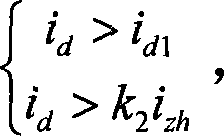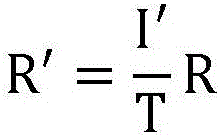Patents
Literature
72 results about "Saturation transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
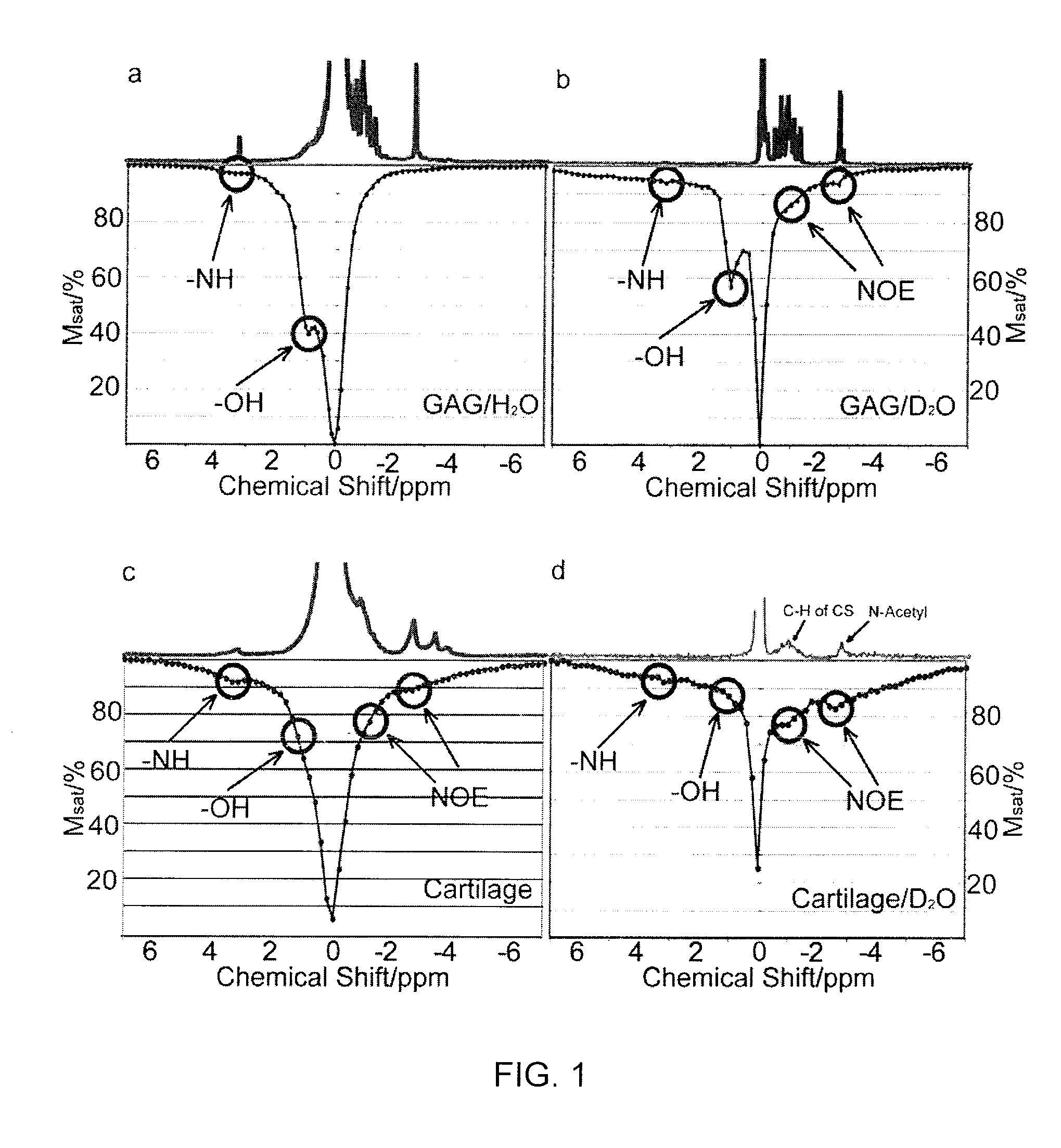
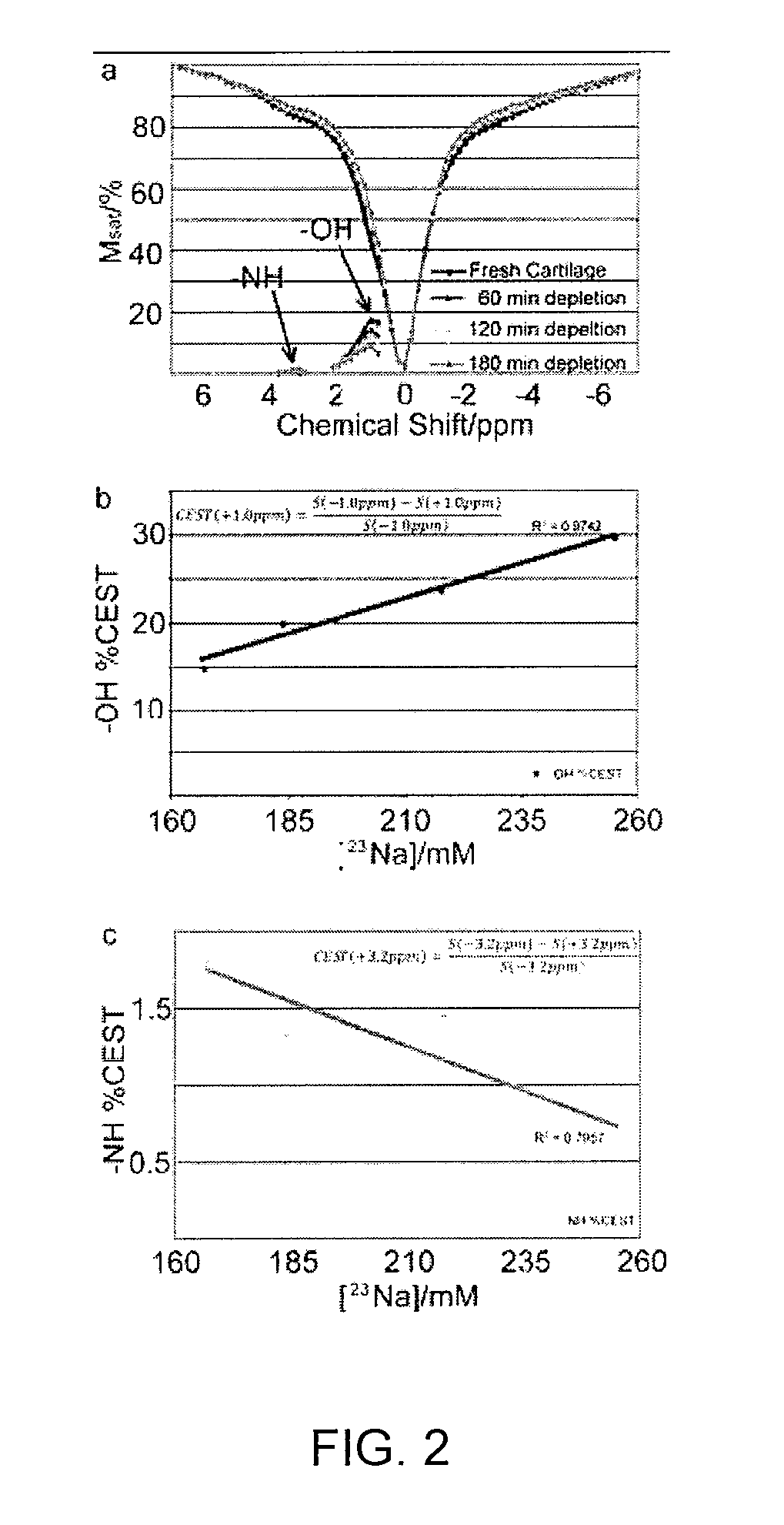
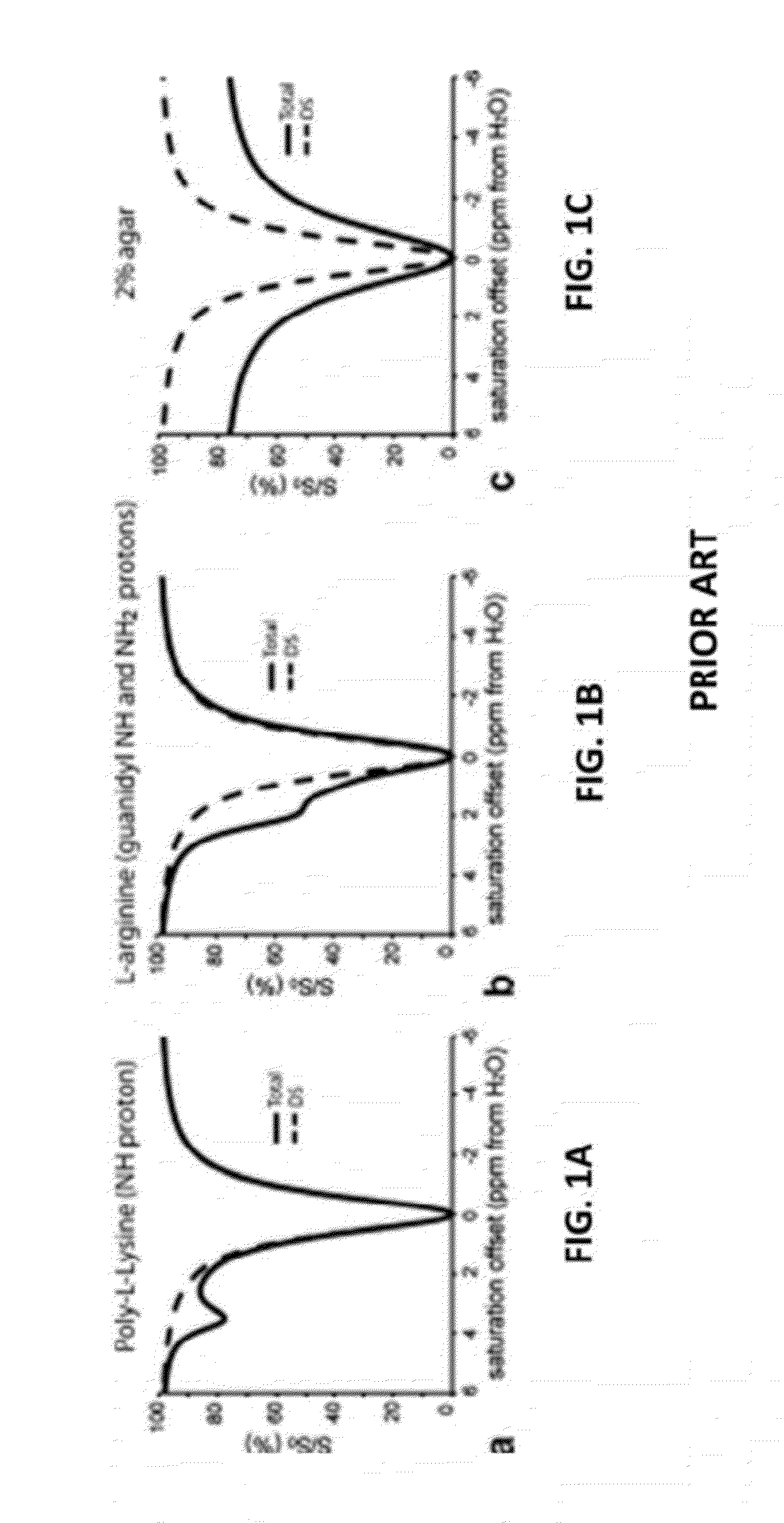
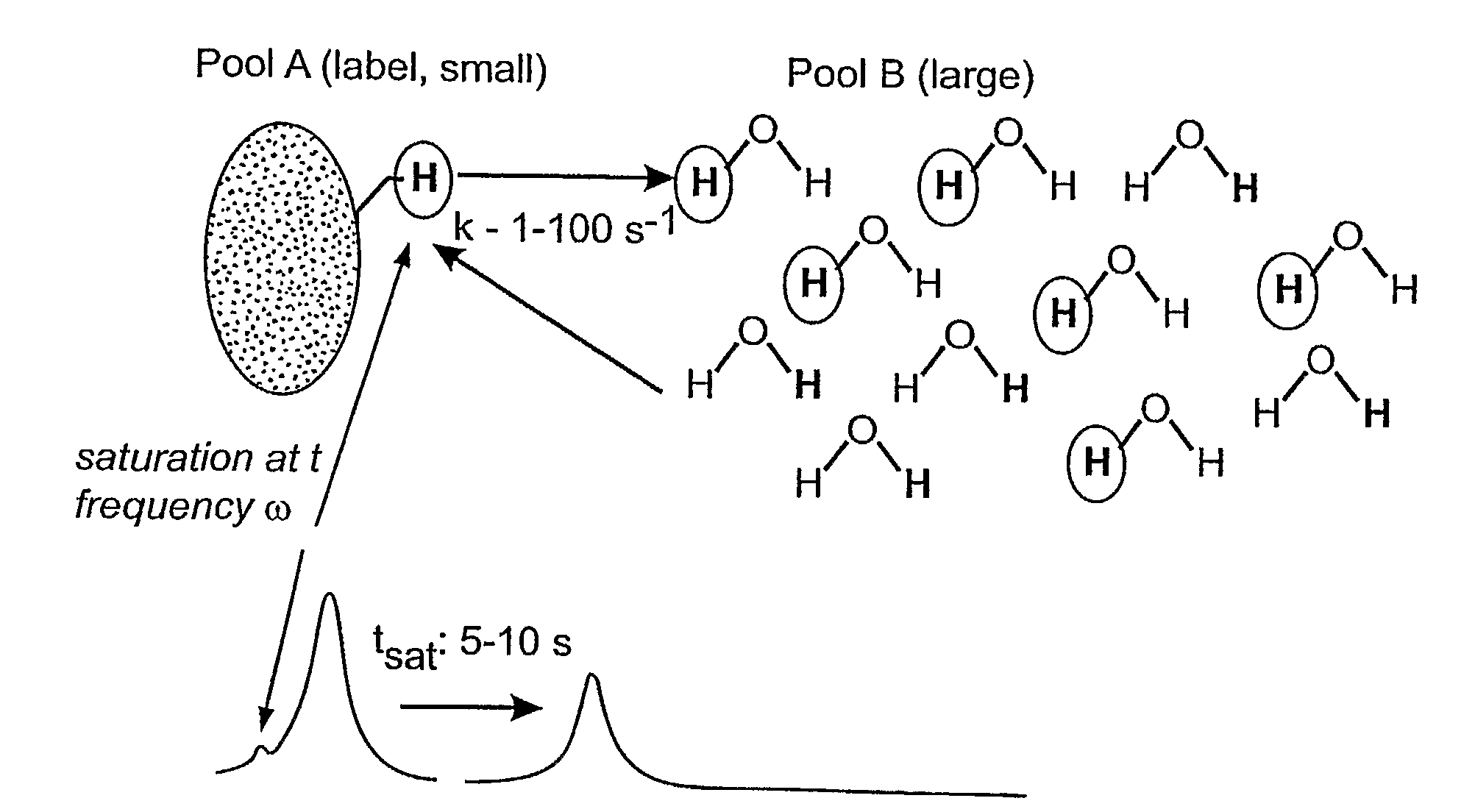
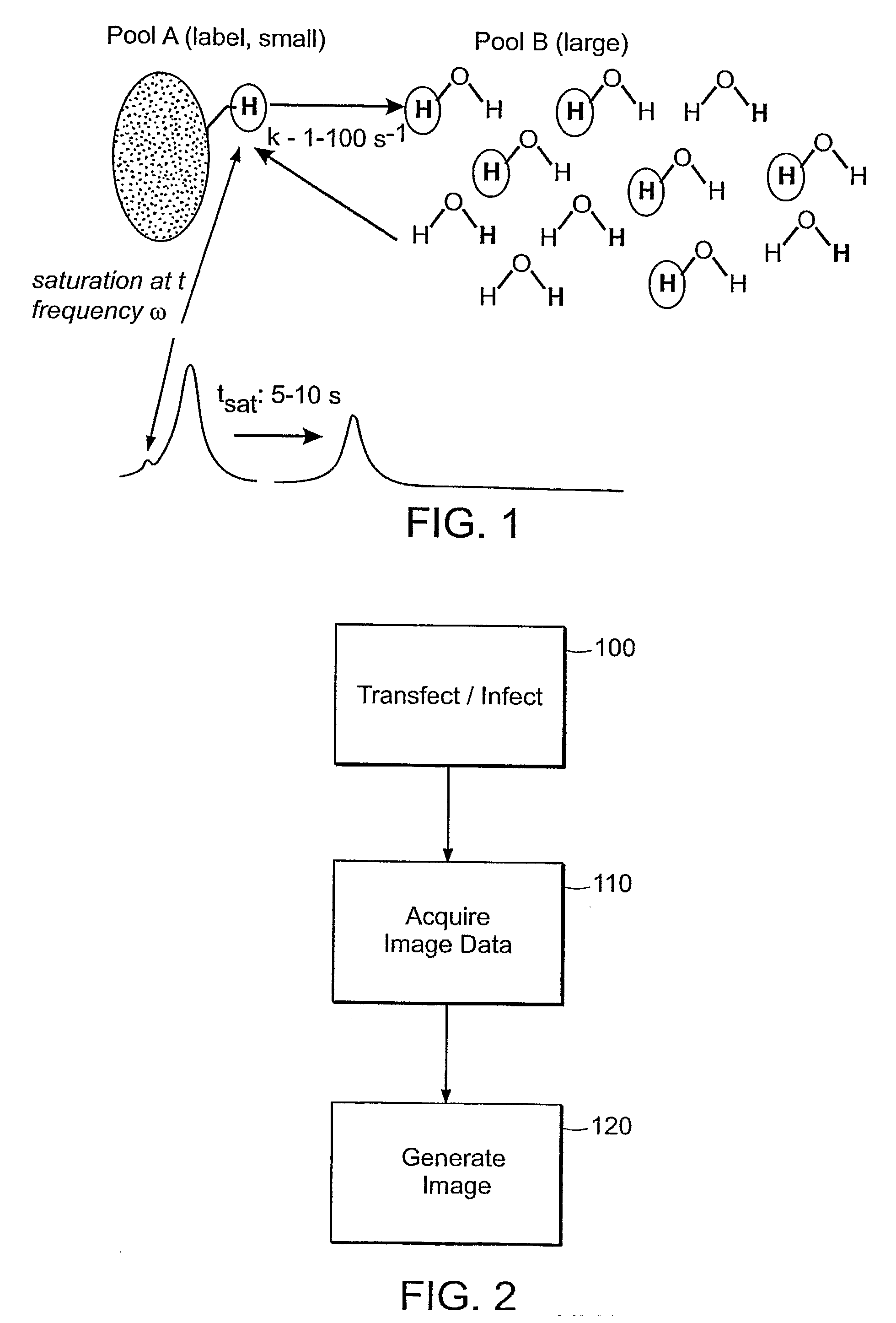
Saturation Transfer. The saturation transfer is an actively driven depolarization process that builds up over time and that strongly depends on the exchange parameters of the noble gas.
