Patents
Literature
38 results about "Fat saturation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
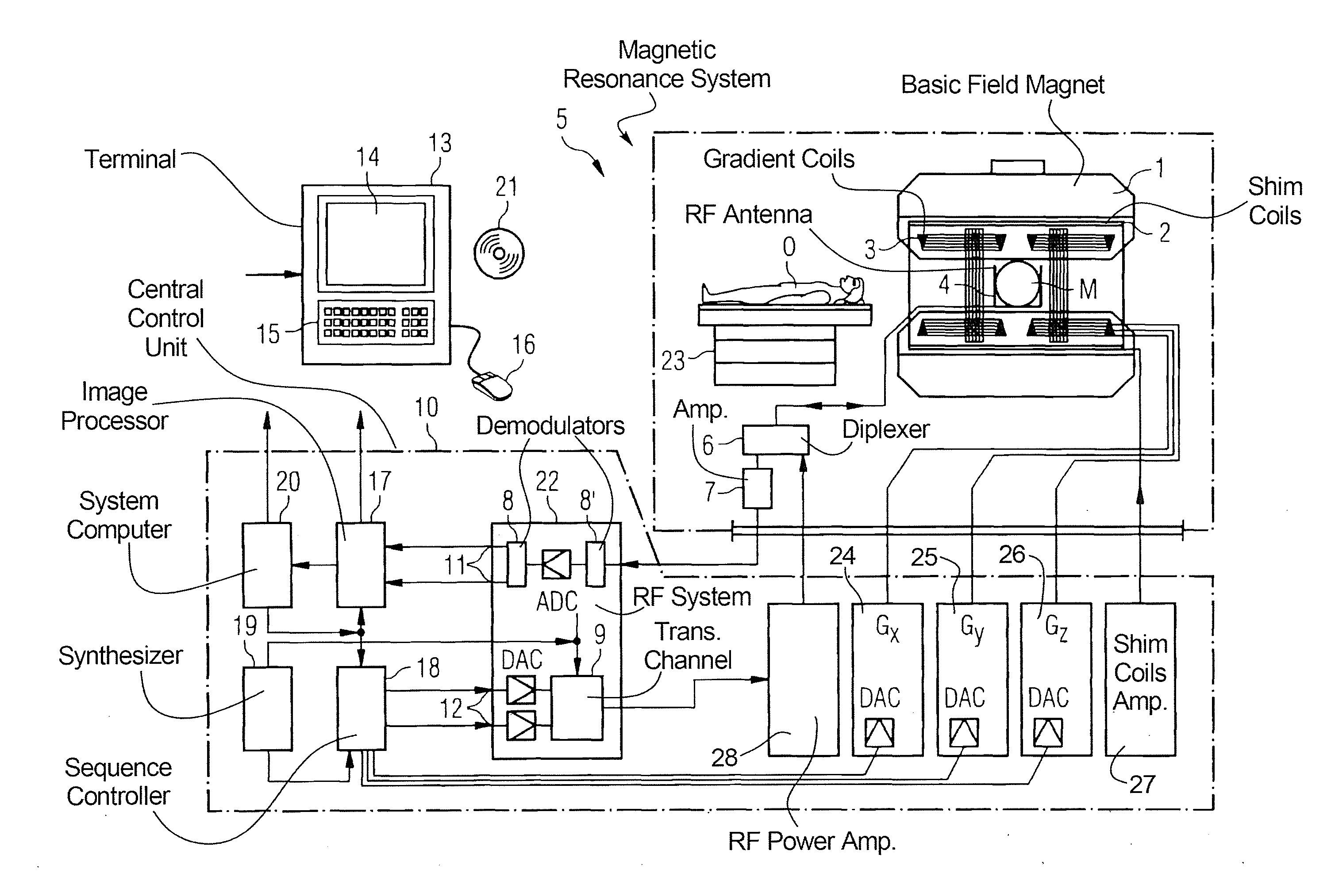
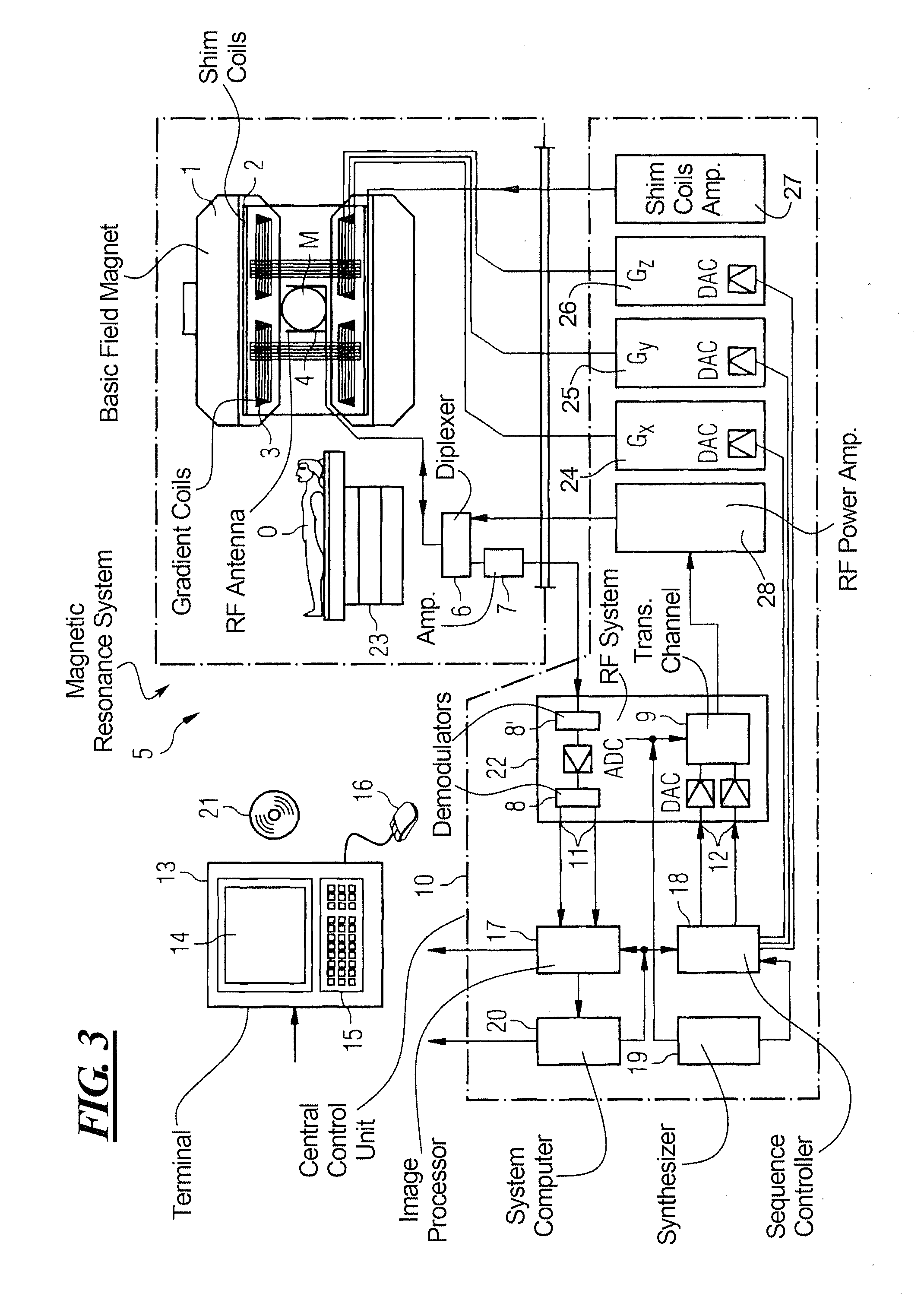
Magnetic resonance imaging concepts
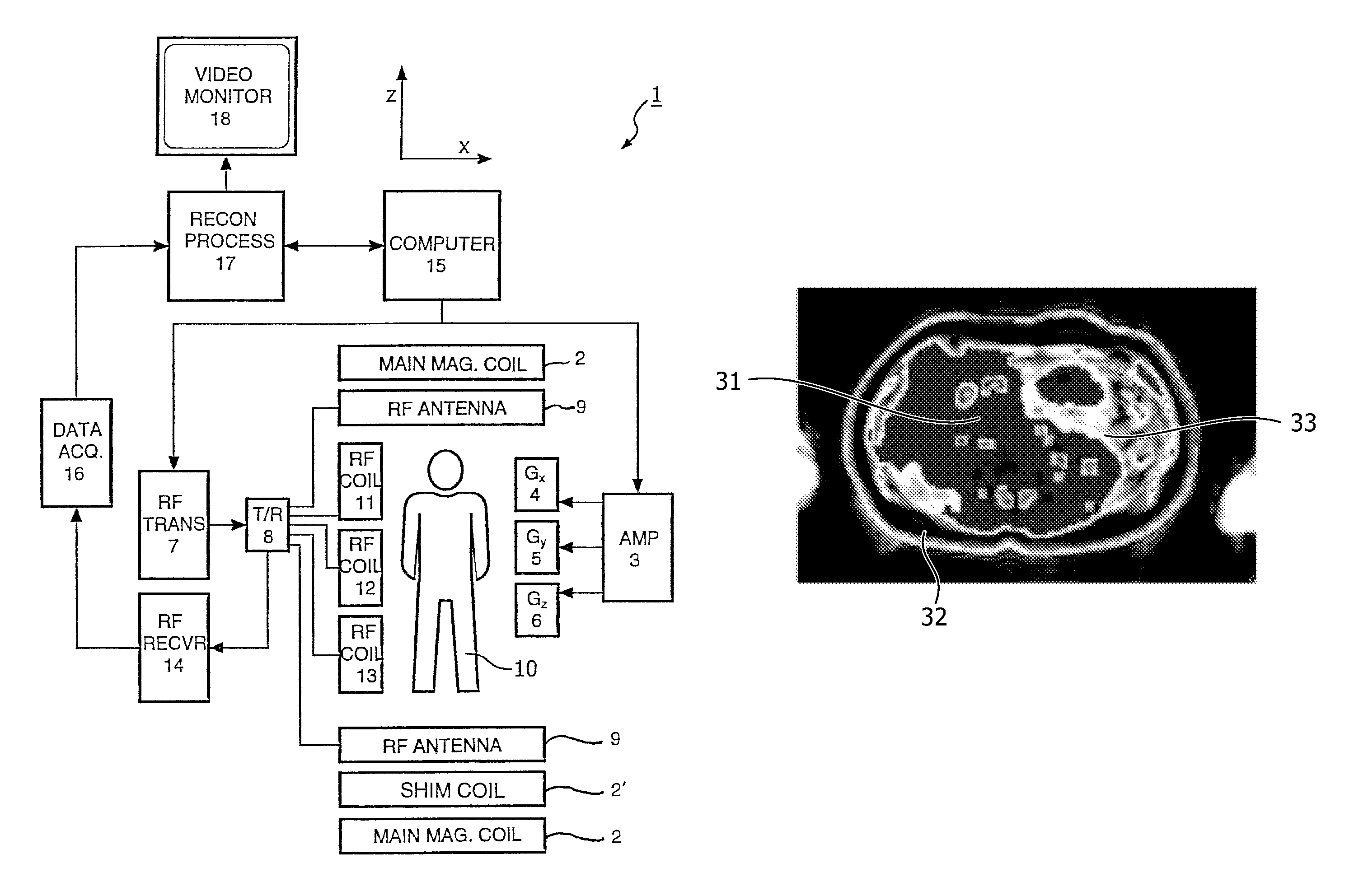
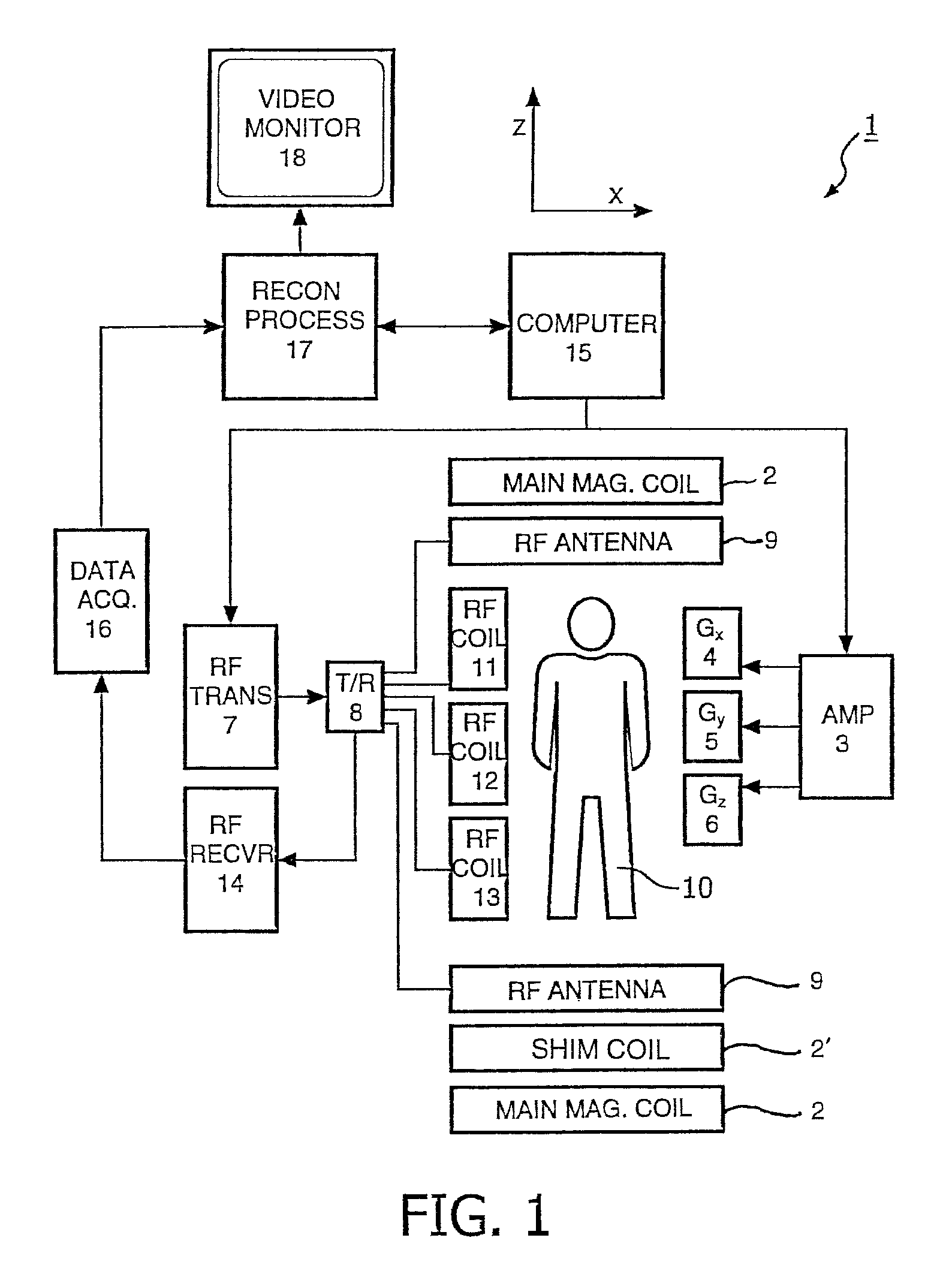
ActiveUS7941204B1Accurate estimateEffective motion suppressionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPresent methodParallel imaging
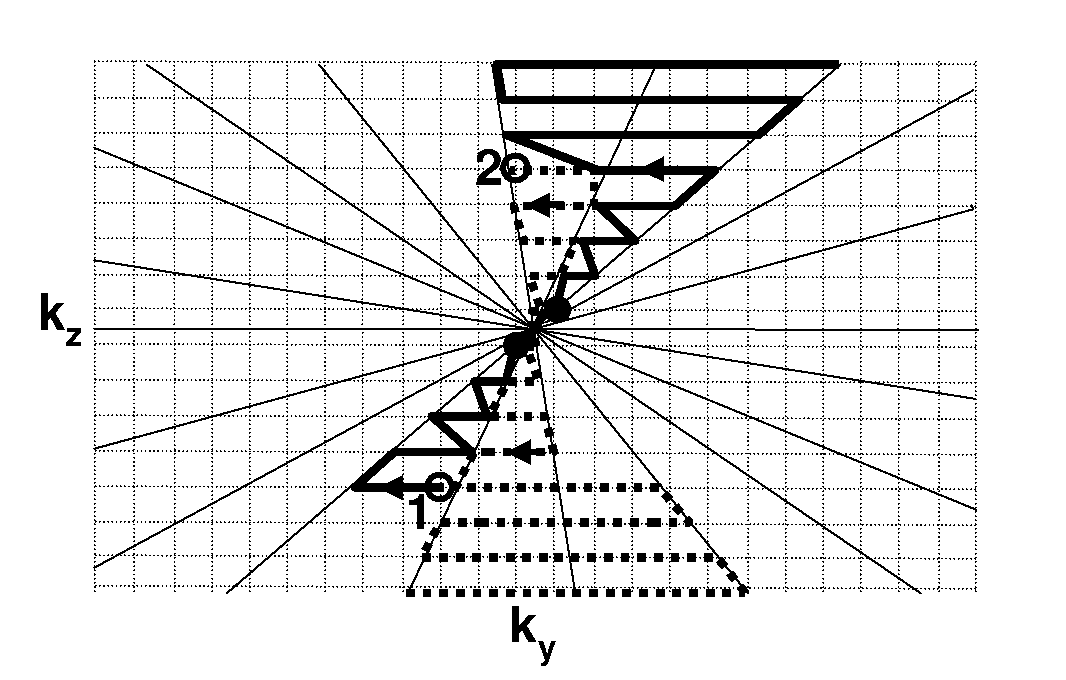
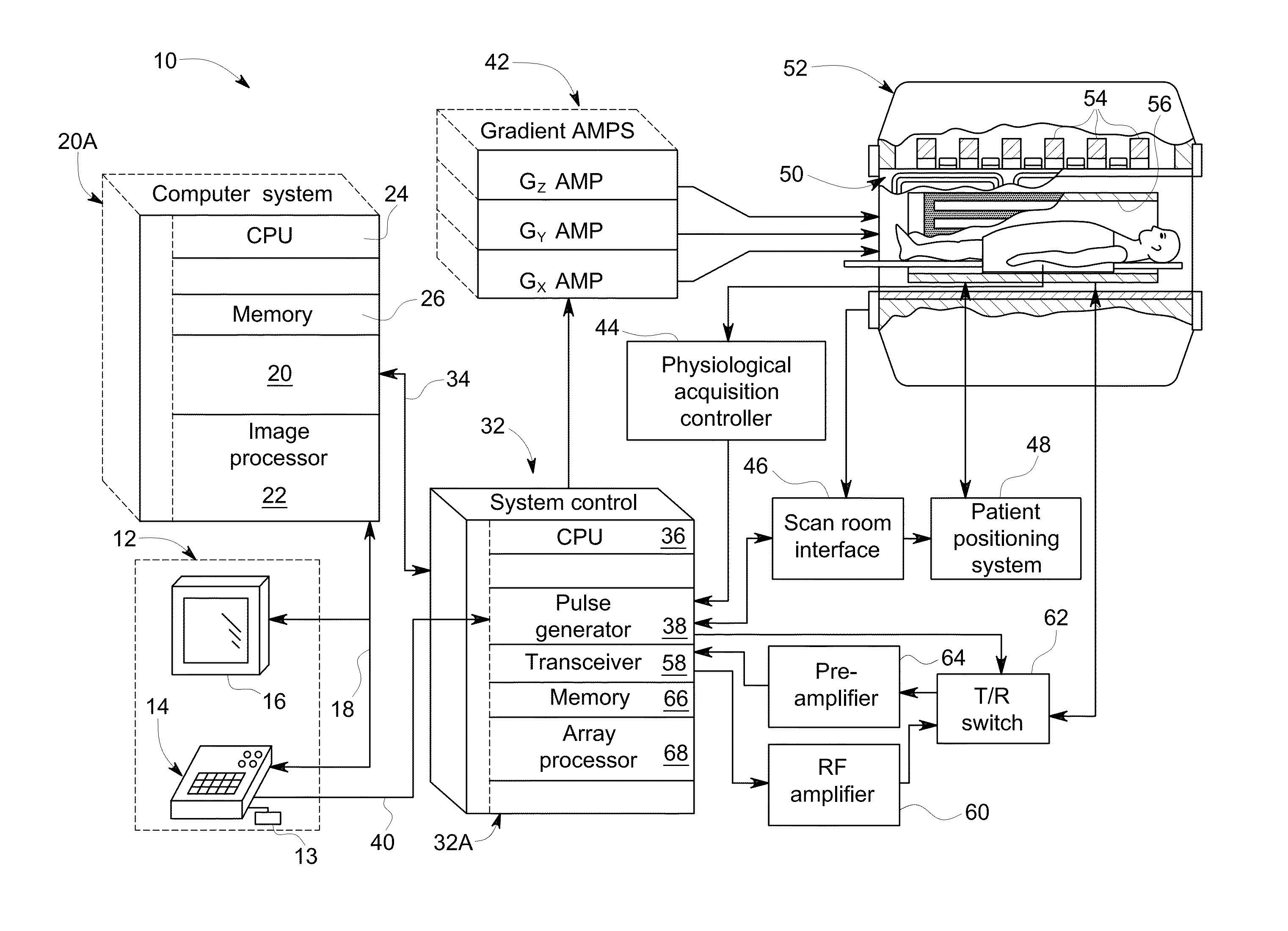
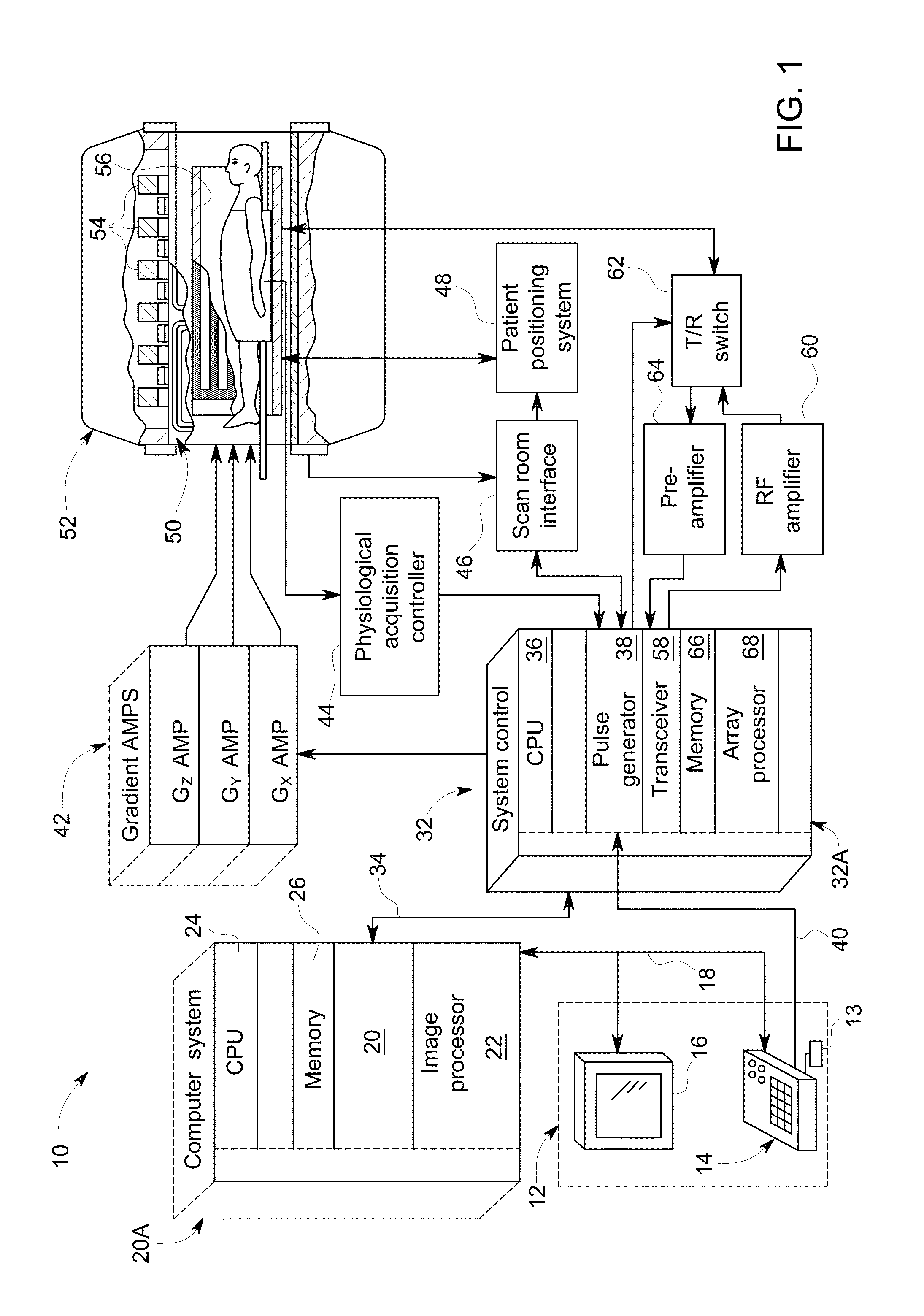
Methods of acquiring magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data for angiography. The present invention includes novel magnetization preparation schemes where the navigator and fat saturation pulses are executed in steady state after the preparatory pulses in order to minimize the delay between the magnetization preparation and the image echoes. The present invention also provides for improved methods of contrast-enhanced MRI where data are collected along non-linear trajectories through k-space and may also involve novel view ordering. In addition, the present methods employ novel motion corrections that minimize motion artifacts. The present invention further provides novel methods of self-calibrated sensitivity-encoded parallel imaging that allow for accurate and rapid scanning of subjects.
