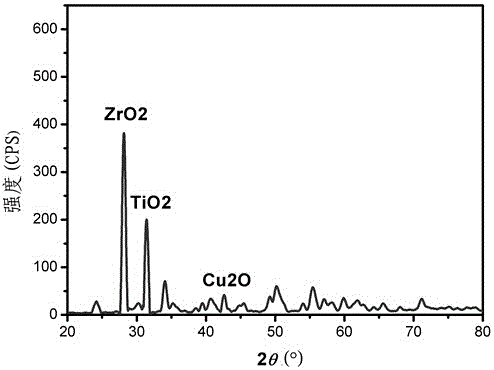
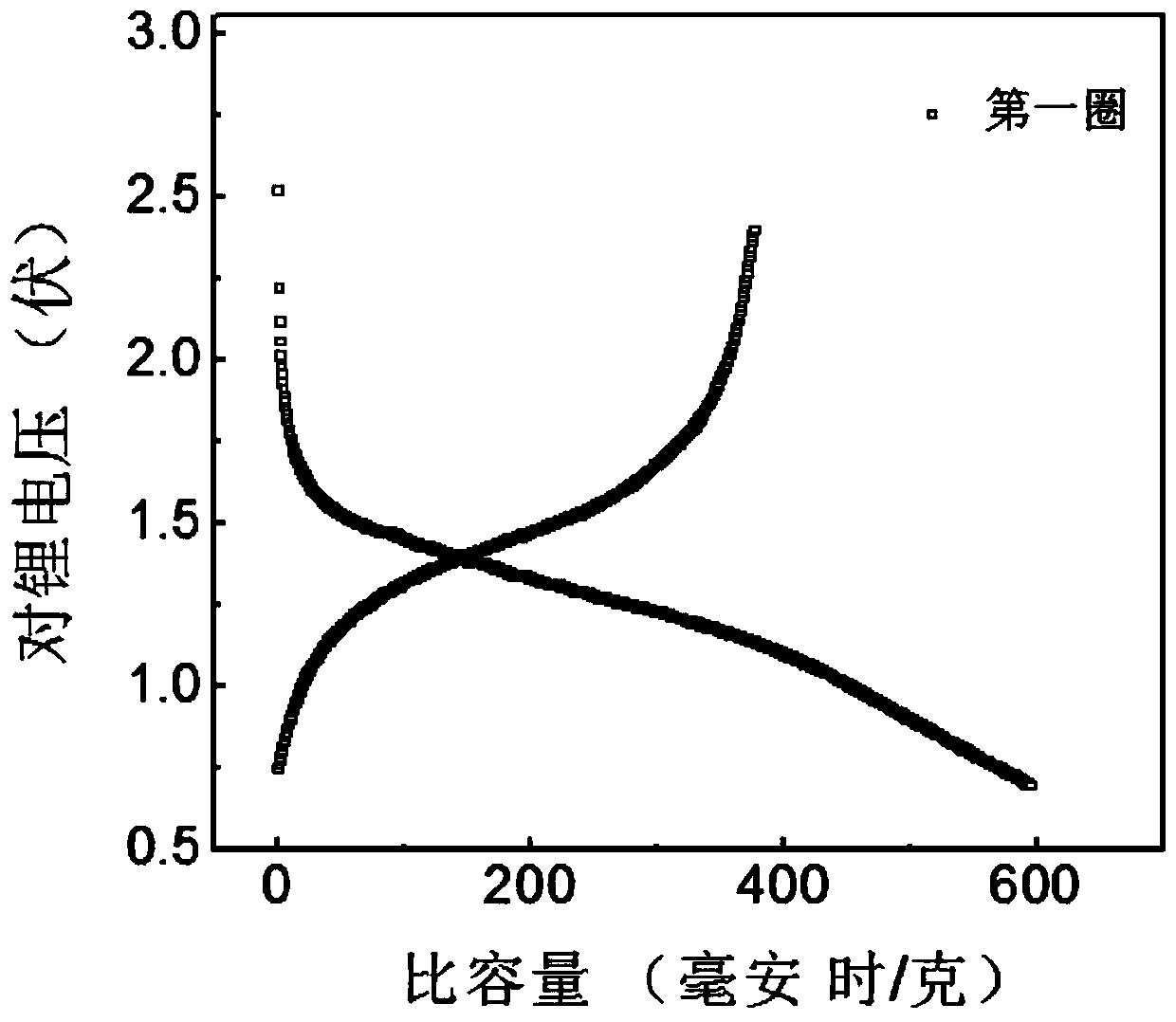
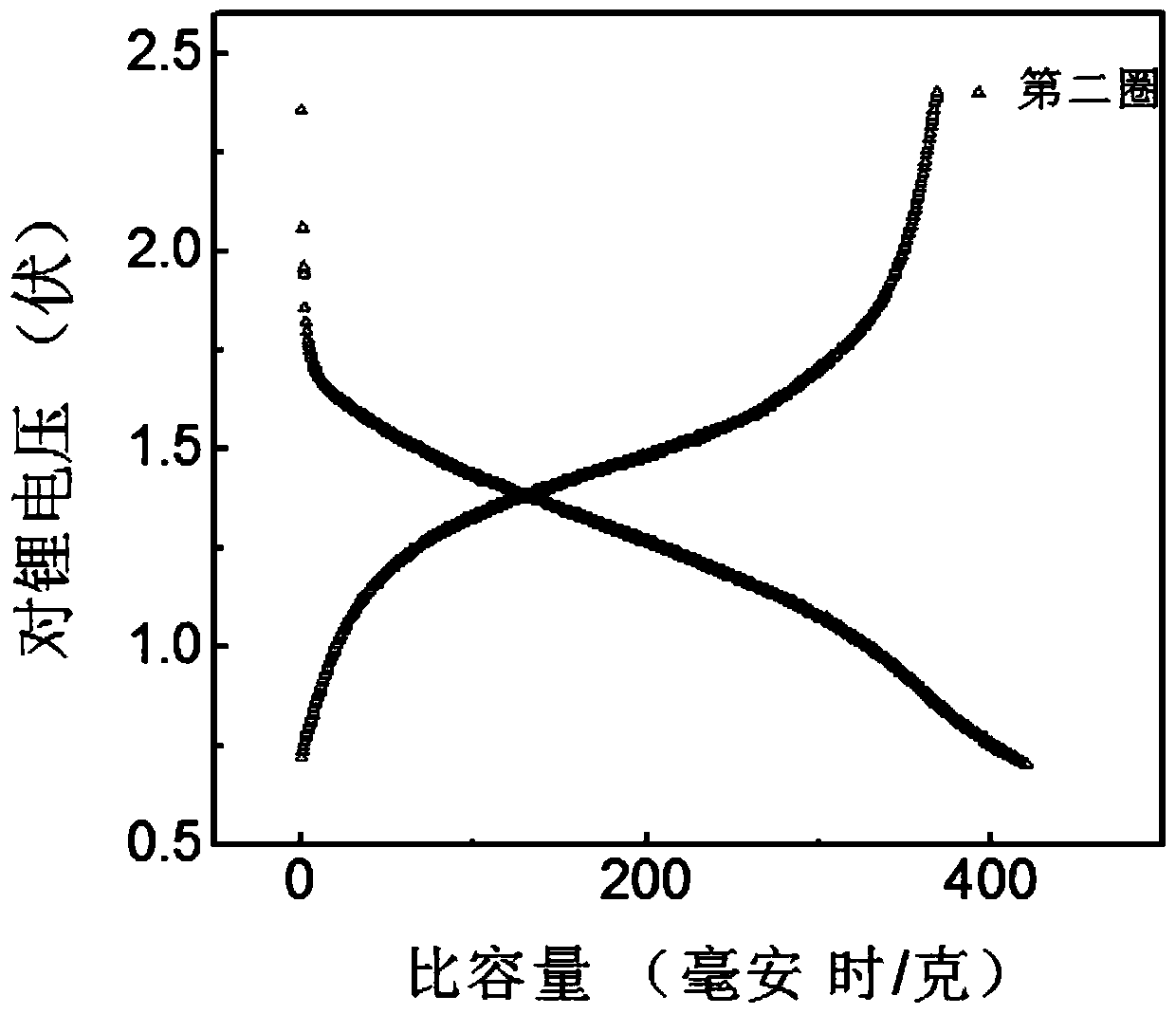
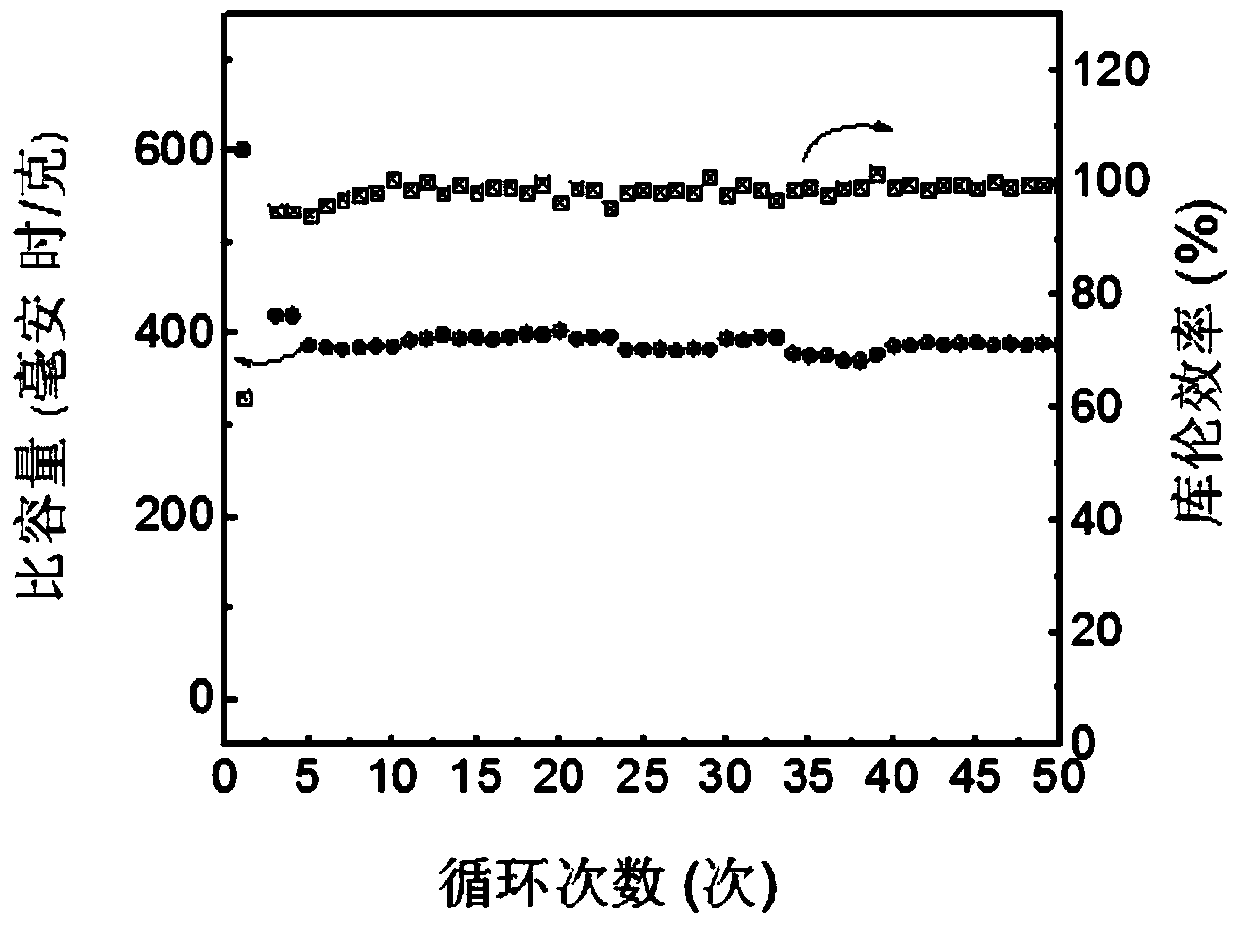
Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Fast reaction kinetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
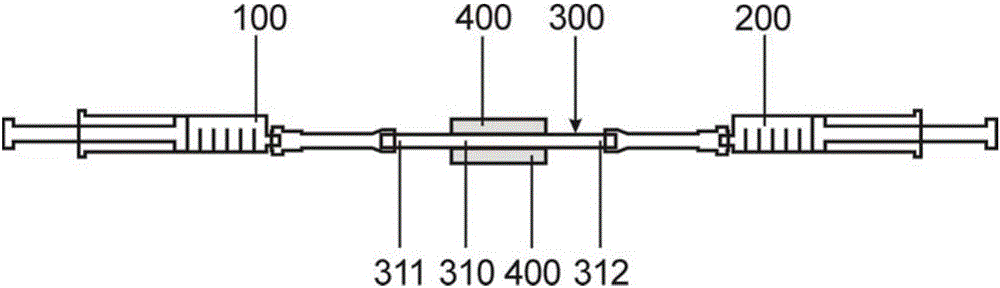
Enriching method of circulating tumor cells
InactiveCN103630440AEasy to detectFast reaction kineticsPreparing sample for investigationMagnetic nanospheresPolymerase chain reaction
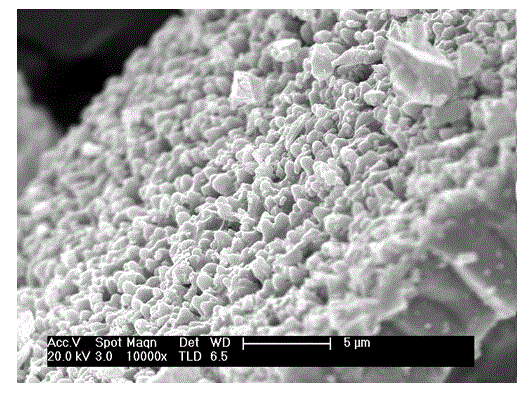
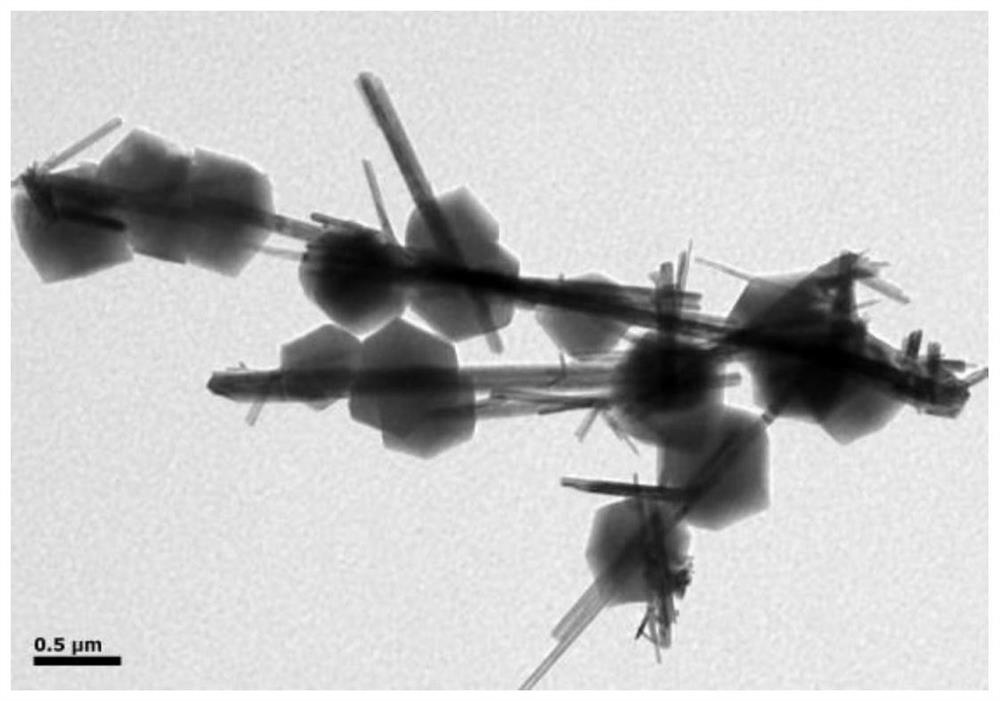
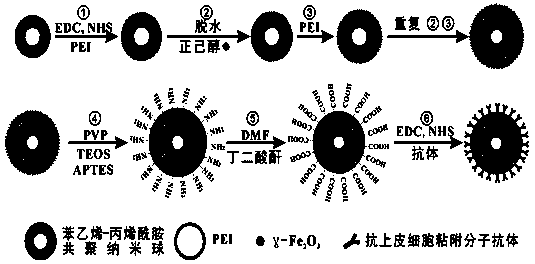
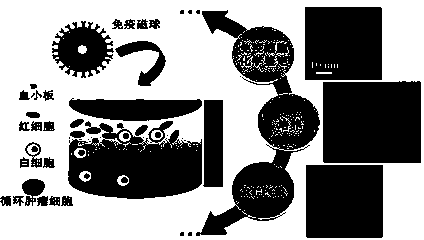
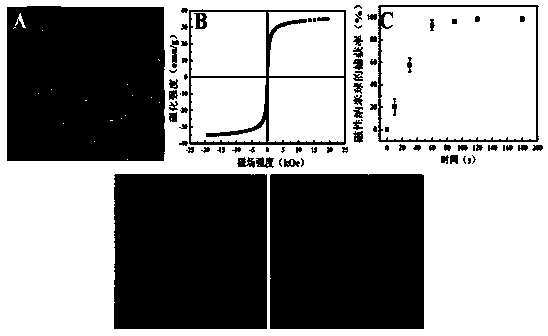
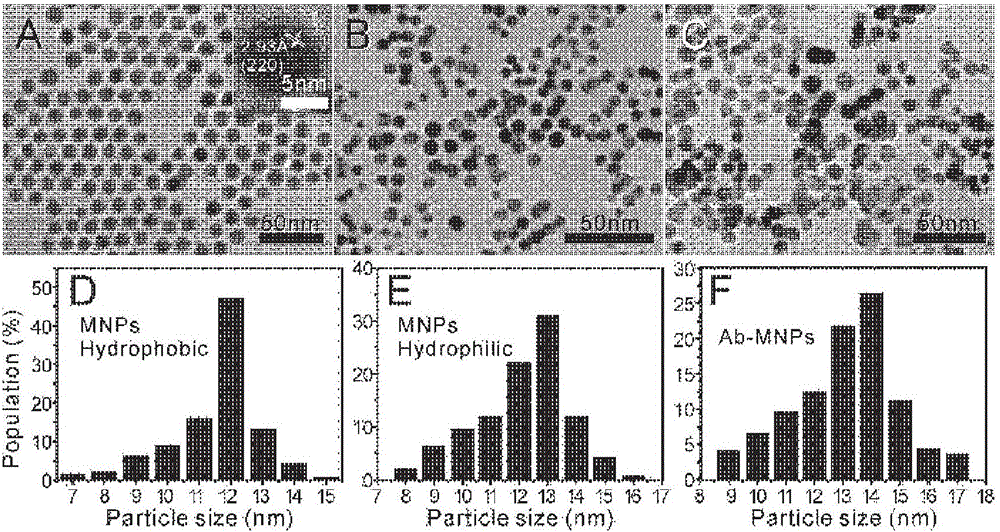
The invention provides an enriching method of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and a kit thereof. The enriching method is applied to quickly and efficiently enriching CTCs from blood. The enriching method comprises the following steps of coupling an anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) antibody onto a magnetic nanosphere to prepare an immune-magnetic bead; adding the immune-magnetic bead into a blood sample for hatching for 5 minutes, and realizing separating, enriching and purifying of CTCs by the steps such as magnetic separating and washing. The enriching method disclosed by the invention is high in capturing efficiency, short in enriching time, good in specificity and very reliable. Activity ratio of the captured cell is kept at (90.5 + / -1.2)%, and the captured cell can be directly used for cultivation, reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immune cell chemical analysis. Besides, the enriching method provides powerful means for detecting and researching CTCs, and has extremely important medical significance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
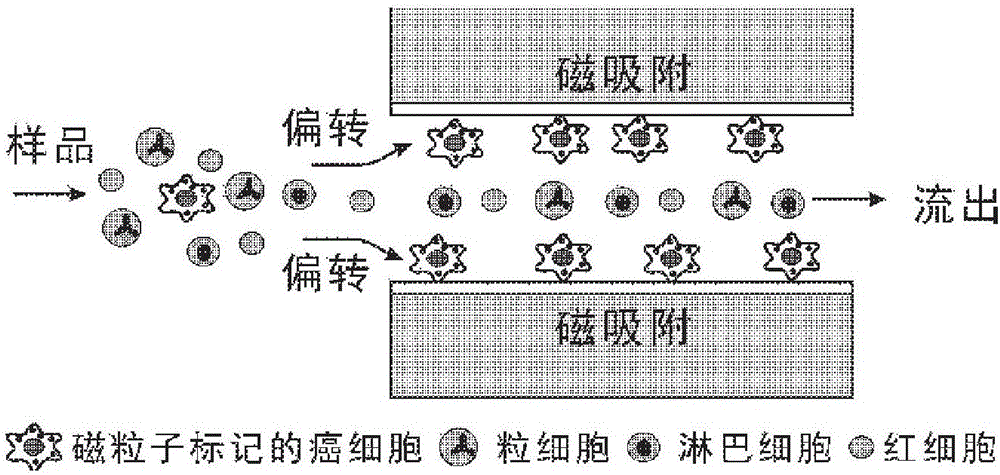
Method for capturing tumor cells by aid of magnetic nano-particles and application of method
InactiveCN106222161AQuick captureEasy to implementBiomass after-treatmentElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentMedicineNanoparticle
The invention discloses a method for capturing cells by the aid of magnetic nano-particles. The method includes that the magnetic nano-particles and samples with the circulating tumor cells (CTC) are blended with one another, the circulating tumor cells CTC and the magnetic nano-particles are combined with one another to obtain circulating tumor cells CTC with magnetic nano-particle markers, the samples with the circulating tumor cells CTC with the magnetic nano-particle markers flow through capillary tubes with the sectional inner diameters of 1 mm at the flow rate of 2-10 ml per hour, magnetic fields are applied to the peripheries of the capillary tubes when the samples flow through the capillary tubes, the circulating tumor cells CTC with the magnetic nano-particle markers can be deflected under the effects of the magnetic fields to be attracted by the magnetic fields, but normal cells which are not marked by the magnetic nano-particles in the samples can continue flowing through magnetic field zones to be collected by sample collecting pools; the magnetic fields on the peripheries of the capillary tubes are removed, the circulating tumor cells CTC, which are adsorbed on the walls of the capillary tubes, with the magnetic nano-particle markers are washed down by solution and are collected to obtain the tumor cells. The method has the advantages that the circulating tumor cells can be quickly captured by the aid of the method, and the method is easy and convenient to implement, easy to operate and high in universality.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
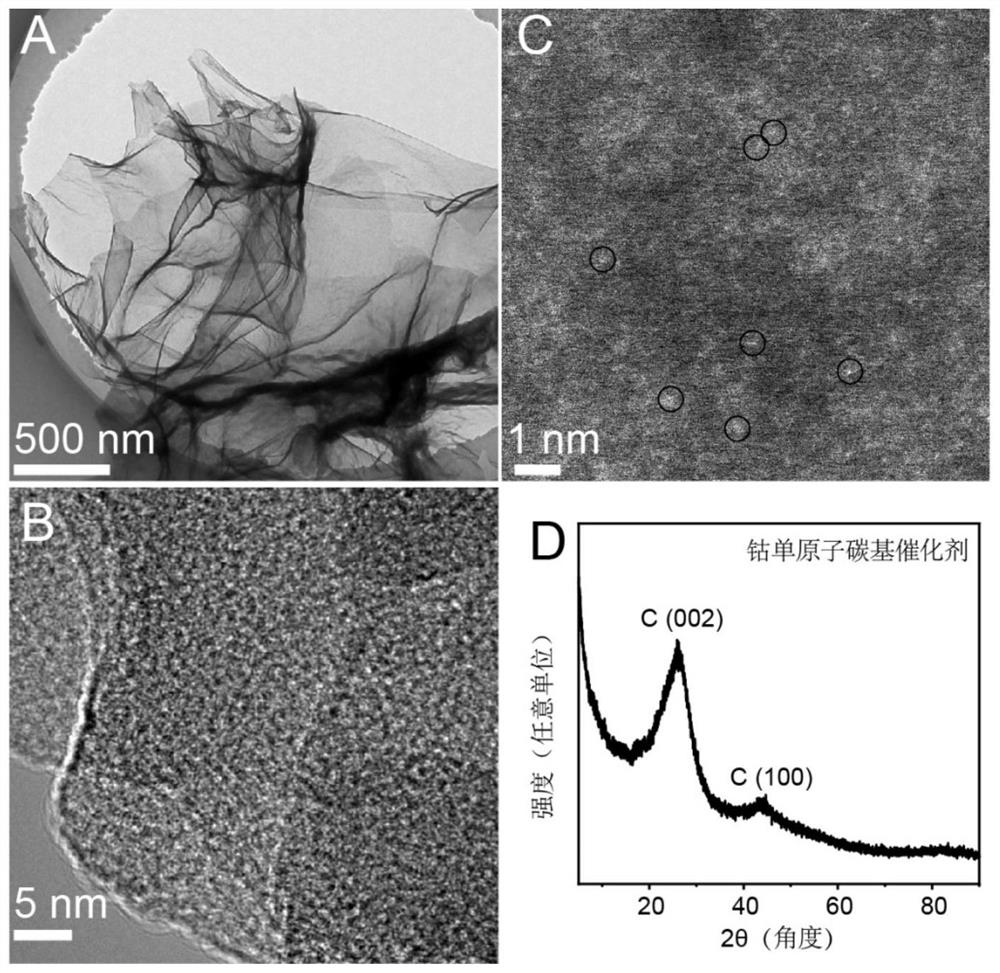
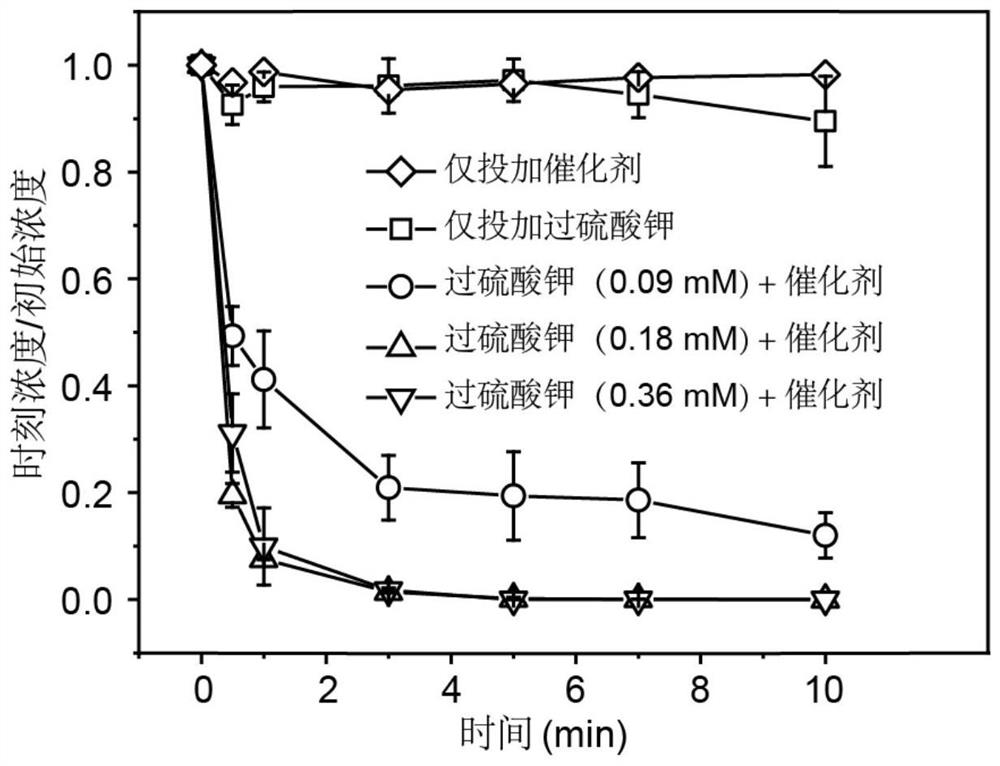
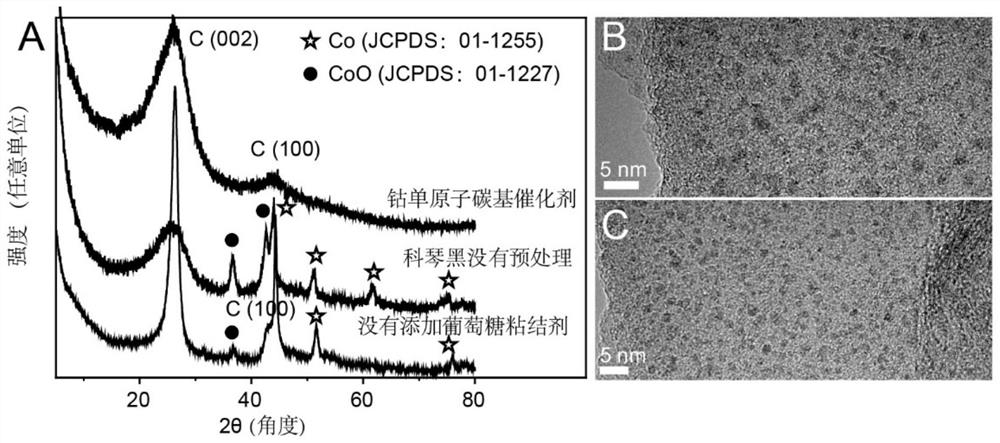
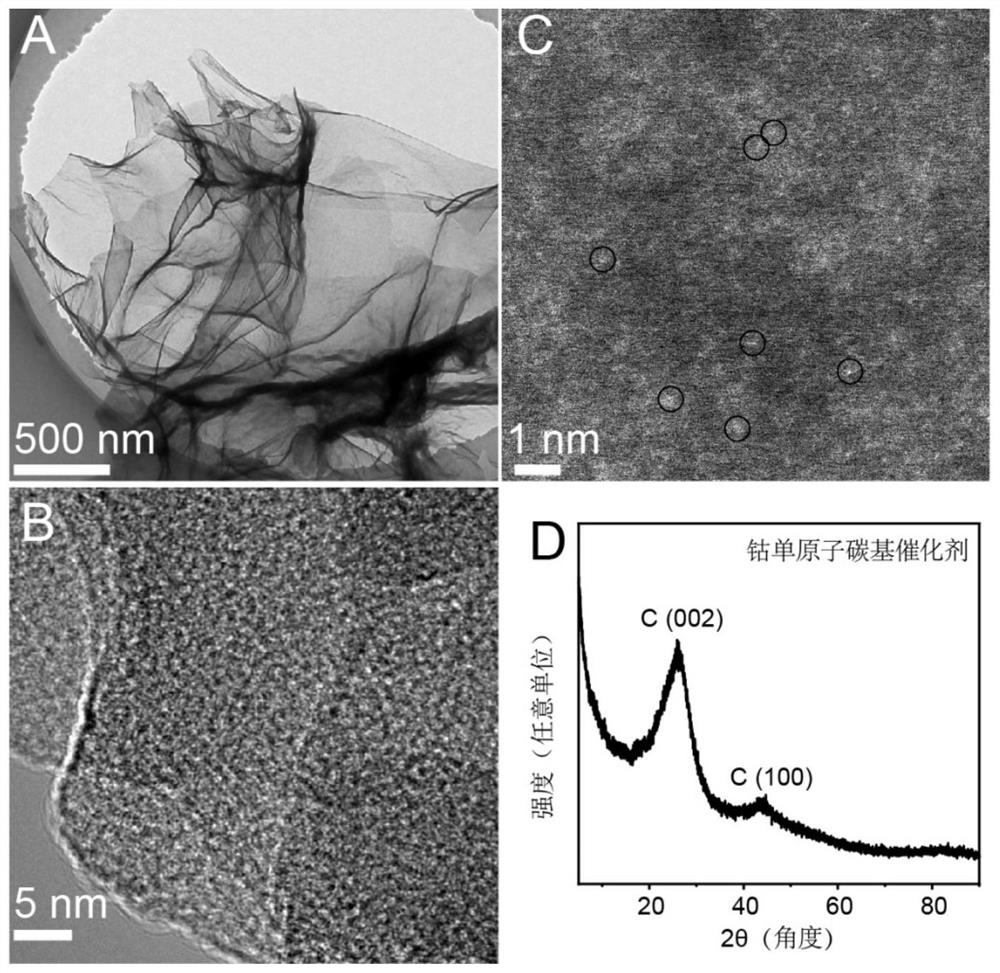
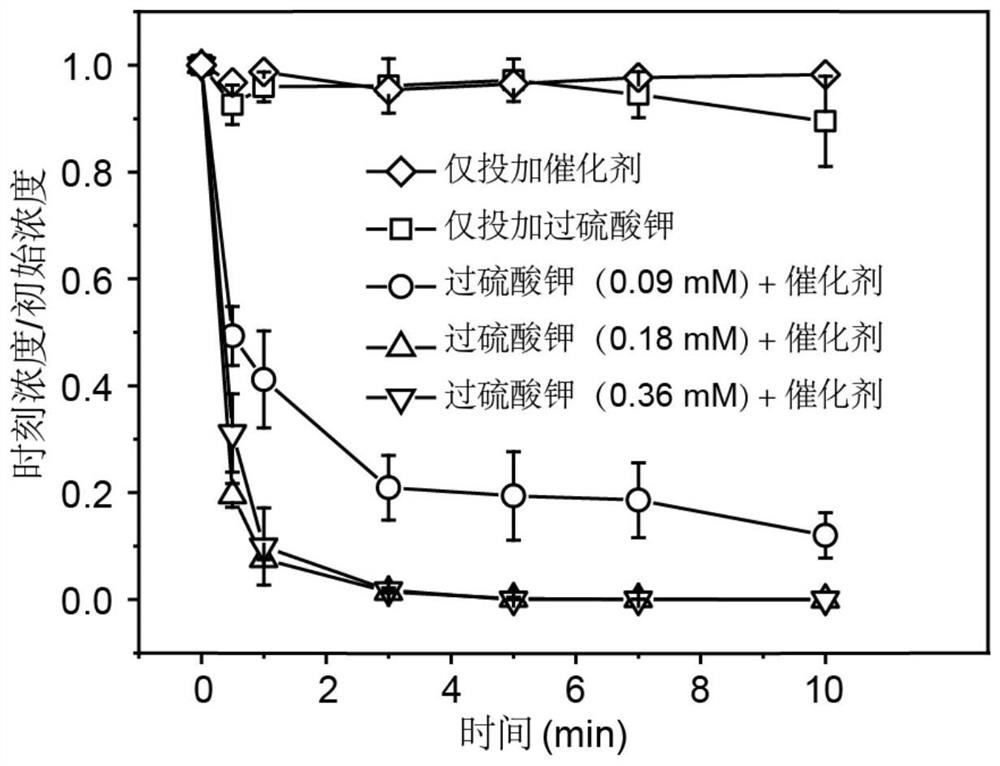
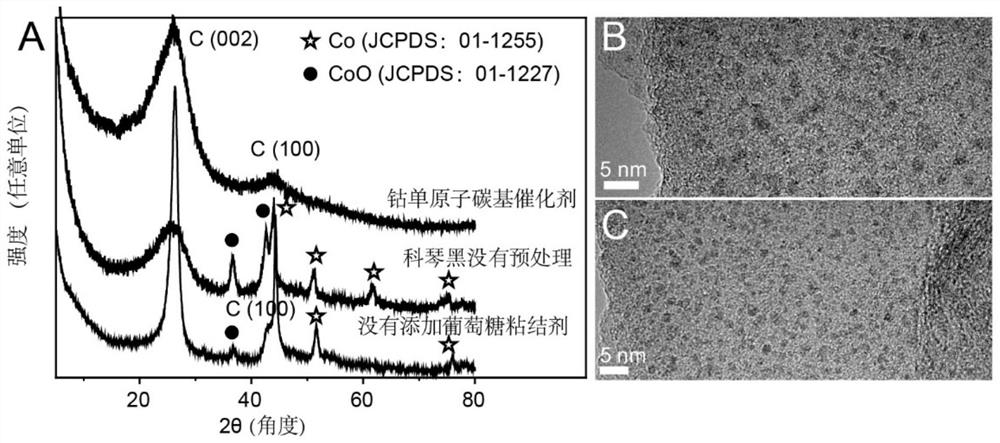
Universal method for preparing metal monatomic carbon-based catalyst and application thereof
ActiveCN112452346AEasy to synthesizeAvoid gatheringPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater contaminantsPtru catalystMetallurgy
The invention discloses a universal method for preparing a metal monatomic carbon-based catalyst and an application thereof. The universal method comprises the following steps: taking a metal compoundas a monatomic precursor, Ketjen black as a carbon skeleton, glucose as a binder and dicyandiamide as a nitrogen element source. All the raw materials are uniformly mixed in an ultrasonic step-by-step dispersion mode, dried and ground, and annealed and cracked at high temperature, so that metal is in monatomic distribution. The prepared metal monatomic carbon-based catalyst is utilized to form aFenton-like system to degrade tetracycline-containing sewage, and has high removal efficiency. According to the invention, a copper monatomic carbon-based catalyst is taken as an example, 10 mg / L tetracycline (20 mL) can be completely removed within 1 min when 0.18 mM of persulfate is activated by 0.1 g / L of the catalyst, and the primary reaction kinetic constant is 4.9 min<-1>.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fluorescent encoding microspheres and arrays and preparation method of fluorescent encoding microsphere
