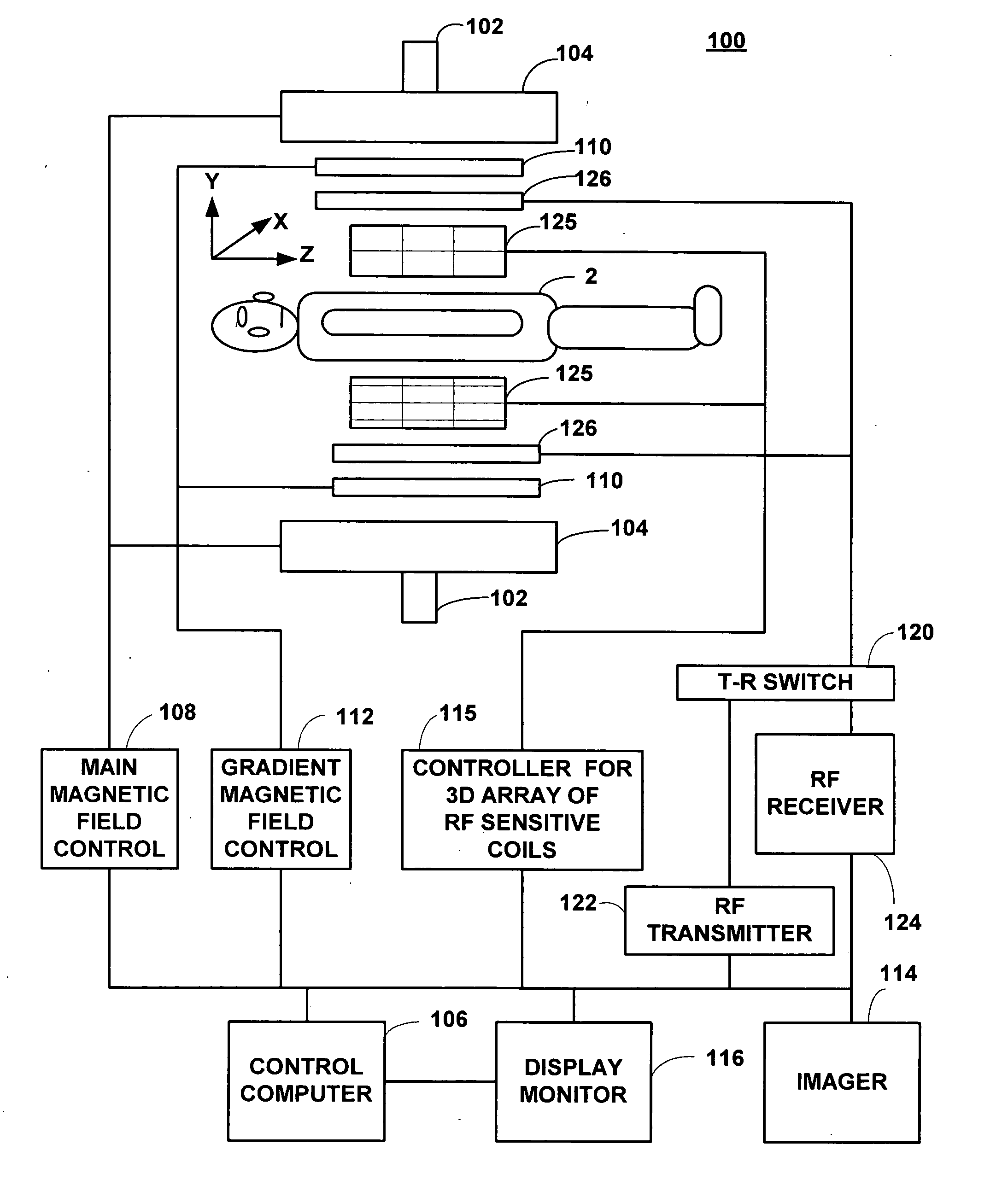
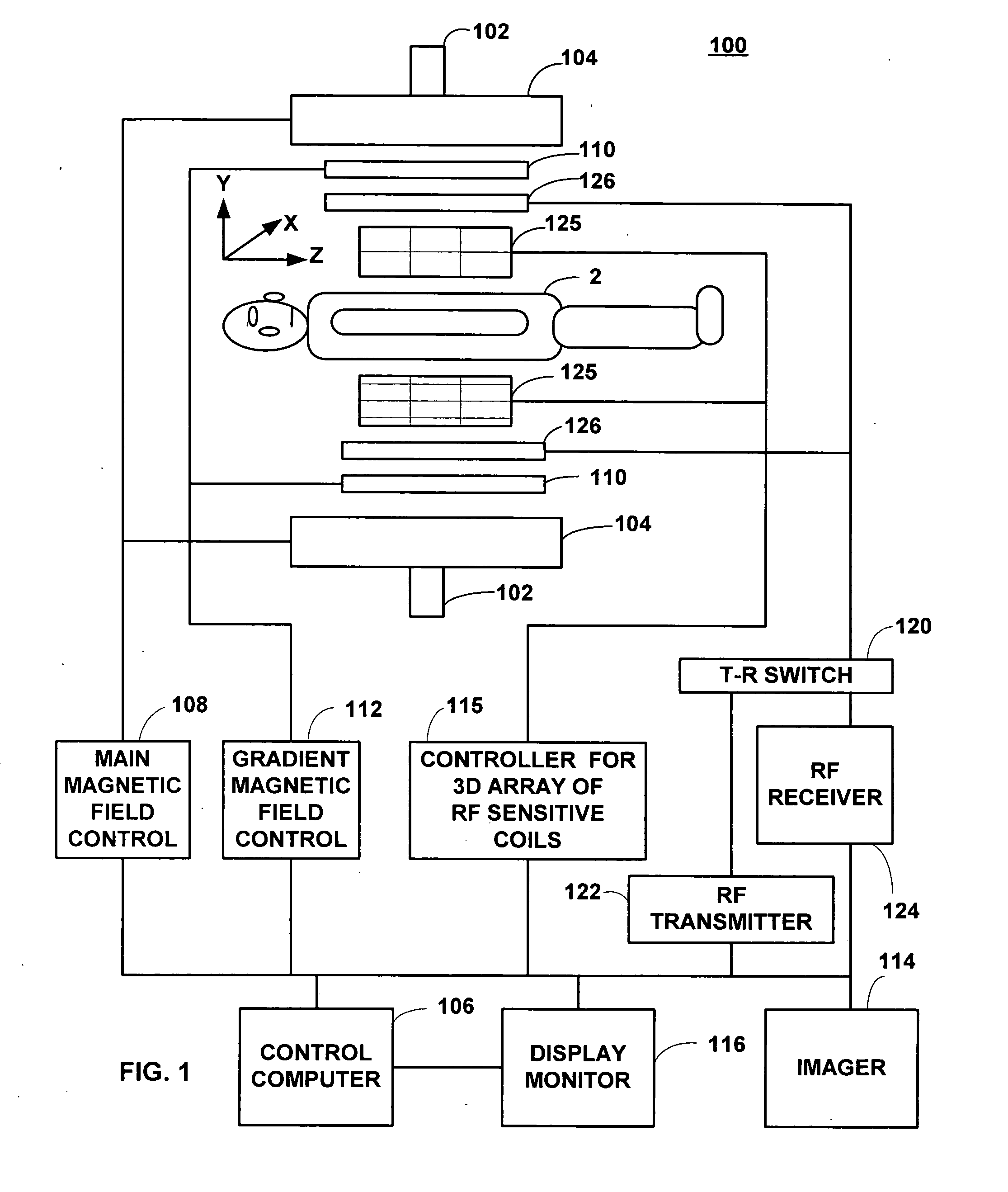
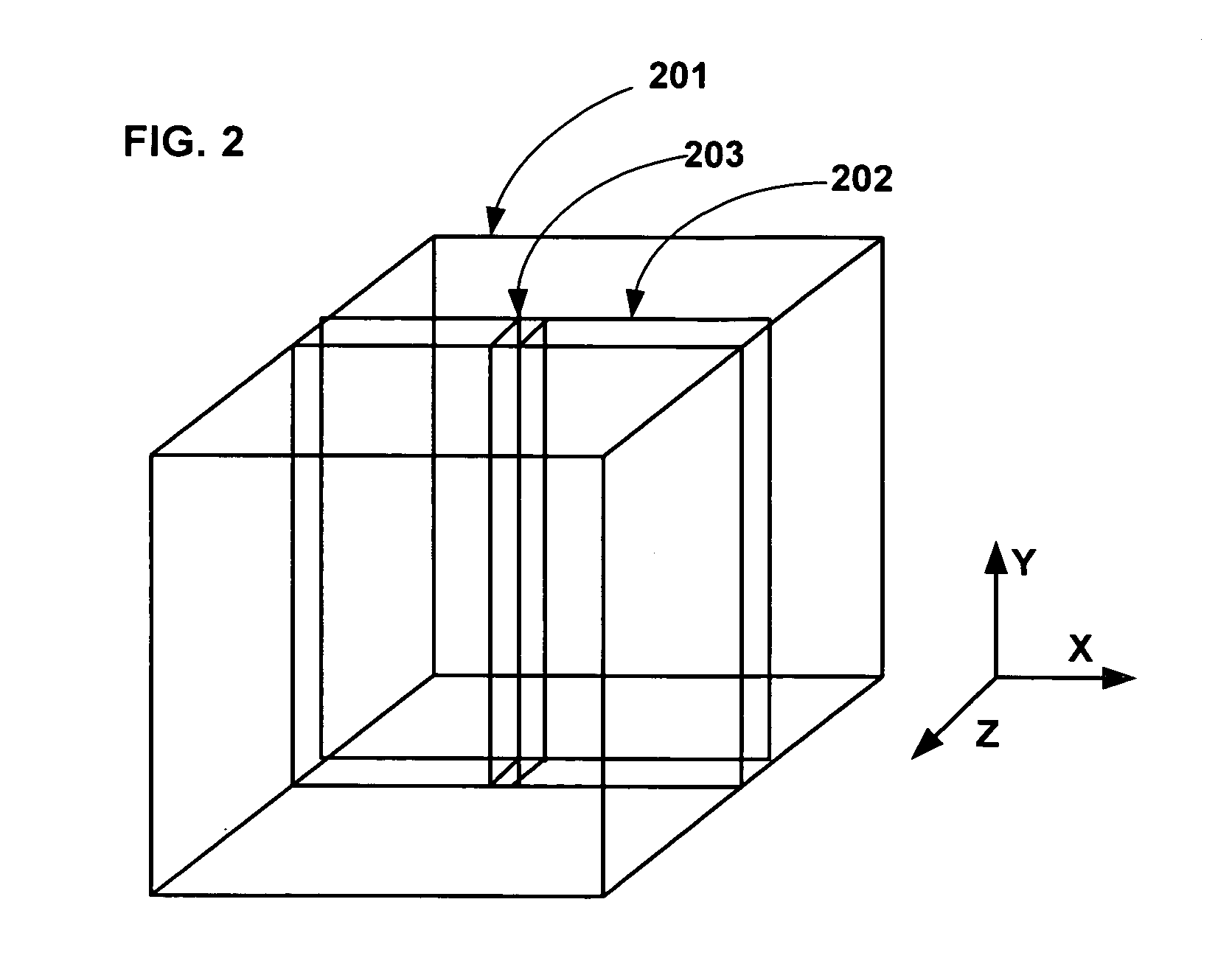
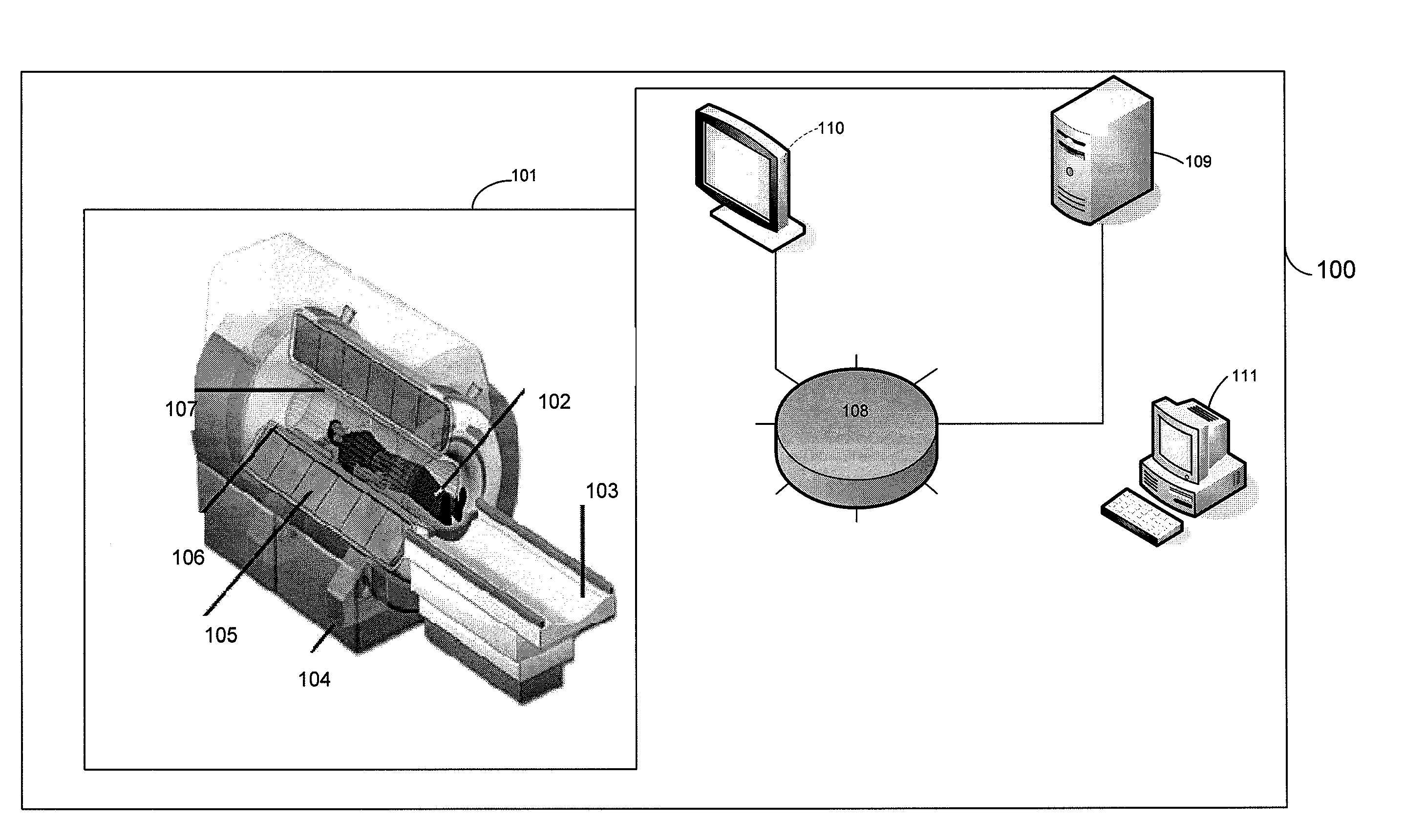
Patents
Literature
1309 results about "Magnetic resonance imagery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), also known as nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, is a scanning technique for creating detailed images of the human body. The scan uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate images of parts of the body that can't be seen as well with X-rays, CT scans or ultrasound.
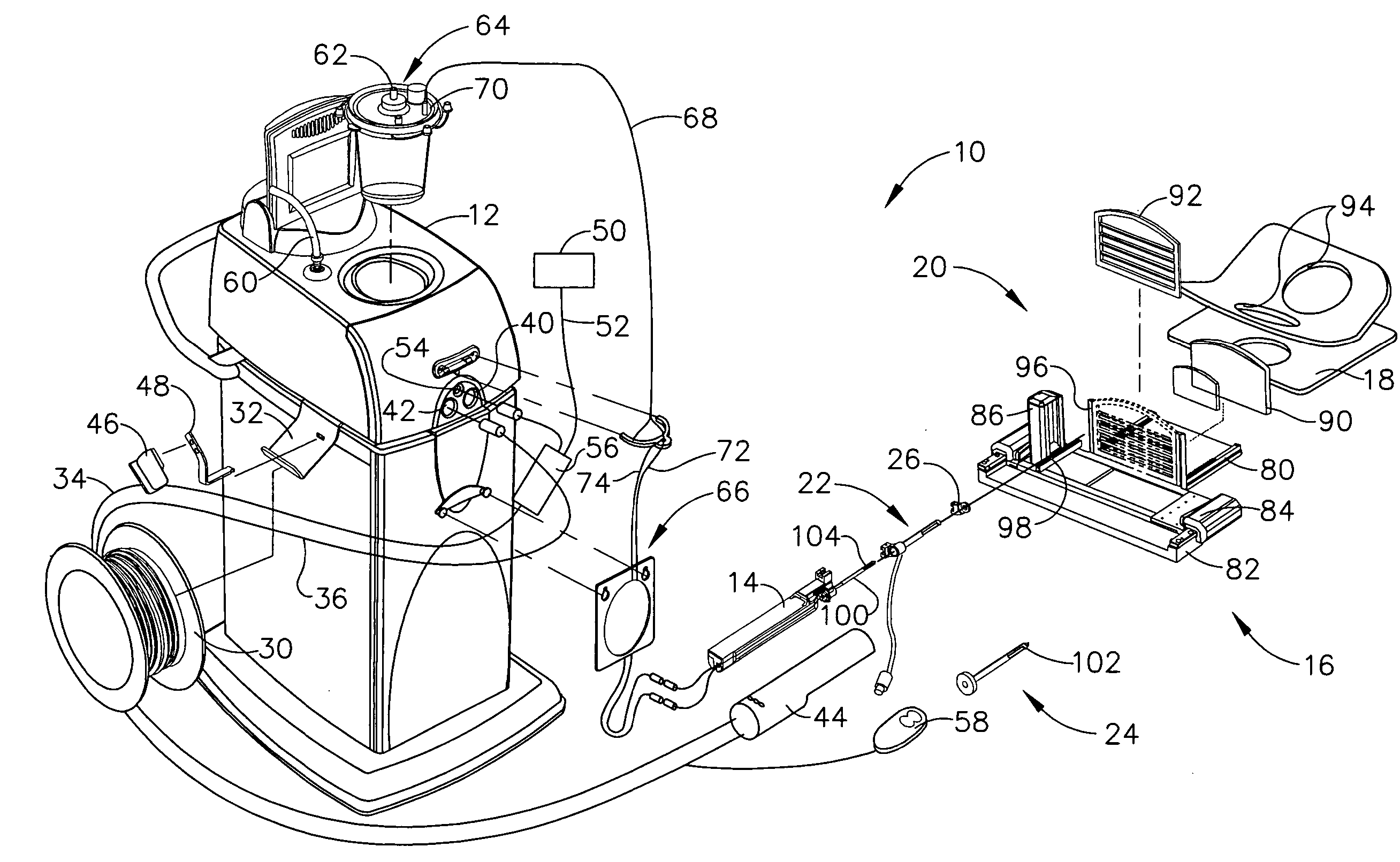
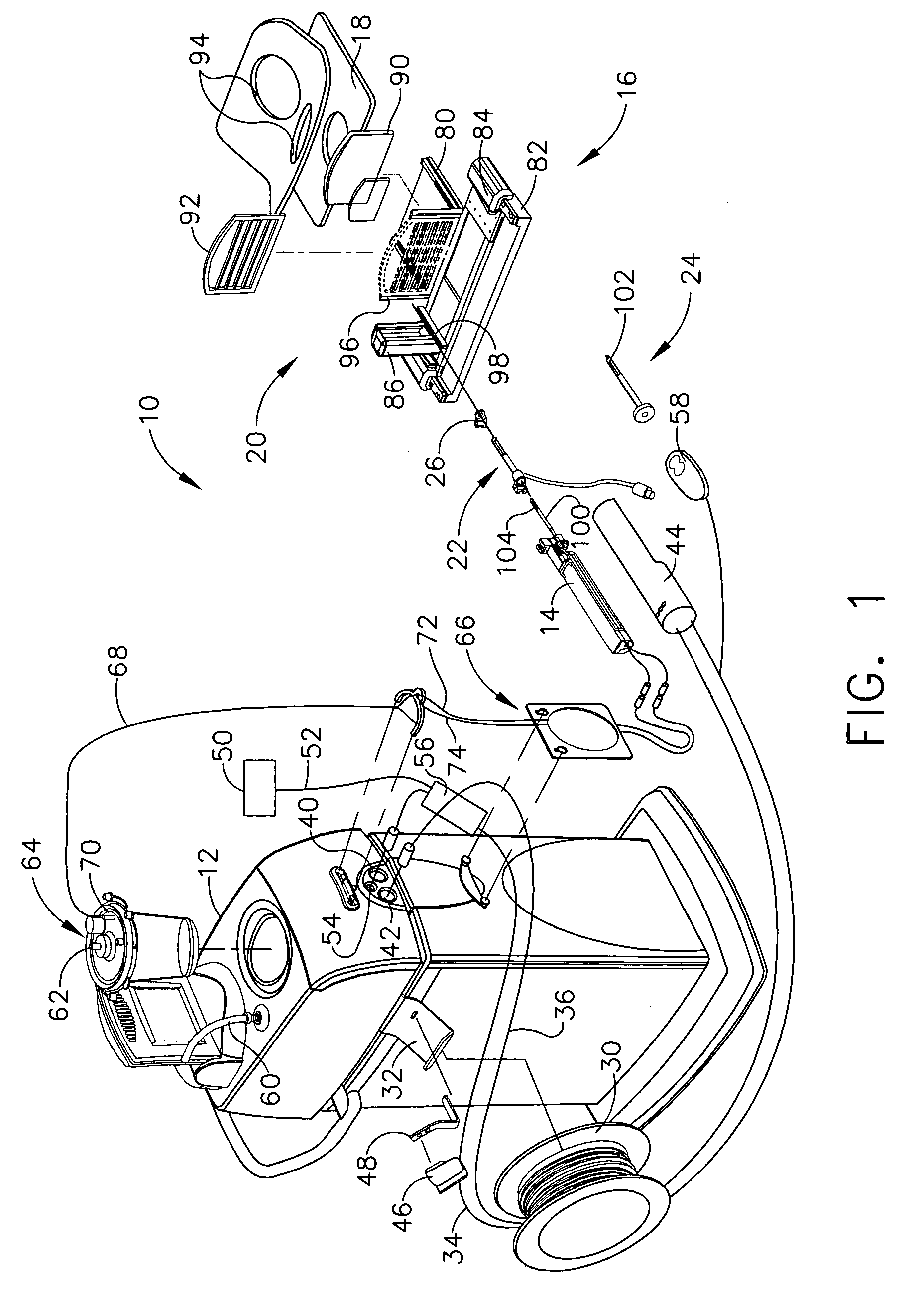
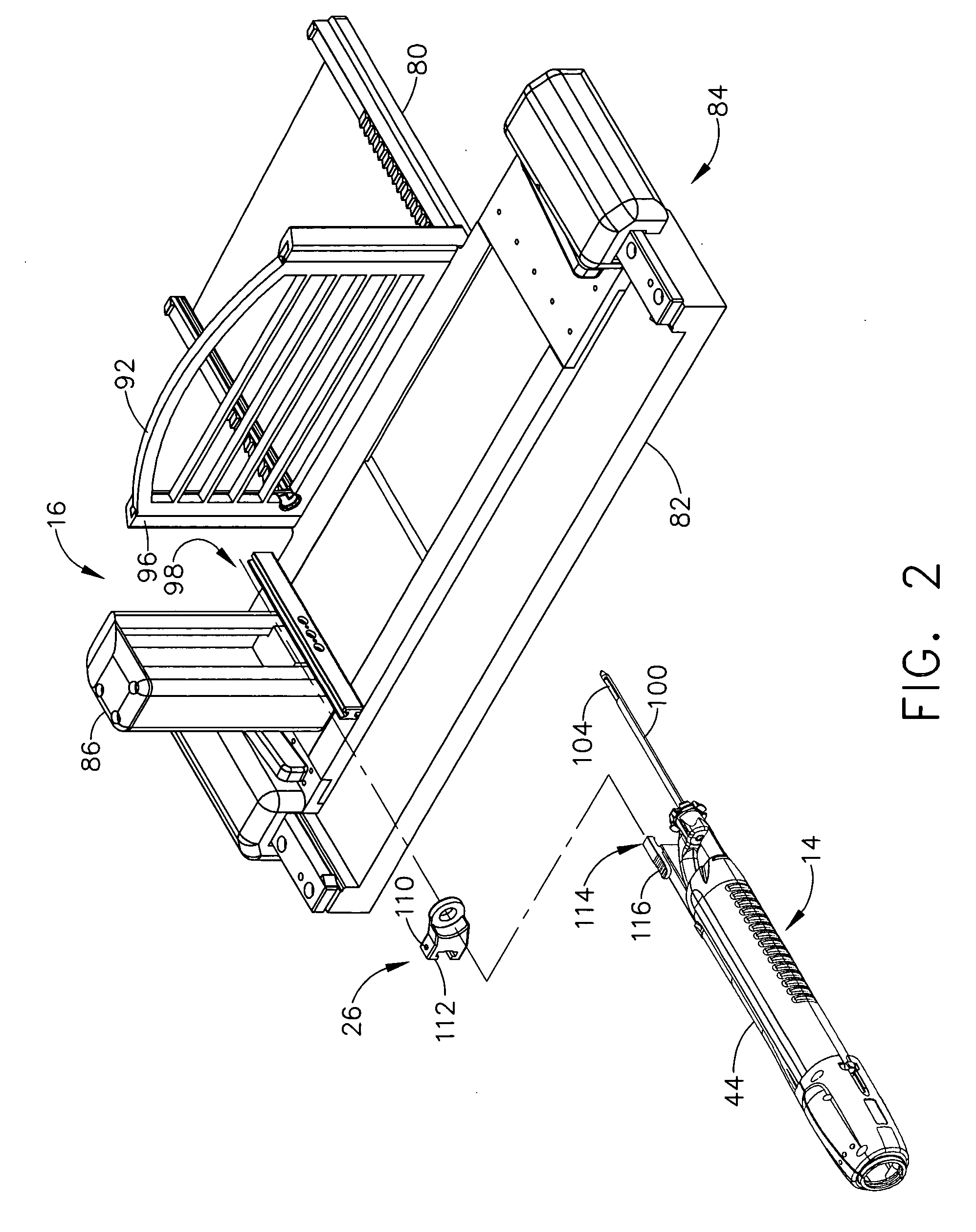
MRI biopsy apparatus incorporating an imageable penetrating portion
An obturator as part of a biopsy system enhances use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) by indicating location of a side aperture in an encompassing cannula. The cannula (e.g., detached probe, sleeve sized to receive a core biopsy probe) includes a side aperture for taking a tissue sample. When the obturator is inserted in lieu of the biopsy device into the cannula, a notch formed in a shaft of the obturator corresponds to the side aperture. A dugout trough into the notch may further accept aqueous material to further accentuate the side aperture. In addition, a series of dimensionally varied apertures (e.g., wells, slats) that communicate through a lateral surface of the shaft and that are proximal to the side aperture receive an aqueous material to accentuate visibility in an MRI image, even in a skewed MRI slice through the cannula / obturator.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
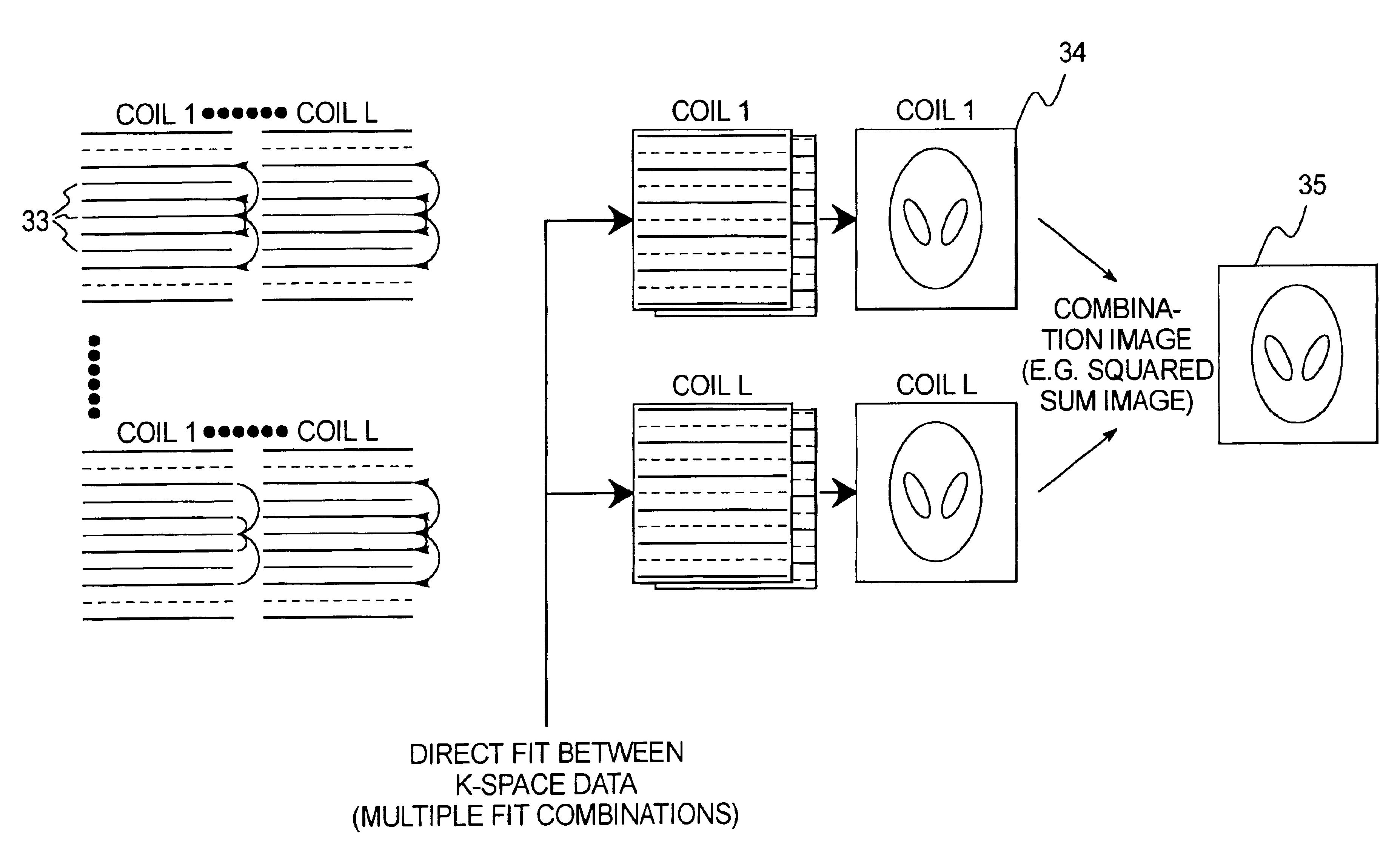
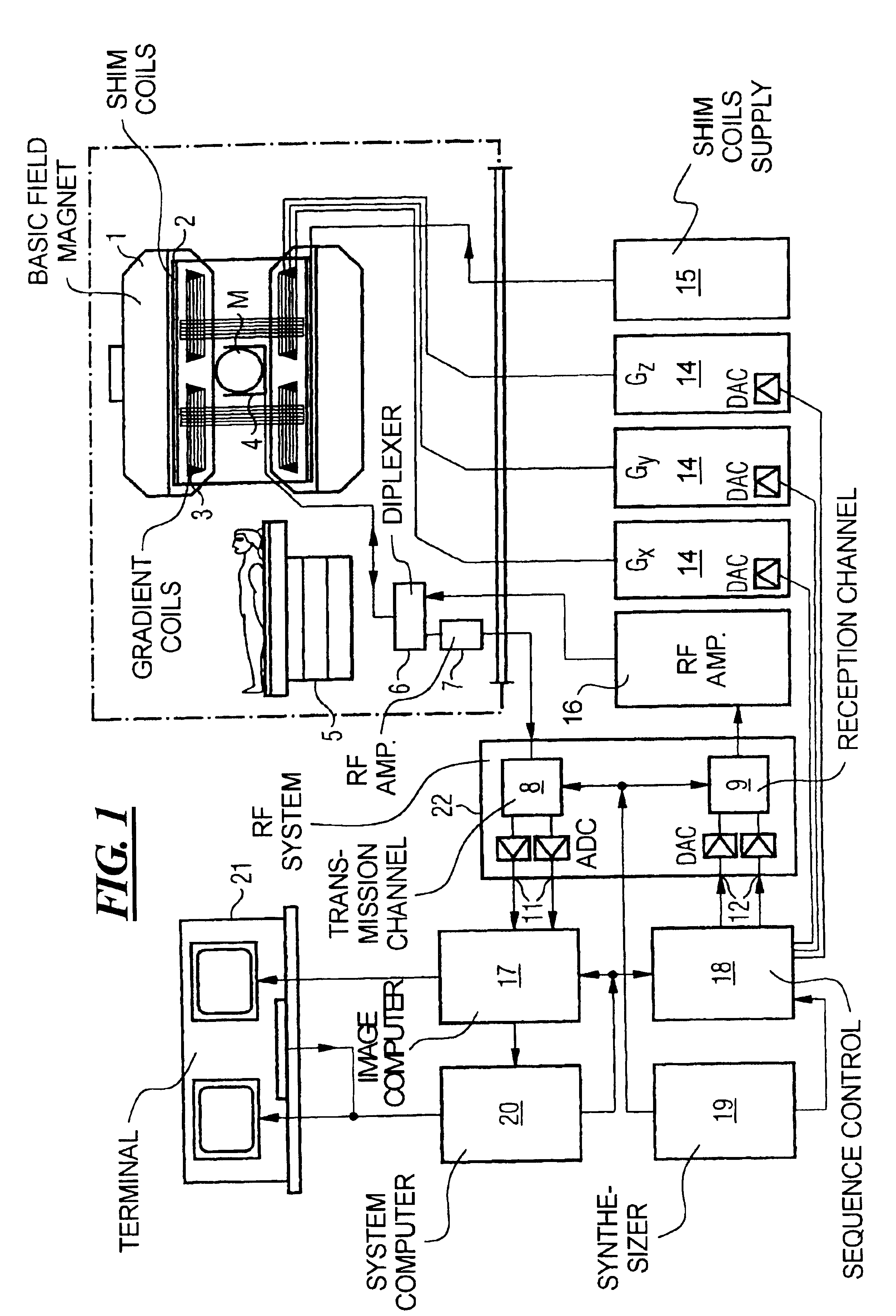
