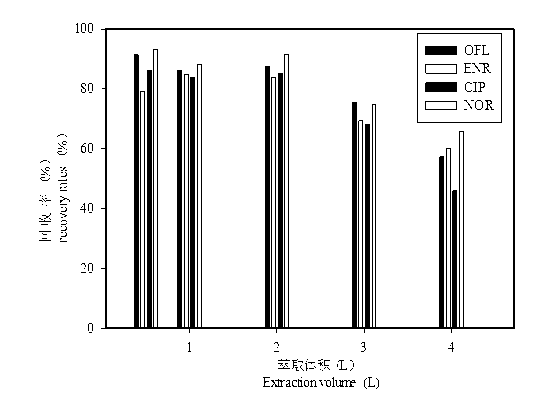
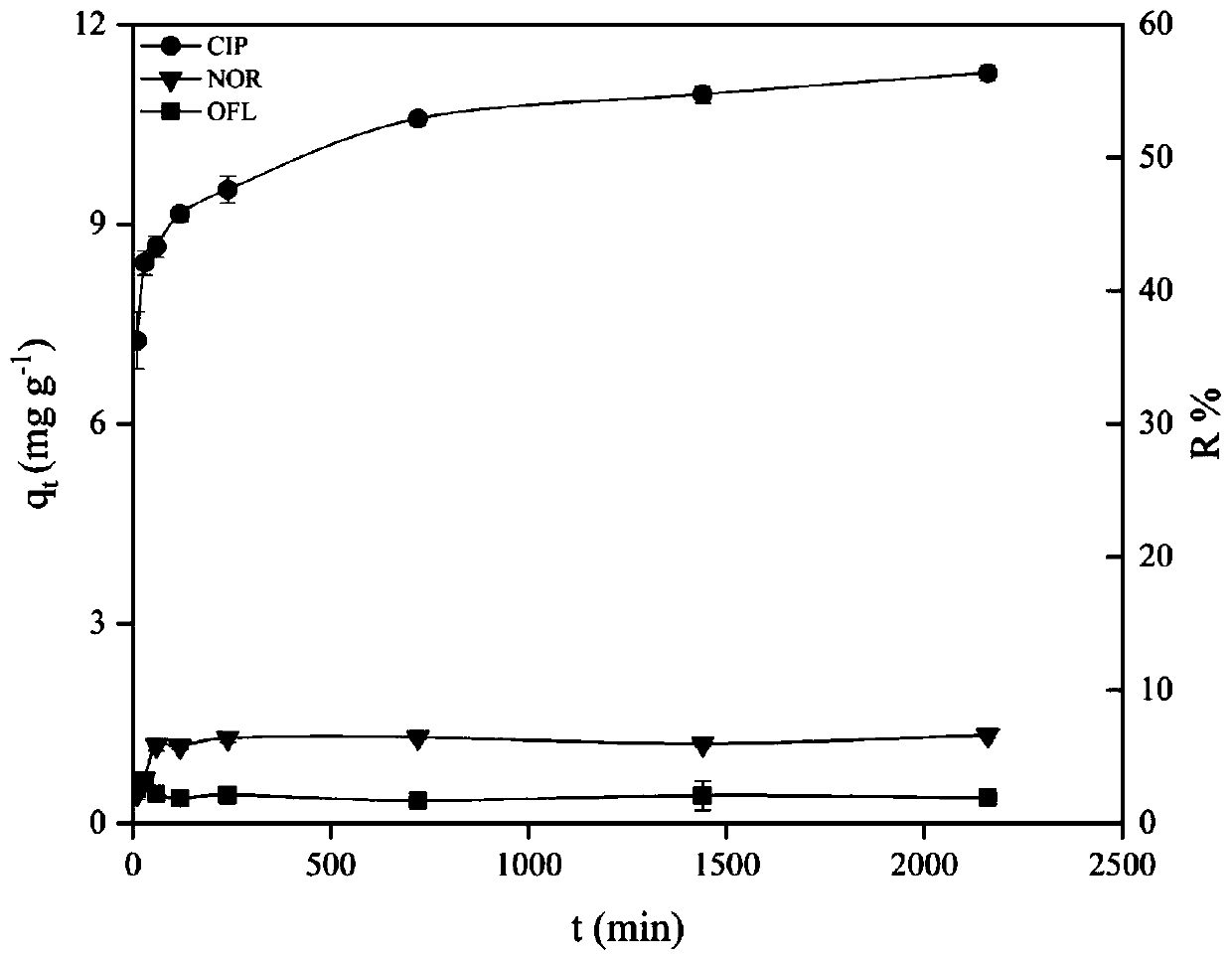
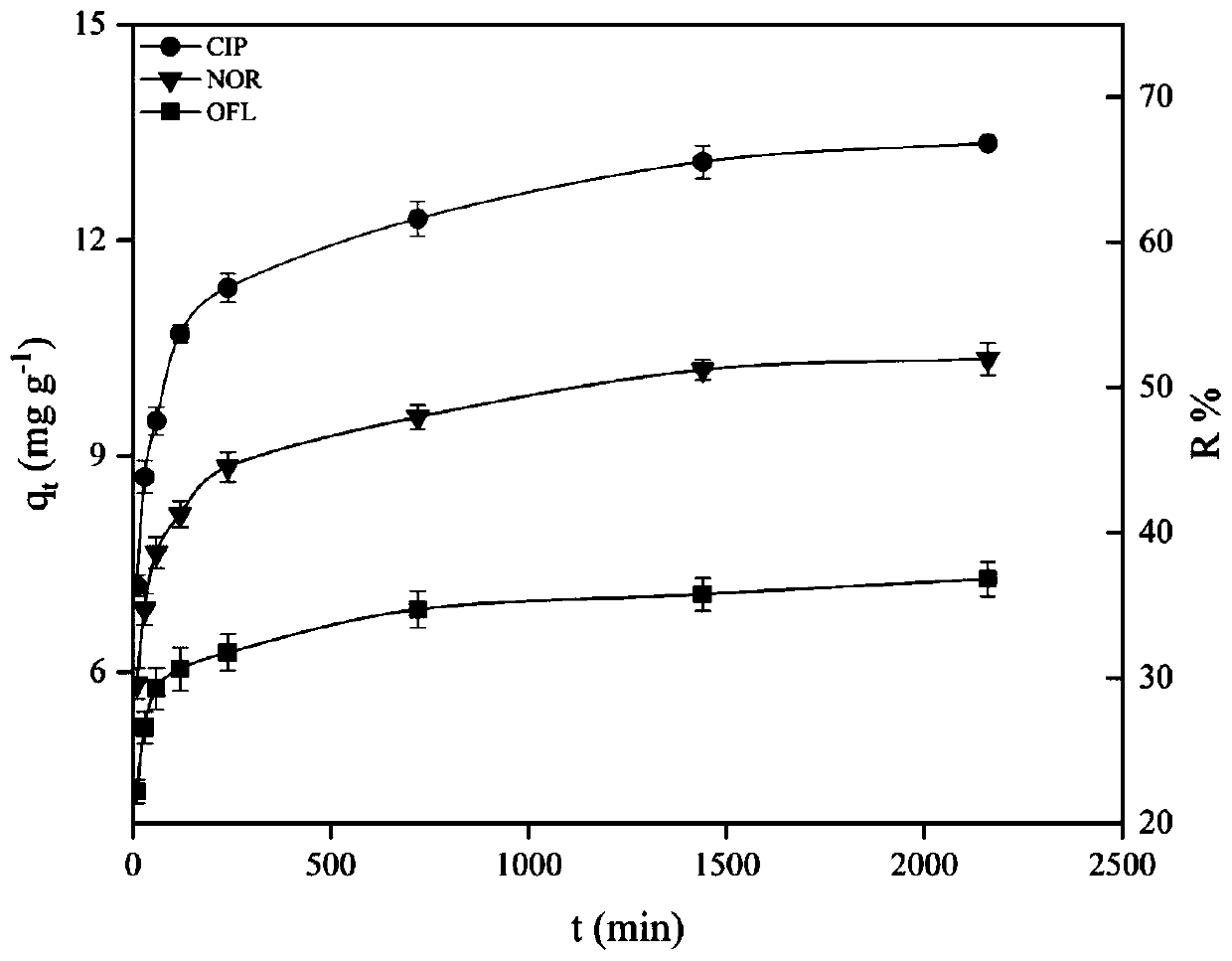
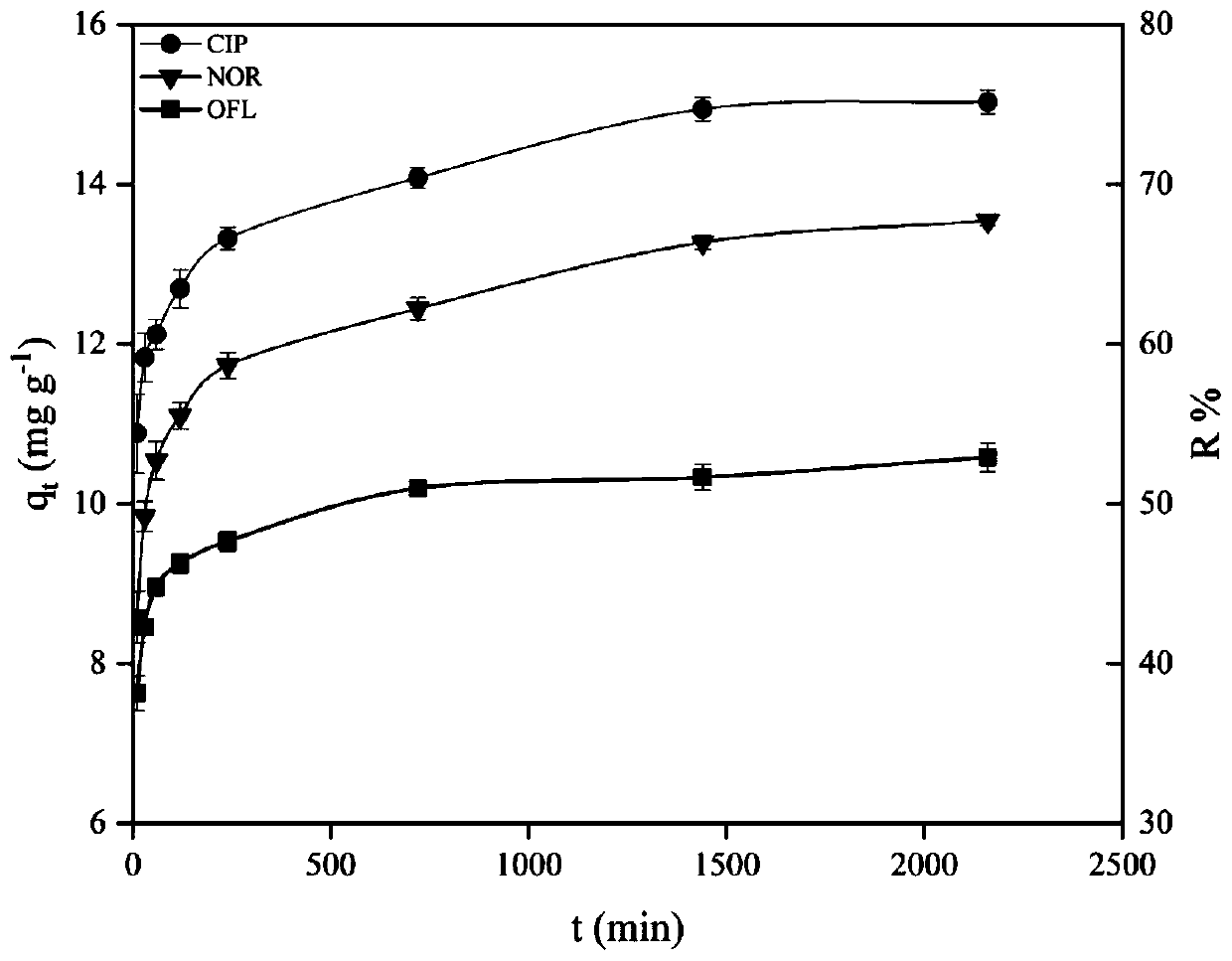
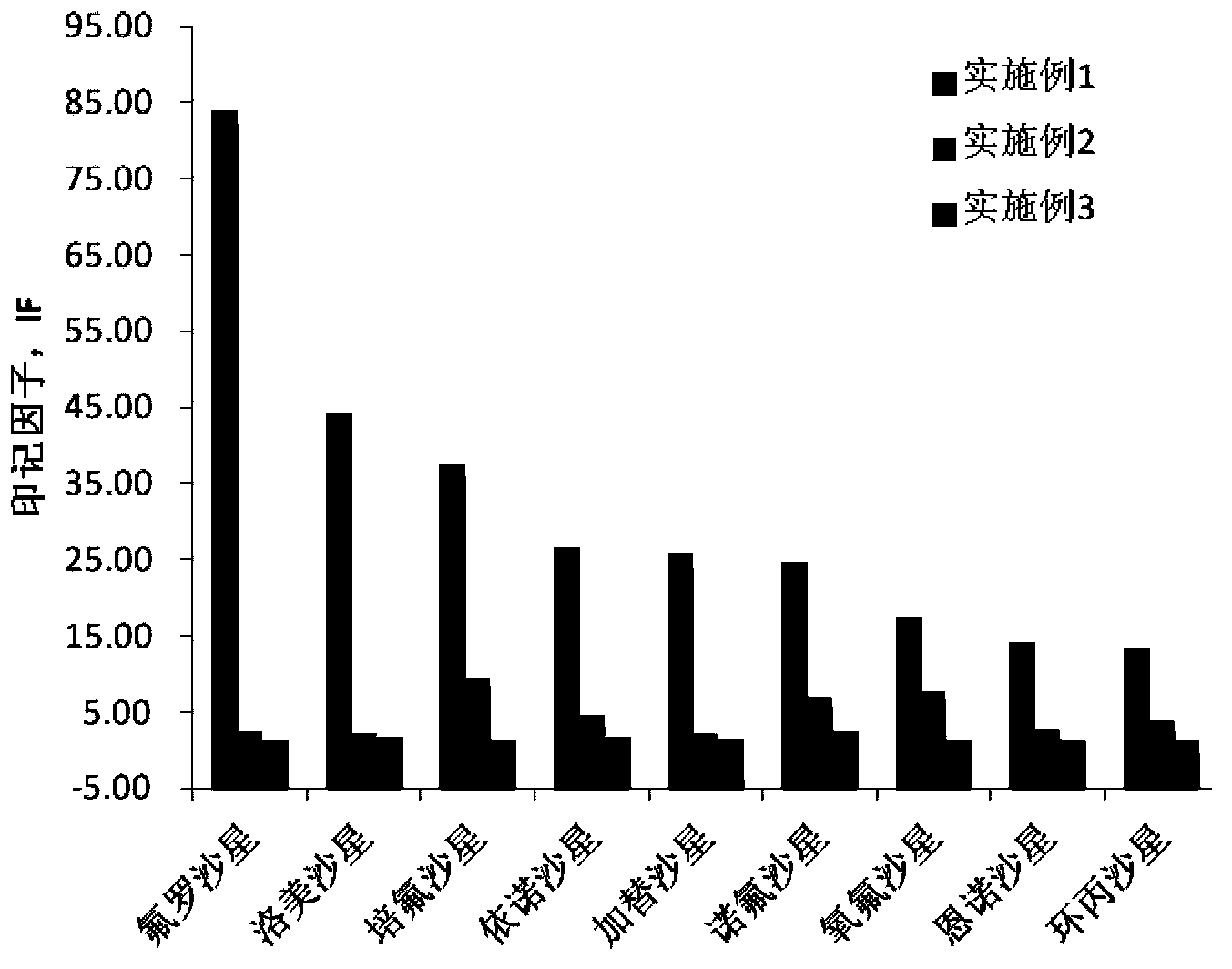
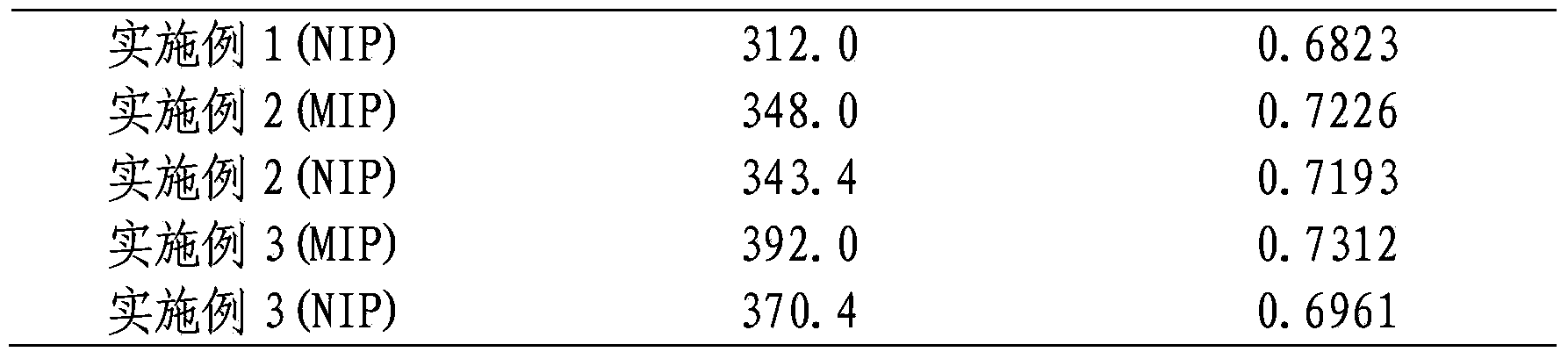
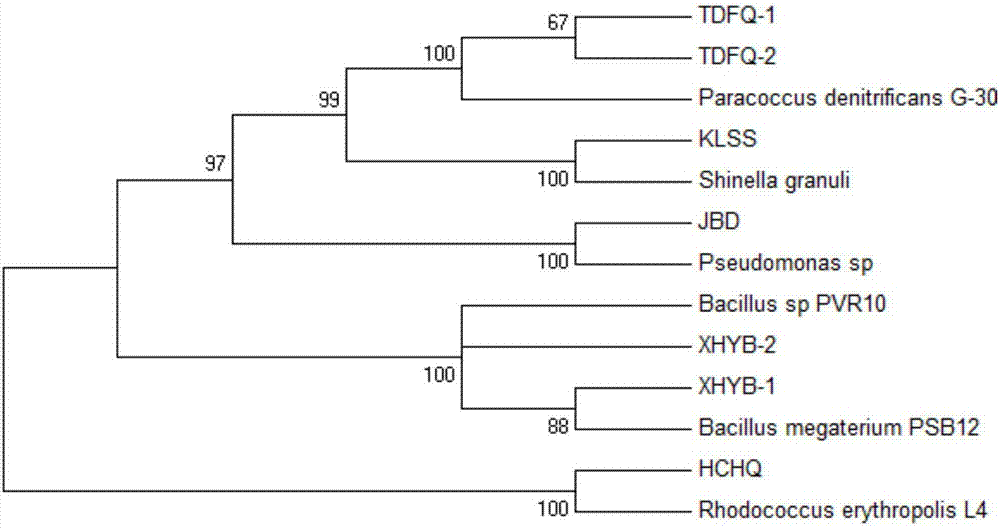
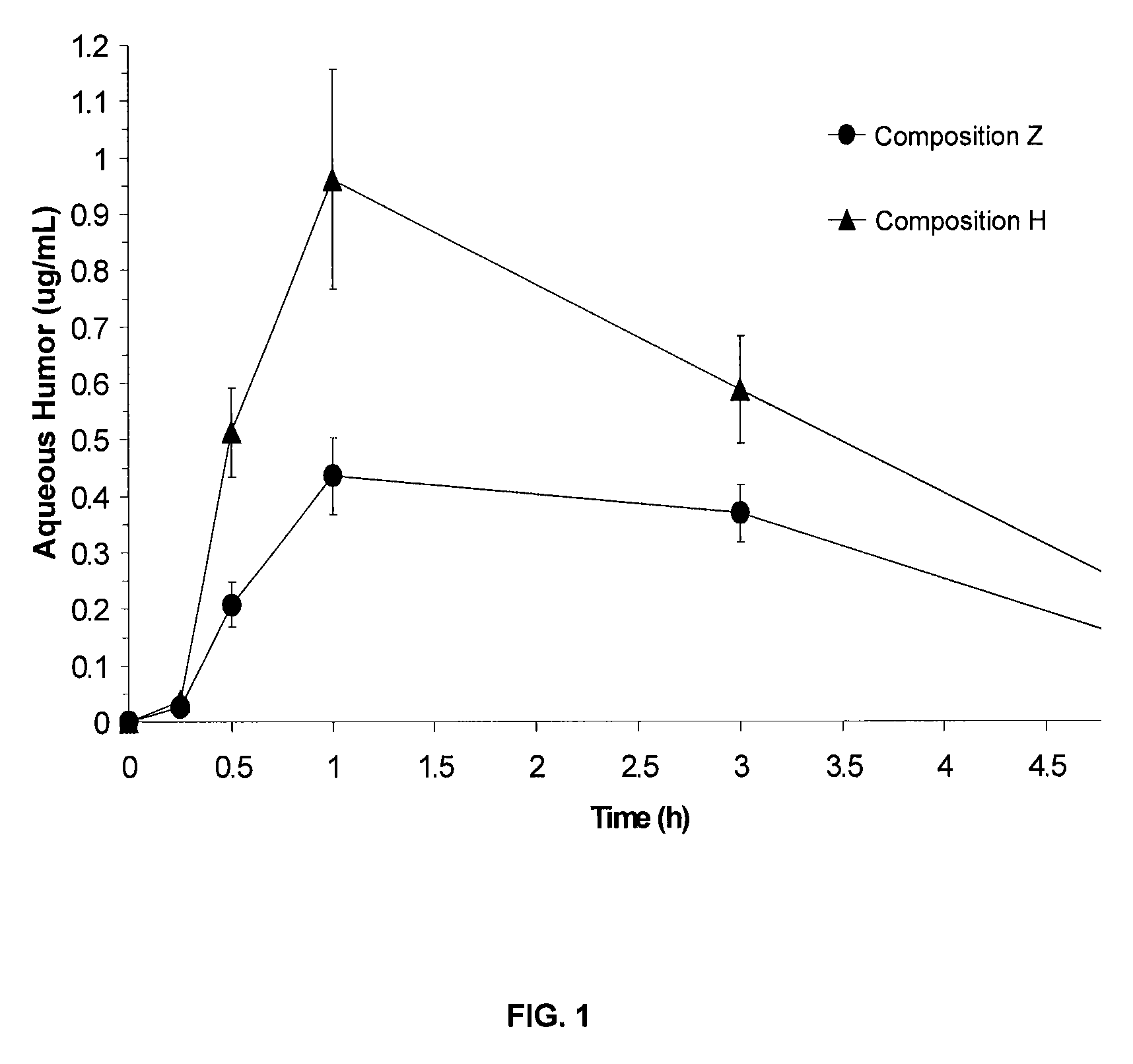
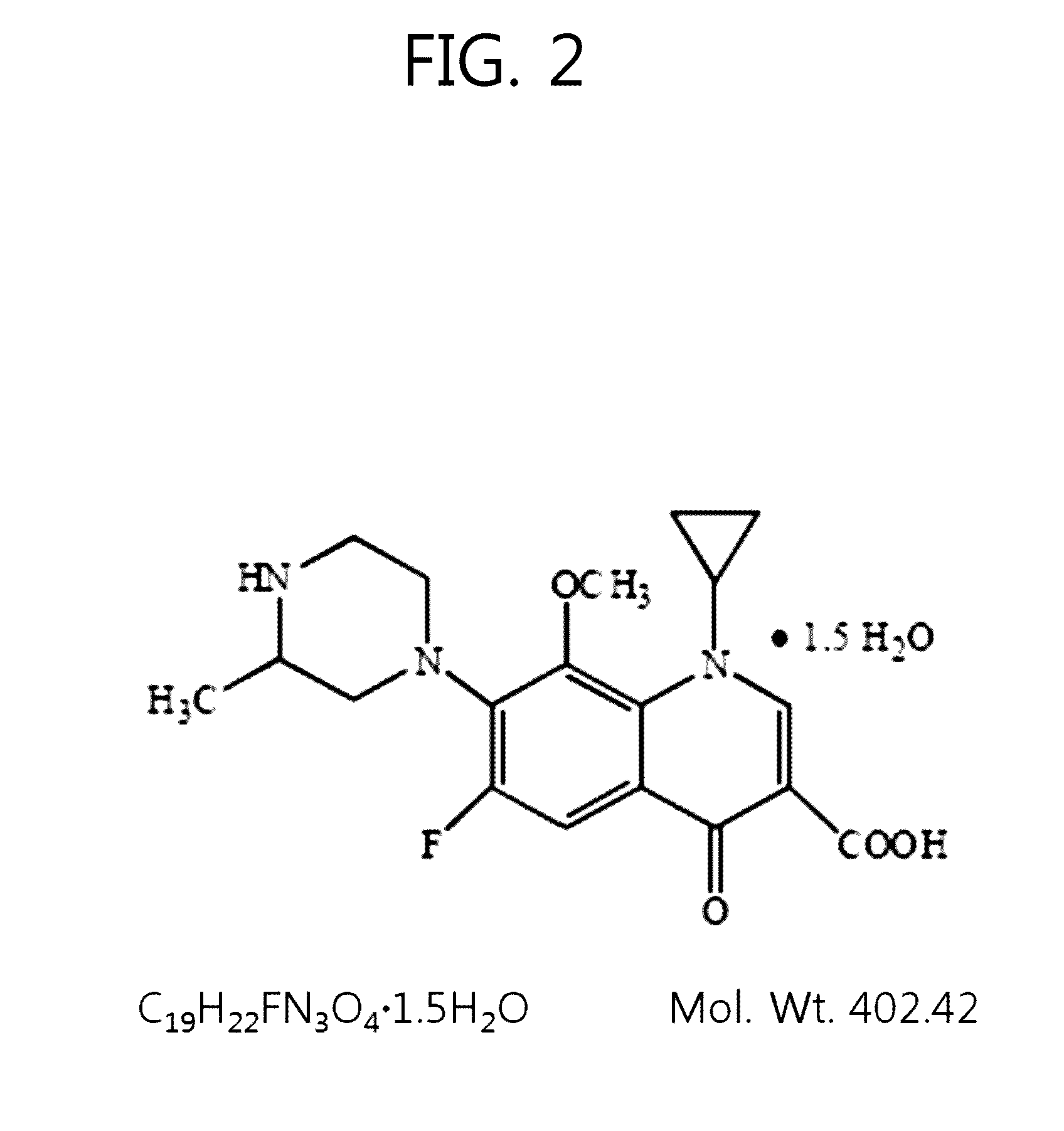
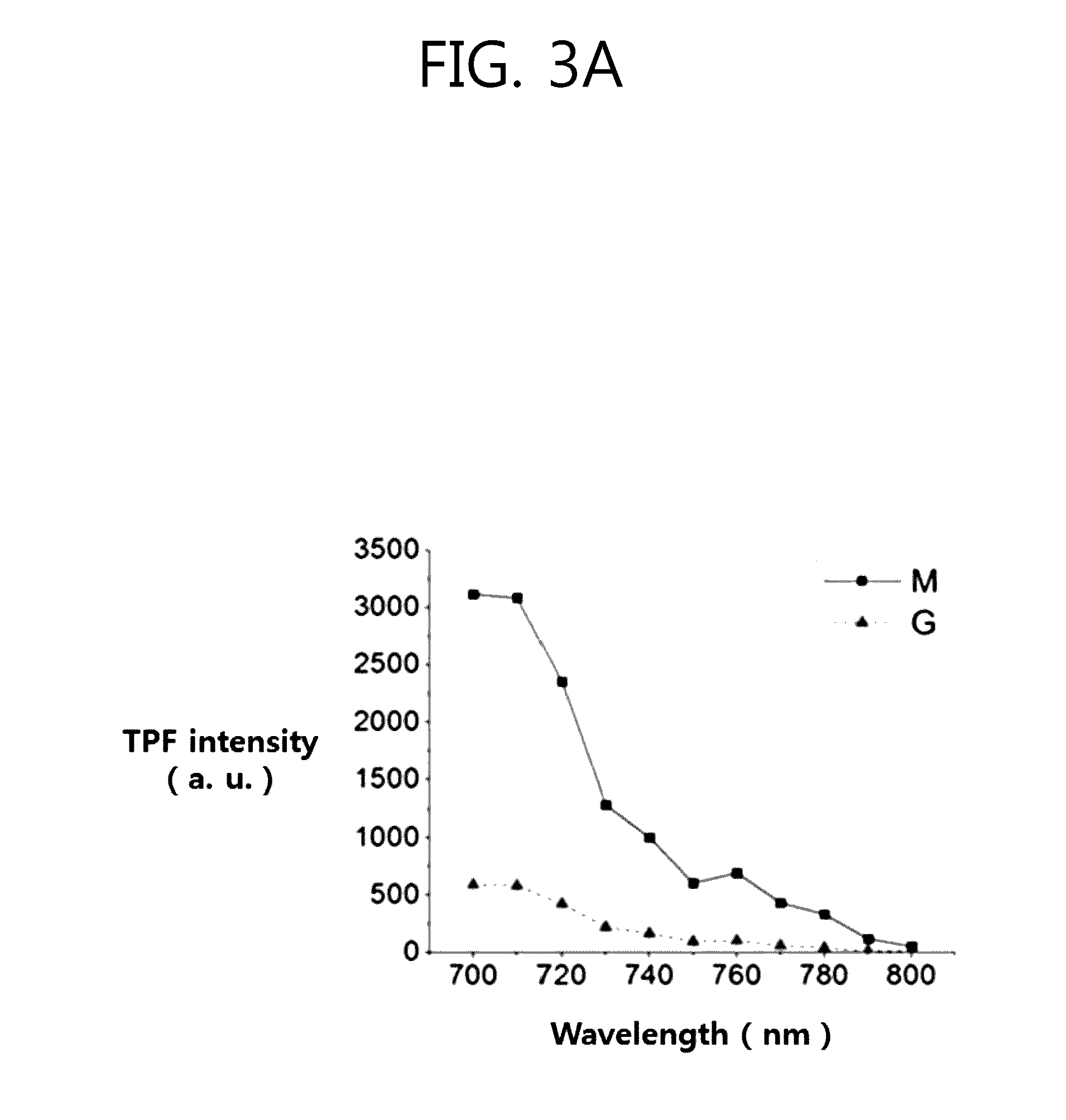
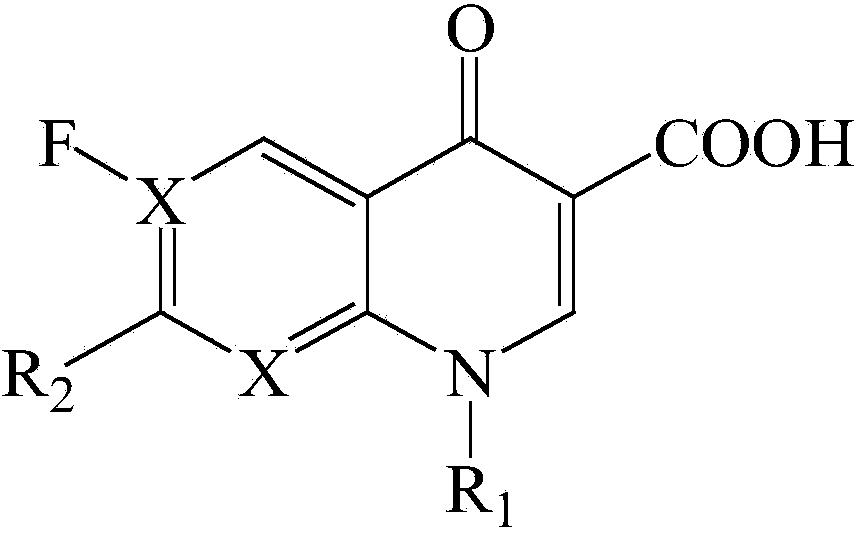
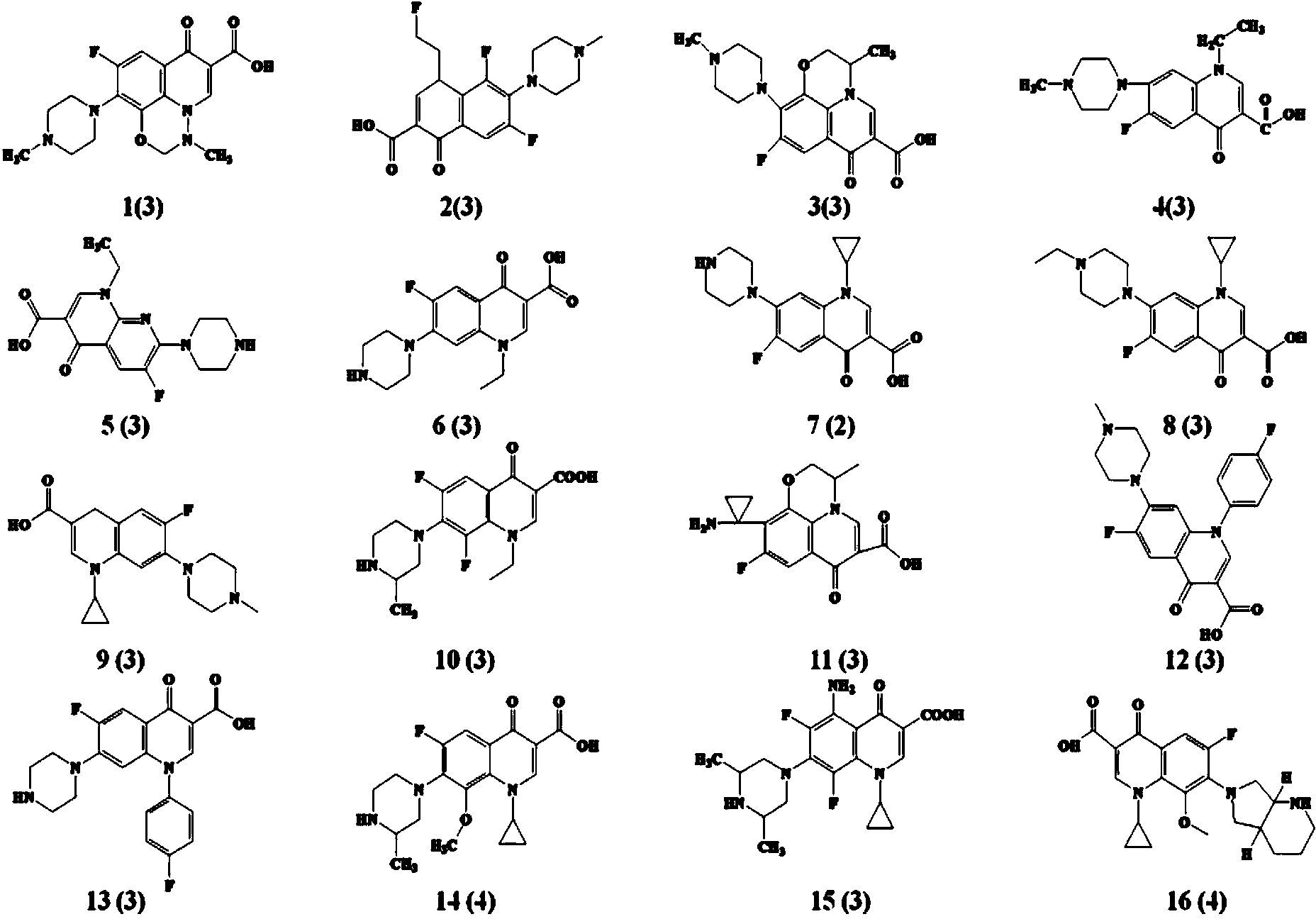
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any quinolone antibiotic with a fluorine (F) atom attached to the quinolone structure, with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Fluoroquinolones diffuse through the bacterial cell wall and act by inhibiting bacterial topoisomerase II, DNA gyrase and/or bacterial topoisomerase IV, which are enzymes involved in bacterial DNA replication. This prevents DNA replication and leads to a blockage of bacterial cell proliferation.