ActiveCN112111268AImplementing Structured EncodingStable Encoding InformationLuminescent compositionsMicroballoon preparationBiochemistryMolecular physics
The invention provides a fluorescent encoding microsphere, an array and a preparation method of the fluorescent encoding microsphere. The encoding microsphere comprises a microsphere carrier, which isa mesoporous microsphere, wherein the microsphere carrier is internally provided with at least one fluorescent marker, the fluorescent marker is formed by connecting a fluorescent dye and an intermediate substance, and the central emission wavelengths of the fluorescent dyes corresponding to the fluorescent markers are different, so that each fluorescent dye defines the coding information of onedimension of the coding microsphere.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAG GENE NANOTECH CO LTD
Carbon Block/Filtration Bed/Conical Reactor with Fluidized Bed System Allowing Small Sorbent Particles to Regenerate Fluid During Extracorporeal Blood Treatment
ActiveUS20180021695A1Simple structureFast reaction kineticsOther chemical processesPeritoneal dialysisBlood treatmentsPorous carbon
Methods and devices for powdered sorbent regeneration of biologic fluids are disclosed. The present invention includes three novel methods, which may be used singly or in any combination, for constraining or immobilizing powders so that they can be perfused with a biological fluid or dialysate: a porous carbon block filter, a filtration bed of very fine powder, and a cone-shaped reactor.
Owner:HEMOCLEANSE TECH
Preparation method of copper-containing metal composite oxide photocatalytic material
ActiveCN104445356ADoes not involve emissionsReduce usageCopper oxides/halidesElectric arc furnaceOxygen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper-containing metal composite oxide photocatalytic material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting copper and zirconium into a vacuum electric arc furnace, performing vacuum pumping, then charging argon, starting smelting, keeping for 60-90 seconds after copper and zirconium are smelted, cooling to obtain an alloy molten ingot, turning over, repeating for 4 to 6 times, putting the alloy molten ingot into rapid melt quenching and melt spinning equipment, performing vacuum pumping, then charging argon, performing smelting by adopting a magnetic induction heating mode to form a melt after completely melting, opening an air pressure valve, spraying the melt on the surface of a copper roller which rapidly rotates to obtain a continuous amorphous alloy ribbon, and putting the amorphous alloy ribbon into a ceramic cup, wherein the ceramic cup comprises a ceramic base, the ceramic base is connected with a ceramic cup cover, the ceramic cup cover is provided with an air inlet hole, an observation view window and a graphite electrode, and the ceramic base is in sliding connection with an ignition graphite electrode; and connecting one end of the amorphous alloy ribbon with the graphite electrode, charging oxygen, then pushing the ignition graphite electrode to the amorphous alloy ribbon, and enabling the ignition graphite electrode to be in contact with the amorphous alloy ribbon to generate electric sparks for igniting an alloy strip material.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method of mesoporous nitrogen-doped graphene-loaded molybdenum disulfide synthesized by laser irradiation and application of mesoporous nitrogen-doped graphene-loaded molybdenum disulfide in electrocatalytic hydrogen production
ActiveCN110586156AGood catalytic activitySimple processPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesCvd grapheneSulfide
The invention relates to a preparation method of mesoporous nitrogen-doped graphene-loaded molybdenum disulfide synthesized by laser irradiation and application of the mesoporous nitrogen-doped graphene-loaded molybdenum disulfide in electrocatalytic hydrogen production. In order to solve the problems that by an existing synthesis process, transition metal oxide / sulfide composite mesoporous nitrogen-doped graphene rich in carbon-pyridine nitrogen metal bonds cannot be synthesized at low temperature and under low pressure, and the content of the carbon-pyridine nitrogen metal bonds in the composite system cannot be regulated and controlled effectively, it is found that the content of the carbon-pyridine nitrogen-molybdenum bonds in the composite catalyst can be improved by irradiating graphene oxide with laser in a range of 177-315 mJ, and in a hydrothermal process, the mass ratio of laser irradiation graphene oxide to tetrathiomolybdic acid as raw materials is 1: 1-1: 8, the loading amount of the molybdenum disulfide on mesoporous graphene can be optimized, thus, while the conductivity of the molybdenum disulfide is improved, the intrinsic activity of the molybdenum disulfide can also be improved synergistically by the carbon-pyridine nitrogen molybdenum bonds at an interface, and the electrocatalysis process of HER is promoted. The preparation method is simple in process, ingenious in design and low in cost, and is safe and environmentally friendly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
