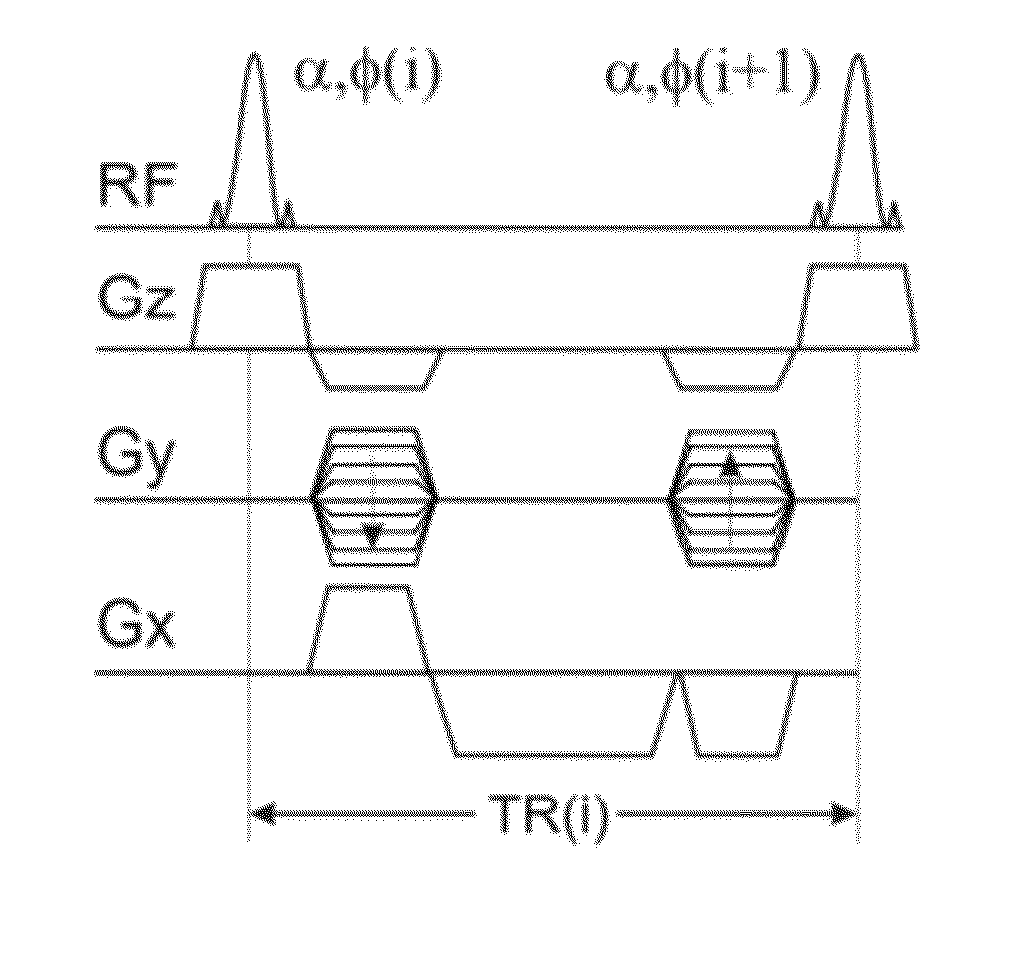
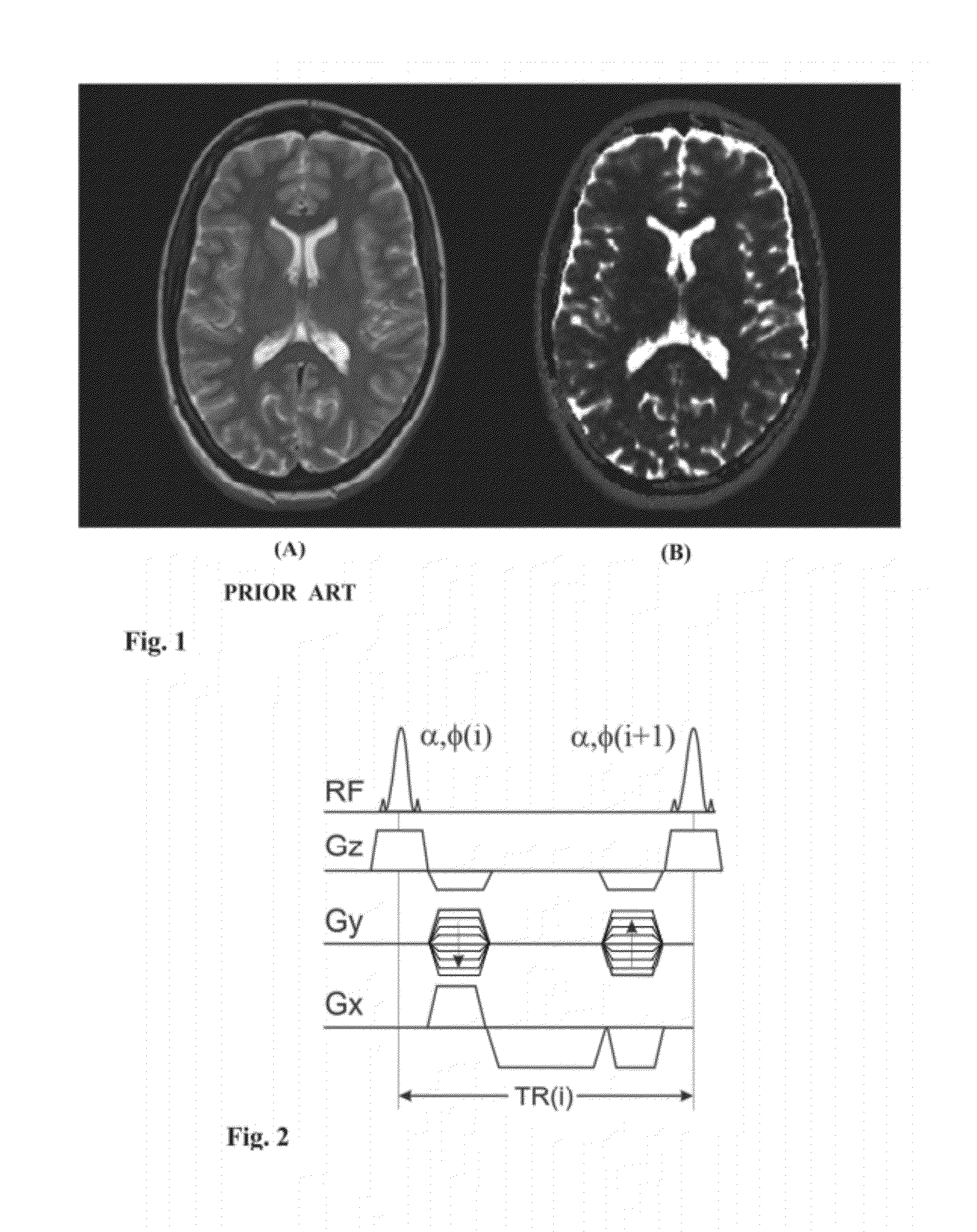
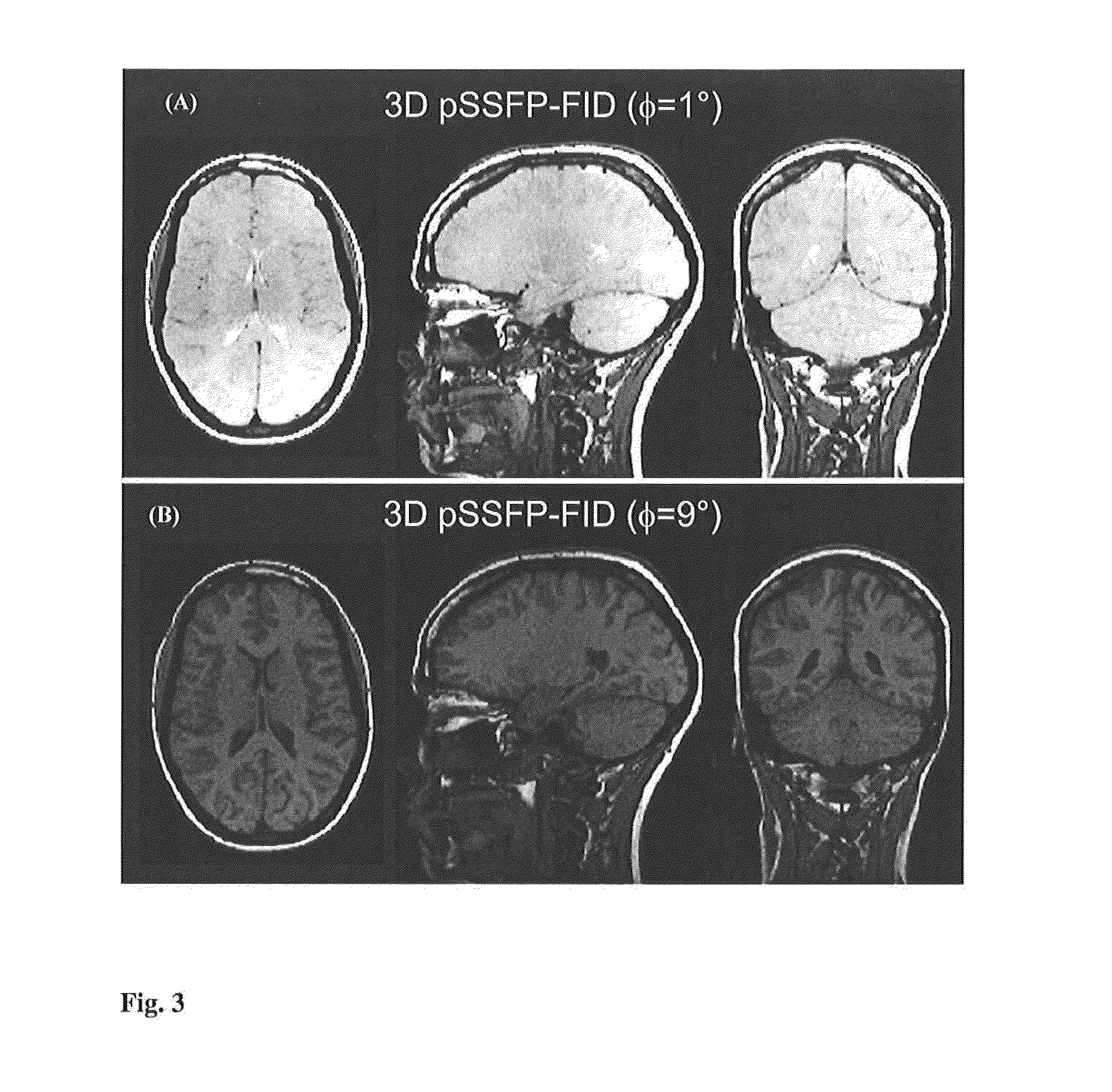
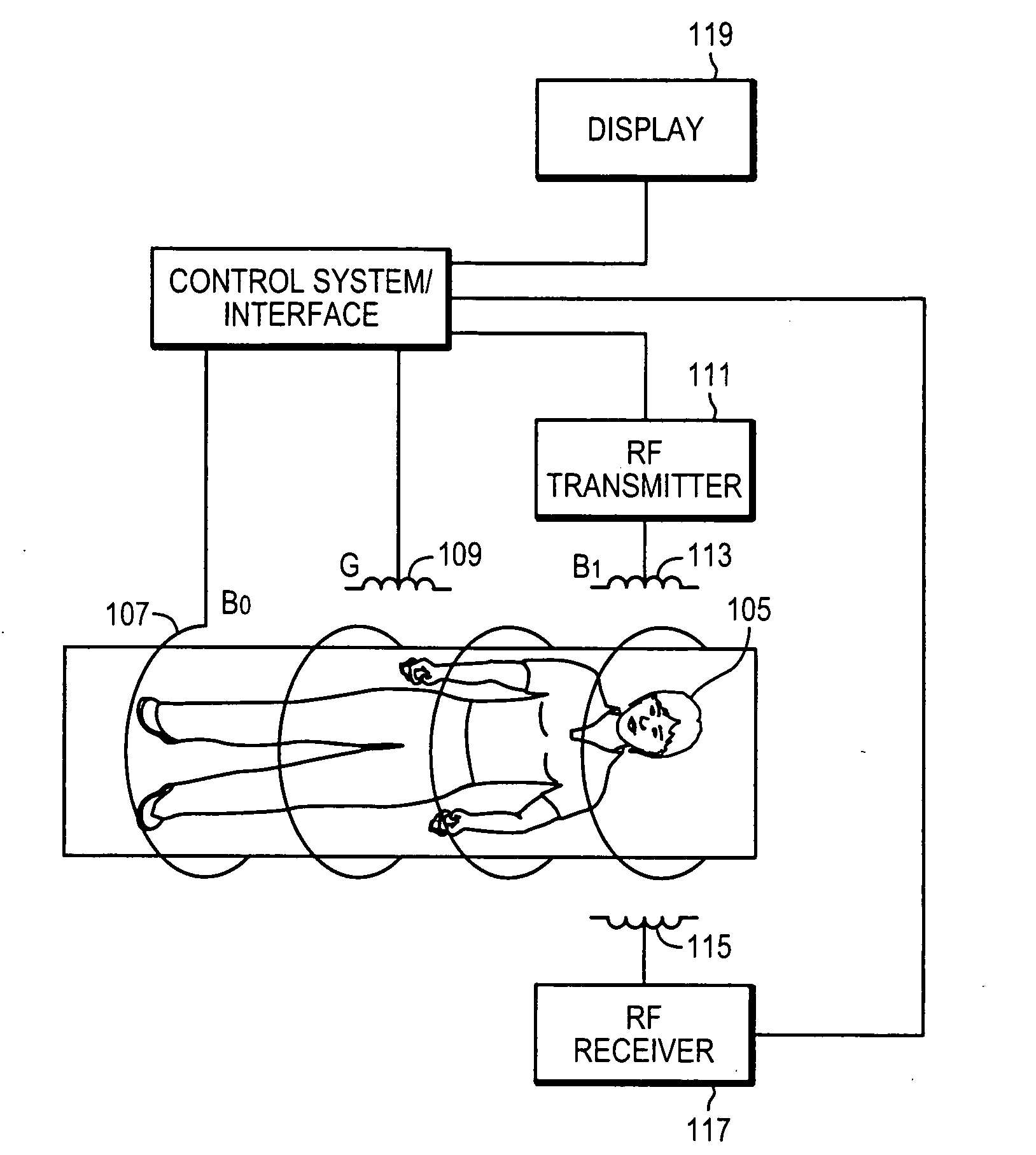
Patents
Literature
108 results about "Magnetization transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
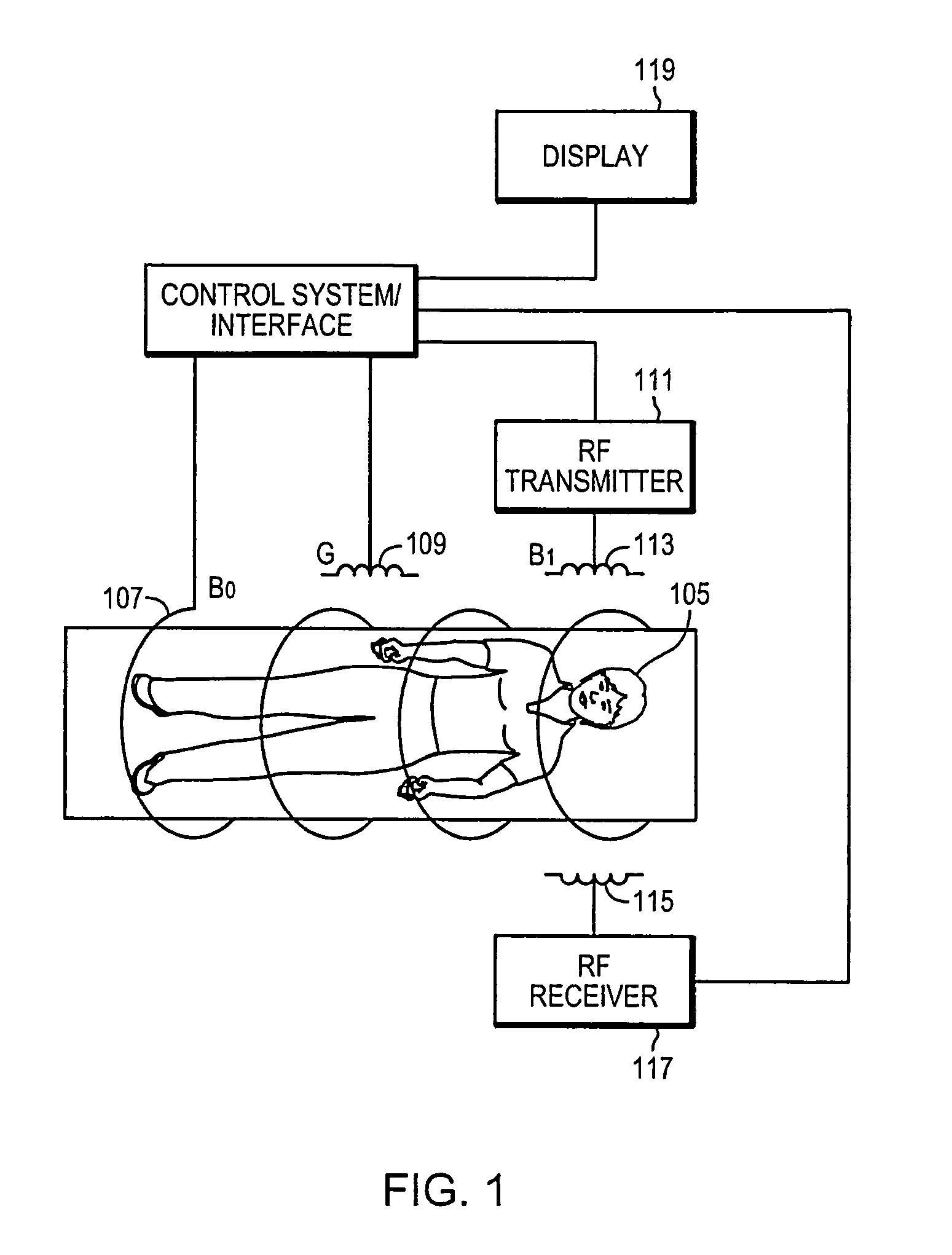
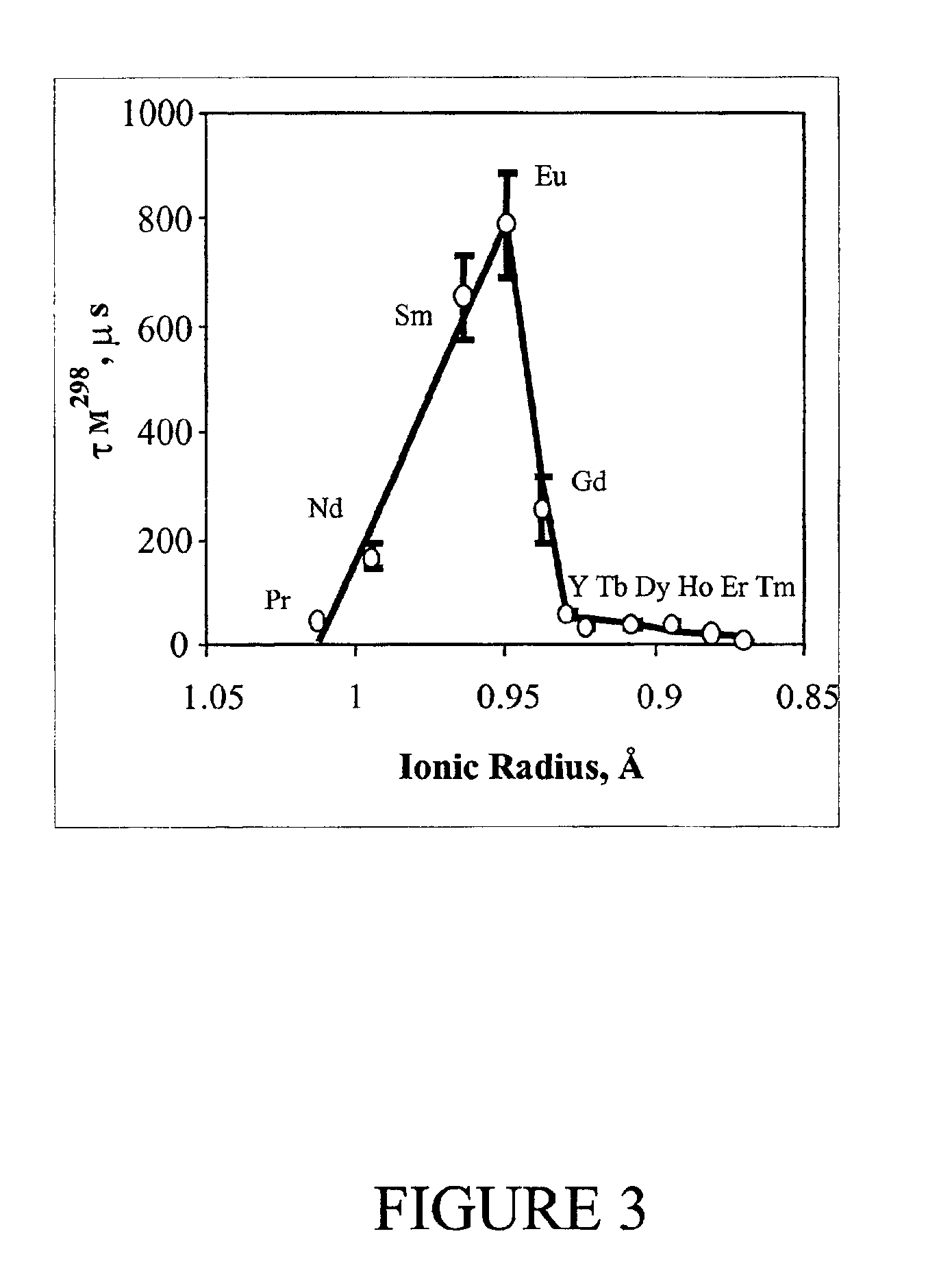
Magnetization transfer (MT), in NMR and MRI, refers to the transfer of nuclear spin polarization and/or spin coherence from one population of nuclei to another population of nuclei, and to techniques that make use of these phenomena. There is some ambiguity regarding the precise definition of magnetization transfer, however the general definition given above encompasses all more specific notions. NMR active nuclei, those with non-zero spin, can be energetically coupled to one another under certain conditions. The mechanisms of nuclear-spin energy-coupling have been extensively characterized and are described in the following articles: Angular momentum coupling, Magnetic dipole–dipole interaction, J-coupling, Residual dipolar coupling, Nuclear Overhauser effect, Spin–spin relaxation, and Spin saturation transfer. Alternatively, some nuclei in a chemical system are labile and exchange between non-equivalent environments. A more specific example of this case is presented in the section Chemical Exchange Magnetization transfer.
