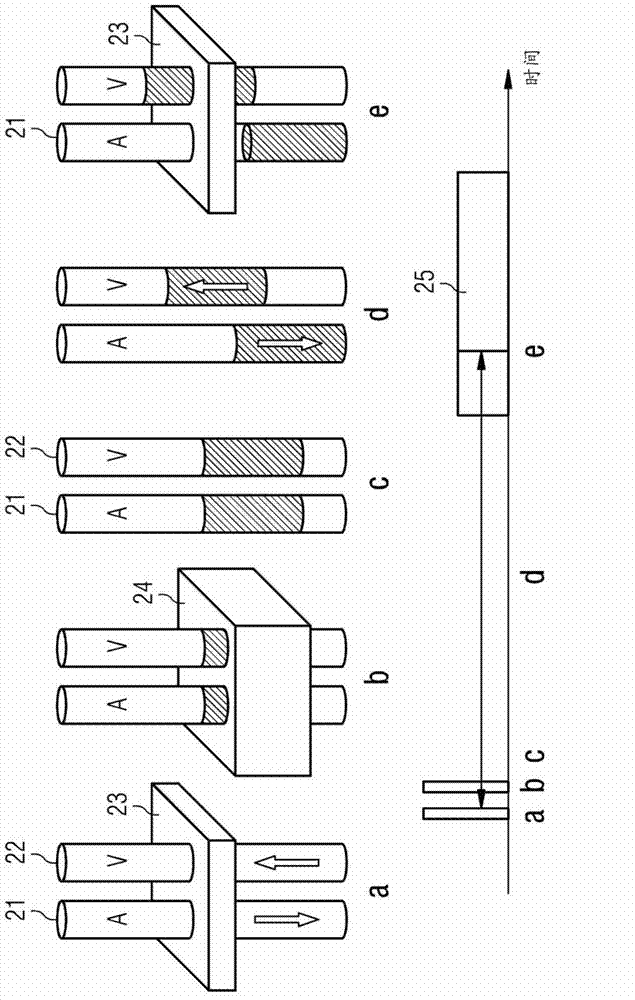
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Saturation pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
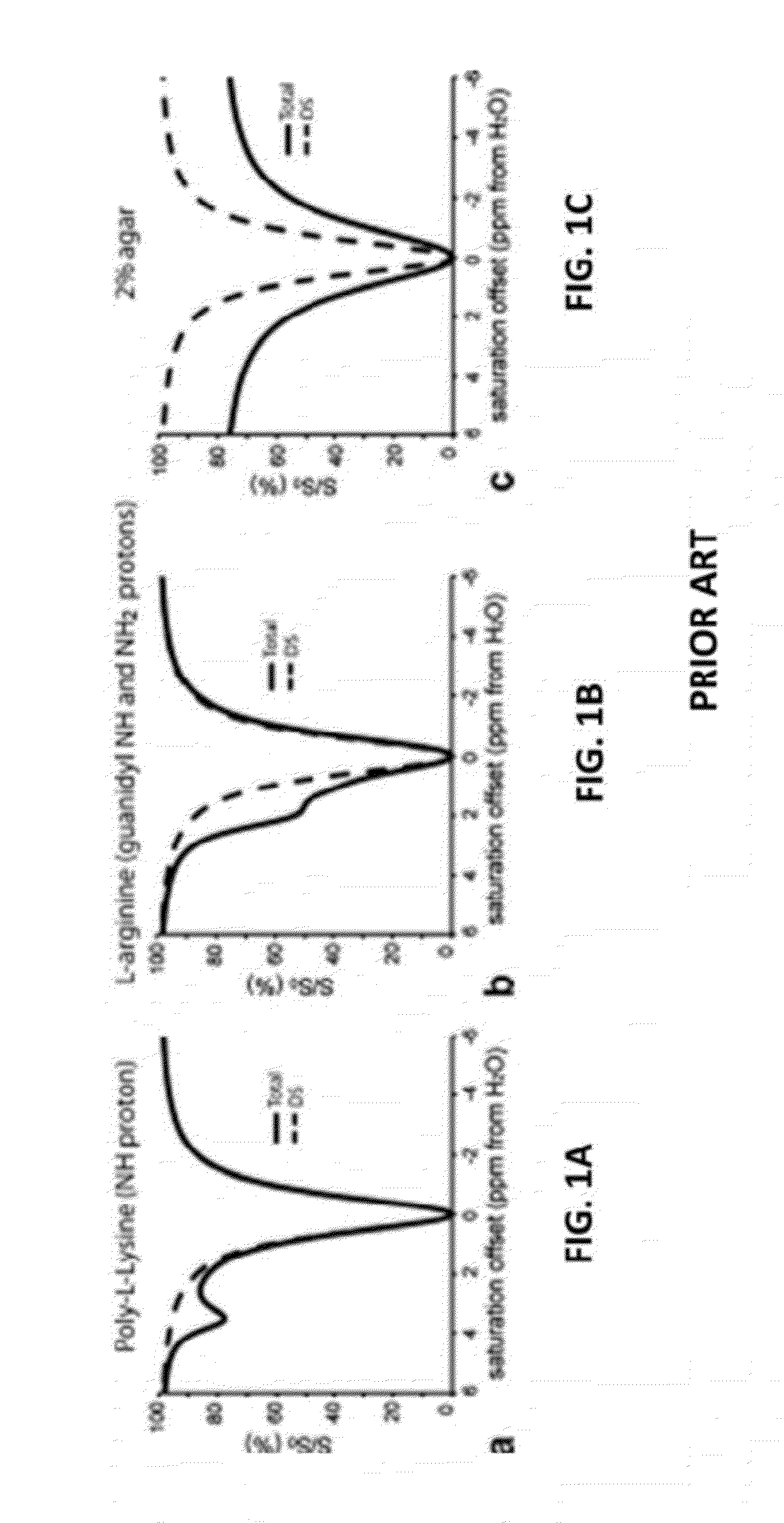
Saturation pulse. a technique for reducing flow or movement artifacts by selectively saturating spins before they enter the imaging plane.
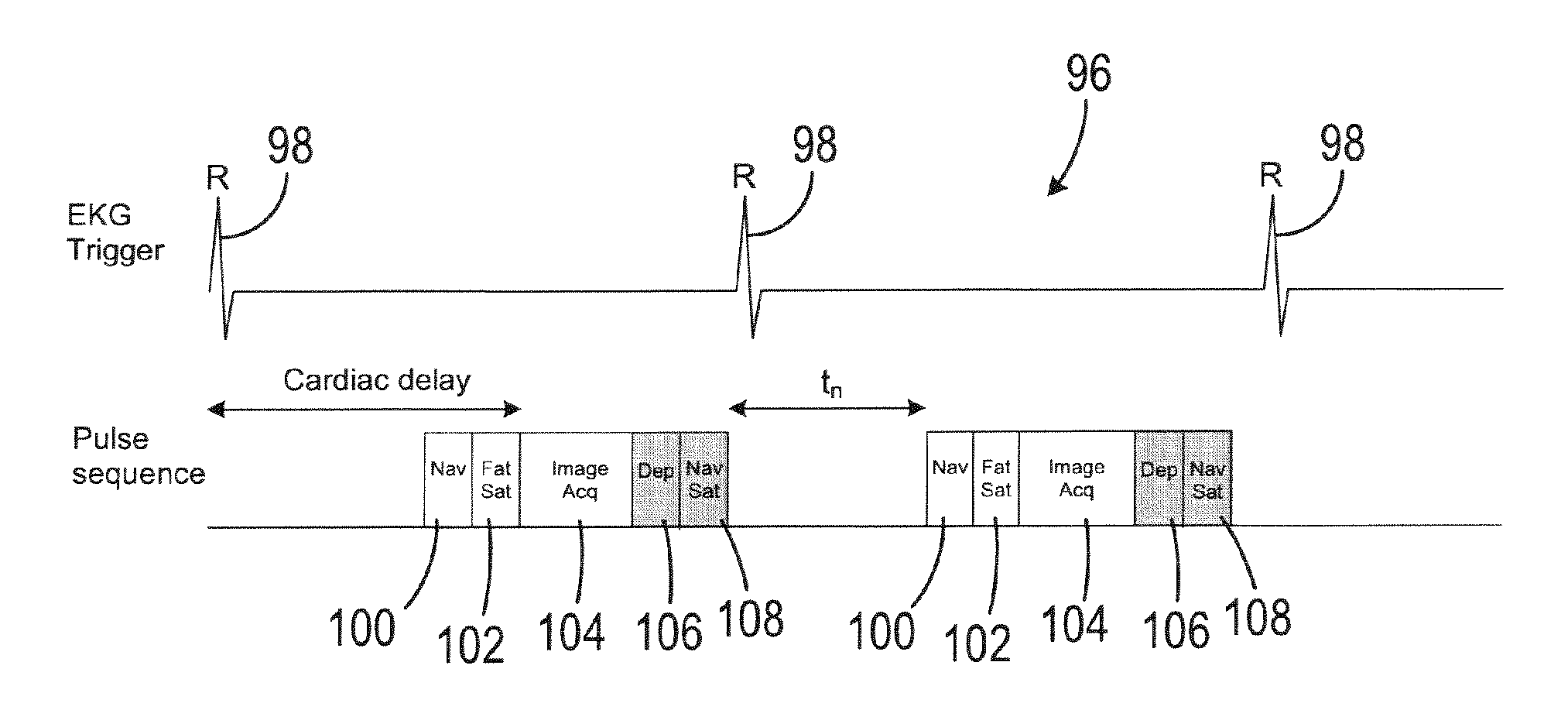
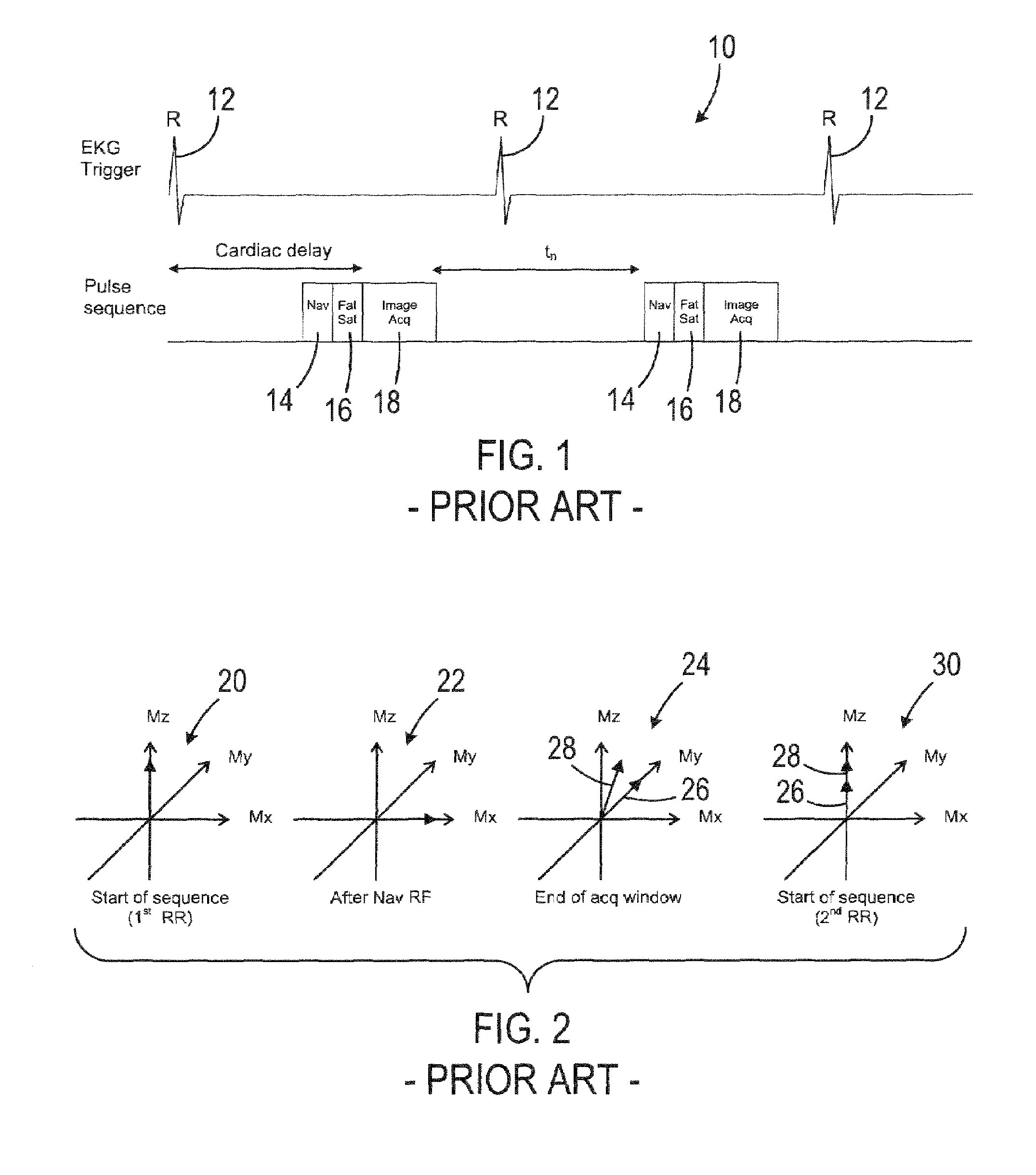
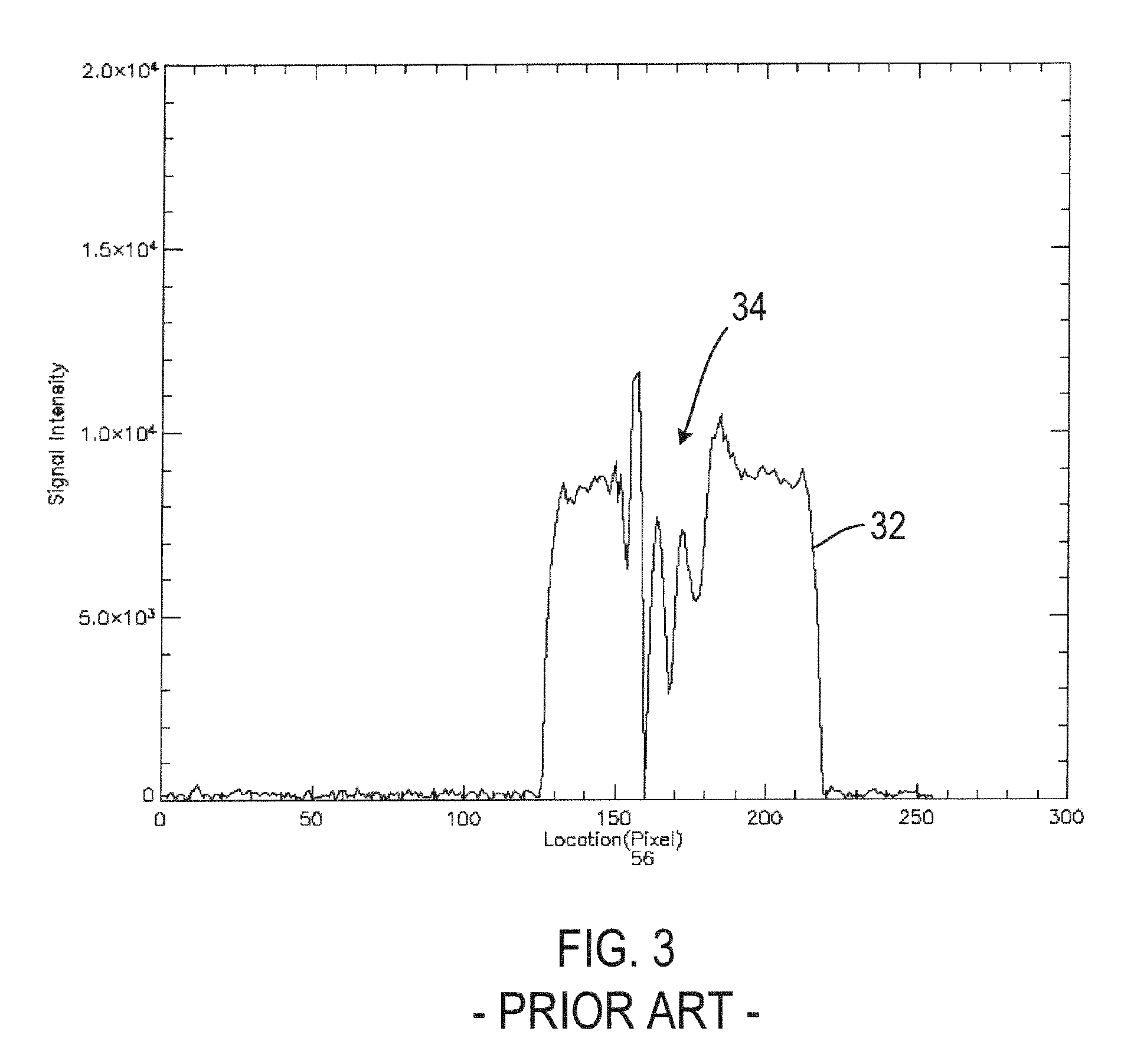
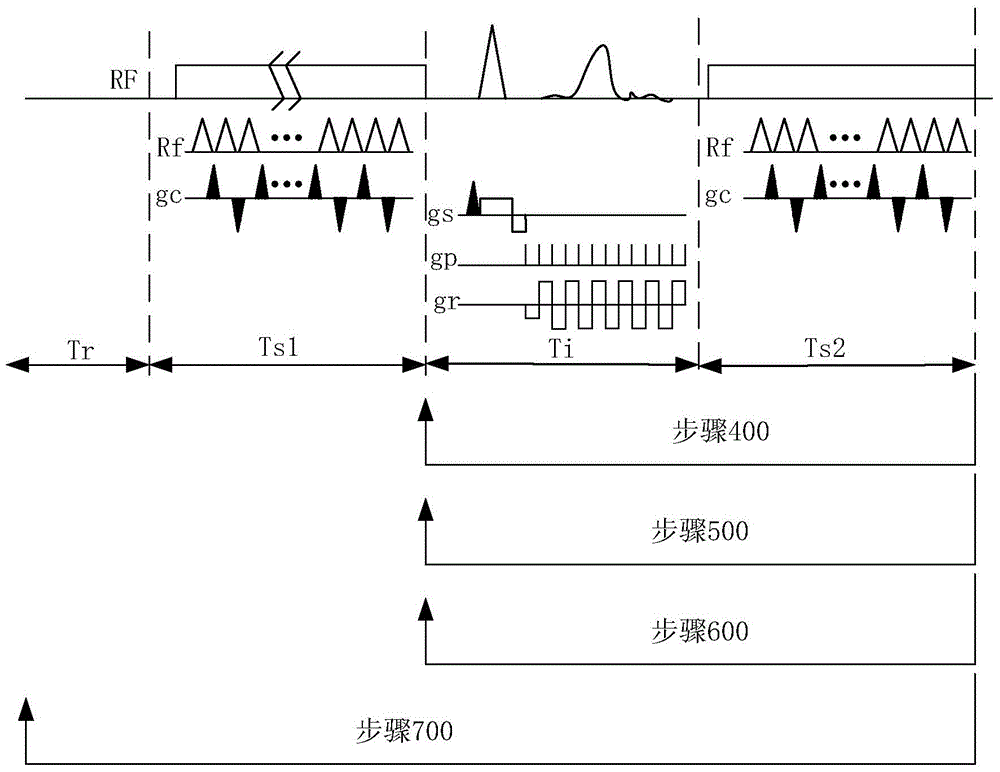
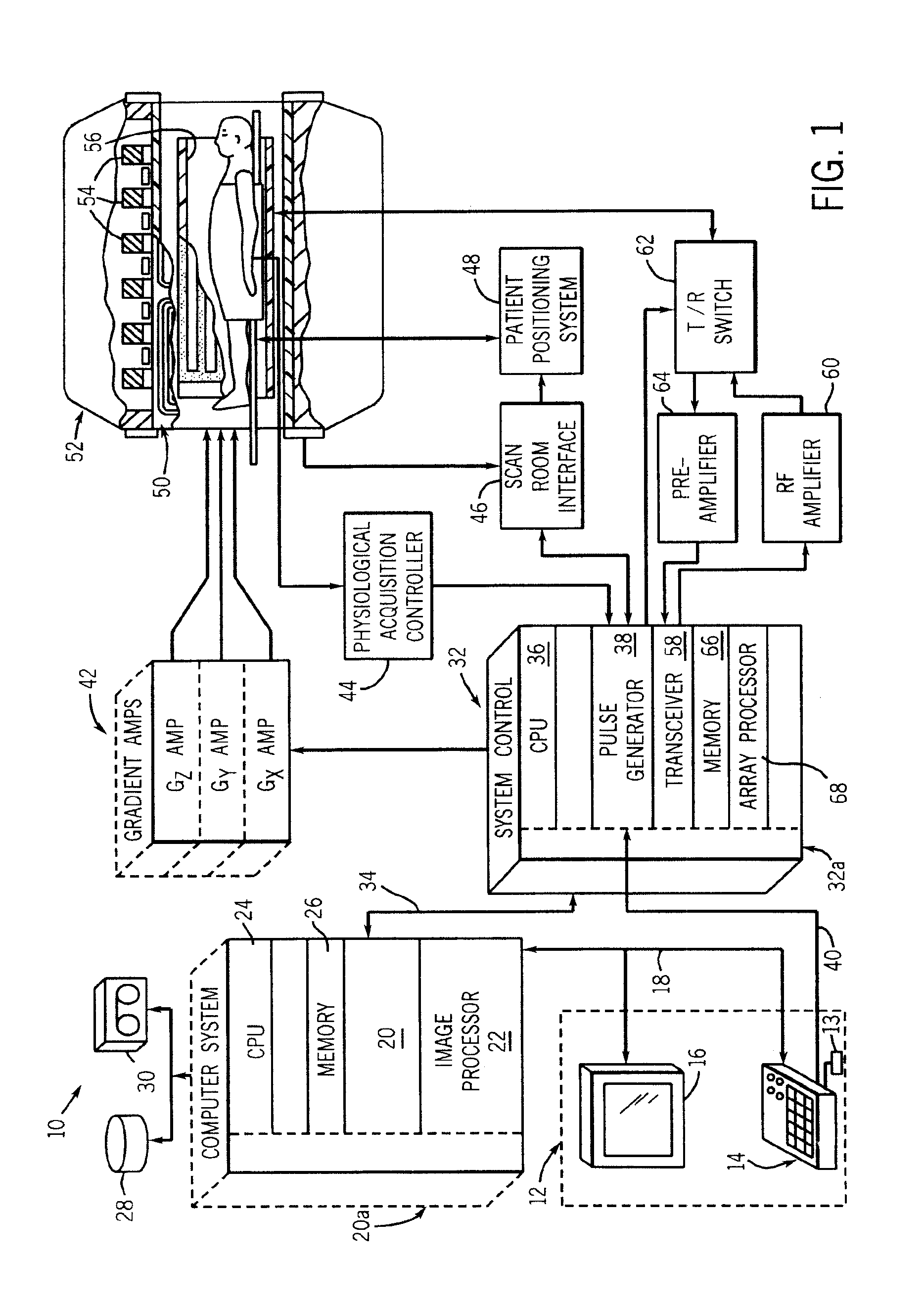
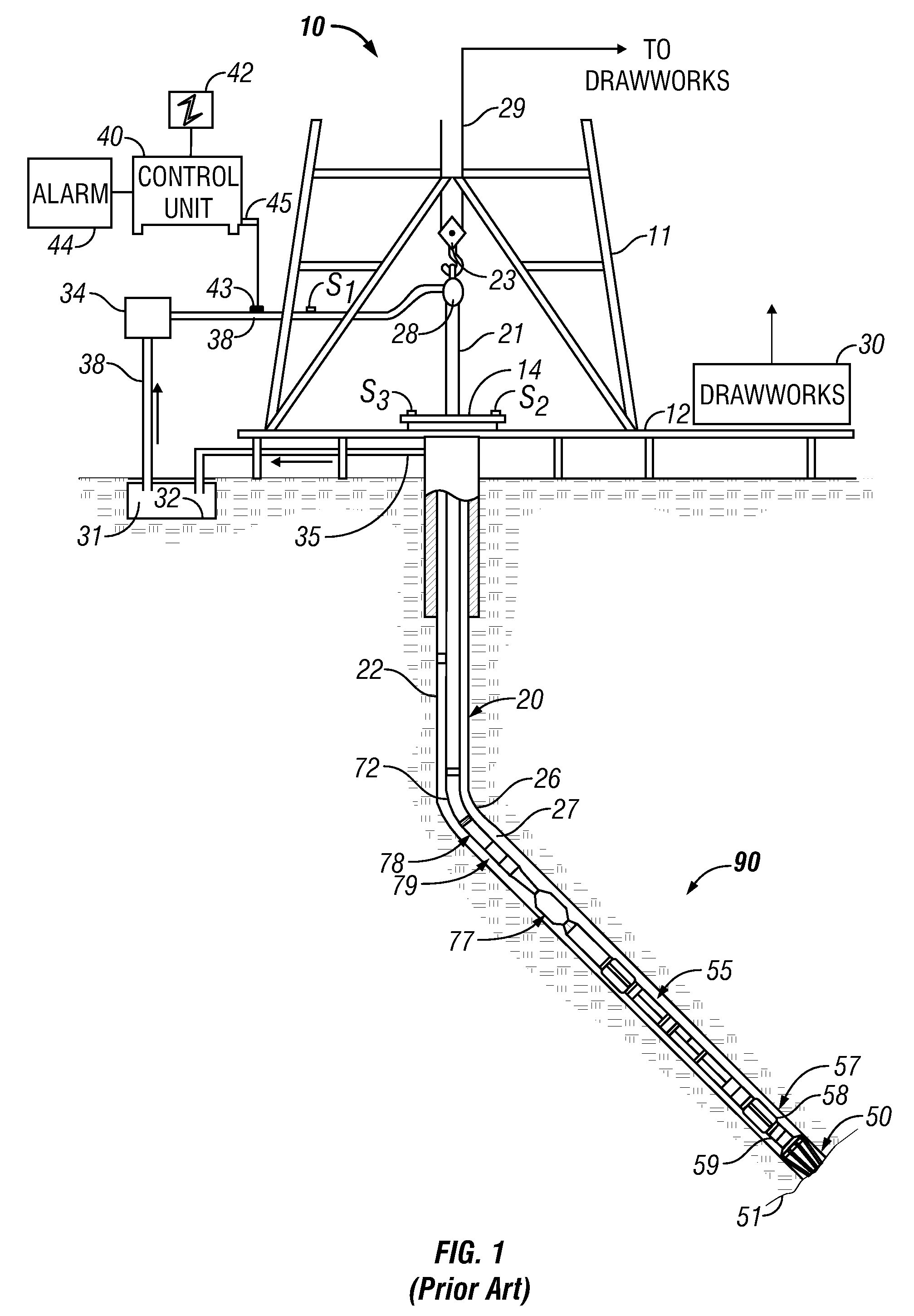
Method and apparatus for acquiring free-breathing MR images using navigator echo with saturation RF pulse
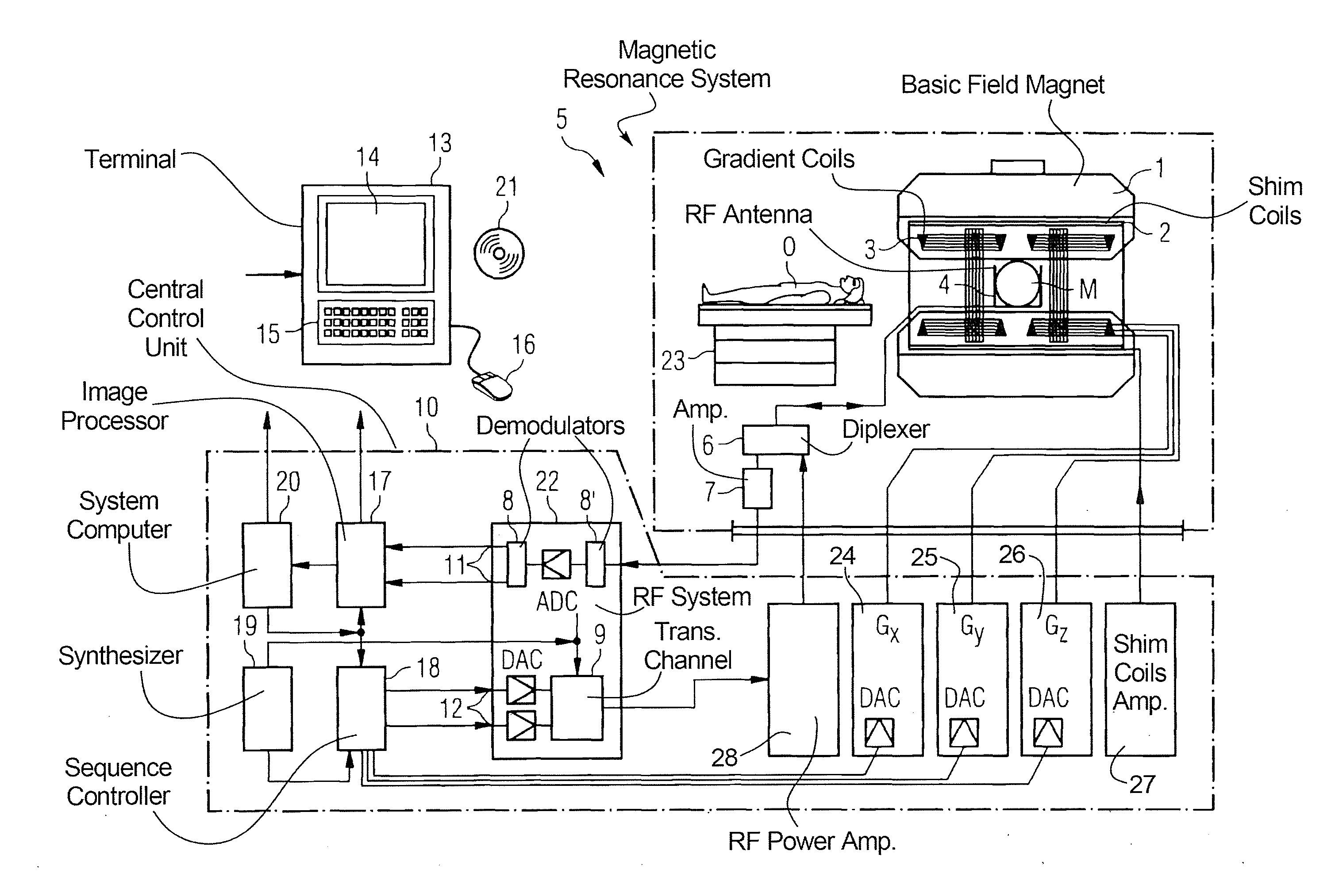
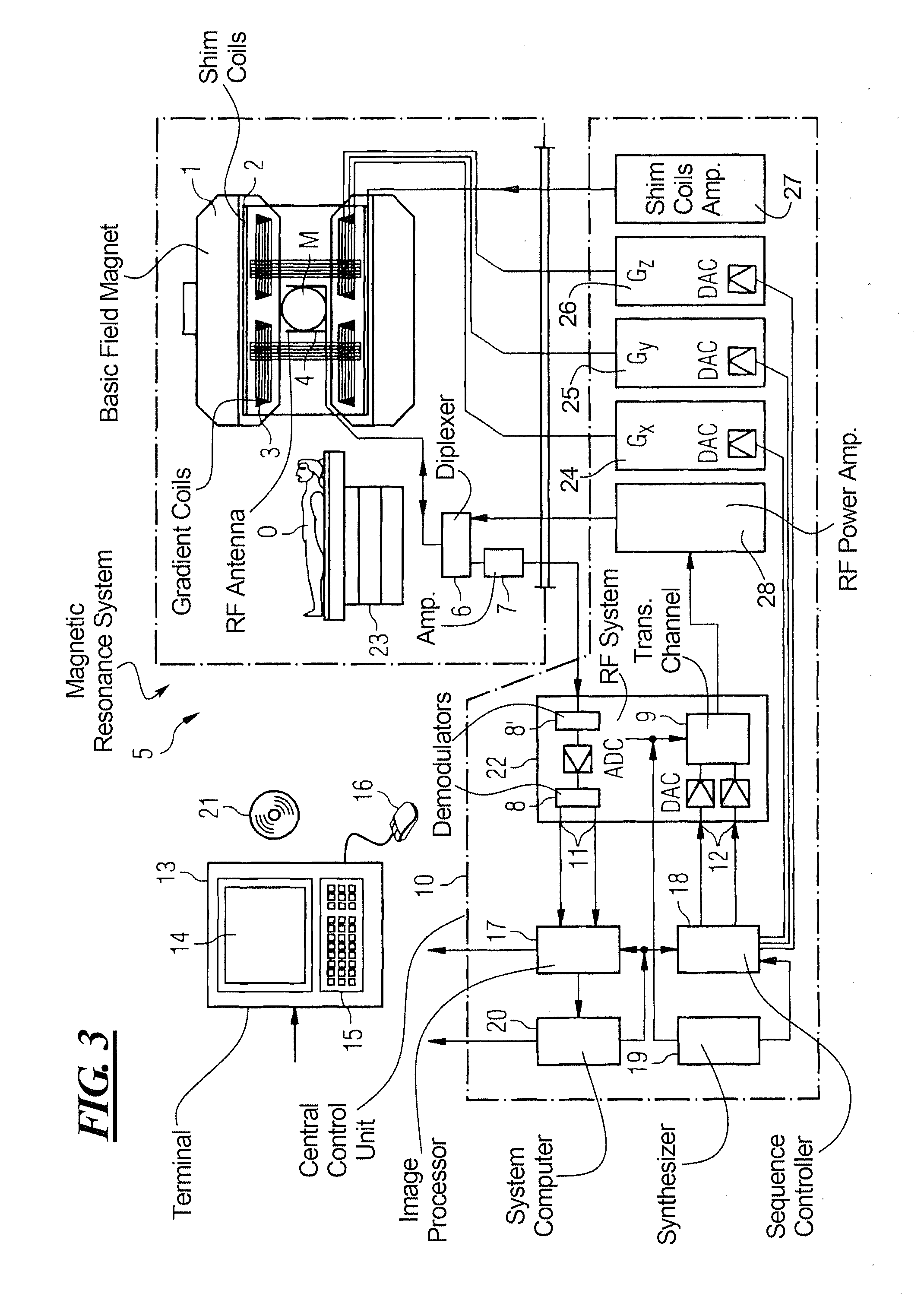
ActiveUS7689263B1Uniform recoveryOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTransverse magnetizationSpins
A system and method of free-breathing MR imaging saturates an entire navigator profile at the end of an imaging segment of physiological motion cycle, e.g., heart cycle, thereby providing a uniform recovery of longitudinal magnetization for the next imaging cycle. Through use of at least one dephaser gradient following the image acquisition segment and a navigator RF saturation pulse, residual transverse magnetization is dephased and spins within a navigator tracker are saturated to ensure a uniform recovery of longitudinal magnetization for the next imaging period.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
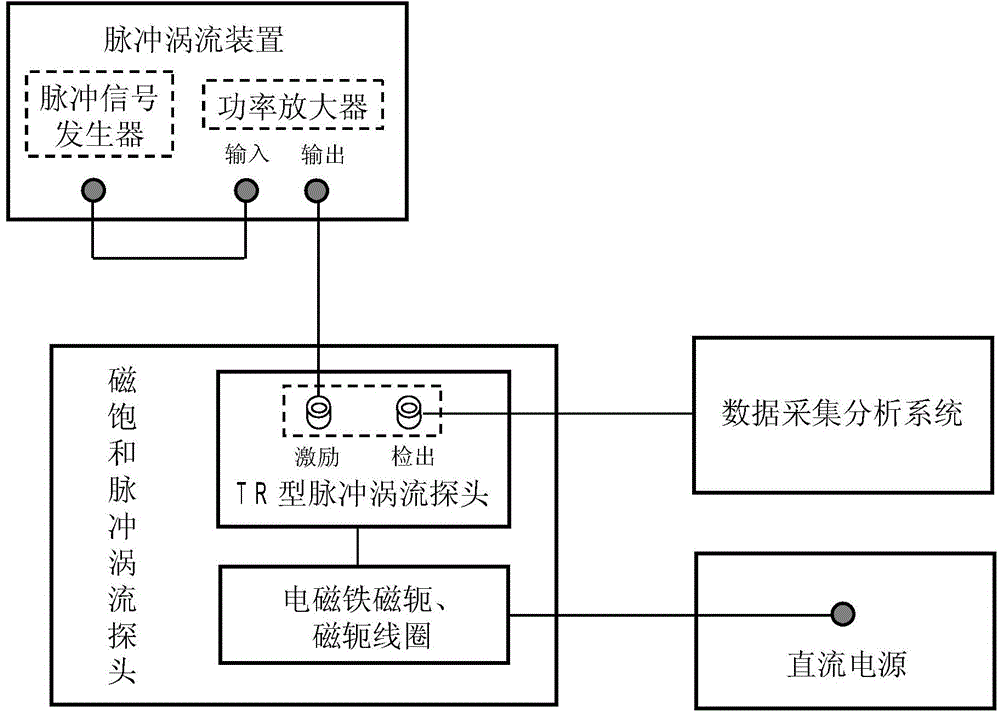
Ferromagnetic pipeline quantitative lossless evaluating method based on nonlinear magnetic saturation pulsed eddy current
ActiveCN104950039AEasy to operateEasy to implementMaterial magnetic variablesPower stationSaturation pulse
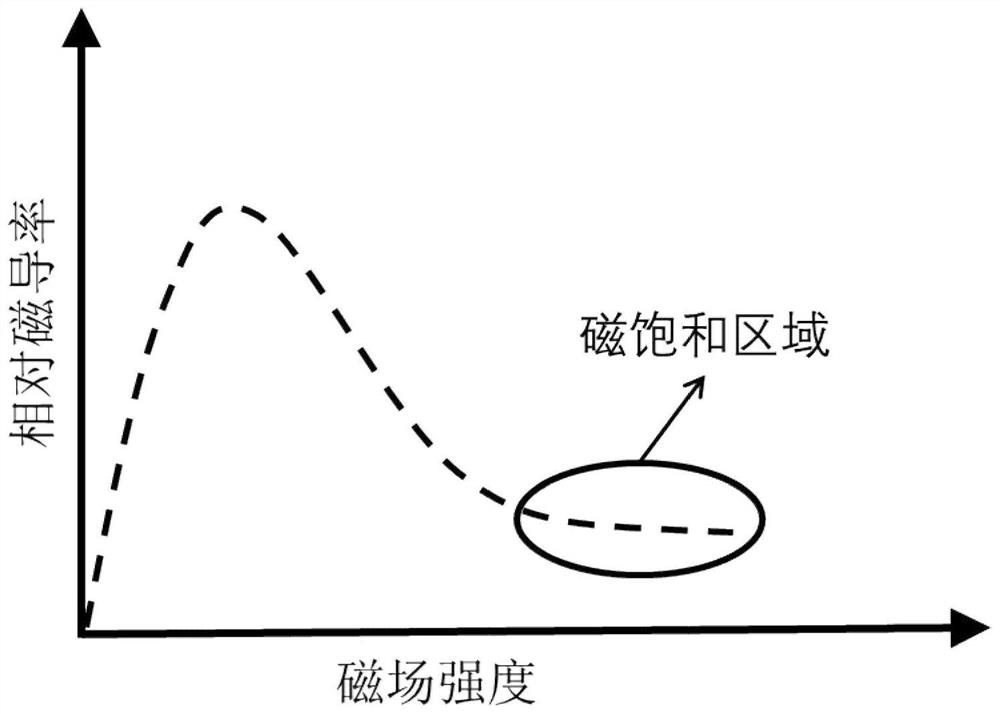
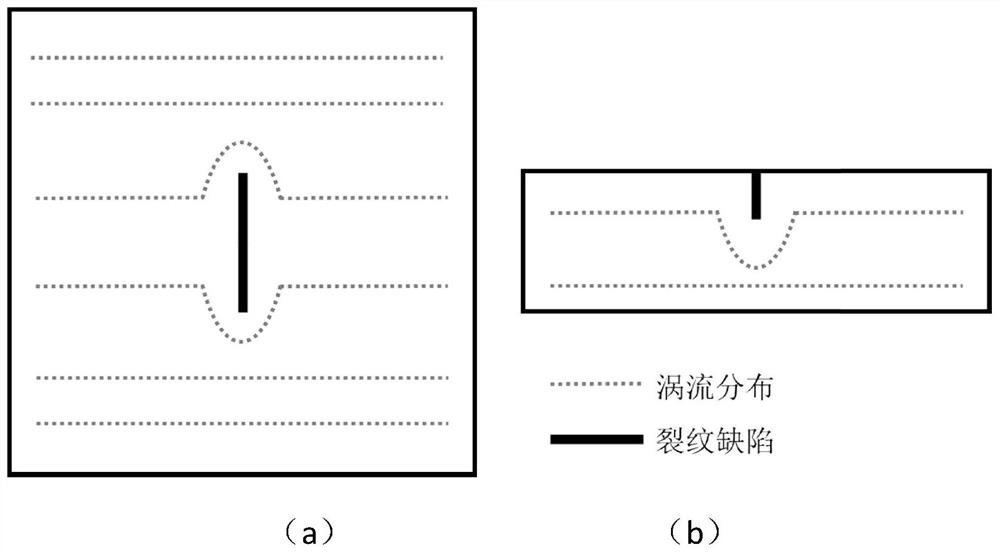
The invention discloses a ferromagnetic pipeline quantitative lossless evaluating method based on nonlinear magnetic saturation pulsed eddy current. An electromagnet coil is conducted with high direct current to form a strong static magnetic field so that a detected object can be magnetically saturated, pulse excitation and pulse signal detection are finished on a TR type pulsed eddy current probe when the detected object is in the magnetic saturation state, and quantitative lossless evaluating on the local thinning defect in a ferromagnetic pipeline is achieved based on a magnetic saturation pulsed eddy current nonlinear efficient direct problem signal simulation method and a defect reconstruction inverse problem algorithm. The method has the advantages of being free of contact, easy to achieve and operate, high in detecting efficiency and the like and can be widely applied to the quantitative lossless evaluating on the local thinning defect of a large number of ferromagnetic material pipeline containers used in a power station, chemical engineering and other structures.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
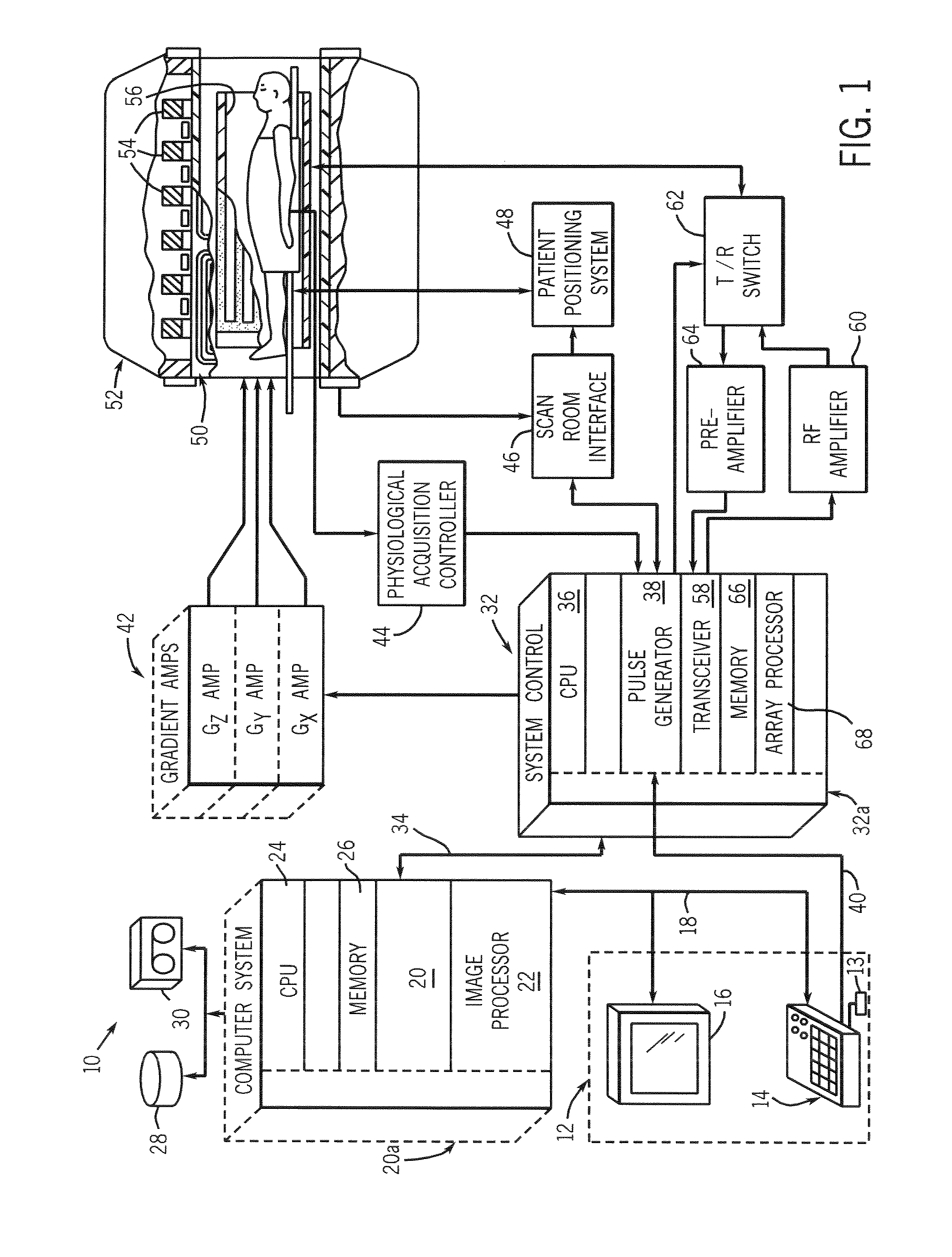
Method and apparatus for generating a magnetic resonance image
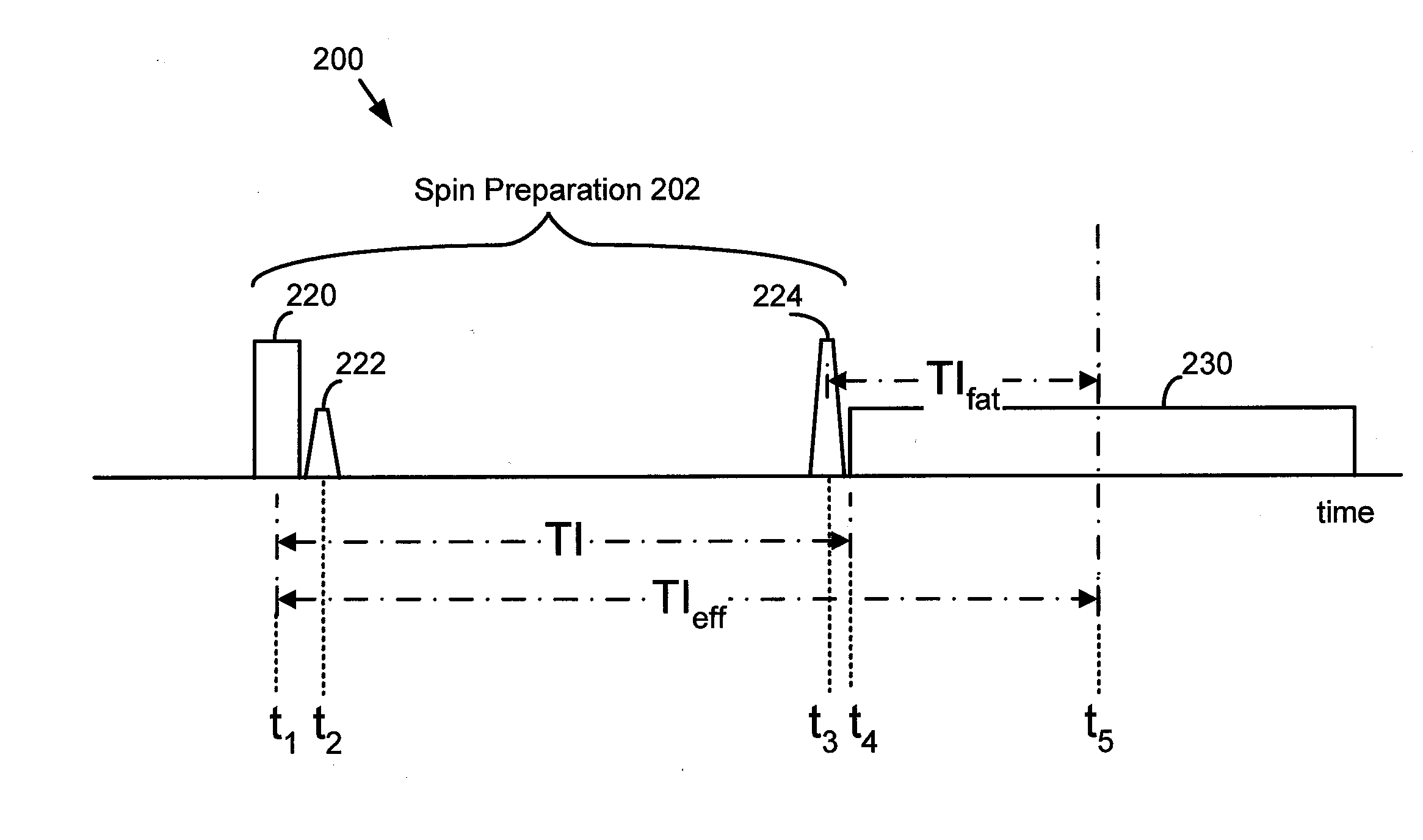
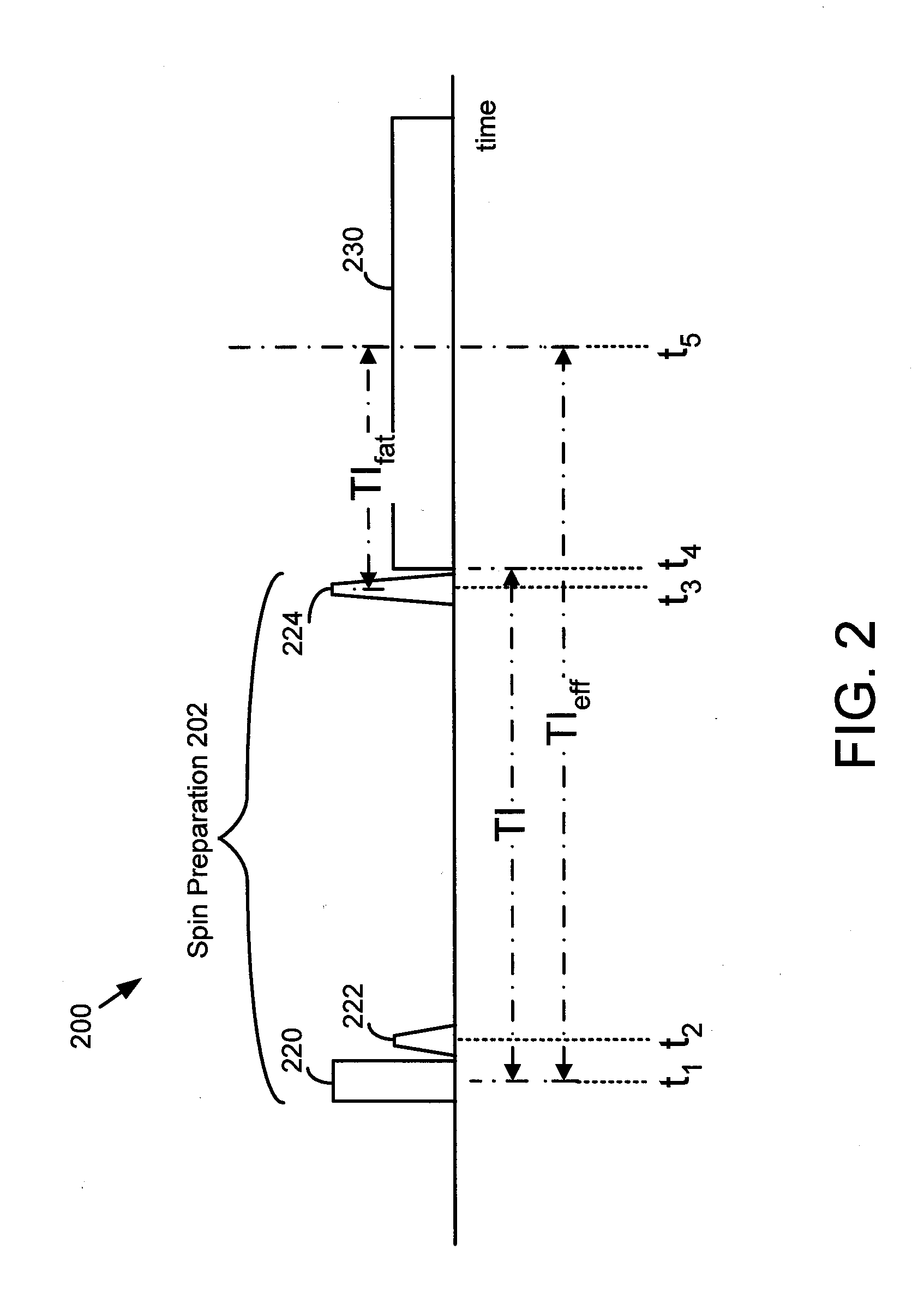
A method for generating a magnetic resonance image includes a series of inversion and saturation pulses, in which the pulses null the MRI signal from both fat and a second tissue for a single MRI acquisition. An inversion pulse is used to provide a null point for the second tissue. A pair of fat-selective saturation and inversion pulses are used to null the MRI signal from fat at approximately the same time as the second tissue reaches its null point. The saturation pulse is used to create a known state for the fat magnetization, allowing the flip angle of the fat-selective inversion pulse to be determined such that the null point of fat approximately coincides with the null point of the second tissue.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method of simultaneous fat suppression, magnetization transfer contrast, and spatial saturation for 3D time-of-flight imaging
ActiveUS7330028B2Improve image qualityIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionImaging quality
