Patents
Literature
201 results about "Magnetic resonance scanner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A magnetic resonance imaging instrument (MRI scanner), or "nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging" scanner as it was originally known, uses powerful magnets to polarize and excite hydrogen nuclei (single proton) in water molecules in human tissue, producing a detectable signal which is spatially encoded, resulting in images of the body.
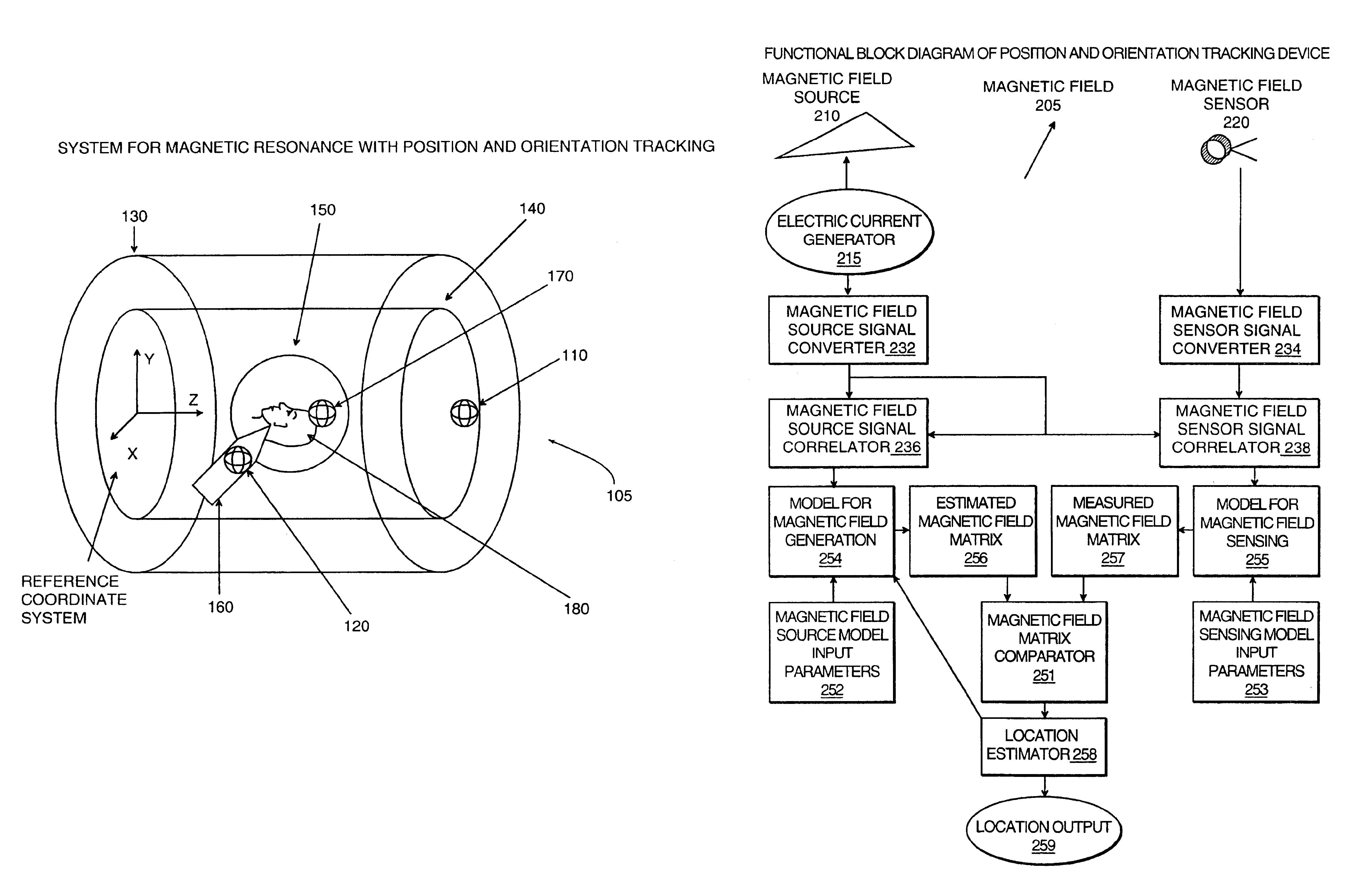
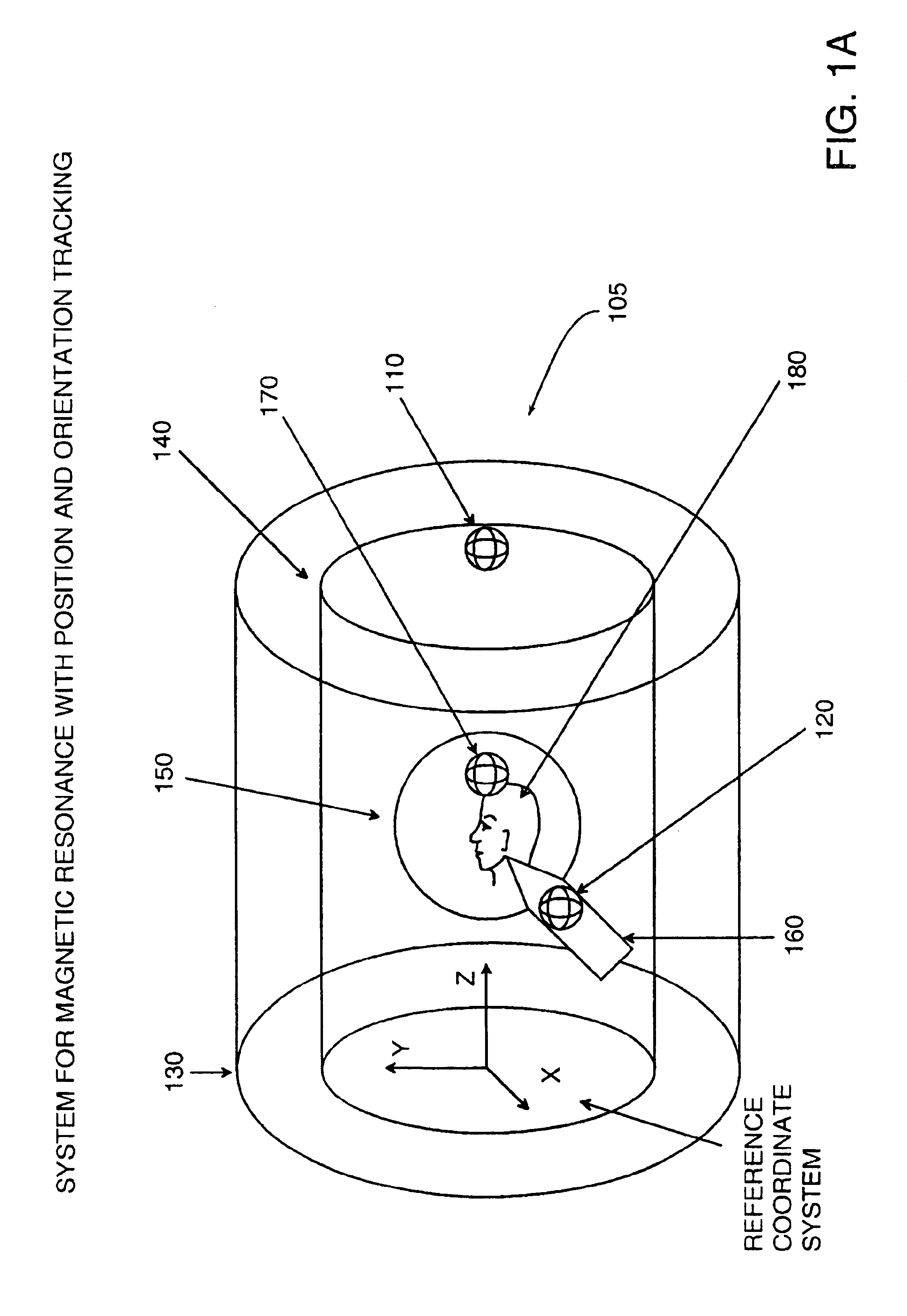
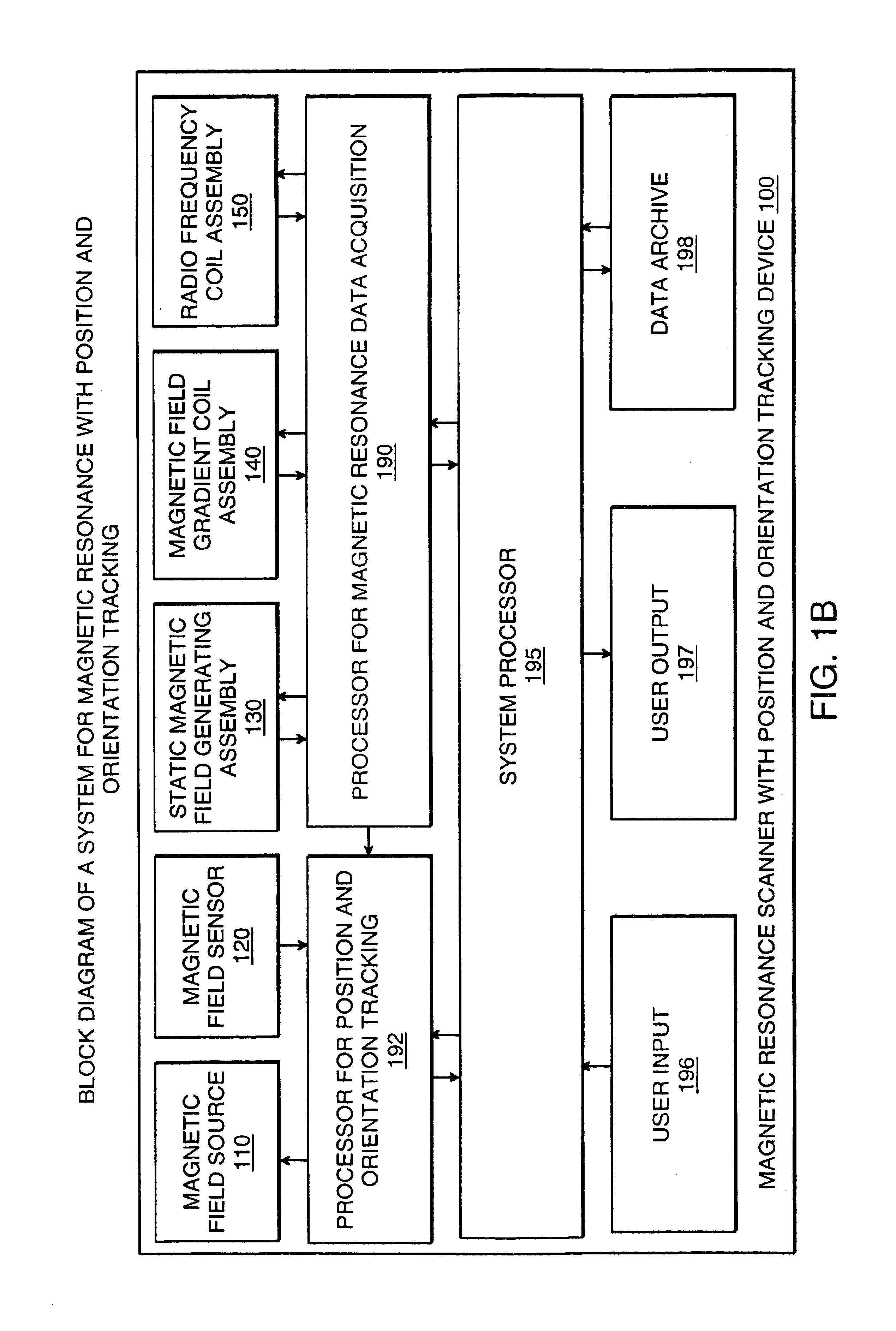
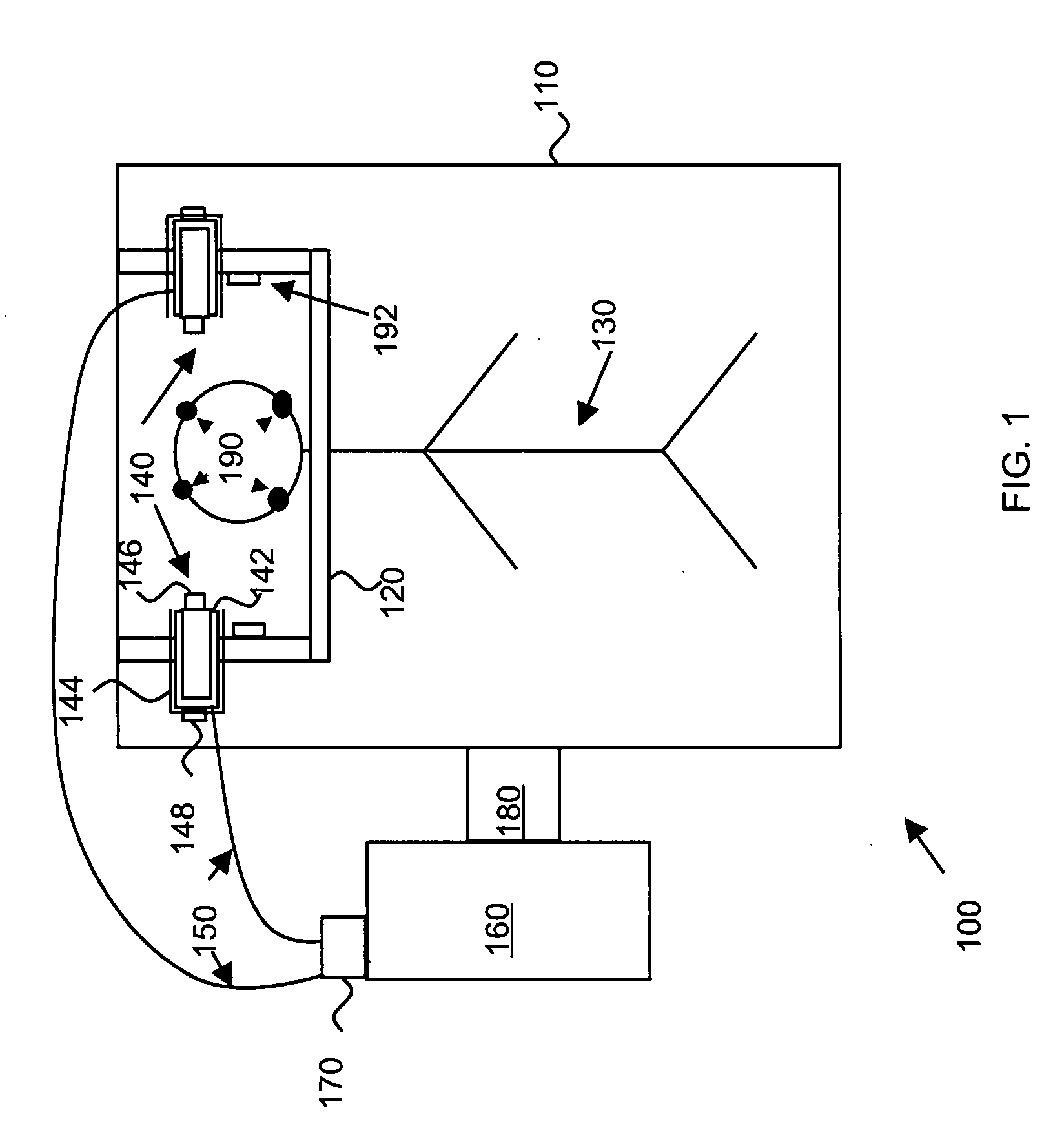
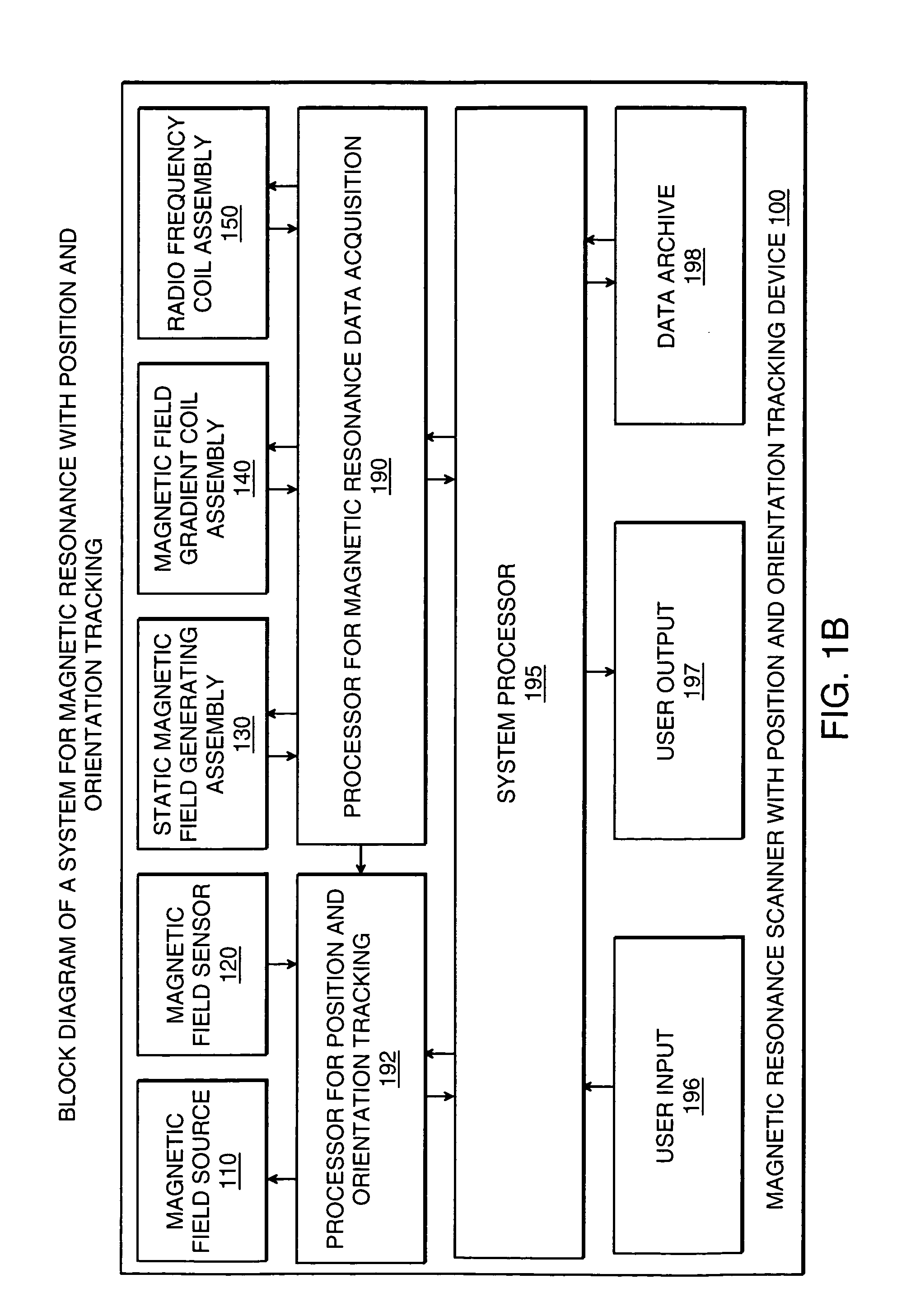
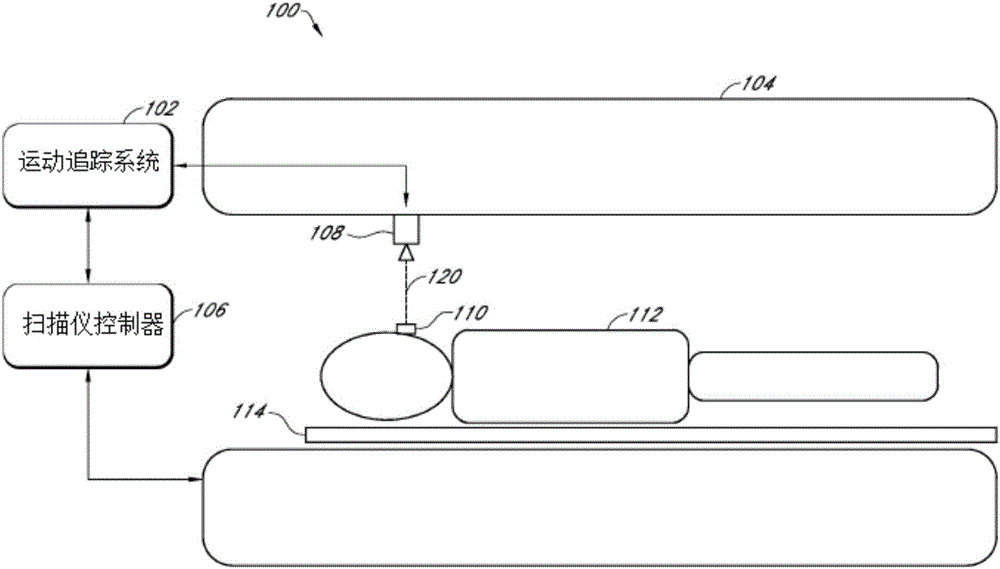
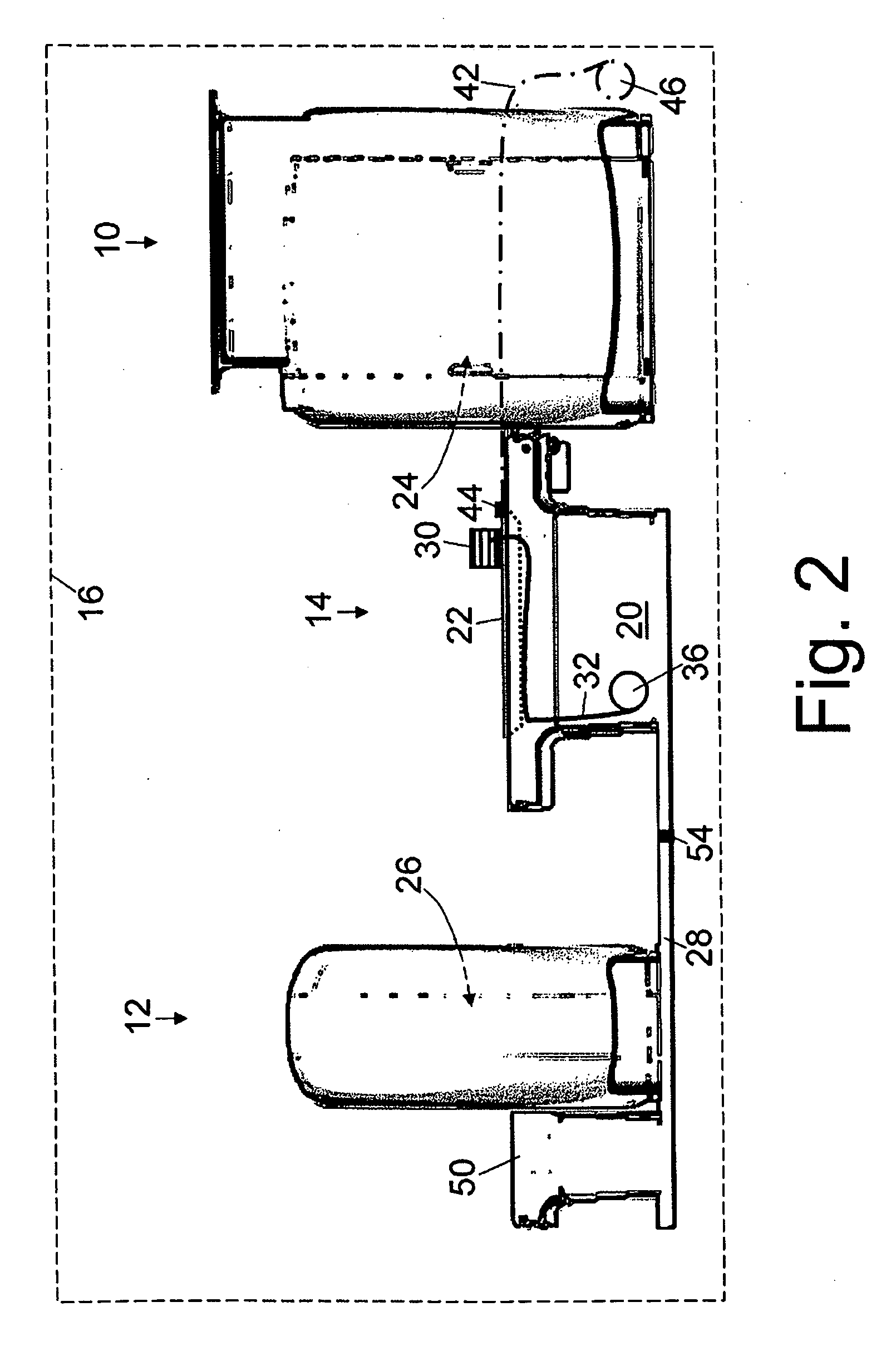
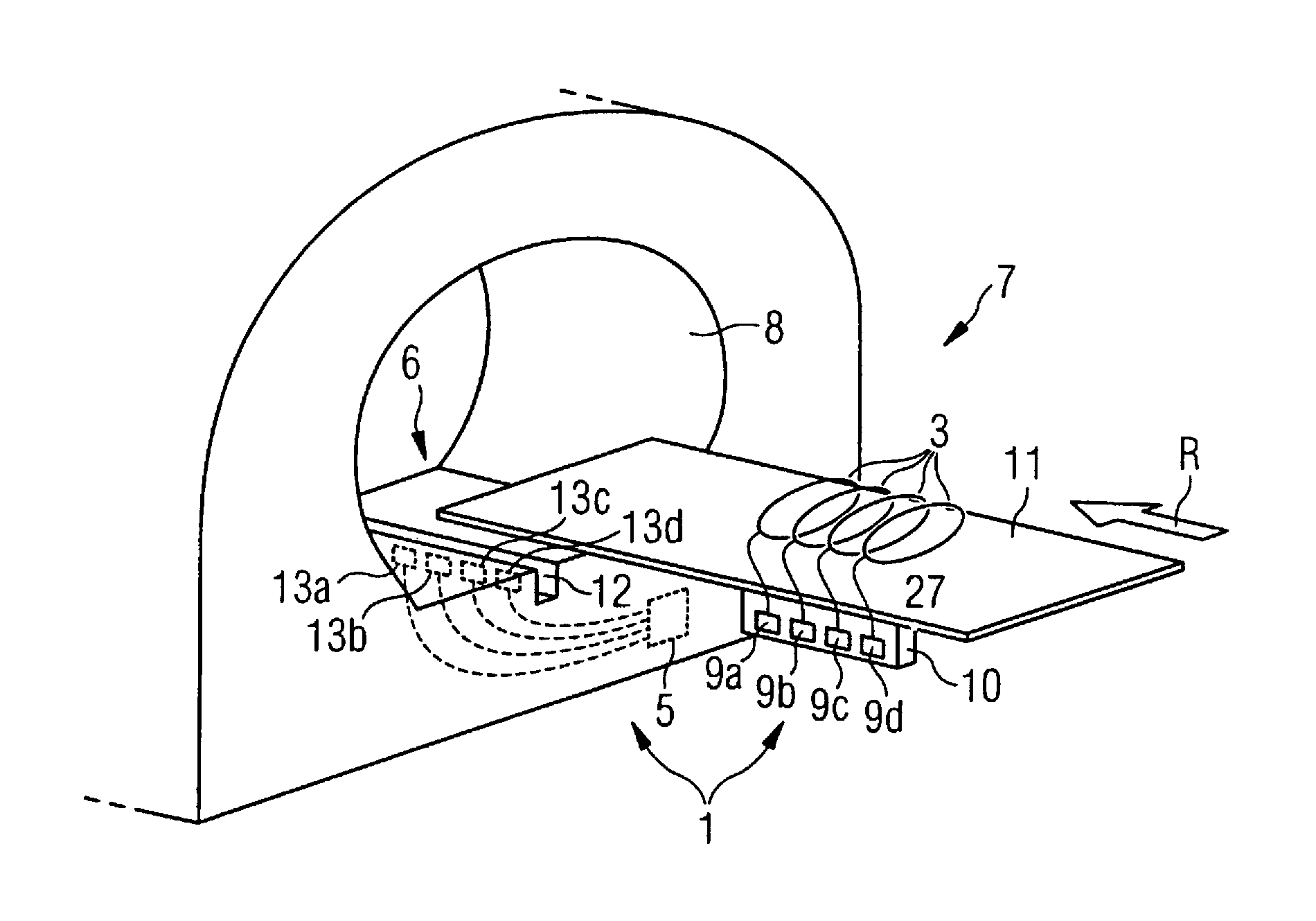
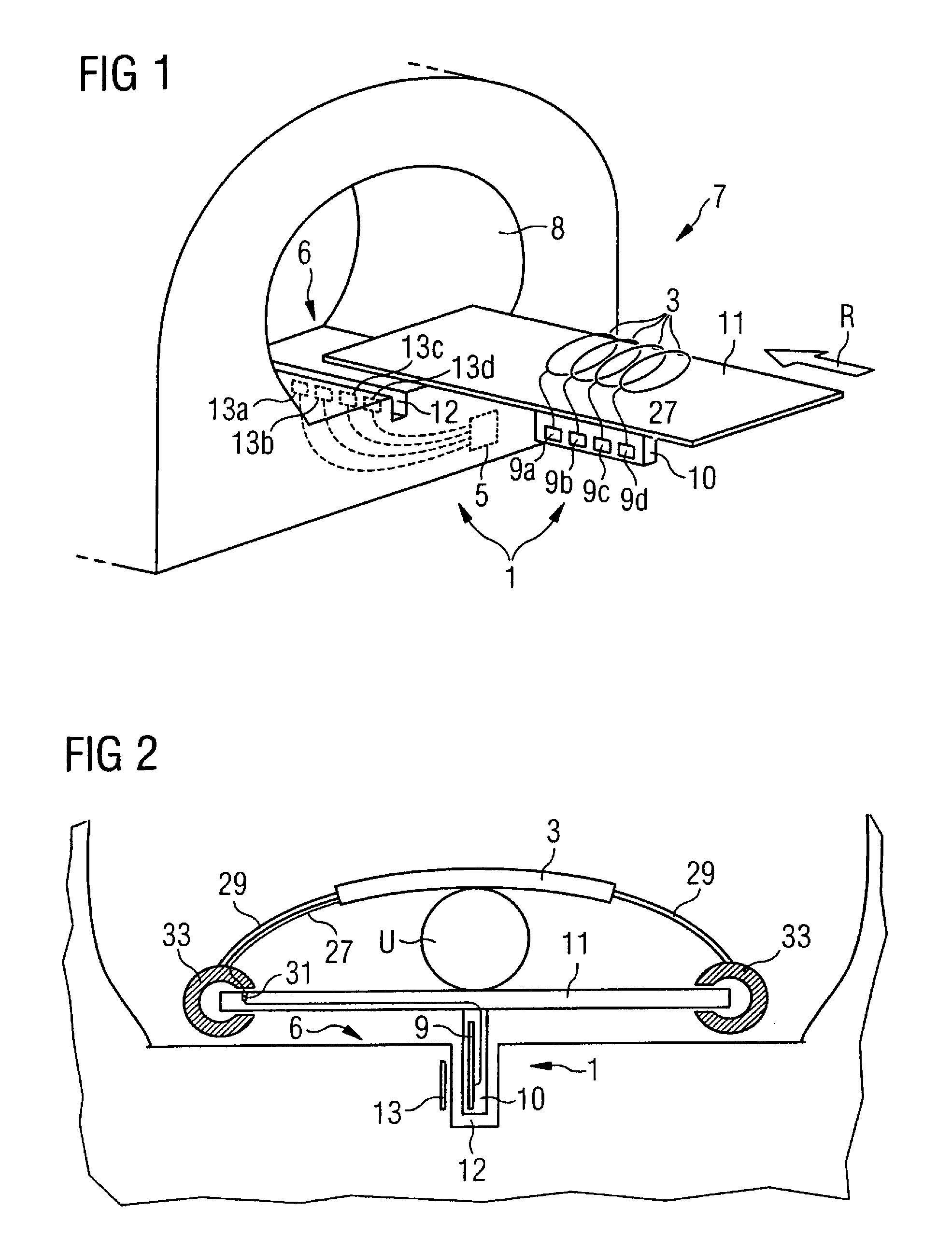
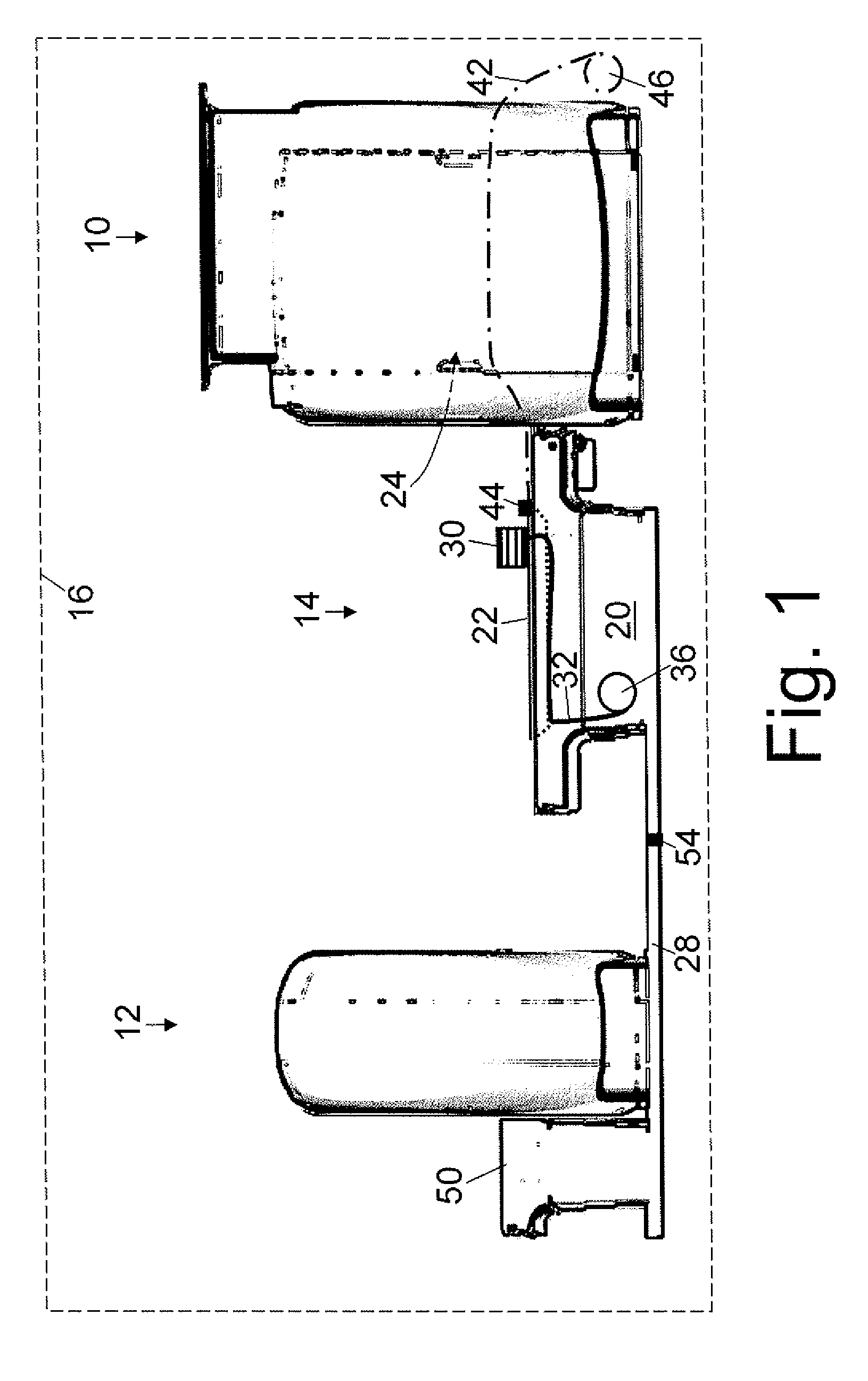
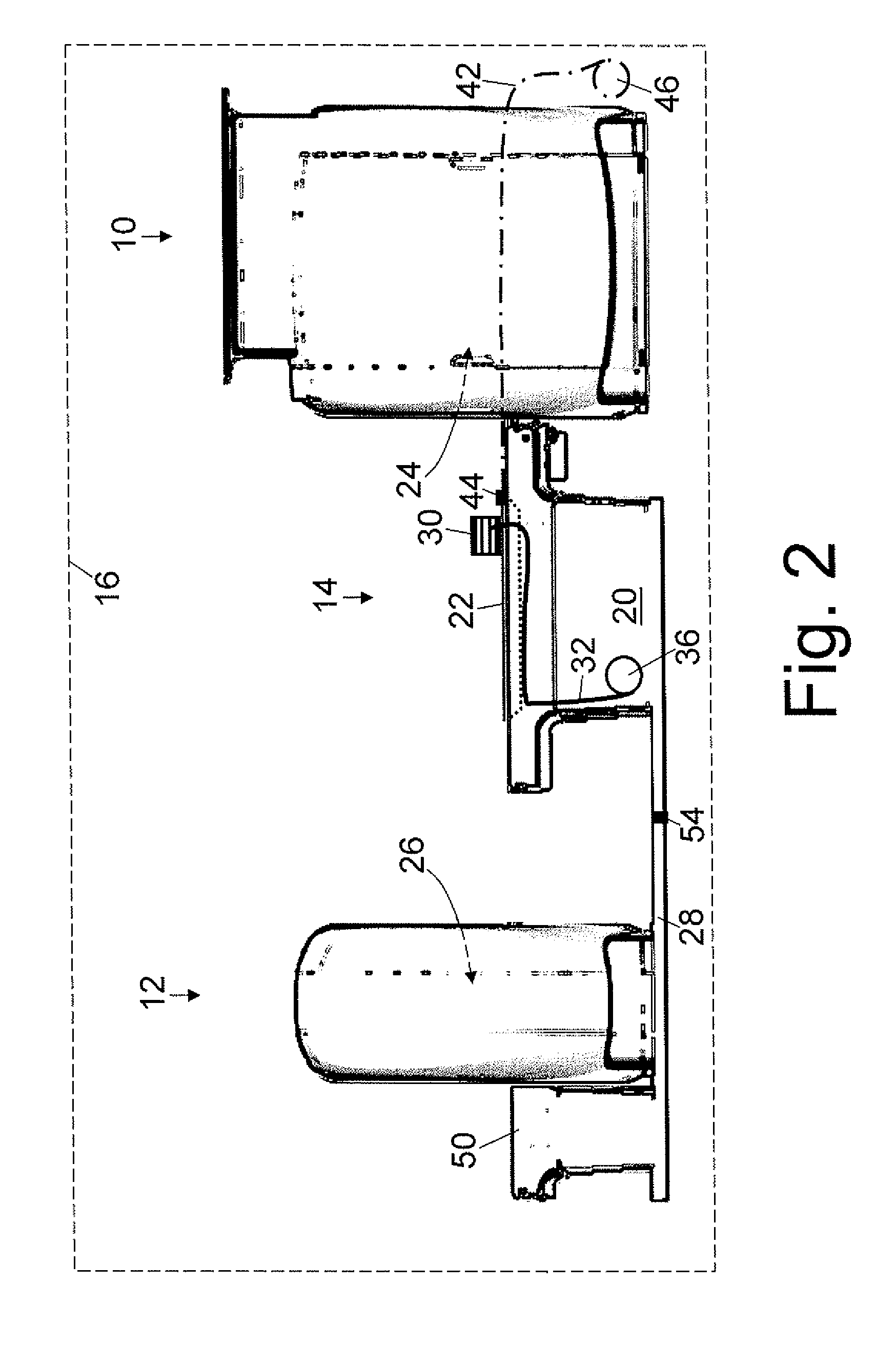
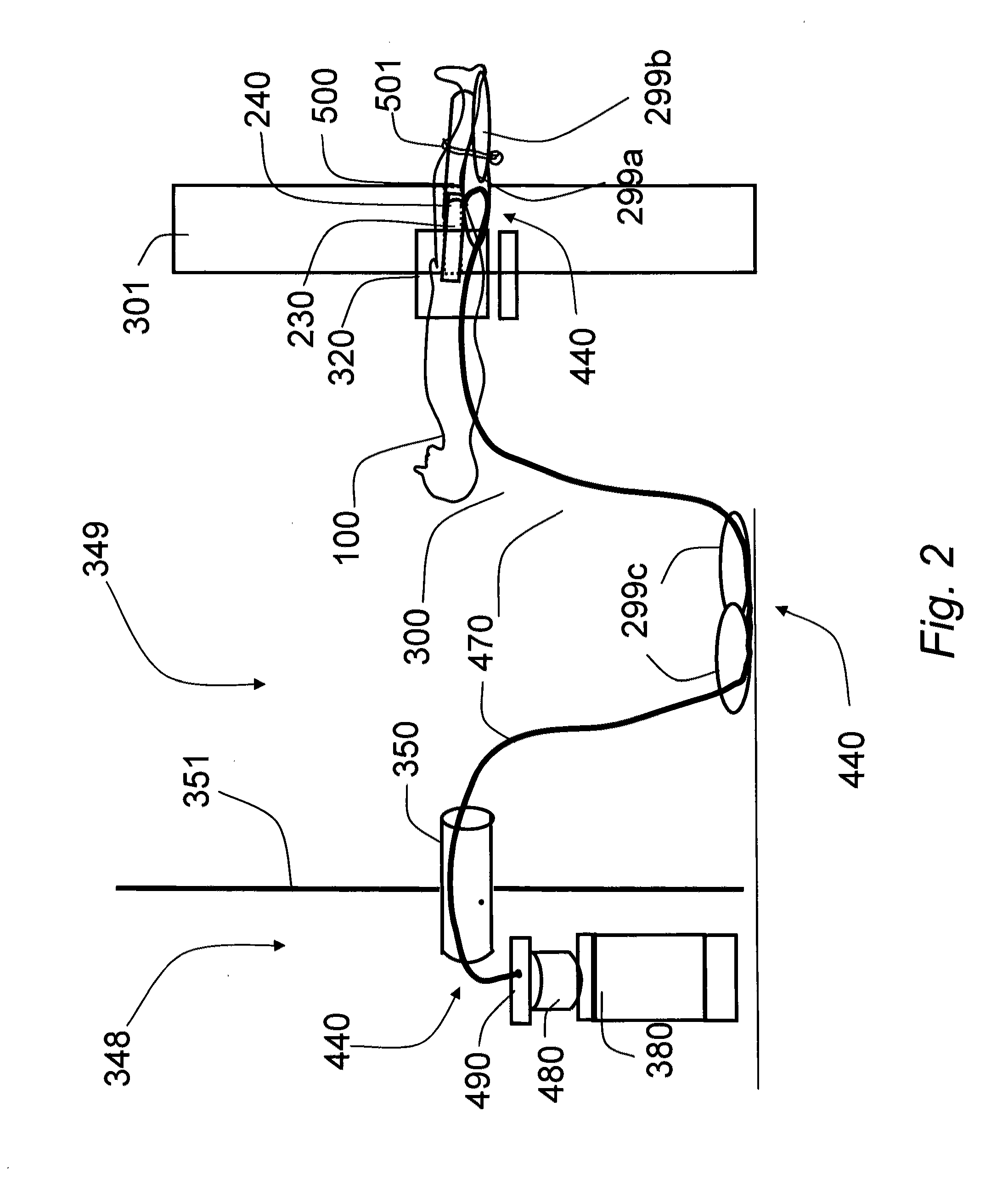
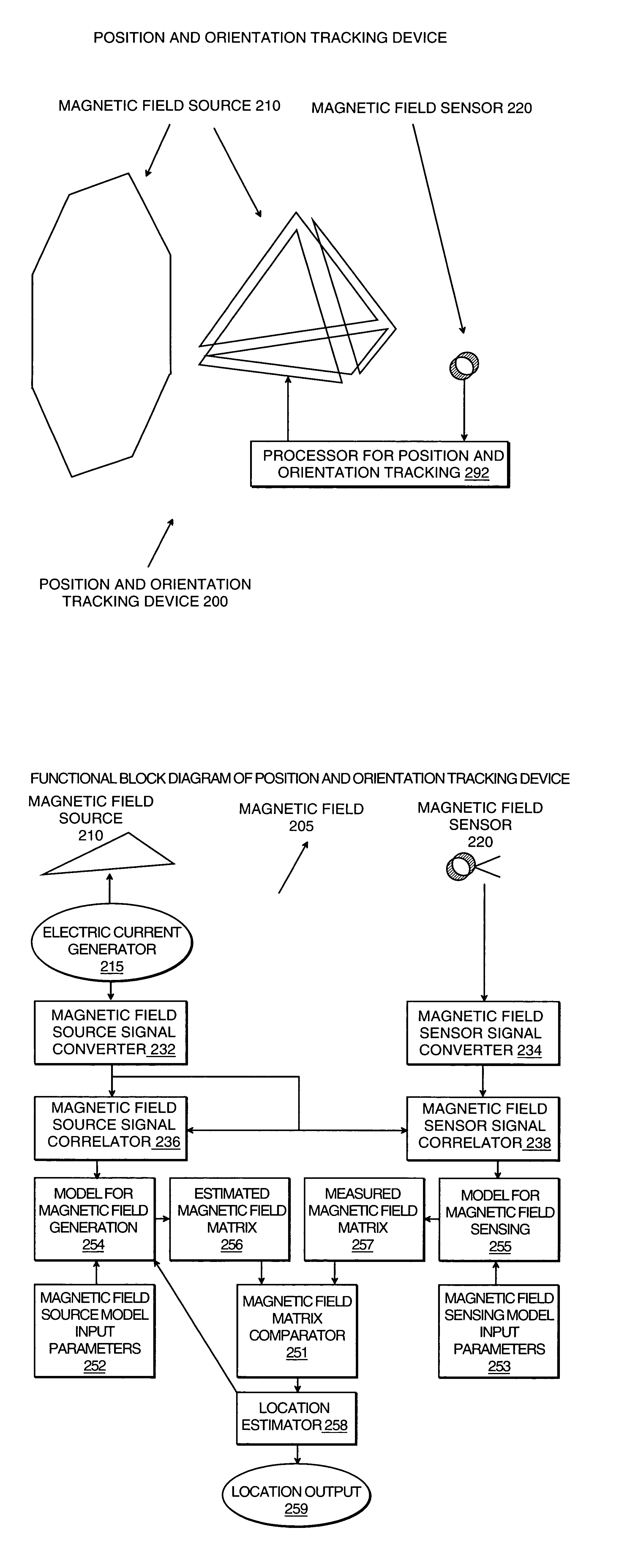
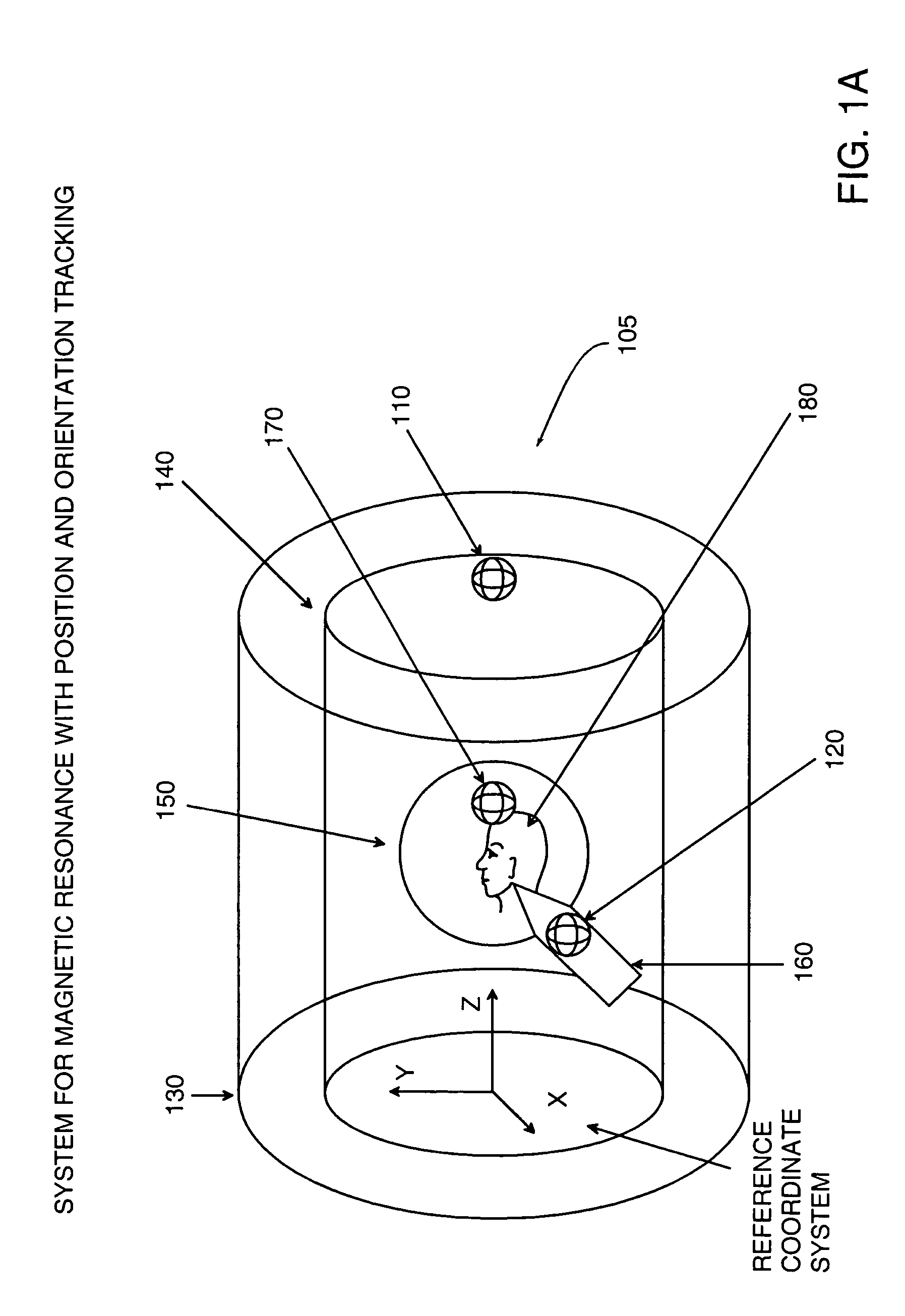
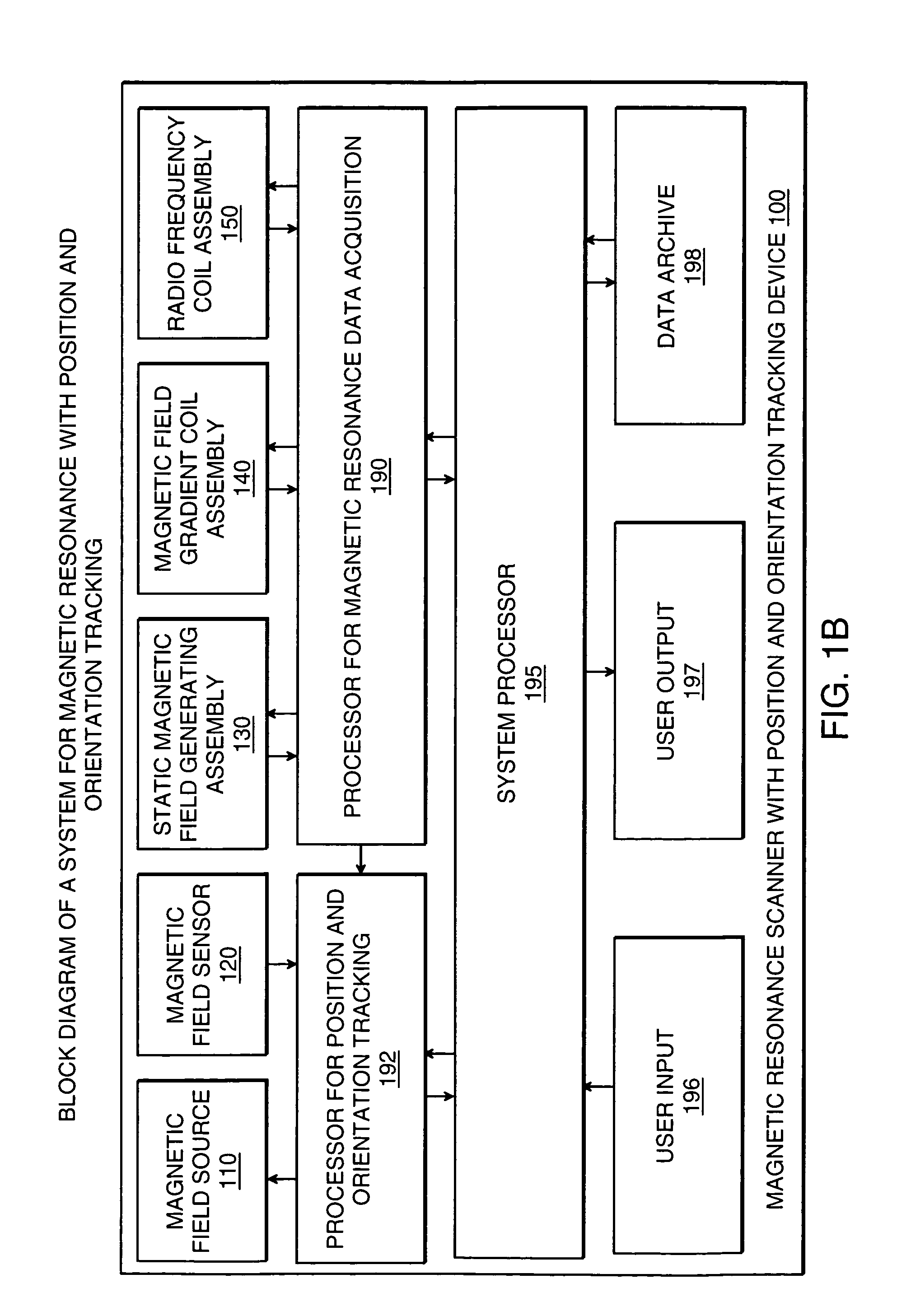
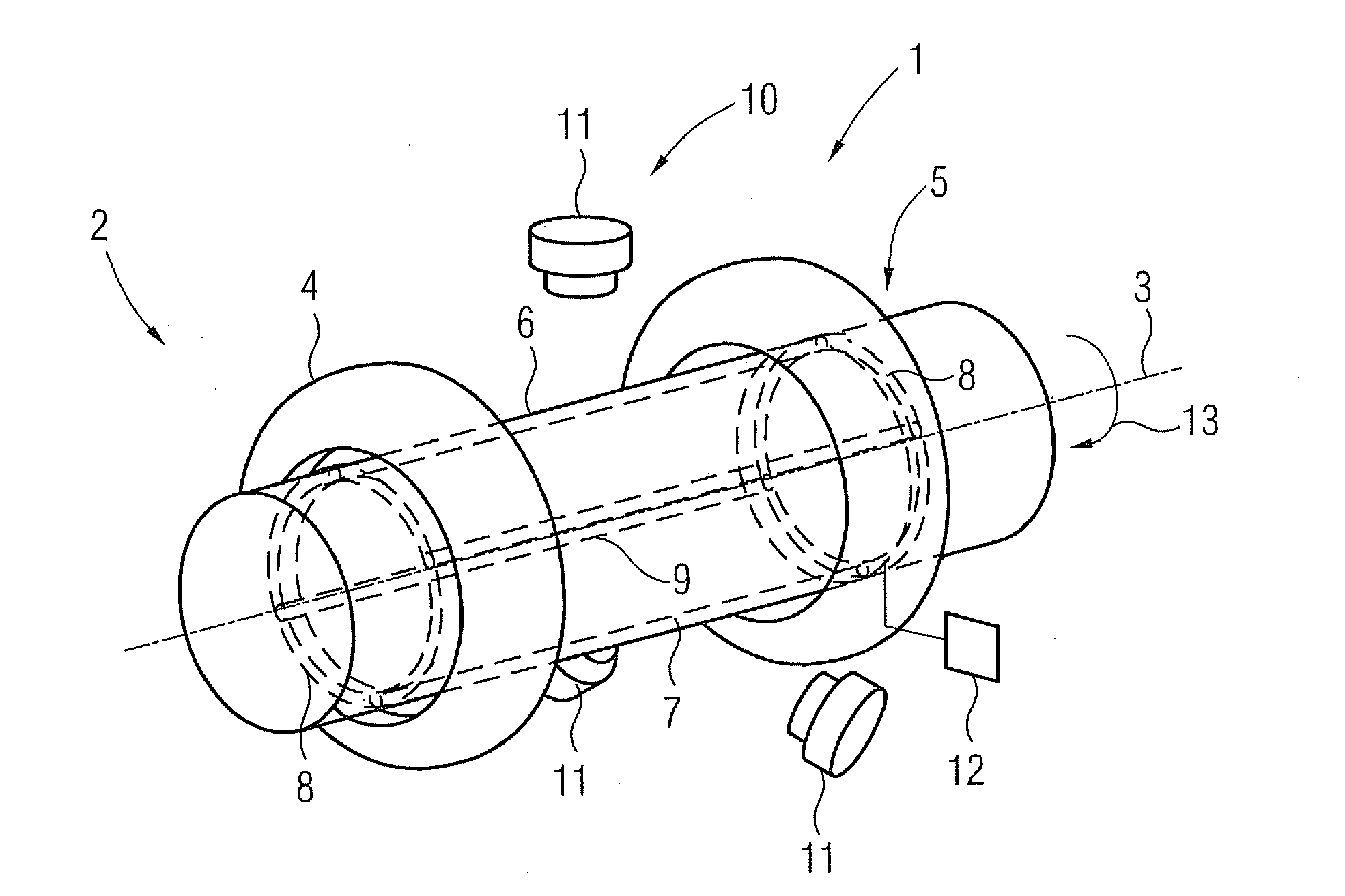
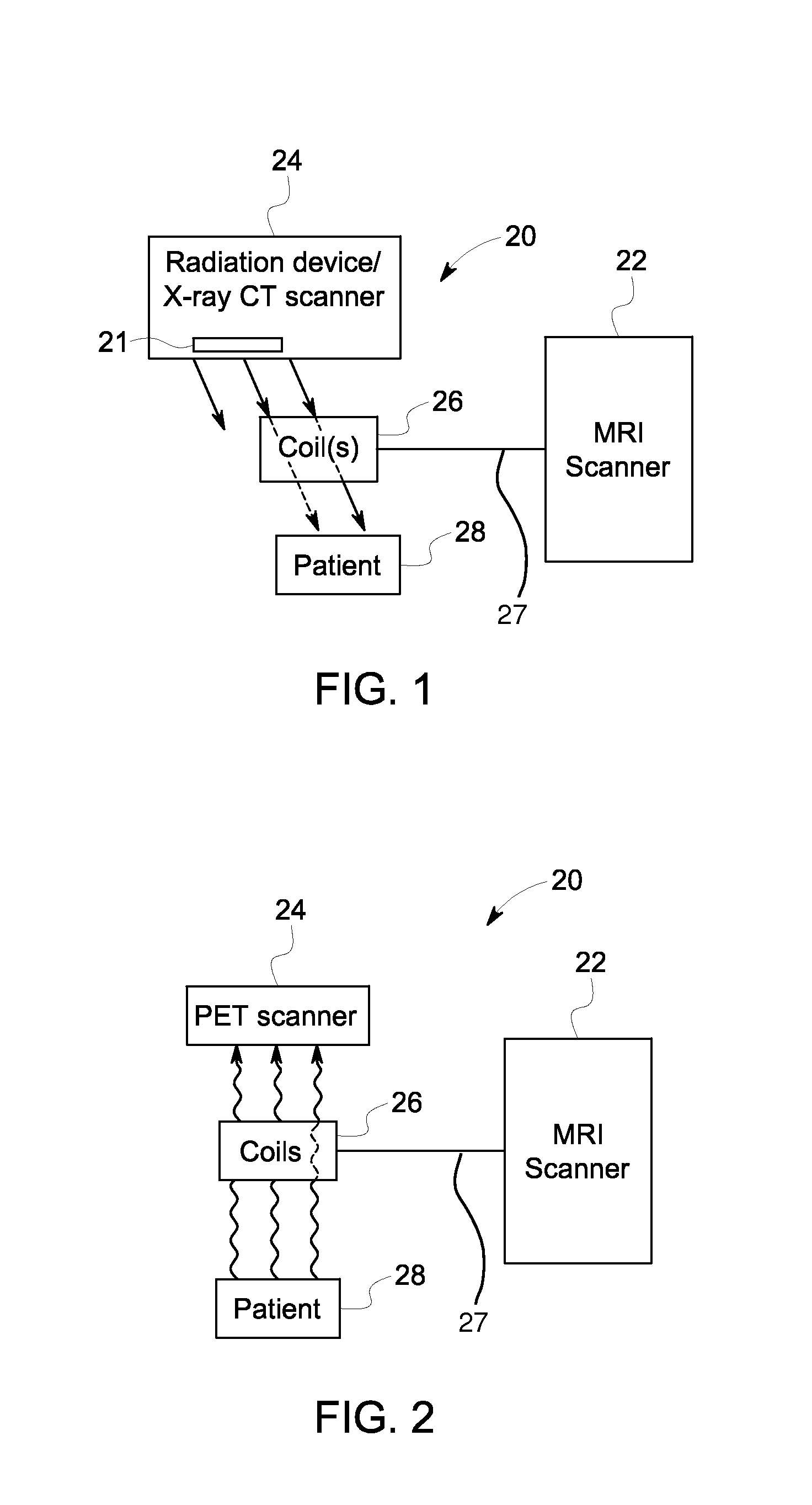
Magnetic resonance scanner with electromagnetic position and orientation tracking device
InactiveUS6879160B2Avoid line of sight limitationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLocation trackingElectromagnetic shielding
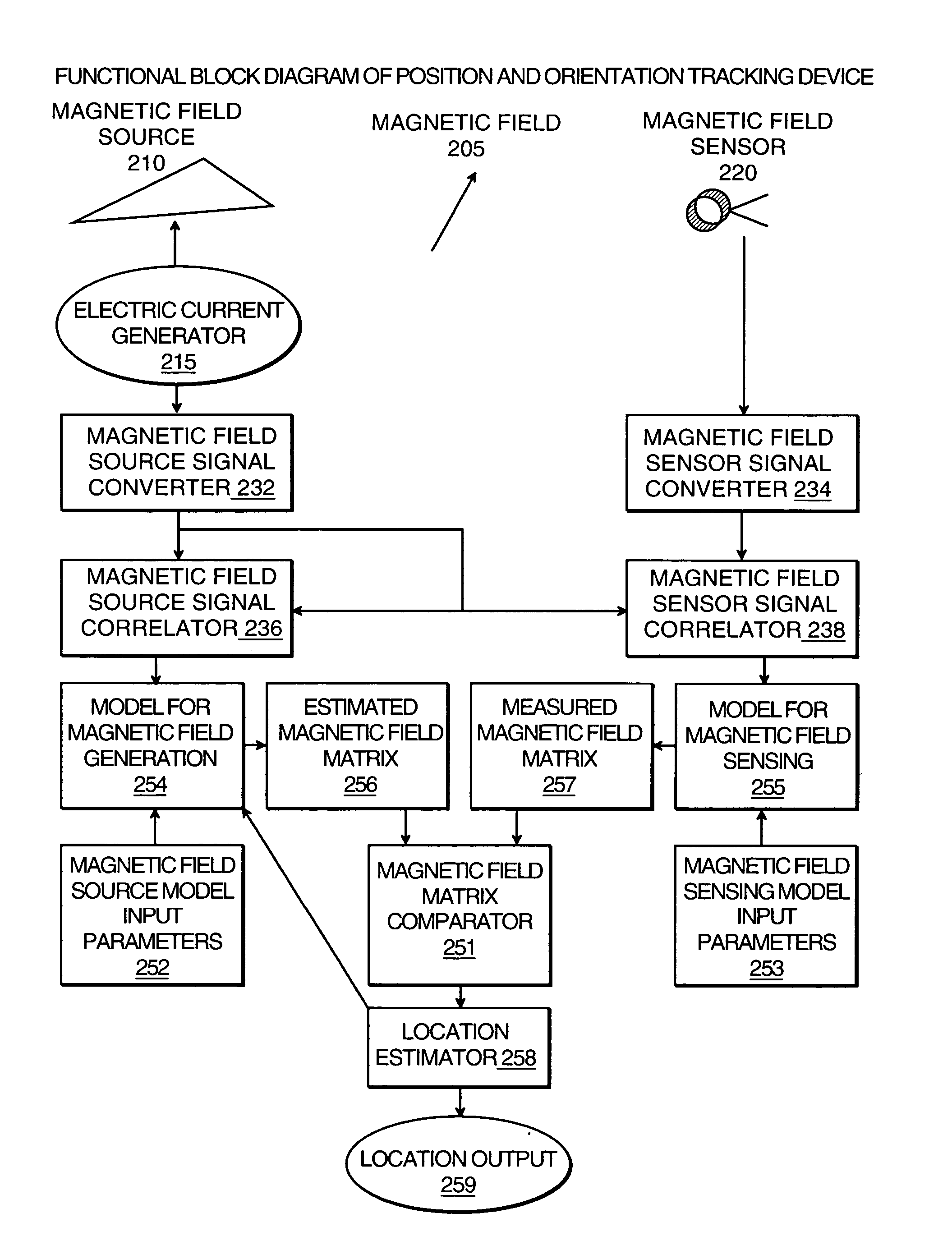
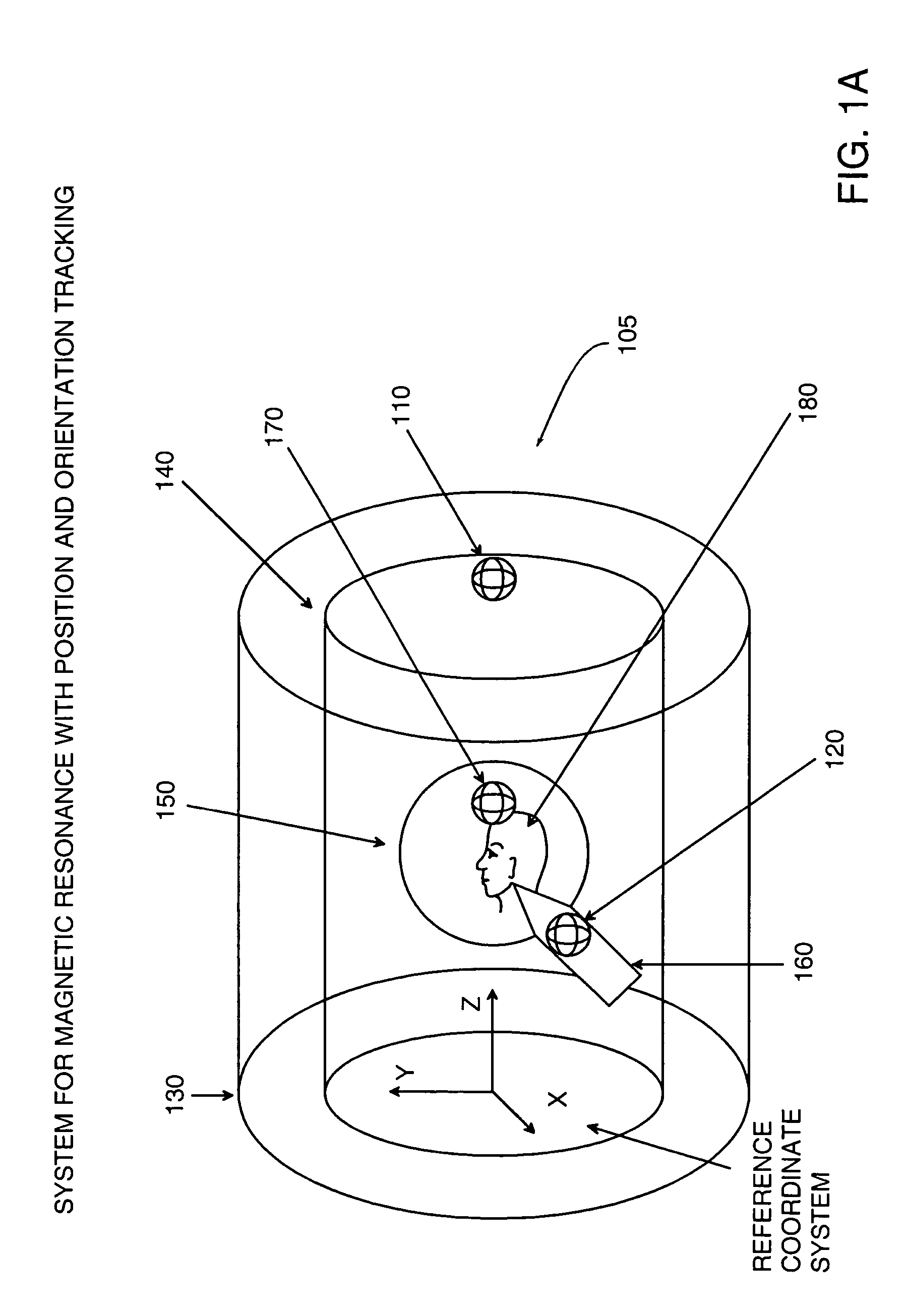
A system for combining electromagnetic position and orientation tracking with magnetic resonance scanner is provided. One embodiment includes a magnetic resonance scanner defining a reference coordinate system for scanning a target. Coupled to the magnetic resonance scanner is a magnetic field source which produces a magnetic field. The magnetic field is sensed by a magnetic field sensor which produces a signal proportional to the magnetic field. The magnetic field sensor has a location relative to the reference coordinate system. The location of the magnetic field sensor relative to the reference coordinate system of the magnetic resonance scanner is determined by a location tracking device using at least a line segment model of the magnetic field source and the signal from the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:JAKAB PETER D