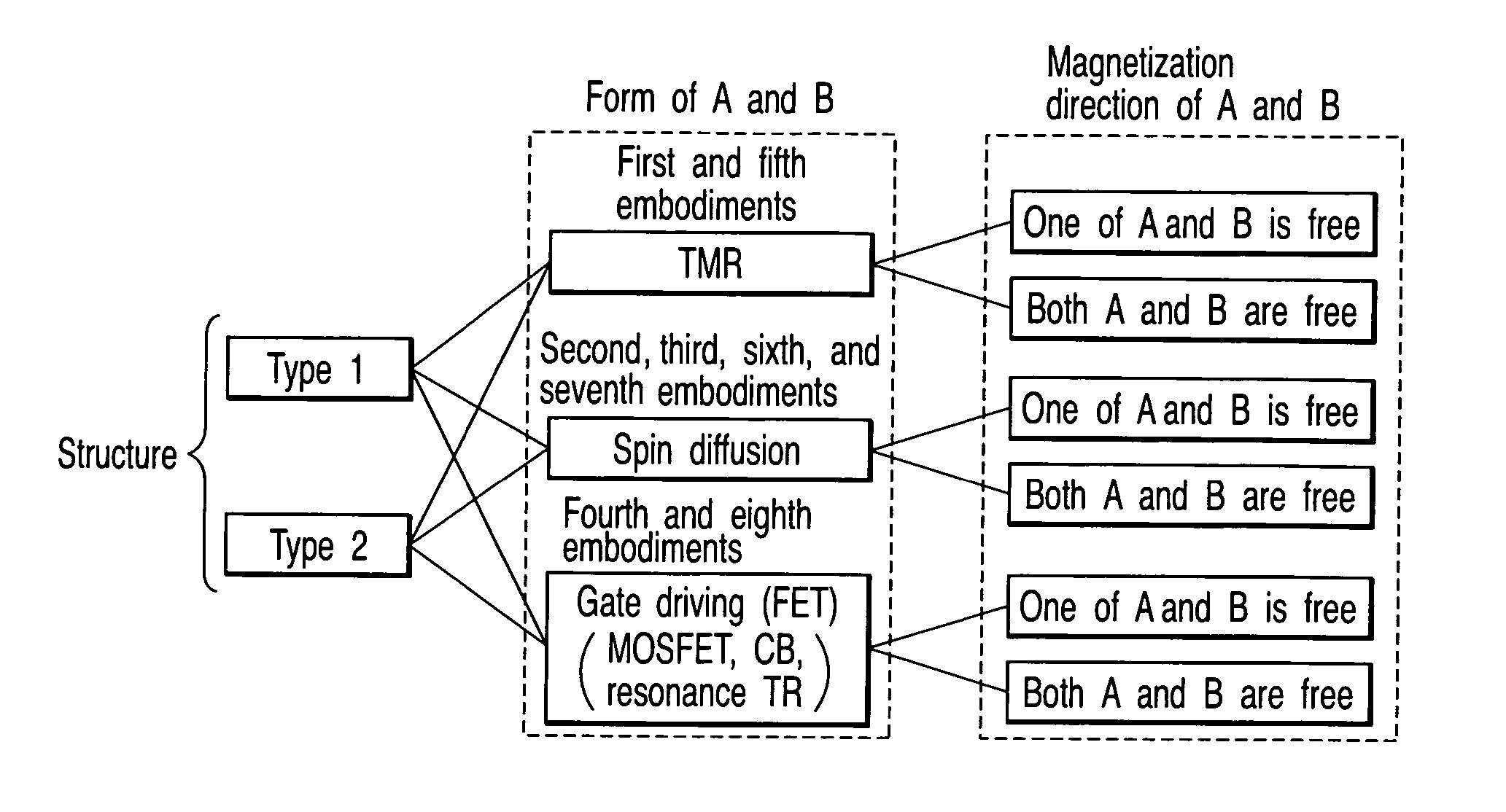
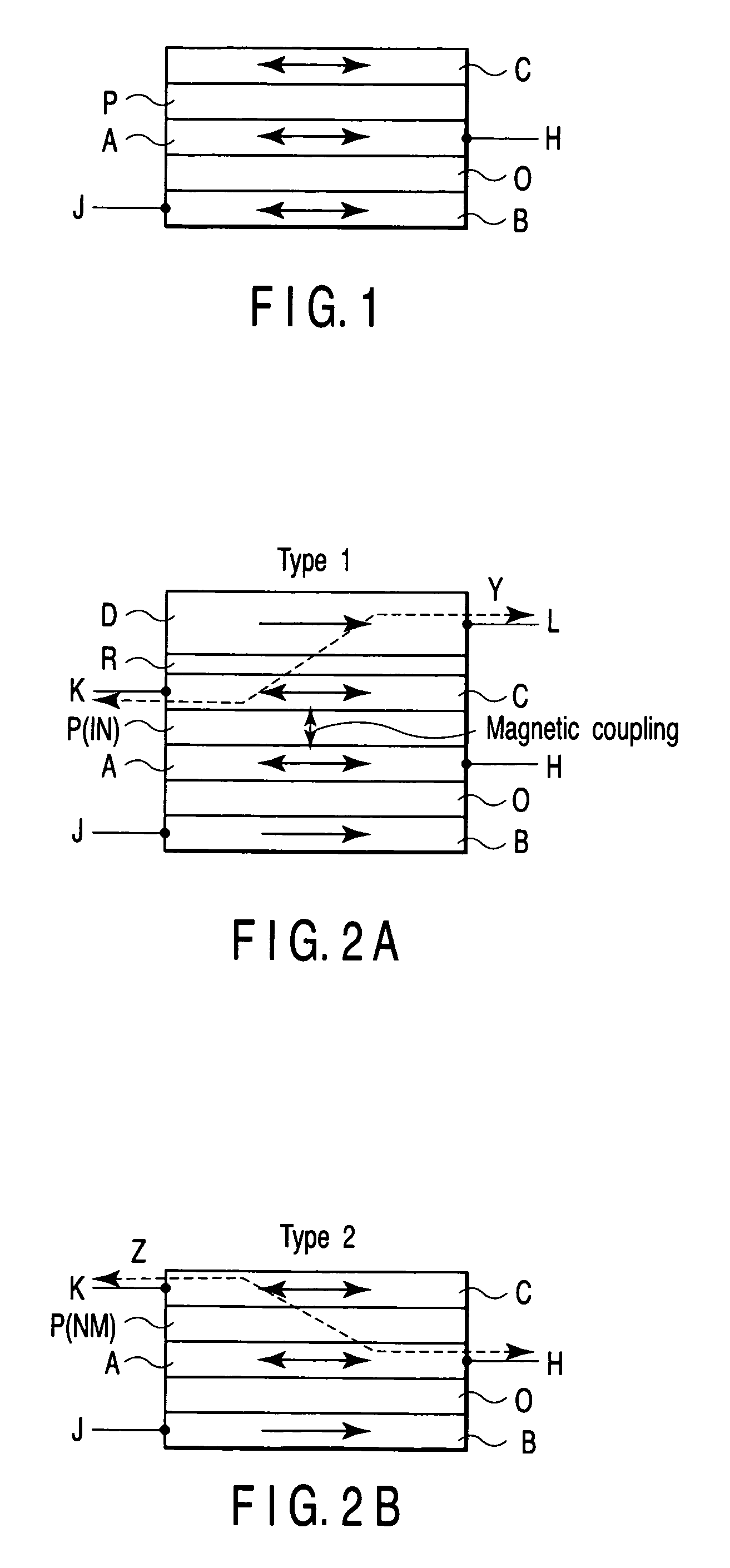
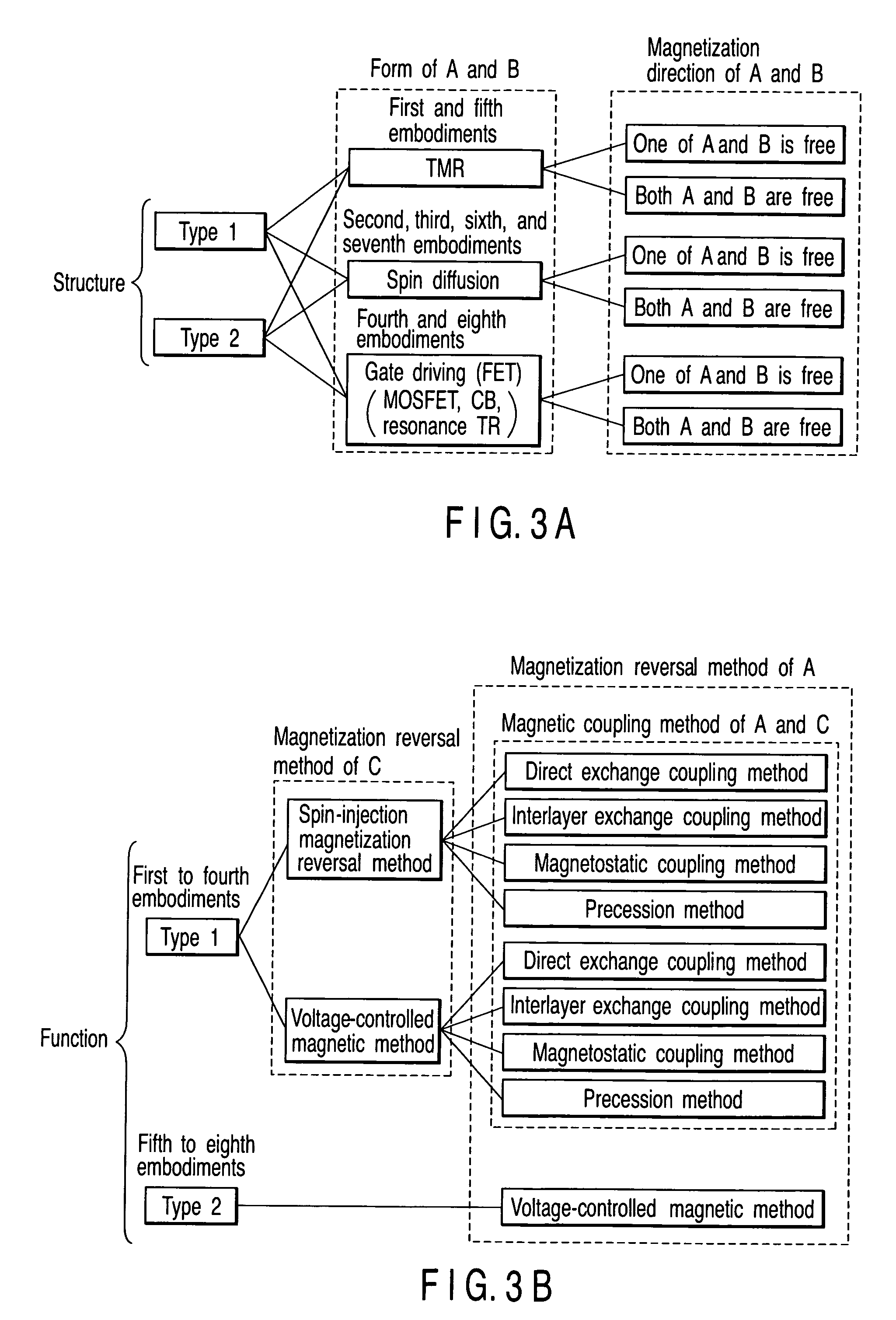
Magnetic element
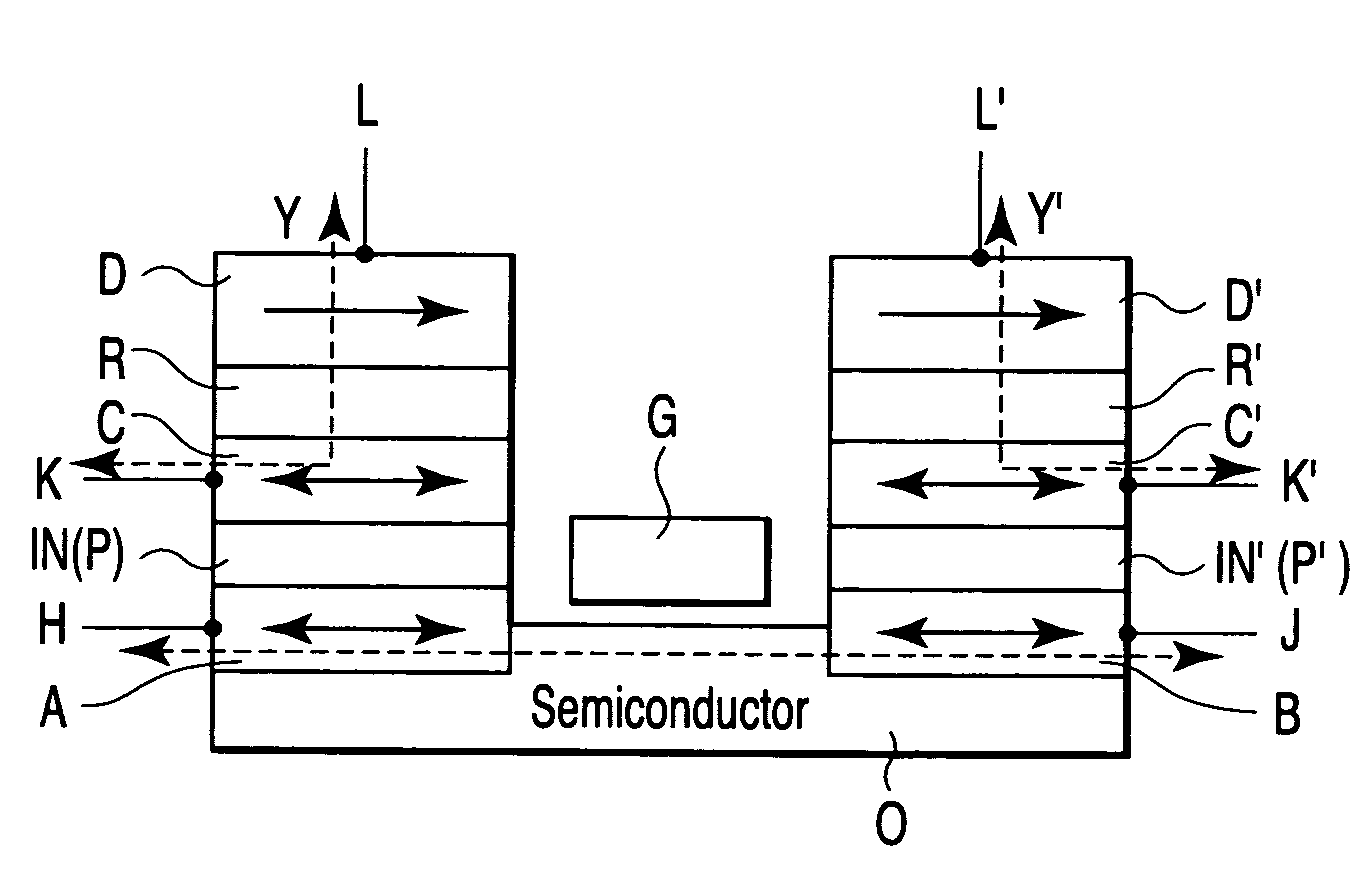
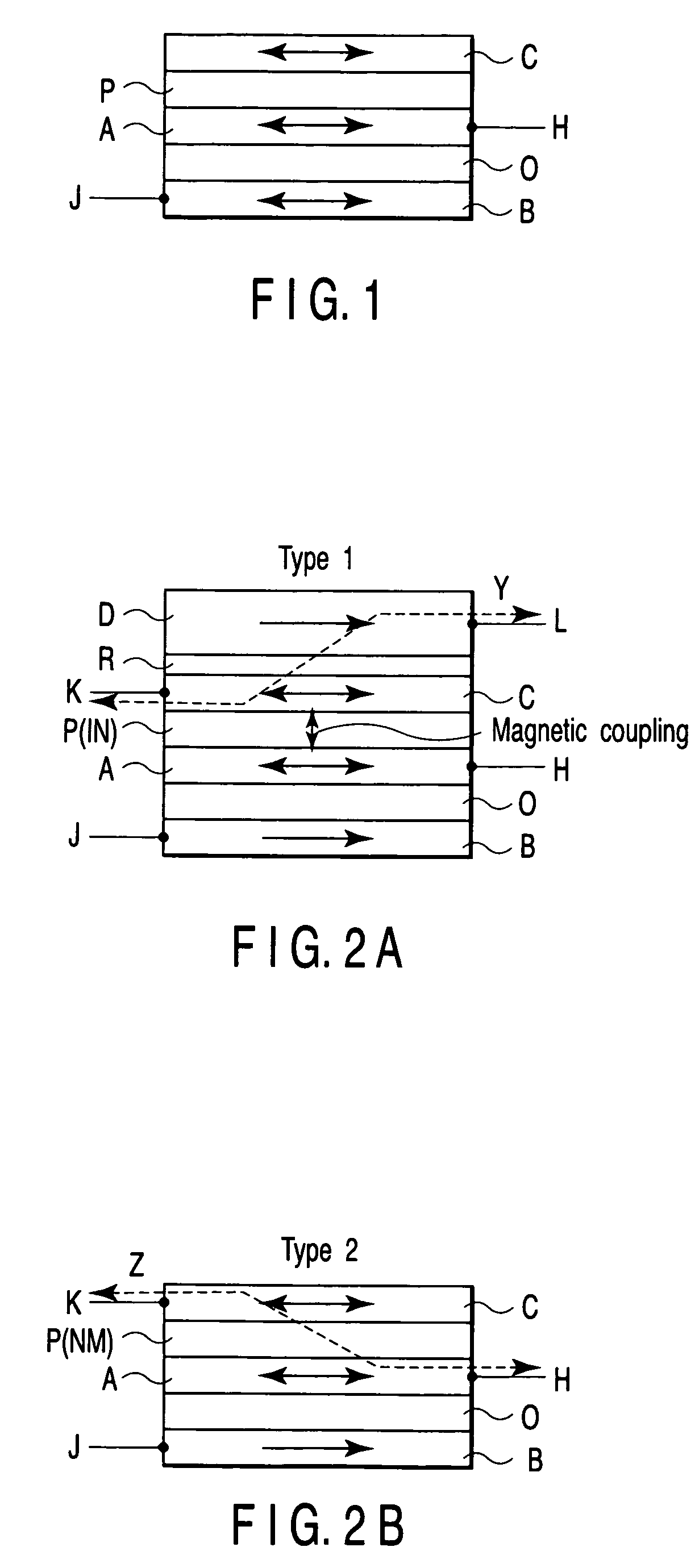
A magnetic element includes a channel layer, a first magnetic electrode which is in contact with the channel layer, a second magnetic electrode which is in contact with the channel layer and is insulated from the first magnetic electrode, a first intermediate layer which is provided adjacent to the first magnetic electrode and has a first insulating layer, a first magnetic layer which is provided in contact with a surface of the first intermediate layer on an opposite side to a surface contacting the first magnetic electrode to transfer magnetization to the first magnetic electrode, a first electrode which is connected to the first magnetic electrode, and a second electrode which is connected to the second magnetic electrode, at least one of the first electrode and the second electrode outputting a first signal which changes depending on a magnetic arrangement of the first magnetic electrode and the second magnetic electrode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
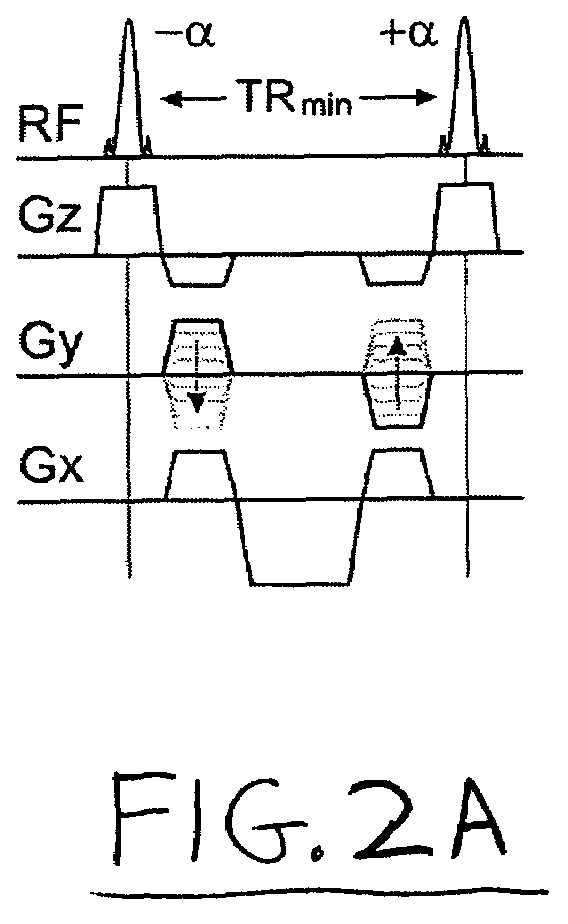
MR imaging using nested pulse sequence involving IR pulse
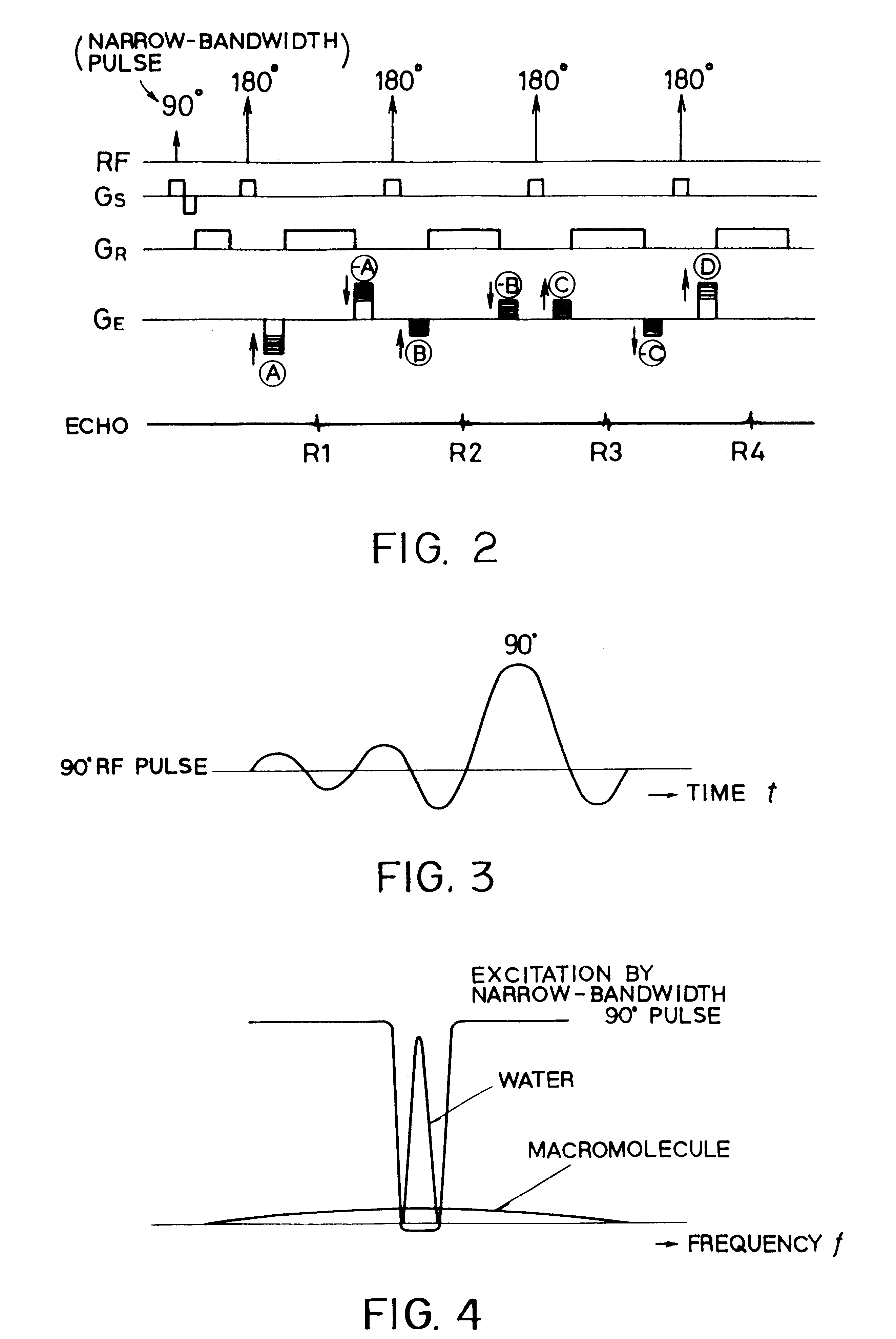
InactiveUS6850793B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSignificant positive effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCross relaxationImage contrast
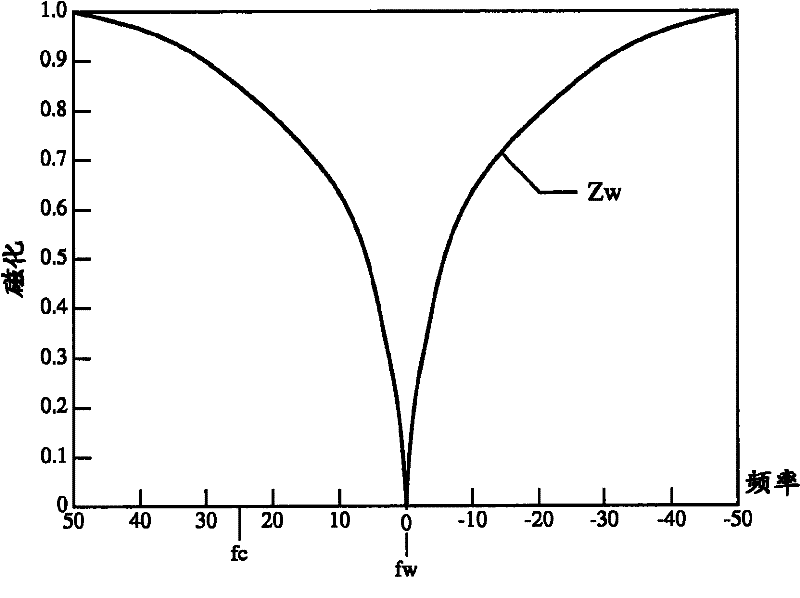
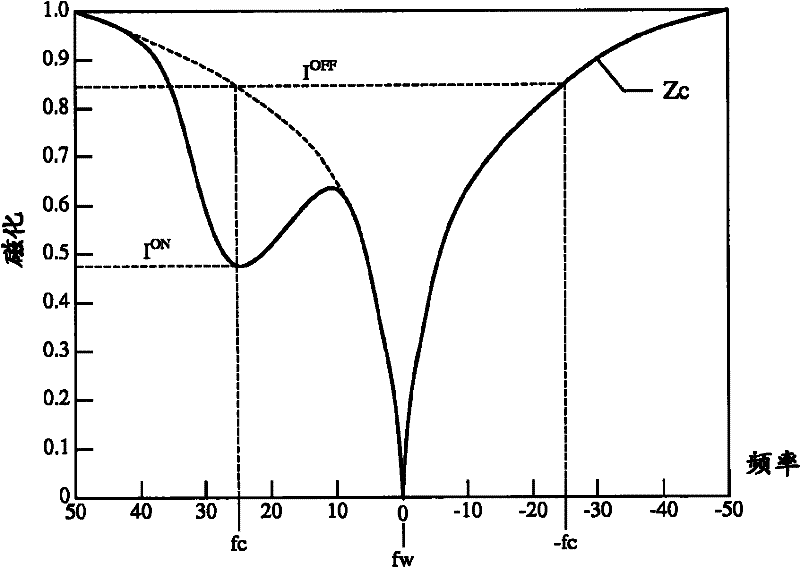
In addition to the known MT (magnetization transfer) effect, an RMT (reverse MT) is newly found, which increases a detected MR signal strength. Both the MT and RMT effects can be explained with mutual interaction, such as phenomena of chemical exchange and / or cross relaxation, acted between a pool of water proton spins and another pool of macromolecule proton spins, for example, within an object. In order to enhance the MT or RMT effect, the frequency bandwidths of RF pulses, such as a 90° RF exciting pulse in a SE or FSE method, an inversion pulse in a FLAIR or fast FLAIR method, and others, are controlled. To enhance the MT effect, the bandwidth is controlled into a wider value (approx. more than 1250 Hz) than the normally (conventionally) used bandwidth, while to obtain the RMT effect, the bandwidth is controlled into a narrower value (approx. less than 1000 Hz) than the normally used bandwidth. Actively controlling the MT or RMT effect permits changed image contrast in MR imaging.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
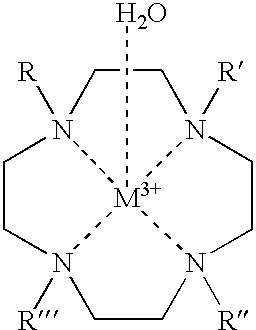
Paramagnetic metal ion-based macrocylic magnetization transfer contrast agents and method of use
InactiveUS20020127182A1Group 3/13 element organic compoundsDiagnostic recording/measuringHydrogenResonance
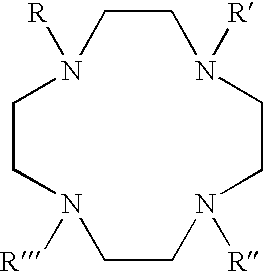
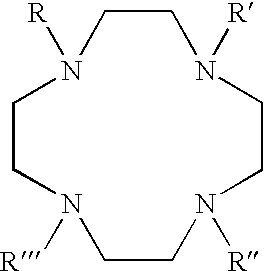
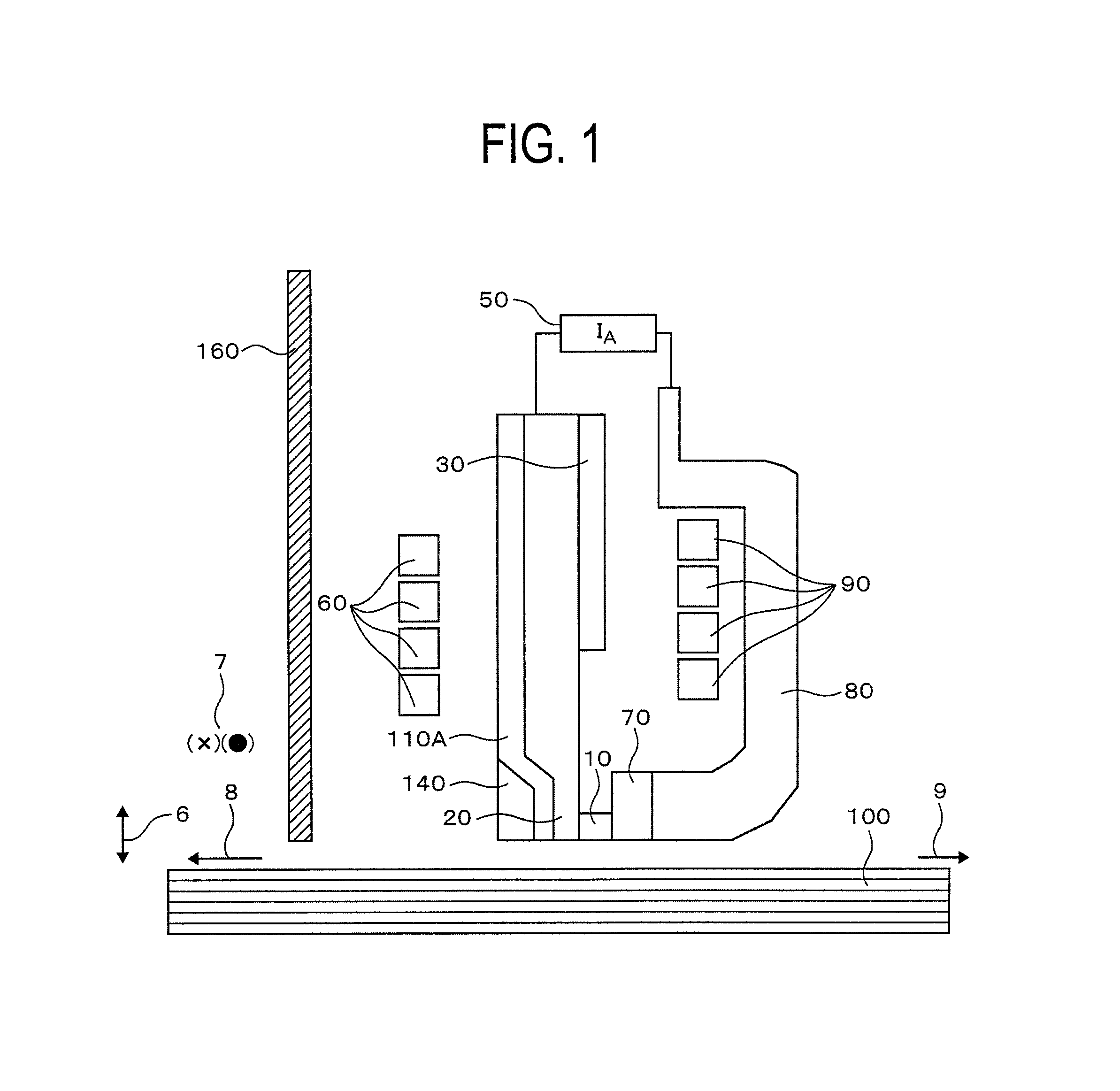