A pulse sequence for time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) includes a fatsat segment, a magnetization transfer segment, and a spatial saturation segment that are applied by an MR apparatus to acquire MR data for image reconstruction with improved image quality. The pulse sequence is constructed such that at the beginning of each iteration of the inner loop of a 3D acquisition, a fatsat pulse is applied. After the fatsat pulse, MR data is acquired in a series of imaging segments with well-suppressed fat signal. Effective fat suppression is achieved by sampling central k-space data first, before signal from fat relaxes back to a pre-saturation level. Each imaging segment is immediately preceded by one of a MT pulse or a spatial saturation pulse and immediately followed by the other one of the MT pulse or the spatial saturation pulse.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
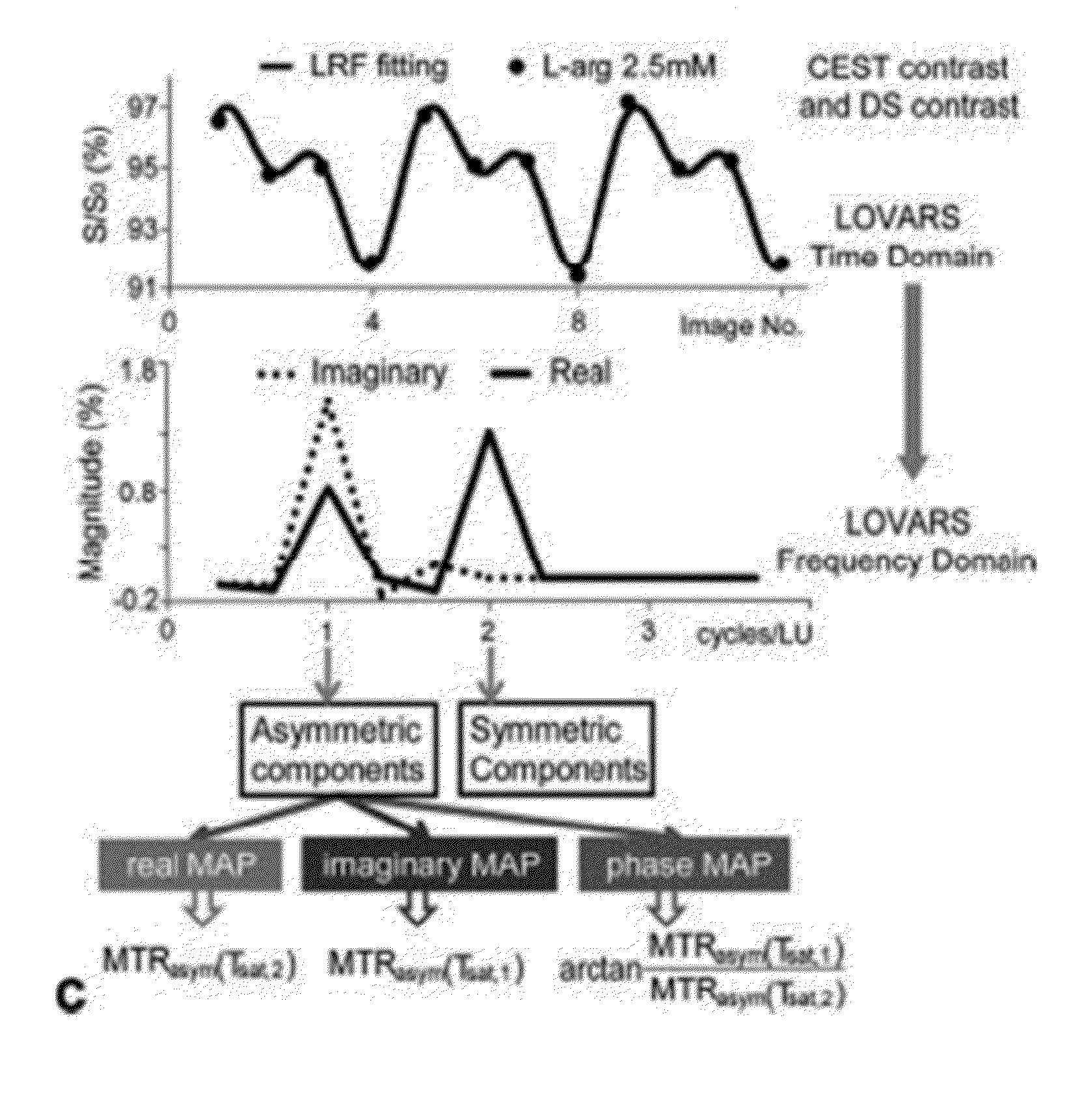
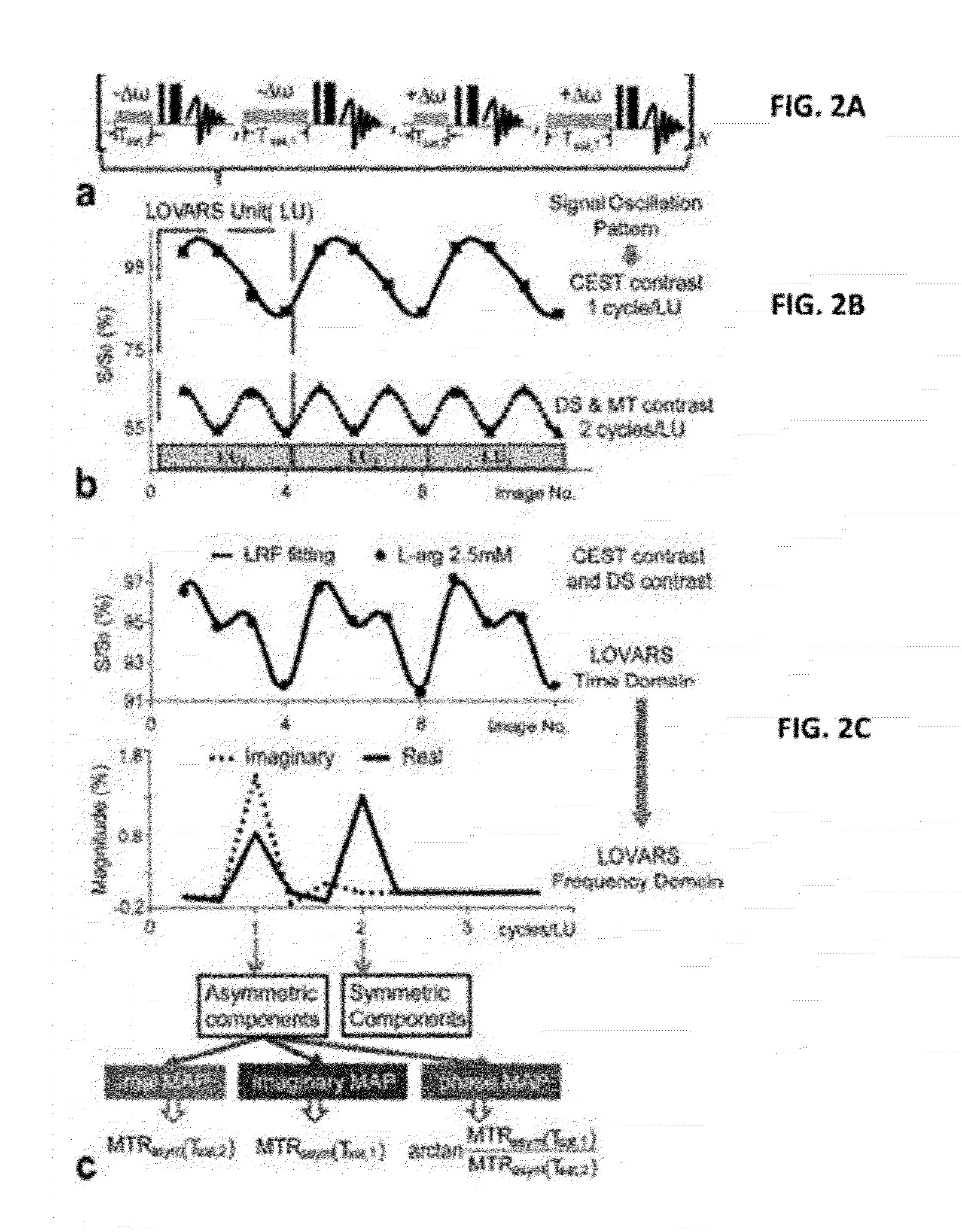
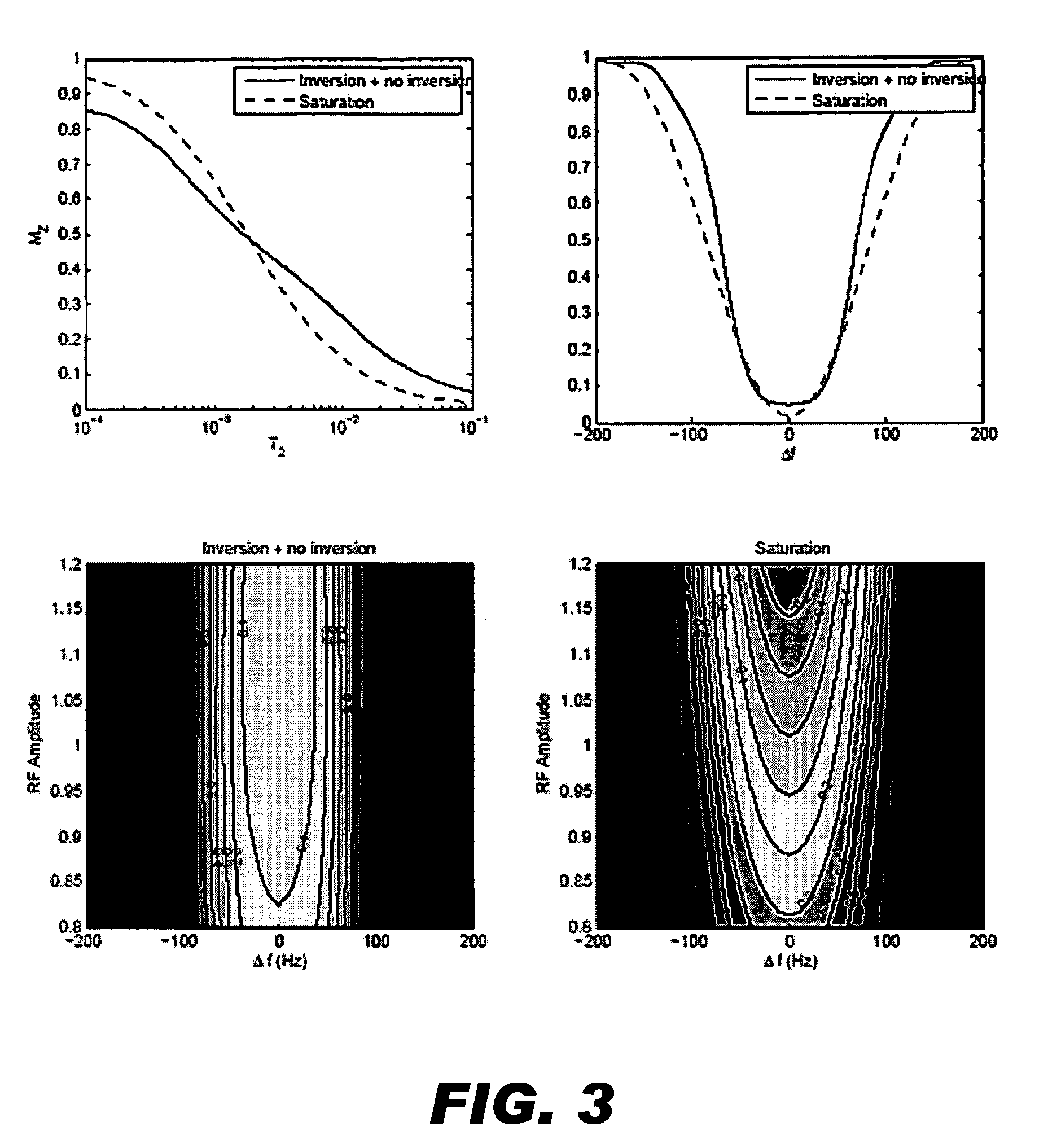
CEST Phase and Magnitude Imaging Using a Multi-Parametric Varied Saturation Scheme
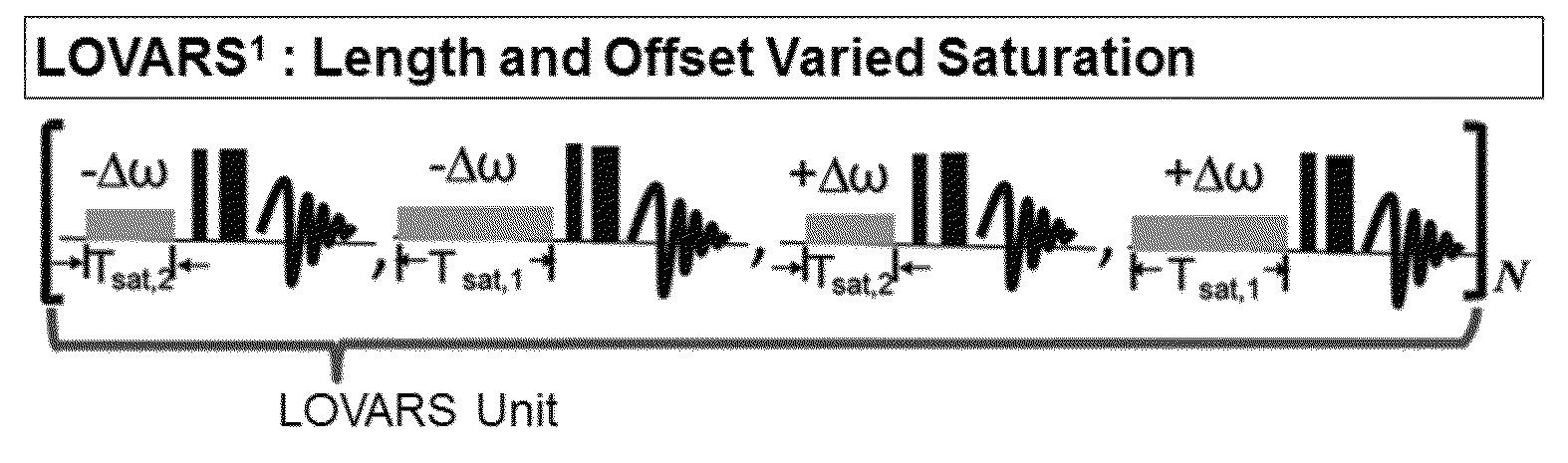
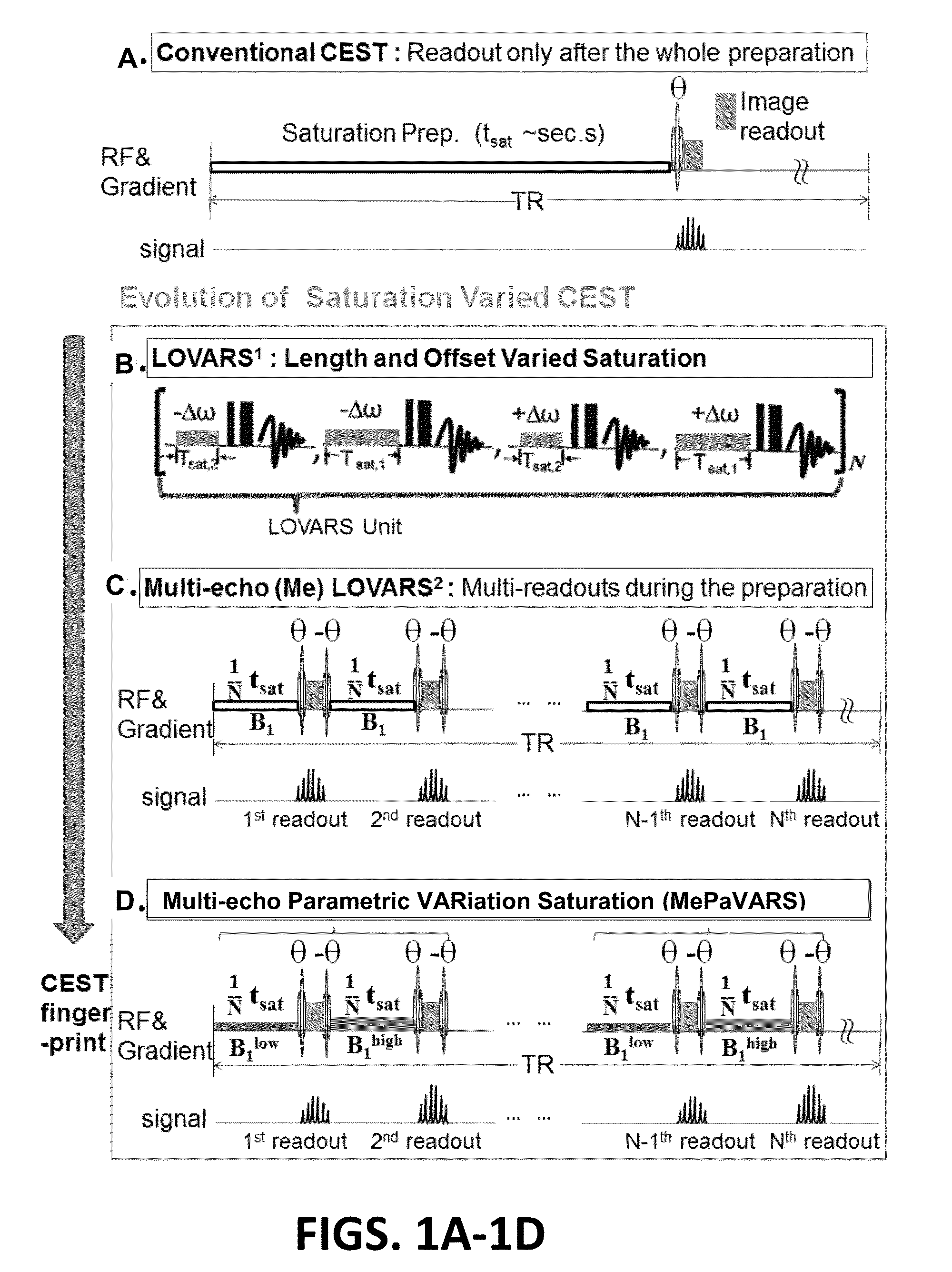
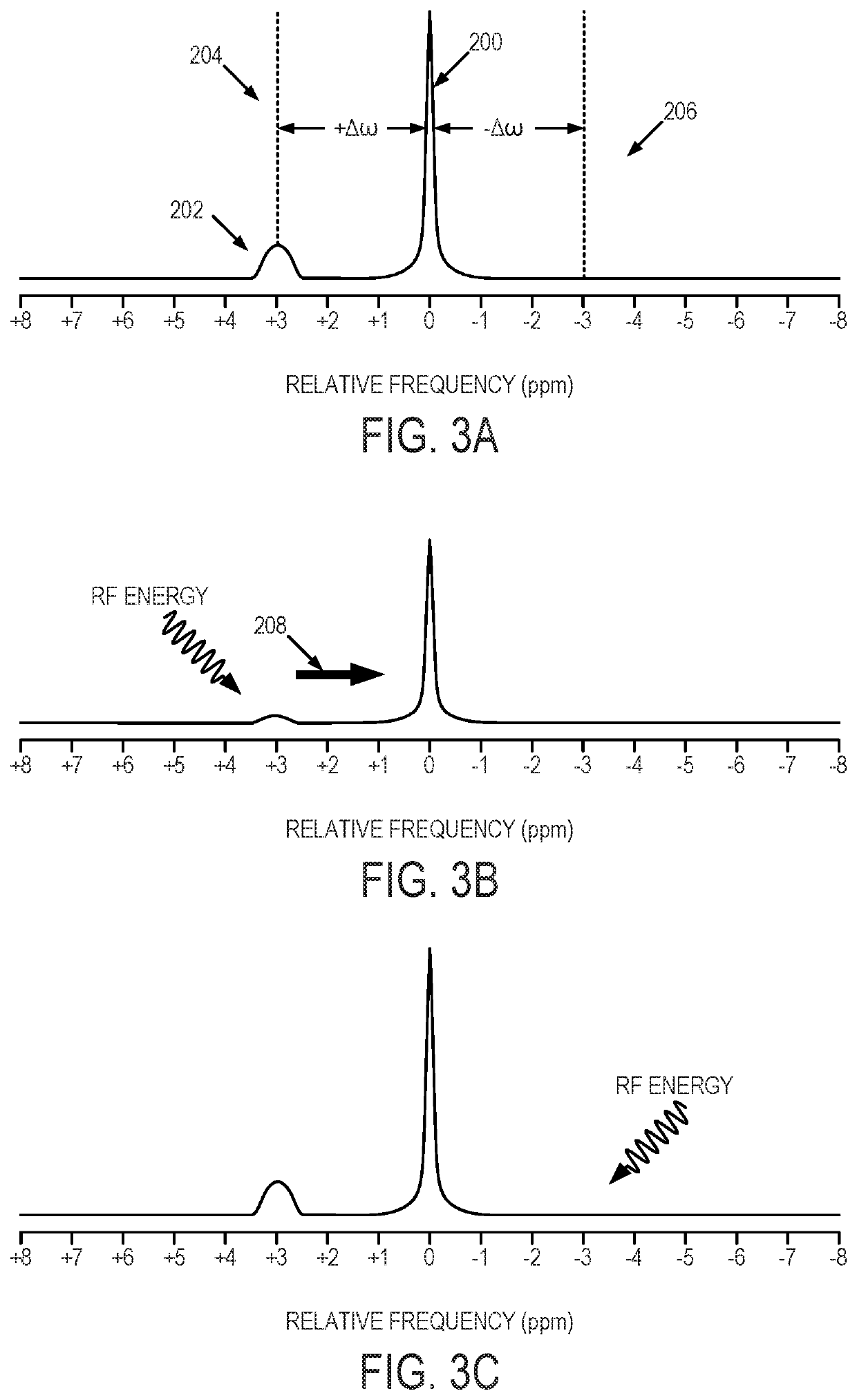
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for obtaining a magnetic resonance image (MRI) or spectrum. The method includes a step of performing a chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) or magnetization transfer (MT) magnetic labeling experiment of a subject using an MRI machine. When performing the CEST or MT magnetic labeling experiment aspects of a saturation pulse or a serial saturation pulse sequence, such as length (tsat), number (Nsat), offset (Δω), modulation frequency (ωs) and power (B1) can be varied in specific-designed schemes. Data is generated from the CEST magnetic labeling experiment and is transmitted to a data processing unit. The data is processed to generate a visual representation of the data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Mr imaging using apt contrast enhancement and sampling at multple echo times
ActiveUS20150051474A1Improved MR imaging techniqueHigh-quality and high contrast-to-noise MR imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientContrast enhancement
The invention relates to a method of CEST or APT MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) placed in a main magnetic field B0 within the examination volume of a MR device. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: •a) subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a saturation RF pulse at a saturation frequency offset; •b) subjecting the portion of the body (10) to an imaging sequence comprising at least one excitation / refocusing RF pulse and switched magnetic field gradients, whereby MR signals are acquired from the portion of the body (10) as spin echo signals; •c) repeating steps a) and b) two or more times, wherein the saturation frequency offset and / or a echo time shift in the imaging sequence are varied, such that a different combination of saturation frequency offset and echo time shift is applied in two or more of the repetitions; •d) reconstructing a MR image and / or B0 field homogeneity corrected APT / CEST images from the acquired MR signals. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) for carrying out the method of the invention and to a computer program to be run on a MR device.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
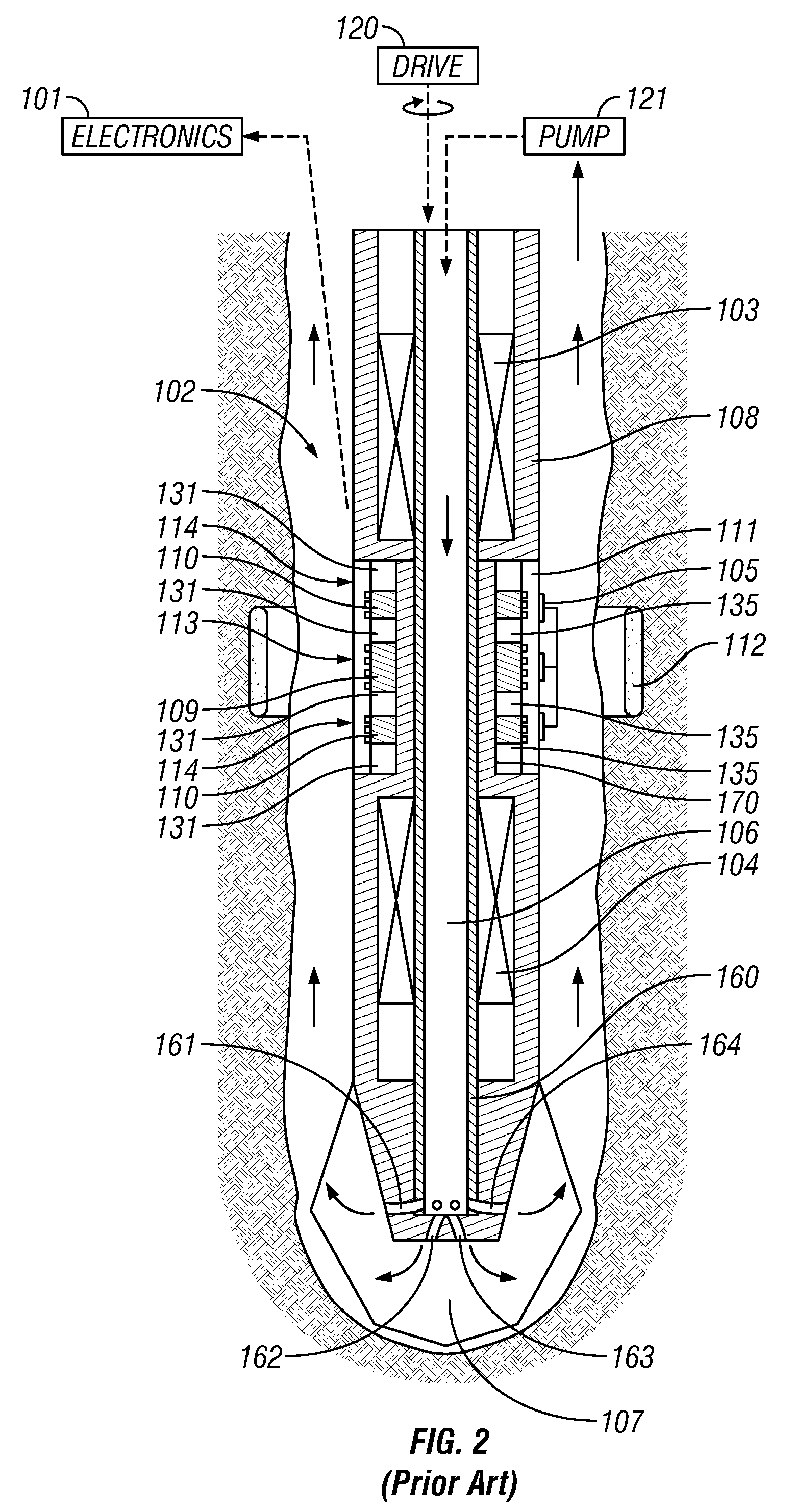
Method and Apparatus for NMR Saturation
ActiveUS20090058416A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpinsSaturation pulse
Saturation pulse sequences are designed to ensure complete saturation of nuclear spins for dual wait time measurements and saturation recovery measurements in the case of axial motion of a downhole NMR logging tool. Frequency and / or phase modulation may be used. An auxiliary saturation coil may be used.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveCN102143707ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSaturation pulseLocal selection