Method for preparing magnetic charcoal material, device adopting method and application
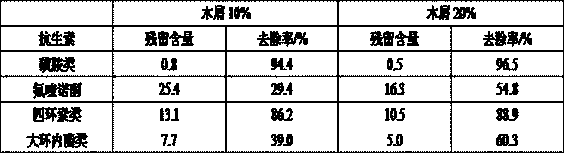
ActiveCN109621897AAvoid resistanceIncrease the active siteOther chemical processesNature of treatment waterSludgeEconomic benefits
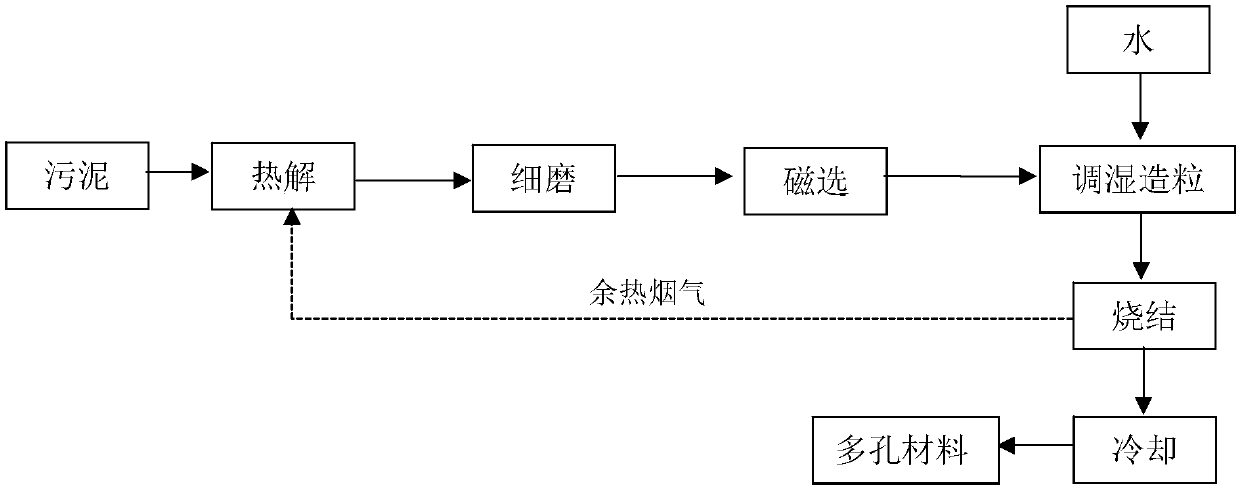
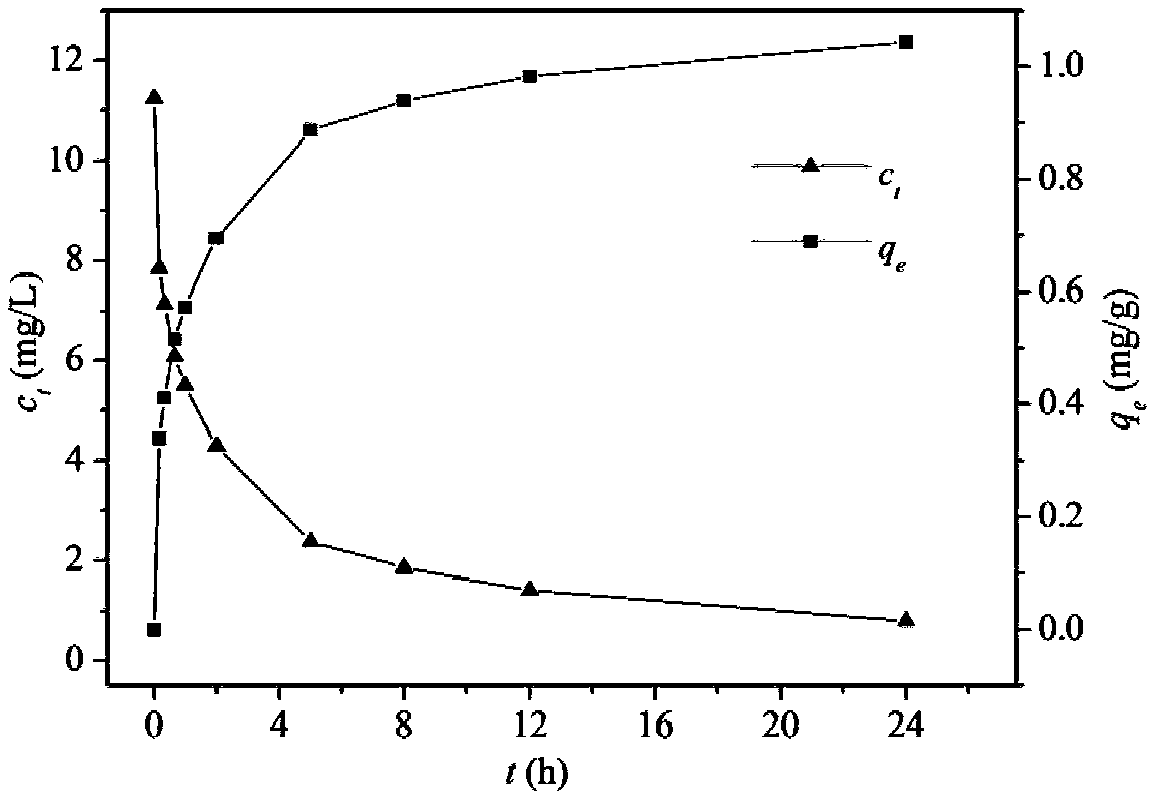
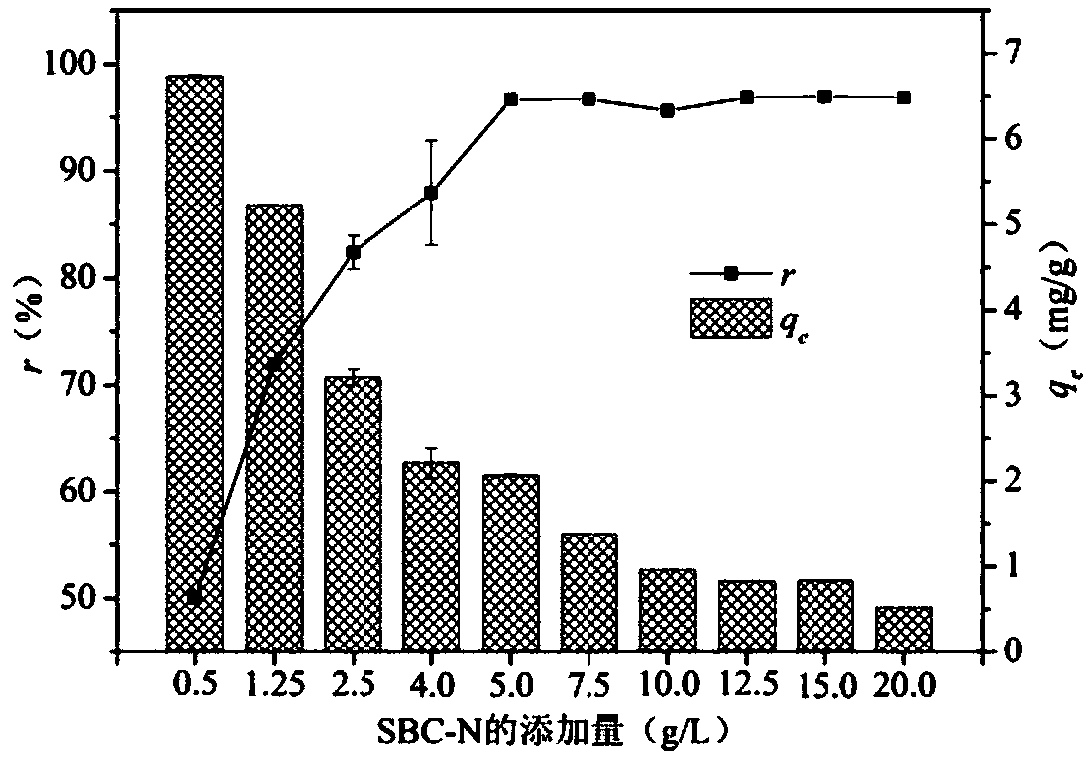
The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnetic charcoal material, a device adopting the method and application. The method comprises the following steps that sewage treatment plant sludgeis subjected to high-temperature anaerobic pyrolysis, and sludge charcoal is obtained; then dry fine grinding is carried out, and charcoal powder is obtained; the sludge charcoal powder is subjected to dry magnetic separation, a magnetic material is obtained, granules obtained after humidifying and pelleting are subjected to high-temperature sintering in protective atmosphere, and sintered materials are obtained; furnace cooling is carried out, and the magnetic charcoal material of a porous structure is obtained. According to the method, the magnetic material is separated out of the sludge pyrolysis product charcoal and is used for preparing the magnetic charcoal material, the magnetic charcoal material is used for efficiently adsorbing and removing quinolone antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, recycling utilization of the sludge charcoal is achieved, the preparation cost of the adsorption materials is reduced, the process is simple, high practicality is achieved, and good economic benefits and environmental benefits are achieved.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid phase extraction and HPLC-fluorescence detection method for fluoroquinolones antibiotics
InactiveCN101696964AMeet the testing requirementsReduce test costsIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationAntibiotic YNorfloxacin
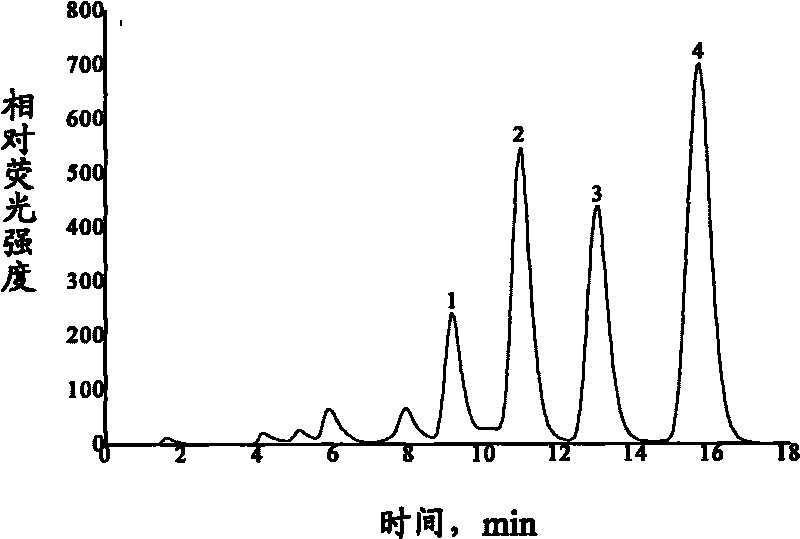
The invention discloses a solid phase extraction and HPLC-fluorescence detection method for fluoroquinolones antibiotics. The method comprises the following steps of passing a pretreated water sample through an activated solid phase extraction column; eluting the solid phase extraction column with a Na2EDTA aqueous solution; then vacuumizing; and finally, eluting the water sample for three times by a concentrated ammonia methanol solution with a concentrated ammonia volume percent concentration of 6 percent by 0.5-2mL each time. An obtained eluent is blow-dried to 0.1-0.4mL in air flow, water is added to reach a constant column of 1.0mL so as to obtain a test sample, and then HPLC-fluorescence detection is carried out. By adopting the solid phase extraction-HPLC-fluorescence detection technology and utilizing a conventional analytical instrument, the method can simultaneously measure the contents of four typical fluoroquinolones antibiotics of ofloxacin, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin in the water sample. The method has simple operation and low cost and can be applied to the measurement of the ultratrace of four typical fluoroquinolones antibiotics in waste water and surface water.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
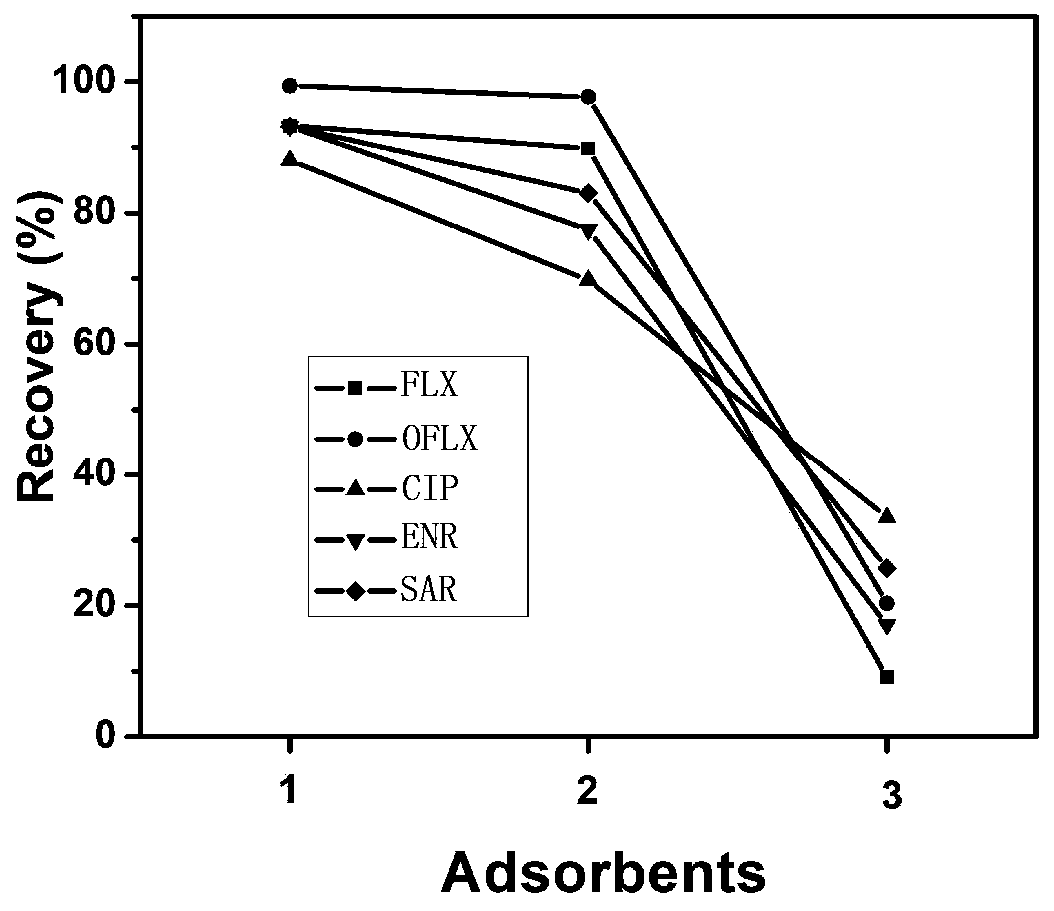
Method for separation enrichment and detection of trace fluoroquinolone antibiotic in water environment
InactiveCN102798689AAntibiotics are effectiveHigh separation, qualitative and quantitative capabilitiesComponent separationFluoro quinolonesSolid phase extraction
The invention relates to a method for separation enrichment and detection of trace fluoroquinolone antibiotic residues in a water environment. According to the method, 2.0-4.0L of a water sample is subjected to solid-phase extraction, and then analysis and detection are carried out by a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry instrument. Being able to well separate and detect a plurality of fluoroquinolone antibiotic substances, the invention has the advantages of low detection limit, high recovery rate, high sensitivity, good selectivity and simple operation, etc., and has substantial effects in the detection study of trace fluoroquinolone antibiotic substances in the water environment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation of Fe-Zn and phosphate modified sludge biochar and application of the same in removal of fluoroquinolones antibiotics from water
ActiveCN110227416AEfficient removalHarm reductionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPhosphateResource utilization
Belonging to the technical field of biochar preparation, the invention discloses preparation of Fe-Zn and phosphate modified sludge biochar and application of the same in removal of fluoroquinolones antibiotics from water. The preparation method includes: dewatering and drying the sludge from a secondary sedimentation tank of a municipal sewage treatment plant, then performing pyrolysis by a hightemperature tubular furnace, then utilizing Fe-Zn and phosphate for modification, and finally conducting two calcining to obtain Fe / Zn+H3PO4-SBC. The Fe / Zn+H3PO4-SBC prepared by the invention has adsorption capacity on fluoroquinolones antibiotics ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin up to 25.43-88.73mg / g. The method provided by the invention adopts municipal sludge as the raw material, reduces the production cost, realizes the resource utilization of municipal sludge and efficient removal of antibiotics from water, also has the advantages of simple operation, low cost and the like, and isa potential removal method for fluoroquinolones antibiotics in water.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Fluoroquinolone substitute template molecularly imprinted polymer and application thereof
ActiveCN104341552AHigh specific selectivityThere is no template leakage problemIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesCross-linkAcetic acid
The invention provides a preparation method and an application method of a fluoroquinolone antibiotic medicine substitute template molecularly imprinted polymer. According to the invention, substitute template molecules, a cross-linking agent, a functional monomer, and an initiator are dissolved in a pore-forming solvent, such that a pre-polymerization solution is prepared; a polymerization reaction is carried out for 24-48h under a temperature of 50-70 DEG C; a white block-shaped polymer obtained in the polymerization reaction is ground, sieved, and settled, such that polymer particles with a particle size of 45-63[mu]m are obtained; the obtained polymer is subjected to Soxhlet extraction or ultrasonic extraction sequentially by using methanol / acetic acid and methanol as extraction solvents, such that residual substitute template molecules and interfering substances are removed, and the substitute template molecularly imprinted polymer is obtained. The substitute template molecularly imprinted polymer has high specific selectivity and enrichment capability upon fluoroquinolone antibiotics. With the material, an imprinting effect is ensured, and a template leakage problem is solved. The polymer can be used in separation, enrichment and purification of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in complex substrate.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for removing antibiotic contamination by adsorption of copper sulphide
InactiveCN103204562ALow costLarge adsorption capacityWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPenicillinMacrolide resistance
The invention provides a method for removing antibiotic contamination by adsorption of copper sulphide, and belongs to the field of water pollution control. The method comprises the steps of filtering waste water containing antibiotic contamination, adjusting pH to 5-9; and filtering the waste water processed in the step (1) through a bed layer containing the copper sulphide, wherein the antibiotic contamination is any one of tetracyclines, penicillins, macrolides, and sulfonamide fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Compared with the traditional removal technology of the antibiotic in a water body, the method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that 1 the antibiotic contamination in the water body can be selectively complexed and removed; and the effluent concentration can be less than 1mug / L; 2, the adsorbing capacity is large; and the adsorbing capacity of copper sulphide can be up to 500mg / g; and 3, the method is fast in adsorption rate, easy to regenerate, simple and convenient to operate, low in cost and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Paracoccus denitrificans and application thereof in treatment of livestock farm wastewater
ActiveCN107090418AReduce pollutionHealth effectsBacteriaWater contaminantsSynechococcusBiotechnology
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to paracoccus denitrificans and an application thereof in treatment of livestock farm wastewater. The paracoccus denitrificans TDFQ-1 is collected at the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2017238. The bacterial strain has the advantages of being high in growth speed, high in environmental tolerance and good in growth in an organic culture medium. The paracoccus denitrificans has a heterotrophic nitrification capability and an aerobic denitrification capability, and is capable of reducing harmful substances, such as ammonia nitrogen and nitrate in water, especially removing the ammonia nitrogen in the livestock farm wastewater with relatively high organic matter content and improving the breeding environment. The bacterial strain is capable of efficiently degrading fluoroquinolone antibiotics when treating the wastewater, reducing the pollution of the antibiotics to soil and water sources and protecting the human health.
Owner:WUHAN KEYUAN BIOLOGICAL DEV CO LTD
Method for removing fluoroquinolones antibiotics in poultry and livestock excrement
InactiveCN105254346AReduce the amount of safetyProduce secondary pollutionBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyAnimal feces
The invention discloses a method for removing fluoroquinolones antibiotics in poultry and livestock excrement. The method includes the steps of 1, preparing compost raw materials, wherein chicken excrement, sawdust, sterile distilled water and high-temperature-resistant fungicide are prepared into the compost raw materials, the mass ratio of the chicken excrement to the sawdust is 5-10 to 1, the water content of the compost raw materials ranges from 55% to 60%, and the high-temperature-resistant fungicide is cellulomonas flavigena; 2, carrying out high-temperature composting, wherein the pile overturning frequency is controlled to enable the compost temperature to range from 45 DEG C to 65 DEG C, and high-temperature fermentation is achieved; 3, carrying out intermediate-temperature composting, wherein after high-temperature fermentation, the manual pile overturning frequency is controlled to enable the temperature of a compost product to range from 30 DEG C to 45 DEG C, and intermediate-temperature fermentation is achieved. According to the method, the fluoroquinolones antibiotics in the poultry and livestock excrement are removed sufficiently through the degradation effect of high-temperature-resistant strains and relative microorganisms, and therefore the fluoroquinolones antibiotics in organic fertilizers are reduced to the safe level.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Mycoplasma clearing reagent and application thereof
InactiveCN101851603AEffectively suppress and killEfficient killingAnimal cellsAntibiotic YMacrolide resistance
The invention relates to a mycoplasma clearing reagent and application thereof. The mycoplasma clearing reagent of the invention comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 1.3 to 1.5 percent of fluoroquinolones antibiotics, 0.3 to 0.5 percent of tetracyclines derivatives, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of macrolides antibiotics and 97.7 to 98.3 percent of buffer solution, can most effectively inhibit and kill mycoplasmas, and has a short period, namely, all the mycoplasmas can be killed in only one week without influencing the metabolism of cells per se; and the treated cells have smooth surfaces, substantially have no black particles and are difficult to be re-infected by the mycoplasmas.