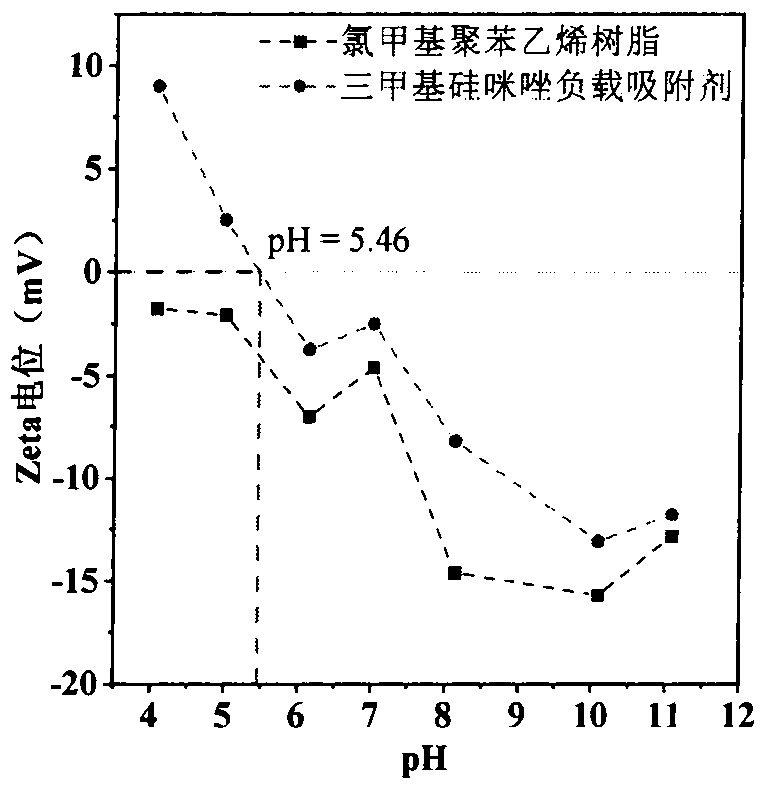
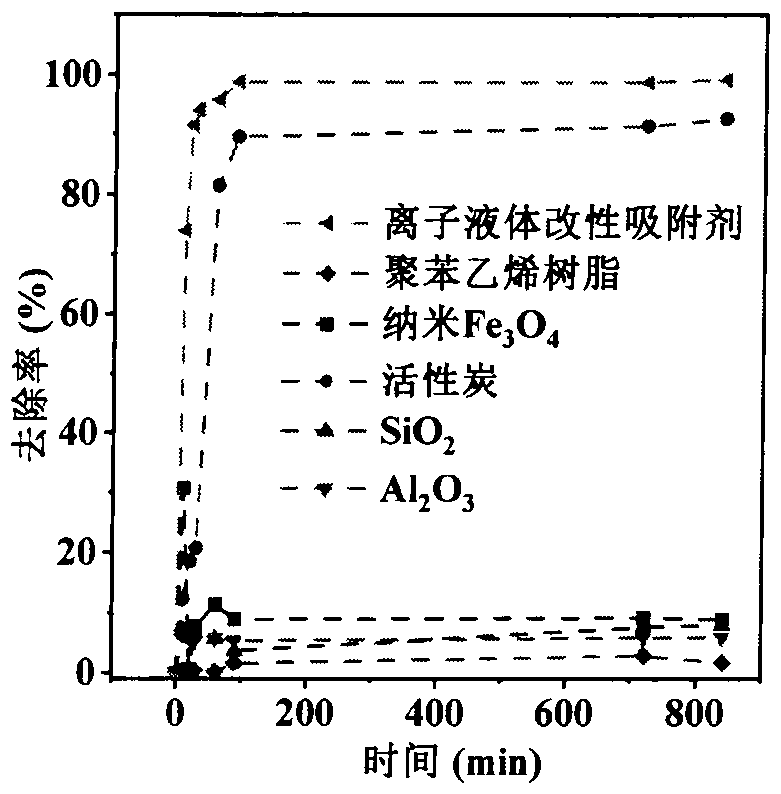
Preparation and application of trimethylsilyl imidazole adsorbentfor antibiotics
PendingCN113600151AImprove adsorption capacityFast reaction kineticsOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPolystyreneSulfanilamide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a 1-(trimethylsilyl) imidazole ionic liquid adsorbent for antibiotics in a water body and an applied synthesis method and application thereoft, and belongs to the technical field of water body organic micropollutant treatment. According to the invention, the 1-(trimethylsilyl) imidazole ionic liquid is grafted on the surface of the chloromethyl polystyrene resin through chemical bonding so that the product is prepared. The specific application effect of the synthesized 1-(trimethylsilyl) imidazole ionic liquid adsorbent in adsorption of four typical antibiotics including beta-lactam antibiotics (ceftiofur), sulfonamide antibiotics (sulfamethoxazole), fluoroquinolone antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) and tetracycline antibiotics (aureomycin) is released for the first time; the synthesis method is simple and convenient to operate and mild in reaction condition, and the product has the advantages of large adsorption quantity, fast reaction kinetics, high adsorption efficiency and the like on various antibiotics.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
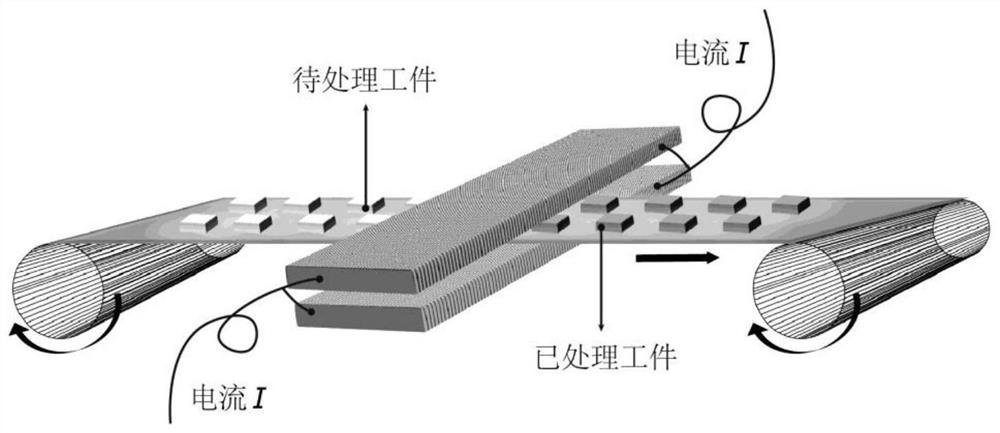
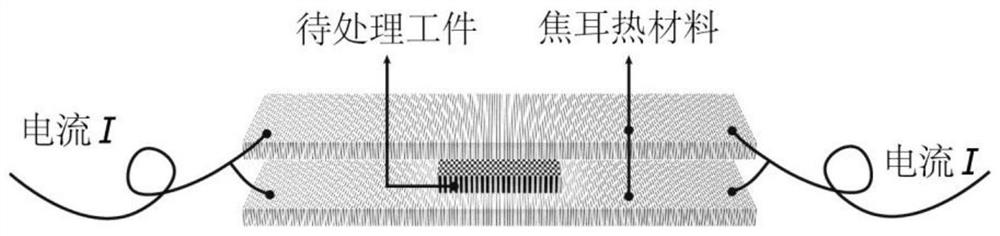
High-temperature adjacent metal heat treatment device and method
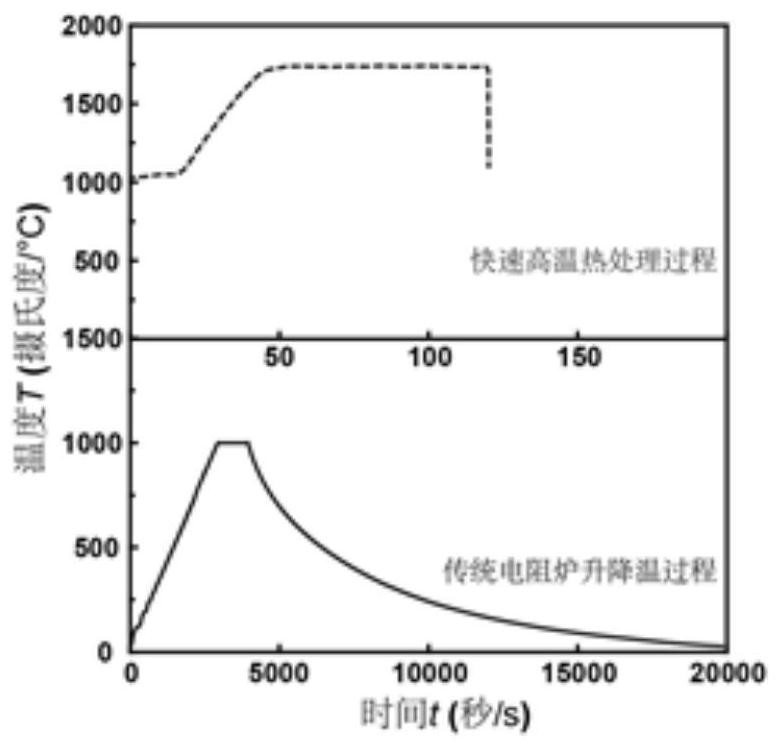
PendingCN113186374AFast reaction kineticsReduce processing timeHeat treatment process controlMetallic materialsElectric current flow
The invention belongs to the related technical field of metal heat treatment, and discloses a high-temperature adjacent metal heat treatment device and method. The device comprises an upper polar plate and a lower polar plate which are oppositely arranged, wherein the upper polar plate and the lower polar plate are both made of Joule thermal materials; a to-be-treated workpiece is placed between the upper polar plate and the lower polar plate; after current is introduced into the upper polar plate and the lower polar plate, the upper polar plate and the lower polar plate are rapidly heated, and the temperature is transmitted to a heat treatment part; and after the current is cut off, the heat treatment part is cooled. the upper polar plate and the lower polar plate are quickly cooled, so that the temperature in the to-be-treated workpiece is reduced, and heat treatment of the to-be-treated workpiece is realized. In the heat treatment process, the processes of atomic diffusion, phase transformation, grain growth and the like all accord with the heat activation process, faster reaction kinetics can be provided, exponential shortening of the heat treatment time is achieved, the heat treatment method which is high in speed and low in energy consumption and can accurately control the performance of the needed metal material is provided, and the method is wide in applicability and good in batch treatment effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
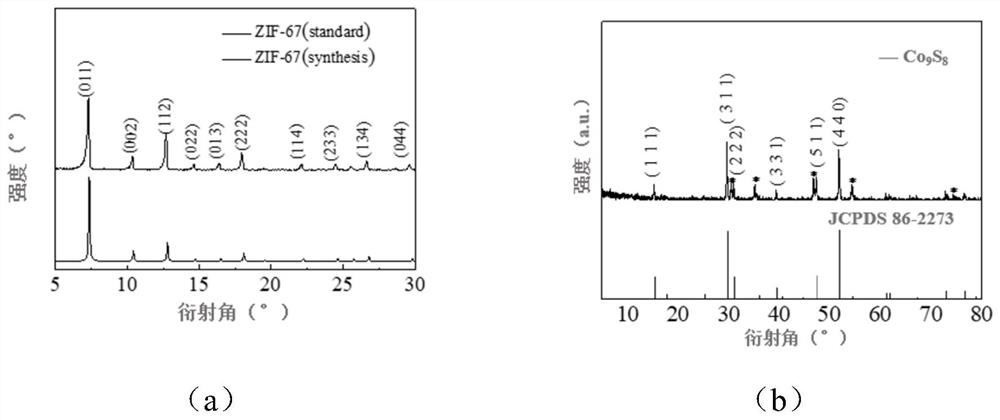
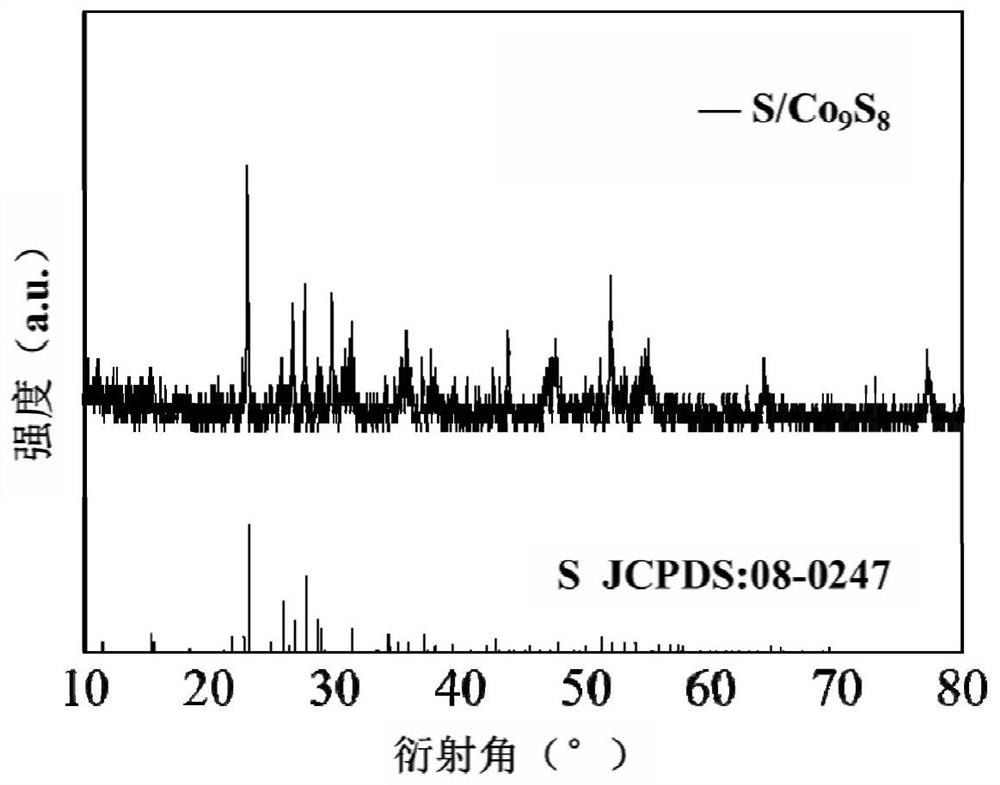
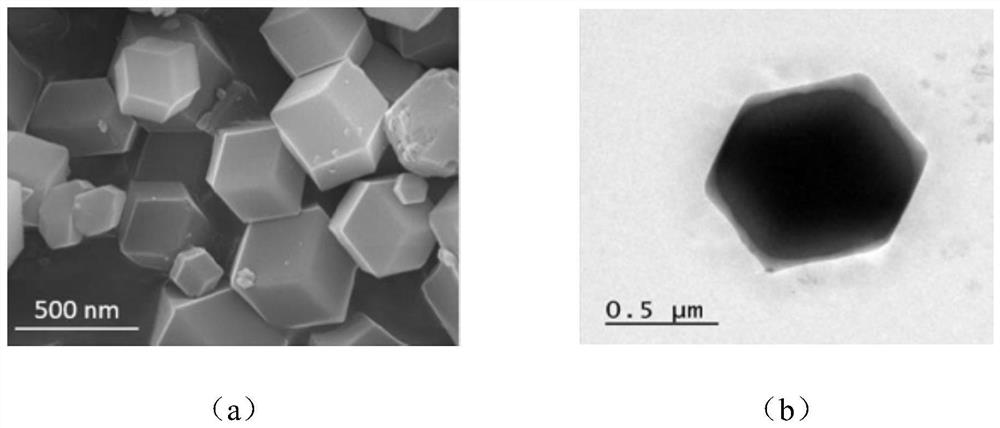
Hollow carbon shell inlaid with metal sulfide, preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113809323ASmall volume changeImprove electrochemical performanceCell electrodesElectrochemical responseElectrical battery
The invention discloses a hollow carbon shell inlaid with metal sulfide, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of lithium-sulfur battery positive electrode materials, wherein a hollow carbon shell polyhedral material inlaid with polar metal sulfide is prepared by taking MOFs as a precursor and performing simple vulcanization and heat treatment. According to the invention, the preparation method is easy to operate, required instruments and equipment are simple, a ZIF-67 precursor template with uniform morphology is prepared by adopting a precipitation method with a mature process, and by using a simple vulcanization process, a hollow structure can be formed due to non-uniform shrinkage in a heat treatment process; and due to the fact that chemical adsorption can be generated on polysulfide, the shuttle effect in the charging and discharging process can be restrained to a certain degree, loss of the active substance sulfur is reduced, the hollow structure can buffer the volume change of sulfur in the electrochemical reaction process, so that the electrochemical performance of the battery can be improved, and the hollow carbon shell can be applied to positive electrode sulfur carriers of lithium-sulfur batteries.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Titanium dioxide coated CoSe2-based nano material as well as preparation method and application thereof
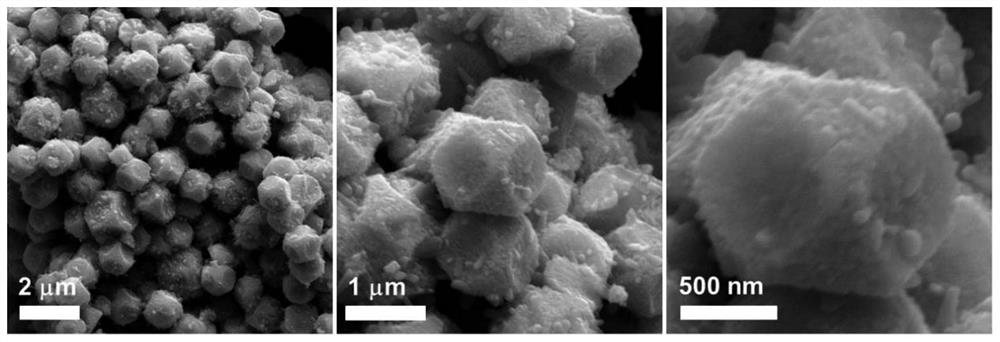
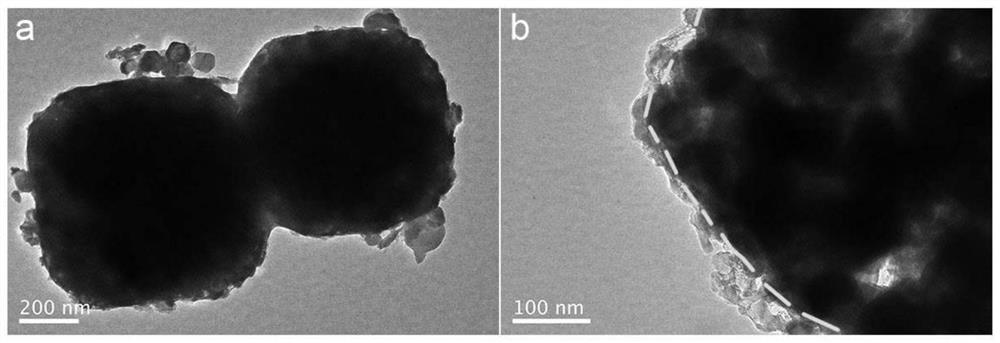
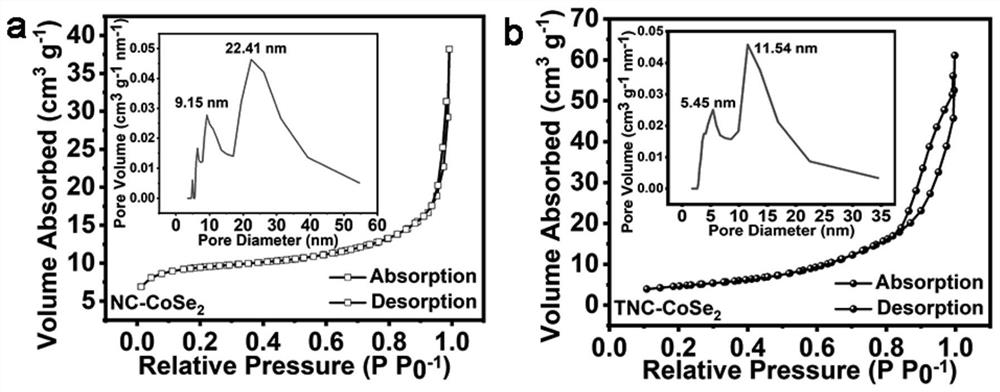
