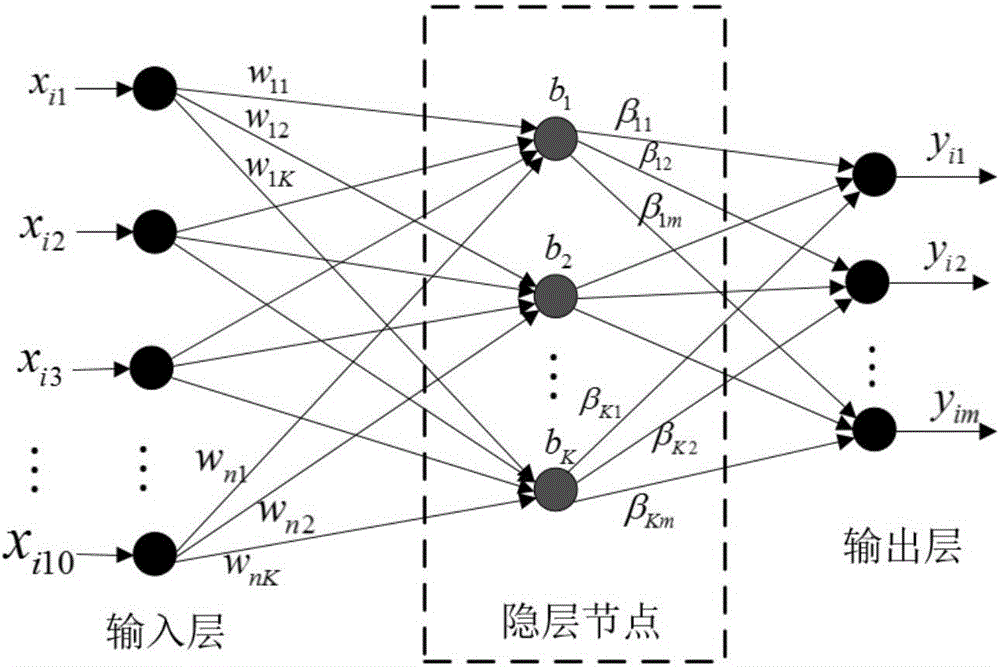
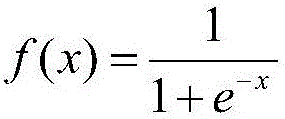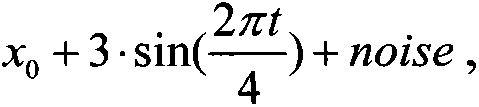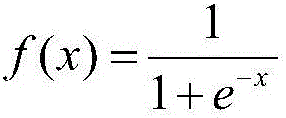Patents
Literature
42 results about "Organ Motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
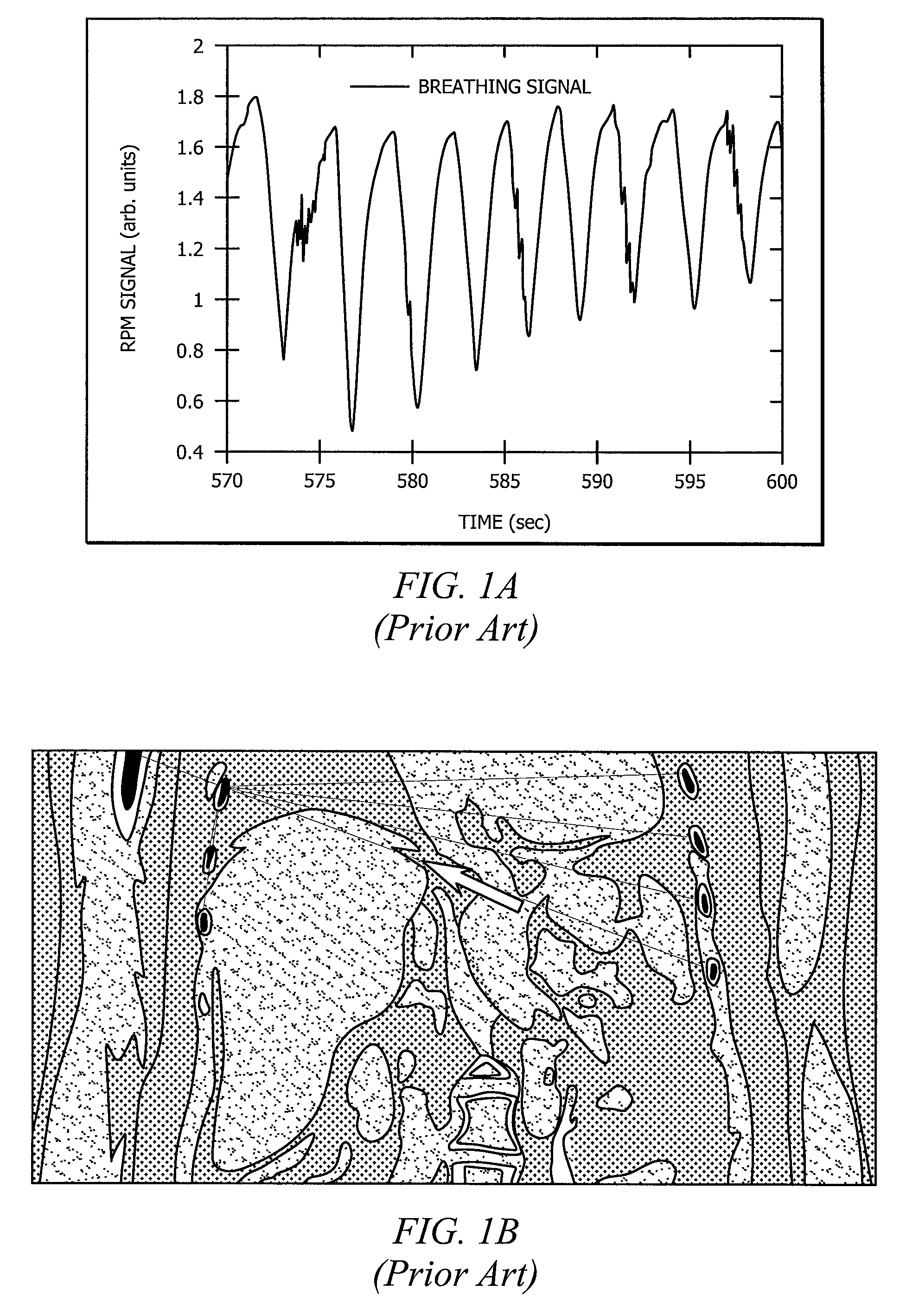
Movement of internal organs due to physiological processes.
Physiological model based non-rigid image registration
InactiveUS7117026B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionData set
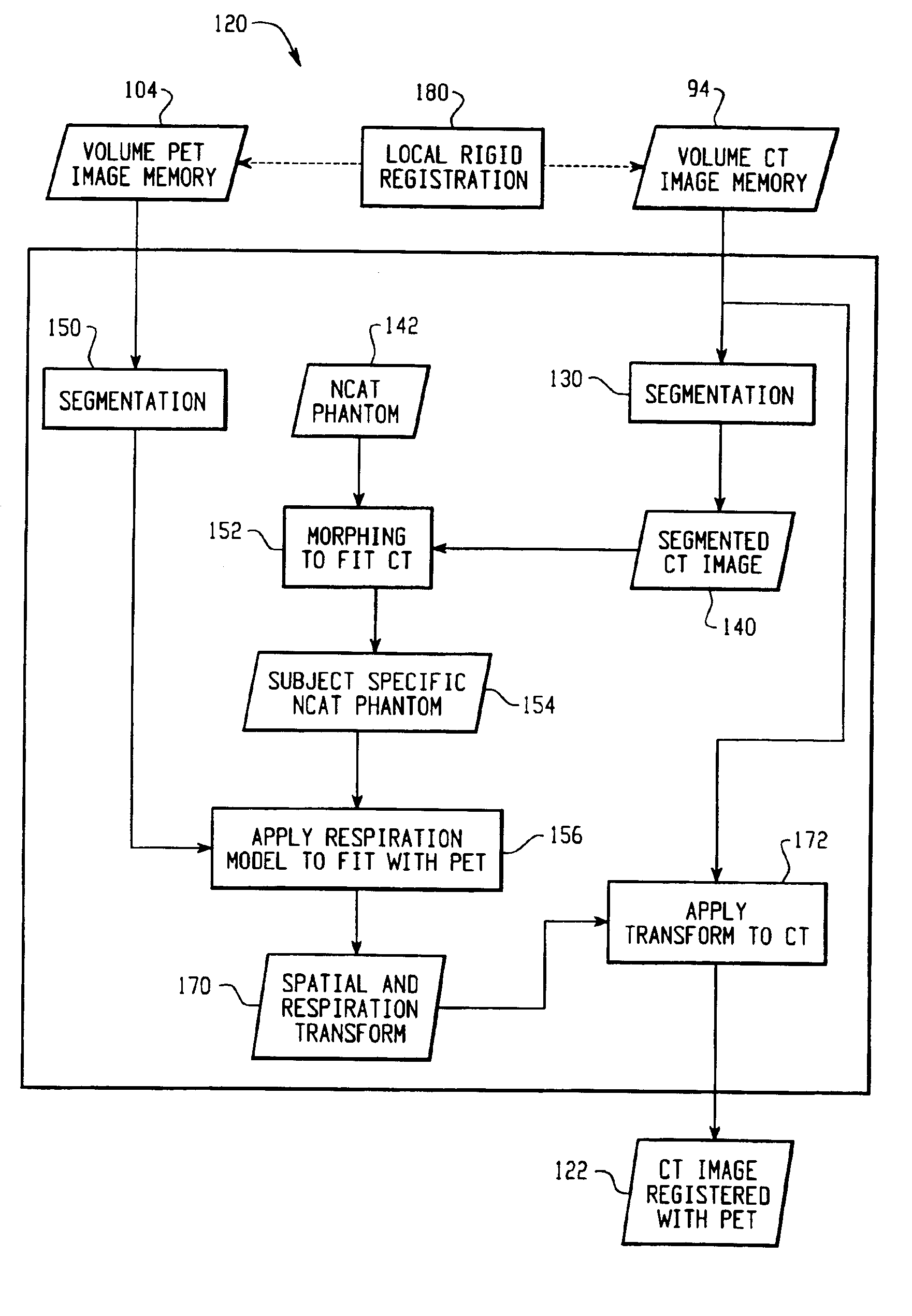
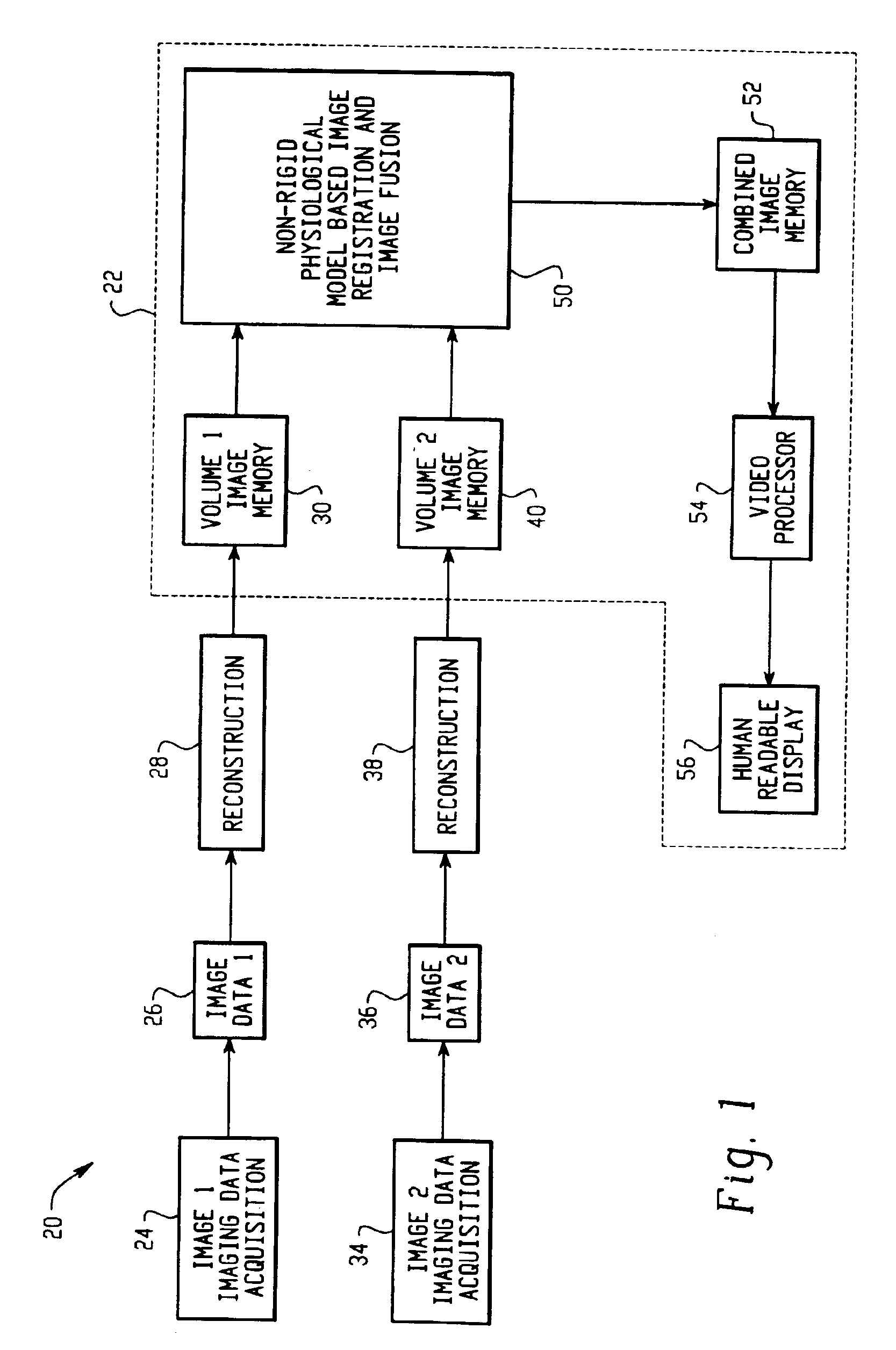
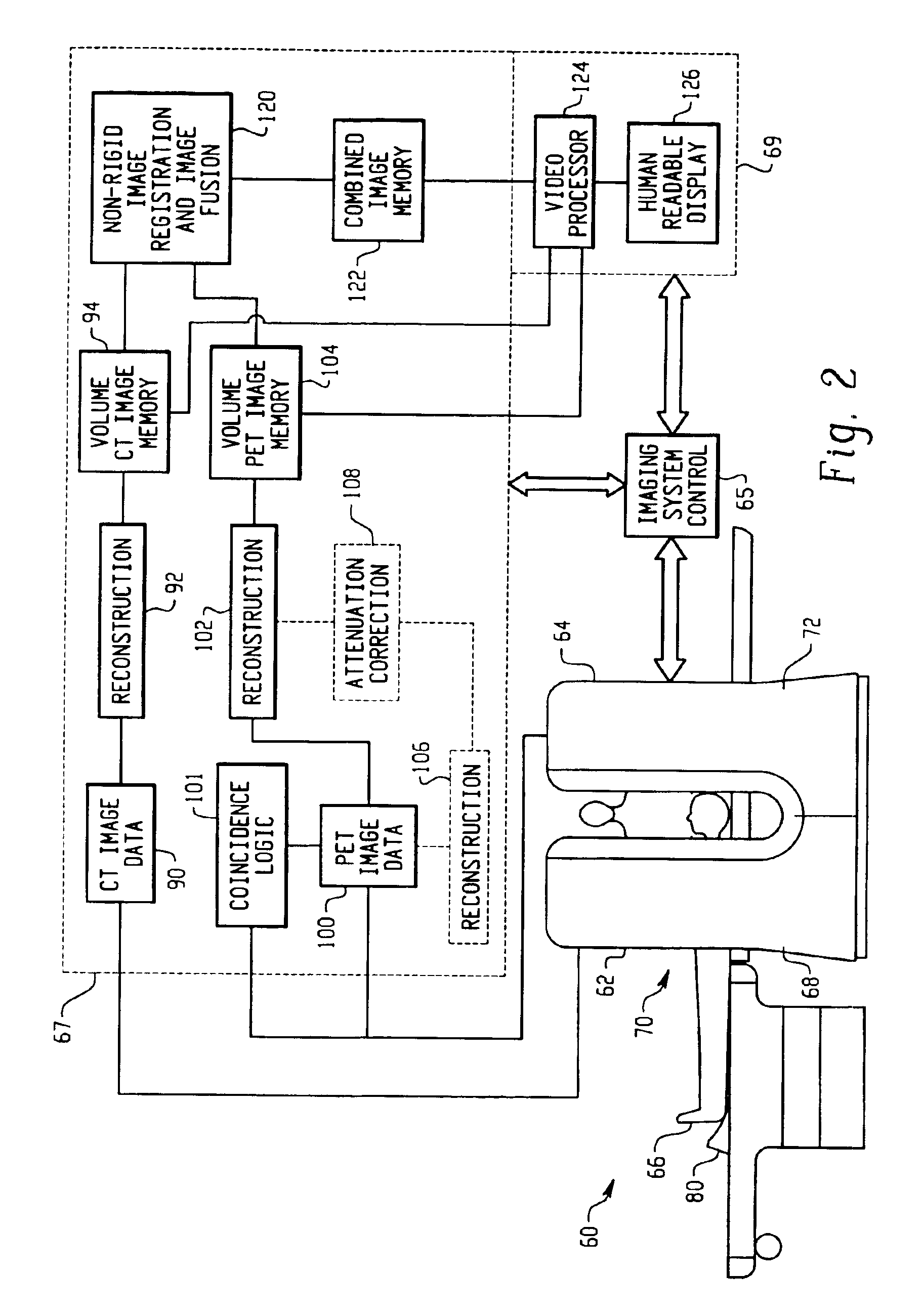
A method for non-rigid registration and fusion of images with physiological modeled organ motions resulting from respiratory motion and cardiac motion that are mathematically modeled with physiological constraints. A method of combining images comprises the steps of obtaining a first image dataset (24) of a region of interest of a subject and obtaining a second image dataset (34) of the region of interest of the subject. Next, a general model of physiological motion for the region of interest is provided (142). The general model of physiological motion is adapted with data derived from the first image data set (140) to provide a subject specific physiological model (154). The subject specific physiological model is applied (172) to the second image dataset (150) to provide a combined image (122).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for tracking motion phase of an object for correcting organ motion artifacts in X-ray CT systems
InactiveUS7085342B2Improve image qualityRemove Motion ArtifactsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationComputed tomography
The present invention relates to a method for tracking motion phase of an object. A plurality of projection data indicative of a cross-sectional image of the object is received. The projection data are processed for determining motion projection data of the object indicative of motion of the object based on the attenuation along at least a same line through the object at different time instances. A motion phase of the object with the object having the least motion is selected. Finally, projection data acquired at time instances within the selected motion phase of the object are selected for tomographical image reconstruction. Reconstructed images clearly show a substantial improvement in image quality by successfully removing motion artifacts using the method for tracking motion phase of an object according to the invention. The method is highly beneficial in cardiac imaging using X-ray CT scan.