Apparatus and method for real-time motion-compensated magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20090209846A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceReal Time Kinematic
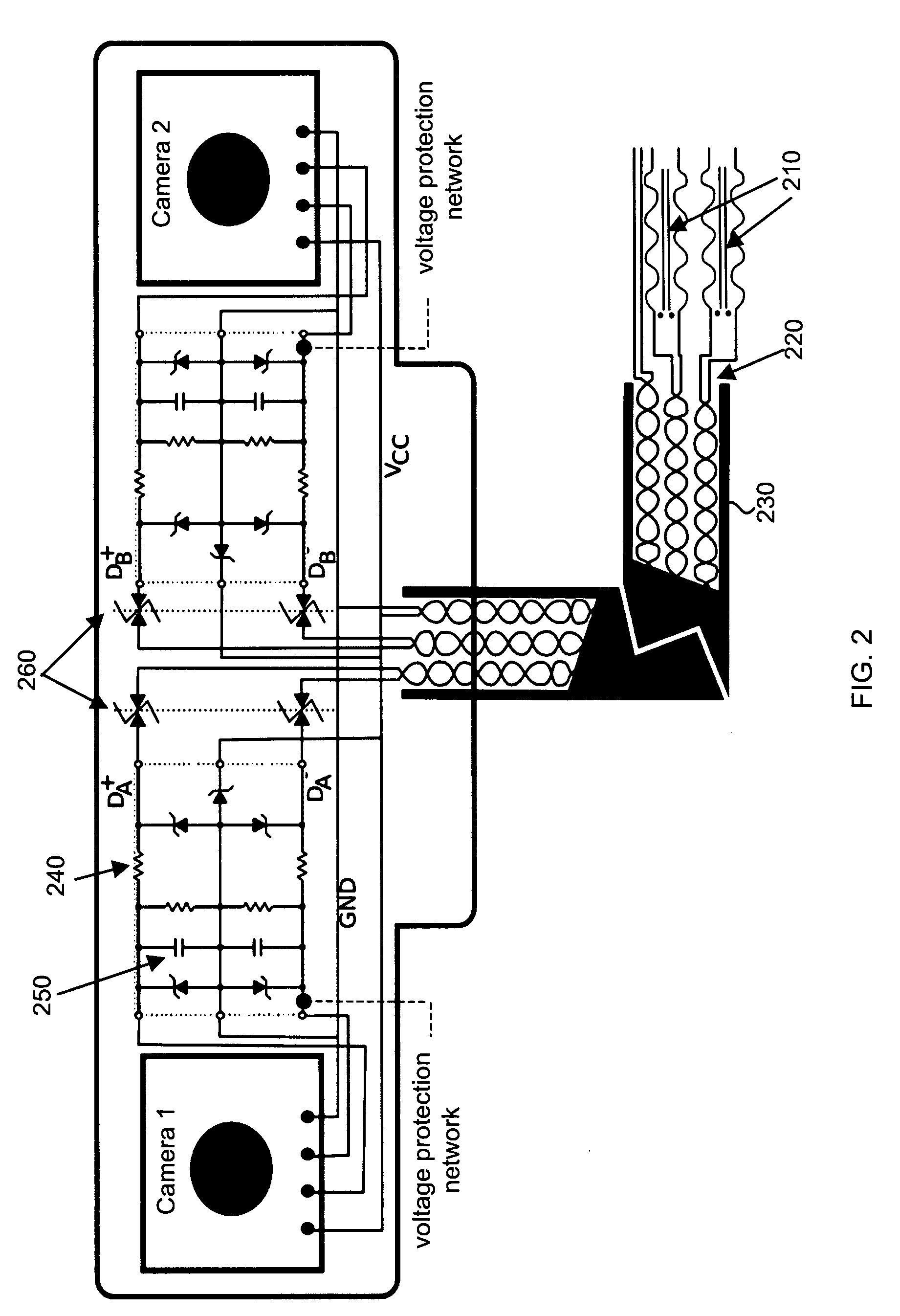
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for real-time motion compensated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a human or animal. The apparatus includes one or more magnetic-resonance compatible cameras mounted on a coil of the MRI device, a calculation and storage device, and an interface operably connected to the MRI device and the calculation and storage device. The apparatus may also include a set of magnetic resonance compatible markers, where the markers are positioned on the human or animal. Alternatively, the apparatus may use a facial recognition algorithm to identify features of the human or animal. For the present invention, the frame of reference is defined by the animal or human being imaged, instead of the typical magnetic resonance coordinate system. Based on continuous positional information, the apparatus controls the magnetic resonance scanner so that it follows the human or animal's motion.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Magnetic resonance scanner with electromagnetic position and orientation tracking device
InactiveUS20050146327A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLocation trackingMagnetic resonance scanner
A system for combining electromagnetic position and orientation tracking with magnetic resonance scanner is provided. One embodiment includes a magnetic resonance scanner defining a reference coordinate system for scanning a target. Coupled to the magnetic resonance scanner is a magnetic field source which produces a magnetic field. The magnetic field is sensed by a magnetic field sensor which produces a signal proportional to the magnetic field. The magnetic field sensor has a location relative to the reference coordinate