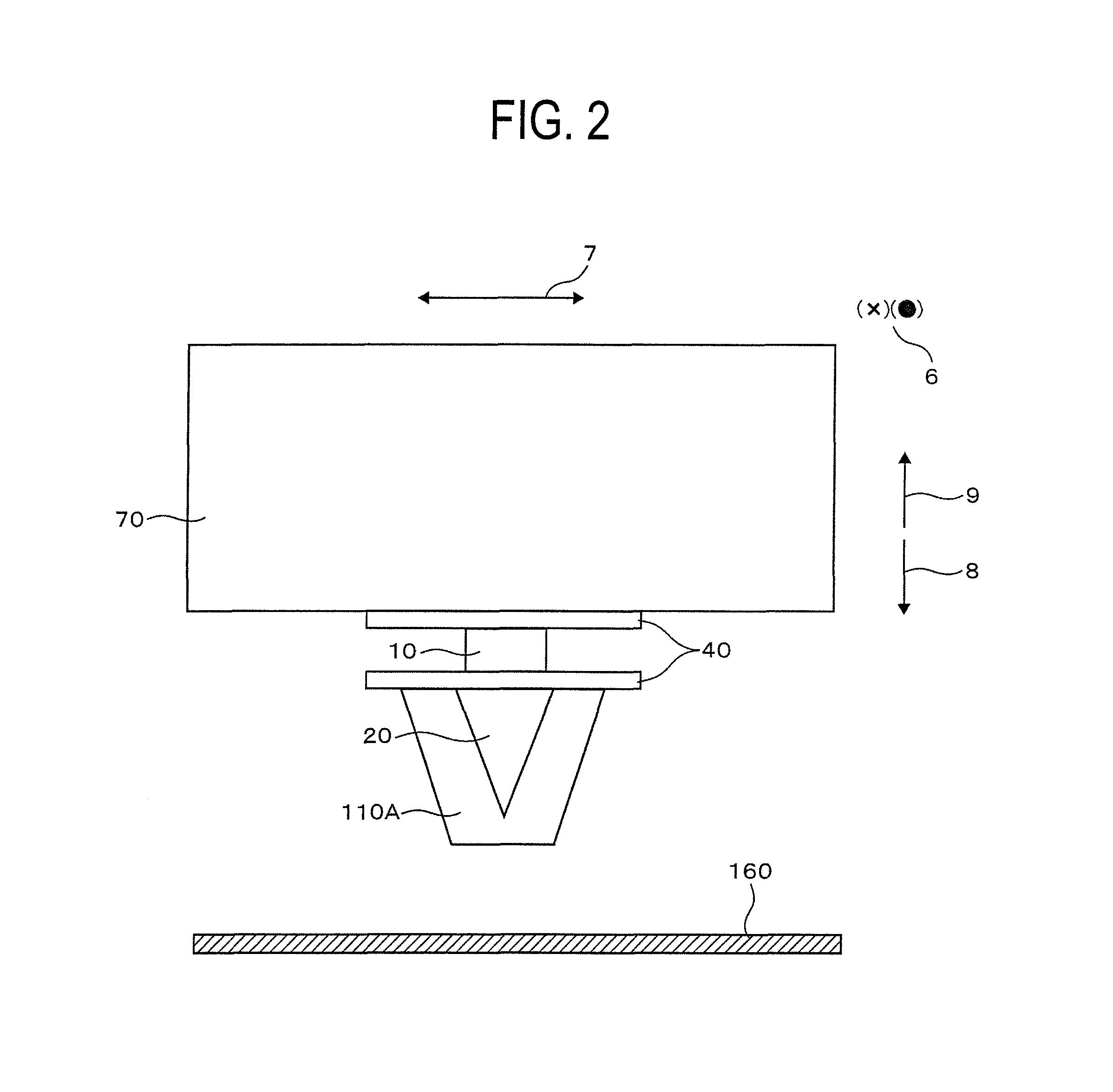
The present invention is directed, in general, to contrast agents (CA), and methods and systems of using such agents for producing image contrast based on a magnetization transfer (MT) mechanism. The CA comprises a tetraazacyclododecane ligand having pendent arms R, R', R" and R"' that are amides having a general formula: --CR.sub.1H--CO--NH--CH.sub.2--R.sub- .2. R.sub.1 includes organic substituents and R.sub.2 is not hydrogen. A paramagnetic metal ion (M) is coordinated to the ligand. The method, comprises subjecting a CA, in a sample, to a radio frequency pulse. The CA has pendent arms R, R', R" and R"' comprising organic substituents and the ligand further includes a M and a water molecule. A signal is obtained by applying a radio frequency pulse at a resonance frequency of the water molecule. The magnetic resonance system, comprises a magnetic resonance apparatus and the CA, the agent containing a ligand having the above described general formula.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
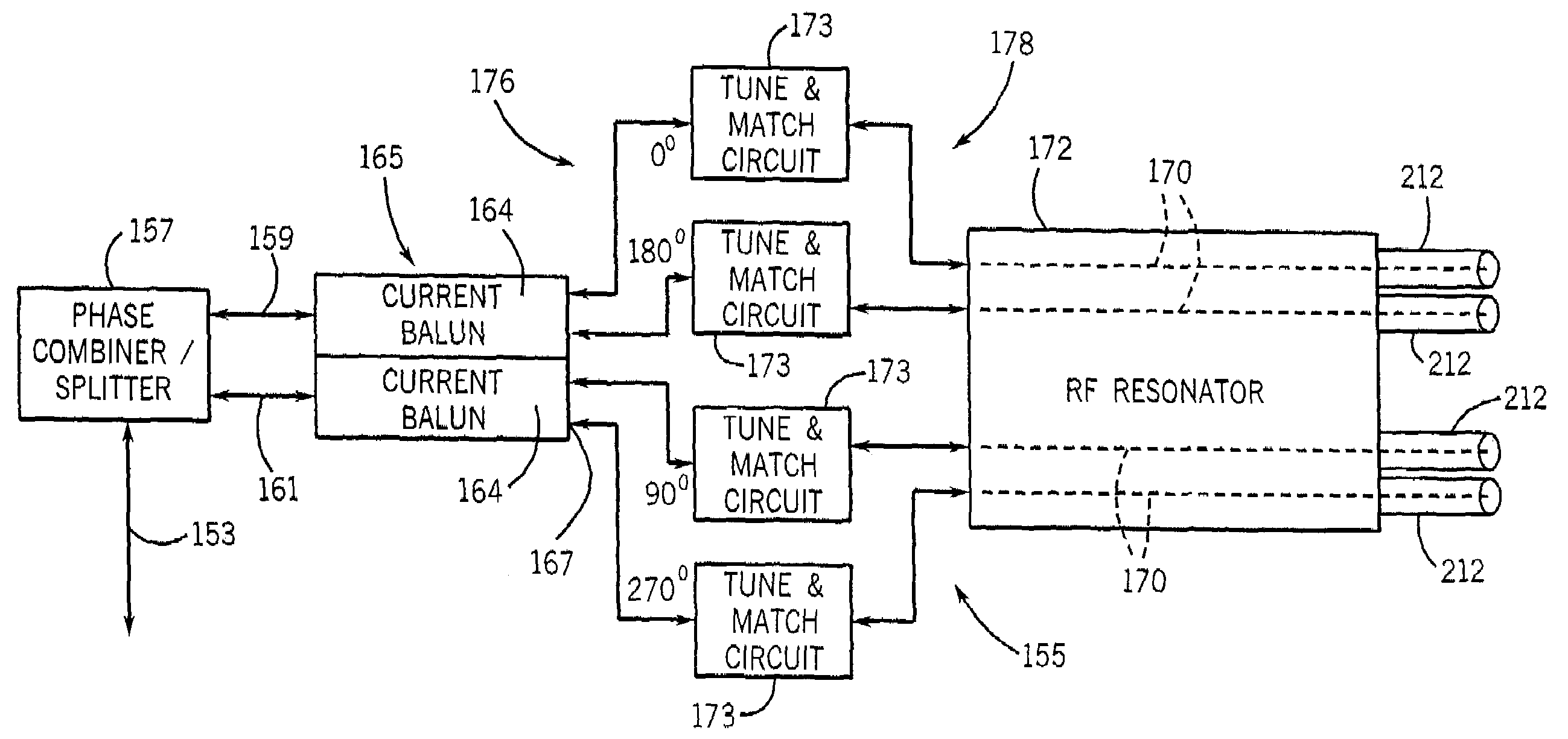
RF coil assembly and method for practicing magnetization transfer on magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy systems
ActiveUS7508212B2Improve isolationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationSpins
An RF coil assembly for an MRI system includes a resonator formed by a cylindrical shield and pairs of opposing conductive legs disposed symmetrically around a central axis and extending the axial length of the shield. One set of conductive leg pairs is tuned to operate at the Larmor frequency of 13C and another set is tuned to operate at the Larmor frequency of 1H. Drive circuitry operates the RF coil assembly to produce 1H spin magnetization which is transferred to 13C magnetization by the nuclear overhauser effect and to acquire MR data from the 13C spins. Multinuclear measurements can be made simultaneously at different Larmor frequencies.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
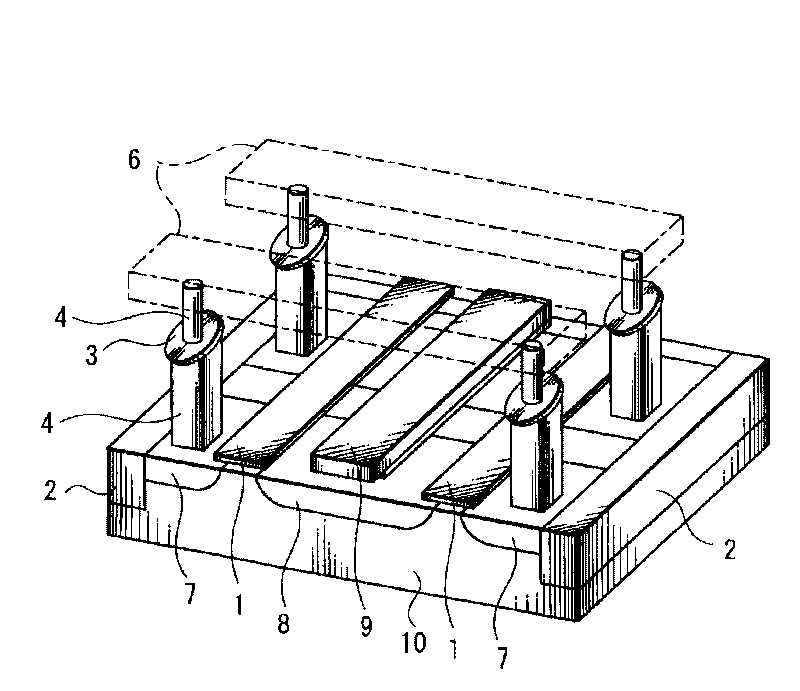
Magnetic element and signal processing device
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
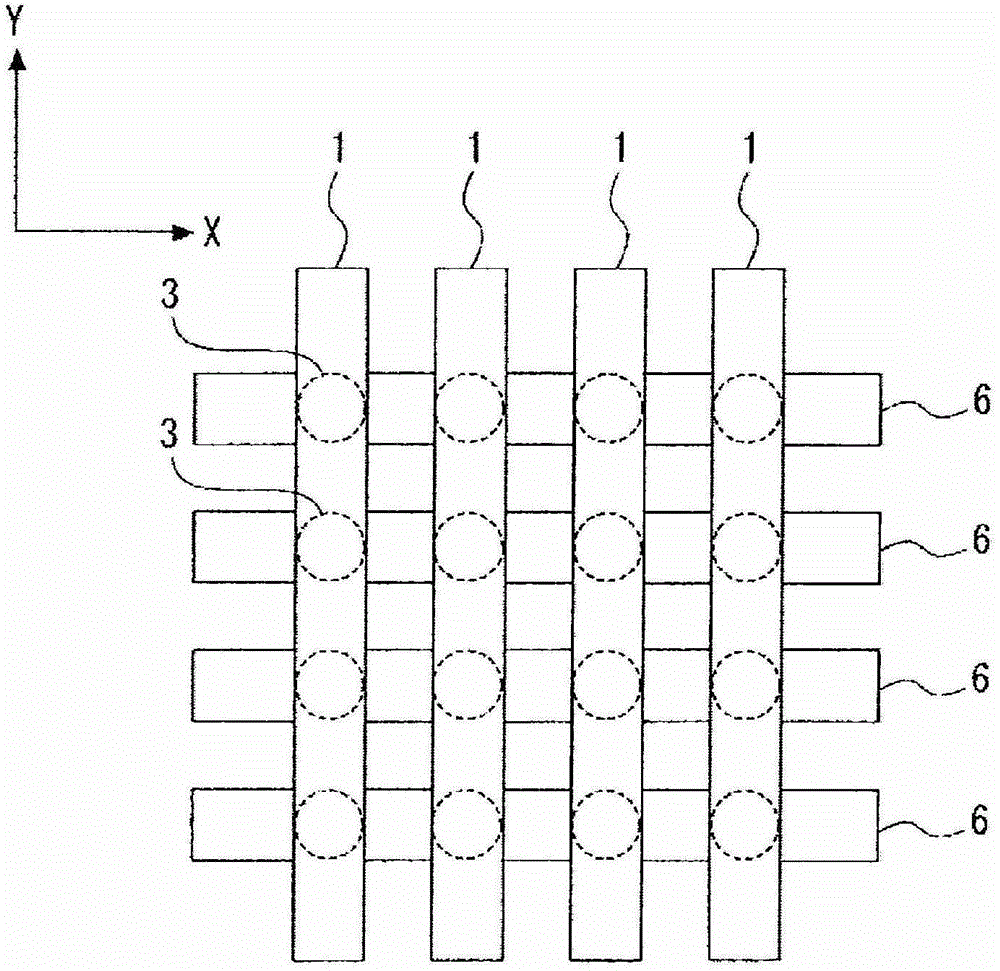
Storage element and memory
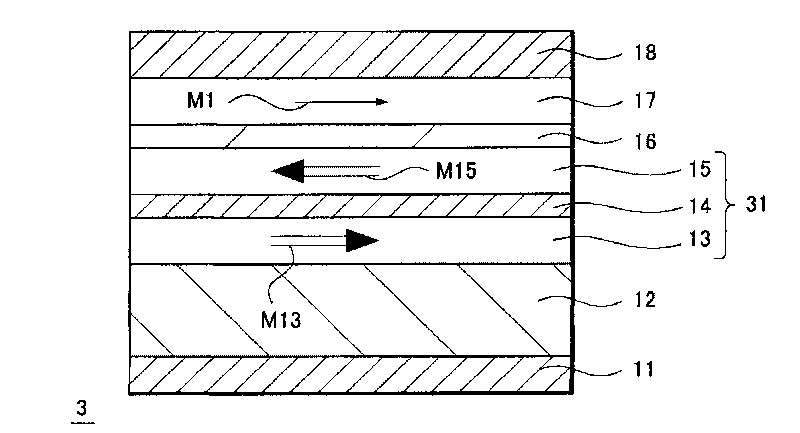
InactiveCN101743634AImprove coercive forceImprove thermal stabilityNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsInsulation layerMagnetization
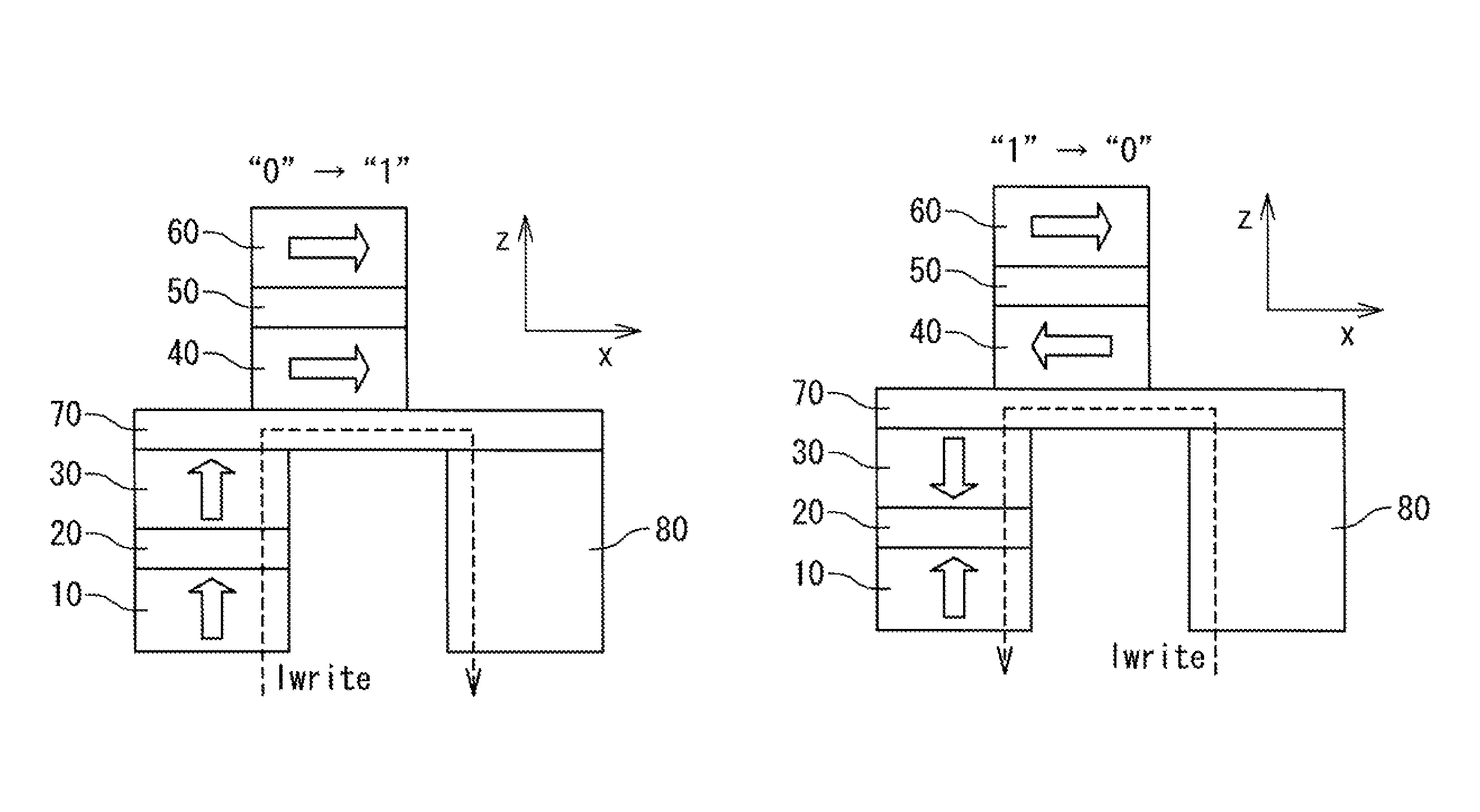
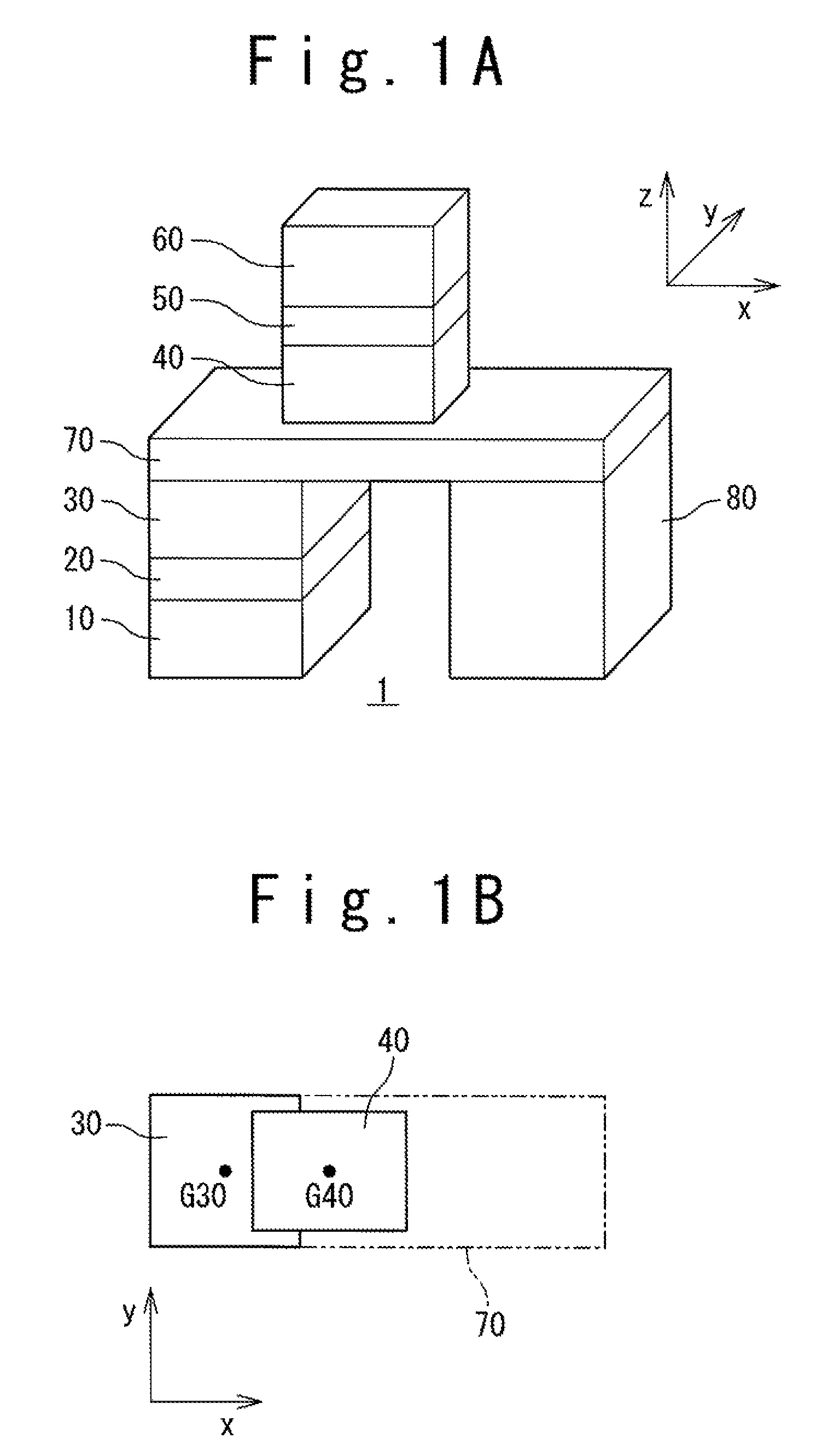
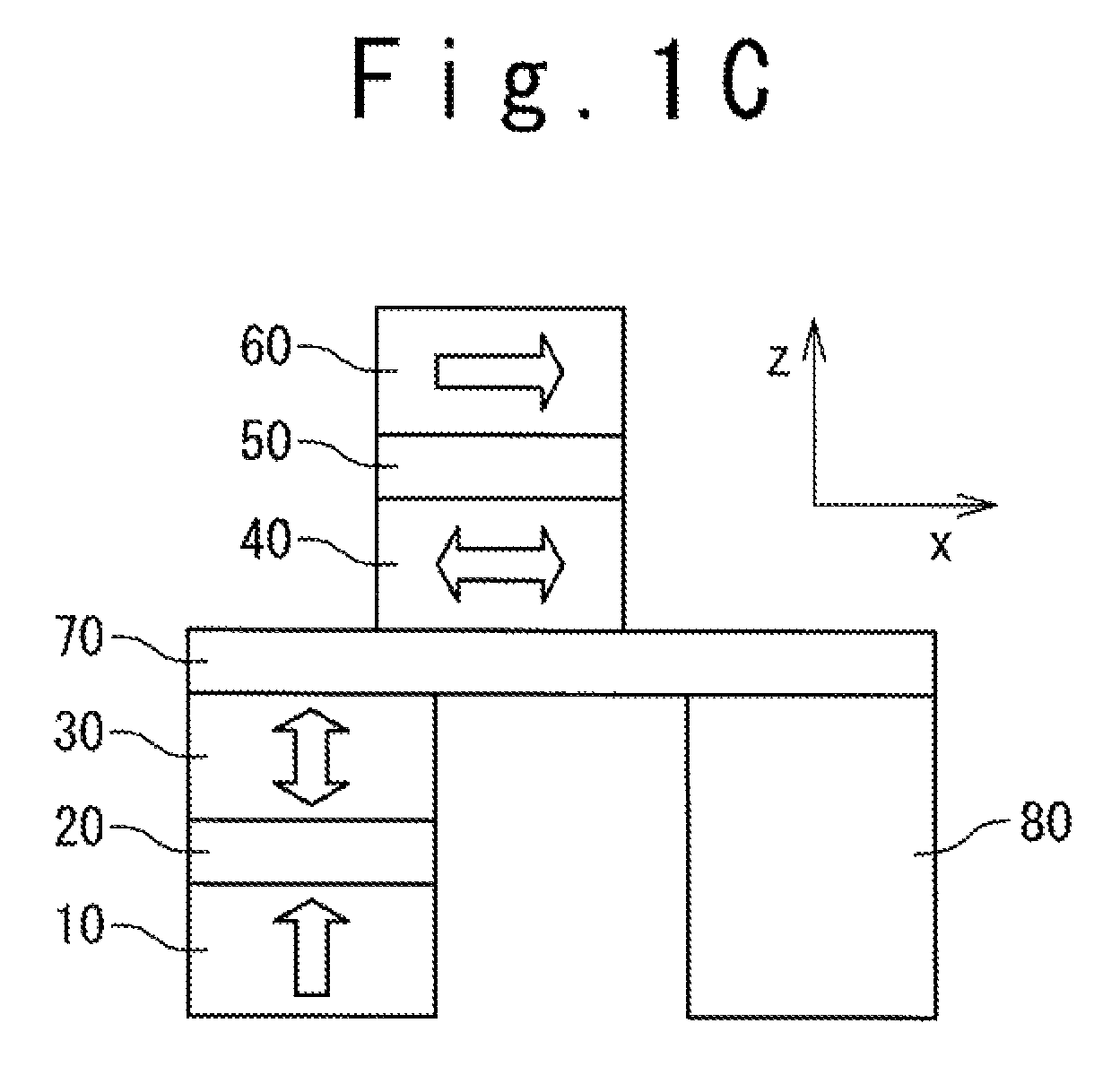
A memory in which thermal stability is improved without increasing the writing current. The memory is provided with a storage element (3) having a storage layer (17) for holding information by the magnetization state of a magnetic body. A magnetization fixation layer (31) is provided on the storage layer (17) through an intermediate layer (16). The intermediate layer (16) consists of an insulator. Direction of magnetization M1 of the storage layer (17) is changed by injecting electrons subjected to spin polarization in the laminating direction, and information is recorded on the storage layer (17). Strain is applied to the storage layer (17)from an insulation layer on the periphery of the storage layer (17) having a smaller coefficient of thermal expansion as compared with the storage layer (17). The memory is also provided with wiring for supplying a current in the laminating direction of the storage element (3).