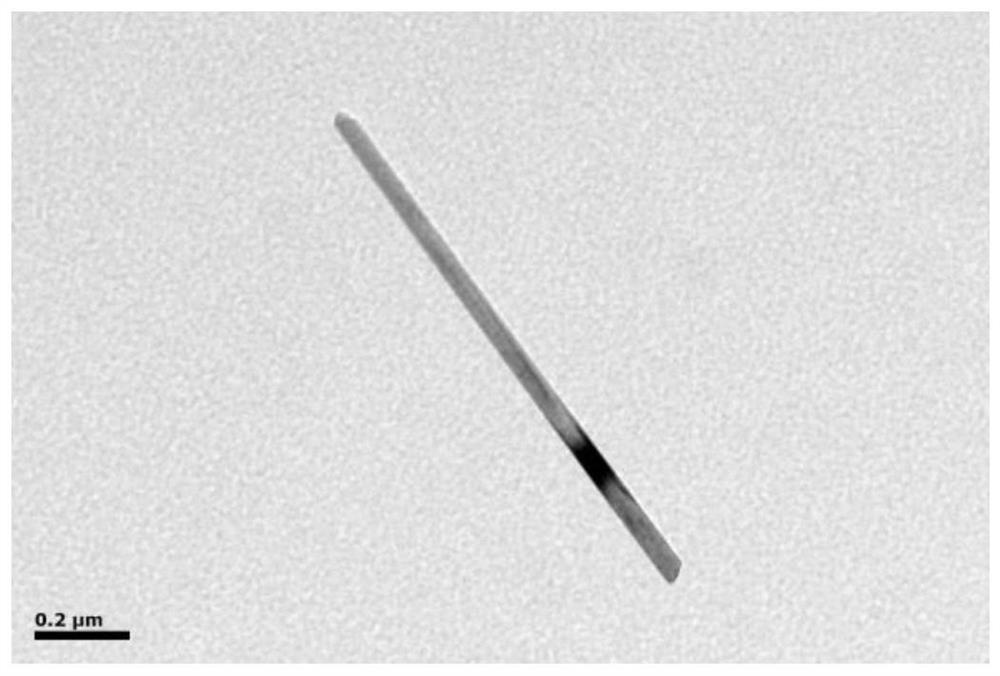
PendingCN114824221AEasy to prepareEasy to operateCell electrodesSecondary cellsTitanium oxideMaterials science
The invention provides a titanium dioxide coated CoSe2-based nano material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a Co-Co PBA microcube with a nanometer size; the Co-Co PBA microcubes are ultrasonically dispersed in a mixed solution of absolute ethyl alcohol and a concentrated ammonia solution, an organic solution of titanium ester is dropwise added into the mixed solution at the speed of 0.5 mLmin <-1 > to 1 mLmin <-1 >, oil bath heating is conducted for 5 h to 8 h at the temperature of 70 DEG C to 100 DEG C, standing is conducted for 20 h to 24 h at the room temperature, after the reaction is finished, a solvent is used for cleaning a product, centrifugal collection is conducted, and Co-Co PBA-at-TiO2 is obtained; the preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly grinding Co-Co PBA-coated TiO2 and selenium powder, and carrying out high-temperature selenylation and carbonization under the protection of inert gas, so as to obtain the titanium dioxide-coated CoSe2-based nano material TNC-CoSe2. The nano material disclosed by the invention is used as a negative electrode material of a sodium-ion battery, and has ultrahigh rate and cycling stability at the same time.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
a cos x @mno 2 Composite material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112853395BThe preparation process steps are simple and controllableShort preparation timeElectrodesPtru catalystOxygen evolution
The invention provides a CoSX@MnO 2 Composite material and its preparation method and application, its preparation method comprises: (1) MnO 2 Preparation of nanotubes; (2) ZIF‑67@MnO 2 Preparation of composite materials; (3) CoS X @MnO 2 Preparation of Catalyst; CoS of the Invention X @MnO 2 The preparation process of the catalyst is simple and controllable, the preparation time is short, and the structure of the obtained catalyst is dendritic MnO 2 penetrating fruit-like CoS X , its structure is stable; in addition, the CoS prepared by the present invention X @MnO 2 During the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction of the catalyst, 10mAcm ‑2 The overpotential at the current density is only 334mV, compared to commercial MnO 2 Catalyst 470mV overpotential drops 136mV; In addition, CoS X @MnO 2 The Tafel slope is 84.8mV dec ‑1 , compared to the commercial MnO 2 Tafel slope 140mV dec ‑1 have a smaller Tafel slope. These all indicate that CoS X Loaded on carrier ZIF‑67@MnO 2 on after exhibited better than commercial MnO 2 more excellent electrocatalytic performance.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
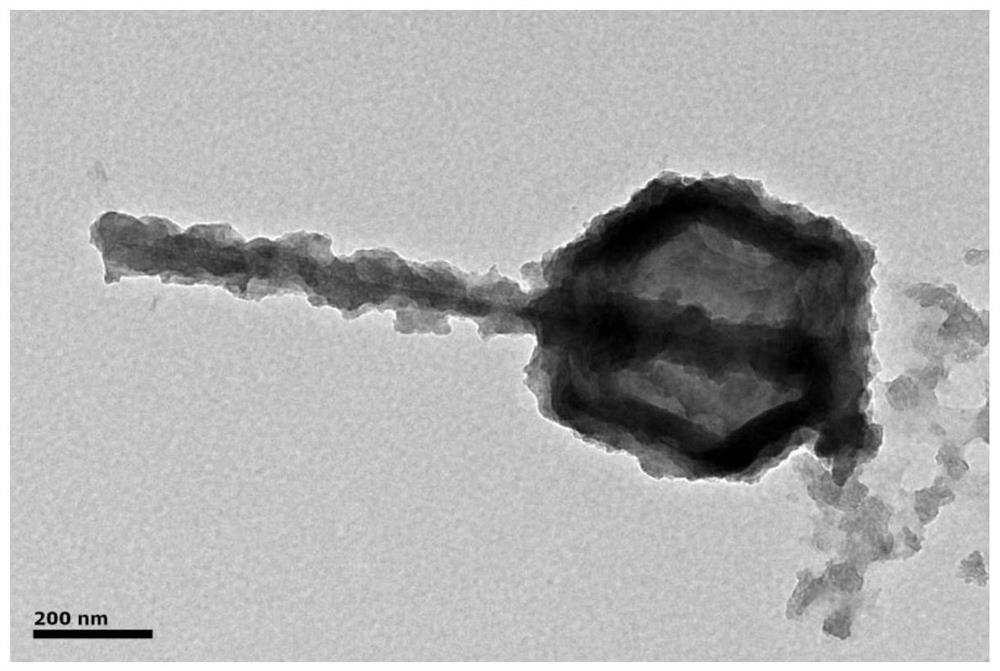
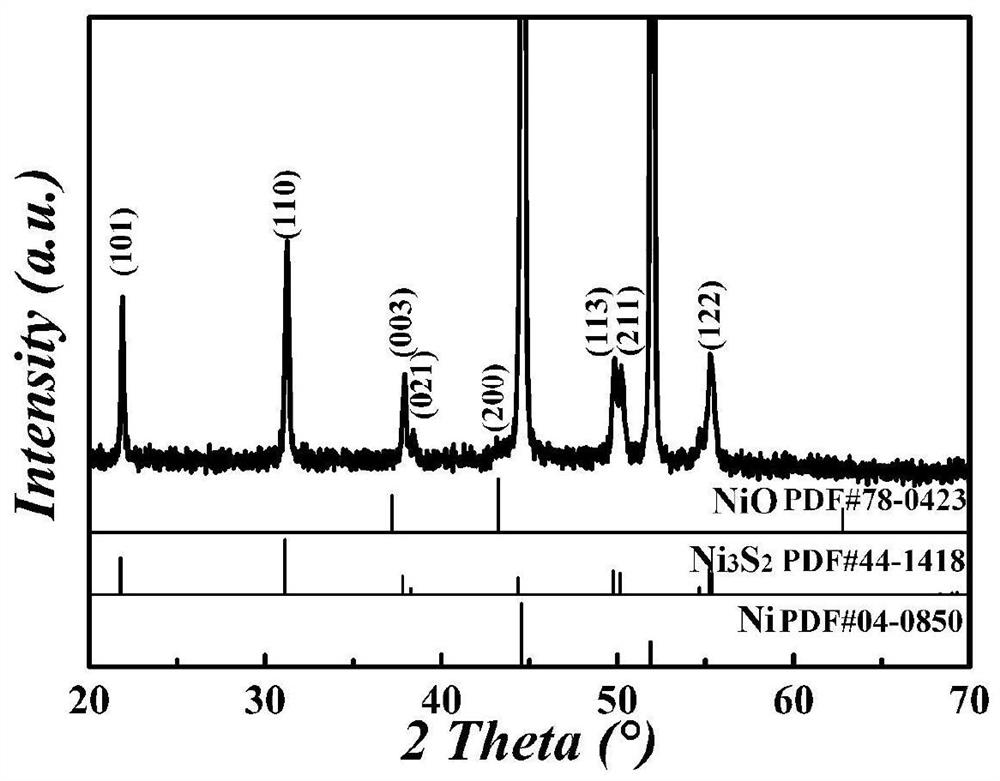
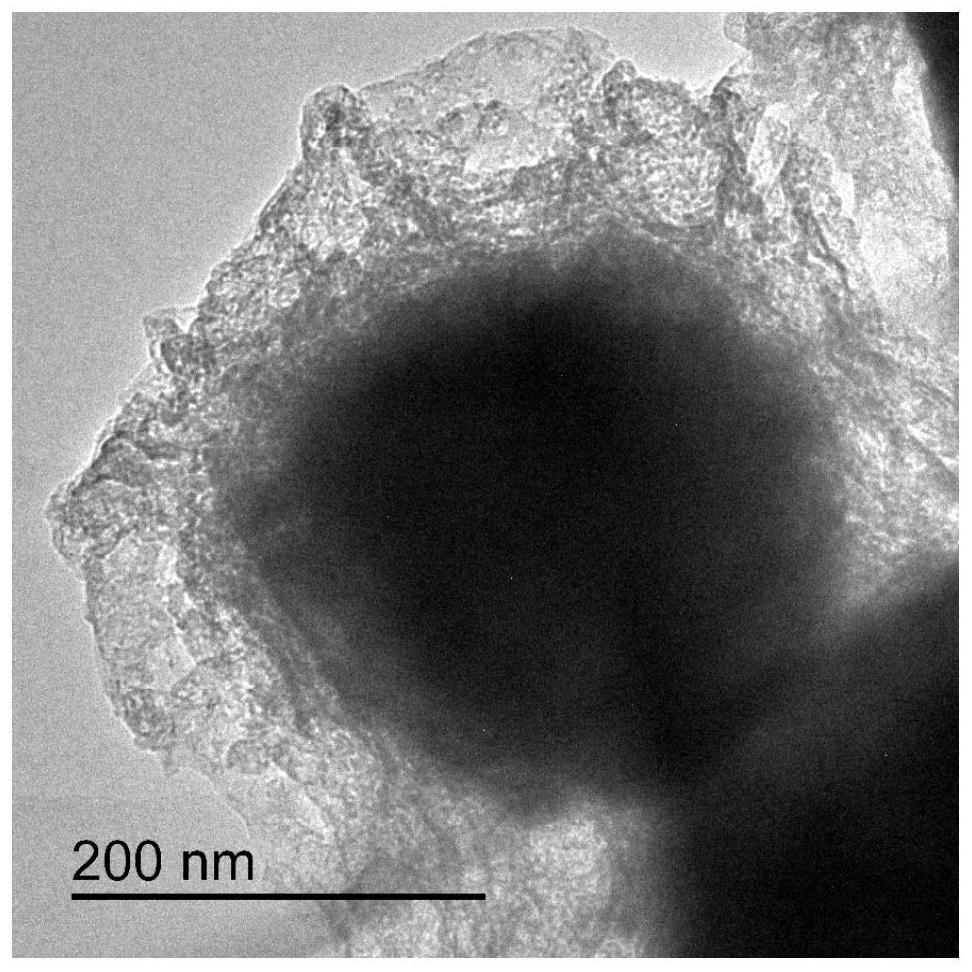
A v-doped ni coated with v-doped nio 3 s 2 Preparation method of core-shell structure
ActiveCN110615488BStrong structural stabilityFacilitated releaseHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionPhysical chemistryVanadium atom
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
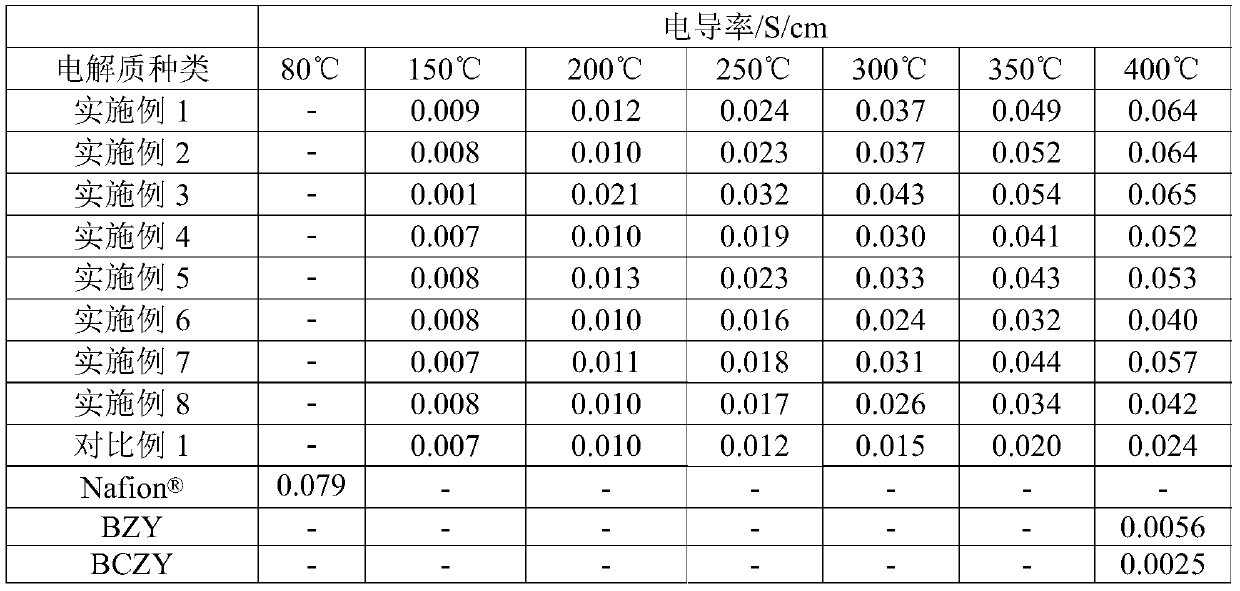
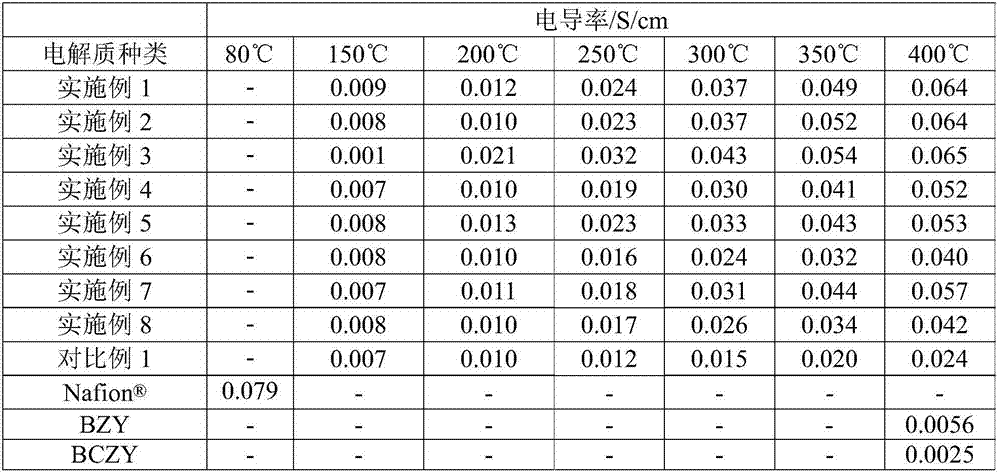
Proton conductor material, its preparation method and application, and medium temperature fuel cell
ActiveCN106887625BBroaden your optionsSimple designSolid electrolytesPhosphorus compoundsElectrical conductorPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to the field of a fuel cell electrolyte and discloses a proton conductor material, a preparation method and application thereof, and an intermediate temperature fuel cell. The chemical formula of the proton conductor material is (NH4)2A1-xBxP4O13, wherein A is one, two or more than two elements of Y, Ti, Nb, Ta, Mo and W; B is one, two or more than two elements of Al, In, Si, Ge and Sn; and x is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.4. When the proton conductor material provided by the invention works in an intermediate temperature (150 to 400 DEG C) range, the proton conductivity is obviously higher than 4*10<-2>S / cm, and application of the proton conductor material to the intermediate temperature fuel cell can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
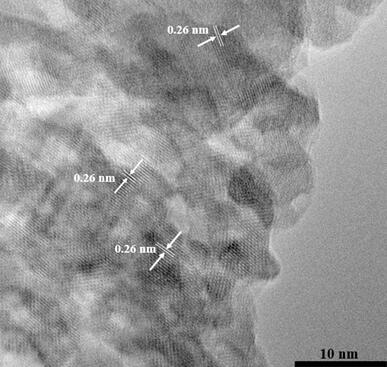
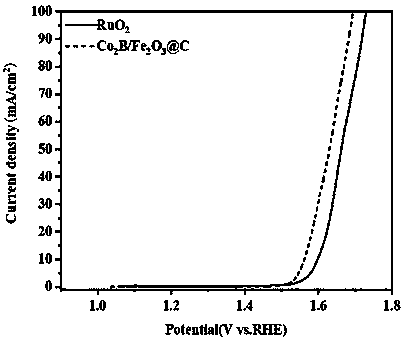
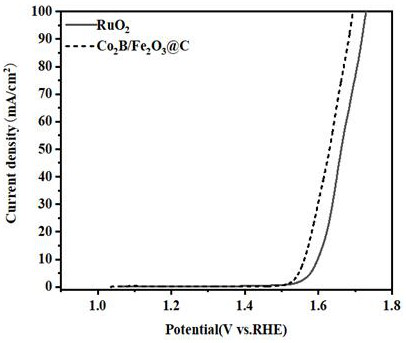
Preparation method of Fe2O3/C@Co2B catalyst and application of Fe2O3/C-coated Co2B catalyst in oxygen evolution reaction