Owner:NGUYEN THANH +4
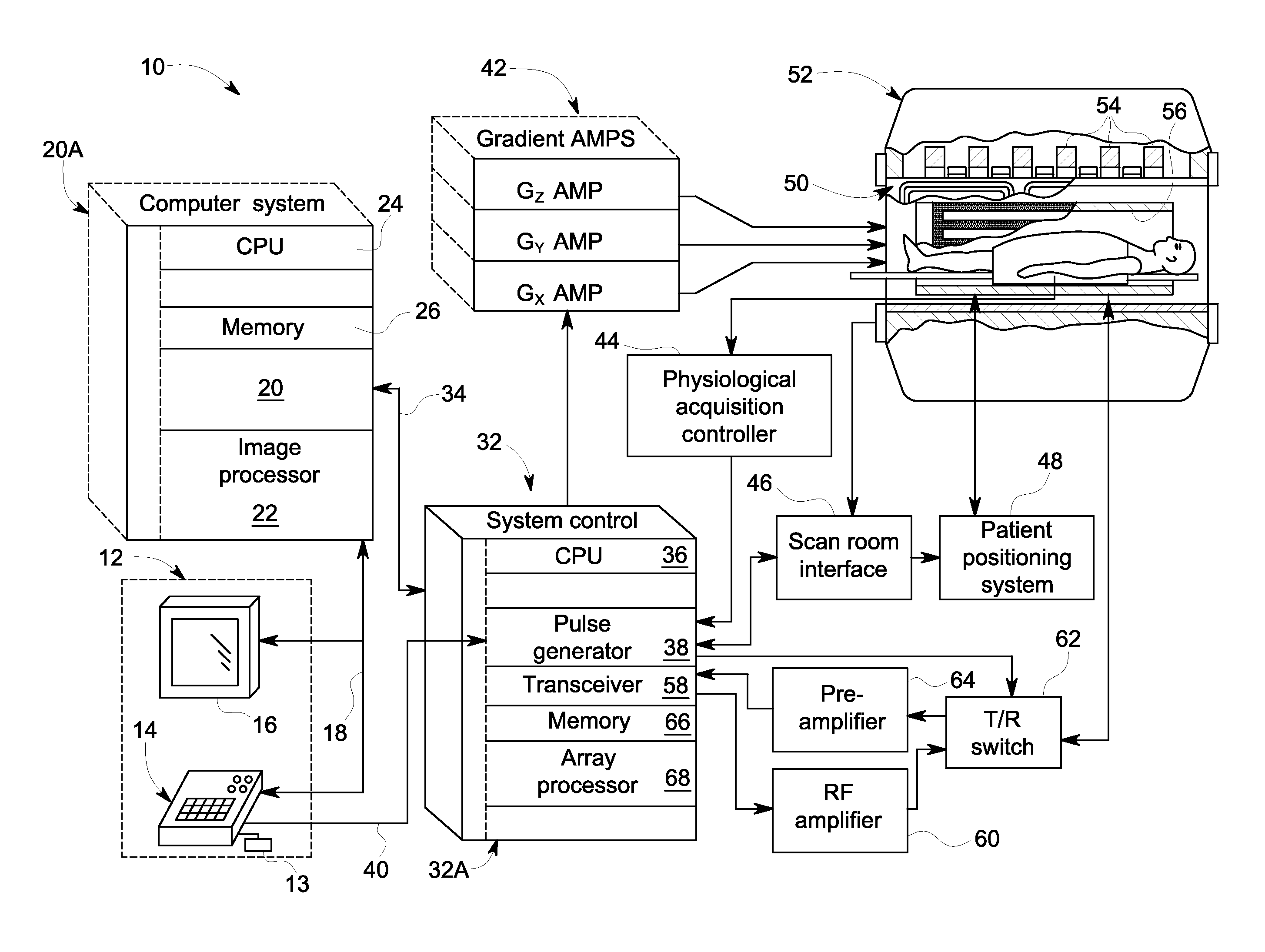
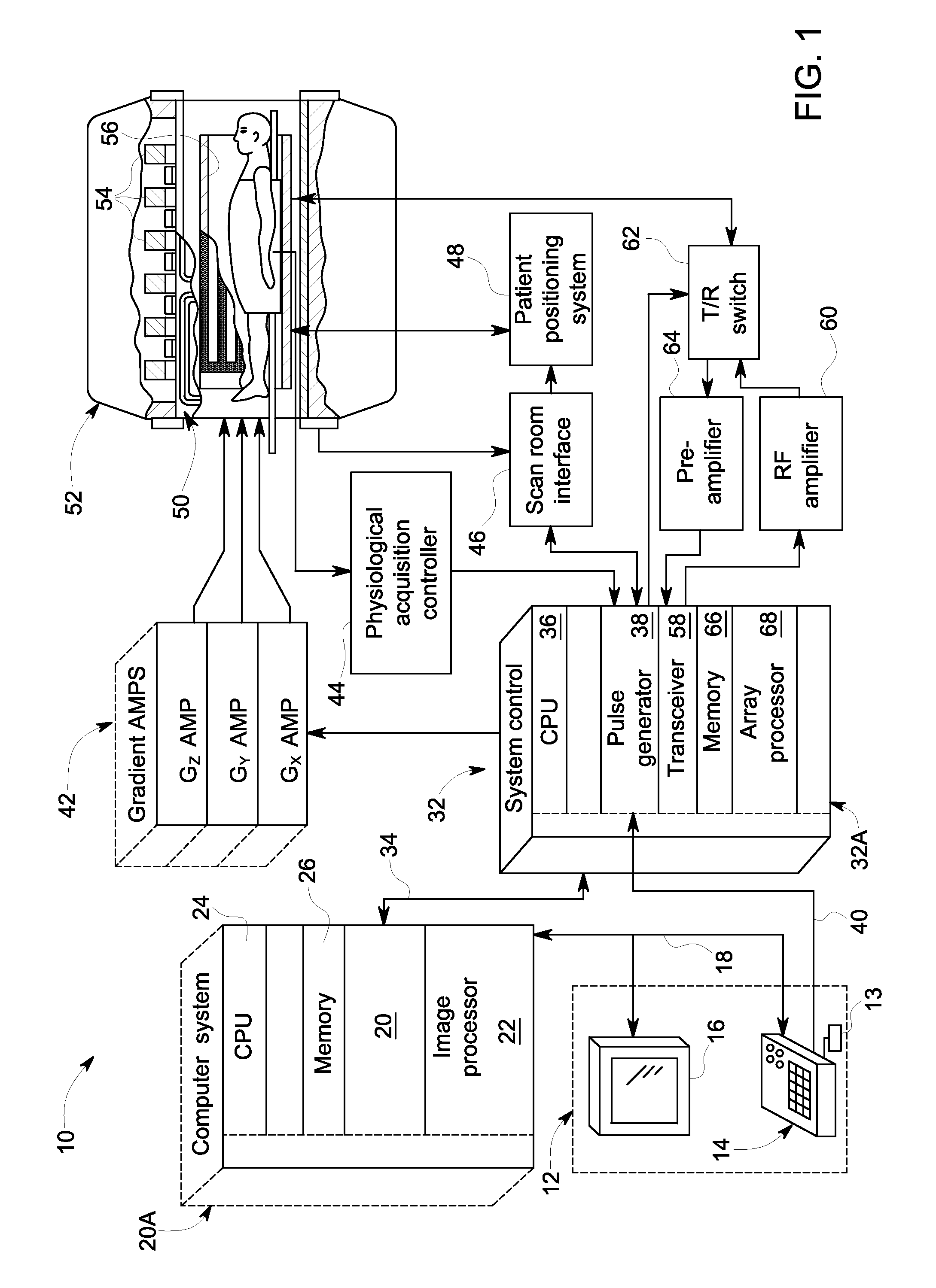
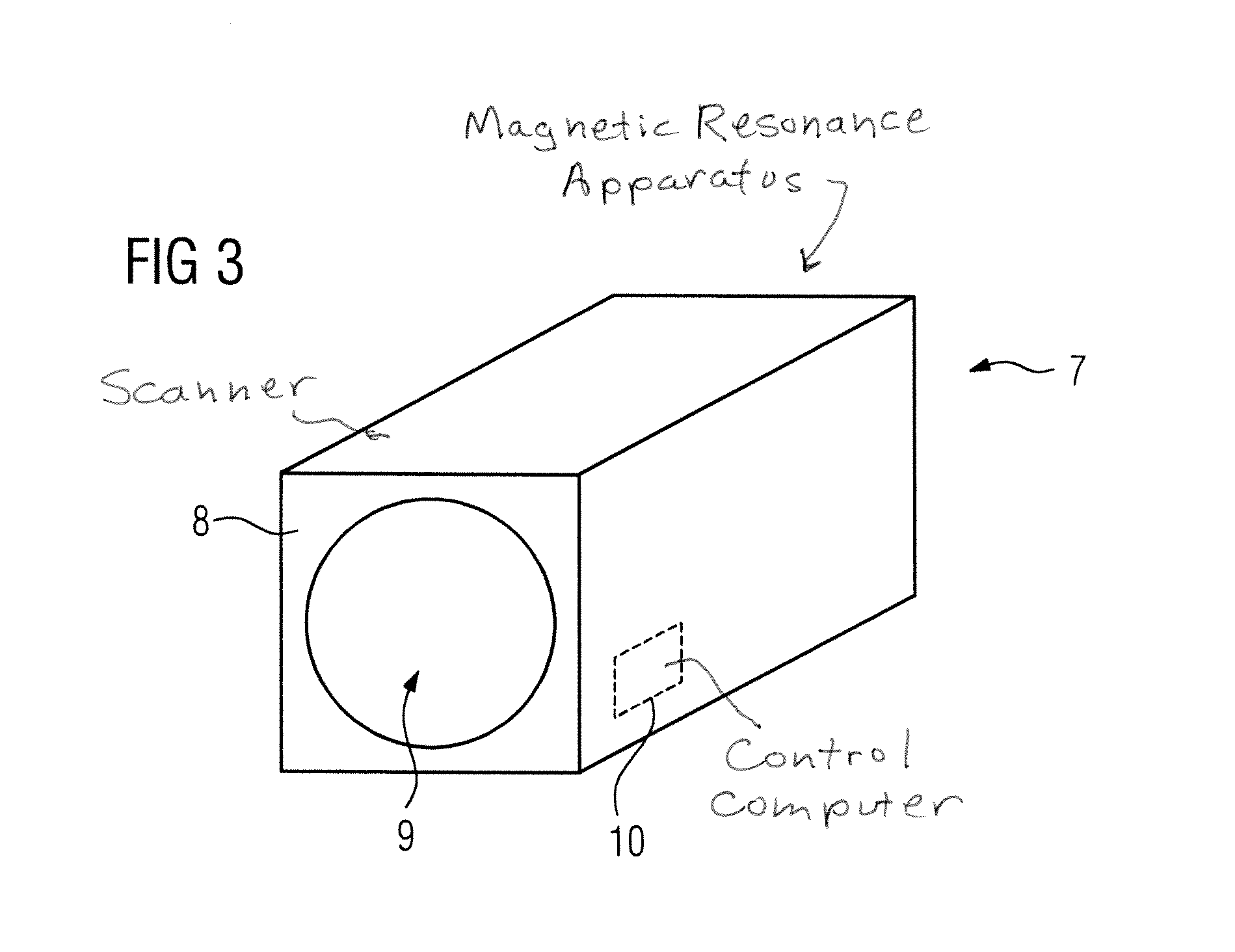
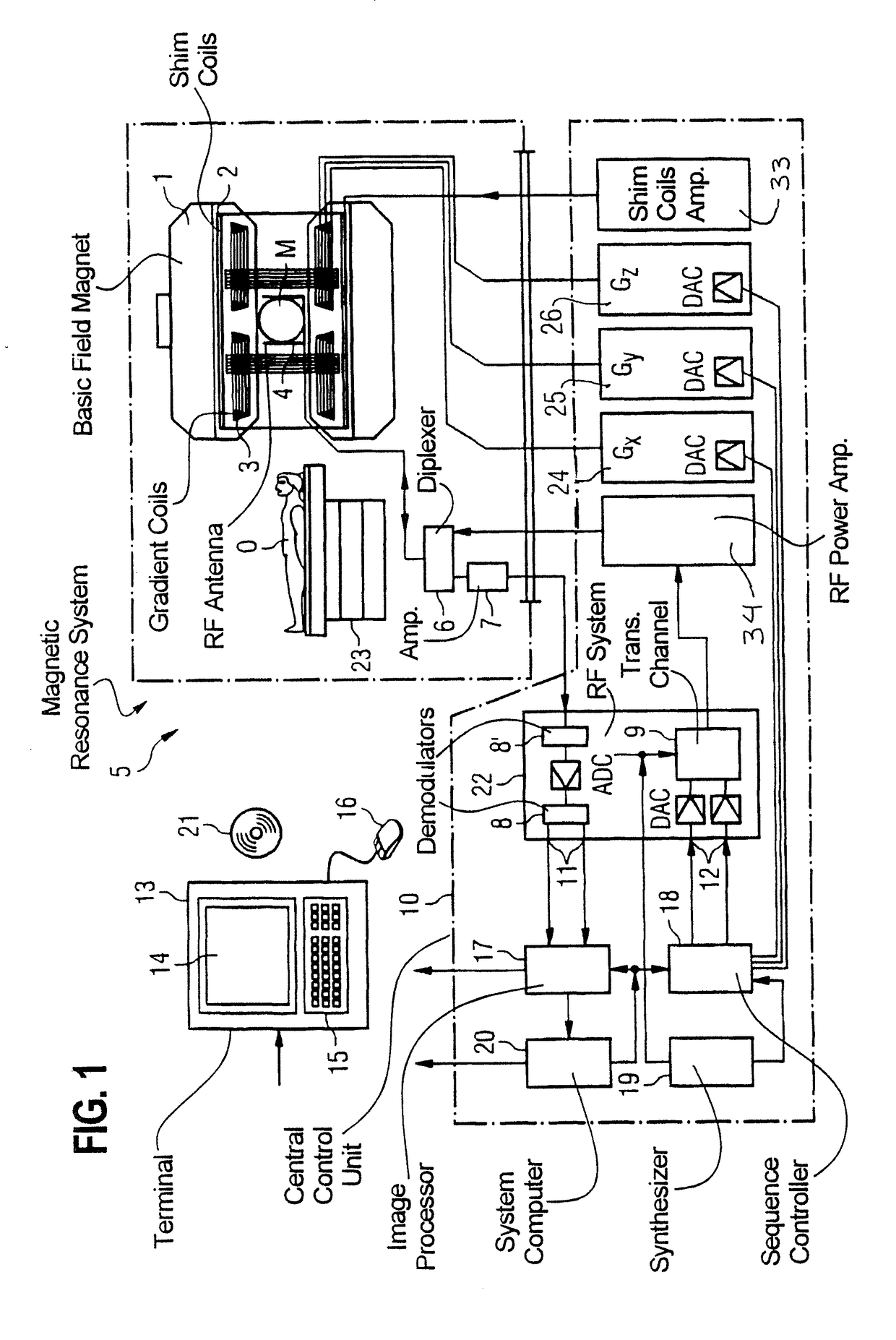
Magnetic resonance imaging device
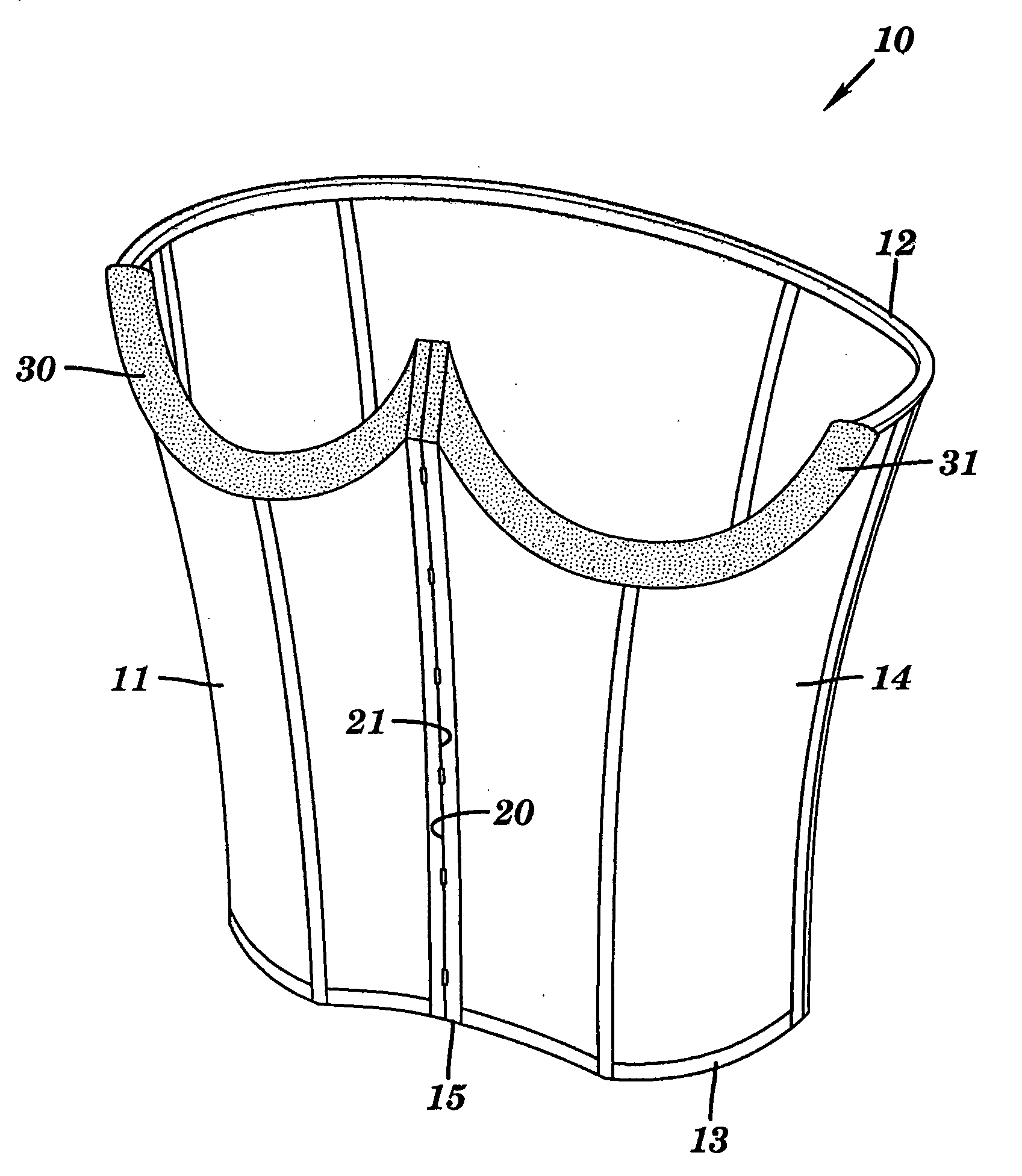
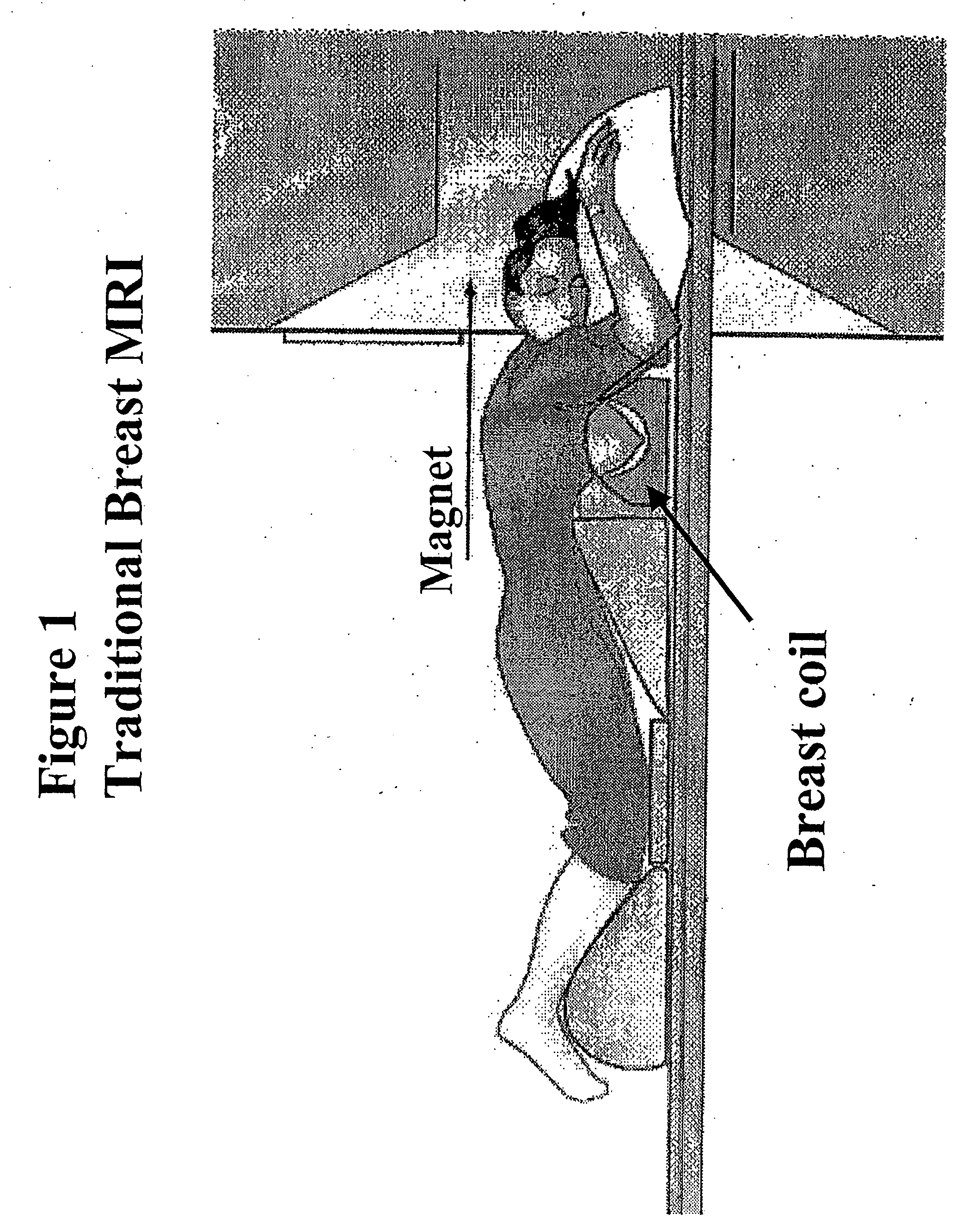
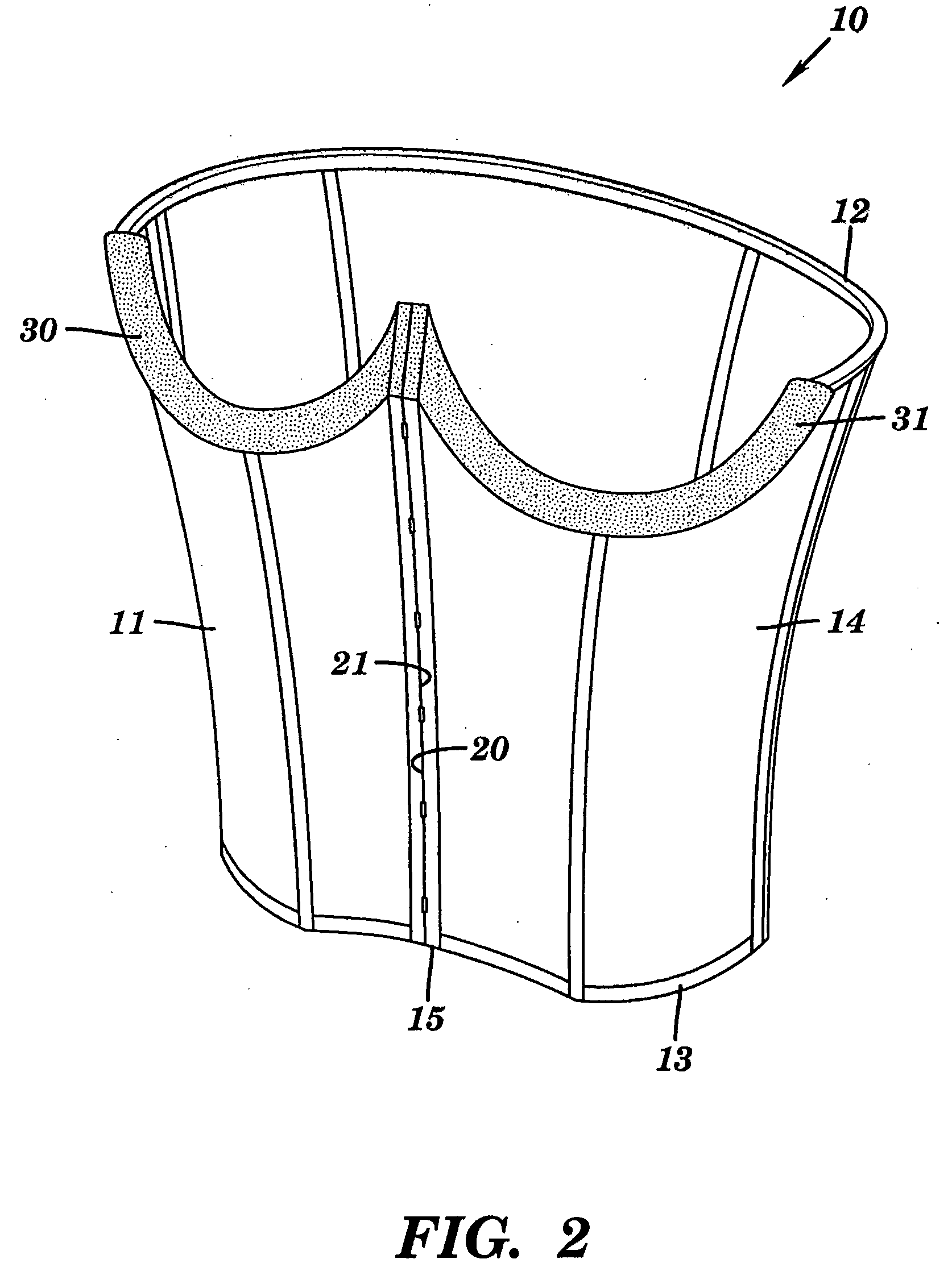
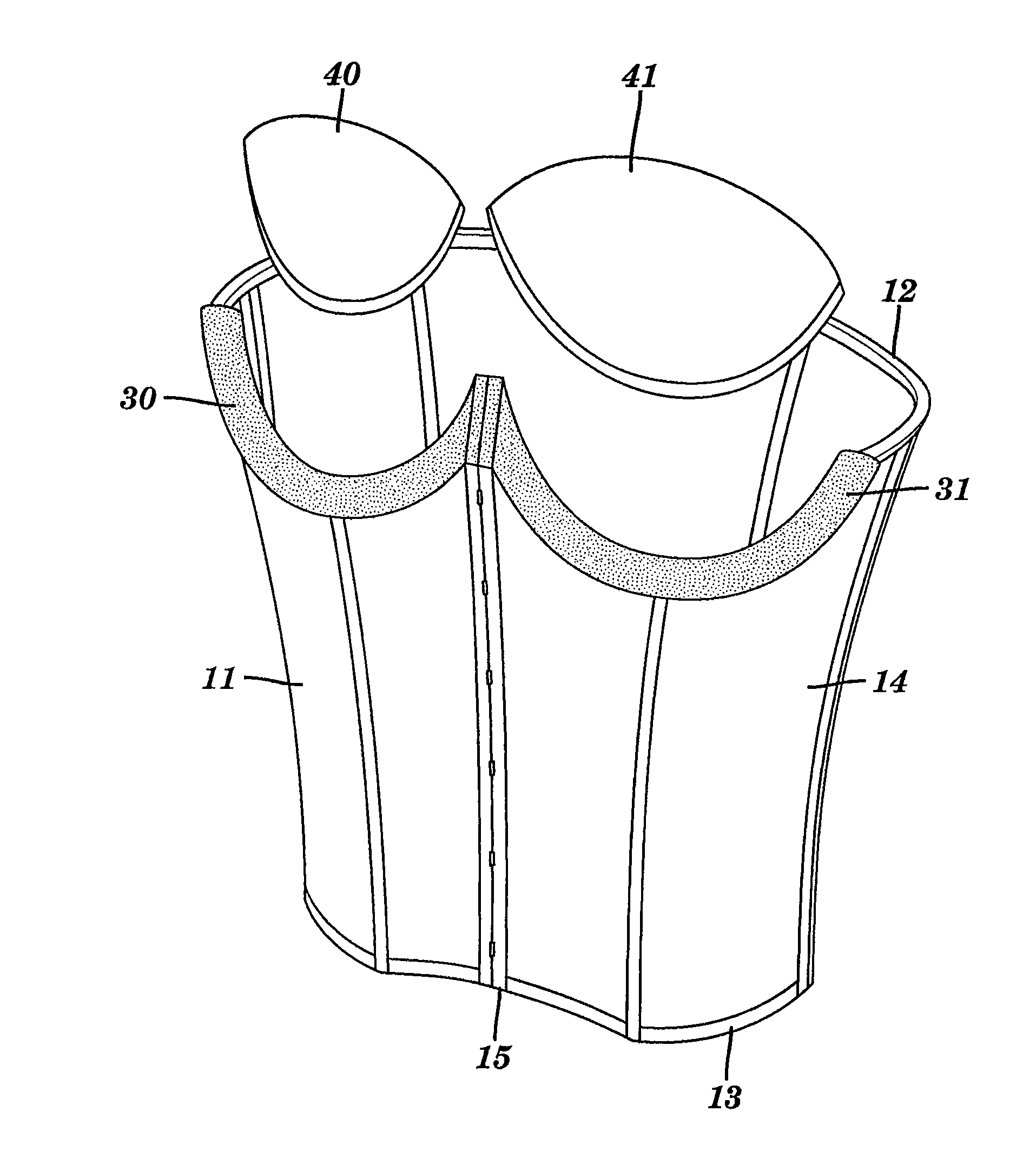
InactiveUS20060270930A1BrassieresDiagnostic recording/measuringFat suppressionMR - Magnetic resonance
The present invention provides a device for use in magnetic resonance imaging of a woman's breasts. The device has breast-supporting cups that comprise an enhanced fat saturation material to facilitate fat suppression during imaging. Significantly, the wearer can put the device on and position it with little or no assistance and without loss of dignity due to manipulation by a technician.
Owner:ORGAMEND
Method for improving magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