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus employing partial parallel acquisition, wherein each coil produces a complete k-space datasheet
InactiveUS6841998B1Quality improvementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDatasheetData set
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an interconnected region of a human body on the basis of a partially parallel acquisition (PPA) by excitation of nuclear spins and measurement of the radio-frequency signals produced by the excited nuclear spins, a number of spin excitations and measurements of an RF response signal are implemented simultaneously in every component coil of a number of RF reception coils. As a result a number of response signals are acquired that form a reduced dataset of received RF signals for each component coil. Additional calibration data points are acquired for each reduced dataset. A complete image dataset is formed for each component coil on the basis of the reduced dataset for that component coil and at least one further, reduced dataset of a different component coil. A spatial transformation of the image dataset of each component coil is implemented in order to form a complete image of each component coil.
Owner:GRISWOLD MARK
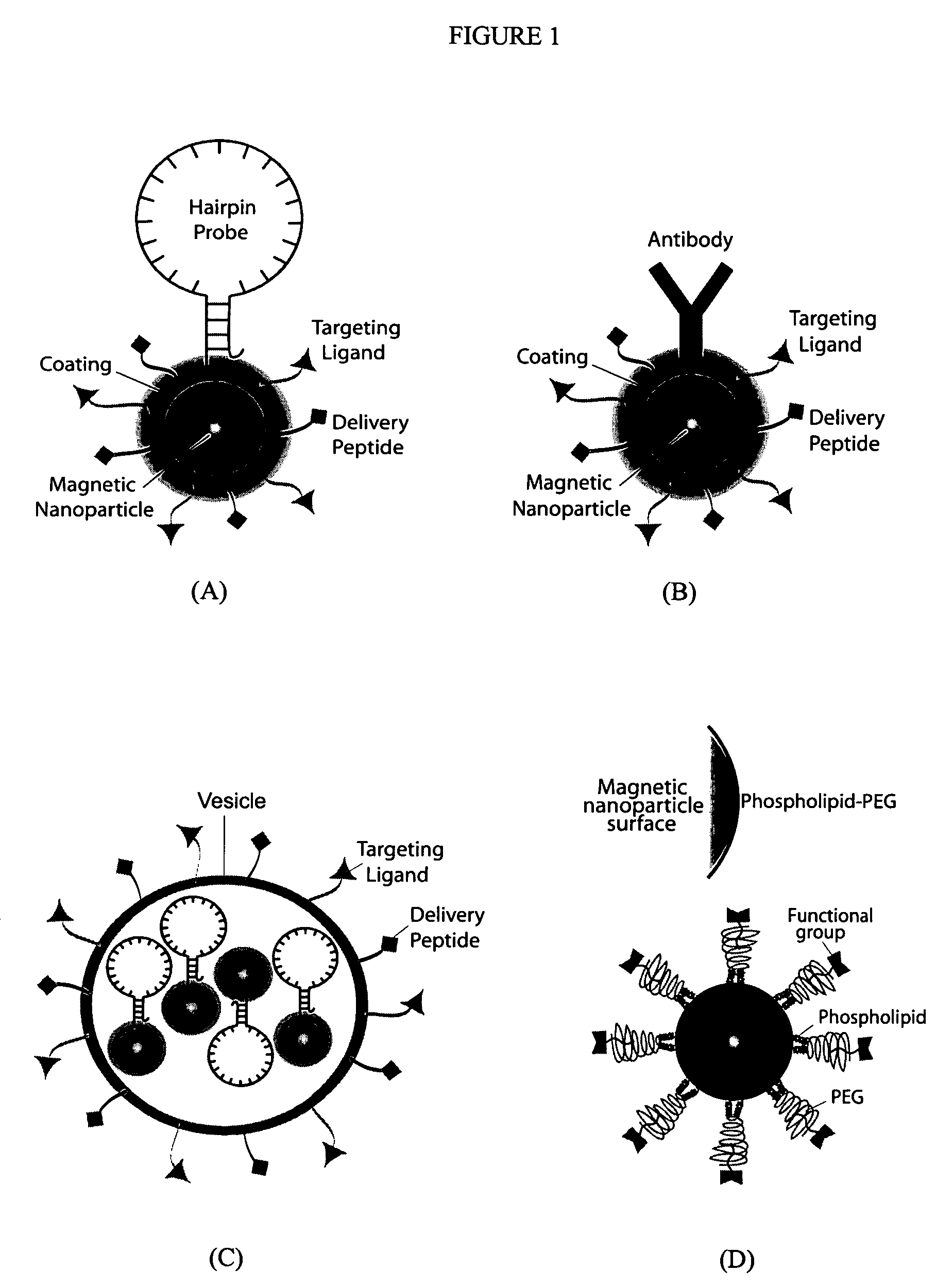
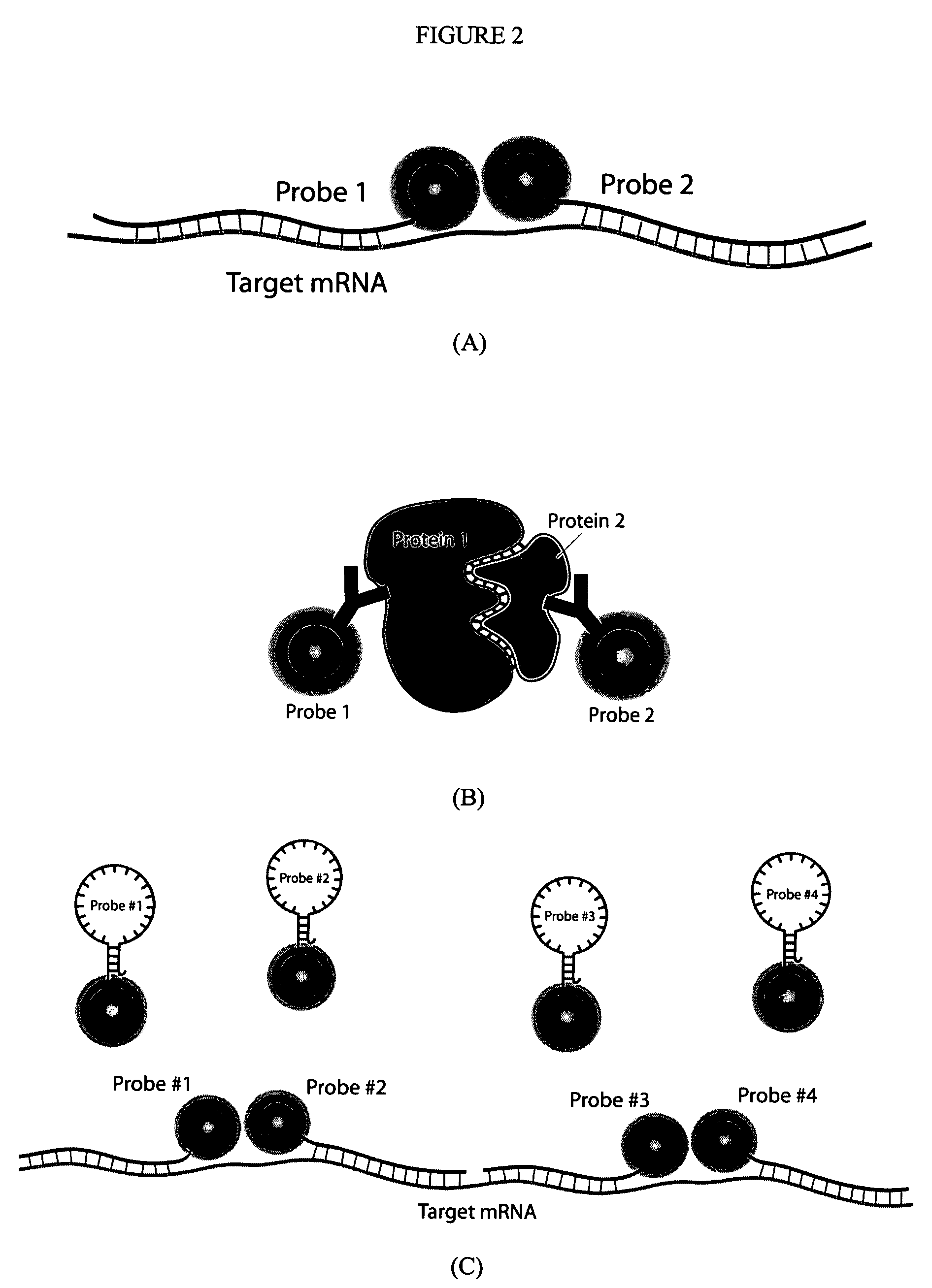
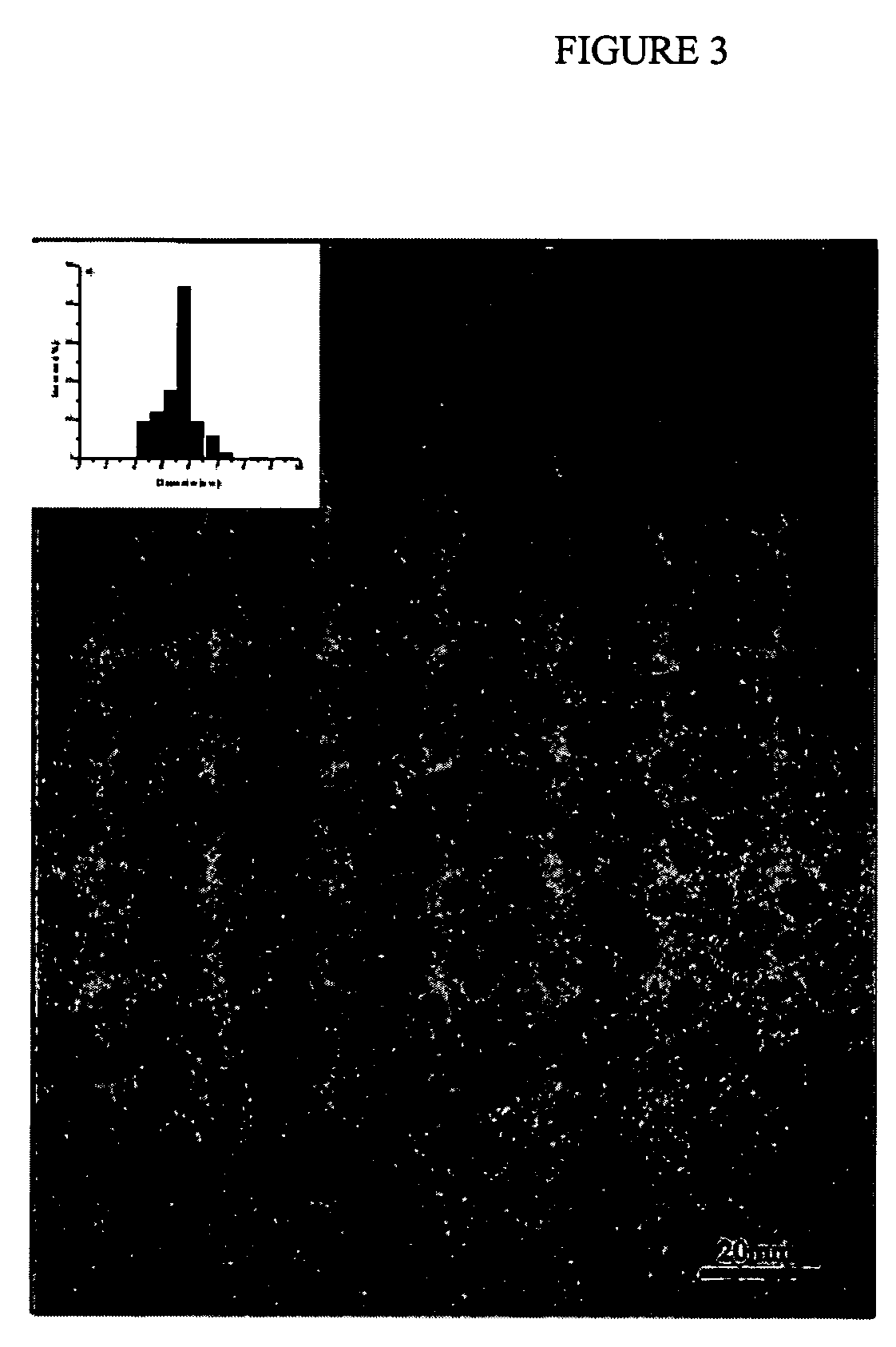
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS7459145B2Efficient internalizationHigh sensitivityBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
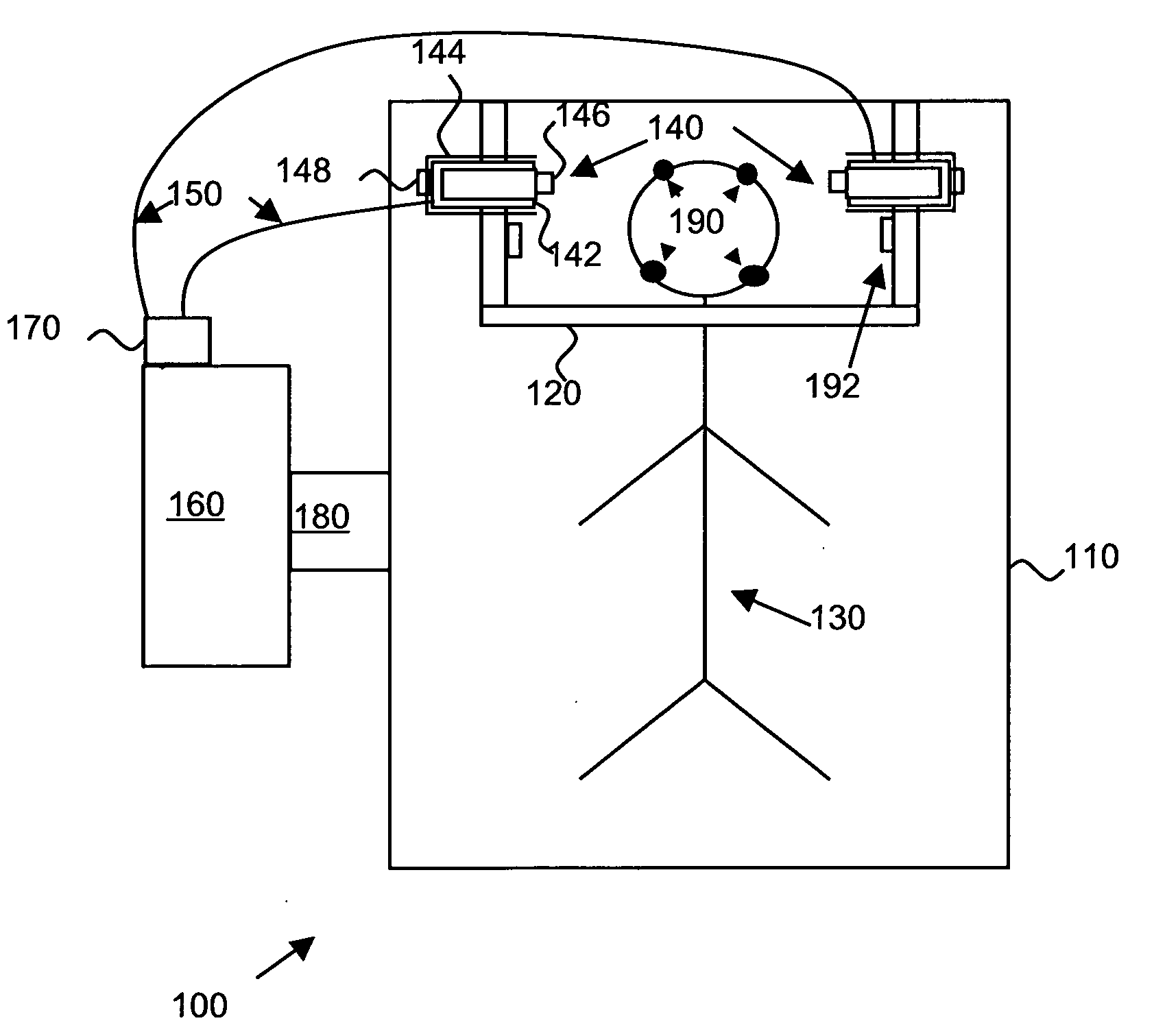
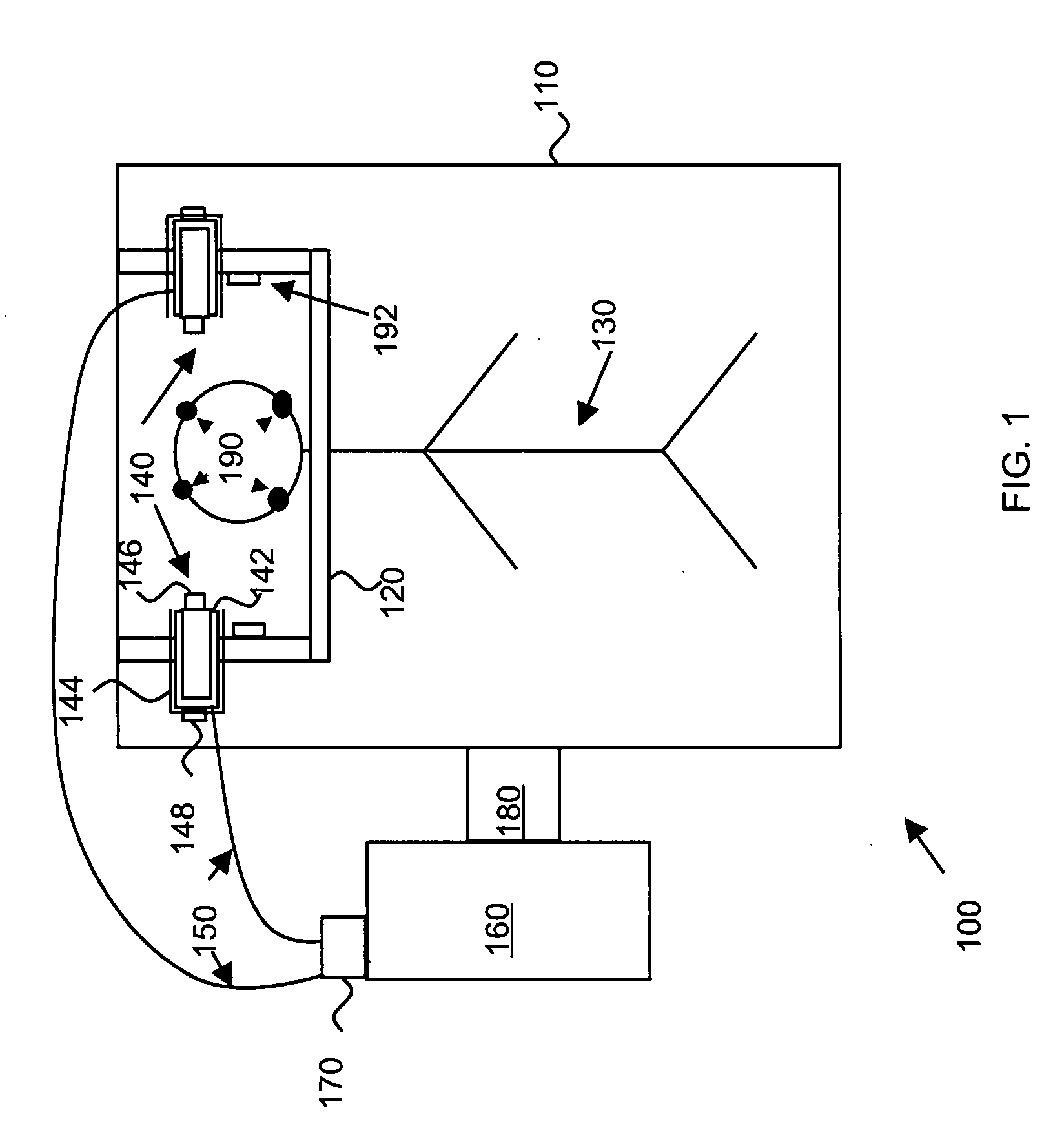
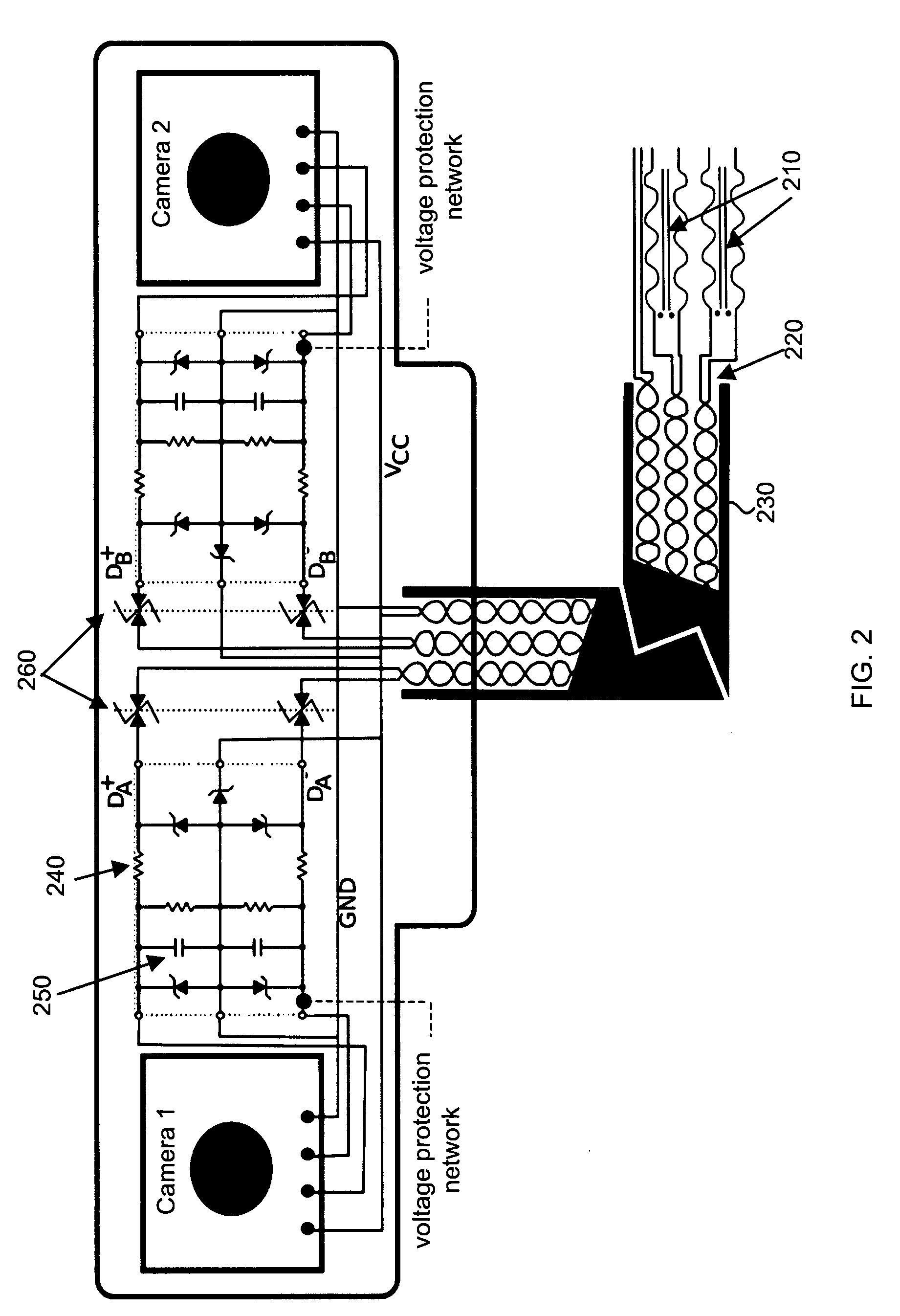
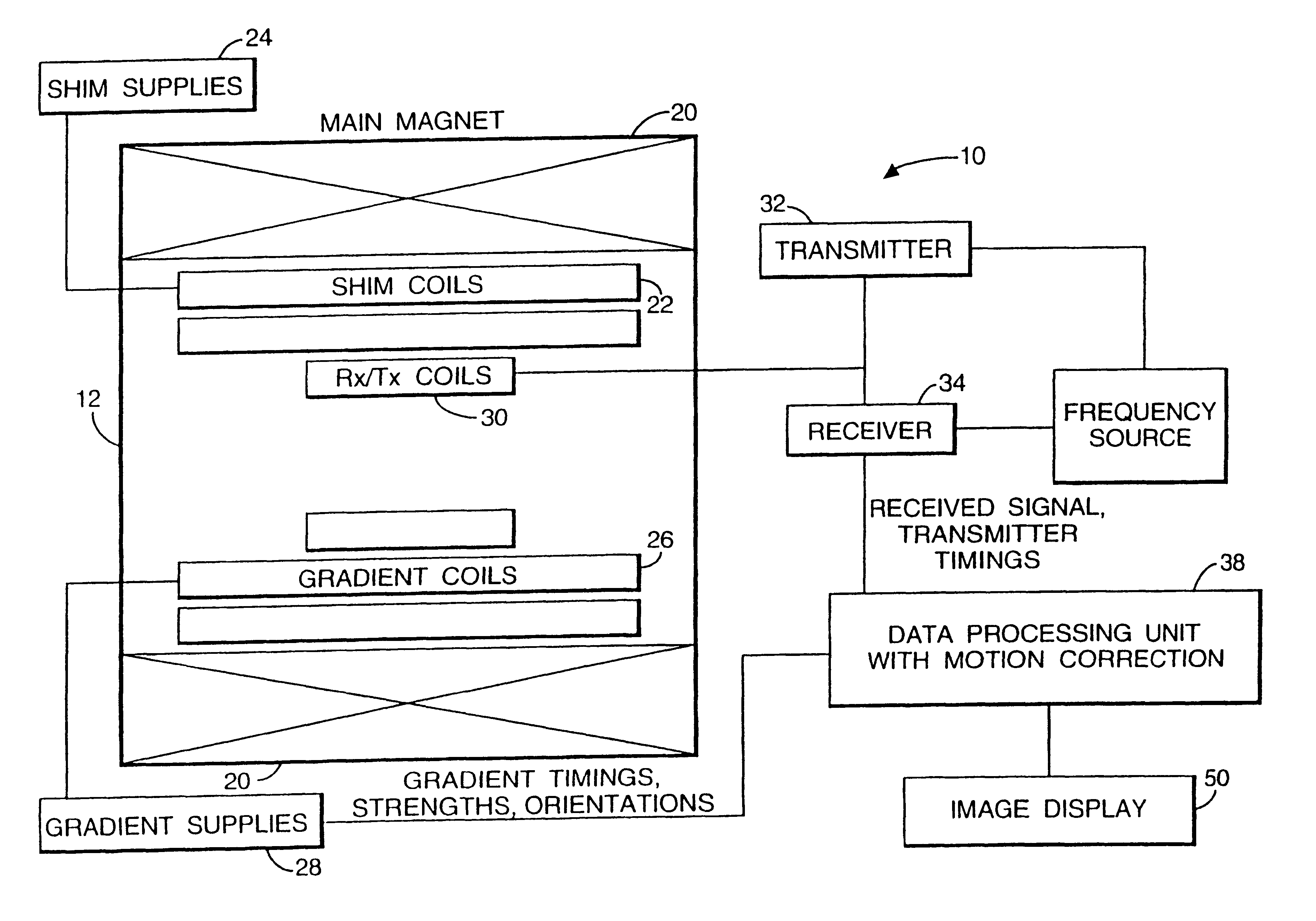
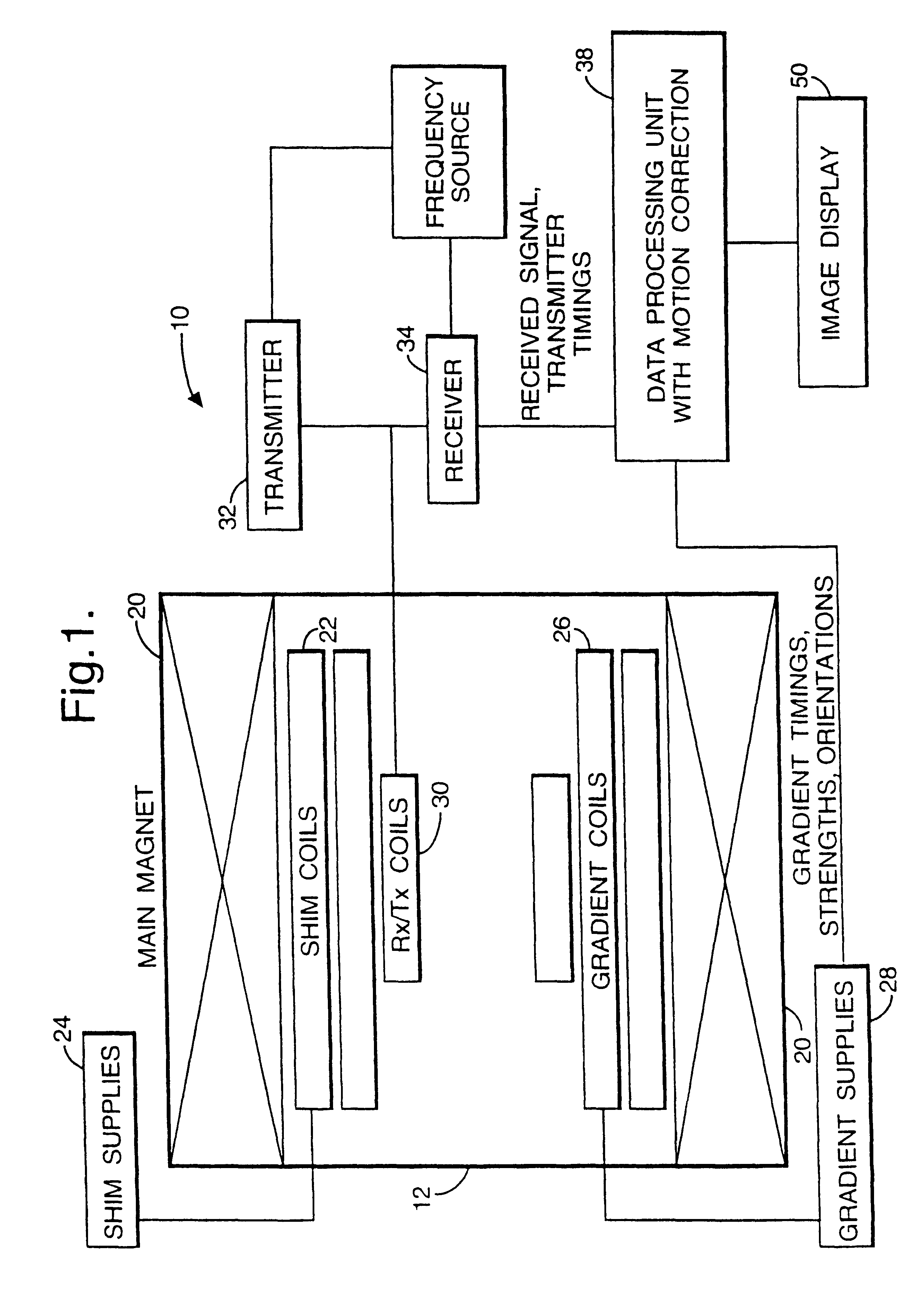
Apparatus and method for real-time motion-compensated magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20090209846A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceReal Time Kinematic