Owner:CANAMET CANADIAN NAT MEDICAL TECH
Image reconstruction incorporating organ motion
InactiveUS20120201428A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioPromote lowerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Systems and methods which implement an image reconstruction framework to incorporate complex motion of structure, such as complex deformation of an object or objects being imaged, in image reconstruction techniques are shown. For example, techniques are provided for tracking organ motion which uses raw time-stamped data provided by any of a number of imaging modalities and simultaneously reconstructs images and estimates deformations in anatomy. Operation according to embodiments reduces artifacts, increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and facilitates reduced image modality energy dosing to patients. The technology also facilitates the incorporation of physical properties of organ motion, such as the conservation of local tissue volume. This approach is accurate and robust against noise and irregular breathing for tracking organ motion.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method and device for correcting organ motion artifacts in MRI systems
InactiveUS6894494B2Improve image qualityRemove Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMotion vectorAnimation
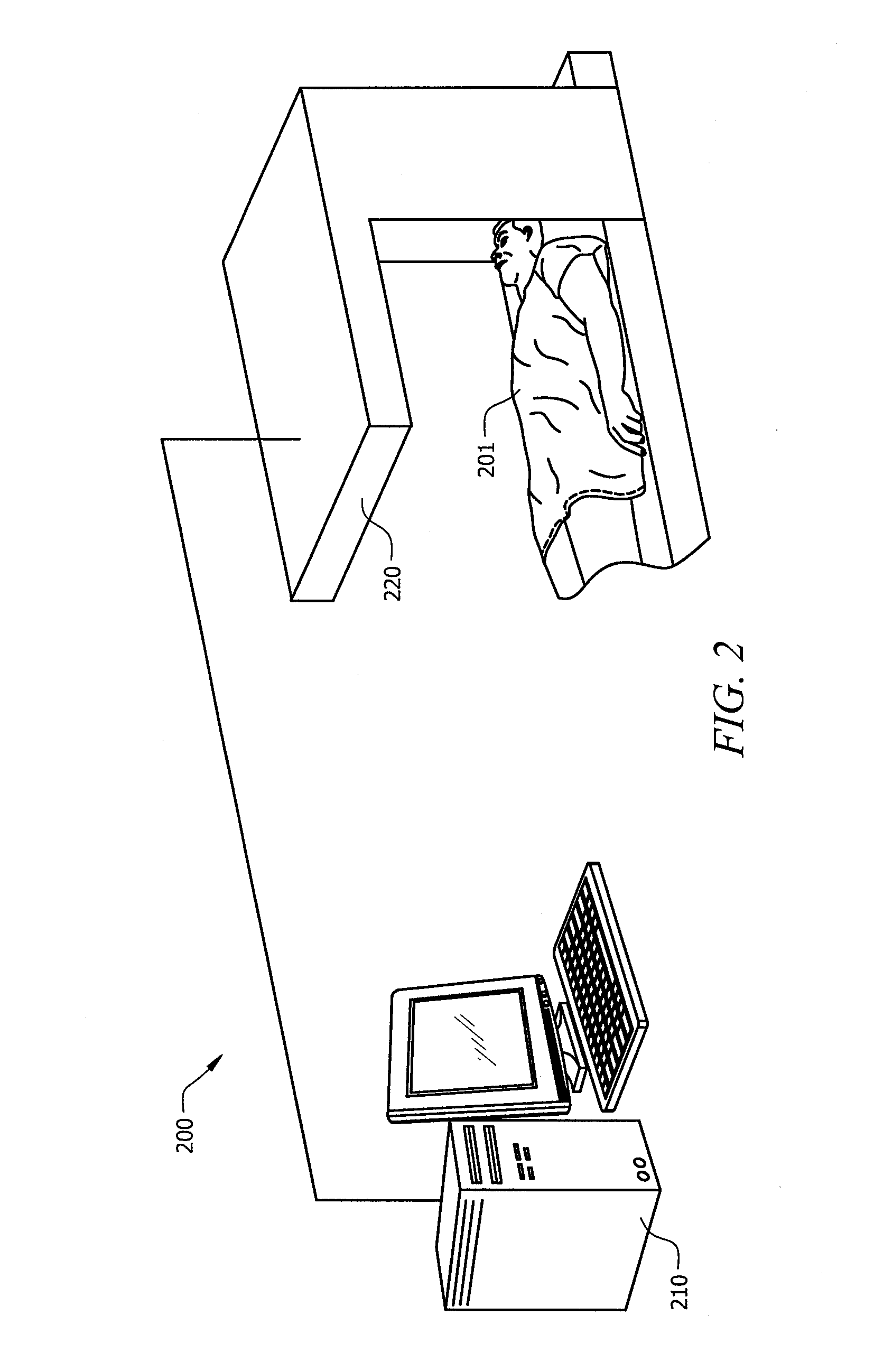
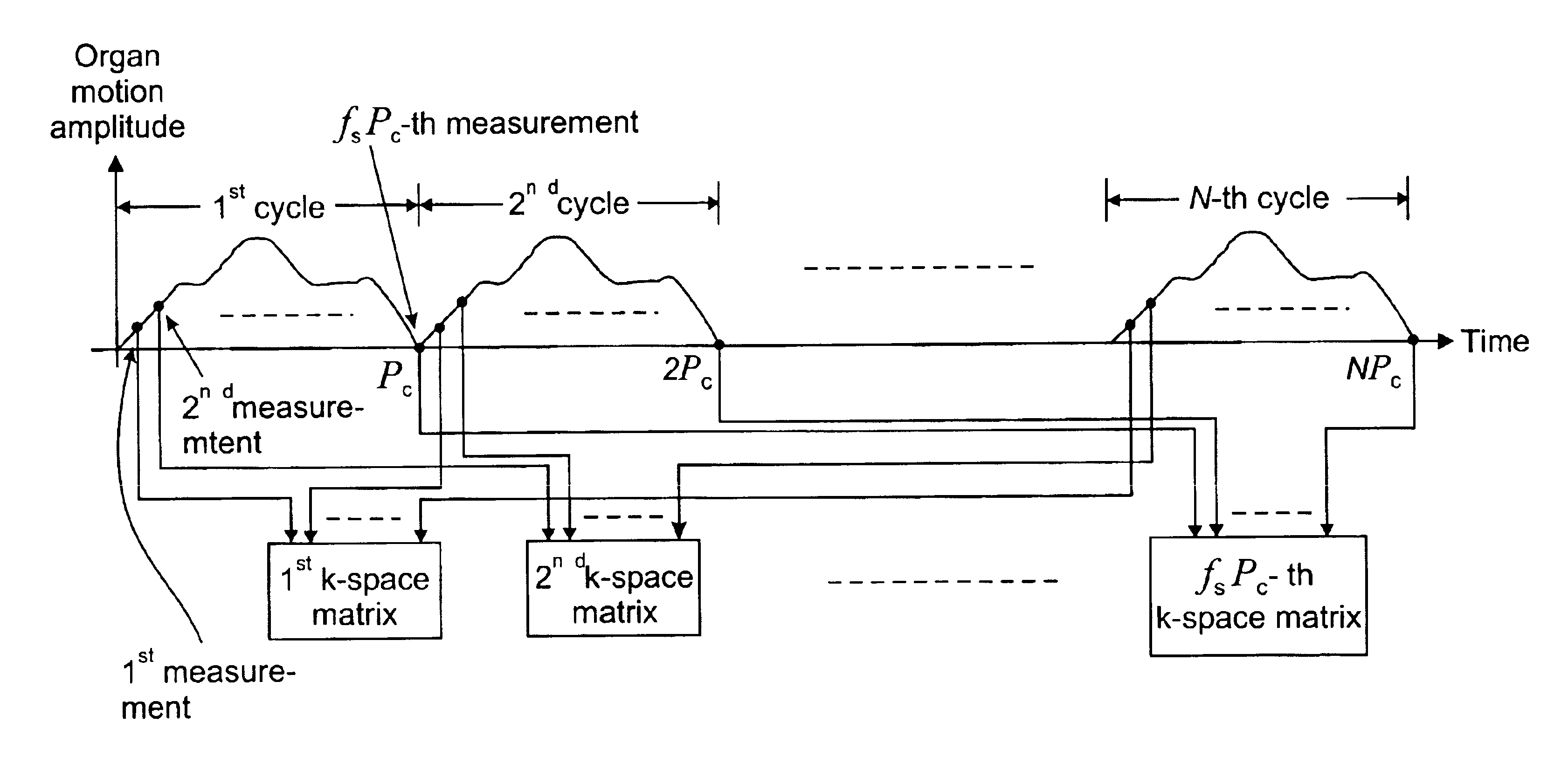
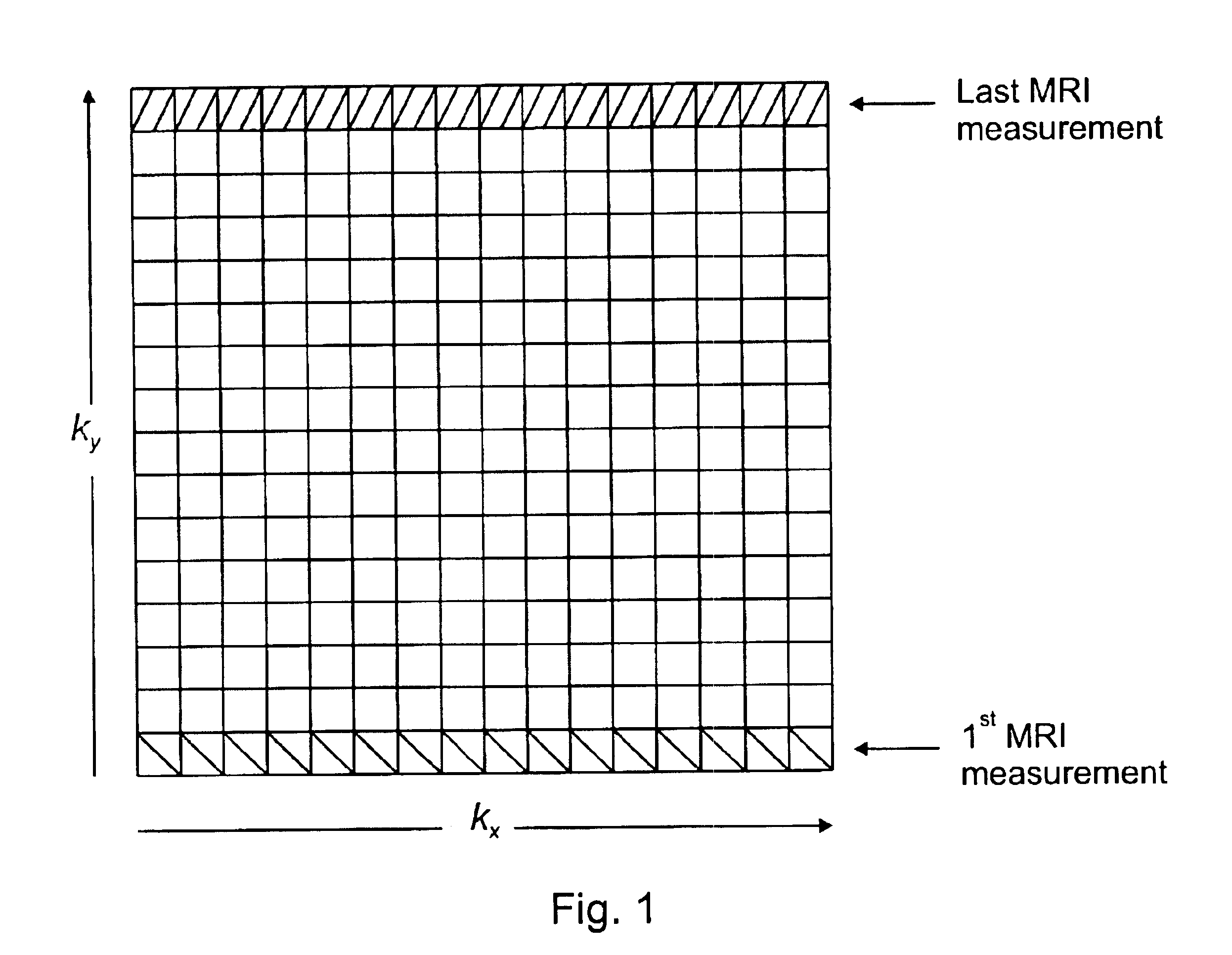
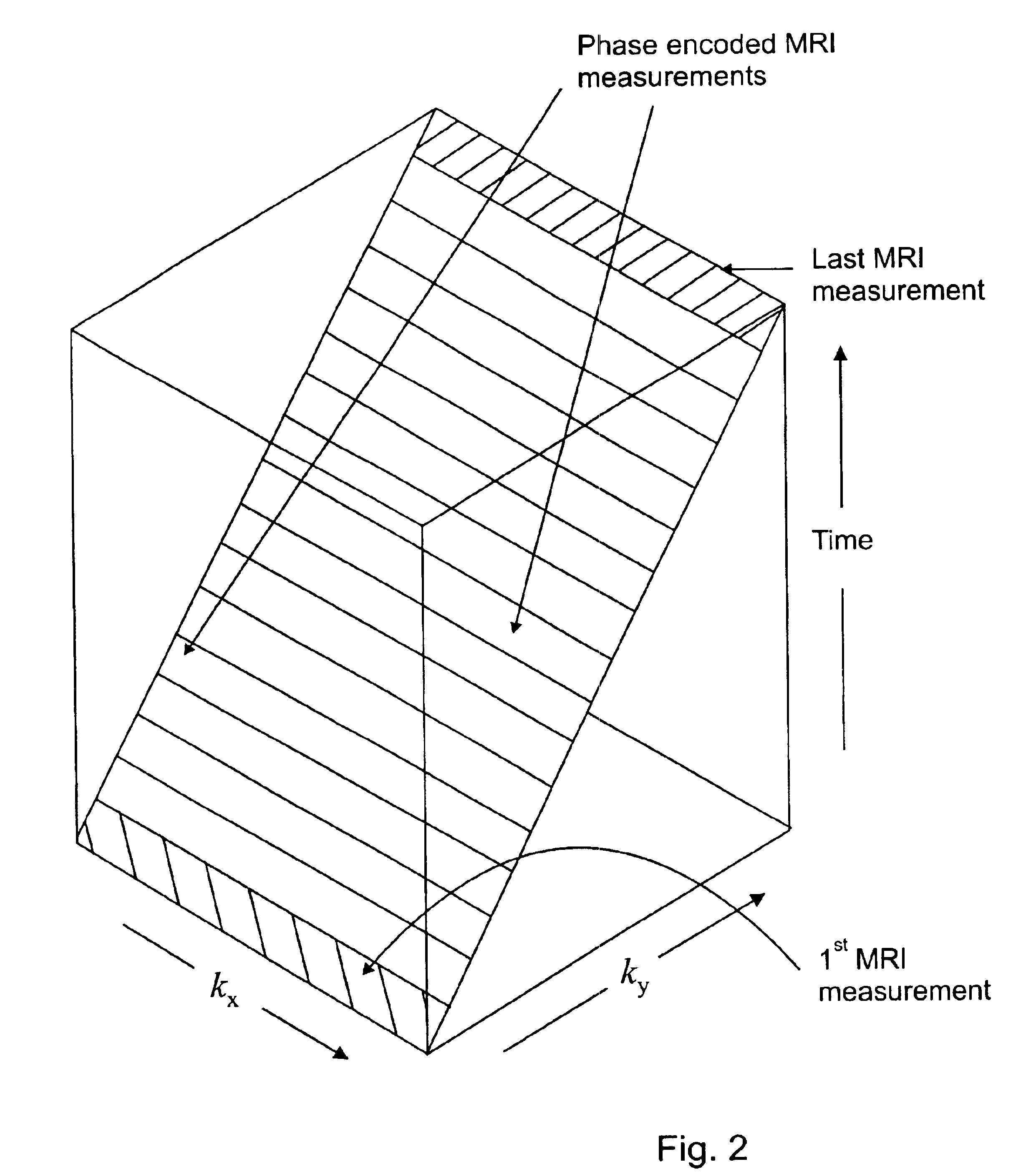
The present invention relates to a signal processing method and system for correcting organ motion artifacts for cardiac and brain imaging. A plurality of sets of MRI measurement data indicative of at least an image of an object is received. Each set corresponds to one row kx of a k-space matrix of at least a k-space matrix. For each set a k-space matrix of the at least a k-space matrix is determined for allocation thereto based on motion information of the object occurring during acquisition of the plurality of sets of the MRI measurement data. In a following step a location within the allocated k-space matrix corresponding to a row of the k-space matrix allocated thereto is determined for each set. At least a k-space matrix is then generated by re-arranging the plurality of sets. Each of the