system. The location of the magnetic field sensor relative to the reference coordinate system of the magnetic resonance scanner is determined by a location tracking device using at least a line segment model of the magnetic field source and the signal from the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:JAKAB PETER D
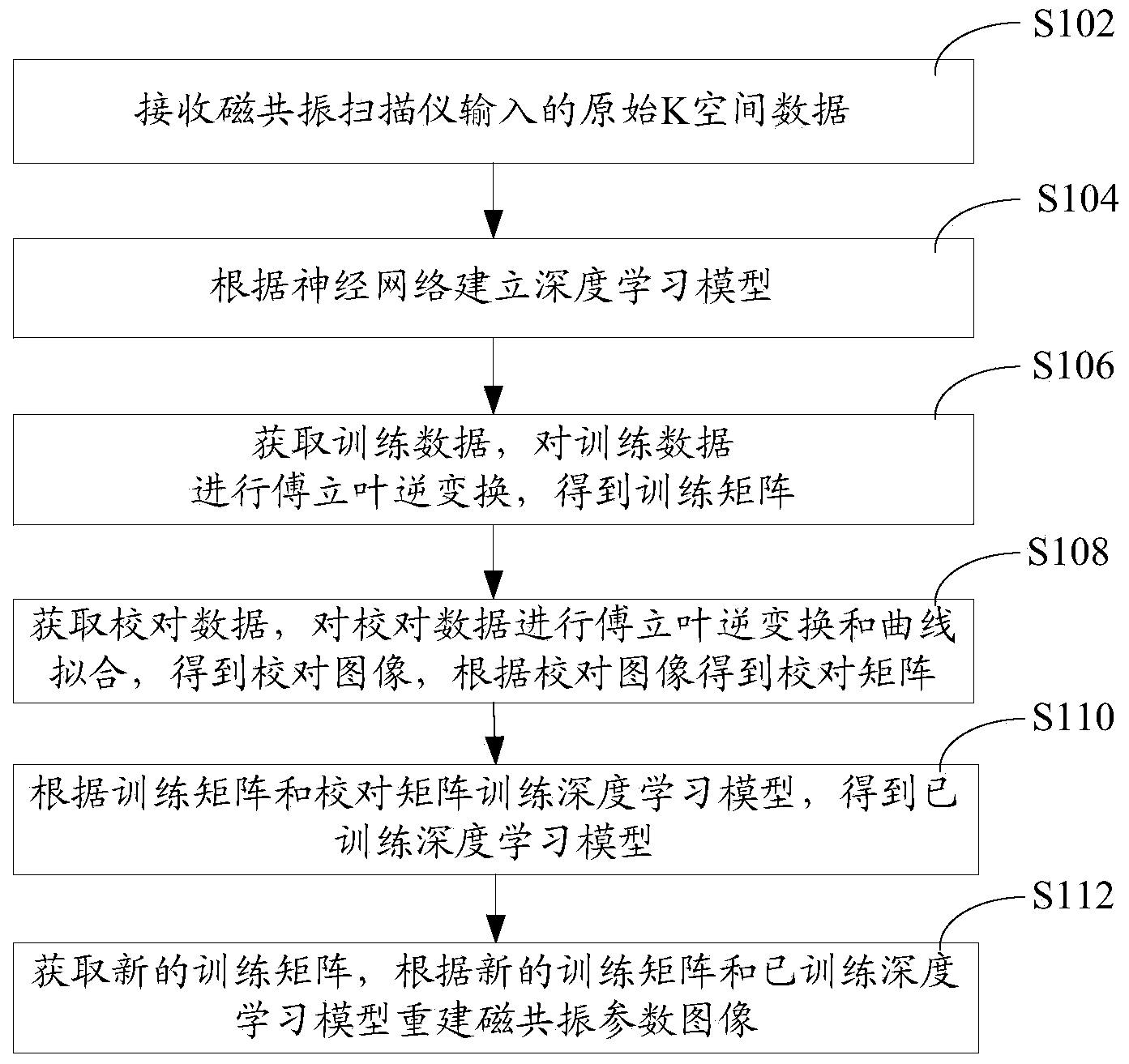
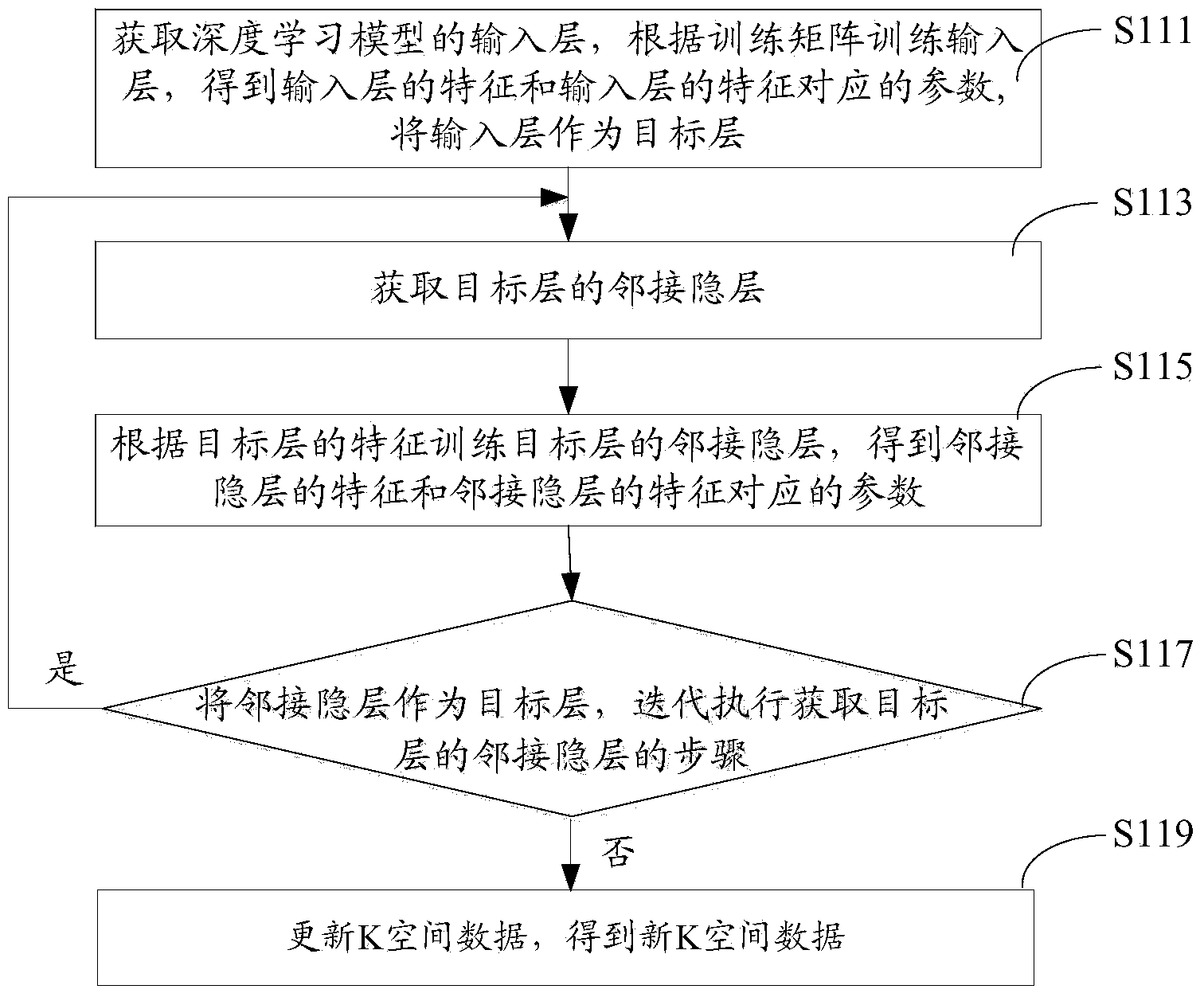
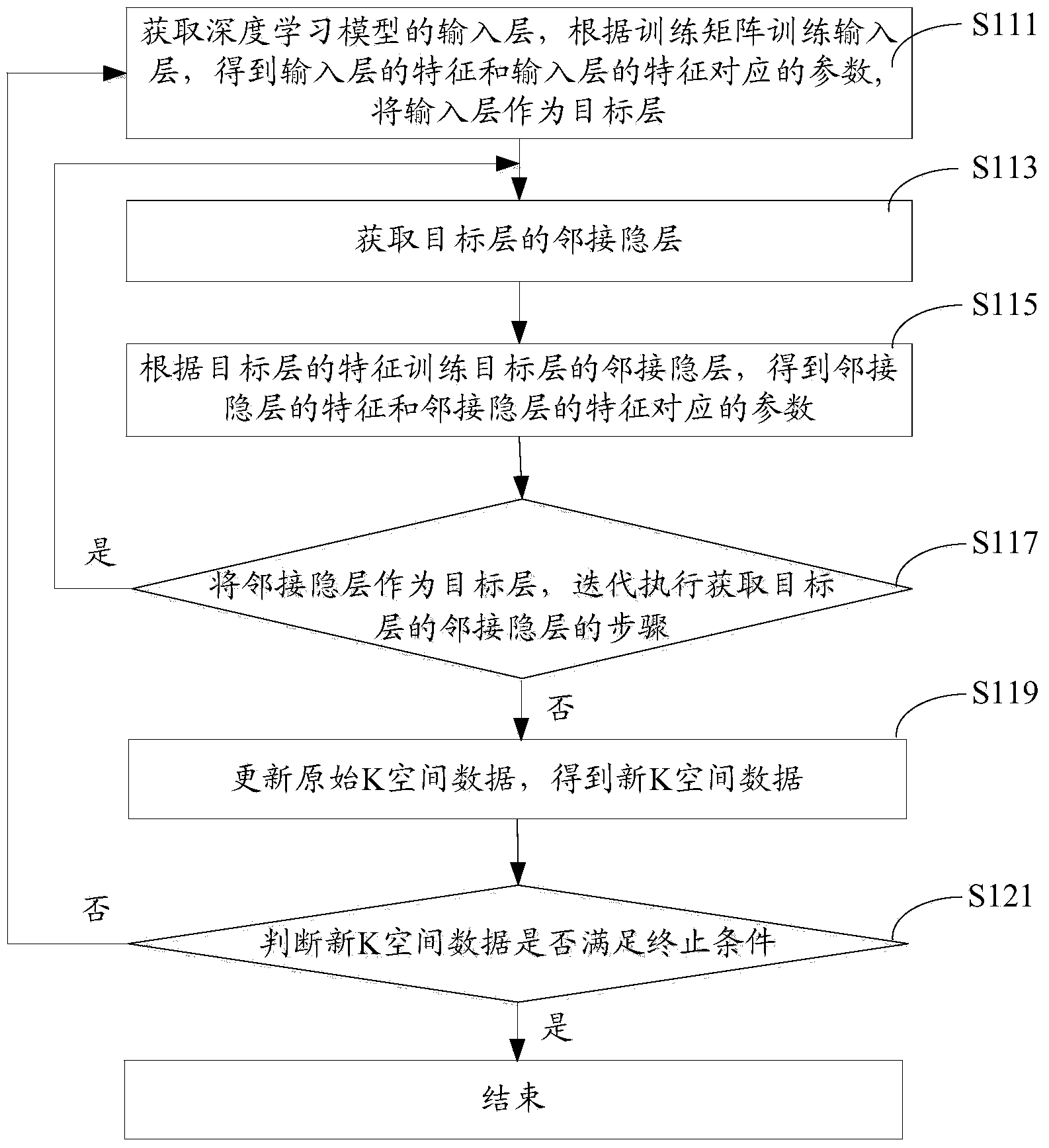
Magnetic resonance rapid parameter imaging method and system
ActiveCN103646410AAvoid errorsQuality improvementImage analysis2D-image generationPattern recognitionNerve network
The invention provides a magnetic resonance rapid parameter imaging method comprising the following steps: original K-space data inputted by a magnetic resonance scanner are received; a deep learning model is established according to a nerve network; training data are acquired, and Fourier inverse transformation is performed on the training data so that a training matrix is obtained; proofreading data are acquired, and Fourier inverse transformation and curve fitting are performed on the proofreading data so that a proofreading image is obtained, and a proofreading matrix is obtained according to the proofreading image; the deep learning model is trained according to the training matrix and the proofreading matrix so that the trained deep learning model is obtained; and a new training matrix is acquired, and a magnetic resonance parameter image is reconstructed according to the new training matrix and the trained deep learning model. Quality of the reconstructed image can be effectively enhanced by using the method. Besides, the invention also provides a magnetic resonance rapid parameter imaging system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
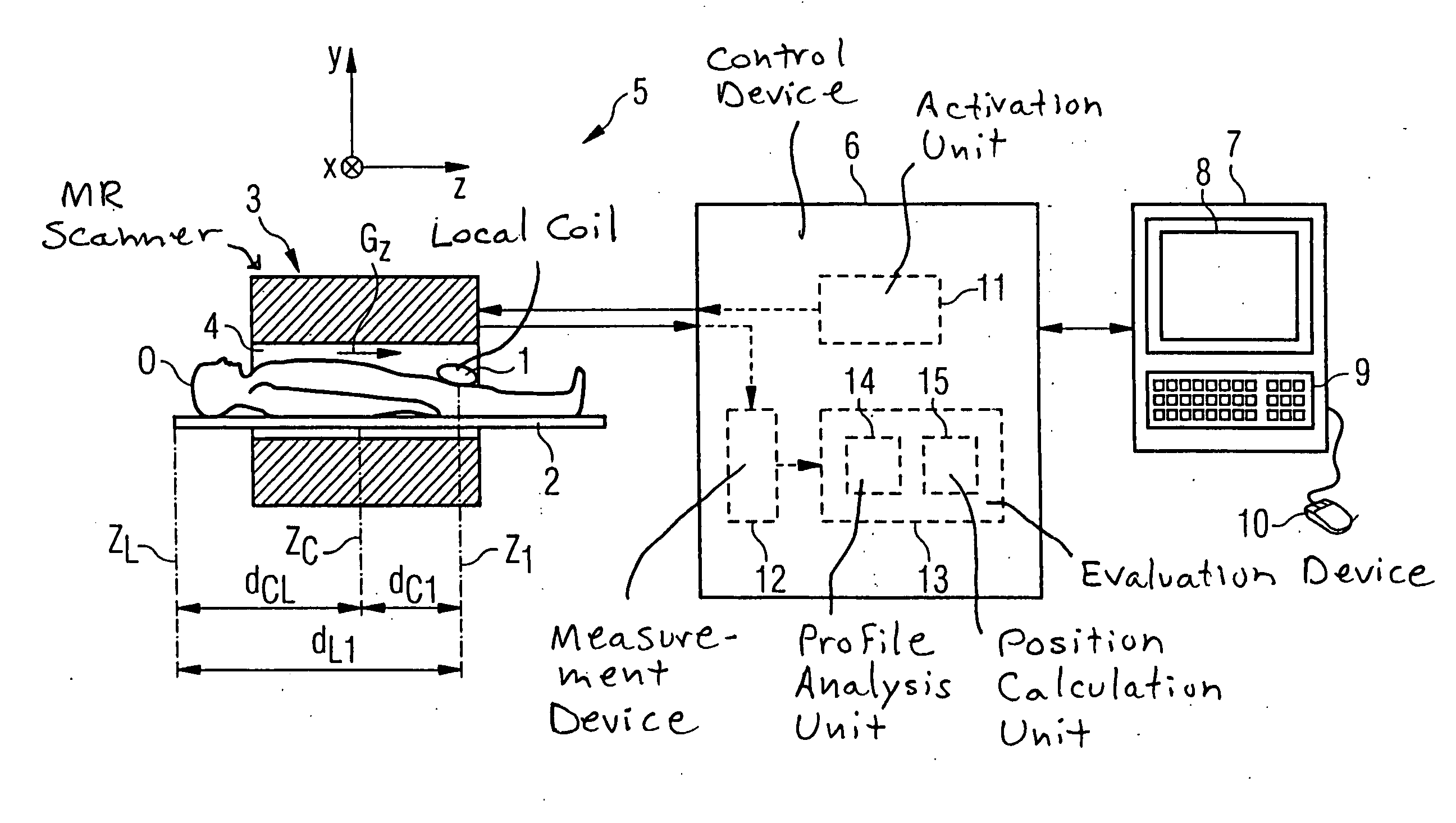
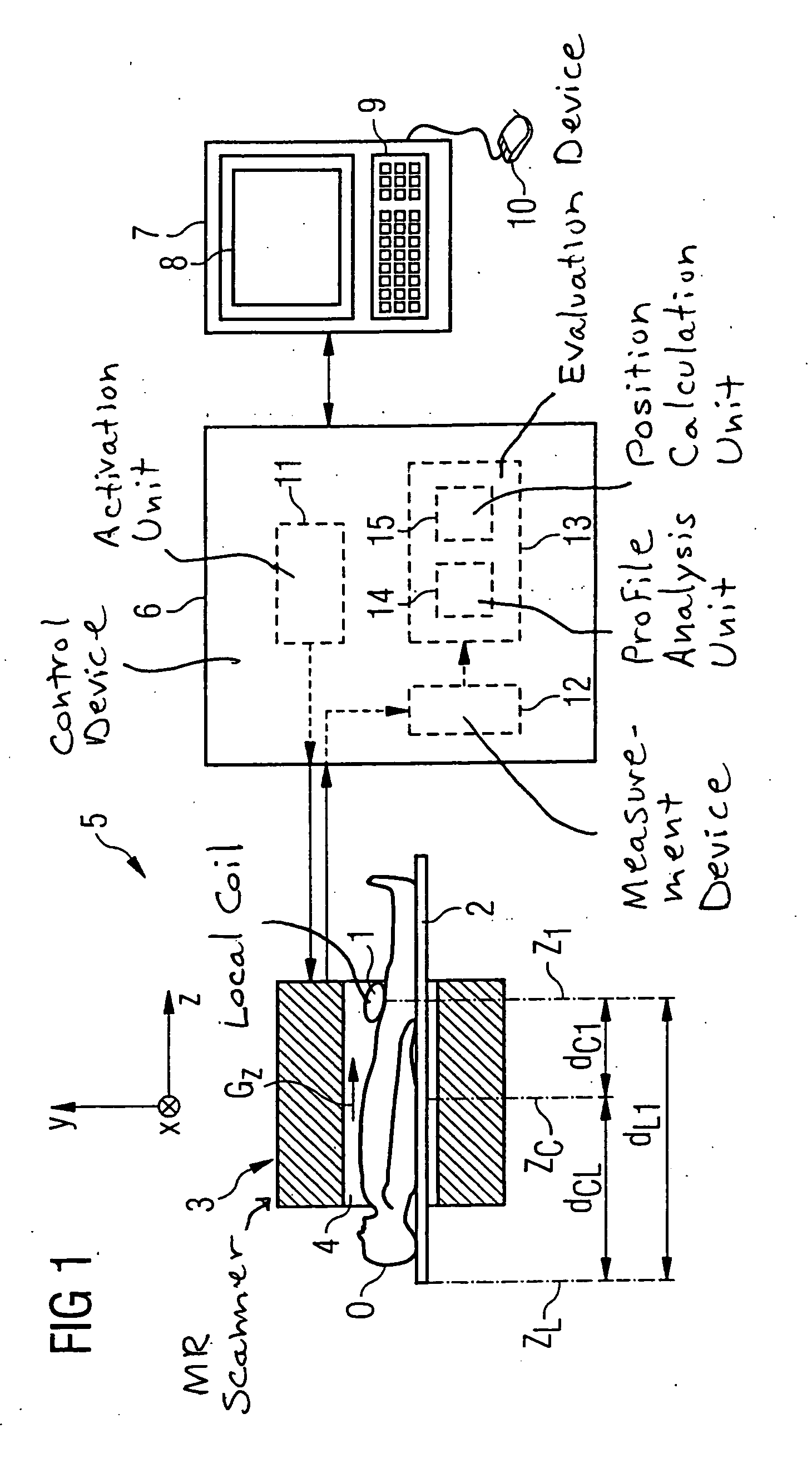
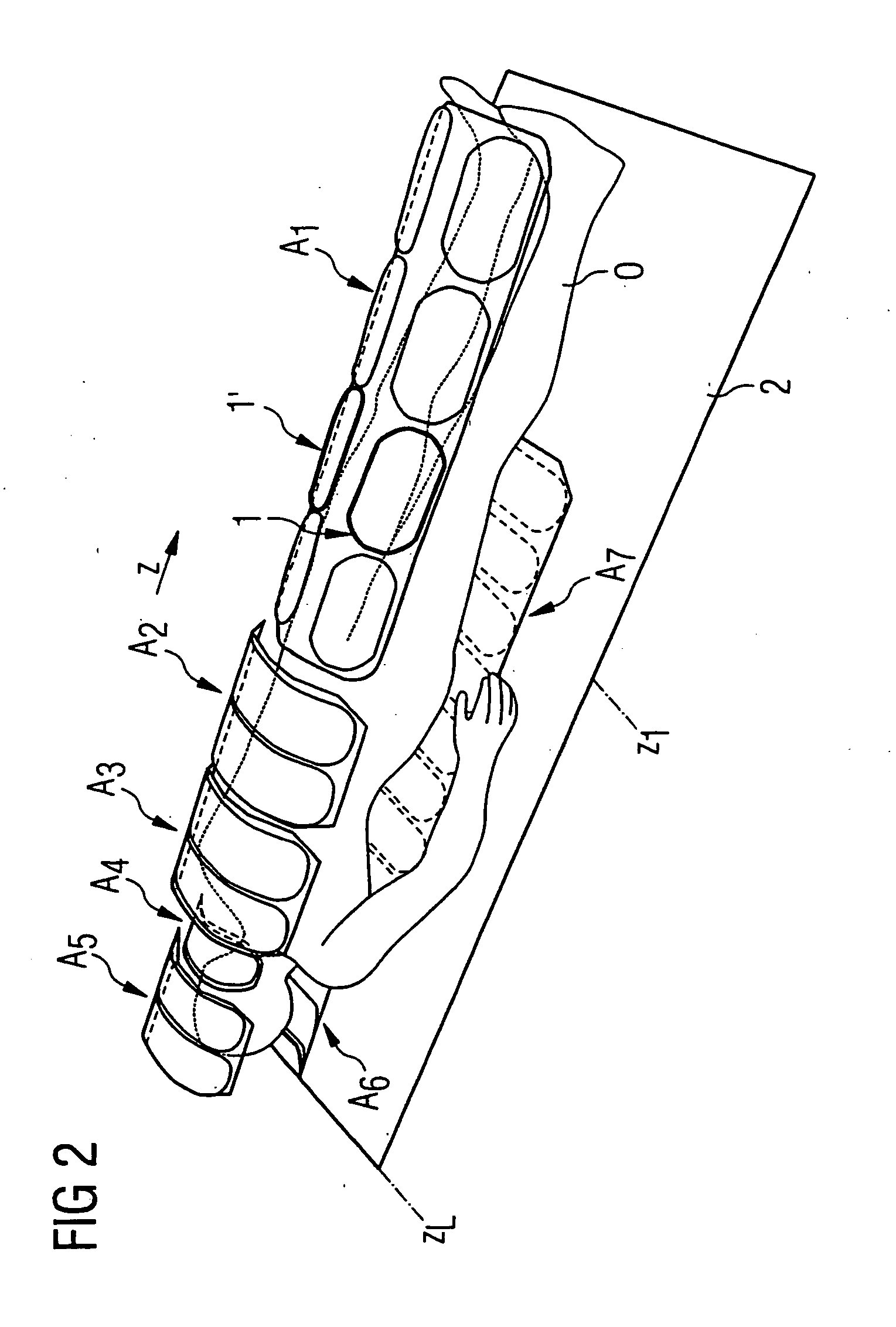
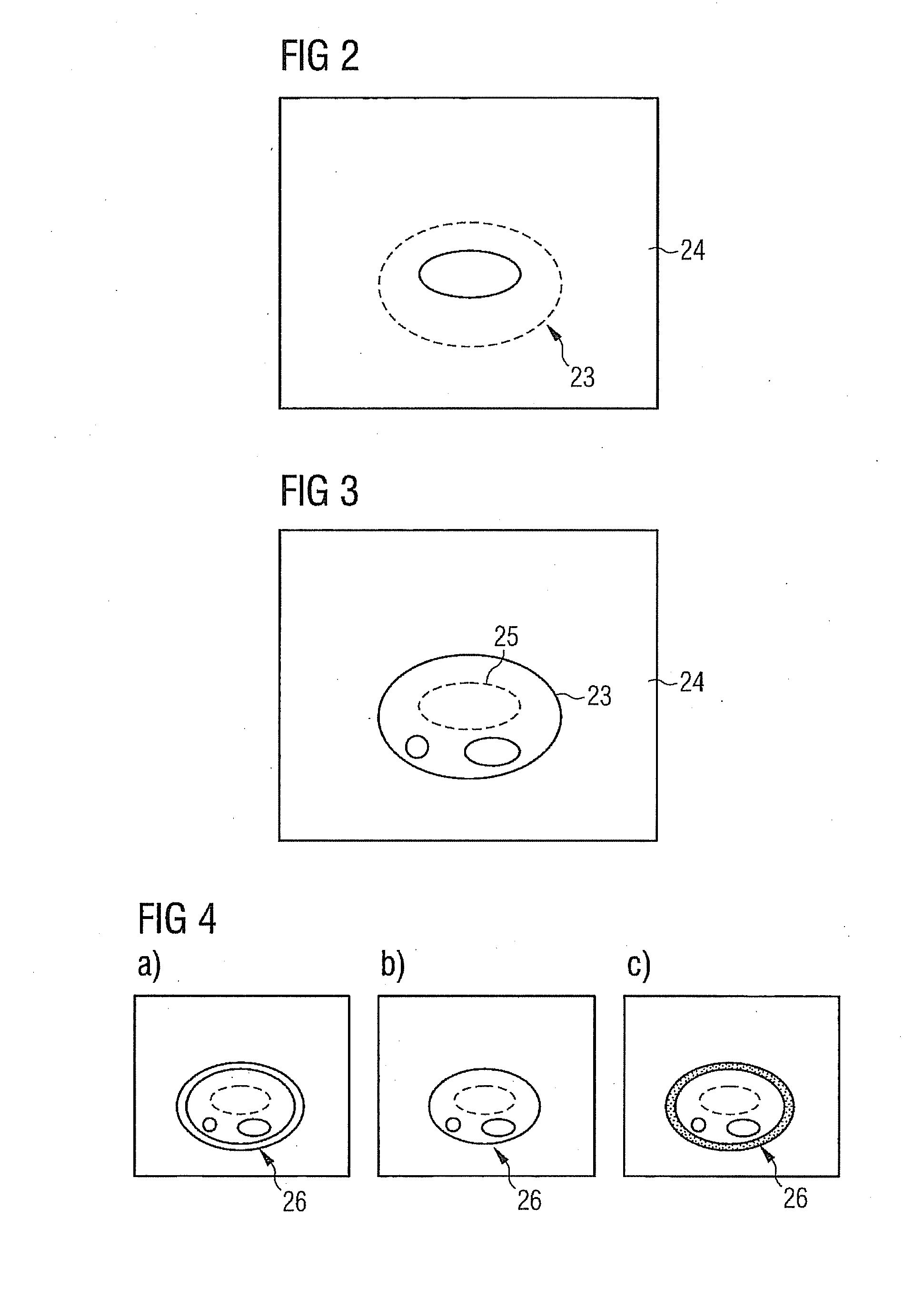
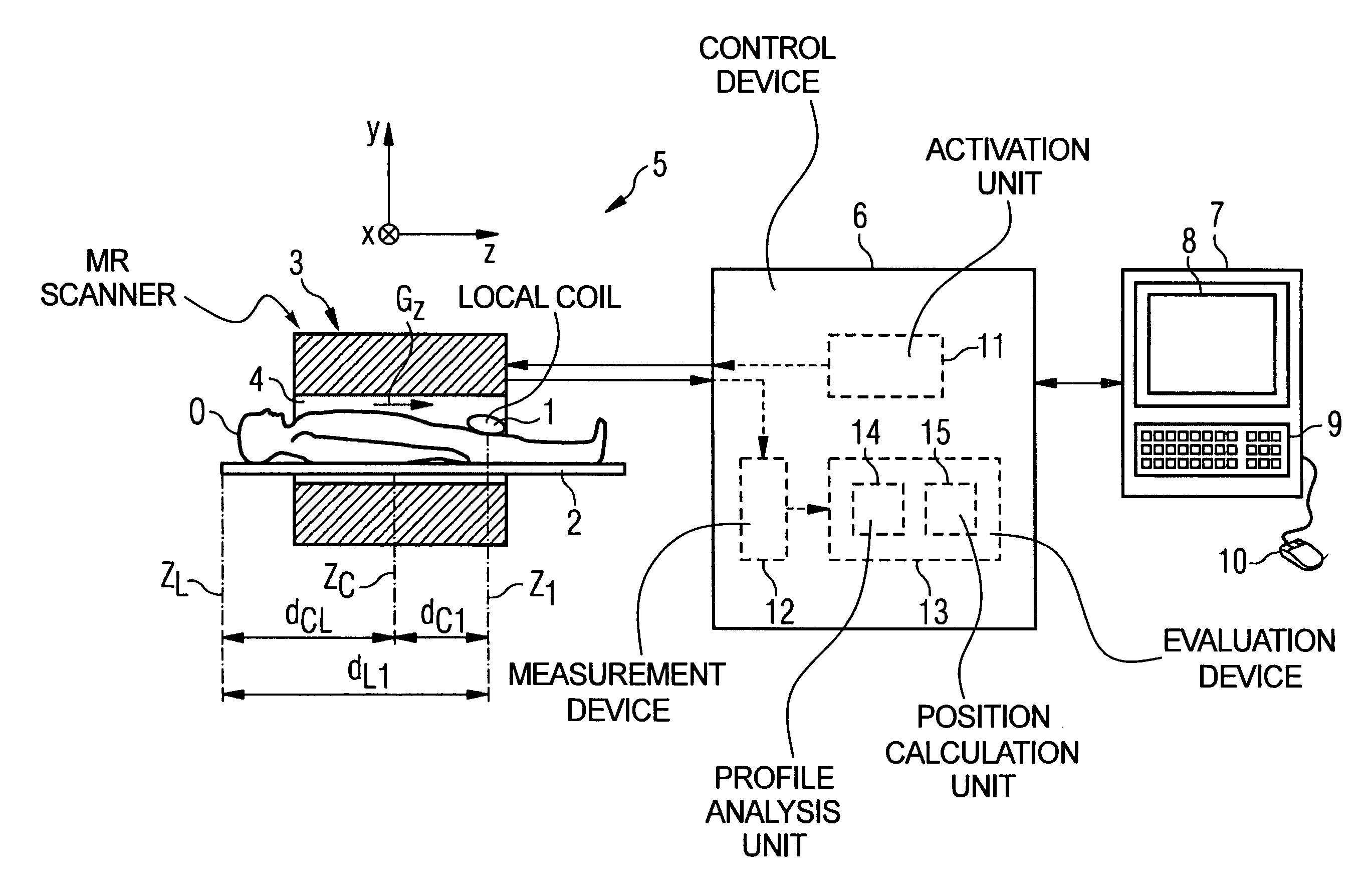
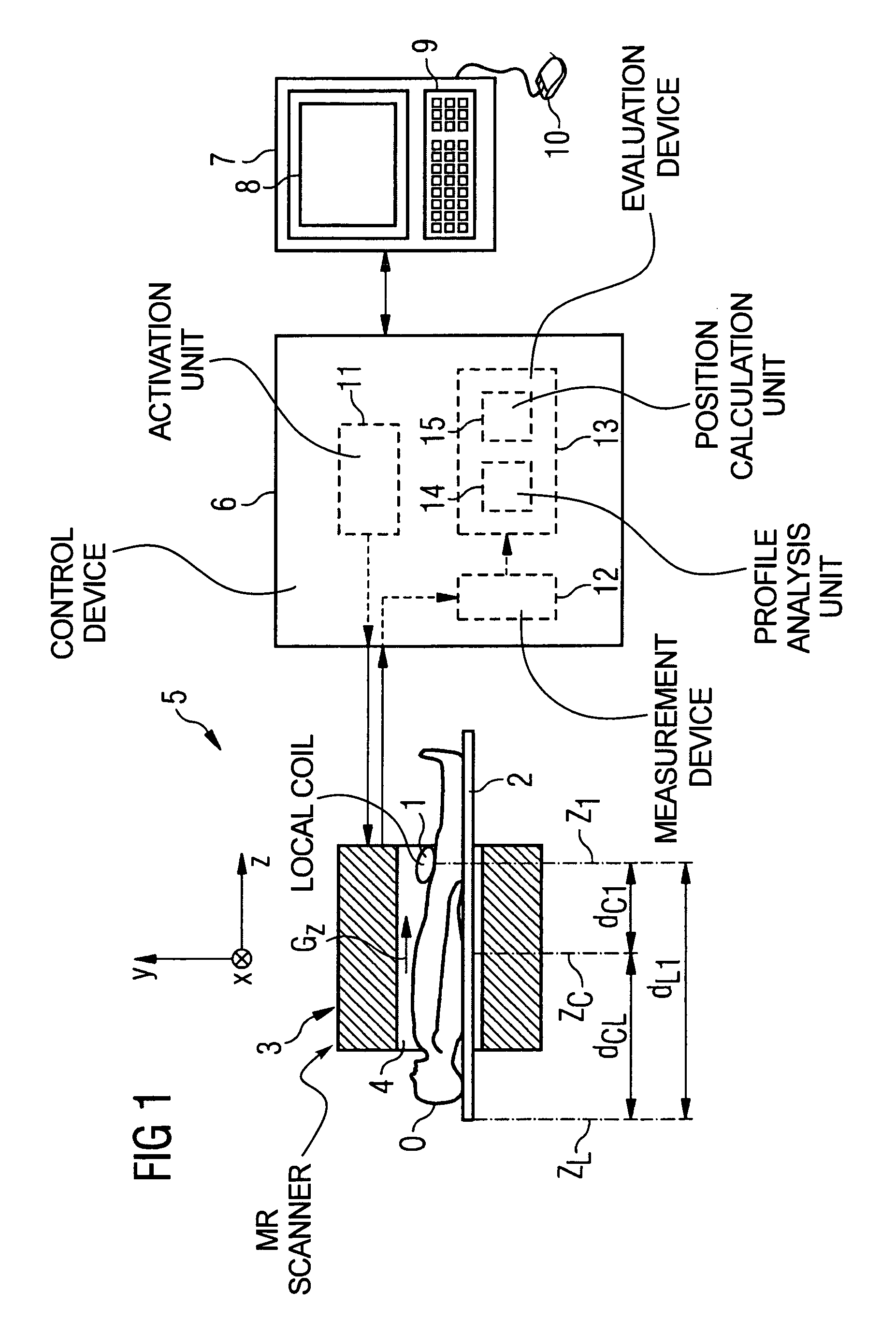
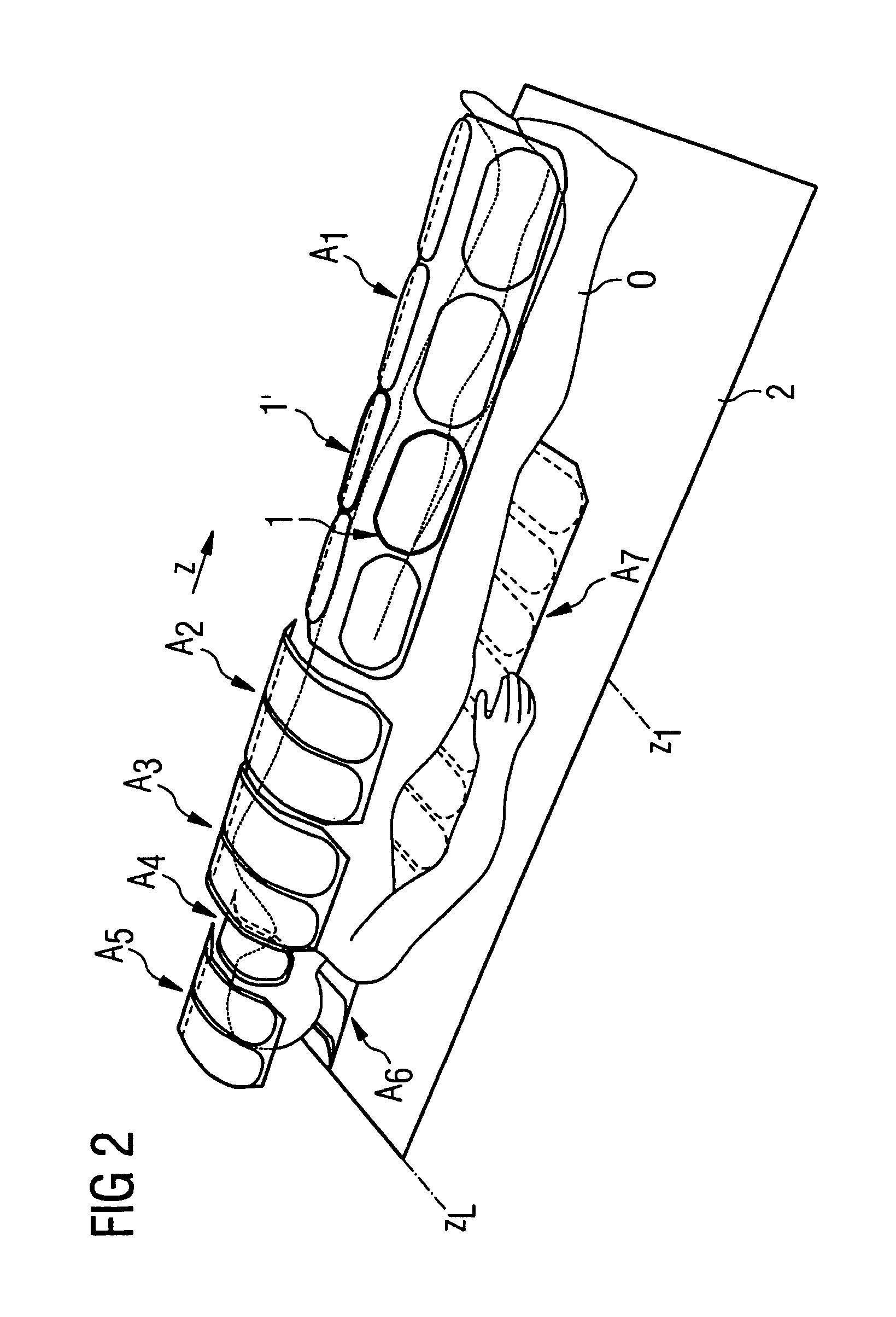
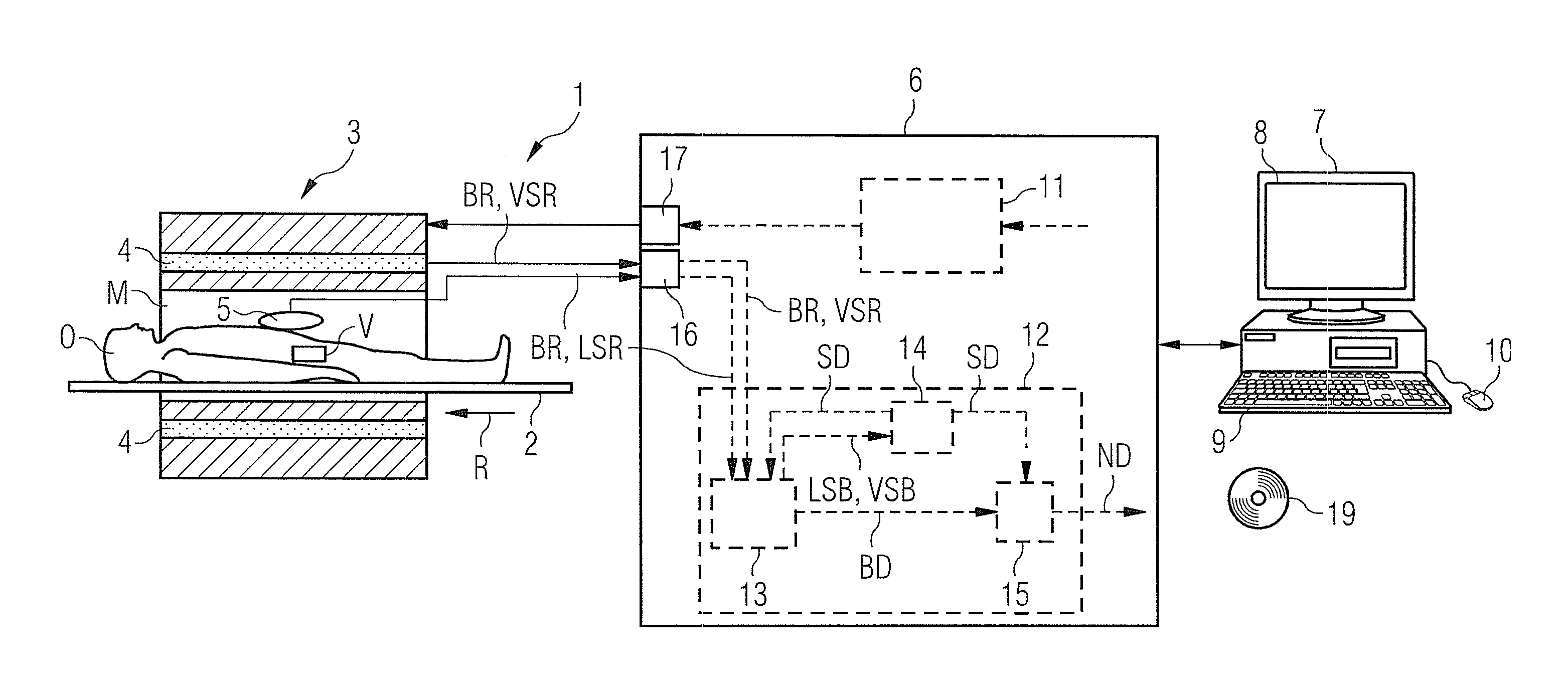
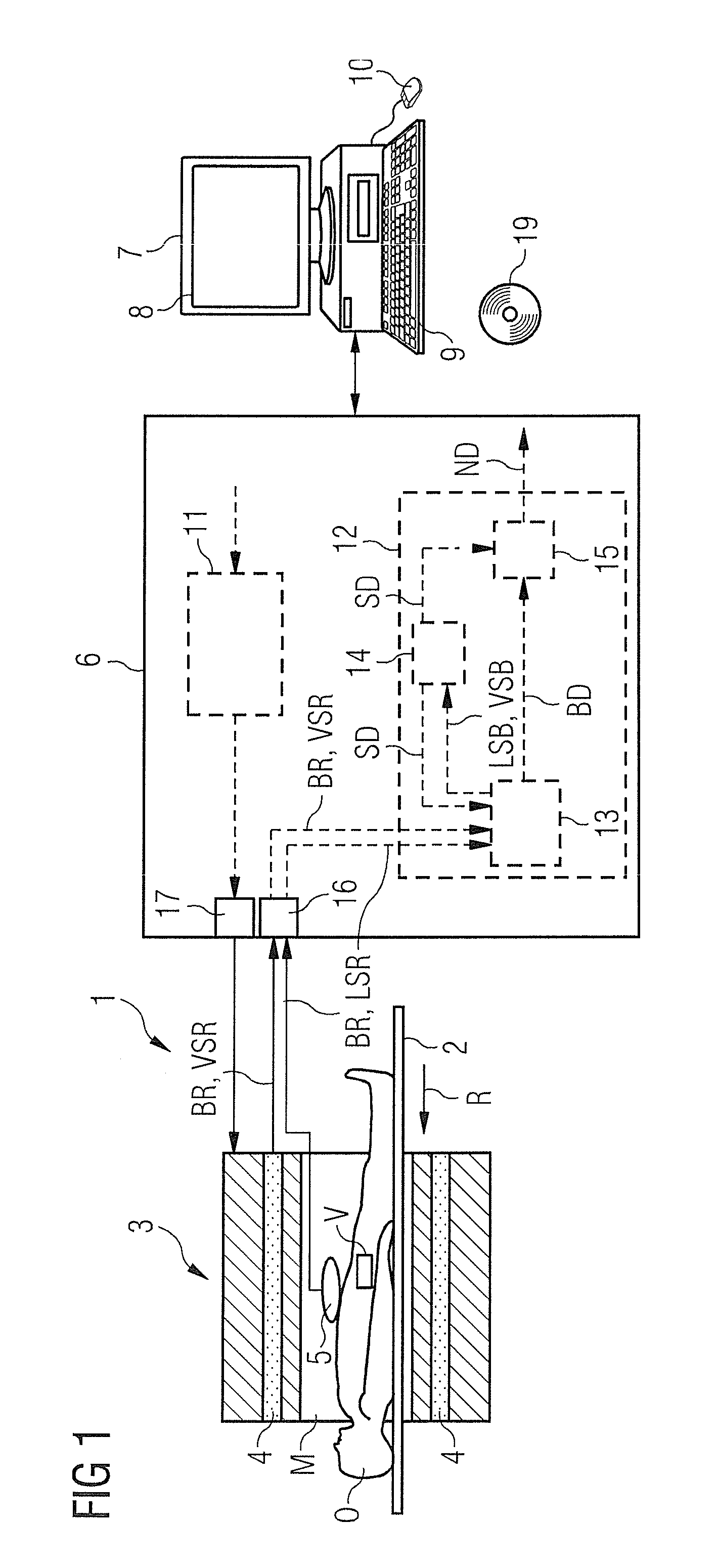
