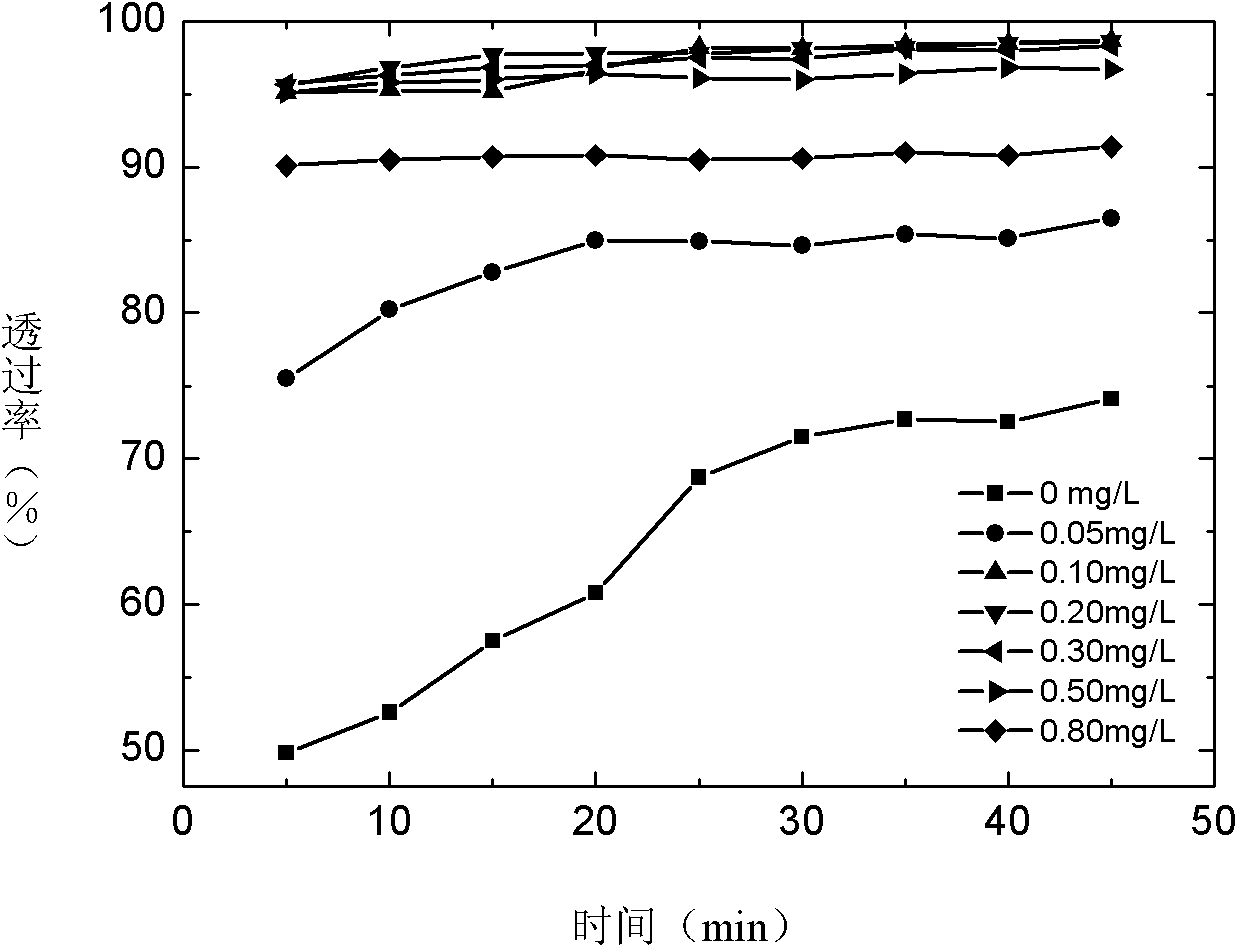
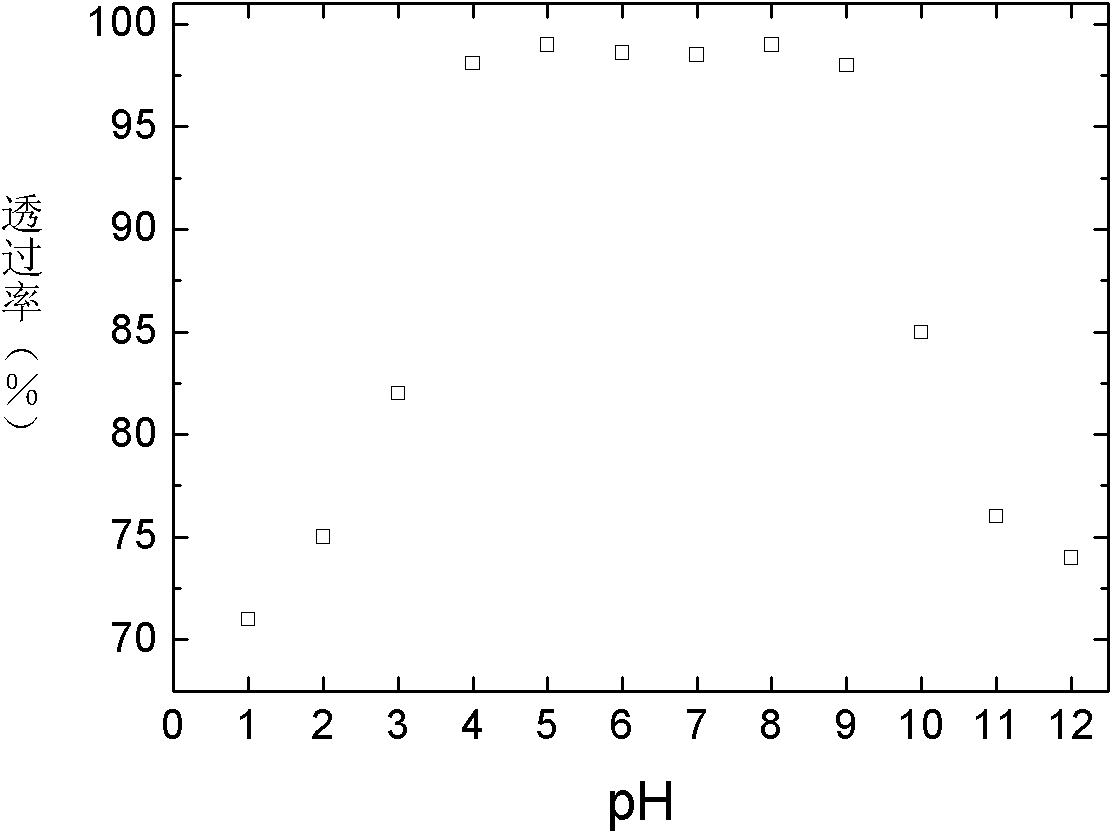
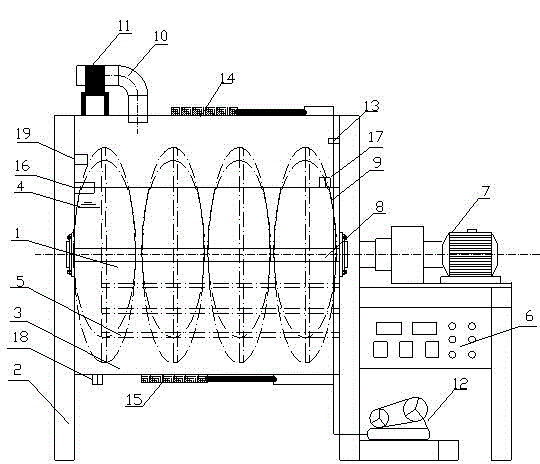
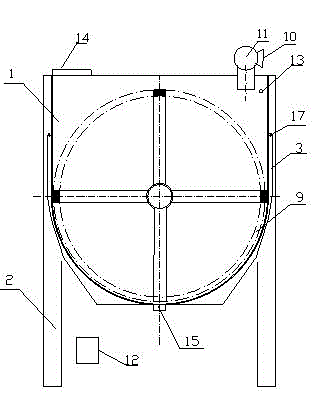
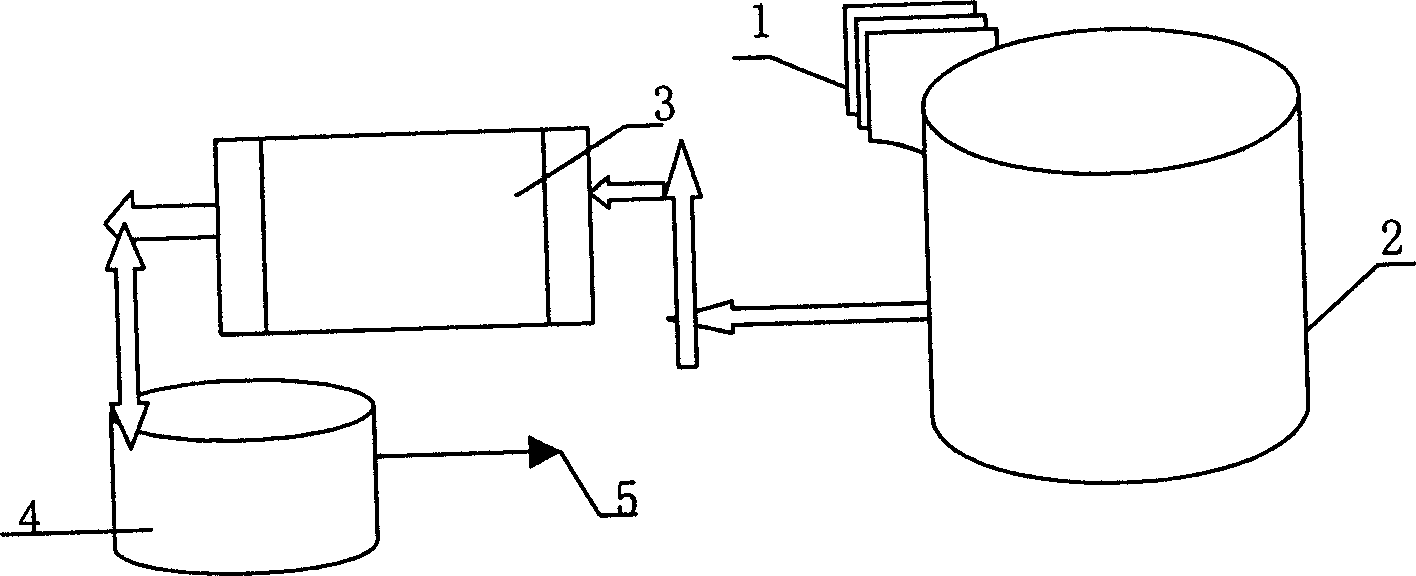
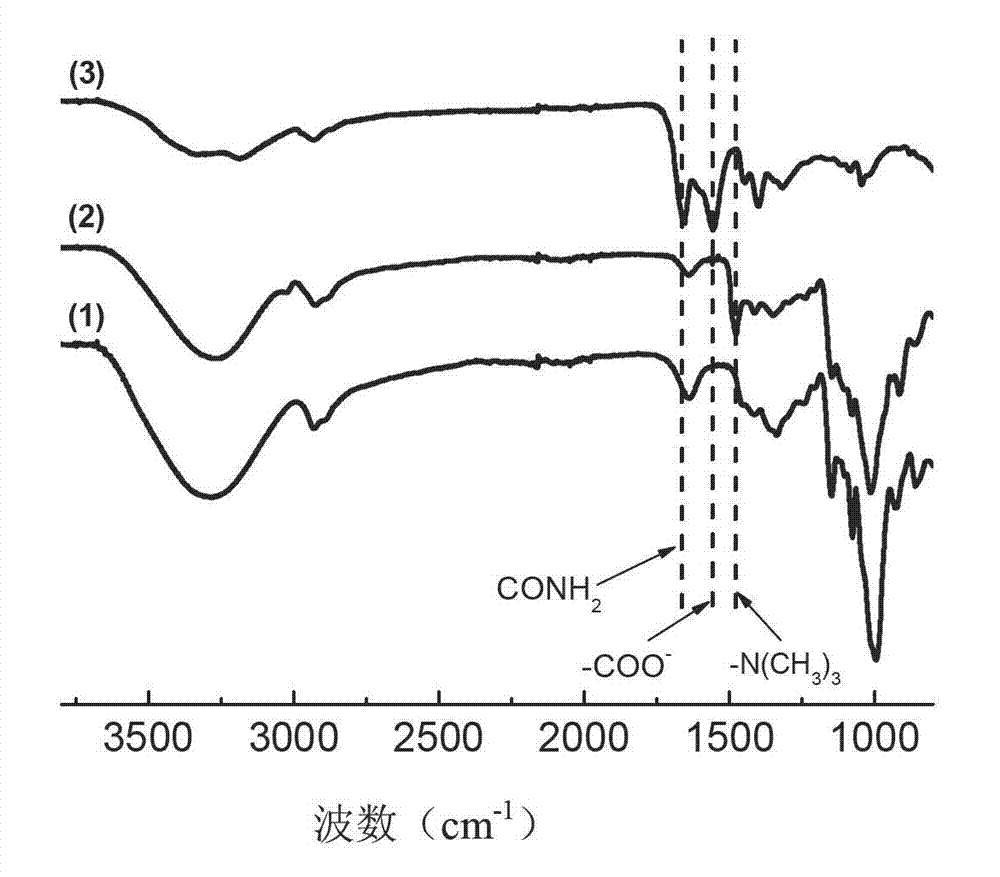
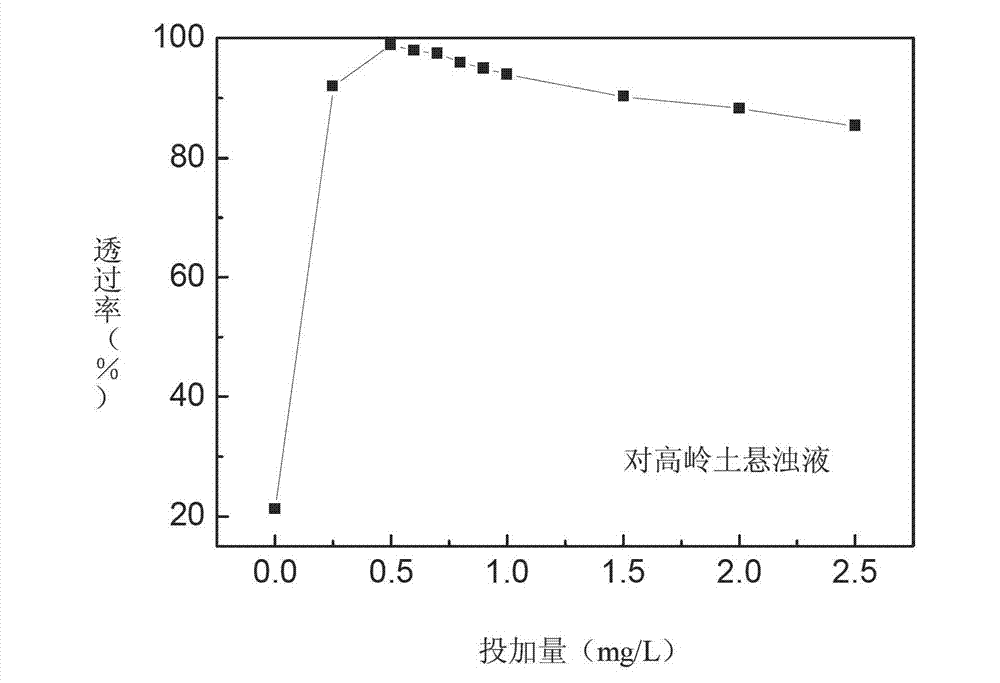
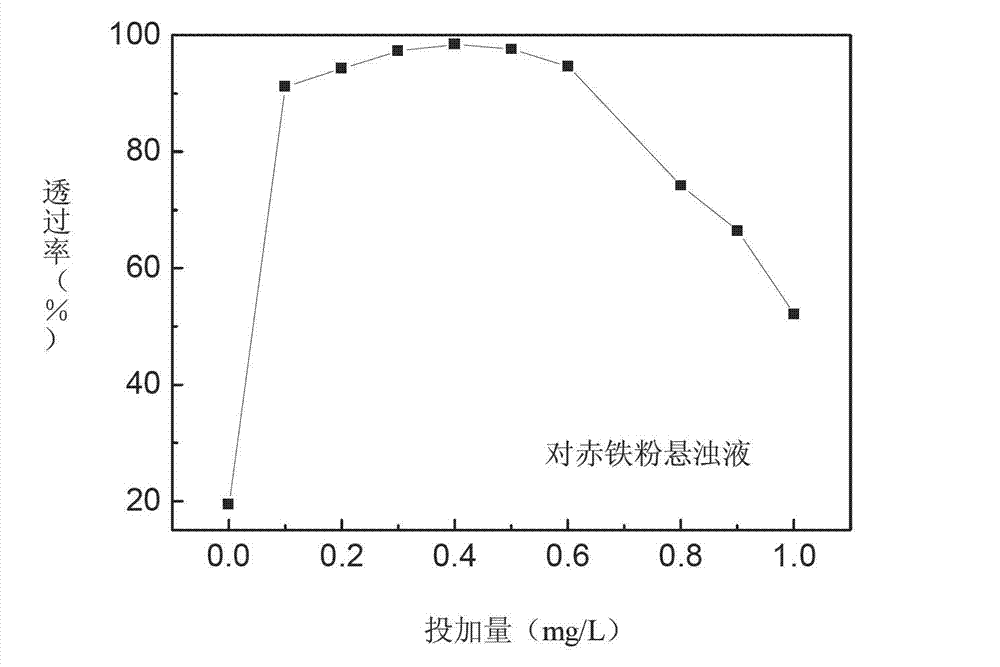
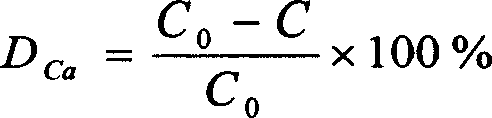Patents
Literature
676results about How to "Produce secondary pollution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intelligent cleaning robot capable of realizing automatic navigation, floor mopping, charging and rag cleaning
InactiveCN104586324ASecondary air pollution will not causeNo pollutionMachine detailsFloor-scrubbing machinesWatering troughMarine navigation
The invention discloses an intelligent cleaning robot capable of realizing automatic navigation, floor mopping, charging and duster cloth cleaning. The intelligent cleaning robot comprises a cleaning robot body and a base station with functions of automatically mopping a floor, charging and cleaning duster cloth, wherein the base station with the functions of automatically mopping the floor, charging and cleaning the duster cloth is an L-shaped fixing device; the cleaning robot body is mutually separated from the base station with the functions of automatically mopping the floor, charging and cleaning the duster cloth; the cleaning robot body and the base station move separately and freely; the front part of the base station with the functions of automatically mopping the floor, charging and cleaning the duster cloth is provided with an automatic charging contact end, and the base station is internally provided with a water filtration and dust extraction system and a water filtration system; the bottom of the base station with the functions of automatically mopping the floor, charging and cleaning the duster cloth is provided with a water trough which is used for automatically cleaning the duster cloth; the cleaning robot body is provided with a navigation component, and the navigation component is a three-coordinate digital gyroscope module. The intelligent cleaning robot has the characteristics of convenience in use, accuracy in positioning, sensitiveness in control response, low cost, small size and the like.
Owner:惠州市鑫沛科技股份有限公司
Passivating agent for governing heavy metal contaminated soil and preparation and use method of passivating agent
ActiveCN104845626AGood stability and good performanceLong-term stabilization/passivationOther chemical processesContaminated soil reclamationClay mineralsSoil science
The invention discloses a passivating agent for governing heavy metal contaminated soil and a preparation and use method of the passivating agent. The passivating agent comprises, in weight percent, 30%-50% of clay minerals, 10%-20% of phosphate, 10%-15% of reducing agents, 10%-15% of sulfide and 15%-20% of alkaline substances. The preparation method includes a step: mixing the clay minerals, the phosphate, the reducing agents, the sulfide and the alkaline substances to mix to obtain the passivating agent. The use method includes the steps: firstly, crushing the heavy metal contaminated soil; secondly, adding the passivating agent into the crushed heavy metal contaminated soil; thirdly, adding water into the crushed heavy metal contaminated soil added the passivating agent to uniformly mix, maintaining the uniformly mixed soil on site, and enabling the passivating agent and heavy metal in the soil to sufficiently react. The passivating agent can effectively meet the urgent requirements of current Chinese heavy metal contaminated soil for high stability, no secondary pollution, durable and stable effect and low cost.