at least a k-space matrix comprises the sets of the plurality of sets of the MRI measurement data allocated thereto. Inverse Fourier transforming of the plurality of k-space matrices provides at least a reconstructed image. Through careful selection of the phases of the cardiac and respiratory cycles and corresponding ranges MRI data acquisition periods are of the order of seconds or a few minutes. Furthermore, integration of motion artifact free MRI images of different phases of organ motion using the coherent k-space synthesis according to the invention allows provision of an animation showing different phases of a cardiac or lung cycle. In an embodiment for correcting motion artifacts for brain imaging a motion vector describing translational and rotational motion of a patient's head is tracked during the MRI data acquisition process. The motion artifacts are then corrected based on coherent k-space synthesis using the motion vector data.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
List Mode-Based Respiratory and Cardiac Gating in Positron Emission Tomography
InactiveUS20100067765A1Health-index calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency spectrumData stream
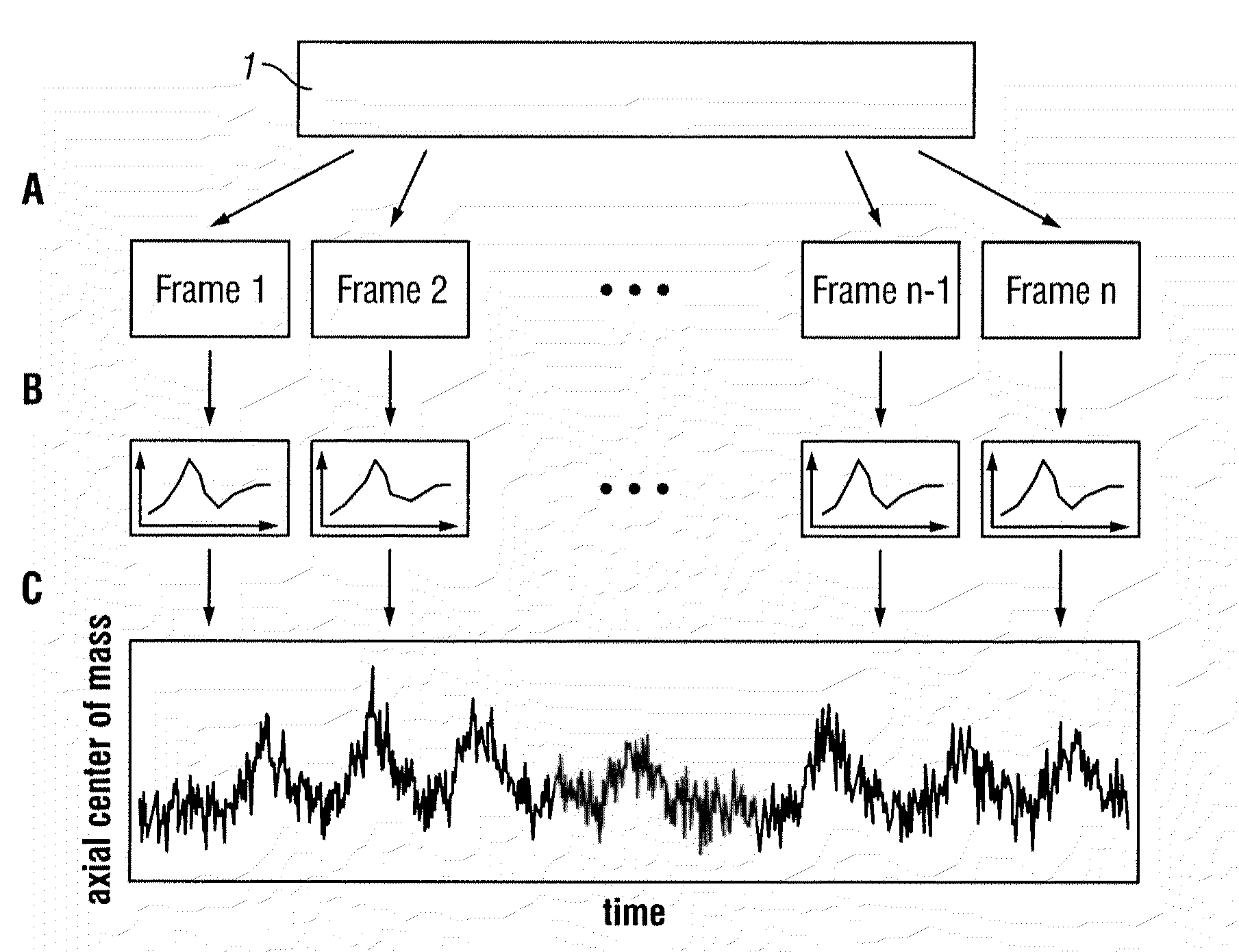
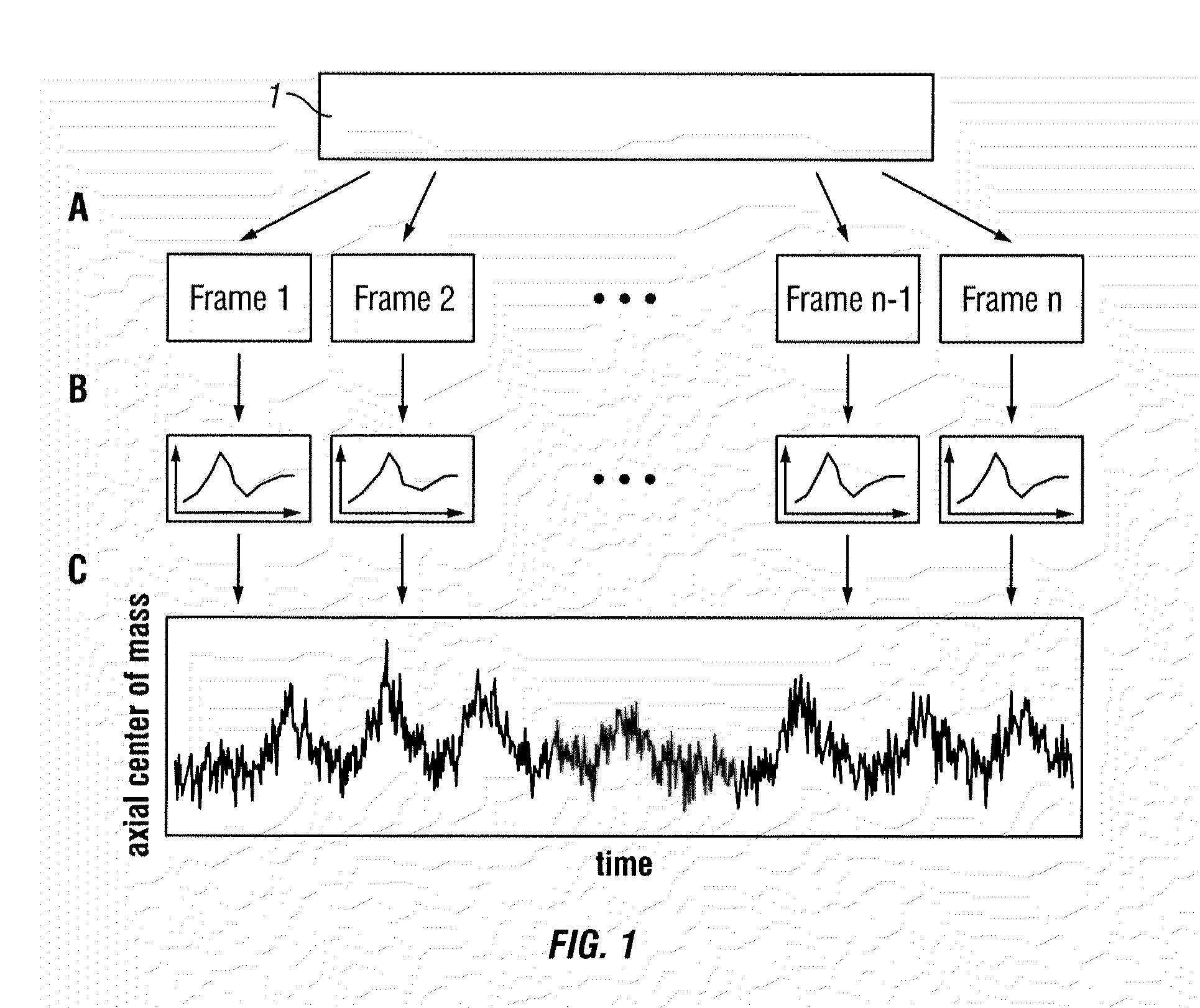
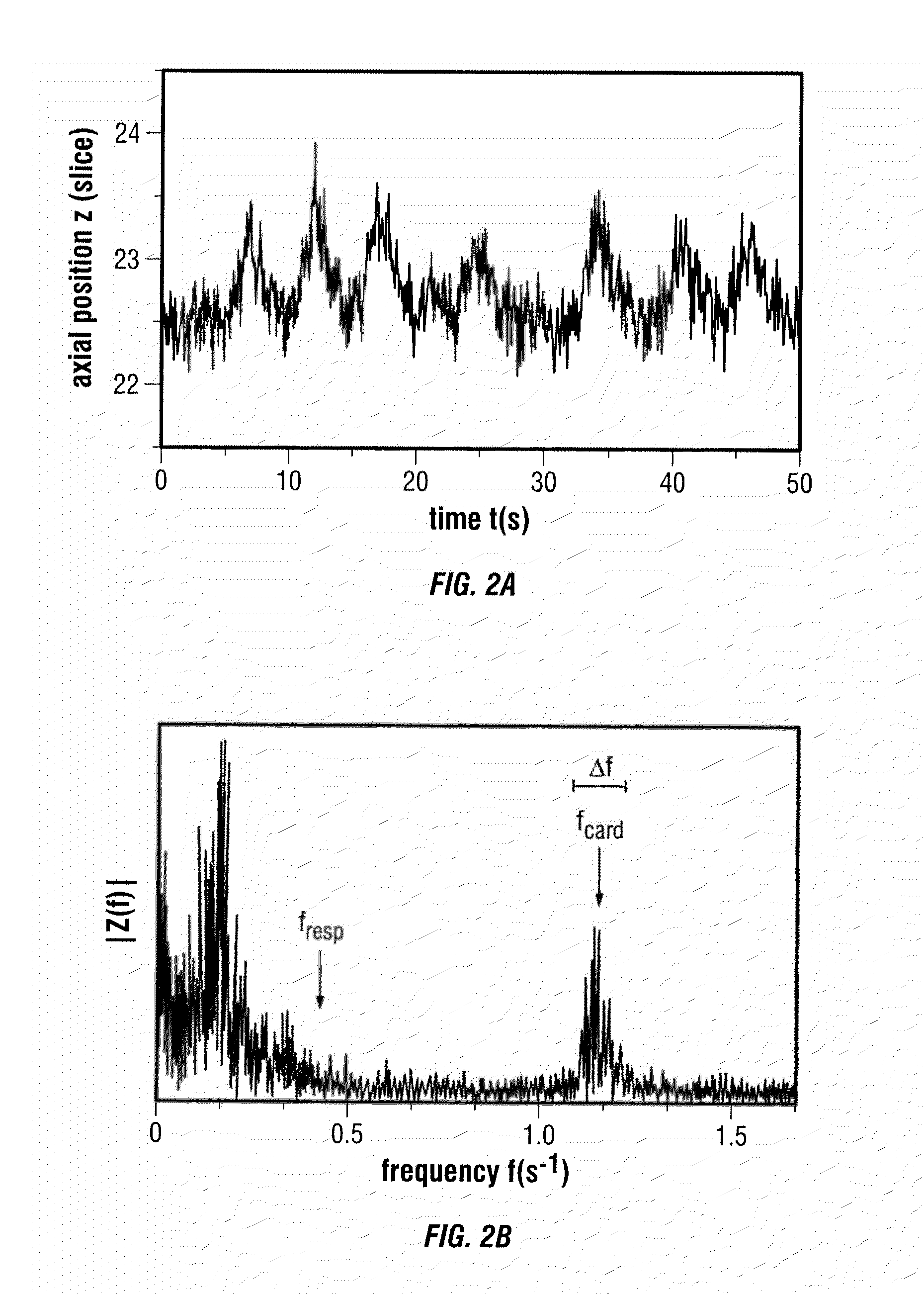
According to a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a method for extracting internal organ motion from positron emission tomography (PET) coincidence data, the method comprising the following steps: generating a data stream of PET coincidence data using the list mode capability of a PET scanner; dividing the data stream into time frames of a given length; computing a histogram A(i, t) of an axial coincidence distribution for a set of time frames; computing the axial center of mass z(t) for each of the time frames in the set of time frames based on the histogram A(i, t); transforming z(t) into the frequency domain; determining either the frequency contribution caused by respiratory motion, given by fresp, or the frequency contribution caused by heart contractions, given by fcard and Δf, identified in the frequency spectrum |Z(f)|; and carrying out further processing of Z(f) leading to curves zresp(t) and zcard(t) with which a gating sequence is established.