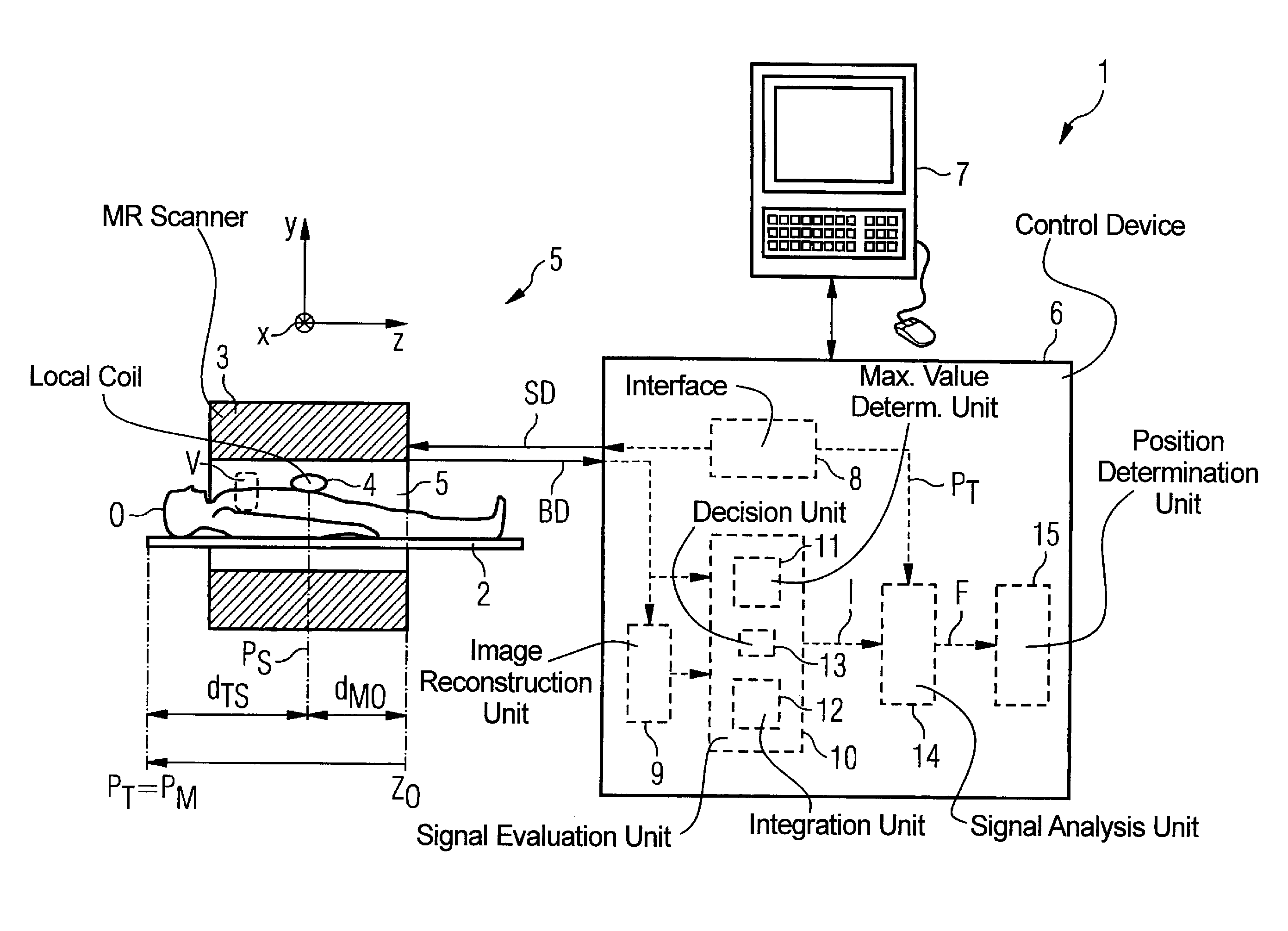
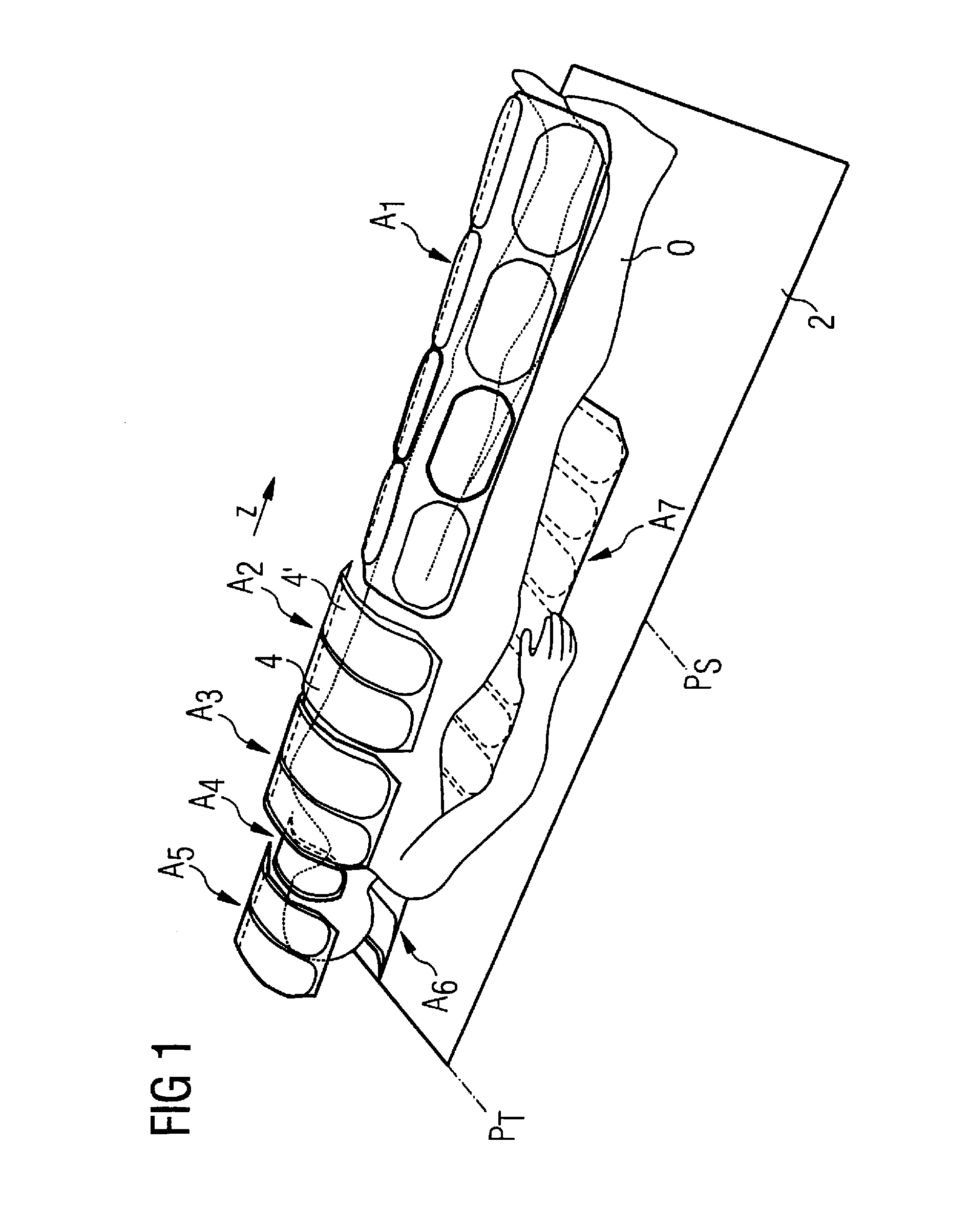
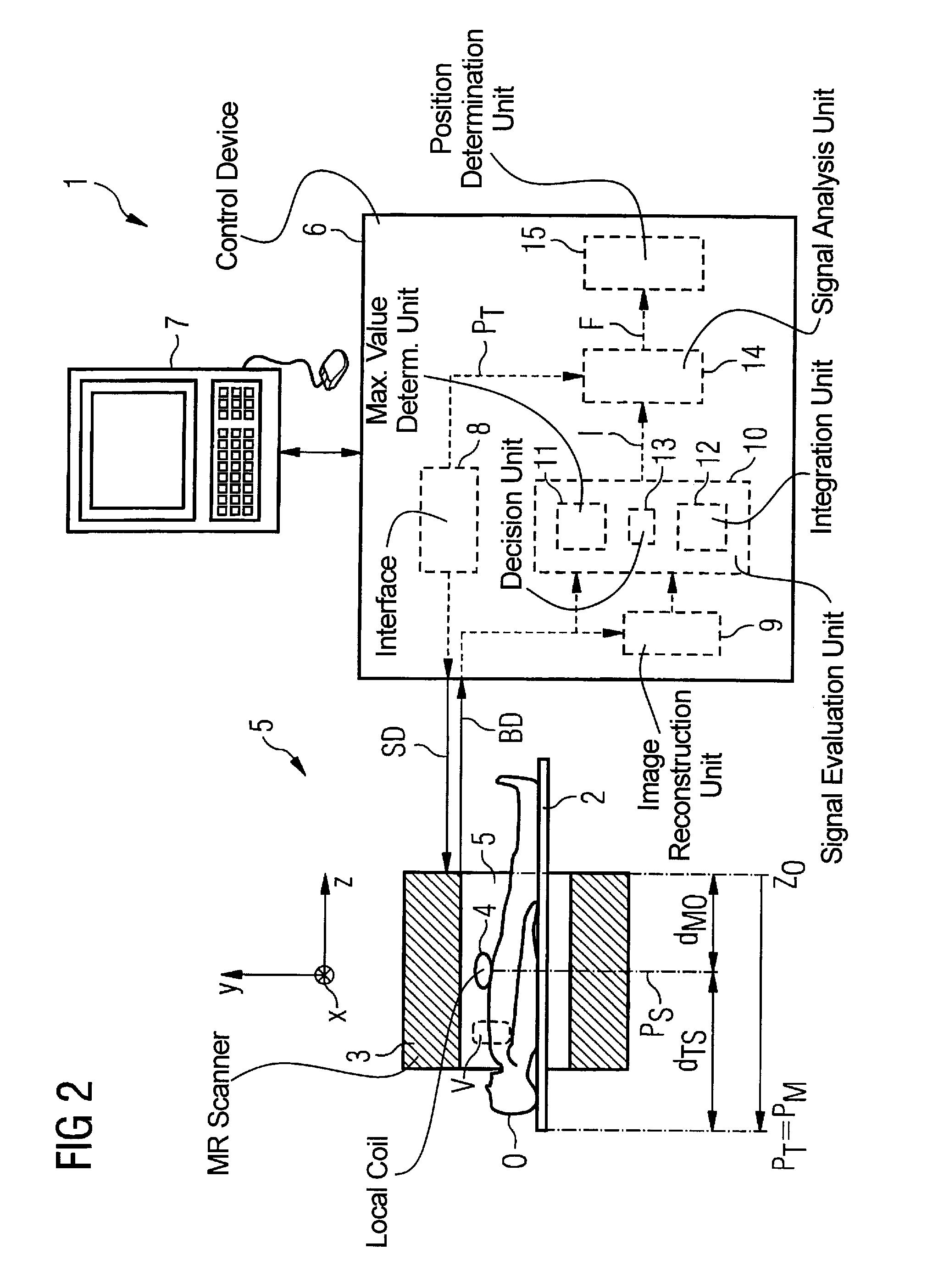
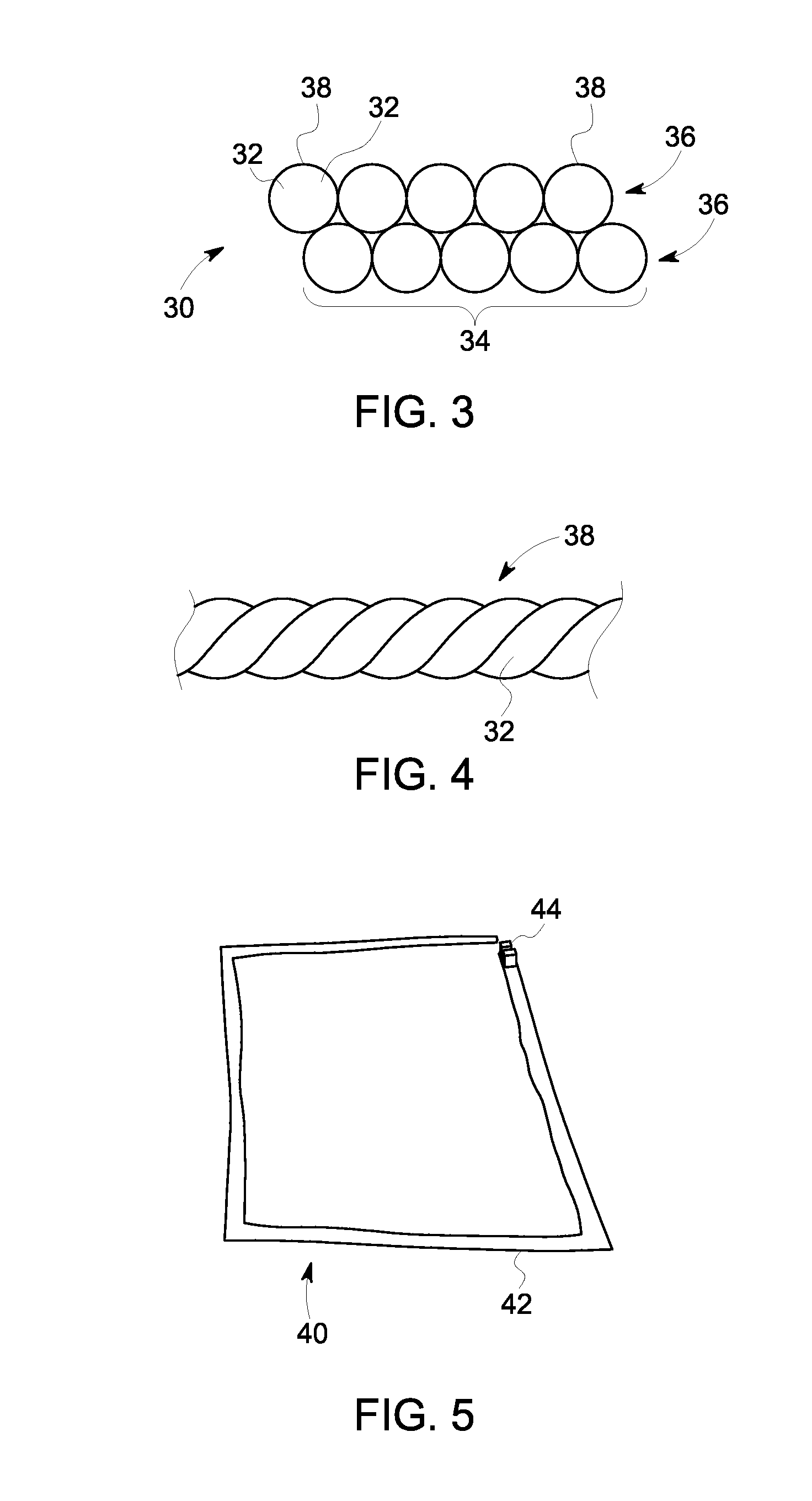
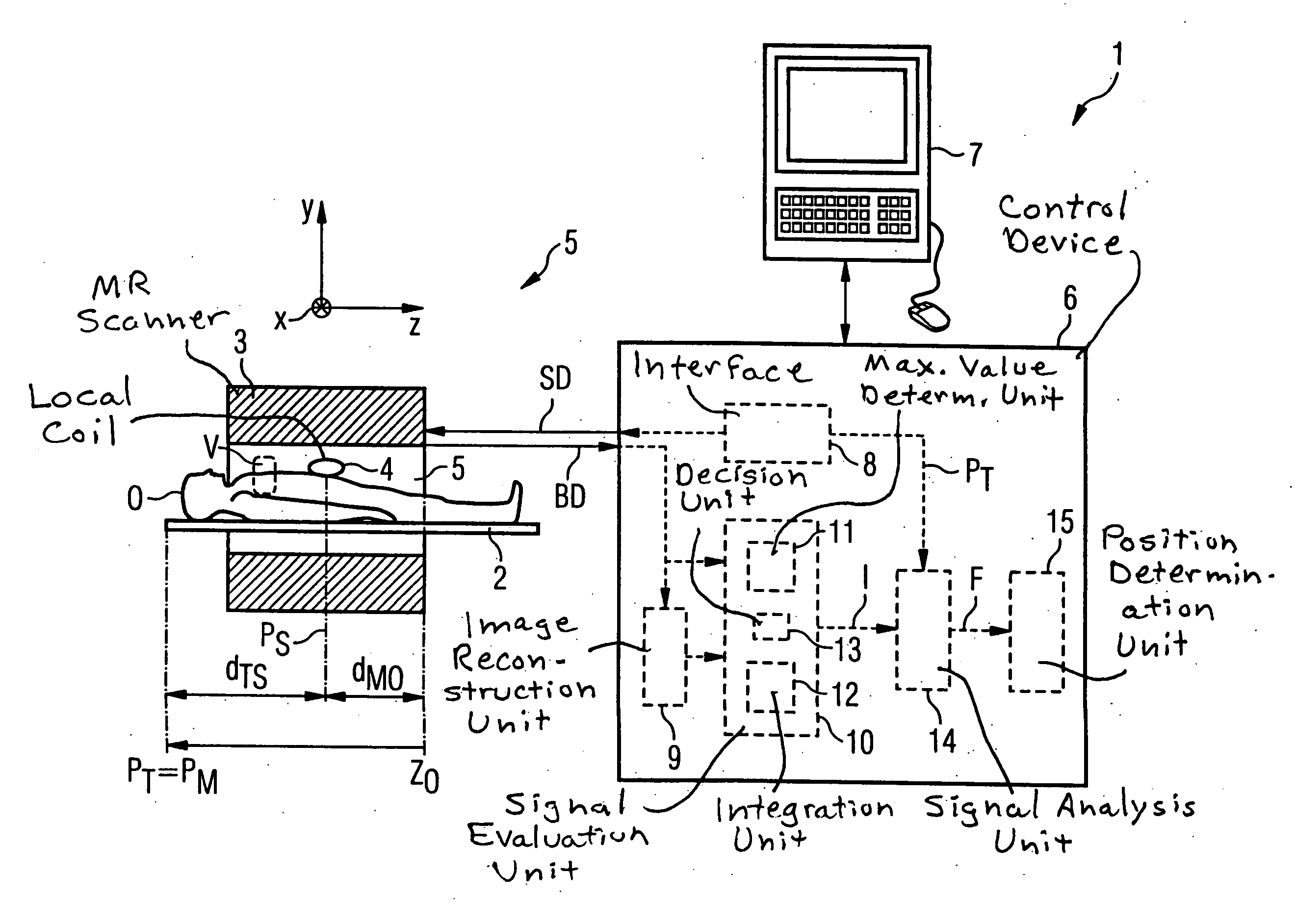
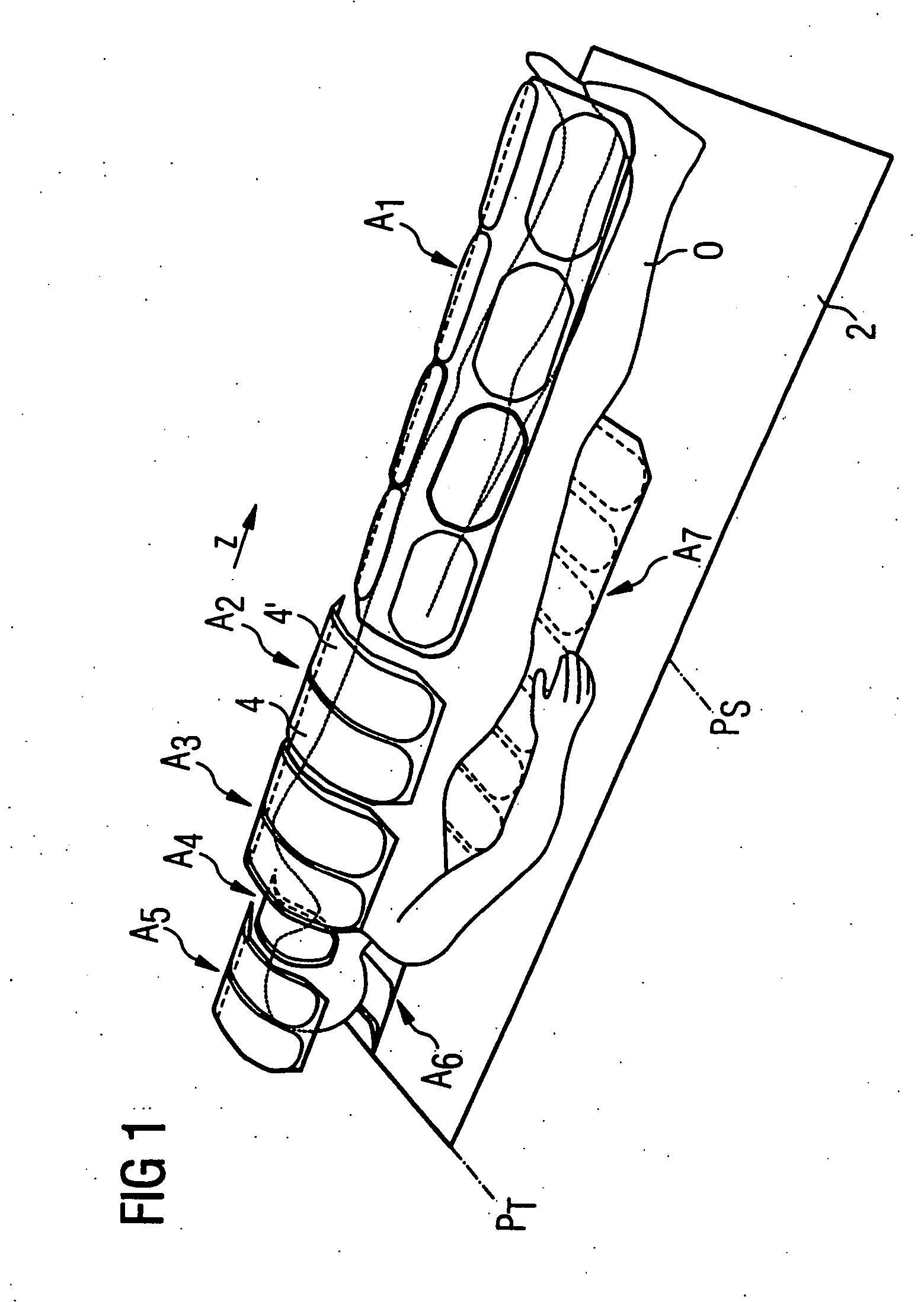
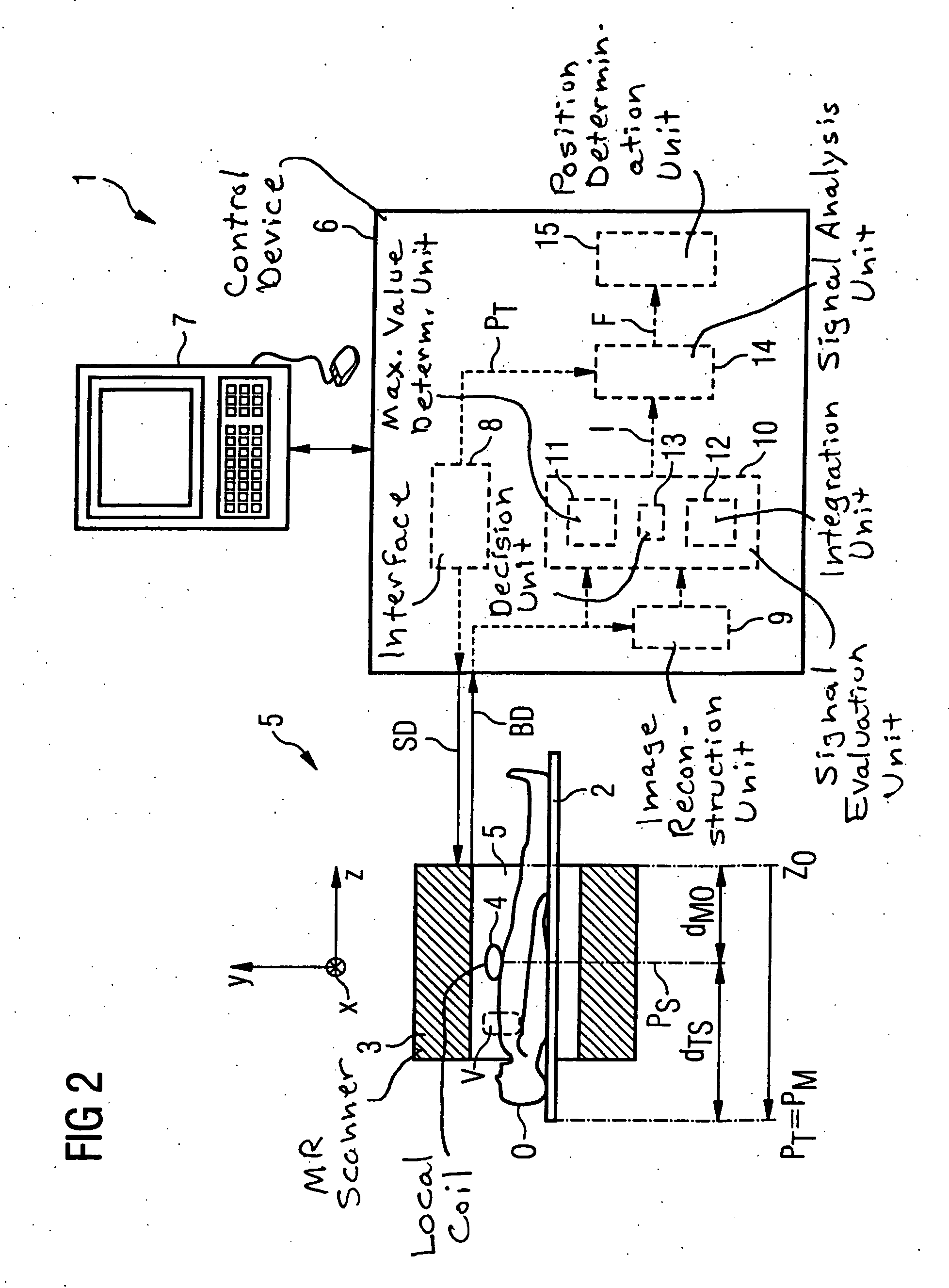
Method and control device for determining the position of a local coil on a patient table of a magnetic resonance scanner
InactiveUS20050253584A1Safely and precisely localizedAvoid problemsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientResonance
In a method and control device for determining the position in at least one spatial direction of a local coil on a patient table in a scanner of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus, a radio-frequency signal is emitted in the presence of a magnetic field gradient applied in the appertaining spatial direction and a signal profile is measured by the local coil along the magnetic field gradient. The signal profile is acquired for each of a number of positions of the patient table relative to the scanner along the magnetic field gradient. Based on the measured signal profile the position of the local coil is determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
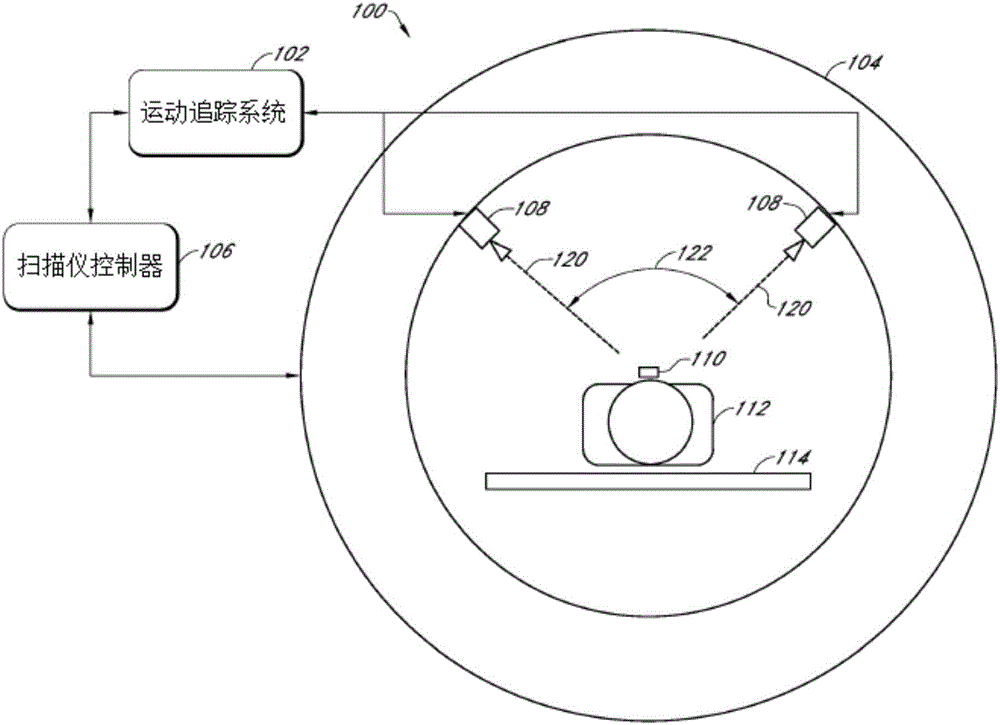
Systems, devices, and methods for tracking and compensating for patient motion during a medical imaging scan
A motion tracking system for dynamic tracking of and compensation for motion of a patient during a magnetic resonance scan comprises a first camera positioned to view an optical marker along a first line of sight; a second camera positioned to view the optical marker along a second line of sight; and a computer system configured to analyze images generated by the first and second cameras to determine changes in position of the optical marker, and to generate tracking data for use by a magnetic resonance scanner to dynamically adjust scans to compensate for the changes in position of the optical marker, wherein the computer system is configured to dynamically adapt its image analysis to utilize images from all cameras that are currently viewing the optical marker.
