Method for efficiently removing antibiotic residues in livestock manure through normal-temperature fermentation
A technology of livestock and poultry manure, normal temperature fermentation, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological sludge treatment, animal husbandry wastewater treatment and other directions, can solve problems such as inability to withstand high temperature, and achieve enhanced degradation, high removal efficiency, and simple temperature control. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Test material: pig manure; the type is free-range pigs raised by farmers; the appearance is dark brown, relatively wet, and the smell is very strong; the original pH is 7.4; 5 kinds of sulfonamides, 5 kinds of quinolones, 3 Four kinds of tetracyclines and three kinds of macrolide antibiotics, of which the total residual concentration of tetracyclines per kilogram of dry pig manure is 77.4mg, the total residual concentration of quinolones is 35.9mg, the total residual concentration of sulfonamides is 15.1mg and macrolides The total residual concentration is 12.8mg.
[0026] A method for efficiently removing antibiotics in livestock and poultry manure by normal temperature fermentation, the method consists of the following steps:
[0027] (1) Add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass ratio of 1% to 500g of fresh pig manure, stir well, and place it at room temperature around 25°C for 1-2 hours;
[0028] (2) Use 10M sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the pig ma...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Test material is the same as embodiment 1.
[0036] A method for efficiently removing antibiotics in livestock and poultry manure by normal temperature fermentation, the method consists of the following steps:
[0037] (1) Add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass ratio of 1% to 500g of fresh pig manure, stir well, and place it at room temperature around 25°C for 1-2 hours;
[0038] (2) Using 10M sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the pig manure treated in step (1) to 5.4;
[0039] (3) Spread the livestock and poultry feces treated in step (2) on an 18cm petri dish, and place them in a light incubator with 24 hours of light and 0 hours of darkness. The light source is LED energy-saving light source, and cultivated at 30°C for 4 -5 days.
[0040] In this example, the control treatment is to spread the livestock and poultry feces treated in step (2) on an 18cm petri dish, use newspapers for shading culture, place them in a light incubator, and cultivate them...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Test material is the same as embodiment 1.
[0043] A method for efficiently removing antibiotics in livestock and poultry manure by normal temperature fermentation, the method consists of the following steps:
[0044](1) According to the weight percentage of 10% and 20%, wood chips are mixed with fresh pig manure;
[0045] (2) Add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass ratio of 3% to the pig manure sawdust mixture treated in step (1), stir evenly, and place it at room temperature around 25°C for 1-2 hours;
[0046] (3) Use 10N sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the sample treated in step (2) to 5.4;
[0047] (4) Spread the sample treated in step (3) on an 18cm petri dish and culture it at 30°C for 4-5 days.
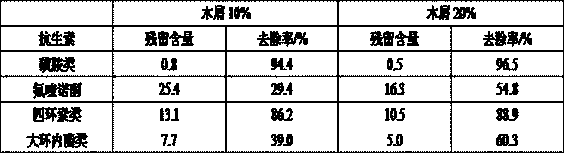
[0048] In this example, after the fermented pig manure samples were freeze-dried, the antibiotic content was determined by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In the present embodiment, after 4-5 days of solid-state ferme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com