Owner:UNIVERSLTAT MUNSTER +1
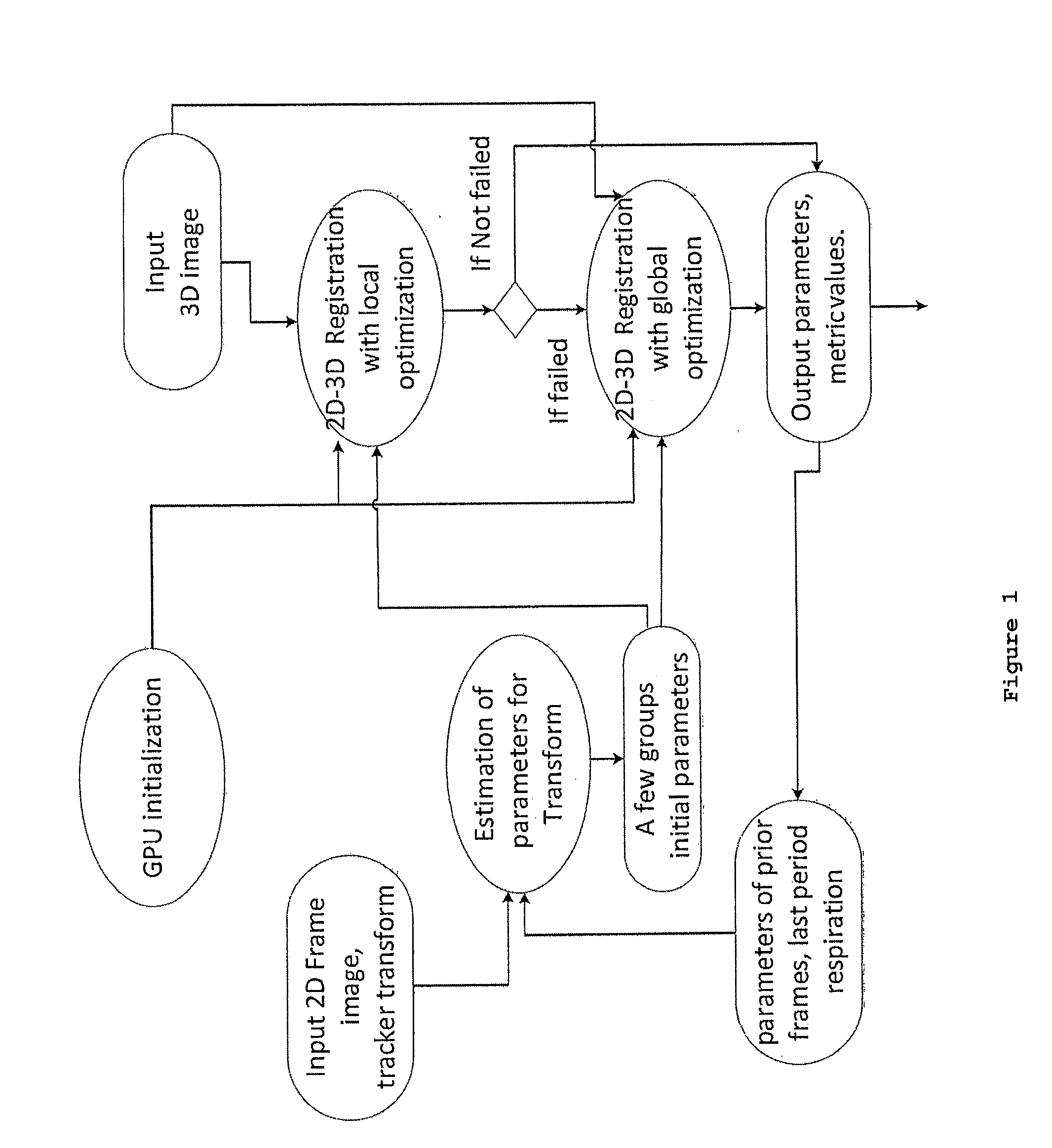
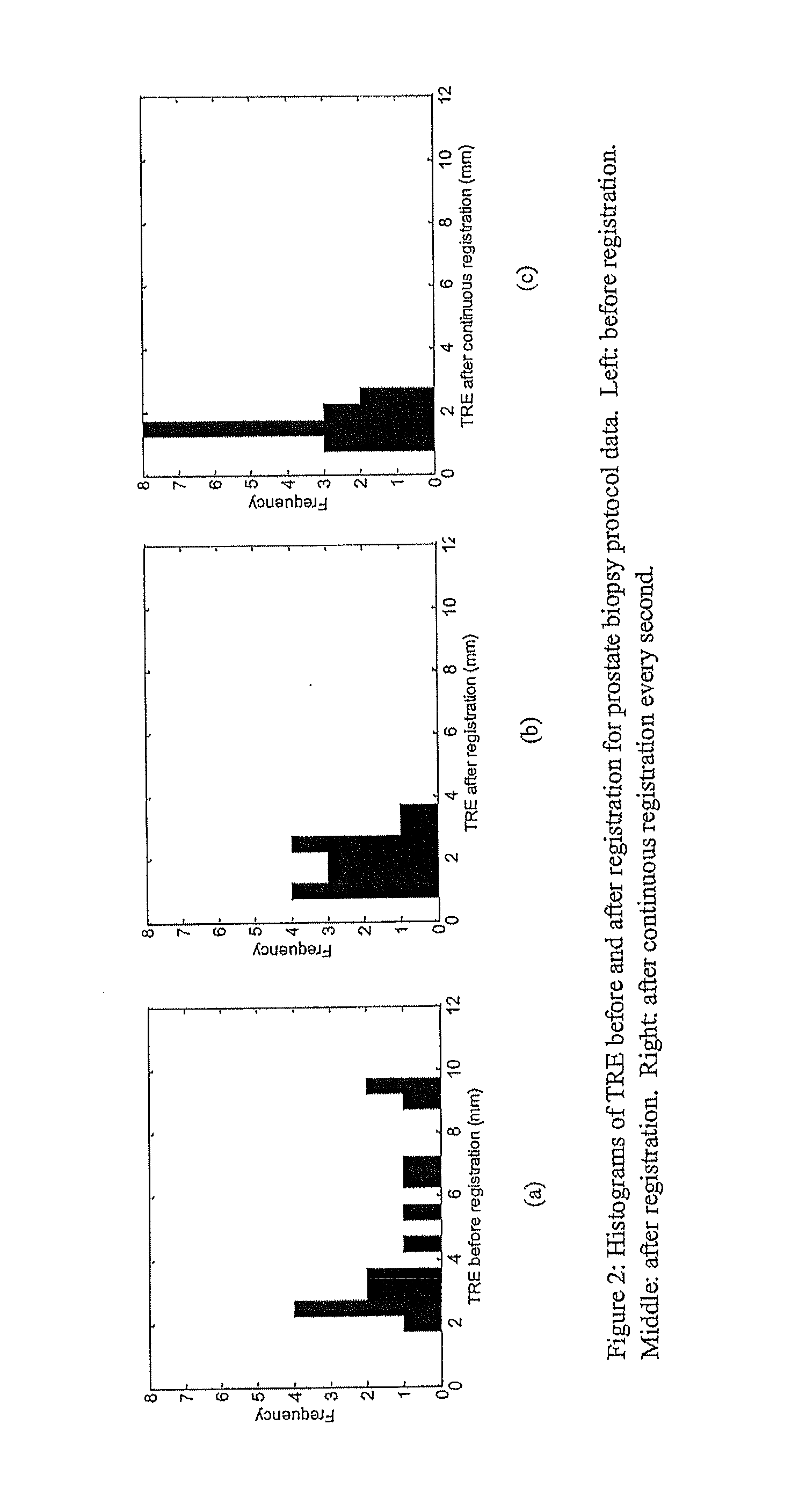
2d-3d rigid registration method to compensate for organ motion during an interventional procedure
InactiveUS20150201910A1Convenient registrationMinimizing errorImage enhancementImage analysisBody movementOrgan Motion
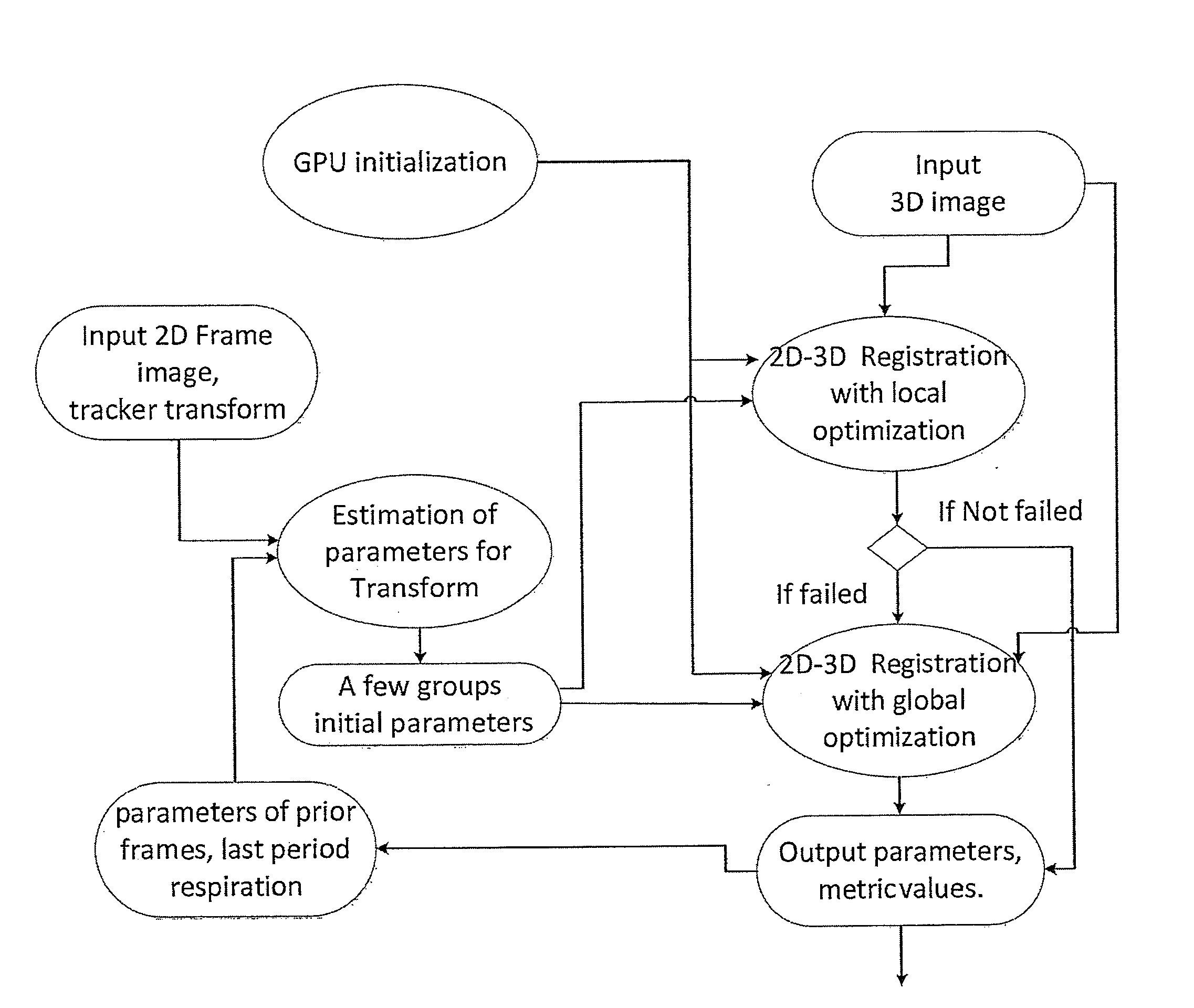
Disclosed herein is a system and method for generating a motion-corrected 2D image of a target. The method comprises acquiring a 3D static image of the target before an interventional procedure. During the procedure, a number of 2D real time images of the target are acquired and displayed. A slice of the 3D static image is acquired and registered with one 2D real time image and then the location of the 3D static image is corrected to be in synchrony with body motion. The motion corrected 2D image of the target is then displayed.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO +1