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveCN108209918ASolve the problem of incomplete suppressionQuality improvementDiagnostic signal processingSensorsResonanceSaturation pulse
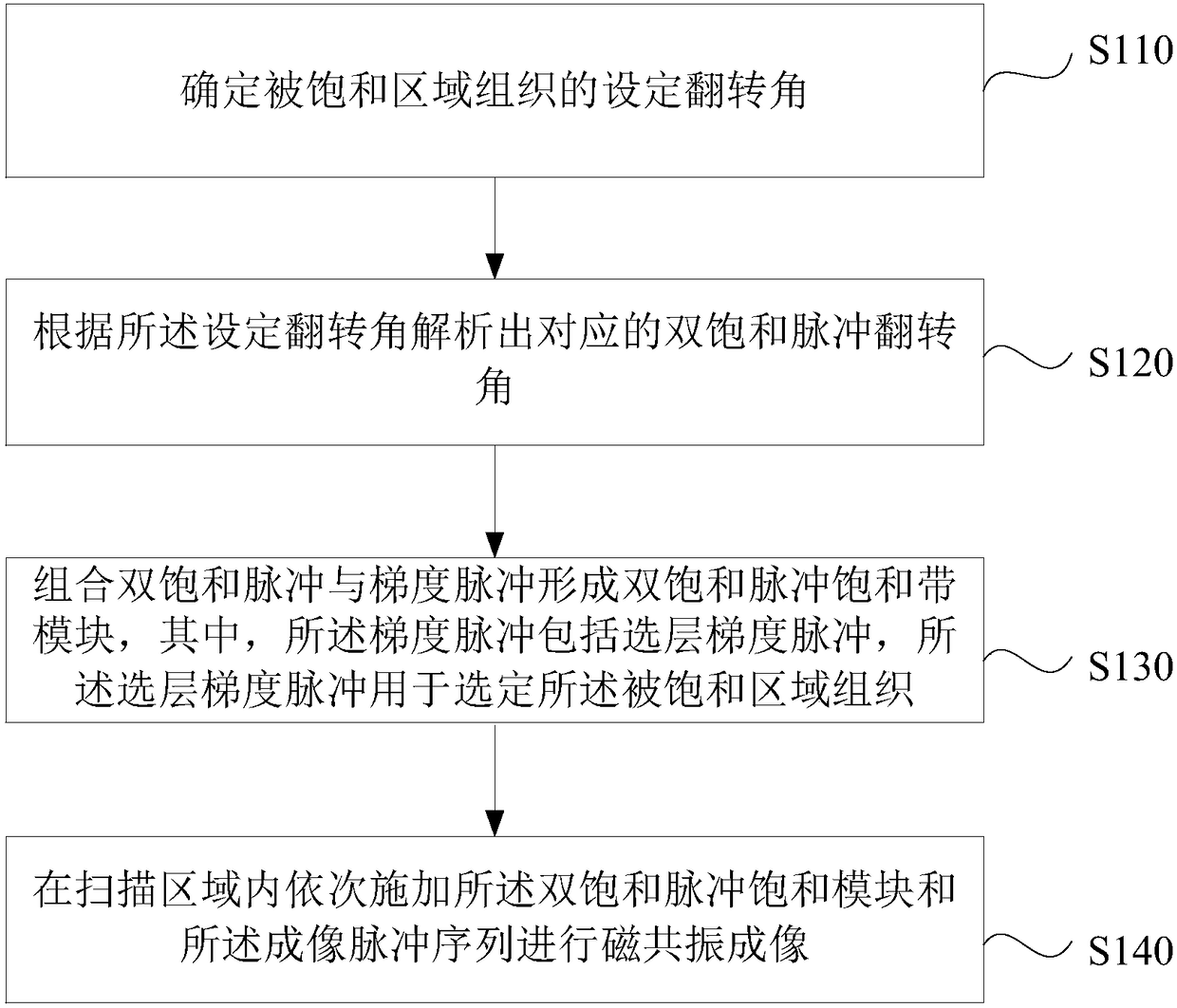
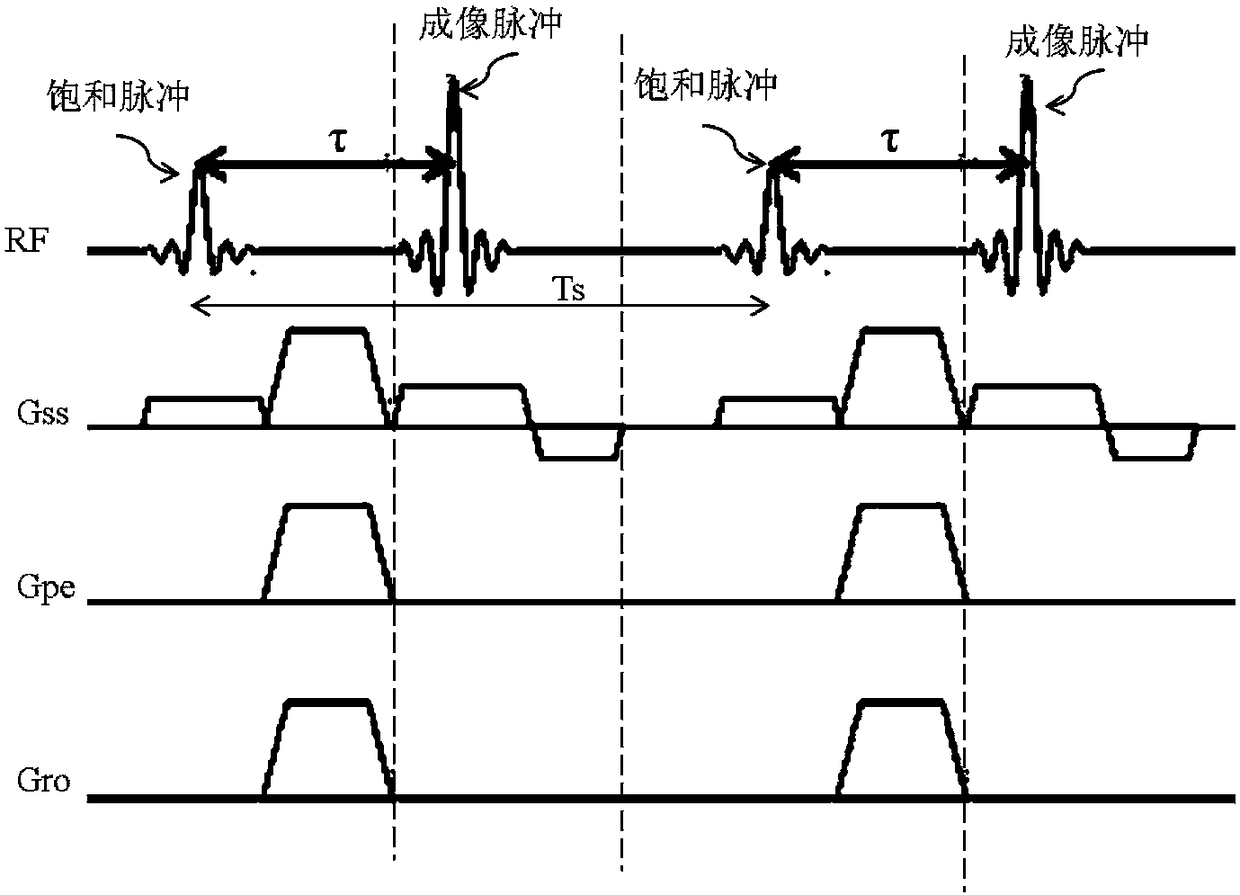
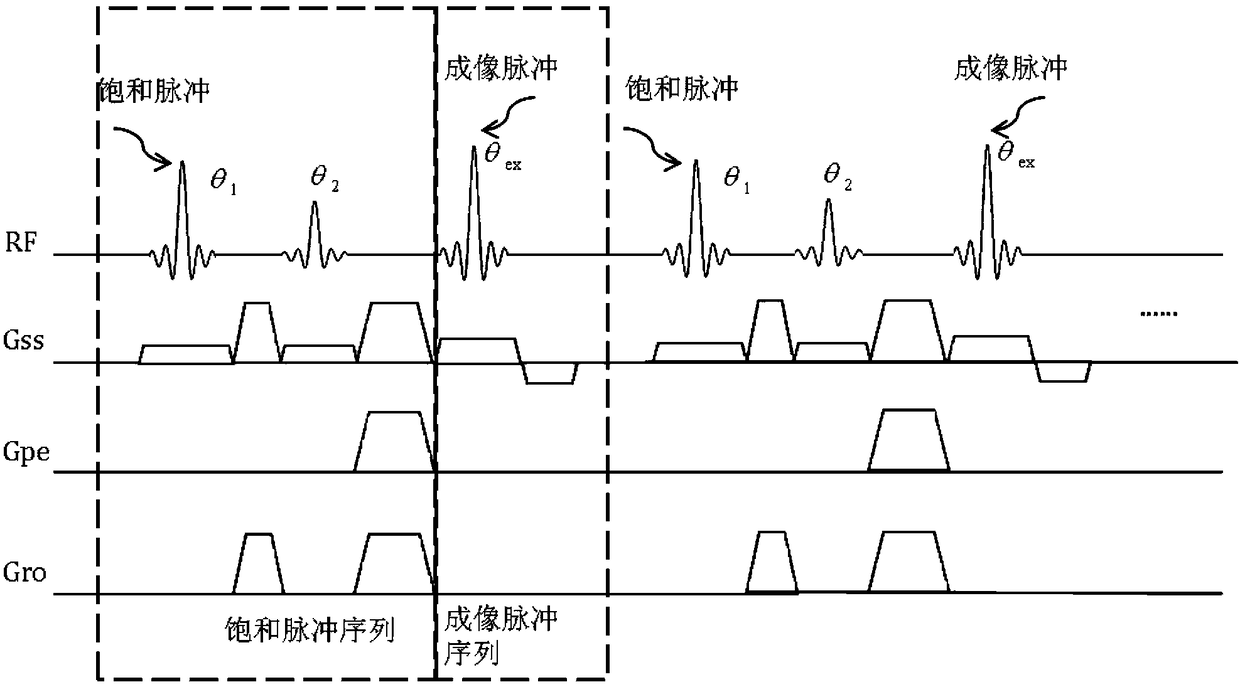
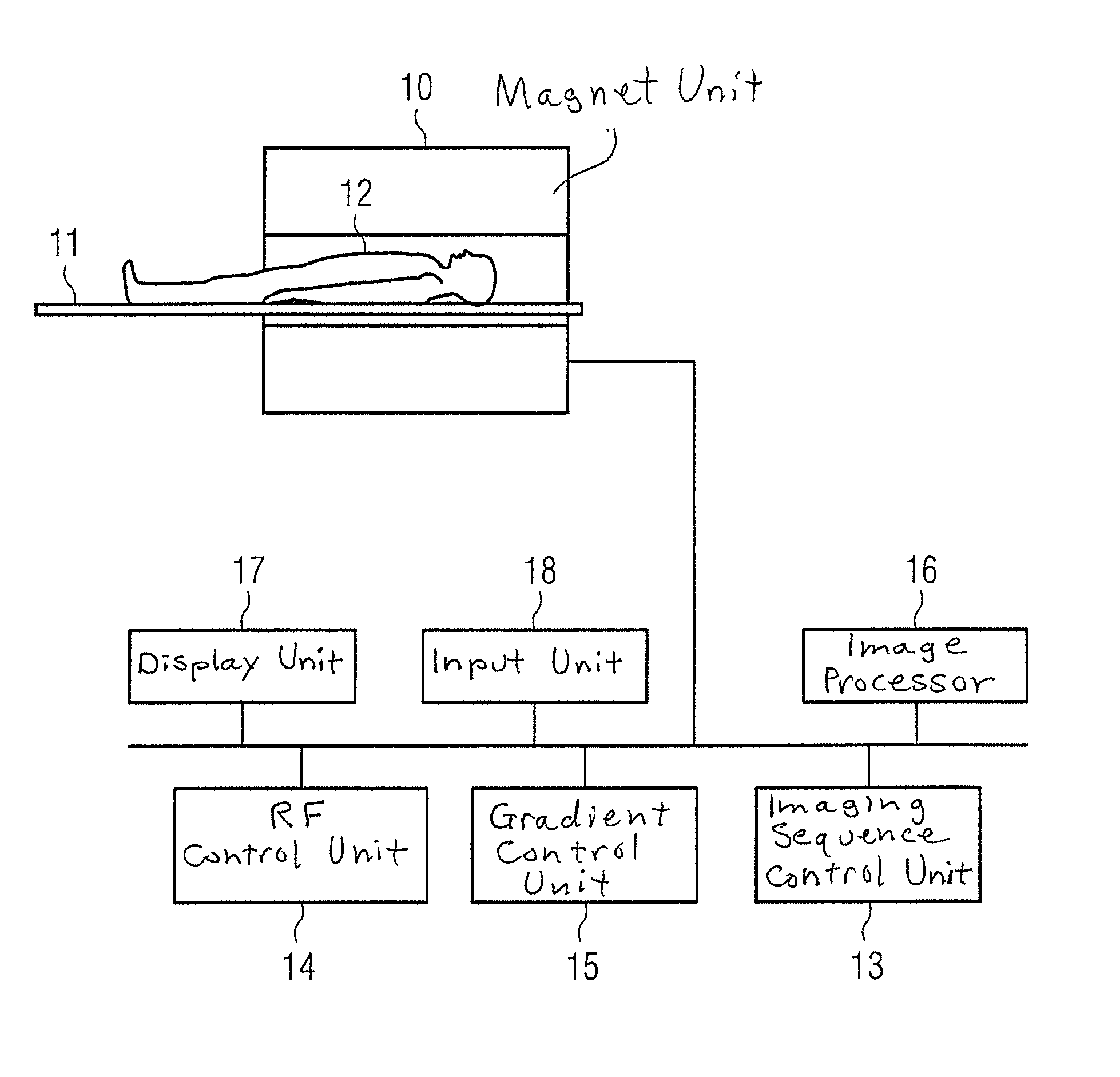
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method and system, wherein the method comprises: before imaging scanning, determining a preset deflection angle of a radio frequency pulse to excite specific tissues; analyzing a corresponding dual-saturated pulse deflection angle according to the preset deflection angle; combining a dual-saturated pulse and a gradient pulse to form a dual-saturated pulse saturation module, wherein the gradient pulse includes a layer-selecting gradient pulse that is used for exciting a corresponding layer of the specific tissues; executing an imaging scanning process, to be specific, applying the dual-saturated pulse saturation module and an imaging pulse sequence sequentially to a scanning area to perform magnetic resonance imaging. By carrying out magnetic resonance imaging through the dual-saturated pulse saturation module and the imaging pulse sequence, saturated band signal inhibition non-uniformity due to non-uniformity of B1 field can be overcome, and motion artifacts due to organ motion, tissue motion and other motions can be inhibited.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
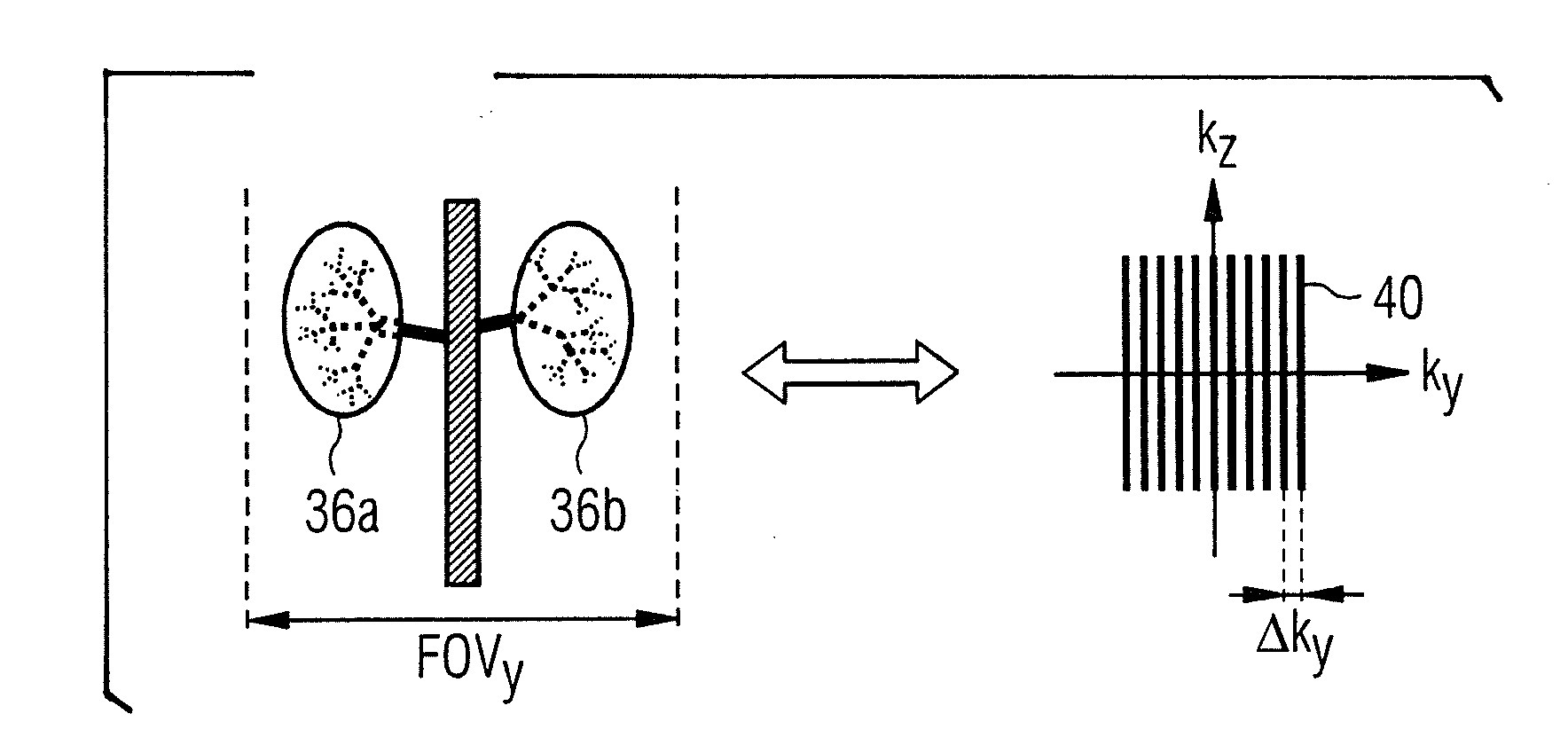
Mr-angiography with non-cartesian signal acquisition
ActiveUS20130006098A1Lengthening measuring time periodImprove spatial resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinsSaturation pulse
In a method and apparatus for the creation of an MR image of a vascular structure of an examination region, the spins in the examination region are saturated by the irradiation of at least one RF saturation signal, which delivers a lower signal intensity as spins in a subsequent MR signal recording for the creation of the MR angiographic image, which flow through at least one blood vessel into the examination region, and are not saturated by the RF saturation pulse. Raw data space of the MR angiographic image is read out with a non-Cartesian trajectory in the MR signal acquisition for the creation of the MR angiographic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging system
ActiveCN105572613AHigh strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceData acquisition
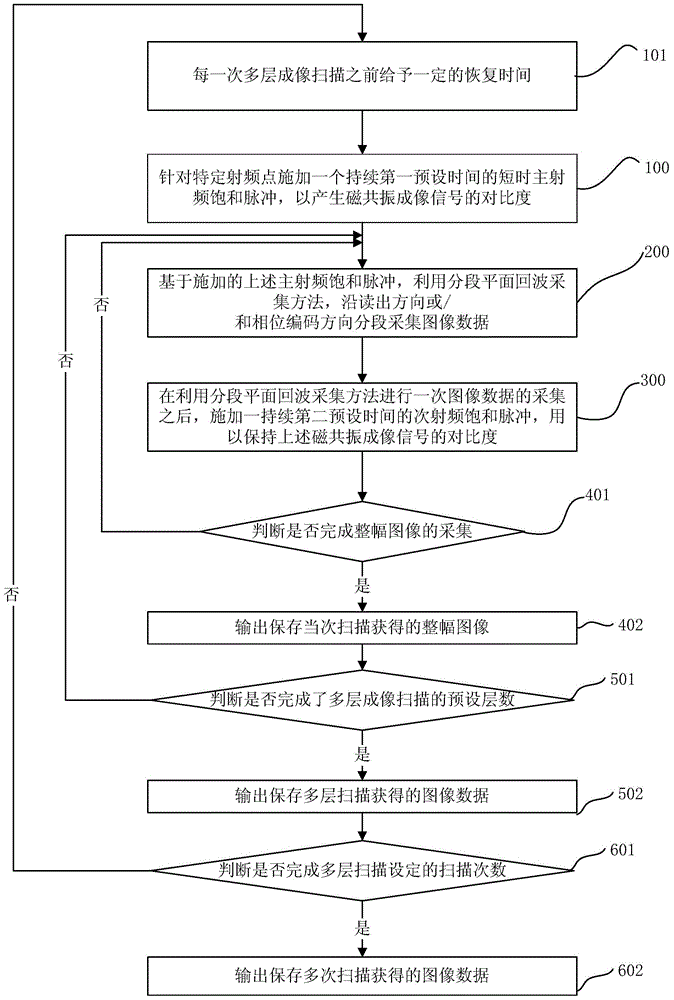
The invention provides a magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and a magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging system. The magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method comprises a main RF pulse generating step, applying a short-time main RF saturation pulse which lasts for a first preset time for aiming at a specific RF point, thereby generating the contrast of a magnetic resonance imaging signal; an image acquisition step, segmentally acquiring image data in a reading-out direction or / and a phase encoding direction based on the applied main RF saturation pulse by means of a segmental planar echo acquisition method; and a sub-RF pulse generating step, after one-time image data acquisition by means of the segmental planar echo acquisition method, applying a sub-RF saturation pulse which lasts for a second preset time, thereby keeping the contrast of the magnetic resonance imaging signal. The magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging method and the magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging system settle problems of low signal sensitivity and low imaging efficiency in existing magnetic resonance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
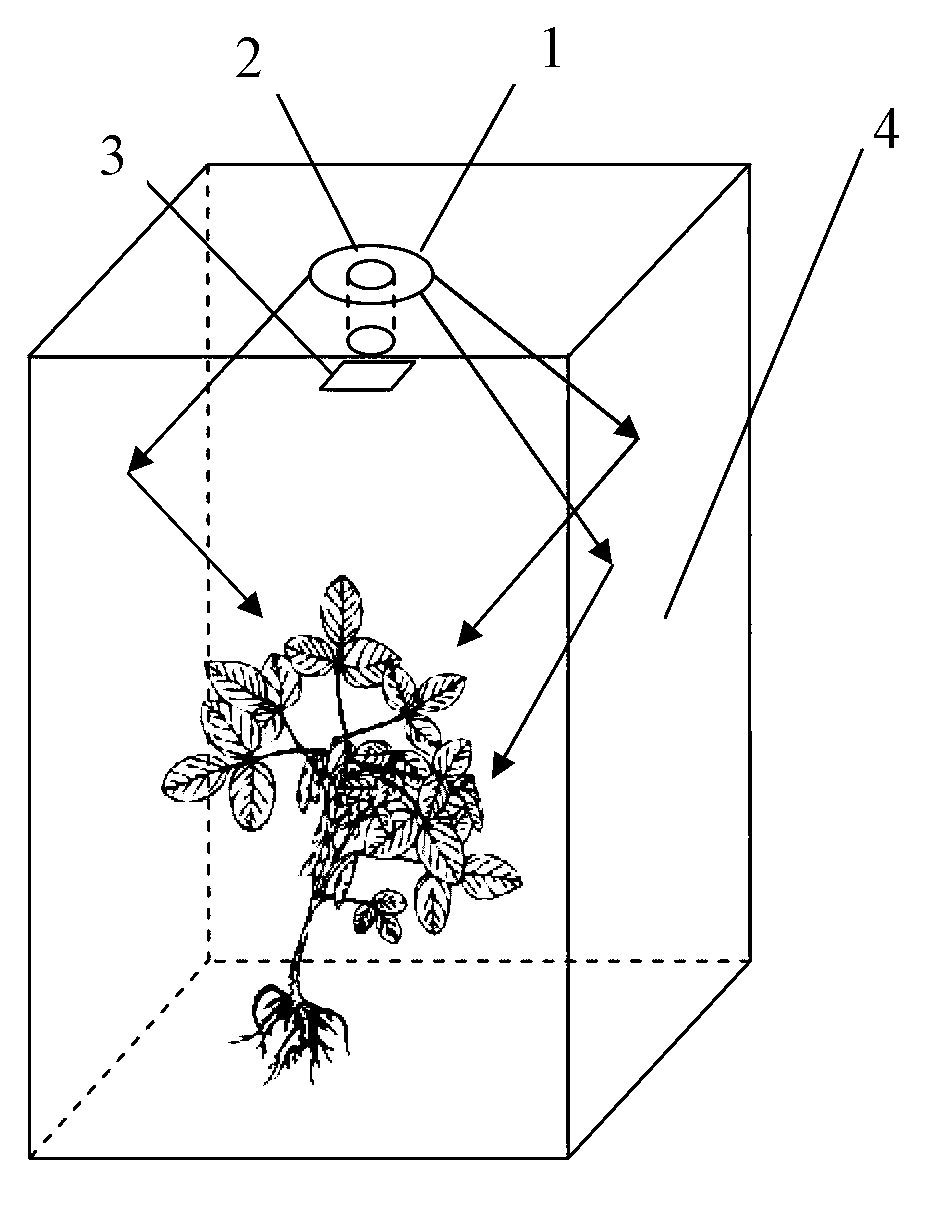
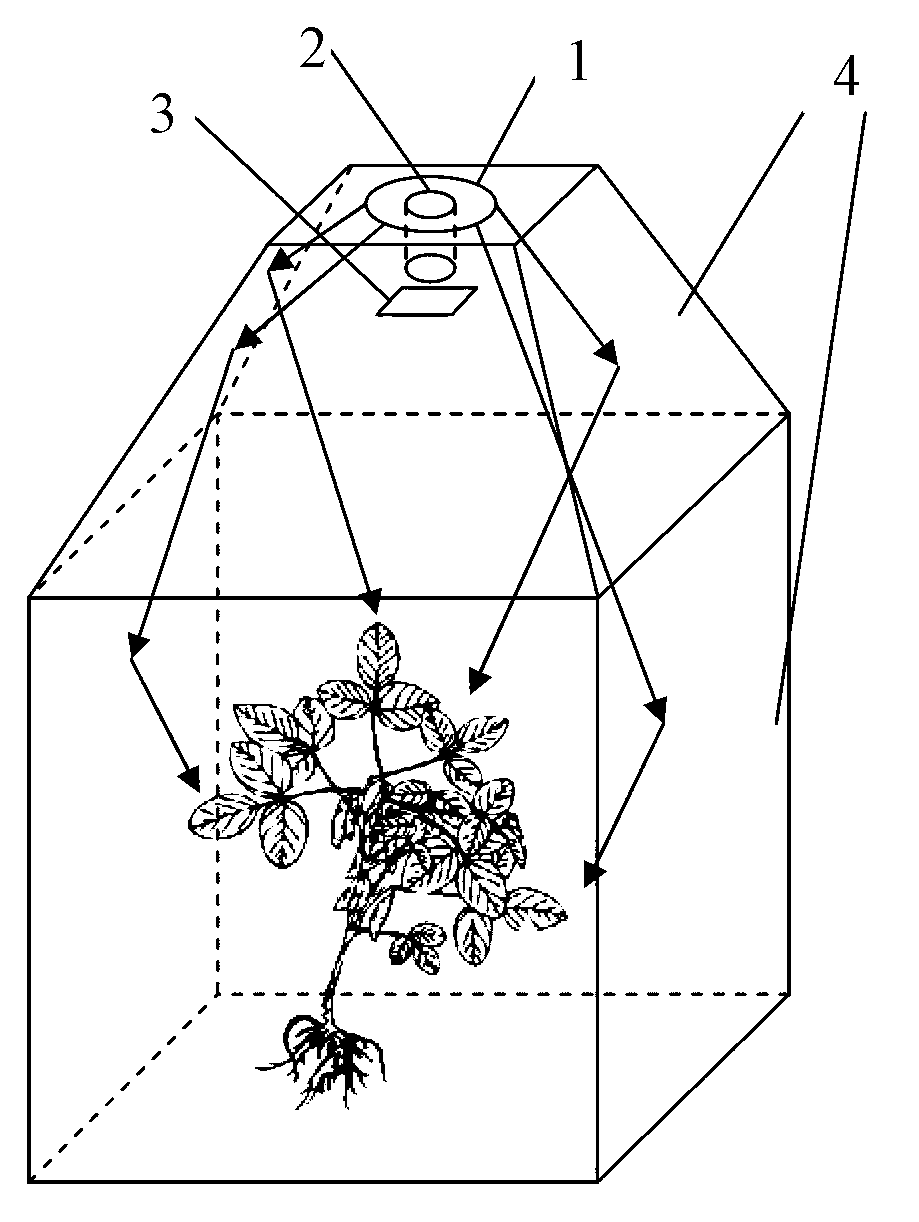
Plant chlorophyll fluorescence detecting device for equalizing irradiation
InactiveCN103018221AUniform lightFluorescence/phosphorescenceArbitrary Fluorescence UnitLight reflection