Owner:SONY CORP
High-saturation-magnetization iron-base amorphous nanocrystal soft magnetic alloy and preparation method thereof
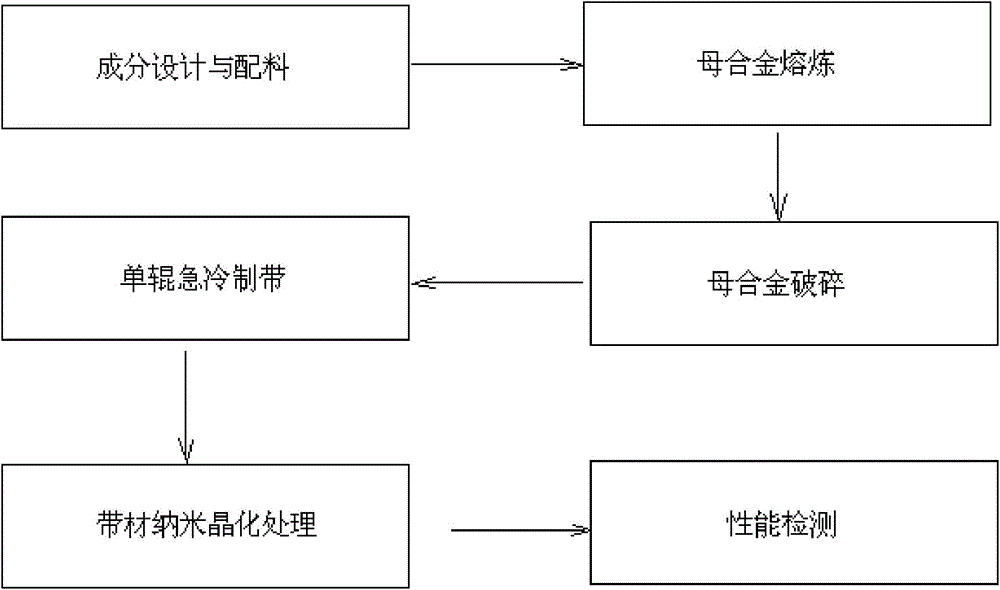
InactiveCN104561841ASolve the problem of low saturation magnetic inductionHigh saturation magnetizationFurnace typesMagnetic materialsMagnetization transferHigh saturation magnetization
The invention relates to a high-saturation-magnetization iron-base amorphous nanocrystal soft magnetic alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy is expressed as FeaMbCucSixByPz, wherein M is one or more of Al, Cr, Mn, Ti and V; and 68<=a<=90, 0<=b<=6, 0<=c<=2, 3<=x<=20, 4<=y<=20, 0<=z<=10, and a+b+c+x+y+z=100. Compared with the prior art, the product has the advantages of high saturation magnetization and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANTAO NANO TECH
Magnetic random access memory with switable switching assist layer
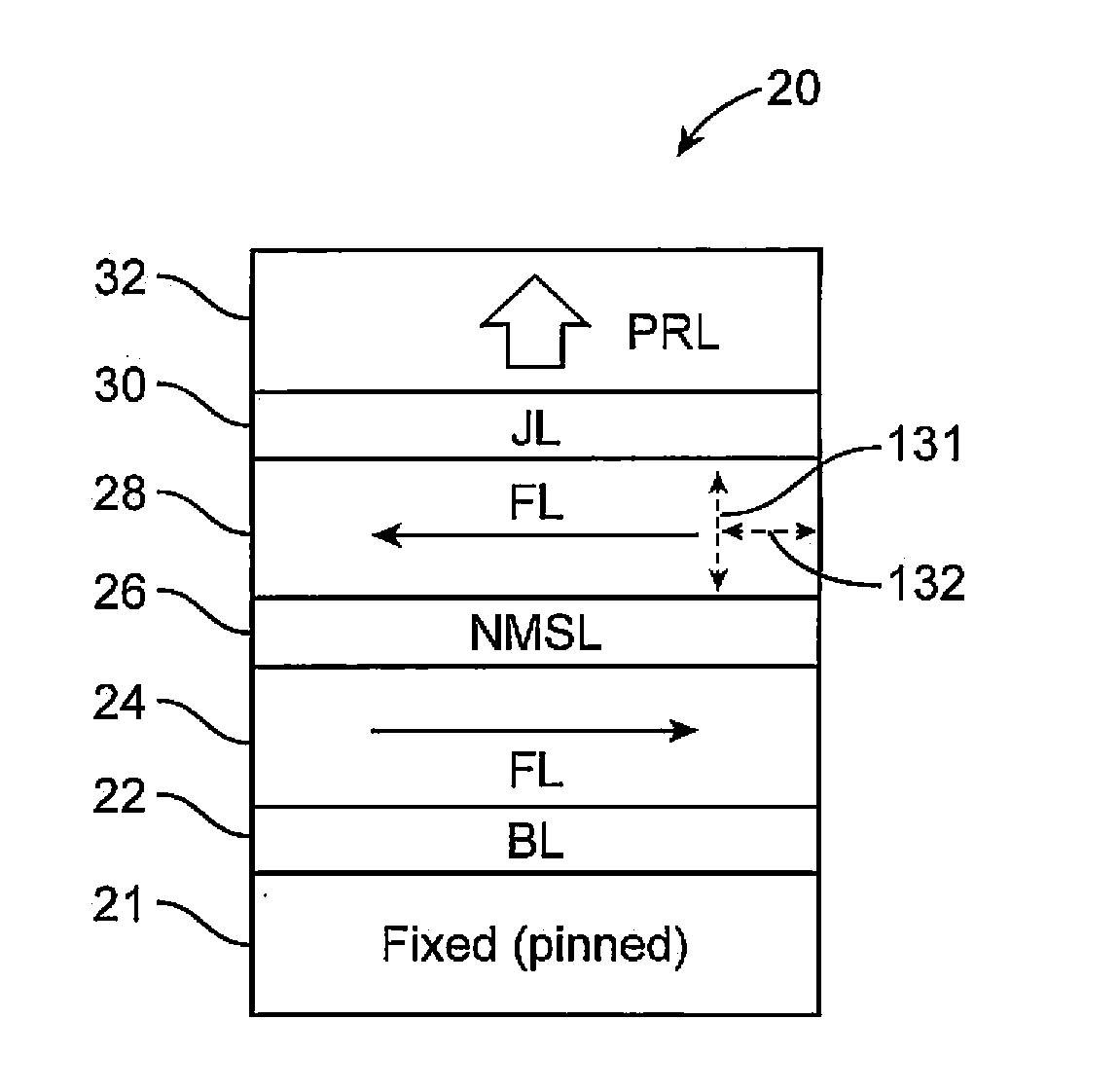
ActiveUS20150061050A1Galvano-magnetic material selectionGalvano-magnetic device detailsIn planeStatic random-access memory
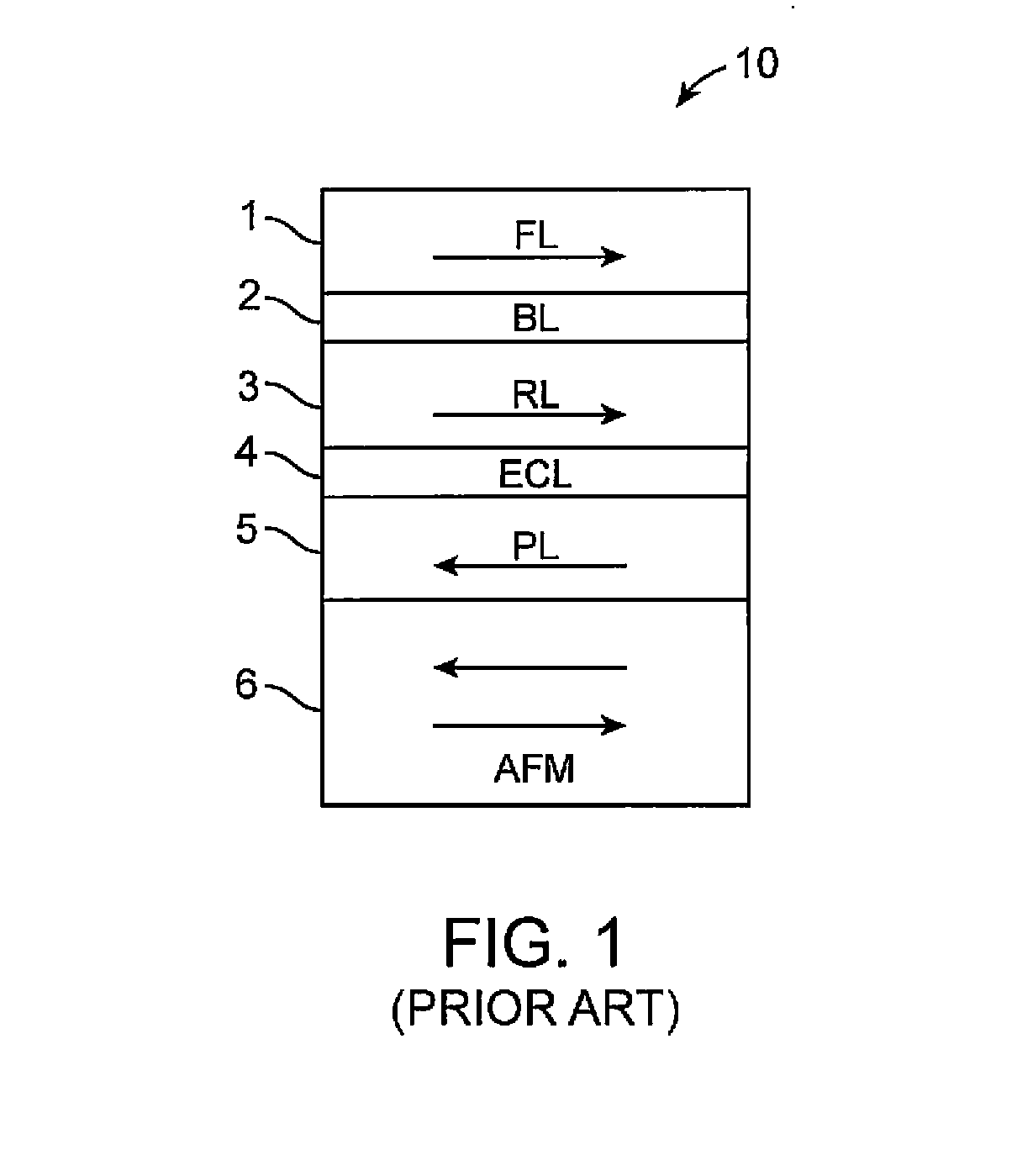
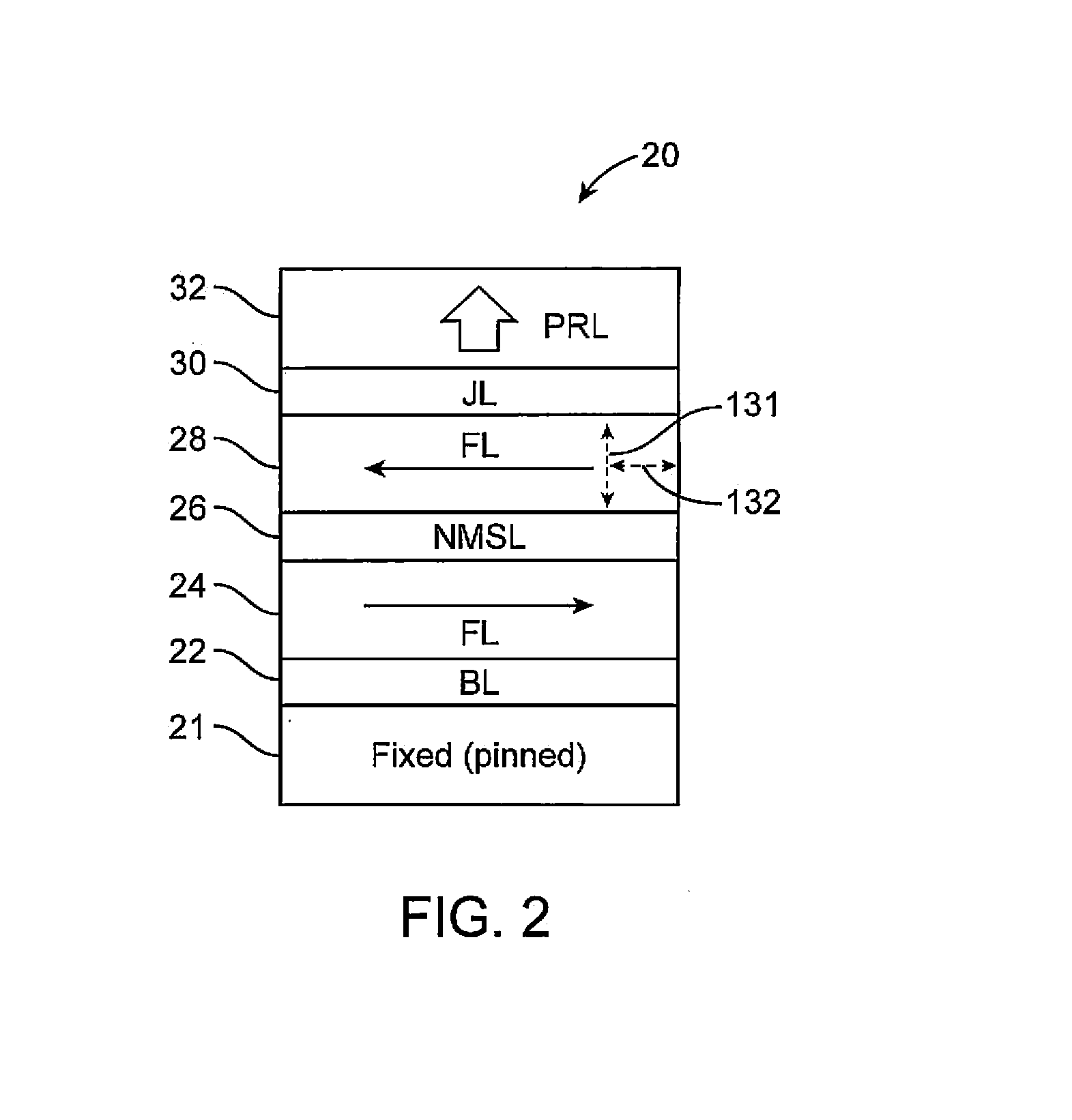
A perpendicular spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory (STTMRAM) element is configured to store a state when electrical current is applied thereto. The perpendicular STTMRAM element includes a magnetization layer having a first free layer and a second free layer, separated by a non-magnetic separation layer (NMSL). The direction of magnetization of the first and second free layers each is in-plane prior to the application of electrical current and after the application of electrical current, the direction of magnetization of the second free layer becomes substantially titled out-of-plane and the direction of magnetization of the first free layer switches. Upon electrical current being discontinued, the direction of magnetization of the second free layer remains in a direction that is substantially opposite to that of the first free layer.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
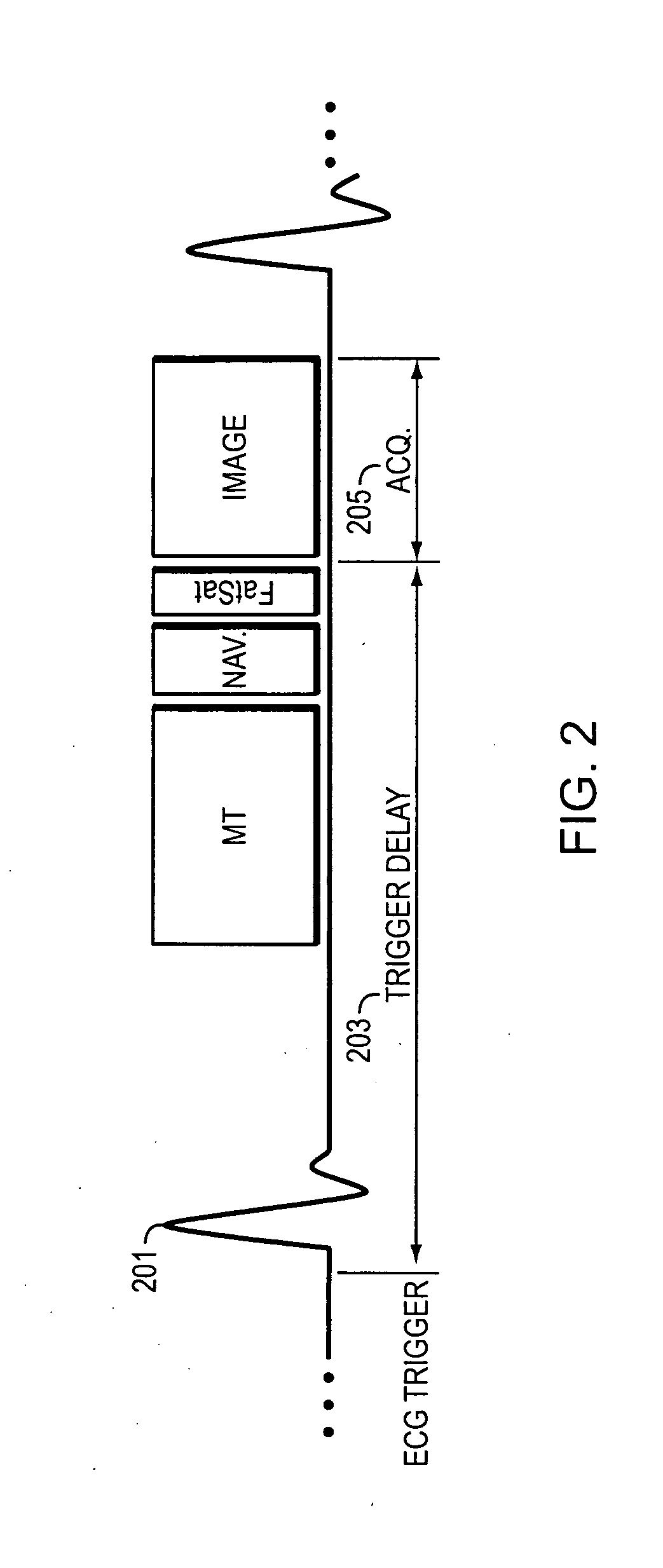
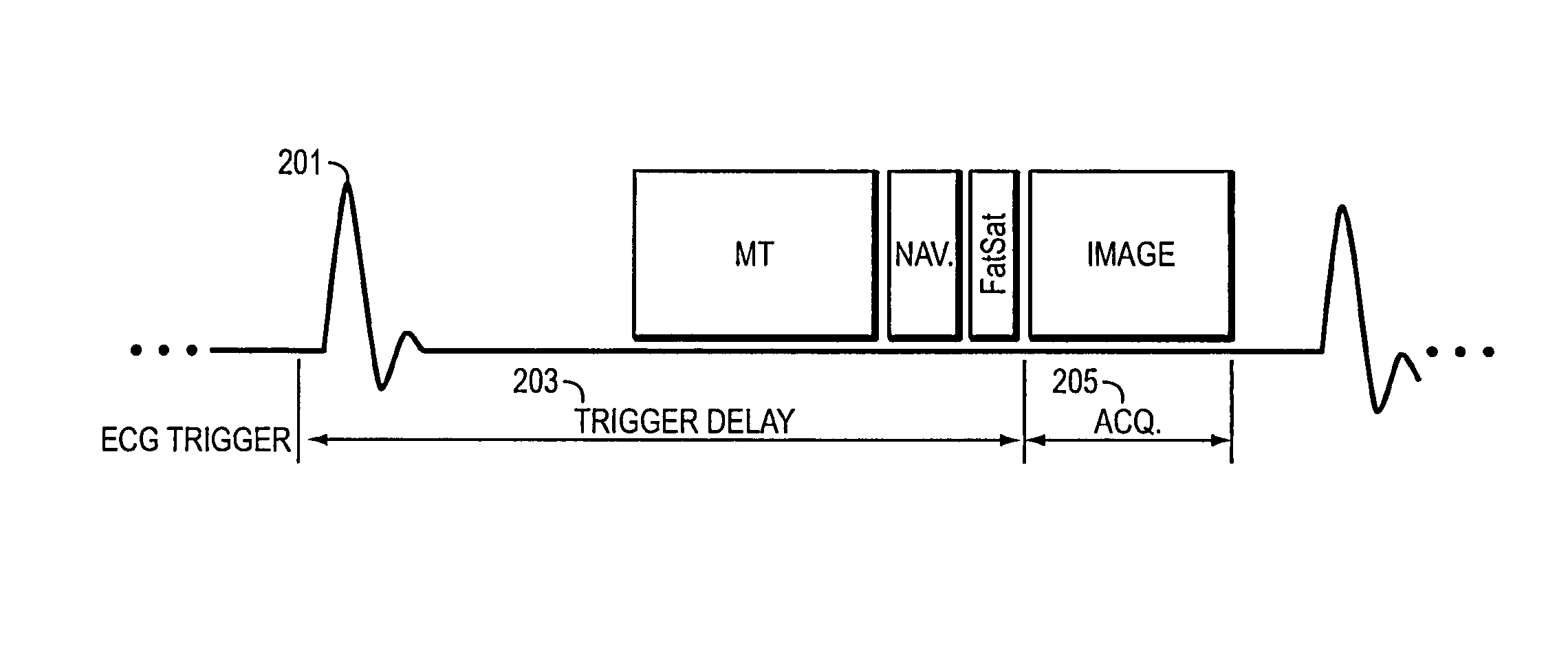
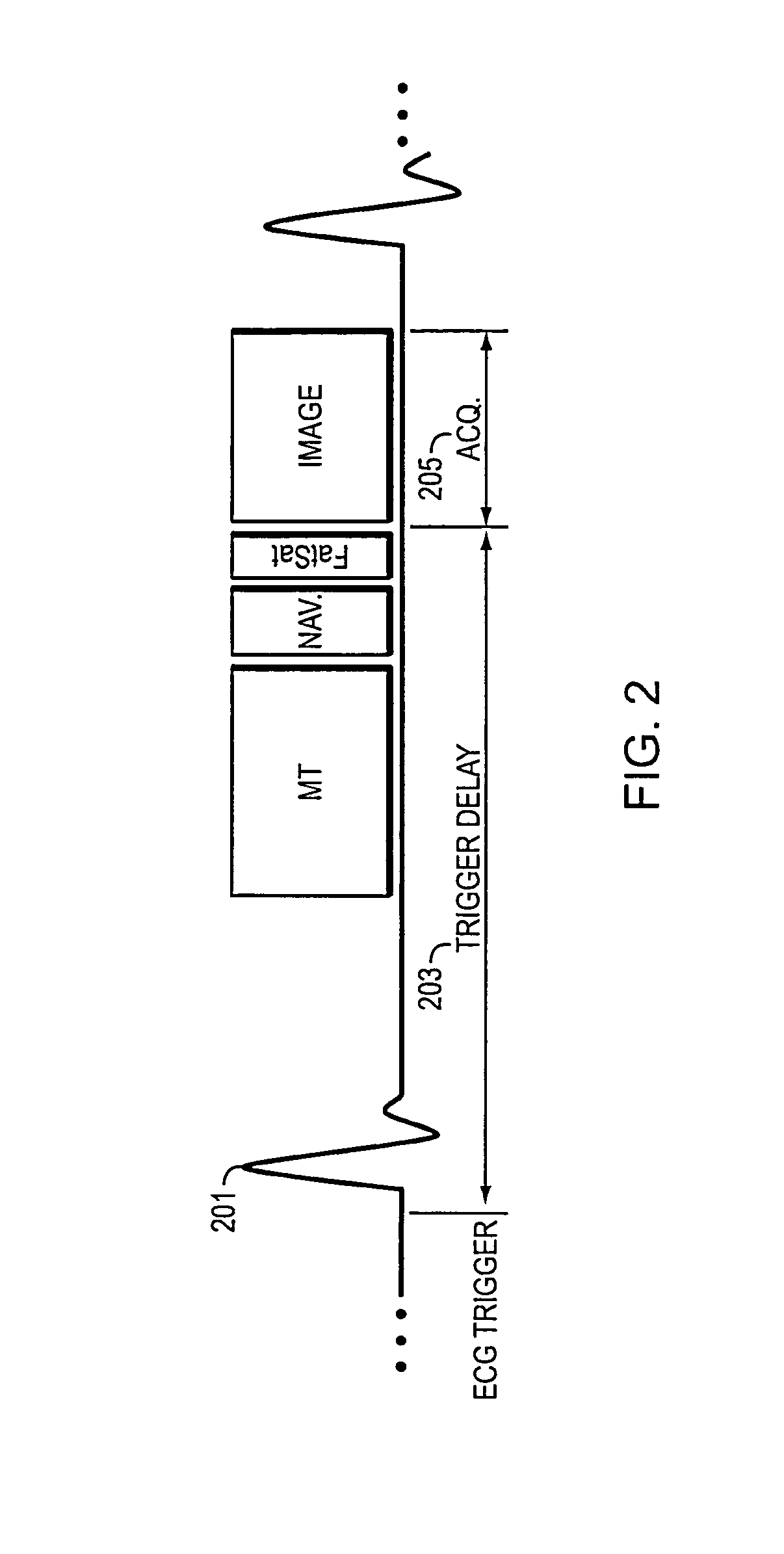
Apparatus and method of simultaneous fat suppression, magnetization transfer contrast, and spatial saturation for 3D time-of-flight imaging
ActiveUS7330028B2Improve image qualityIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionImaging quality