Owner:CHANGSHA HASKY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH DEV CO LTD
Preparation method of grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant
InactiveCN101880356AHigh molecular weightEnhanced bonding and bridging flocculationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSolubilityAcetic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of a grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant, comprising the following steps: carrying out graft copolymerization between carboxymethyl chitosan and polyacrylamide to obtain the grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant, wherein the substituted ratio of a carboxyl group is 5%-90%, and the mass of the polyacrylamide is 40%-80% of the grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant. The carboxymethyl chitosan can be obtained by separation after carboxylation reaction between chitosan and chloroacetic acid. The chitosan can adopt various commercially available products, and preferably, molecular weight of the chitosan is not less than 50,000, more preferably 750,000-850,000. The carboxymethyl chitosan grafting polyacrylamide flocculant prepared by the method of the invention improves water solubility of the chitosan, is applicable to treating water with different electric charges, and has good salt tolerance; and the flocculant can be also widely applied to an acid medium and an alkaline medium, and has wide adaptability to the pH value range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Method and device for high-temperature rapid fermentation on agricultural waste to produce organic fertilizer
ActiveCN104609916ANo secondary pollutionNo smellBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser apparatusAutomatic controlMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a method and a device for high-temperature rapid fermentation on agricultural waste to produce an organic fertilizer. The device comprises a material storage system, a heating system, a stirring system, a dehumidification and biodeodorization system, an oxygenation system, a feeding and discharging system and electric automatic control systems, wherein the material storage system comprises a U-shaped fermentation tank and an overall rack; the heating system comprises a heating insulating jacket, heat-conducting oil and an electric heating tube; the stirring system comprises a gear motor, a stirring shaft and a dual-layer spiral mixing blade; dehumidification and biodeodorization system comprises a dehumidifier and a biodeodorization filter material; the oxygenation system comprises an air compressor and an oxygen delivery pipeline; the feeding and discharging system comprises a feeding hole and a discharge hole; the electric automatic control systems of various units are uniformly connected to an electric control box. According to the method and the device, agricultural waste and thermophilic composite microbial agents can be evenly stirred and mixed, and are rapidly heated, so that the temperature in the device reaches 80-100 DEG C; harmful microorganisms and pathogens in the waste can be effectively inactivated; meanwhile, the activity of the thermophilic composite microbial agents is activated; and the organic fertilizer product is produced within 9 hours.