The invention discloses a plant chlorophyll fluorescence detecting device for equalizing irradiation. The plant chlorophyll fluorescence detecting device for equalizing irradiation comprises a light source, a camera, a light filler and a light reflection mirror, wherein the light source is used for transmitting detection light for a to-be-detected sample; the camera is used for collecting light rays from the to-be-detected sample; the light filler is arranged between the camera and the to-be-detected sample; and the light reflection mirror is used for reflecting detecting light from the light source to the to-be-detected sample. The plant chlorophyll fluorescence detecting device for equalizing irradiation provided by the invention can provide three kinds of irradiation including measurement light, saturation pulse light and actinic light; the light emitted by the light source is reflected by the light reflection mirror; and a space with equal irradiation is formed in the device, so that irradiation imaging can be carried out on laminas of plants with different heights.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
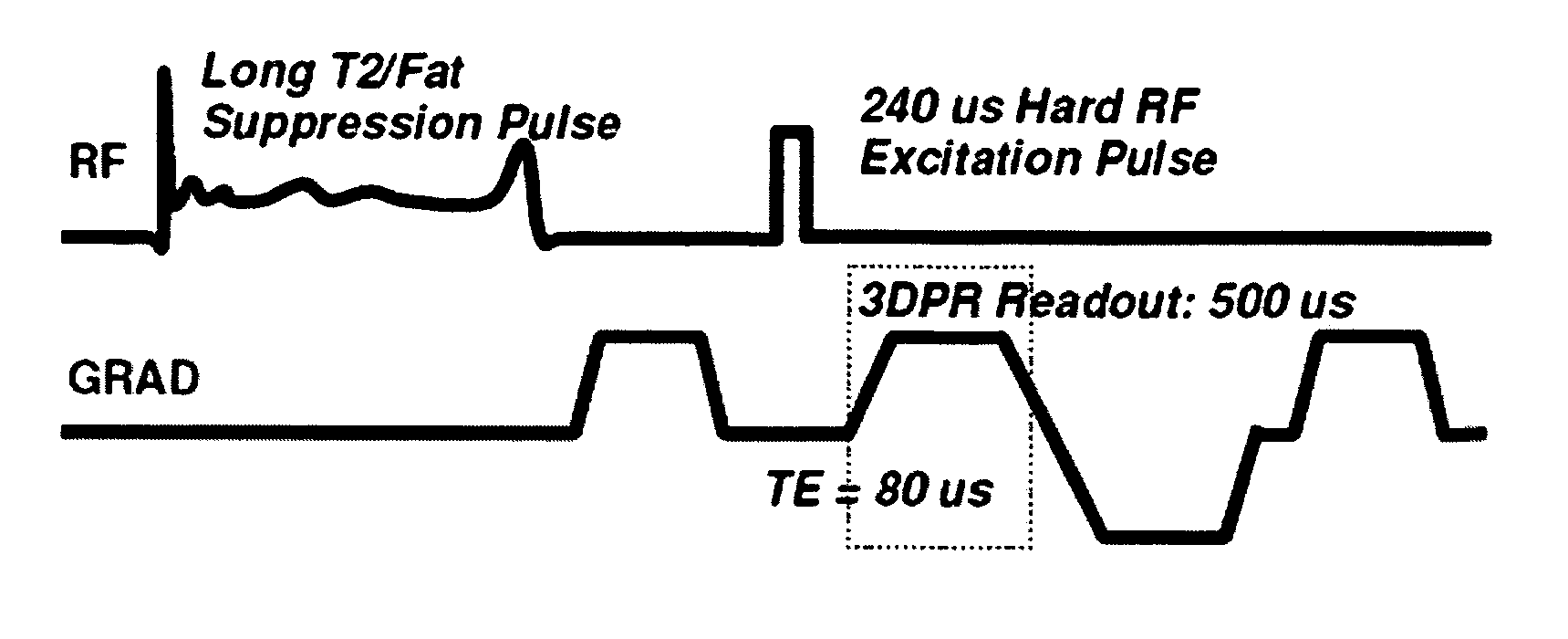
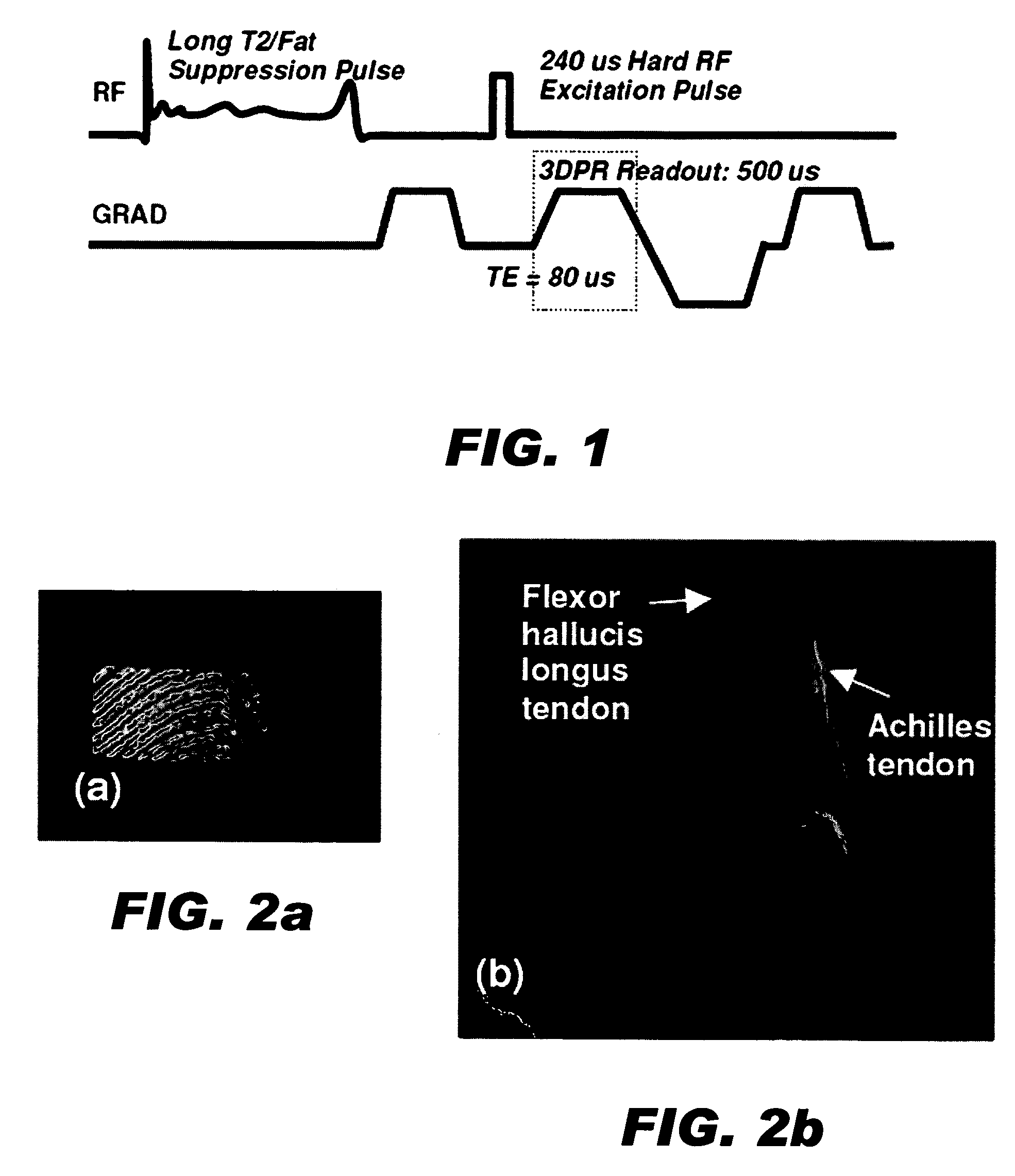
RF pulses for long T2 suppression in MRI
ActiveUS7288936B2Minimal interferenceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse planePulse sequence
In imaging a first species having a short T2 magnetic resonance parameter in the presence of a second and third species having longer T2 parameters, a method of suppressing signals from the longer T2 species comprises the steps of: a) applying a RF saturation pulse with multiple suppression bands for the second and third species to excite nuclei spins of the longer T2 species with the magnitude of the RF pulse being sufficiently low so as not to excite nuclei spins of the short T2 species, the RF saturation pulse being sufficiently long to rotate the longer T2 species nuclei spins into a transverse plane, and b) dephasing the longer T2 species nuclei spins in the transverse plane. An imaging pulse sequence is then applied to image the short T2 species. Alternatively, the method can comprise the steps of a) applying a first inversion pulse for selective inverting species of the second longer T2 species, b) obtaining first image signals after step a, c) applying a second inversion pulse for selectively inverting species of the third longer T2 species, d) obtaining second image signals after step c), and e) combining the first image signals and the second image signal to image the first short T2 species with the longer second and third species cancelling in the combination. In each of these methods, either the second or third longer T2 species can be suppressed without suppressing the other by applying the RF saturation or inversion pulse only to the species to be suppressed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
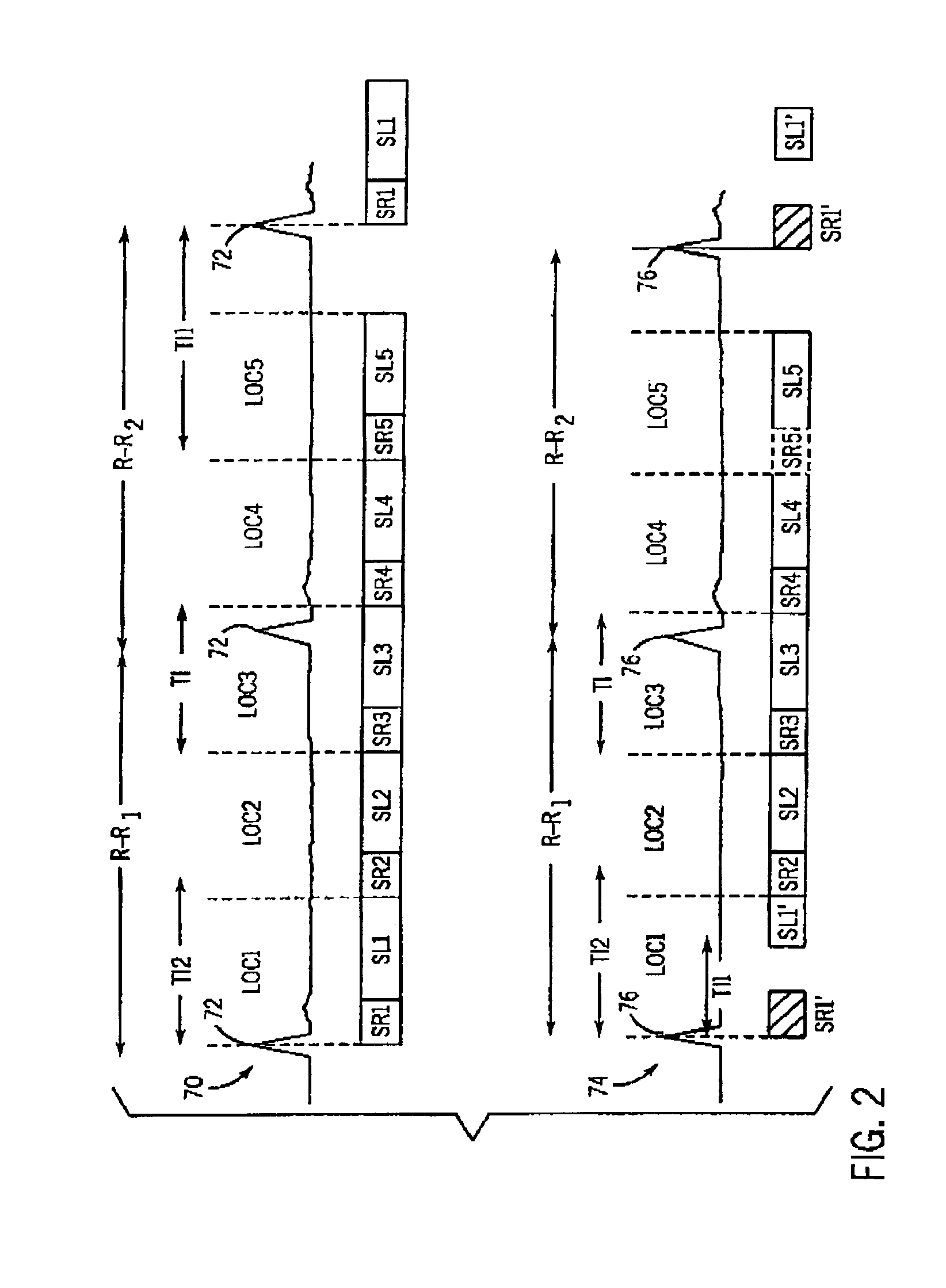
Method and apparatus for MR perfusion image acquisition using non-selective and notched RF saturation pulses
InactiveUS6903548B2Addressing Insufficient CoverageImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSaturation pulseBlood pool
A non-selective saturation pulse together with a series of notched RF saturation pulses are used to acquire MR perfusion data. The non-selective saturation recovery RF pulse is non-selective and is designed to be effective at blood pool suppression for a first slice as well as a next slice in a series of slice locations. The first slice. location may be placed at an angle or plane that is not necessarily coaxial with the other slice locations to be imaged. The present invention supports the acquisition of MR data with efficient spatial coverage and a calibration slice of data that provides a linear measure of signal intensity versus contrast concentration in a blood pool.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
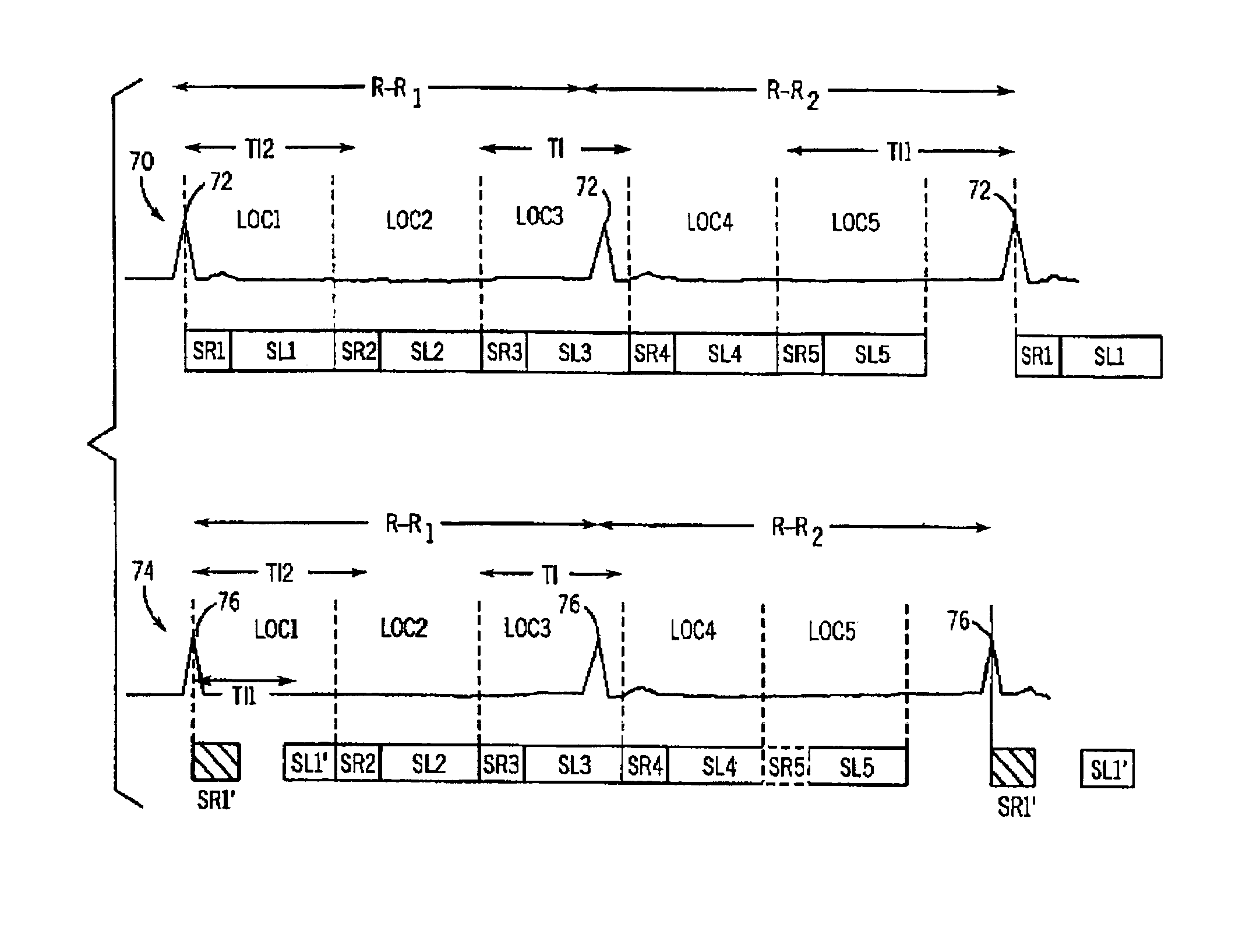
System and methods for active suppression of superior tagging in flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery
InactiveUS20100164496A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionInversion recoverySaturation pulse