ActiveCN111514896AThe preparation process steps are simple and controllableShort preparation timeMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Fe2O3 / C@Co2B catalyst and application of the Fe2O3 / C@Co2B catalyst in an oxygen evolution reaction. According to the invention, Fe2O3 / C is prepared byusing a liquid plasma arc discharge method; The Fe2O3 / C@Co2B catalyst with a core-shell structure is prepared by using a chemical reduction method. After being washed and dried, a catalyst sample isapplied to the process of an electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Results show that under a current density of 10 mA / cm<2>, the overpotential of the Fe2O3 / C@Co2B catalyst is only 332 mV, a reduction of 33 mV compared with the overpotential (365 mV) of a commercial RuO2 catalyst. Furthermore, the Tafel slopes of Fe2O3 / C@Co2B and RuO2 are 48 mV / dec and 68 mV / dec respectively, so compared withcommercial RuO2, Fe2O3 / C@Co2B has a smaller Tafel slope, which indicates that Fe2O3 / C@Co2B has faster reaction kinetics. Moreover, the stability of Fe2O3 / C@Co2B is obviously improved compared with the stability of Co2B; and Fe2O3 / C@Co2B can stably catalyze water electrolysis for 12 hours without obvious reduction, and the overpotential of Fe2O3 / C@Co2B is not obviously increased after 2000 CV cycles.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
A universal method for the preparation of metal single-atom carbon-based catalysts and its application
ActiveCN112452346BEasy to synthesizeAvoid gatheringPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater contaminantsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a universal method and application for preparing a metal single-atom carbon-based catalyst, comprising the following steps: using a metal compound as a single-atom precursor, Ketjen black as a carbon skeleton, glucose as a binder, and dicyandiamide as a source of nitrogen. By means of ultrasonic dispersion step by step, all raw materials are mixed evenly, then dried and ground, annealed and cracked at high temperature, so that the metal presents a single atom distribution. The invention uses the prepared metal monoatomic carbon-based catalyst to form a Fenton-like system to degrade tetracycline-containing sewage, and has high removal efficiency. Taking the copper single-atom carbon-based catalyst as an example, 0.1g / L catalyst activated 0.18mM persulfate can completely remove 10mg / L tetracycline (20mL) in 1min, and the kinetic constant of the first order reaction is 4.9min ‑1 .
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Core-shell structure sulfur cathode material, preparation method and application in lithium-sulfur batteries
ActiveCN112421044BHigh degree of coatingGuaranteed electrical conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyPositive electrodesAcid etchingElectrical battery
The invention discloses a sulfur cathode material with a core-shell structure, a preparation method and an application in a lithium-sulfur battery. The core-shell structure nano cage adopts a one-step method to directly generate a metal coordination gel from a transition metal salt and an organic ligand as a skeleton After freeze-drying and high-temperature calcination, the coating material C@Fe 3 o 4 , in order to make the active material evenly distributed and give full play to the structural advantages, part of the Fe is etched by acid 3 o 4 Get the core-shell structure (YCF), using carbon shell and Fe 3 o 4 The gap between them encapsulates sulfur, resulting in S / YCF material. The synergistic effect of the carbon shell and the polar core as a physical barrier and a chemical adsorbent can effectively inhibit the shuttle effect of polysulfides, and by regulating Fe 3 o 4 The content of polar balls can balance the maximum sulfur loading, inhibit polysulfide shuttling and accommodate volume expansion, and realize the preparation of high Coulombic efficiency and long-life positive electrodes.
Owner:北京理工大学重庆创新中心 +1
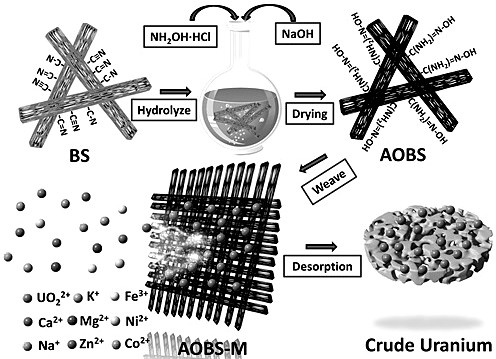
A weavable seawater uranium extraction adsorption material and its flexible control preparation method
ActiveCN113231038BLower synthesis costEasy to operateOther chemical processesSeawater treatmentMineralogyEnvironmental chemistry
A weavable seawater uranium extraction material and its flexible control preparation method relate to the technical field of adsorption materials, in particular a weavable seawater uranium extraction material and its flexible control preparation method. After sonicating bamboo strips with acetone, ethanol, and deionized water, select H 2 o 2 As a solvent, hydrothermal method is used to carry out hydroxylation treatment on it, and finally NH 2 Amidoximation reaction was carried out in alkaline solution of OH·HCl to prepare amidoximated bamboo strips. The method is simple in preparation and operation, low in cost, and can be built into a macroscopic large-area shaped adsorption material. In addition, the oxime nitrogen, amino nitrogen and oxime oxygen in the amidoxime functional group can be chemically coordinated with uranyl ions, which can effectively improve the selectivity of bamboo sticks to uranyl ions and achieve the effect of specifically capturing uranyl ions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
fe 2 o 3 /c@co 2 The preparation method of b catalyst and its application in oxygen evolution reaction
ActiveCN111514896BThe preparation process steps are simple and controllableShort preparation timeMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesPtru catalystElectrolysis