Owner:天津市生态环境科学研究院
Method and device for decomposing and recycling photovoltaic component
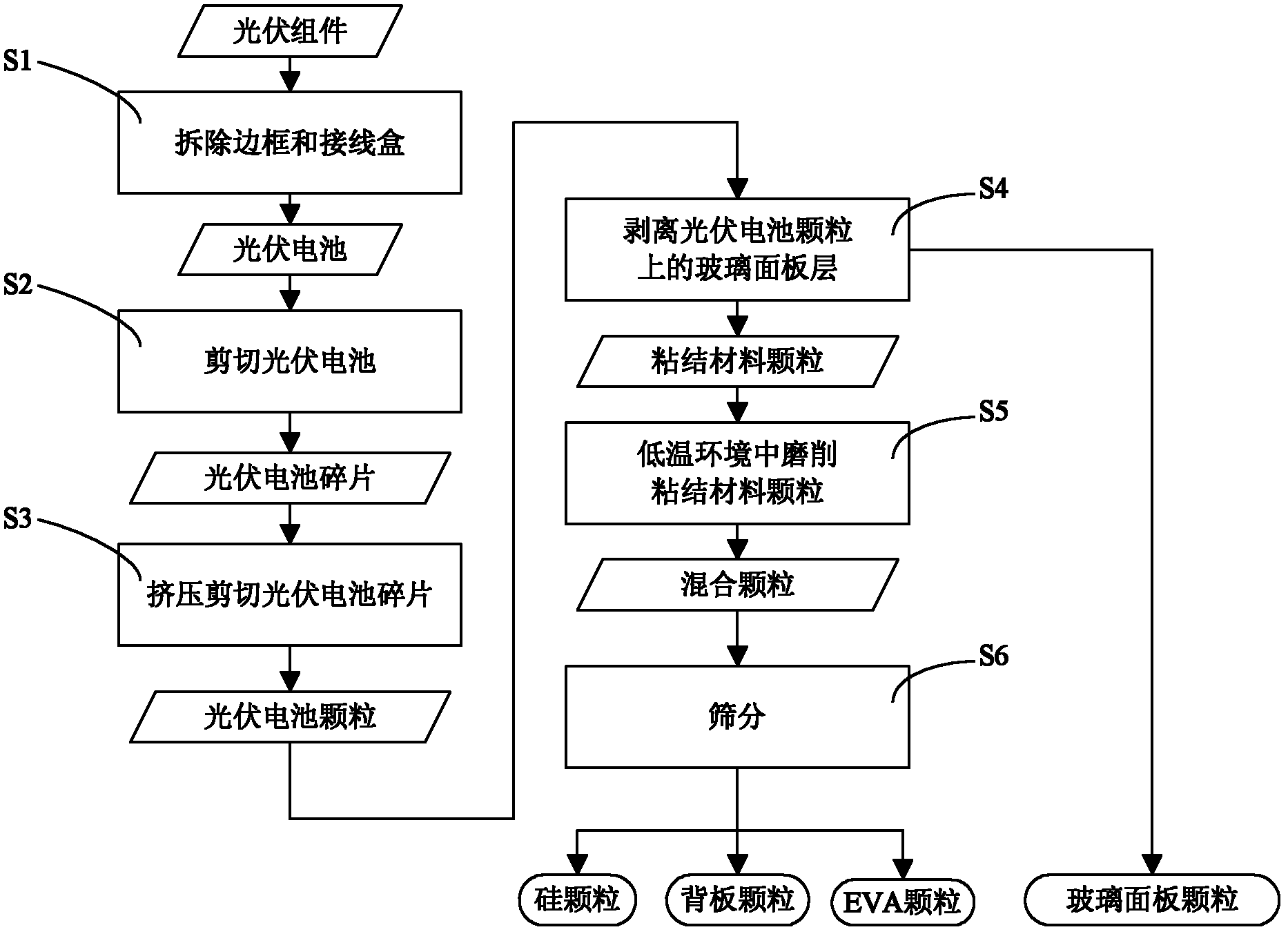
ActiveCN102544239ANo secondary pollutionReduce energy consumptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesChemical treatmentState of art
The invention discloses a method for decomposing and recycling a photovoltaic component. According to the method, glass panel particles, ethylene-vinlacetate (EVA) particles, backboard particles and silicon particles are recycled from the photovoltaic component subjected to border and junction box removal by using methods for shearing, squeezing and shearing, grinding at low temperature, vibrating and screening, and the like. Compared with a method for decomposing and recycling the photovoltaic component by adopting thermal treatment and chemical treatment in the prior art, the method for decomposing and recycling the photovoltaic component has the advantages that: the photovoltaic component is decomposed and recycled by adopting mechanical methods for crushing, grinding at low temperature, vibrating and screening, and the like, thermal treatment is not required during treatment, and the energy consumption is relatively low; and furthermore, according to the method for decomposing and recycling the photovoltaic component, chemical reagents are not used, so that secondary pollution to the environment is avoided, and the method is relatively environment-friendly. The invention also provides a device for decomposing and recycling the photovoltaic component.
Owner:YINGLI GRP
Method used for producing sulfur-based urea compound fertilizer from ammonia desulphurization by-products
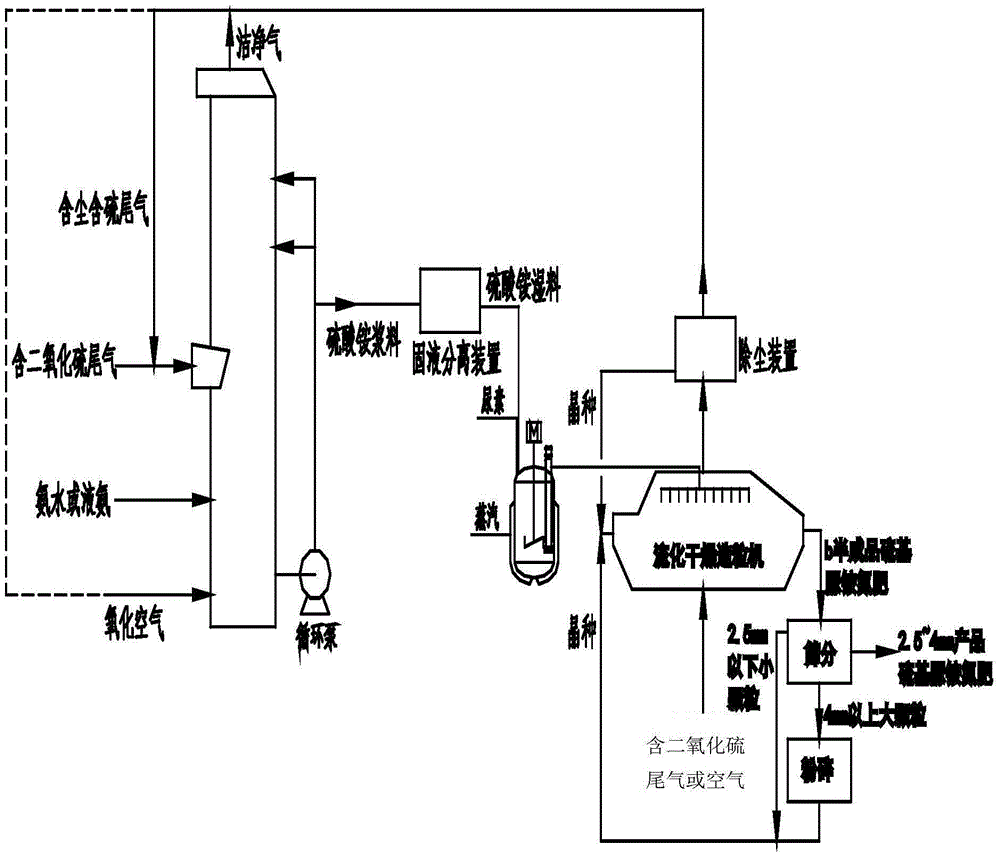
The invention discloses a method used for producing sulfur-based urea compound fertilizer from ammonia desulphurization by-products. The method comprises following steps: sulfur dioxide-containing tail gas is delivered into a desulfurizing tower; ammonium hydroxide or liquid ammonia is sprayed so as to absorb sulfur dioxide, ammonium sulfite is oxidized with air, and an obtained product is subjected to concentration so as to obtain an ammonium sulfate slurry, and the ammonium sulfate slurry is subjected to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain an ammonium sulfate wet material; the ammonium sulfate wet material is delivered into a molten urea groove via a conveyor, solid urea is delivered into the molten urea groove via another hopper, and an obtained mixture is subjected to heating melting, or liquid urea is added directly; fluidization granulation is carried out, wherein dried seed crystal is delivered into a fluidized bed through one end, and is driven to flow to the other end of the fluidized bed in the fluidized bed; a mixed ammonium sulfate-urea composite solution is pumped into the fluidized bed, and multistage spraying is carried out; the sulfur dioxide-containing tail gas is delivered into the fluidized bed or / and fluidized drying with hot air is carried out, and semi-finished product sulfur-based urea compound fertilizer is obtained via seed crystal growth; and a obtained fluidization tail gas is subjected to dust separation, and is delivered into an ammonia desulphurization tower. According to the method, ammonium sulfate low in additional value is changed into sulfur-based urea high in additional value at low investment and operation cost.
Owner:JIANGSU NEW CENTURY JIANGNAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
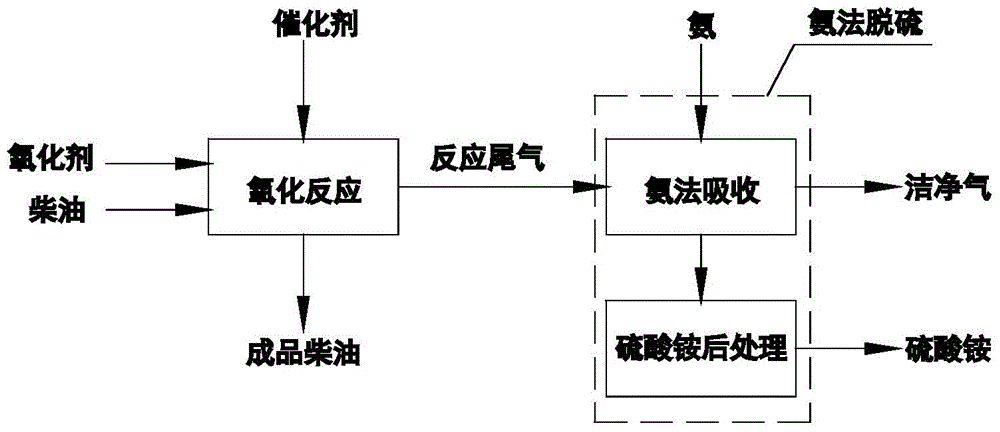
Diesel oxidation ammonia desulfurization method
InactiveCN104927894ASimple processSuitable for mass productionRefining with oxygen compoundsDispersed particle separationSulfur containingPetroleum
The present invention discloses a diesel oxidation ammonia desulfurization method (DOA), comprising steps of:1) oxidation reaction. In the presence of a catalyst, using an oxidant and selectively oxidizing sulfur-containing compounds of diesel to obtain a finished diesel with the sulfur dioxide reaction exhaust and sulfur content amount is not more than 10ppm; 2) ammonia desulfurization. Using an ammonia desulfurization method to process the sulfur dioxide reaction exhaust, converting the sulfur dioxide into an ammonia sulfate fertilizer and emitting clean gas under required standards; and in the presence of the catalyst, using the oxidant and selectively oxidizing sulfur-containing compounds of diesel (mainly mercaptans, sulphides, and thiophenes sulfur-containing compounds). The method is simple in process with no secondary pollution and can be widely used in petroleum refining industry.