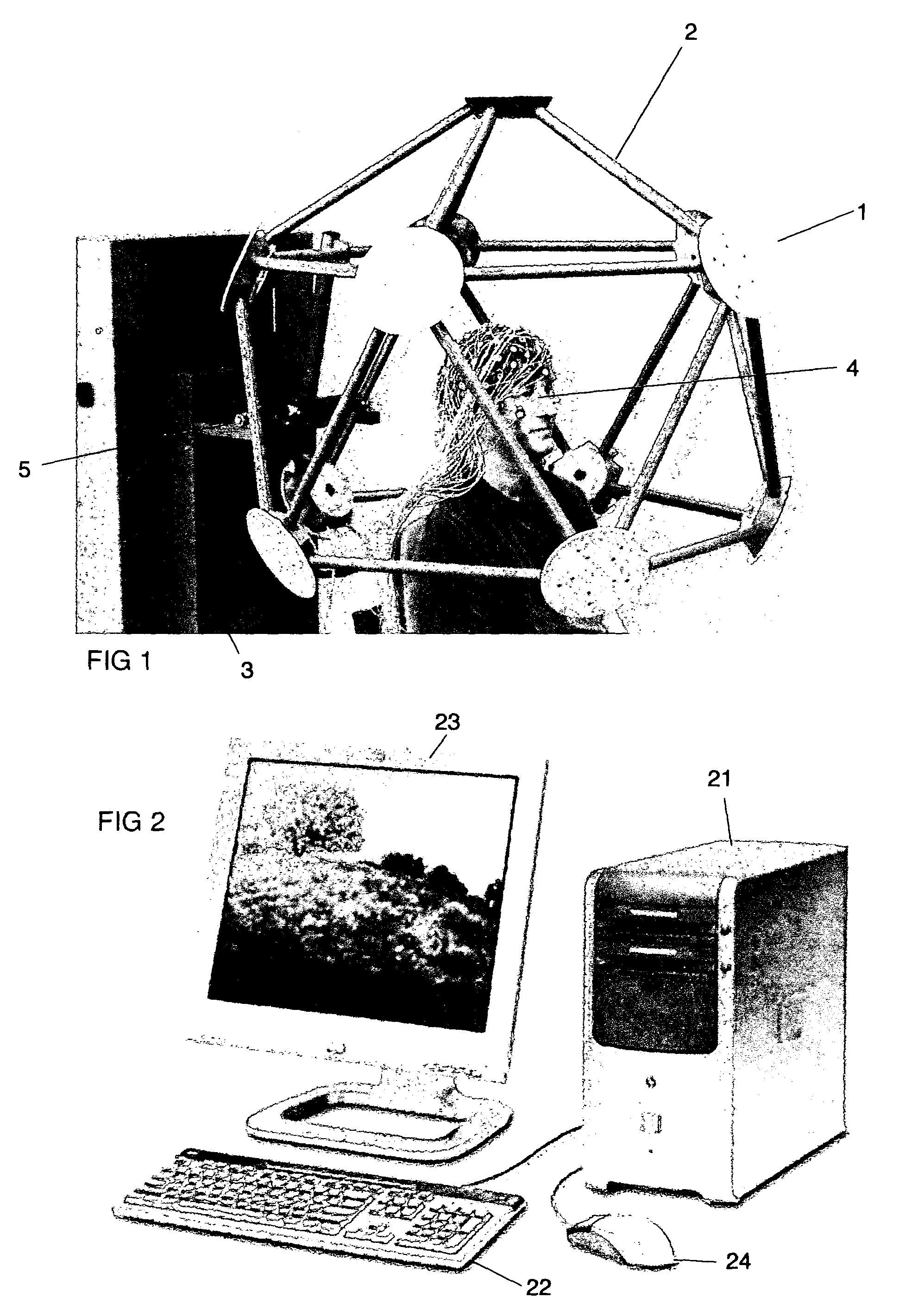
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for real-time motion compensated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a human or animal. The apparatus includes one or more magnetic-resonance compatible cameras mounted on a coil of the MRI device, a calculation and storage device, and an interface operably connected to the MRI device and the calculation and storage device. The apparatus may also include a set of magnetic resonance compatible markers, where the markers are positioned on the human or animal. Alternatively, the apparatus may use a facial recognition algorithm to identify features of the human or animal. For the present invention, the frame of reference is defined by the animal or human being imaged, instead of the typical magnetic resonance coordinate system. Based on continuous positional information, the apparatus controls the magnetic resonance scanner so that it follows the human or animal's motion.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
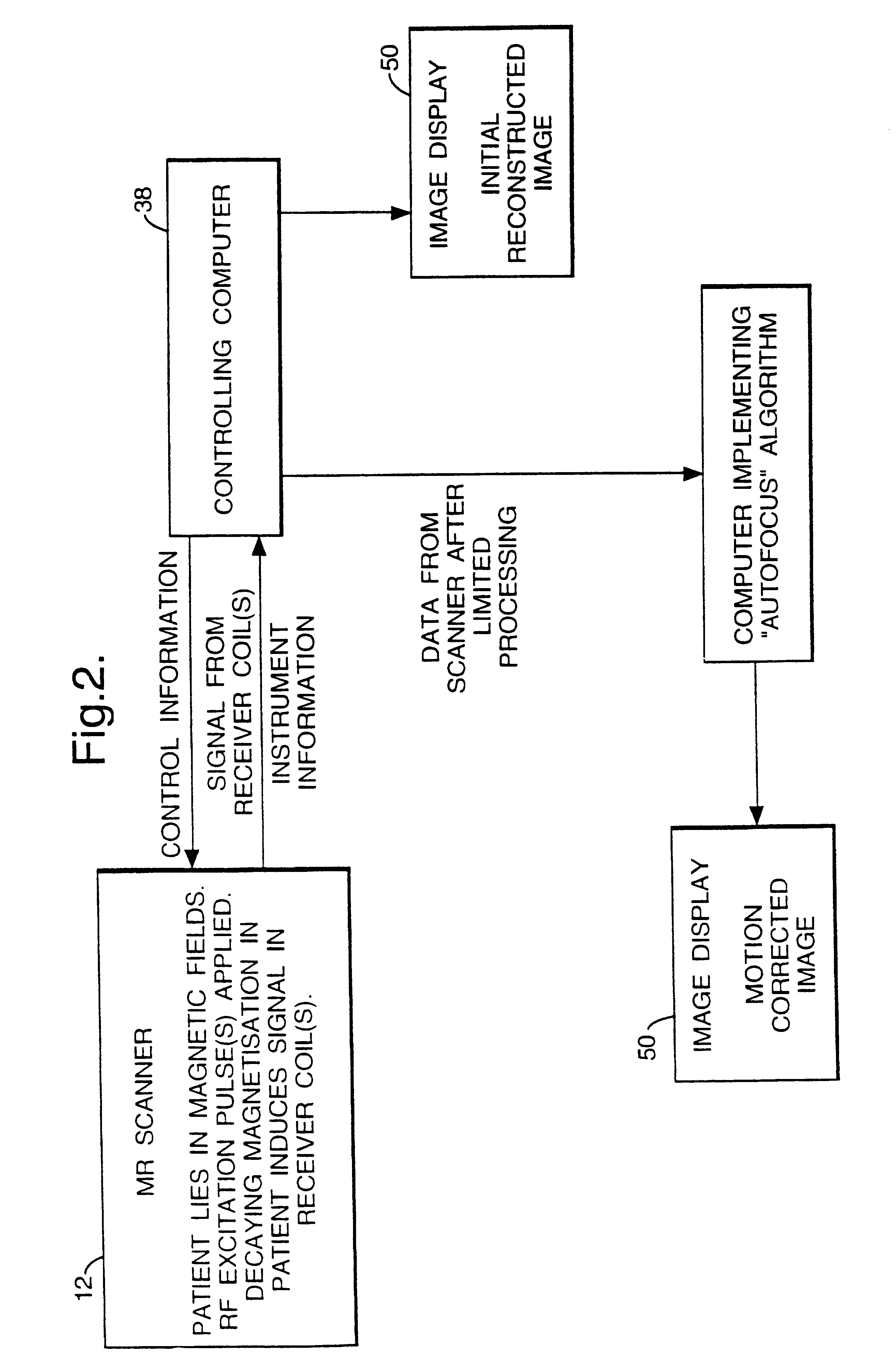
Method and apparatus for imaging artefact reduction
InactiveUS6341179B1Improve image qualityReduce impactReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionImage ArtifactComputer science
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for reducing imaging artifacts in physiological images, such as magnetic resonance imaging images. A model of a physical cause for the image artifact is modelled and the effects of perturbing this model on a focus criterion of the image analyzed so as to optimize the focus criterion. For an optimized focus criterion, the model should reflect the actual physical cause of the image artifact. A focus criterion is a measure of entropy of the image, with an optimized image having reduced entropy.