Fe 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 Preparation method of B catalyst and its application in oxygen evolution reaction, Fe is prepared by liquid plasma arc discharge method 2 O 3 / C. Fe with core-shell structure was prepared using chemical reduction method 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 B catalyst. After the catalyst sample is washed and dried, it is used in the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction process. The results show that at 10 mA / cm 2 At the current density of Fe 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 The overpotential of B catalyst is only 332 mV, which is higher than that of commercial RuO 2 The overpotential of the catalyst (365 mV) dropped by 33 mV. In addition, Fe 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 B and RuO 2 The Tafel slopes are 48 mV / dec and 68 mV / dec respectively, Fe 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 B relative to commercial RuO 2 has a smaller Tafel slope, indicating that Fe 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 B has faster reaction kinetics. Furthermore, Fe 2 O 3 / C@Co 2 The stability of B and Co 2 Compared with B, it has also been significantly improved. It can stably catalyze water electrolysis for 12 hours without significant decrease. After 2000 CV cycles, the overpotential does not increase significantly.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
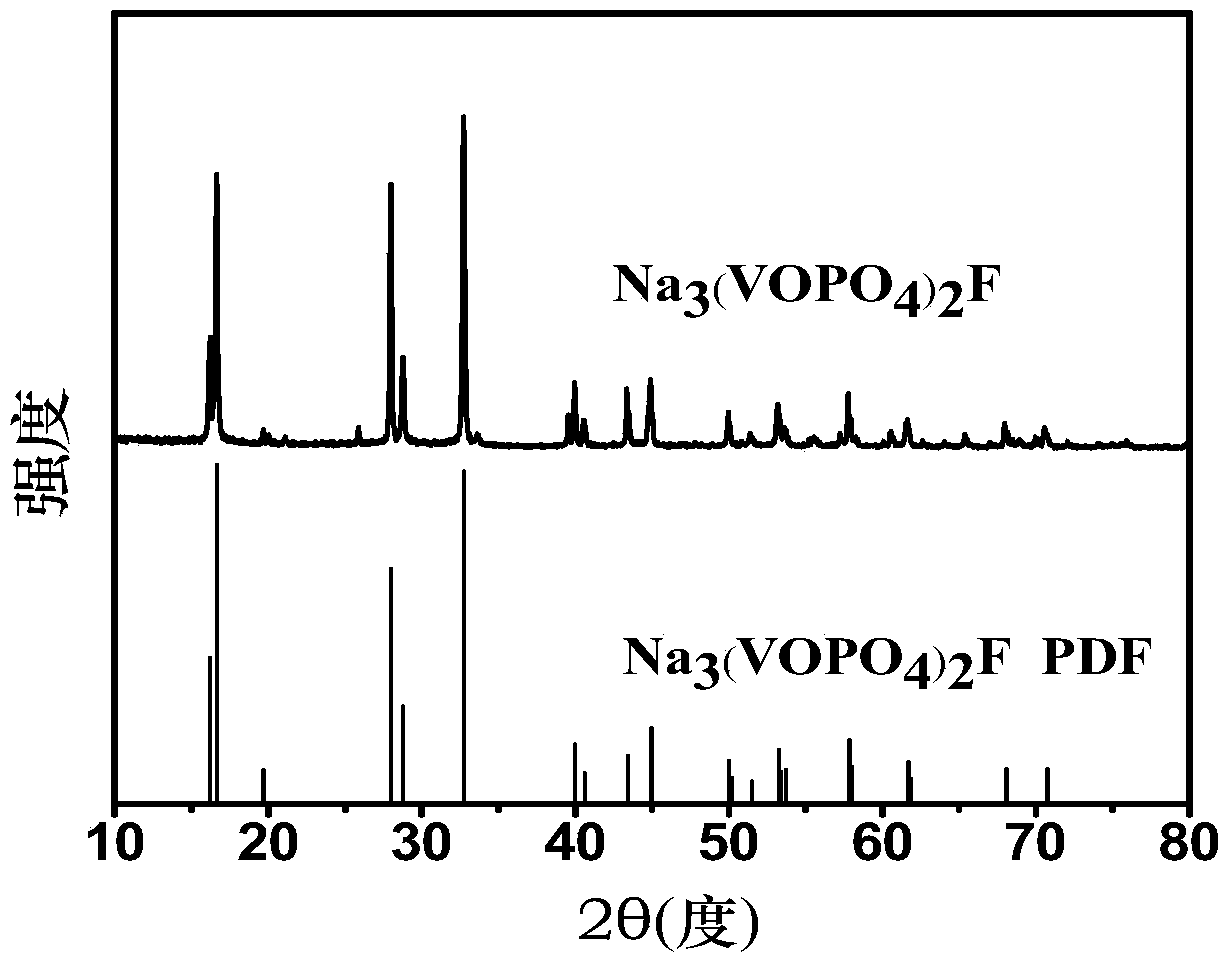
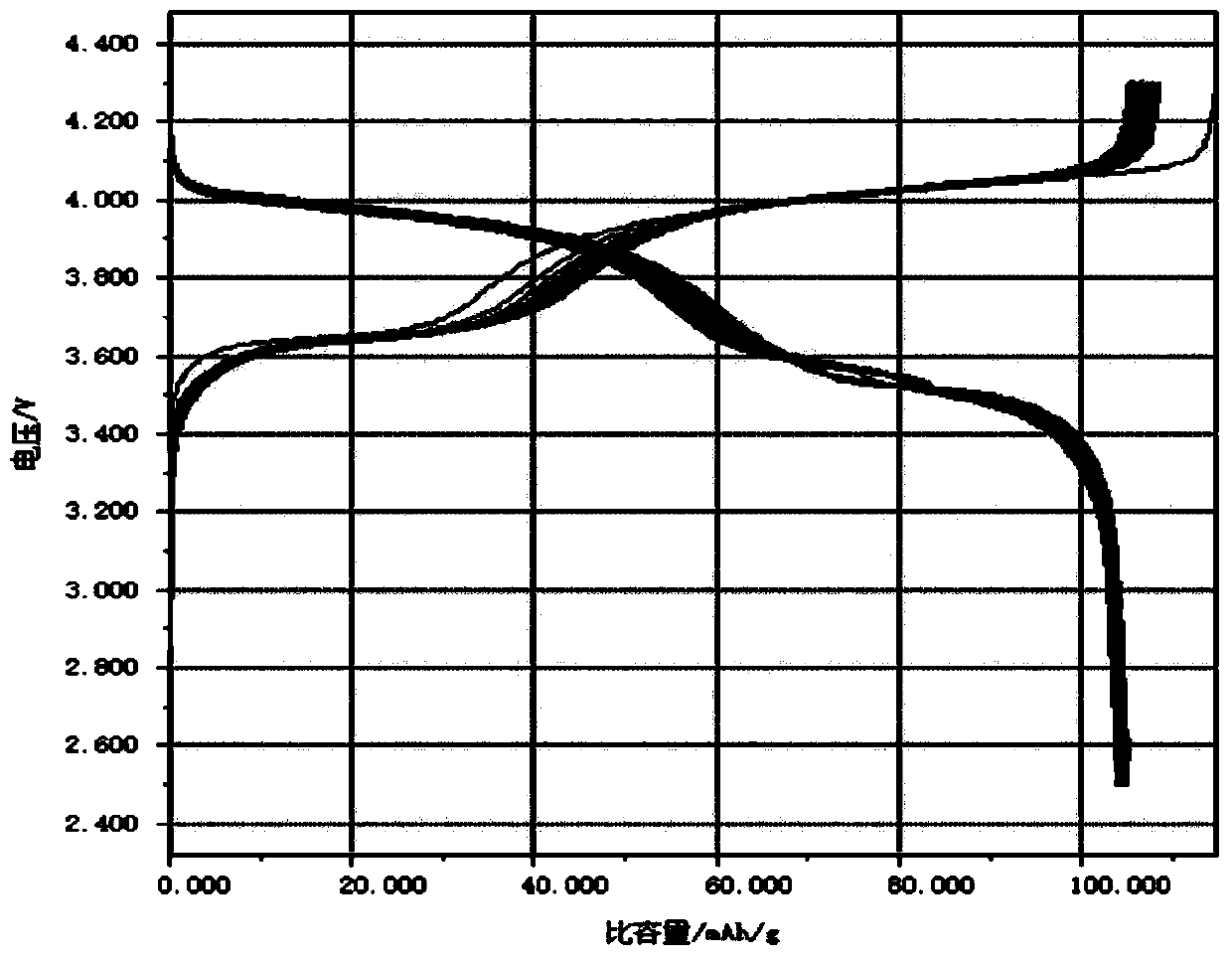
A kind of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate and its preparation method and application
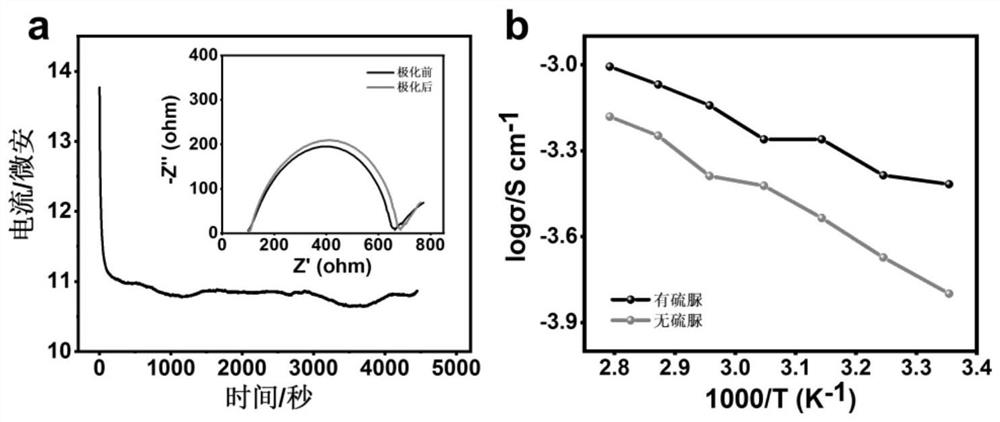
ActiveCN107154493BSynthesis temperature is lowFast reaction kineticsCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrical batteryNanoparticle
The present invention provides a sodium vanadium fluorophosphate, a preparation method and uses thereof, wherein the molecular formula of the sodium vanadium fluorophosphate is Na3(VOxPO4)2F3-2x, x is more than or equal to 0 and is less than or equal to 1, the morphology is a spherical wool ball, loose hollow ball or nanoparticle aggregate, and the size is from nanometer to micron. The preparation method comprises: (1) dissolving a vanadium source in water to obtain a vanadium source solution; (2) adding a phosphorus source, a fluorine source and a sodium source to the vanadium source solution to obtain a reaction mixture; and (3) post-treating the obtained reaction mixture to obtain the sodium vanadium fluorophosphate. According to the present invention, the water is directly used as the solvent so as to provide the advantage of no pollution; the sodium vanadium fluorophosphates can be directly synthesized at the room temperature of 10-35 DEG C, such that the temperature is low, the reaction kinetics is rapid, and the large-scale preparation of the sodium vanadium fluorophosphates can be achieved; the morphology and the crystallinity of the sodium vanadium fluorophosphate can be adjusted; the pentavalent vanadium industrial product can be used as the vanadium source so as to substantially reduce the cost of the vanadium source; and the prepared material has good electrochemical properties, and is suitable for the sodium ion battery positive electrode material.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Proton conductor material, preparation method and application thereof, and intermediate temperature fuel cell
ActiveCN106887625AImprove proton conductivityEasy to operateSolid electrolytesFuel cellsElectrical conductorMetallurgy
The invention relates to the field of a fuel cell electrolyte and discloses a proton conductor material, a preparation method and application thereof, and an intermediate temperature fuel cell. The chemical formula of the proton conductor material is (NH4)2A1-xBxP4O13, wherein A is one, two or more than two elements of Y, Ti, Nb, Ta, Mo and W; B is one, two or more than two elements of Al, In, Si, Ge and Sn; and x is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.4. When the proton conductor material provided by the invention works in an intermediate temperature (150 to 400 DEG C) range, the proton conductivity is obviously higher than 4*10<-2>S / cm, and application of the proton conductor material to the intermediate temperature fuel cell can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Preparation method of copper-containing metal composite oxide photocatalytic material
ActiveCN104445356BDoes not involve emissionsReduce usageCopper oxides/halidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectric arc furnaceOxygen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper-containing metal composite oxide photocatalytic material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting copper and zirconium into a vacuum electric arc furnace, performing vacuum pumping, then charging argon, starting smelting, keeping for 60-90 seconds after copper and zirconium are smelted, cooling to obtain an alloy molten ingot, turning over, repeating for 4 to 6 times, putting the alloy molten ingot into rapid melt quenching and melt spinning equipment, performing vacuum pumping, then charging argon, performing smelting by adopting a magnetic induction heating mode to form a melt after completely melting, opening an air pressure valve, spraying the melt on the surface of a copper roller which rapidly rotates to obtain a continuous amorphous alloy ribbon, and putting the amorphous alloy ribbon into a ceramic cup, wherein the ceramic cup comprises a ceramic base, the ceramic base is connected with a ceramic cup cover, the ceramic cup cover is provided with an air inlet hole, an observation view window and a graphite electrode, and the ceramic base is in sliding connection with an ignition graphite electrode; and connecting one end of the amorphous alloy ribbon with the graphite electrode, charging oxygen, then pushing the ignition graphite electrode to the amorphous alloy ribbon, and enabling the ignition graphite electrode to be in contact with the amorphous alloy ribbon to generate electric sparks for igniting an alloy strip material.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A kind of metal sodium secondary battery and its application