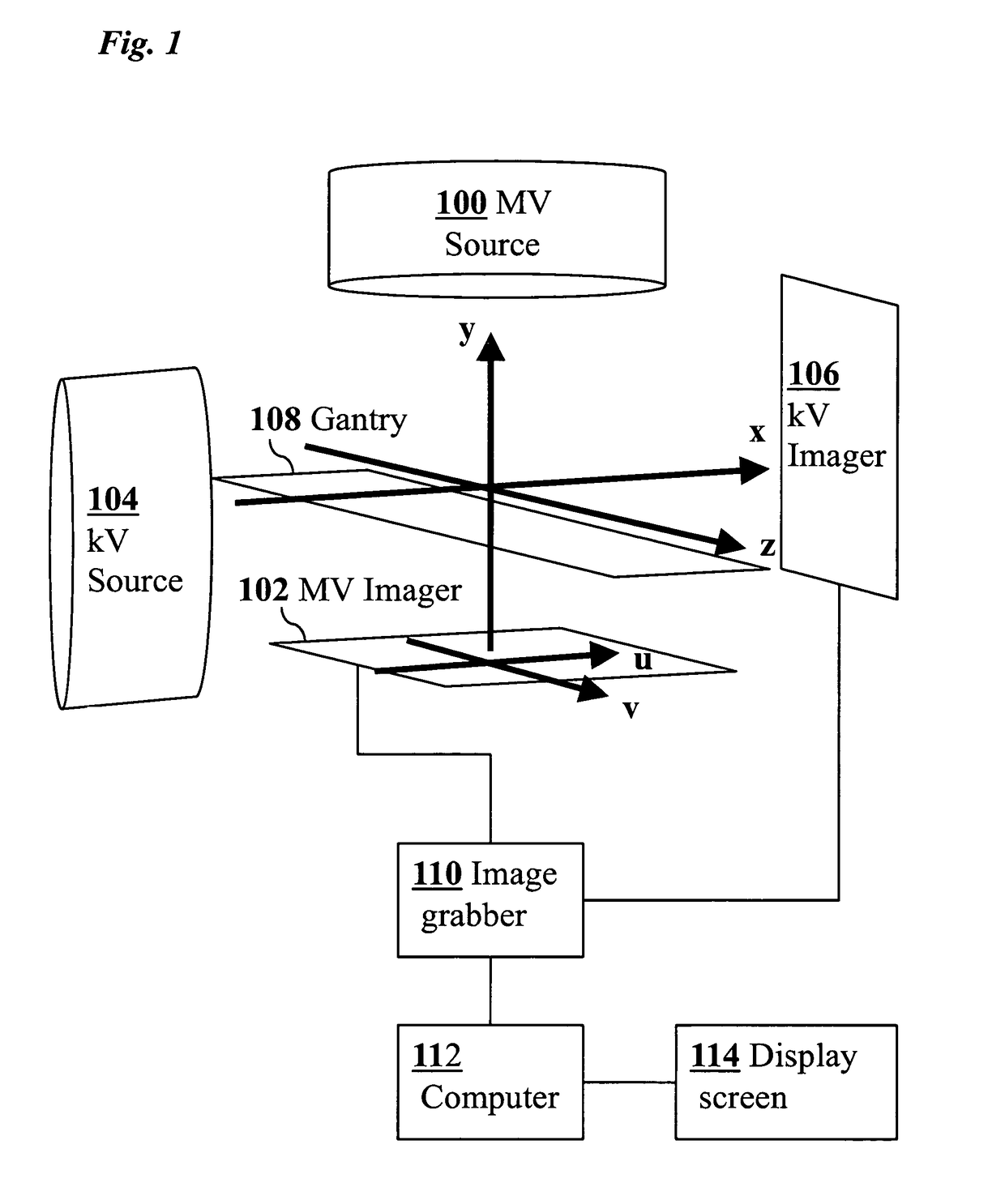
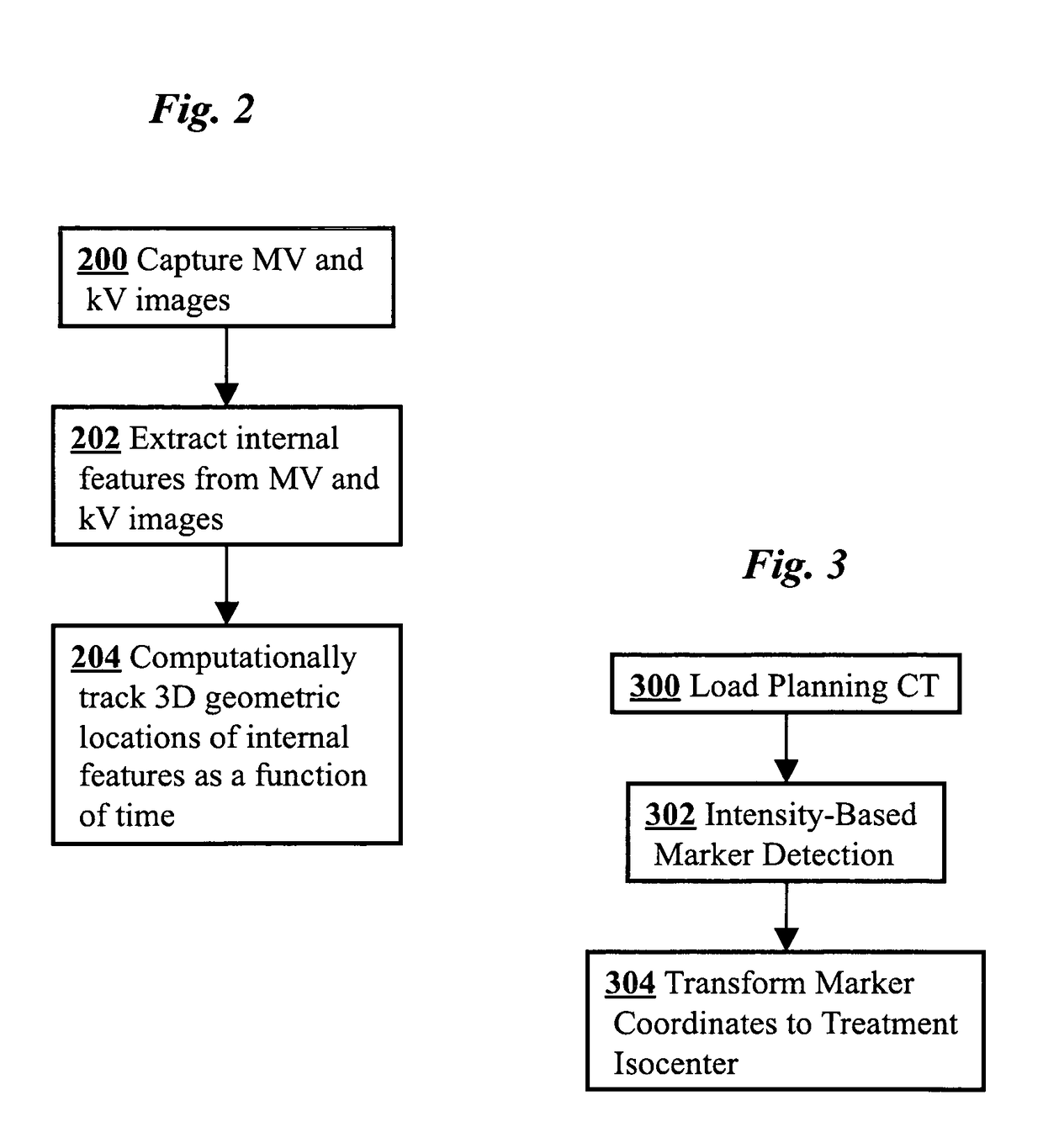
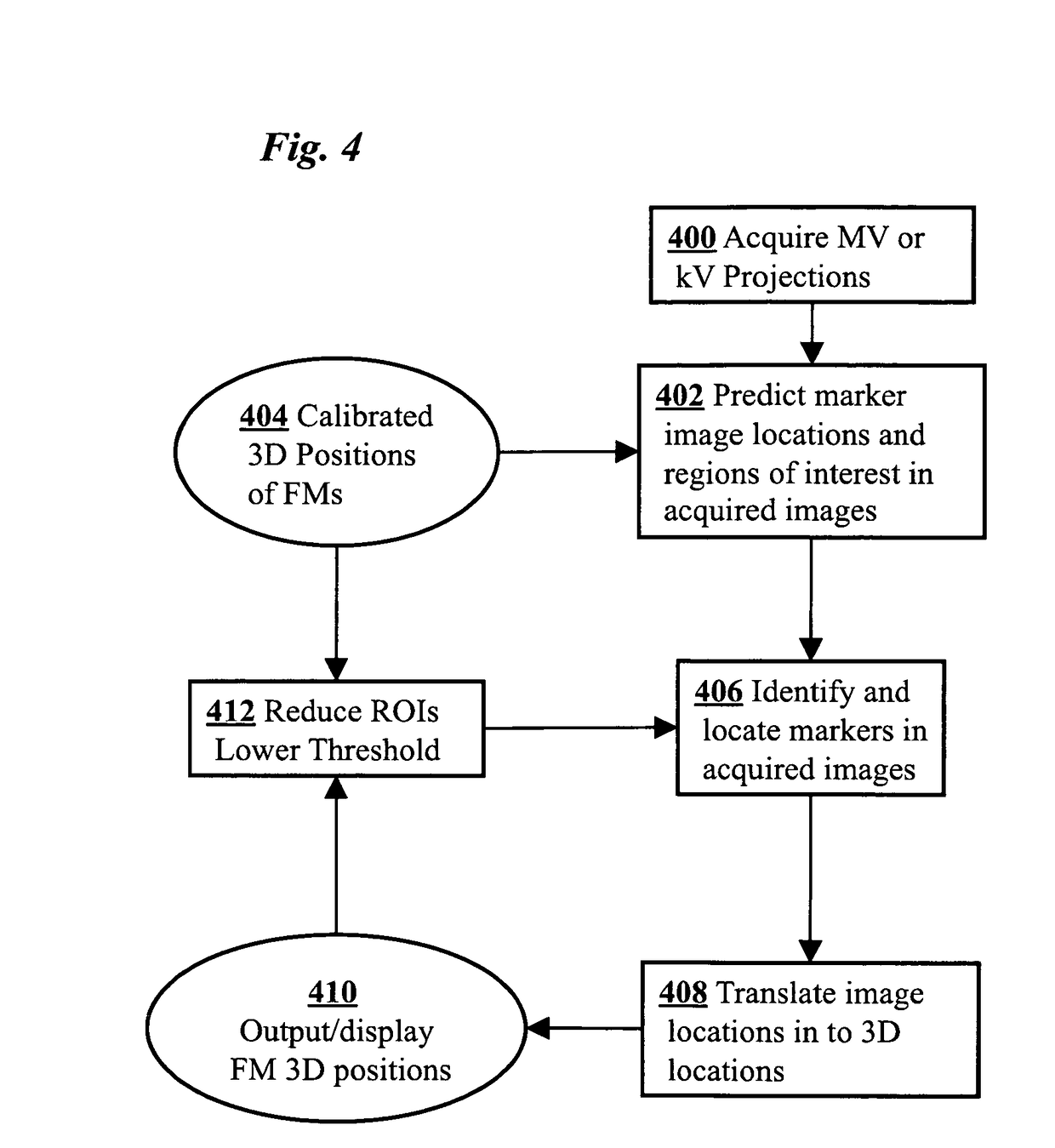
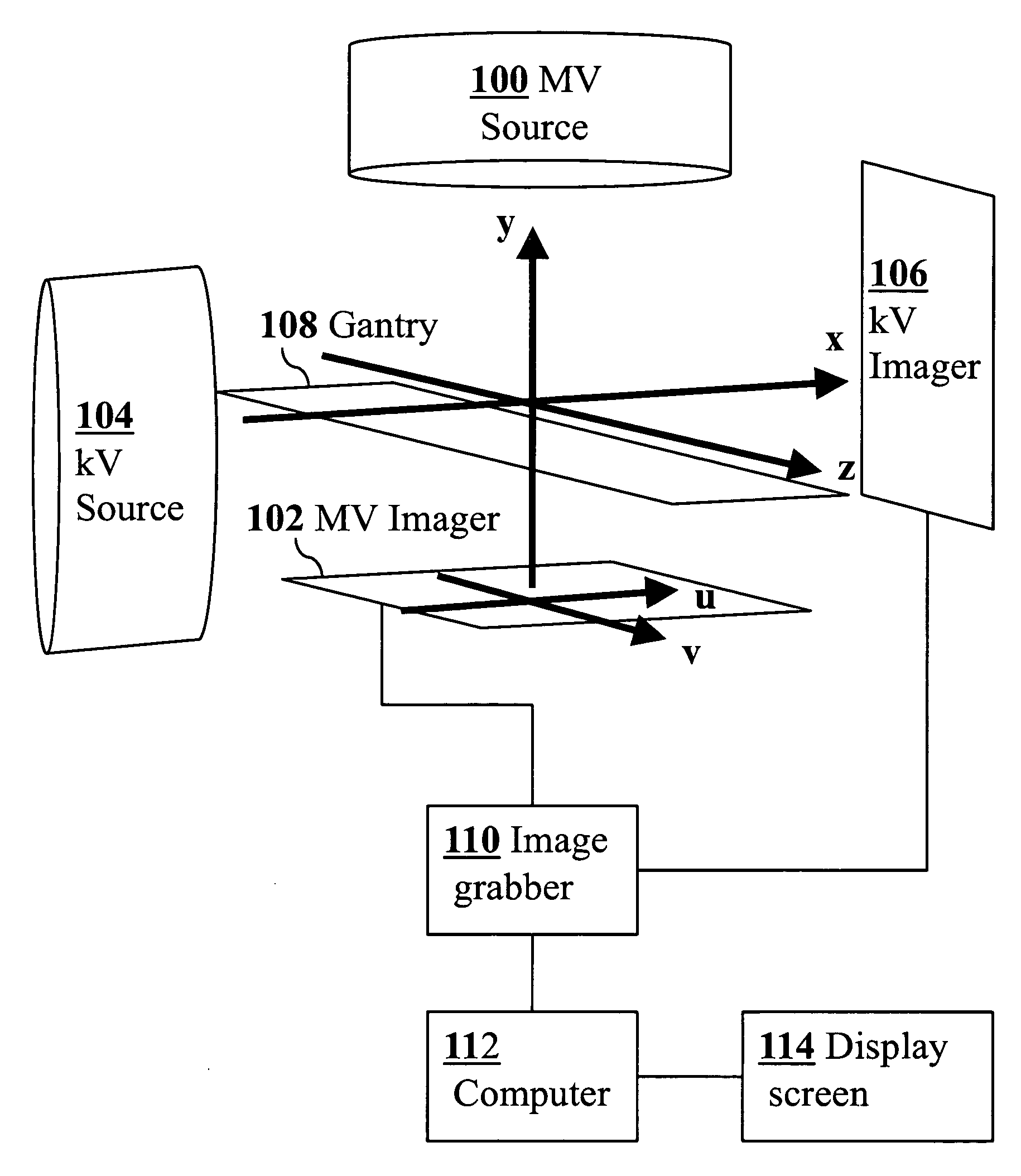
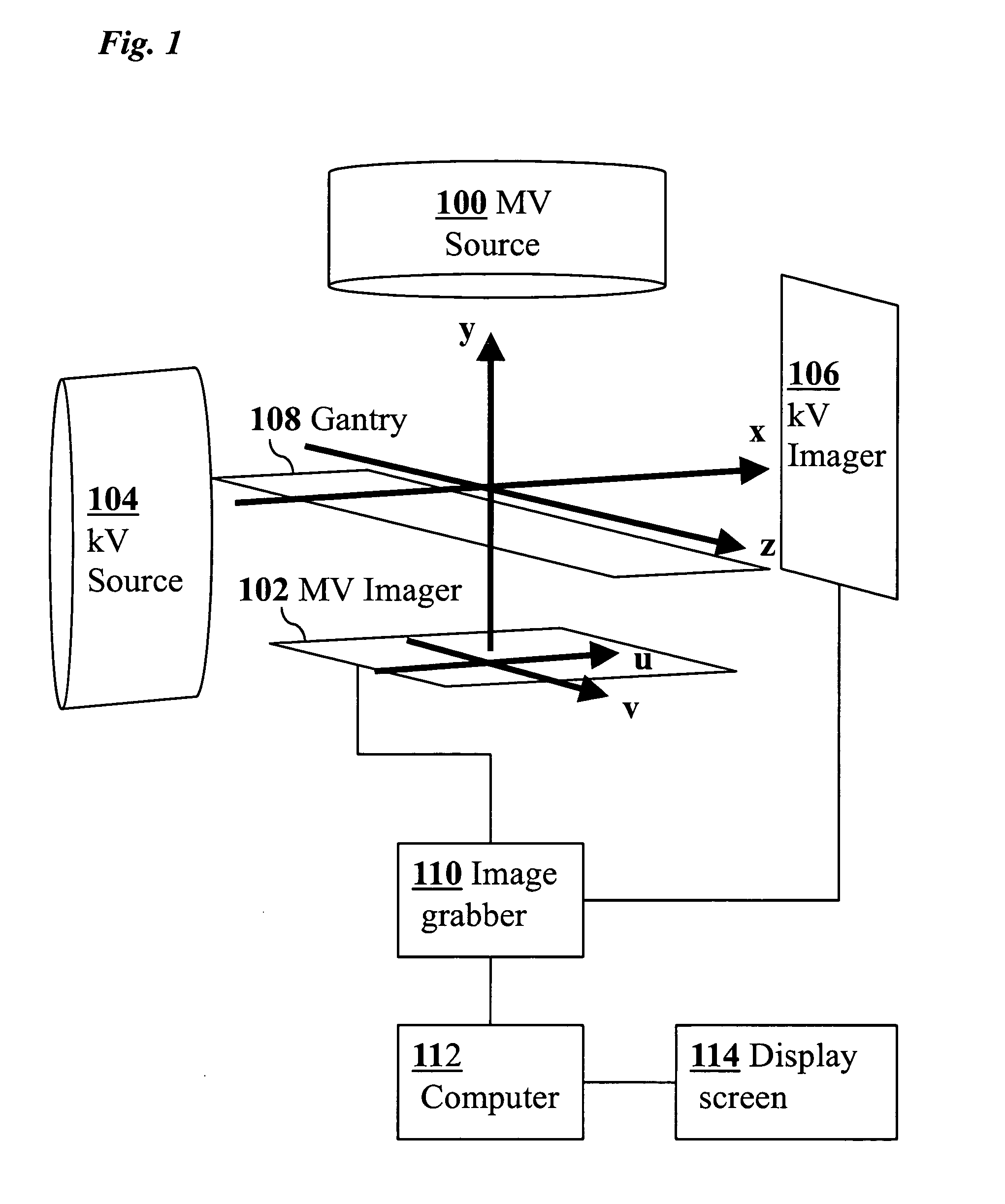
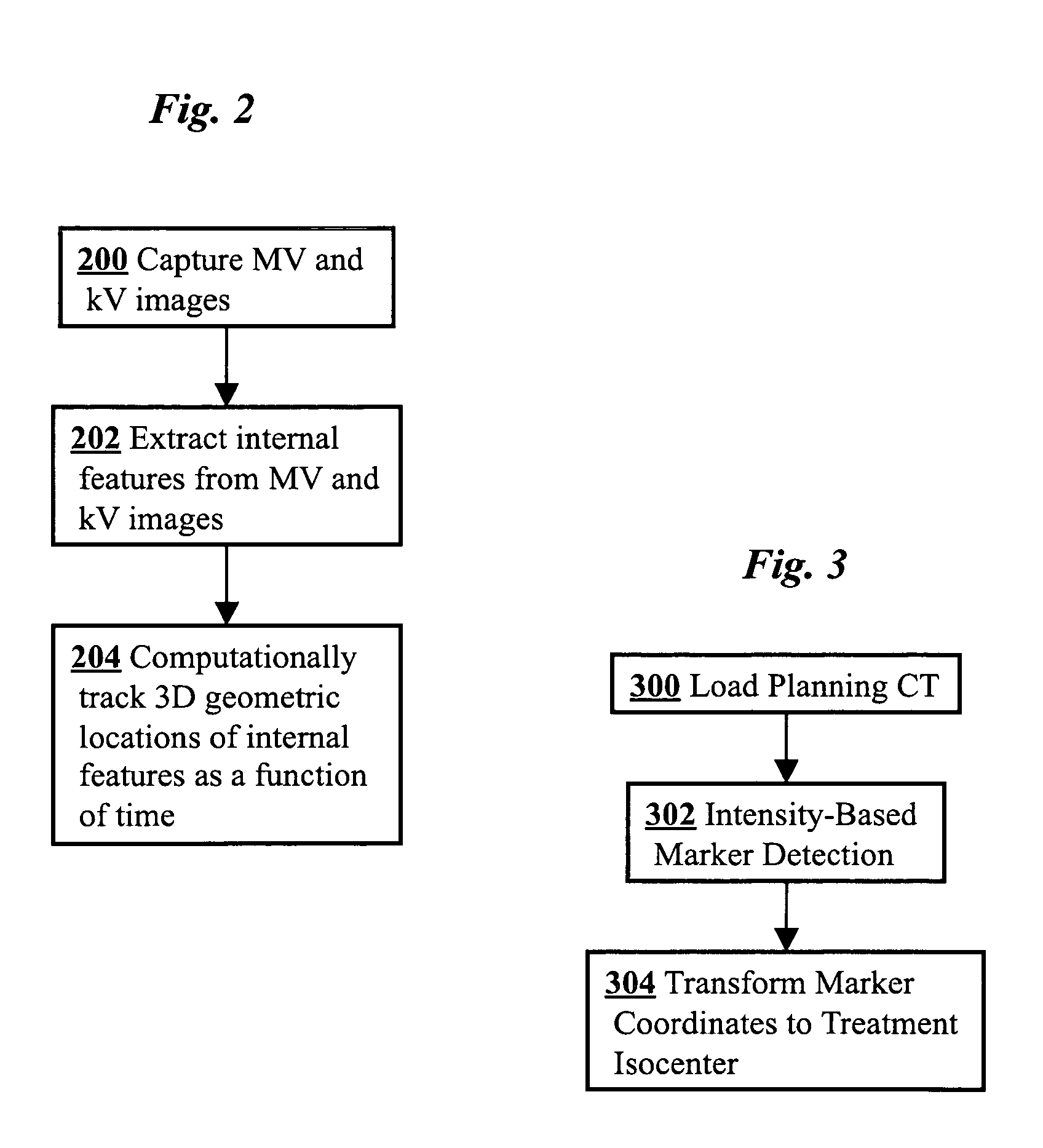
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
ActiveUS8121368B2Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
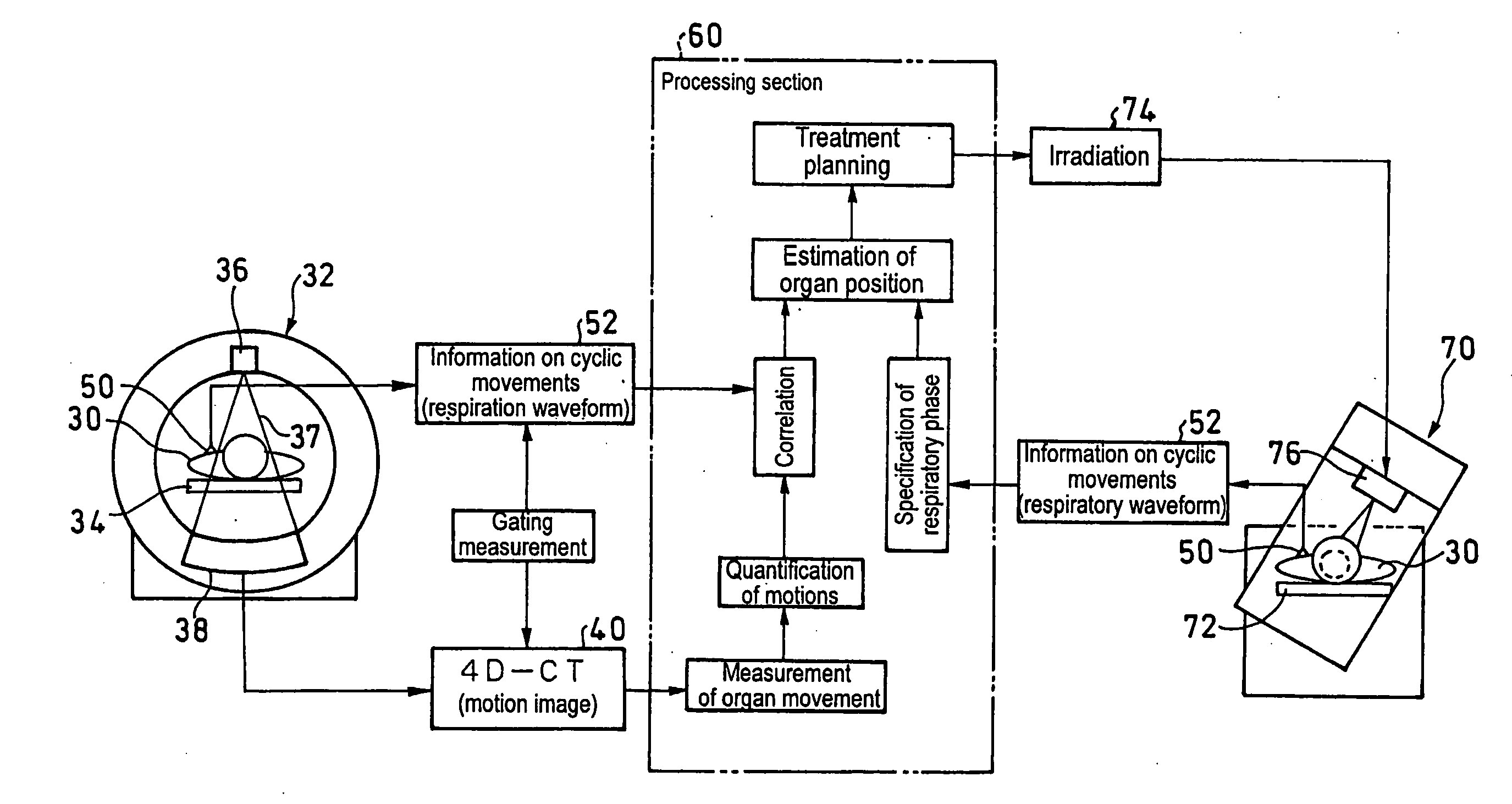
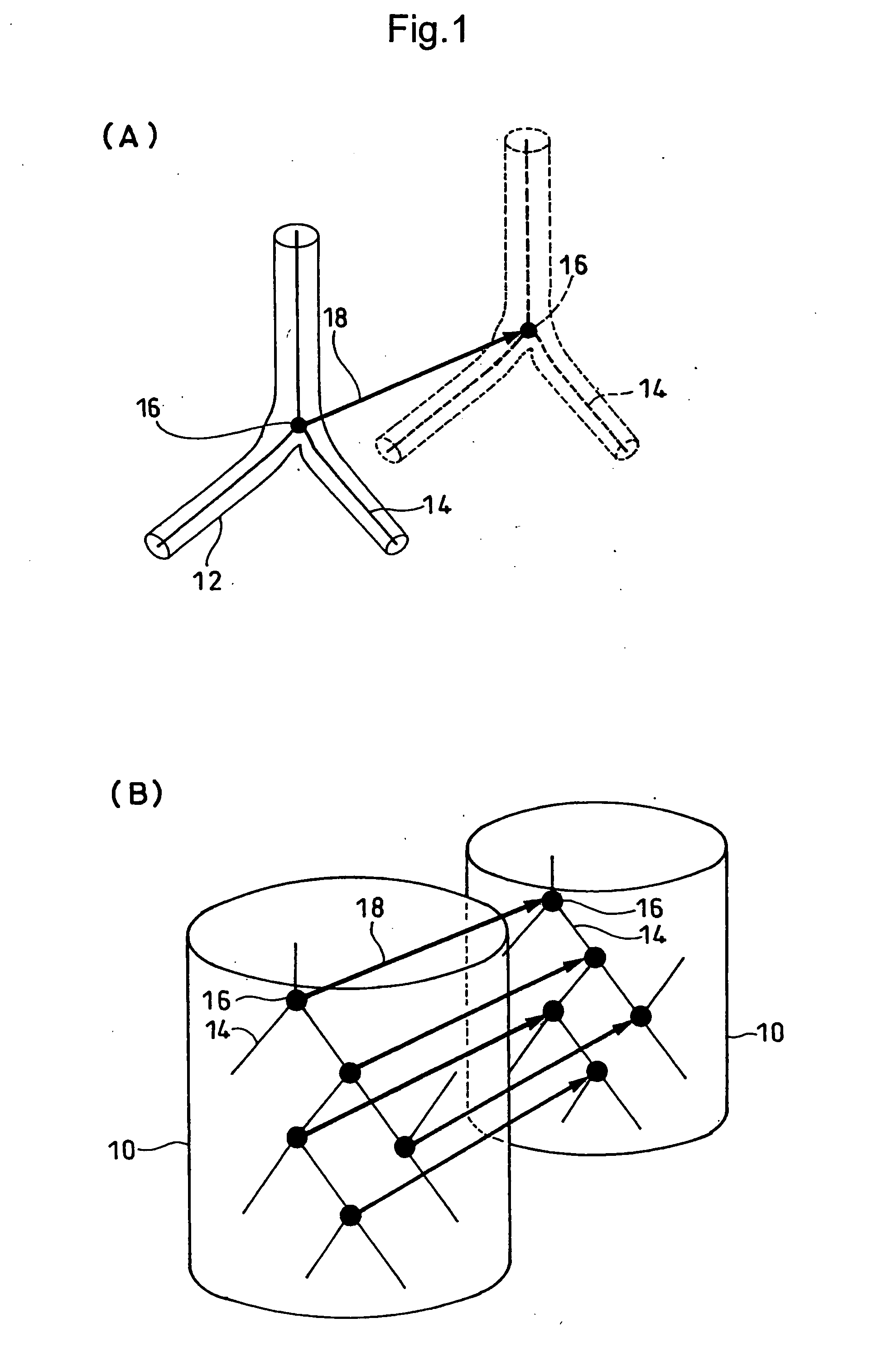
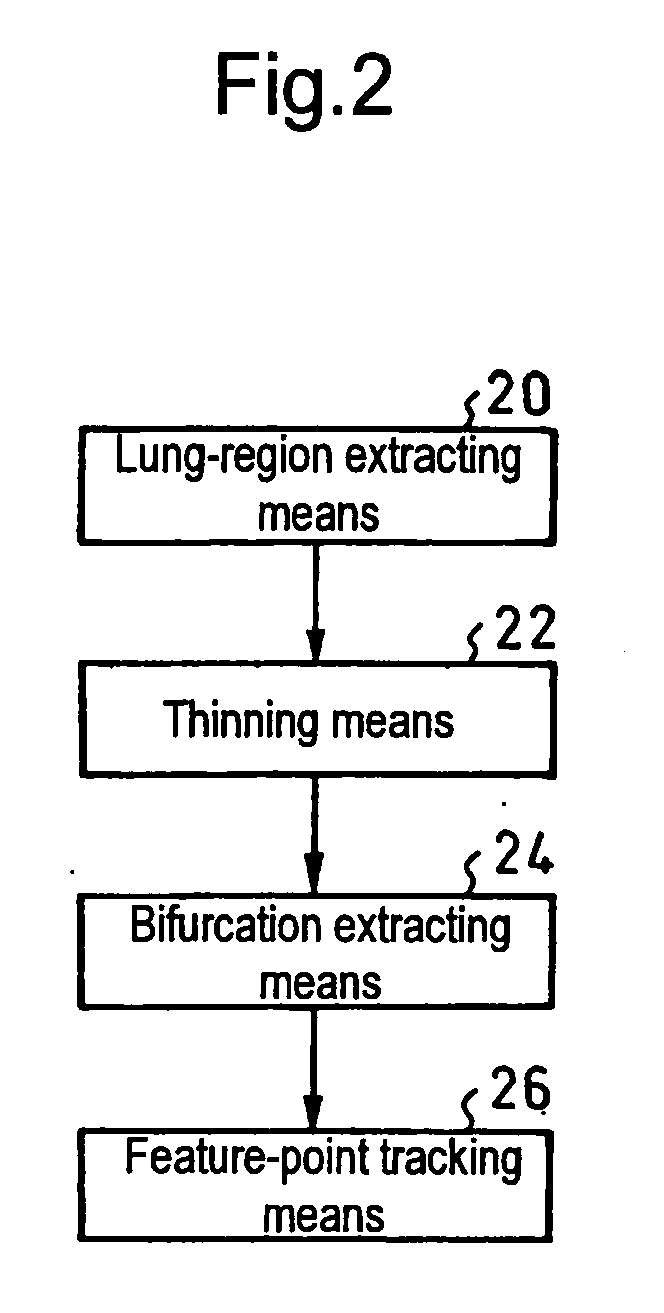
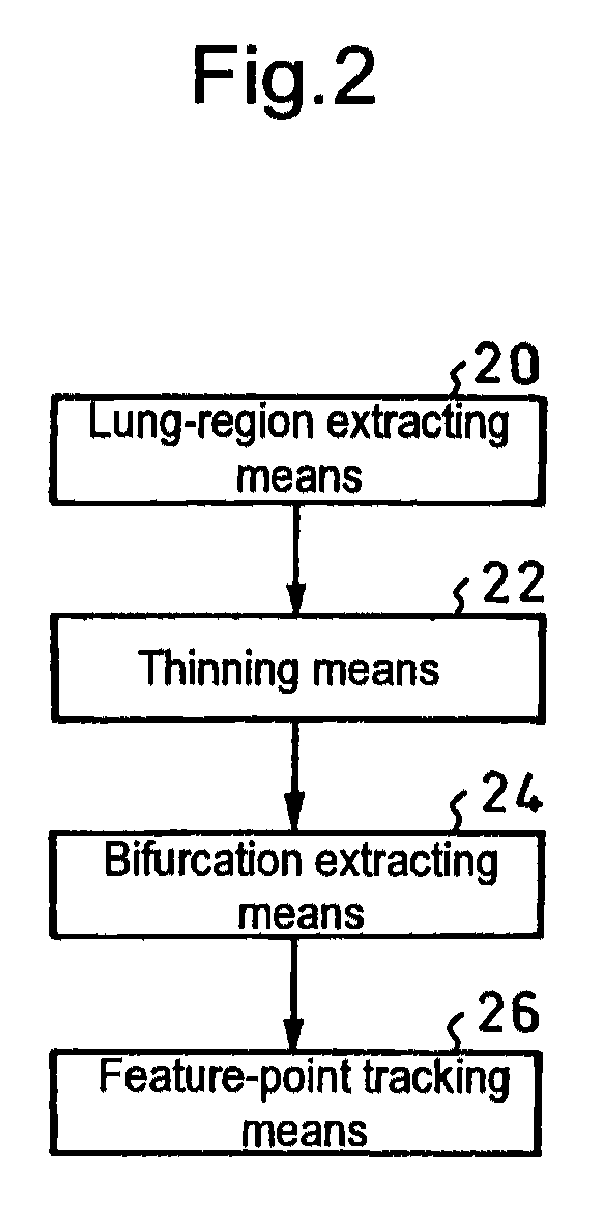
Method for Quantifying Organ Motion, Apparatus Therefor, Method for Estimating Organ Position, Apparatus Therefor, Method for Irradiating Radiation, Apparatus Therefor, and Apparatus for Detecting Abnormal Organ