Owner:NANOGEN RECOGNOMICS BMBH +1
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110254548A1Reliable separationLarge possible separationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
A method for multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging, in which image data is acquired simultaneously from multiple slice locations using a radio frequency coil array, is provided. By way of example, a modified EPI pulse sequence is provided, and includes a series of magnetic gradient field “blips” that are applied along a slice-encoding direction contemporaneously with phase-encoding blips common to EPI sequences. The slice-encoding blips are designed such that phase accruals along the phase-encoding direction are substantially mitigated, while providing that signal information for each sequentially adjacent slice location is cumulatively shifted by a percentage of the imaging FOV. This percentage FOV shift in the image domain provides for more reliable separation of the aliased signal information using parallel image reconstruction methods such as SENSE. In addition, the mitigation of phase accruals in the phase-encoding direction provides for the substantial suppression of pixel tilt and blurring in the reconstructed images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
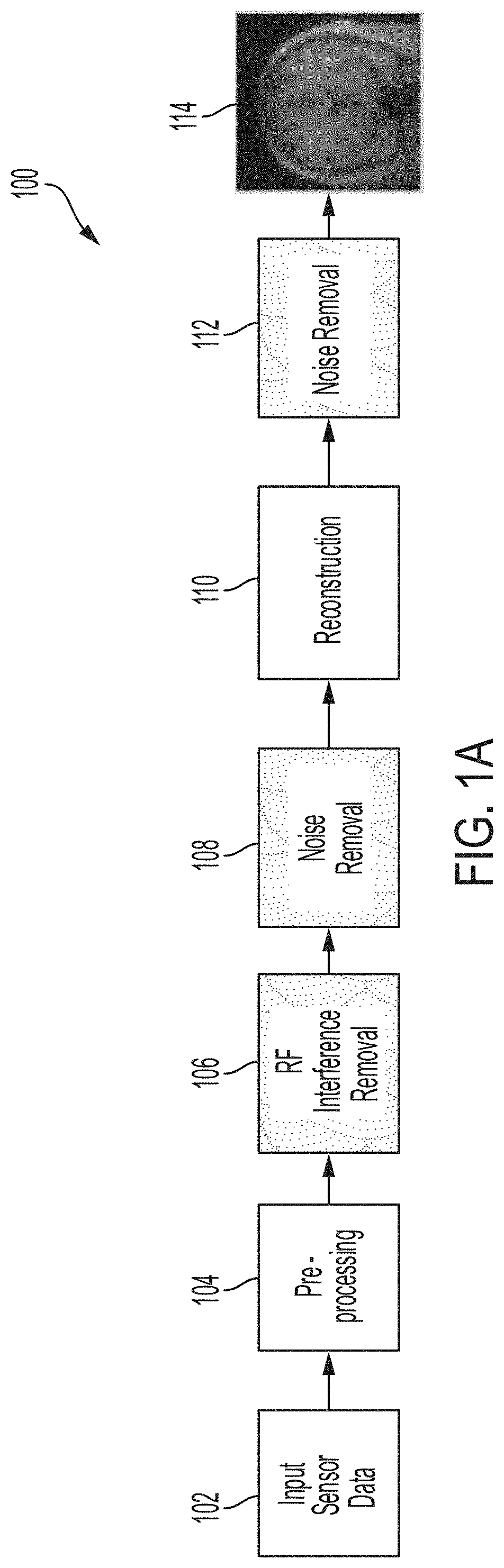
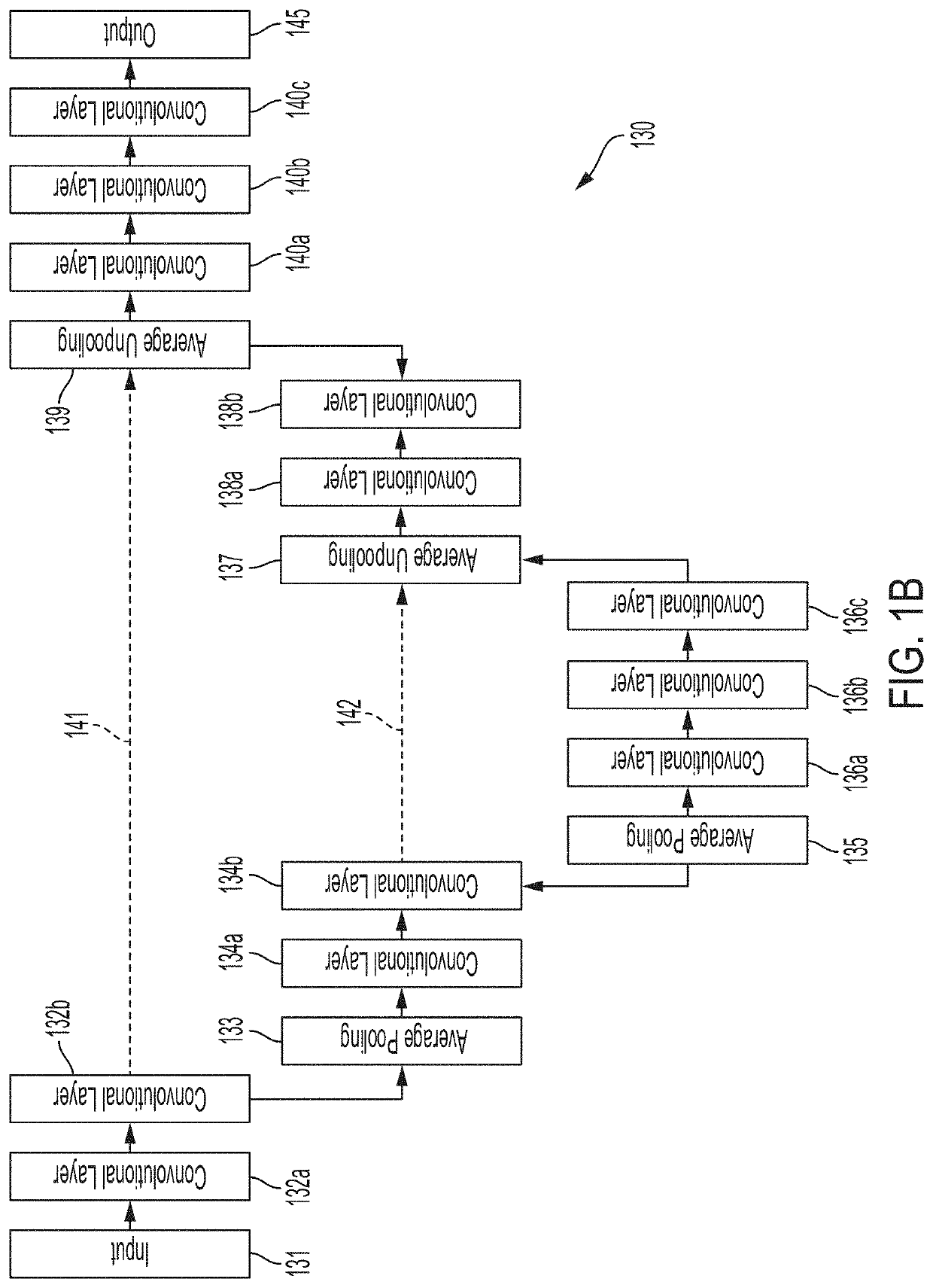
Deep learning techniques for suppressing artefacts in magnetic resonance images
Techniques for removing artefacts, such as RF interference and / or noise, from magnetic resonance data. The techniques include: obtaining input magnetic resonance (MR) data using at least one radio-frequency (RF) coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system; and generating an MR image from input MR data at least in part by using a neural network model to suppress at least one artefact in the input MR data.
Owner:HYPERFINE OPERATIONS INC
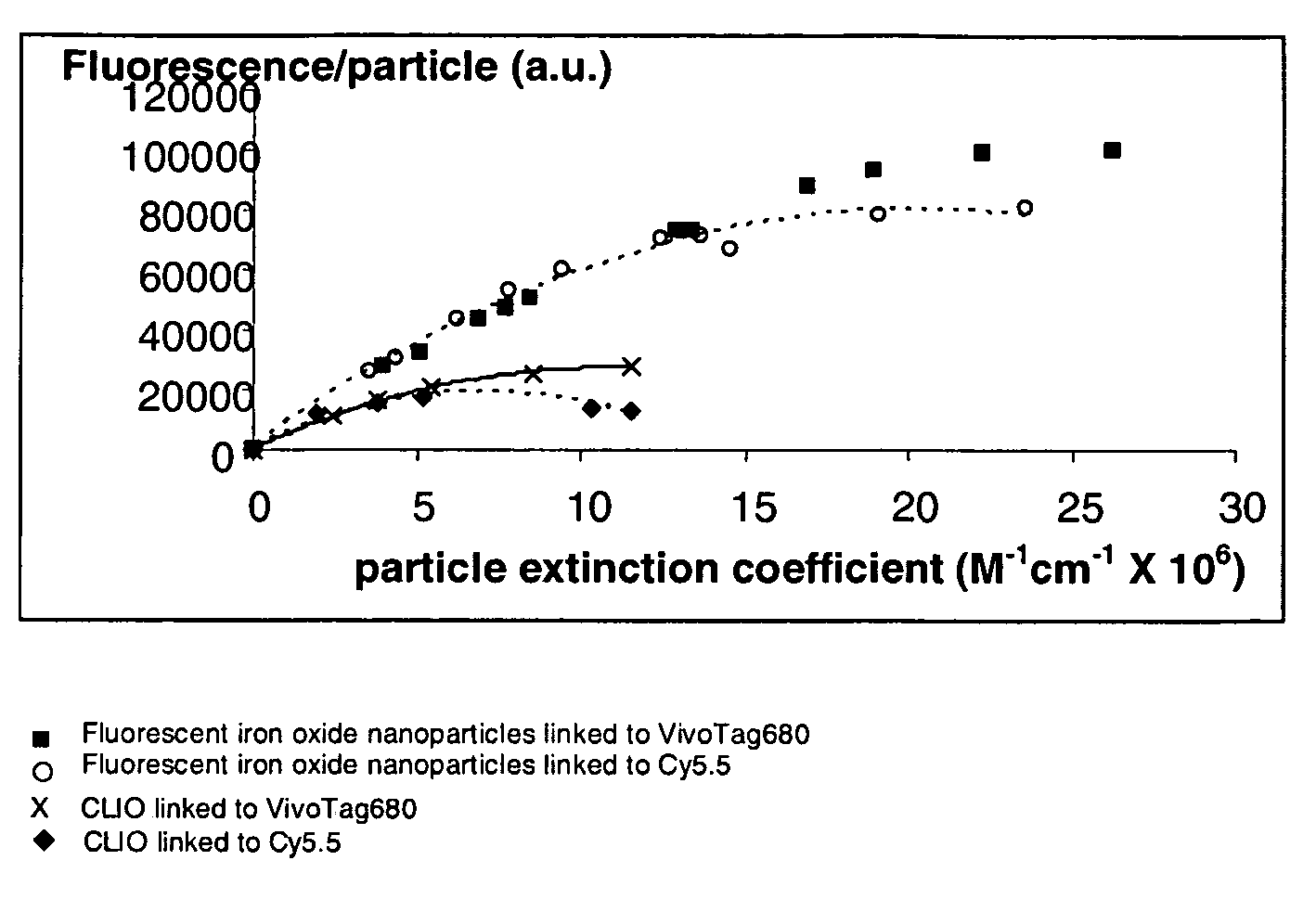
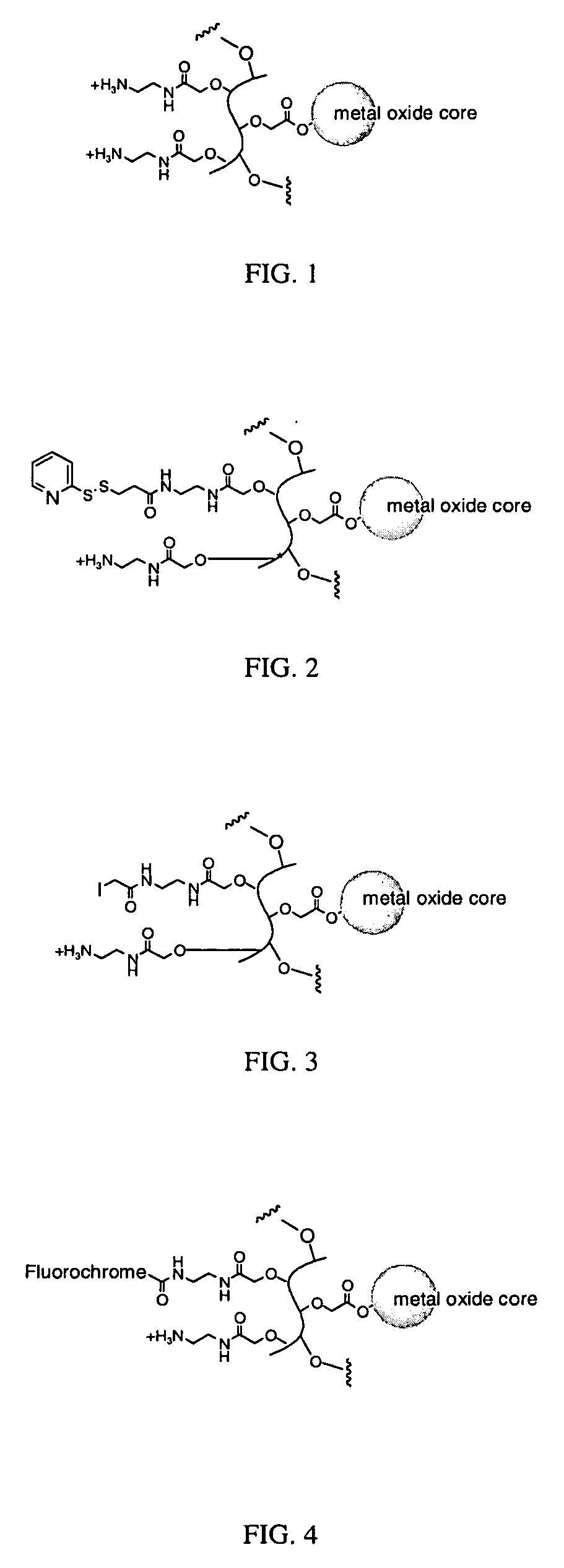
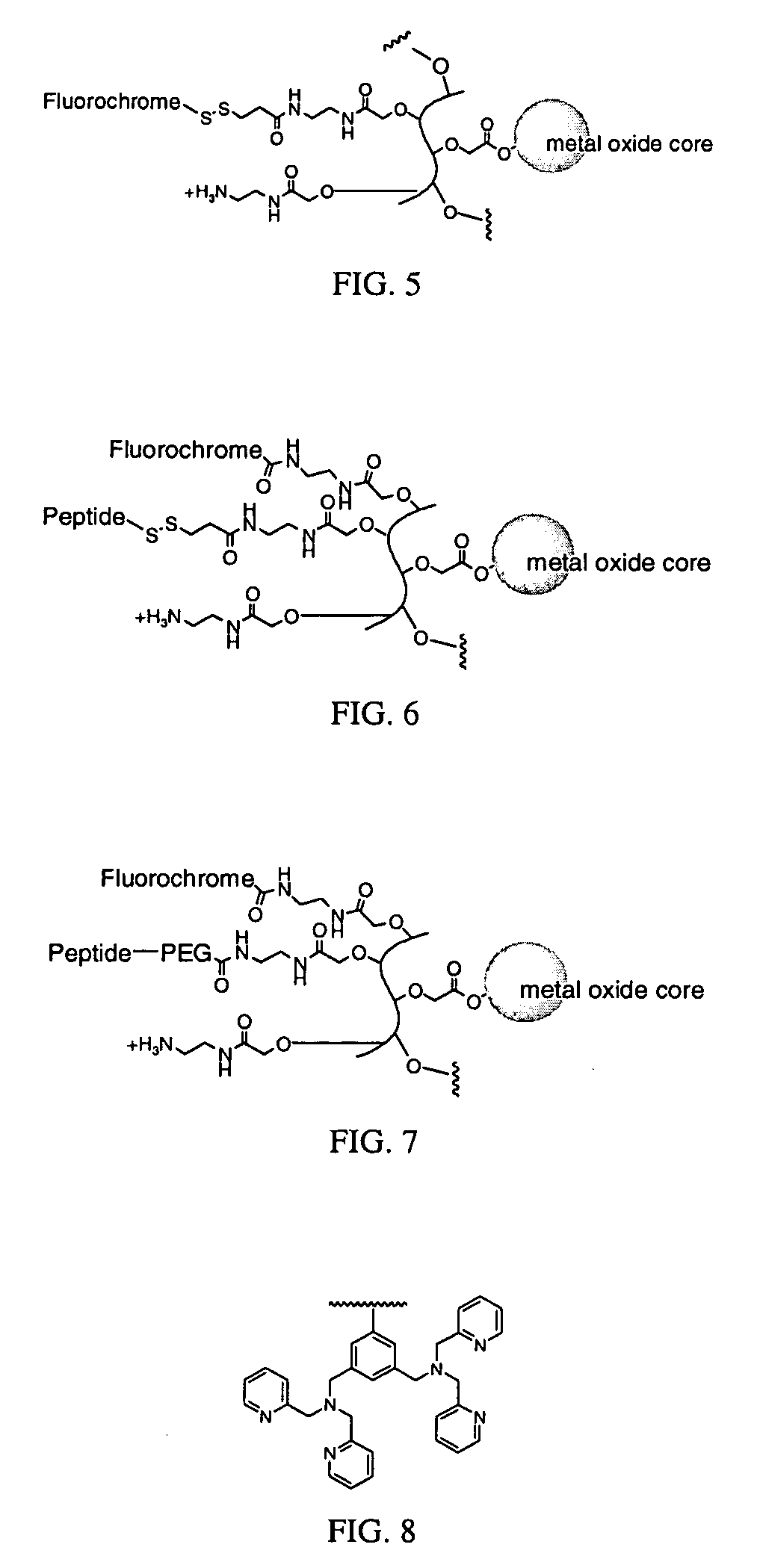
Biocompatible fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080226562A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryMetal oxide nanoparticlesChemical ligation
The invention relates to highly fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles to which biomolecules and other compounds can be chemically linked to form biocompatible, stable optical imaging agents for in vitro and in vivo applications. The fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles may also be used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), thus providing a multi modality imaging agent.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Method and apparatus for evaluation of contrast agent uptake based on derived parametric images
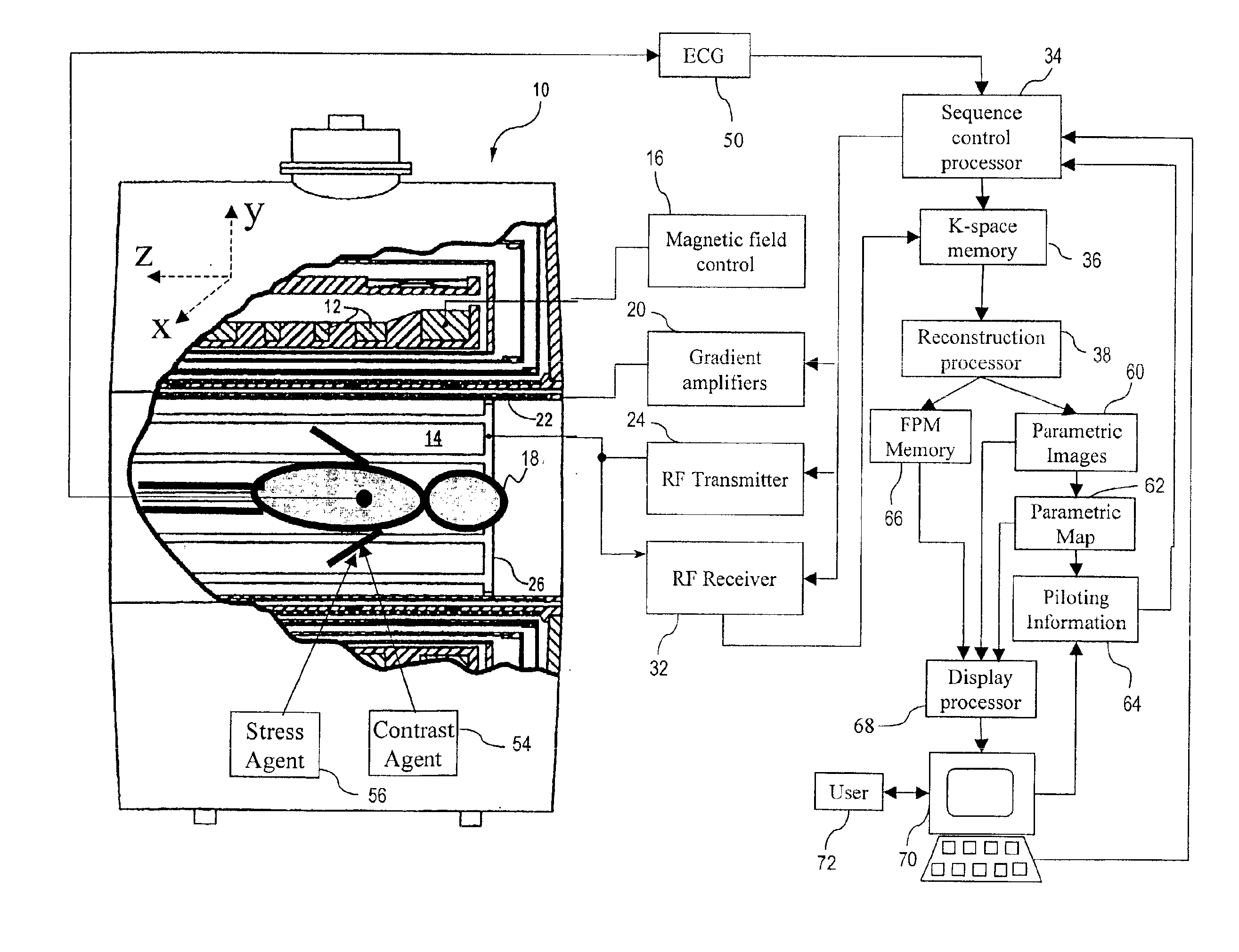
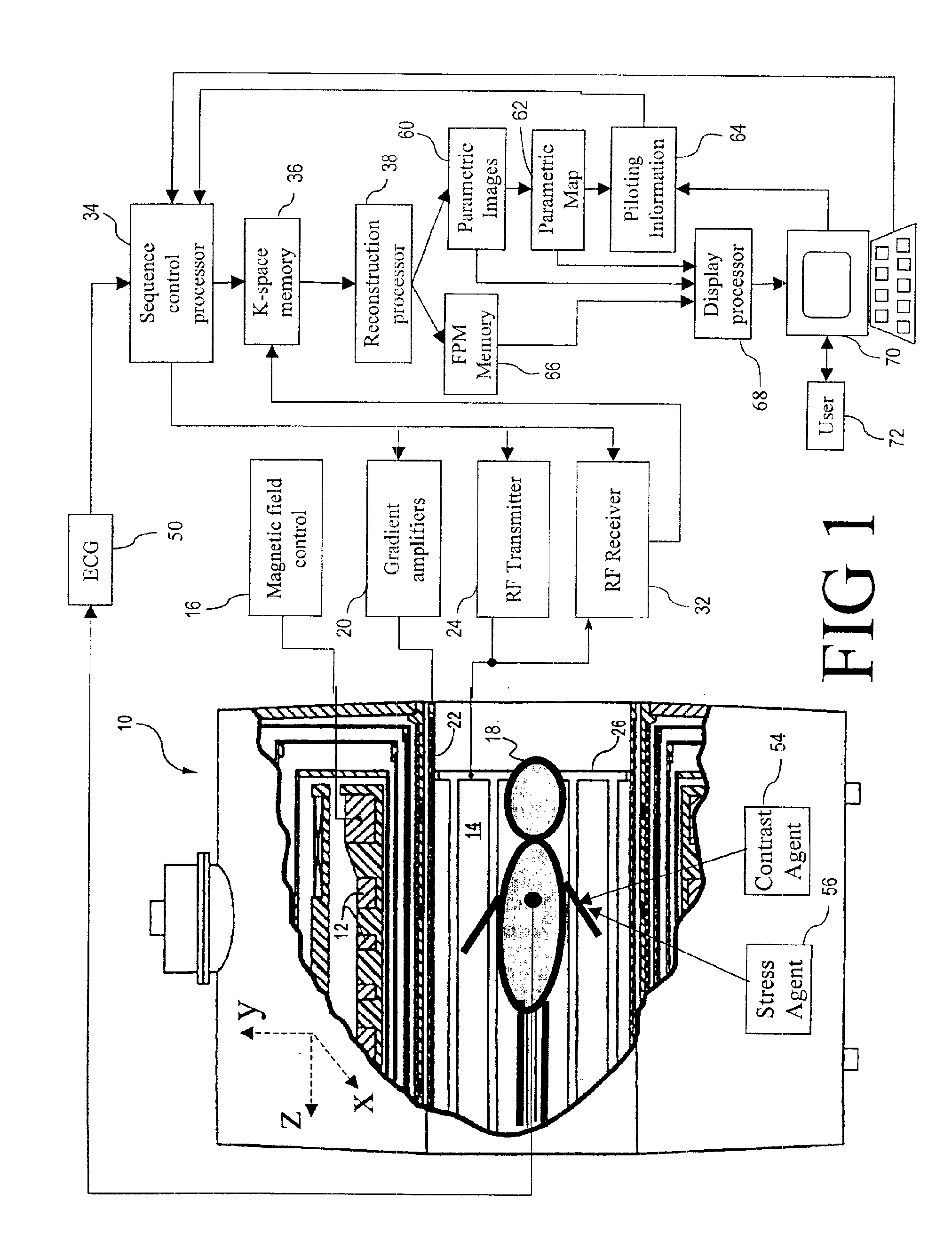
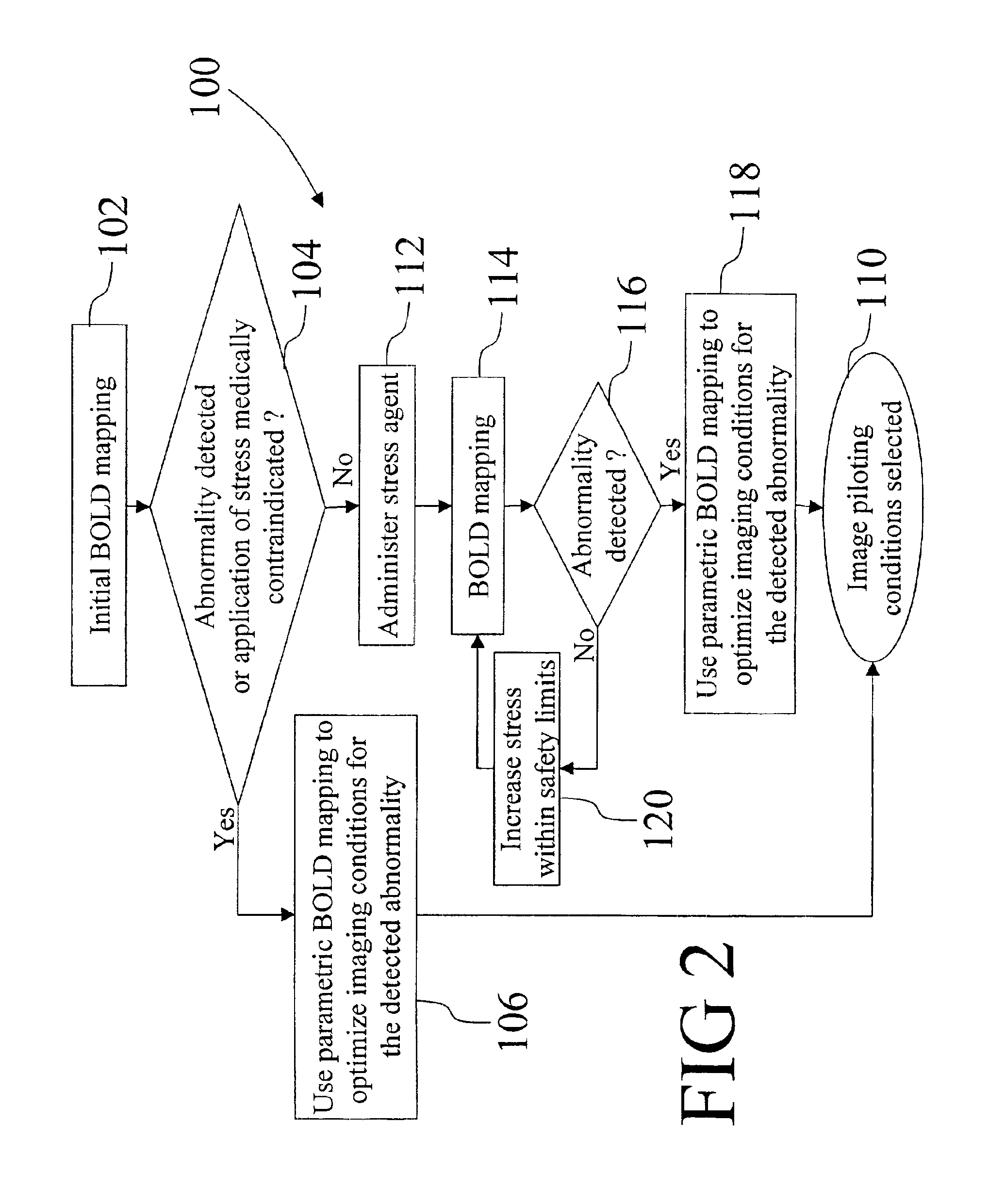
InactiveUS6904306B1Improved clinical work flowMaximize probabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsComputer scienceVolume of interest
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus (10) acquires a plurality of parametric images (60) with at least one varying imaging parameter. A parametric map (62) is constructed from the plurality of parametric images (60). At least one pilot parameter (64) is identified from at least the parametric map (62). The at least one identified pilot parameter (64) includes at least a volume of interest for a diagnostic image. A contrast agent (54) is administered to the patient (18). The identified volume of interest is imaged during influx of the administered contrast agent (54) into the identified volume of interest. The imaging uses the at least one identified pilot parameter (64).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Magnetic resonance imaging concepts
ActiveUS7941204B1Accurate estimateEffective motion suppressionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPresent methodParallel imaging
Methods of acquiring magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data for angiography. The present invention includes novel magnetization preparation schemes where the navigator and fat saturation pulses are executed in steady state after the preparatory pulses in order to minimize the delay between the magnetization preparation and the image echoes. The present invention also provides for improved methods of contrast-enhanced MRI where data are collected along non-linear trajectories through k-space and may also involve novel view ordering. In addition, the present methods employ novel motion corrections that minimize motion artifacts. The present invention further provides novel methods of self-calibrated sensitivity-encoded parallel imaging that allow for accurate and rapid scanning of subjects.