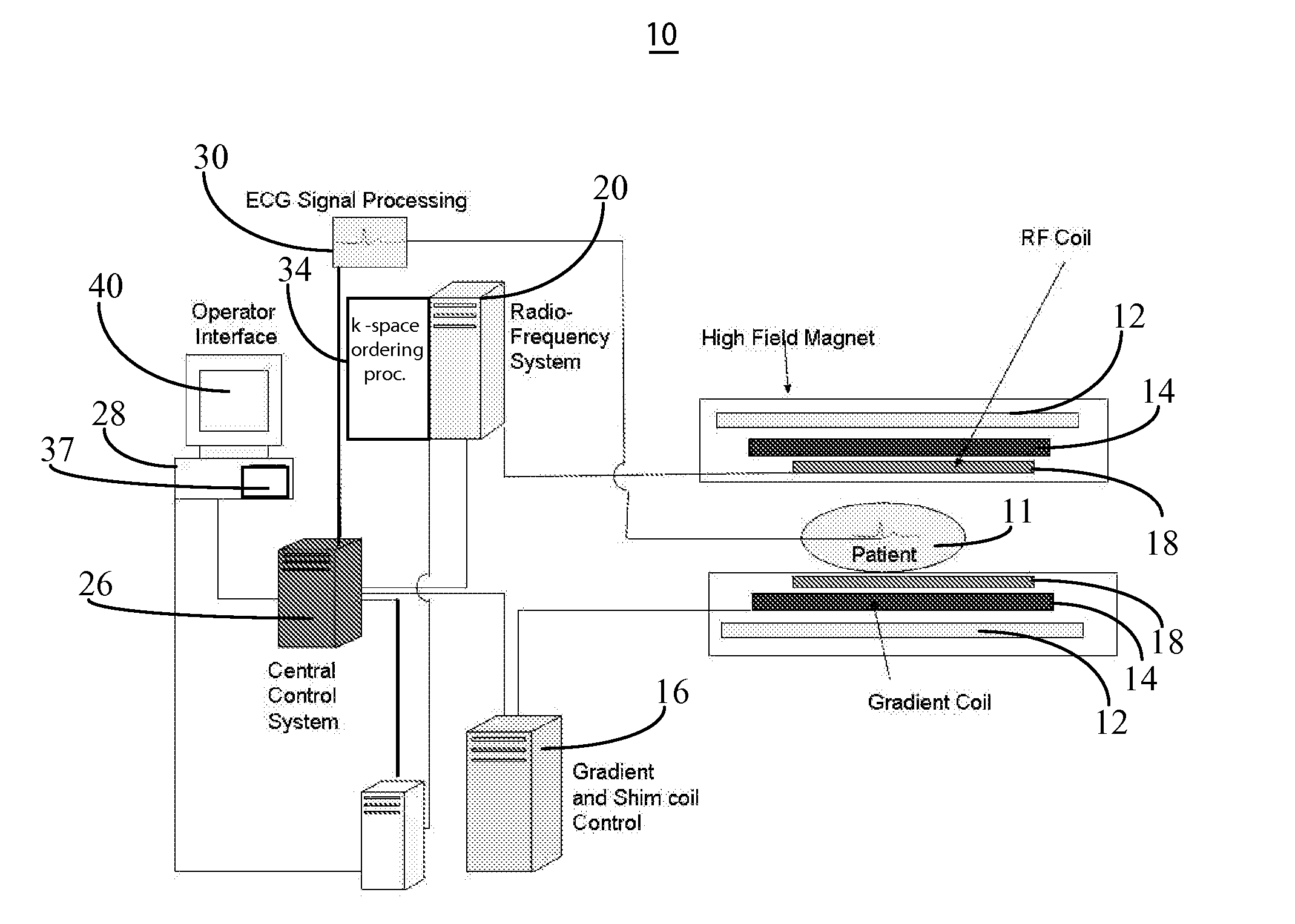
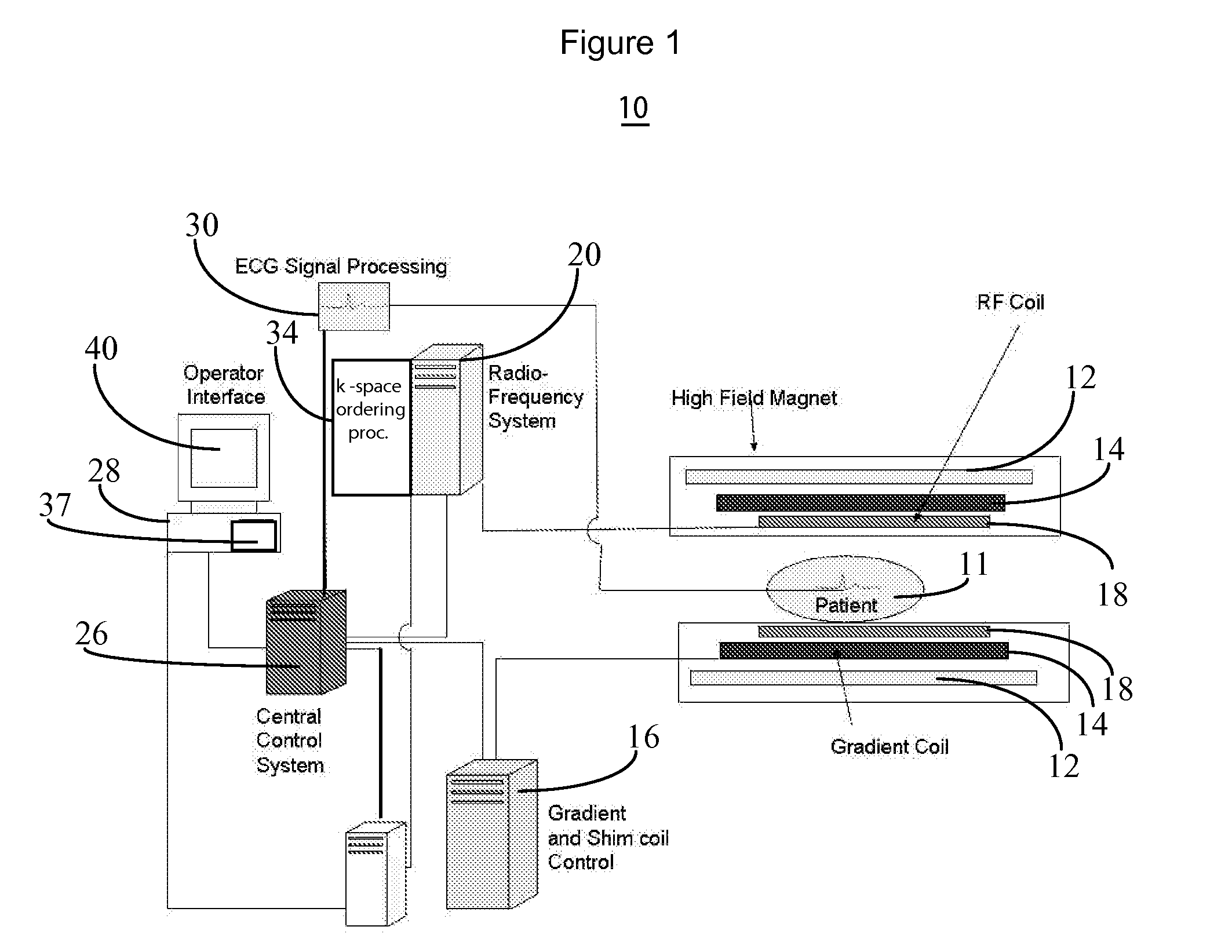
Method, System, and Computer-Accessible Medium for Assessment of Glycosaminoglycan Concentration in Vivo by Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer
InactiveUS20110054299A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringCross relaxationResonance
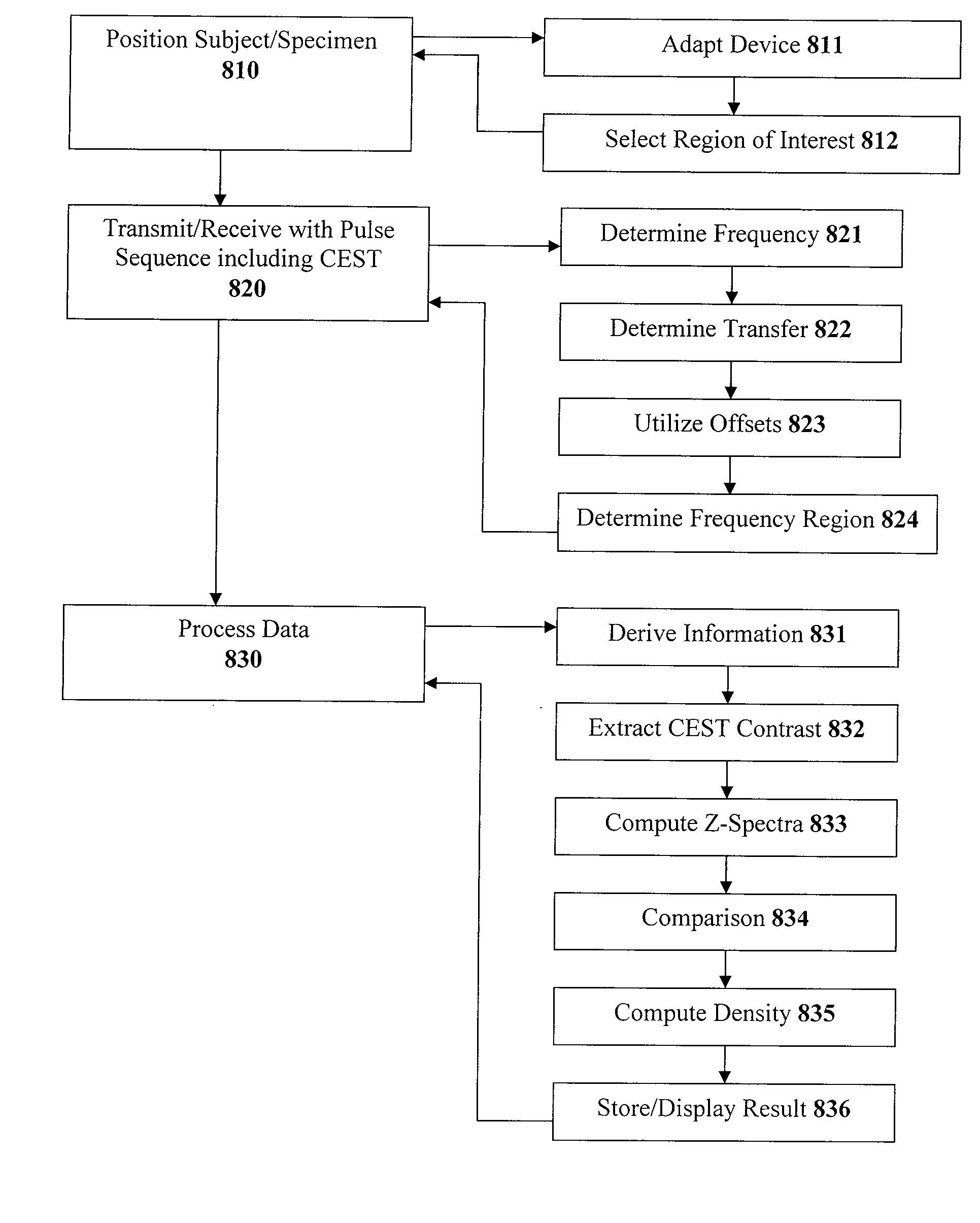
An exemplary methodology, procedure, system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided to determine one or more particular frequencies of cross-relaxation between at least one molecule and at least one particular compound, determine a chemical exchange based on magnetic resonance data using a further frequency which is different from the one or more particular frequencies, and derive particular information about the anatomical region of interest based on the chemical exchange.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
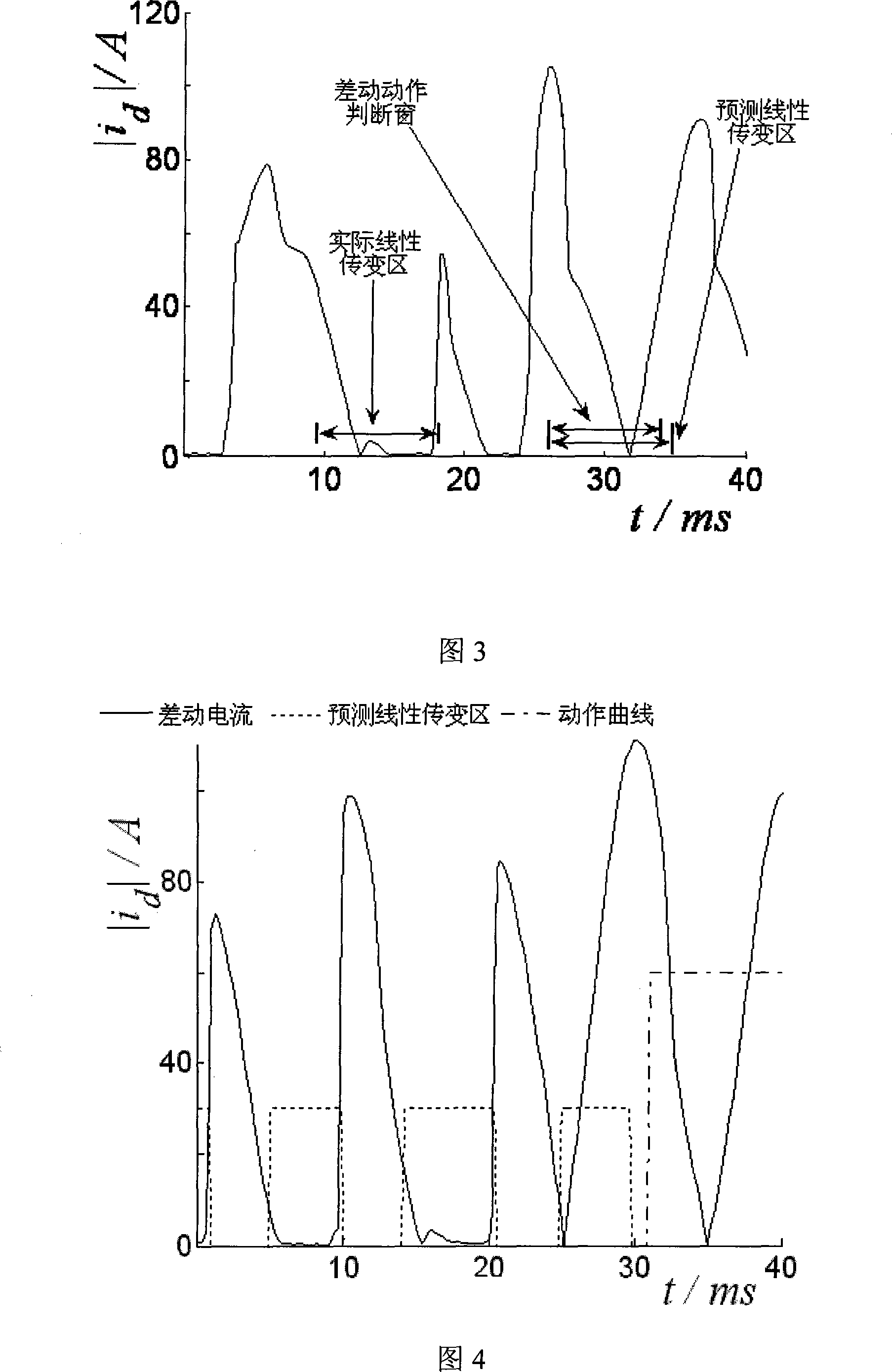
Anti-CT saturated sampling value differential protection of predicting CT linear transform area
ActiveCN101183786AMeet safe operation requirementsMove quicklyEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLinear predictionLinear transform
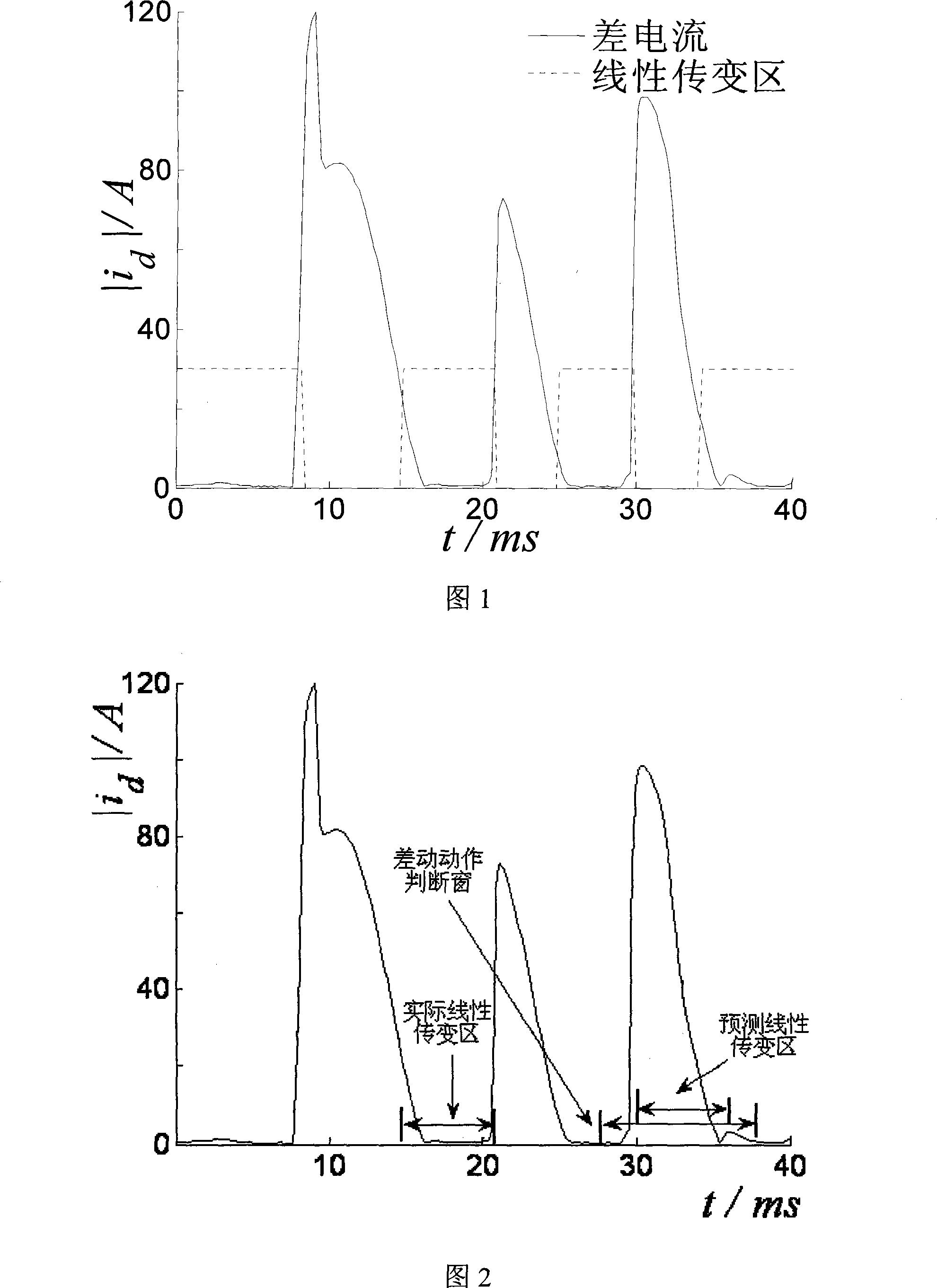
The invention relates to an anti-CT saturation sampling value differential protection for predicting the CT linear transmission area, including: detecting the CT linear transmission area; predicting the linear transmission area after one cycle according to the currently known position of the linear transmission area location; in the predicted linear transmission area, apply the sampling value difference criterion to judge; if it is an internal fault, there is no linear transmission area, and the protection action; for an external fault, if it develops into the area, the sampling value difference If the fault is still outside the area, continue the above-mentioned protection judgment process of detecting the linear change area prediction, predicting the linear change area, and performing differential judgment of sampling values in the predicted linear change area, and so on until Protective action or start return. The invention can judge the CT saturation, and can act quickly when the fault outside the zone is CT saturated and transfers to the zone; it is not affected by the degree of saturation; there is no limit to whether the CT is saturated when the fault is switched; it has high action sensitivity and reliability sex.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
MR Parallel Imaging System Reducing Imaging Time
ActiveUS20140070803A1Good effectIncreased RF pulse sequence duty cycleMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingPulse sequence
An MR imaging system uses multiple RF coils, for reducing image acquisition time, suitable for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging. Multiple RF (Radio Frequency) coils provide CEST imaging preparation in an anatomical volume by providing multiple interleaved RF pulses. The multiple interleaved RF pulses provide substantially increased RF pulse sequence duty cycle in the multiple RF coils relative to a duty cycle provided by a single coil of the multiple RF coils. The multiple RF coils subsequently provide RF excitation pulses in a reduced anatomical volume using k-space undersampling in an accelerated imaging method using the multiple RF coils and enable subsequent acquisition of associated RF echo data for deriving a CEST image.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
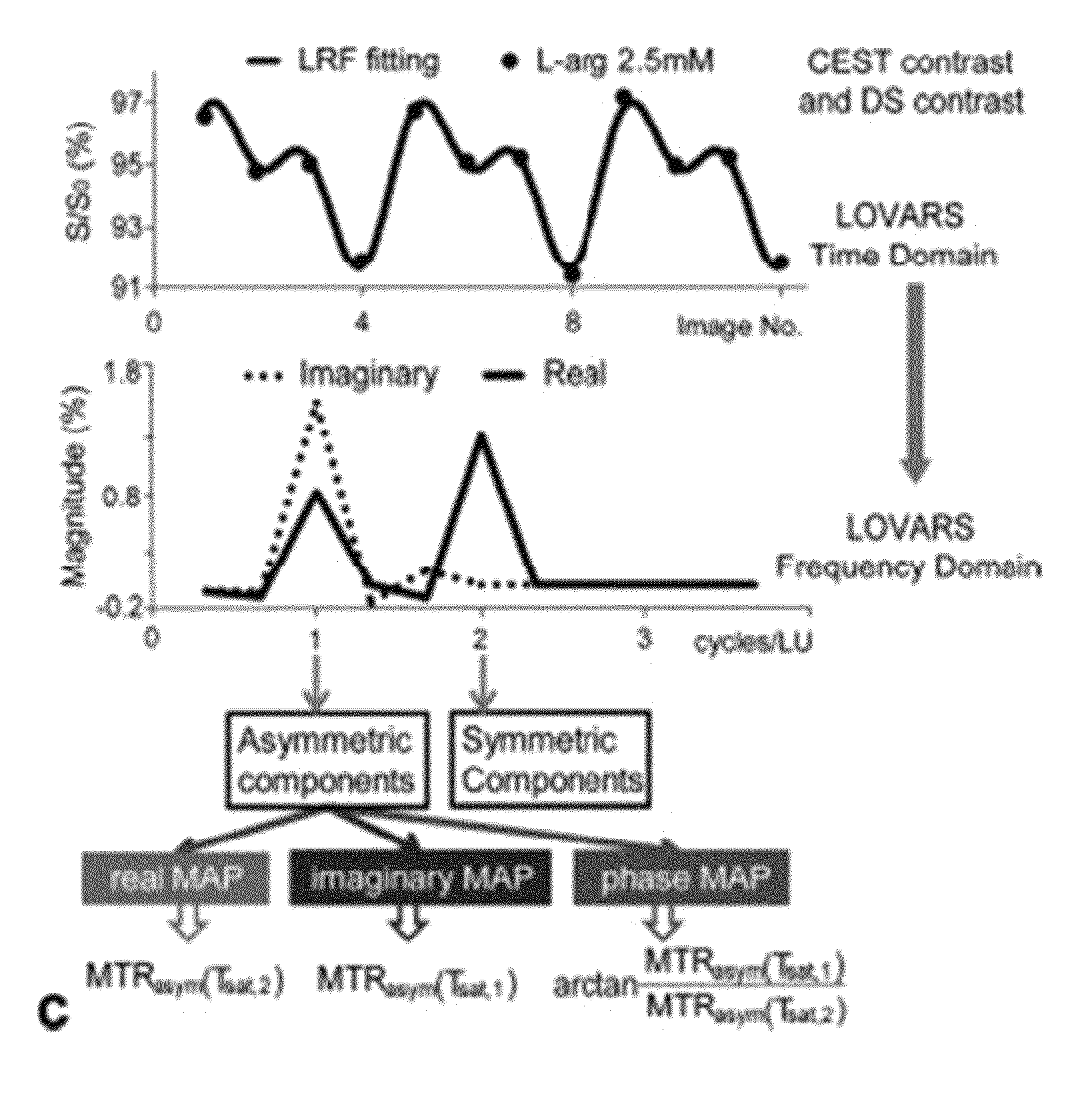
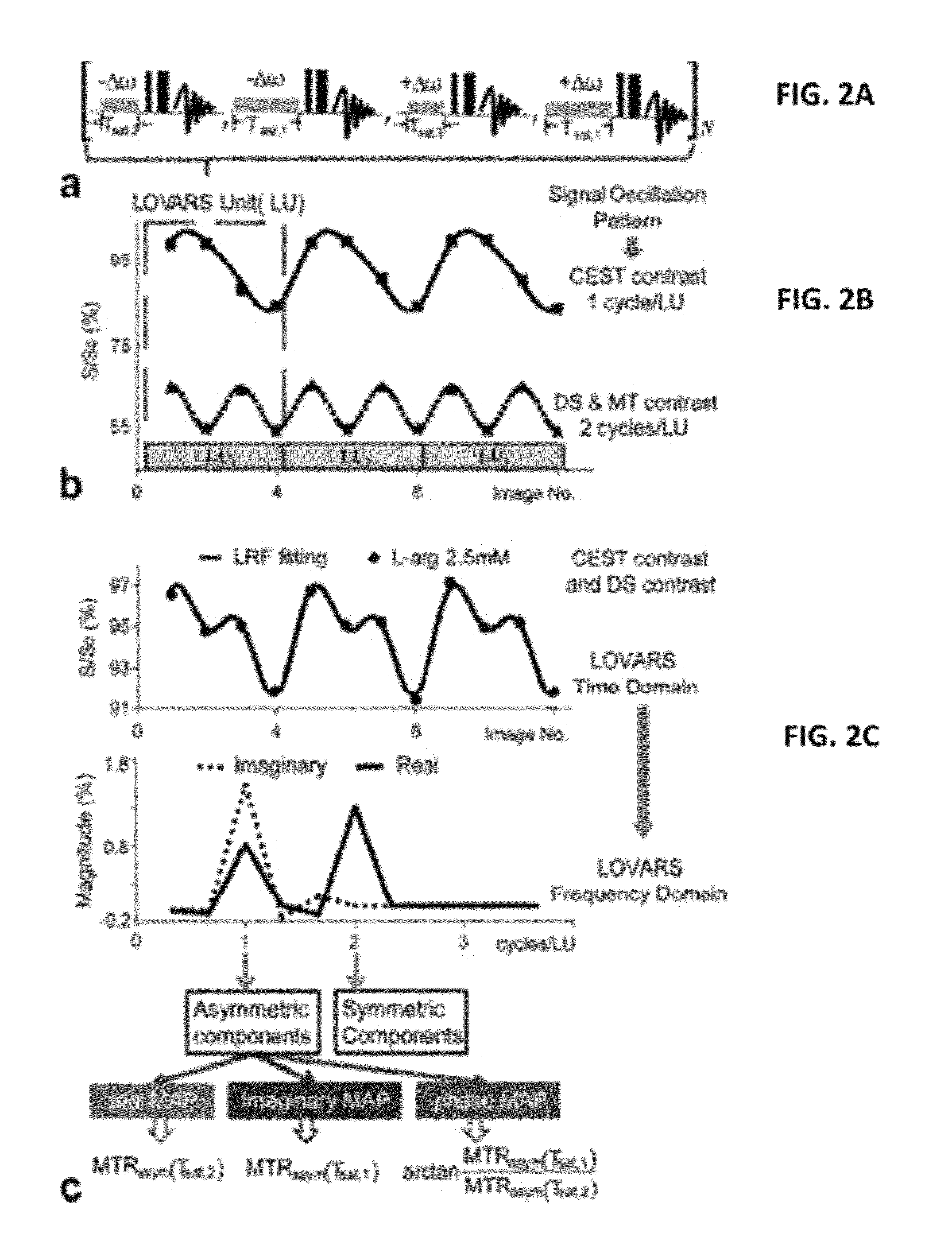
CEST Phase and Magnitude Imaging Using a Multi-Parametric Varied Saturation Scheme
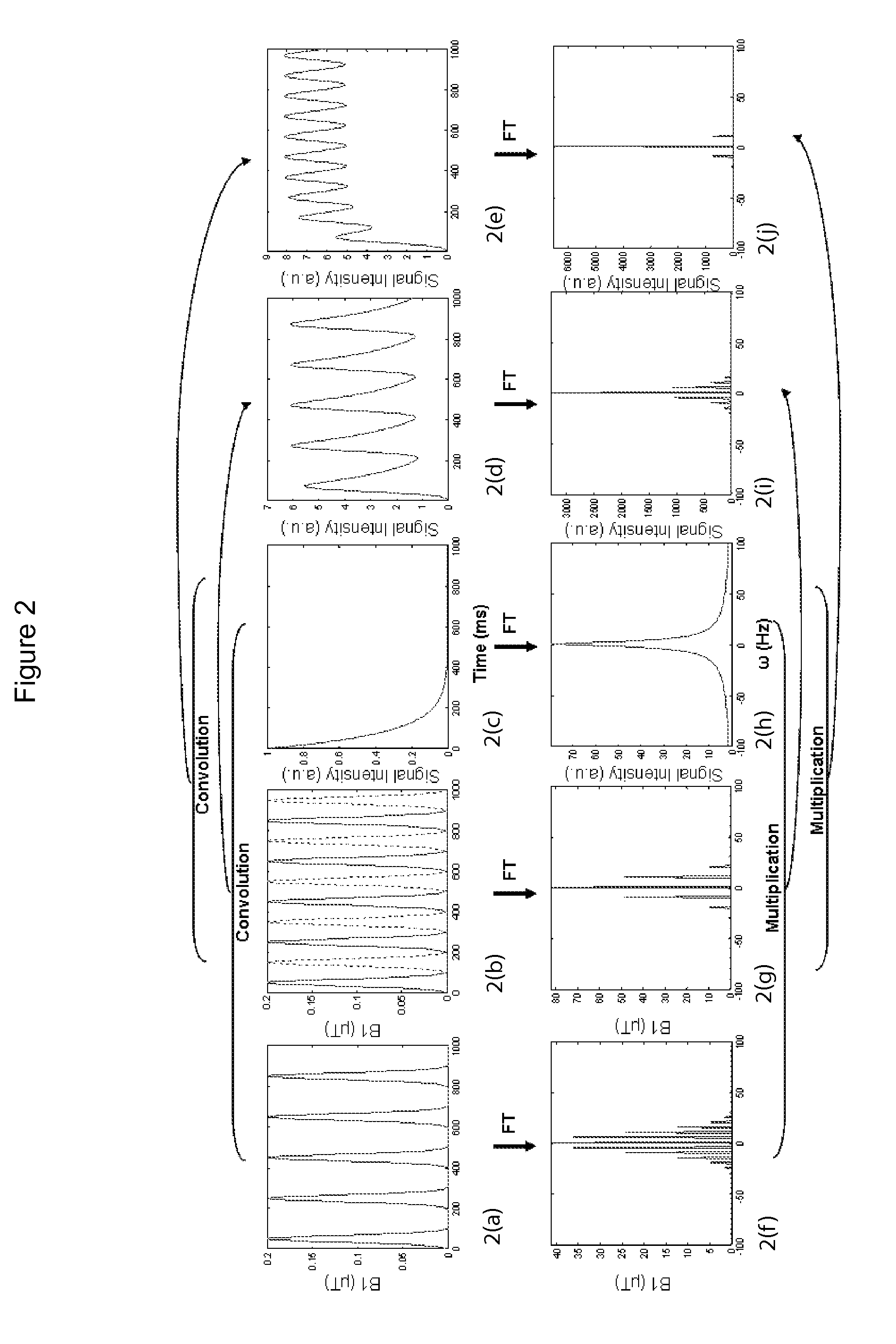
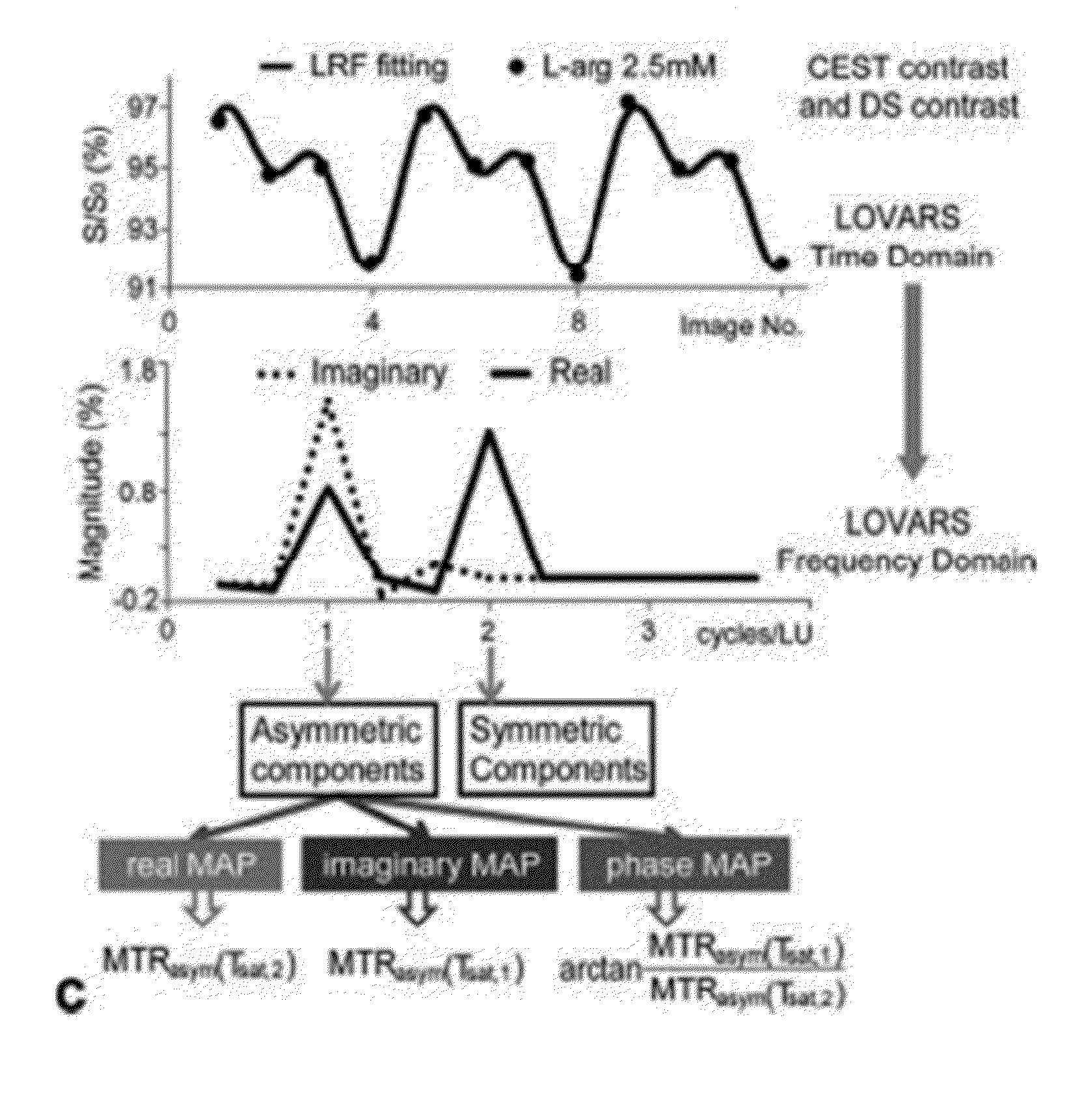
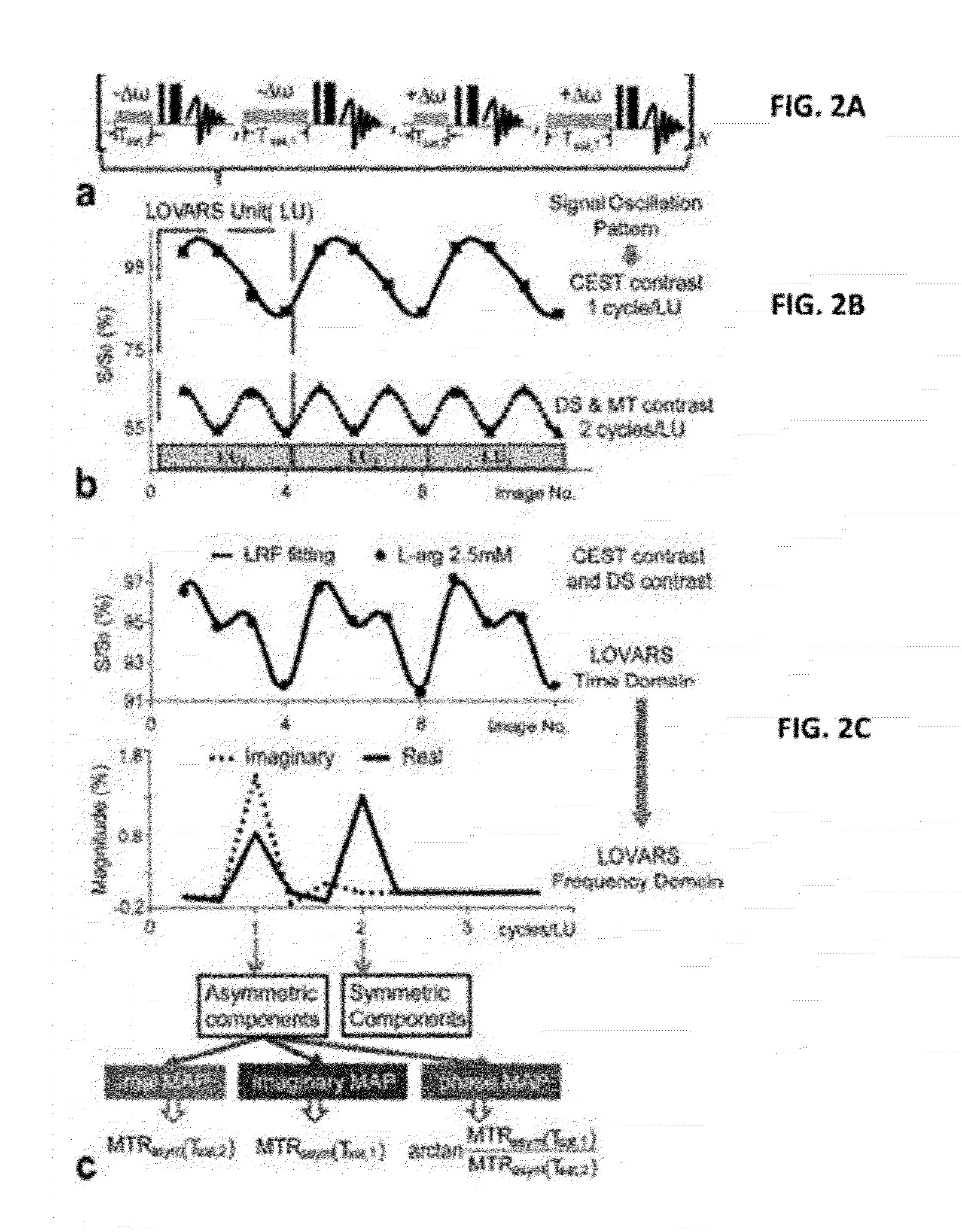
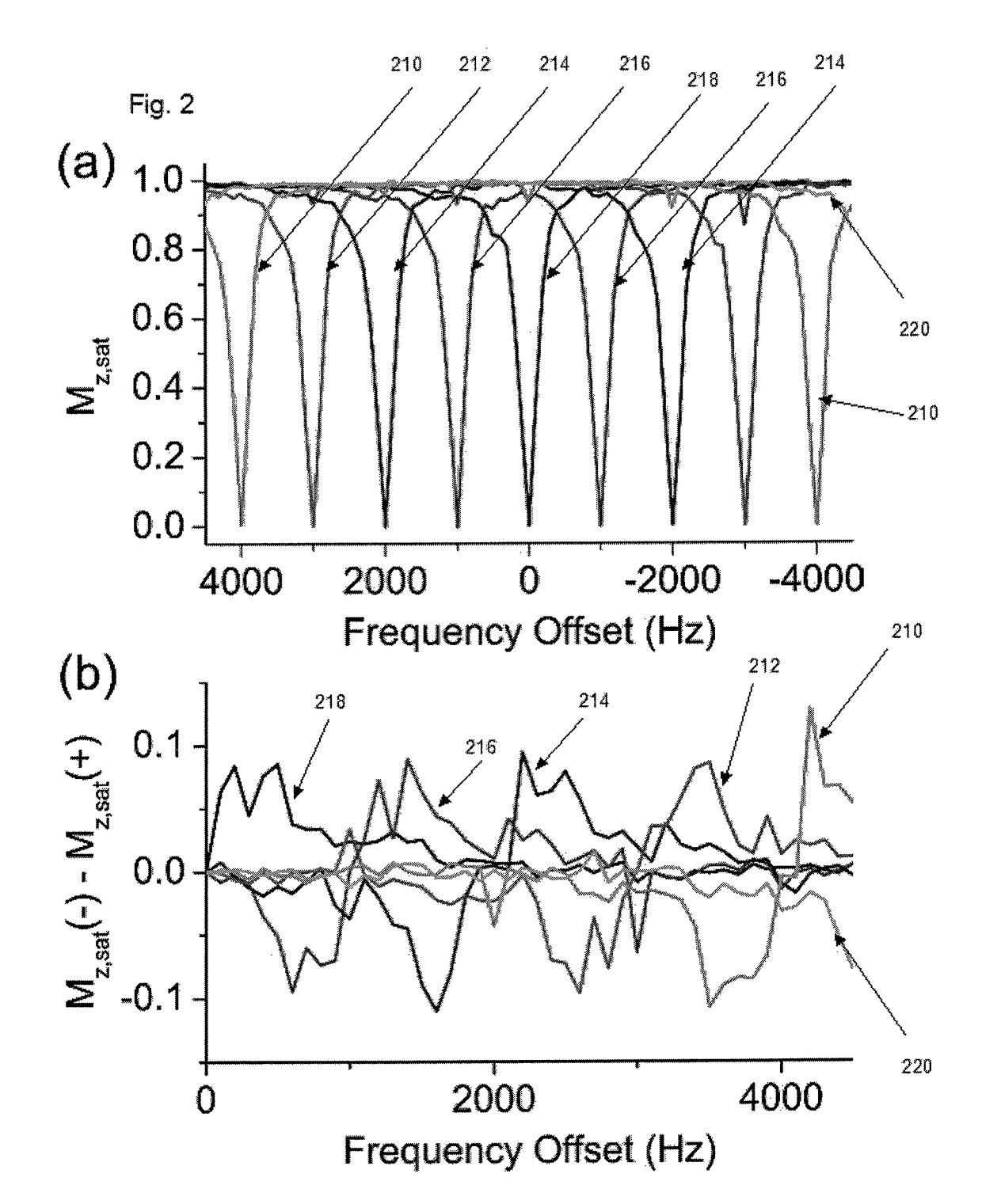
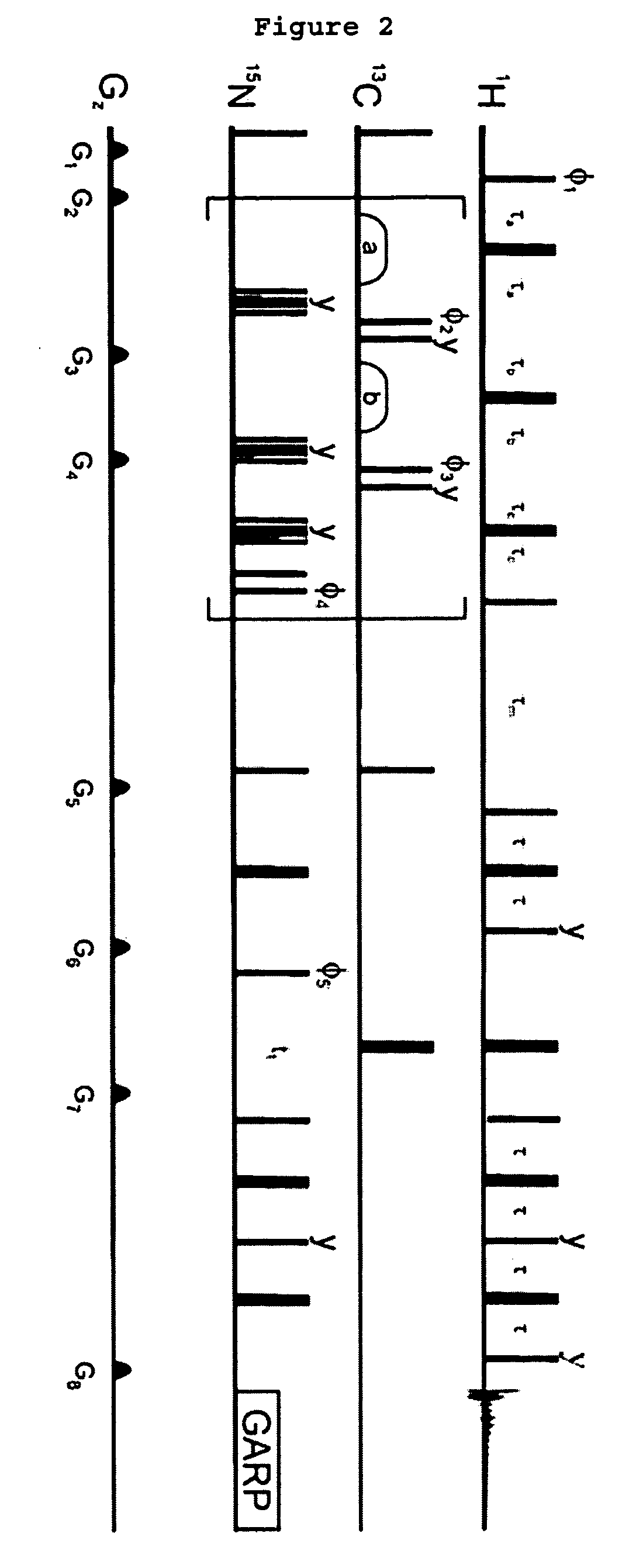
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for obtaining a magnetic resonance image (MRI) or spectrum. The method includes a step of performing a chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) or magnetization transfer (MT) magnetic labeling experiment of a subject using an MRI machine. When performing the CEST or MT magnetic labeling experiment aspects of a saturation pulse or a serial saturation pulse sequence, such as length (tsat), number (Nsat), offset (Δω), modulation frequency (ωs) and power (B1) can be varied in specific-designed schemes. Data is generated from the CEST magnetic labeling experiment and is transmitted to a data processing unit. The data is processed to generate a visual representation of the data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging system