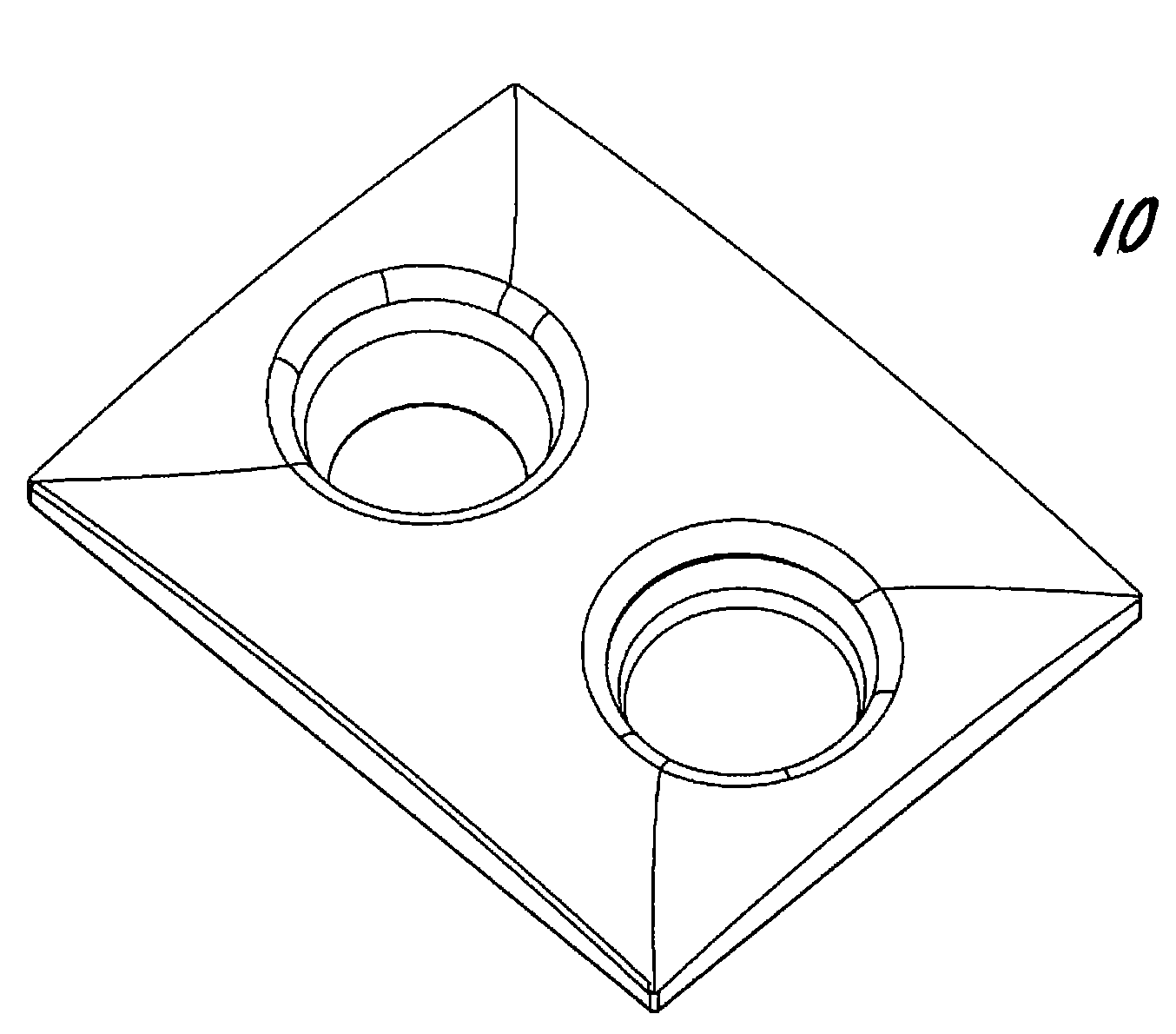
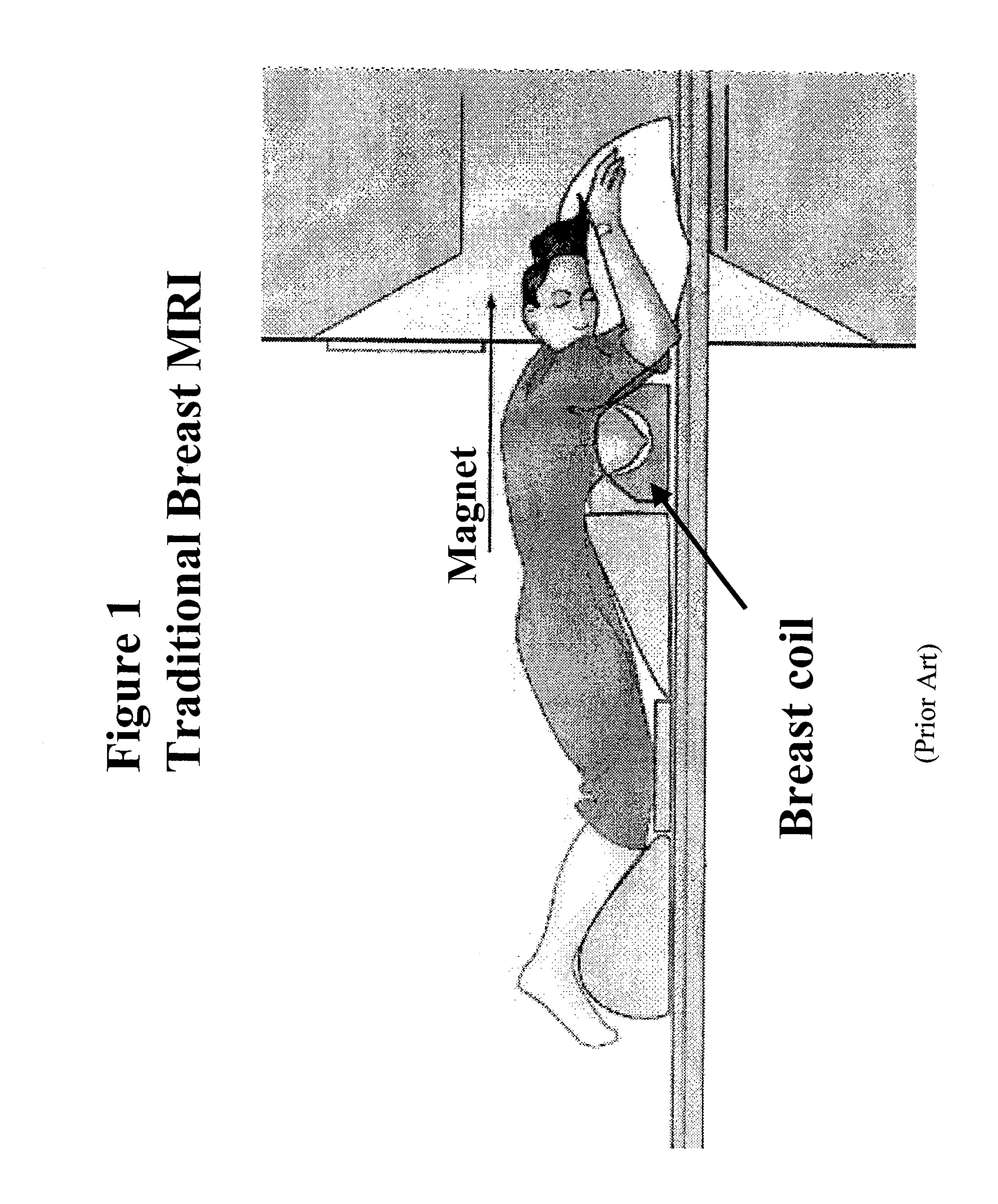
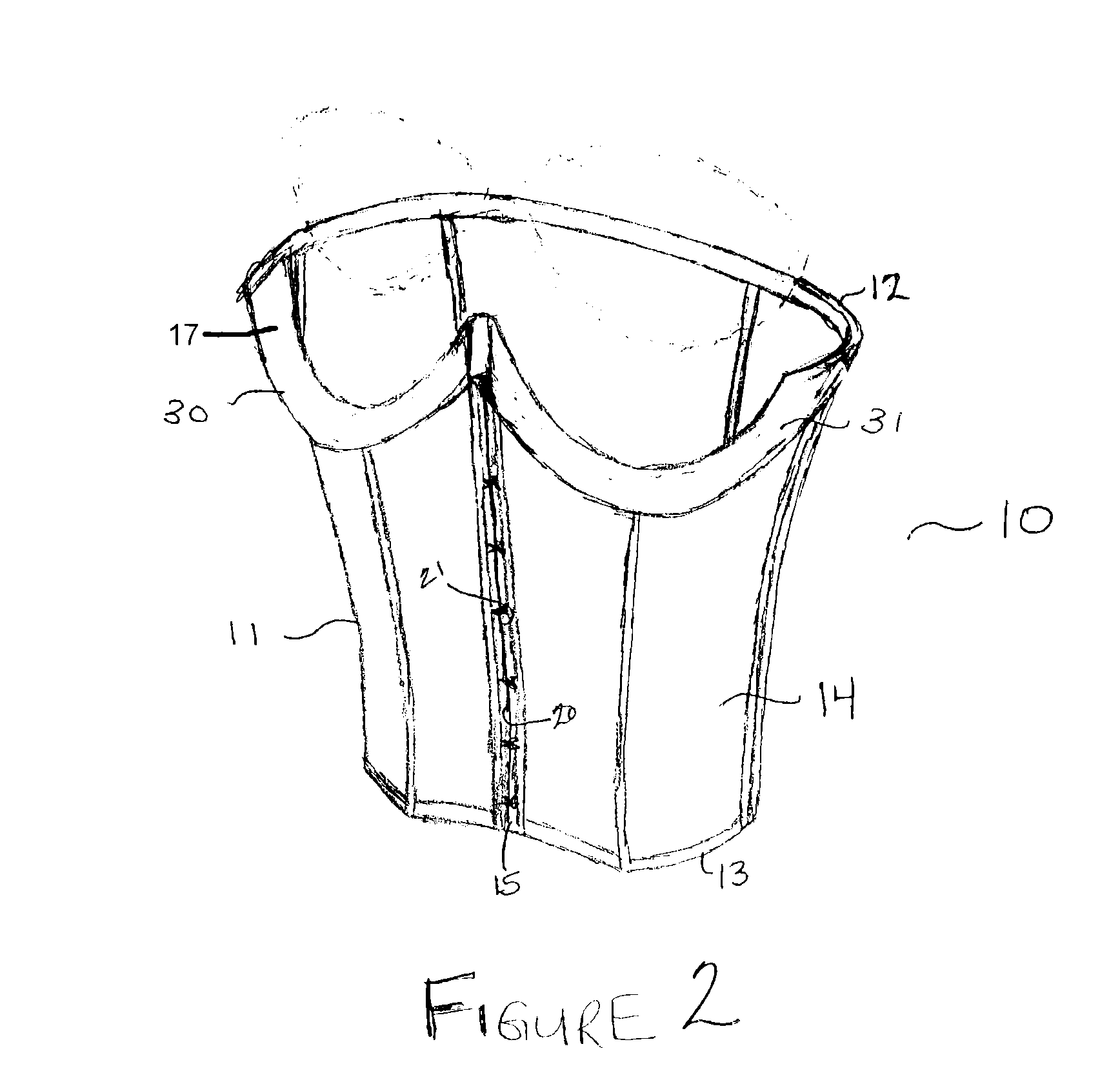
InactiveUS20080214930A1Enhancing magnetic resonance (MR) imageCut skinDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAir interfaceMedicine
The present invention provides a fat saturation device to be used in conjunction with a magnetice resonance imaging (MRI) breast coil, which provides padding for the comfort of the patient being imaged while eliminating the skin-air interface, thereby reducing the level of artefacts in the image. The device comprises a coil surface pad that contacts the surface of the coil, the pad having apertures therein through which the patients breasts extend when the patient is positioned on the coil for imaging. Aperture sleeves that are removable or retractable extend from the bottom surface of the coil surface into the apertures of the breast coil. The device comprises a fat saturation material.