ActiveCN105185958BImprove securityHigh specific capacityCell electrodesSecondary cellsTe elementSodium-ion battery
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
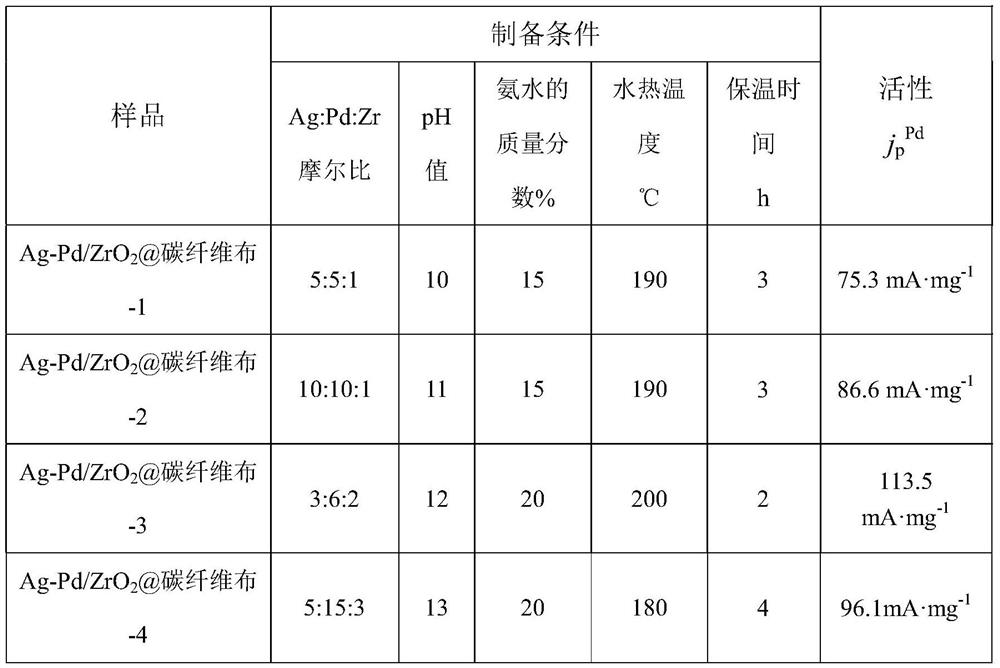
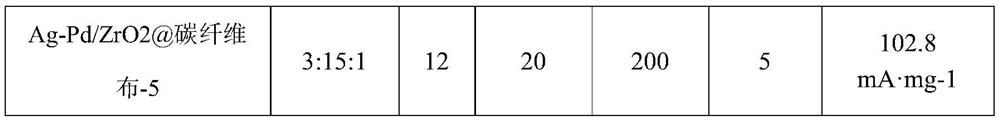
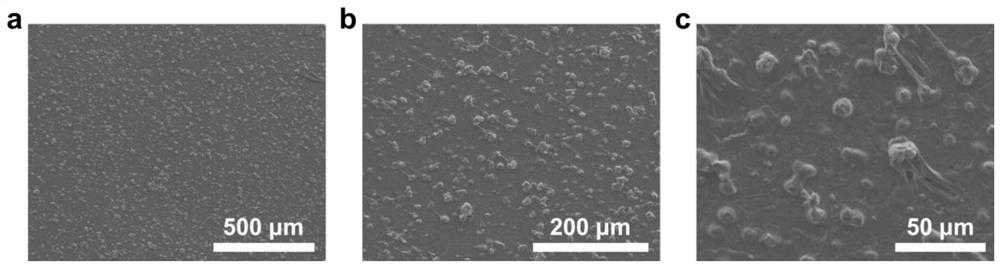
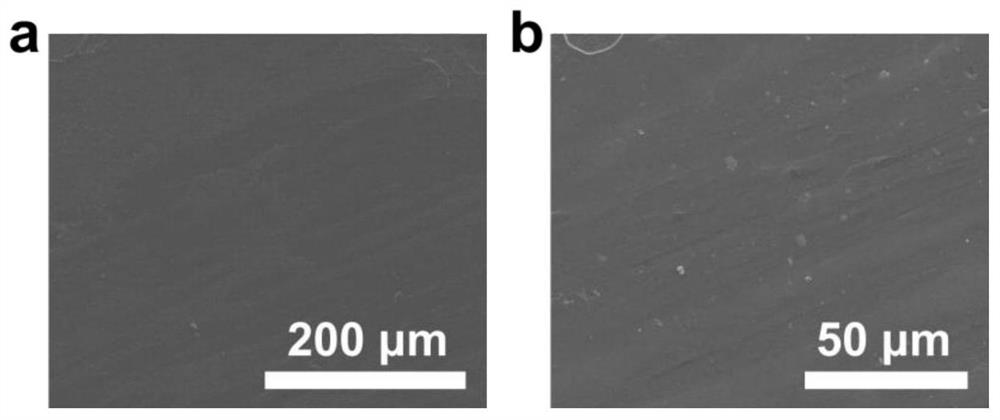
Preparation method of flexible Ag-Pd/ZrO2@carbon fiber cloth catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a flexible Ag-Pd / ZrO2@carbon fiber cloth catalyst, which comprises the following steps: dissolving carbon fiber cloth in an acetone solution, carrying out ultrasonic cleaning, sequentially carrying out ultrasonic cleaning with deionized water and alcohol, drying, putting the carbon fiber cloth in a ZrOCl2. 8H2O, PdCl2 and AgCl2 mixed solution, carrying out ultrasonic treatment, and dropwisely adding ammonia water into an obtained mixed solution until the pH value is 8-14, introducing the mixed solution into a reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction, at last washing a reaction solution with deionized water, and drying to obtain the flexible Ag-Pd / ZrO2@carbon fiber cloth catalyst. The flexible Ag-Pd / ZrO2@carbon fiber cloth catalyst prepared by the method has the advantages that the components, the nanoparticle size and the crystallization degree can be regulated and controlled, the binding force between the loaded nanoparticles and a flexible carrier is strong, and the stability is high; and the cost of the catalyst is effectively reduced under the condition of keeping high catalytic performance. And meanwhile, excellent conductivityis achieved.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of graphene composite sponge of Li-S battery cathode material
InactiveCN110010868AEasy transferIncrease transfer rateCell electrodesGraphenePorous grapheneMaterials science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene composite sponge of a Li-S battery cathode material. The method comprises the following steps of: taking sodium bis(2-ethylhexylhexyl) sulfosuccinate powder, adding the sodium bis(2-ethylhexylhexyl) sulfosuccinate powder into deionized water to obtain a microemulsion precursor solution; taking sheet-shaped graphene oxide powder (GO) intothe N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) to prepare a GO-NMP solution, slowly dropping the GO-NMP solution into the microemulsion precursor solution, namely preparing a graphene microemulsion; taking elemental sulfur particles, performing microwave reduction of the elemental sulfur particles after ball milling, then adding the elemental sulfur particles into an organic solvent, and slowly dropping the mixture into the microemulsion precursor solution to prepare a sulfur microemulsion; and slowly dropping the sulfur microemulsion into the graphene microemulsion for continuous stirring by employing ultrasound, and performing filtering to obtain granular precipitates, namely preparing the sulfur-coated graphene composite sponge material. The three-dimensional porous graphene framework facilitates achievement of the rapid reaction kinetic, and the sulfur-coated graphene composite sponge can develop a higher active material utilization rate.
Owner:SHANDONG XINGHUO SCI TECH INSTITYTE
Asymmetric semi-solid electrolyte, preparation method and metal lithium secondary battery
ActiveCN111009683BEnsure interface contactIncrease migration rateFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufactureSolid state electrolyteMetallic lithium
The invention provides an asymmetric semi-solid electrolyte, a preparation method and a metal lithium secondary battery. By coating different solid electrolyte components on both sides of the separator, the electrolyte membrane on the side facing the positive electrode is composed of lithium salt, a polymer matrix that can conduct lithium ions, and inorganic ceramic powder. The electrolyte membrane on the side facing the negative electrode is A gel electrolyte formed of a polymer and a pore-forming agent. Such an asymmetric design, compared with the traditional pure asymmetric all-solid-state electrolyte system, not only solves the problem that the solid electrolyte needs to withstand high voltage on the positive side, but also regulates the deposition and growth of lithium on the negative side, avoiding the The generation of dendrites accelerates the reaction kinetics, which can be effectively applied in high energy density metal lithium secondary battery systems, greatly improving its cycle life.