InactiveUS20090022379A1Quantitative precisionImage enhancementImage analysisFluenceThree-dimensional space
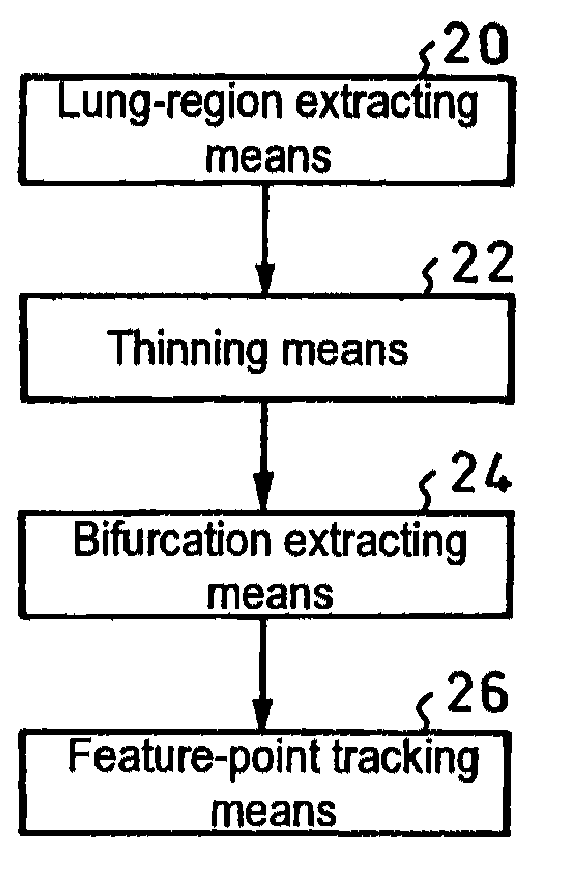
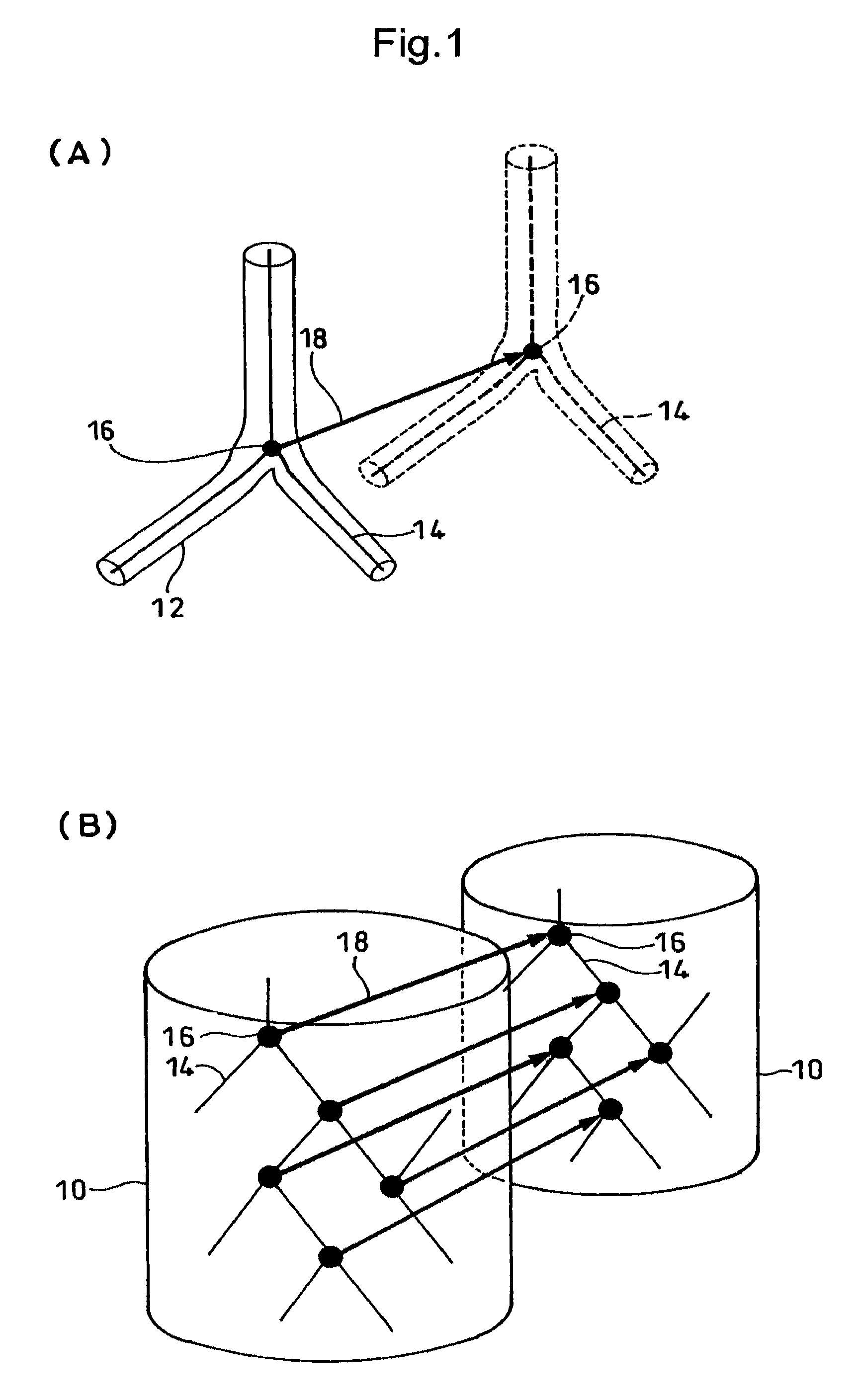
A plurality of CT images of an organ (10) which has undergone a subtle variation or deformation are used as input data, blood vessels and trachea 12 distributed inside the organ are extracted and subjected to thinning, the thus thinned images 14 are used to extract the coordinates of bifurcations 16 and connections, the thus extracted coordinates are used as feature points to track the motion of individual points between a plurality of CT images in a three dimensional space, thereby measuring the movement of the organ (10). Thus, it is possible to realize a local motion tracking at an arbitrary point over an entire region inside an organ, which would be impossible by using a metal marker.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