A pulse sequence for time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) includes a fatsat segment, a magnetization transfer segment, and a spatial saturation segment that are applied by an MR apparatus to acquire MR data for image reconstruction with improved image quality. The pulse sequence is constructed such that at the beginning of each iteration of the inner loop of a 3D acquisition, a fatsat pulse is applied. After the fatsat pulse, MR data is acquired in a series of imaging segments with well-suppressed fat signal. Effective fat suppression is achieved by sampling central k-space data first, before signal from fat relaxes back to a pre-saturation level. Each imaging segment is immediately preceded by one of a MT pulse or a spatial saturation pulse and immediately followed by the other one of the MT pulse or the spatial saturation pulse.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
CEST Phase and Magnitude Imaging Using a Multi-Parametric Varied Saturation Scheme
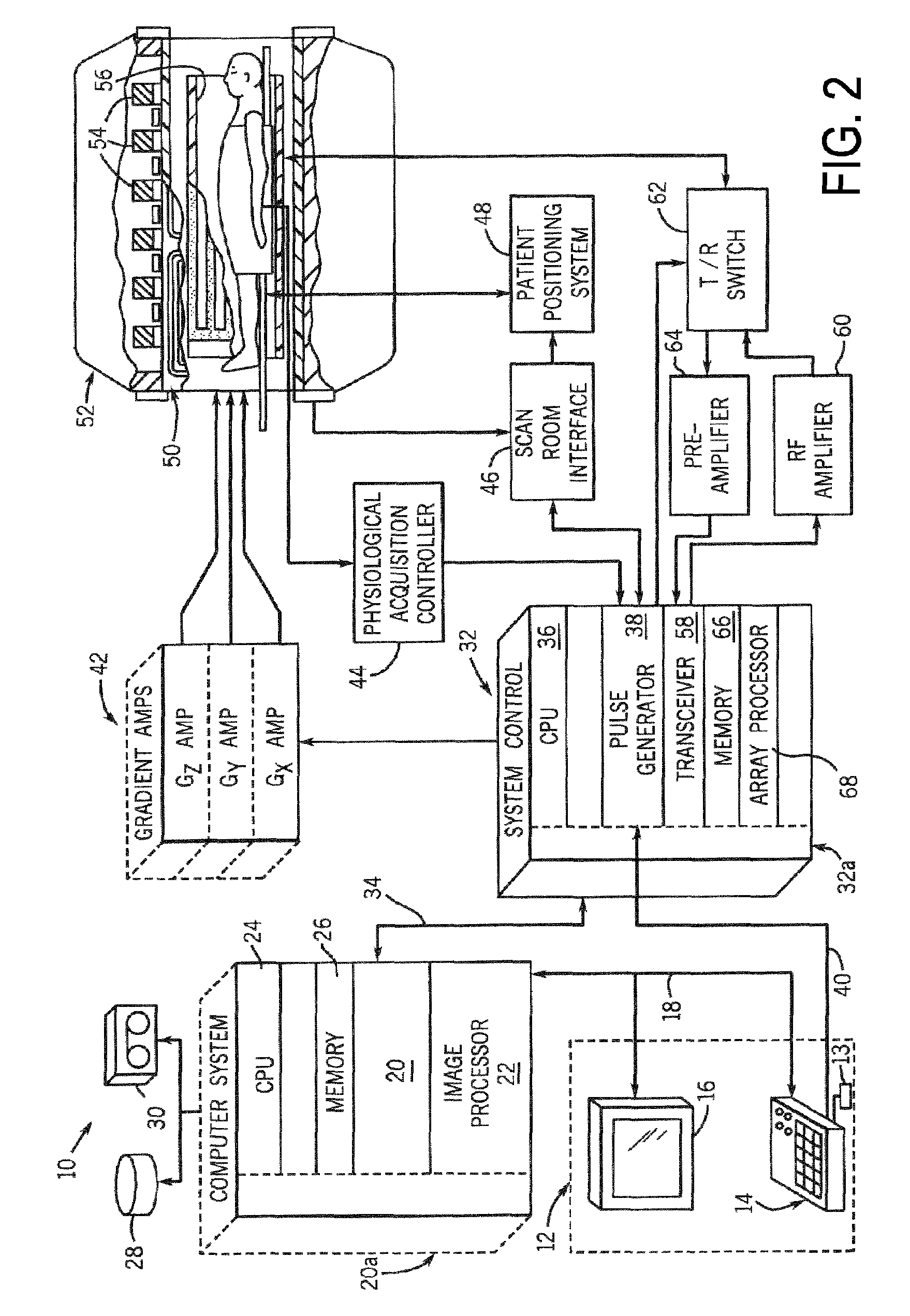
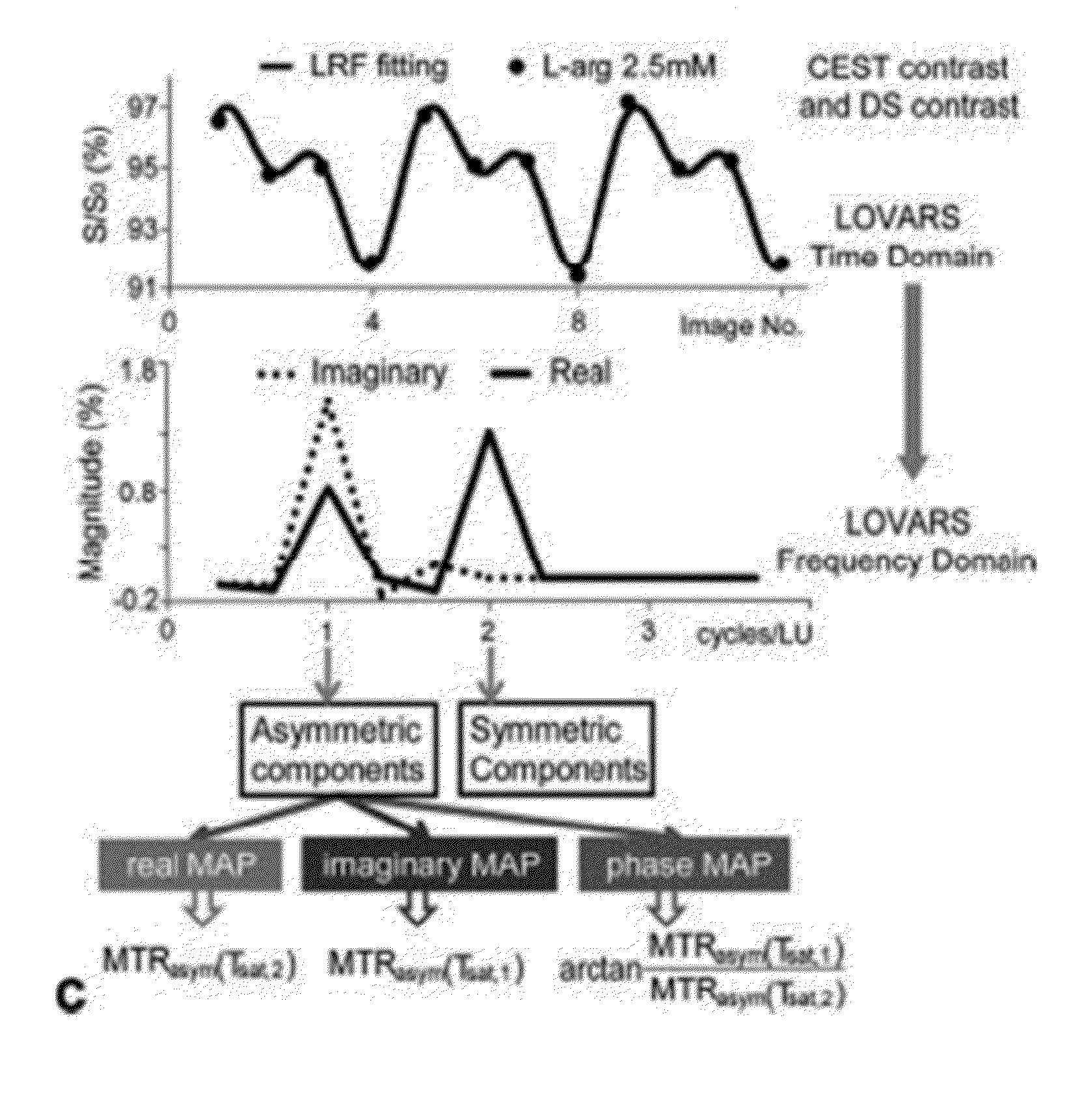
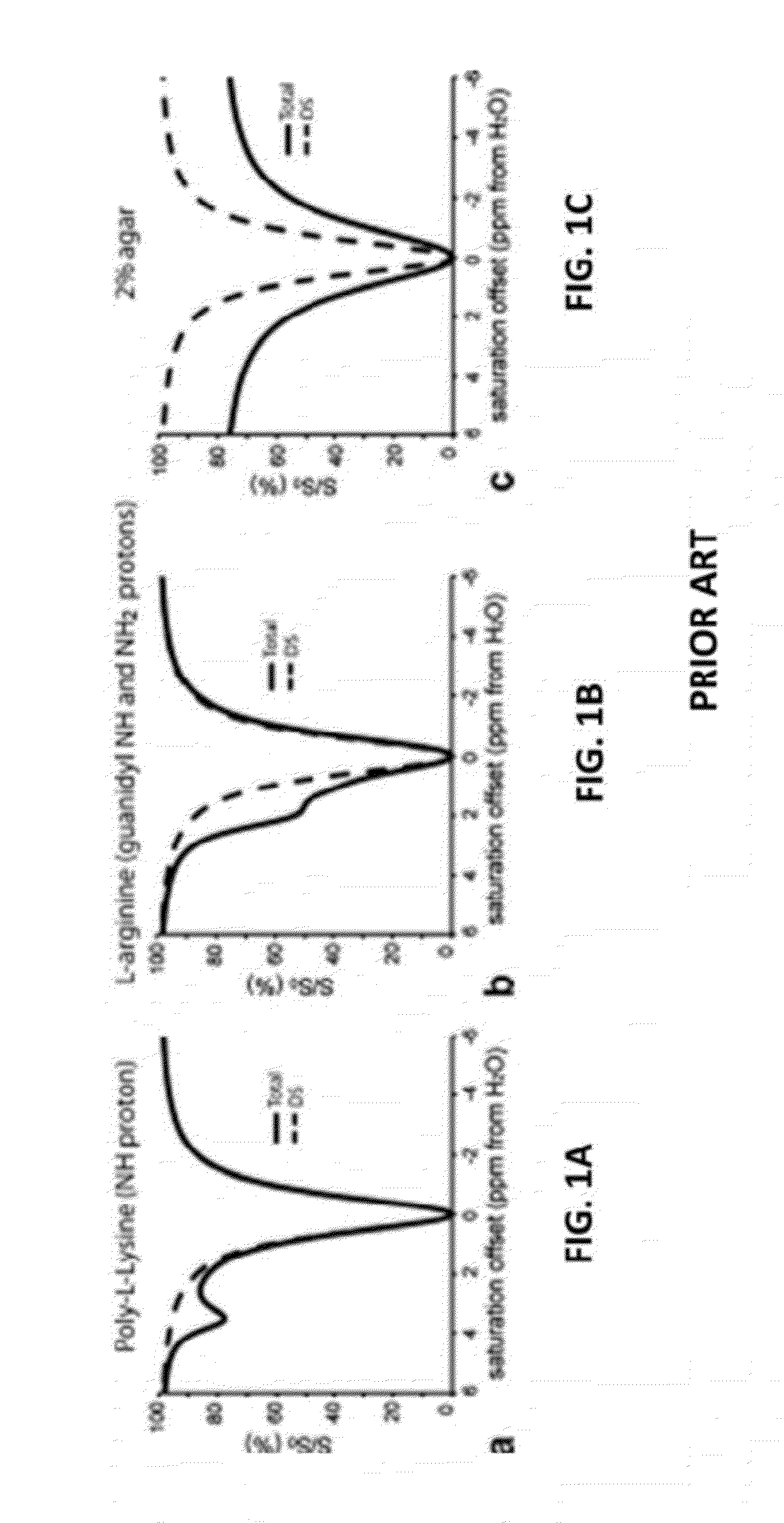
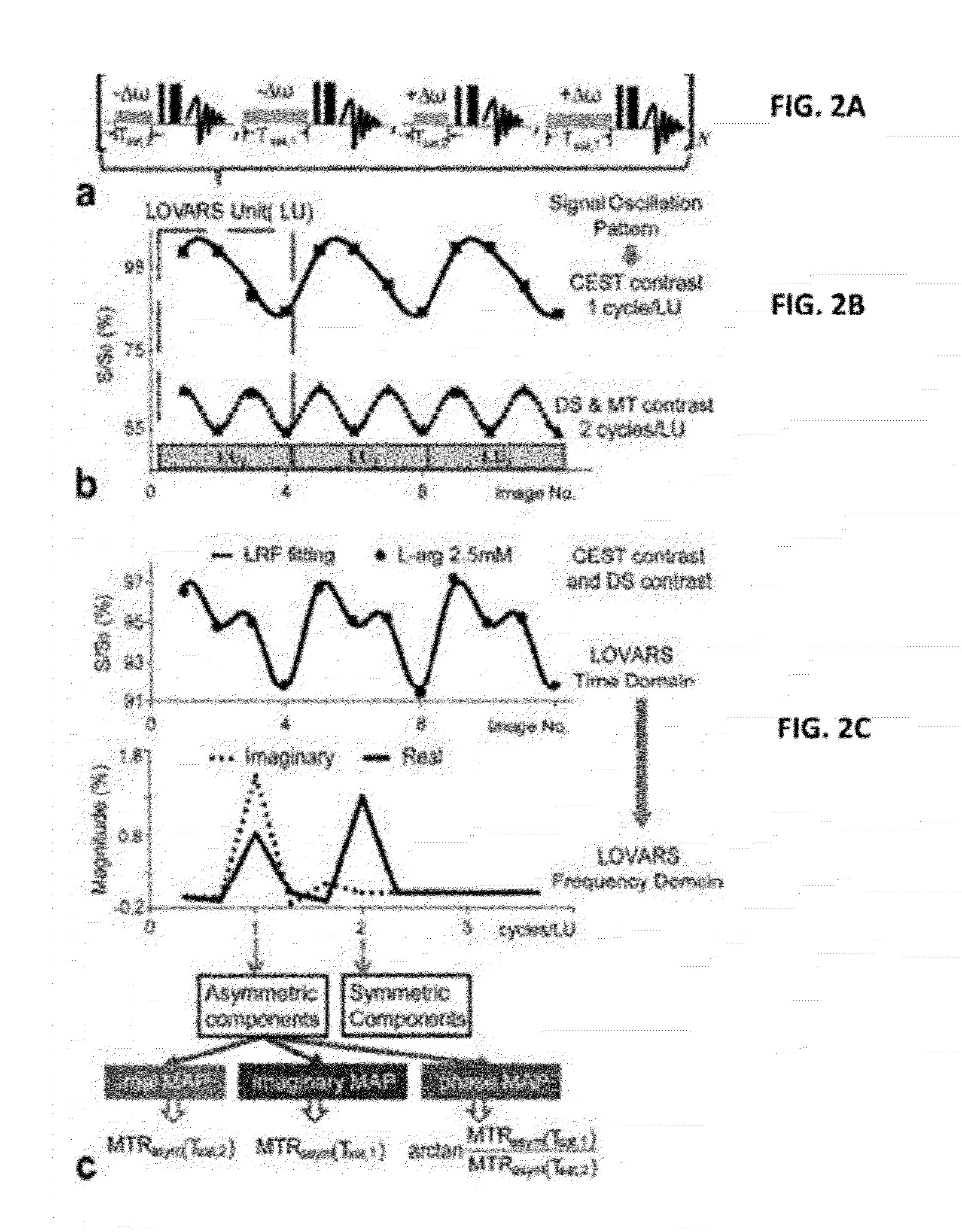
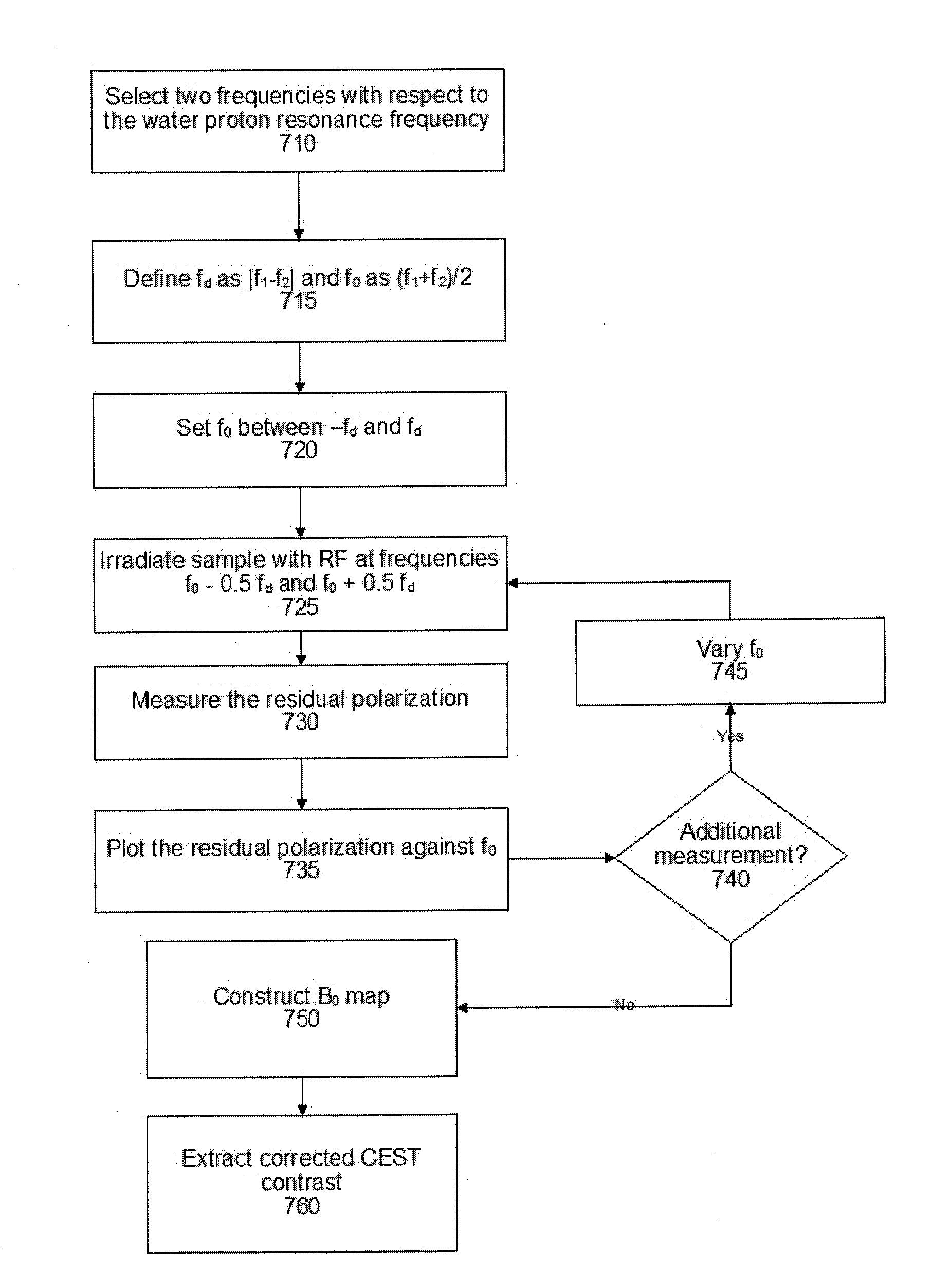
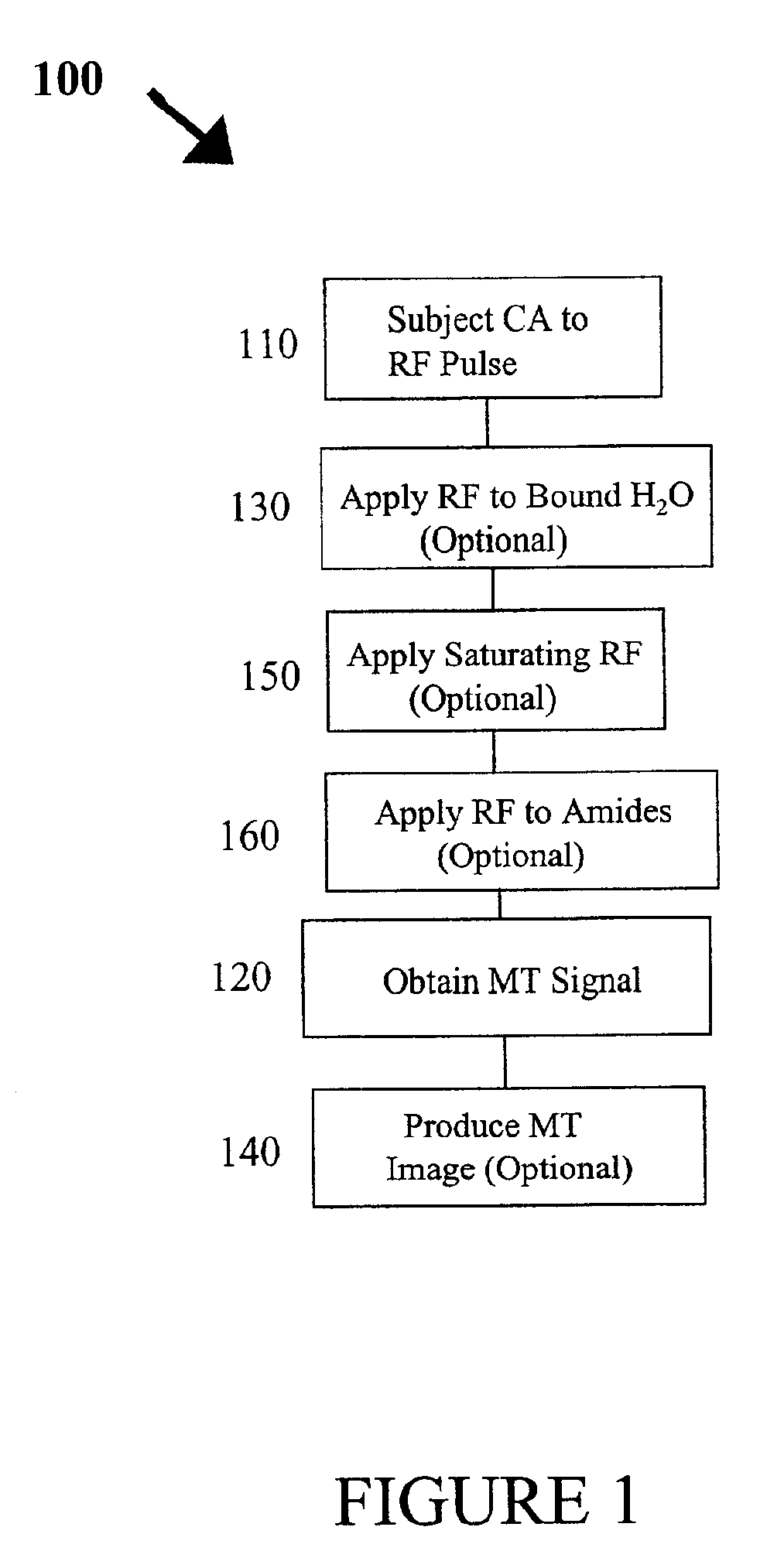
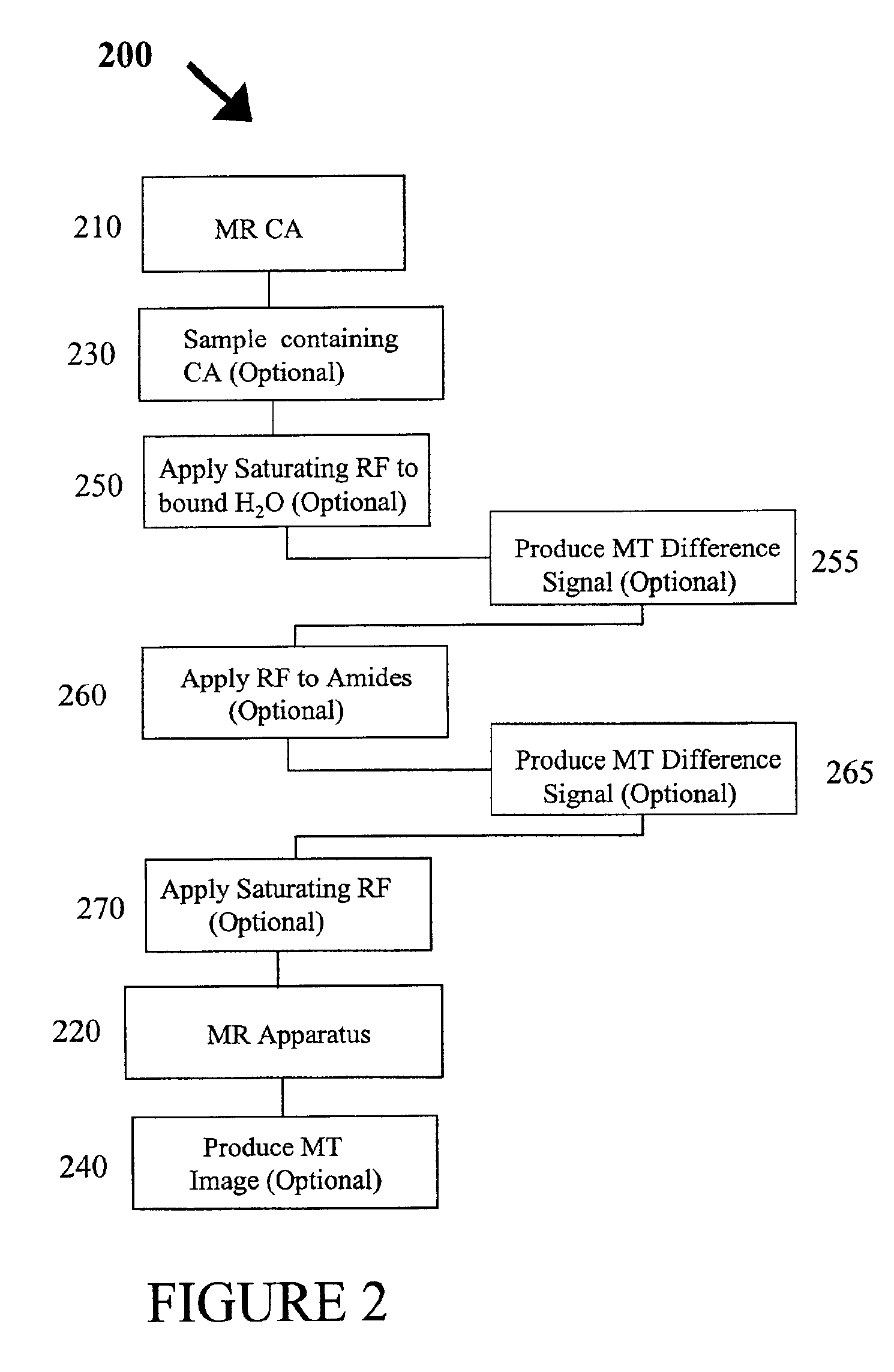
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for obtaining a magnetic resonance image (MRI) or spectrum. The method includes a step of performing a chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) or magnetization transfer (MT) magnetic labeling experiment of a subject using an MRI machine. When performing the CEST or MT magnetic labeling experiment aspects of a saturation pulse or a serial saturation pulse sequence, such as length (tsat), number (Nsat), offset (Δω), modulation frequency (ωs) and power (B1) can be varied in specific-designed schemes. Data is generated from the CEST magnetic labeling experiment and is transmitted to a data processing unit. The data is processed to generate a visual representation of the data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Magnetic resonance method for quantification of transverse relaxation times
ActiveUS8314618B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionRapid imagingTransverse relaxation
Apparatus and methods for quantification of transverse relaxation times (T2) using steady-state free precession sequences (generally known as fast imaging sequences) and their sensitivity to a quadratic increase of the RF pulse phase, also known as RF spoiling. Using at least two image acquisitions with different partial RF spoiling increments, T2 can be assessed with high precision and with short acquisition times in the limit of large excitation angles being independent on the longitudinal relaxation time (T1) and magnetization transfer effects as compared to other SSFP based quantitative T2 methods. This invention is not restricted to any kind of target and may be applied in 3D as well as in 2D.
Owner:UNIV HOSPITAL OF BASEL
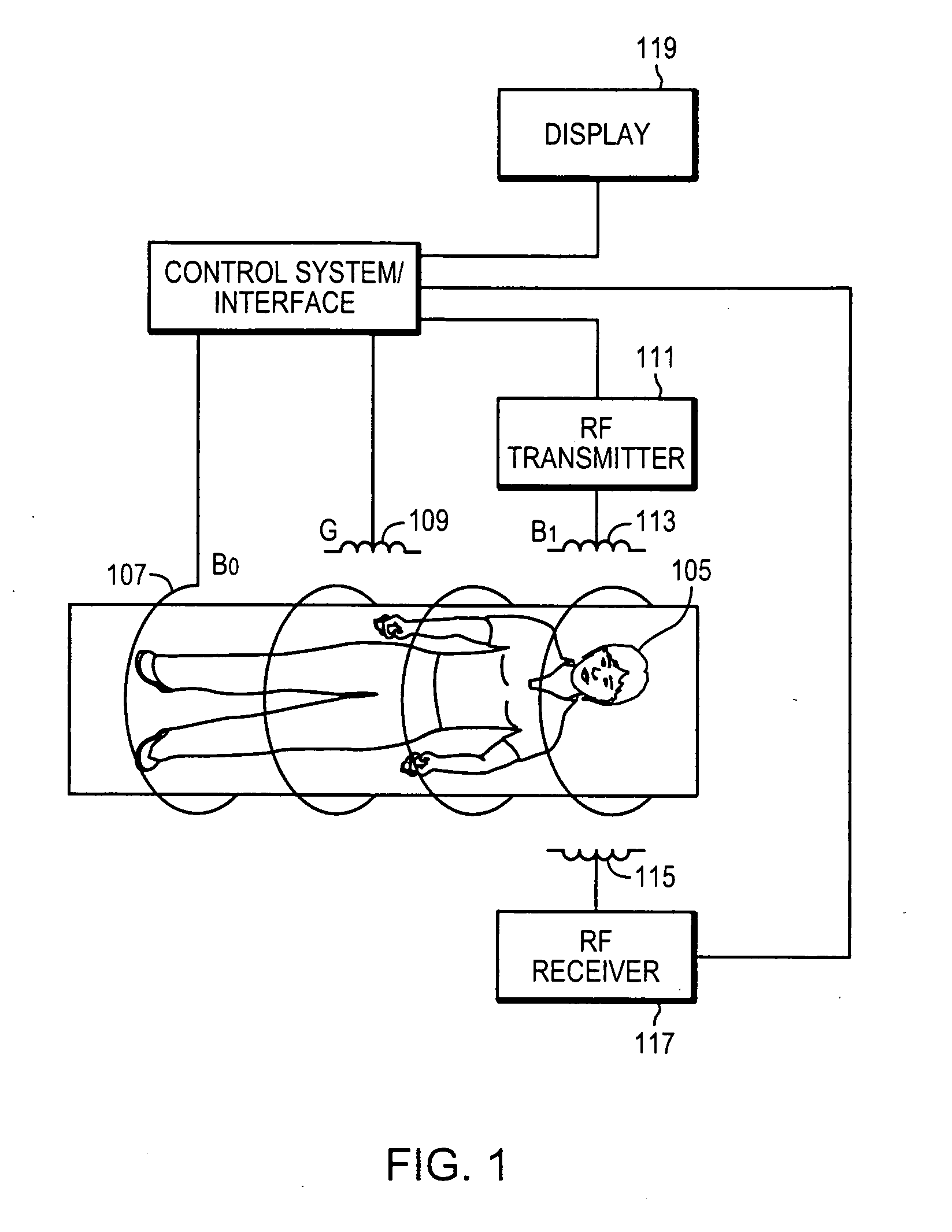
Magnetic resonance imaging of coronary venous structures