ActiveCN105572613AHigh strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceData acquisition
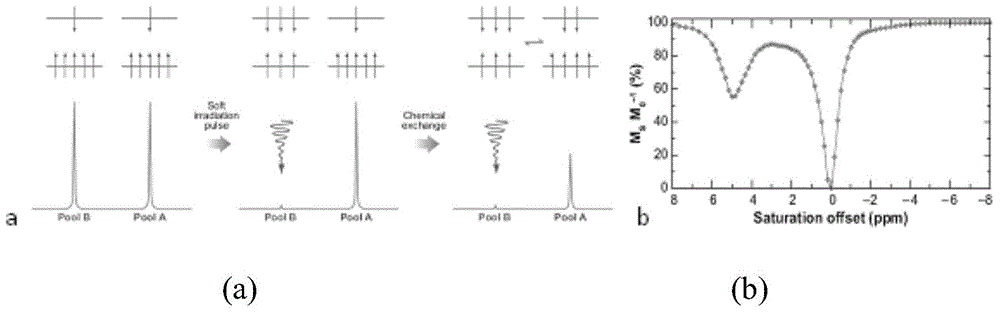
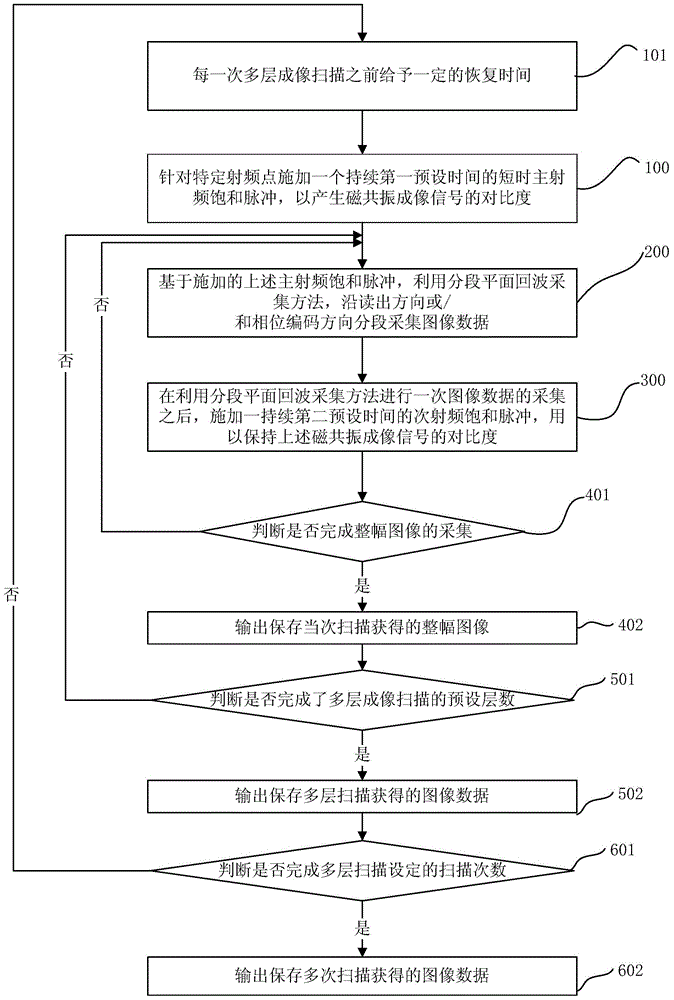
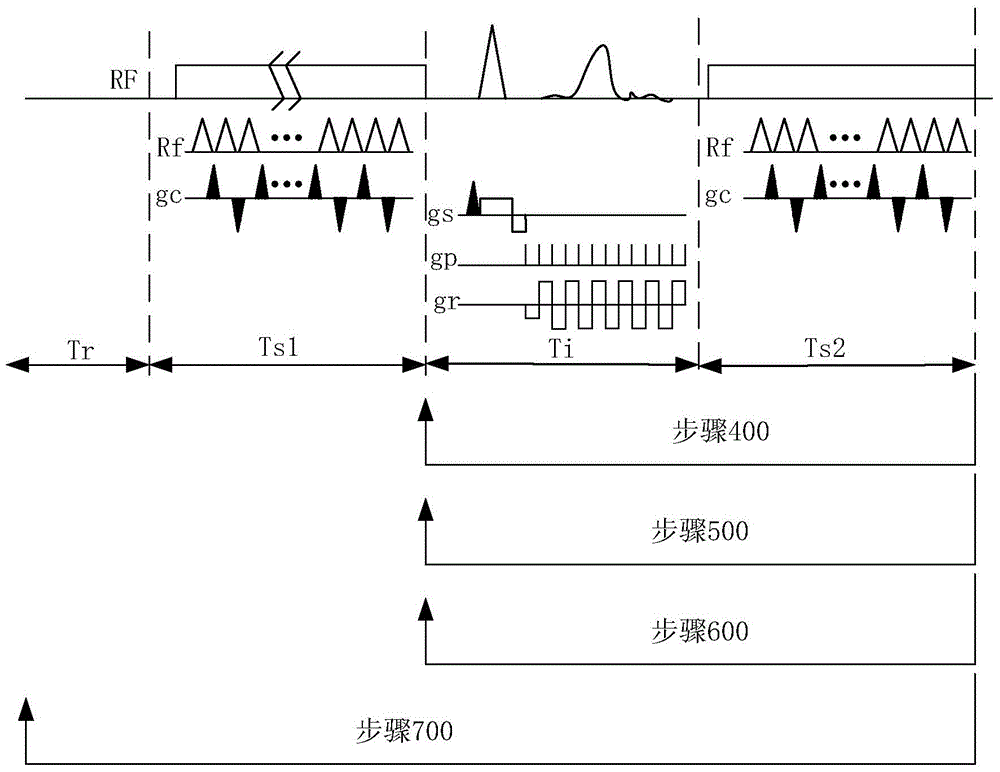
The invention provides a magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and a magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging system. The magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method comprises a main RF pulse generating step, applying a short-time main RF saturation pulse which lasts for a first preset time for aiming at a specific RF point, thereby generating the contrast of a magnetic resonance imaging signal; an image acquisition step, segmentally acquiring image data in a reading-out direction or / and a phase encoding direction based on the applied main RF saturation pulse by means of a segmental planar echo acquisition method; and a sub-RF pulse generating step, after one-time image data acquisition by means of the segmental planar echo acquisition method, applying a sub-RF saturation pulse which lasts for a second preset time, thereby keeping the contrast of the magnetic resonance imaging signal. The magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and the magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging system settle problems of low signal sensitivity and low imaging efficiency in existing magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
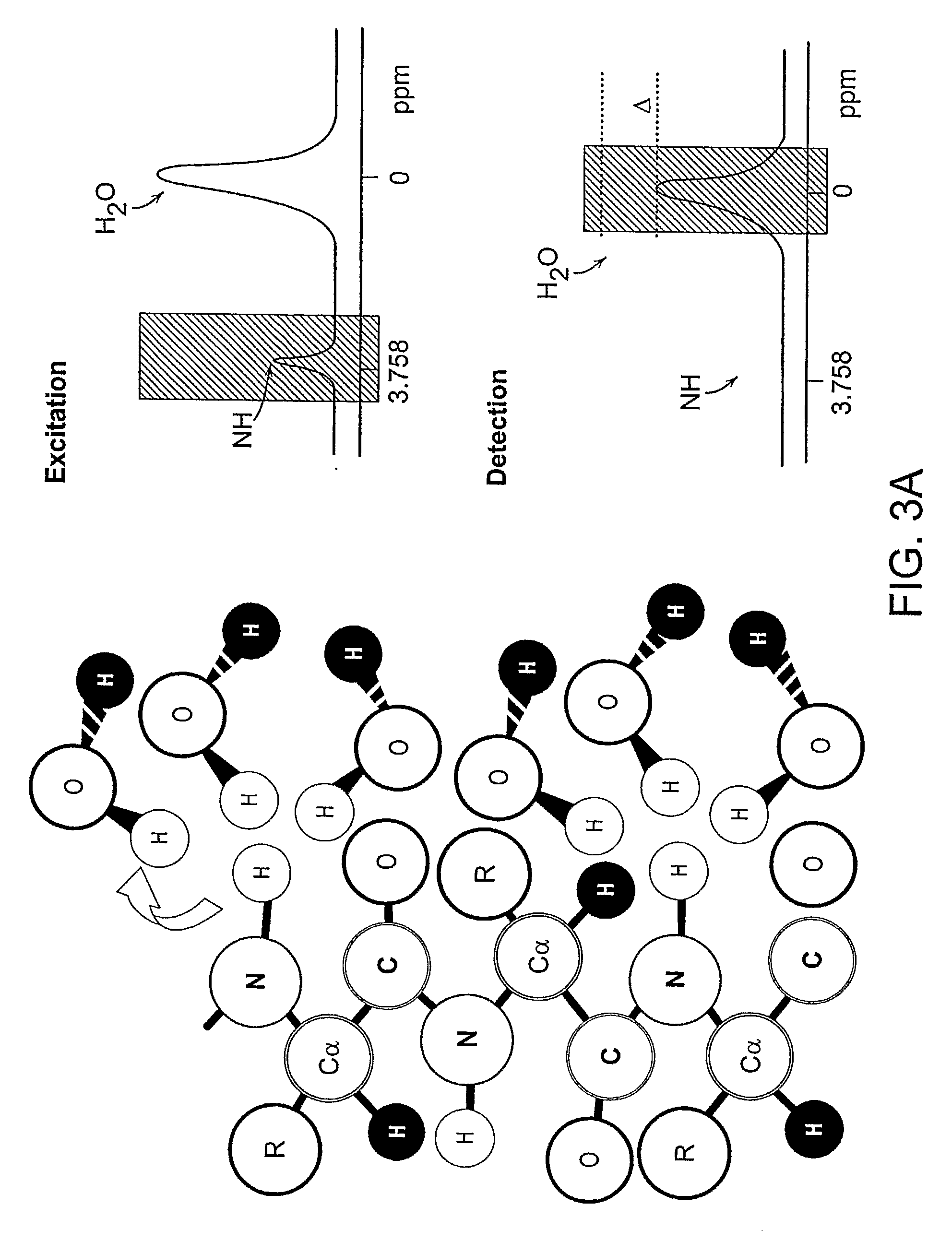
Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Based Mri Using Reporter Genes and Mri Methods Related Thereto
ActiveUS20080284427A1Advantageous biodistributionEliminate needSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMr contrastRadio frequency
Featured are a new class of reporter genes including reporter compositions as well as methods, MRI systems and MRI imaging kits related thereto. The genes according to the present invention provide MR contrast when the sample / subject is irradiated at a specific off-resonance radio-frequency (RF frequency), where the contrast mechanism utilizes chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) technique for imaging.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
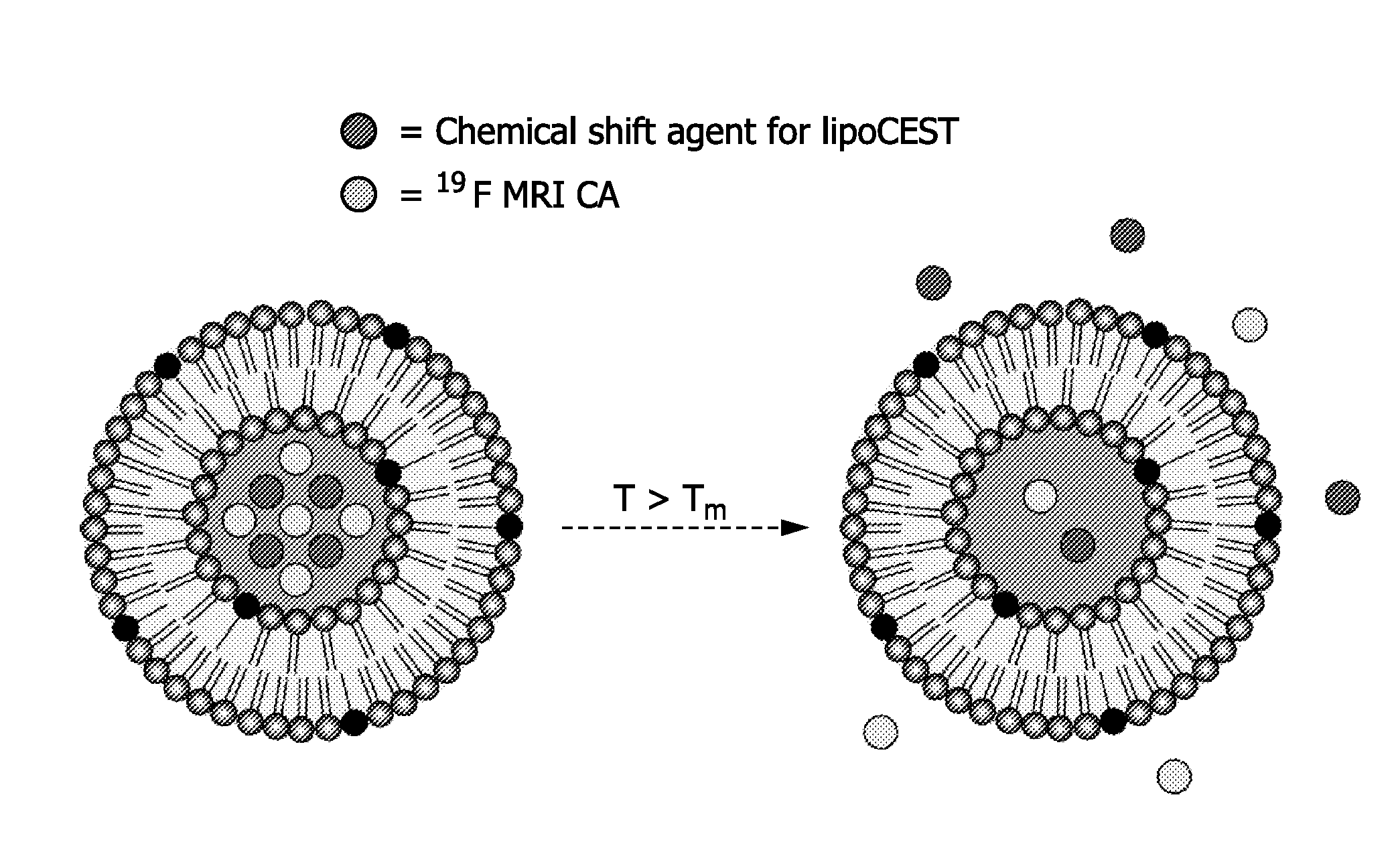
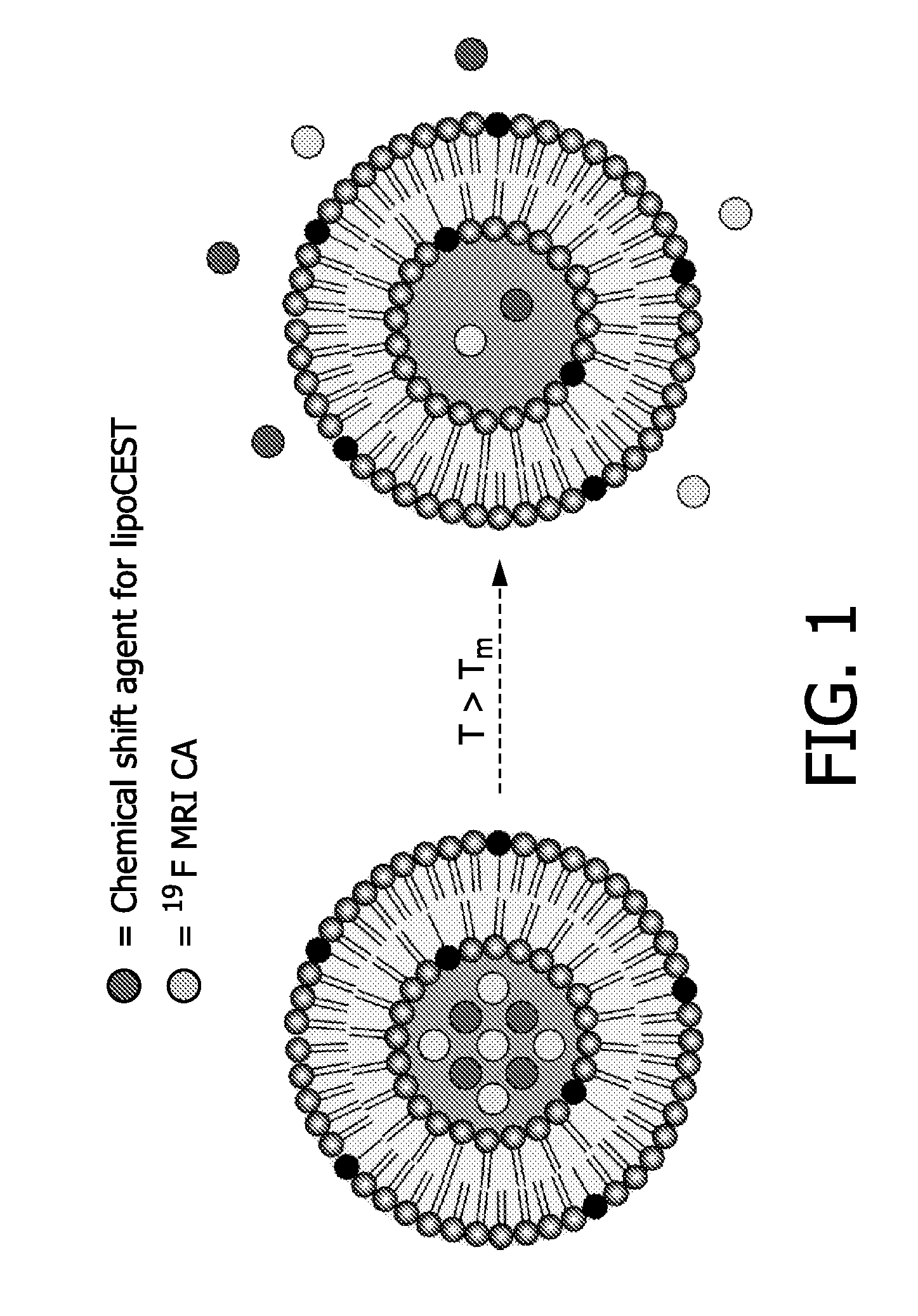
Drug carrier providing MRI contrast enhancement
Described are drug carriers useful in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided drug release comprising a shell capable of releasing an enclosed biologically active agent as a result of a local stimulus, e.g. energy input, such as heat, wherein the shell encloses a 19F MR contrast agent. Preferably, the carrier also acts as a contrast enhancement agent for MRI based on the principle of Chemical Exchange-dependent Saturation Transfer (CEST). To this end the shell encloses a cavity that comprises a paramagnetic chemical shift reagent, a pool of proton analytes, and the 19F contrast agent, and wherein the shell allows diffusion of the proton analytes.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
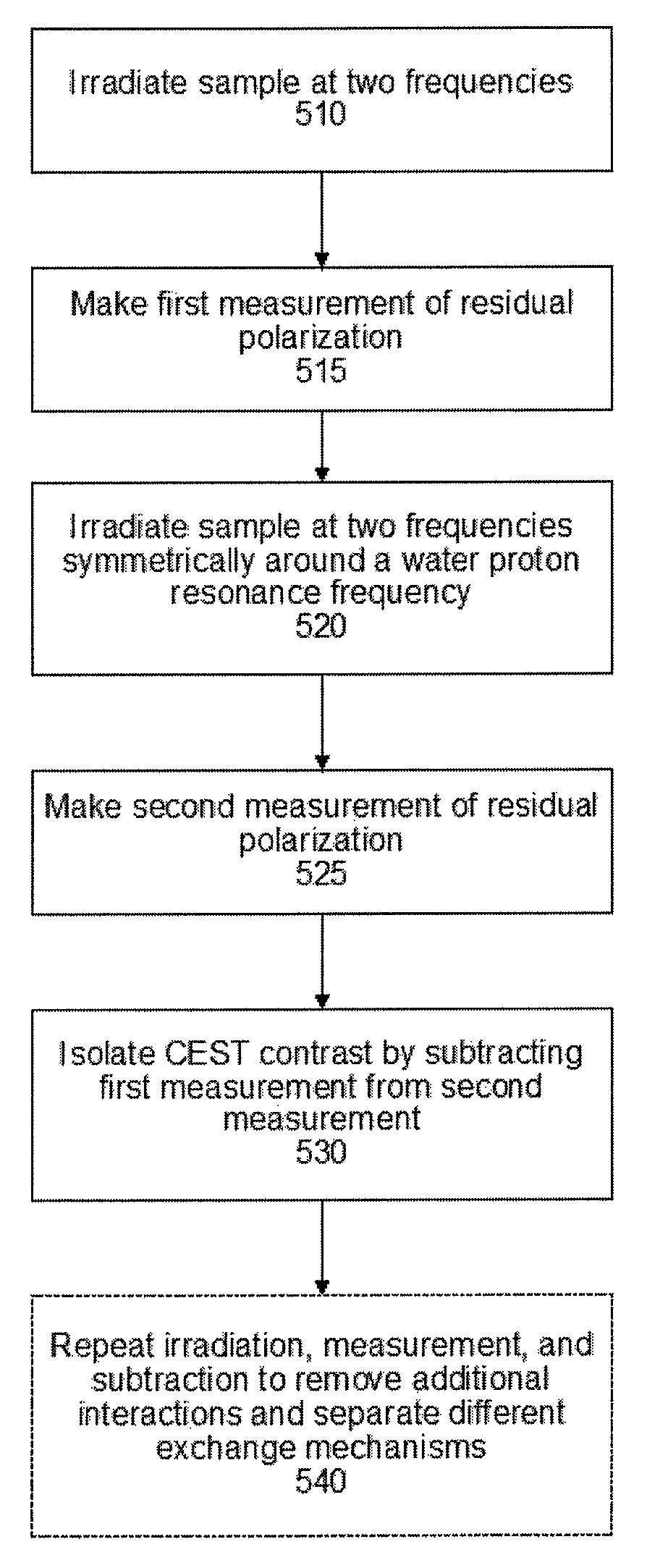
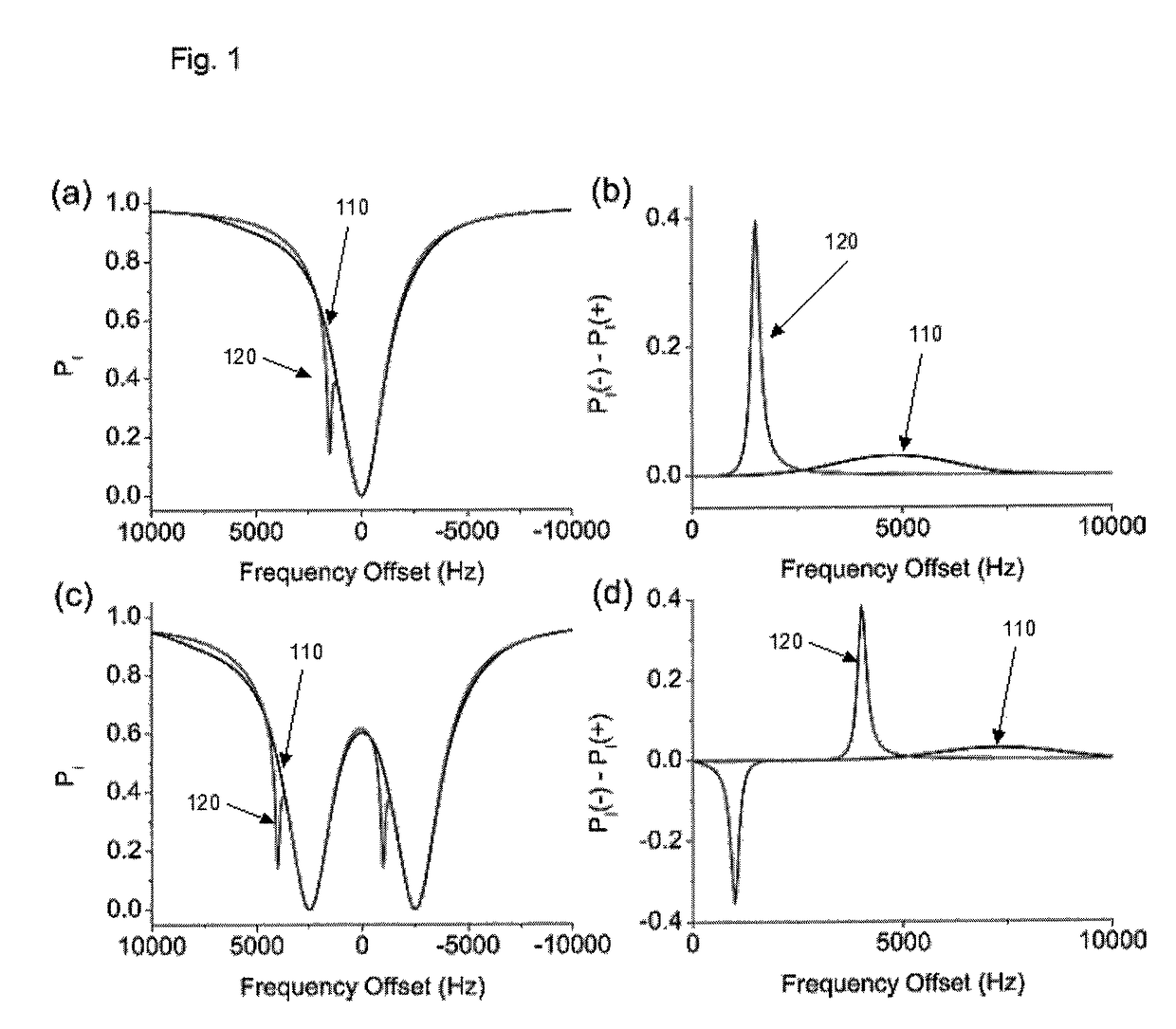
Apparatus, system, method and computer-readable medium for isolating chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast from magnetization transfer asymmetry under two-frequency RF irradiation
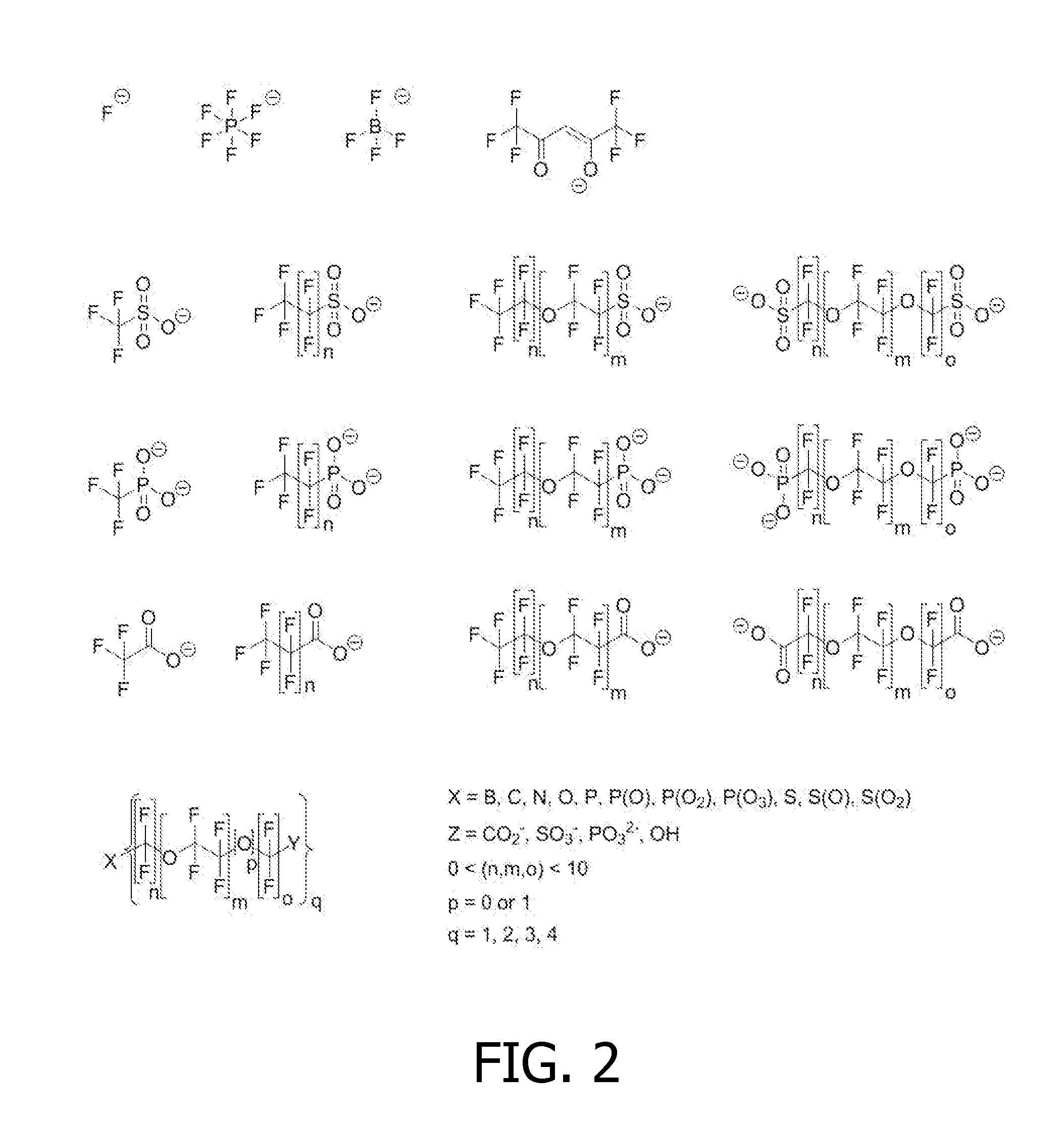
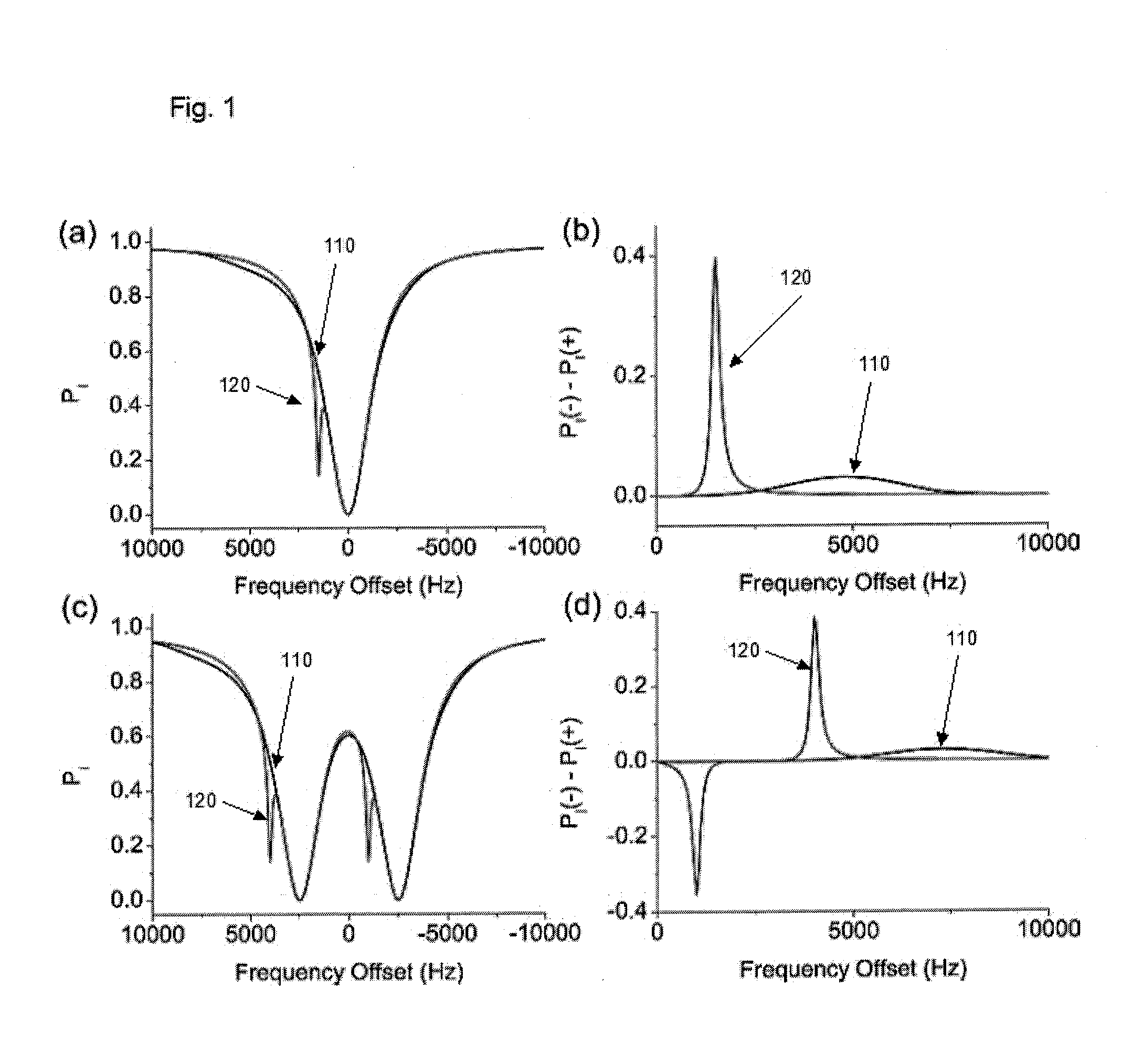
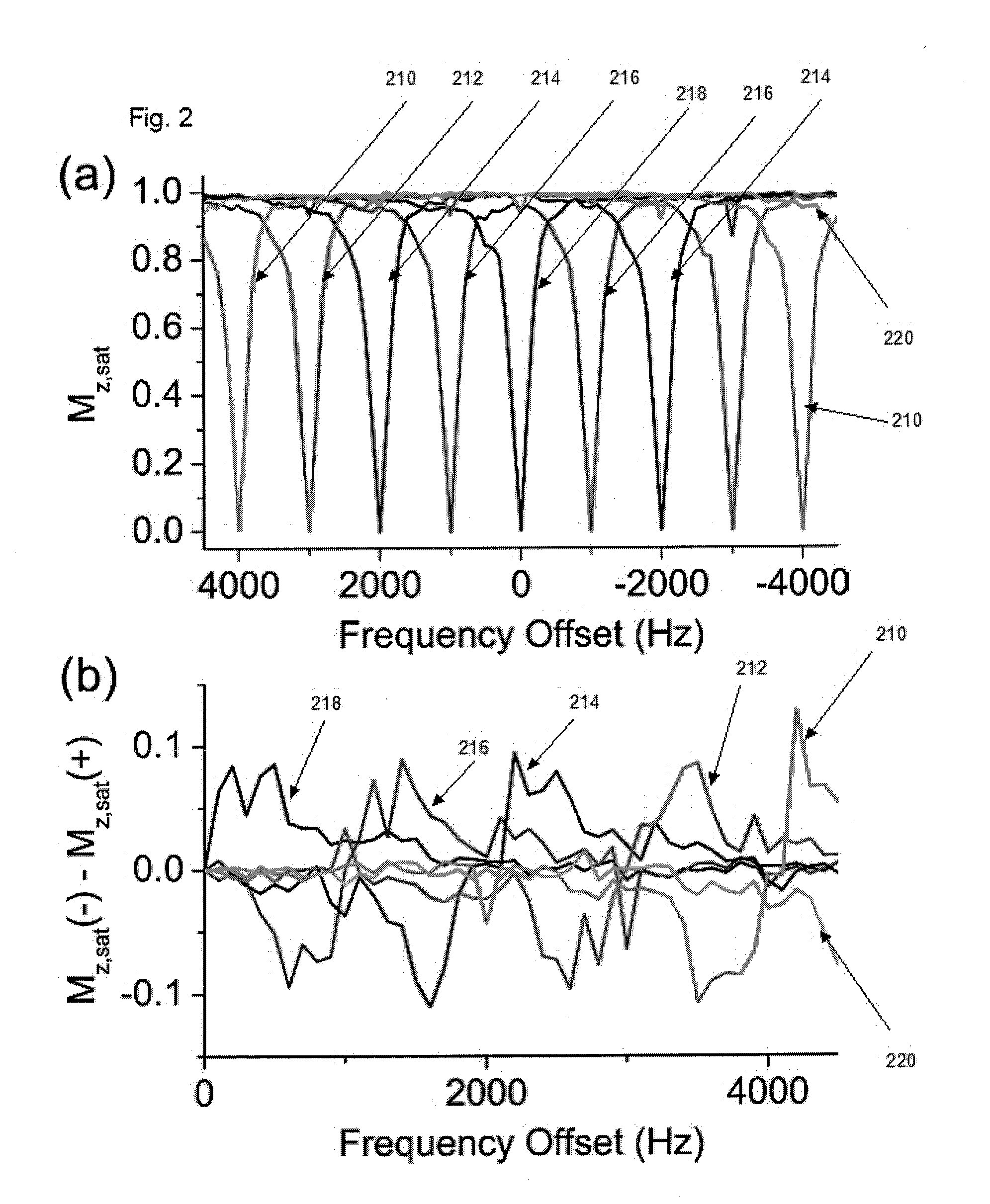
ActiveUS20130166226A1Eliminate contributionMagnetic measurementsChemical machine learningDual frequencyFrequency spectrum
Apparatus, system, method and computer-readable medium for isolating chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast from magnetization transfer asymmetry under two-frequency RF irradiation. A two-pool model for magnetization transfer (MT) can be established fully based on Provotorov's theory of saturation, and then extended to the situation of simultaneous two-frequency RF irradiation. Numerical simulations and experimental results demonstrate that two-frequency RF irradiation can make MT effects independent of irradiation frequency over a wide range, and thus can suppress MT asymmetry. Exemplary embodiments can be provided to isolate chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrast from MT asymmetry contrast by using the two-frequency RF irradiation technique. A further embodiment can isolate a narrow-frequency spectrum MT mechanism from a broad-frequency spectrum MT mechanism.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging with gating synchronized acquisition