Owner:上海龙鼎医药科技有限公司
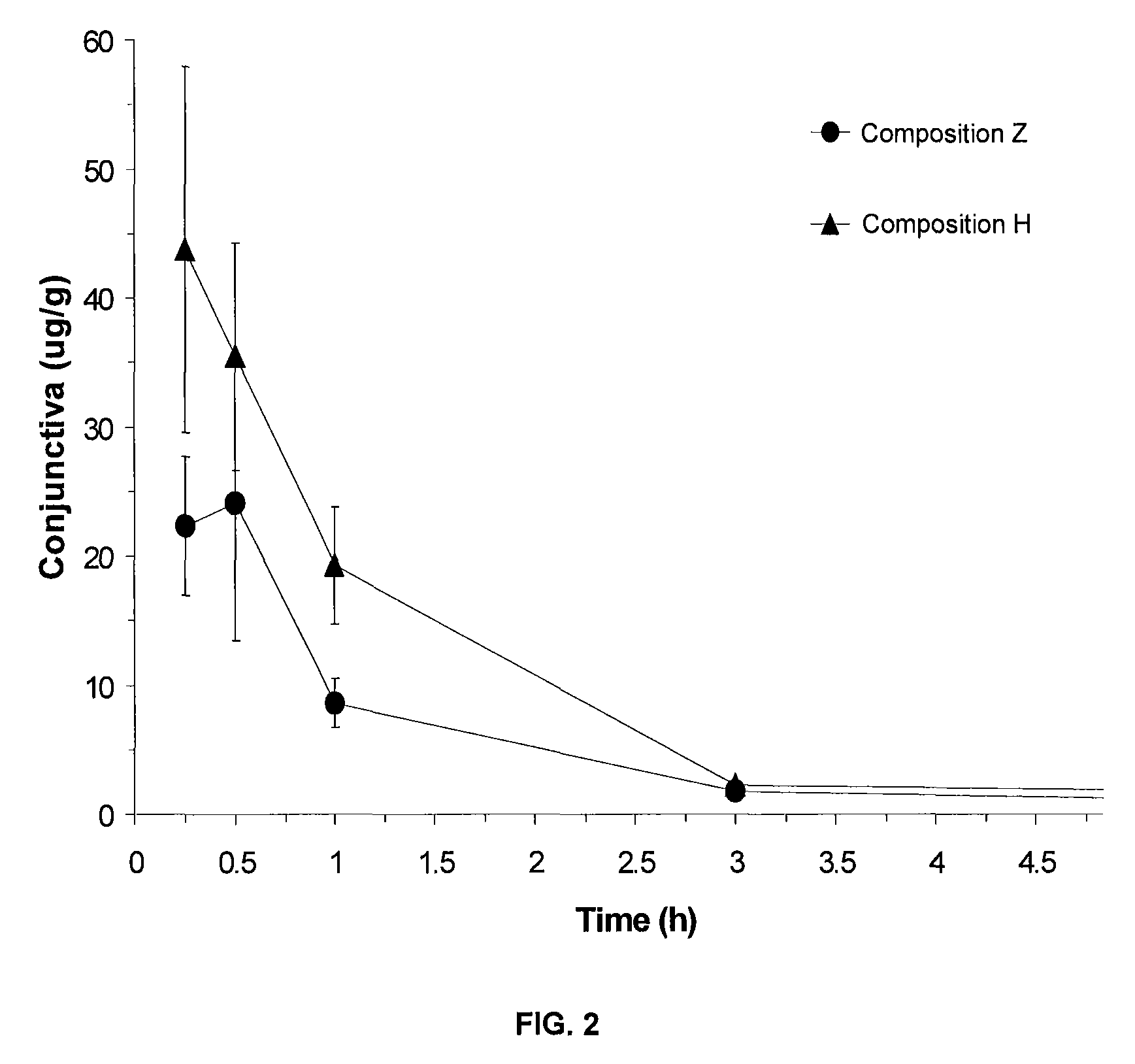
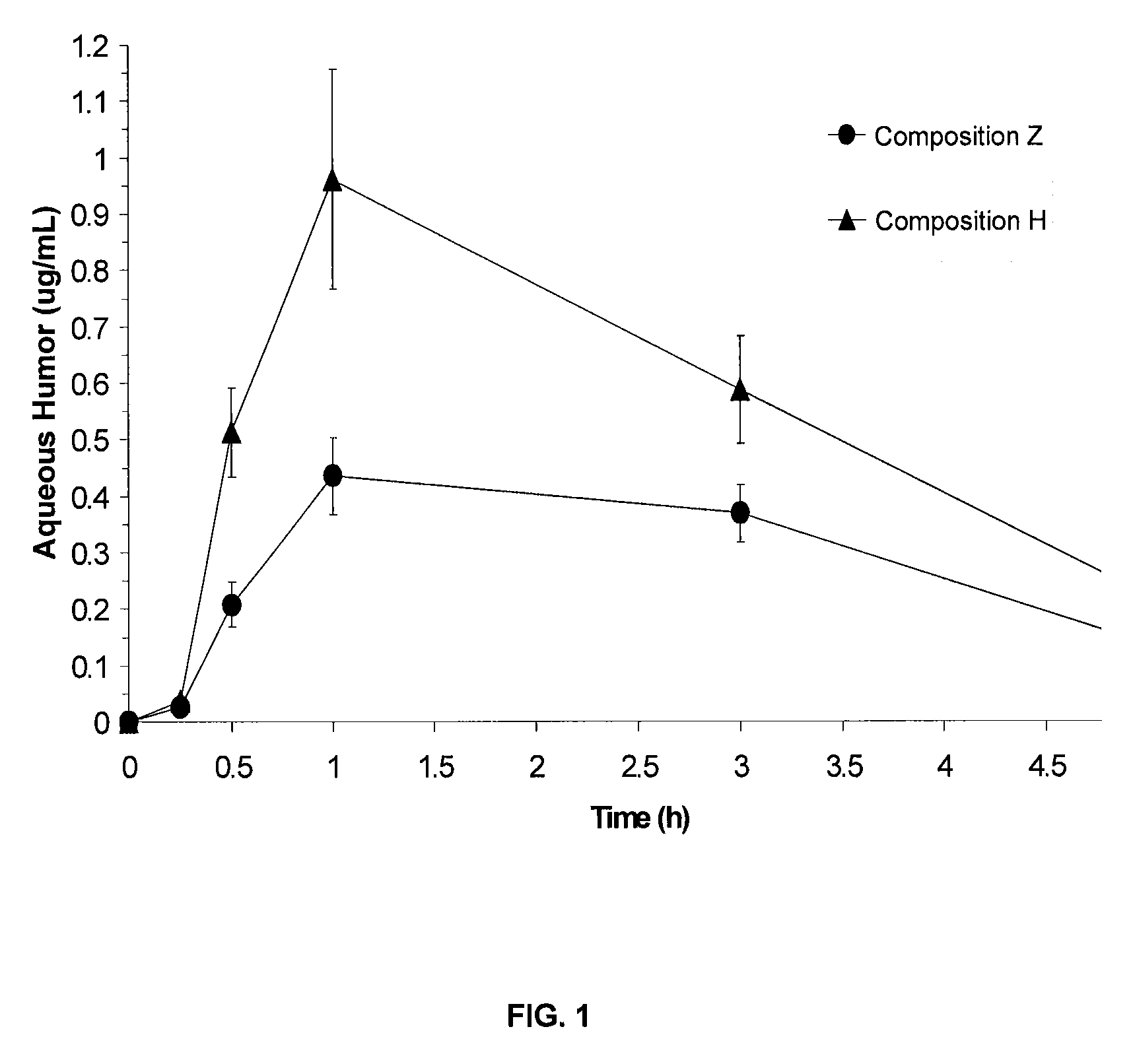
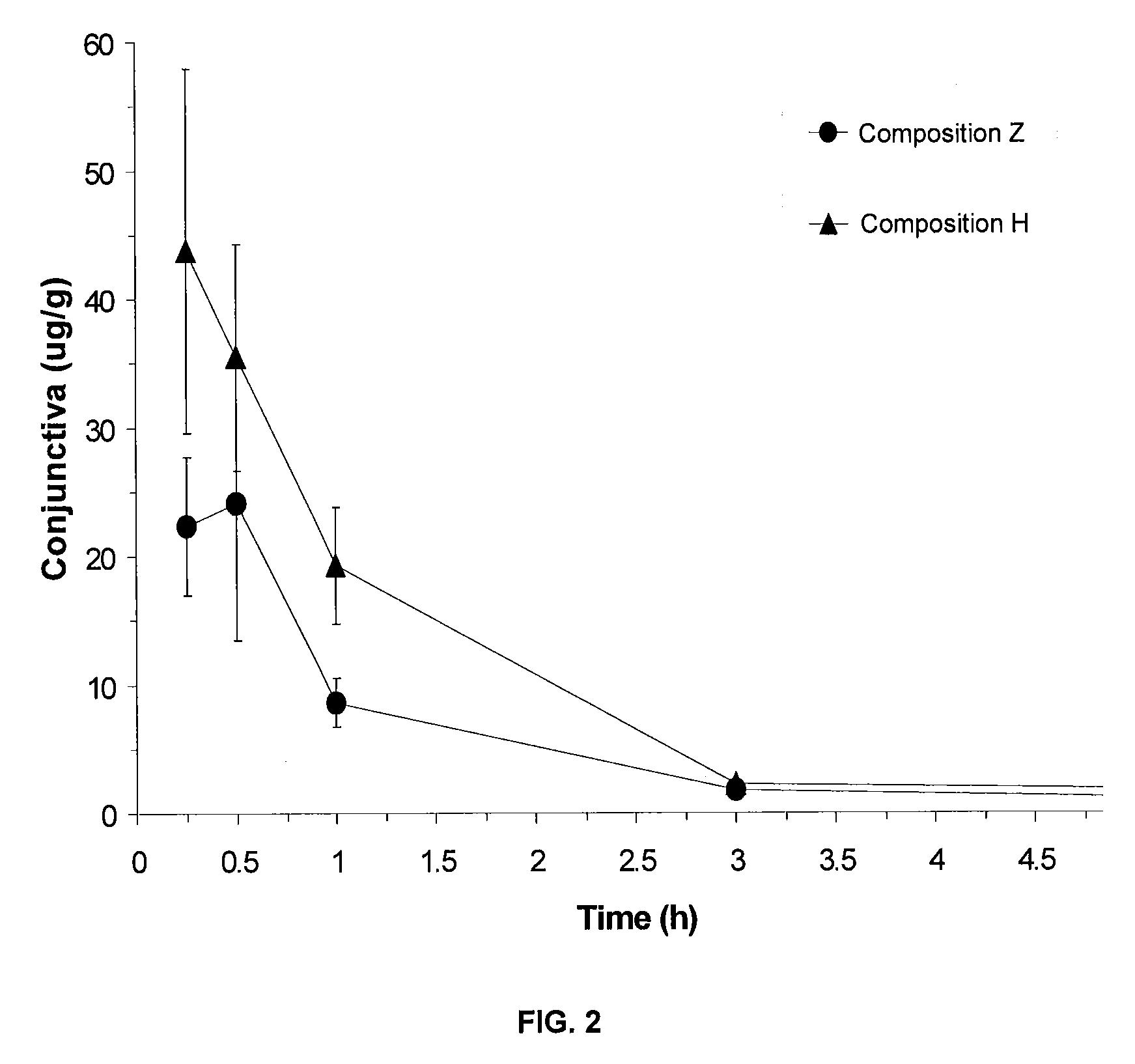
Pharmaceutical compositions containing a fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug
ActiveUS8450311B2Improve homogeneityEqually distributedAntibacterial agentsBiocideBioavailabilityFluoroquinolone Antibiotic
Pharmaceutical compositions containing a fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug are disclosed. The compositions exhibit improved homogeneity, improved bioavailability, lower turbidity or a combination thereof. The composition can be use as otic or nasal compositions, but are particularly useful as ophthalmic compositions.
Owner:HARROW HEALTH INC
Method for efficiently removing antibiotic residues in livestock manure through normal-temperature fermentation
ActiveCN105502864AEasy temperature controlGood removal effectWaste water treatment from animal husbandryBiological sludge treatmentBiotechnologyLivestock manure
The invention provides a method for efficiently removing antibiotic residues in livestock manure through normal-temperature fermentation. The method includes the following steps that 1, concentrated sulfuric acid with the mass ratio of 1%-3% is added into the livestock manure, and acid regulating treatment is carried out for 1-2 hours; 2, pH is adjusted to range from 4.5 to 6.0; 3, the treated manure is spread to a sealed or semi-sealed container, the temperature is controlled to range from 28 DEG C to 35 DEG C, and solid state fermentation is carried out for 4-6 days. A light source is arranged in a fermenting container for illumination cultivation, and wood shavings are added into the livestock manure, so that degradation of antibiotics is accelerated. The antibiotic pollutants can be any one of tetracycline antibiotics, sulfonamide antibiotics and fluoroquinolone antibiotics or a mixture of several of tetracycline antibiotics, sulfonamide antibiotics and fluoroquinolone antibiotics, and the method is particularly suitable for removing tetracycline antibiotics and sulfonamide antibiotics. Compared with an existing technology for removing antibiotics in the livestock manure, it can be achieved that the content of the antibiotics in the livestock manure is reduced in a short time under the normal temperature condition, and the method does not depend on the high temperature condition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Magnetic nano-microsphere and method for extracting and analyzing five trace quinolone antibiotics in water body by virtue of magnetic nano-microsphere
InactiveCN108896676APromote enrichmentEasy extractionComponent separationOther chemical processesFluoro quinolonesMicrosphere
The invention provides a magnetic nano-microsphere and a method for extracting and analyzing five trace quinolone antibiotics in a water body by virtue of the magnetic nano-microsphere. The magnetic nano-microsphere is Fe3O4@Cys@MIL125-NH2. By taking a magnetic solid phase extraction technique as the basis and the magnetic nano-microsphere as an adsorbent, the quinolone antibiotics in a to-be-tested water body are pretreated and enriched, so that the sensitivity of the method for detecting the trace quinolone antibiotics in the water body is greatly improved.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
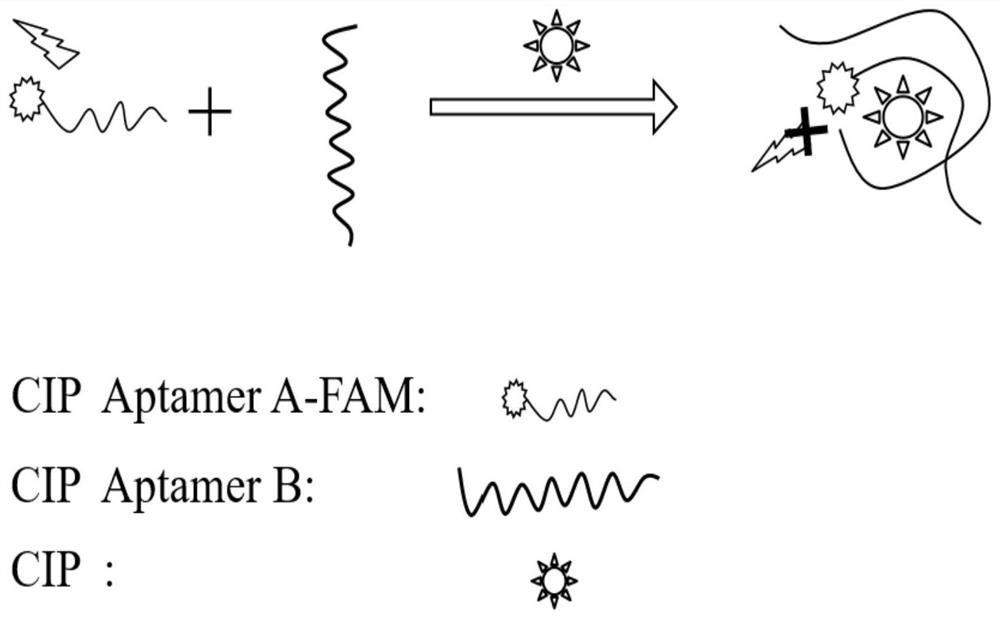
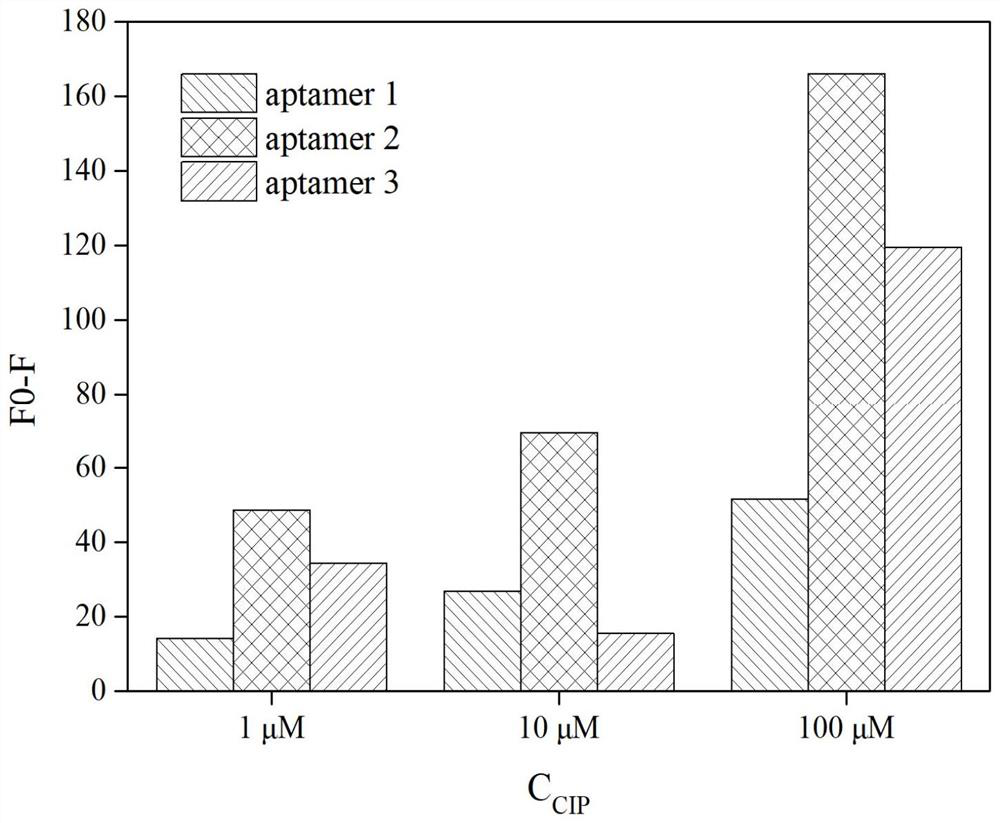
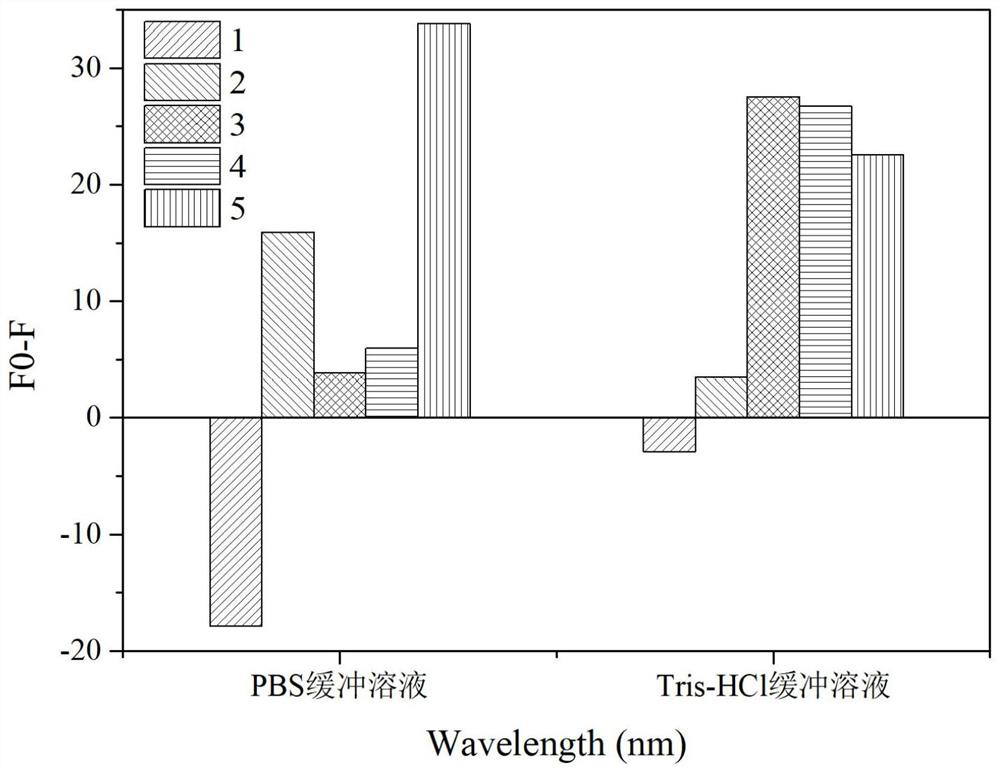
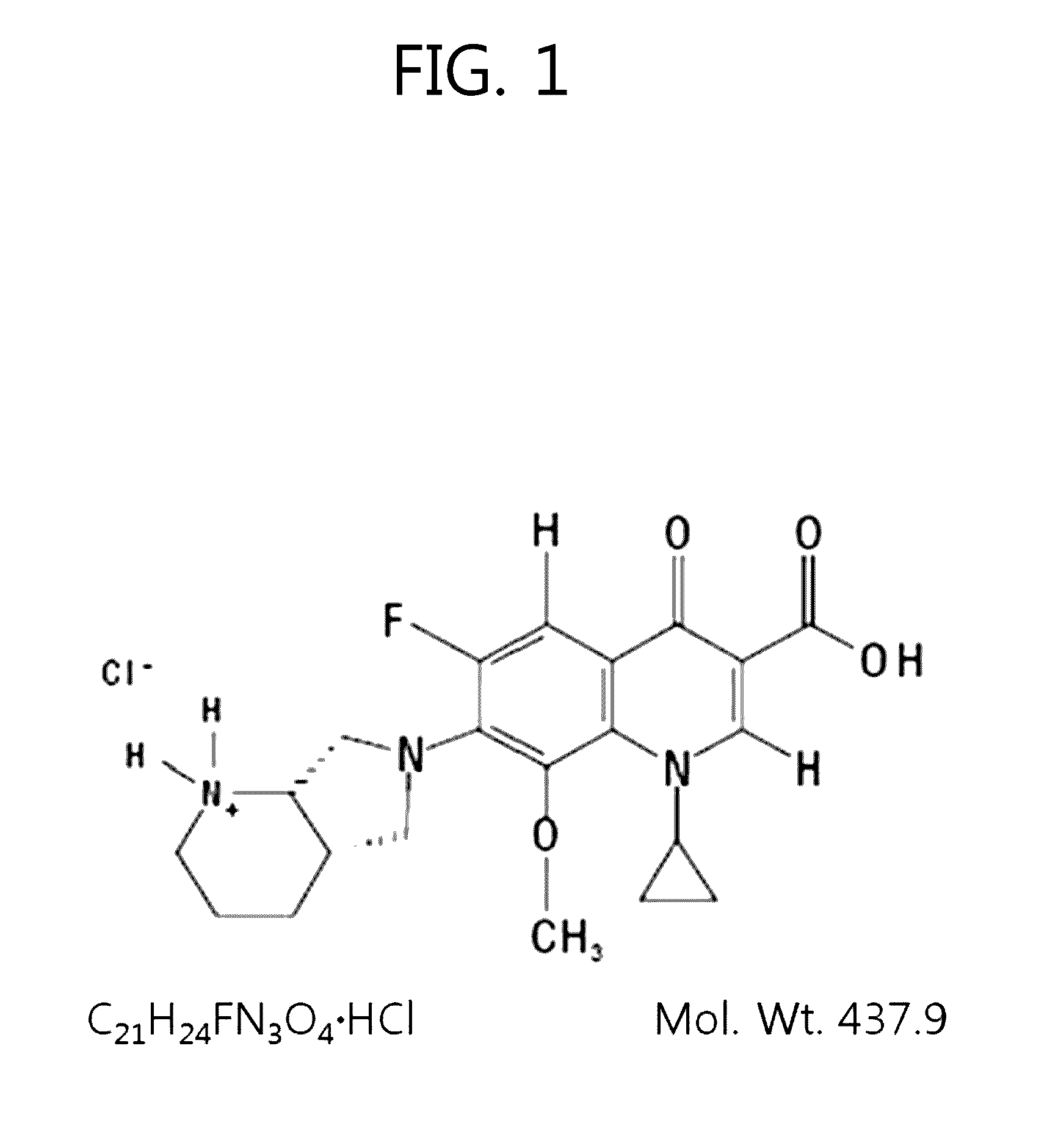
Split nucleic acid aptamer for specifically detecting ciprofloxacin and application of split nucleic acid aptamer
ActiveCN113430204ACutting costsEasy to operateBiological testingDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerQuinolone
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer for specifically detecting ciprofloxacin and application of the nucleic acid aptamer, and belongs to the field of detection of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. The invention provides two nucleic acid sequences, one of which is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the other one of which is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. A detection experiment result on ciprofloxacin in a buffer solution after FAM is modified at a 5'-end of the segment with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 shows that the nucleic acid aptamer provided by the invention is high in combination specificity with ciprofloxacin and is slightly interfered by other fluoroquinolone antibiotics, and the lowest detection limit is as low as 5nM; And the method has the advantages of low requirements on detection environment and time, simplicity in operation and rapidness in detection.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics
ActiveUS20160341734A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingLimited resourcesComputer network
Provided are a method and an apparatus for coordinating inter-cell interference. A user equipment receives from a serving cell information on a downlink timing offset between an interfering cell and an interfered cell and a limited resource measurement, and applies the downlink timing offset to perform measurement using a radio resource indicated for the limited resource measurement, thereby allowing the user equipment to be provided services through the radio resource which substantially mitigates interference, and enhancing connectivity with a network.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Rapid detection method and rapid detection kit of fluoroquinolone antibiotics
InactiveCN101692079AMeet the needs of supervision and inspectionReduce analysis costsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsRural areaPositive control
The invention discloses a rapid detection method and a rapid detection kit of fluoroquinolone antibiotics added in drugs, health care products and foods. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing acid solution to carry out extracting treatment on drugs, health care products and foods, filtering the extracting solution and then carrying out fading process with potassium permanganate solution, adding ferric trichloride solution for coloration, and judging according to the coloration result. The kit of the invention comprises acid solution, potassium permanganate solution, ferric trichloride solution, strainer head, injector and positive control. The method of the invention has low analysis cost, strong ability of resisting interference of coexisting substances, no need for special equipment, high sensitivity, obvious and easily judged coloration result and high accuracy of detection conclusion, and is suitable for rapidly detecting whether fluoroquinolone antibiotics are added in drugs, health care products and foods. The rapid detection kit can be prepared according to the rapid detection method of the invention, thereby meeting the demand for developing food and drug supervision detection in rural areas.
Owner:广东省汕尾市药品检验所
Method for testing fluoroquinolones antibiotics in cosmetics
ActiveCN103969383AImprove detection limitRaise the limit of quantitationComponent separationHybrid typeAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a method for testing fluoroquinolones antibiotics in cosmetics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing a sample: performing vortex oscillation and ultrasonic extraction on the sample by using a 2% formic acid solution and acetonitrile as solvents according to the volume ratio of 2:1, and performing centrifugal treatment and Water Oasis MCM mixed type solid-phase extraction small column purification on an extracting solution so as to obtain a purified solution; (2) testing the purified solution through a machine, and performing a qualitative and quantitative analysis on the target substance by adopting a liquid chromatogram-mass spectrum / mass spectrum method. The method for testing fluoroquinolones antibiotics in the cosmetics is accurate, high in stability, reliable, and high in sensitivity.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Fluoroquinolone antibiotic degrading bacterium and application thereof in compost
ActiveCN113308413AEfficient degradationImprove securityBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyFeces
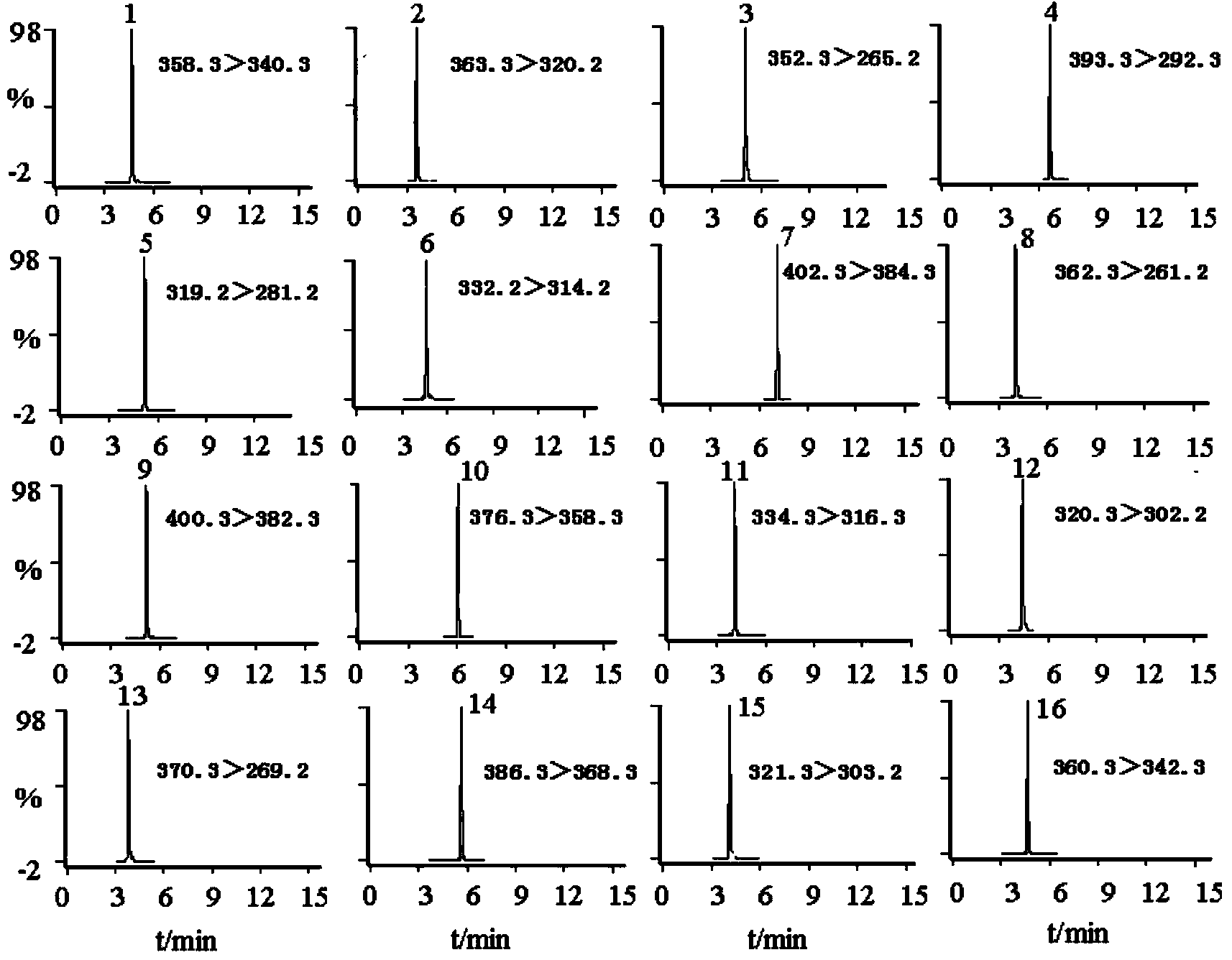
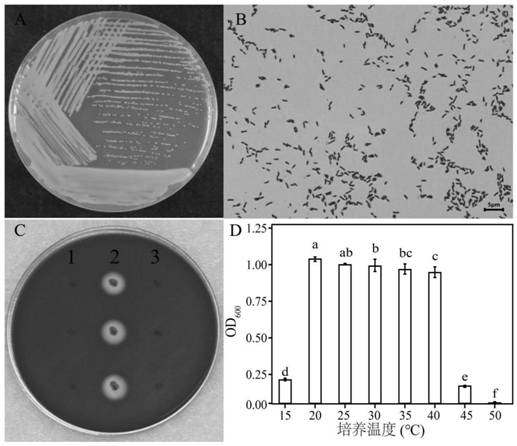
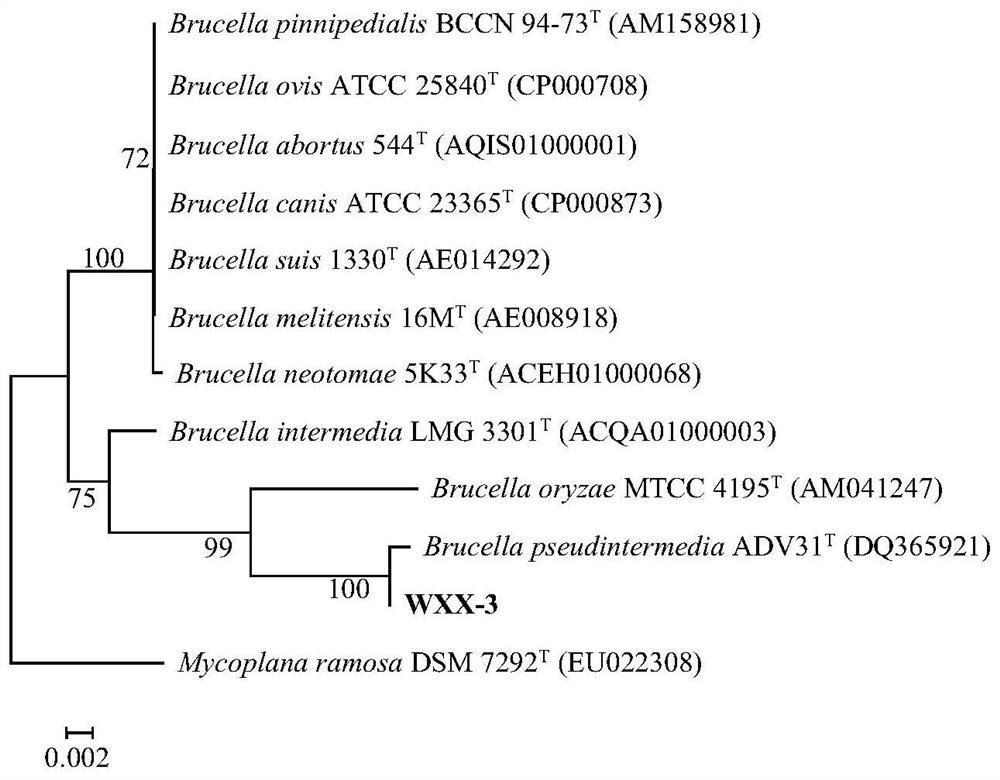
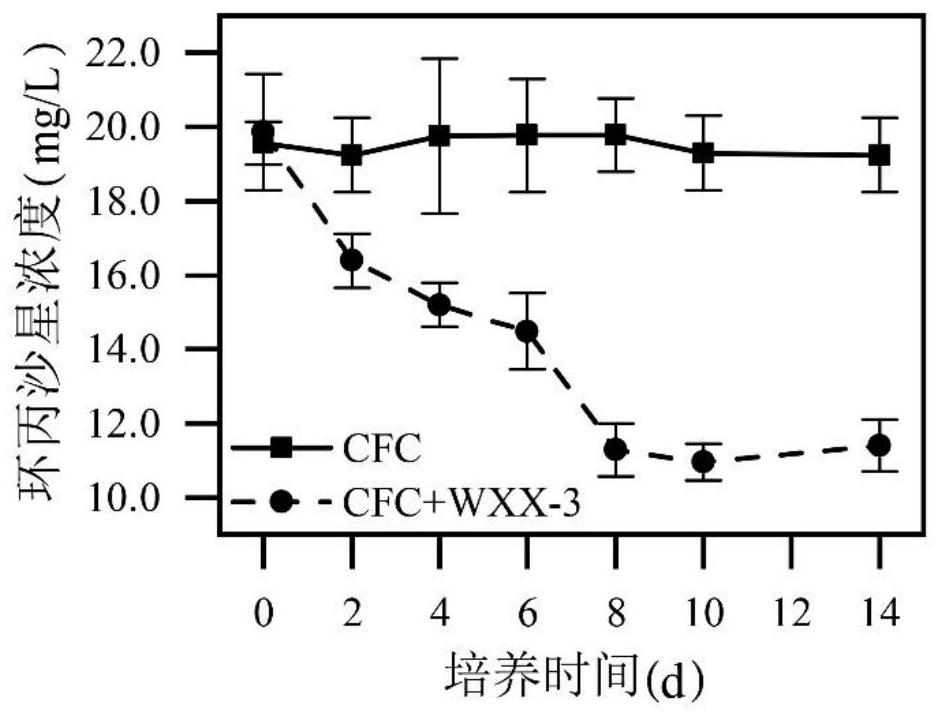
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to a Brucella WXX-3 strain and application of the Brucella WXX-3 strain in degradation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. The preservation number of the strain provided by the invention is CGMCC NO.22259. The WXX-3 strain provided by the invention can efficiently degrade fluoroquinolone antibiotics, and according to the embodiment, the highest degradation rate of ciprofloxacin reaches 44.7% after the strain is added into an LB liquid culture medium containing 20mg / L ciprofloxacin and is cultured in a dark place; besides, the strain is inoculated into livestock and poultry manure for propagation expanding for 8-10 days, then conditioning agents such as wood chips and straw are added for conventional composting for 30 days, and the degradation rate of ciprofloxacin can reach 85.7%; meanwhile, compost prepared from the strain can degrade antibiotic resistance genes, so that the safety of compost products is improved, and the strain is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
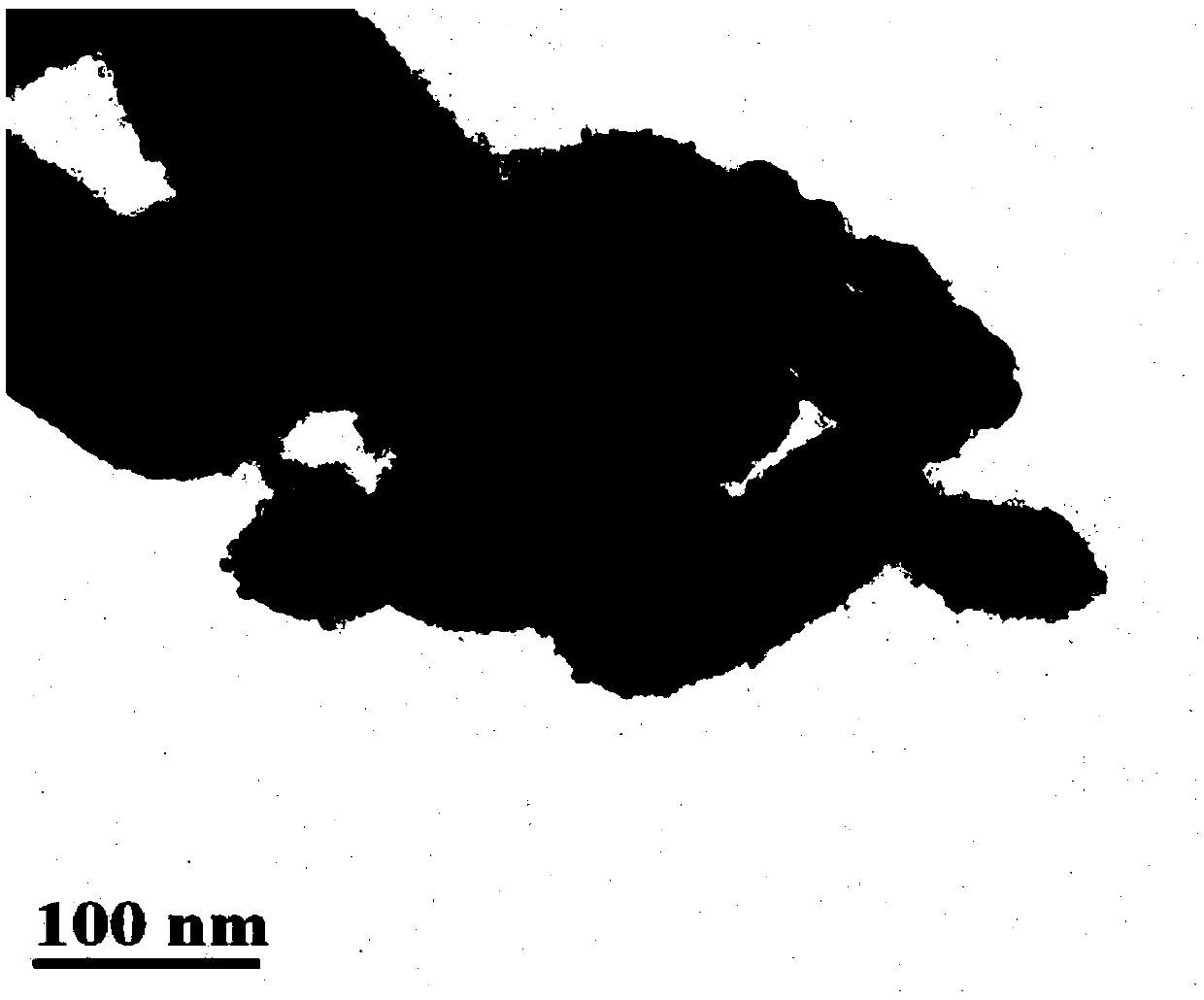