InactiveUS20080221429A1Improve blood-myocardium contrastSuppresses coronary vein signalMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringVenous blood specimenVenous blood
A method and system for magnetic resonance imaging comprises applying at least one radiofrequency magnetization transfer (MT) pulse to a coronary venous region of a subject positioned within a magnetic field, and acquiring magnetic resonance imaging data from the coronary venous region to produce an image of a coronary venous structure. This technique can be utilized as part of a 3D free-breathing, ECG-triggered gradient-echo Cartesian acquisition of the coronary region. One or more magnetization transfer (MT) preparation pulses are used to enhance the contrast between venous blood and myocardium. The MT preparation results in myocardial signal suppression without any significant signal loss in the arterial or venous blood so as to maintain venous blood signal-to-noise ratio while improving contrast between myocardium and veins. The coronary venous structure can comprise one or more of a coronary sinus, a lateral vein and a posterior vein. The image of a coronary venous structure can be acquired in connection with an interventional cardiovascular procedure, such as a cardiac resynchronization therapy.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
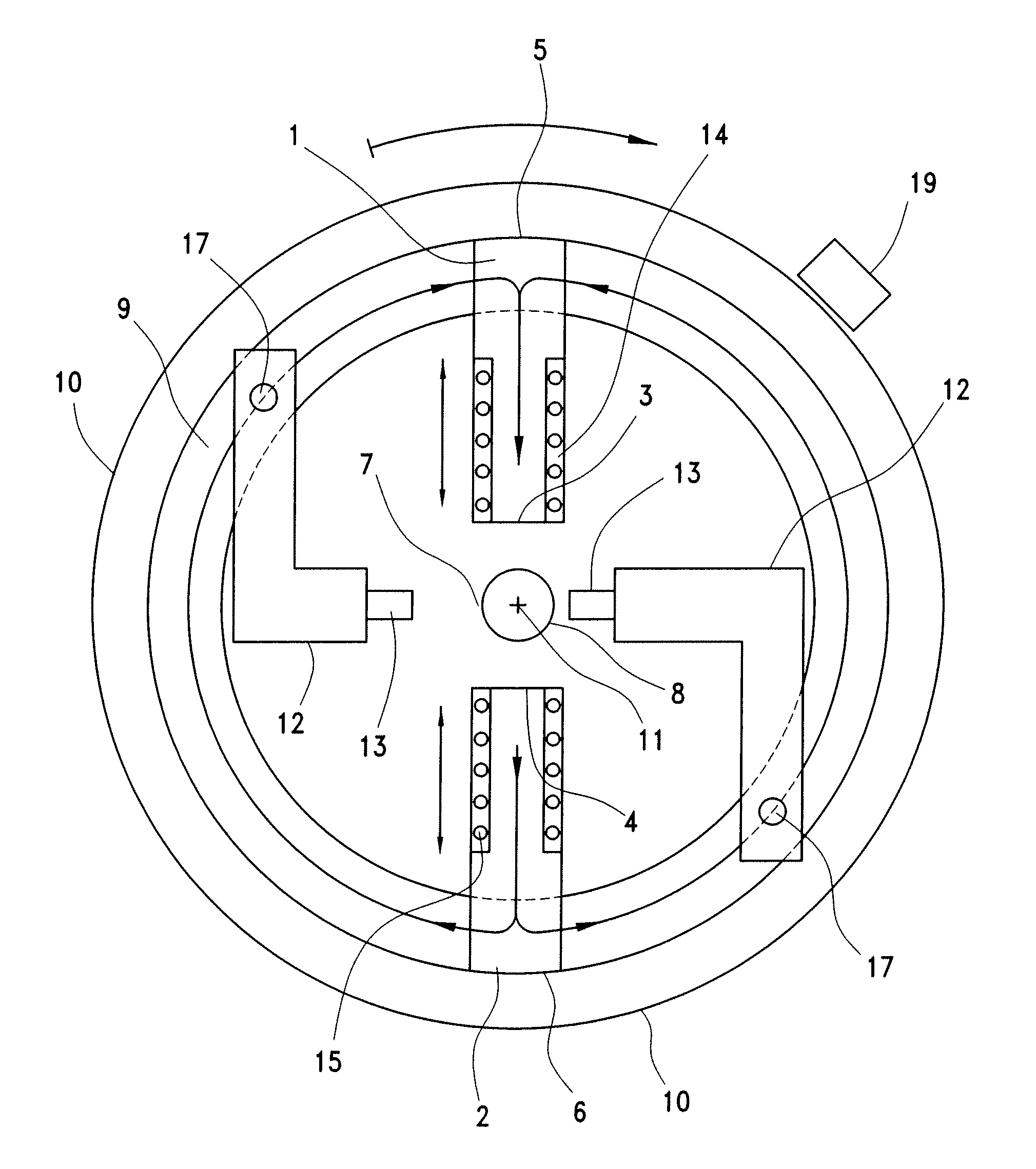
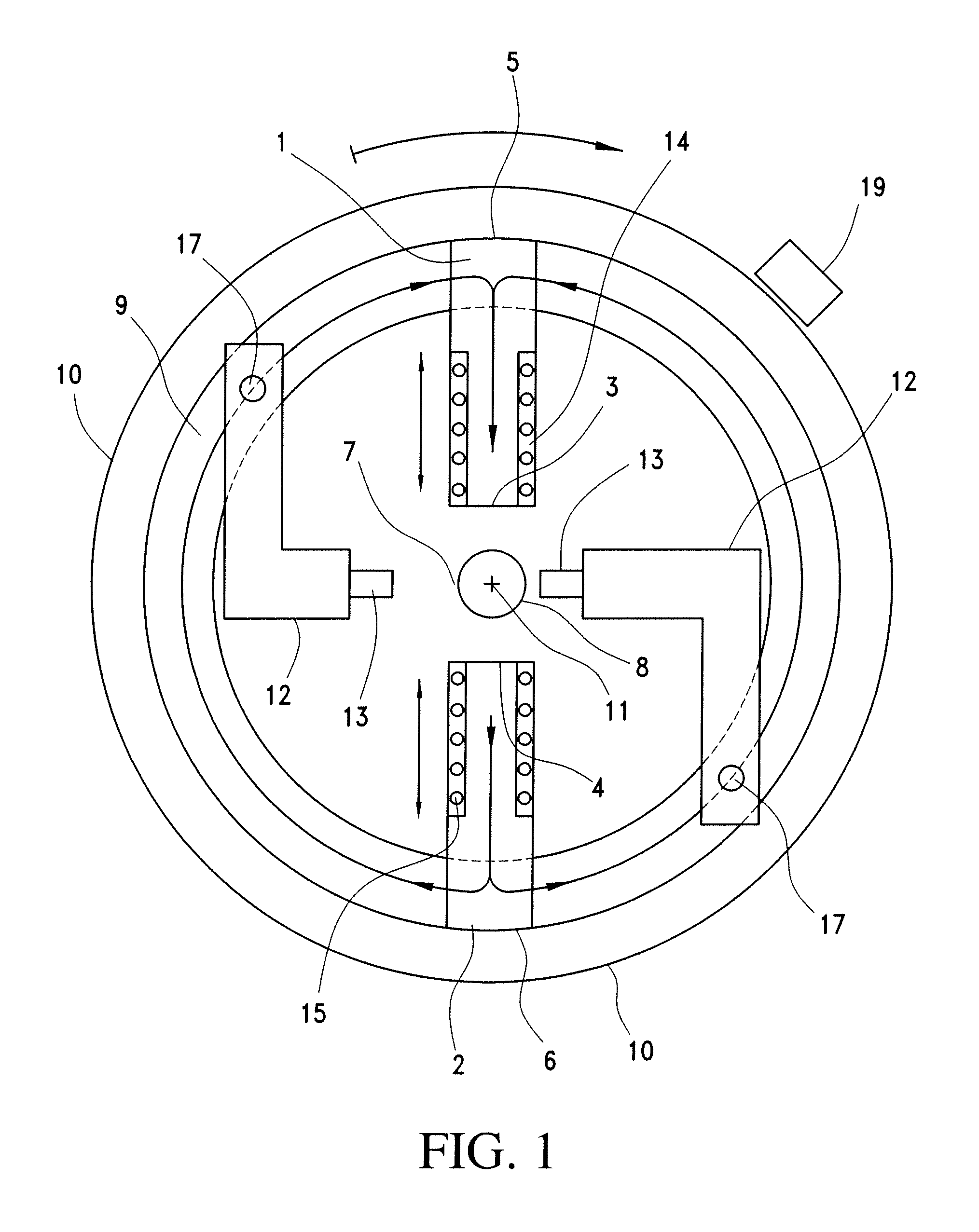
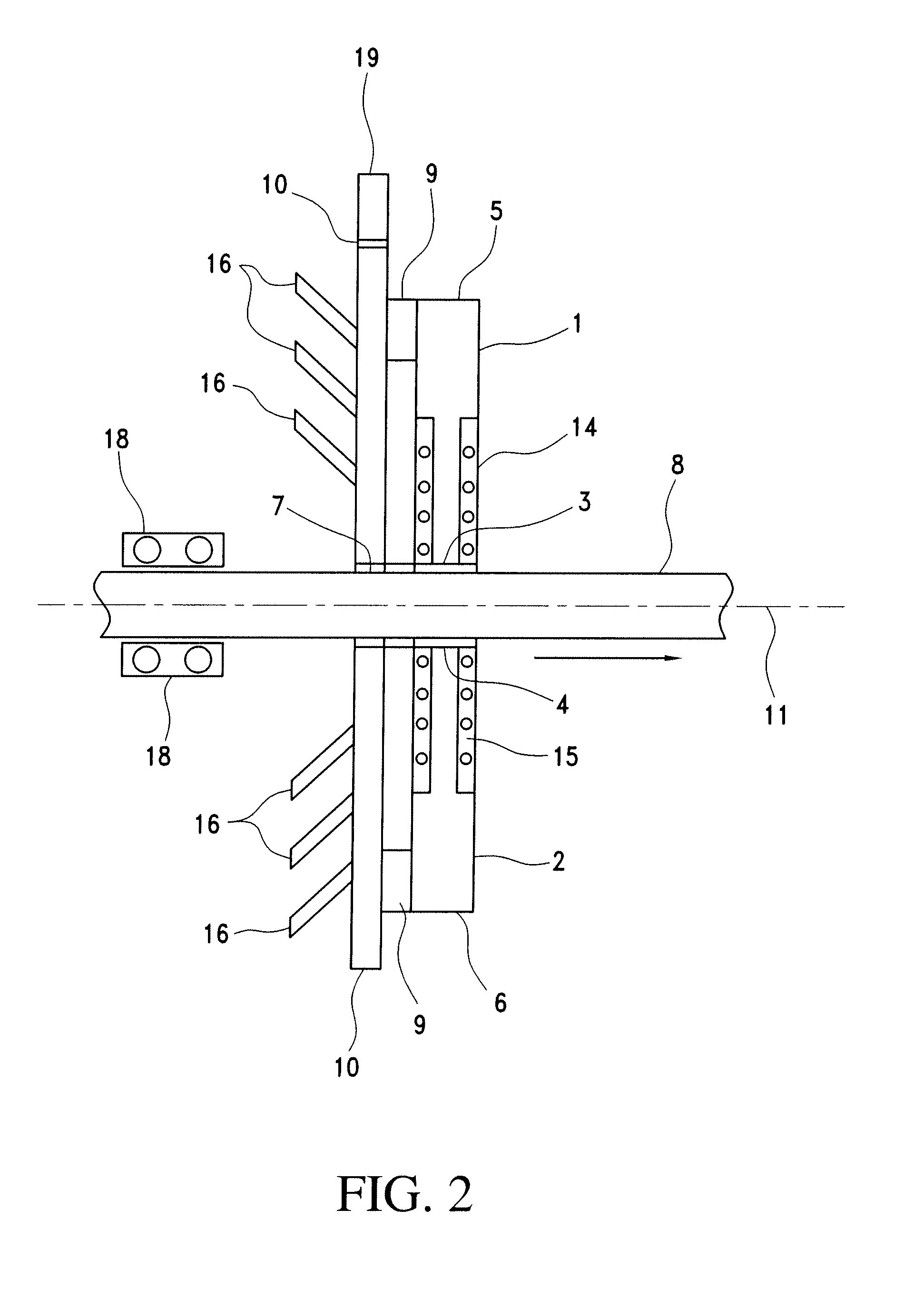
Stirring-type liquid magnetization device
PendingCN105271483AIncrease magnetic fluxIncrease magnetic inductionScale removal and water softeningWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetic tension forceMagnetization
The invention relates to a stirring-type liquid magnetization device. A main body rack is driven to rotate by utilization of a counter-acting force generated during flow injection of a water input pipe, a group of vertical magnetic columns on the main body rack can be driven to rotate or revolve in a horizontal direction, the magnetic columns are composed of a plurality of neodymium iron boron permanent magnetism cylindrical magnets, and the magnetic line direction and the magnetic column axial direction are consistent and are vertical directions. Orthogonal cutting of a liquid is carried out in a rotating tangential direction during rotation and the purpose of magnetizing the liquid is achieved. The main body rack also can be changed to be driven by a motor. The stirring-type liquid magnetization device is a magnetization device which can be installed in a reservoir, continuous production can be achieved, the magnetization time and degree can be controlled, and various magnetic fields and fluid relative speeds can be covered. The magnetization device can be widely applied in industrial pipe and heat exchange circulating water magnetization for preventing scale, removing scale and preventing rust, concrete mixing water magnetization for enhancing the intensity and fishery culture water magnetization for resisting diseases and increasing the yield, and can provide a lot of agricultural magnetization water.