Owner:ORGAMEND
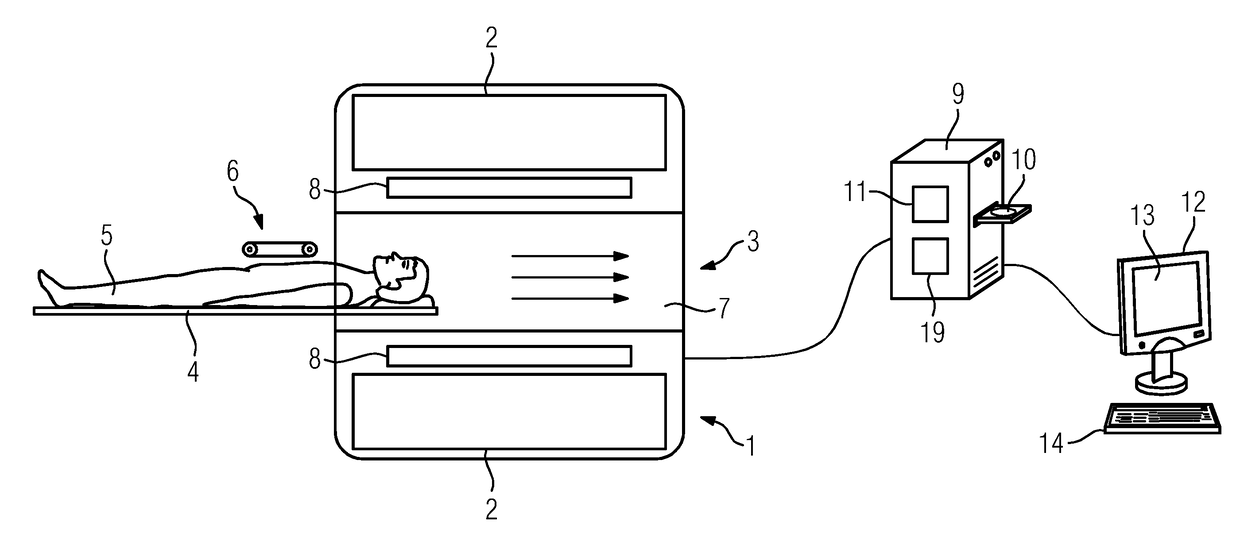
MR imaging using a multi-point dixon technique
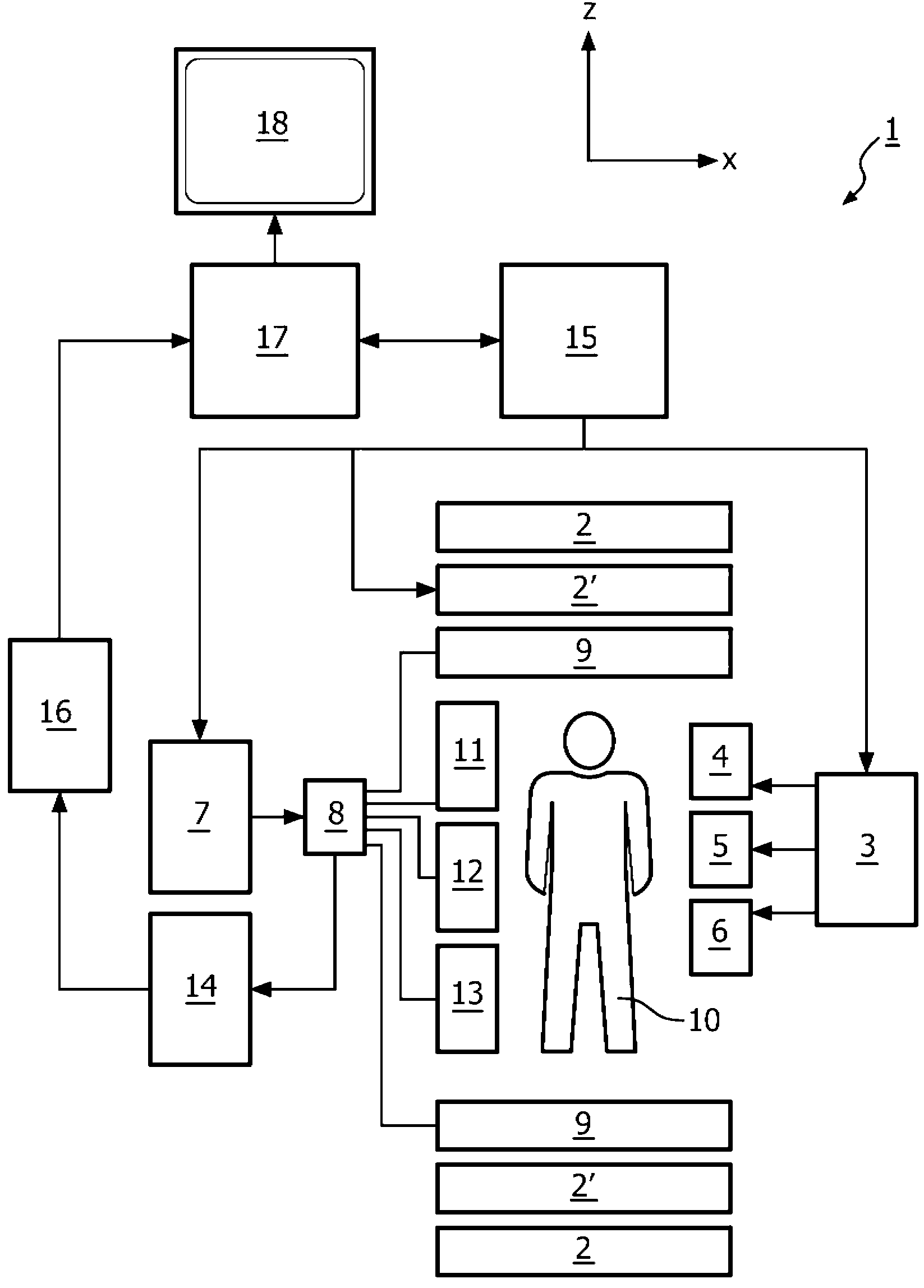
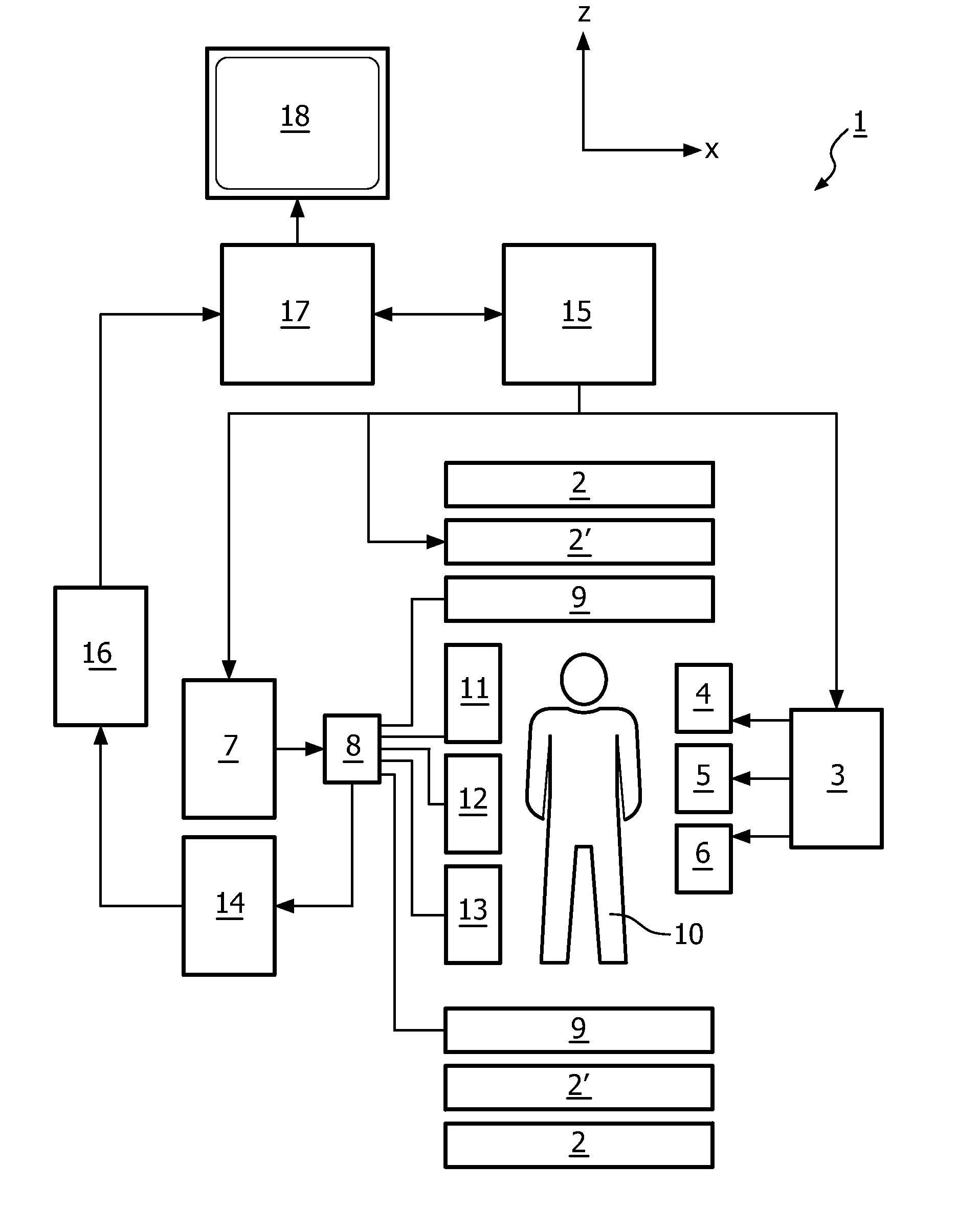
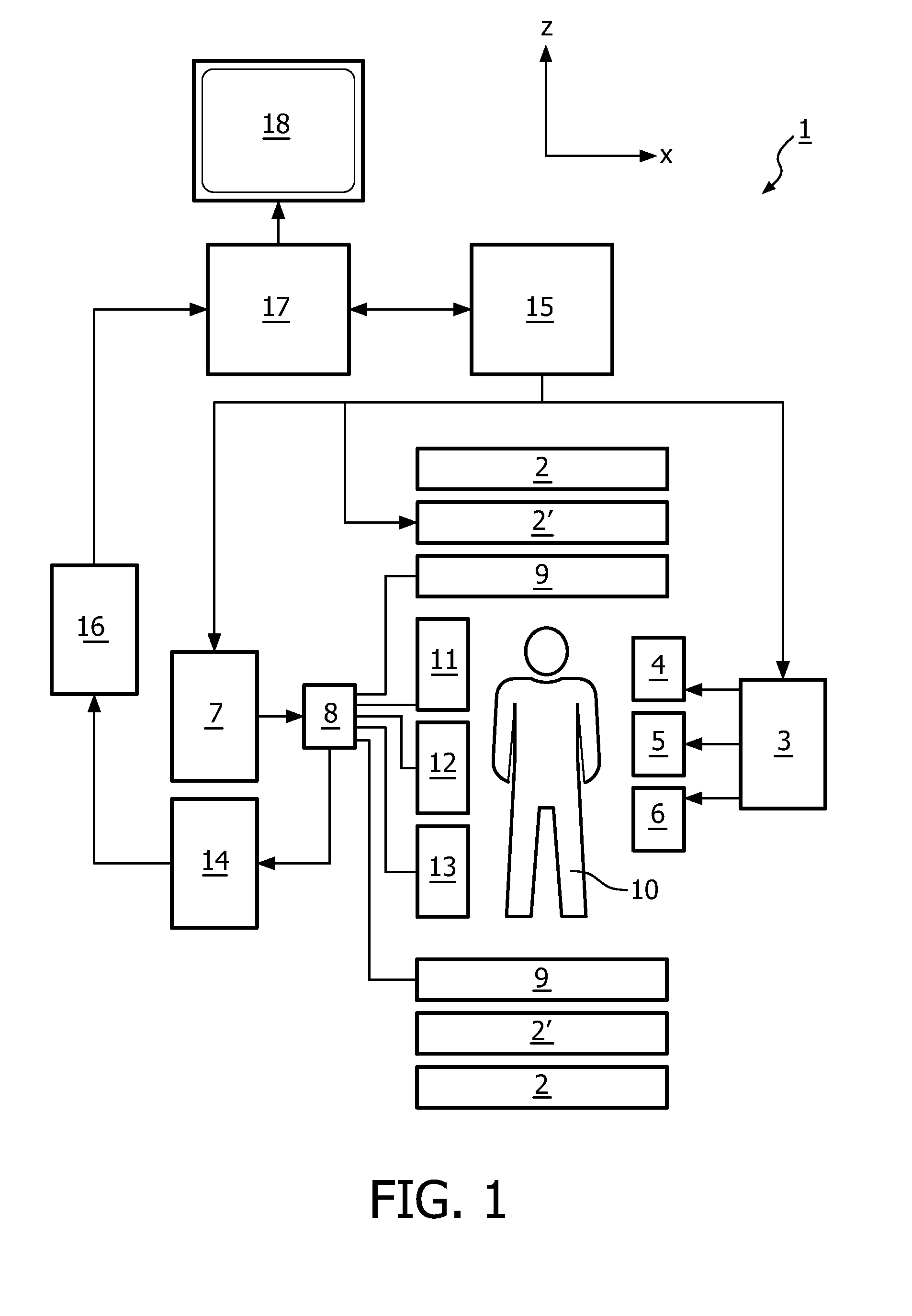
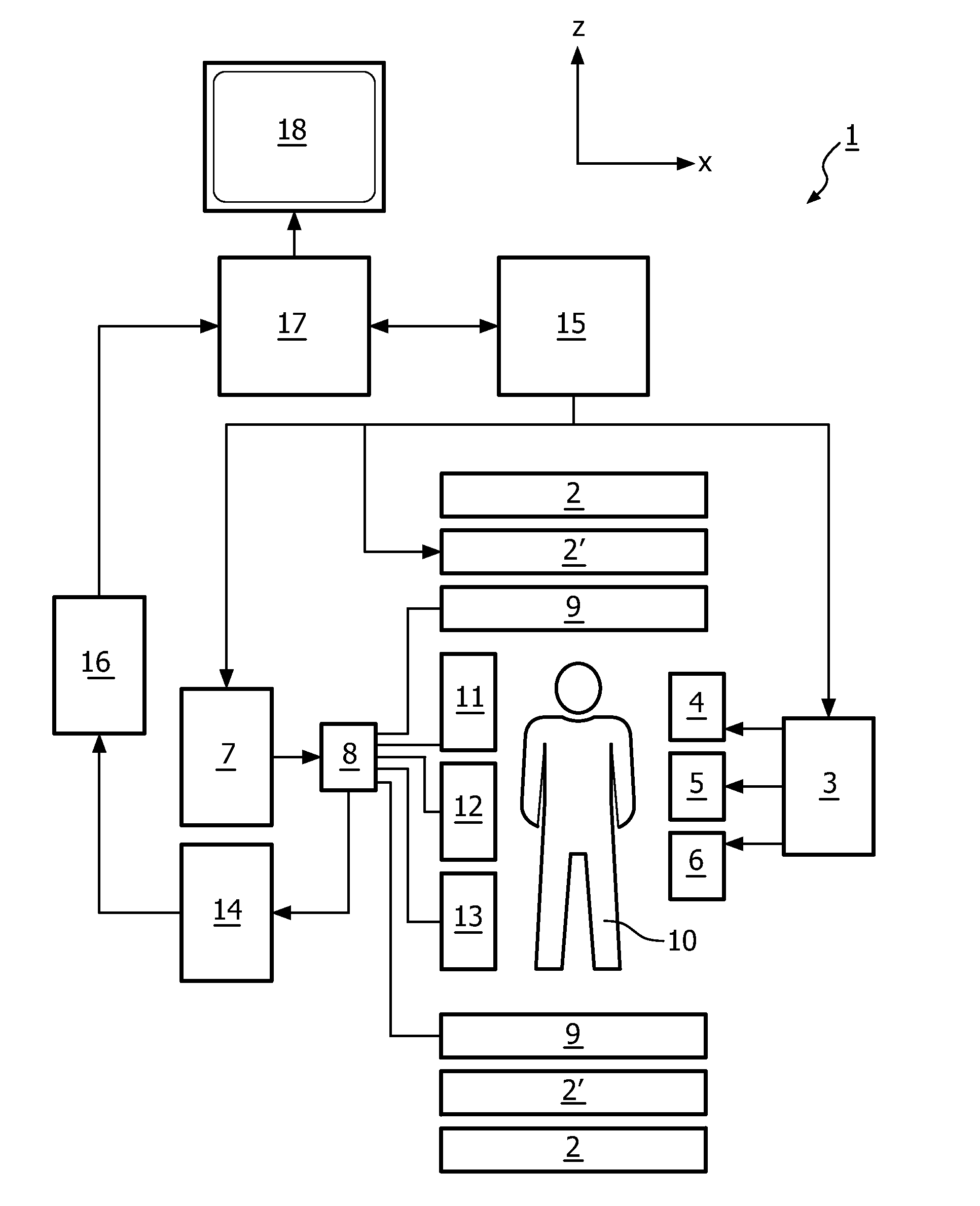
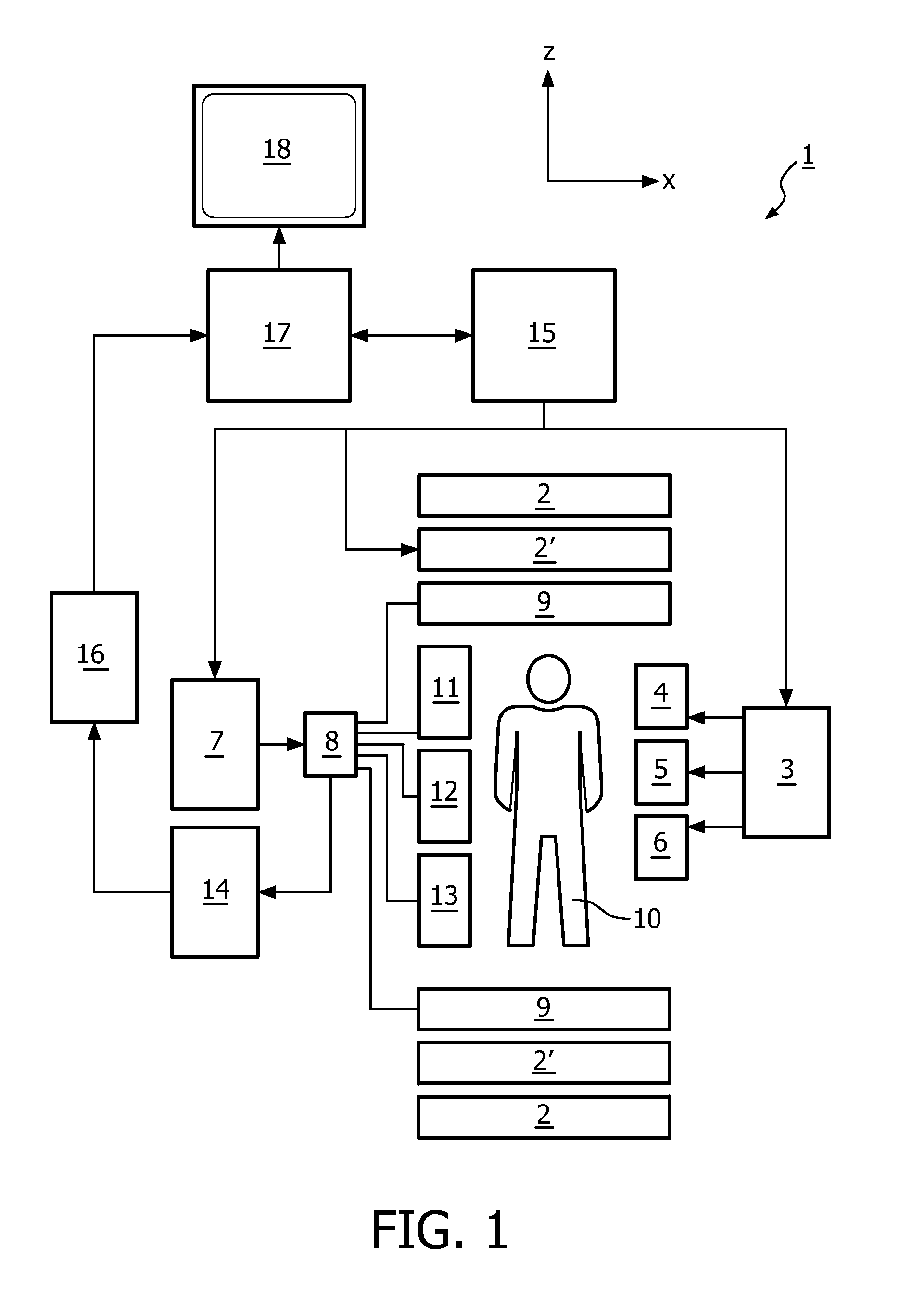
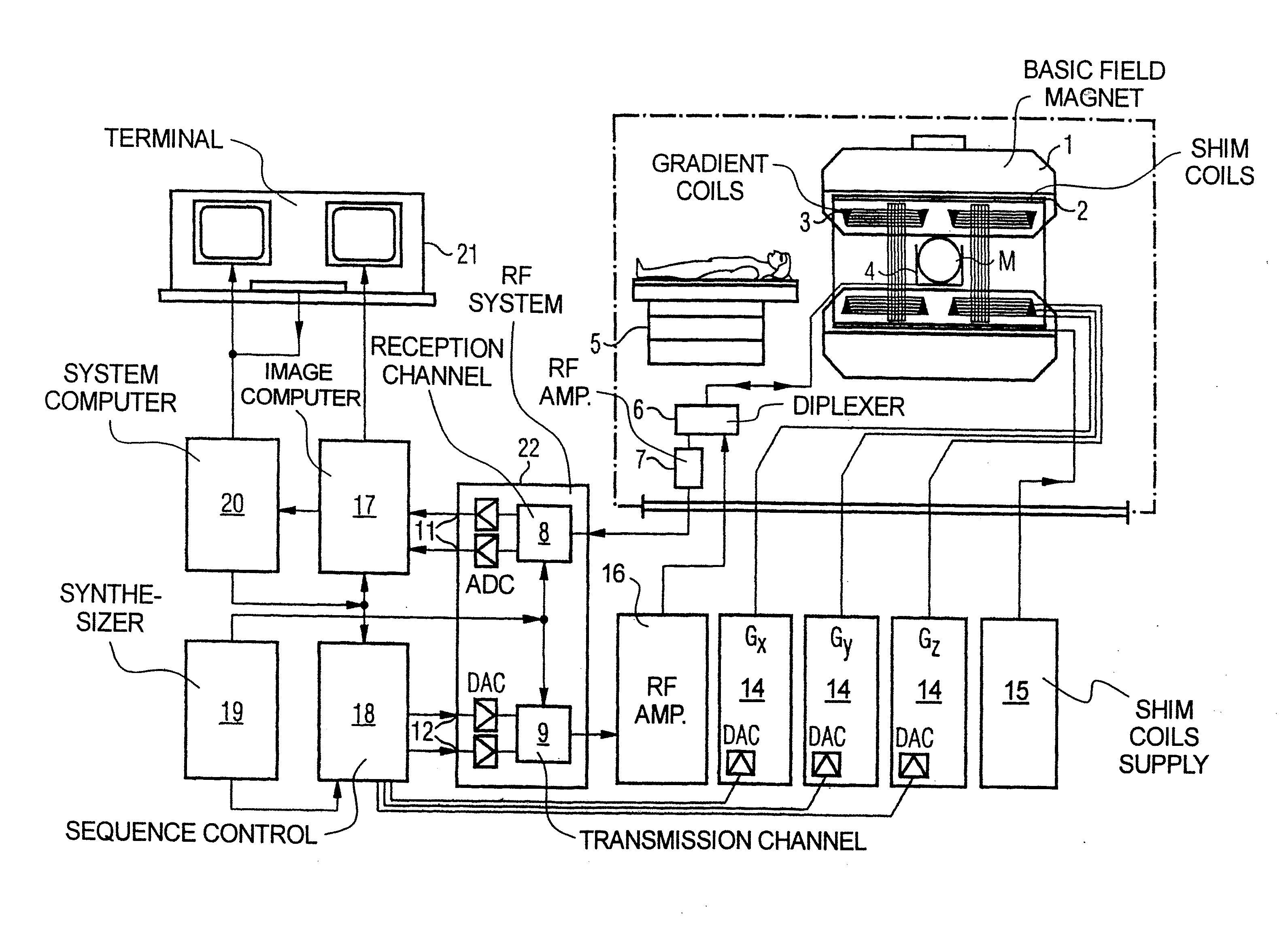
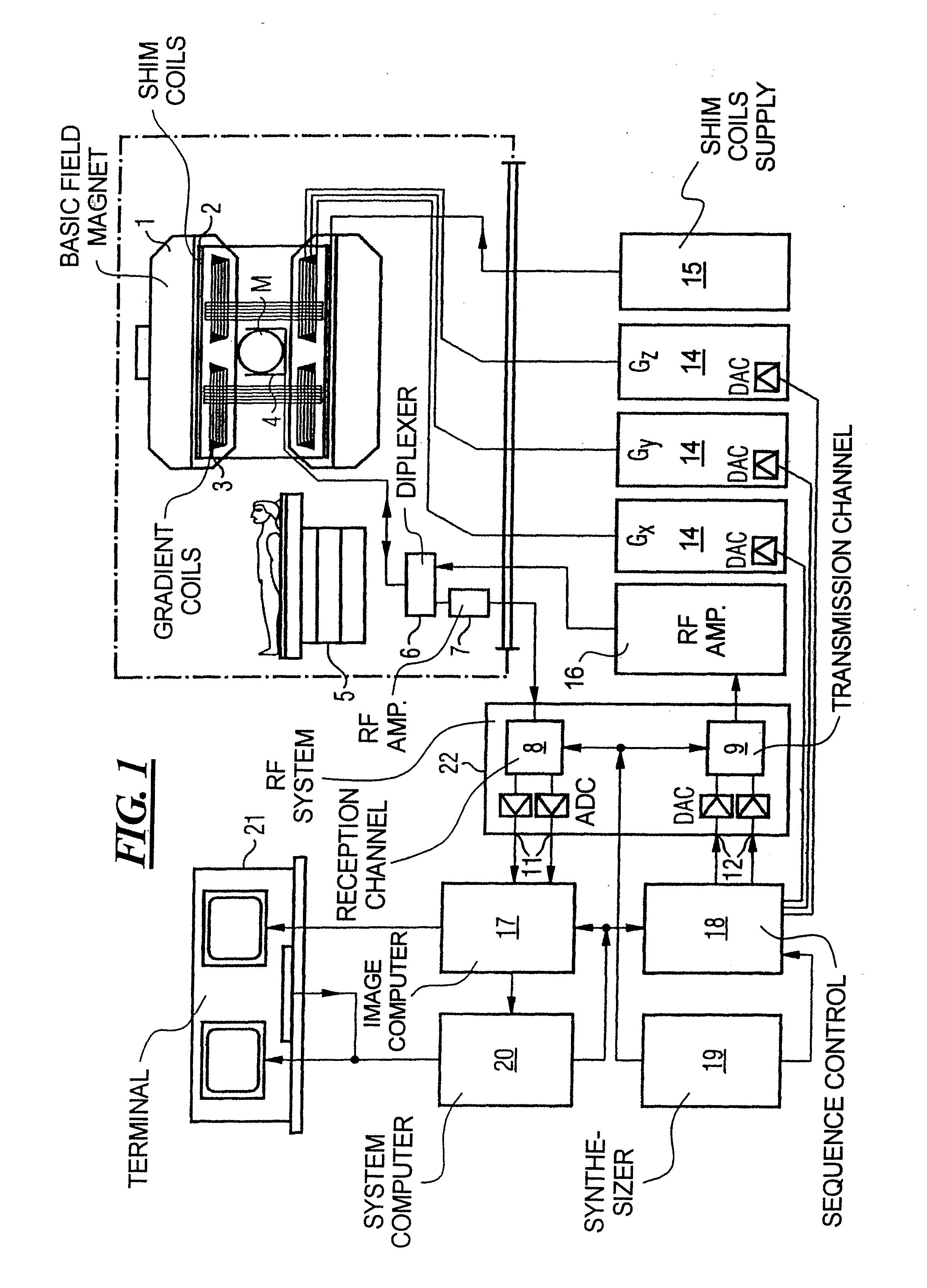
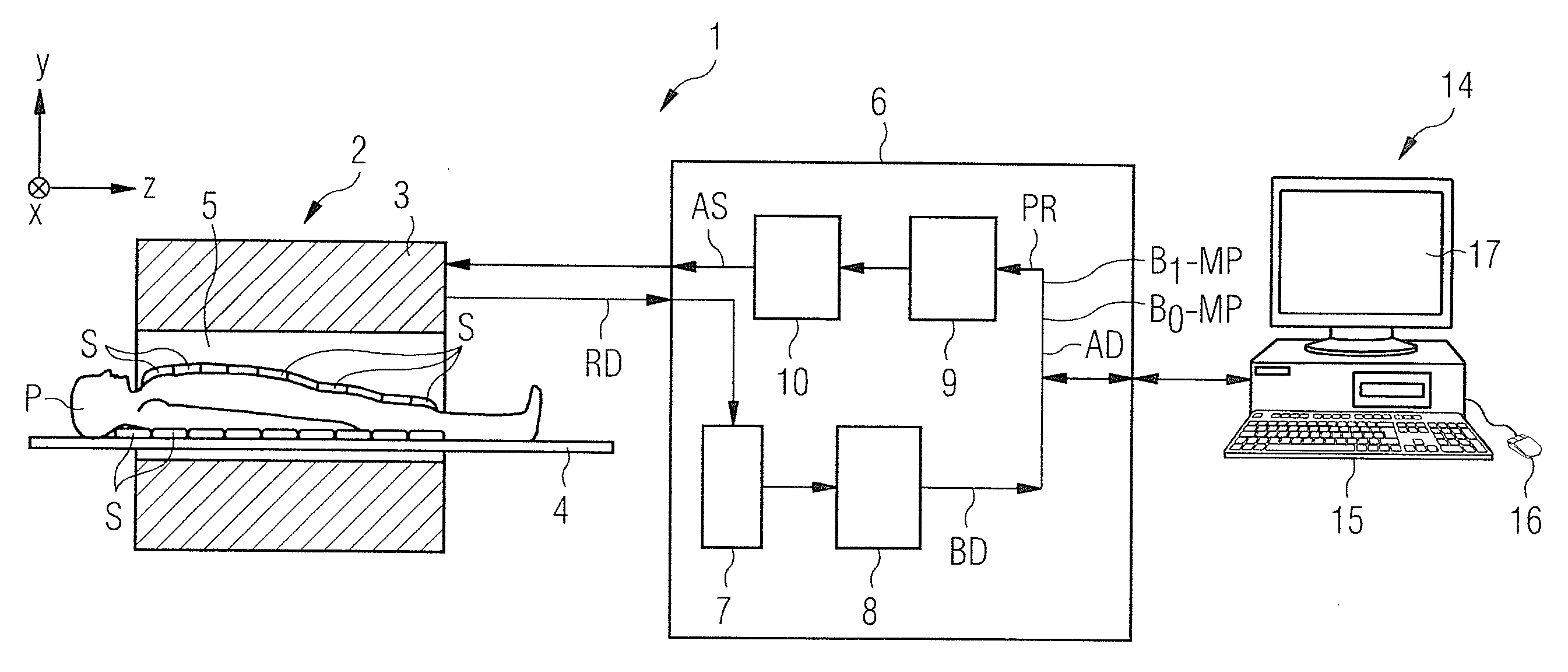
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) of a patient positioned in an examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to provide a method that enables improved fat saturation. The method of the invention comprises the steps of: - subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a calibration sequence comprising RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a calibration signal data set is acquired by means of a multi-point Dixon technique at a first image resolution; - deriving calibration parameters from the calibration signal data set; - controlling the MR device (1) according to the derived calibration parameters; - subjecting the portion of the body (10) to an imaging sequence comprising RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a diagnostic signal data set is acquired at a second image resolution which is higher than the first image resolution; and - reconstructing a diagnostic MR image from the diagnostic signal data set. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) for carrying out the method and to a computer program to be run on a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Mr imaging using a multi-point dixon technique
ActiveUS20130249553A1MinimizeMinimize biasMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData set
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) of a patient positioned in an examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to provide a method that enables improved fat saturation. The method of the invention comprises the steps of:—subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a calibration sequence comprising RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a calibration signal data set is acquired by means of a multi-point Dixon technique at a first image resolution;—deriving calibration parameters from the calibration signal data set;—controlling the MR device (1) according to the derived calibration parameters;—subjecting the portion of the body (10) to an imaging sequence comprising RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a diagnostic signal data set is acquired at a second image resolution which is higher than the first image resolution; and—reconstructing a diagnostic MR image from the diagnostic signal data set. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) for carrying out the method and to a computer program to be run on a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Mr imaging using a multi-point dixon technique
ActiveUS20130249554A1Information can be usedEasy accessMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData set
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) of a patient positioned in an examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to provide a method that enables improved fat saturation. The method of the invention comprises the steps of: subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a calibration sequence comprising RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a calibration signal data set is acquired by means of a multi-point Dixon technique at a first image resolution; deriving calibration parameters from the calibration signal data set; subjecting the portion of the body (10) to an imaging sequence comprising RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a diagnostic signal data set is acquired at a second image resolution which is higher than the first image resolution; and reconstructing a diagnostic MR image from the diagnostic signal data set, wherein the MR device (1) is operated according to the derived calibration parameters during acquisition of the diagnostic signal data set and / or during reconstruction of the diagnostic MR image. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) for carrying out the method and to a computer program to be run on a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Transmitting frequency calibration method for chemical saturation in MRI and MRI system