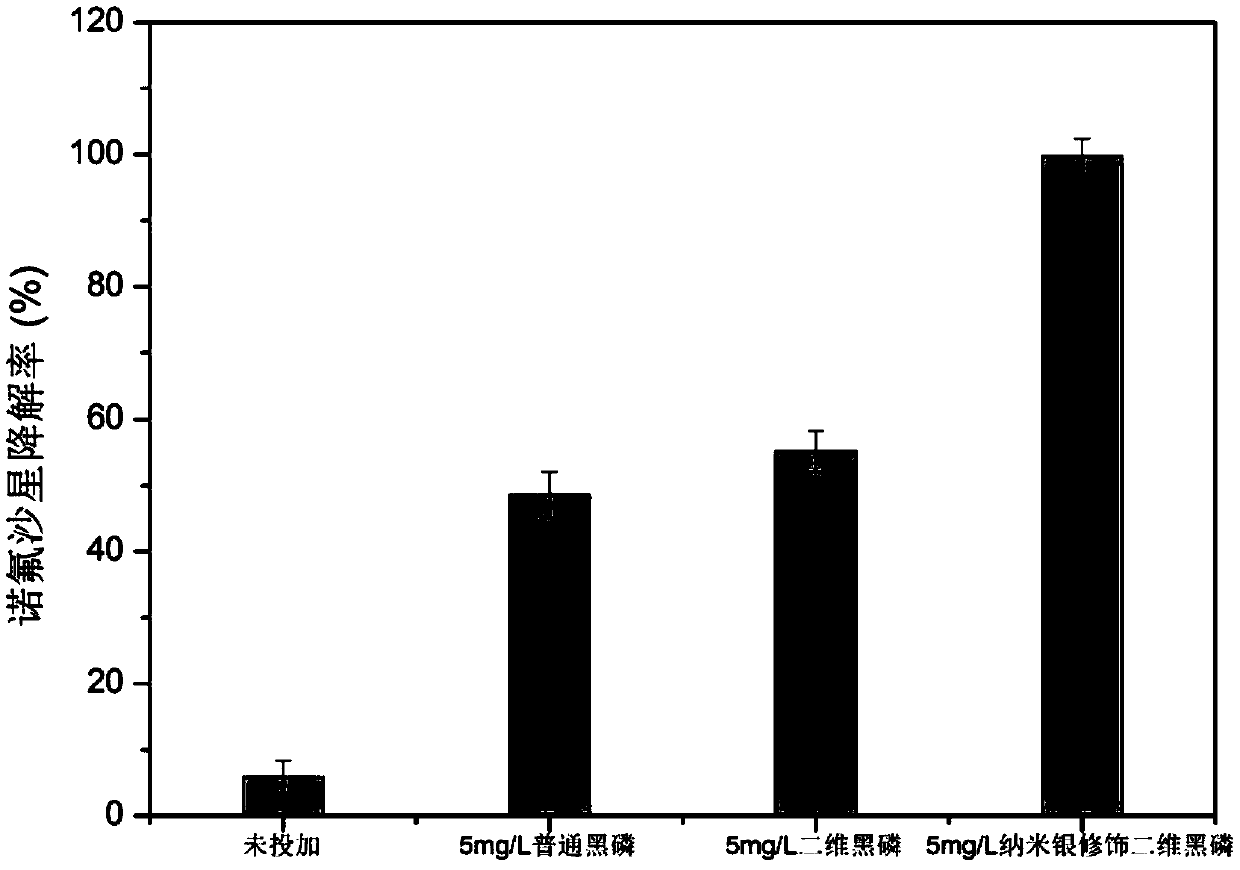
Preparation method of nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material and application of nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material in efficient photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic pollutants
InactiveCN109647449AEasy to operateFast degradationPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFluoro quinolonesUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material and an application of the nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material in efficient photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic pollutants. The method comprises the following steps of: taking the nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material as a degradation material, adding the nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material into wastewater containing antibiotic pollutants, uniformly mixing, andcarrying out magnetic stirring reaction under the condition of ultraviolet light irradiation so as to complete the degradation and removal of antibiotic pollutants in the wastewater. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, high degradation speed and high degradation efficiency; the prepared nano-silver modified two-dimensional black phosphorus composite material has higher specific surface area and photocatalytic activity, is used for carrying out high-efficiency photocatalytic degradation on fluoroquinolone antibiotics such as norfloxacin in wastewater, and has important application prospect and commercial value in the aspect of treating the wastewater containing antibiotics.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of fluoroquinolone antibiotic adsorbent
InactiveCN109225144AImprove adsorption efficiencyLarge adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsN dimethylformamideSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fluoroquinolone antibiotic adsorbent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving metal salt and an organic ligand in N,N-dimethylformamide to obtain a solution A; 2) transferring the solution A into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and reacting for 20-30h at 100-160 DEG C; cooling to room temperature; performing centrifugation, washing and drying to obtain an intermediate product; 3) dissolving the intermediate product and cobalt sulfate in an organic solvent, performing magnetic stirring and cooling to room temperature;performing centrifugation and drying to obtain the quinolone antibiotic adsorbent. The pore diameter of the adsorbent is 1.5-3.2nm, and the specific surface area is 698-1,143m<2> / g. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation steps, low cost, high removal efficiency of quinolone antibiotic pollutants and broad application prospect.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
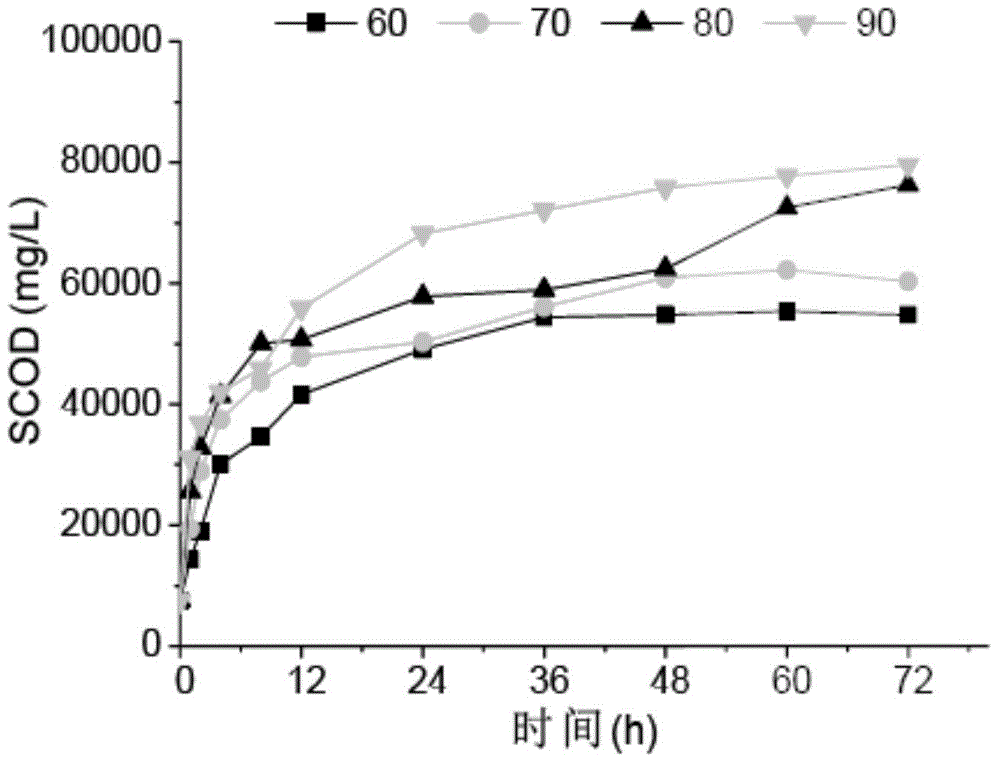
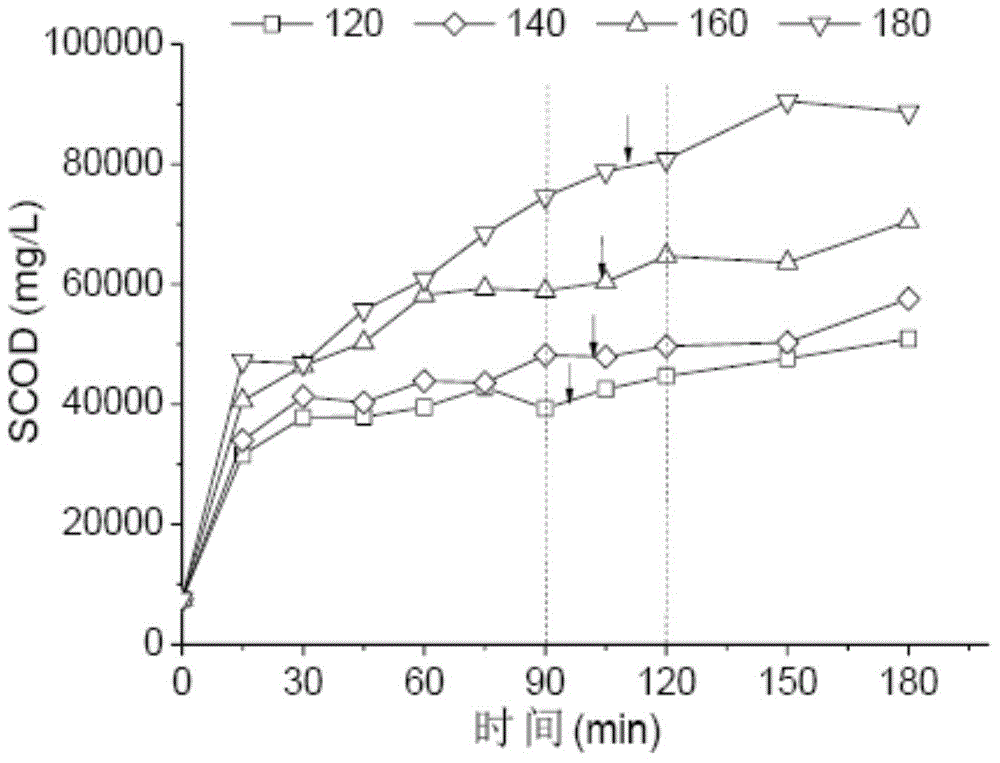
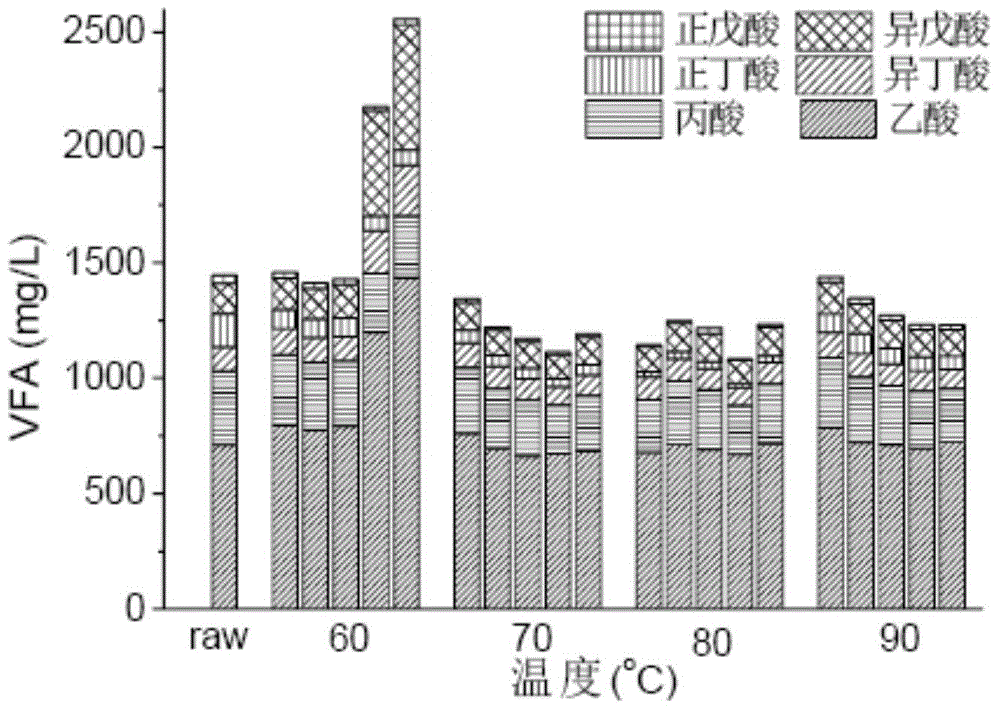
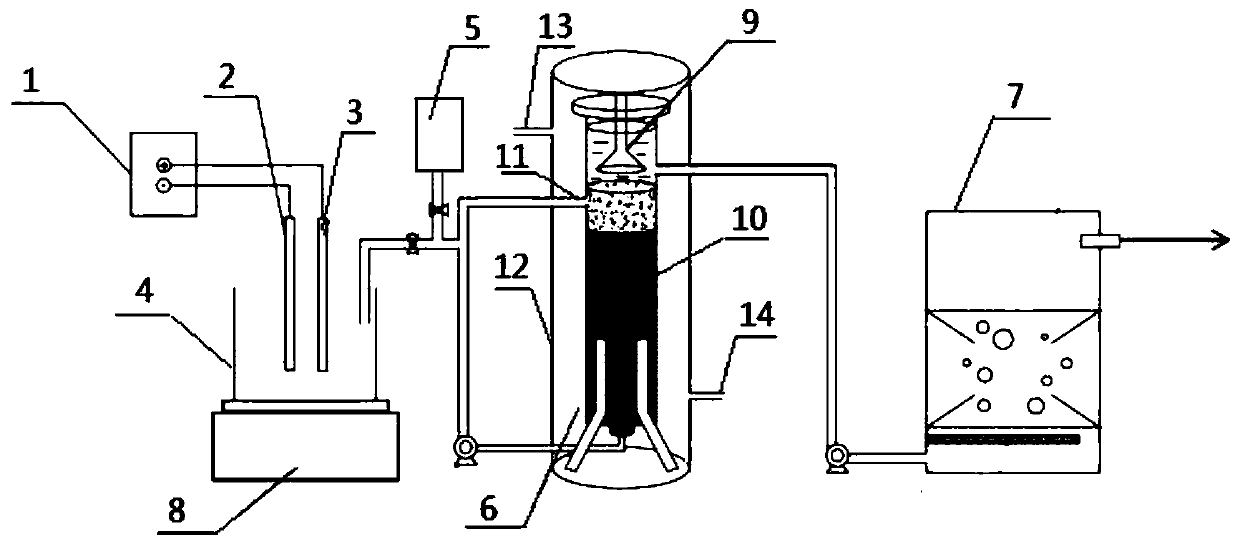
Method for degrading fluoroquinolone antibiotics in sludge through pyrohydrolysis pretreatment and anaerobic digestion
ActiveCN104909533AImprove solubilitySpeed up the hydrolysis stepSludge treatment by pyrolysisWaste based fuelGeneration rateMethane yield
The invention discloses a method for degrading fluoroquinolone antibiotics in sludge through pyrohydrolysis pretreatment and anaerobic digestion, comprising the following steps: (1) pyrohydrolysis pretreatment: 70 grams of dewatered sludge is added into a 100-milliliter inner container made from polytetrafluoroethylene, and the inner container is put into a reaction kettle; the thermocouple of a digital thermometer is attached on the outer surface of the reaction kettle, and the temperature of the outer surface is detected on line; a reaction tank is put into an oven of which the temperature is set to be 120-180 DEG C, the tank is taken out after 180min, and the tank is cooled down to the indoor temperature, and then the tank body is opened for sampling; (2) dissolving out organic matter: a sample subjected to the pyrohydrolysis pretreatment generates dissolved organic matter; (3) anaerobic digestion: the standing time of the sludge subjected to the pyrohydrolysis pretreatment is controlled to be 12-16 days, and the gas production rate and the total gas production rate are monitored; under the test condition of the abovementioned steps, the degradation of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics is realized. The method can enhance the hydrolysis effect and shorten the hydrolysis time to improve the anaerobic digestion performance of the sludge, accelerate the gas generation rate and increase the methane yield, thereby improving the degradation of the antibiotics in the sludge.