Owner:JIANGSU NEW CENTURY JIANGNAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Preparation method of catalyst for catalyzing ozonation for advanced treatment of coal chemical wastewater
InactiveCN103111290AReduce pollution pressureLarge specific surface areaCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSolubilityHazardous substance
The invention discloses a preparation method of a catalyst for catalyzing ozonation for advanced treatment of coal chemical wastewater and relates to a preparation method for the catalyst. The preparation method is used for solving the technical problems that the existing ozonation method is poor in ozone water solubility and low in degradation rate, successfully applied to the advanced treatment of the coal chemical wastewater, and capable of removing the degradation-resistant hazardous substances in water, improving the biodegradability of the wastewater and enabling the quality of the outlet water to reach the first-grade national emission standards. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, washing active carbon particles; secondly, soaking the active carbon in a metal nitrate solution, shaking for mixing and reacting, and taking out the active carbon 12 hours later; and thirdly, drying the active carbon and putting the dried active carbon to a muffle furnace, heating the muffle furnace to 200 DEG C by adopting nitrogen gas as the protective gas, roasting for one hour, continuing heating the muffle furnace to 600 DEG C and roasting for 3 hours at 600 DEG C to obtain the catalyst for treating the coal chemical wastewater. By using the catalyst prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the utilization rate of ozone is greatly improved, and the catalyst is very suitable for the field of coal chemical wastewater treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
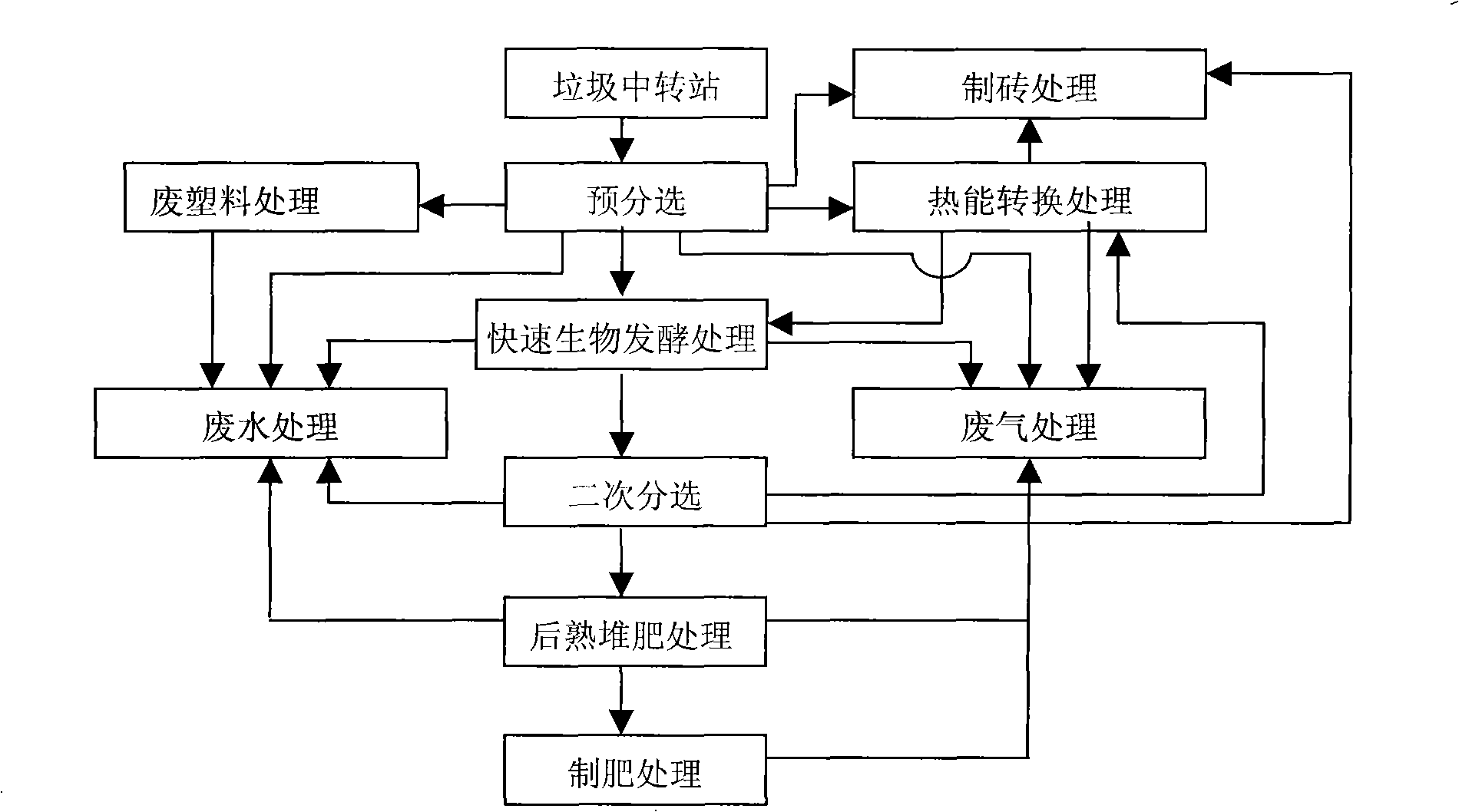
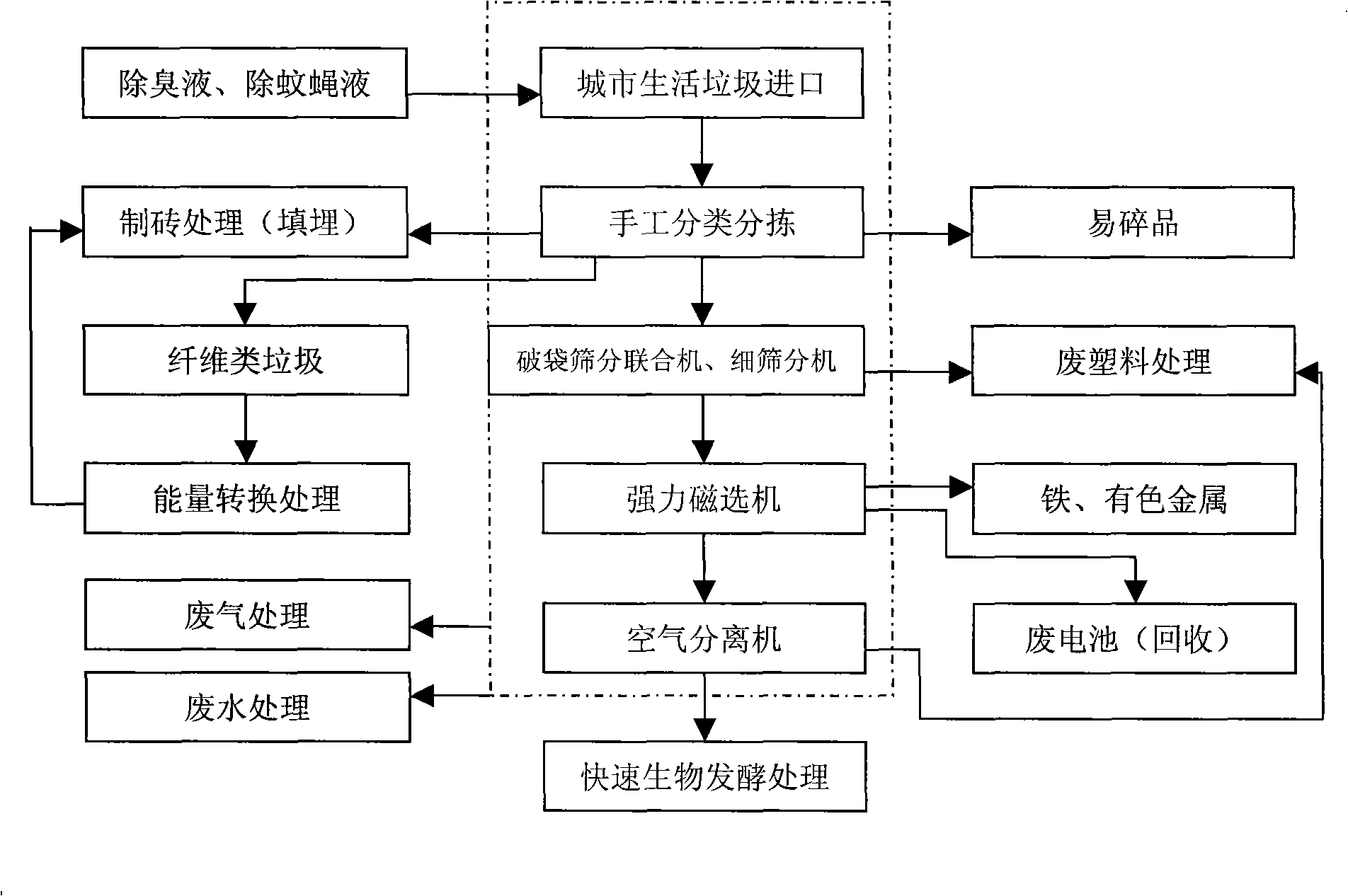
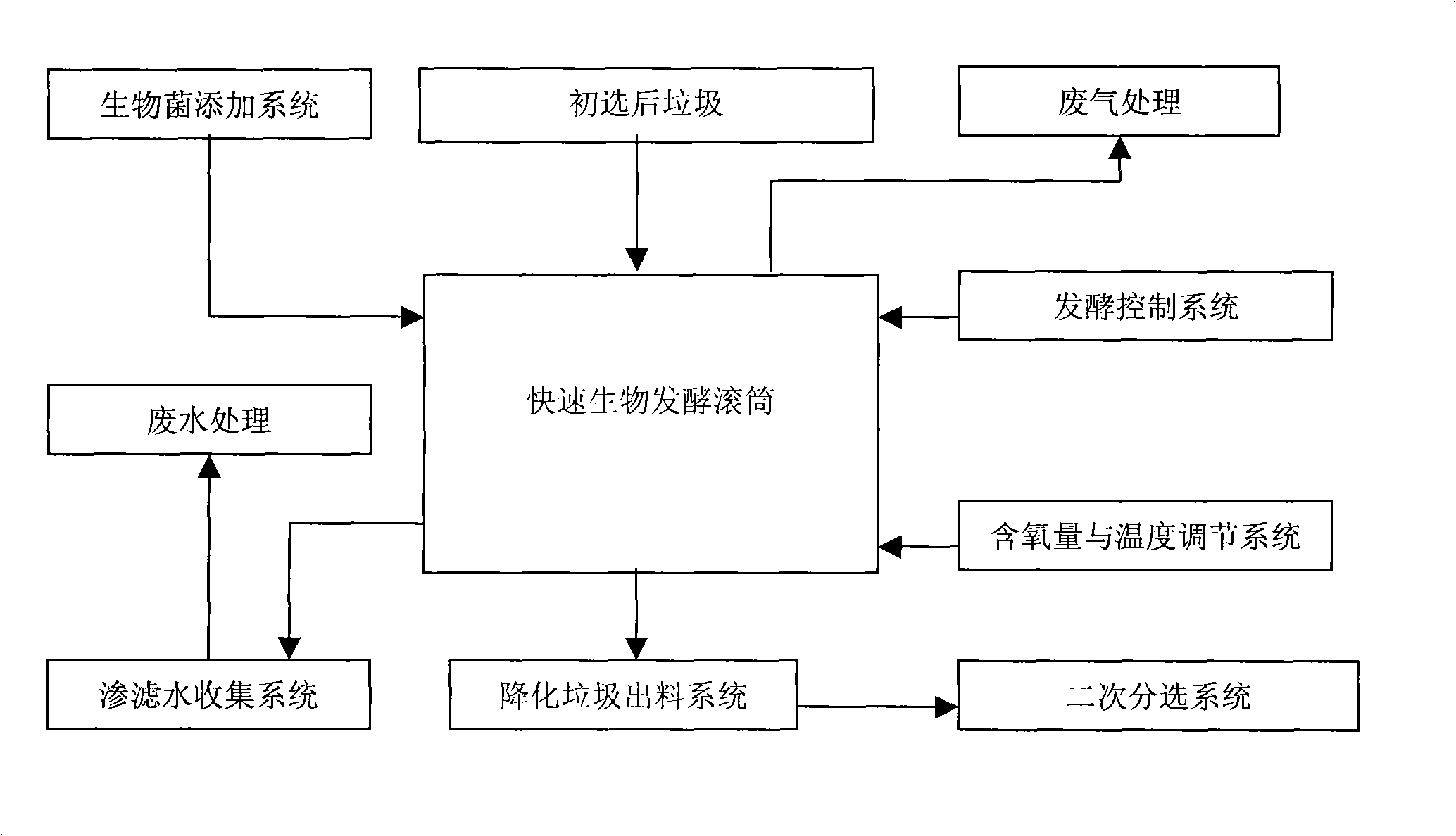
Integral treatment method for city household refuse
InactiveCN101289336ANo secondary pollutionHigh degree of harmlessnessSolid waste disposalClimate change adaptationFiberBrick
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
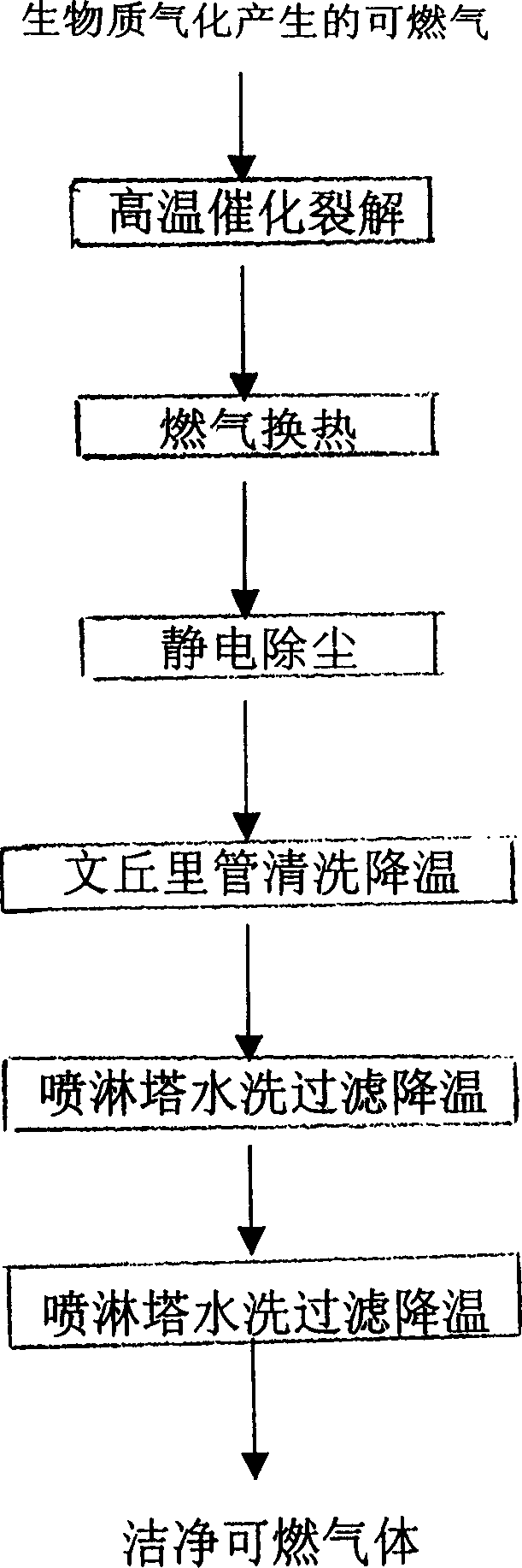
Cracking purification method for combustible gas produced by gasifying crude material
InactiveCN1485415AEfficient recyclingAffect operationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentPurification methodsHigh pressure
A method of degrading and cleansing combustible gases produced during gasifying biological matters. It comprises) passing a cracking machine with a moving bed, the combustible gases will be cracked by high-temperature and catalysis in the charcoal bed at 800-1200degree C, most of tar is removed; b)reducing the temperature of combustible gases from 800degree C to 300-350degree C; c) dedusting by static electricity at a high-voltage electric field of 80000 volts, reducing the temperature to 250-300degree Cú”(d) washed by water, debusting and detarring, reducing the temperature to 60-80degree Cú”(E) washing, filtering and reducing the temperature to below 40degree C, the contents of tar and dust in the combustible gases will be reduced below 50mg / Nm3. The invention could remove completely dust and tar in combustible gases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Humic acid bioactive fertilizer produced by using activation technology and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN102320881AThe effect of increasing production is obviousIncrease profitFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesPhosphatePotassium
The invention relates to a humic acid bioactive fertilizer produced by using an activation technology and preparation and application thereof. The fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-70 parts of weathered brown coal, 5-15 parts of urea, 5-20 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 4-15 parts of potassium chloride, 2-5 parts of trace elements, 3-5 parts of initiator, 1-5 parts of bioactivator and 5-15 parts o bonding agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding the initiator which is diluted by 2-3 times into the weathered brown coal; uniformly mixing; adding the bioactivator, uniformly stirring and standing; adding the urea, monoammonium, potassium chloride, trace elements and bonding agent in sequence; mixing; and granulating. Due tothe adoption of the activated weathered brown coal, the transition speed and transition rate of organic matters in soil are increased, various trace elements exist in chelation state, the absorbing rate, and utilization rate and soil physical and chemical properties of nutrients are remarkably increased and improved. The humic acid bioactive fertilizer can be applied to field and economical cropssuch as rice, vegetables, fruits and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG LIANGYUAN BIOLOGICAL ORGANIC FERTILIZER
Method for preparing dust suppressing covering agent
InactiveCN102558579AWide variety of sourcesReliable sourceOther chemical processesPolymer scienceCross linker
The invention relates to a method for preparing a dust suppressing covering agent, comprising the following steps: preparing raw materials including 3-10 parts of natural starch, 35-50 parts of water, 10-20 parts of acrylic acid, 30-40 parts of 30% sodium hydroxide, 1-5 parts of cross-linking agent and 5-15 parts of initiator; mixing the acrylic acid and the 30% sodium hydroxide to prepare sodium acrylate solution, and filling the sodium acrylate solution into a sodium acrylate solution storage tank for later use; fully mixing the natural starch and the water, and filling starch slurry into a starch slurry storage tank; pumping the starch slurry into a stirring reactor by using a starch slurry pump, heating for 75-80 DEG C by using a clamp sleeve of the stirring reactor, and gelatinizing for 1 hour at constant temperature; stopping heating, decreasing the temperature in the stirring reactor to 45-50 DEG C, keeping the temperature constant, and introducing nitrogen into the stirring reactor to replace the air inside the stirring reactor; adding the prepared sodium acrylate solution, the initiator and the cross-linking agent into the stirring reactor in sequence, introducing nitrogen into the stirring reactor continuously, and the stirring slowly for reaction of 3 hours at constant temperature.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Biodegradable coated carbamide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101723751AReduce releaseReduce rateUrea compound fertilisersFertilizer mixturesCoated ureaNitrification inhibitors