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for suppression of venous artifacts from superior tagging in flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery. The systems may include an image capture device and a controller. The controller may be configured to cause the image capture device to perform a labeling experiment, capture a first image of a slice of body tissue, perform a control experiment, and capture a second image of the slice of body tissue. The systems may be configured to perform a ninety (90) degree RF saturation pulse directed to a portion of body tissue that is superior to the first slice of body tissue imaged during at least one of the labeling experiment and / or the control experiment, and to apply a spoiler gradient subsequent to the saturation pulse during at least one of the labeling experiment and / or the control experiment.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Apparatus and method of simultaneous fat suppression, magnetization transfer contrast, and spatial saturation for 3D time-of-flight imaging
ActiveUS20070069724A1Improve image qualityEffective applicationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionImaging quality
A pulse sequence for time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) includes a fatsat segment, a magnetization transfer segment, and a spatial saturation segment that are applied by an MR apparatus to acquire MR data for image reconstruction with improved image quality. The pulse sequence is constructed such that at the beginning of each iteration of the inner loop of a 3D acquisition, a fatsat pulse is applied. After the fatsat pulse, MR data is acquired in a series of imaging segments with well-suppressed fat signal. Effective fat suppression is achieved by sampling central k-space data first, before signal from fat relaxes back to a pre-saturation level. Each imaging segment is immediately preceded by one of a MT pulse or a spatial saturation pulse and immediately followed by the other one of the MT pulse or the spatial saturation pulse.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method for reducing unnecessary contrast
ActiveUS20150355304A1Reducing unnecessary contrastHigh quality imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRecovery periodResonance
In multi-echo imaging, in imaging in which pulses other than a 180° pulse are included in refocus RF pulses, a high-quality image in which the intended contrast is emphasized is obtained by reducing unnecessary contrast. Therefore, imaging parameters are adjusted so as to reduce the unnecessary contrast. The adjustment is performed so that, for echo signals from tissues having the same relaxation time to cause intended contrast among echo signals from a plurality of tissues having different relaxation times, the difference between the signal strengths of echo signals to determine the contrast, such as echo signals at the k-space center, is reduced. Imaging parameters to be adjusted include a repetition time, the FA of a DE pulse, the FA of a saturation pulse, the application timing of the saturation pulse, the application strength of a gradient magnetic field in a recovery period, application timing, and the like.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Multi-echo parametric variation saturation (mepavars) for cest imaging and other mr imaging
ActiveUS20160187445A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSaturation pulseImaging agent
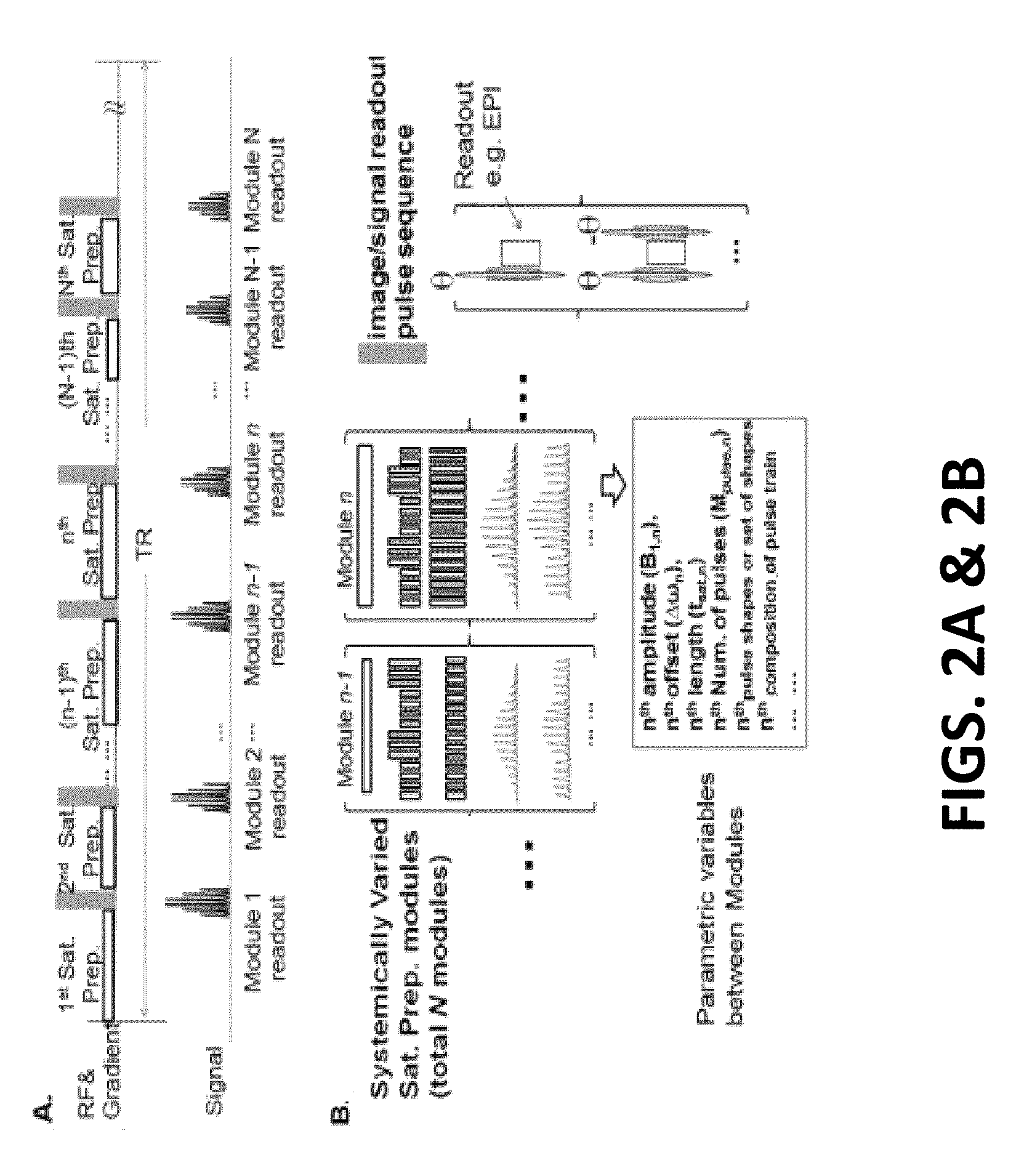
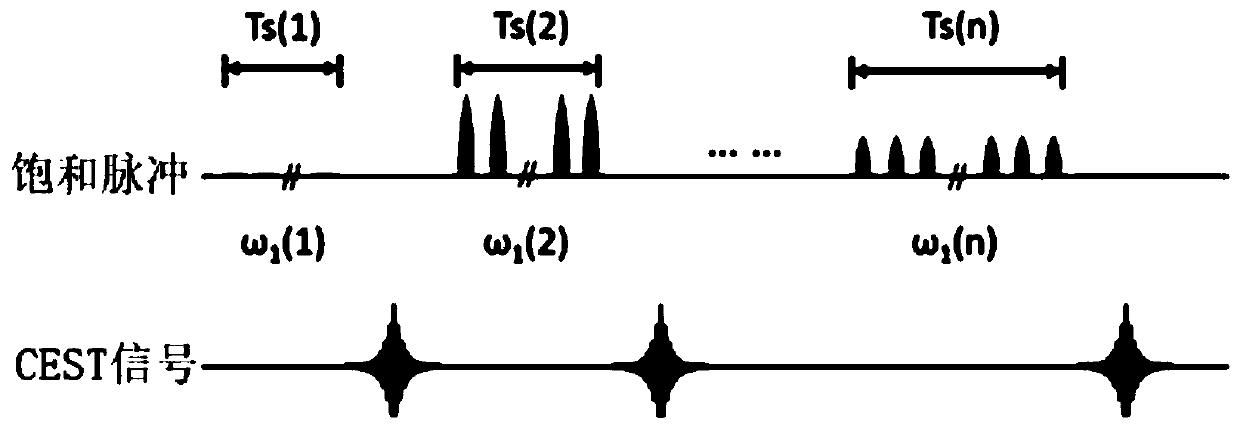
The present invention provides a novel approach for CEST MR imaging, called Multi-echo Parametric VARiation Saturation (Me-PaVARS) CEST. This method places multiple image readouts in between a series of saturation pulses. The saturation pulse parameters are varied in a designated systematic pattern, which allows the generation of CEST contrast maps by encoding the patterns of signal loss into the images for better discrimination between various CEST imaging agents. The saturation parameter changes include, but are not limited to, saturation amplitude (B1), saturation length (tsat), number of pulses, shape of saturation pulses, amplitude of saturation pulses, saturation offset frequency, or a combination of these variations.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS7684847B2Improve image qualityReduce intensityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSaturation pulseMagnetization