Methods and systems for producing a magnetic resonance (MR) image of a subject include acquiring a first physiological monitoring signal related to a first physiological process of the subject and acquiring a second physiological monitoring signal related to a second physiological process of the subject. The method also includes analyzing the first physiological monitoring signal and the second physiological monitoring signal to identify at least a first trigger point and a second trigger point and, upon identifying the first trigger point, applying a radiofrequency (RF) saturation module at a selected frequency to saturate a selected spin species in the subject. Upon identifying the second trigger point, the method includes performing a chemical exchange striation transfer (CEST) readout to acquire CEST data and then reconstructing the CEST data to produce a CEST image of the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Magnetic resonance image processing method and device
ActiveCN107133957AShort processReduce complexityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingResonance
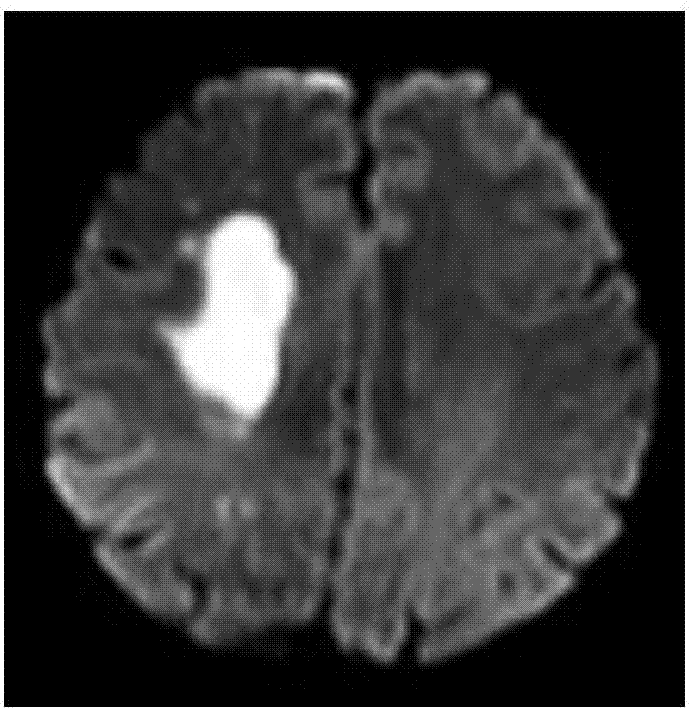
The embodiment of the invention discloses a magnetic resonance image processing method and device. The method comprises the steps that diffusion weighted imaging scanning and pulse parameter modulation imaging scanning based on chemical exchange saturation transfer are performed on the area of interest of the brain, and a diffusion weighted image and a chemical exchange saturation transfer image are acquired; when the chemical exchange saturation transfer image presents low signal shadow in comparison with the preset benchmark template, arterial spin mark imaging scanning is performed on the area of interest of the brain so as to acquire an arterial spin mark image; the diffusion weighted image is compared with the arterial spin mark image so as to determine a first mismatch area; the diffusion weighted image is compared with the chemical exchange saturation transfer image so as to determine a second mismatch area; and the second mismatch area is removed out of the first mismatch area, and the residual area of the first mismatch area is determined as an ischemic penumbra area. The accuracy of the ischemic penumbra can be enhanced, the image processing flow can be saved, the complexity can be reduced and the safety can be enhanced.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS LTD +2
Method for using CEST contrast agents in MRI
InactiveCN101166987AEliminate dependenciesElimination of concentration dependenceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic variable regulationMedicineProton
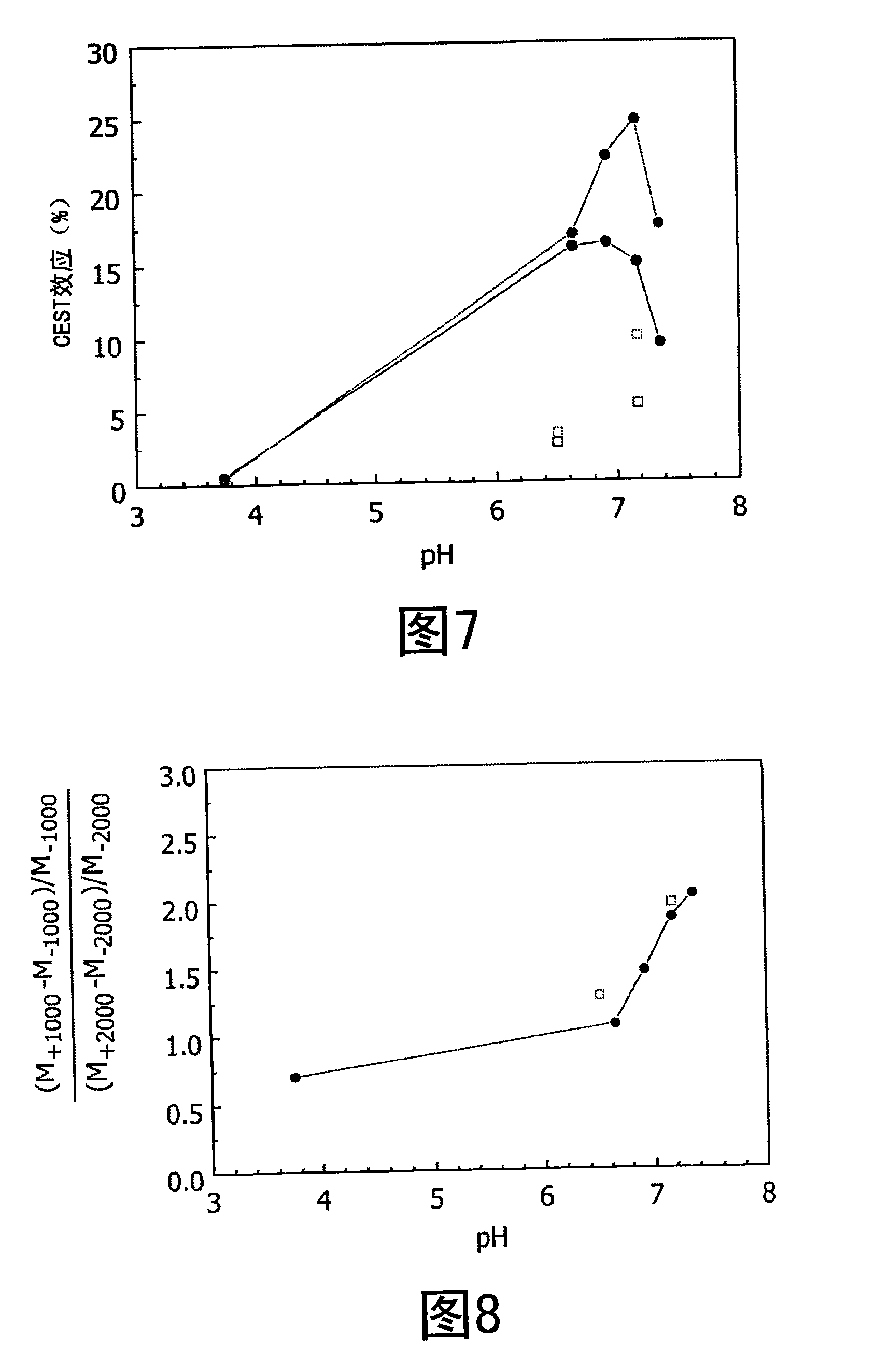
The invention relates to a method for mapping of a physico-chemical parameter such as pH value, temperature, PO2 or metabolite concentration, using a chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agent in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. This method may be used with agents having only one exchangeable entity pool, e.g. proton pool, by applying two different RF frequencies for pre-saturation of the contrast agent.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Targeted mr imaging agents
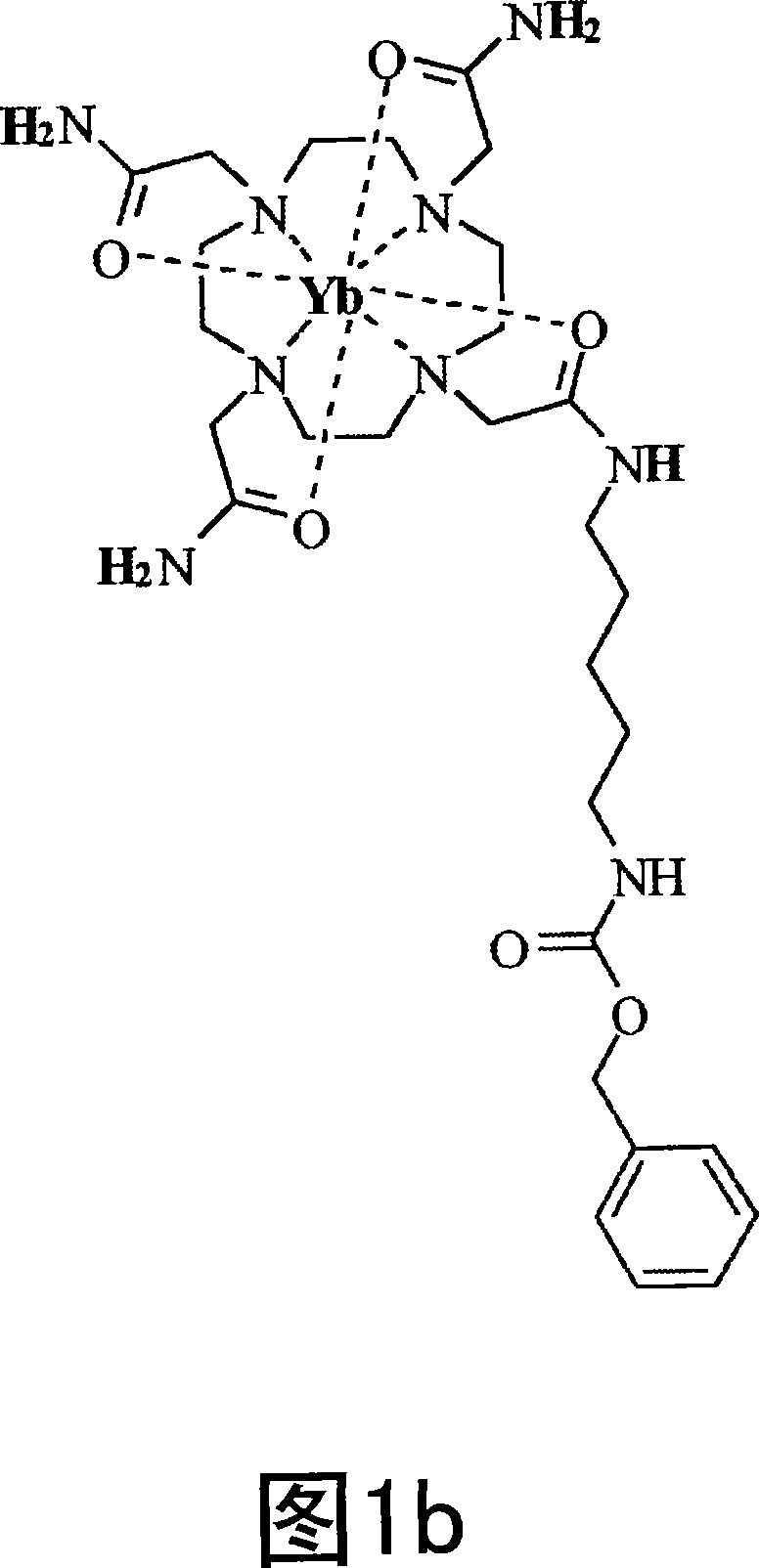
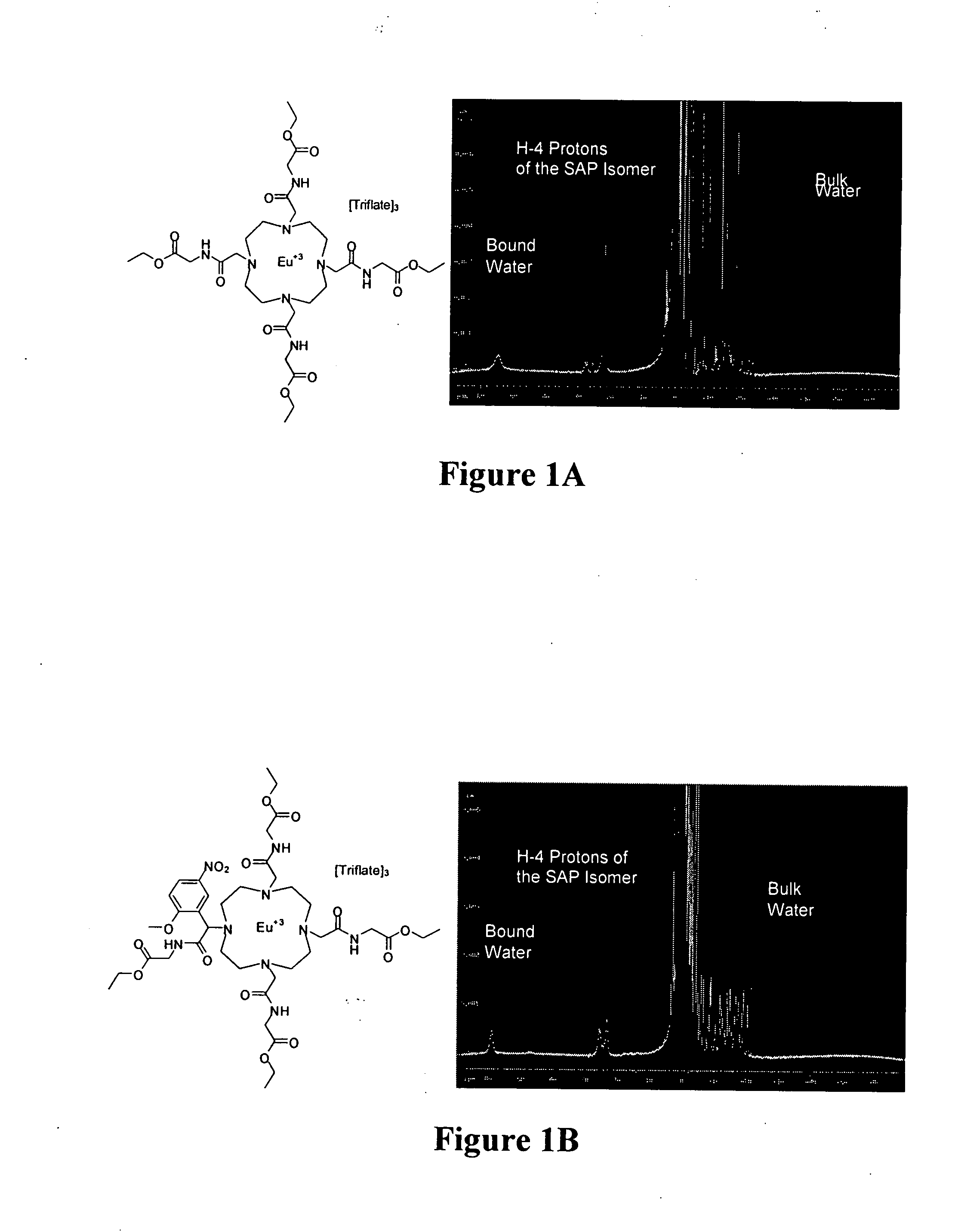
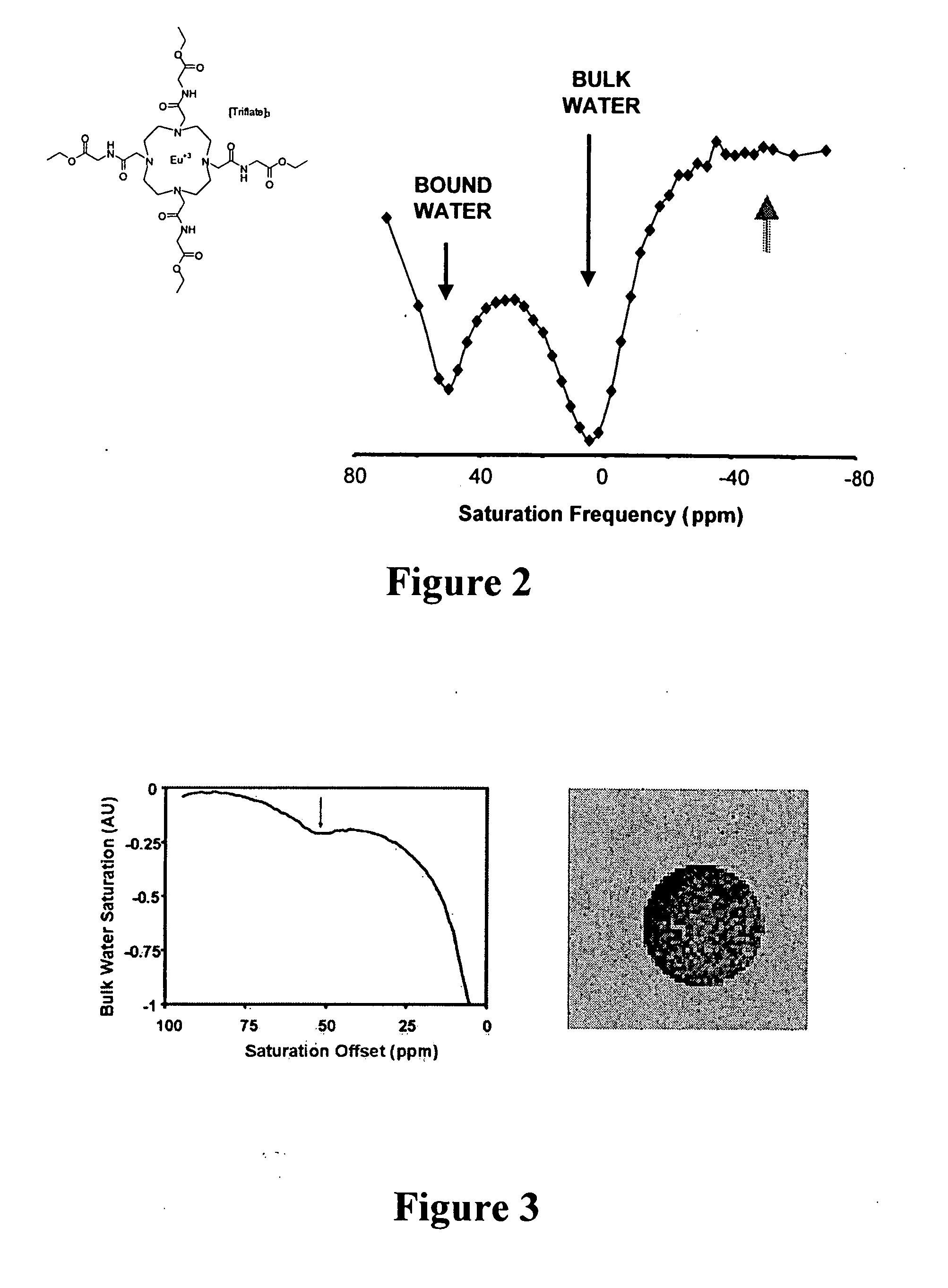
InactiveUS20070237721A1Weakening rangeEfficient switchingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDispersion deliveryParticulatesMRI contrast agent
MRI contrast agents that employ paramagnetic agents and chemical exchange saturation transfer (paraCEST) and which are coupled to targeted particulate delivery vehicles provide sufficient concentration of the paraCEST contrast agents to obtain useful images of target tissues or organs. In addition, the image contrast may be switched on or off with a presaturation radio frequency pulse, avoiding the necessity obtaining pre-injection and post-injection images.
Owner:BARNES JEWISH HOSPITAL
Ph-weighted MRI using fast amine chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging
ActiveUS20180164393A1Easy to optimizeReduce scan timeDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMetaboliteNon invasive
A pH-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method and system are provided that works by indirectly measuring the NMR signal from amine protons found on the backbones of amino acids and other metabolites, which resonate at a frequency of +2.8-3.2 ppm with respect to bulk water protons. The technique uses a modified magnetization transfer radiofrequency saturation pulse for the generation of image contrast. A train of three 100 ms Gaussian pulses at high amplitude (6 uT) or Sinc3 pulses are played at a particular frequency off-resonance from bulk water prior to a fast echo planar imaging (EPI) readout, with one full image acquired at each offset frequency. This non-invasive pH-weighted MRI technique does not require exogenous contrast agents and can be used in preclinical investigations and clinical monitoring in patients with malignant glioma, stroke, and other ailments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