Owner:KINETICOR
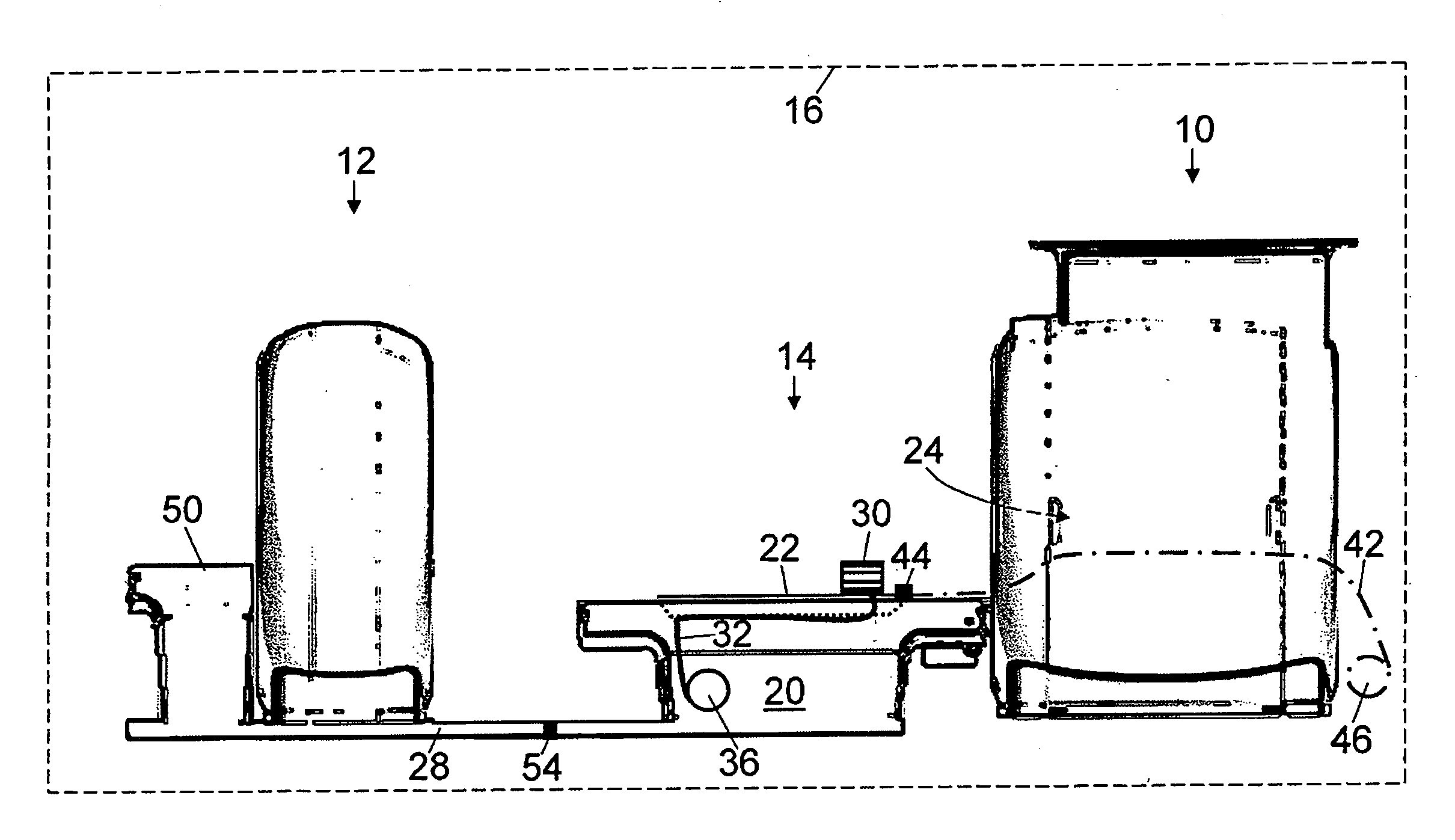
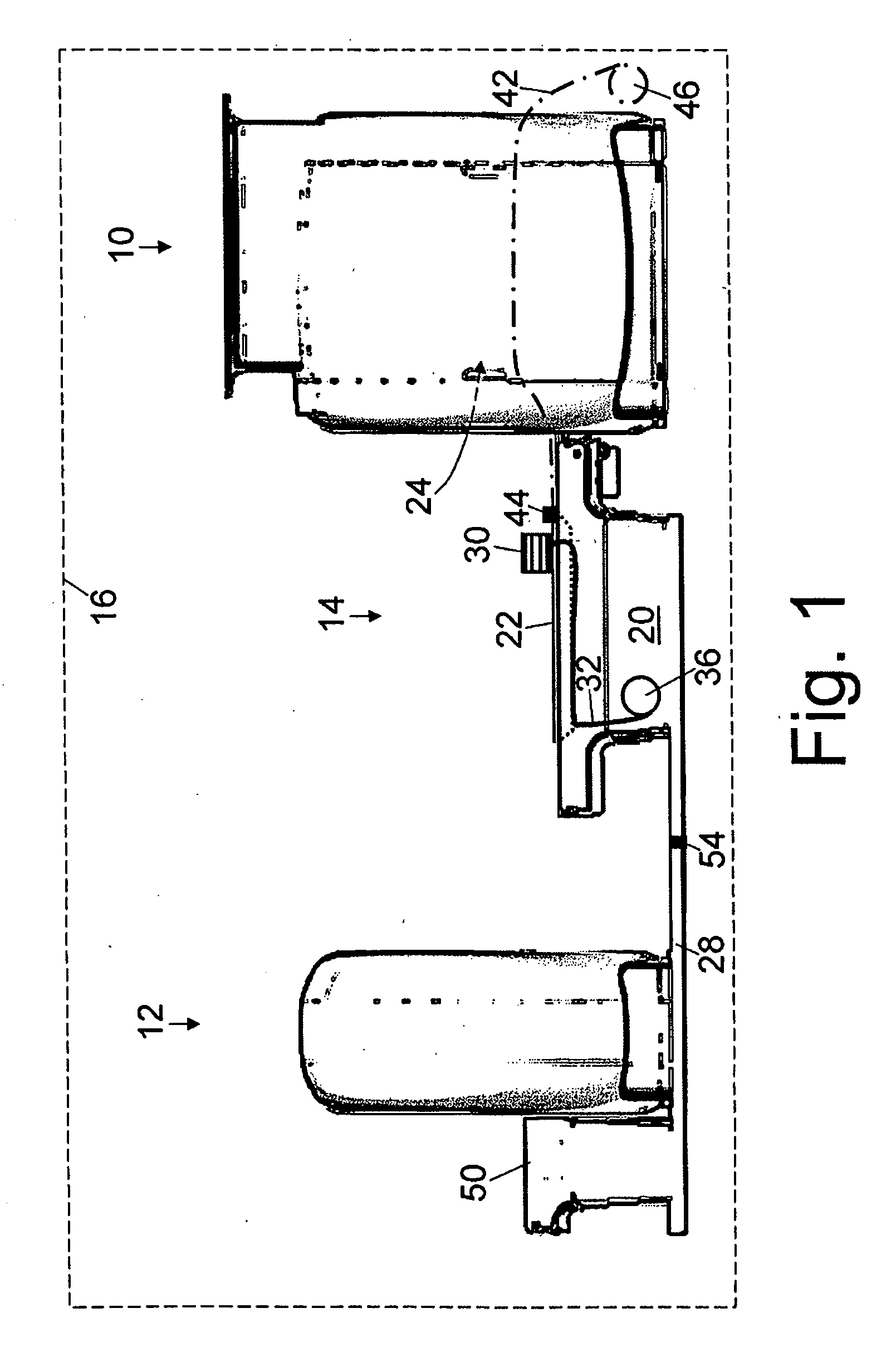
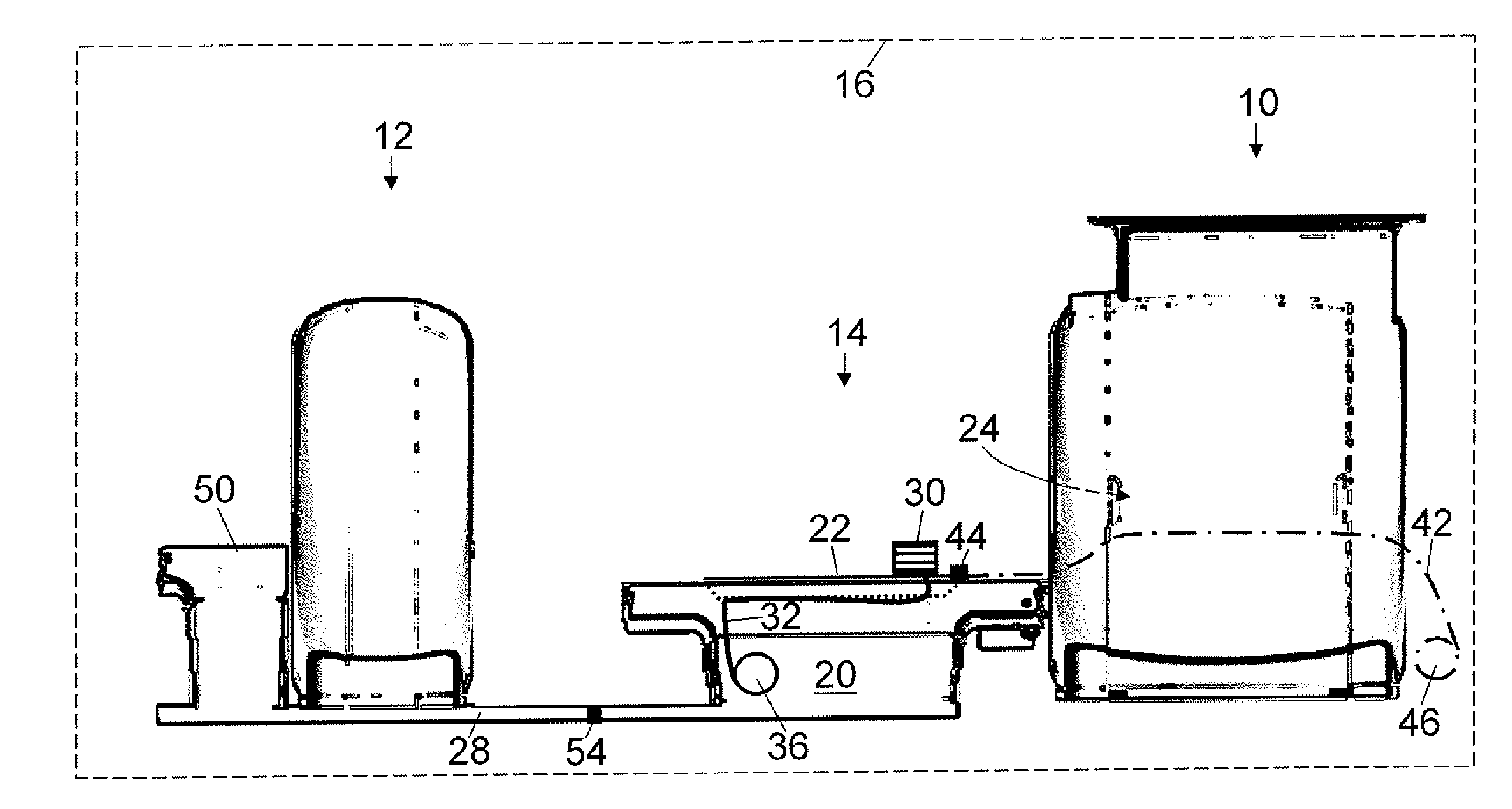
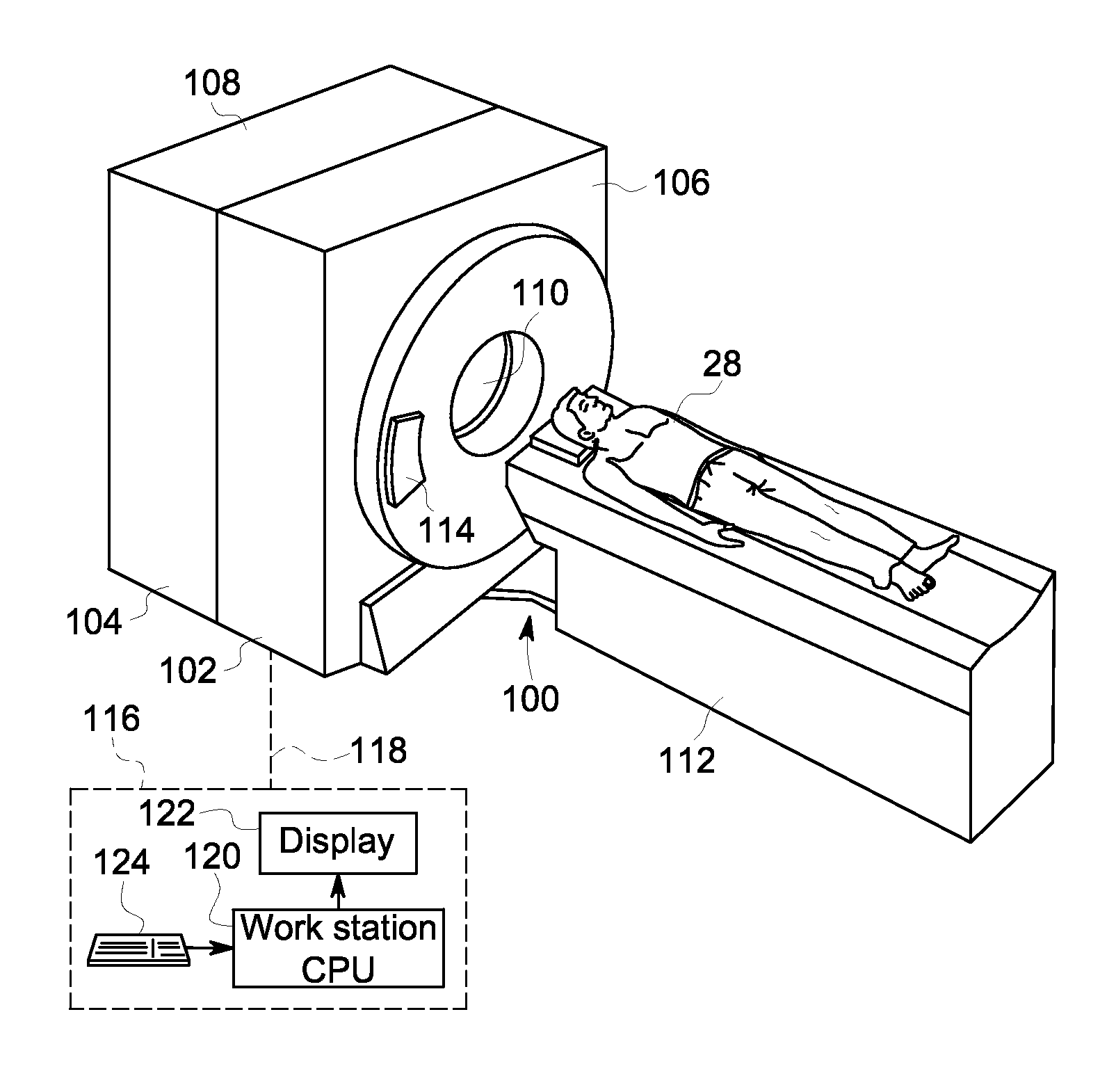
Patient bed for pet/mr imaging systems
ActiveUS20090209844A1Without compromising easeEasy to placePatient positioning for diagnosticsCabinetsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityEngineering
A hybrid imaging system and a patient bed for same are disclosed. The hybrid imaging system includes a magnetic resonance scanner and a second modality imaging system spaced apart from the magnetic resonance scanner by a gap. In some embodiments, the gap is less than seven meters. The patient bed is disposed at least partially in the gap between the magnetic resonance scanner and the second modality imaging system, and includes a linearly translatable patient support pallet aligned to be selectively moved into an examination region of the magnetic resonance scanner for magnetic resonance imaging and into an examination region of the second modality imaging system for second modality imaging. In some embodiments, a linear translation range of the linearly translatable pallet is less than five times a length of the patient support pallet along the direction of linear translation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Multi-b-value DWI (diffusion weighted image) noise reduction method based on mutual information
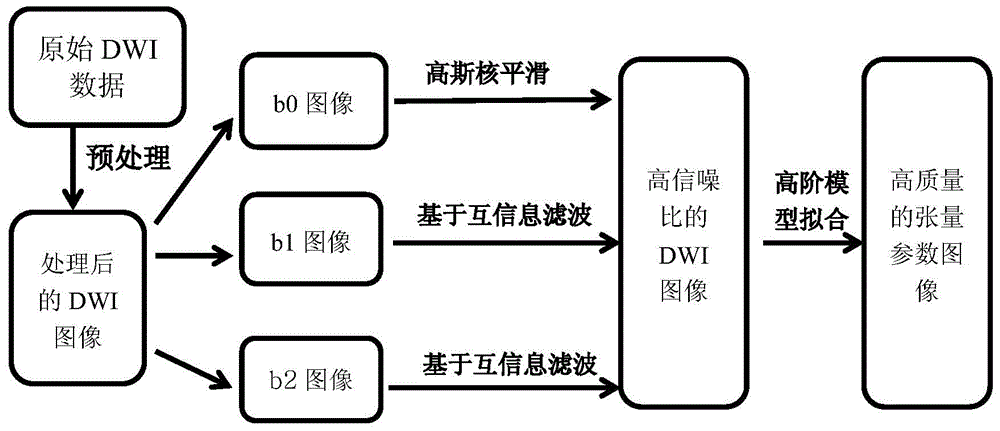
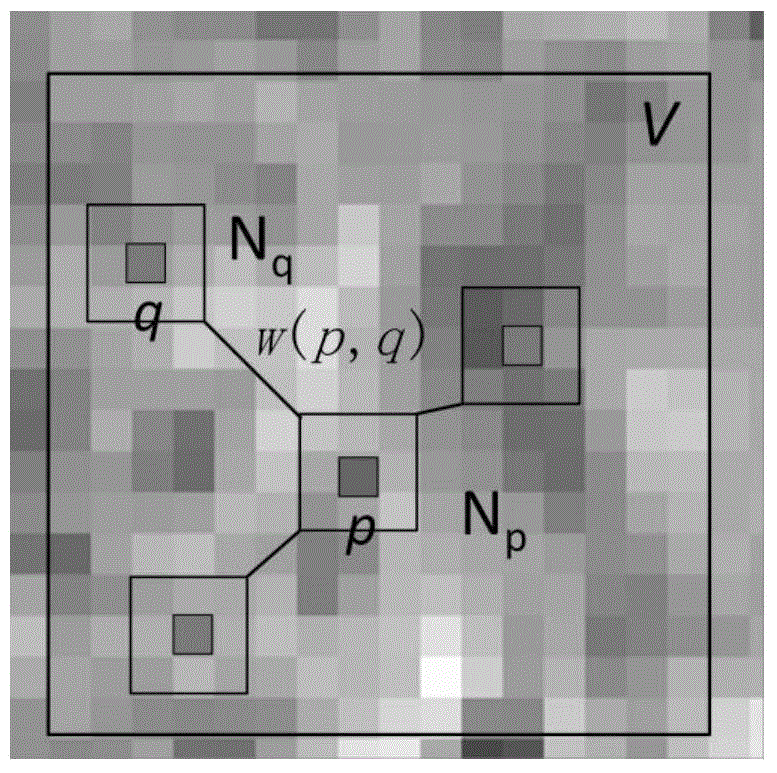
ActiveCN104574298AReduce mistakesLess singular valueImage enhancementDiagnostic recording/measuringHead movementsImaging quality
The invention discloses a multi-b-value DWI (diffusion weighted image) noise reduction method based on mutual information. The method comprises steps as follows: acquiring to-be-tested multi-b-value DWIs in multiple diffusion sensitive gradient directions by a magnetic resonance scanner; performing preprocessing such as head movement correction, eddy current correction and the like on the images; estimating different b-value image signal-to-noise ratios; performing noise reduction processing on the images through setting parameters of an optimal noise reduction algorithm so as to acquire DWIs with higher signal-to-noise ratios. The method fully considers features of different images, and three-dimensional structural features of the processed images are reserved as many as possible while noises are eliminated. During establishment of a high-order complex model, different b images have higher image quality, so that acquired high-order parameter images can have smaller errors and fewer singular values. The method can be better applied to preprocessing of a high-order model imaging technology and plays an active role in further research on white matter fiber structures.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
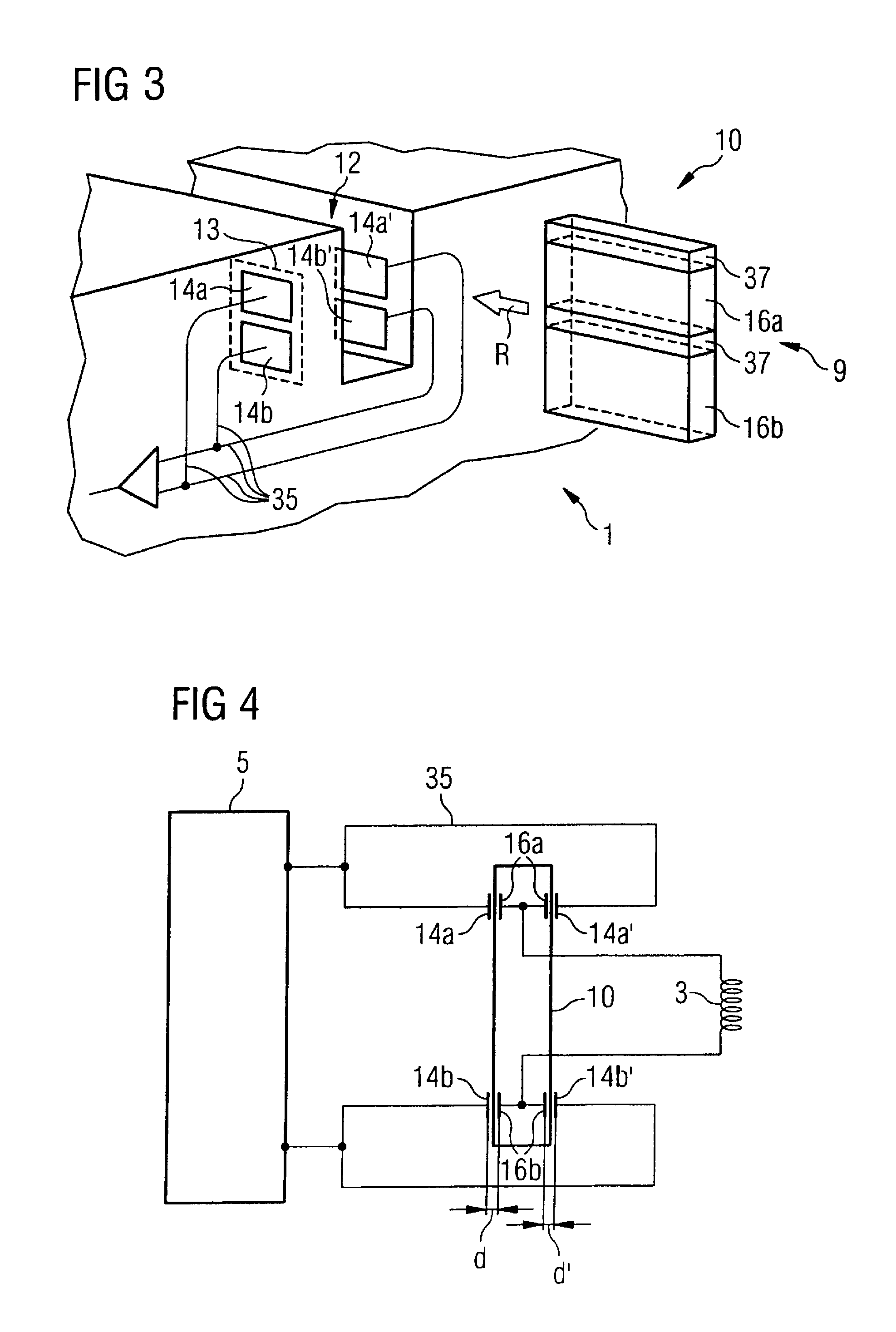
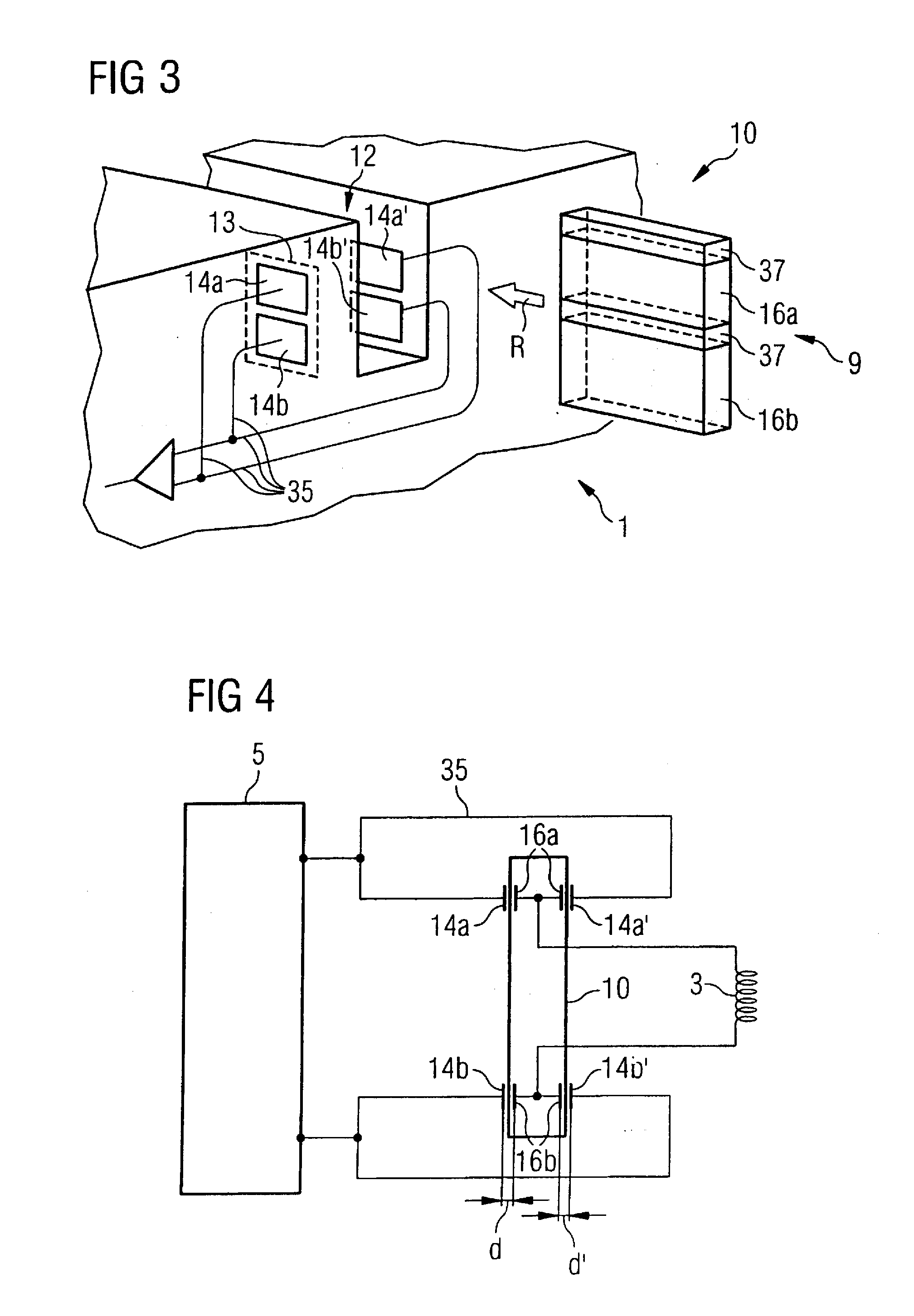
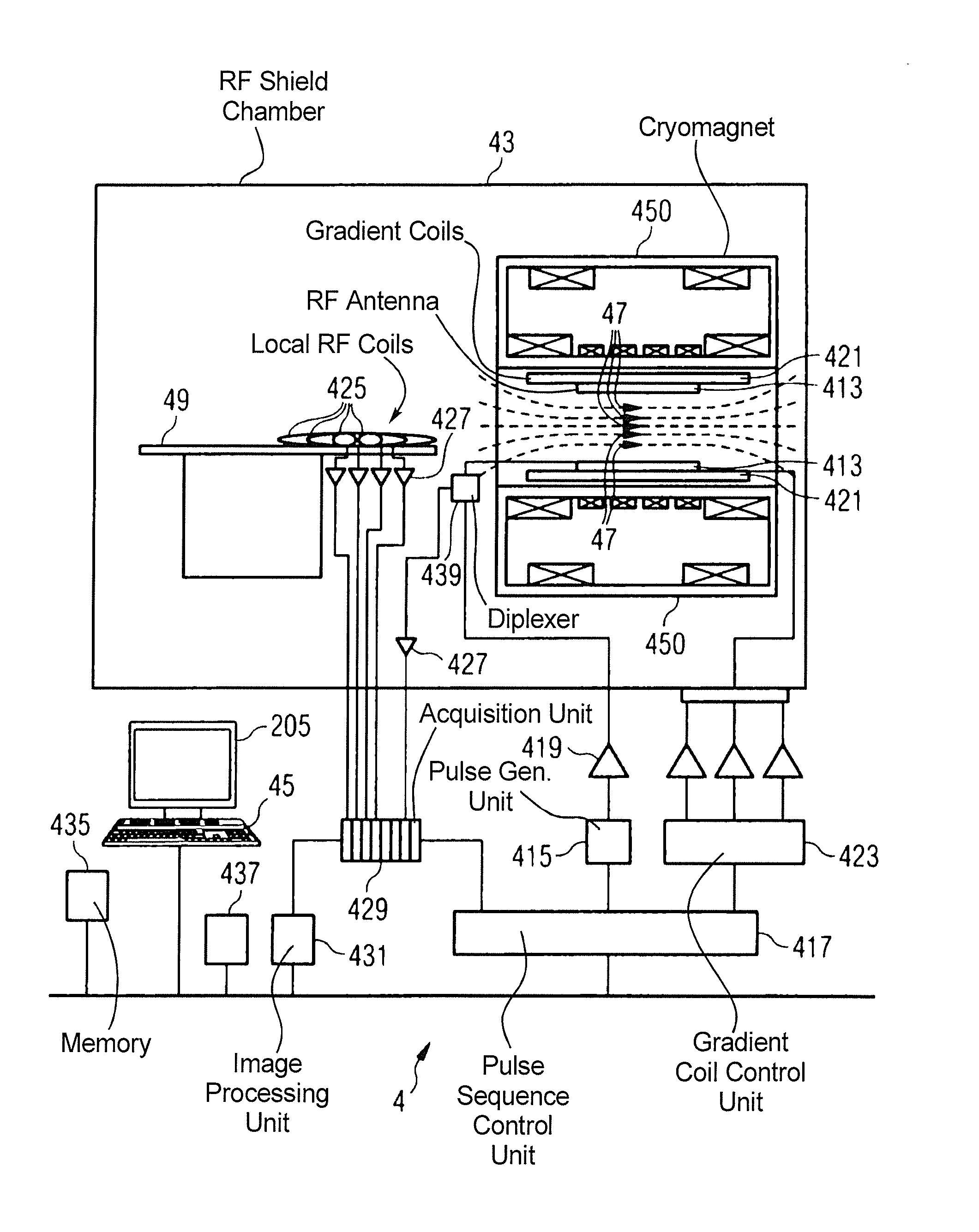
System and method for electrically contacting local coils with a signal processor remote therefrom in a magnetic resonance scanner
InactiveUS7990147B2Convenient ArrangementContinuous motionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectricityResonance
In a contacting system and method for contacting magnetic resonance local coils with a unit for additional signal processing of a magnetic resonance data acquisition unit, a number of coil coupler elements are electrically connected with the magnetic resonance local coils and apparatus coupler elements are mounted at the magnetic resonance tomograph, and are electrically connected with a unit for signal processing. The coil coupler elements and the apparatus coupler elements are fashioned so that, given a movement of the local coils along a movement path in the magnetic resonance data acquisition unit, a successive contacting of at least a portion of the coil coupler elements with apparatus coupler elements ensues at least over a specific path segment of the movement.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Hybrid pet/mr imaging systems
ActiveUS20080312526A1Reduce interactionImprove workflow efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHigh energyHigh energy photon
A hybrid imaging system includes a magnetic resonance scanner and a second modality imaging system disposed in the same radio frequency isolation space. The second modality imaging system includes radiation detectors configured to detect at least one of high energy particles and high energy photons. In some embodiments a retractable radio frequency screen is selectively extendible into a gap between the magnetic resonance scanner and the second modality imaging system. In some embodiments shim coils are disposed with the magnetic resonance scanner and are configured to compensate for distortion of the static magnetic field of the magnetic resonance scanner produced by proximity of the second modality imaging system.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
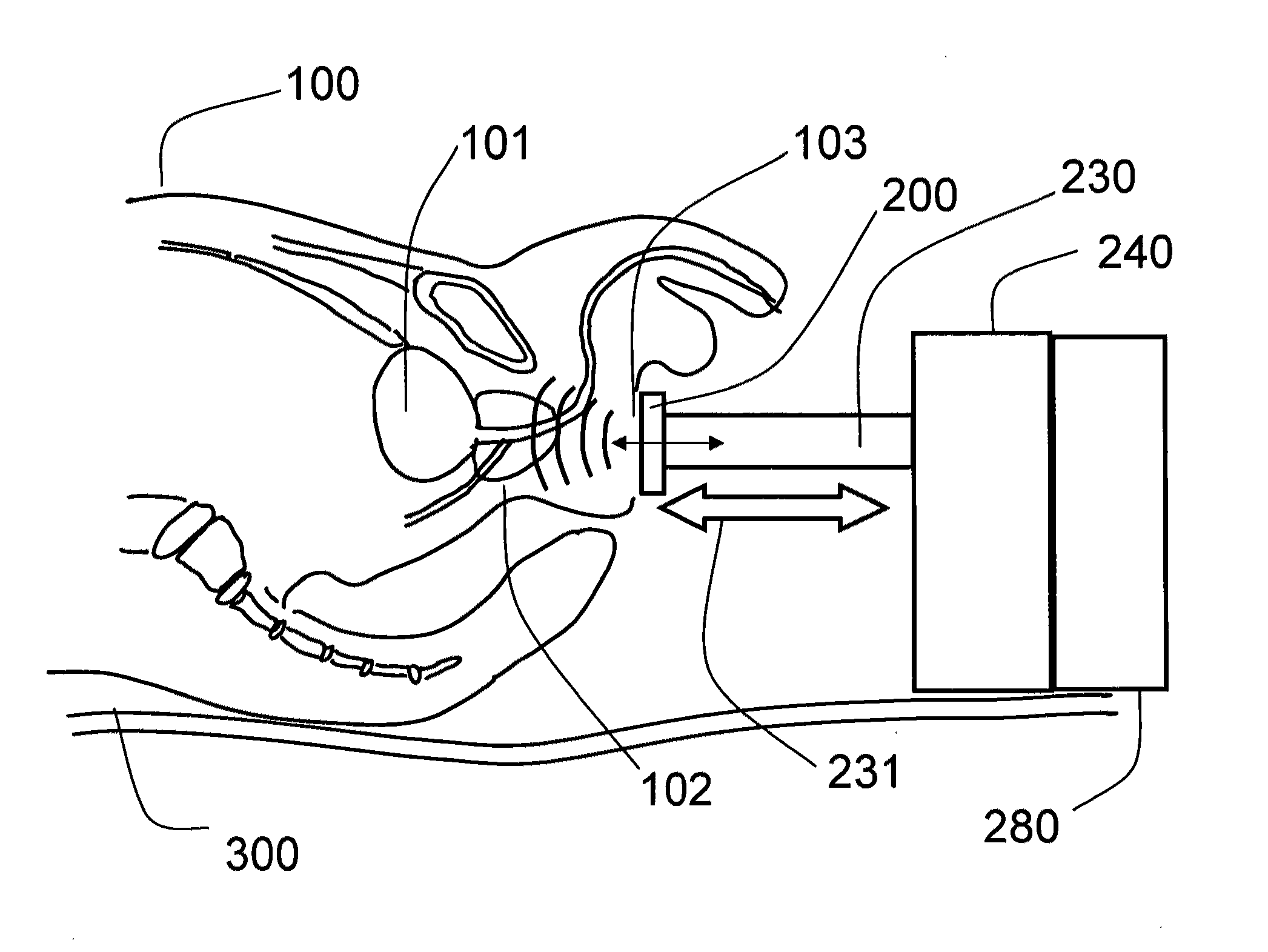
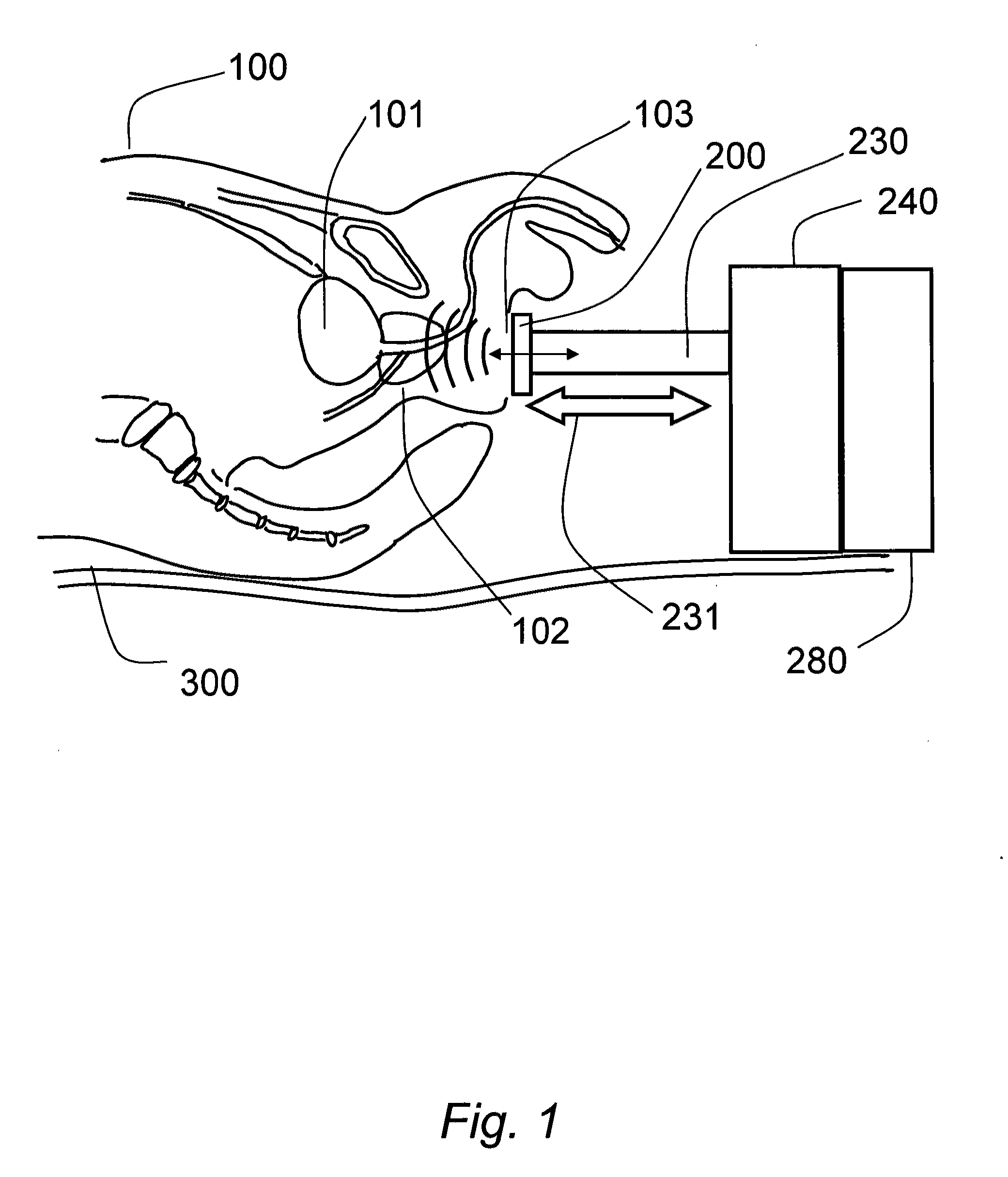
Trans-perineal prostate MR elastography
InactiveUS20120053450A1Travel efficientlyMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsRadiologyMagnetic resonance scanner
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for imaging the mechanical properties of the prostate of a patient non-invasively. The apparatus generally comprises a magnetic resonance scanner, a vibration assembly coupled to the perineal region of the patient, and a driver that drives the mechanical exciter. The method generally comprises positioning the vibration assembly against the perineal region of the patient, vibrating the mechanical exciter to cause deformational excitation of a tissue region contacted in the perineum, capturing a series of images in time (snapshots) of the tissue region using the MR scanner, and finally processing the displacement images to generate maps of mechanical properties of images tissue.
Owner:SALCUDEAN SEPTIMIU +2
System and method for electrically contacting local coils with a signal processor remote therefrom in a magnetic resonance scanner
InactiveUS20090315556A1Easy access connectionContinuous motionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRElectricityResonance
In a contacting system and method for contacting magnetic resonance local coils with a unit for additional signal processing of a magnetic resonance data acquisition unit, a number of coil coupler elements are electrically connected with the magnetic resonance local coils and apparatus coupler elements are mounted at the magnetic resonance tomograph, and are electrically connected with a unit for signal processing. The coil coupler elements and the apparatus coupler elements are fashioned so that, given a movement of the local coils along a movement path in the magnetic resonance data acquisition unit, a successive contacting of at least a portion of the coil coupler elements with apparatus coupler elements ensues at least over a specific path segment of the movement.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance scanner with electromagnetic position and orientation tracking device
A system for combining electromagnetic position and orientation tracking with magnetic resonance scanner is provided. One embodiment includes a magnetic resonance scanner defining a reference coordinate system for scanning a target. Coupled to the magnetic resonance scanner is a magnetic field source which produces a magnetic field. The magnetic field is sensed by a magnetic field sensor which produces a signal proportional to the magnetic field. The magnetic field sensor has a location relative to the reference coordinate system. The location of the magnetic field sensor relative to the reference coordinate system of the magnetic resonance scanner is determined by a location tracking device using at least a line segment model of the magnetic field source and the signal from the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:JAKAB PETER D
Method and device for automated generation of a formal description of a magnetic resonance system measurement sequence, using a sequence model
InactiveUS8299789B2Easy to controlReduce effortDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceSequence model
A magnetic resonance sequence model that is a formal description of a measurement sequence is used to automate measurement sequence programming. The sequence model allows a system-independent specification of the measurement sequence for execution in a magnetic resonance scanner. The sequence model is as formal as possible; it is limited to the minimum required information for description of a measurement sequence without limiting the flexibility in the sequence programming. A method for formal description of the measurement sequence describes the measurement sequence by a number of parameters to be parameterized. The parameterization of the measurement sequence can ensue automatically from the formalized description of the measurement sequence, except for a set of parameters that are still be determined. For automatic generation of an executable measurement sequence, the method determines the parameters to be determined using a solver, under consideration of boundary conditions, so that a consistent set of parameters is created that completely describes the measurement sequence. This complete description of parameter values of the measurement sequence is then be translated automatically into a programming language that can be directly executed in the magnetic resonance scanner.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method For Generating MR Images And An Appropriately Designed Magnetic Resonance System
ActiveUS20120010495A1Quality improvementImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceComputer science
An embodiment of the invention relates to the generation of MR images of a volume section within an examination object by way of a magnetic resonance scanner. In at least one embodiment, the following steps are performed: generating at least one of the MR images; automatically performing a number of quality inspections on the at least one MR image; and, should one of these quality inspections fail, an action is automatically performed in order to improve a quality when generating more of the MR images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
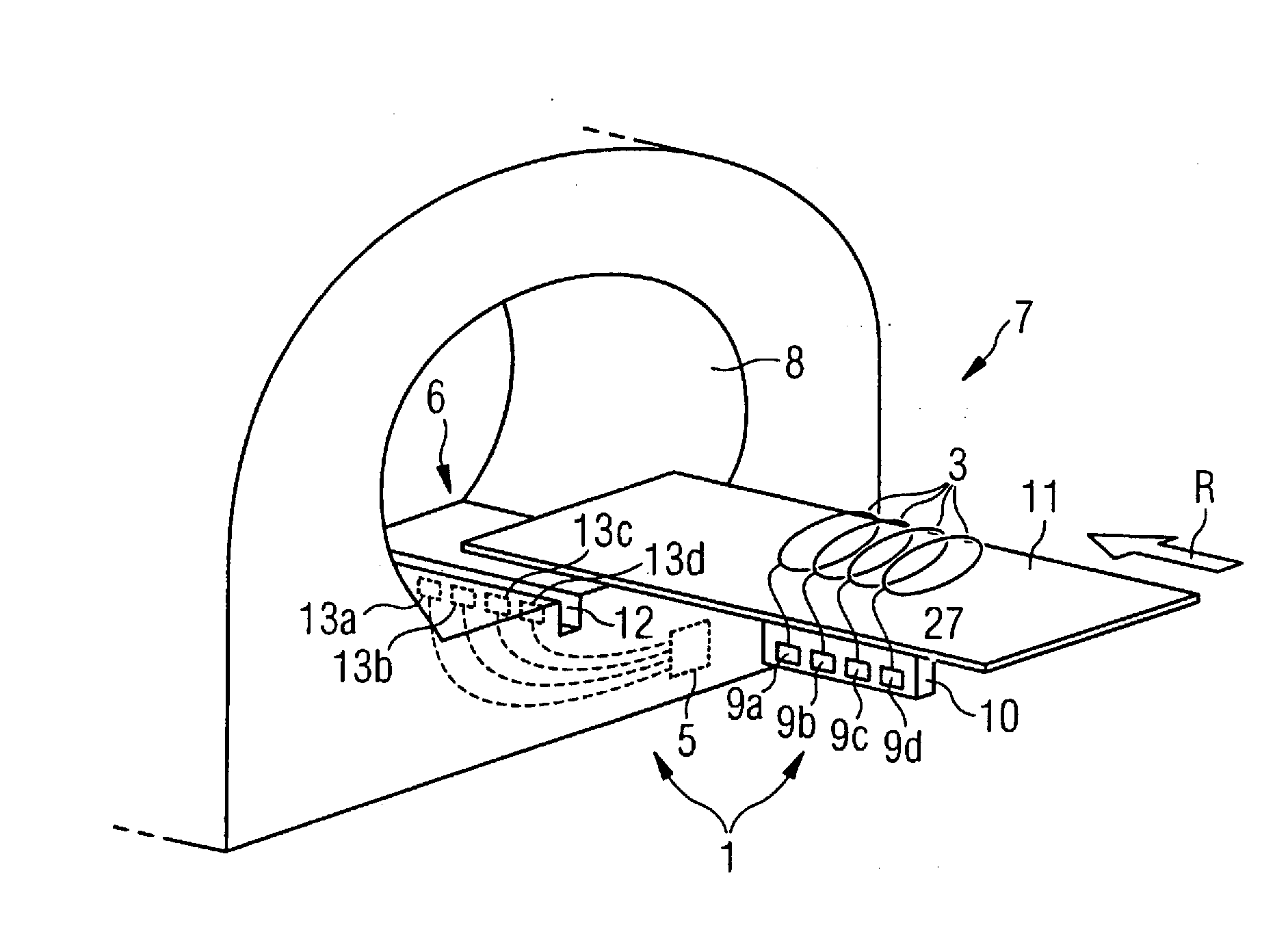
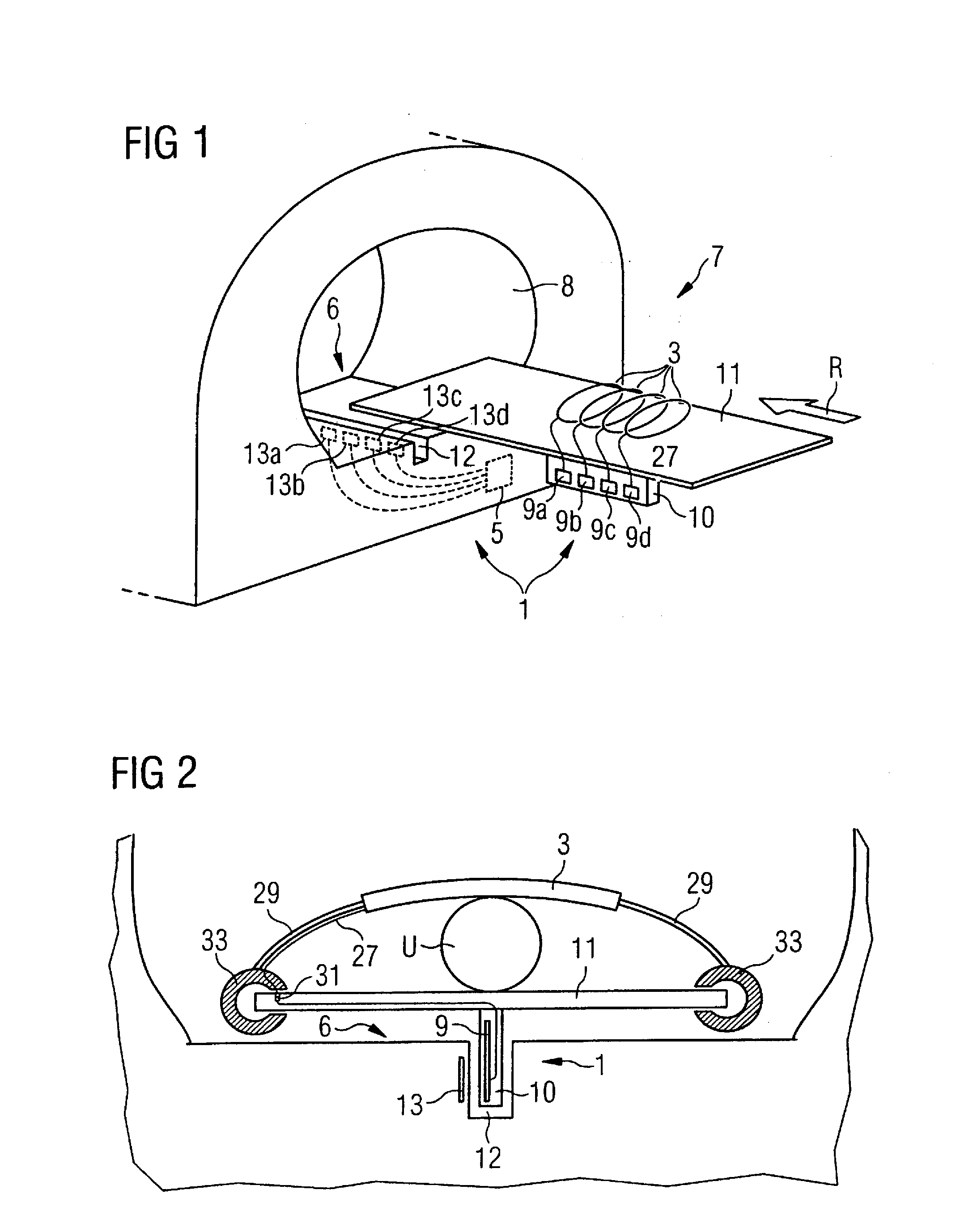
Whole-Body Coil Arrangement for an Open Magnetic Resonance Scanner for Use With a Second Diagnostic and/or Therapeutic Modality
ActiveUS20110043207A1Suitability manufactureMechanical stabilityTomographyElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical conductorWhole body
A whole-body coil arrangement for an open magnetic resonance scanner for use with a second diagnostic and / or therapeutic modality is proposed. The whole-body coil arrangement includes at least one coil conductor and a radio-frequency shield. The whole-body coil arrangement is embodied at least in part as essentially transparent to the second modality.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
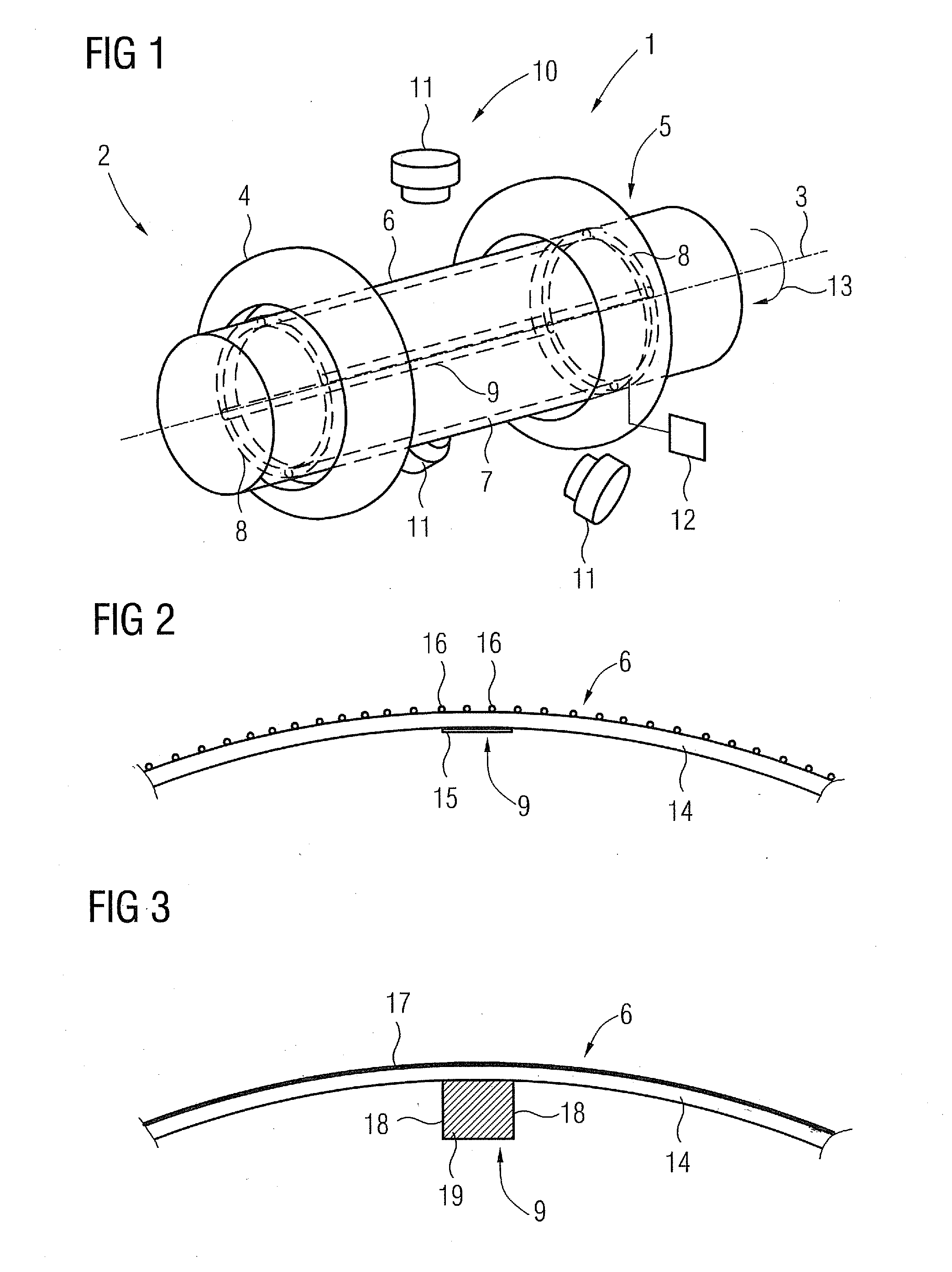
Method and control device for determining the position of a local coil on a patient table of a magnetic resonance scanner
InactiveUS7141976B2Safely and precisely localizedEasy to identifyMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientResonance
In a method and control device for determining the position in at least one spatial direction of a local coil on a patient table in a scanner of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus, a radio-frequency signal is emitted in the presence of a magnetic field gradient applied in the appertaining spatial direction and a signal profile is measured by the local coil along the magnetic field gradient. The signal profile is acquired for each of a number of positions of the patient table relative to the scanner along the magnetic field gradient. Based on the measured signal profile the position of the local coil is determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
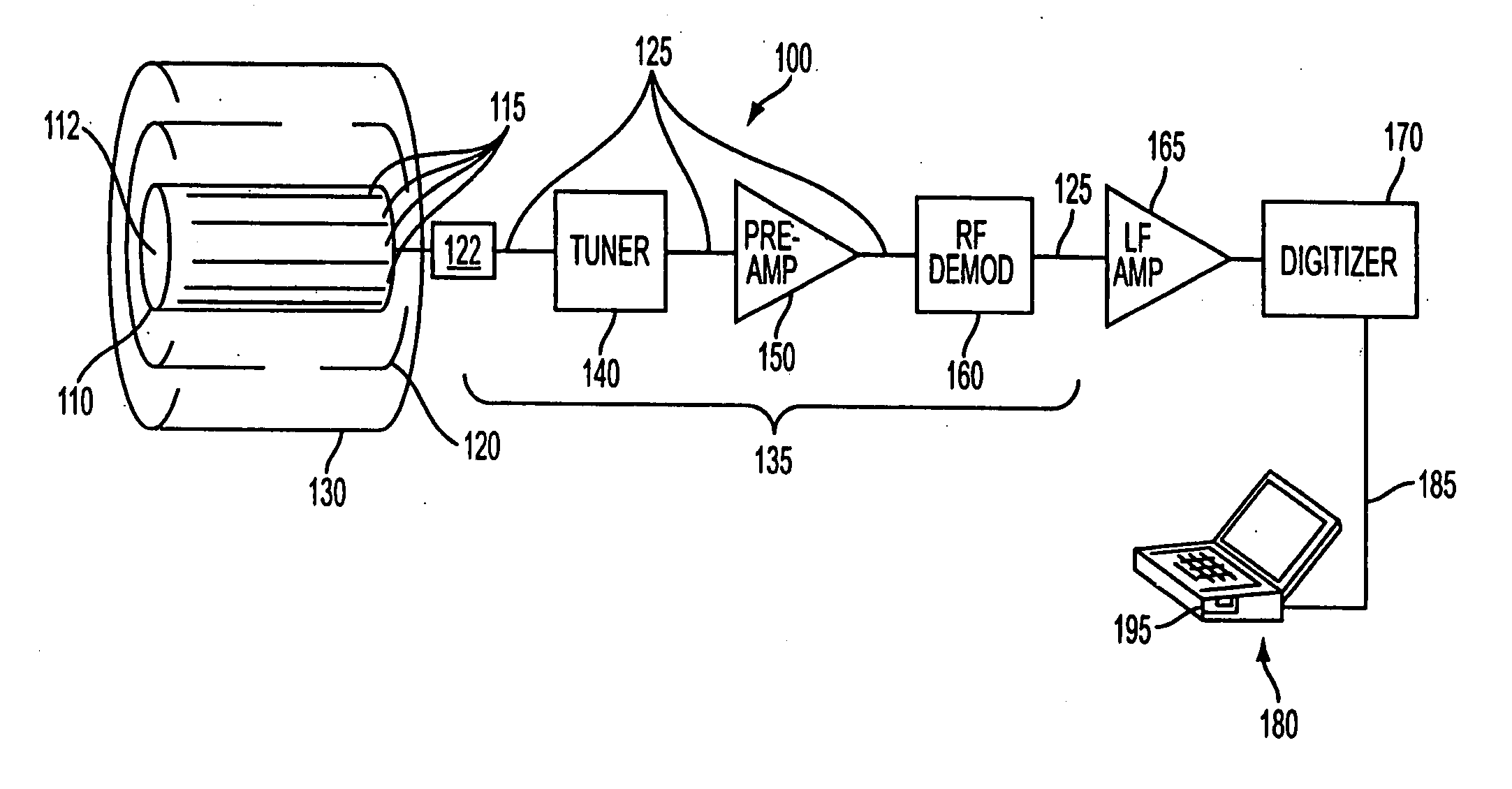
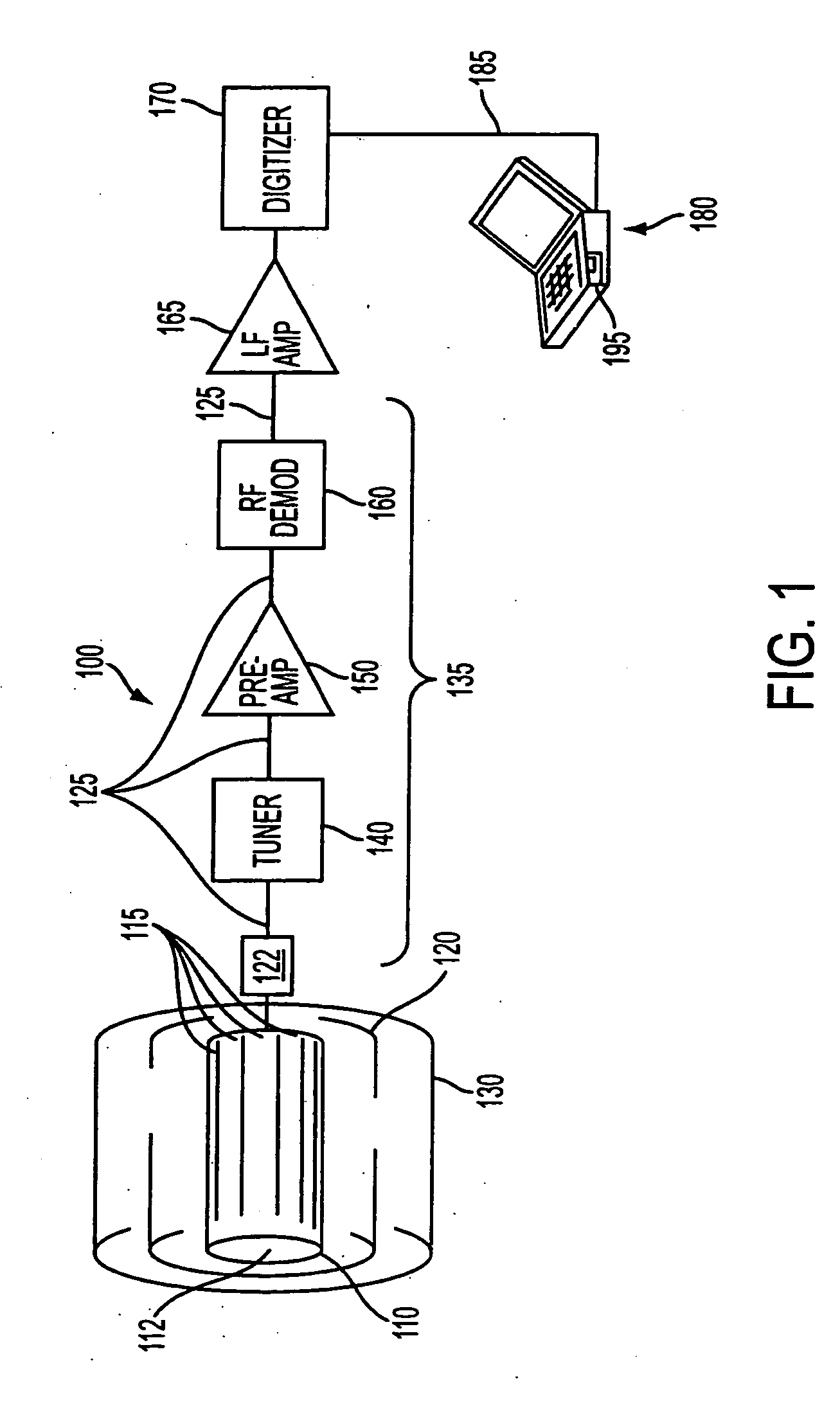
Radiometric Approach to Temperature Monitoring Using a Magnetic Resonance Scanner
InactiveUS20070293753A1Accurate and absolute non-invasive thermal imagingEffective diagnosisBody temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic shieldingTemperature monitoring
Disclosed is a method and system for acquiring absolute temperature imagery using an MR scanner. The method involves using the RF coil as a passive antenna, and performing radiometric measurements of the noise variance of the target within the field of view of the RF coil. The noise variance corresponds to the absolute temperature of the volume within the field of view of the RF coil. The room of the MR scanner is used for electromagnetic shielding during the acquisition of radiometric data. This method may be performed with minimal or no add-ons to existing MR scanner hardware. Disclosed are a method for calibrating an MR scanner for radiometric temperature measurements, and a method for acquiring and generating thermal imagery with a calibrated MR scanner.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