Owner:东华(西藏)低碳科技有限责任公司
Harmless treatment method for macrolide and fluoroquinolone antibiotics in livestock and poultry manure
ActiveCN112125709ALow costReduce energy consumptionBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersBiotechnologyLivestock manure
The invention belongs to the technical field of solid waste treatment, and discloses a harmless treatment method for macrolide and fluoroquinolone antibiotics in livestock manure, which realizes resourceful treatment of the livestock manure by adopting microbial fermentation and hermetia illucens culture, and realizes harmless treatment of the livestock manure by virtue of the biological decomposition and biological conversion effects of microorganisms and hermetia illucens, which realizes efficient degradation of the residual antibiotics, does not need to add any chemical substances in the whole process, does not need to hold various reaction conditions such as temperature, saves the livestock manure treatment cost, reduces the treatment energy consumption, and greatly reduces the antibiotic content of the treated livestock manure, and finally, no waste is generated in the whole livestock and poultry manure treatment process, growth of hermetia illucens is achieved after hermetia illucens is bred, the bred hermetia illucens has certain economic value, good economic benefits can be generated, and therefore the method has good application and popularization value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Device and method for treating wastewater containing fluoroquinolone antibiotics
PendingCN109824214AReduce inhibitionPromote degradationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationWater quality
The invention relates to a device and method for treating wastewater containing fluoroquinolone antibiotics, wherein the device comprises a direct current regulated power supply, a cathode, an anode,an electrolytic cell, a domestic sewage collection tank, an upflow sulfate reduction anaerobic sludge bed reactor and a biological contact oxidation tank, the method comprises the following steps of:firstly, pouring wastewater containing fluoroquinolone antibiotics into the electrolytic cell for electrolytic treatment; secondly, pumping the treated wastewater and domestic sewage into the upflow sulfate reduction anaerobic sludge bed reactor for anaerobic treatment; and finally, pumping the anaerobic treated wastewater into the biological contact oxidation tank for biological oxidation treatment.The device is simple to construct, the process is reasonable and the operation is easy; high-concentration pharmaceutical wastewater can be treated to reduce antibiotic residues in sludge; the treatment time can be shortened; the energy consumption can be reduced; the removal rate of the whole system is up to 99.80%; the TOC and COD of effluent are below 20 and 30 mg / L; the effluent has good quality and no odor.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
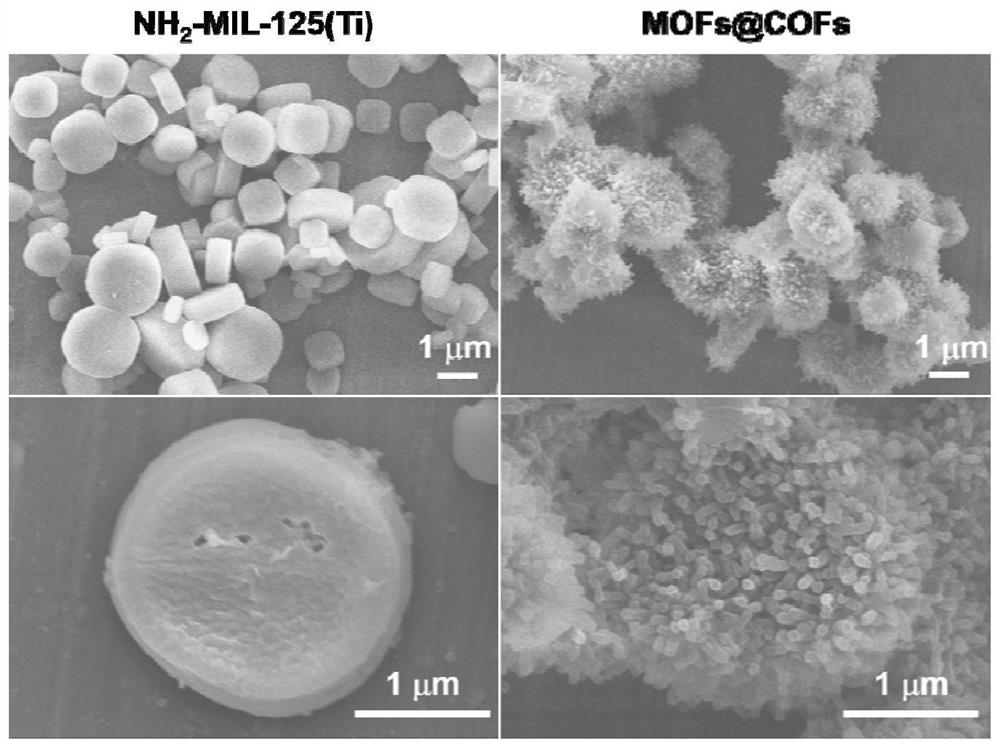
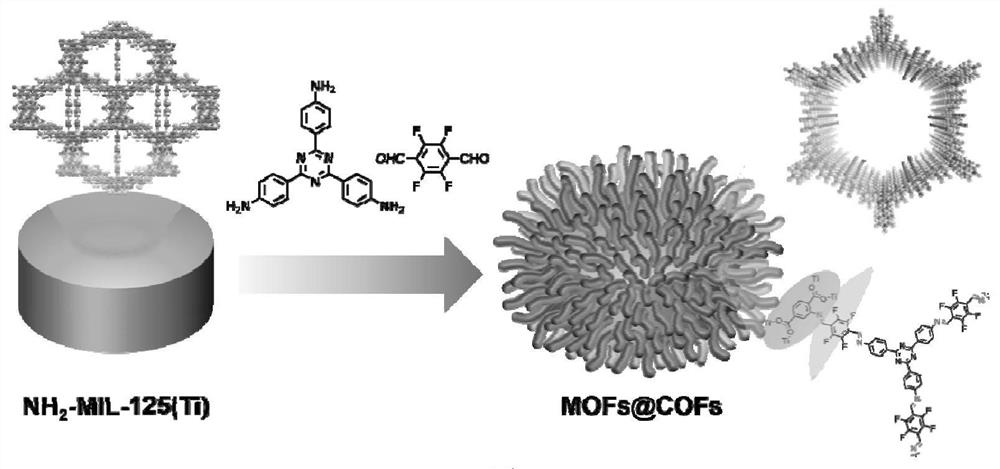
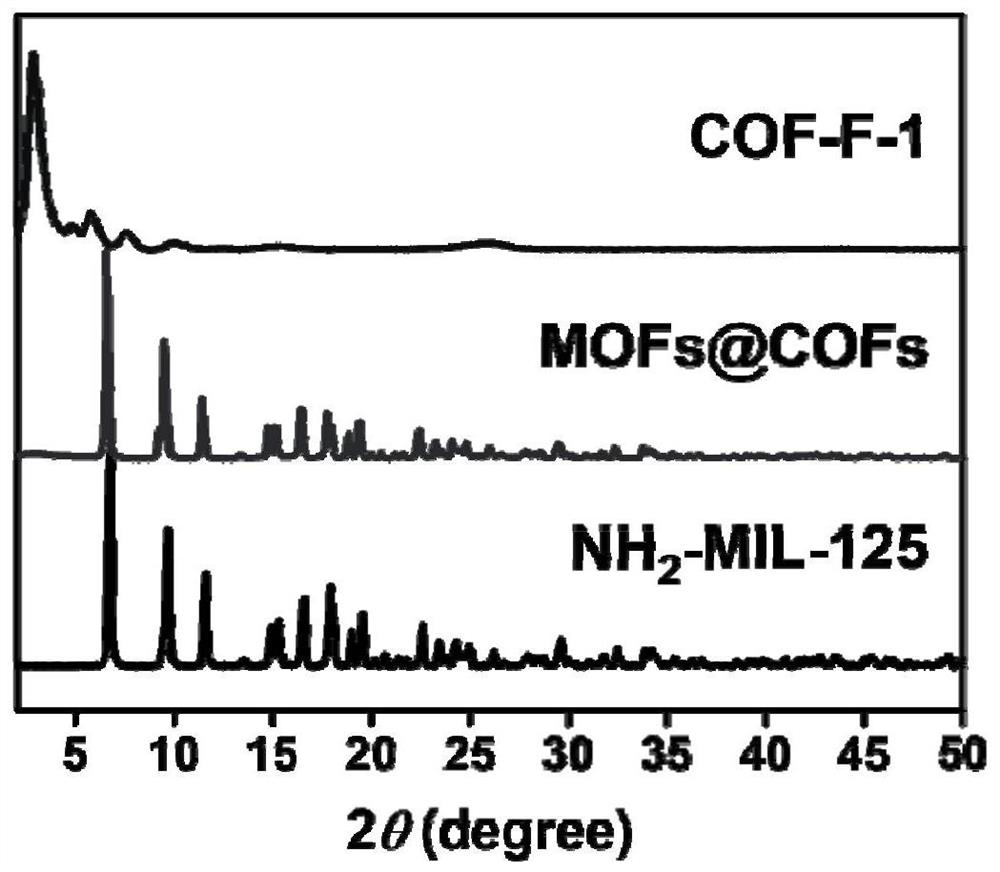
Sea urchin-shaped MOFs@COFs core-shell structure material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113842901AEfficient deliveryEasy to separateIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesSorbentSea urchin
The invention discloses a sea urchin-shaped MOFs@COFs core-shell structure material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of synthetic materials. The sea urchin-shaped MOFs@COFs core-shell structure material disclosed by the invention is prepared from NH2-MIL-125 (Ti) and COFs; according to the COFs, an imine bond connecting structure of 2, 3, 5, 6-tetrafluoro p-dibenzaldehyde and 2, 4, 6-tri (4-aminophenyl)-1, 3, 5-triazine is used as a structural unit. The material presents a sea urchin-like morphology with an NH2-MIL-125 (Ti) nanowafer as a core and a COFs nanowire as a shell layer, the material can be used as an adsorbent and an auxiliary matrix to effectively enrich fluoroquinolone antibiotics in a complex environment and a biological liquid sample, and then surface-assisted laser desorption plasma mass spectrometry is used for analyzing, relatively high analysis speed and relatively high sensitivity are achieved.
Owner:INST OF ANALYSIS GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI (CHINA NAT ANALYTICAL
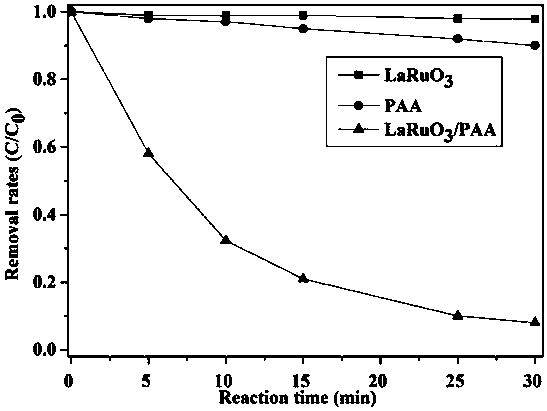
Method of using lanthanum ruthenate-bearing perovskite to activate peracetic acid to degrade fluoroquinolone antibiotics
ActiveCN109574317ANo secondary pollutionHigh catalytic efficiencyWater contaminantsRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsHigh activationActivation technique
The invention discloses a method of using a lanthanum ruthenate-bearing perovskite (LaRuO3) catalyst to heterogeneously activate peracetic acid to treat fluoroquinolone antibiotics wastewater, and relates to the field of water treatment. The invention is intended to solve the problem that existing peracetic acid catalytic activation techniques have low efficiency and may cause secondary pollution,and develops a more efficient, economical and environment-friendly method. In the method, lanthanum ruthenate-bearing perovskite is used for the first time to activate peracetic acid to generate hydroxy free radicals via activation, thereby further oxidizing fluoroquinolone antibiotics in wastewater. The method has evident effect in removing the typical fluoroquinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin, with removal rate reaching about 92% in 30 min. The method has the advantages of high activation efficiency, high efficiency and speed of pollutant removal, wide pH applicable range, lower cost owing to LaRuO3 reusability, good operational convenience and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
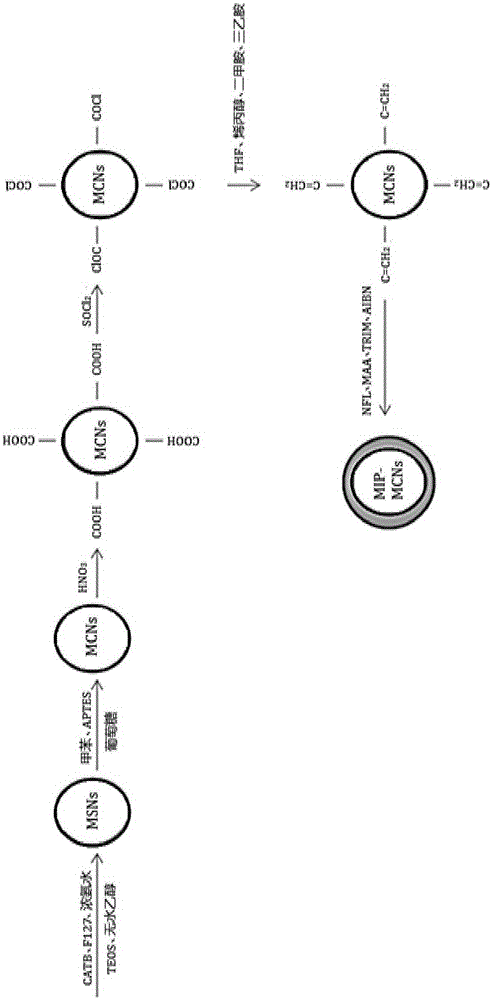
Preparation method of molecularly imprinted polymer packing for fluoroquinolone antibiotics
InactiveCN105175611AImprove bindingImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesMethacrylateAntibiotic Y
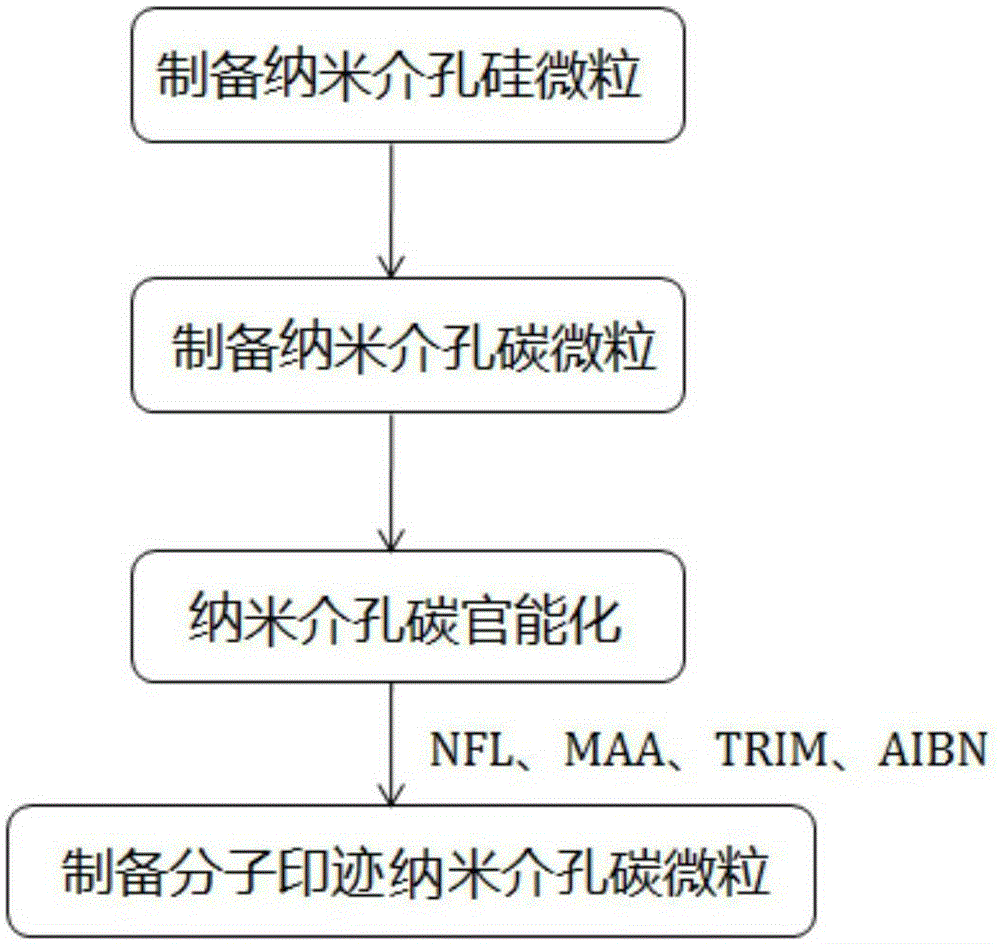
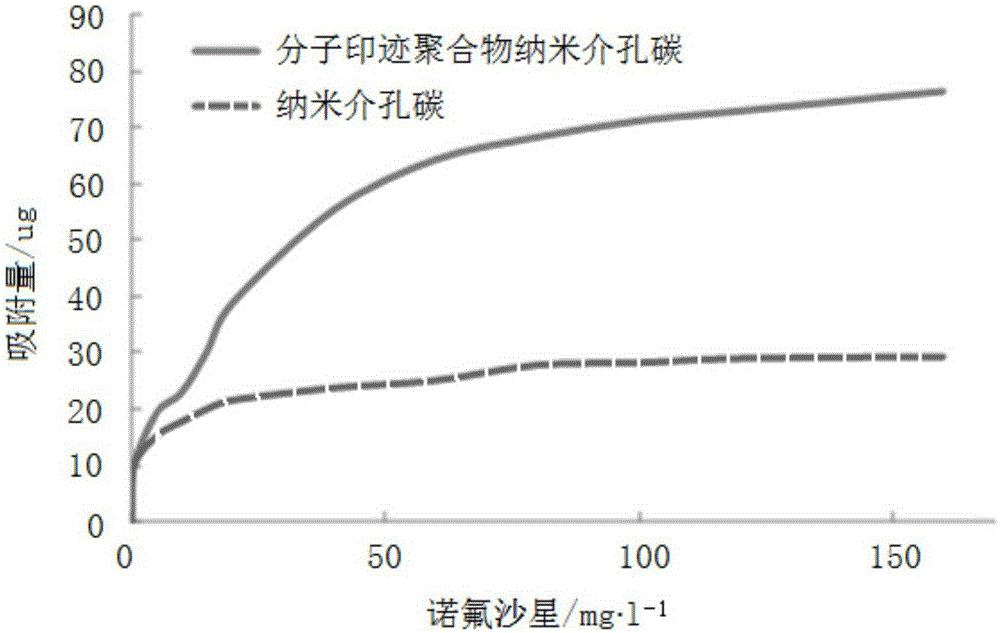
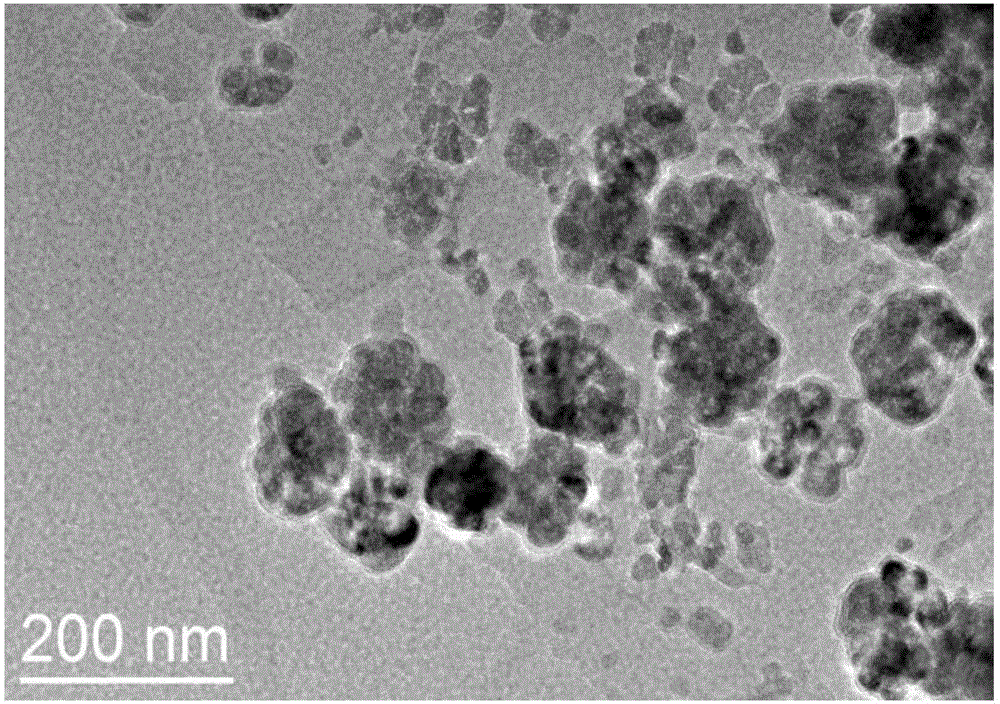
The invention provides a preparation method of molecularly imprinted polymer packing for fluoroquinolone antibiotics. The method includes the steps that tetraethoxysilane serves as a silicon source, polyether F127 serves as a template, and nanometer meso-porous silicon particles are prepared in a CTAB-water system; the nanometer meso-porous silicon particles are subjected to amino-group functionalization, and glucose serves as a carbon source to prepare unloaded nanometer mesoporous carbon particles; methacrylic acid serves as monomers, trimethoxy propyl acrylate serves as a crosslinking agent, MCNs and norfloxacin to which functional groups are added serve as template molecules, and nanometer mesoporous carbon loaded with molecularly imprinted polymer is prepared. The molecularly imprinted polymer packing has the recognition and selective adsorption functions on the fluoroquinolone antibiotics, the adsorption effect is remarkably improved, and recovery and regeneration are easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