The invention relates to coated carbamide, in particular to a totally biodegradable coated carbamide and a preparation method thereof. The coated carbamide consists of a coated layer and a carbamide core. The main body of the coated layer is polylactic acid and / or polybutylene succinate. The coating process adopts fluidized bed spraying-coated technology, and comprises the following steps: dissolving polylactic acid and / or polybutylene succinate in trichloromethane, adding carboxymethylcellulose, organic and / or inorganic conditioner, urease and / or nitrification inhibitor in the solution, spraying and coating the surfaces of the fluidized carbamide after uniformly mixing the mixture under the stirring of a stirrer to form the uniform and complete organic polymeric membrane layer. The process has the advantages of easy implementation, and capacity of effectively slowing down the release of the nutrient to the outside and the conversion rate of nitrogen in soils, effectively controlling the release of the nitrogen nutrient in soils, and reducing the pressure on environment caused by the rapid release of nutrient. The coated material can be totally biodegradable, and the degradation products have no secondary pollution to the environment.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graphene oxide/chitosan porous composite microspheres and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN105642246AWide variety of sourcesBiodegradableOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCross-linkMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene oxide / chitosan porous composite microspheres. The preparation method of the graphene oxide / chitosan porous composite microspheres comprises the following steps of (1), uniformly dispersing chitosan and graphene oxide in an acetic acid solution to obtain a graphene oxide / chitosan solution; (2), dropwise adding the graphene oxide / chitosan solution into a sodium hydroxide solution to solidify an obtained mixture into the microspheres, cleaning the microspheres to be neutral by using deionized water, and carrying out freeze drying on the microspheres to obtain the graphene oxide / chitosan porous composite microspheres. The microspheres prepared by the preparation method are controllable and uniform in size and appearance; a carboxyl group on the graphene oxide interacts with an amino group on the chitosan, so that a honeycomb structure of the chitosan is assembled together with a porous layer structure of the graphene oxide layer by layer; meanwhile, the graphene oxide also plays the role of a cross-linking agent; the strength of the composite microsphere is improved; the microsphere which is favorable in performance is obtained, and can be applied to the adsorption treatment of dye wastewater.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Method for ultrasonically repairing heavy metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN104607452AShort repair timeHigh removal rateContaminated soil reclamationContaminated soilsUltrasonic assisted
The invention discloses a method for ultrasonically repairing heavy metal contaminated soil. The method comprises at least following steps: preparation of an extracting agent- citric acid solution; mixing of an extracting agent and polluted soil; mechanical oscillation extraction or ultrasonic-assisted extraction for soil; centrifugal separation and filtration of soil after extraction. According to the method, citric acid is selected as the extracting agent, so that the cost is relatively lower, influence on basic physicochemical property of soil is smaller, secondary pollution cannot be caused, the citric acid is an environment-friendly extracting agent, and four heavy metals including cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in the soil can be effectively removed when the extracting agent and ultrasonic waves are jointly applied to repairing of the heavy metal contaminated soil. The method has the characteristics of good removal effect, small extracting agent dosage and short repairing time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Underwater cavitating cleaner for ship
InactiveCN101850836AImprove cleaning efficiencySimple and efficient operationVessel cleaningHullsPollutantEngineering
The invention discloses an underwater cavitating cleaner for a ship, consisting of a hand slap bracket, a disc-shaped shell, a hollow rotary shaft, a cleaning effuser, a high pressure liquid input pipe and a propelling effuser. A plurality of water inlets are arranged at the top of the disc-shaped shell. The hand slap bracket is arranged on the upper side of the disc-shaped shell and connected with the disc-shaped shell. The hollow rotary shaft is arranged on the disc-shaped shell. The cleaning effuser is arranged in the disc-shaped shell and communicated with the hollow rotary shaft. A turbine nozzle is arranged at the end of the cleaning effuser. The high-pressure liquid input pipe and the propelling effuser are respectively communicated with the hollow rotary shaft and located on the upper side of the disc-shaped shell. The high pressure liquid input pipe and the propelling effuser are provided with control valves, respectively. The invention has the advantages of high cleaning efficiency, safety and reliability and is suitably used on irregular and hardly-closed surfaces. By using the cleaner, hard pollutants are cleaned more rapidly than by other methods. Paint is not damaged during cleaning, and secondary pollution to environment can be avoided.
