Method for degrading fluoroquinolone antibiotics in sludge through pyrohydrolysis pretreatment and anaerobic digestion
A fluoroquinolone and anaerobic digestion technology, which is applied in the field of solid waste recycling, can solve the problems of slow hydrolysis rate of microbial cell walls and cell membranes, low gas production, and slow gas production rate, so as to shorten residence time and speed up hydrolysis steps , the effect of fluidity improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A method for thermal hydrolysis pretreatment anaerobic digestion to degrade fluoroquinolone antibiotics in sludge, characterized in that the specific steps are as follows:
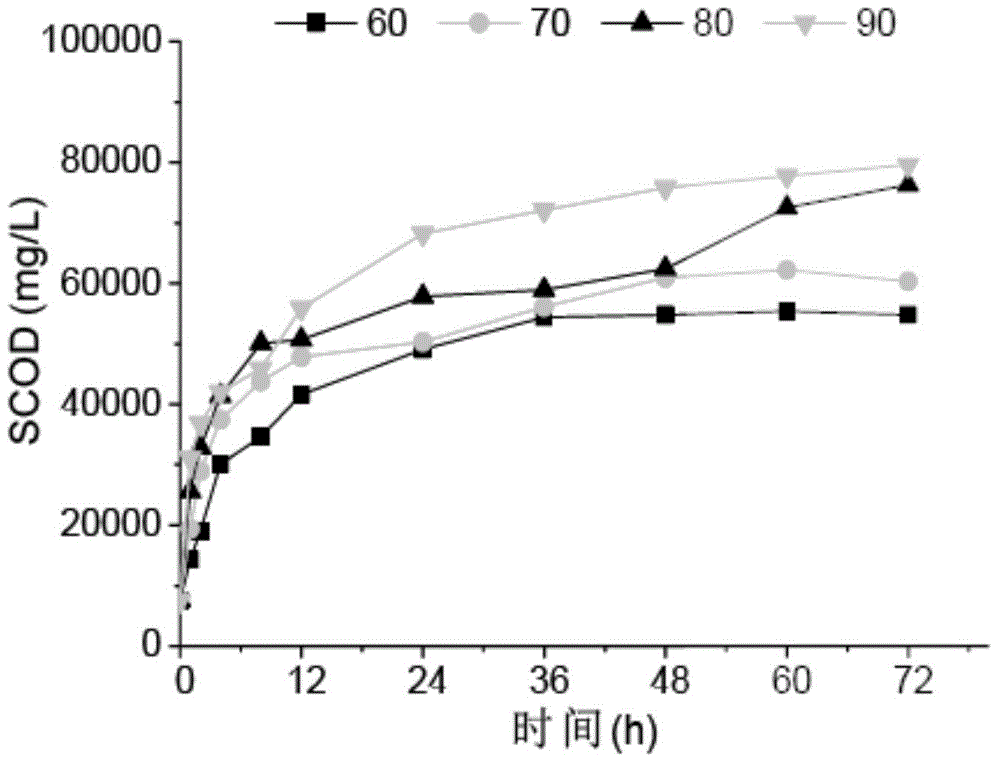
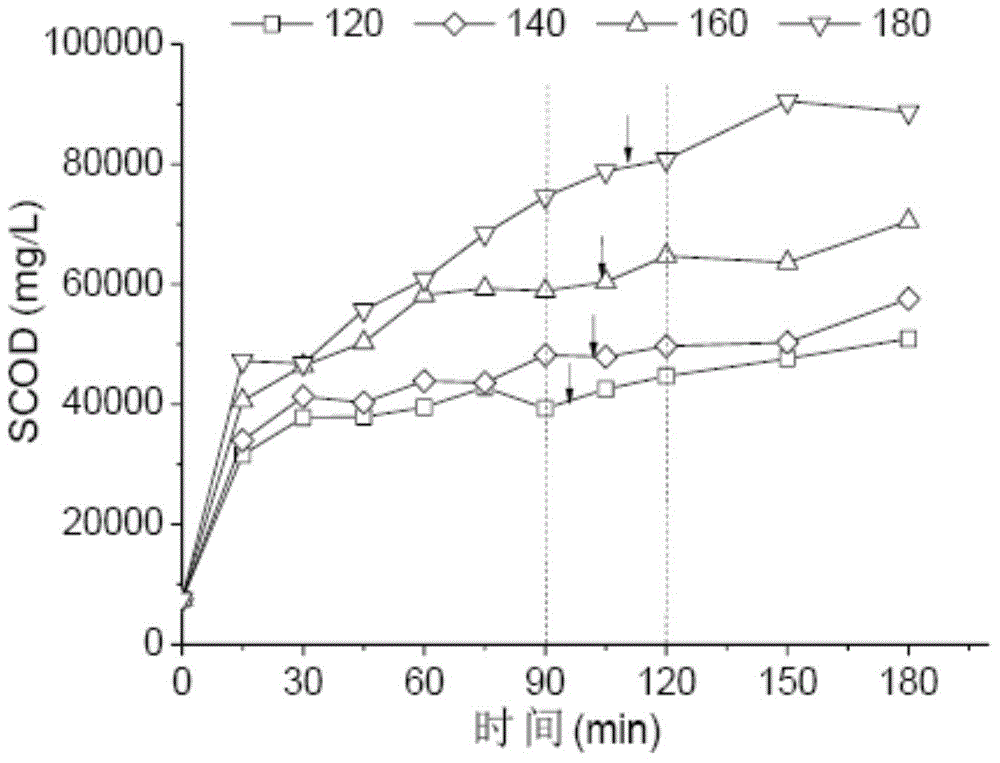