ActiveCN101744616ARobust suppressionSaturation emission frequency is goodDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFat suppressionImaging quality
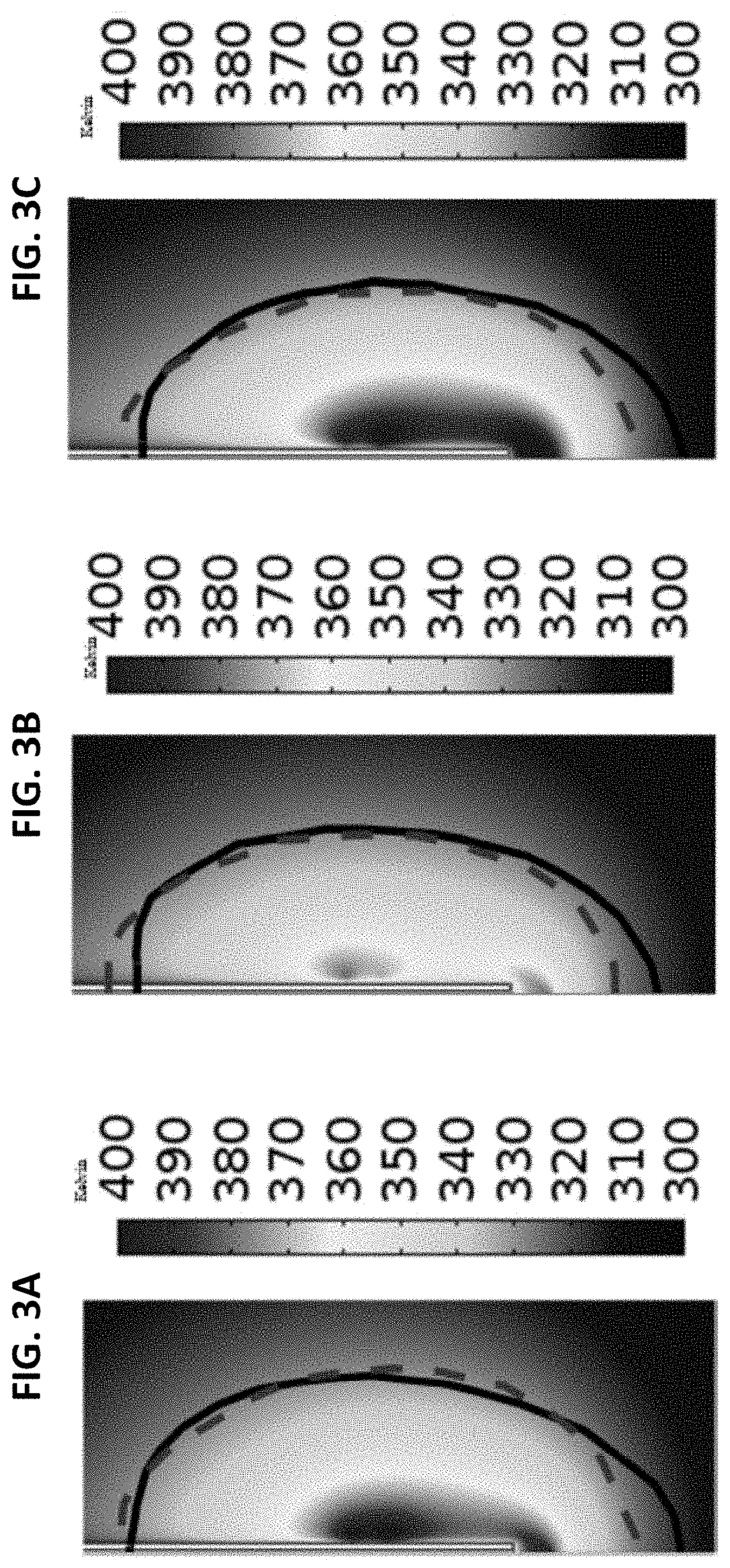
The invention relates to a transmitting frequency calibration method for chemical saturation in MRI and a MRI system. The invention provides a transmitting frequency calibration method for chemical saturation, which relates to the chemical saturation imaging technology of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology. The method of the invention adopts the decrease of water signal amplitude as standard to judge that the fat is fully saturated, therefore obtaining the transmitting frequency of fat saturation. And in addition, the invention also can confirm the best saturation transmitting frequency through combining with other prescan method. With the method of the invention, the fat-suppression effect is stable than before, and the method is less rely on the experience of the operator, and the image quality of chemical saturation (particularly the image quality of chemical saturation in low field MRI) is improved.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
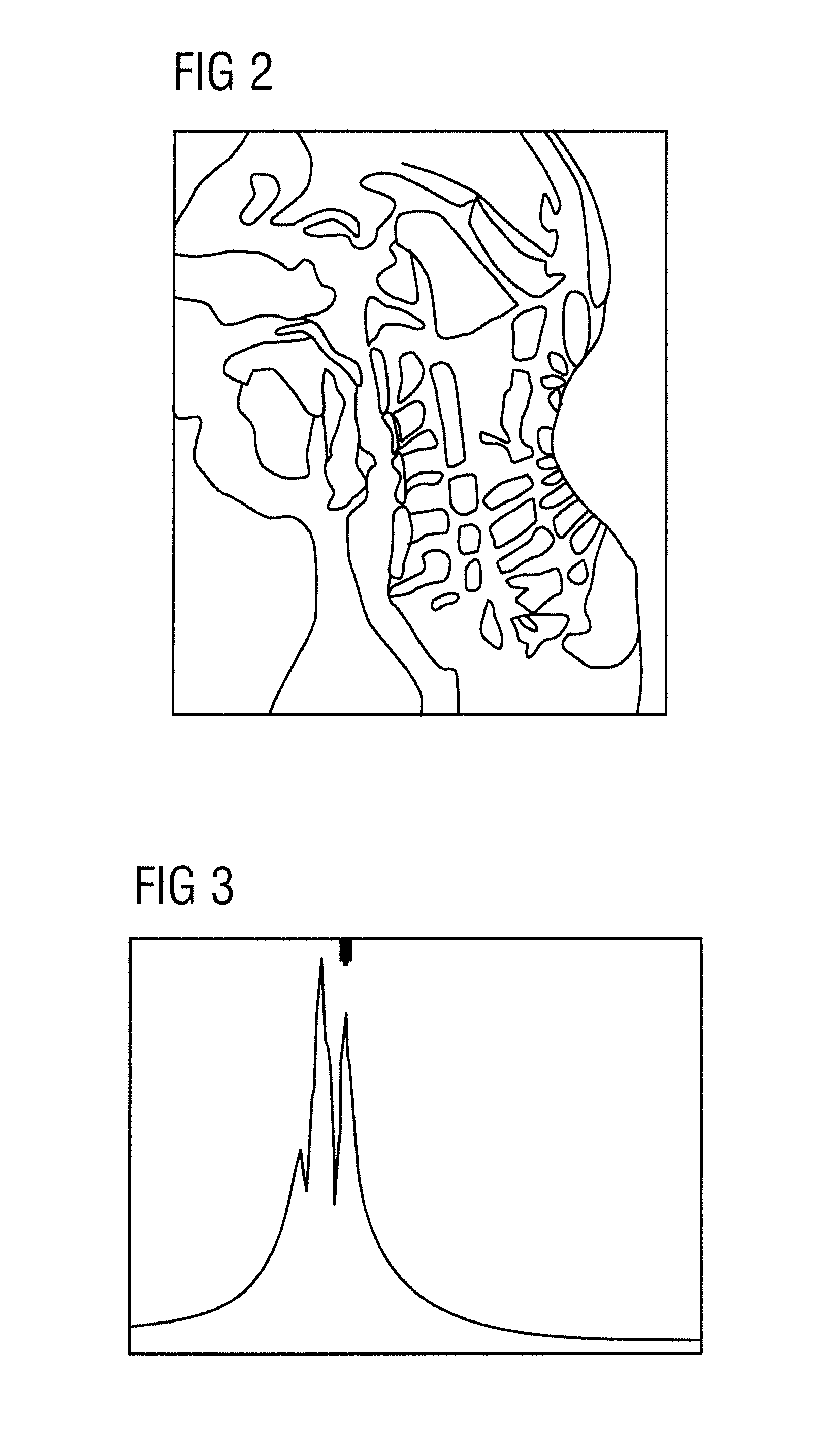
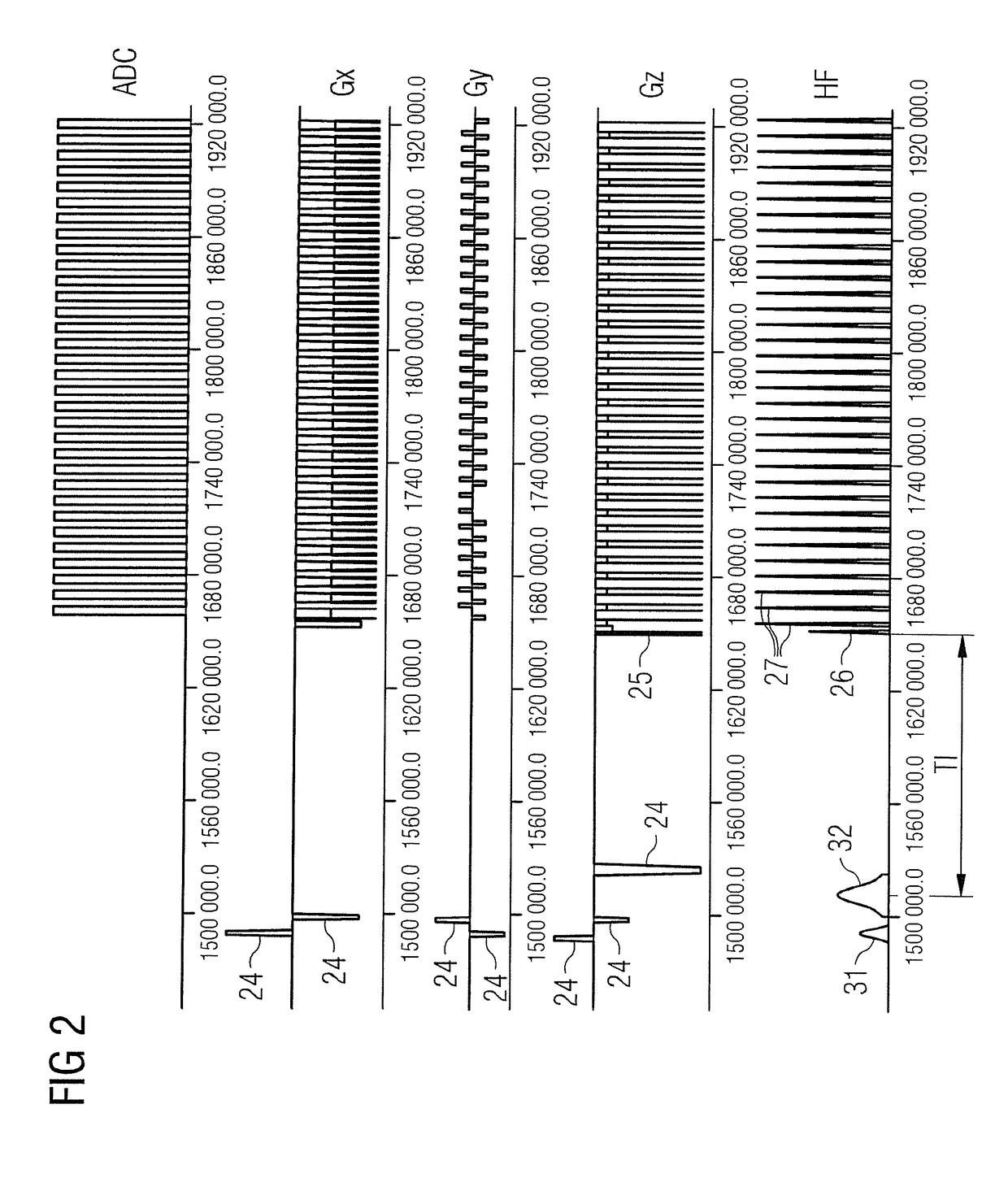
Method for imaging in magnetic resonance tomography with spectral fat saturation or spectral water excitation
InactiveUS20100271023A1Improve image qualityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceTomography
A magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) method with spectral fat saturation or spectral water excitation in a tissue region that is to be represented of a patient who is to be examined, includes the following steps: (Step 1) frequency adjustment measurement of a region of a patient that is to be represented with a selected first partial coil of the MRT system, (Step 2) precise determination of the resonance frequency of water with the aid of the spectrum obtained in Step 1 exhibiting the resonance frequencies of fat and water, (Step 3) repetition of Steps 1 and 2 with at least one additionally selected second partial coil of the MRT system adjacent to the first partial coil, (Step 4) measuring of a k space data record with a partial coil or a partial coil combination on the basis of the water resonance frequency assigned to these partial coils, (Step 5) repetition of Step 4 with other partial coils or other partial coil combinations until the entire tissue region to be represented has been measured, (Step 6) combining of the measuring results obtained in Steps 4 and 5, and (Step 7) representing of the results obtained in Step 6 in the image space in the form of an overall image of the tissue region to be represented.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for reducing localized signal fluctuation
ActiveUS20120146638A1Reducing localized signal fluctuationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransceiverEngineering
A system and method is disclosed for eliminating localized fluctuation artifacts caused by fat signal contamination in MR images, the system includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system having a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet, and an RF transceiver system and an RF switch controlled by a pulse module to transmit RF signals to an RF coil assembly to acquire MR images, and a computer programmed to apply a spectral-spatial fat saturation pulse, apply a slice selection gradient pulse, acquire imaging data of an imaging slice of interest, and generate an image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