Owner:NGUYEN THANH +4
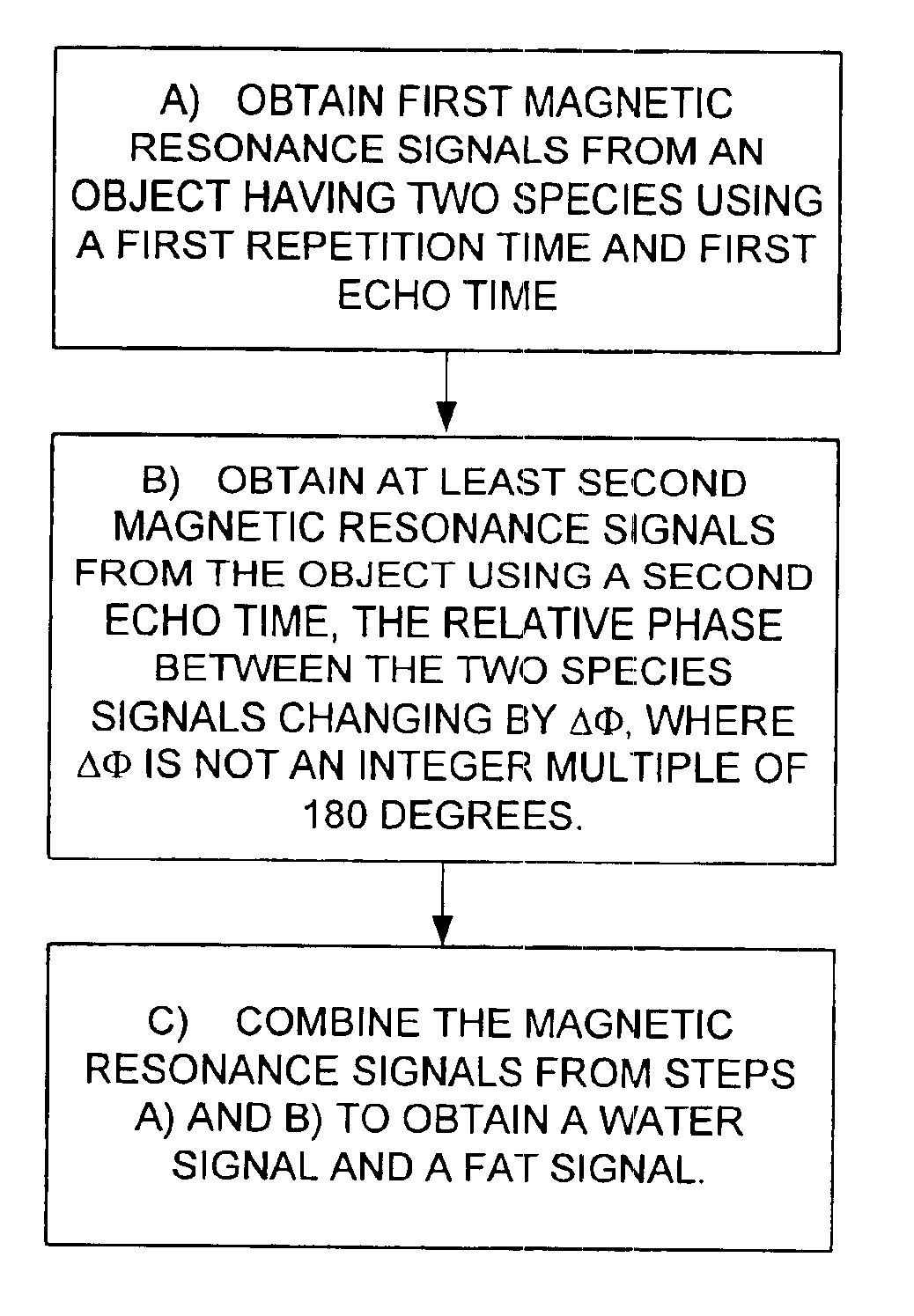
Magnetic resonance imaging with fat-water signal separation
InactiveUS6856134B1Fast imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionArticular cartilageMR - Magnetic resonance
A generalized multi-point fat-water separation process is combined with steady-state free precession (SSFP) to obtain high quality images of articular cartilage with reduced imaging time.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
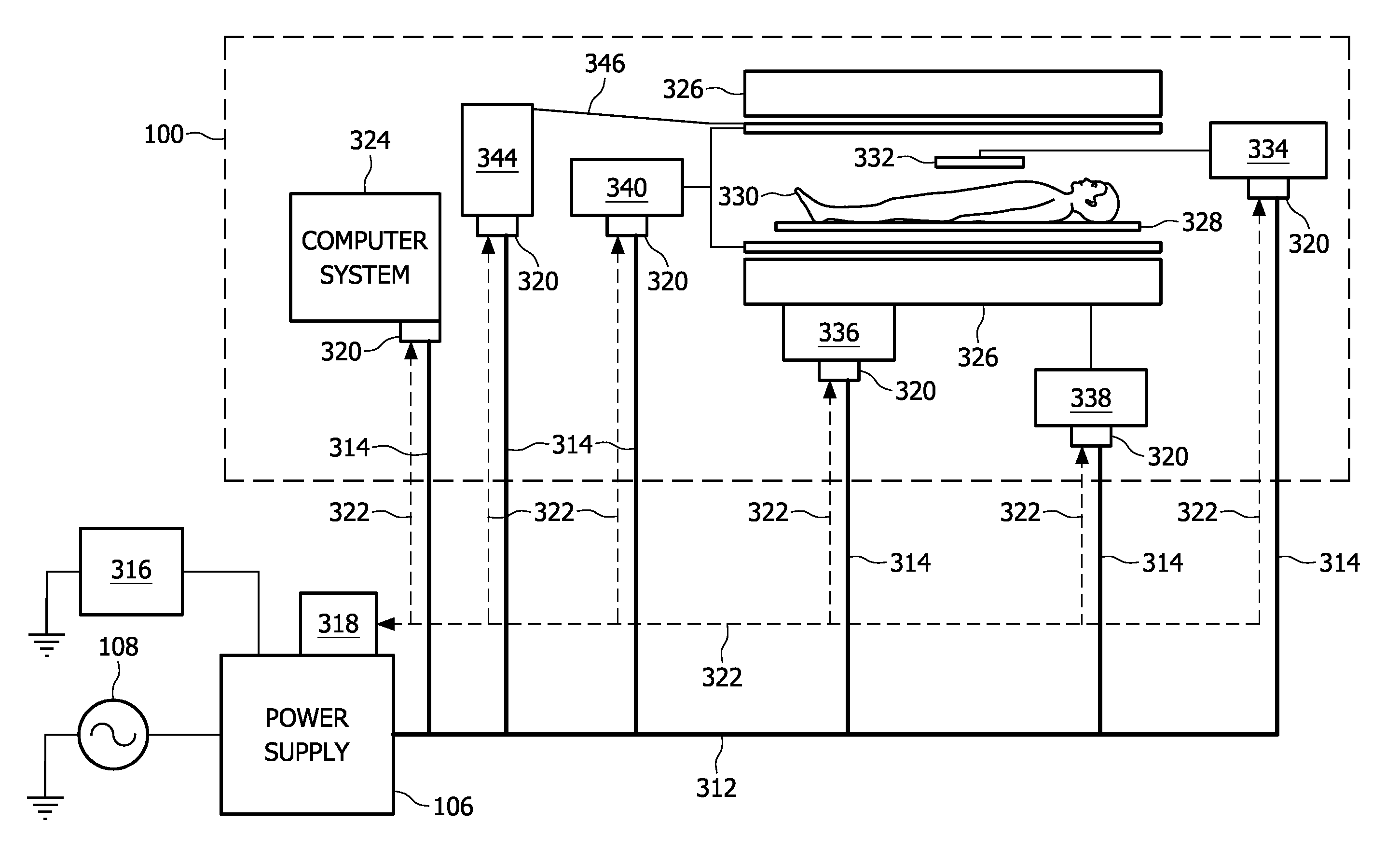
Magnetic resonance imaging system comprising a power supply unit adapted for providing direct current electrical power
ActiveUS20110210739A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerAC - Alternating currentData acquisition
A MRI system for acquiring MRI image data comprising a data acquisition means comprising a plurality of subunits for acquiring MRI image data, a power distribution means for providing the means for acquiring MRI image data with electrical power, the power distribution means comprising: a power supply unit adapted for providing direct current electrical power from an alternating current electrical mains, a power bus adapted for supplying the subunits with the direct current electrical power, control means for controlling the supply of direct current electrical power by the power bus to the subunits.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Open architecture imaging apparatus and coil system for magnetic resonance imaging
Apparatus and method for using radio frequency coil systems for magnetic resonance imaging within an open architecture apparatus is provided. The MRI coil system includes a support structure with an open architecture in which secondary support structures, compression systems and plates containing RF coil systems may be introduced. These structures and RF coils can be moved relative to the patient, or removed entirely from the system. In one embodiment the system consists of a tabletop coil system, while another embodiment consists of a dedicated stretcher design.
Owner:INVIVO CORP +1
Transceiver apparatus, system and methodology for superior In-Vivo imaging of human anatomy
ActiveUS20120112748A1Maximize efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRHuman anatomyDisease
The inventive subject matter as a whole is an improved transceiver apparatus and system for diagnostic evaluations of living subject, human or animal; and is particularly effective as a clinical tool for the spectroscopic scanning or magnetic resonance imaging of humans suspected of being afflicted with a particular disease, disorder, or pathology. The improved transceiver apparatus is used as an essential component in a computer controlled system suitable for magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”), or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (“MRS”), and / or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (“MRSI”); and the present improvement of these electromagnetic signaling systems will provide far more accurate and precise visual images and accumulated data for the clinician or surgeon, as well as serve as a basis upon which to make a diagnosis and decide upon a mode of therapeutic treatment for that individual.
Owner:HETHERINGTON HOBY P +2
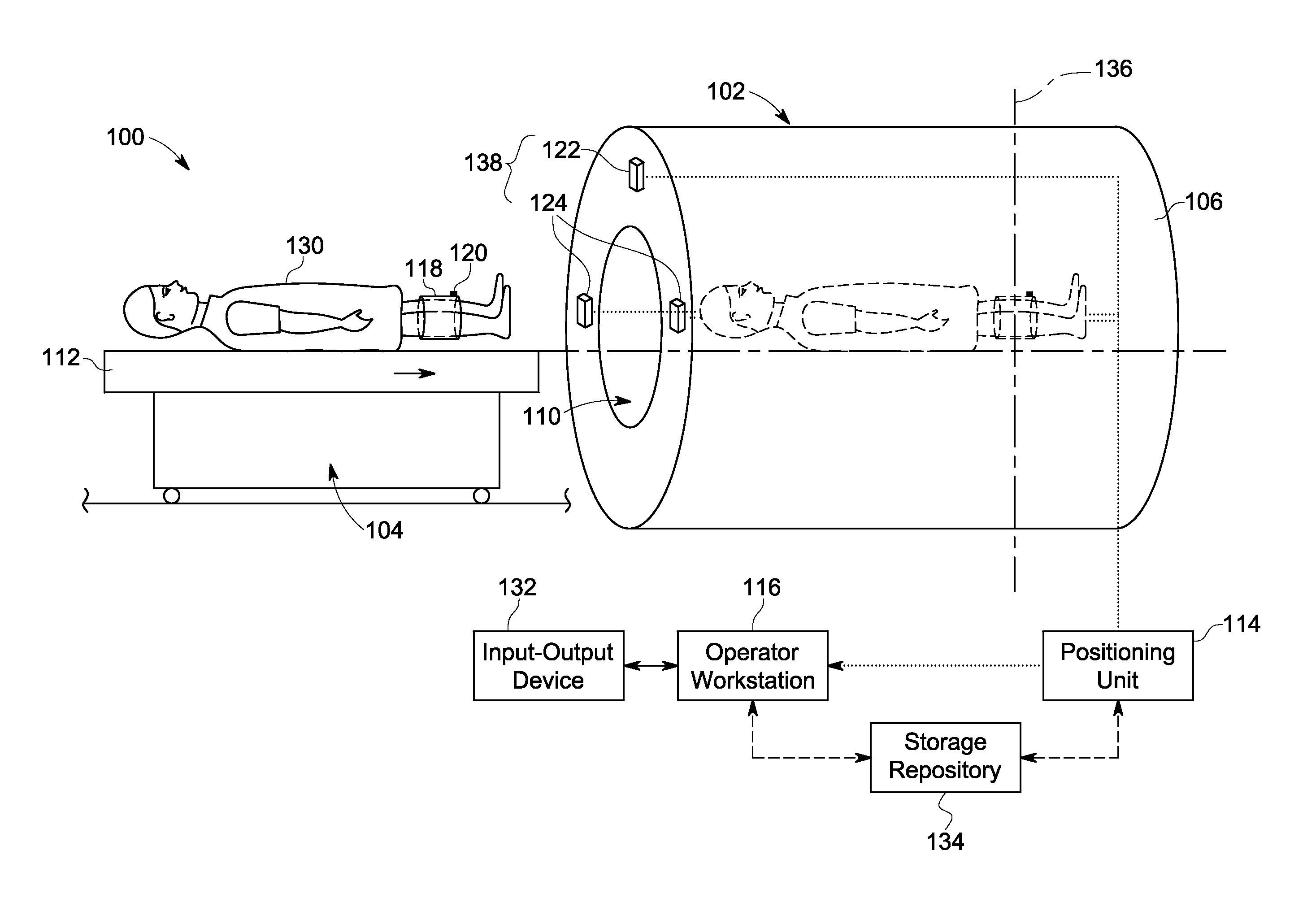
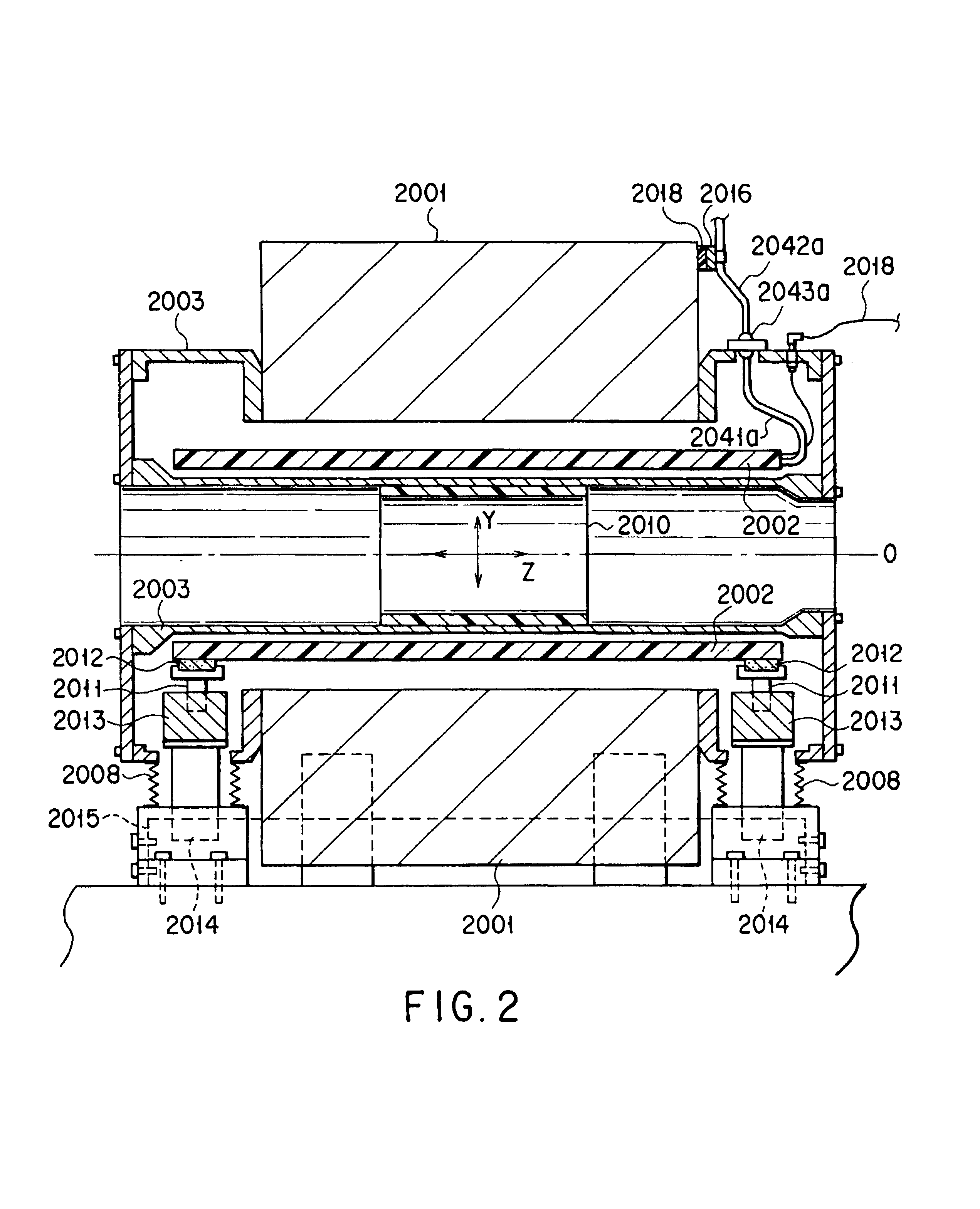
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20050187459A1Small magnetic structureSmall structureDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVertical planeMR - Magnetic resonance
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus including a magnetic structure having two opposite and spaced apart poles and a column or wall transverse to the poles and connecting the poles; the poles defining two opposite walls delimiting a patient-imaging space, the two opposite walls extending along substantially parallel planes which are substantially parallel to a vertical plane; and a patient positioning table which is slidably connected to a supporting frame between the two poles; the table being positioned with its longitudinal axis substantially parallel to the two opposite parallel walls of the poles and the table being oriented with its transverse axis perpendicular to at least one of the two opposite walls.