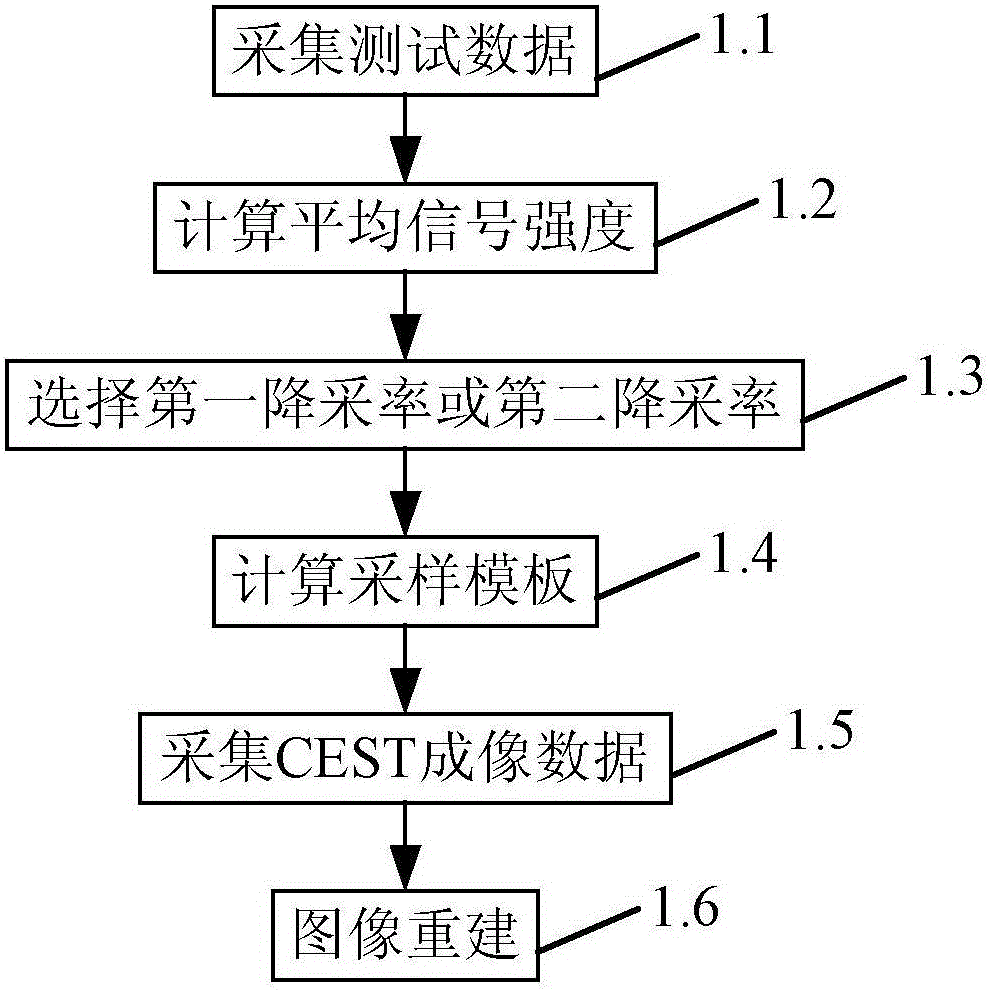
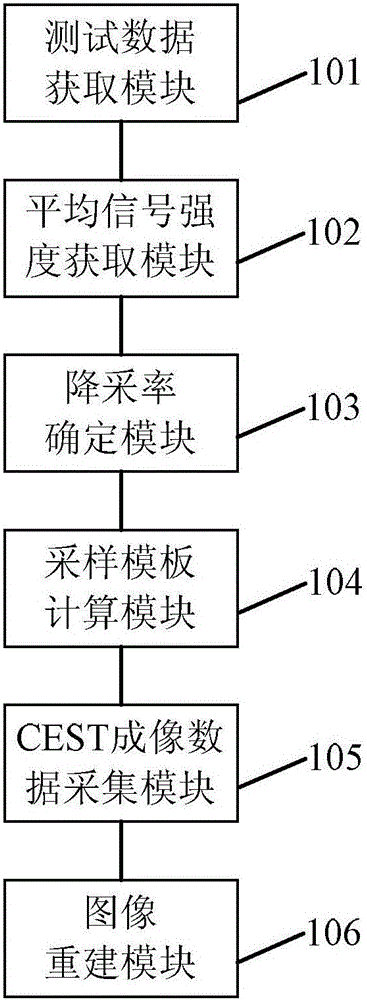
Rapid chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and system
ActiveCN105759233ASolve the problem that it is difficult to achieve good reconstruction resultsFast imagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a rapid chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and system, and the method determines that a current image employs a first downsampling rate or a second downsampling rate through judging the relation between the mean signal intensity of the image and a preset signal intensity threshold value; The method solves a problem that a low signal to noise ratio image is difficult to achieve a better reconstruction result because all CEST images employ the same downsampling rate, achieves the adaptivity of a CEST imaging undersampling mode, improves the CEST imaging speed, and guarantees the reconstruction quality of an CEST image.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
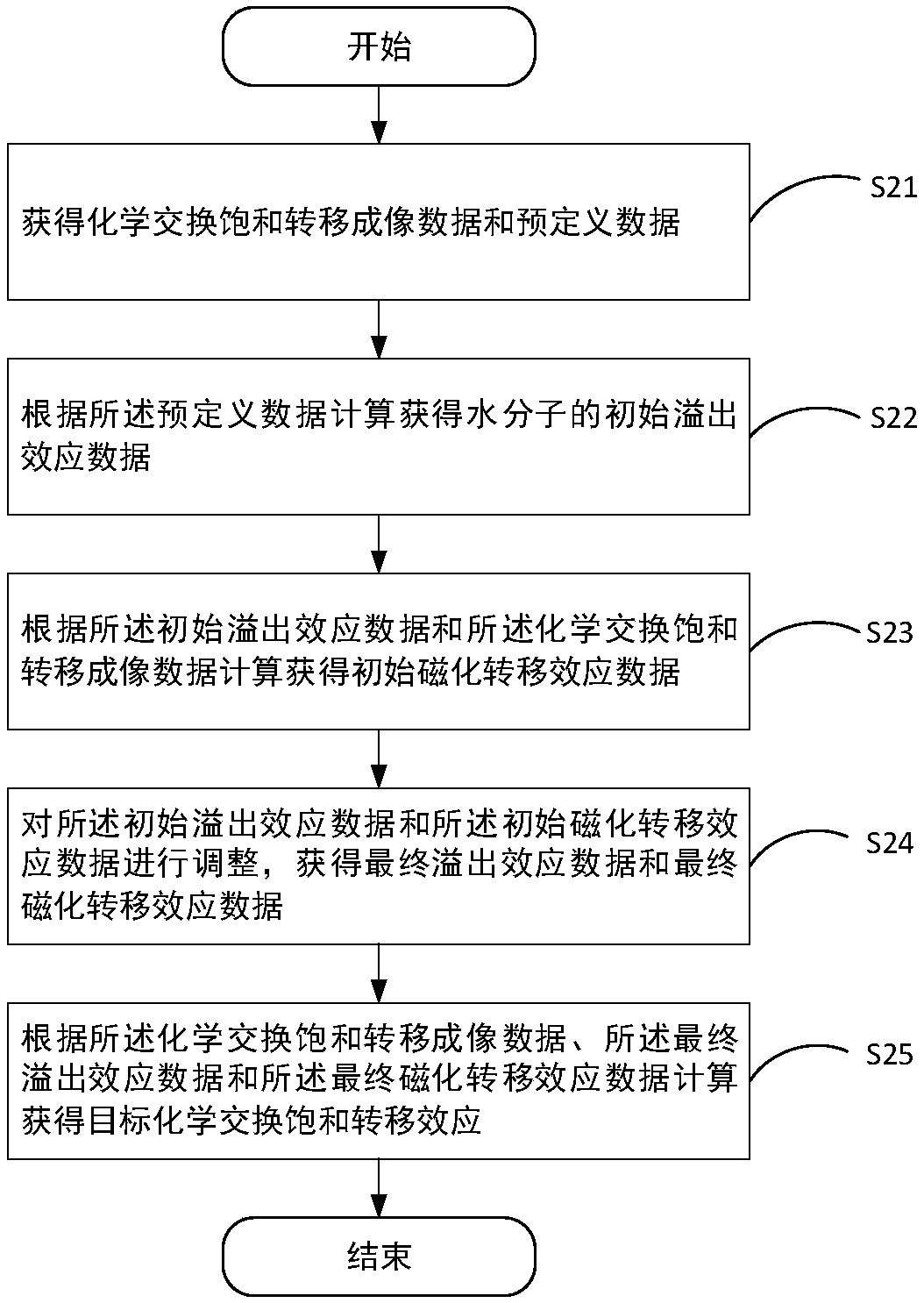
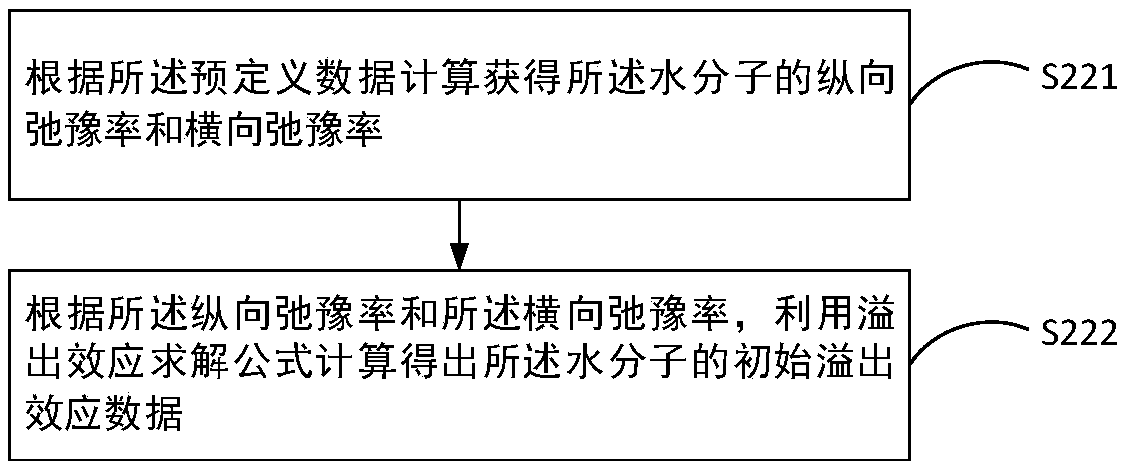
Chemical exchange saturation transfer effect quantification method and device, and electronic device
ActiveCN108051765AAccurate analysisAccurate calculation of initial spillover dataMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsQuantification methodsMagnetization transfer
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Hyperpolarization <129>Xe switch type magnetic resonance molecular probe for identifying diamine oxidase
InactiveCN109082457AImprove targetingNot immune to fluorescence quenching effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisResonanceMolecular probe
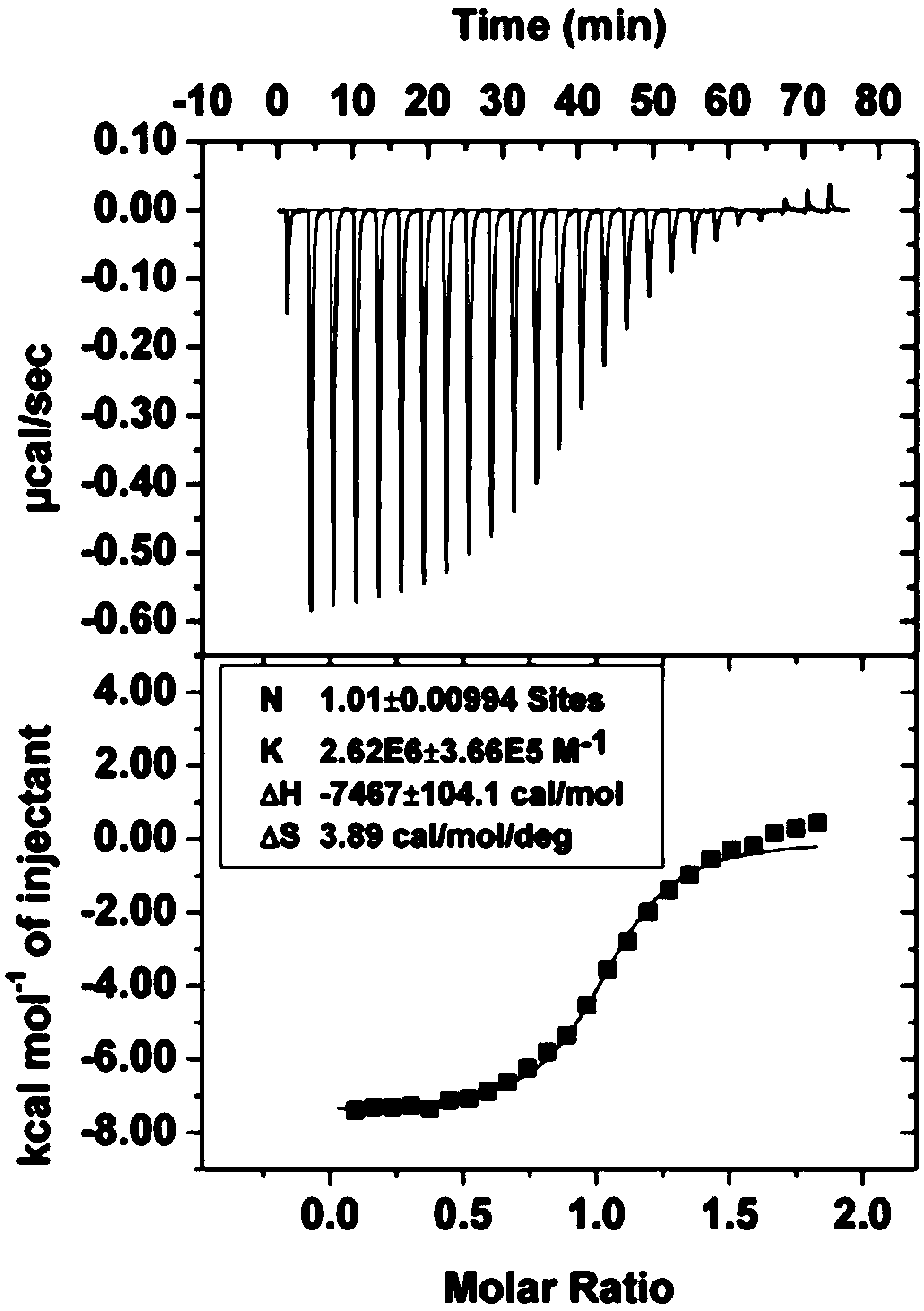
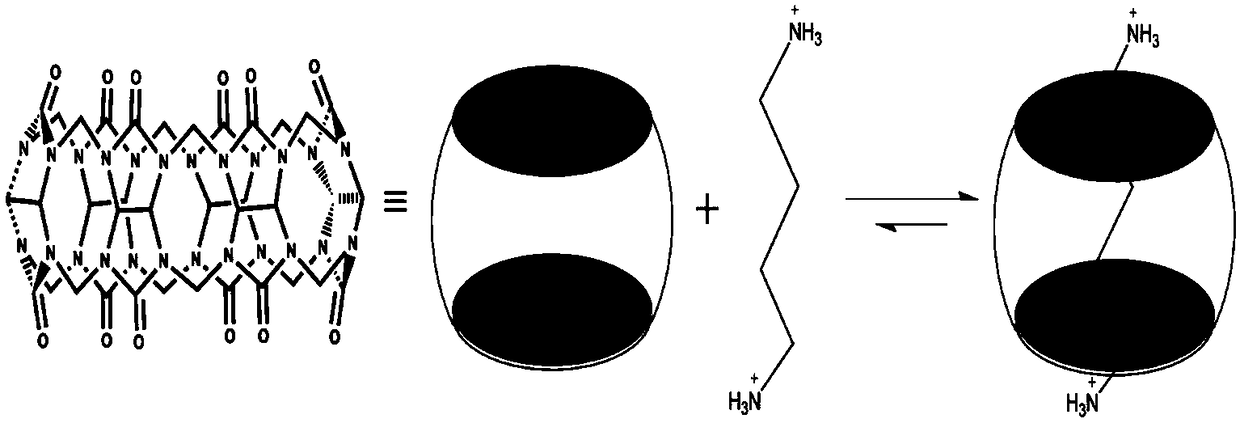
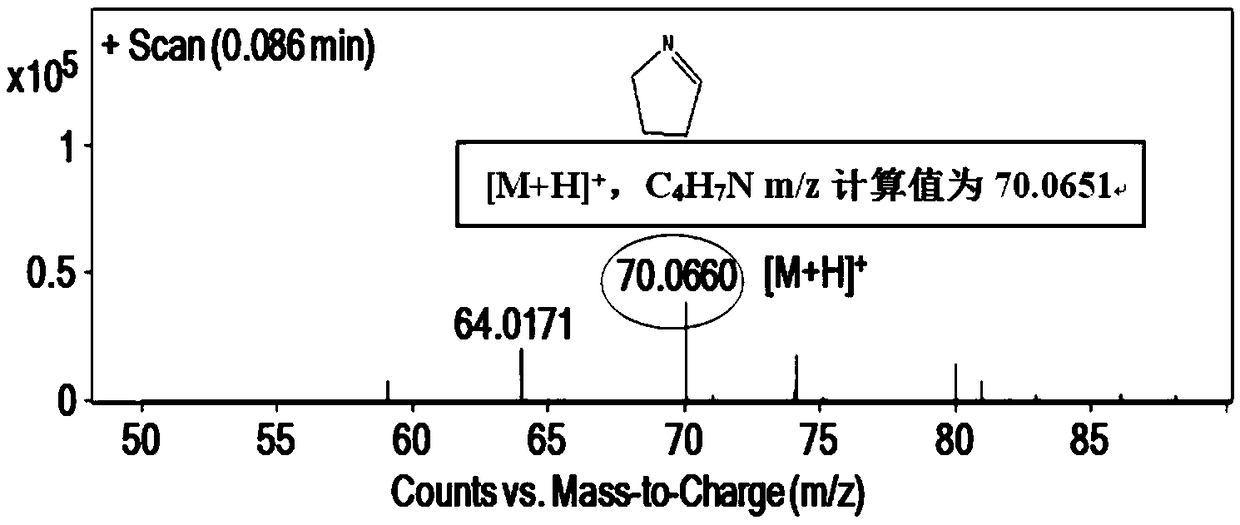
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical analysis and particularly relates to a hyperpolarization <129>Xe switch type magnetic resonance molecular probe for identifying diamine oxidase. The hyperpolarization <129>Xe switch type magnetic resonance molecular probe comprises cucurbit[6]uril and putrescine hydrochloride. The principle of the molecular probe is characterized in thata substrate (putrescine hydrochloride) with high cucurbit[6]uril binding force is converted by diamine oxidase into a product (1-pyrroline) which does not combine with cucurbit[6]uril; before enzymatic reaction, a <129>Xe hyperpolarization chemical exchange saturation transfer signal in the cucurbit[6]uril is inhibited by strong cucurbit[6]uril conjugate until the enzymatic reaction oxidizes the substrate into the product; due to the fact that the binding constant of putrescine hydrochloride@cucurbit[6]uril is several magnitude orders larger than that of <129>Xe@cucurbit[6]uril and (1-pyrroline)@cucurbit[6]uril cannot combine, the <129>Xe hyperpolarization chemical exchange saturation transfer signal in the cucurbit[6]uril appears after the enzymatic reaction through enhanced <129>Xe cucurbit[6]uril interaction, and diamine oxidase identification is achieved through the <129>Xe hyperpolarization chemical exchange saturation transfer signal in the cucurbit[6]uril.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Simultaneous ph and oxygen weighted MRI contrast using multi-echo chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging (me-cest)
ActiveUS20200158803A1Fast and and high resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRadio frequencyMR - Magnetic resonance
A method is provided that includes applying at least one radiofrequency saturation pulse at a frequency or a range of frequencies to substantially saturate magnetization corresponding to an exchangeable proton in the ROI to generate magnetic resonance (MR) data. The MR data is then acquired using an echo-planar imaging readout, which is configured to sample a series of gradient echo pulse trains at a series of gradient echo times and a series of spin echo pulse trains at a series of spin echo times. One or more relaxometry measurement is then computed using the MR data sampled at the gradient echo times and the spin echo times. An oxygen-weighted image is then generated using the one or more relaxometry measurement, and a pH-weighted image is generated using MR data sampled at one or more of the spin echo times or gradient echo times.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Non-invasive sensing of free metal ions using ion chemical exchange saturation transfer