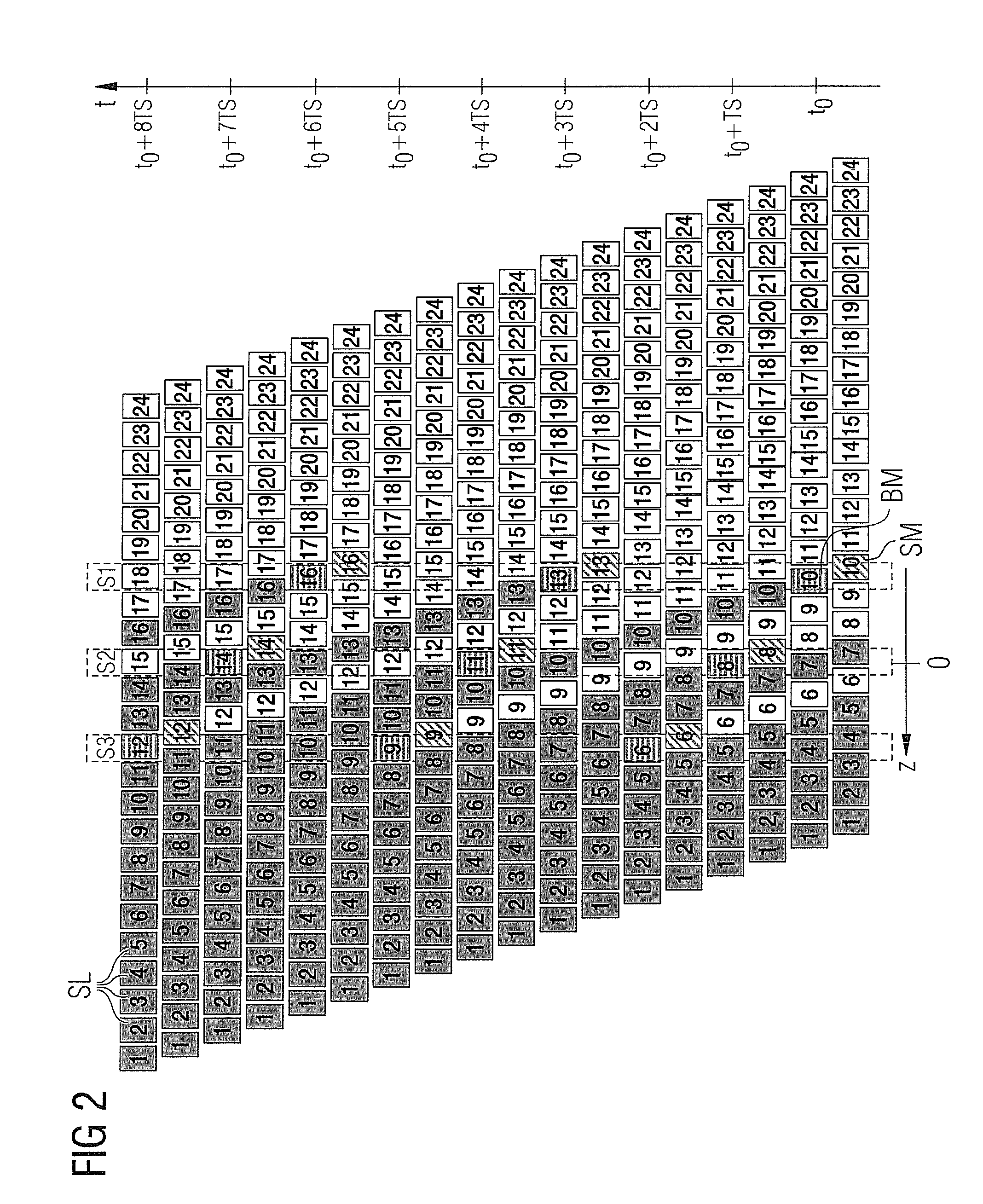
Method and magnetic resonance tomography system to generate magnetic resonance image data of an examination subject
ActiveUS20120229136A1Avoid problemsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRMagnetic resonance scannerTomography
A method and magnetic resonance tomography system to generate magnetic resonance image data of an examination subject, raw imaging data are acquired from multiple slices of a predetermined volume region of the examination subject using local coils during a table feed in the magnetic resonance scanner. Image data of the slices are reconstructed on the basis of the raw imaging data. A normalization of the image data is subsequently implemented on the basis of measured coil sensitivity data of the local coils that are used.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
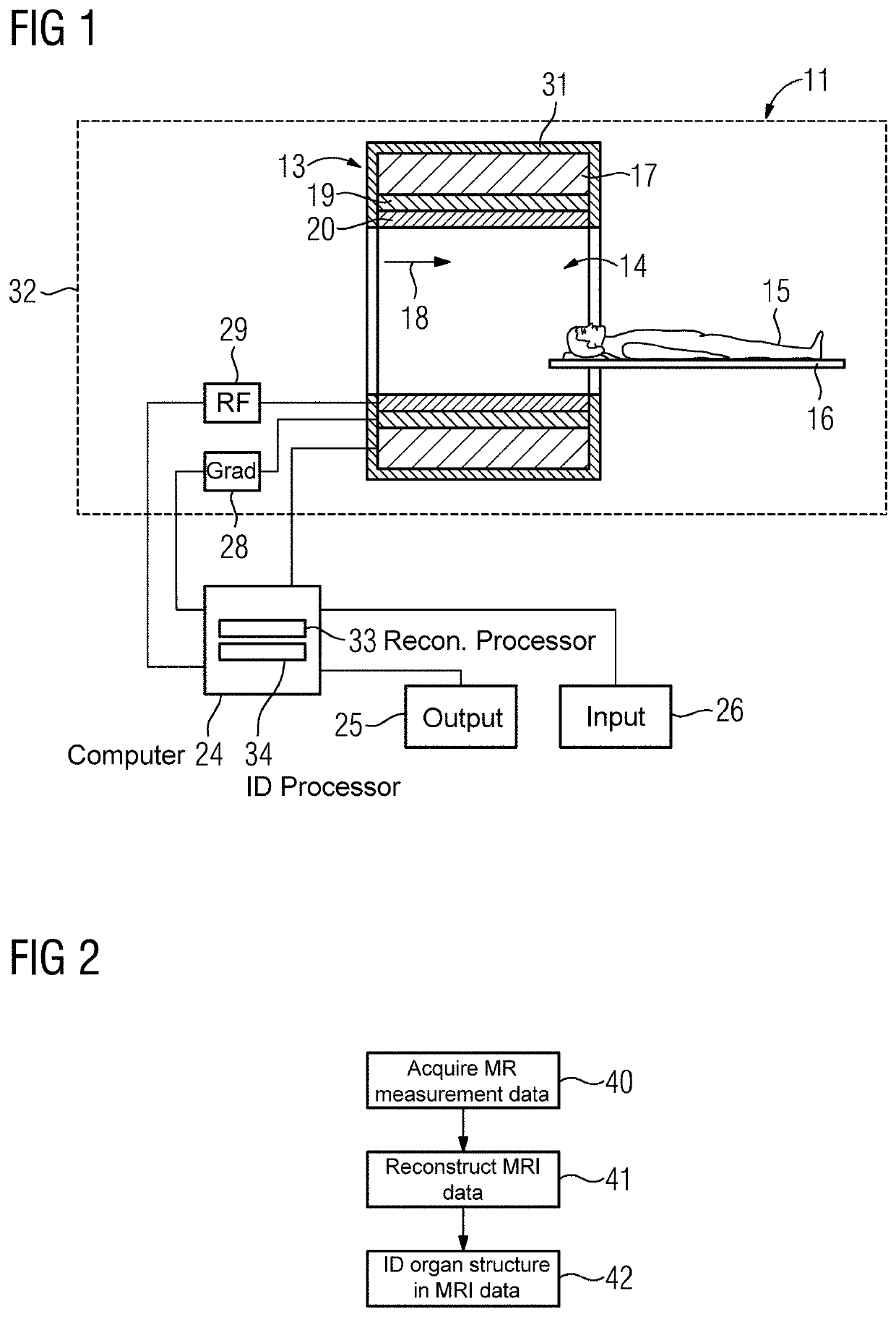
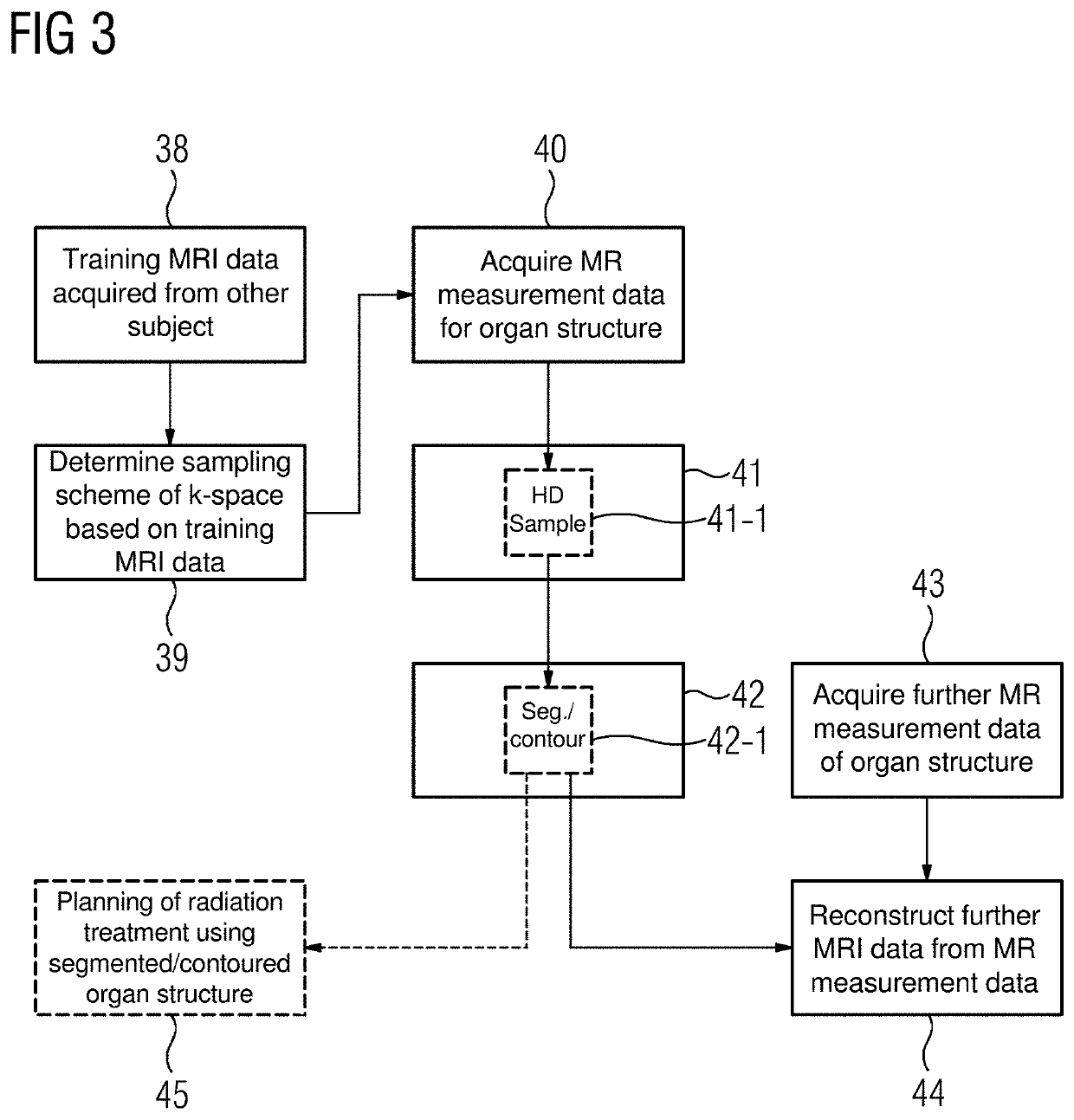
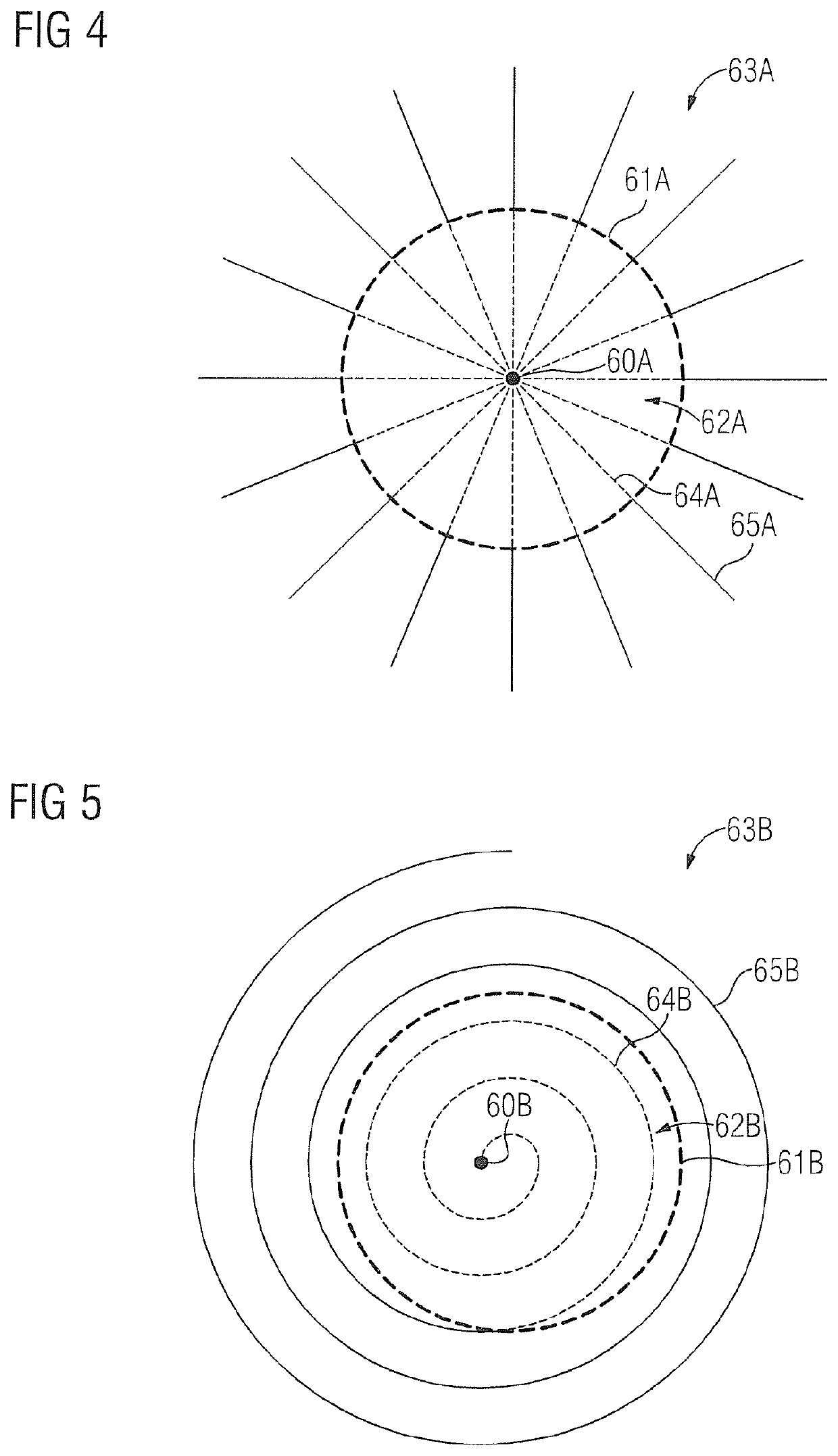
Method and apparatus for identifying an organ structure of an examined object in magnetic resonance image data
ActiveUS10702186B2Quality improvementMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementMri image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and control device for determination of the position of a local coil in a magnetic resonance apparatus
InactiveUS7598737B2Fast and cost-effective methodReliable detectionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementSpatial direction
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance radio-frequency coil and method of manufacturing
ActiveUS20130027040A1NanosensorsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrical conductorResonance
A Magnetic Resonance (MR) Radio-Frequency (RF) coil and method of manufacturing are provided for a multi-modality imaging system. The multi-modality imaging system includes a Magnetic Resonance (MR) scanner portion configured to acquired MR data of a patient using one or more MR Radio-Frequency (RF) coils. The one or more MR RF coils are formed from carbon nanotube conductors. The multi-modality imaging system also includes a radiation potion configured to transmit radiation through or detect radiation from the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and control device for determination of the position of a local coil in a magnetic resonance apparatus
InactiveUS20070103157A1Fast and cost-effectiveSafely localizingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementSpatial direction
In a method for determination of a position of a local coil on a bed in at least one spatial direction within a magnetic resonance scanner, a signal intensity value is initially, extracted from magnetic resonance measurements implemented with the appertaining local coil for acquisition of magnetic resonance images of an examination subject and / or for measurement of further system parameters at each of various positions of the recumbent bed relative to the tomograph. The functional dependency of the extracted signal intensity values on the position of the bed relative to the scanner is then determined. The position of the local coil on the bed is determined on the basis of the determined functional dependency. A corresponding control device for a magnetic resonance system and a computer program product implement the method.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
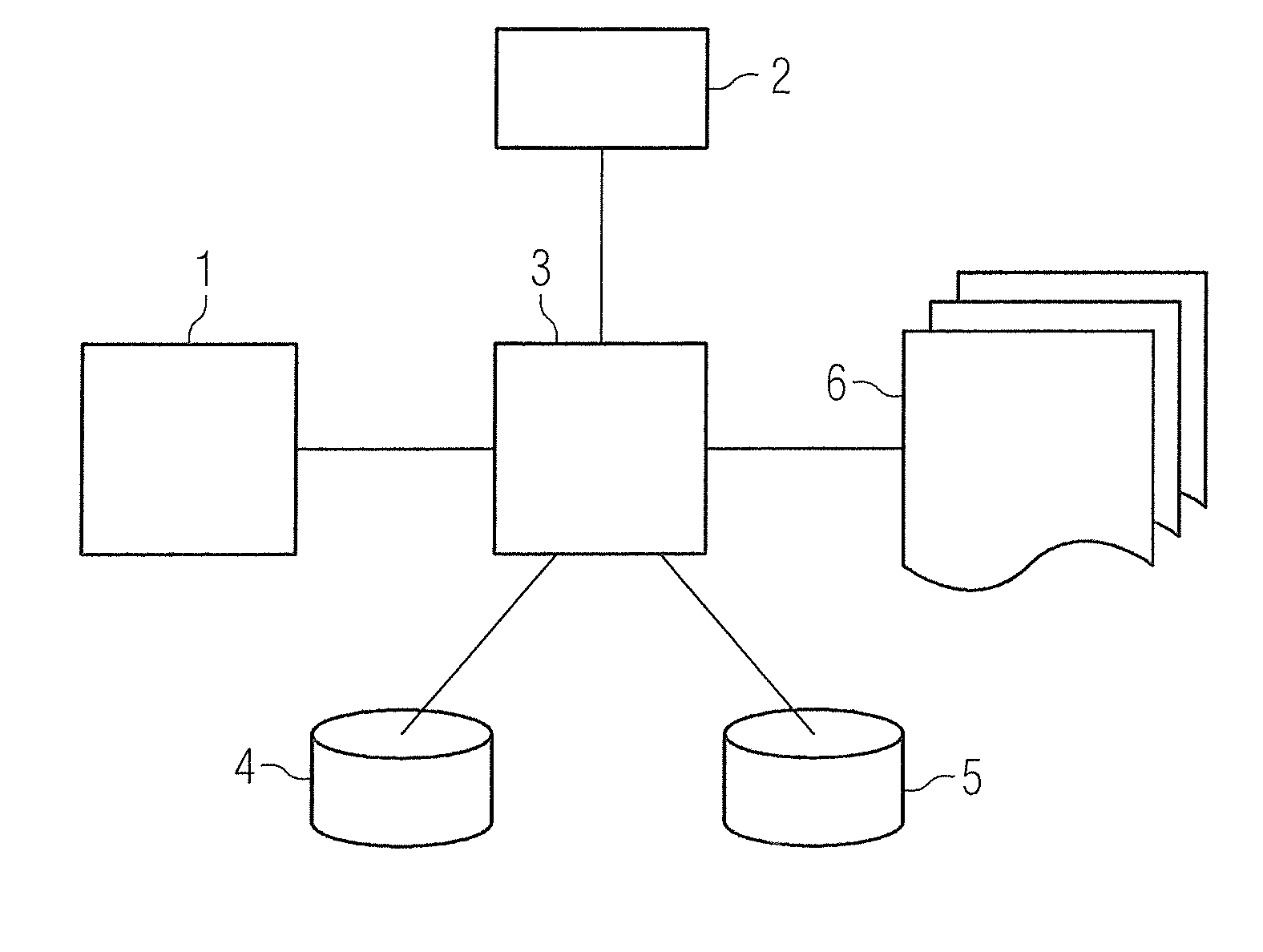
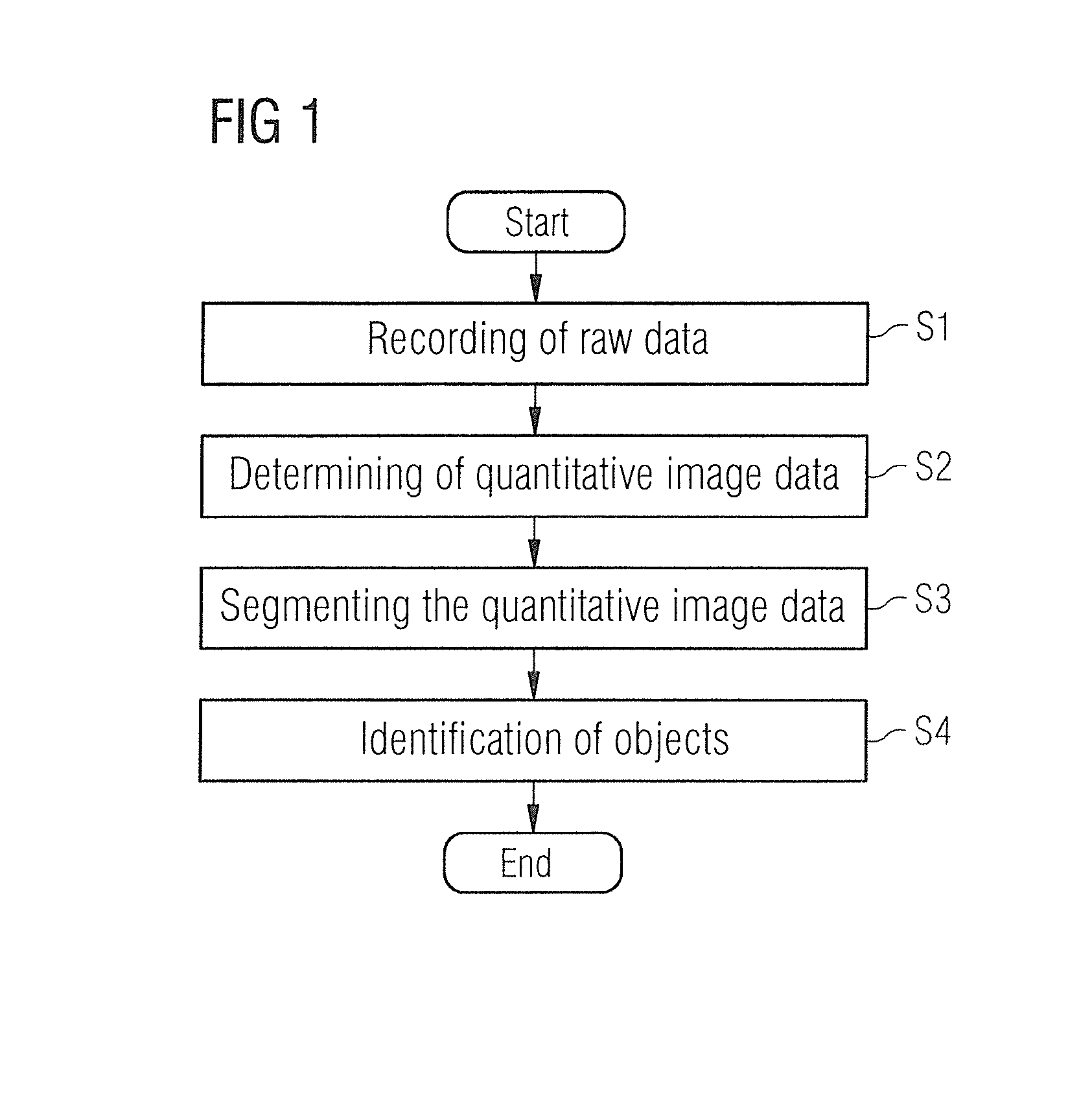
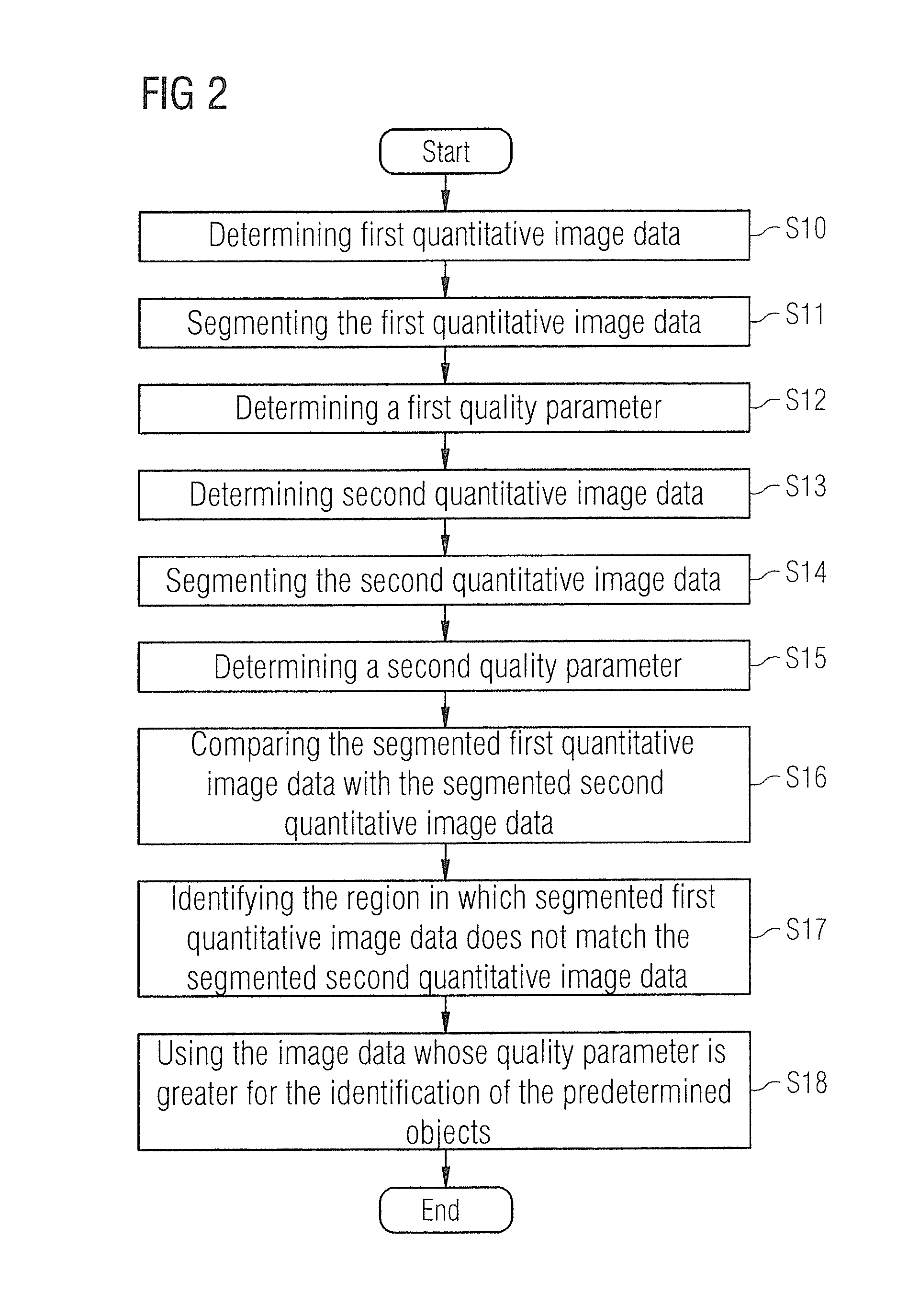
Method and device for segmenting a medical examination object with quantitative magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20160155238A1Avoid disadvantagesPromote reproductionImage enhancementMedical imagingResonanceQuantitative magnetic resonance imaging
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for segmenting image data of an examination object, raw data of the examination object are achieved with the operation of a magnetic resonance scanner. Quantitative image data of the examination object are then calculated in a processor from the raw data. At least one physical variable of the examination object is quantitatively ascertained pixelwise and is displayed. The quantitative image data are segmented for identification of predetermined objects in the quantitative image data, and displayed in a display unit.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
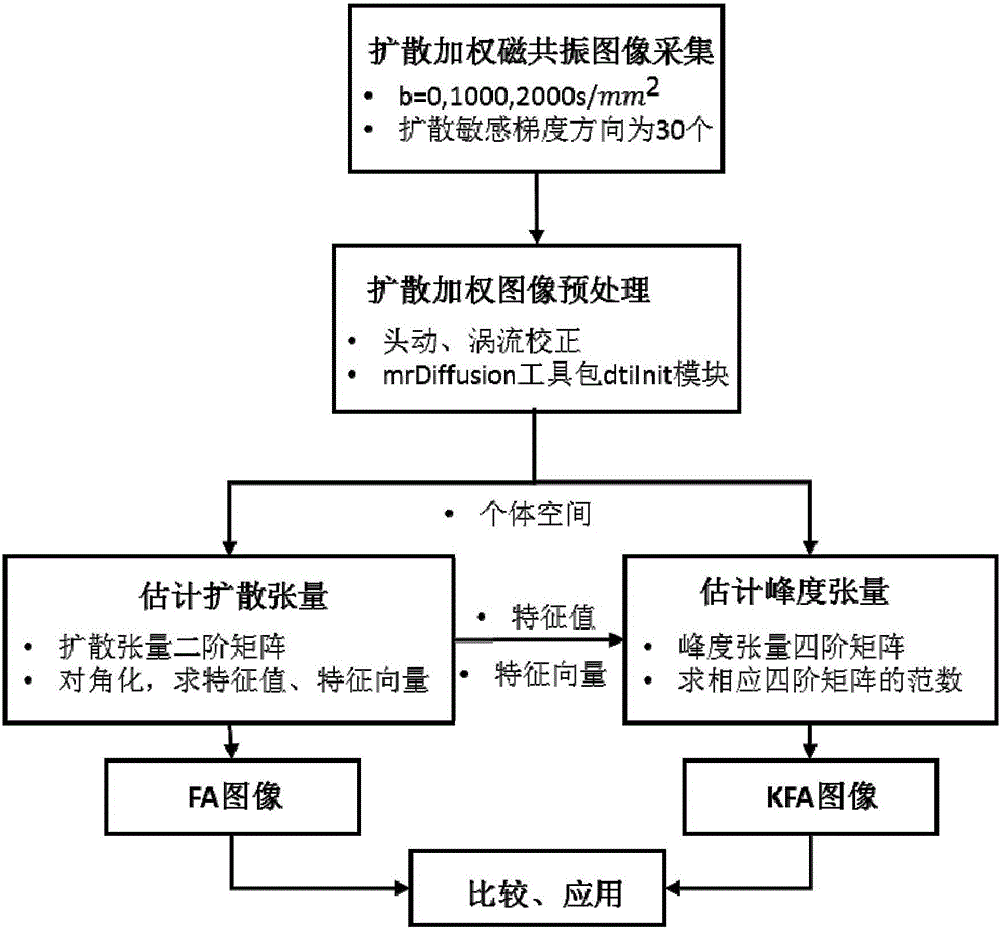
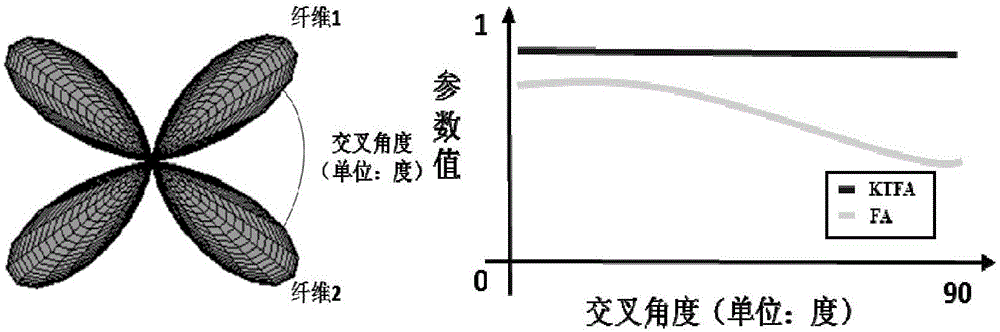
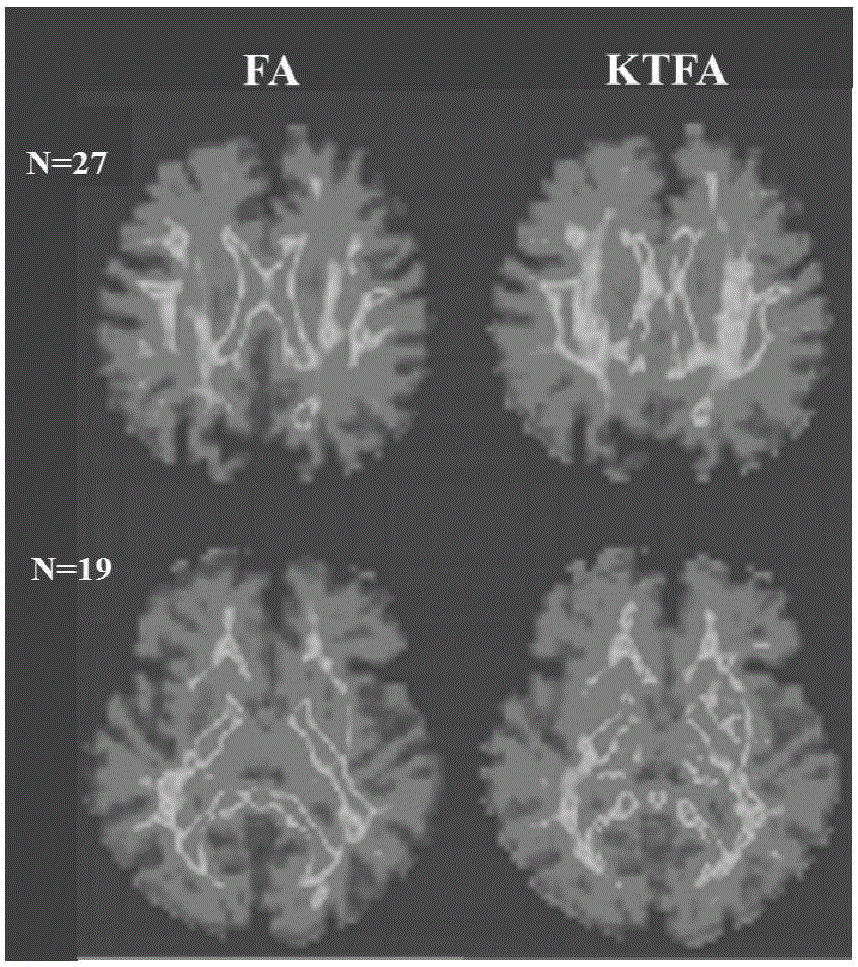
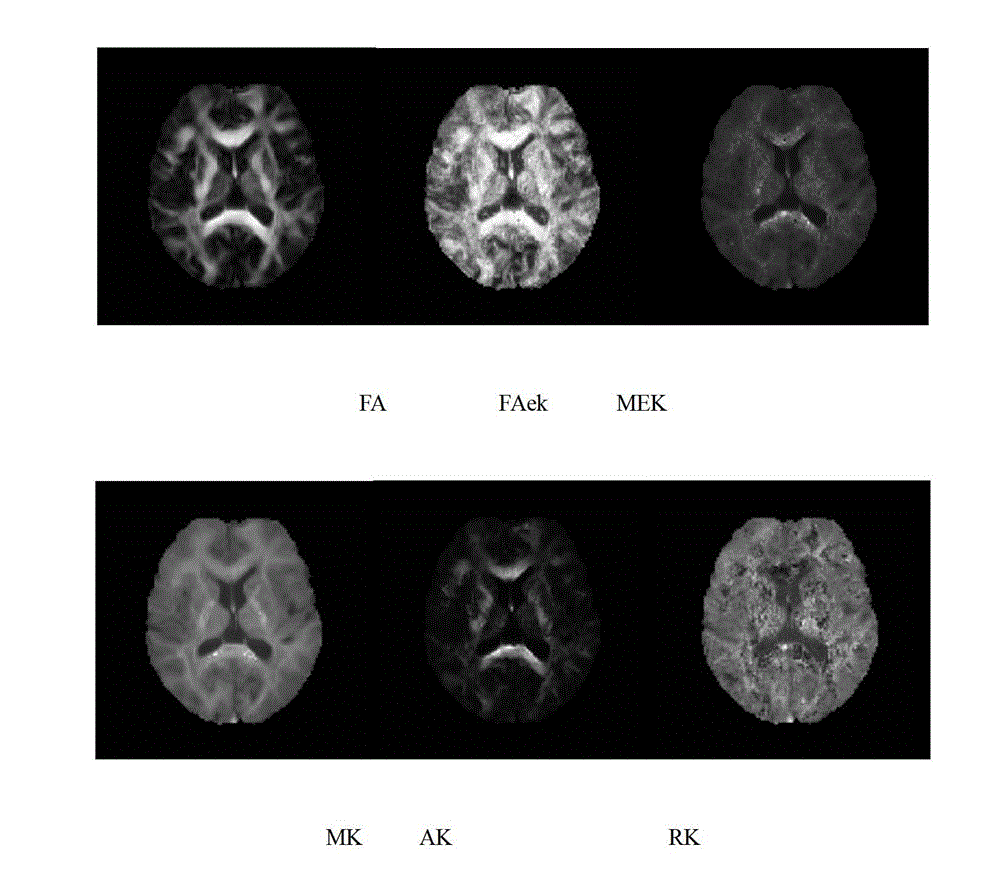
Fractional anisotropy microstructure characteristic extraction method based on kurtosis tensor and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN105842642ALow number of crossoversDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFiberMedical equipment
The invention relates to the image processing and medical instrument technology field and provides a burgeoning parameter extraction method of biological tissue anisotropy detection, wherein the method is used for clinic application. An analysis method of reconstructing and quantizing a clear, refine and highly-stable biological-tissue microcosmic anisotropy characteristic and a correlation apparatus are obtained. In a technical scheme used in the invention, based on the kurtosis-tensor fractional anisotropy microstructure characteristic extraction method, a subject collects multiple b value diffusion weight images of tissues along a plurality of diffusion sensitivity gradient directions on a magnetic resonance scanner; after the diffusion weight images are preprocessed, in an individual space, a second-order diffusion tensor and a fourth-order kurtosis tensor matrix reflecting a water molecule diffusion distribution probability density function characteristic in the tissues are acquired through fitting; through matrix operation, the corresponding fractional anisotropy FA and kurtosis tensor fractional anisotropy KTFA are acquired; and combining a characteristic parameter, a nerve fiber microstructure characteristic is acquired. The method and the apparatus are mainly used in medical equipment designing and manufacturing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