Owner:高明雄
Apparatus, system, method and computer-readable medium for isolating chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast from magnetization transfer asymmetry under two-frequency RF irradiation
ActiveUS20130166226A1Eliminate contributionMagnetic measurementsChemical machine learningDual frequencyFrequency spectrum
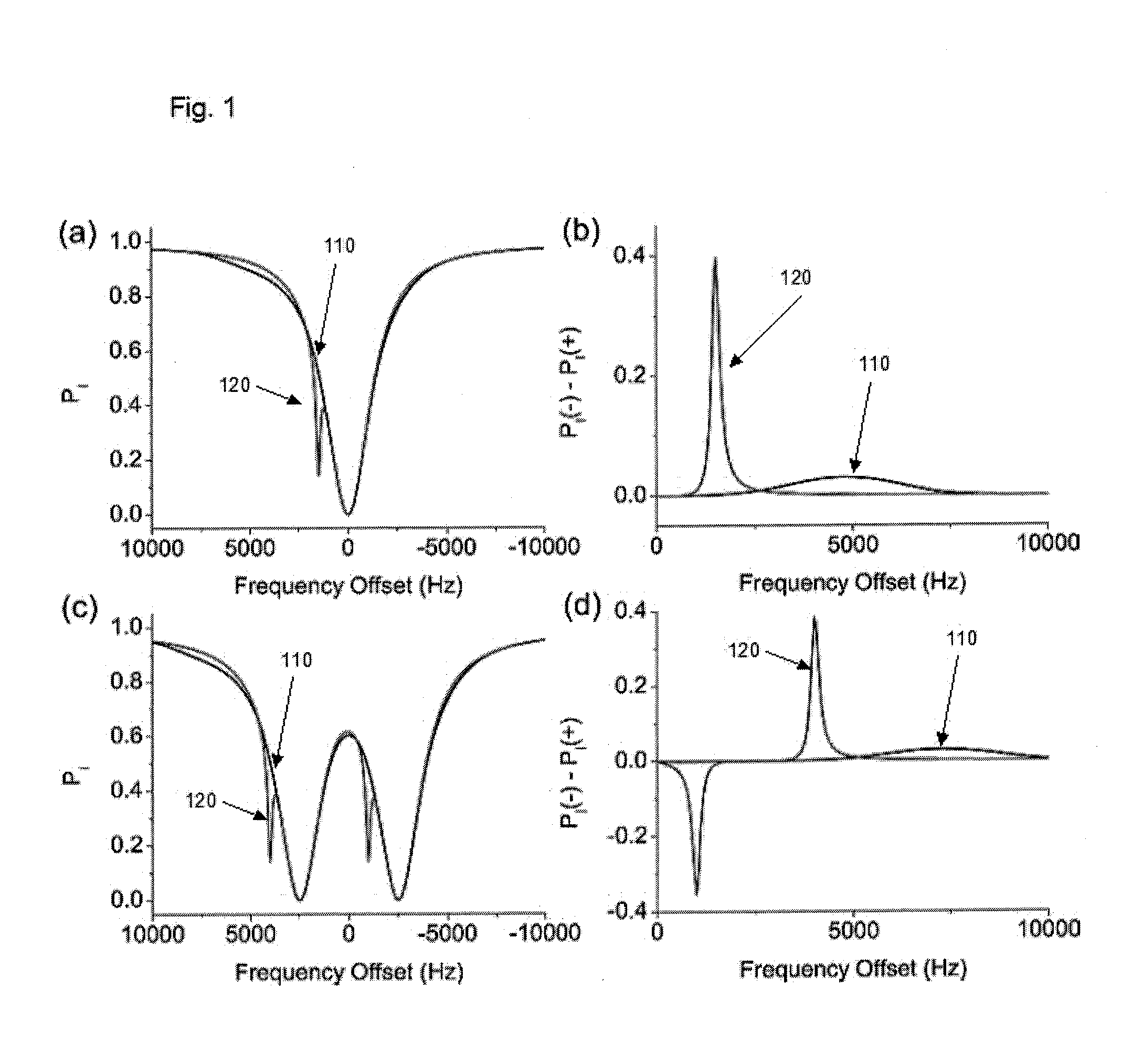
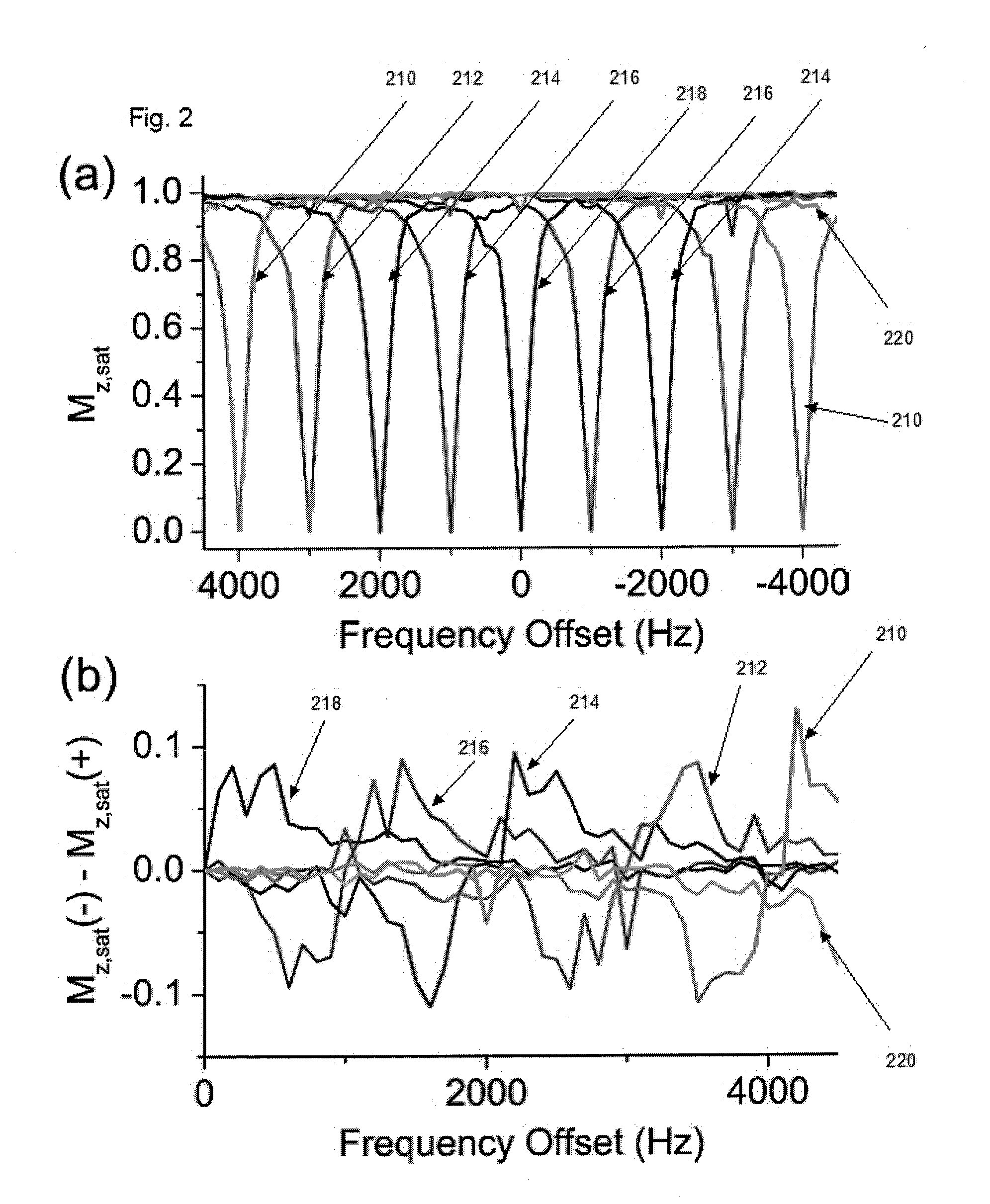
Apparatus, system, method and computer-readable medium for isolating chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast from magnetization transfer asymmetry under two-frequency RF irradiation. A two-pool model for magnetization transfer (MT) can be established fully based on Provotorov's theory of saturation, and then extended to the situation of simultaneous two-frequency RF irradiation. Numerical simulations and experimental results demonstrate that two-frequency RF irradiation can make MT effects independent of irradiation frequency over a wide range, and thus can suppress MT asymmetry. Exemplary embodiments can be provided to isolate chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrast from MT asymmetry contrast by using the two-frequency RF irradiation technique. A further embodiment can isolate a narrow-frequency spectrum MT mechanism from a broad-frequency spectrum MT mechanism.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
MRI-CEST diagnostic technique based on non-punctual analysis
ActiveCN102132169AMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic variable regulationFrequency spectrumResonance
A solution in the MRI-CEST field is proposed for analyzing a body-part, which includes a CEST agent providing a magnetization transfer with a bulk substrate of the body-part. A corresponding diagnostic system (100) includes input means (505-550) for providing an input map including a plurality of input elements each one for a corresponding location of the body-part; each input element is indicative of a spectrum of a magnetic response of the location, which spectrum includes the magnetic response at an agent frequency of resonance of the contrast agent (with the agent frequency that is at an agent offset of frequency from a bulk frequency of resonance of the bulk substance), and at a reference frequency at the opposite of the agent offset from the bulk frequency. The system further includes calculation means (555,563) for calculating an agent value and a reference value for each one of a set of selected locations; the agent value is calculated in a non-punctual agent range of frequencies including the agent frequency e.g. by integrating the spectrum, and the reference value is calculated in a non-punctual reference range of frequencies including the reference frequency e.g. by integrating the spectrum. Comparison means (565) is then provided for calculating a parametric value for each selected location by comparison between the agent value and the reference value of the selected location.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Apparatus and method of simultaneous fat suppression, magnetization transfer contrast, and spatial saturation for 3D time-of-flight imaging
ActiveUS20070069724A1Improve image qualityEffective applicationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionImaging quality
A pulse sequence for time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) includes a fatsat segment, a magnetization transfer segment, and a spatial saturation segment that are applied by an MR apparatus to acquire MR data for image reconstruction with improved image quality. The pulse sequence is constructed such that at the beginning of each iteration of the inner loop of a 3D acquisition, a fatsat pulse is applied. After the fatsat pulse, MR data is acquired in a series of imaging segments with well-suppressed fat signal. Effective fat suppression is achieved by sampling central k-space data first, before signal from fat relaxes back to a pre-saturation level. Each imaging segment is immediately preceded by one of a MT pulse or a spatial saturation pulse and immediately followed by the other one of the MT pulse or the spatial saturation pulse.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for differentiating tissues in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20060020197A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue DifferentiationPulse sequence
A method of differentiating tissues in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) comprising applying a Magnetization Transfer (MT) pre-pulse in combination with the Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) pulse sequence to obtain an image of the tissue under evaluation. Analysis maps and / or measurements are generated from the obtained image, from which values representative of the macromolecular content are computed for obtaining tissue differentiation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High performance magnetic core transverse magnetic field heat treatment furnace
InactiveCN103103332AImprove performanceMagnetically stableFurnace typesInductances/transformers/magnets manufacturePower flowMagnetization
The invention discloses a high performance magnetic core transverse magnetic field heat treatment furnace, which includes a furnace liner and a material rack fixedly disposed in the furnace liner. The furnace liner is connected to a vacuum pump through a pipeline, a heating wire twines around the furnace liner externally, and an air duct and a magnetized coil are arranged outside the heating wire for separation. An air cooler for cooling the upper air duct is mounted at the furnace liner bottom. The magnetized coil is connected to a control cabinet through a pipeline. For the heating wire and the magnetized coil, power supply control is provided through the control cabinet, and the magnetized coil controls the magnetic field magnitude through current. The iron-based nanocrystalline alloy magnetic core transverse magnetic field heat treatment furnace with the structure combines the advantages of vacuum heat treatment and magnetic heat treatment. As the magnetization treatment is conducted in a vacuum state, the magnetic core has a bright surface and excellent performance. Meanwhile, because of the magnetization treatment, the magnetic performance is stable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BUSINESS TECH INST
Mr imaging with an RF pulse producing reduced magnetization transfer
ActiveUS20070236216A1Reduce and limit amountMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationK space trajectory
A system and method are provided herein for designing and transmitting RF pulses which cause a reduced off-resonance magnetization transfer saturation. An RF pulse shape may be optimized according to a set of Bloch solutions defining a desired magnetization profile. An RF pulse may be transmitted according to this optimized shape according to a k-space trajectory which traverses a high amplitude portion of the RF pulse more times than one or more low amplitude portions. In addition, a generally alternating slice select gradient may be applied during transmission of the RF pulse.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Magnetic resonance imaging of coronary venous structures
InactiveUS8457711B2Increase contrastSuppresses coronary vein signalsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringVenous bloodCardiovascular procedures
A method and system for magnetic resonance imaging comprises applying at least one radiofrequency magnetization transfer (MT) pulse to a coronary venous region of a subject positioned within a magnetic field, and acquiring magnetic resonance imaging data from the coronary venous region to produce an image of a coronary venous structure. This technique can be utilized as part of a 3D free-breathing, ECG-triggered gradient-echo Cartesian acquisition of the coronary region. One or more magnetization transfer (MT) preparation pulses are used to enhance the contrast between venous blood and myocardium. The MT preparation results in myocardial signal suppression without any significant signal loss in the arterial or venous blood so as to maintain venous blood signal-to-noise ratio while improving contrast between myocardium and veins. The image of a coronary venous structure can be acquired in connection with an interventional cardiovascular procedure, such as a cardiac resynchronization therapy.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Magnetic recording head, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic disk device
InactiveUS8837086B2Sufficient effectHigh densityManufacture head surfaceDriving/moving recording headsLine resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A magnetic recording head used for microwave-assisted magnetic recording includes: a main pole; a spin torque oscillator provided on the main pole, including a high-speed rotating magnetization layer in which the magnetization is rapidly rotated by a spin torque; a trailing shield provided on the spin torque oscillator; and a sub pole magnetically coupled to the trailing shield provided in a medium-facing surface, extending in a vertical direction to the medium-facing surface. Then, a non-magnetic electrode is provided on the outside of a trailing gap in which the spin torque oscillator is provided with respect to a magnetic material of the main pole, the trailing shield, or the sub pole, to prevent the line resistance variation due to the AMR effect or the eddy current. Thus, the variation of the current flowing to the spin torque oscillator can be controlled to achieve stable oscillation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Paramagnetic metal ion-based macrocyclic magnetization transfer contrast agents and method of use
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS8159872B2Suppress mutationImprove featuresNanotechMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeStatic random-access memory
An MRAM has: a memory cell including a first magnetoresistance element; and a reference cell including a second magnetoresistance element. The first magnetoresistance element has a first magnetization fixed layer, a first magnetization free layer, a first nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the first magnetization fixed layer and the first magnetization free layer, a second magnetization fixed layer, a second magnetization free layer and a second nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the second magnetization fixed layer and the second magnetization free layer. The first magnetization fixed layer and the first magnetization free layer have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, and the second magnetization fixed layer and the second magnetization free layer have in-plane magnetic anisotropy. The first magnetization free layer and the second magnetization free layer are magnetically coupled to each other. Center of the second magnetization free layer is displaced in a first direction from center of the first magnetization free layer in a plane parallel to each layer. Whereas, the second magnetoresistance element has: a third magnetization free layer whose magnetization easy axis is parallel to a second direction; a third magnetization fixed layer whose magnetization direction is fixed in a third direction perpendicular to the second direction; and a third nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the third magnetization fixed layer and the third magnetization free layer. The third magnetization fixed layer and the third magnetization free layer have in-plane magnetic anisotropy.
Owner:NEC CORP
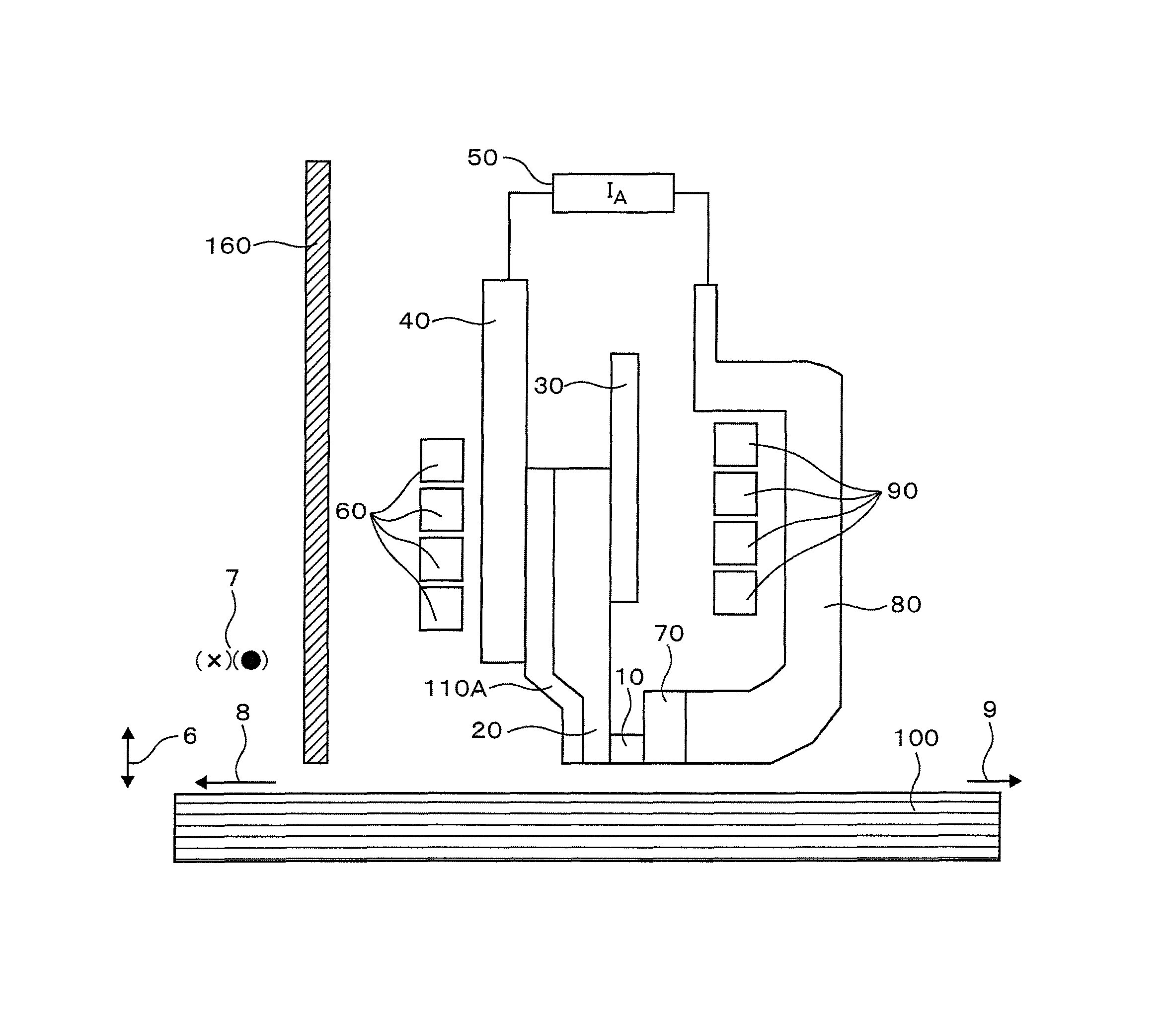
Device for testing a test specimen for surface faults by magnetization means and by means of induction probes as measurement sensors
ActiveUS7242186B2Easily and economically adapted to different test specimensImprove cooling effectMagnetic property measurementsCores/yokesElectrical conductorHigh energy
A device for testing a test specimen for surface faults is equipped for delivering a magnetic flux into the specimen and has induction probes measurement sensors. At least two yoke legs have opposed gap-forming ends with oppositely poled exciter coils between which the test specimen can be guided. Outside ends of the yoke legs opposite the gap-forming ends are connected to one another by a magnetic flux conductor so that the magnetic flux runs perpendicular to the lengthwise direction through the test specimen. To adapt to test specimens of different cross section, the yoke legs can be moved and fixed. Testing of test specimens by means of high-energy magnetic alternating fields improved because the high heat losses produced in this process are adequately dissipated. The device is especially well suited to determine the quality of bars, pipes and the like in a hot rolling mill with high-energy alternating magnetic fields.