The invention features a novel non-invasive approach for imaging, detecting and / or sensing metal ions with improved sensitivity and specificity in a biological sample or tissue. In certain embodiments, the invention provides a MR contrast-based approach for imaging, detecting and / or sensing metal ions in the biological sample / tissue containing various background ions by using 19F-based chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) technique.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
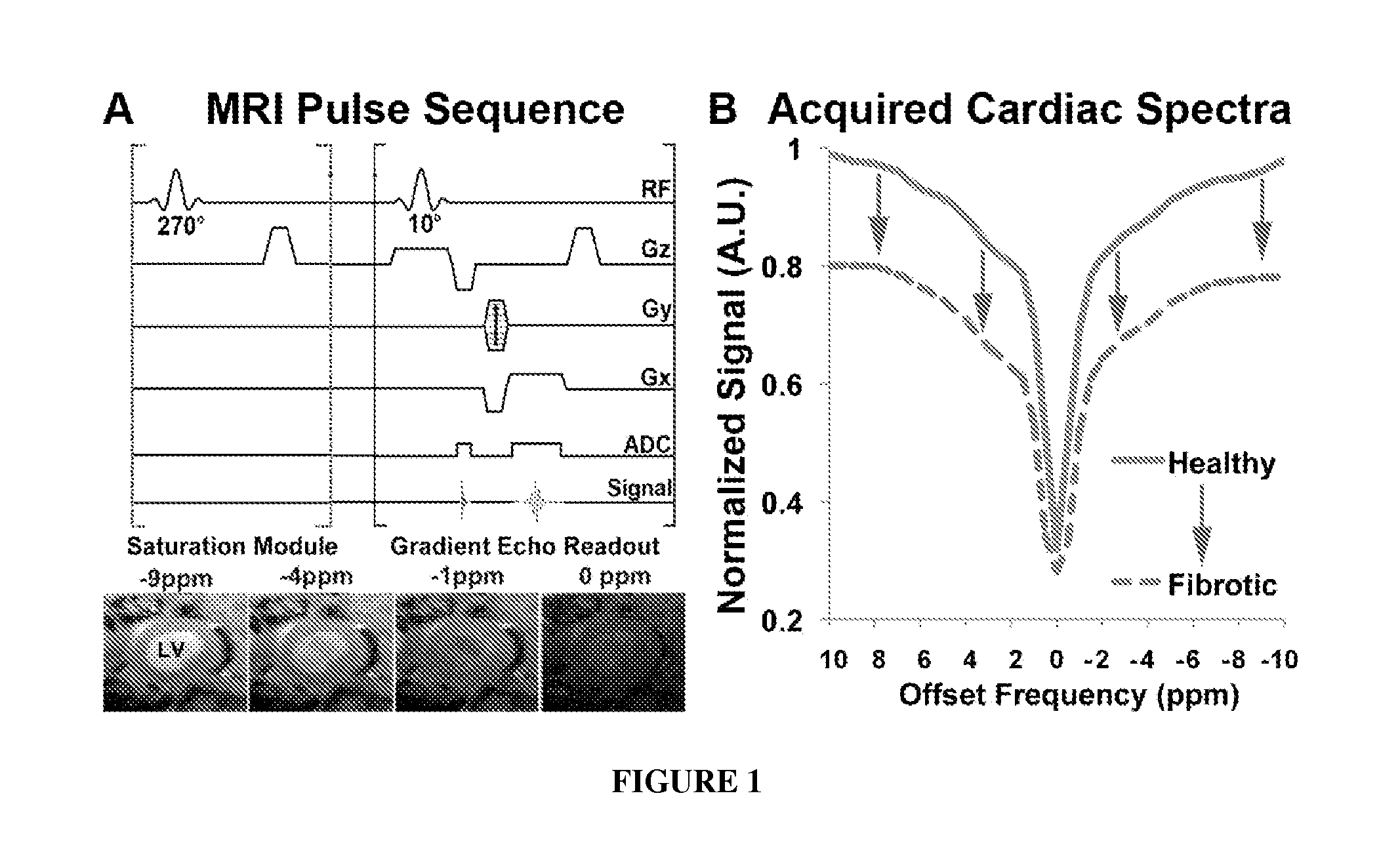
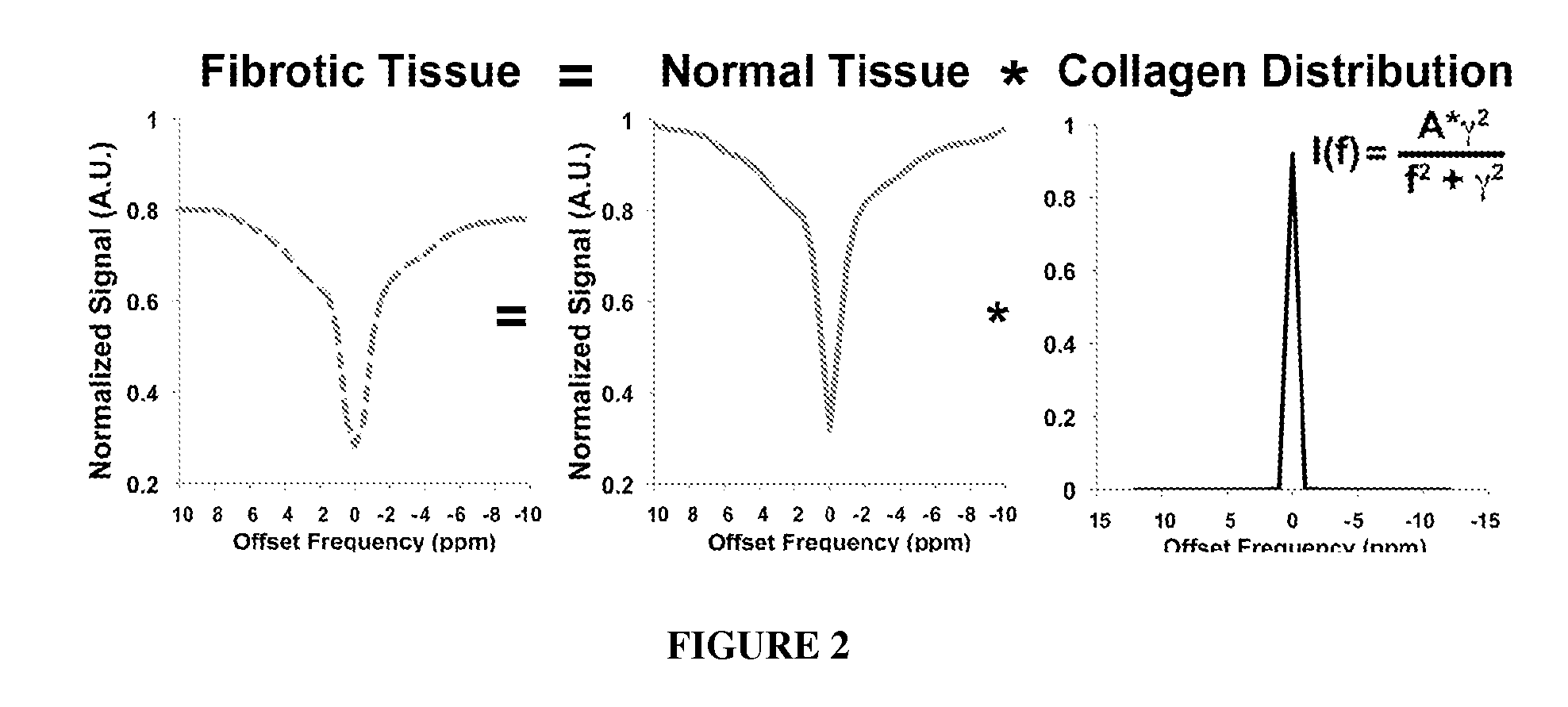
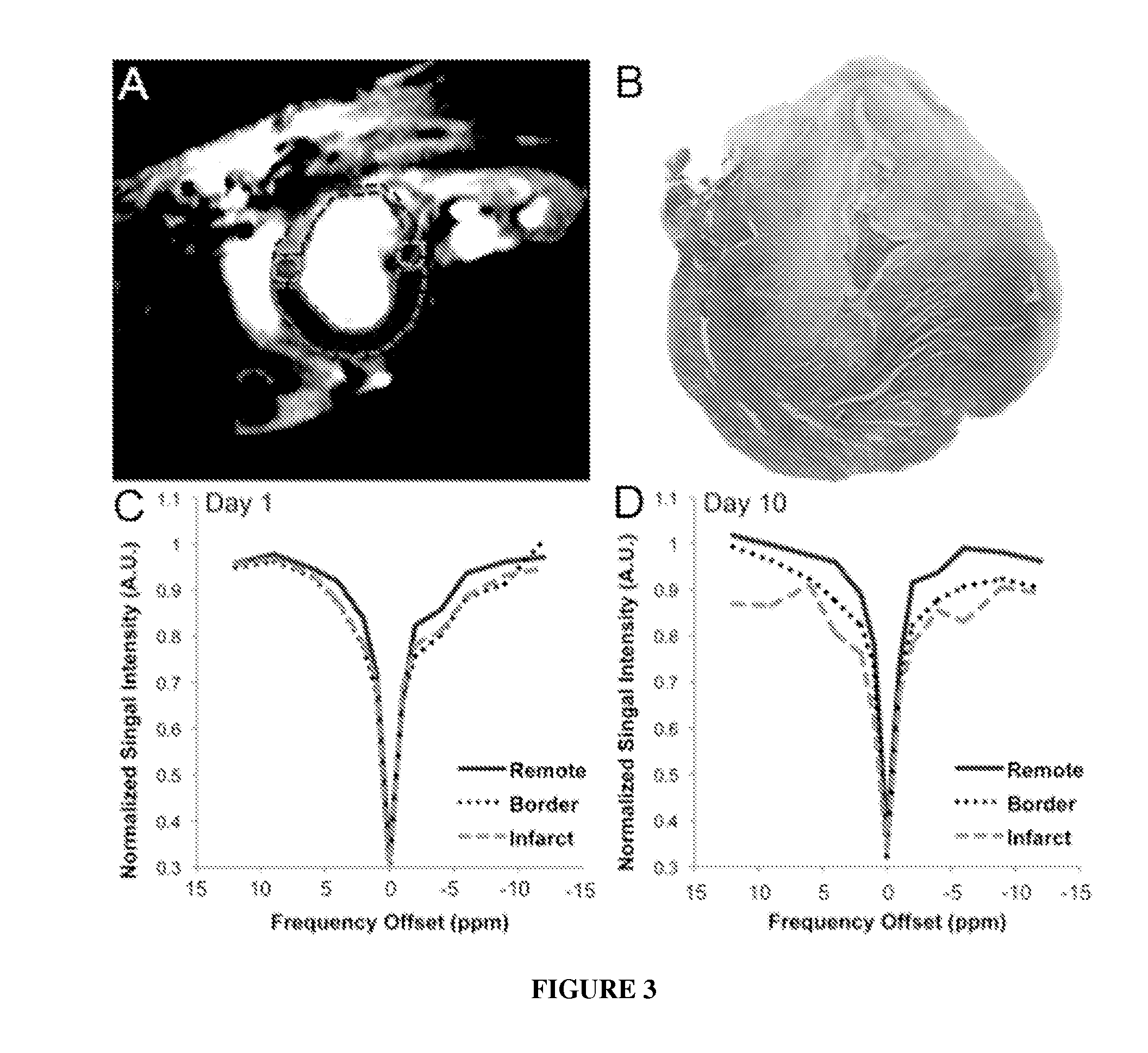
Magnetic resonance imaging for detecting cardiac diseases
The invention provides magnetic resonance imaging methods for detecting cardiac diseases including myocardial fibrosis. Specifically, the invention provides a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) pulse sequence that could be used to perform magnetization transfer (MT) or chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) in the heart.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
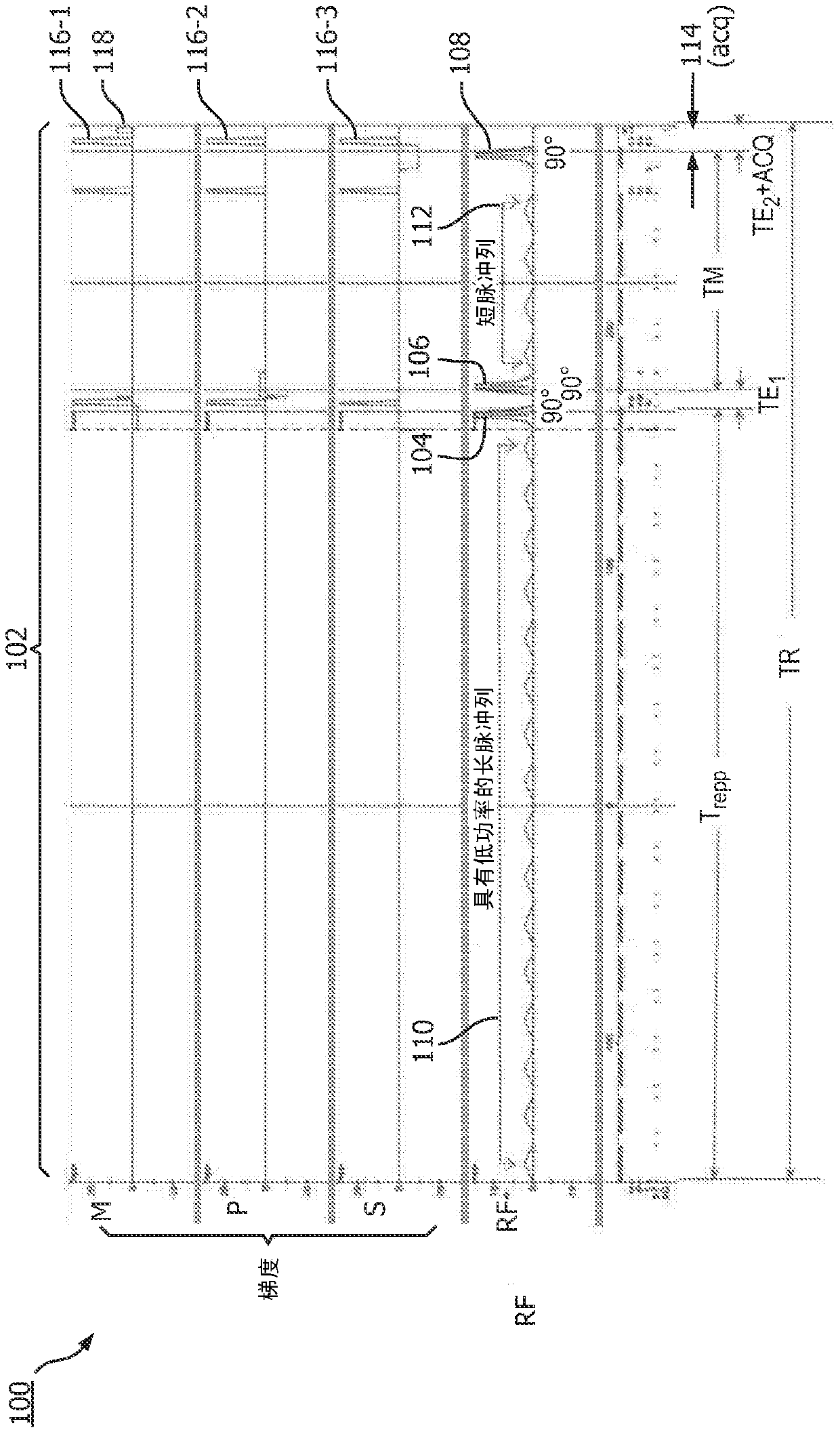
Magnetization transfer contrast technique for chemical exchange saturation transfer (cest) mri by localized steam and method of operation thereof
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system (600),for acquiring magnetic resonance (MR) information of a volume, includes at least one controller (610) configured generate at least a portion of a stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) CESTsequence including first through third 90degree radio frequency (RF) pulses, and a first pulse train situated before the first 90degree RF pulse. The first pulse train has first number of pulses. The controller (610) is further configured to generate at least another portion of the STEAM CEST sequence comprising a second pulse train situated between the second and third 90degree RF pulses, the second pulse train comprising a second number of pulses which is less than the first number of pulses;generating end of spoil gradients;and / or to acquire MR information during an acquisition window which is stated at least partially after the end of spoil gradients.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
CEST phase and magnitude imaging using a multi-parametric varied saturation scheme
ActiveUS9121917B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceSaturation pulse
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for obtaining a magnetic resonance image (MRI) or spectrum. The method includes a step of performing a chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) or magnetization transfer (MT) magnetic labeling experiment of a subject using an MRI machine. When performing the CEST or MT magnetic labeling experiment aspects of a saturation pulse or a serial saturation pulse sequence, such as length (tsat), number (Nsat), offset (Δω), modulation frequency (ωs) and power (B1) can be varied in specific-designed schemes. Data is generated from the CEST magnetic labeling experiment and is transmitted to a data processing unit. The data is processed to generate a visual representation of the data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Apparatus, system, method and computer-readable medium for isolating chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast from magnetization transfer asymmetry under two-frequency RF irradiation
ActiveUS9709511B2Eliminate contributionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsChemical machine learningDual frequencyFrequency spectrum
Apparatus, system, method and computer-readable medium for isolating chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast from magnetization transfer asymmetry under two-frequency RF irradiation. A two-pool model for magnetization transfer (MT) can be established fully based on Provotorov's theory of saturation, and then extended to the situation of simultaneous two-frequency RF irradiation. Numerical simulations and experimental results demonstrate that two-frequency RF irradiation can make MT effects independent of irradiation frequency over a wide range, and thus can suppress MT asymmetry. Exemplary embodiments can be provided to isolate chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrast from MT asymmetry contrast by using the two-frequency RF irradiation technique. A further embodiment can isolate a narrow-frequency spectrum MT mechanism from a broad-frequency spectrum MT mechanism.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
System and method for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) magnetic resonance fingerprinting