Owner:ZHANJIANG SEA DOWN WATER CLEANOUT TECH
New type of ecological cement and its prepn and application
InactiveCN1609031AImprove corrosion resistanceHas gelling propertiesCement productionUltimate tensile strengthNatural mineral
The new type of ecological cement and its preparation and application belongs to the field of cementing material technology. The materials includes aluminum-rich material F, aluminum-poor material P and guide crystal seed D, and material F and material P are selected from various industrial wastes and natural minerals. Material F has the molar ratio of Si / Ca in 0.5-1.7 and Si / Al in 1.5-3.0, and material P has the molar ratio of Si / Ca in 0.3-1.0 and Si / Al in 1.0-2.6. During use, material F, material P and material D are mixed while adding water to form cementing matter with high strength. The present invention changes industrial wastes into useful material, and has no secondary environmental pollution.
Owner:张立省
Preparation method of grafted amphoteric starch flocculants
InactiveCN103087265AImprove solubilityGood flocculation effectWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationSalt resistance
The invention discloses a preparation method of grafted amphoteric starch flocculants, which is implemented by carrying out graft copolymerization on cationic starches, acrylamide and an acrylic acid so as to obtain a grafted amphoteric starch flocculant, and the grafted amphoteric starch flocculant has the following structure shown in the abstract. The method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages that because a molecular chain is rich in anion-cation groups and has amphoteric characteristics, not only is the flocculation property of materials improved, and also the dissolving property of starches is improved; high polymer materials are wide in resource and low in cost, so that the grafted amphoteric starch flocculant has a high performance price ratio; starches have biodegradability and are non-toxic, so that starches do not produce secondary pollution to water bodies; the grafted amphoteric starch flocculant has various good effects such as flocculation, metal ion adsorption, bacteriostasis, deodorization, decoloring, and capability of effectively reducing the COD value; the grafted amphoteric starch flocculant has a characteristic of high efficiency, and is low in putting amount, and the putting amount is generally 0.1-10mg / L; and the the grafted amphoteric starch flocculant is suitable for treating water bodies with different charges, good in salt resistance and wide in applied pH range, and can be applied when the pH value is 1-12.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Nano-hydroxyapatite/sodium alginate composite material, preparation method and application of nano-hydroxyapatite/sodium alginate composite material
ActiveCN104117341AWide variety of sourcesLow costOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesApatiteFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of nano-hydroxyapatite / sodium alginate composite material. The obtained material can be used for sewage treatment and used for adsorbing and removing heavy metal ions. The method comprises the following steps: quickly pouring a diammonium hydrogen phosphate aqueous solution in the aqueous solution of calcium nitrate, uniformly stirring and mixing, centrifuging to obtain a precipitate, washing the precipitate by using deionized water, re-dispersing the washed precipitate to the deionized water; adding a stabilizer in the obtained suspension, ultrasonically dispersing to obtain stable hydroxyapatite suspension; controlling the mass ratio of hydroxyapatite to sodium alginate, adding sodium alginate in the hydroxyapatite suspension; continuously heating and stirring, controlling the reaction time, evaporating water, carrying out freeze-drying to obtain the product. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation process is simple and controllable, the raw material resource is wide, the cost is low, environment is protected, the pollution does not exist, the uniform compounding of the hydroxyapatite nano-particles and sodium alginate is realized, and the uniform dispersion and the non-reunion of the hydroxyapatite nano-particles are guaranteed.
Owner:武汉华威生物材料工程有限公司
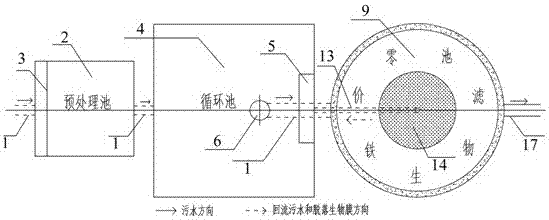
Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthened treatment of rural domestic wastewater
ActiveCN107055754AImprove effluent qualityGood removal effectTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesRural areaLand resources
The invention discloses a circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthened treatment of rural domestic wastewater. The circulating zero-valent iron biofilter is structurally characterized in that a plurality of wastewater treatment units are arranged underground; the rural domestic wastewater is collected into the wastewater treatment units for circulating and strengthened treatment through a water pipeline system; the treated domestic wastewater is used as agricultural irrigation water or for supplementing groundwater or is directly discharged into a river; each wastewater treatment unit comprises a pretreatment pool, a circulating pool and a zero-valent iron biofilter; and the treatment units are structurally independent of one another and communicate through pipes. The circulating zero-valent iron biofilter has the advantages of low maintenance, low energy consumption, water quality impact resistance and high wastewater treatment efficiency; the advantages of intensive and ecological technical routes are coupled through only one pump, complicated drainage conditions of rural areas are coped with easily and the stability of effluent quality is ensured; and meanwhile, surface land resources are saved and the circulating zero-valent iron biofilter is simple and applicable, and is convenient to operate and manage and low in cost.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Composite sodium salt for producing sodium stannate from cassiterite concentrate and application of composite sodium salt
The invention discloses a composite sodium salt for producing sodium stannate from cassiterite concentrate and an application of the composite sodium salt. The composite sodium salt consists of 70%-90% of sodium carbonate, 5%-20% of sodium bicarbonate, 2.5%-5% of sodium borate and 2.5%-5% of sodium humate by mass. When the composite sodium salt is used, the composite sodium salt is ground to the particles with the size fraction of minus 0.1mm being no less than 90% by mass, the cassiterite concentrate of the fine fraction and the composite sodium salt are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:(0.5-2), pelletized and dried, coke powder or anthracite is taken as a reducing agent, the mixture is calcined for 30 minutes-90minutes at the temperature of 800 DEG C-950 DEG C, and the cooled calcined product is ground, leached, filtered, purified, concentrated and crystallized, so that the sodium stannate product is obtained. The adopted composite sodium salt is reasonable in component, can be widely obtained, is low in price, is easy to obtain and does not cause pollution to the environment. With the composite sodium salt, the stable crystal structure of the cassiterite concentrate can be obviously damaged, and the composite sodium salt can be widely applied to various cassiterite concentrates so as to directly produce sodium stannate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