MR imaging using a multi-point dixon technique
ActiveUS9575154B2Information can be usedEasy accessMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData set
At least a portion of a body (10) of a patient is positioned in an examination volume of a MR device (1). The portion of the body (10) is subject to a calibration sequence including RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a calibration signal data set is acquired by a multi-point Dixon technique at a first image resolution. Calibration parameters are derived from the calibration signal data set. The portion of the body (10) is subject to an imaging sequence including RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients controlled in such a manner that a diagnostic signal data set is acquired at a second image resolution which is higher than the first image resolution A diagnostic MR image is reconstructed from the diagnostic signal data set. The MR device (1) is operated according to the derived calibration parameters with fat saturation during acquisition of the diagnostic signal data set and / or during reconstruction of the diagnostic MR image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
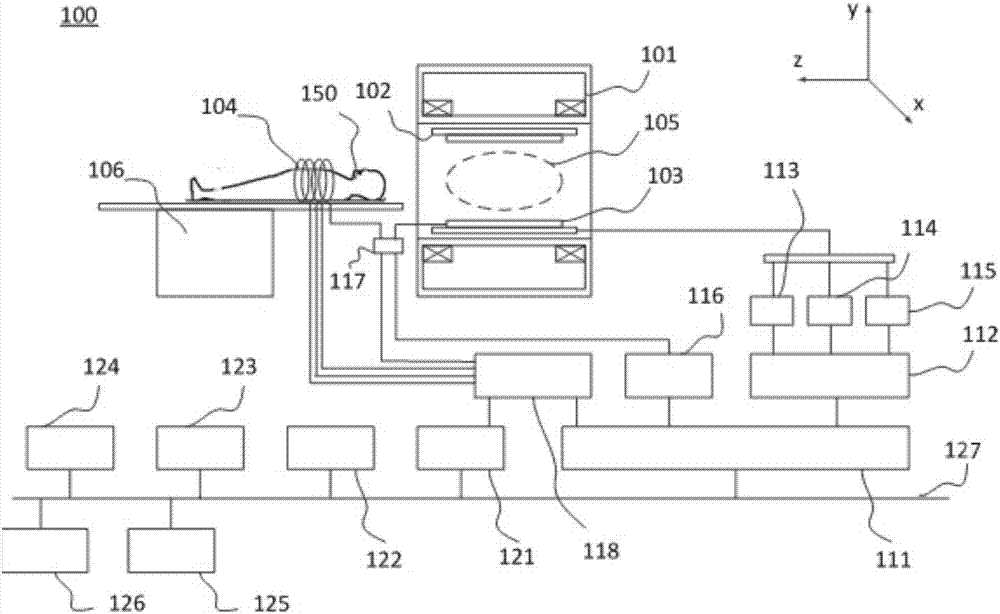
Magnetic resonance data acquisition method and apparatus saturation with spin dependent on the anatomical structures to be imaged
ActiveUS20160291111A1Easy to upgradeIncrease loadMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnatomical structuresFat suppression
In a method, computer and magnetic resonance imaging system for determining a control sequence for operating the magnetic resonance imaging system to generate magnetic resonance image data of a region to be imaged of an examination subject, from which magnetic resonance raw data are acquired, information describing the anatomical structure of the region to be imaged is made available in the computer, and a surrounding area and a central area are specified in the region to be imaged dependent on the determined anatomical structure. Furthermore, a one-dimensional water / fat saturation pulse sequence for saturating the surrounding areas is determined and a multidimensional water / fat saturation pulse sequence for saturating the central area is determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
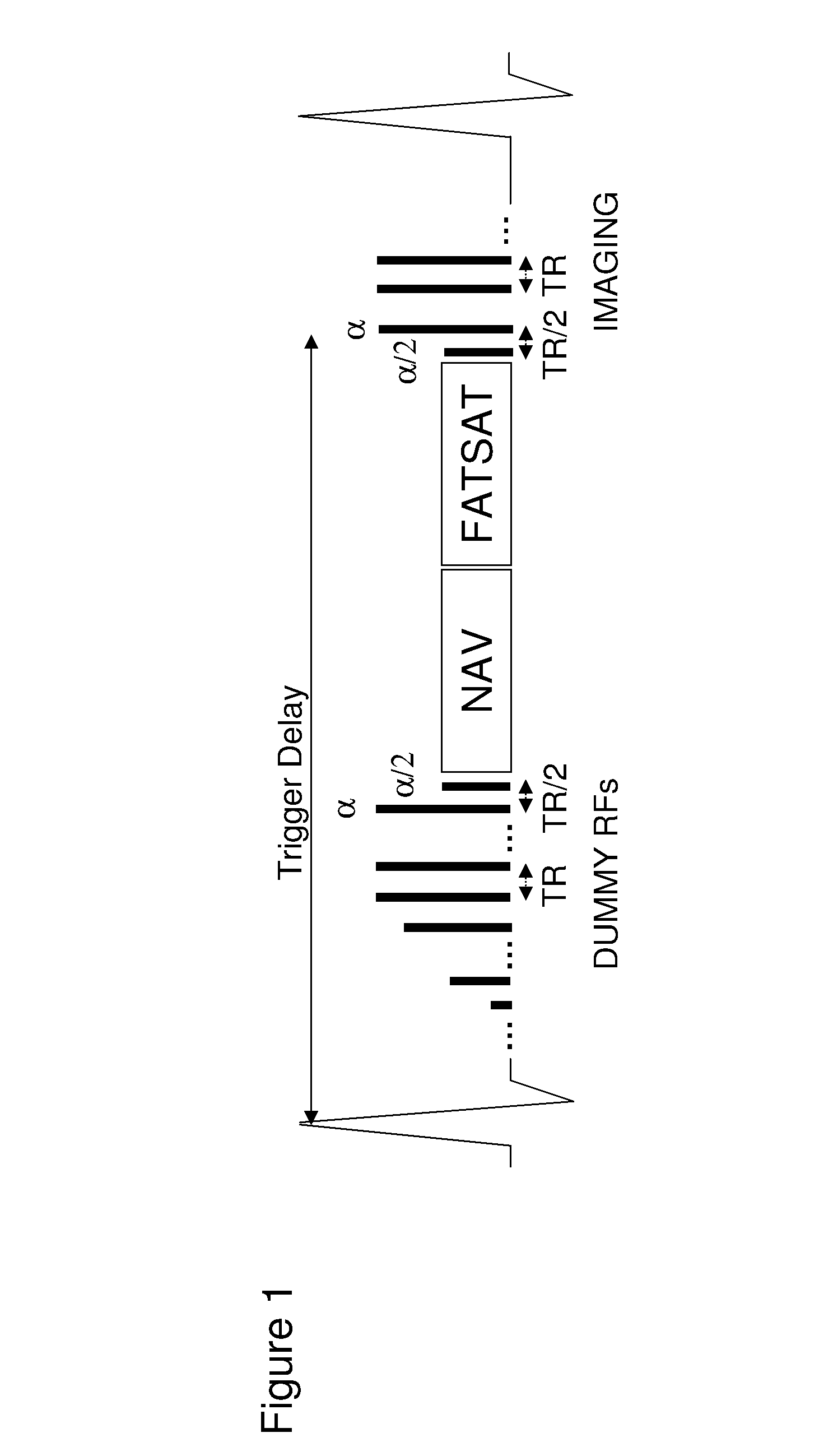
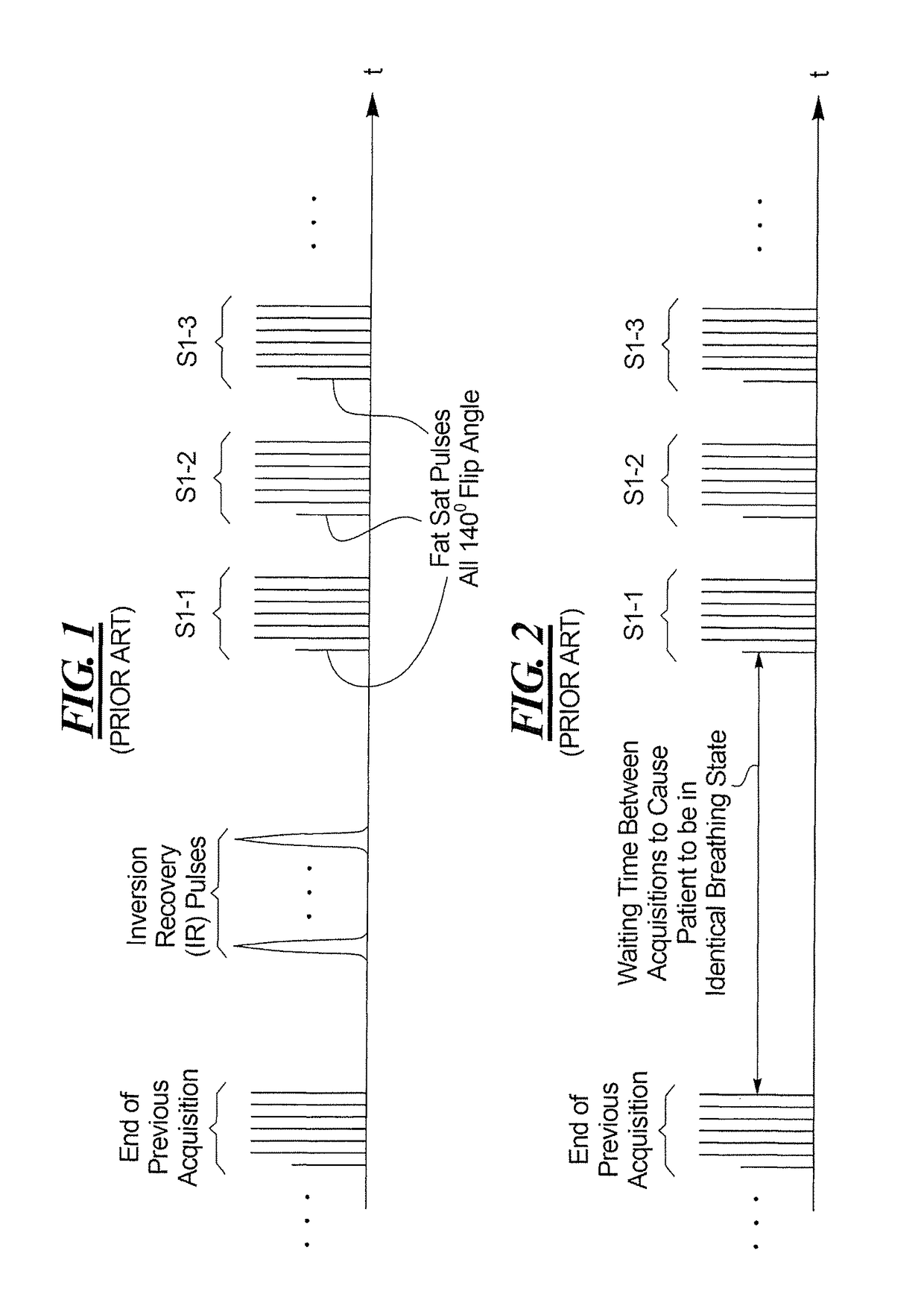
Method and apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance data from a target region while the target region moves due to respiration
ActiveUS20160069976A1Reduced conversion timeLarge in inversion timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceInversion Time
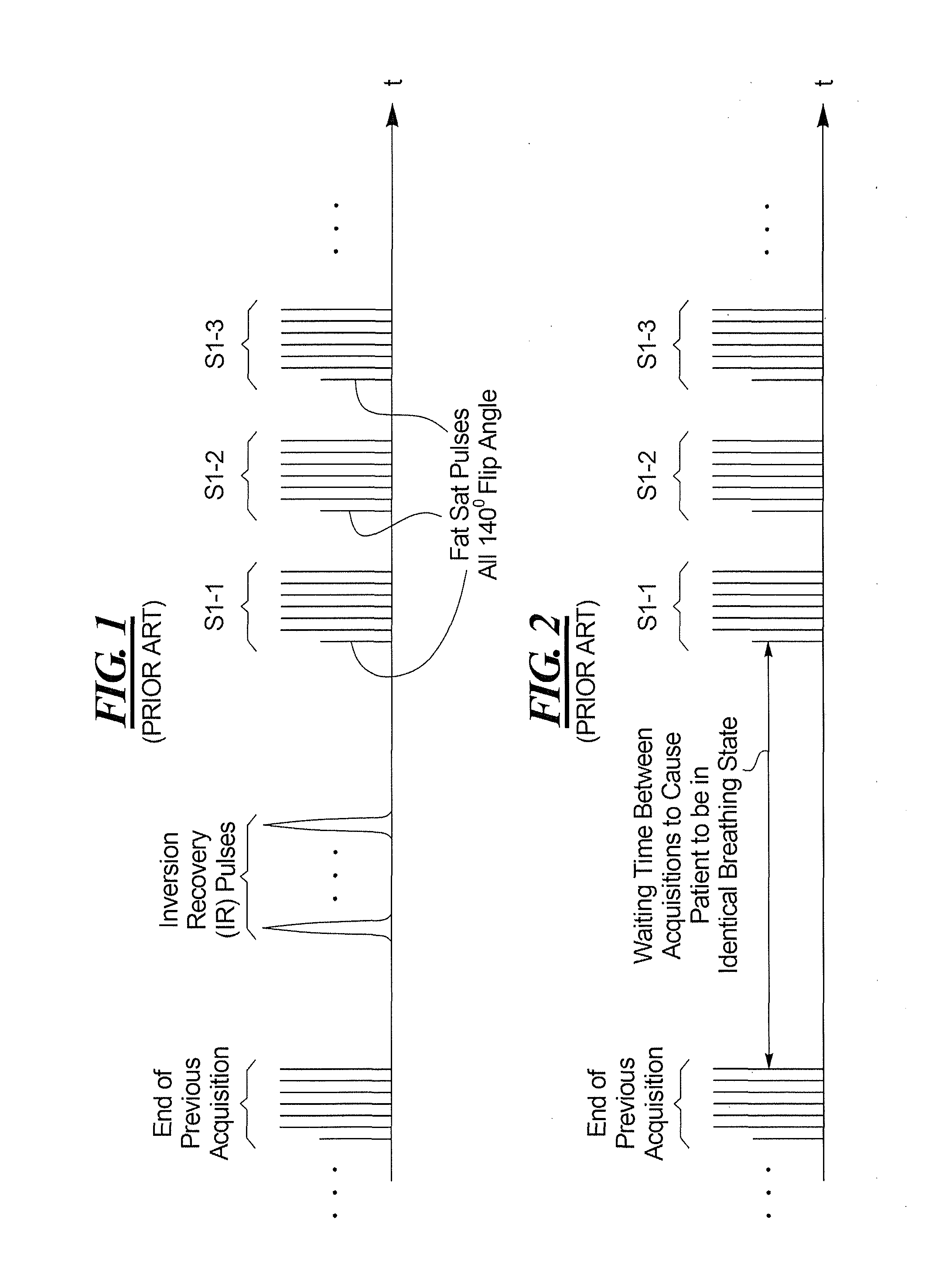
In a method for recording magnetic resonance data in a target region of a patient while the target region moves due to respiration a single-shot turbo spin echo sequence is used as a magnetic resonance sequence in a magnetic resonance apparatus. SPAIR fat saturation is used by emitting an inversion pulse at an inversion time before the data recording with the magnetic resonance apparatus. Multiple repetitions of the sequence of an inversion pulse, an inversion time and a data recording using the magnetic resonance sequence are triggered by a respiratory signal describing the respiratory cycle, each repetition occurring upon fulfillment of a recording criterion. At least one further inversion pulse is emitted in a waiting time between the sequences.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
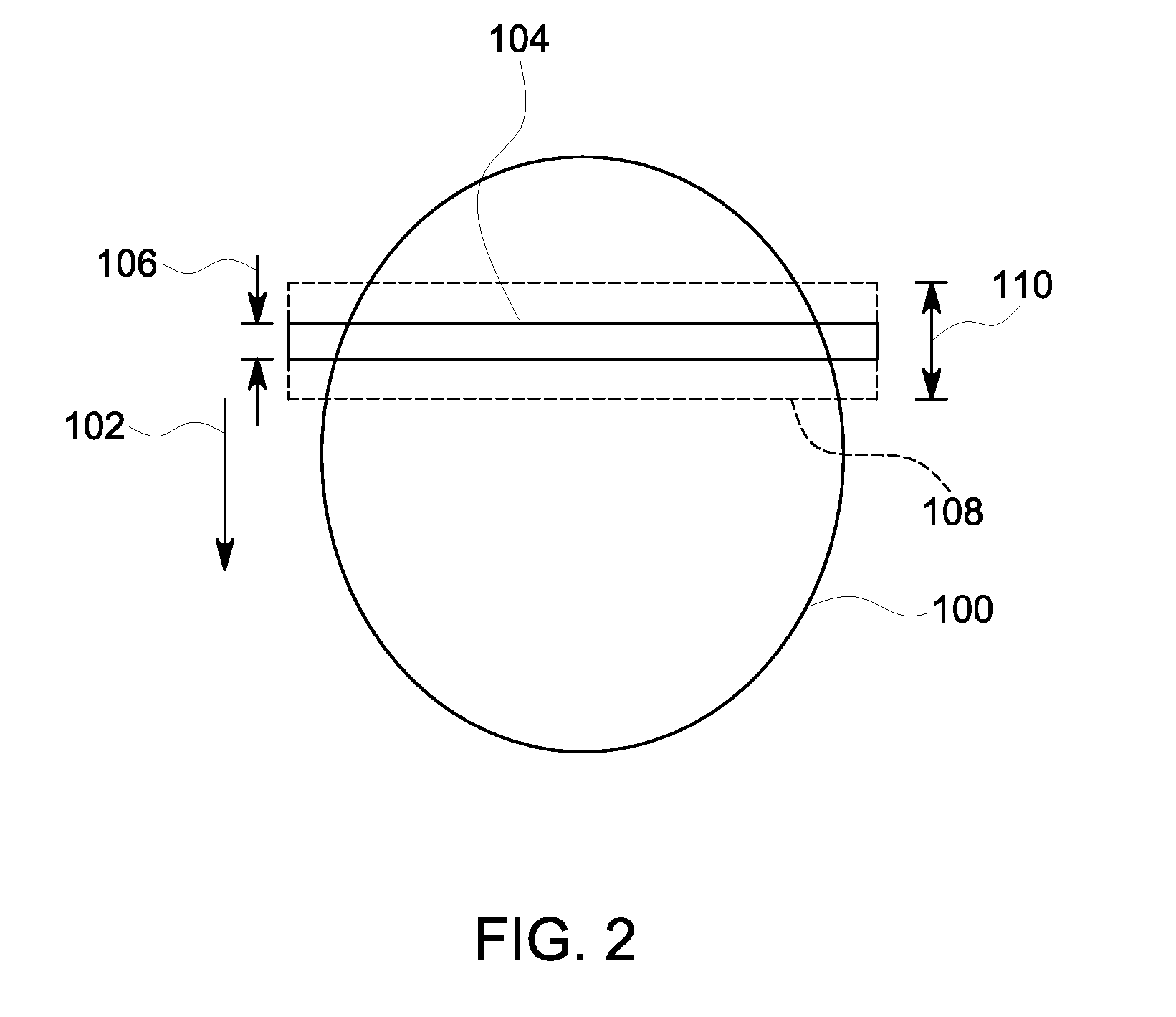