A system and method of use includes (a) directing a magnetic resonance (MR) system to perform a pulse sequences block in which radio frequency (RF) energy is applied to the subject to substantially saturate magnetization corresponding to an exchangeable proton. The method includes (b), following step (a), acquiring data from the subject with the MR system and (c) repeating step (a) a plurality of times where parameters of the pulse sequence sub-block differ in at least some pulse sequence sub-blocks by at least an amount of RF energy applied to saturate the magnetization. The method further includes (d), after each repetition of step (a), repeating step (b) to acquire data representing signal evolutions from the subject. Additionally, the method includes (e) comparing the signal evolutions with a dictionary database comprising a plurality of different signal evolution templates to determine quantitative chemical exchange or exchangeable proton information of the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
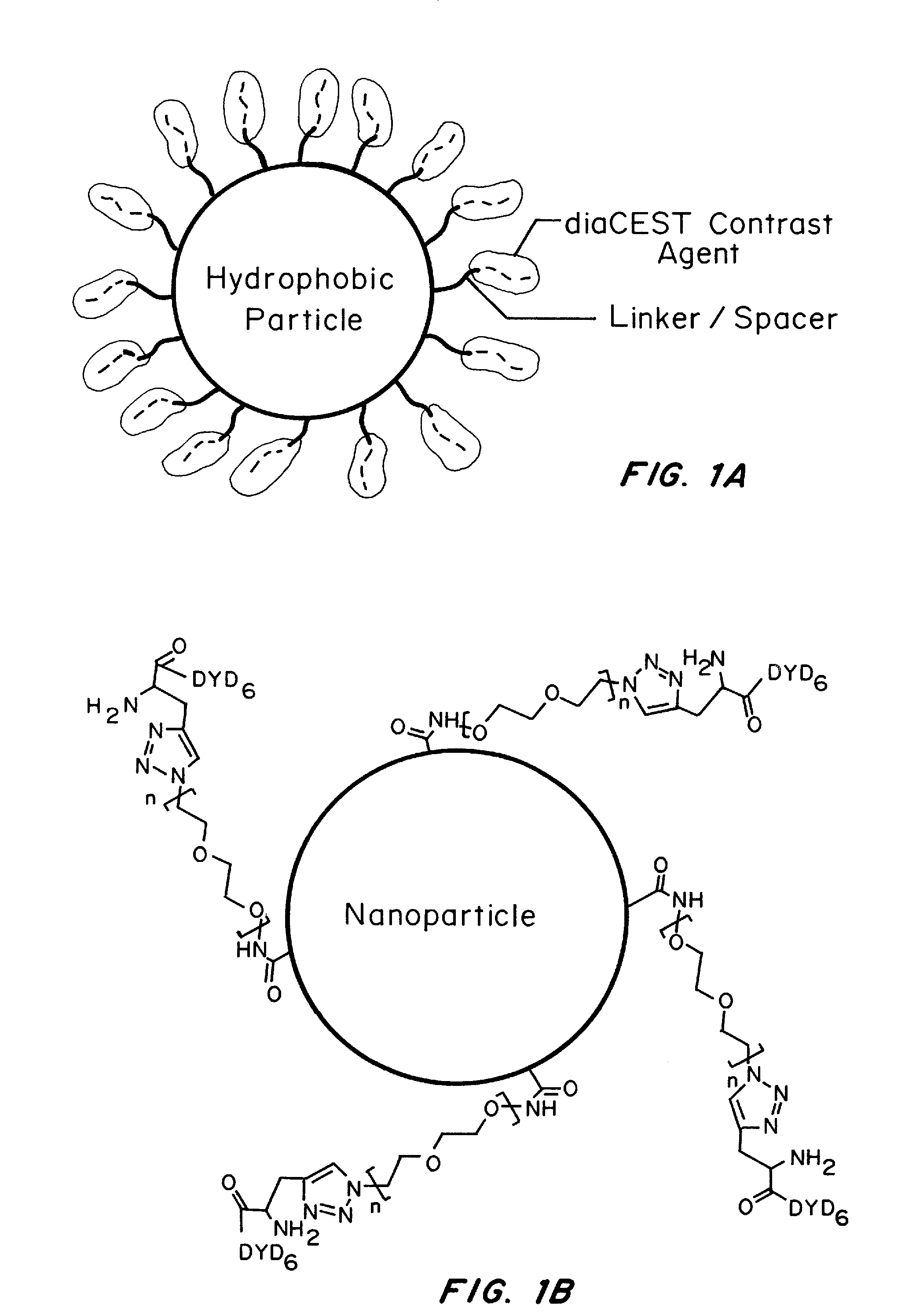
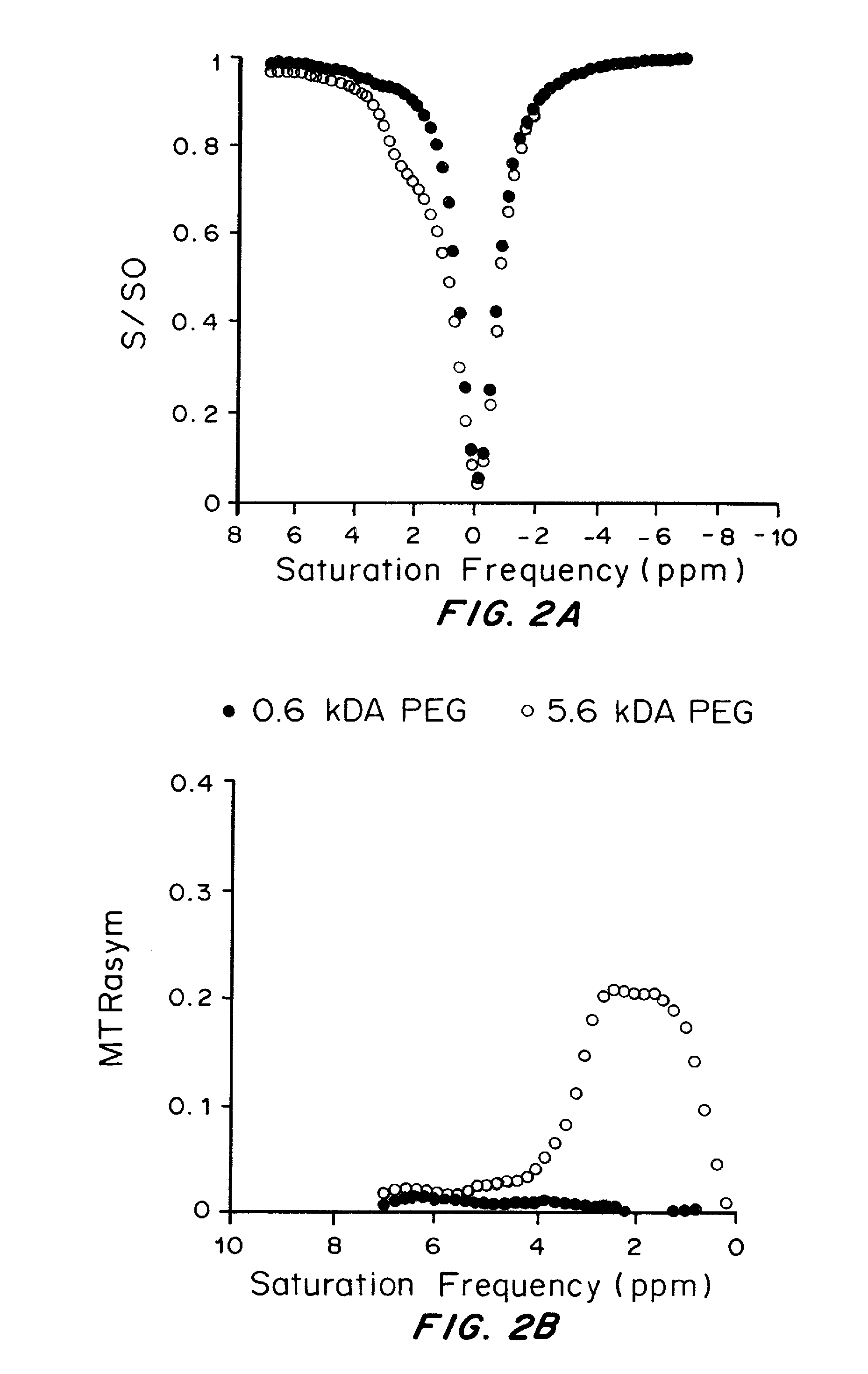
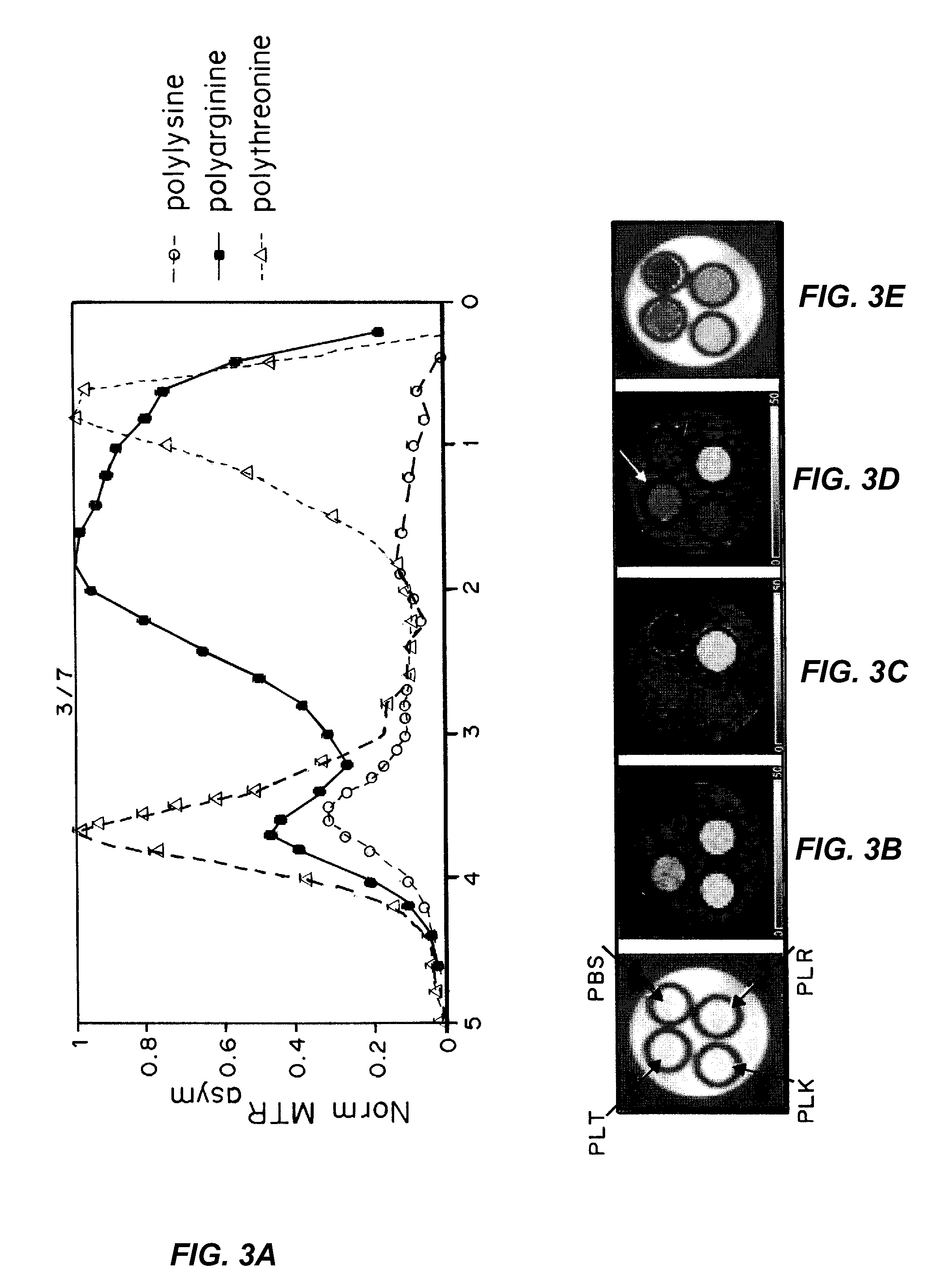
Nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging tracking and methods of making and using thereof
ActiveUS20160206760A1Effective mergerEffective imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMRI contrast agentSuperparamagnetism
Surface conjugated diamagnetic Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (diaCEST) agent carriers and methods of making and using are described herein. The particles are safe alternatives to conventional paramagnetic or superparamagnetic metal-based MRI contrast agents that are often toxic and therefore not biocompatible. The carriers described herein can provide simultaneous monitoring of multiple particle types labeled with ‘multicolor’ diaCEST contrast agents. In some embodiments, the carriers are micro- and / or nanoparticles. In other embodiments, the carriers are liposomes. In some embodiments, the particles and / or liposomes are mucus penetrating. In other embodiments, the particles and / or liposomes are not mucus penetrating.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
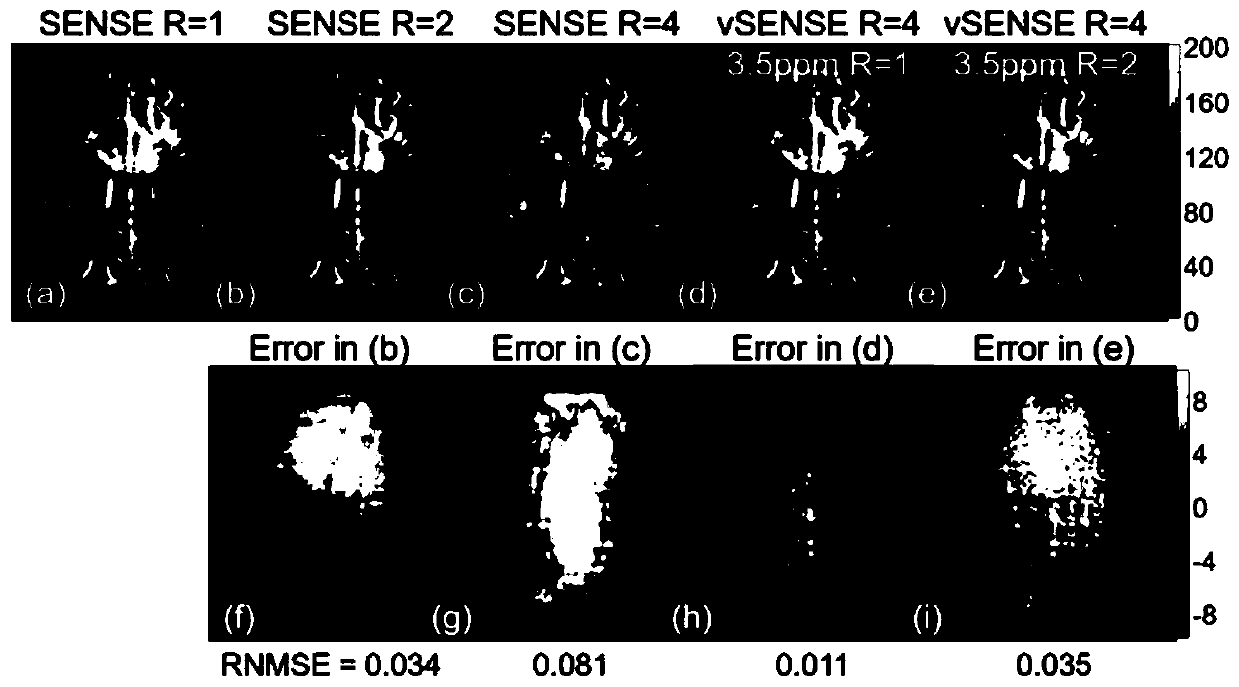
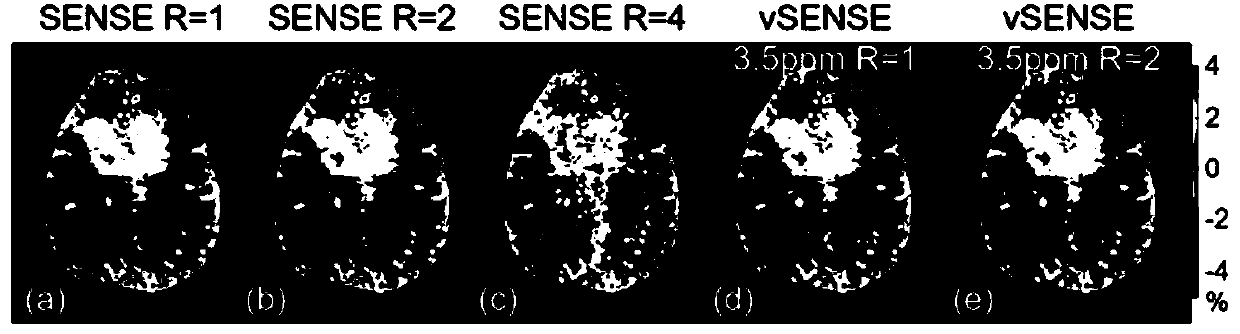
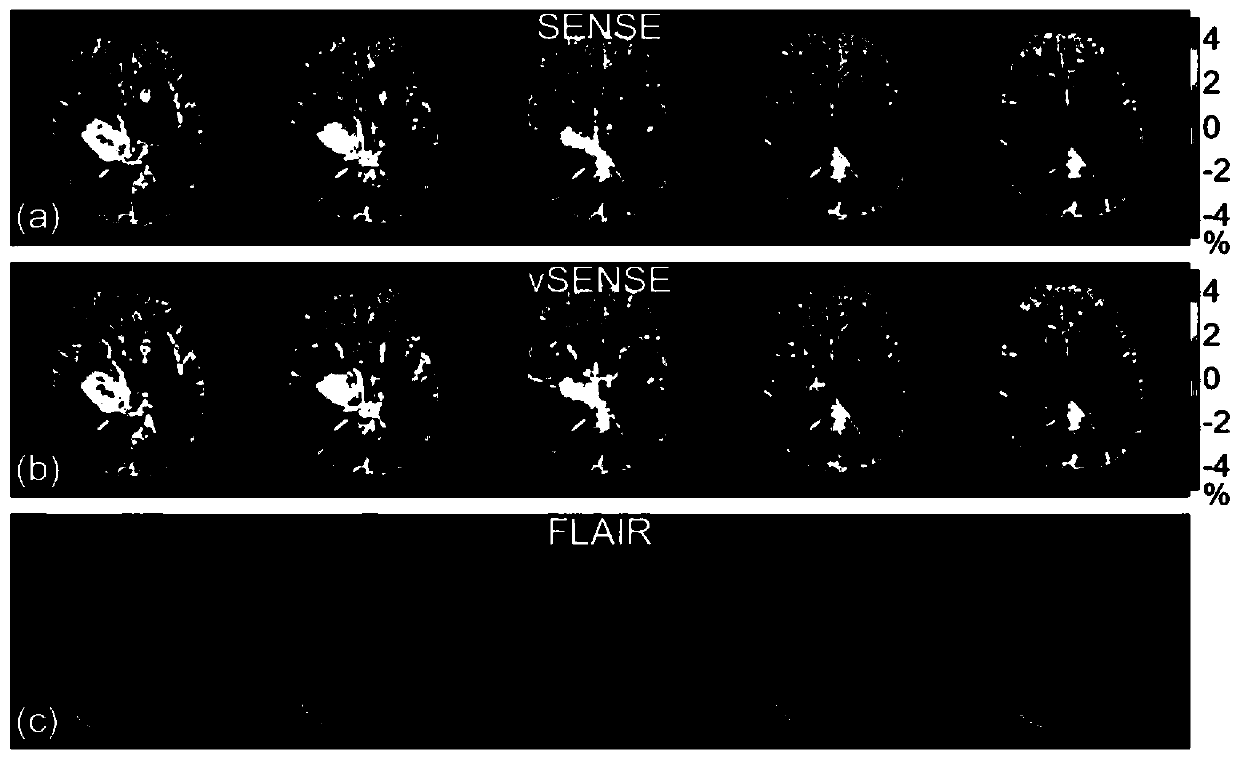
CEST (Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer) image reconstruction method and device based on variable acceleration sensitivity encoding
ActiveCN109839607AEliminate artifacts2D-image generationDiagnostic recording/measuringAcceleration factorVoxel
The invention discloses a chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging method and device based on a variable acceleration sensitivity encoding method, and belongs to the field of magnetic resonance imaging. In the method, Fourier transform is carried out on K-space data formed by a measured object in CEST imaging to obtain image space folding data of each voxel, wherein the image space folding data includes at least one undersampled frame accurate image with the acceleration factor R1 being greater than or equal to 1 and a plurality of other to-be-reconstructed undersampled frame images with the acceleration factor being not less than R1; and then image reconstruction is carried out on the to-be-reconstructed undersampled frame images with the acceleration factor being R2. The sensitivity map of the traditional SENSE method can be modified by using undersampled frames. The reconstruction error of the method is basically the same as that of the traditional SNESE method which applies a low acceleration factor in a CEST source image, but the speed of the method is twice or more the speed of the traditional SENSE method. Since it is unnecessary to adopt fully sampled frames, the method is particularly applicable to three-dimensional (3D) CEST imaging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
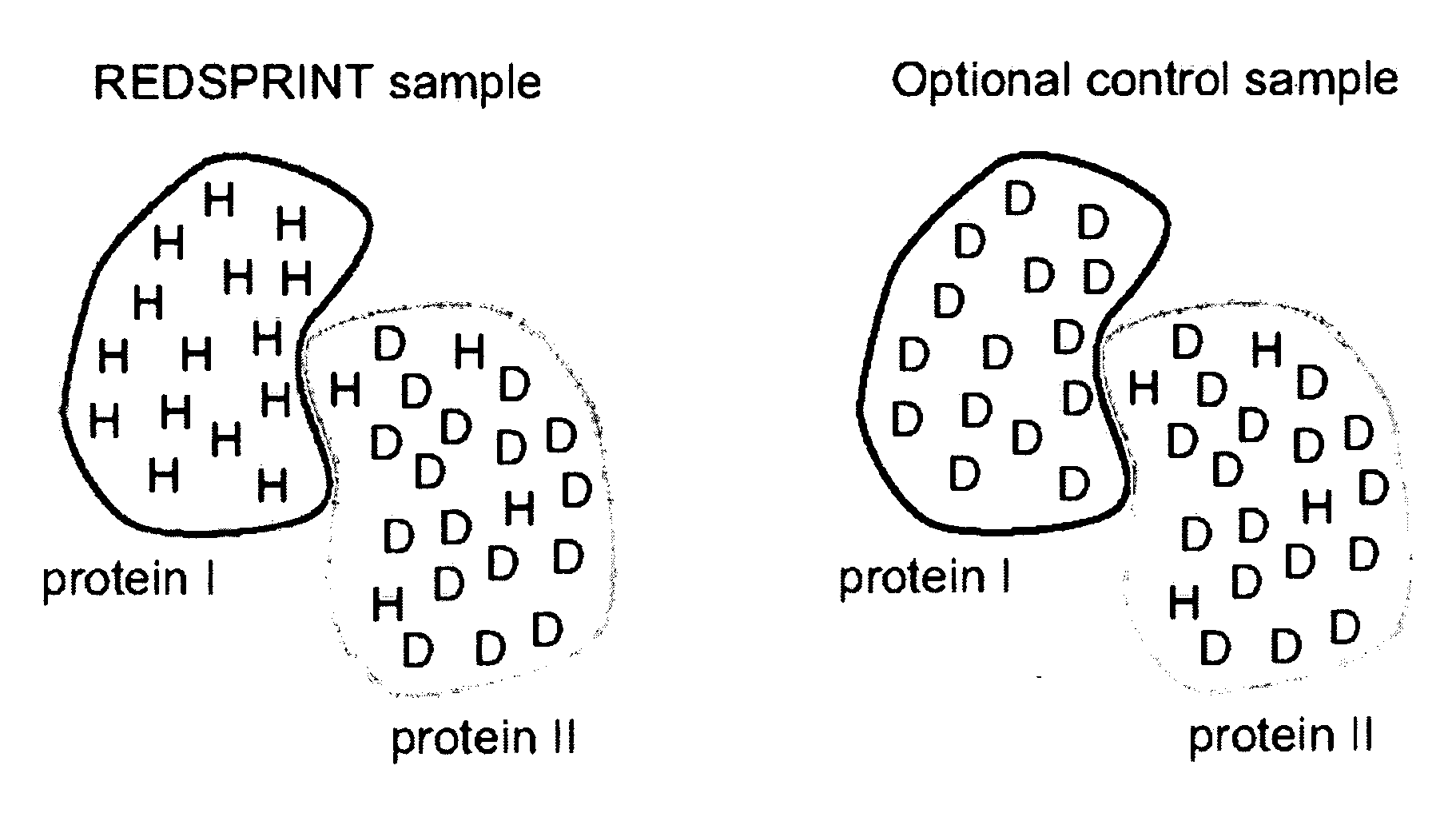
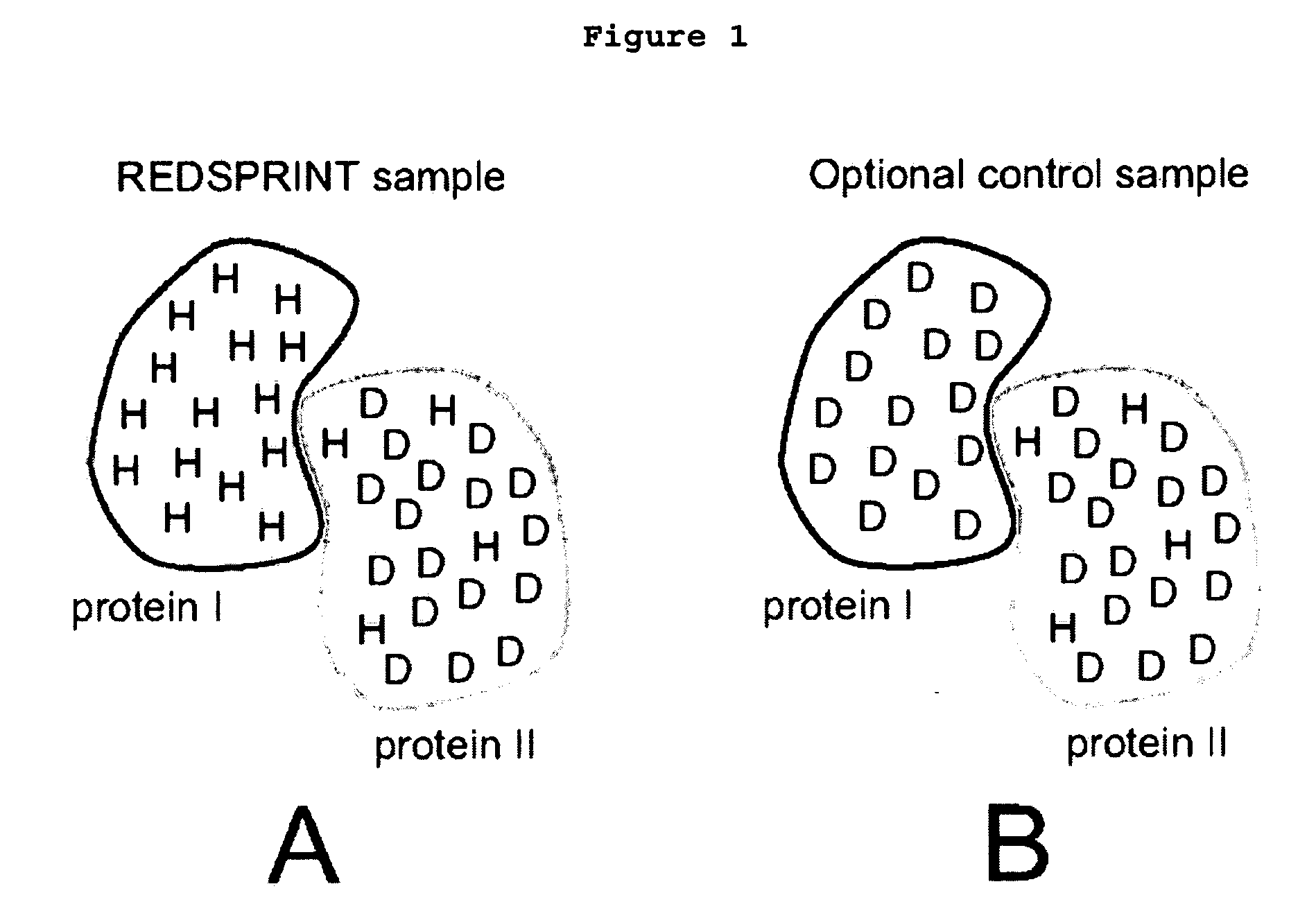
Methods and devices for characterizing macromolecular complexes using isotope labeling techniques
InactiveUS20060183157A1Reduces H densityMagnetic measurementsBiological testingIsotopic labelingSpectroscopy
A method for characterizing interactions in macromolecular complexes, such as protein-protein or protein-ligand complexes, by selective isotopic labeling of the target molecule to reduce the 1H density in a selected spectral region; by irradiating the target; and by monitoring the polarization using filtered nuclear Overhauser spectroscopy (NOESY) and / or by performing selective saturation transfer experiments to determine the docking potential of the macromolecular complex.