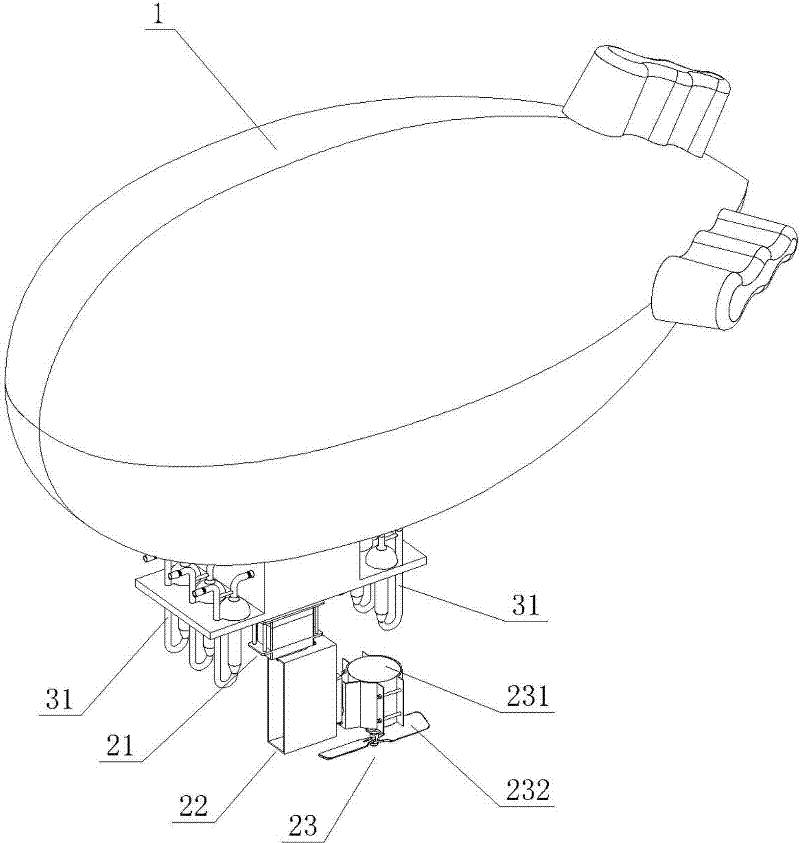
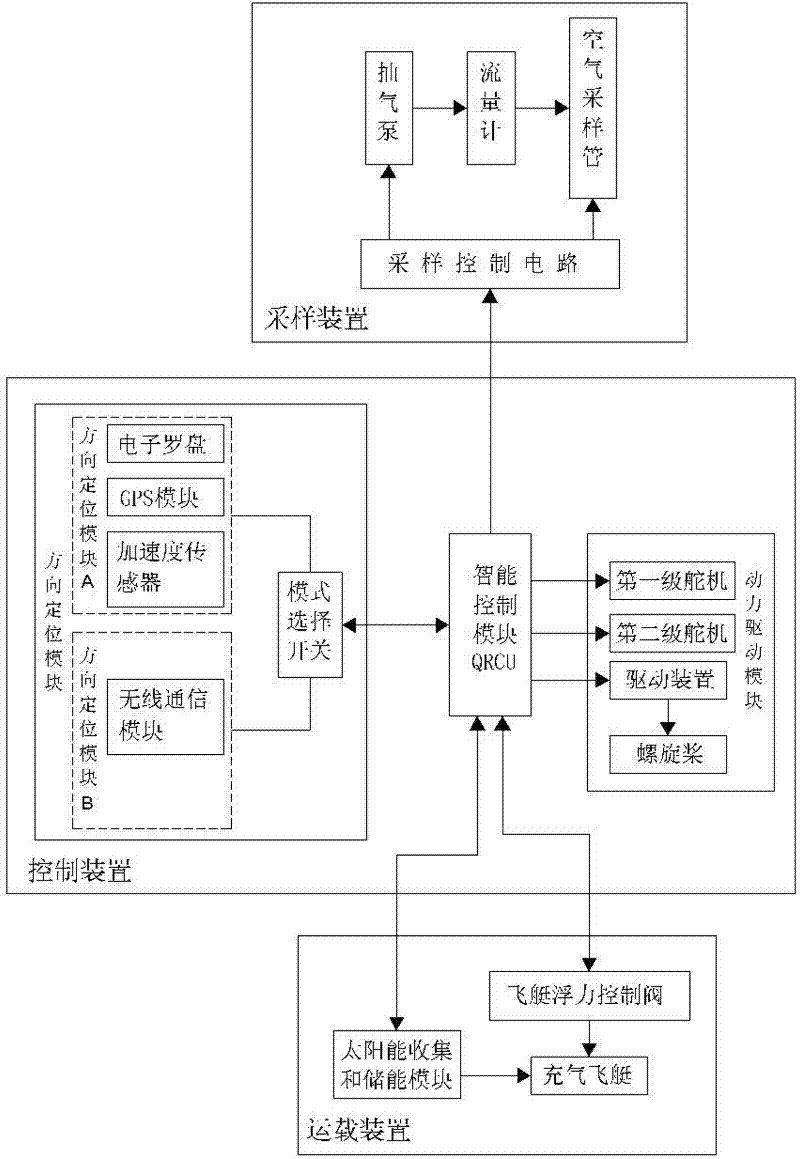
Air sampling aircraft and air sampling method
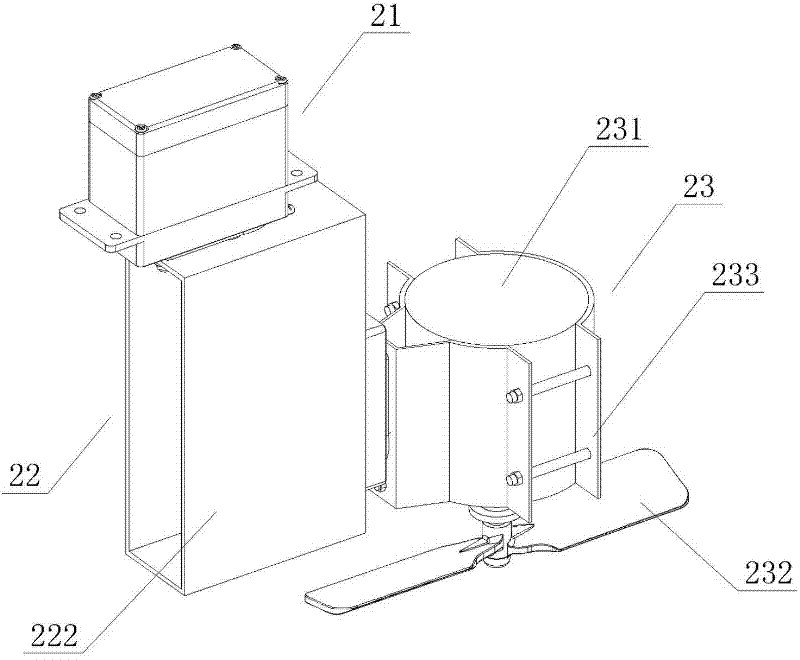
InactiveCN102249002AProtect life safetyNo secondary pollutionWithdrawing sample devicesAircraftsPropellerTerrain
The invention provides an air sampling aircraft which comprises a flight main body, a control device and a sampling device which are disposed on the flight main body, wherein the control device comprises an intelligent control module, a direction positioning module which is connected to the intelligent control module and is used to control and adjust the flying direction of the flight main body and to position the sampling device, and a power driving module which is connected to the intelligent control module and is used to driving the operation of the flight main body, and the power driving module comprises a first-grade actuator, a second-grade actuator, a driving motor, a propeller, and a driving device. Because a combined structure of the flight main body, the control device, and the air sampling device is employed, not only air samples can be collected automatically, but also the time and regional restriction is broken through; more importantly, with the automatic technology, notonly air sampling by sampling technicians is convenient, but also the life safety of sampling personnel is protected during air sampling under certain specific conditions such as regions with inaccessible and strategic terrain or a lot of toxic gas.
Owner:杨当立
Method utilizing charcoal to achieve rural non-point source pollution denitrogenating
InactiveCN103130337AWide variety of sourcesLow priceTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiocharChemical agent
A method utilizing charcoal to achieve rural non-point source pollution denitrogenating includes the steps of modifying agricultural wastes in metal ionic solution, achieving air drying for the agricultural wastes for later using, placing the agriculture wastes after air drying in a sealed stainless container, obtaining charcoal through anoxycausis, taking out and smashing the prepared charcoal, burying the charcoal under an agricultural non-point pollution waste water collecting ditch pond, and mixing soil under the ditch pond with the charcoal to enable microbes in the soil under the ditch pond to be attached on the charcoal. When rural non-point source waste water is generated, the waste water is stored in the collecting ditch pond. Accordingly, when the waste water is infiltrated into the soil, ammonia nitrogen is absorbed by the charcoal, and nitrate nitrogen is taken as a slow-release carbon source by the charcoal to achieve denitrification under the function of the microbes in the soil. According to the method utilizing charcoal to achieve rural non-point source pollution denitrogenating, raw material is extensive in source and low in price, and secondary pollution is not generated to the soil due to fact that chemical agent is not added in a whole process. In addition, the operation process is very simple, the requirement for management is low, the quantity of reform for rural local non-point source pollution devices is relatively small, and cost is low.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103172790AHigh molecular weightEnhanced bonding and bridging flocculationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSodium carboxymethylcellulosePolyacrylamide
The invention discloses a hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent. The hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent is characterized by being obtained by carrying out hydrolysis reaction onto graft carboxymethyl cellulose under alkali condition, wherein the hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent has the structure shown in the specification; the mass of polyacrylamide is 5%-65% of that of the hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent; and the mass of the polyacrylic acid is 5%-70% of the that of the hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent. The hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent disclosed by the invention has the triple characteristic of carboxymethyl anionic group, polyacrylamide and polyacrylic acid. Moreover, the carboxymethyl anionic group, polyacrylamide and polyacrylic acid are linked by chemical bonds, so that the molecular weight of carboxymethyl cellulose is improved and the bonding and bridging flocculation is enhanced. Besides, the soluble pH range of the hydrolysis graft strengthened anionic carboxymethyl cellulose flocculating agent is expanded due to the existence of the grafting chain, and therefore, the pH sensitivity of the flocculation effect of carboxymethyl cellulose is effectively restrained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Process for demetalizating of hydrocarbon oil
InactiveCN1693424ANo secondary pollutionReduce the impact of processingHydrocarbon oils refiningOil processingDemulsifier
A demetallating process for the hydrocarbon oil includes such steps as mixing the acetylacetone as demetalating agent with raw hydrocarbon oil, water and demulsifier, and oil-water separation. Its advantage is high effect to remove Ca, Mg, Fe, etc.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
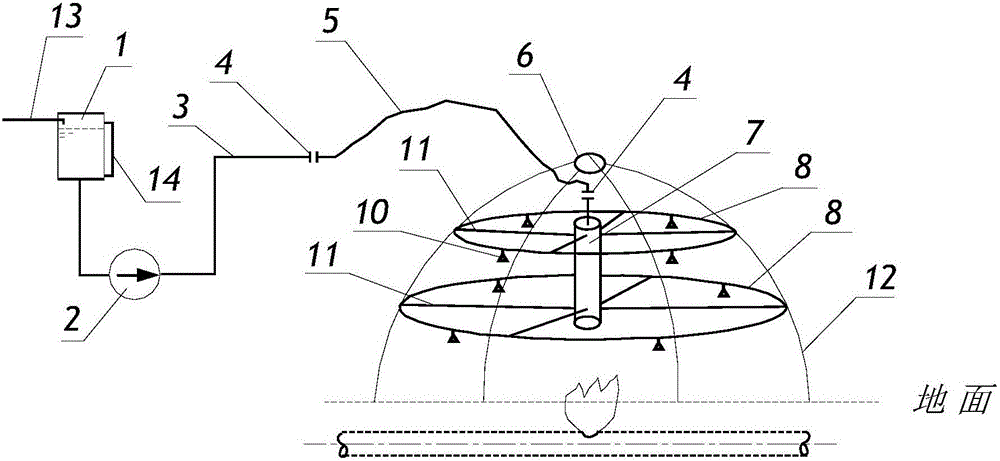
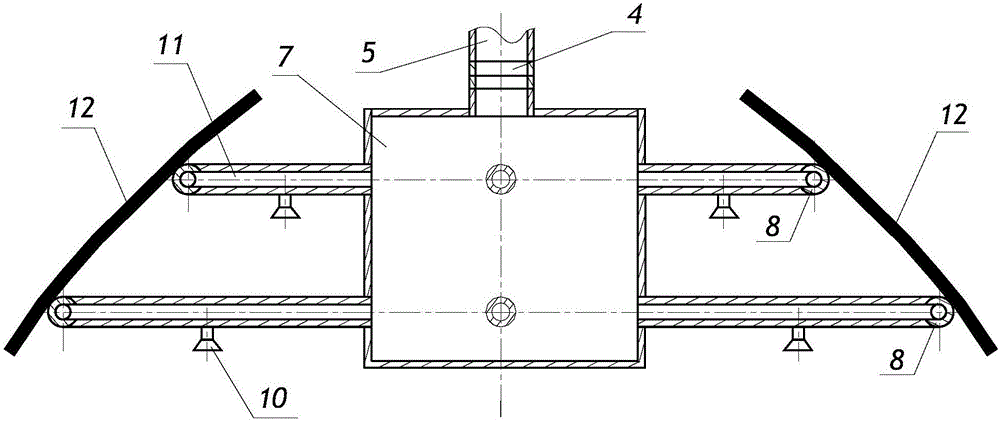
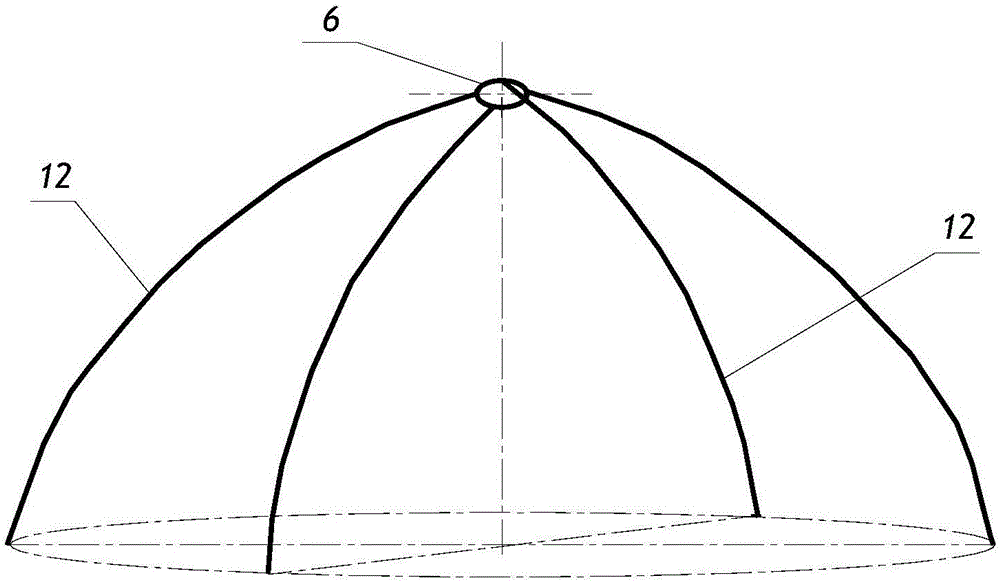
Annular fine water mist fire extinguishing cover system
ActiveCN106581891AFire extinguishing speedImprove fire extinguishing efficiencyFire rescueSpray nozzleWater pipe
The invention discloses an annular fine water mist fire extinguishing cover system. The annular fine water mist fire extinguishing cover system comprises a fine water mist spraying mechanism; the fine water mist spraying mechanism includes a high-pressure water distributor and more than two annular water pipes; each annular water pipe is communicated with the high-pressure water distributor through more than high-pressure water distribution pipes; and each annular water pipe is respectively provided with more than two fine water mist nozzles. The annular fine water mist fire extinguishing cover system is fast in fire extinguishing speed and high in fire extinguishing efficiency, and cannot generate secondary pollution to surrounding environments. The annular fine water mist fire extinguishing cover system can be used for cooling exposed combustible gas or liquid pipes after fire extinguishing, overcomes the defects of low fire extinguishing efficiency and bad fire extinguishing agent waste in a traditional spraying dry powder fire extinguishing agent, and satisfies the purposes and the technical requirements of effectively extinguishing the oil tank fire.