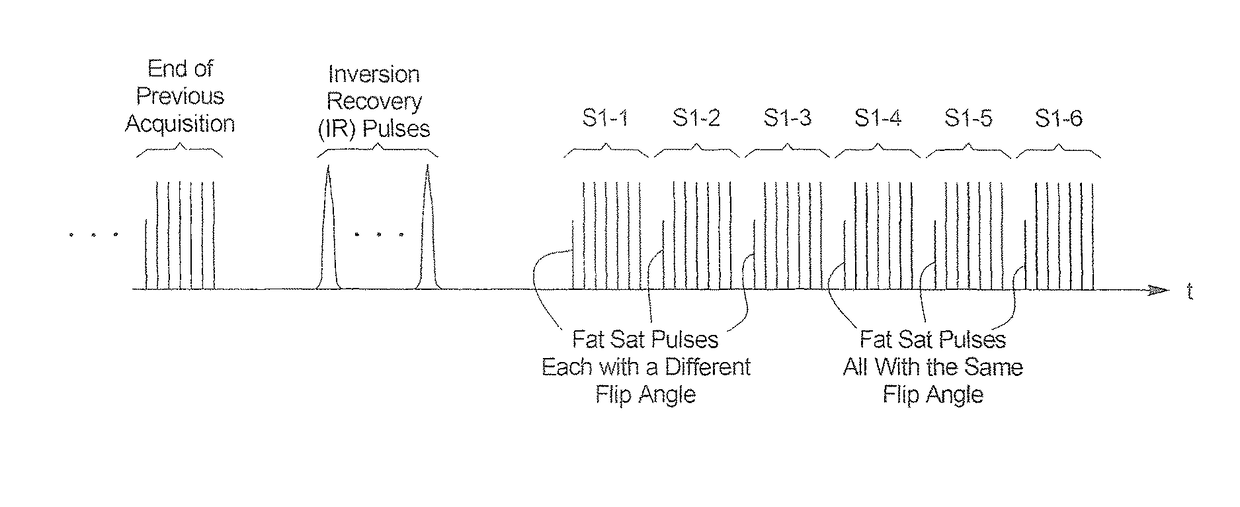
Method and apparatus for acquisition of magnetic resonance data with fat saturation pulses radiated with respectively different flip angles
ActiveUS20150268319A1Accelerated programUniform fat saturationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSaturation pulse
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an examination subject using an acquisition sequence that includes at least one acquisition cycle, wherein the acquisition cycle includes a readout block set with at least two readout blocks, and a saturation pulse set with at least two saturation pulses, the saturation pulses of the saturation pulse set are respectively associated with respective readout blocks of the readout block set, and the saturation pulses of the saturation pulse set have respectively varying flip angles.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
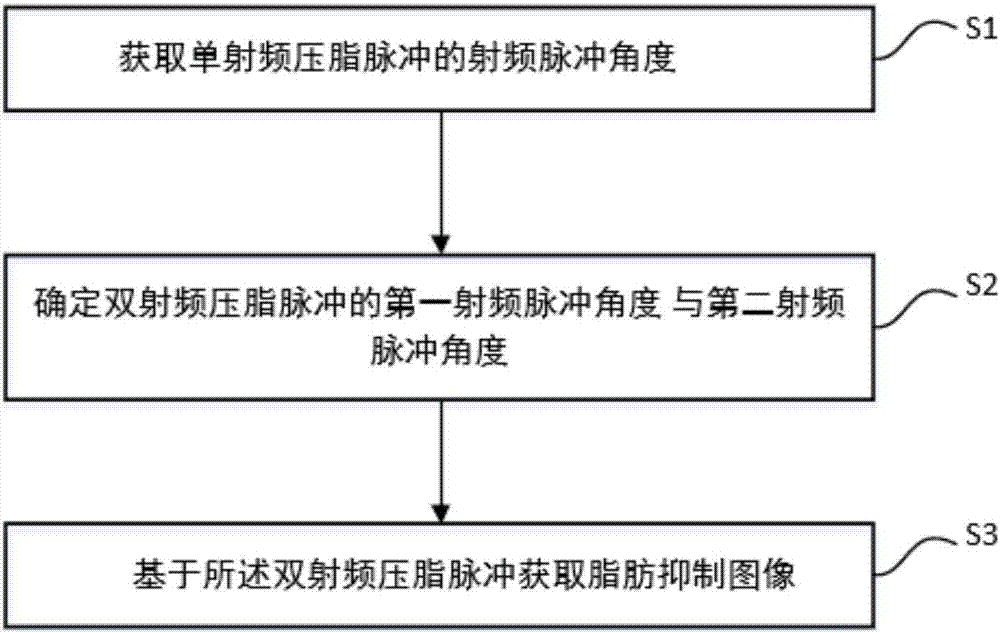
Method for acquiring magnetic resonance fat-suppression image, storage medium and scanning system
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a magnetic resonance fat-suppression image. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a radio-frequency pulse angle alpha of a single radio-frequency fat saturation pulse; determining a first radio-frequency pulse angle alpha1 and a second radio-frequency pulse angle alpha2 of a dual radio-frequency fat saturation pulse through the radio-frequency pulse angle alpha of the single radio-frequency fat saturation pulse; and acquiring the fat saturation image based on the first radio-frequency pulse angle alpha1 and the second radio-frequency pulse angle alpha2 of the dual radio-frequency fat saturation pulse. With the method for acquiring the magnetic resonance fat-suppression image, the sensitivity of fat saturation uniformity to a radio-frequency emission field can be remarkably reduced. The invention also relates to a storage medium and a scanning system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Automated spectral fat saturation
ActiveUS9632159B2Easy to separateImprove homogeneityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAutoanalysisResonance
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Therapeutic guidance compute node controller
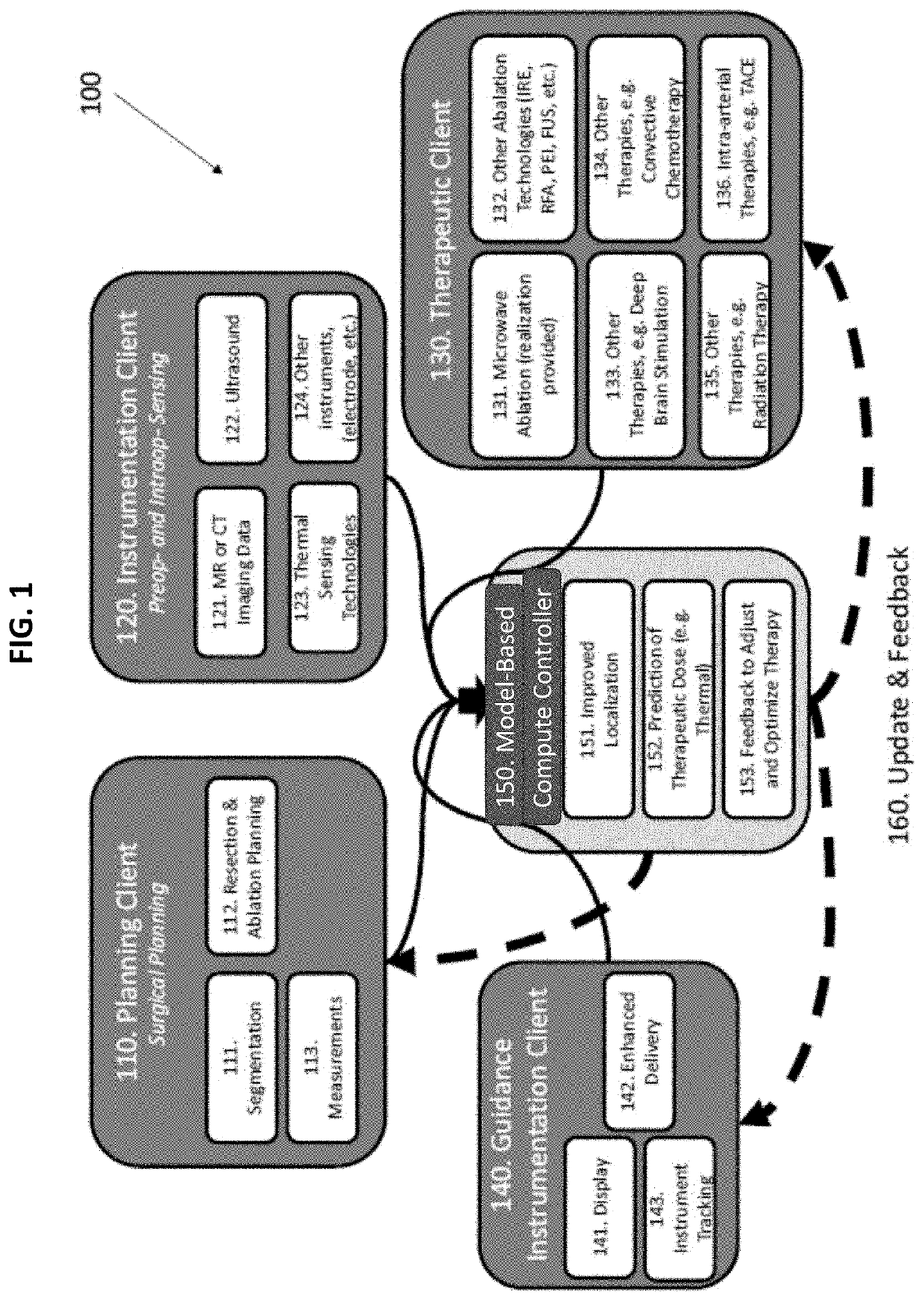
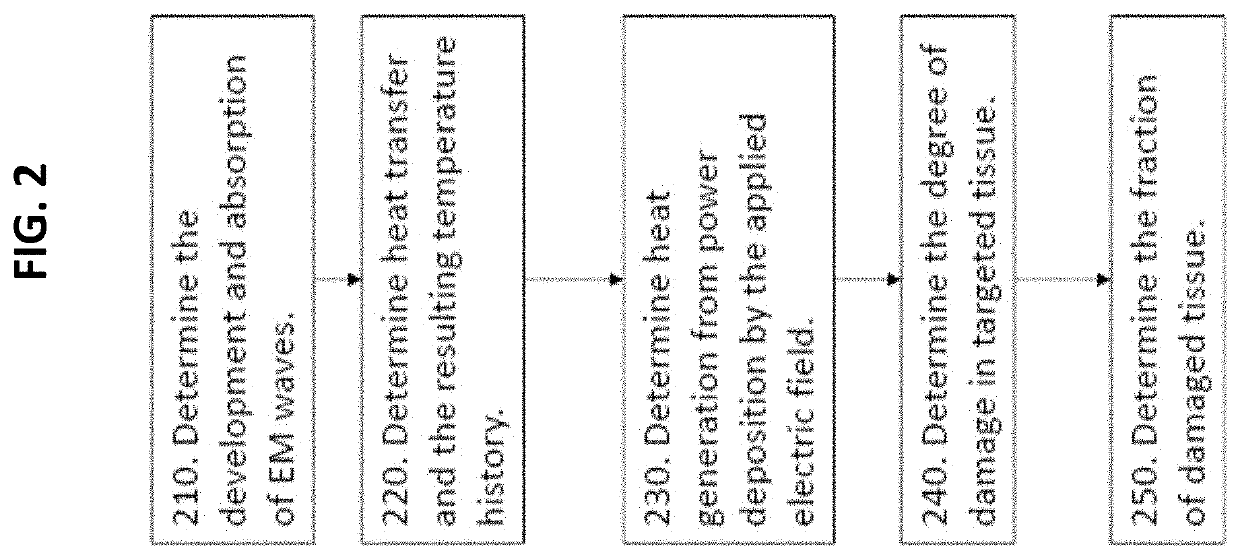
The various examples of the present disclosure are directed towards a multi-physics controller that can predict and monitor ablation procedures. In some examples of the present disclosure, fat saturation images can be used to create custom microwave ablation bioelectric / biothermal models. In some examples of the present disclosure, a deformation correction methodology can be used. Thereby, microwave and mechanics computational models can forecast therapeutic delivery intraoperatively while correcting for deformation.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
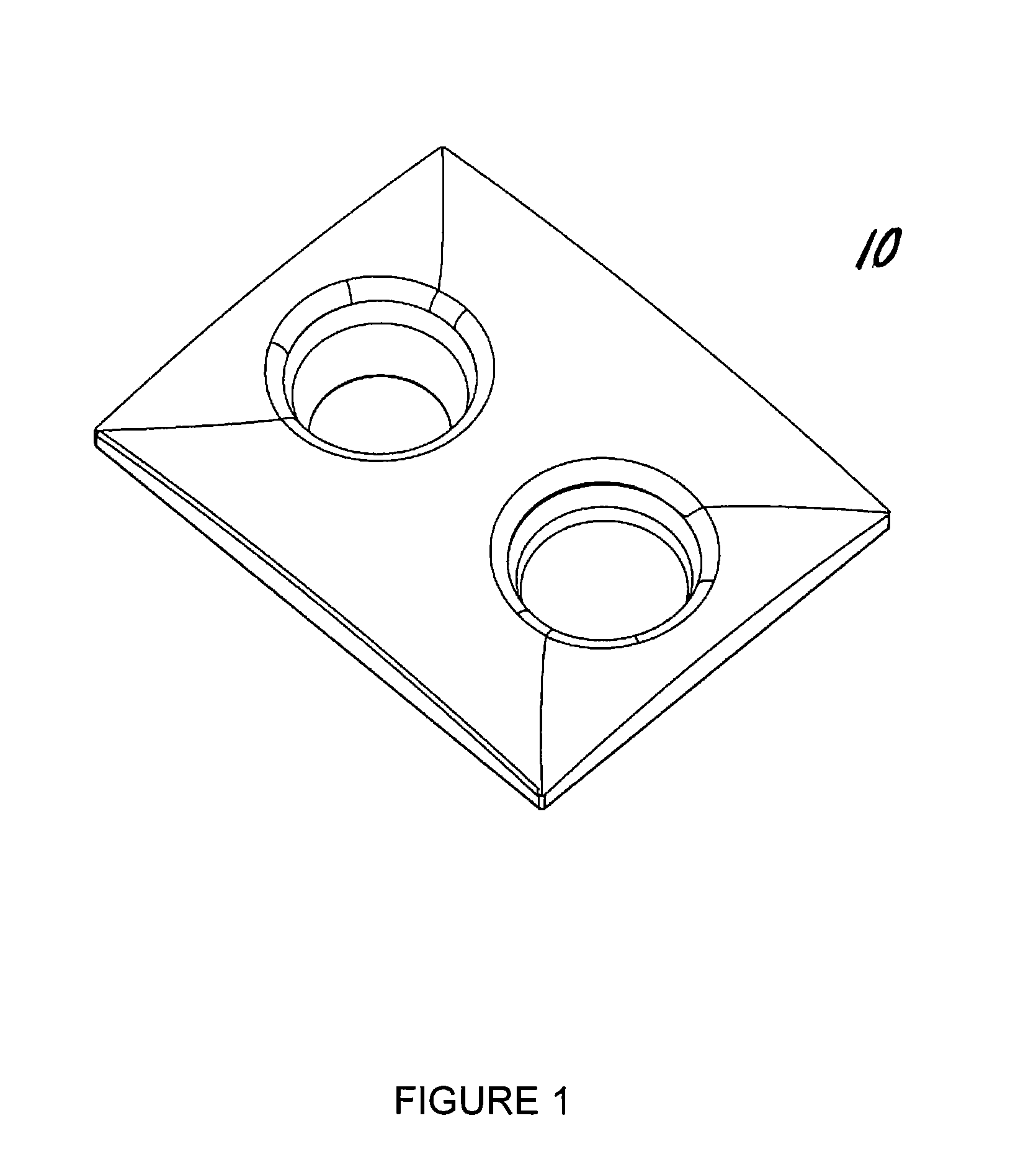
Method for improving magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
InactiveUS8078260B2Enhancing magnetic resonance (MR) imageIncrease elasticityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineAir interface
The present invention provides a fat saturation device to be used in conjunction with a magnetice resonance imaging (MRI) breast coil, which provides padding for the comfort of the patient being imaged while eliminating the skin-air interface, thereby reducing the level of artefacts in the image. The device comprises a coil surface pad that contacts the surface of the coil, the pad having apertures therein through which the patients breasts extend when the patient is positioned on the coil for imaging. Aperture sleeves that are removable or retractable extend from the bottom surface of the coil surface into the apertures of the breast coil. The device comprises a fat saturation material.