Owner:ESAOTE
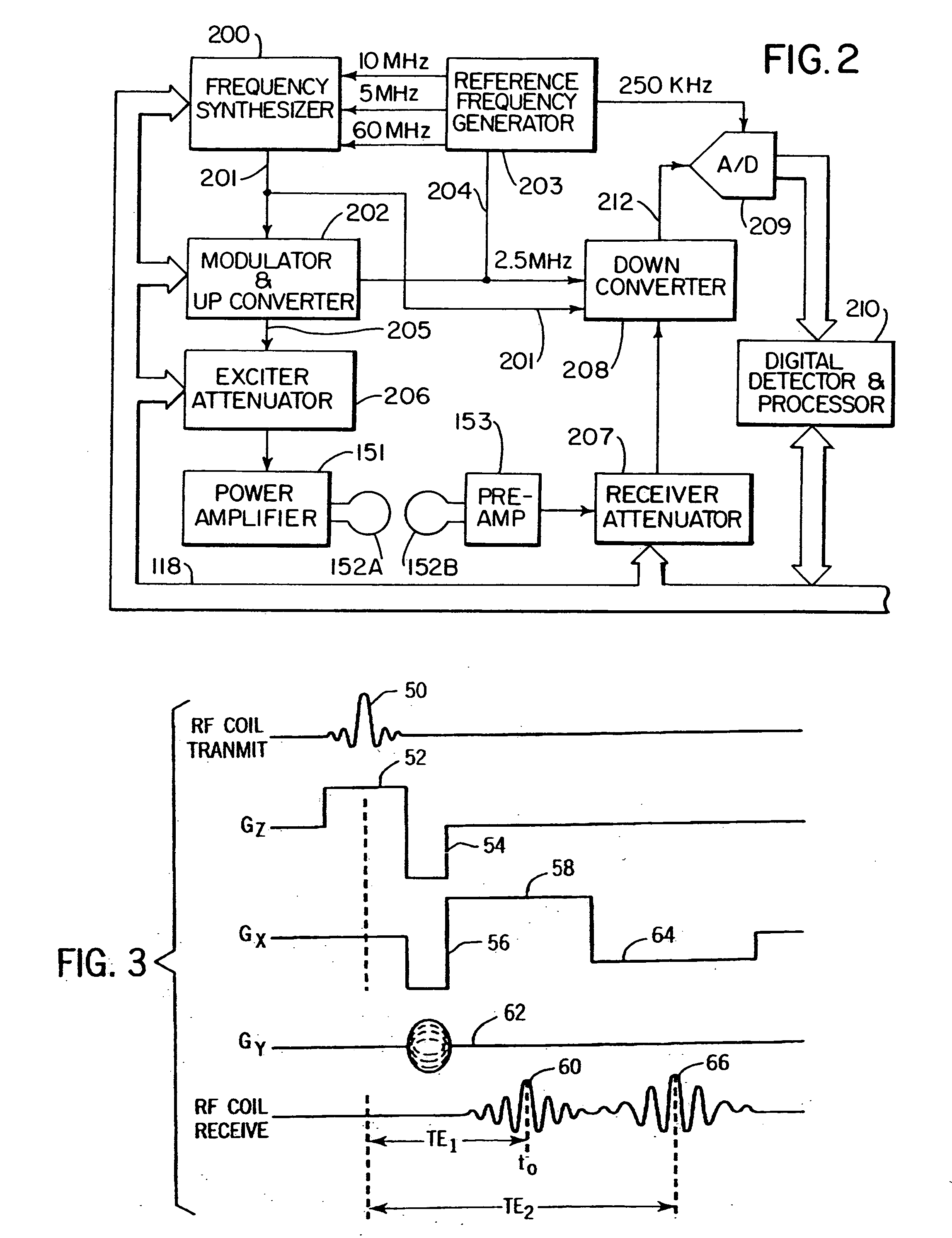
Correcting method for quick-speed spin echo pulse sequence and uses thereof
InactiveCN101162262AResolve ArtifactsEliminate image quality effectsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoStimulated echo
The invention provides a method for correcting fast spin echo sequence, aiming at solving the problem that the prior FSE images have the factors of an imaging system such as artifacts, magnetic field stability, eddy current, etc. which have impact on the quality of images. The method can be used to correct the parameter of the fast spin echo (FSE) sequence of a magnetic resonance diagnostic, in particular to correct the parameter of the fast spin echo (FSE) sequence of a magnetic resonance diagnostic which can switch frequence of a transmitter and a receiver. The method for correcting fast spin echo sequence of the invention eliminates the impact of the factors of the imaging system such as artifacts, magnetic field stability, eddy current, etc. on the quality of the images; and as the parameter which is obtained by the correcting method and used in the pre-scanning is the optimal parameter, thereby solving the problem of artifacts of the prior FSE images.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Mri Compatible Devices
InactiveUS20070280850A1Sufficient radiopacityMammary implantsSurgeryMagnetic susceptibilityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A medical device suitable for use with magnetic resonance imaging techniques includes a component that is formed from a refractory metal, a precious metal, an alloy comprising a refractory metal, an alloy comprising a precious metal, and / or alloy comprising at least one refractory metal and at least one precious metal. The component has a magnetic susceptibility less than about 300×10−6 cgs, and has a low radiopacity such that the component can be visualized under fluoroscopy.
Owner:COOK INC
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system for eliminating motion artifact based on dynamic tracking technology
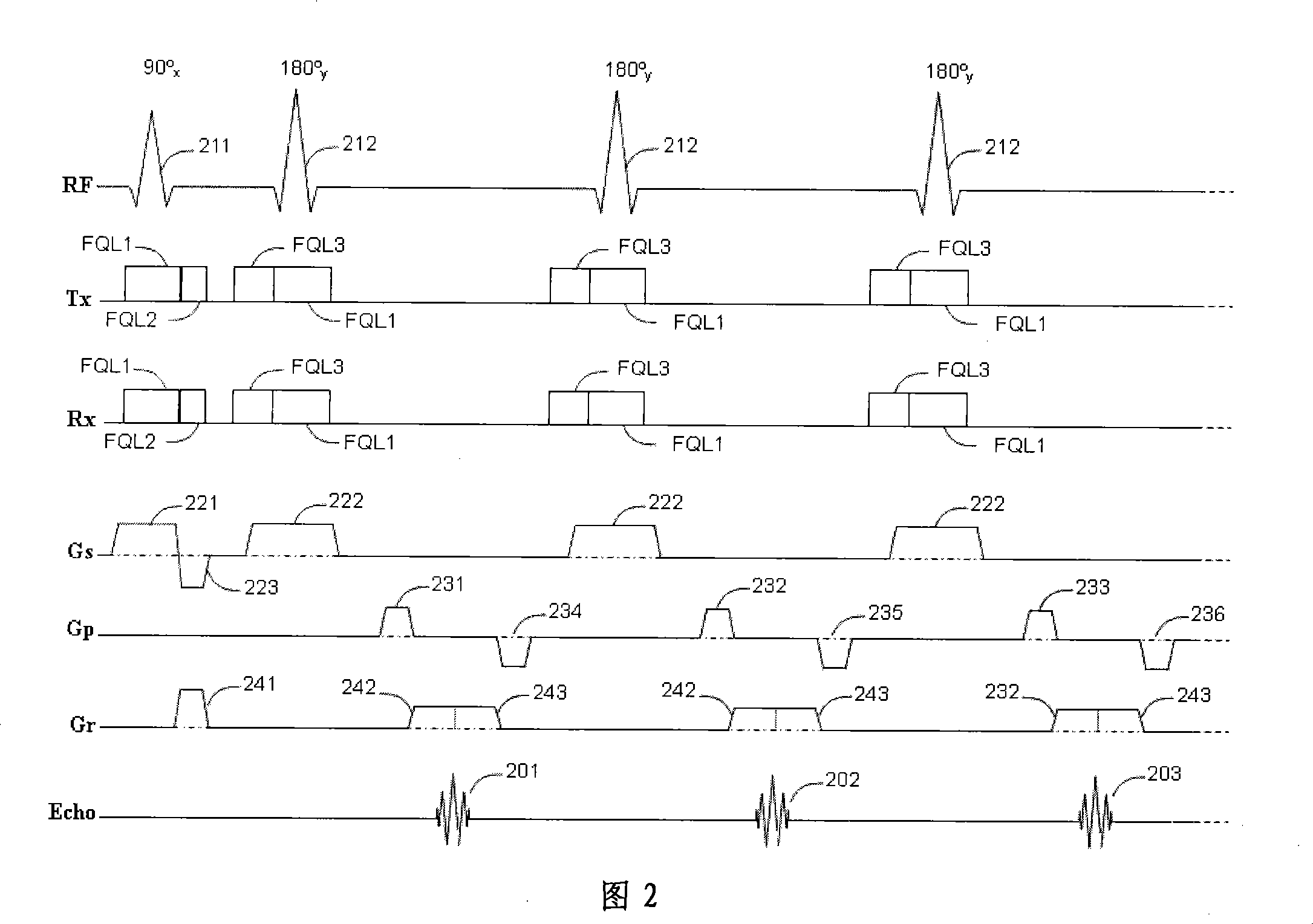
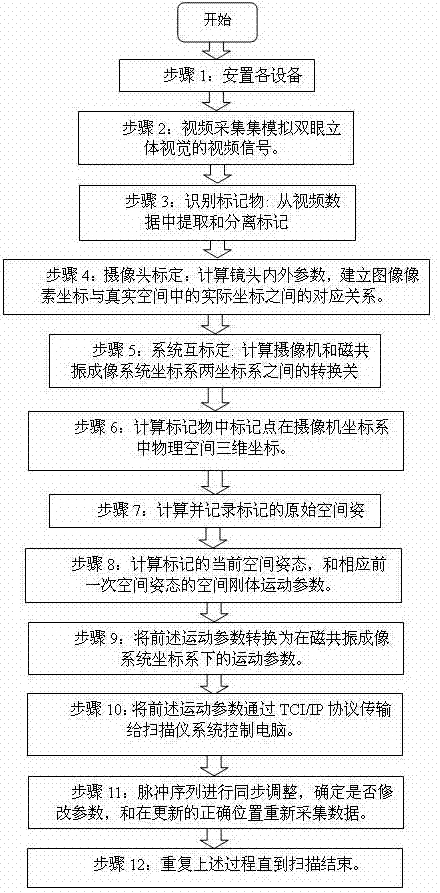
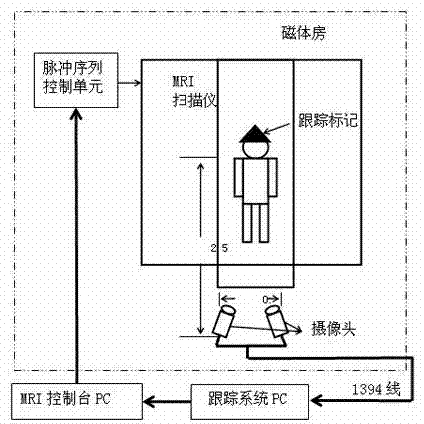
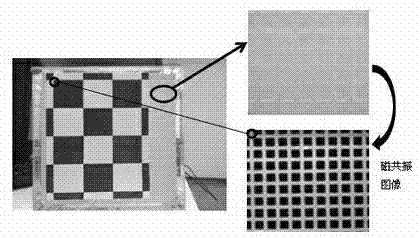
ActiveCN103315739AImprove resolutionAcquisition speed is fastImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringNuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic resonance imagery
The invention relates to the research field of magnetic resonance imaging and provides a method and a system for tracking a tested space attitude, dynamically adjusting imaging parameters of a scanner in real time and avoiding acquisition of motion artifact images in the acquisition process of magnetic resonance imaging data based on a computer vision target recognition and tracking technology. By adopting at least two video cameras for simulating stereoscopic vision of human eyes, a target is recognized, the tested space attitude is calculated, and space motion of the space attitude is monitored and judged. Once the motion occurs, parameters of the corrected space attitude are calculated immediately and are transmitted to the scanner through a transmission control protocol / internet protocol (TCP / IP), the imaging parameters of the scanner are adjusted in real time, the scanner is ensured to be capable of acquiring image data at a correct space position under the condition that the motion of the tested space attitude exists, and accordingly finally-obtained images are like images acquired under the condition that the motion of the tested space attitude does not occur. Therefore, acquired image data are stable and reliable in quality, the motion artifact is eliminated completely, and motion correction is not required in post-processing.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
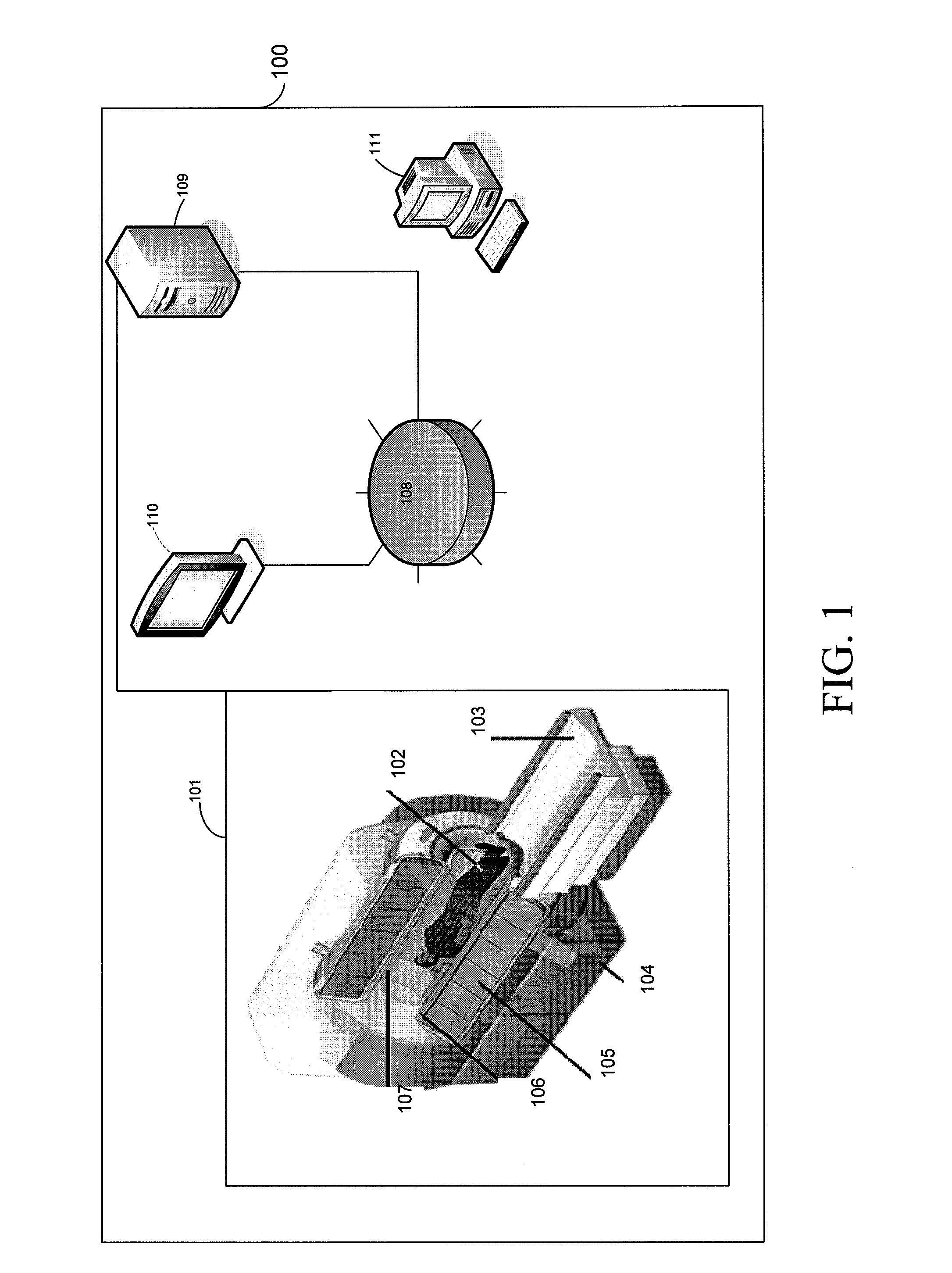
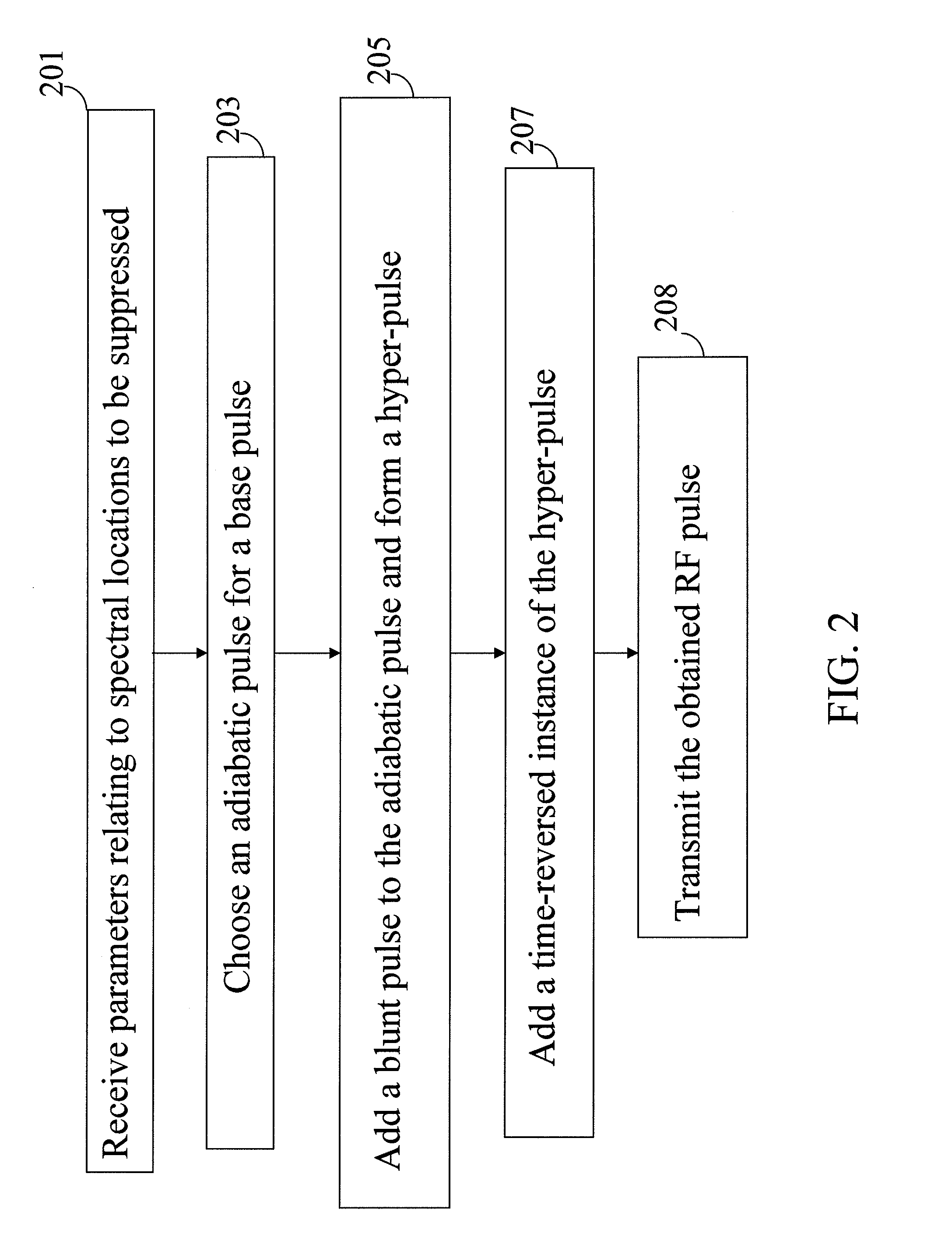
Adiabatic multi-band RF pulses for selective signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110144474A1Suppression problemDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMulti bandChemical composition