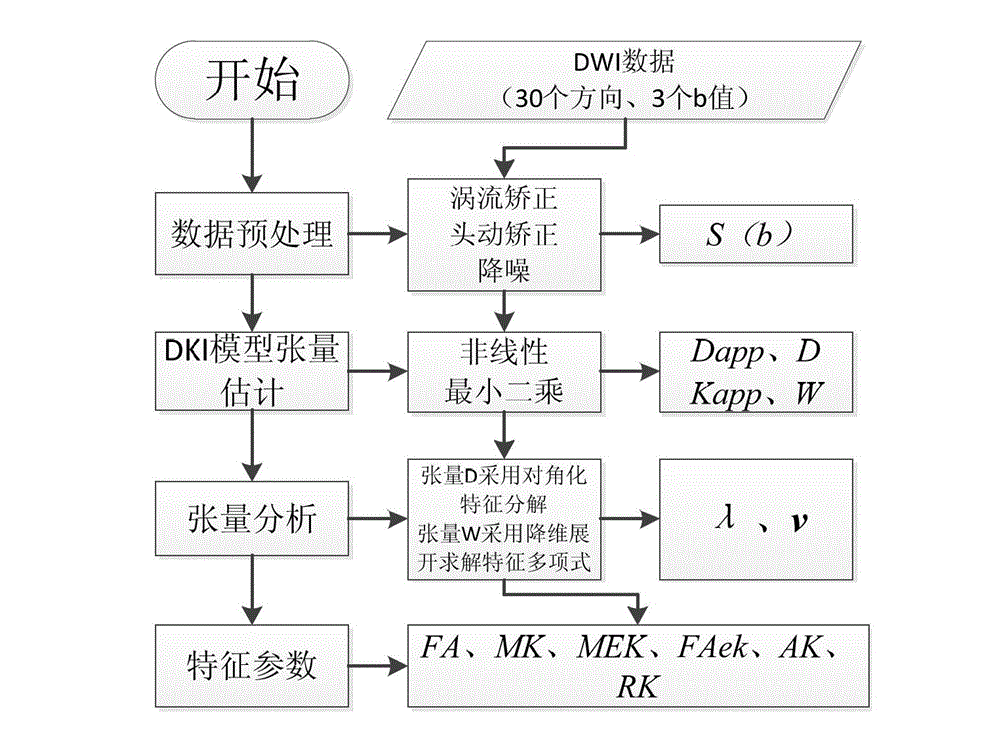
Method for extracting high-order tensor characteristic parameters of diffusion kurtosis tensor imaging
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, provides a novel practical method for extracting MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) parameters of structural abnormality of white matters of a human brain, and aims to achieve the purpose of objectively evaluate the lesion degree by analyzing anisotropy of tissues through a certain characteristic extraction method. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the method for extracting high-order tensor characteristic parameters of diffusion kurtosis tensor imaging comprises the following steps: a subject collects diffusion weighted signals of tissues along a plurality of directions on a magnetic resonance scanner, then a second-order or fourth-order tensor that reflects diffusion and distribution probability density function of water molecules in the tissues can be obtained through fitting, and lesion characteristics of diffusion and distribution abnormality of the water molecules, caused by structural abnormality of the tissues, can be obtained through certain tensor analysis, wherein parameters from two different angles, including diffusion coefficient and kurtosis coefficient, are mainly included. The invention is mainly applied to design and manufacture of medical instruments.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
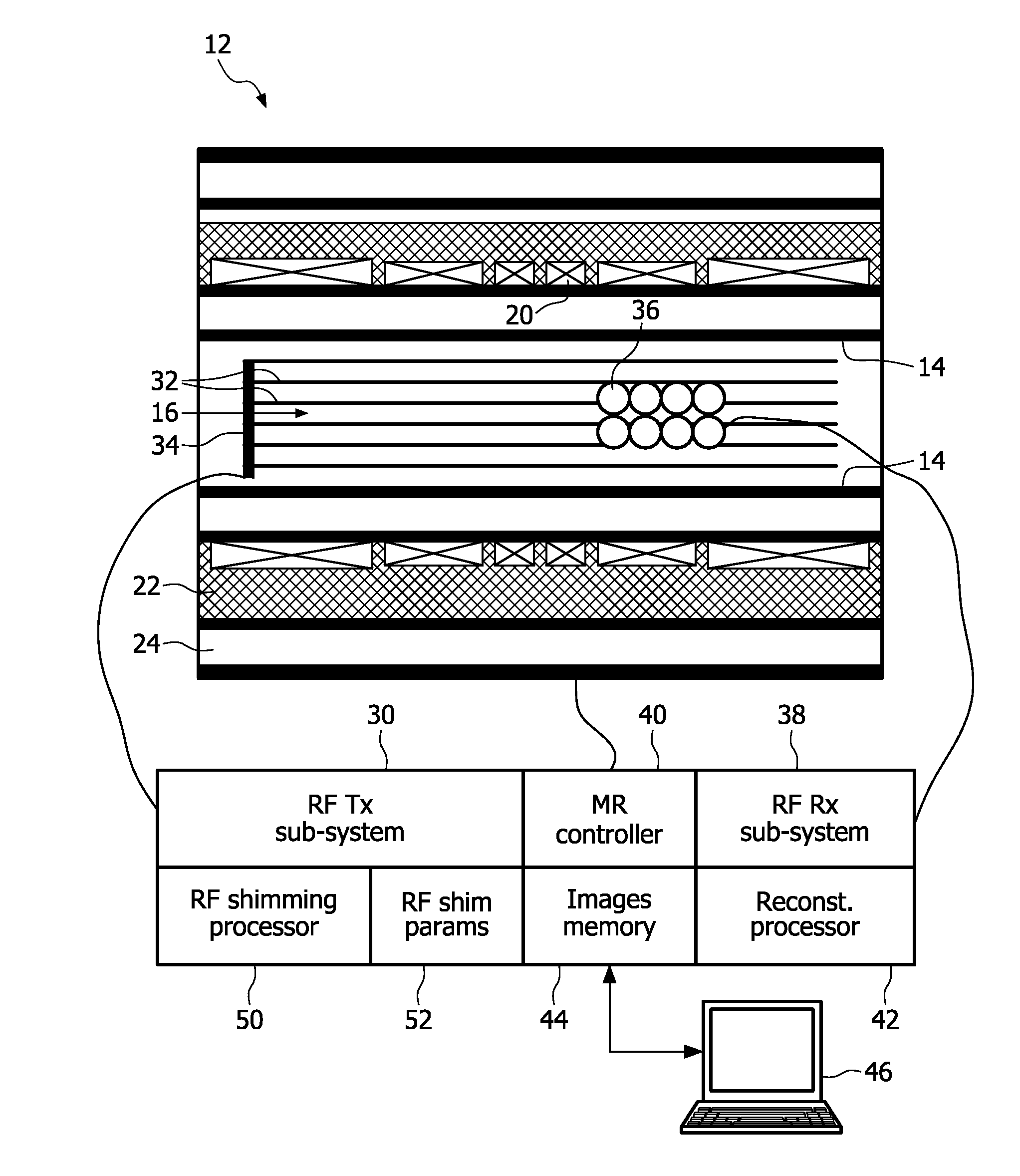
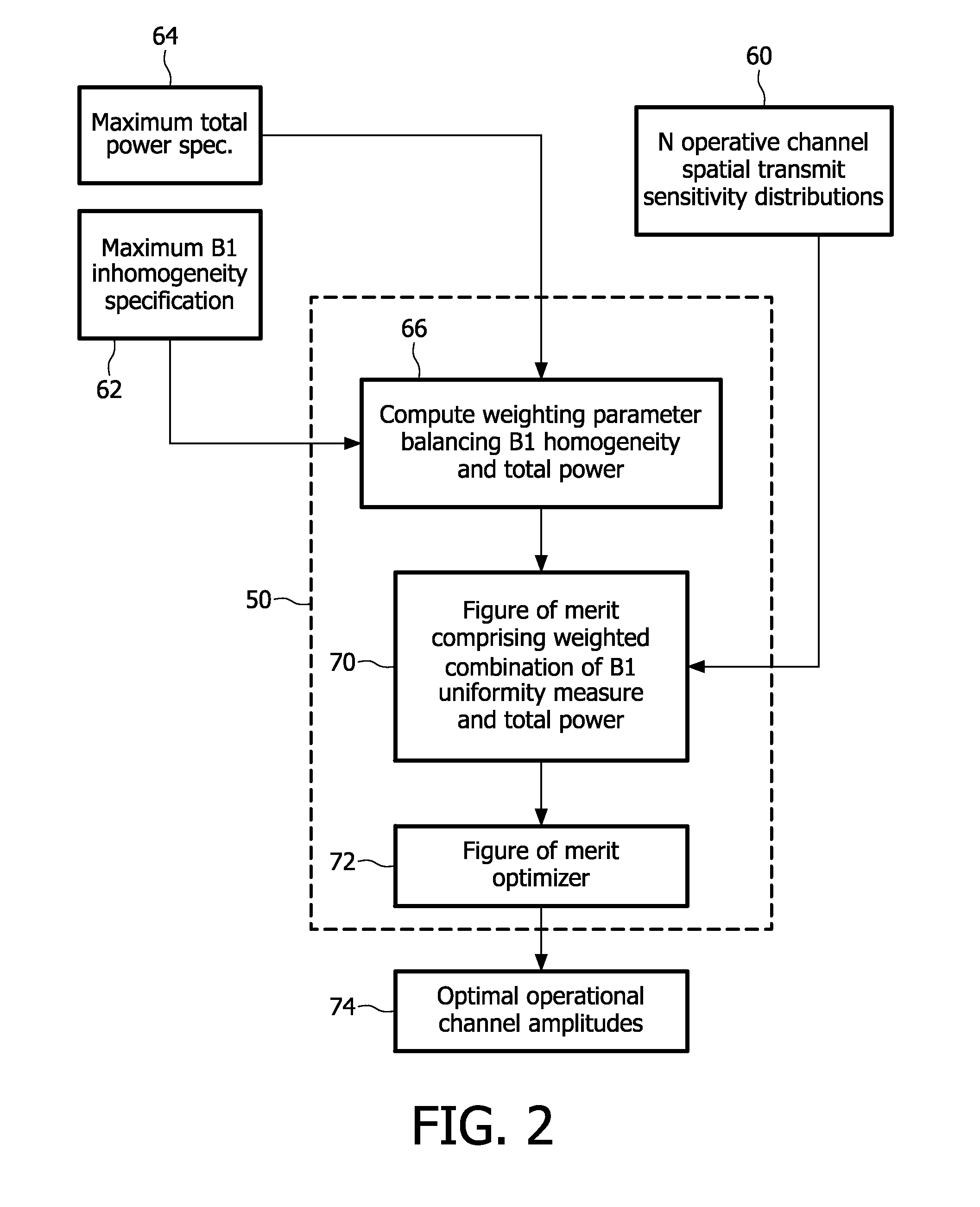
RF shimming with RF power regularization using a multi-channel RF transmit system for MRI
InactiveUS20110163749A1Effective planningElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRComplex amplitudeResonance
A magnetic resonance system comprises: a magnetic resonance scanner (12) including a multi-channel RF transmit system (32, 34); an RF shimming processor (50) configured to compute complex amplitude values for operative channels of the multi-channel RF transmit system based on a figure-of-merit (70) comprising a weighted combination of a B1 uniformity measure and a total power measure; and an RF transmit sub-system (30) configured to drive the multi-channel RF transmit system to excite magnetic resonance using the complex amplitude values computed by the RF shimming processor for the operative channels of the multi-channel RF transmit system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Local coil and construction method, magnetic resonance apparatus and method for measuring magnetic resonance signals
InactiveCN102288930AHigh acceleration factorMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic resonance scannerInductance
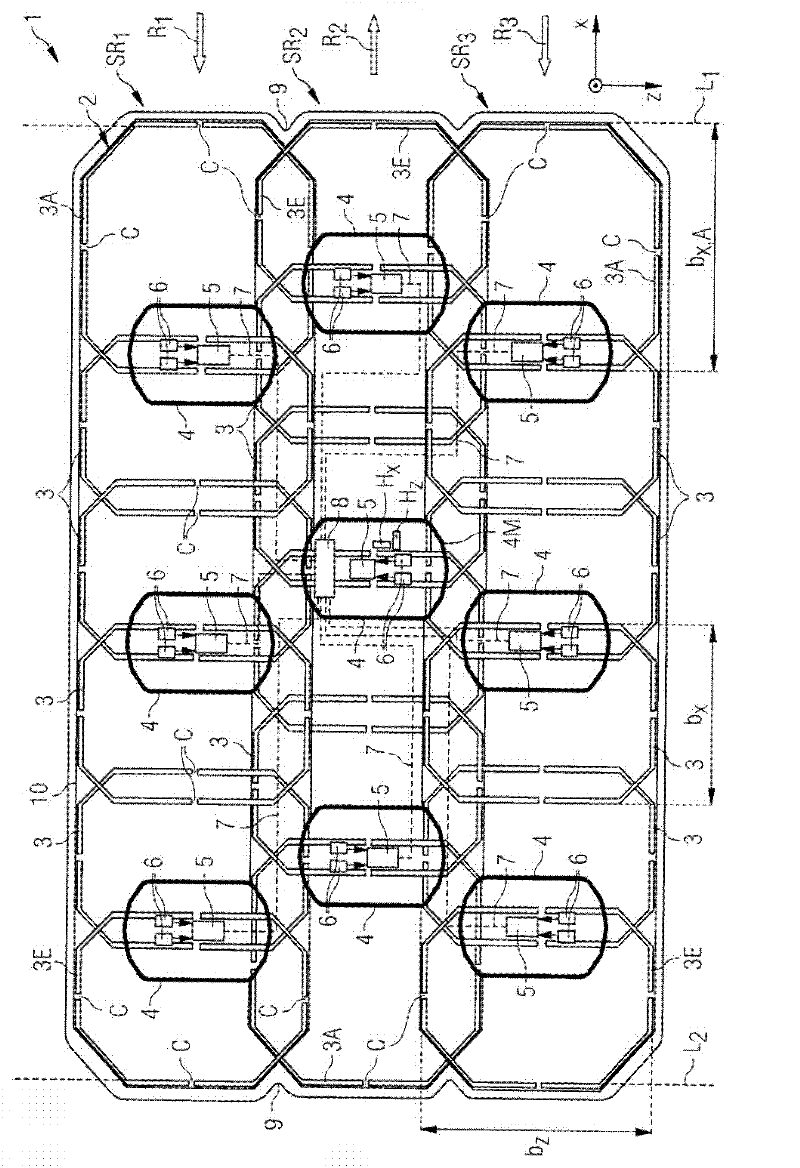
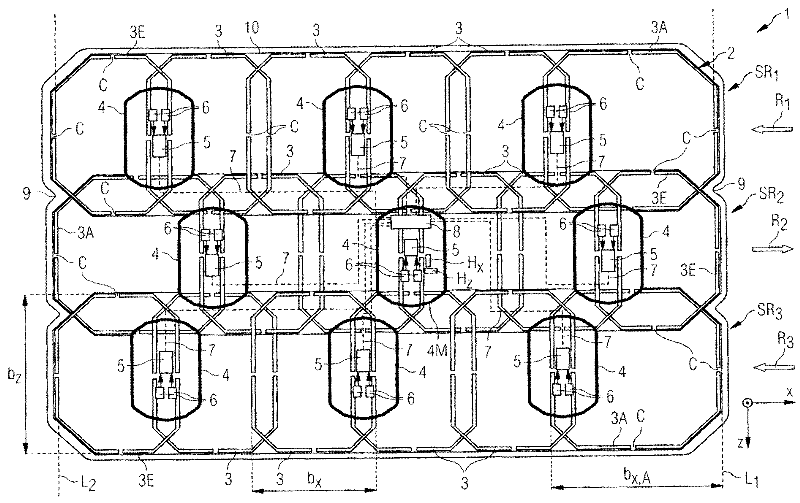
The invention relates to a local coil (1) with a magnetic resonance antenna group (2) comprising a plurality of antenna turns (3, 3A, 3E) arranged in adjacent rows (SR1, SR2, SR3) ), the antenna turns arranged adjacent to each other are inductively decoupled from each other through geometric overlap (UX, UZ), and the antenna turns are staggered in alternate directions (R1, R2, R3), so that two in a row The overlapping area of the antenna turns is staggered from the overlapping area of two antenna turns in an adjacent row, at least some of the antenna turns are designed to compensate for the stagger, so that they are redrawn as different areas and thus the antenna lines Adjacent rows of turns in the stagger direction terminate substantially at the front end and at the rear end, respectively, on a straight line ( L1 , L2 ) transverse to the stagger direction. The invention also relates to a magnetic resonance apparatus with such a local coil, a method for constructing such a local coil and a method for measuring magnetic resonance signals.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for Compensating for Respiratory Motion in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveUS20120319685A1Accurate modelingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMedicineResonance
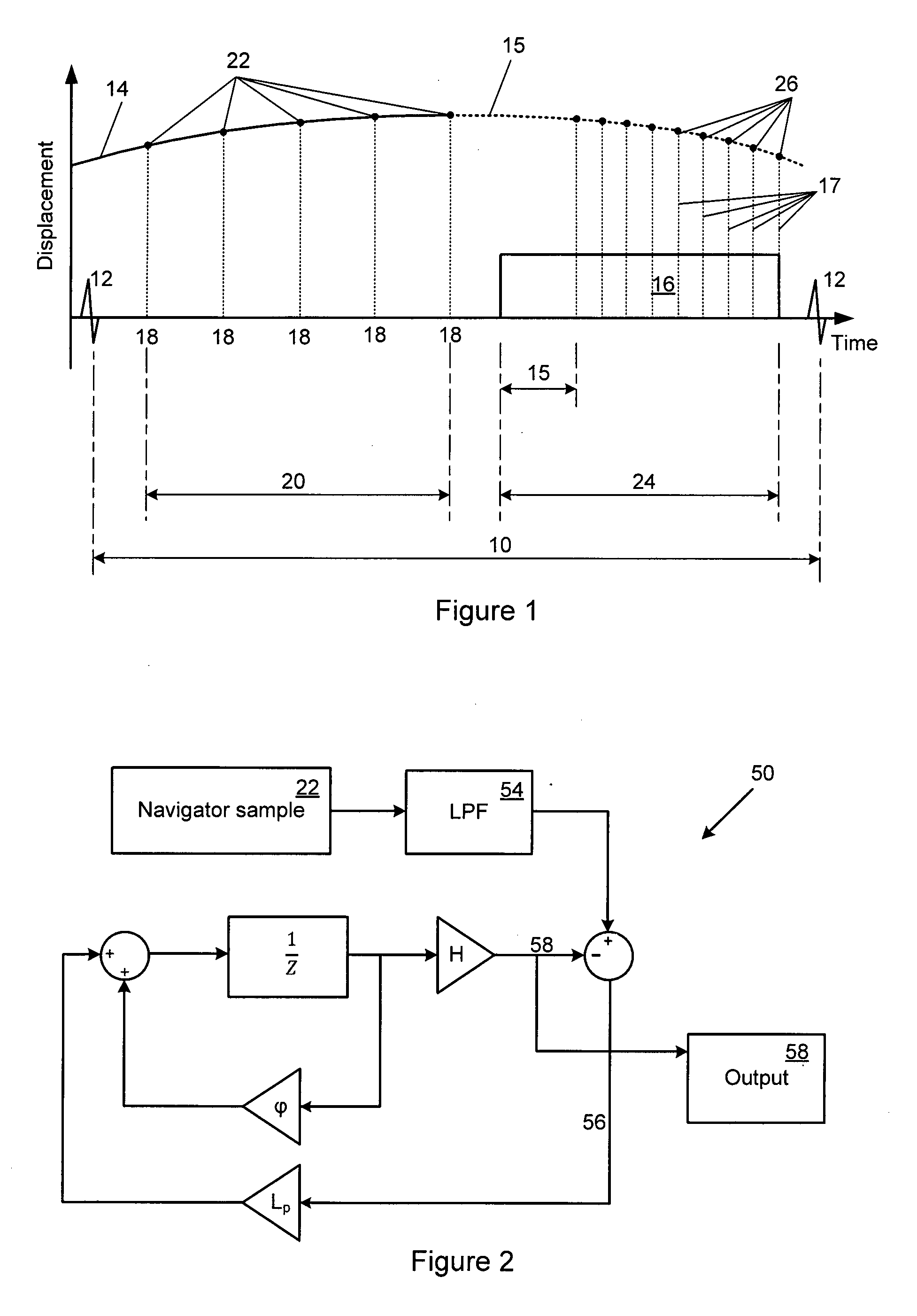
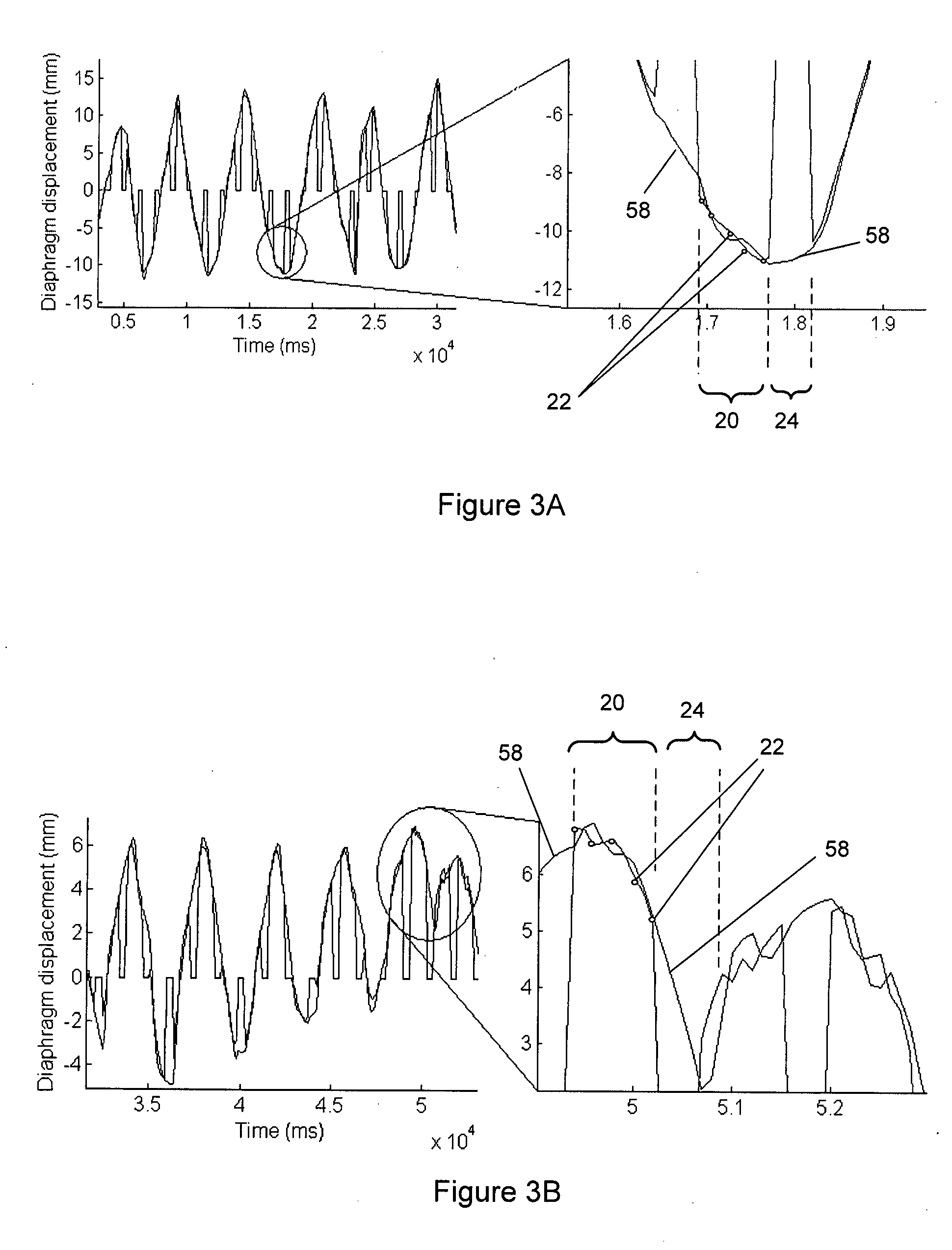
A method for compensating for respiratory motion of a structure imaged by a magnetic resonance (MR) scanner, such as heart, is disclosed. The method comprises obtaining a sequence of navigator samples (22) representative of the progressive displacement of the structure during a first time interval (20), and adjusting a waveform (14) of predefined initial parameters to follow the sequence of navigator samples. During a second time interval (24) which follows the first time interval and during which the magnetic resonance scanner takes a number of image projection views or lines (17), the expected respiratory displacement of the structure is estimated at the times that the image projection lines are taken, by extrapolating the waveform model and estimating the displacements (26) predicted by the extrapolated waveform, so that the position at which the image projection lines are taken can be adjusted to compensate for the respiratory motion, so as to yield a sharper magnetic resonance image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN
Diffusion-weighted imaging method
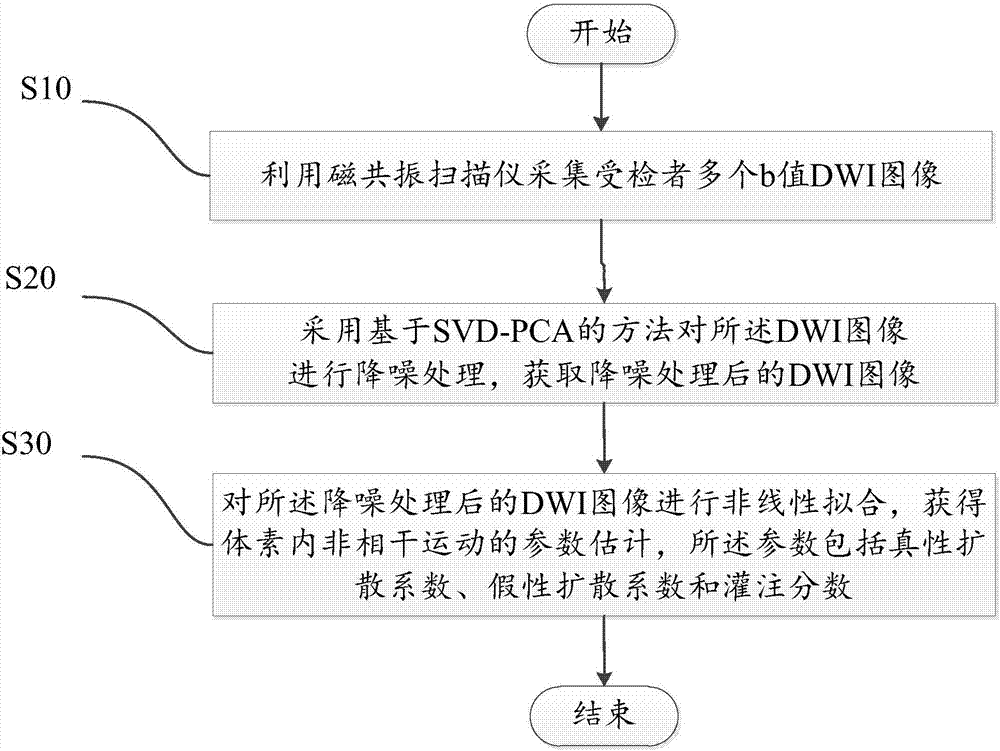
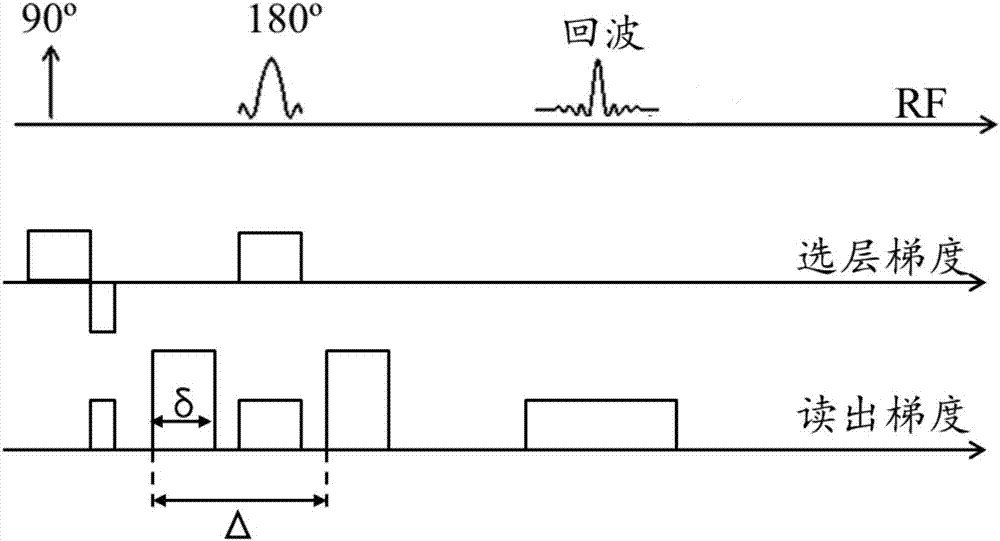
ActiveCN107240125ARemove noise componentsImprove reliabilityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiffusionVoxel
The invention discloses a diffusion-weighted imaging method comprising the following steps: a plurality of b-value DWI images of a testee are collected via a magnetic resonance scanner, and noise reduction operation is performed on the DWI images via an SVD-PCA-based method; after the noise reduction operation, the DWI images are obtained and subjected to non-linear fitting operation, and estimated parameters of noncoherent motion in voxel can be obtained; the parameters comprise true diffusion coefficients, false diffusion coefficients and perfusion scores. According to the diffusion-weighted imaging method, after singular values of a vector composite matrix are filtered, noise components of the DWI images can be effectively removed; a signal to noise ratio can be improved, and therefore reliability of the estimated parameters of the noncoherent motion in the voxel can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com