Owner:COWBURN DAVID +3
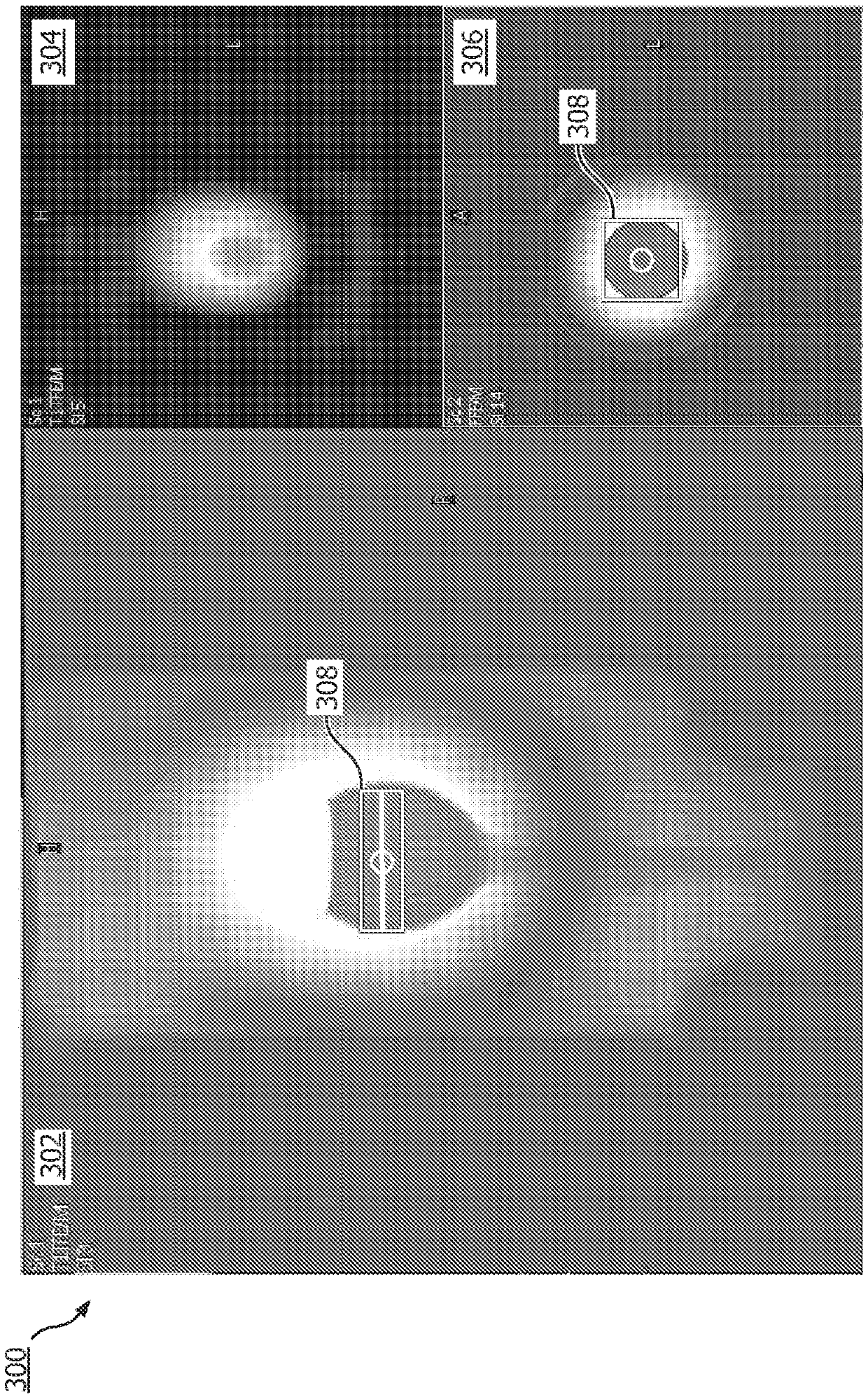
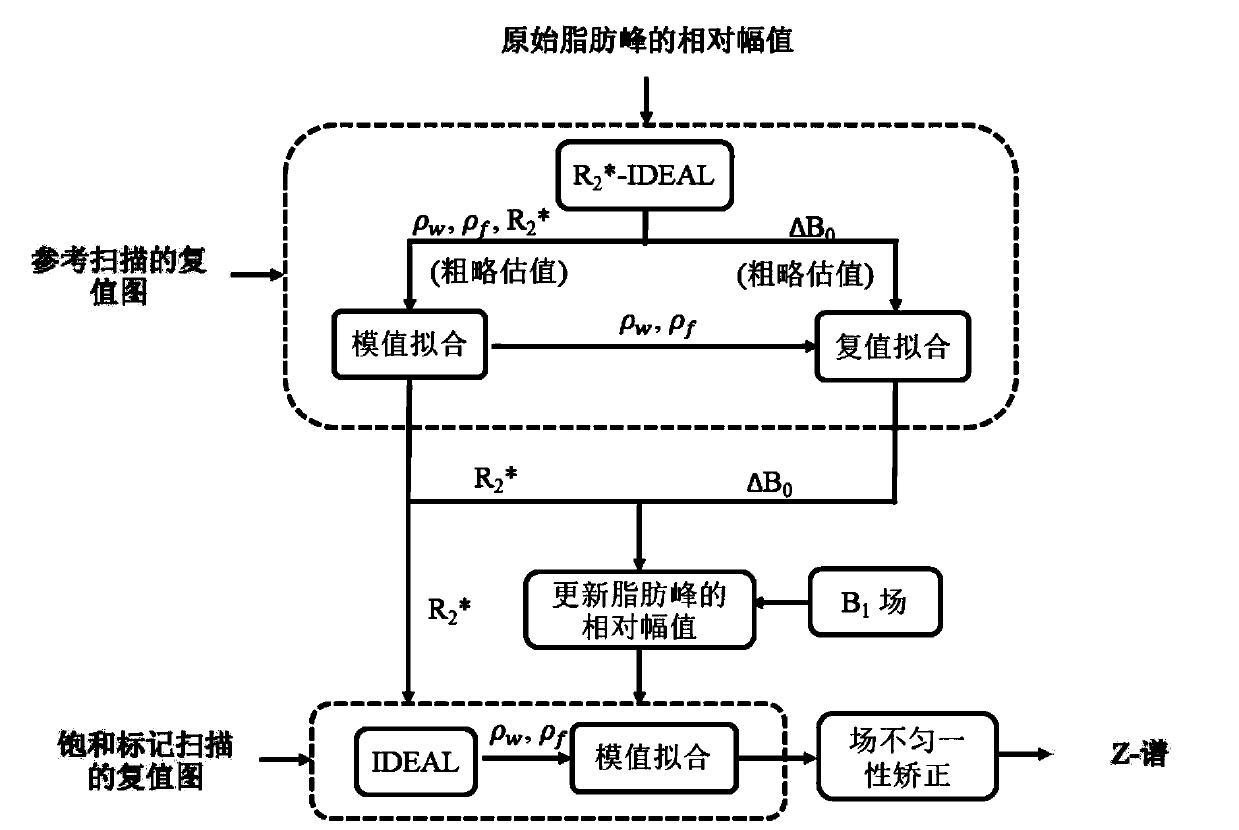
Single-point dixon method for fat-water separation in chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging
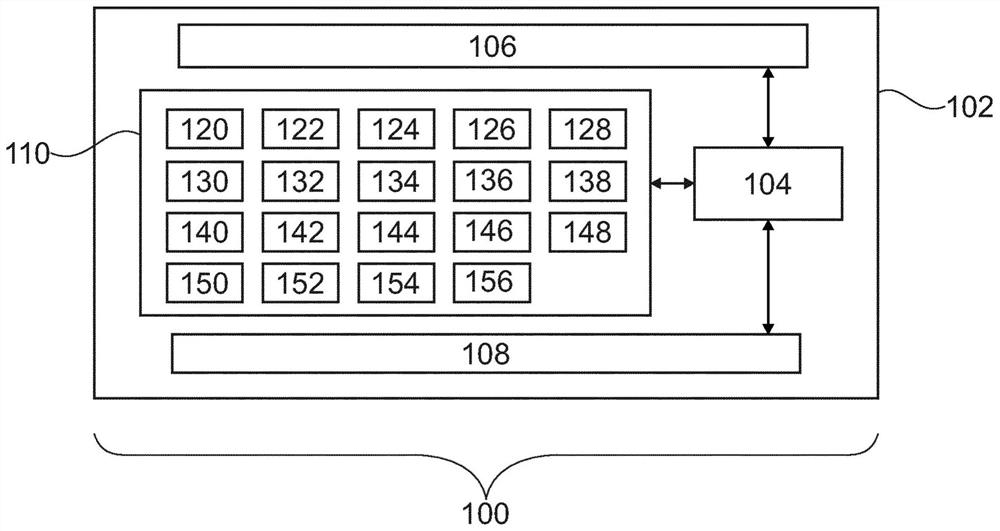
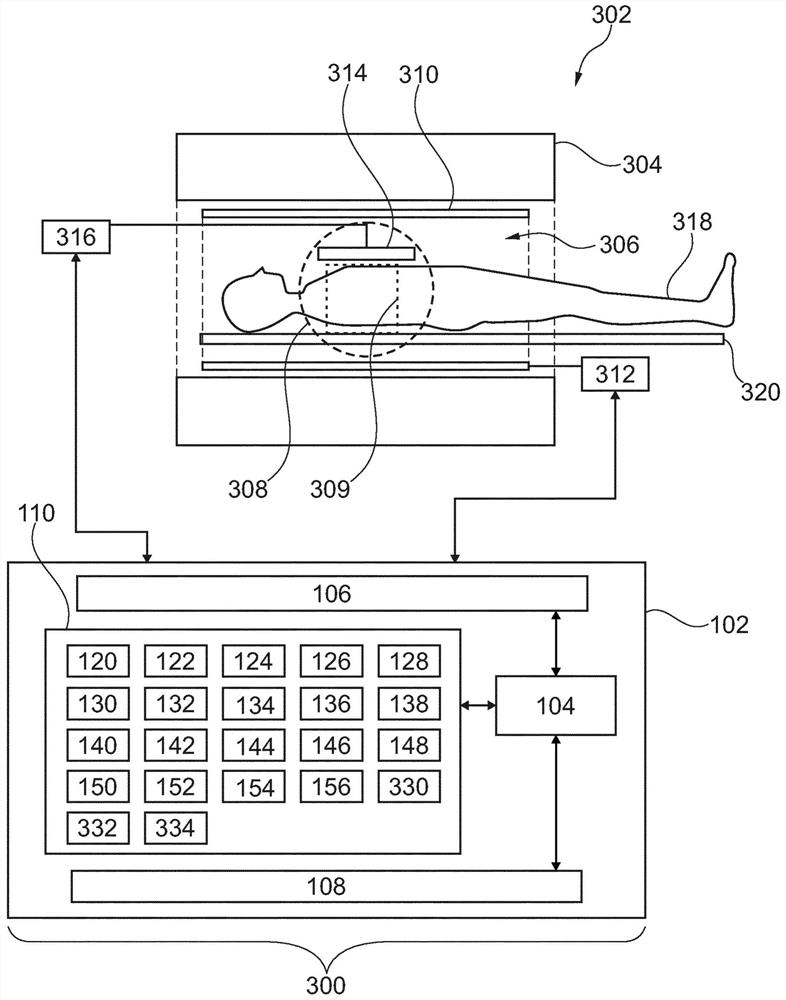
ActiveUS20200348382A1Enhance the imageDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelImaging data
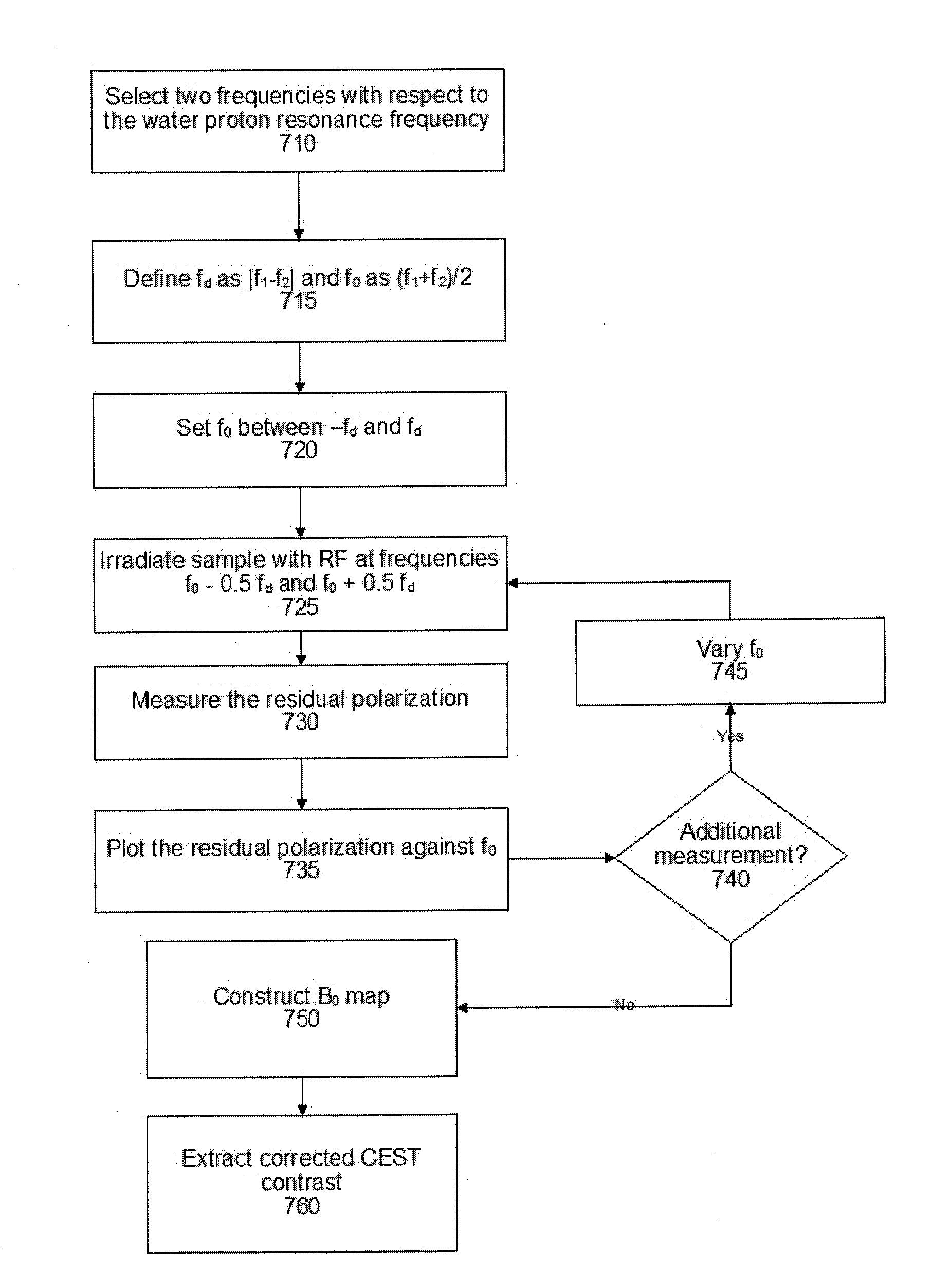
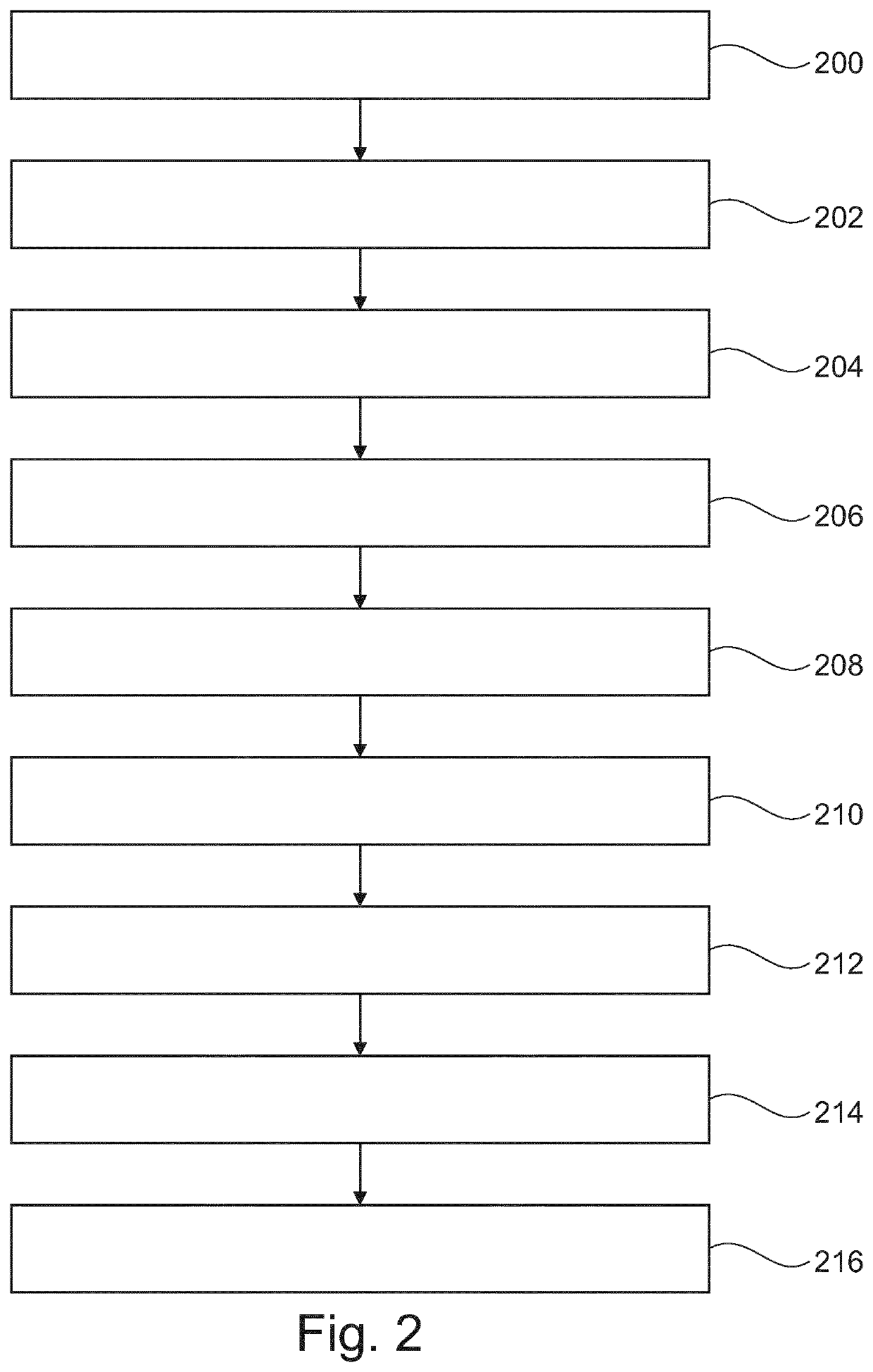
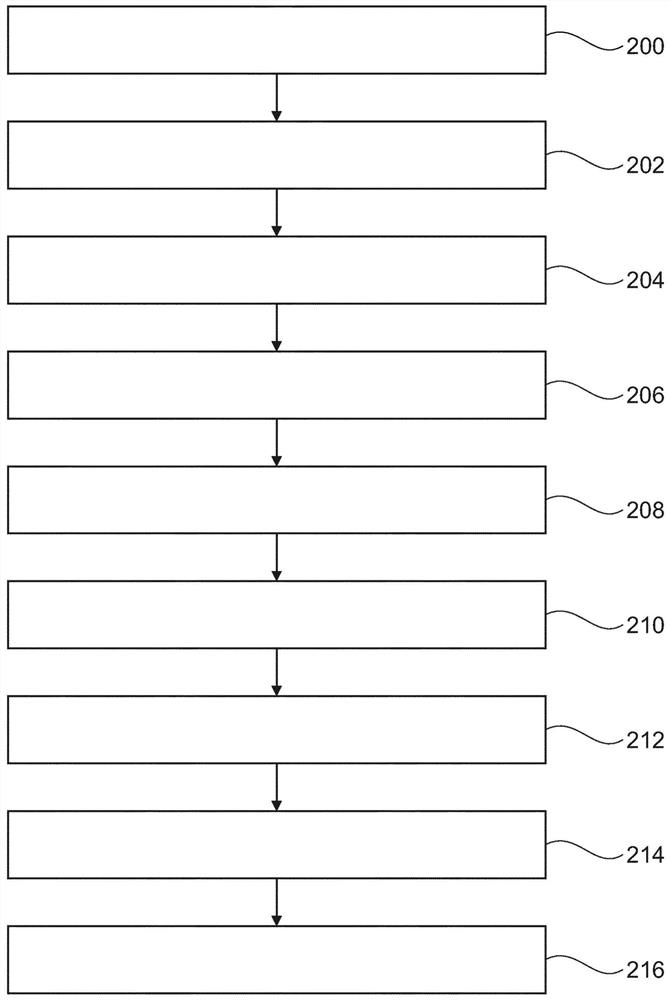
The invention provides for a medical imaging system (100, 300). The medical imaging system comprises a processor (104). Execution of machine executable instructions (120) causes the processor to: receive (200) magnetic resonance imaging data (122) comprising a Z-spectrum acquisition (124) for a set of saturation frequency offsets (126) and at least one reference saturation frequency offset (128); reconstruct (202) saturation frequency offset complex image data (130); reconstruct (204) a B0 map (132), a water image (134), and a fat image (136) according to a Dixon-type magnetic resonance imaging protocol; calculate (206) a water phase angle (138) using the water image and / or the fat image; calculate (208) rotated complex image data (140) by rotating the phase of the saturation frequency offset complex image data such that the complex water signal is aligned with a real axis for each voxel; perform (210) a B0 correction by calculating shifted complex image data (142); calculate (212) a frequency dependent phase angle (144) descriptive of a phase angle between the complex water signal and the complex fat signal for each of the set of saturation frequency offsets using a fat signal model comprising at least two fat species; calculate (214) a residual fat component correction factor (150) by projecting the complex fat signal onto the real axis for each of the set of saturation frequency offsets; and calculate (216) corrected water Z-spectrum image data (152) by subtracting the residual fat component correction factor for each of the set of saturation frequency offsets from the real component of the shifted complex image data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Single-point dixon method for fat-water separation in chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN111837047ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelImaging data
The invention provides for a medical imaging system (100, 300). The medical imaging system comprises a processor (104). Execution of machine executable instructions (120) causes the processor to: receive (200) magnetic resonance imaging data (122) comprising a Z-spectrum acquisition (124) for a set of saturation frequency offsets (126) and at least one reference saturation frequency offset (128);reconstruct (202) saturation frequency offset complex image data (130); reconstruct (204) a B0 map (132), a water image (134), and a fat image (136) according to a Dixon-type magnetic resonance imaging protocol; calculate (206) a water phase angle (138) using the water image and / or the fat image; calculate (208) rotated complex image data (140) by rotating the phase of the saturation frequency offset complex image data such that the complex water signal is aligned with a real axis for each voxel; perform (210) a B0 correction by calculating shifted complex image data (142); calculate (212) afrequency dependent phase angle (144) descriptive of a phase angle between the complex water signal and the complex fat signal for each of the set of saturation frequency offsets using a fat signal model comprising at least two fat species; calculate (214) a residual fat component correction factor (150) by projecting the complex fat signal onto the real axis for each of the set of saturation frequency offsets; and calculate (216) corrected water Z-spectrum image data (152) by subtracting the residual fat component correction factor for each of the set of saturation frequency offsets from thereal component of the shifted complex image data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method for eliminating fat artifact
ActiveCN110068783AAccurate reconstructionGuaranteed interferenceMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringVoxelRadio frequency
The invention discloses a chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method for eliminating fat artifacts, which comprises the steps of image acquisition and image reconstruction, wherein the imageacquisition is to acquire a model image and a phase image of magnetic resonance imaging by adopting a multi-echo gradient echo sequence under the condition of unsaturated radio frequency irradiationand the condition of saturated radio frequency irradiation of different frequencies; the image reconstruction comprises reconstructing a water map, a fat map, a field map and a map based on data collected under irradiation of the multimodal fat model on unsaturated radio frequency; fat models in data acquired after saturated radio frequency irradiation of different frequencies is updated on a per-entity basis by using a numerical method; a water map and a fat map are reconstructed based on the data acquired by the updated fat model under the saturated radio frequency irradiation of different frequencies; and the accurate water-fat reconstruction ensures that no fat signal interference exists in the water map, fat artifacts occurring in chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging are effectively eliminated, and the chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method for eliminating fat artifacts can improve the accuracy of the chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Targeted MR imaging agents
InactiveUS8003078B2Weakening rangeEfficient switchingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDispersion deliveryParticulatesContrast level
MRI contrast agents that employ paramagnetic agents and chemical exchange saturation transfer (paraCEST) and which are coupled to targeted particulate delivery vehicles provide sufficient concentration of the paraCEST contrast agents to obtain useful images of target tissues or organs. In addition, the image contrast may be switched on or off with a presaturation radio frequency pulse, avoiding the necessity obtaining pre-injection and post-injection images.
Owner:BARNES JEWISH HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com