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a magnetic resonance imaging scanner comprising: a main magnet providing a substantially uniform main magnetic field B0 for a subject under observation; and a radio frequency (RF) coil configured to irradiate a radio frequency (RF) pulse into a region of interest of the subject under observation, wherein the RF pulse comprises a base pulse comprising an adiabatic pulse having a first bandwidth time product (BWTP), wherein the RF pulse selectively suppresses magnetic resonance signals from more than one chemical component or more than one spatial region within the region of interest of the subject under observation, and wherein the adiabatic pulse is characterized by an amplitude modulation function and a frequency modulation function.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
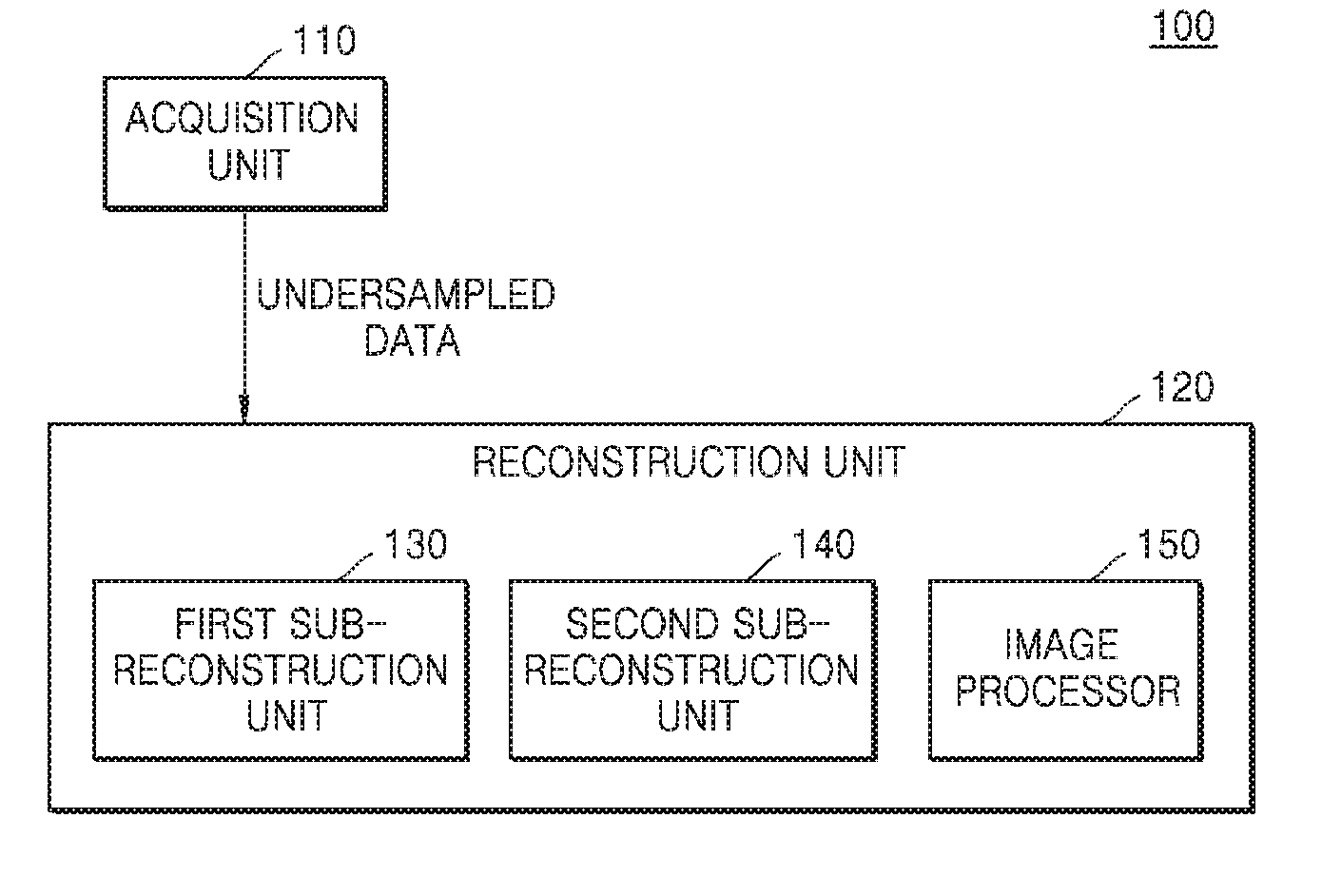
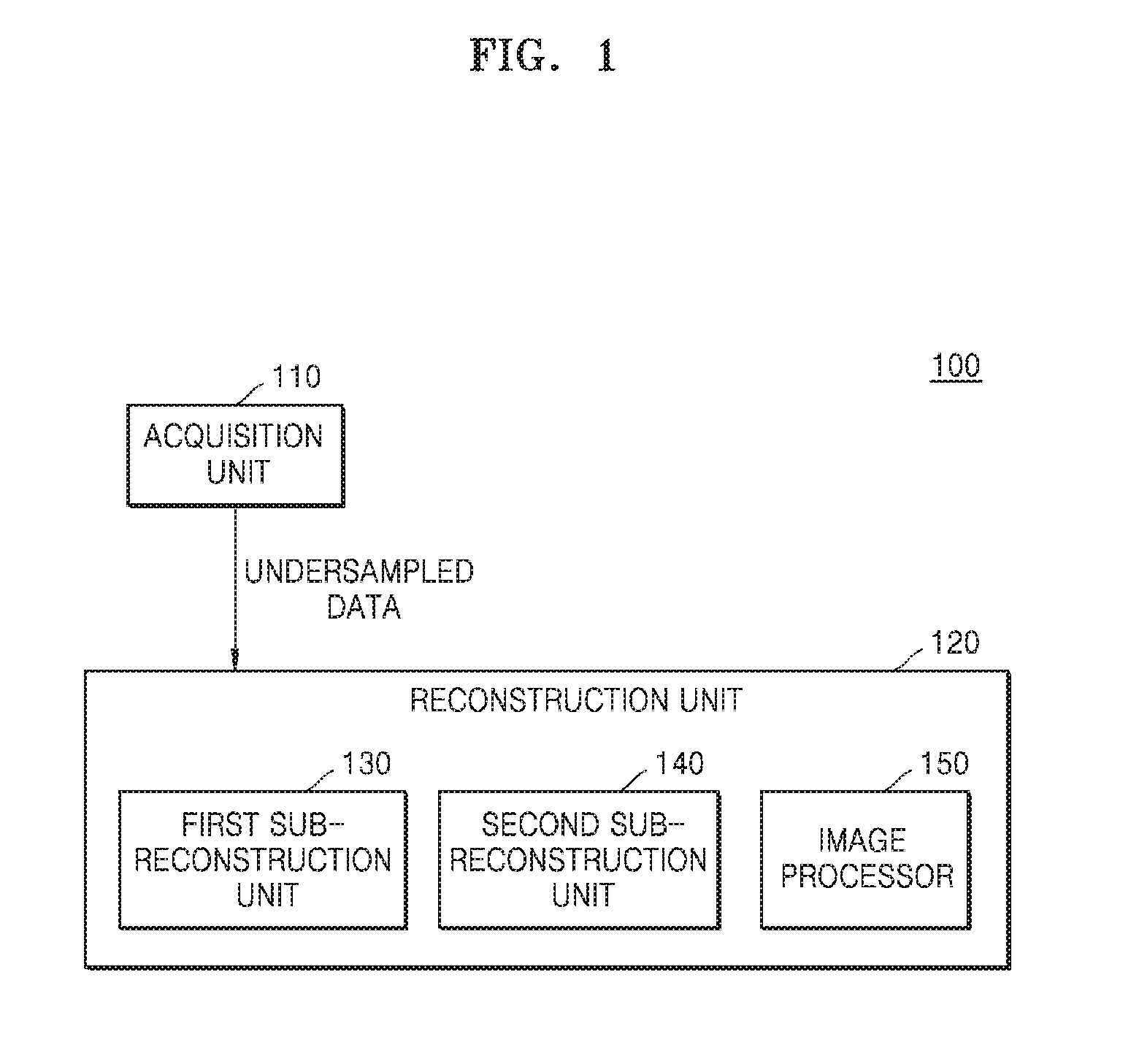
Magnetic resonance imaging device and method for generating magnetic resonance image
ActiveUS20170053402A1Increase speedAccelerate the computational algorithmsImage enhancementMedical imagingDictionary learningFrequency spectrum
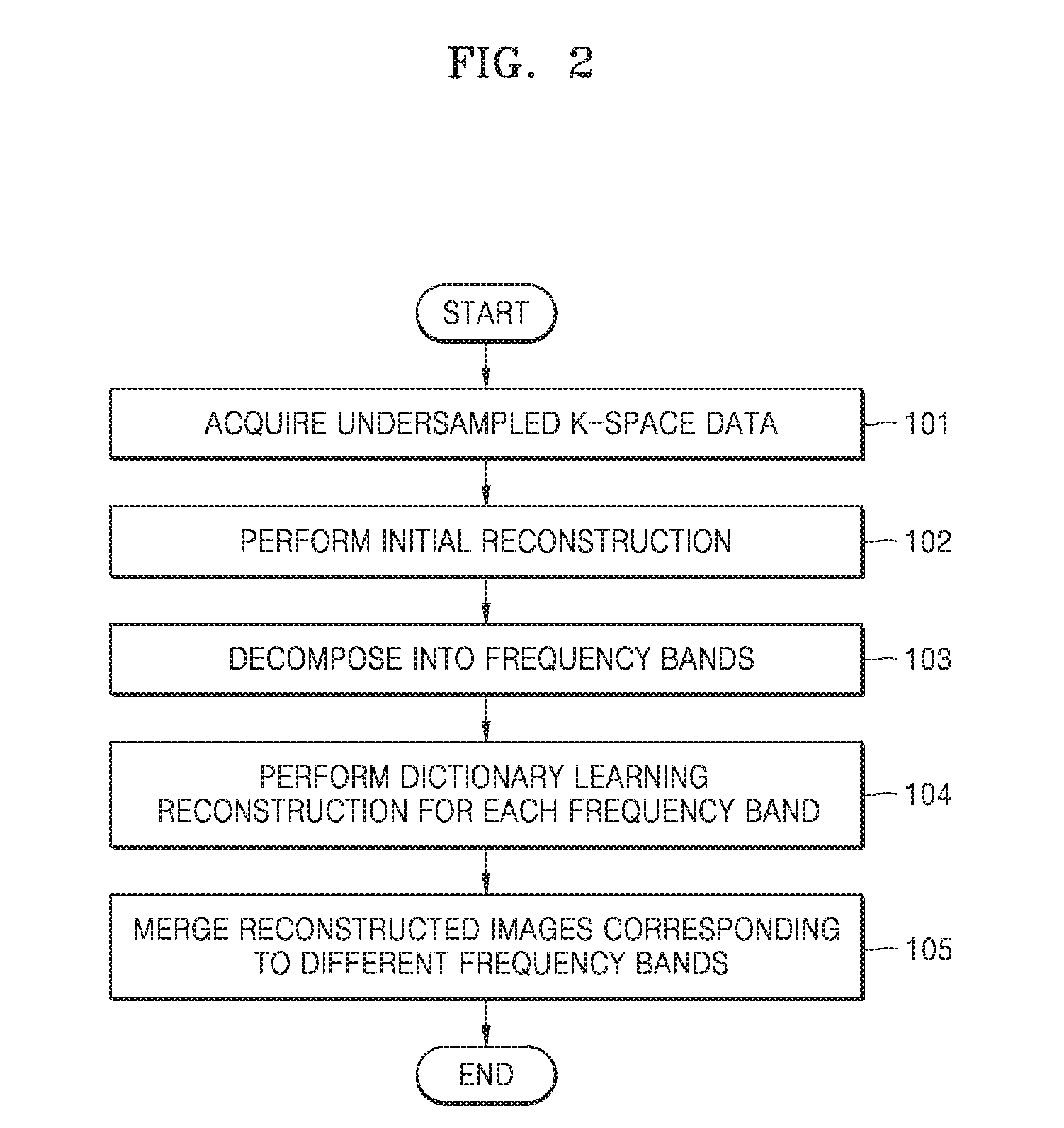
Provided is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus including an acquisition unit configured to acquire an undersampled spectrum in a k-space and a reconstruction unit configured to generate a target image based on the undersampled spectrum, wherein the reconstruction unit includes: a first sub-reconstruction unit configured to perform initial reconstruction on data corresponding to unsampled positions in the k-space by using a Split Bregman algorithm or approximate sparse coding; a second sub-reconstruction unit configured to decompose the initially reconstructed spectrum in the k-space into multiple frequency bands to thereby generate a plurality of individual spectra and perform dictionary learning reconstruction on images respectively corresponding to the decomposed multiple frequency bands by alternating sparse approximation and reconstructing of measured frequencies; and an image generator configured to generate a target image by merging together the reconstructed images respectively corresponding to the multiple frequency bands.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
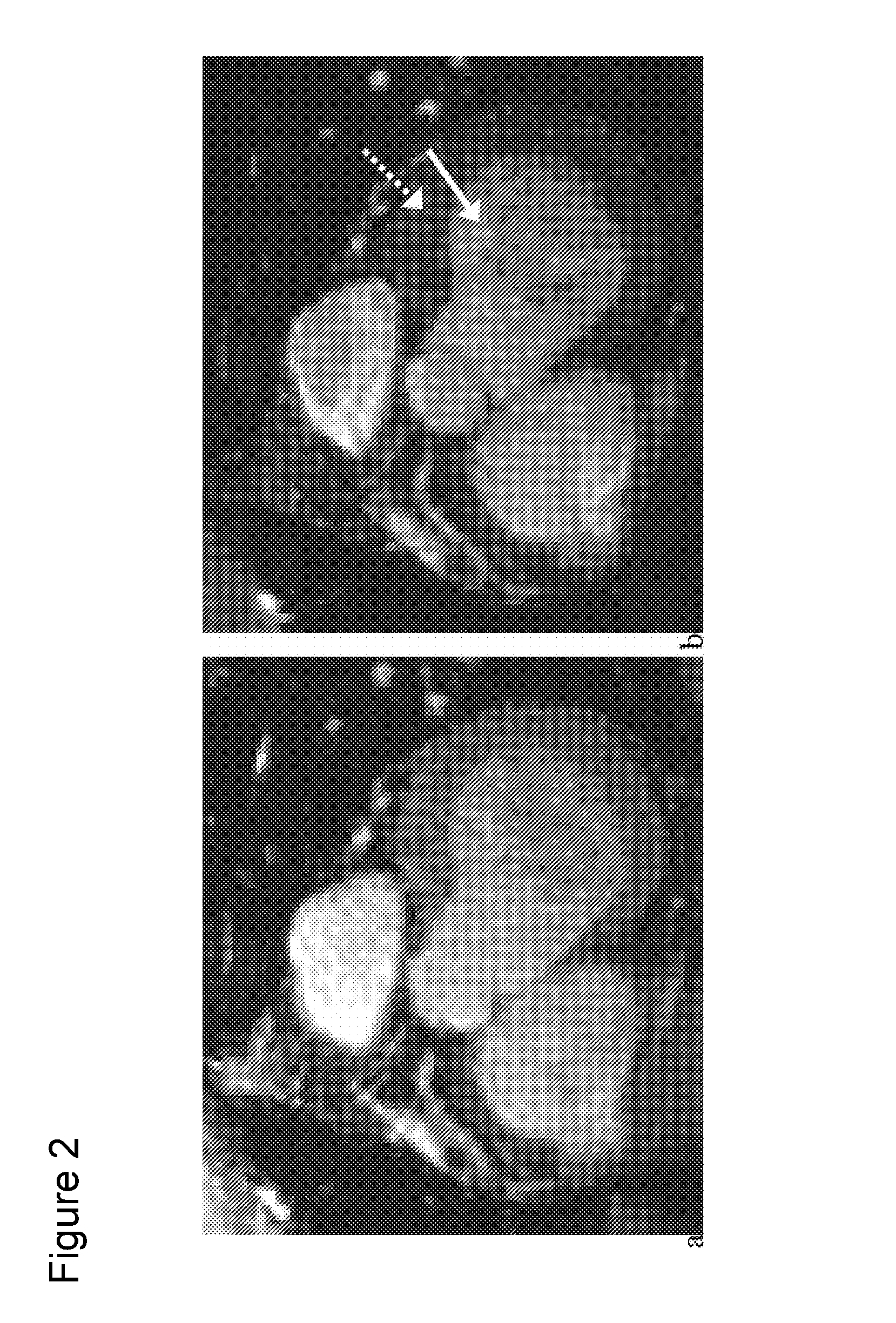
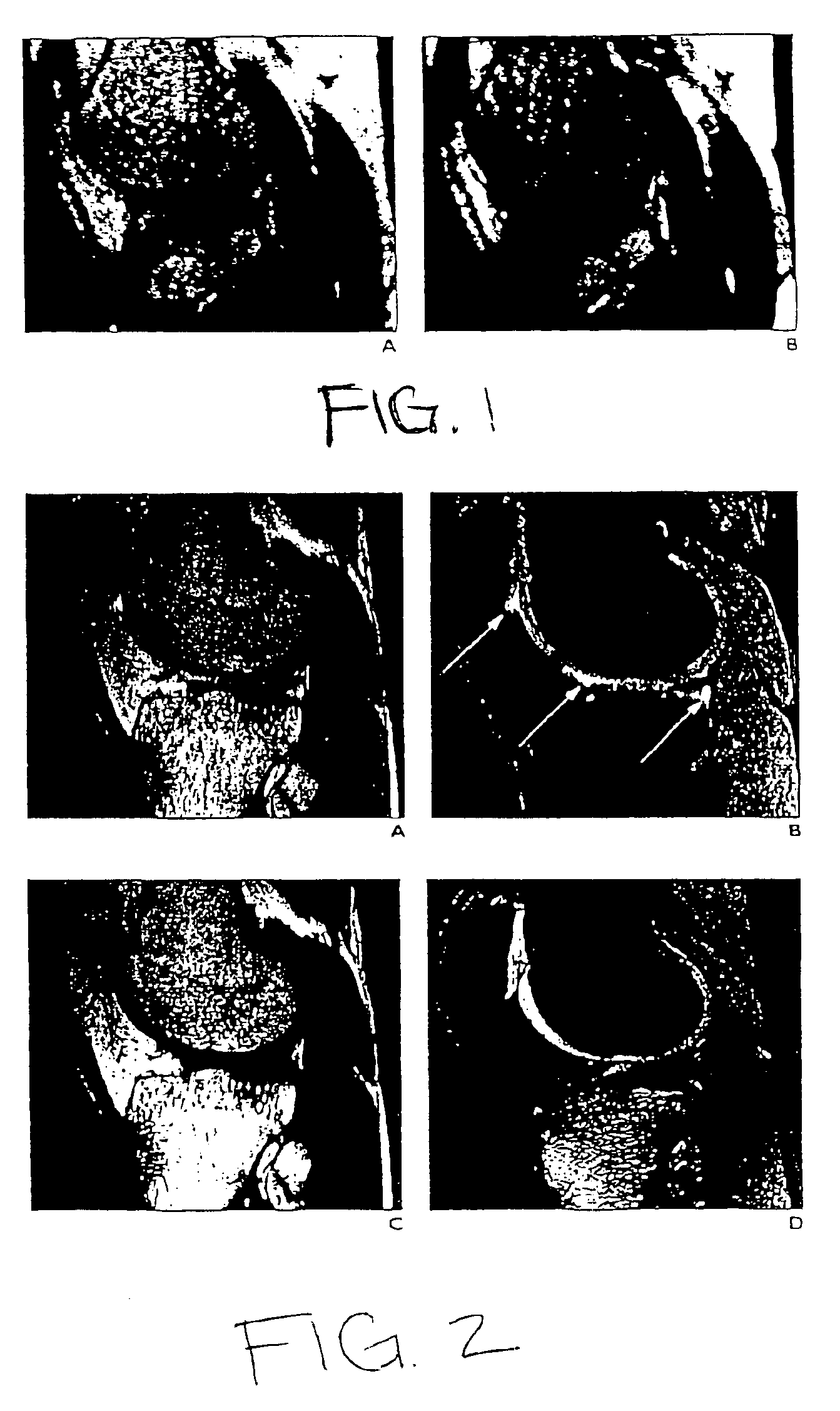
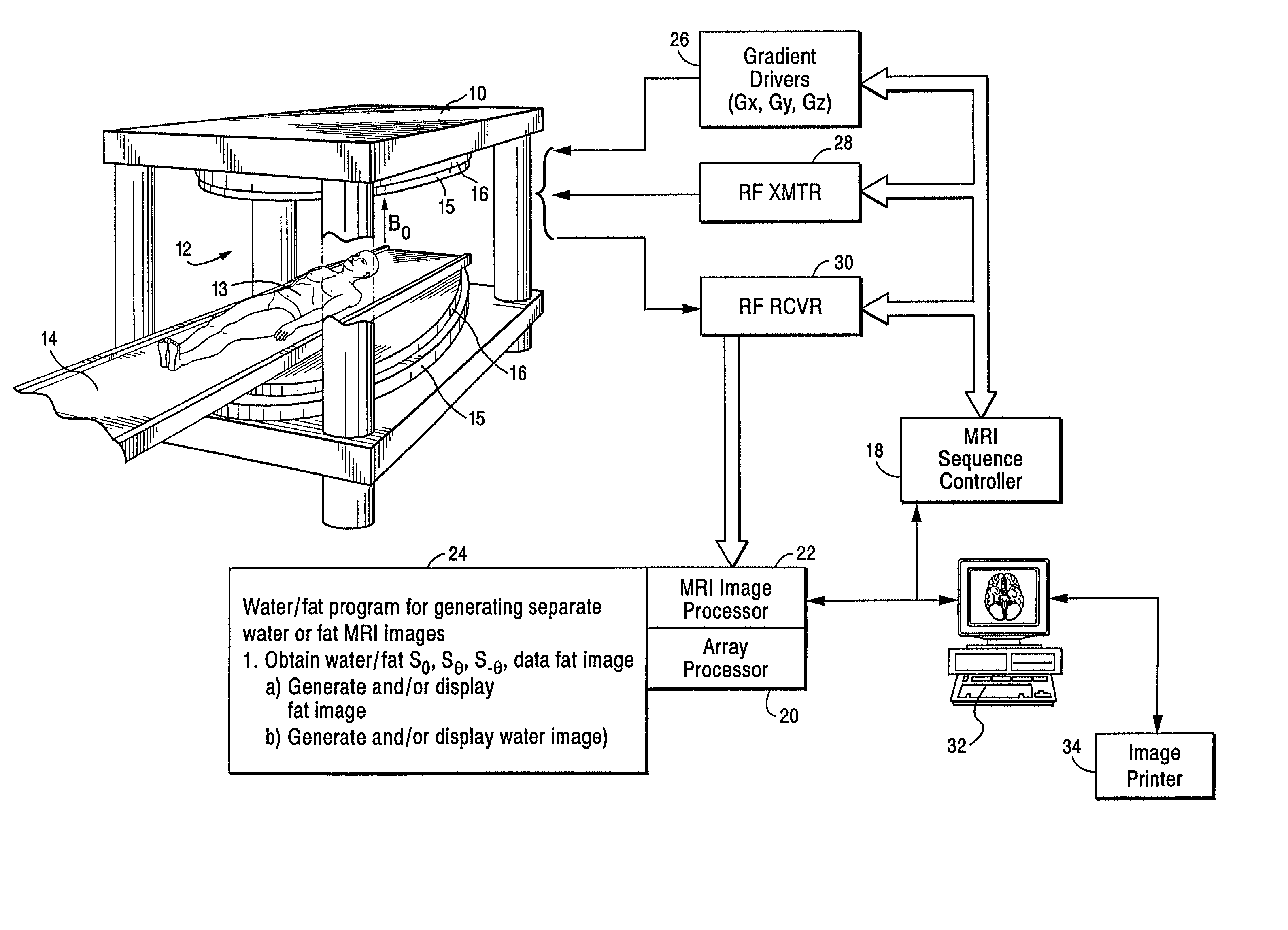
Separation and identification of water and fat MR images at mid-field strength with reduced T2/T2* weighting
InactiveUS20030060697A1Eliminate the effects ofCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringField strengthMr images
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method is disclosed for generating and identifying water and fat separated MR images. Image data is first acquired to obtain two echo images with the water and fat signals orthogonal in the first echo image, and parallel / anti-parallel in the second echo image. The effect of background field inhomogeneties are removed, and water and fat images are separated from each other. The separated water and fat images are identified according to the difference of their precessing frequencies.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Embolism material composition as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN103550834AGood biocompatibilityEasy to checkSurgeryX-ray constrast preparationsBiocompatibility TestingX ray image
The invention provides an embolism material composition as well as preparation method and use thereof, the embolism material composition is prepared from reactant raw materials, wherein the reactant raw materials comprise a biocompatibility material, a roentgenopaque substance and a magnetic resonance imaging substance, the roentgenopaque substance and the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) substance are covered by the biocompatibility material. The embolism material composition not only can be directly detected by an X-ray image device, but also can be directly detected by the MRI, so that a doctor can select a detection method according to self condition of a patient and the medical device condition.