When performing imaging in synchronization with a biological movement of an examinee by using a pulse sequence applying a pre-saturation pulse, it is possible to reduce irregularities of echo signal intensity and artifact on the image generated by the irregularities. Especially, it is possible to prevent artifact attributed to blood in the ventricle when performing delay contrast imaging. For this, before measuring the echo signal, an IR pulse or the like for adjusting magnetization to a desired state is applied so as to suppress irregularities of the echo signal intensity and prevent artifact.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic resonance image acquisition with suppression of background tissues and RF water excitation at offset frequency
InactiveUS20080272776A1Eliminate orientation dependenceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging agentSaturation pulse
Background tissue signals such as water and / or fat are suppressed in an MR image by using an imaging agent that chemically shifts the tissue spins of interest. An imaging pulse sequence is used to acquire the image data using an RF excitation pulse that is tuned to the off-resonance tissue spins of interest with the saturation pulse sequences being interleaved with the imaging pulse sequences to selectively suppress signals from on-resonance background tissues such as water and / or fat.
Owner:EVANSTON NORTHWESTERN HEALTHCARE RES INST
Method and apparatus for mr perfusion image acquisition using non-selective and notched RF saturation pulses
InactiveUS20050083053A1Addressing Insufficient CoverageImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSaturation pulseBlood pool
A non-selective saturation pulse together with a series of notched RF saturation pulses are used to acquire MR perfusion data. The non-selective saturation recovery RF pulse is non-selective and is designed to be effective at blood pool suppression for a first slice as well as a next slice in a series of slice locations. The first slice location may be placed at an angle or plane that is not necessarily coaxial with the other slice locations to be imaged. The present invention supports the acquisition of MR data with efficient spatial coverage and a calibration slice of data that provides a linear measure of signal intensity versus contrast concentration in a blood pool.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ph-weighted MRI using fast amine chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging
ActiveUS20180164393A1Easy to optimizeReduce scan timeDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMetaboliteNon invasive
A pH-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method and system are provided that works by indirectly measuring the NMR signal from amine protons found on the backbones of amino acids and other metabolites, which resonate at a frequency of +2.8-3.2 ppm with respect to bulk water protons. The technique uses a modified magnetization transfer radiofrequency saturation pulse for the generation of image contrast. A train of three 100 ms Gaussian pulses at high amplitude (6 uT) or Sinc3 pulses are played at a particular frequency off-resonance from bulk water prior to a fast echo planar imaging (EPI) readout, with one full image acquired at each offset frequency. This non-invasive pH-weighted MRI technique does not require exogenous contrast agents and can be used in preclinical investigations and clinical monitoring in patients with malignant glioma, stroke, and other ailments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
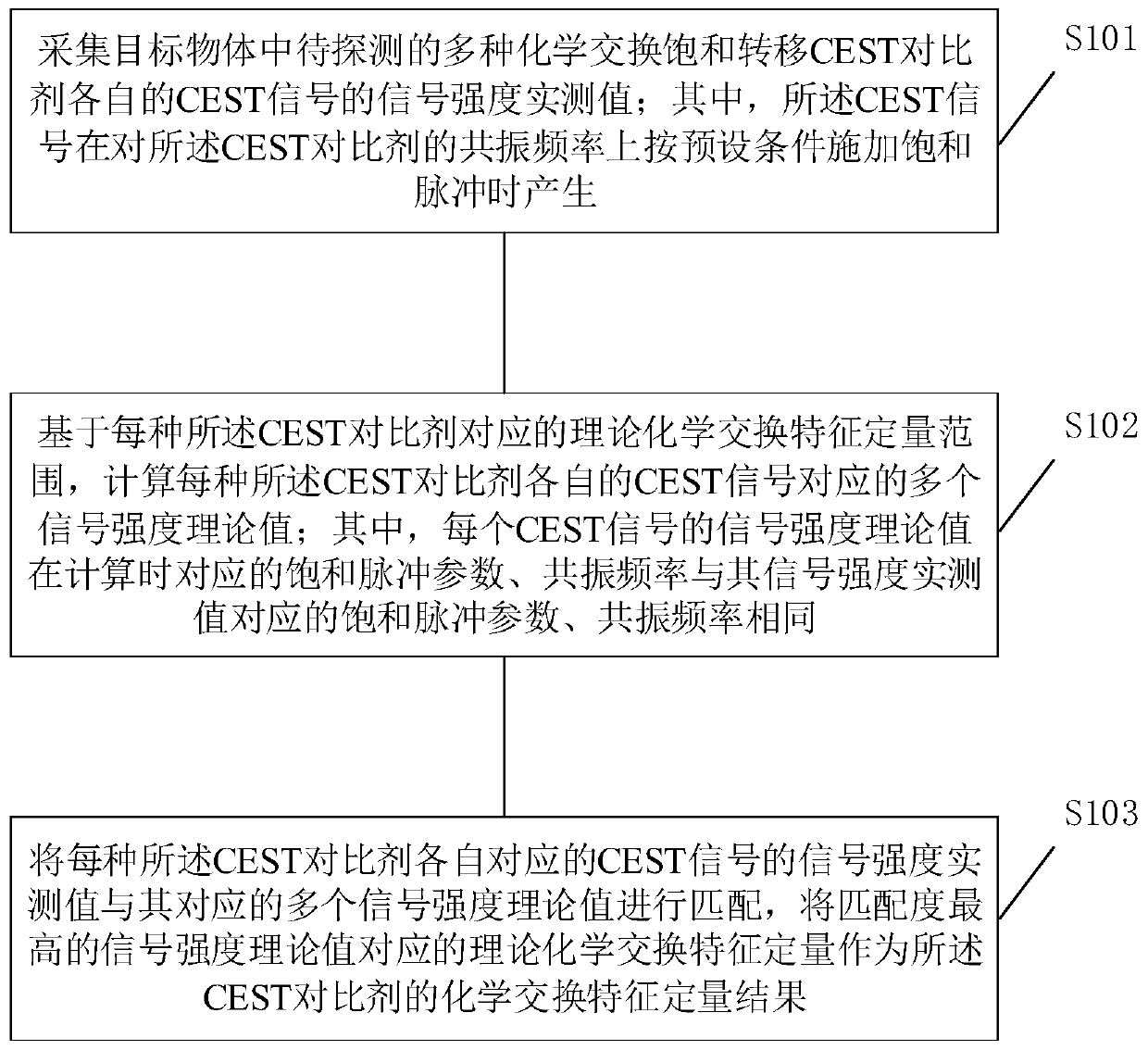
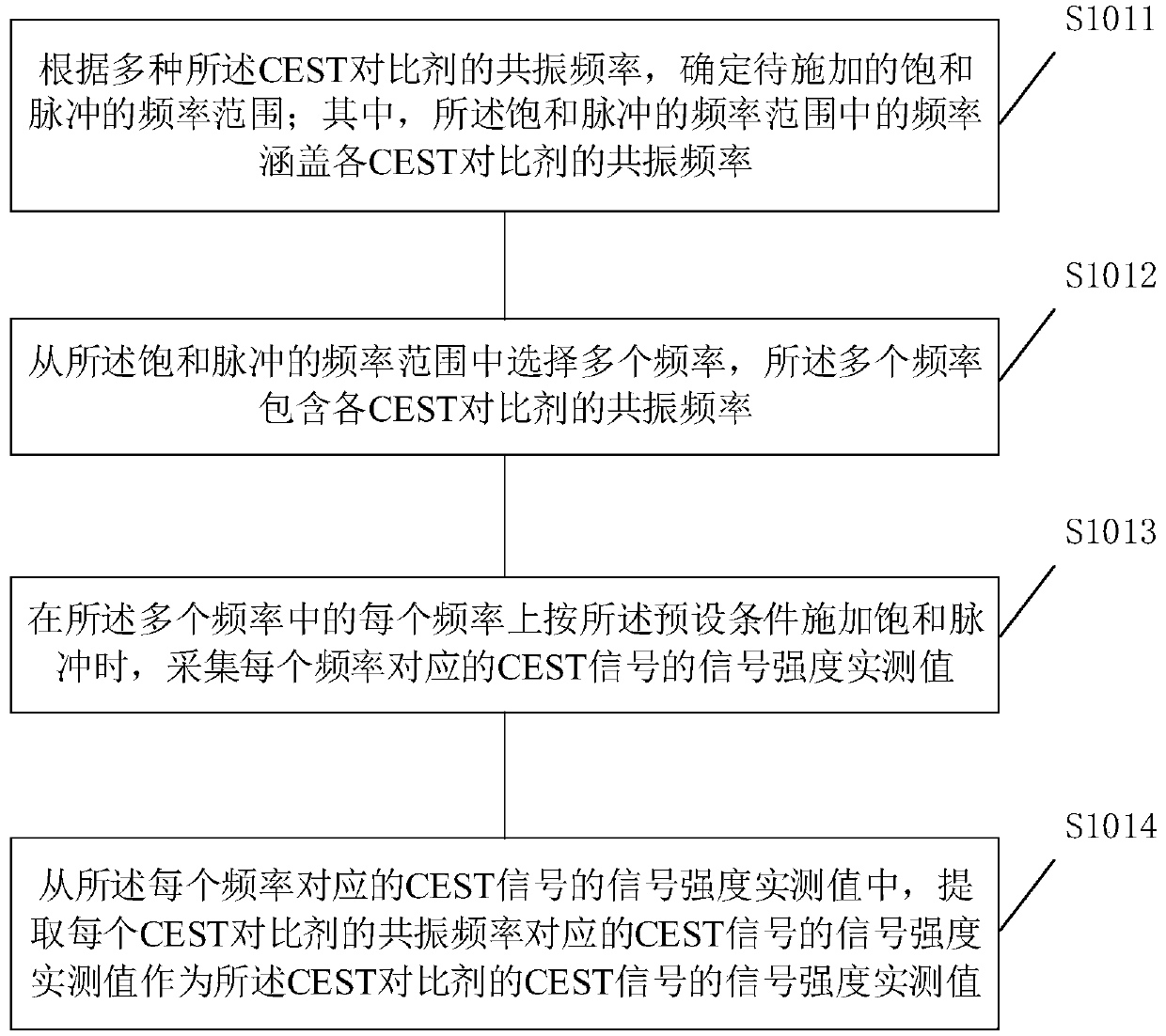
Chemical exchange characteristic quantification method and equipment
ActiveCN110824398AExact matchImprove accuracyMagnetic measurementsChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