ActiveUS20090208074A1Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
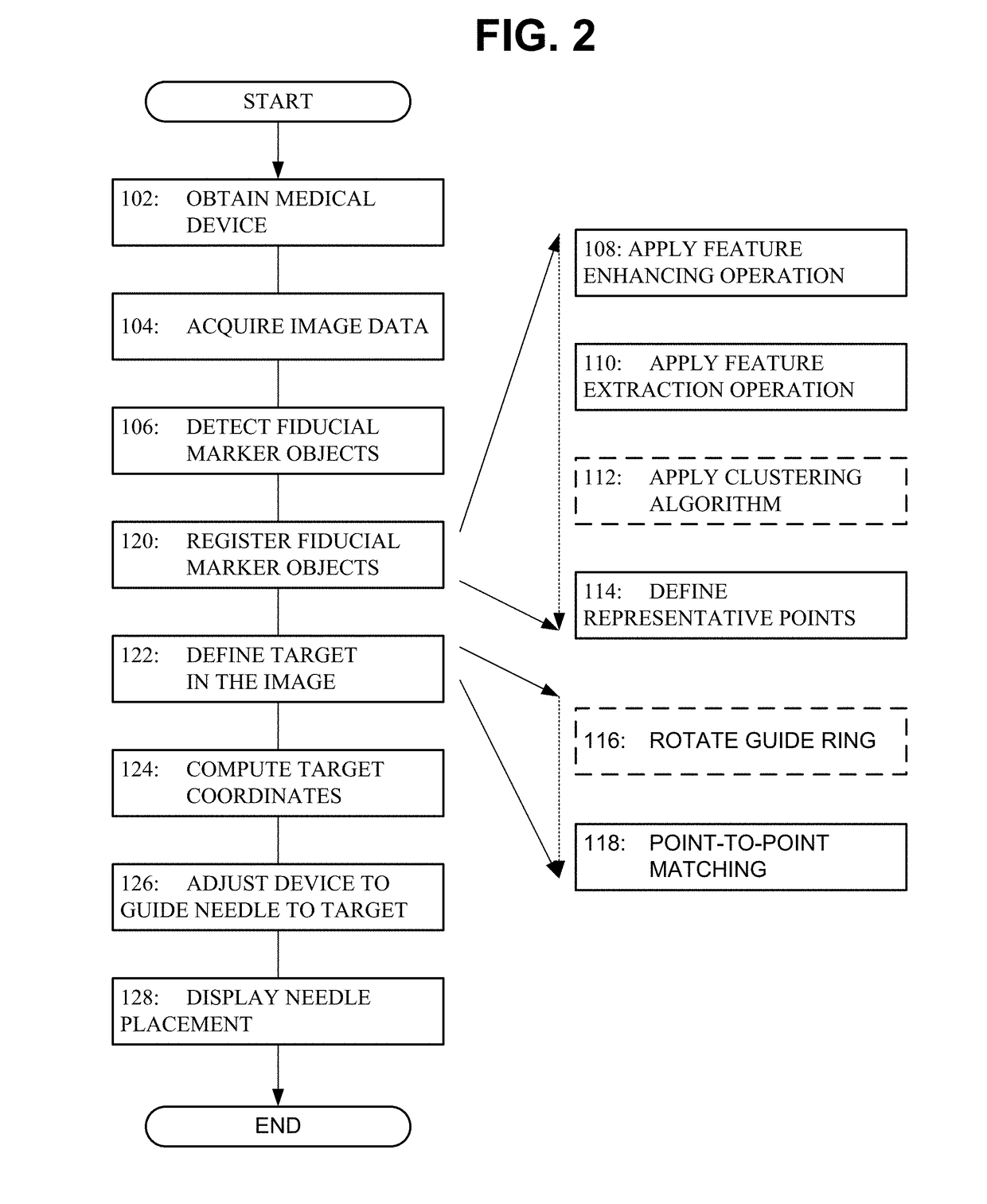
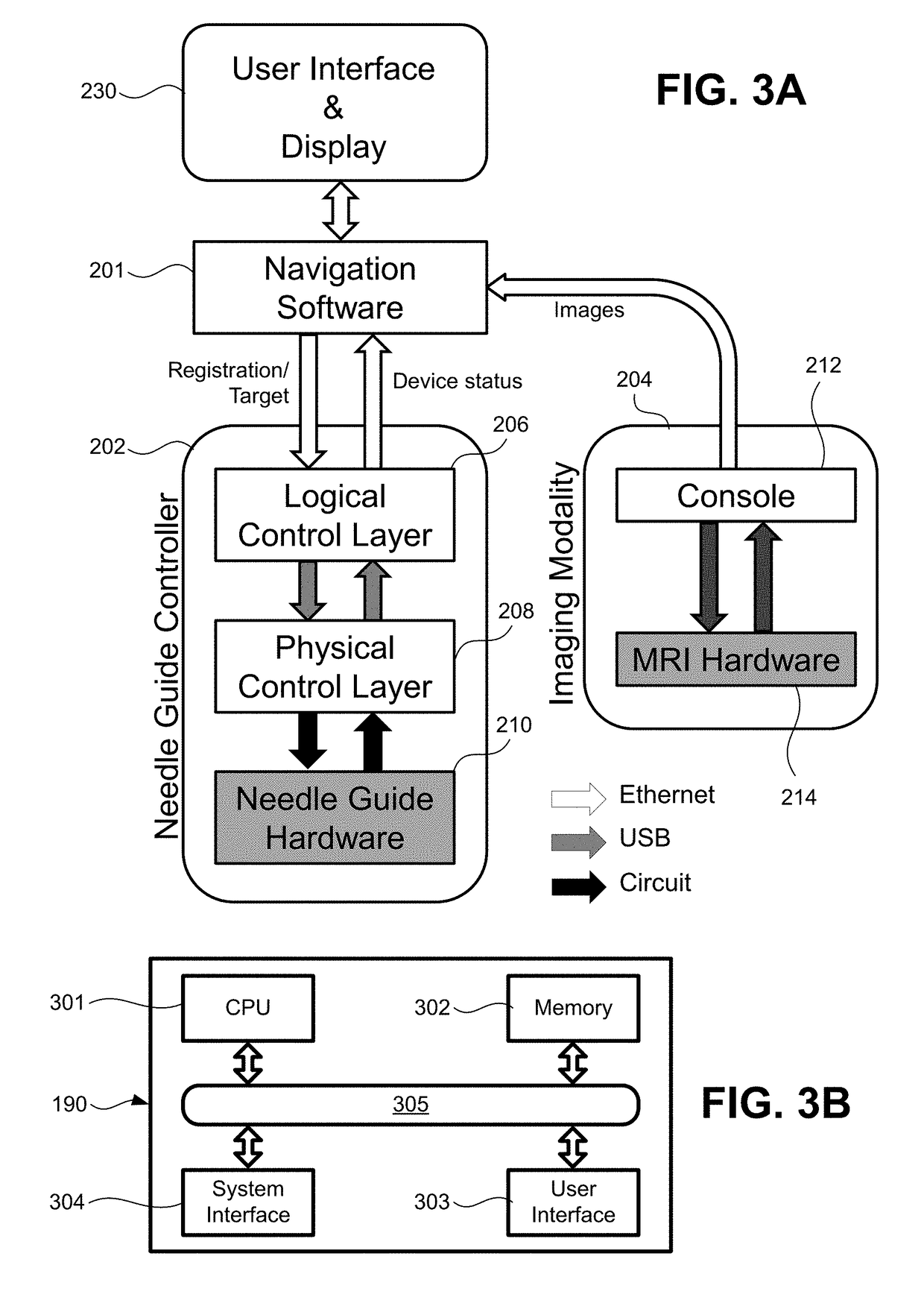
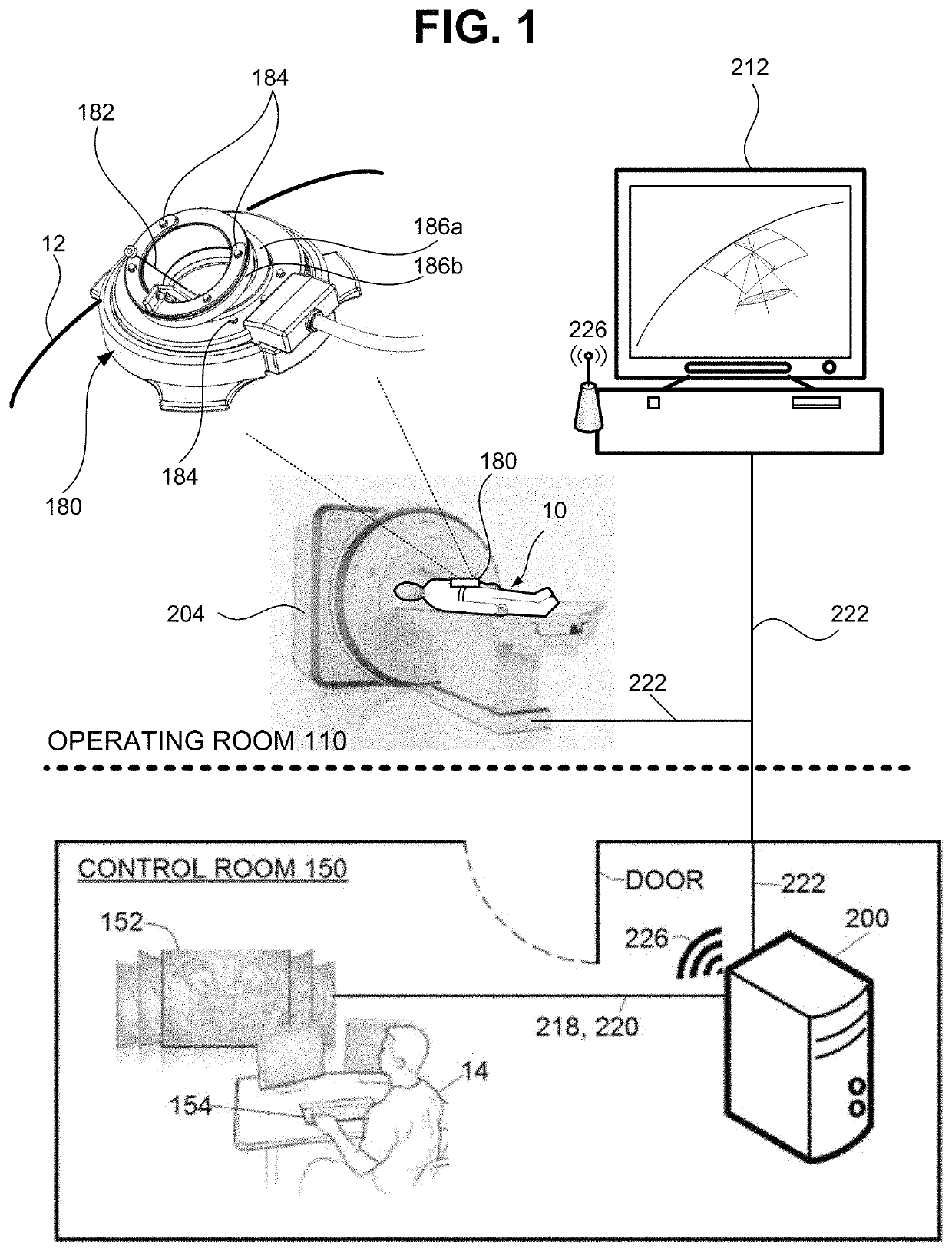
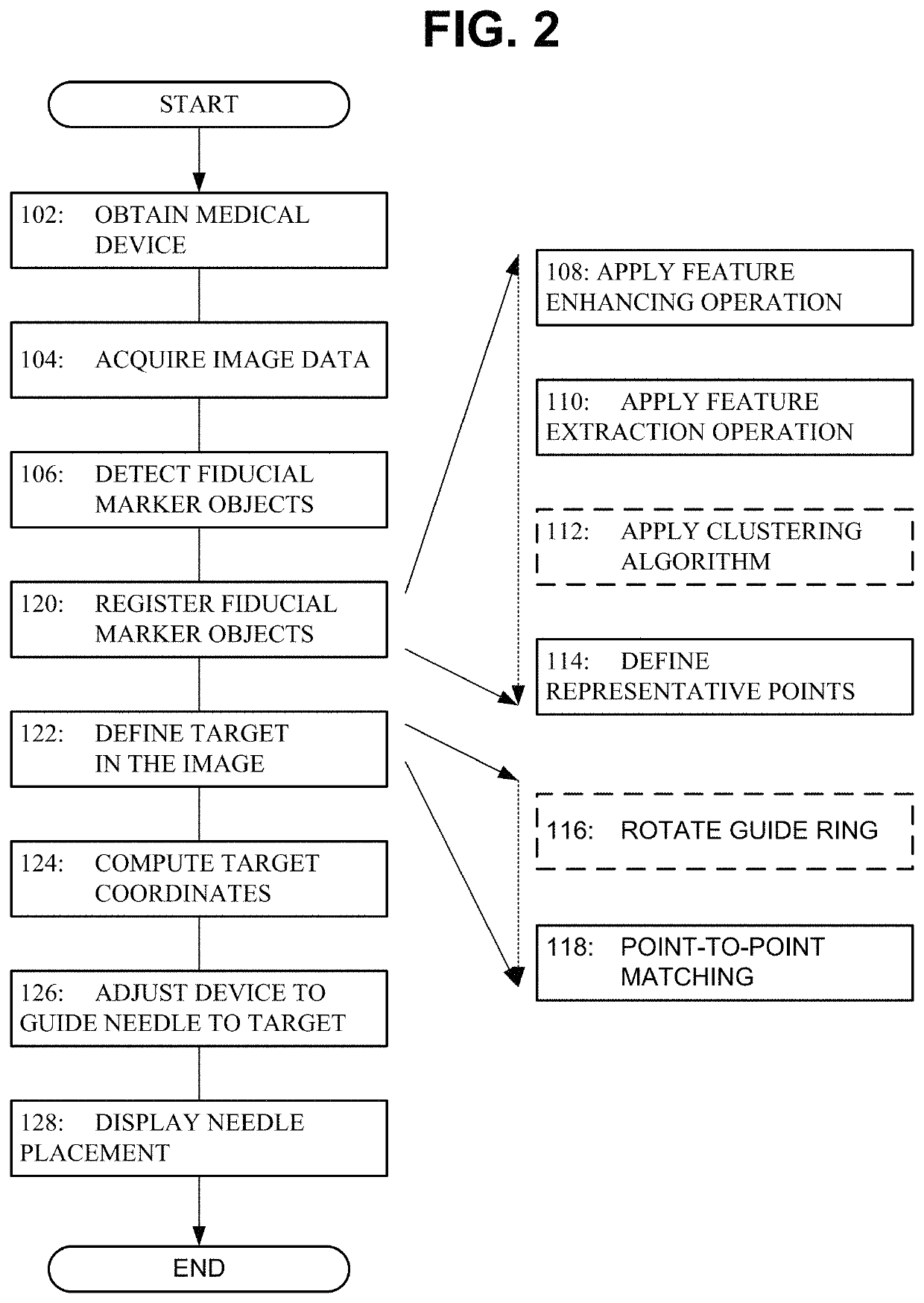
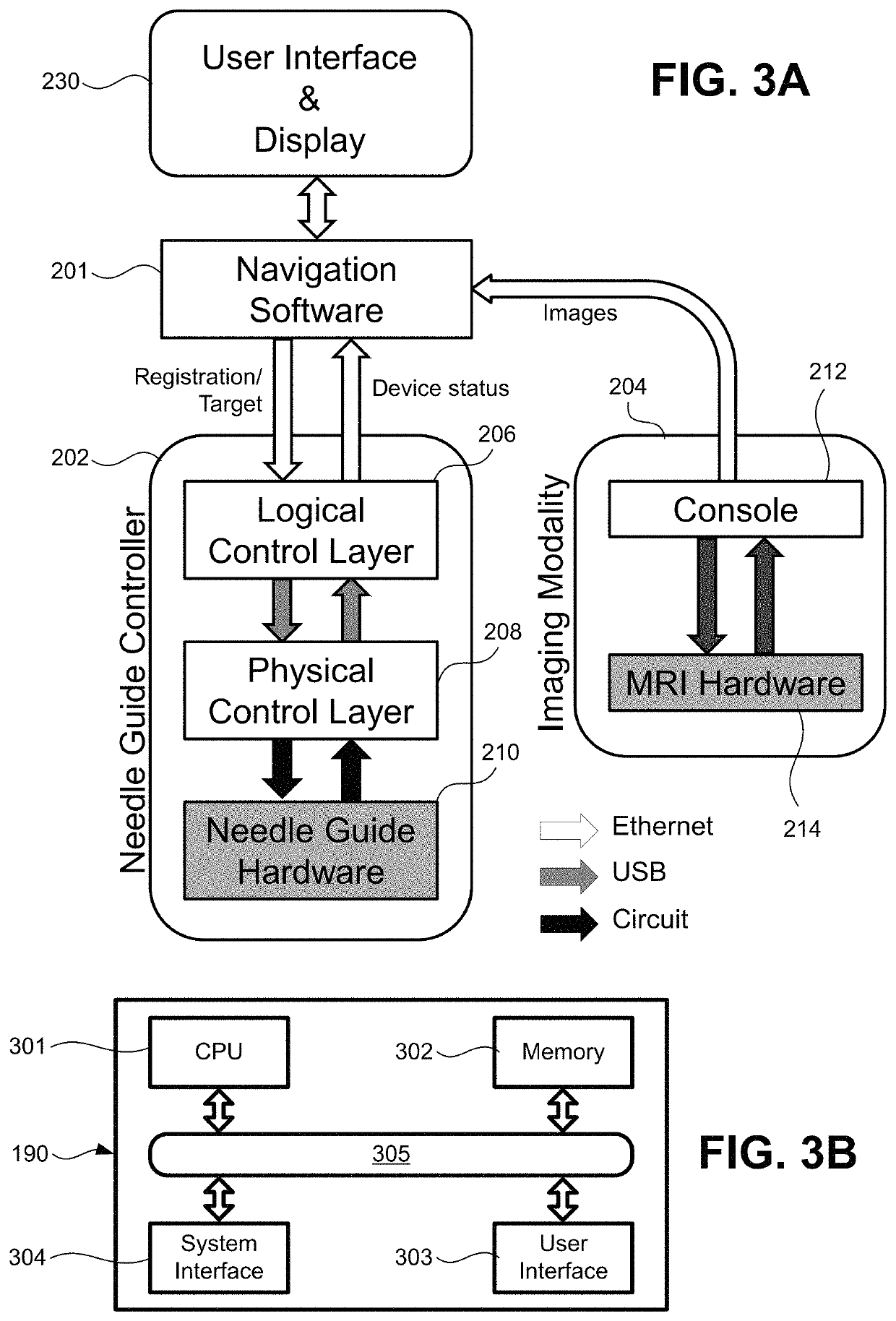
Registration and motion compensation for patient-mounted needle guide
Exemplary methods, apparatus, and systems are disclosed for automated registration and motion compensation of patient-mounted needle guide medical devices using fiducial markers, and processing algorithms where a re-registration step is provided. These methods, apparati, and systems adaptively compensate for the displacement of the medical device and / or target location due to the patient movement or internal organ motion.