Owner:ORGAMEND
System and method for reducing localized signal fluctuation
A system and method is disclosed for eliminating localized fluctuation artifacts caused by fat signal contamination in MR images, the system includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system having a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet, and an RF transceiver system and an RF switch controlled by a pulse module to transmit RF signals to an RF coil assembly to acquire MR images, and a computer programmed to apply a spectral-spatial fat saturation pulse, apply a slice selection gradient pulse, acquire imaging data of an imaging slice of interest, and generate an image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for enhanced fat saturation during MRI
InactiveUS6933721B2Improve the uniformity of the magnetic fieldMinimize interactionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceEngineeringSilicon dioxide
The present invention provides for a method for using a silicon dioxide (SiO2) material that is equally effective in improving magnetic field homogeneity during MR imaging. The present invention further provides for using silicon dioxide in its granular state. The granular silicon dioxide can then be poured inside a flexible container and the flexible container can be formed to fit any contour of the body.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method for imaging in magnetic resonance tomography with spectral fat saturation or spectral water excitation
InactiveUS8395387B2Improve image qualityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceTomography
A magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) method with spectral fat saturation or spectral water excitation in a tissue region that is to be represented of a patient who is to be examined, includes the following steps: (Step 1) frequency adjustment measurement of a region of a patient that is to be represented with a selected first partial coil of the MRT system, (Step 2) precise determination of the resonance frequency of water with the aid of the spectrum obtained in Step 1 exhibiting the resonance frequencies of fat and water, (Step 3) repetition of Steps 1 and 2 with at least one additionally selected second partial coil of the MRT system adjacent to the first partial coil, (Step 4) measuring of a k space data record with a partial coil or a partial coil combination on the basis of the water resonance frequency assigned to these partial coils, (Step 5) repetition of Step 4 with other partial coils or other partial coil combinations until the entire tissue region to be represented has been measured, (Step 6) combining of the measuring results obtained in Steps 4 and 5, and (Step 7) representing of the results obtained in Step 6 in the image space in the form of an overall image of the tissue region to be represented.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and magnetic resonance scanner for acquiring a magnetic resonance data set
ActiveUS20150226819A1Uniform fat saturationHigh saturationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) scanner for acquiring an MR data set of multiple slices of a volume of interest of an examination object (patient), on receipt of a trigger signal relating to the patient's respiration and indicating the start of an acquisition time window, a fat saturation technique is begun and, in one of a number of acquisition blocks having a number of echo trains each relating to a single slice and a single portion of k-space, wherein all the echo trains of each individual acquisition block relate to different slices, magnetic resonance data for the different slices are acquired. A magnetic resonance image of each slice is determined for that slice by combining magnetic resonance data acquired in different acquisition blocks and relating to a portion of k-space. For at least two of the acquisition blocks, a different sequence of the slices to be acquired by the echo trains is used within the acquisition block.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and magnetic resonance scanner for acquiring a magnetic resonance data set
ActiveUS10088541B2Uniform fat saturationHigh saturationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) scanner for acquiring an MR data set of multiple slices of a volume of interest of an examination object (patient), on receipt of a trigger signal relating to the patient's respiration and indicating the start of an acquisition time window, a fat saturation technique is begun and, in one of a number of acquisition blocks having a number of echo trains each relating to a single slice and a single portion of k-space, wherein all the echo trains of each individual acquisition block relate to different slices, magnetic resonance data for the different slices are acquired. A magnetic resonance image of each slice is determined for that slice by combining magnetic resonance data acquired in different acquisition blocks and relating to a portion of k-space. For at least two of the acquisition blocks, a different sequence of the slices to be acquired by the echo trains is used within the acquisition block.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance apparatus and method for vascular imaging
ActiveUS20180335497A1Sharp contrastSuppressing background signalMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMagnetization transfer
In a magnetic resonance method and apparatus for time-of-flight vascular imaging, a magnetic field is applied to an imaging volume and an inflow volume, from which liquid enters into the imaging volume, of an examination person. The imaging volume is excited by an RF pulse, which fulfills a magnetization transfer function and a fat saturation function, while the magnetic field is being applied. The RF pulse has a frequency distribution whose frequencies are higher than the center frequency of water in the imaging volume, and that includes the fat frequency in the imaging volume. The magnetic field has a field distribution with an apex with essentially no spatial gradient in the imaging volume and having a higher spatial gradient in the inflow volume, so that the center frequency of water in the inflow volume is shifted in the direction of lower frequencies and is no longer affected by the RF pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance imaging device
Owner:ORGAMEND
Non-invasive temperature mapping using temperature-responsive water saturation shift referencing (T-WASSR) MRI
ActiveUS10274564B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWater useTemperature response
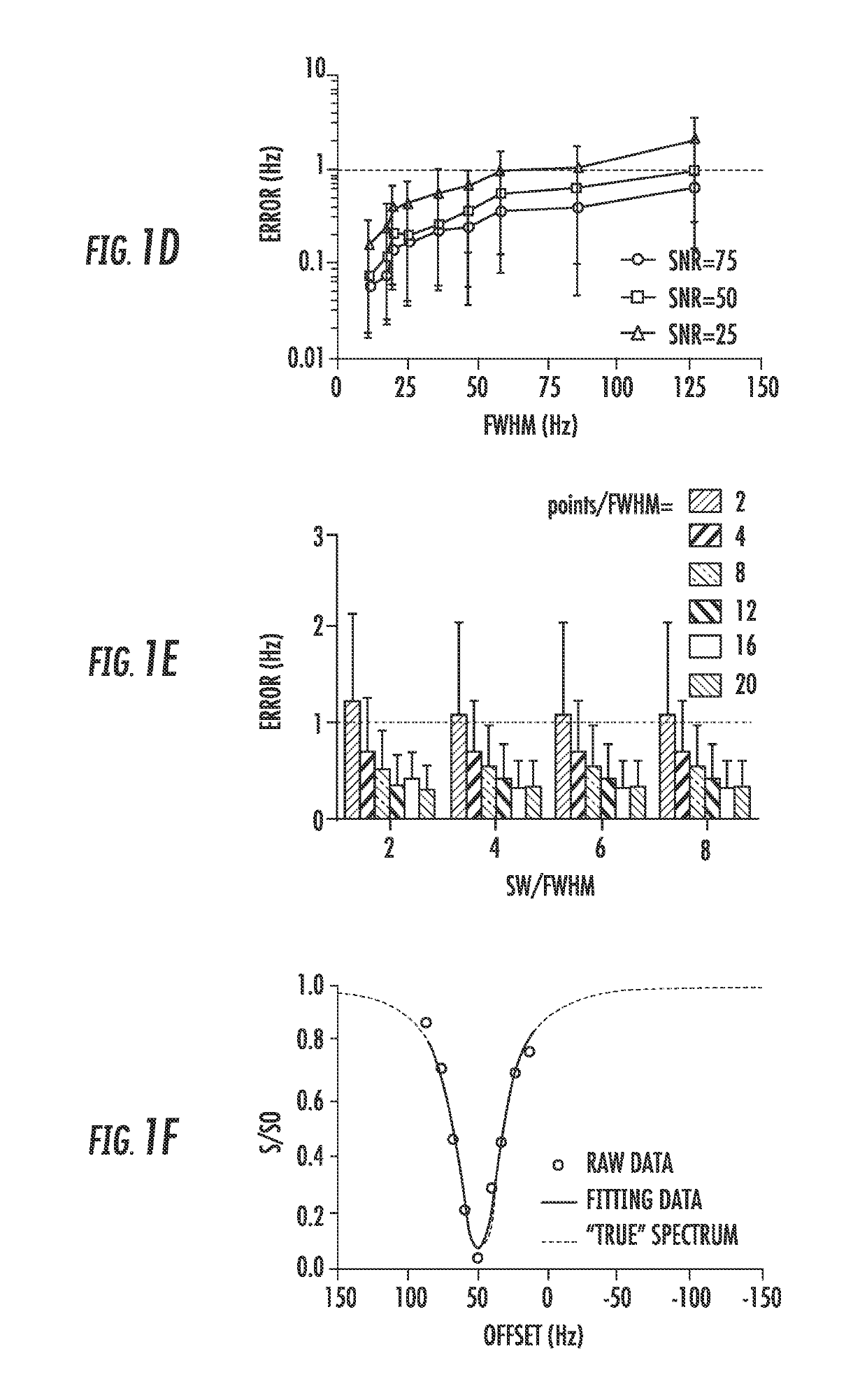
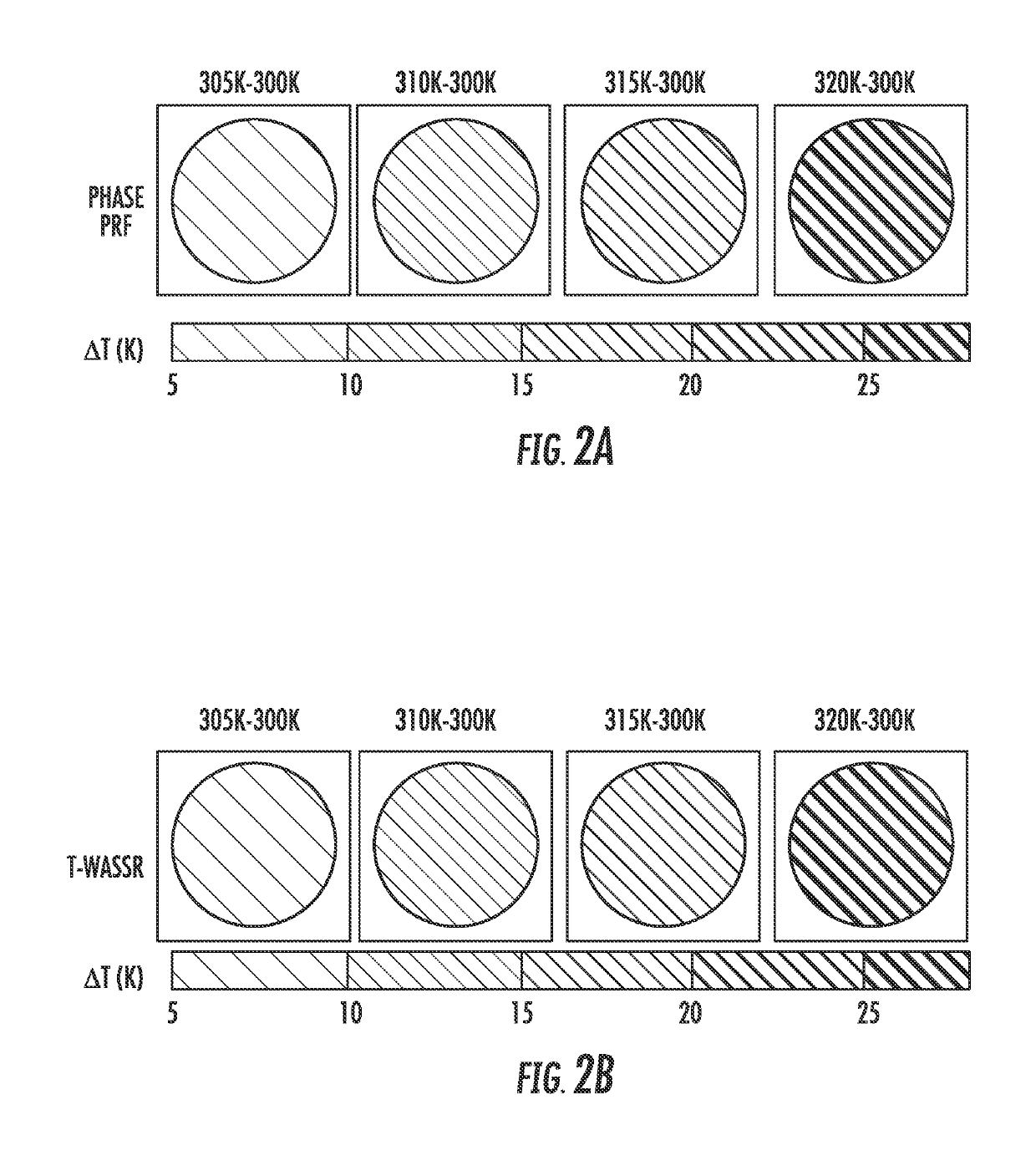
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method of non-invasively detecting and imaging temperature or temperature changes by assessing the temperature induced shifts in the saturation spectrum of water using MRI, namely saturation shift referencing. This procedure includes the MRI procedures to assess water saturation spectrum and the data processing steps to determine the temperature induced shifts of water resonance frequency and consequently to estimate the temperature change. This procedure also includes the procedure of assessing fat saturation spectrum and estimating fat resonance frequency. This method can be used as a clinical procedure for temperature mapping in multiple applications, especially where a significant amount of fat is present. One application is to monitor the temperature of the targeted tumor and its surrounding tissues during the procedure of hyperthermia. Such local hyperthermia can be applied, using high-intensity focus-ultrasound for deep-seated tissues or heating supplies for superficial tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method and apparatus for acquisition of magnetic resonance data with fat saturation pulses radiated with respectively different flip angles
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an examination subject using an acquisition sequence that includes at least one acquisition cycle, wherein the acquisition cycle includes a readout block set with at least two readout blocks, and a saturation pulse set with at least two saturation pulses, the saturation pulses of the saturation pulse set are respectively associated with respective readout blocks of the readout block set, and the saturation pulses of the saturation pulse set have respectively varying flip angles.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance data acquisition method and apparatus saturation with spin dependent on the anatomical structures to be imaged
ActiveUS10317492B2Easy to upgradeIncrease loadMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnatomical structuresResonance
In a method, computer and magnetic resonance imaging system for determining a control sequence for operating the magnetic resonance imaging system to generate magnetic resonance image data of a region to be imaged of an examination subject, from which magnetic resonance raw data are acquired, information describing the anatomical structure of the region to be imaged is made available in the computer, and a surrounding area and a central area are specified in the region to be imaged dependent on the determined anatomical structure. Furthermore, a one-dimensional water / fat saturation pulse sequence for saturating the surrounding areas is determined and a multidimensional water / fat saturation pulse sequence for saturating the central area is determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
3D gradient spin echo diffusion imaging method for inversion recovery preparation, medium and equipment
PendingCN113476031AInhibit ADC valueReduce scan timeMedical imagingDiagnostic signal processingInversion recoveryNoise (radio)
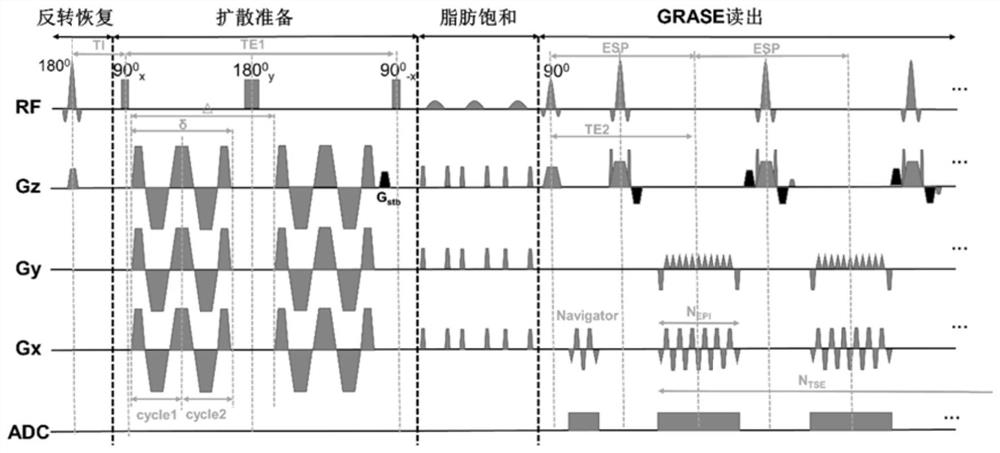
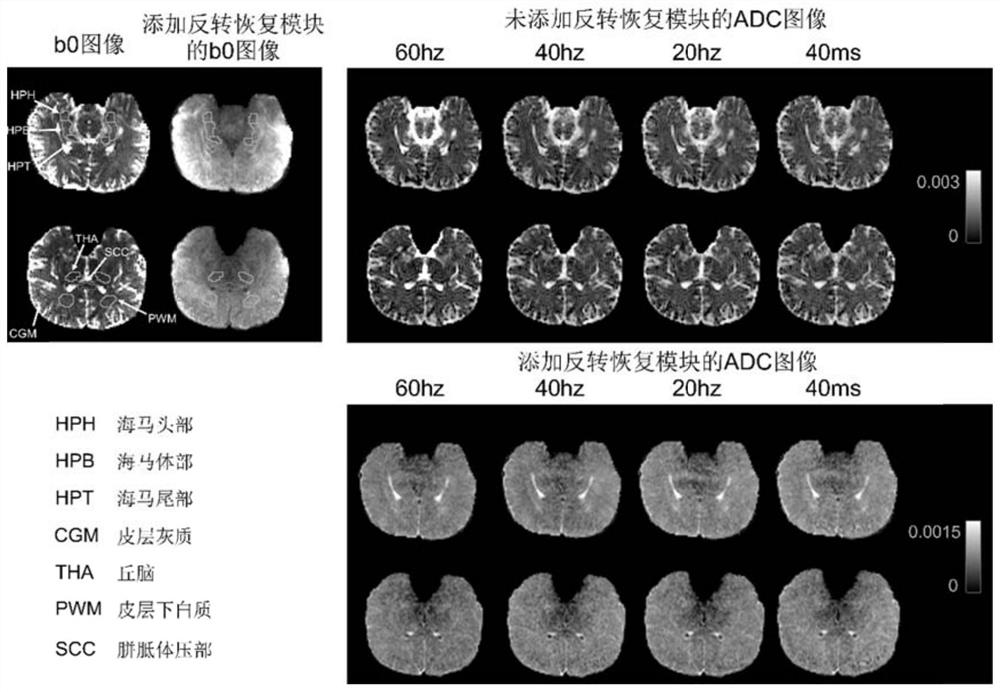
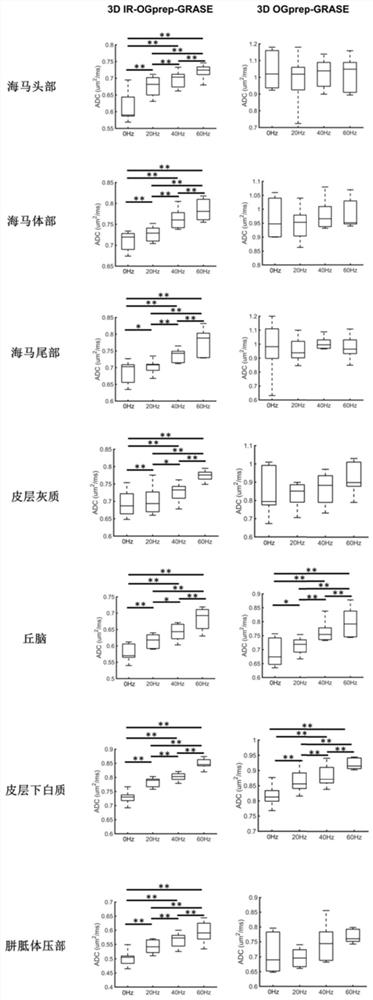
The invention discloses a 3D gradient spin echo diffusion imaging method for inversion recovery preparation, a medium and equipment. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, in an inversion recovery preparation module, applying 180-degree inversion radio frequency pulse, and setting corresponding inversion recovery time to inhibit cerebrospinal fluid and free water signals; secondly, embedding a pair of trapezoidal cosine oscillation gradients or pulse gradients into 90-degree x-180-degree y-90-degree-x radio frequency pulses through a diffusion coding module, and separating diffusion coding from signal acquisition; then, inhibiting a fat signal by using a fat saturation module; and finally, collecting signals by adopting a 3D gradient spin echo reading mode. The time and the signal-to-noise ratio of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging are improved, accurate measurement of brain tissue diffusion magnetic resonance signal time dependence is facilitated, the effect is especially obvious for a brain area which is near a ventricle and is influenced by the cerebrospinal fluid due to a partial volume effect, and the clinical transformation of a time-dependent diffusion magnetic resonance technology is effectively promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and magnetic resonance system for fat saturation
ActiveUS9971005B2Choose simpleHigh saturationMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceSPAIR
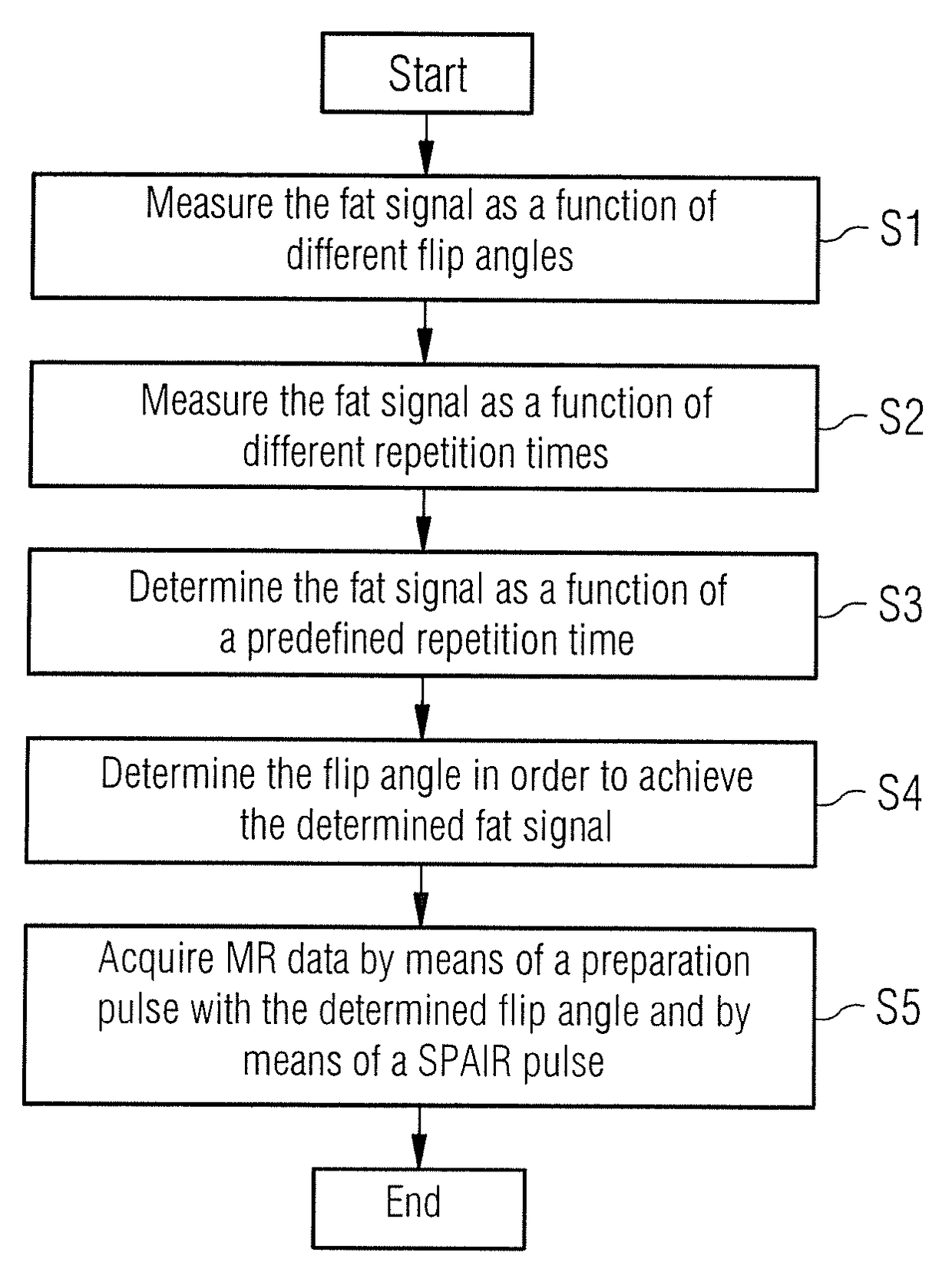
In a method and a magnetic resonance (MR) system for fat saturation when acquiring MR data in a predetermined volume segment of an examination object (O), a flip angle is determined as a function of a predetermined requirement for a fat signal that is acquired by the magnetic resonance system in the volume segment, and an RF preparation pulse is emitted that has the determined flip angle. This is followed by emission of a SPAIR pulse, followed by acquisition of the MR data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
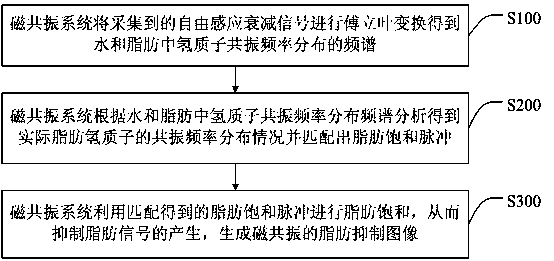
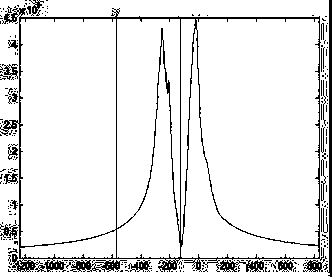
A kind of image processing method and device for suppressing fat signal
ActiveCN106952261BInhibitionEnhanced inhibitory effectImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumFat suppression
The invention discloses an image processing method and an image processing device for suppressing a fat signal. The image processing method comprises the steps that: a magnetic resonance system carries out Fourier transform on a collected free induction decay signal to obtain a resonance frequency distribution spectrum of hydrogen protons in water and fat; the magnetic resonance system analyses the resonance frequency distribution spectrum of the hydrogen protons in water and fat, so as to obtain resonance frequency distribution situations of actual fat hydrogen protons and match fat saturation pulses; and the magnetic resonance system performs fat saturation by utilizing the fat saturation pulses obtained through matching, so as to suppress the generation of the fat signal and generate a fat suppression image of magnetic resonance. The image processing method and the image processing device apply the fat saturation pulses with different bandwidths and central frequencies according to the resonance frequency distribution situations of actual fat hydrogen protons, suppress the fat signal by means of the fat saturation pulses, and improve the success rate of fat suppression, thereby acquiring the magnetic resonance image with obvious fat suppression effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com