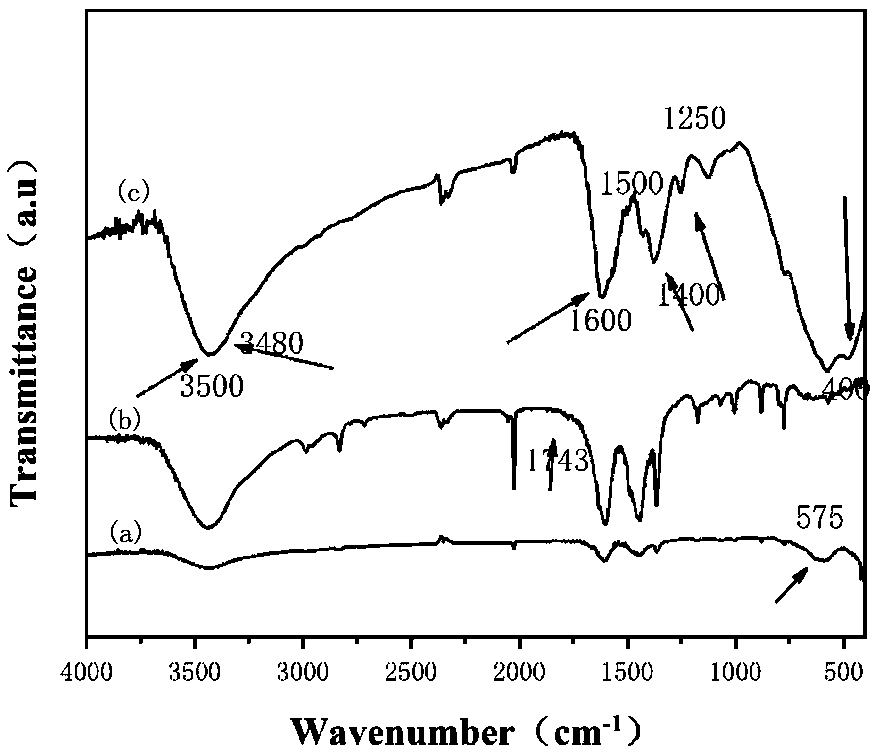
Preparation method of magnetic molecular imprinted nanometer material
InactiveCN105854843ALarge specific surface areaLarge adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAntibiotic YSolvent
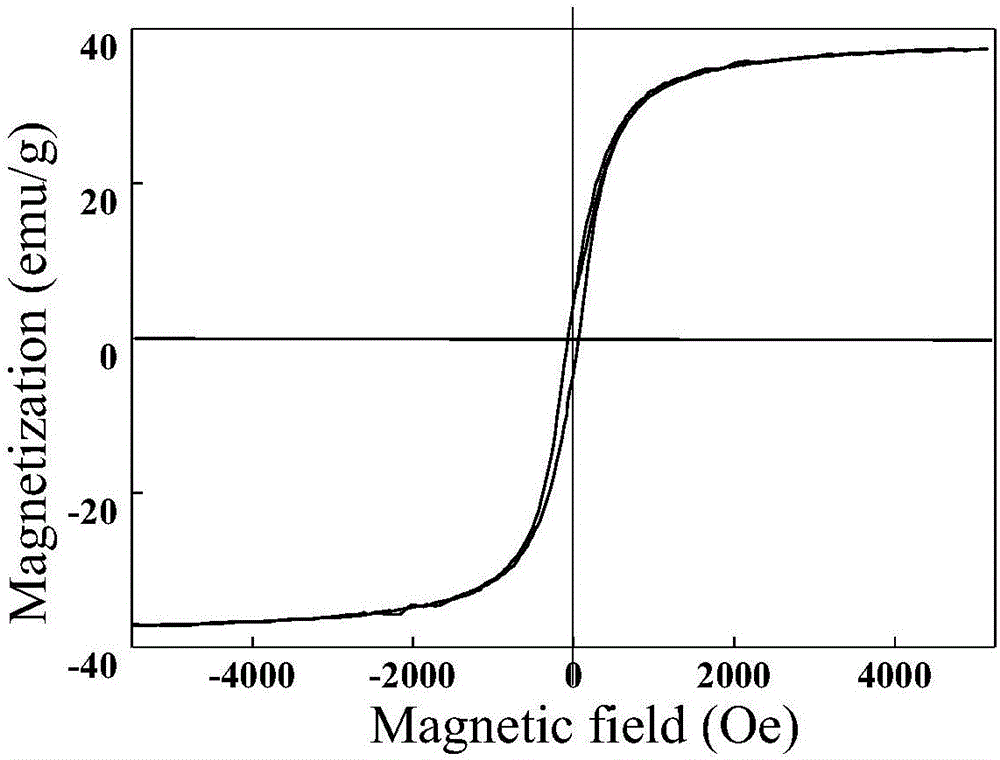
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic graphene molecular imprinted nanometer material and belongs to the fields of environmental pollutant removal and detection. The magnetic molecular imprinted nanometer material is of a core-shell structure formed by wrapping grapheme / Fe3O4 with dopamine molecularly imprinted polymer. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing graphene oxide and FeCl3, then conducting a hydrothermal reaction to prepare grapheme / Fe3O4, adopting sarafloxacin as template molecules, adopting dopamine as a monomer, adopting Tris-HCl solvent with pH being 8.5 as solvent, after the materials are mixed, conducting polymerization under an oscillation condition, collecting products of a polymerization reaction with magnets, and after the template molecules are eluted, conducting drying, so that the magnetic molecular imprinted nanometer material is obtained. The magnetic graphene molecular imprinted nanometer material has a high adsorption rate, a high adsorption capacity and a high specificity for fluoroquinolone antibiotics, and has great application value in the field of adsorbing and removing the fluoroquinolone antibiotics in a water body.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation and application of trimethylsilyl imidazole adsorbentfor antibiotics
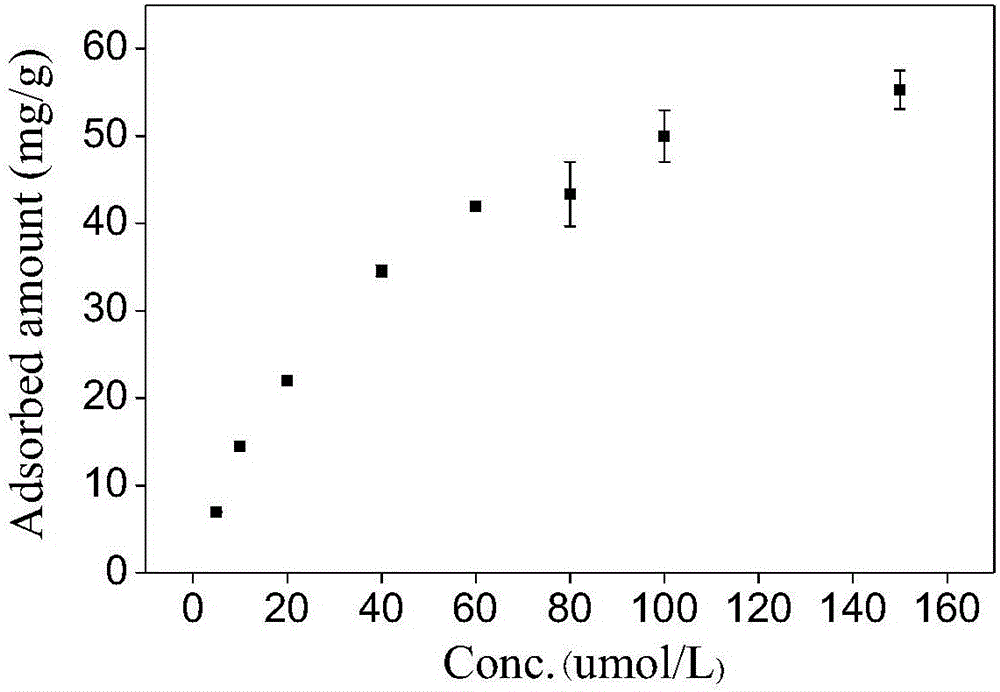
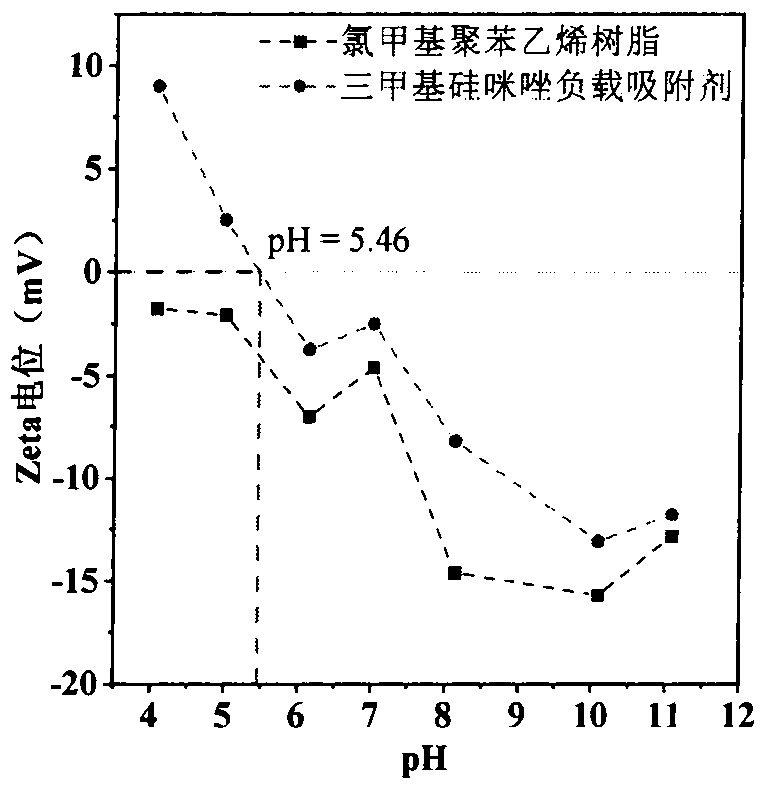
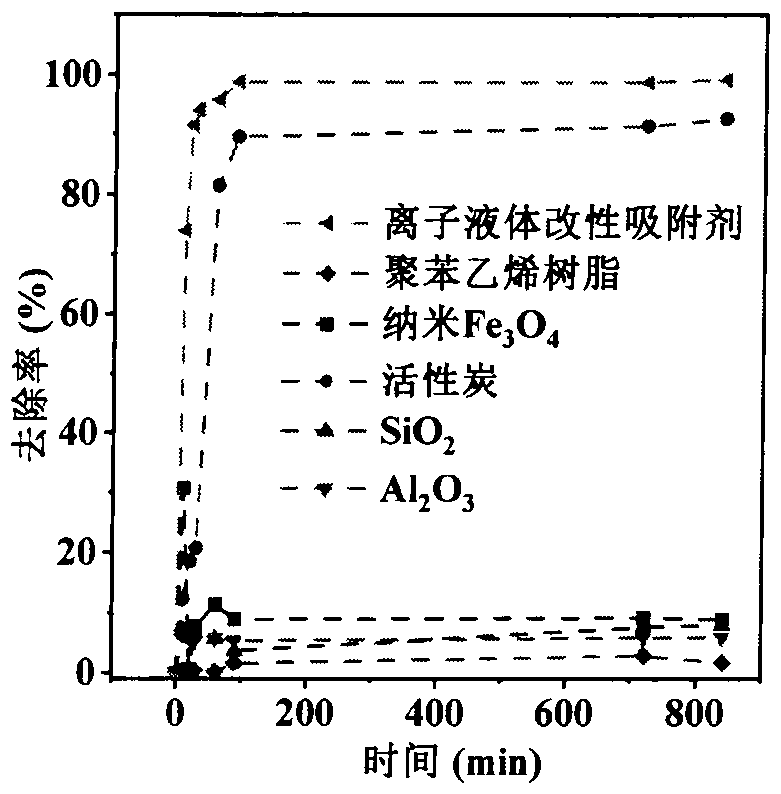
PendingCN113600151AImprove adsorption capacityFast reaction kineticsOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPolystyreneSulfanilamide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a 1-(trimethylsilyl) imidazole ionic liquid adsorbent for antibiotics in a water body and an applied synthesis method and application thereoft, and belongs to the technical field of water body organic micropollutant treatment. According to the invention, the 1-(trimethylsilyl) imidazole ionic liquid is grafted on the surface of the chloromethyl polystyrene resin through chemical bonding so that the product is prepared. The specific application effect of the synthesized 1-(trimethylsilyl) imidazole ionic liquid adsorbent in adsorption of four typical antibiotics including beta-lactam antibiotics (ceftiofur), sulfonamide antibiotics (sulfamethoxazole), fluoroquinolone antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) and tetracycline antibiotics (aureomycin) is released for the first time; the synthesis method is simple and convenient to operate and mild in reaction condition, and the product has the advantages of large adsorption quantity, fast reaction kinetics, high adsorption efficiency and the like on various antibiotics.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pharmaceutical compositions containing a fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug
ActiveUS20090306128A1Improve homogeneityEqually distributedAntibacterial agentsBiocideBioavailabilityFluoroquinolone Antibiotic
Pharmaceutical compositions containing a fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug are disclosed. The compositions exhibit improved homogeneity, improved bioavailability, lower turbidity or a combination thereof. The composition can be use as otic or nasal compositions, but are particularly useful as ophthalmic compositions.
Owner:HARROW HEALTH INC
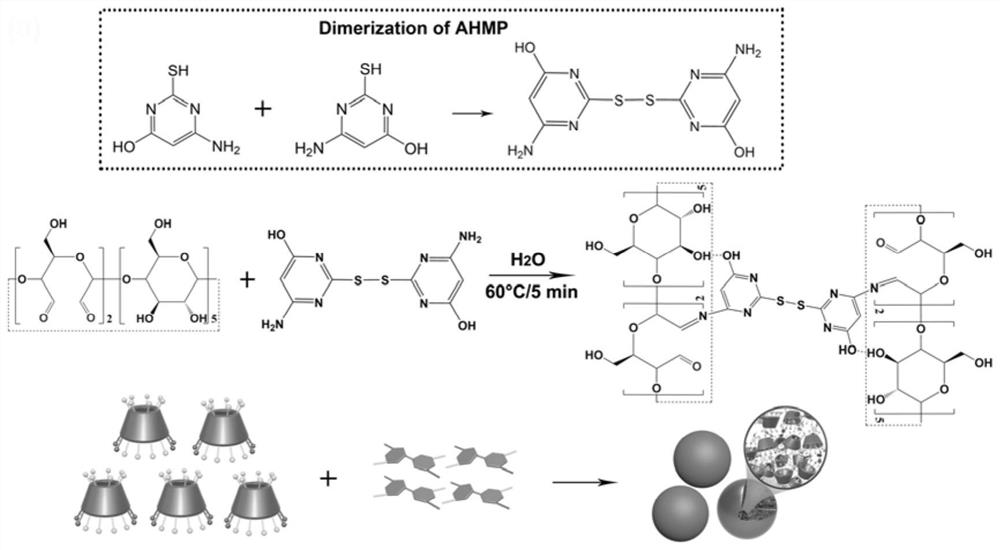
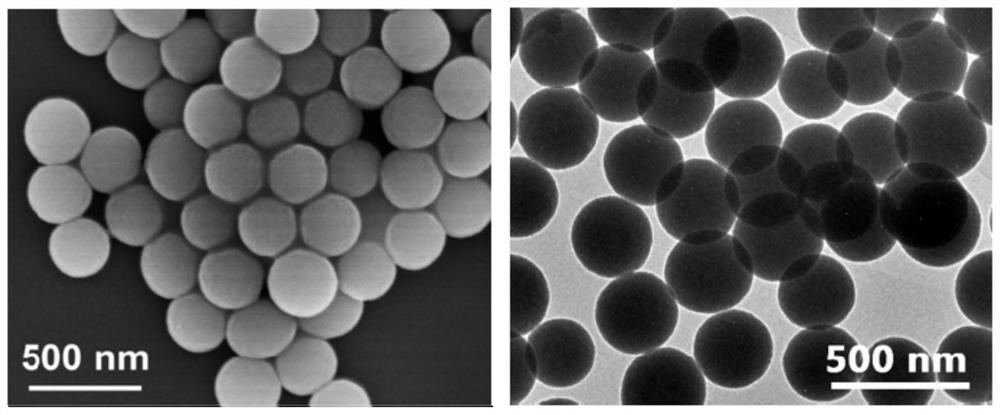
Rapid water-phase synthesis method of multifunctional cyclodextrin polymerized microspheres
ActiveCN112516112AHas an alkaline response functionHas alkaline response decomposition propertiesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicrosphereCyclodextrin
The invention relates to a rapid water-phase synthesis method of multifunctional cyclodextrin polymerized microspheres. The rapid water-phase synthesis method comprises the following steps of: pre-oxidizing beta-cyclodextrin by using sodium periodate to obtain aldehyde cyclodextrin at first; then, preparing an aldehyde cyclodextrin aqueous solution and performing heating; and then adding a cross-linking agent 4-amino-6-hydroxyl-2-mercaptopyrimidine, performing stirring for reaction, and carrying out post-treatment to obtain cyclodextrin polymerized microspheres; meanwhile, before the cross-linking agent is added, an active drug or a modifier can be introduced into a reaction system, so that the loading of the active drug and the preparation of the modified cyclodextrin polymerized microspheres can be realized. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, mild and green, and can quickly react in an open water-phase system under a low-temperature condition; the product has a good alkaline response function and can be used for various oral intestinal drug delivery systems; and in addition, the boron-modified cyclodextrin polymerized microspheres show an excellent rapid adsorption effect on fluoroquinolone antibiotics, and have a better application prospect in the field of waste drug treatment.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
In metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) material based on tridentate carboxylic acid ligands, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110776648AImprove stabilityStrong fluorescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsCarboxylic acidSolvothermal reaction
The invention discloses an In metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) material based on tridentate carboxylic acid ligands as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technicalfield of crystalline materials. The In MOFs material based on the tridentate carboxylic acid ligands have a chemical formula as [In(3)-(OH)(3)-(CTTA)(2)], wherein the H(3)-CTTA is 5'-(4-carboxyphenyl)-2',4',6'-trimethyl-[1',1':3',1''-p-terphenyl]-4,4''-dicarboxylic acid. The In MOFs material based on the tridentate carboxylic acid ligands is synthesized under closed conditions by the step of allowing solvothermal reaction of the organic ligands 5'-(4-carboxyphenyl)-2',4',6'-trimethyl-[1',1':3',1''-p-terphenyl]-4,4''-dicarboxylic acid (the 'H(3)-CTTA') with indium nitrate in N,N-dimethylformamide, thereby obtaining crystals of the MOFs material. The In MOFs material based on the tridentate carboxylic acid ligands displays rare water stability of In MOFs, and shows selective quenching by fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com