Owner:广州福勒自动控制设备科技有限公司
Treating system, separating apparatus and treating method for oily sludge
PendingCN106630514AExpand the scope of applicationLow oil contentWaste water treatment from quariesSievingOil contentHandling system
The invention discloses a treating system, separating apparatus and treating method for oily sludge. The separating apparatus comprises a stirring drum, a first drive unit, a stirring shaft, multiple layers of separator plates and stirring members, wherein the stirring shaft is arranged in the stirring drum; the multiple layers of separator plates divide the stirring drum into multiple layers of space; each of the multiple layers of space is provided with one stirring member which is connected with the stirring shaft; the upper part of the stirring drum is provided with a sludge inlet and first floating oil discharge outlet; the lower part of the stirring drum is provided with a sludge outlet; and the bottom or lower part of the stirring drum is provided with a feed inlet for one or more selected from a group consisting of an extractant, air-dissolved water and solid foam particles. The treating system is applicable to dehydration of a variety of oily sludge, enables the oil content of oily sludge to be decreased to 3% or below, can maximally recover oil and does not produce secondary pollution like waste water.
Owner:仇霞霞
Amphoteric polysaccharide/cross-linked graphene oxide double-network composite hydrogel adsorption material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107570121AWide variety of sourcesLow priceOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCvd grapheneIon
The invention discloses an amphoteric polysaccharide / cross-linked graphene oxide double-network composite hydrogel adsorption material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, after uniformly mixing graphene oxide, a polysaccharide and an amphoteric ionic monomer (or a mixture of a cationic monomer and an anionic monomer), preparing single-network composite hydrogel through a microwave assisted grafting and copolymerization manner; then, crossly linking the single-network composite hydrogel with the graphene oxide in a water solution of apolyamino or amino-terminated polymer to obtain the double-network composite hydrogel adsorption material. The double-network composite hydrogel adsorption material prepared by the preparation methodhas excellent mechanical properties and can be used for removing heavy metal ions and organic pollutants at the same time; the double-network composite hydrogel adsorption material has a relatively high adsorption amount and a relatively rapid adsorption speed on the heavy metal ions and the organic pollutants.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Amino-acid-modified chitosan flocculating agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105601764AAvoid pollutionAvoid the risk of secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationChemical reaction
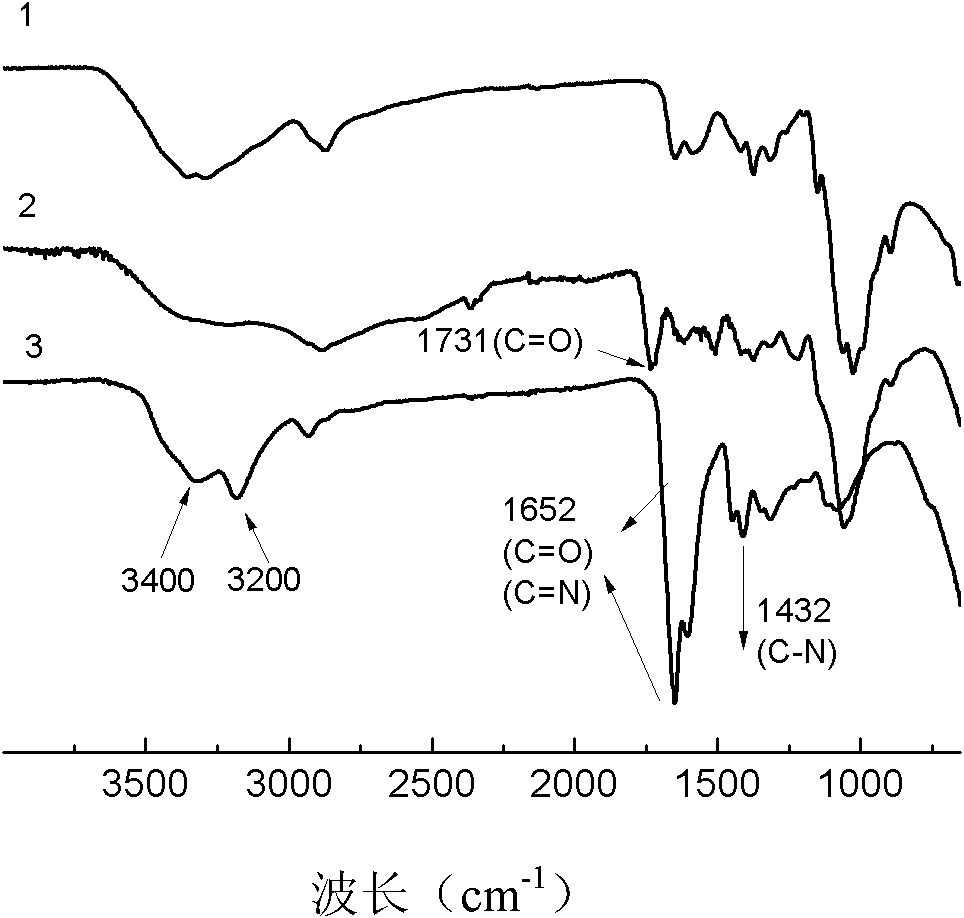
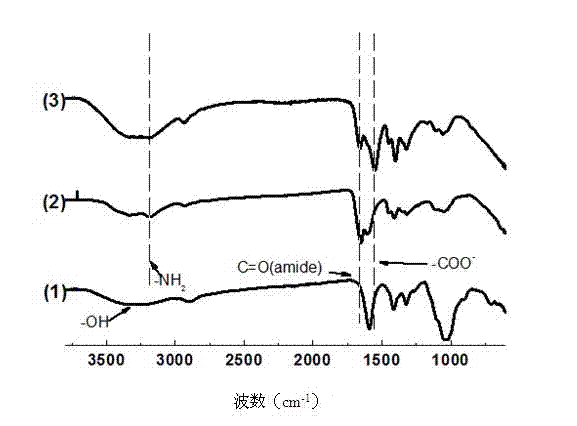
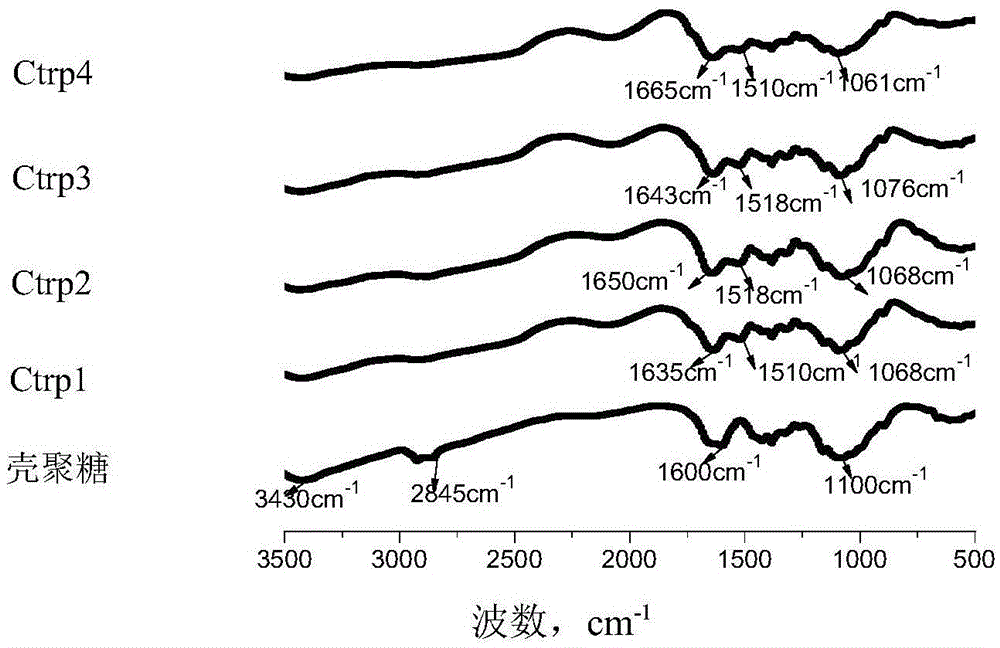
The invention discloses an amino-acid-modified chitosan flocculating agent and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of organic synthesis of high polymer materials. The flocculating agent is prepared from chitosan and amino acid through a chemical reaction, the amino acid is one of tryptophan or tyrosine or phenylalanine, the molecular weight of the chitosan is 110-840 thousand, and the deacetylation degree is 65-95%; the infrared spectrogram of the amino-acid-modified chitosan flocculating agent is provided with a characteristic absorption peak within the range of 1500-1520cm<-1>. By means of the flocculating agent, the molecular weight is increased, the bridging flocculation effect is enhanced, furthermore, the requirement that the residual flocculating agent causes no secondary pollution to a water body can be met, an introduced amino acid functional group contains an aromatic ring structure, and good flocculation capability is achieved for antibiotics in the water body.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Formaldehyde scavenger and preparation method thereof
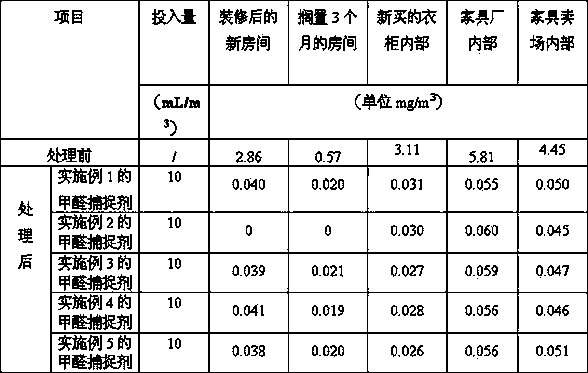
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical preparations and particularly relates to a formaldehyde scavenger and a preparation method thereof. The formaldehyde scavenger comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-20 parts of amino acid, 10-20 parts of starch, 5-10 parts of casein, 5-10 parts of polysorbate, 10-15 parts of isoamyl alcohol, 30-50 parts of plant flower extracts, 5-10 parts of active carbon carboxymethylcellulose, 6-8 parts of a penetrant, 5-10 parts of pillared rectorite, 10-20 parts of chitosan and 80-120 parts of deionized water. The formaldehyde scavenger provided by the invention is high in absorption efficiency and capable of eliminating free formaldehyde in air, reducing the release amount of formaldehyde in a decorated product and simultaneously improving the stability of the formaldehyde in the decorated product so as to solve the problem of formaldehyde pollution caused after indoor decoration and the health of people is beneficial.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com