Preparation method and application of antibiotic molecular imprinting adsorption membrane
A technology of molecular imprinting and antibiotics, which is applied in the field of pollutant control and detection, can solve the problems of non-selectivity and decline in sampling performance, and achieve the effect of low cost, simple operation and good hydrophilicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
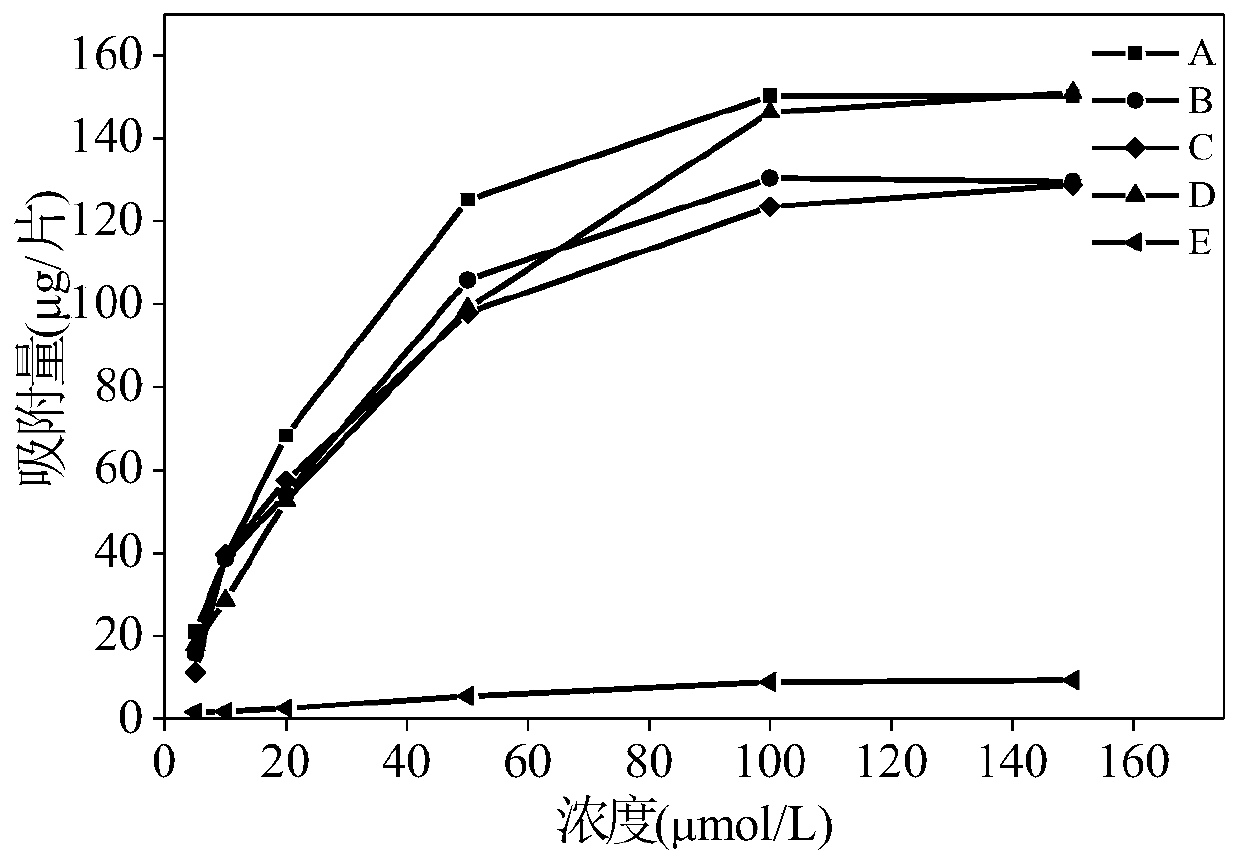
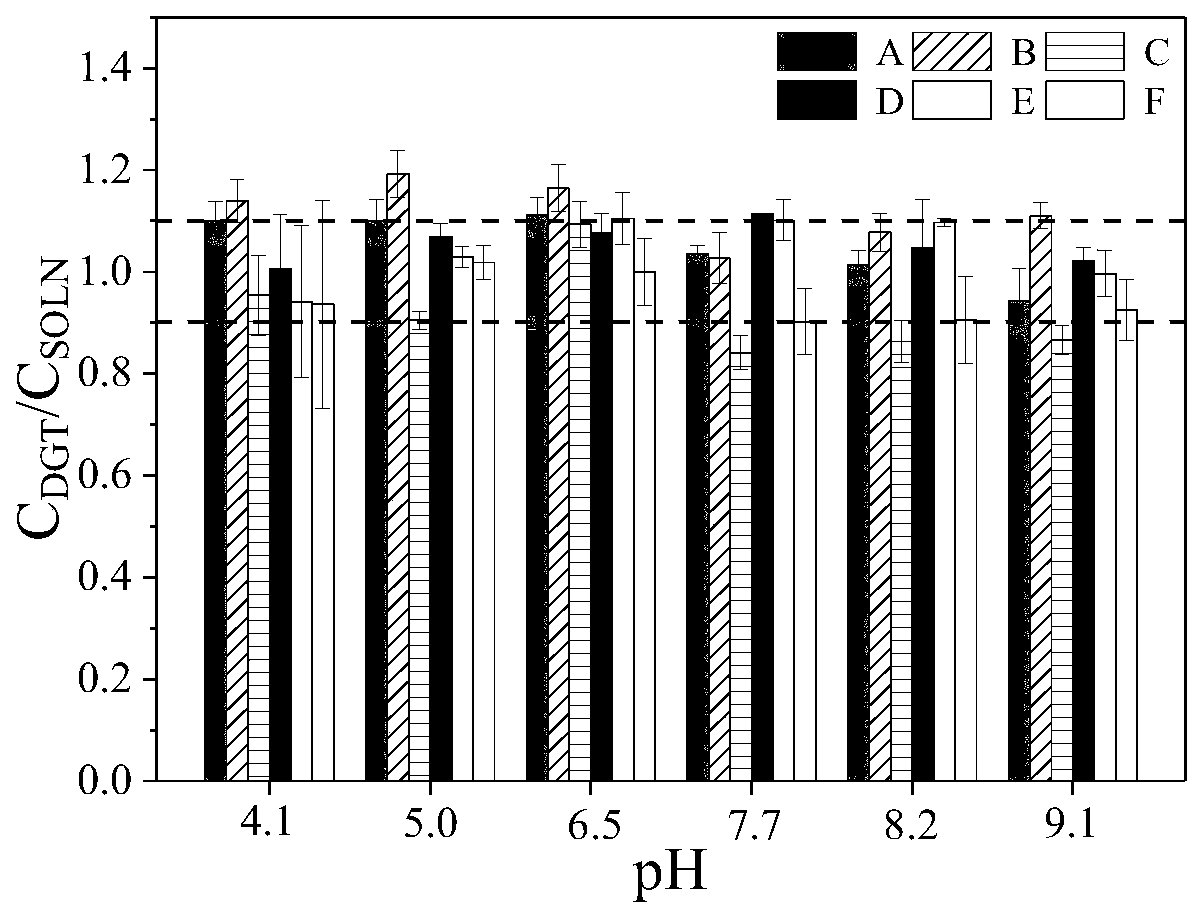
[0033] With baloxacin as a template molecule, methacrylic acid as a functional monomer, and divinylbenzene as a crosslinking agent, it was dissolved in 100 mL of acetonitrile according to a molar ratio of 1:4:12, and 120 mg of azobisisobutyronitrile was added to the solution , passing nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, reacting at 60° C. at a speed of 100 rpm for 8 hours, centrifuging to collect precipitates, eluting template molecules, and drying to obtain fluoroquinolone antibiotic molecularly imprinted materials.
[0034] Prepare an agarose solution with a mass concentration of 1%, mix the fluoroquinolone antibiotic molecularly imprinted material with the agarose solution at a ratio of 0.4%, and quickly inject it into a glass plate with a plastic septum (thickness 0.5mm) on the edge, after the air bubbles are discharged , placed at room temperature for 1 hour, after the solution was gelled, the glass plate and septum were removed, soaked in ultrapure water for 24 hours, and cut ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] With sulfadoxine as a template molecule, methacrylic acid as a functional monomer, and divinylbenzene