Owner:PRUTECHNIK DIETER BUSCH AG
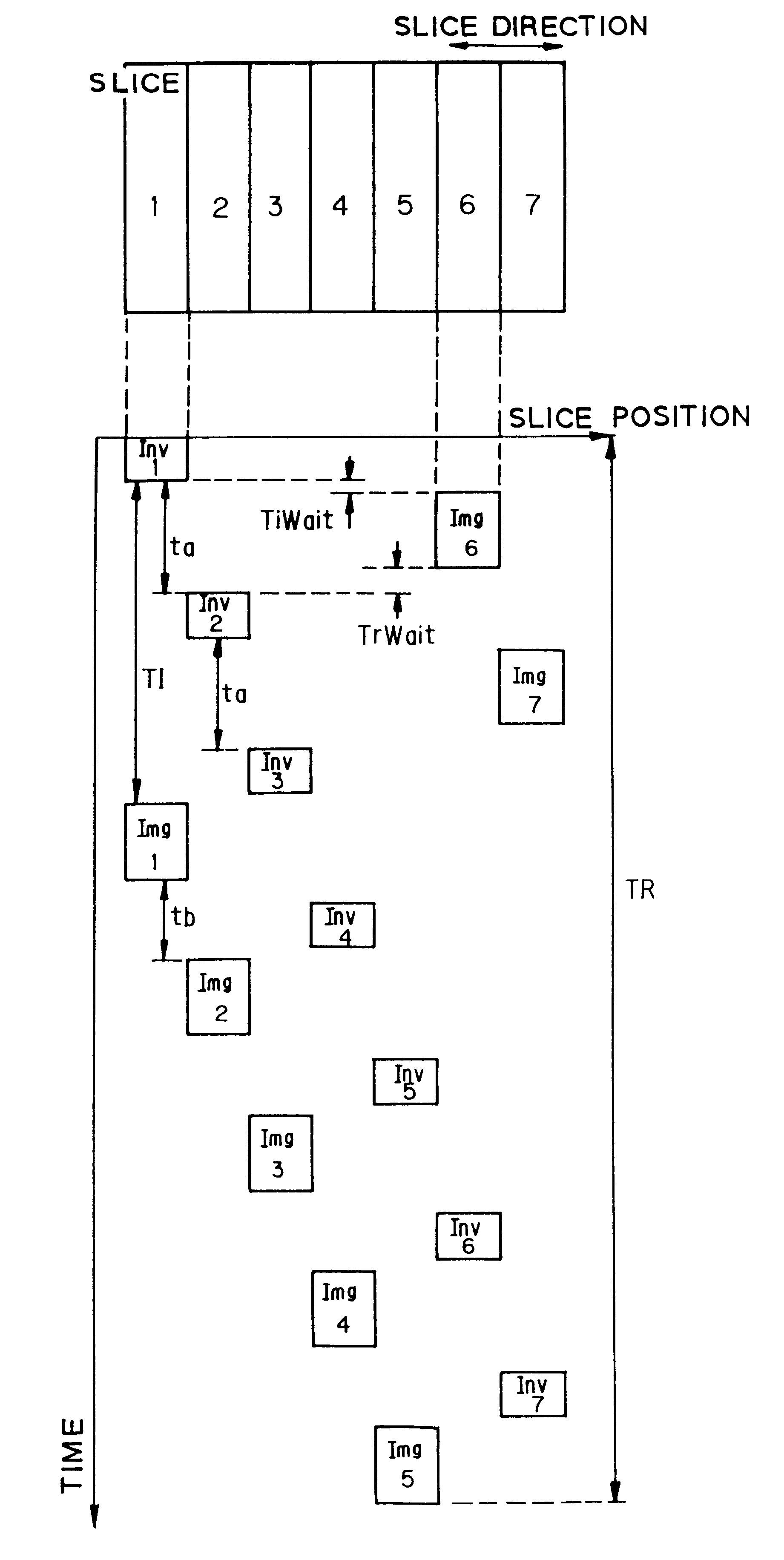
Multi-slice magnetic resonance data acquisition method and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20160178719A1Reduce crosstalk effectsReduce transfer effectMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionComplete dataMulti slice
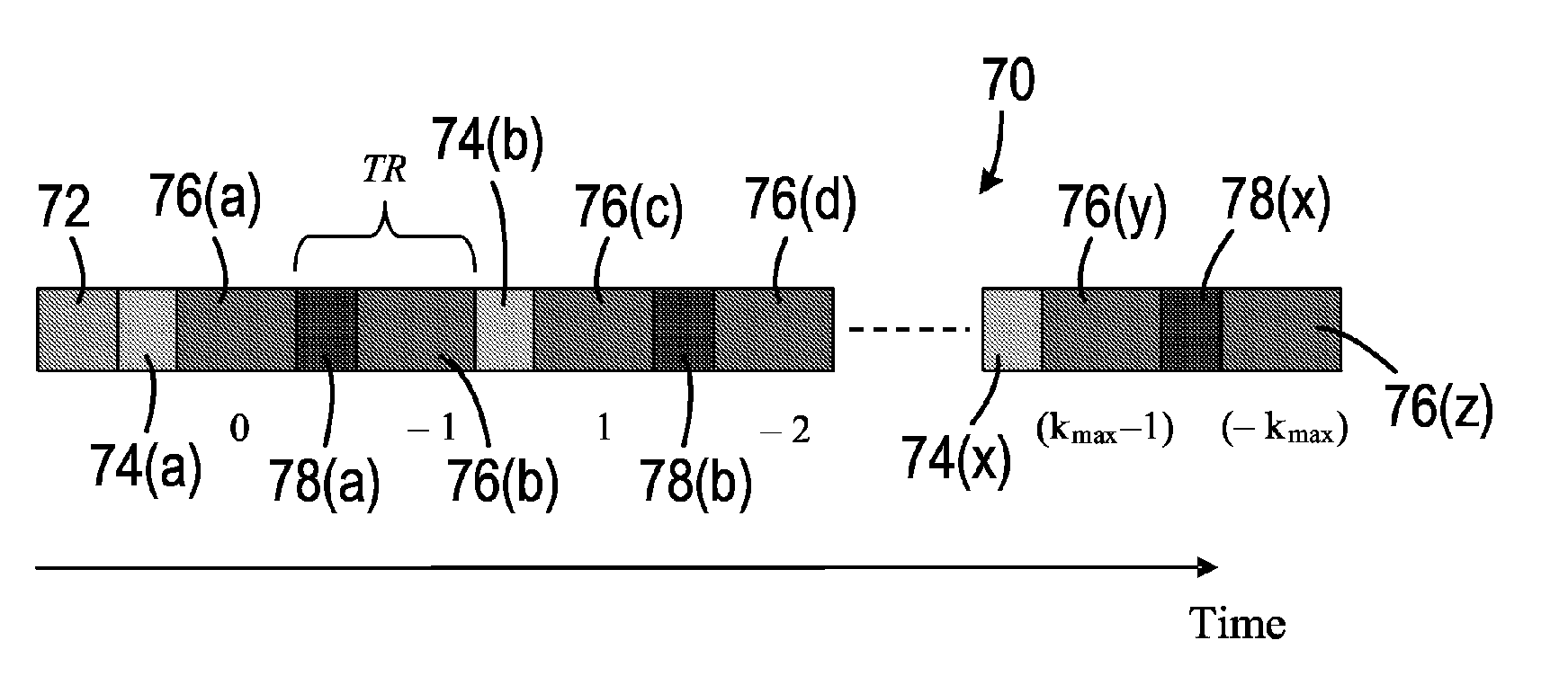
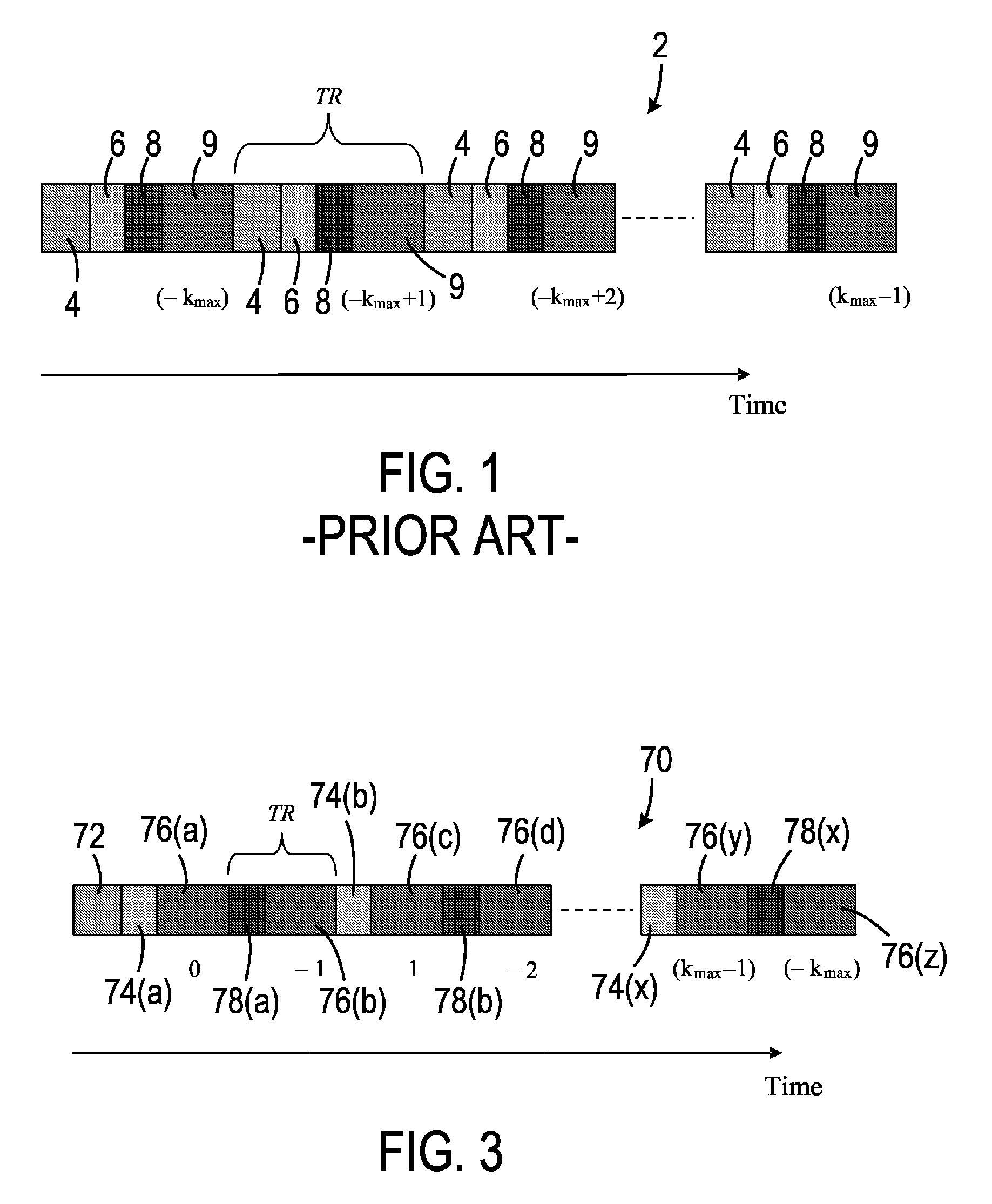
In a multi-slice data acquisition method and device and a magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus, a number NC of fractional acquisitions and a number NS of slice individual, complete data acquisition of the multi-slice data acquisition are determined. Using an iterative odd / even arranging method, a slice data acquisition order of each of the fractional acquisitions is arranged according to an ideal number of iterations. The ideal number of iterations is obtained from multiple undetermined numbers j of iterations of the iterative odd / even arranging method according to the number NS of slice data and the number NC of fractional acquisitions. This multi-slice data acquisition method optimizes the slice data acquisition order so as to significantly reduce the effect of magnetization transfer and crosstalk.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for generation of magnetization transfer contrast in steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7372267B2Shorten Image Acquisition TimeImprove rendering capabilitiesMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Transverse relaxation
Apparatus and methods of generating magnetization transfer contrast images in which signal to noise ratios are improved and / or in which image acquisition times are reduced. In certain embodiments, apparatus and methods which utilize sensitivity and / or non-sensitivity to magnetization transfer effects to improve the contrast of images which are generated. In certain additional embodiments, apparatus and methods for generating magnetization transfer contrast images which exhibit sensitivity to longitudinal and transverse relaxation times of bound and free proton pools, respectively.
Owner:BASEL UNIV OF
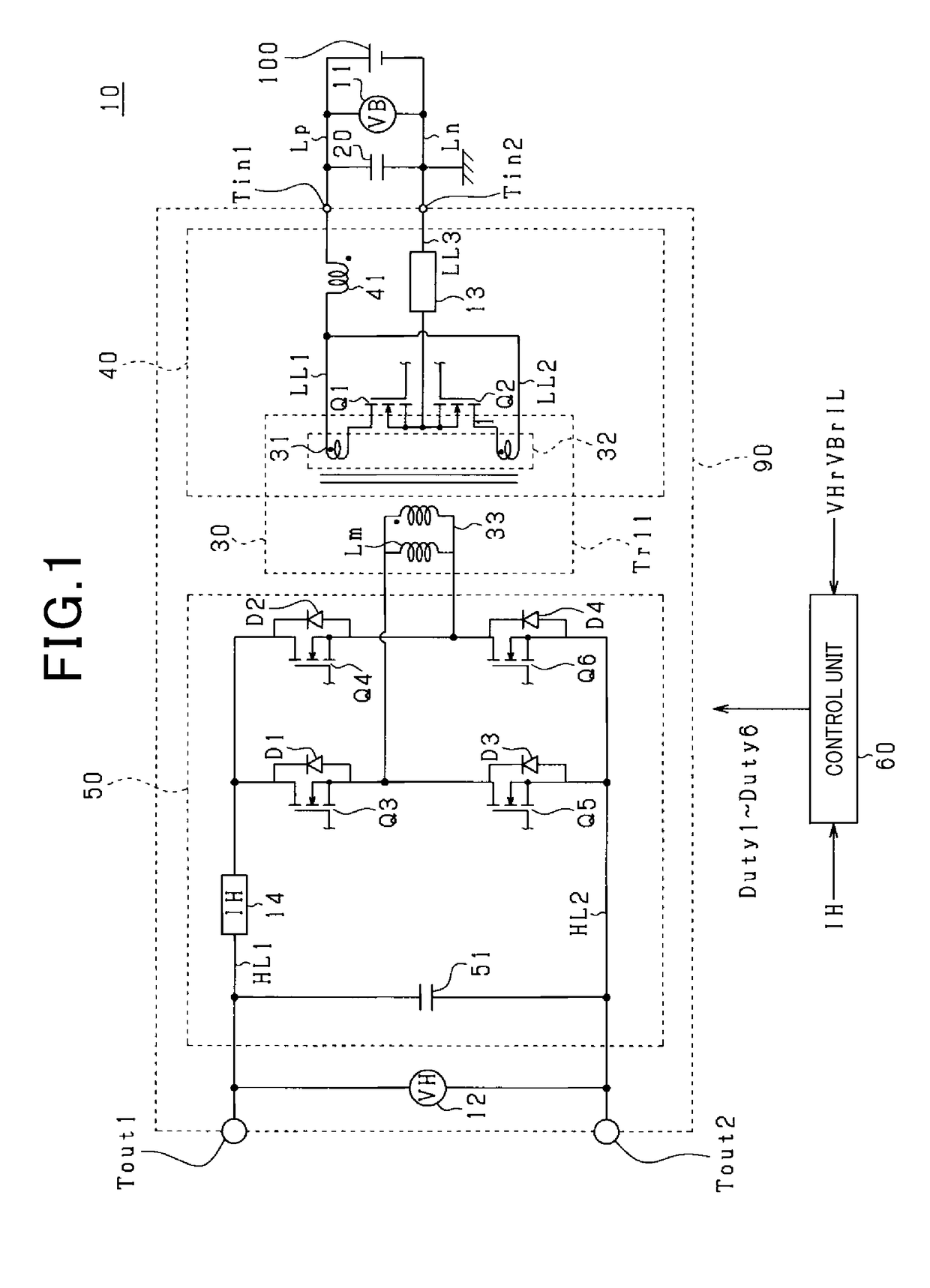
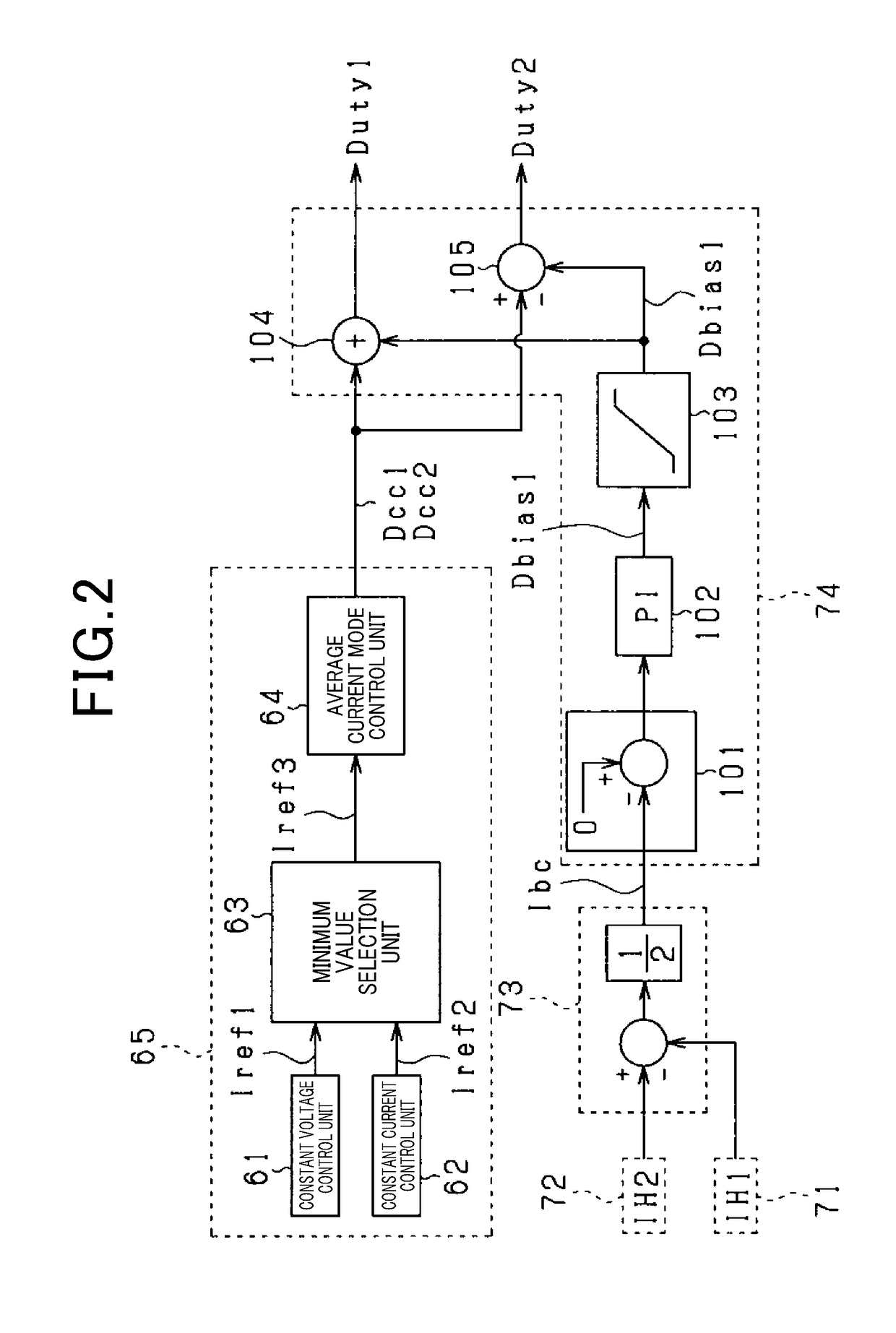
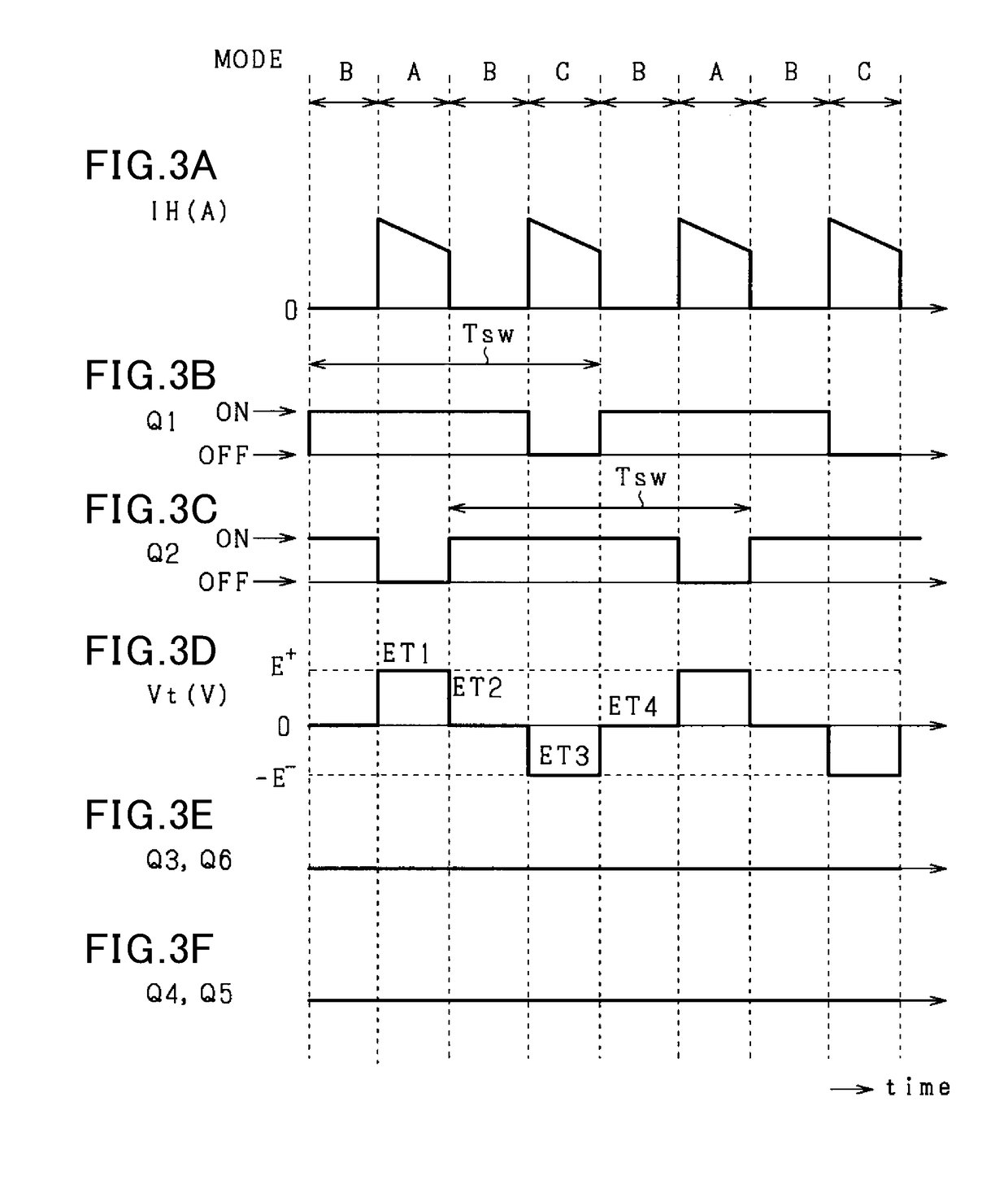
Control apparatus
ActiveUS20180342942A1Reduce magnetization biasAvoid mistakesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationExcitation currentTransformer
A control unit capable of accurately calculating a magnetization bias of a transformer is provided, thereby appropriately reducing the magnetization bias. The control unit acquires first and second currents that flow through a transformer during a period where either first or second switches individually turn ON. The control unit predicts an amount of magnetization bias in either positive side or negative side of the excitation current that flows through the transformer. The control unit reduces the magnetization bias of the transformer based on the predicted amount of magnetization bias.
Owner:SOKEN CO LTD +1
Magnetic field superposed pipeline fluid magnetization treater
InactiveCN101982857ASimple structureImprove the magnetization effectMagnetic bodiesWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetizationUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a magnetic field superposed pipeline fluid magnetization treater, belonging to the water treatment equipment. The treater is characterized in that the structural patterns of bipoles of two permanent magnets or multi-poles of three or four permanent magnets are correspondingly arranged on the same circumferential section of the outer wall of a fluid pipe; or various poles such as the bipoles or multi-poles are set as a plurality of magnet magnetization groups and repeated magnetization structure patterns in the length direction of the pipe; the poles correspond to each other (namely N-N or S-S) and the magnetic lines of force of N-S poles of the magnets are vertical to the length direction of the pipe axle; and various installation methods are adopted. The treater has the following advantages: the structure is simple; the magnetic field intensity can be more than n times that of the single magnet; the magnetization time can be adjusted according to the requirement; and compared with the existing magnetization pattern structures, the magnetization effect of the treater is obviously improved.
Owner:廖一
Multi-slice data acquisition method and magnetic resonance imaging method thereof
ActiveCN105785297AOptimize collection orderRepetition time shortenedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData acquisitionMagnetization transfer
The invention discloses a multi-slice data acquisition method and a magnetic resonance imaging method thereof. The multi-slice data acquisition and sequencing method includes the steps of determination and sequencing. According to the determination step, times-based acquisition quantity NC and slice data quantity NS of multi-slice data acquisition are determined. According to the sequencing step, an iterative odd-even sequencing method is adopted to arrange a multi-slice data acquisition sequence of each times-based acquisition according to an ideal number of iterations, wherein the ideal number of iterations is obtained from a plurality of numbers j of iterations to be determined of the iterative odd-even sequencing method according to the slice data quantity NS and the times-based acquisition quantity NC. With the multi-slice data acquisition method provided by the embodiments of the invention adopted, the slice data acquisition sequence can be optimized, so that cross interference and magnetization transfer can be significantly reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS SHENZHEN MAGNETIC RESONANCE
Storage element, storage apparatus, and magnetic head
InactiveCN104662686AImprove thermal stabilityEasy to operateNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMagnetizationComputational physics
There is provided a storage element including a layered construction including a storage layer that has magnetization perpendicular to a surface of the storage layer and whose direction of magnetization is changed corresponding to information, a pinned magnetization layer that has magnetization perpendicular to a surface of the pinned magnetization layer and serves as a standard for information stored in the storage layer, and an insulating layer that is composed of a non-magnetic material and is provided between the storage layer and the pinned magnetization layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com