Owner:HYGEA MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
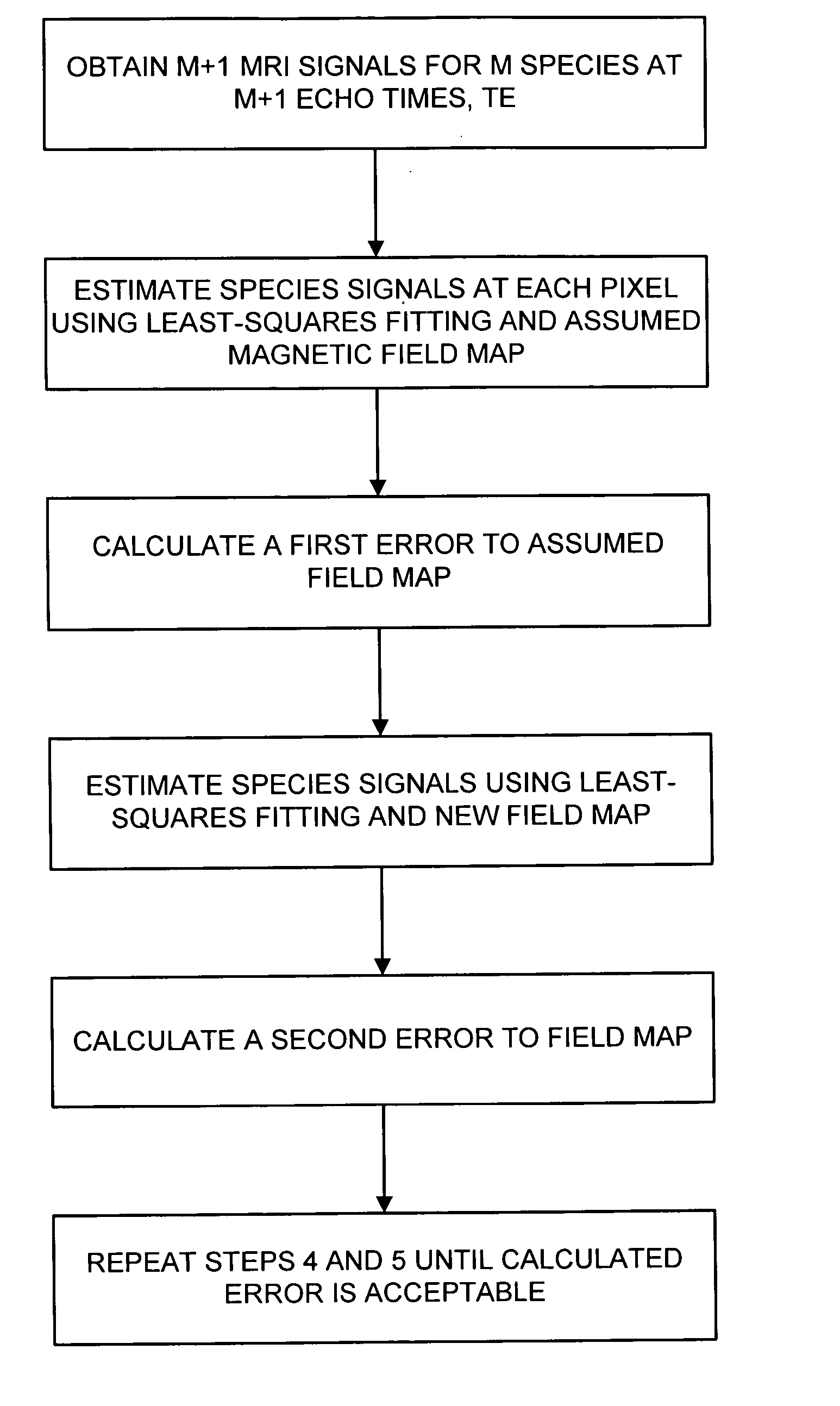
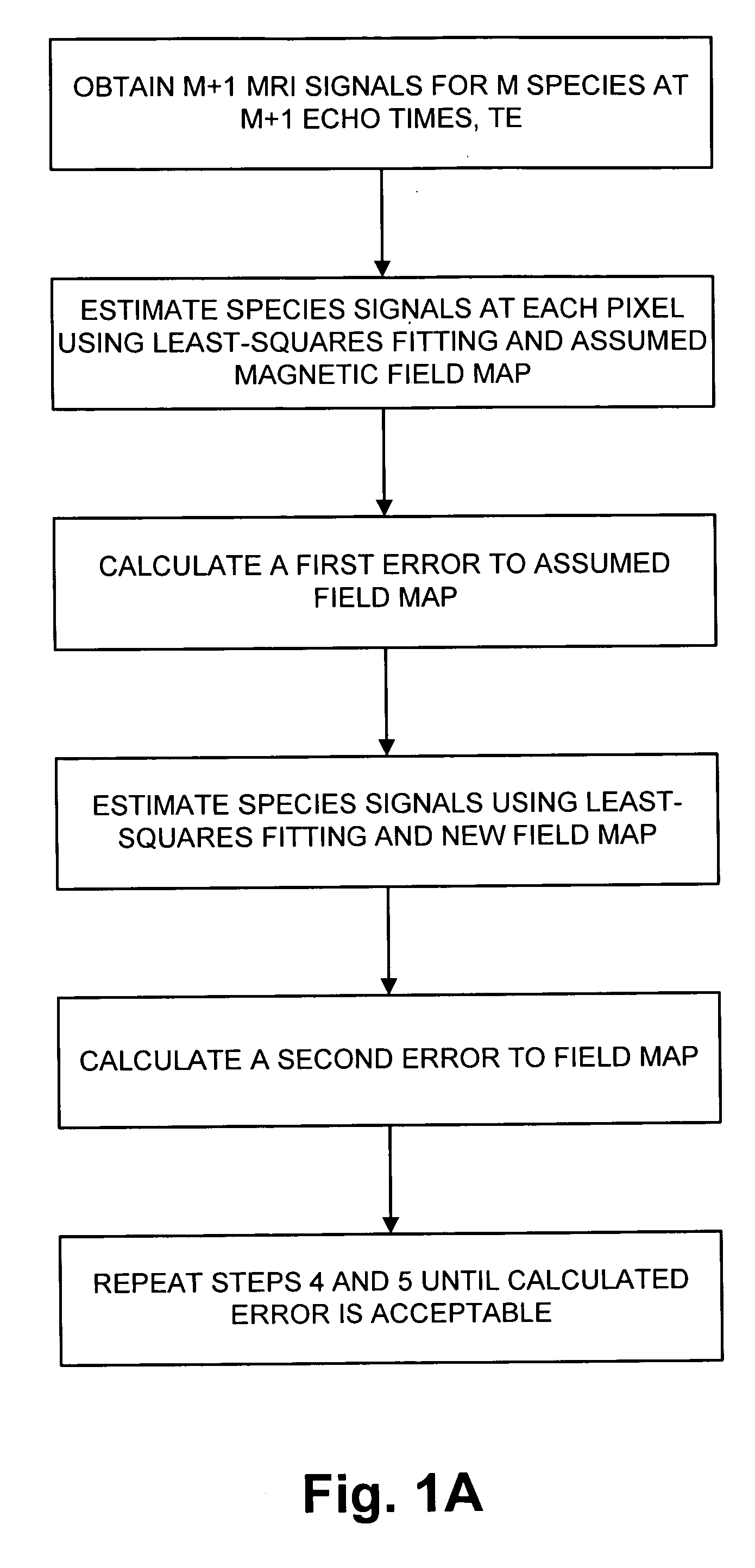
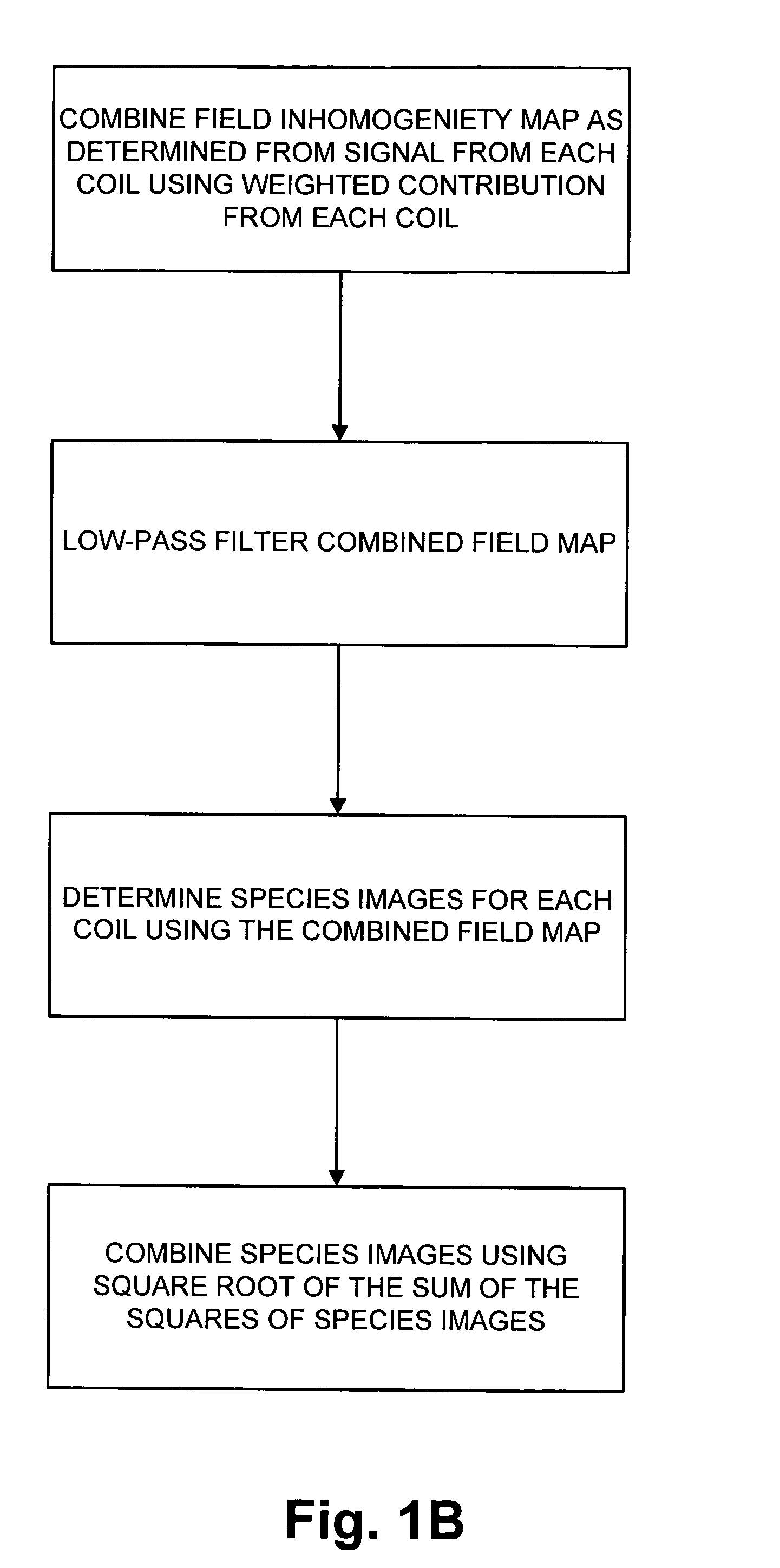
Magnetic resonance imaging of different chemical species in a system having magnetic field heterogeneities
ActiveUS20050085713A1Good estimateImprove Noise PerformanceDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsShort echo timeSource image
A multi-point chemical species (e.g., water, fat) separation process which is compatible with rapid gradient echo imaging such as SSFP uses an iterative least squares method that decomposes water and fat images from source images acquired at short echo time increments. The single coil algorithm extends to multi-coil reconstruction with minimal additional complexity.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
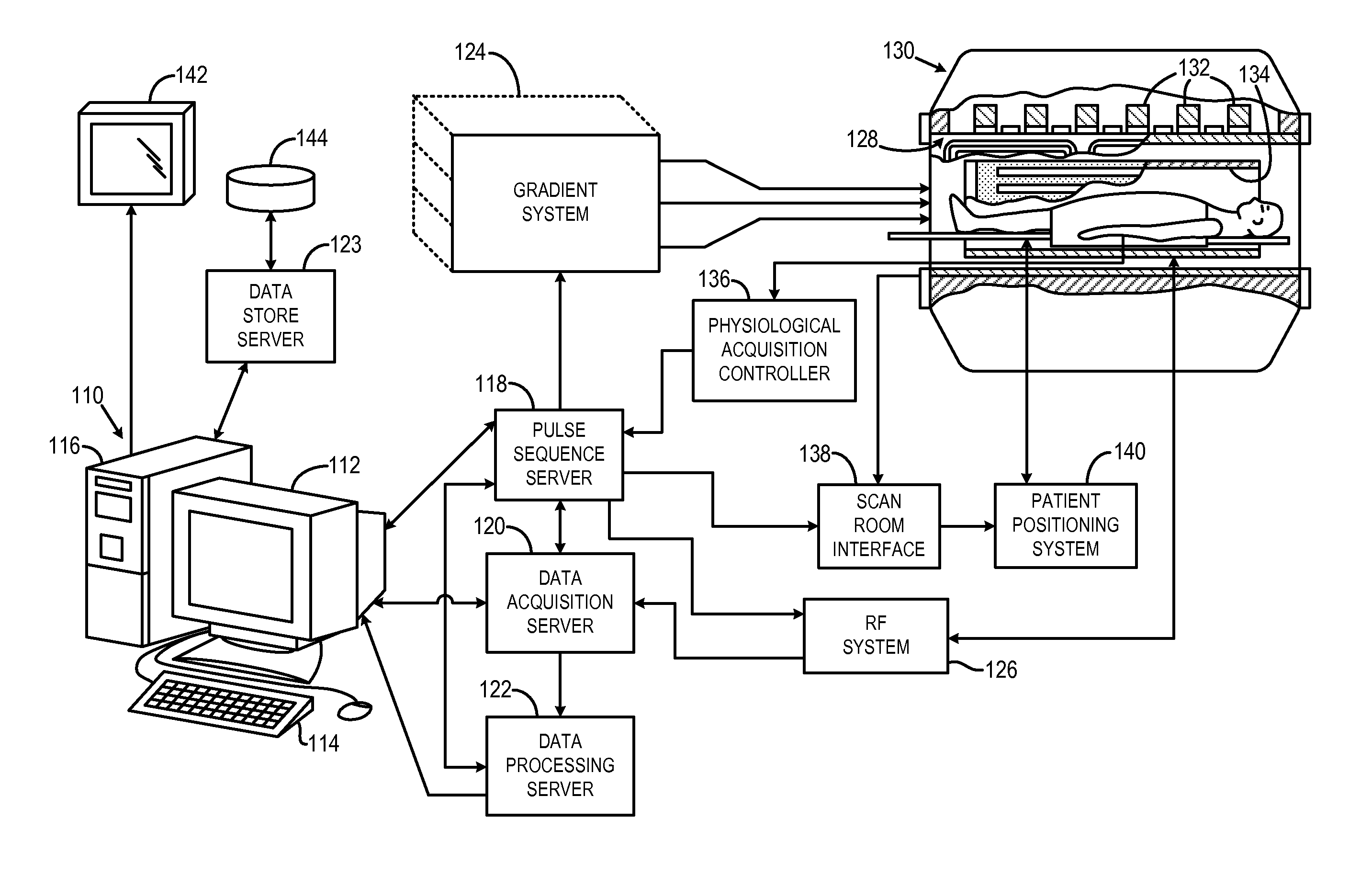
Systems and methods for landmark correction in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20130279779A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionMedicineMR - Magnetic resonance
Systems and methods for landmark correction in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are provided. One method includes acquiring at least one calibration image or at least one localizer image of an object, identifying in the calibration or localizer images a region of the object as a reference point, wherein the reference point defines a landmark position. The method further includes determining an offset between an initial landmark position and the identified landmark position. The method also includes using the determined offset for MRI.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
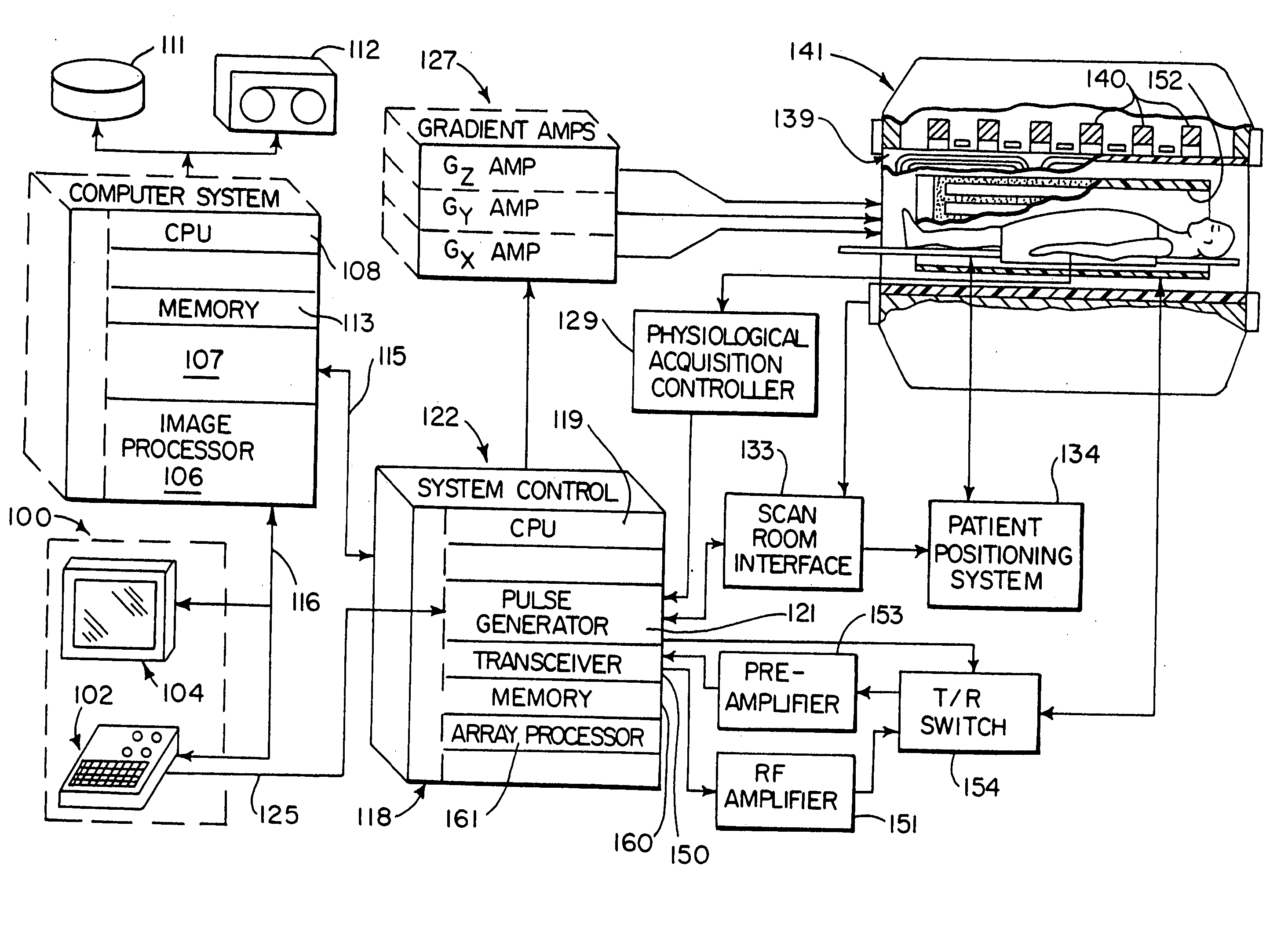
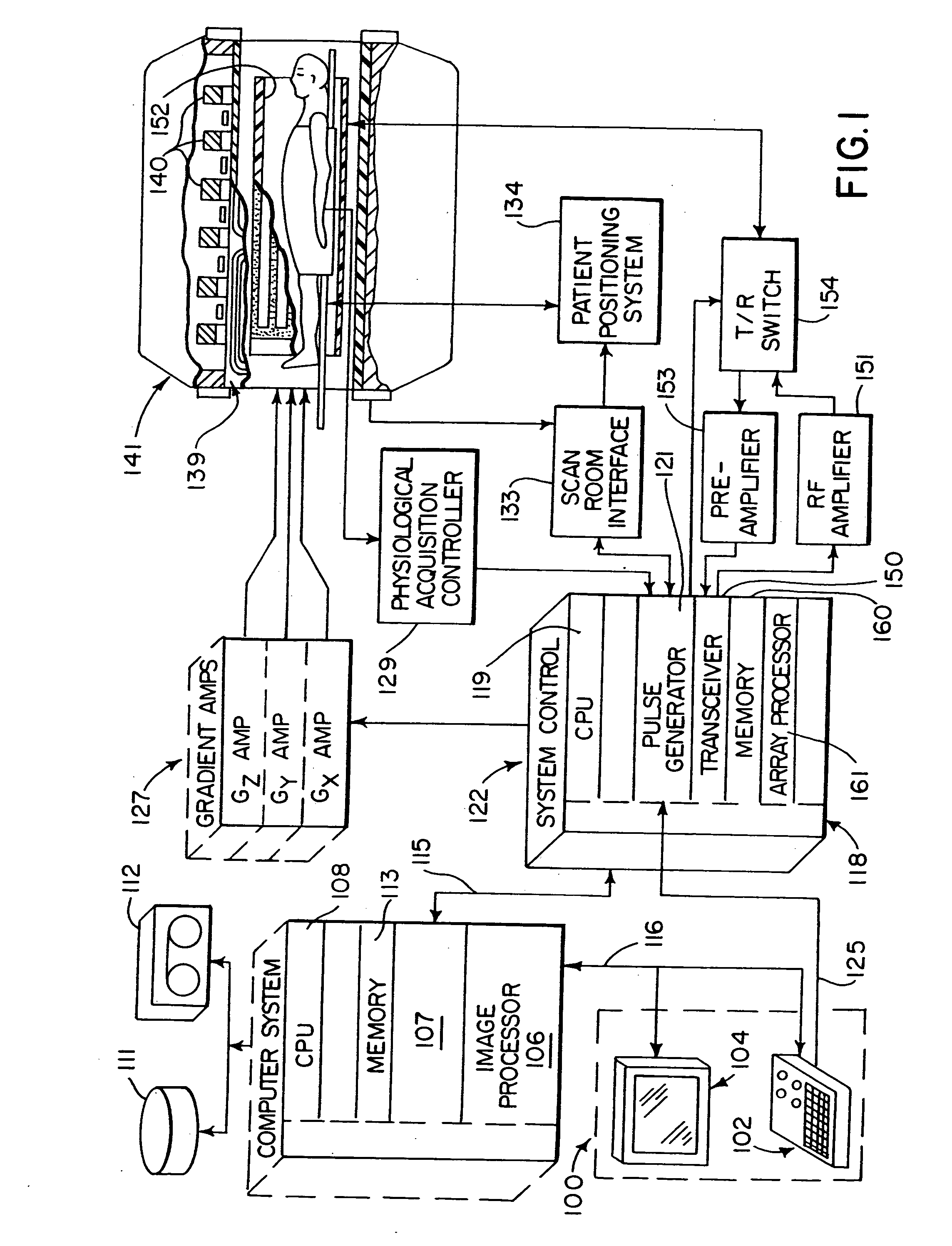
InactiveUS7071693B2Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectron flowField coil
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus generates an MR signal from an object to be examined by applying a gradient field pulse generated by a gradient field coil and a high-frequency magnetic field pulse generated by a high-frequency coil to the object in a static field generated by a static field magnet, and reconstructs an image on the basis of the MR signal. The gradient field coil is housed in a sealed vessel. Numerous techniques are disclosed to reduce adverse effects of vibrations caused by rapidly changing gradient coil currents. By judicious use of non-conducting connection components between gantry components at some joint portions requiring electrical contact and at some other portions not requiring electrical contact, the generation of adverse B waves, and / or induced electron flow in response to physical vibration between joint components can be reduced.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Separation and identification of water and fat MR images at mid-field strength with reduced T2/T2* weighting
InactiveUS6603990B2Reducing T.sub.2 and T.sub.2 * weightingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringMr imagesMR - Magnetic resonance
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method is disclosed for generating and identifying water and fat separated MR images. Image data is first acquired to obtain two echo images with the water and fat signals orthogonal in the first echo image, and parallel / anti-parallel in the second echo image. The effect of background field inhomogeneties are removed, and water and fat images are separated from each other. The separated water and fat images are identified according to the difference of their precessing frequencies.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Method for monitoring thermal heating during magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20060064002A1Accurate detectionReduce scan timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicinePulse sequence
The SAR exposure of a subject undergoing an MRI examination is measured by acquiring a thermal image that indicates that temperature increase caused by the SAR exposure. This measurement may be used in a prescan process to adjust the SAR load produced by a prescribed imaging pulse sequence, and it can be used during the scan to adjust the SAR load produced by the prescribed imaging pulse sequence.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com