as a crosslinking agent, it is dissolved in 100mL of acetonitrile according to a molar ratio of 1:4:12, and 110mg of azobisisobutyronitrile is added to the solution. Nitrogen was introduced to remove oxygen, reacted at 60° C. for 16 hours at 150 rpm, centrifuged to collect precipitates, eluted template molecules, and dried to obtain sulfonamide antibiotic molecularly imprinted materials.
[0037] Prepare an agarose solution with a mass concentration of 1.5%, mix the sulfonamide antibiotic molecularly imprinted material with the agarose solution at a ratio of 1%, and quickly inject it into a glass plate with a plastic septum (thickness 0.5mm). After the solution is gelled, remove the glass plate and septum, soak in ultrapure water for 30 hours, take it out and cut it into a sulfonamide antibiotic molecularly imprinted adsorption membrane with a diameter of 2 cm.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Prepare an agarose solution with a mass concentration of 3%, mix the fluoroquinolone antibiotic molecularly imprinted material prepared in Example 1 with the sulfonamide antibiotic molecularly imprinted material prepared in Example 2 and mix it with the agarose solution at a ratio of 3%, and quickly Pour into a glass plate with a plastic septum (thickness 0.8mm) on the edge, let it stand at room temperature for 5 hours after the air bubbles are discharged, and after the solution gels, remove the glass plate and septum, and soak in ultrapure water for 32 hours , taken out and cut into a 2.5cm diameter antibiotic molecularly imprinted adsorption membrane (such as figure 1 shown).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com