Owner:BEIJING TAIFENG XIANXING NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD +1
Peroxidase catalyzed cell surface protein labeling method
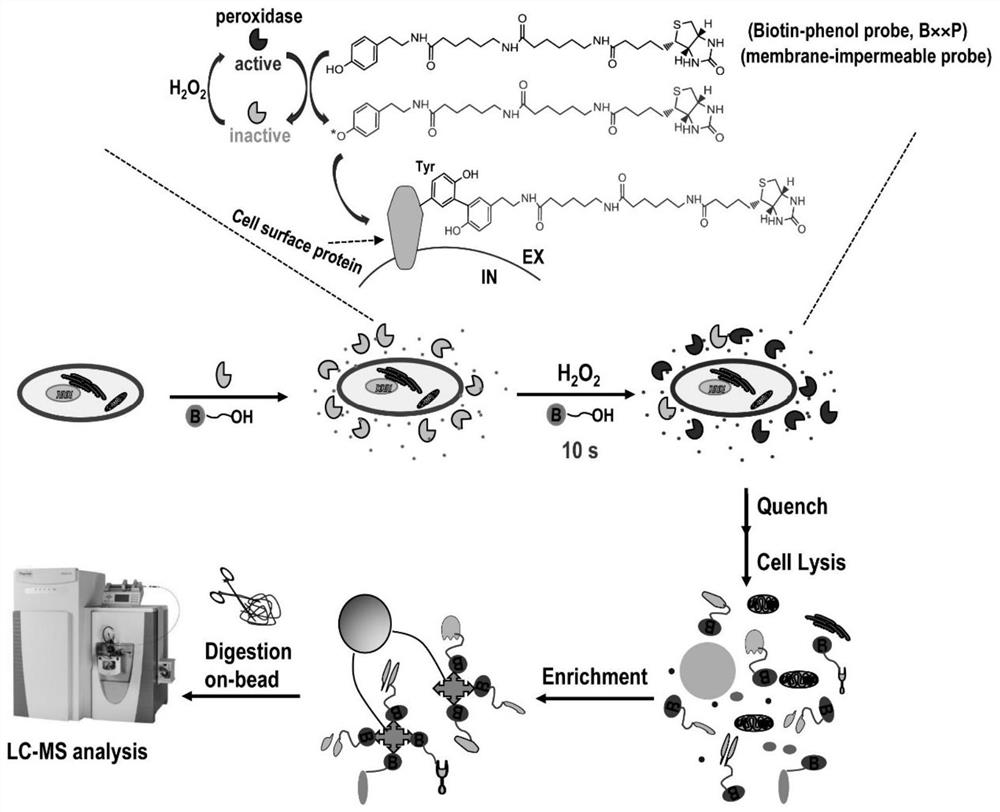
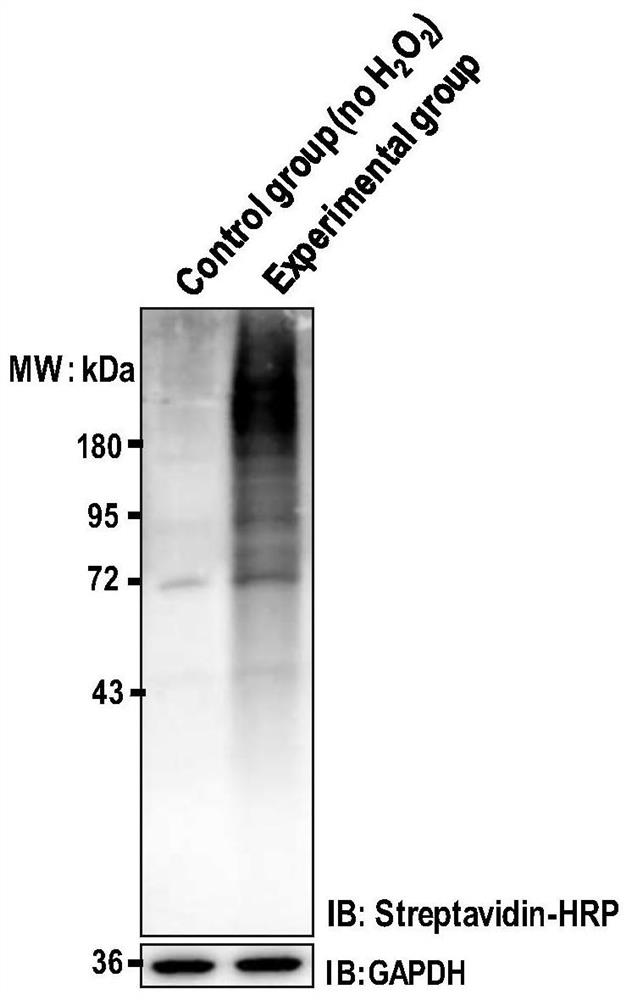
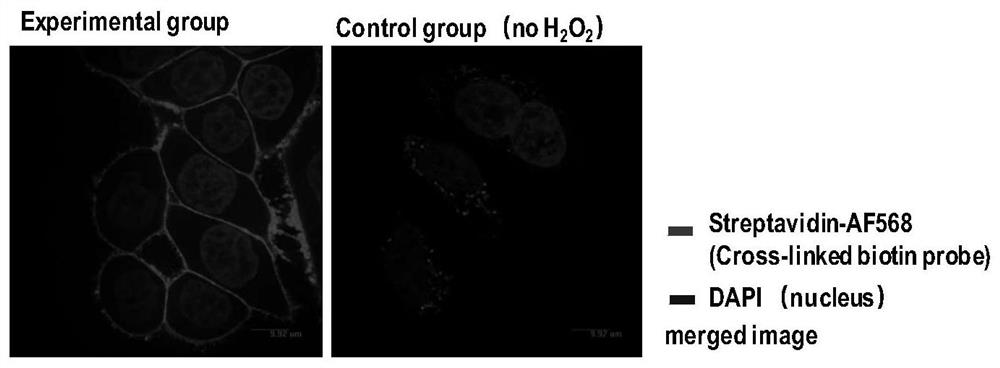
ActiveCN113702341AUnbiasedNo preferenceBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell Surface ProteinsPeroxidase
The invention discloses a peroxidase catalyzed cell surface protein labeling method. Exogenous peroxidase is introduced outside a cell to catalyze a chemical probe to generate free radicals with high activity and a short service life to selectively and covalently label protein groups exposed on the outer side of a cytoplasmic membrane. After reacting for a period of time, a sealing buffer solution is added to terminate the labeling reaction; and then, proteomic analysis is performed on the labeled protein by using a capturing group on the chemical probe. The free radical of the chemical probe can be covalently linked with one or more than two of amino acids with higher electron density, such as tyrosine, tryptophan, histidine, cysteine and the like, on an adjacent protein. The labeling strategy is simple to operate, good in selectivity and high in reaction rate, does not damage glycoforms of cell surface proteins, can be applied to analysis of cell surface proteome (or plasma membrane proteome) and a dynamic change thereof, and can also be applied to research of a cell surface protein-protein interaction, a cell-cell interaction and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescence-encoded microspheres and arrays and preparation methods
ActiveCN112111268BImplementing Structured EncodingStable Encoding InformationLuminescent compositionsMicroballoon preparationMicrosphereFluorescent light
Owner:SHANGHAI MAG GENE NANOTECH CO LTD
Preparation method and application of a carbon nanofiber-hydrotalcite composite adsorbent
ActiveCN107876006BGood environmental stabilityExcellent physical and chemical propertiesOther chemical processesWater contaminantsFiberNanowire
The invention discloses a method for preparing a carbon nanofiber-hydrotalcite composite material adsorbent. The method adopts tellurium nanowire as a template and glucose as a carbon source to prepare carbon nanofibers by a 'one-step method', hydrotalcite further grows outside the carbon nanofibers by a hydro-thermal method, and the carbon nanofiber-hydrotalcite composite material is obtained. The carbon nanofibers well carry on the one-dimensional appearance and three-dimensional reticular structure of the template, a great number of oxygen-containing functional groups are on the surface, and the stability of the carbon nanofibers in an aqueous solution can be reinforced by adding the hydrotalcite material. The preparation method is simple, convenient and feasible; and the adsorbent hashigh adsorption capacity for radionuclide, has relatively rapid reaction kinetics, does not have second pollution in the adsorbing process, and has an excellent effect for removing radionuclide in waste water.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
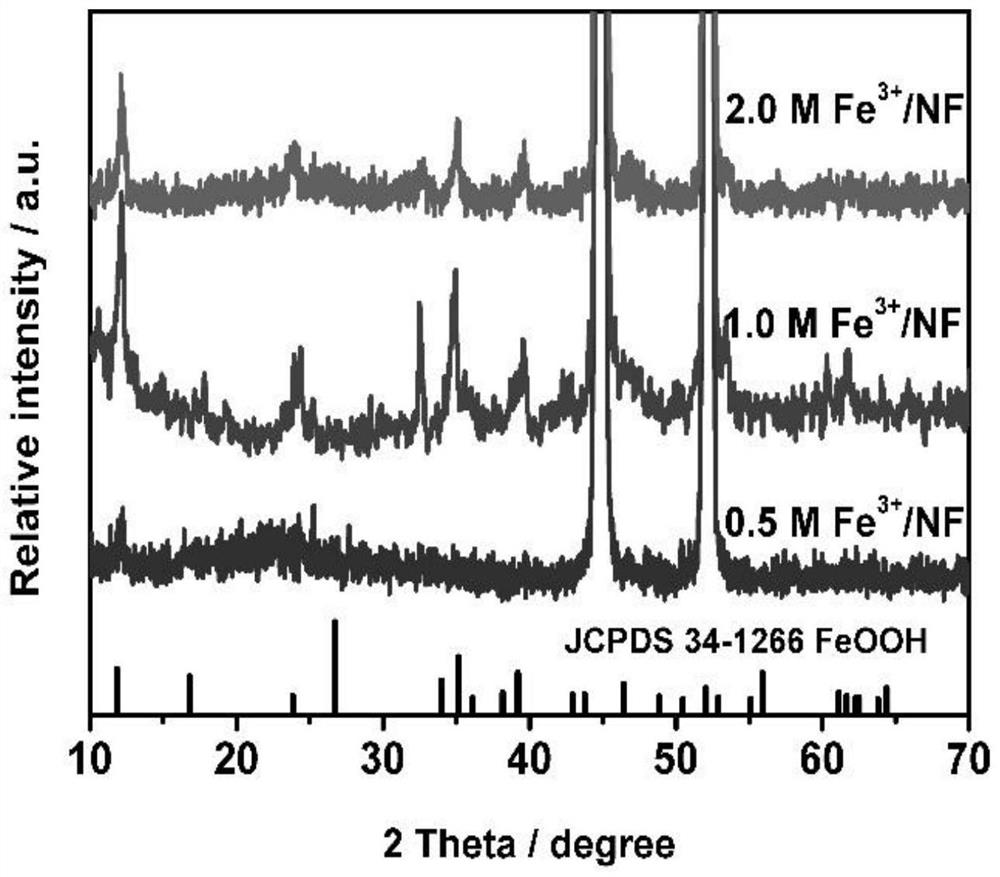
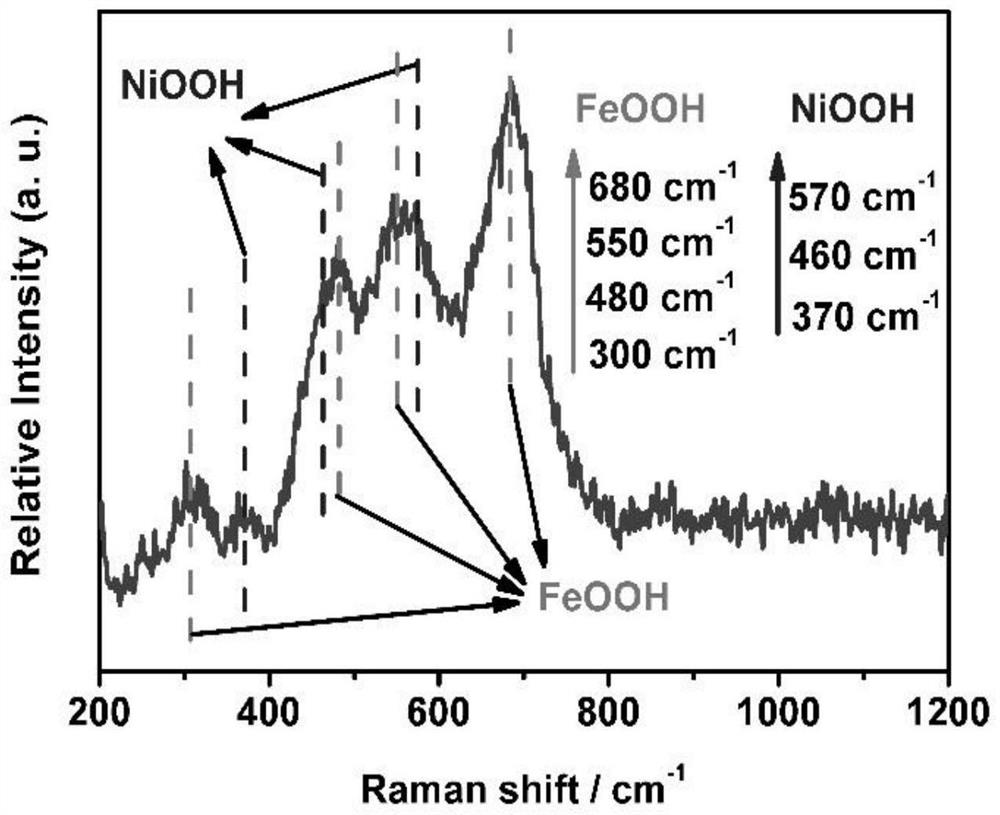
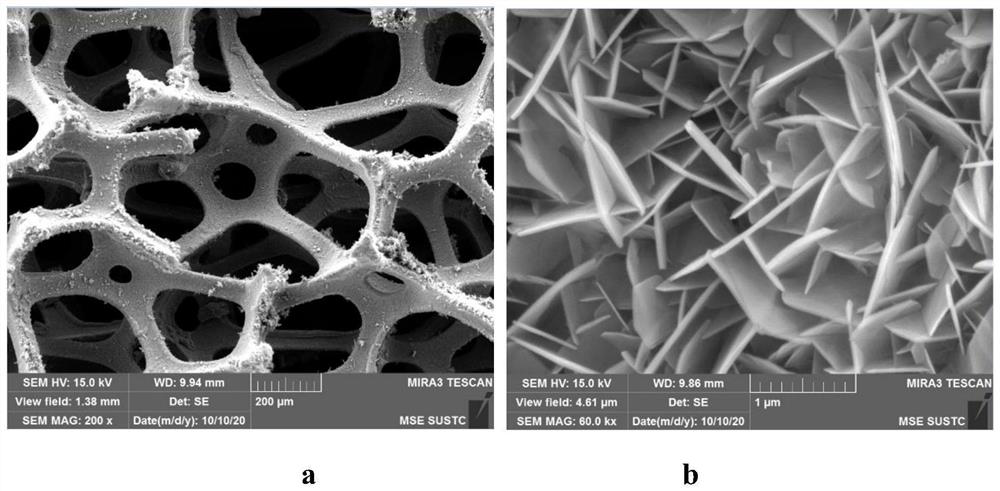
Self-source etching preparation method and application of nickel-doped iron oxyhydroxide self-supporting electrode material
PendingCN114277400AMild treatment conditionsShort reaction timeElectrodesPtru catalystNickel substrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrocatalytic materials, and discloses a self-source etching preparation method and application of a nickel-doped iron oxyhydroxide self-supporting electrode material. The method comprises the following steps: by taking a common foamed nickel substrate as a nickel source, carrying out Fe < 3 + > hydrolysis etching under a low-temperature hydrothermal condition, and then carrying out a secondary hydrothermal precipitation process to obtain the nickel-doped FeOOH catalyst on the in-situ grown foamed nickel substrate. By virtue of the three-dimensional self-supporting structure, the charge transfer resistance can be reduced, the exposed number of active sites of the catalyst is greatly increased, and the material shows relatively excellent electrocatalytic activity when being used for electrocatalytic water oxidation. In addition, the technology is green and environment-friendly, the raw materials used in the technology are cheap and easily available, the treatment time is short, the reaction is mild, the energy consumption is low, and the method has very high application value and very good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com