The invention is suitable for the field of biomedical engineering, and provides a chemical exchange characteristic quantification method and chemical exchange characteristic quantification equipment.The chemical exchange characteristic quantification method comprises the steps of: acquiring signal intensity measured values of CEST signals of various CEST contrast agents; respectively calculatingcorresponding signal intensity theoretical values under the same saturation pulse parameter and resonance frequency as the signal intensity measured values based on a theoretical chemical exchange characteristic quantitative range of each CEST contrast agent; and regarding theoretical chemical exchange characteristic quantification corresponding to the theoretical value with the highest matching degree as a chemical exchange characteristic quantification result of the CEST contrast agents. According to the chemical exchange characteristic quantification method and the chemical exchange characteristic quantification equipment, the chemical exchange characteristic quantification process does not need to select a reference signal, thus is not susceptible to other chemical exchange effects, the theoretical chemical exchange characteristic quantification corresponding to the matching result can represent the actual chemical exchange specific quantity more precisely, and the precision of thechemical exchange specific quantity is effectively improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
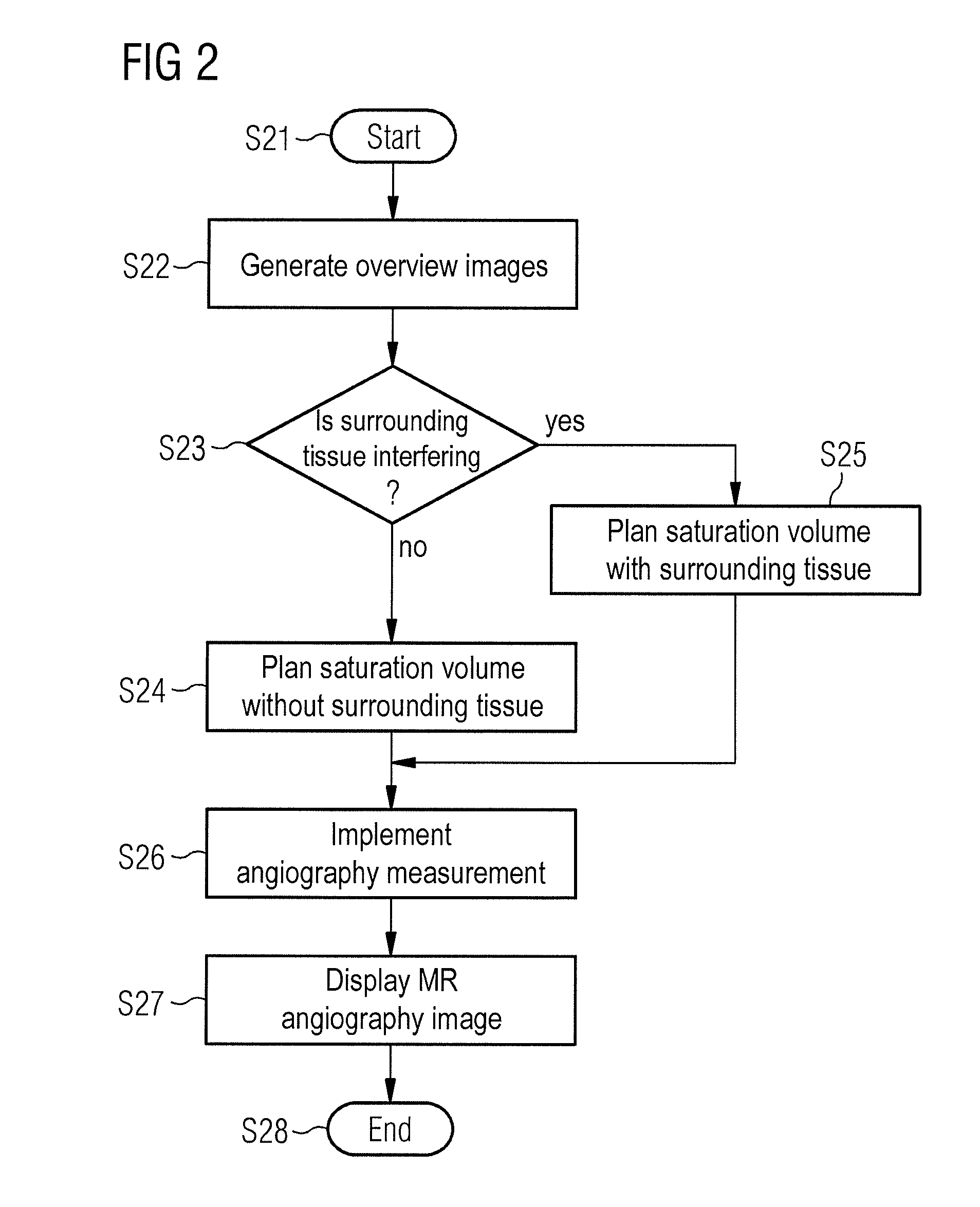
Method and apparatus to generate magnetic resonance angiography images
ActiveUS20120271158A1Quality improvementReduce intensityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPeri-aorticVascular structure
In a magnetic (MR) method and apparatus to generate an MR angiography image of a vascular structure of an examination region, spins in the examination region are saturated by an RF saturation pulse to cause these spins to produce a lower signal intensity in the angiography image than spins that flow from a major artery via a feed artery into the examination region, which are not saturated by the RF saturation pulse. A saturation volume is established that is saturated by the RF saturation pulse in order to be able to depict substantially all the vascular structure, such that the major artery and the tissue surrounding the major artery are not situated at the level of the branching of the feed artery in the saturation volume. The MR angiography image is generated using the established saturation volume.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
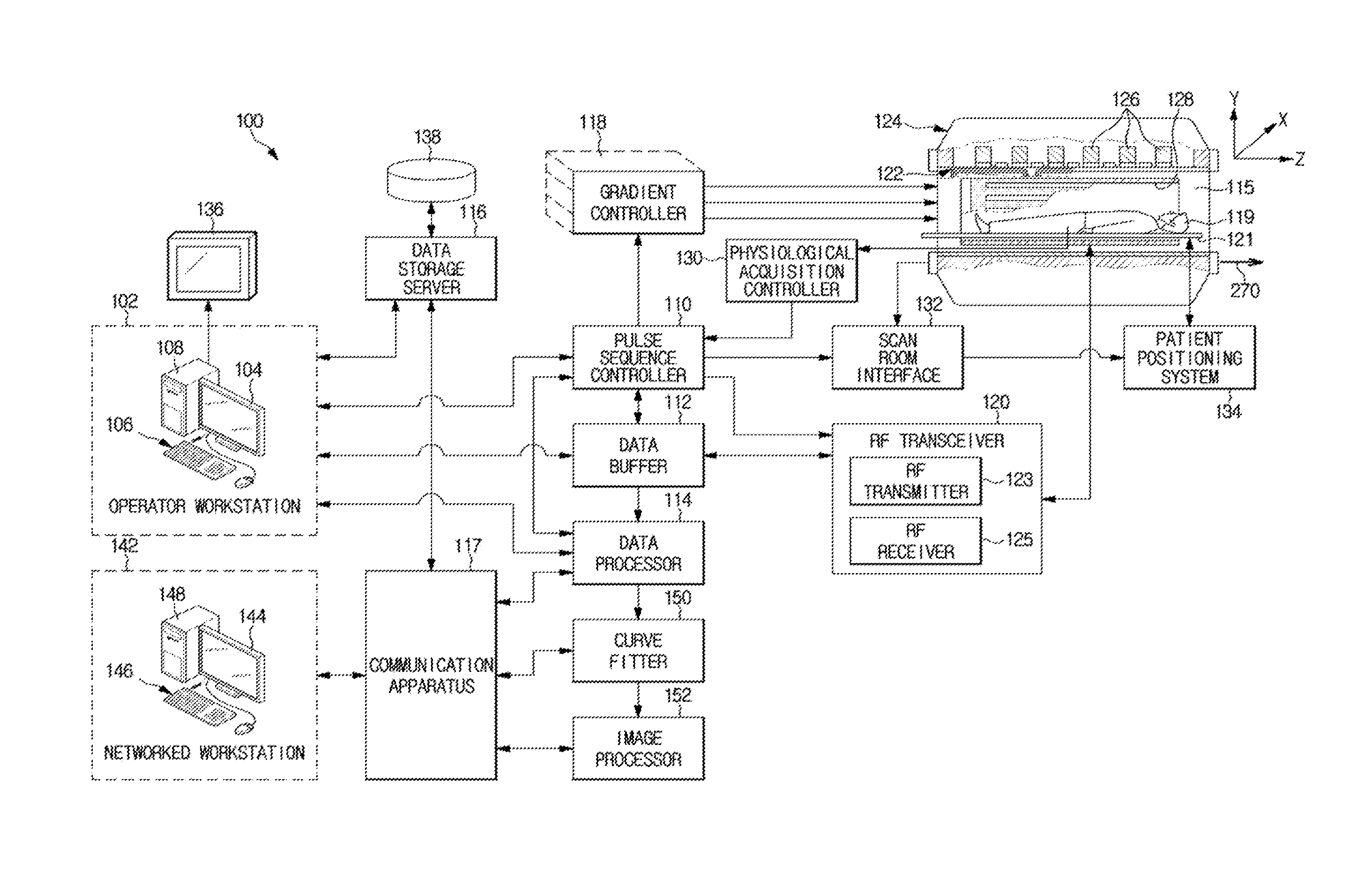
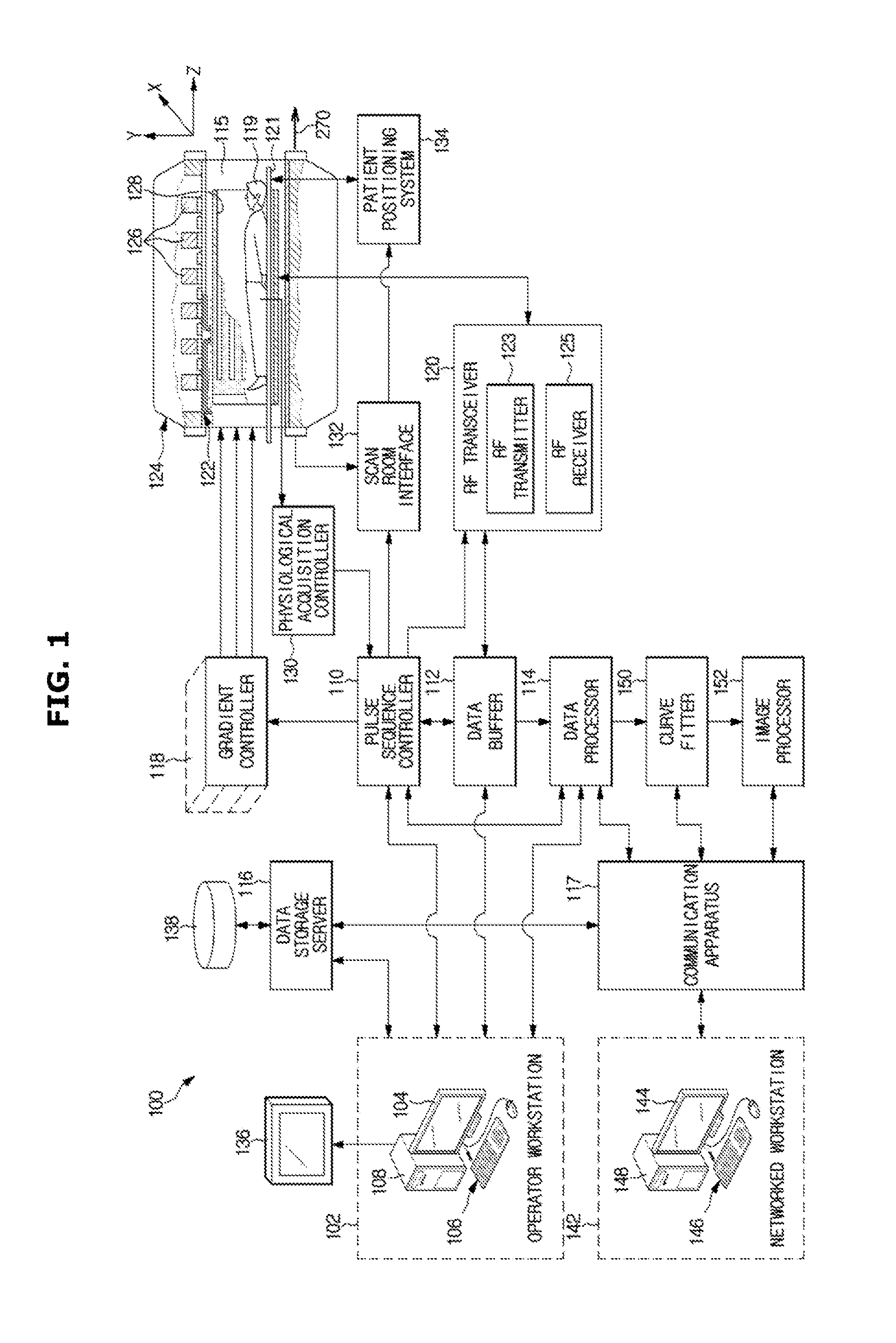
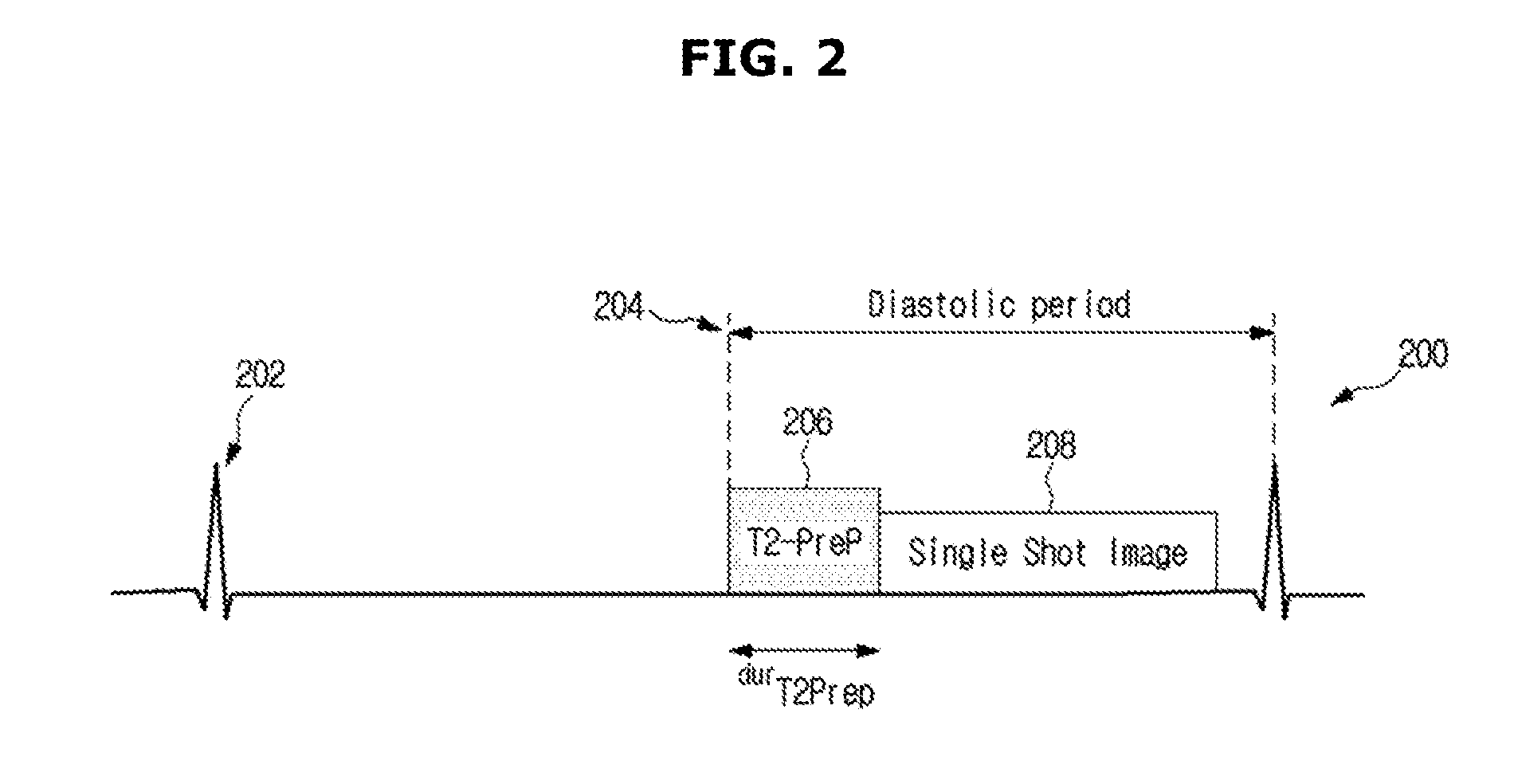
System and method for assessing t2-relaxation times with improved accuracy
InactiveUS20150268320A1Quantitative precisionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedCurve fitting
An MRI apparatus includes: a data processor configured to acquire a first set of T2-weighted imaging data and a second set of T2-weighted imaging data; a pulse sequence controller configured to generate a pulse sequence and apply the generated pulse sequence to a gradient coil assembly and RF coil assembly, the generated pulse sequence including: T2-preparation modules and associated imaging modules to acquire the first set of T2-weighted imaging data, and a saturation pulse sequence and an associated saturation imaging module to acquire the second set of T2-weighted imaging data; a curve fitter configured to apply the first and second sets of T2-weighted imaging data to a three-parameter model for T2 decay, to determine a T2 value at a plurality of locations; and an image processor configured to generate a T2 map of the object based on the T2 value determined at the plurality of locations.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method and apparatus for NMR saturation
ActiveUS7825661B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSaturation pulseSpins
Saturation pulse sequences are designed to ensure complete saturation of nuclear spins for dual wait time measurements and saturation recovery measurements in the case of axial motion of a downhole NMR logging tool. Frequency and / or phase modulation may be used. An auxiliary saturation coil may be used.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Simultaneous ph and oxygen weighted MRI contrast using multi-echo chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging (me-cest)