[0045](1) Thermal hydrolysis pretreatment: Add 70g of dewatered sludge into a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene liner, put the liner into the reactor, cover and rotate until tight; attach the thermocouple of the digital thermometer to the reactor The temperature of the outer surface is detected online, which is close to the temperature of the sludge inside the tank. Put the reaction tank into an oven set at 140°C, take out the tank after 180 minutes, and open the tank to take samples after cooling to room temperature;
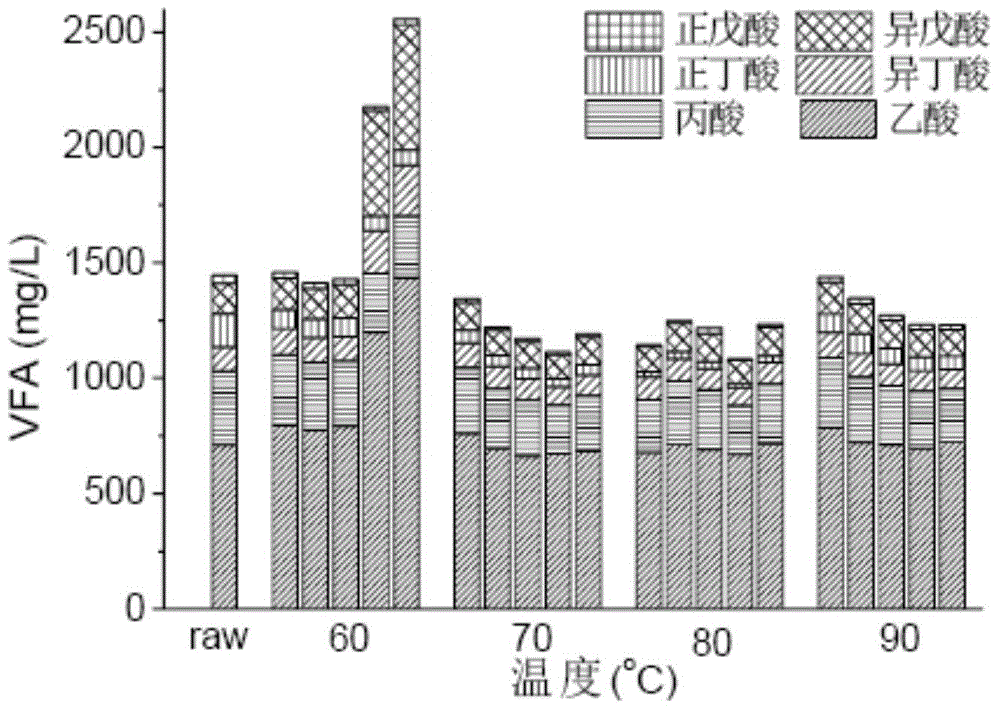
[0046] (2) Dissolution of organic matter: the sample after thermal hydrolysis pretreatment produces soluble organic matter including carbohydrates, proteins, and soluble volatile fatty acids;
[0047] (3) Anaerobic digestion: the sludge after thermal hydrolysis treatment is controlled t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com