ActiveUS20200158803A1Fast and and high resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRadio frequencyMR - Magnetic resonance
A method is provided that includes applying at least one radiofrequency saturation pulse at a frequency or a range of frequencies to substantially saturate magnetization corresponding to an exchangeable proton in the ROI to generate magnetic resonance (MR) data. The MR data is then acquired using an echo-planar imaging readout, which is configured to sample a series of gradient echo pulse trains at a series of gradient echo times and a series of spin echo pulse trains at a series of spin echo times. One or more relaxometry measurement is then computed using the MR data sampled at the gradient echo times and the spin echo times. An oxygen-weighted image is then generated using the one or more relaxometry measurement, and a pH-weighted image is generated using MR data sampled at one or more of the spin echo times or gradient echo times.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for acquisition of magnetic resonance data with fat saturation pulses radiated with respectively different flip angles
ActiveUS20150268319A1Accelerated programUniform fat saturationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSaturation pulse
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an examination subject using an acquisition sequence that includes at least one acquisition cycle, wherein the acquisition cycle includes a readout block set with at least two readout blocks, and a saturation pulse set with at least two saturation pulses, the saturation pulses of the saturation pulse set are respectively associated with respective readout blocks of the readout block set, and the saturation pulses of the saturation pulse set have respectively varying flip angles.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Permanent magnet-based magnetic saturation pulsed eddy current infrared nondestructive evaluation method
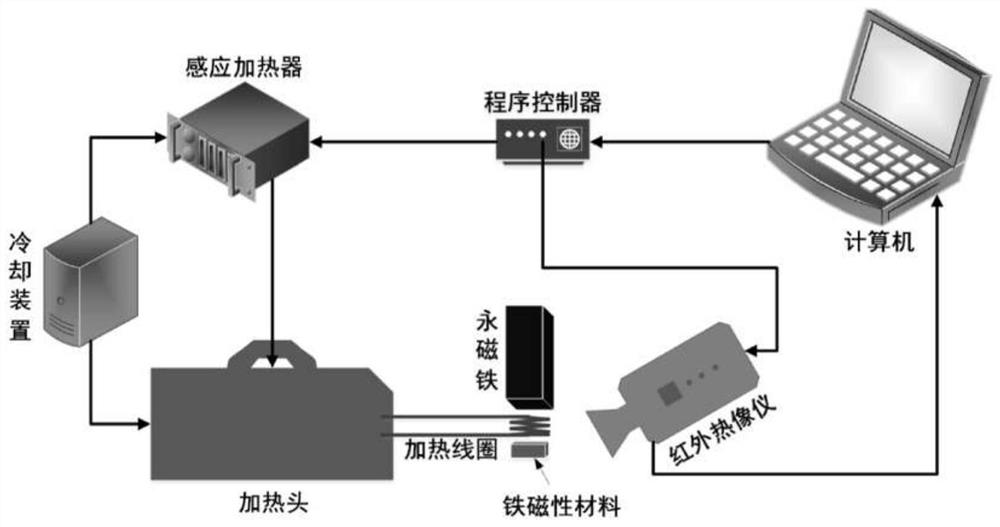
PendingCN111982967AExpand the scope of observationHigh resolutionCoil arrangementsMaterial flaws investigationFerromagnetismThermal infrared
The invention discloses a permanent magnet-based magnetic saturation pulsed eddy current infrared nondestructive evaluation method. Firstly, a computer controls a program controller to synchronously trigger an induction heater and a thermal infrared imager, the induction heater applies pulse current excitation to a heating coil connected with a heating head while receiving a trigger signal, and acooling device cools the induction heater, the heating head and the heating coil at the same time; a strong static magnetic field is generated around the permanent magnet, a ferromagnetic material reaches magnetic saturation under the action of a permanent magnet, then joule heat is generated under the action of the heating coil, and the surface temperature of the material is changed through heatconduction; and finally, temperature changes are collected through a thermal infrared imager, and defect nondestructive evaluation is conducted on the ferromagnetic material by analyzing the collectedimage sequence. Compared with a traditional pulsed eddy current infrared nondestructive detection method, the method has the advantages that the detection depth of the ferromagnetic material is larger, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:RES INST OF NUCLEAR POWER OPERATION +2
MR-angiography with non-cartesian signal acquisition
In a method and apparatus for the creation of an MR image of a vascular structure of an examination region, the spins in the examination region are saturated by the irradiation of at least one RF saturation signal, which delivers a lower signal intensity as spins in a subsequent MR signal recording for the creation of the MR angiographic image, which flow through at least one blood vessel into the examination region, and are not saturated by the RF saturation pulse. Raw data space of the MR angiographic image is read out with a non-Cartesian trajectory in the MR signal acquisition for the creation of the MR angiographic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com