Owner:CANON USA +1
Respiration correction technique in positron emission tomography
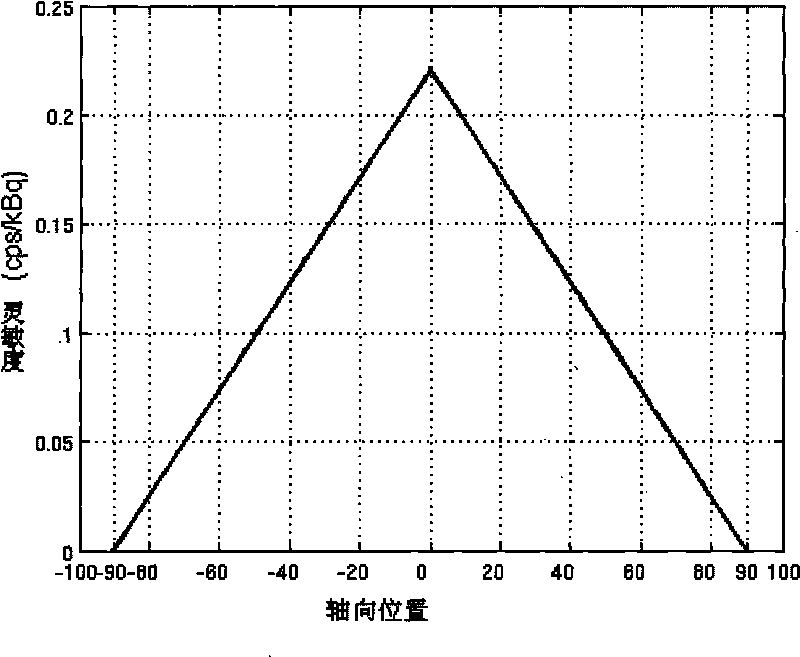
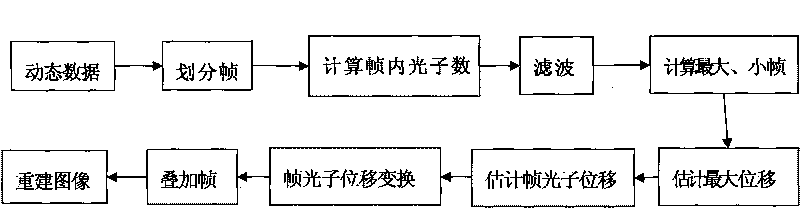
InactiveCN101702232AImprove the correct diagnosis rateCompensate for image artifactsImage enhancement3D-image renderingDetector geometryCorrection technique
The invention relates to a respiration correction technique in positron emission tomography, in particular to a technique for correcting the artifact of respiration tomography on the basis of the sensitivity characteristics of a three-dimensional positron emission detector, belonging to the field of nuclear medical tomography. The correction method provided by the invention can effectively compensate for the image artifact caused by respiration, thereby improving the diagnostic accuracy of doctors. The correction method comprises the following steps: frame segmentation is carried out on the acquired dynamic data by using the variation characteristics of the geometric sensitivity of a scanning detector in the three-dimensional PET, wherein the number of intra-frame photons can reflect the phase position of the organ motion, and the number of photons of each phase position has a linear relation with the motion displacement thereof; accordingly, each phase position is moved to certain reference phase position point for correcting; and the image reconstructed at last constitutes the image artifact caused by the respiration in the PET improved by correction. Compared with the prior art like the gating correction technique, the method of the invention dispenses with hardware equipment and extra preparation by patients or clinic before scanning, therefore, the method is easier, more effective and more reliable in actual application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for tracking motion phase of an object for correcting organ motion artifacts in X-ray CT systems
InactiveUS20050238135A1Improve image qualityEnhance the imageReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationObject based
The present invention relates to a method for tracking motion phase of an object. A plurality of projection data indicative of a cross-sectional image of the object is received. The projection data are processed for determining motion projection data of the object indicative of motion of the object based on the attenuation along at least a same line through the object at different time instances. A motion phase of the object with the object having the least motion is selected. Finally, projection data acquired at time instances within the selected motion phase of the object are selected for tomographical image reconstruction. Reconstructed images clearly show a substantial improvement in image quality by successfully removing motion artifacts using the method for tracking motion phase of an object according to the invention. The method is highly beneficial in cardiac imaging using X-ray CT scan.
Owner:CANAMET CANADIAN NAT MEDICAL TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveCN108209918ASolve the problem of incomplete suppressionQuality improvementDiagnostic signal processingSensorsResonanceSaturation pulse
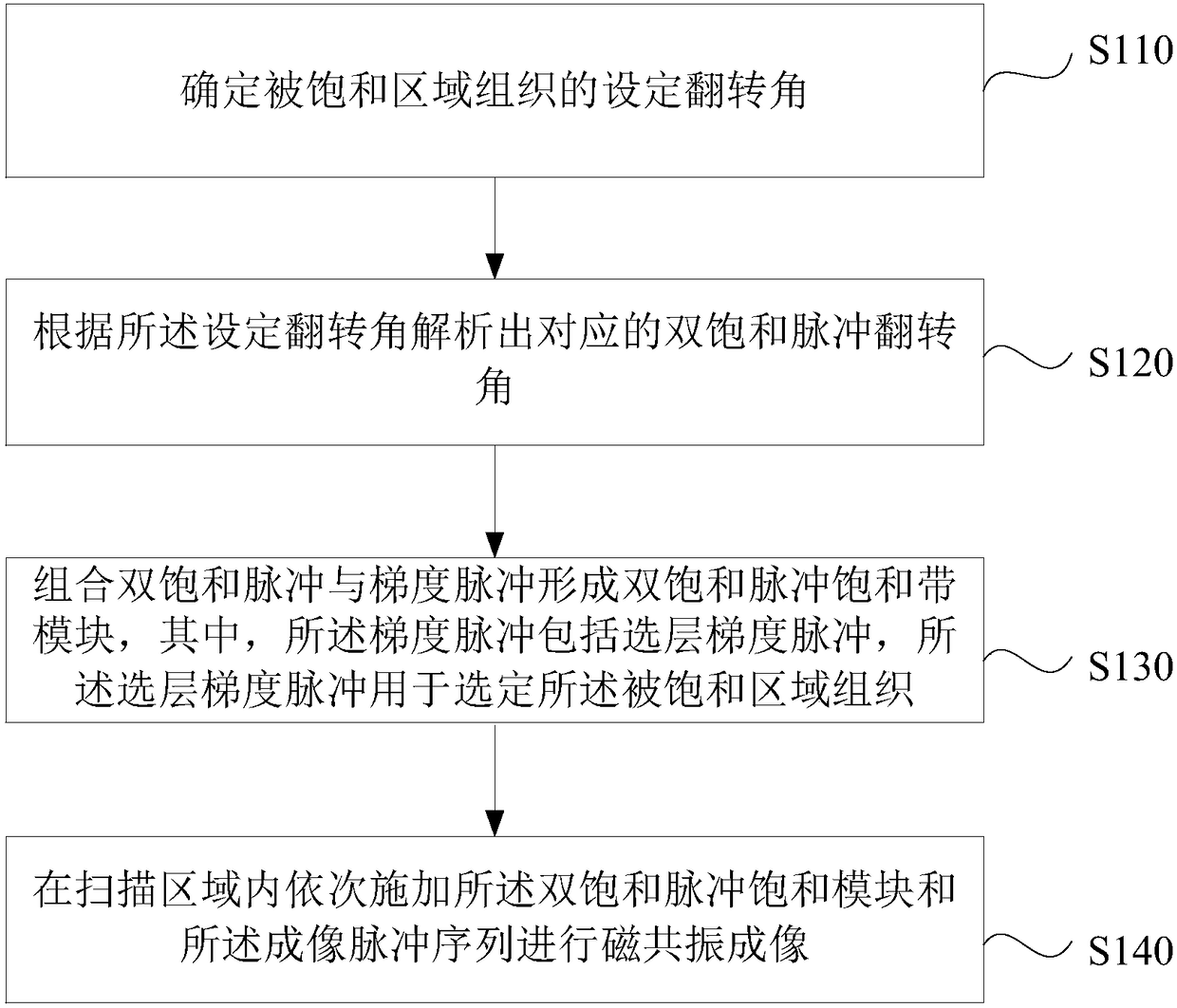
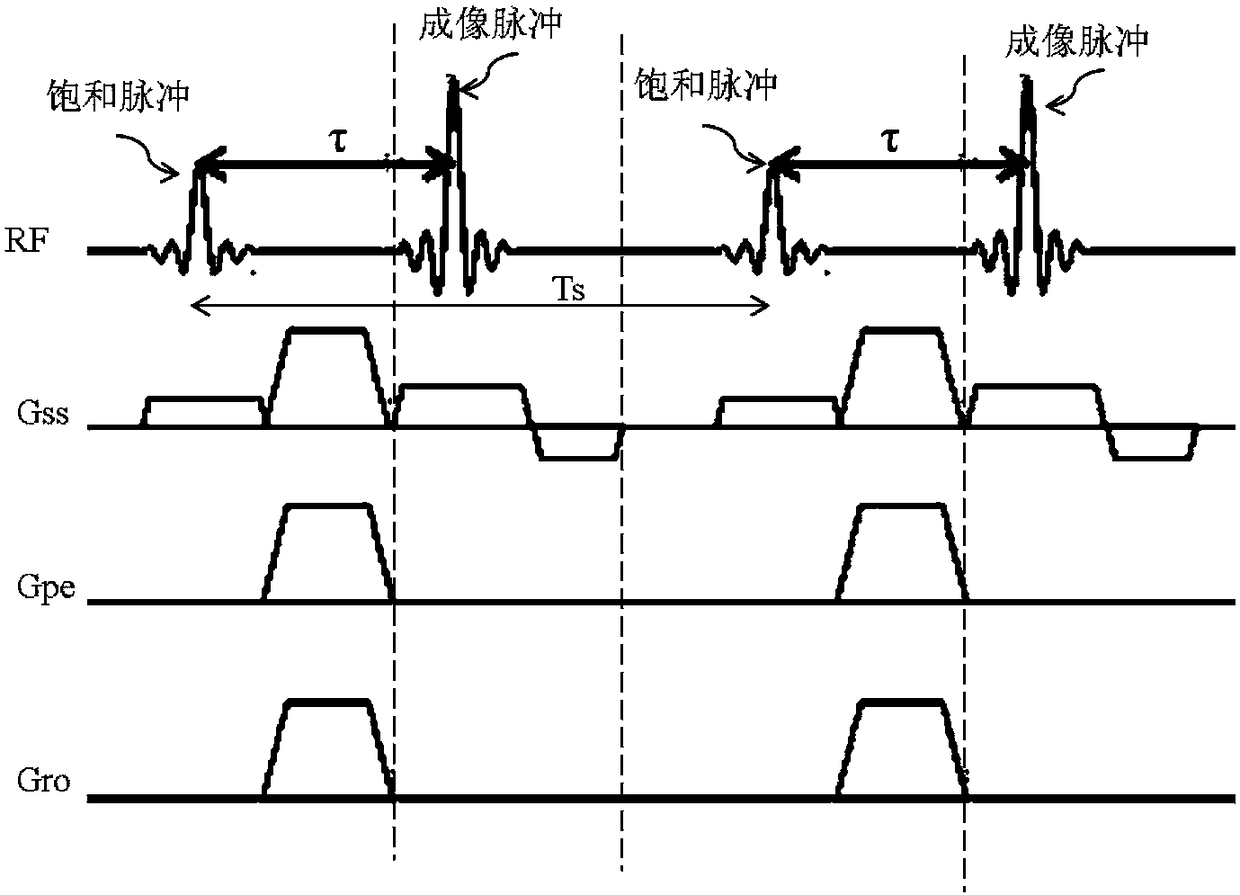
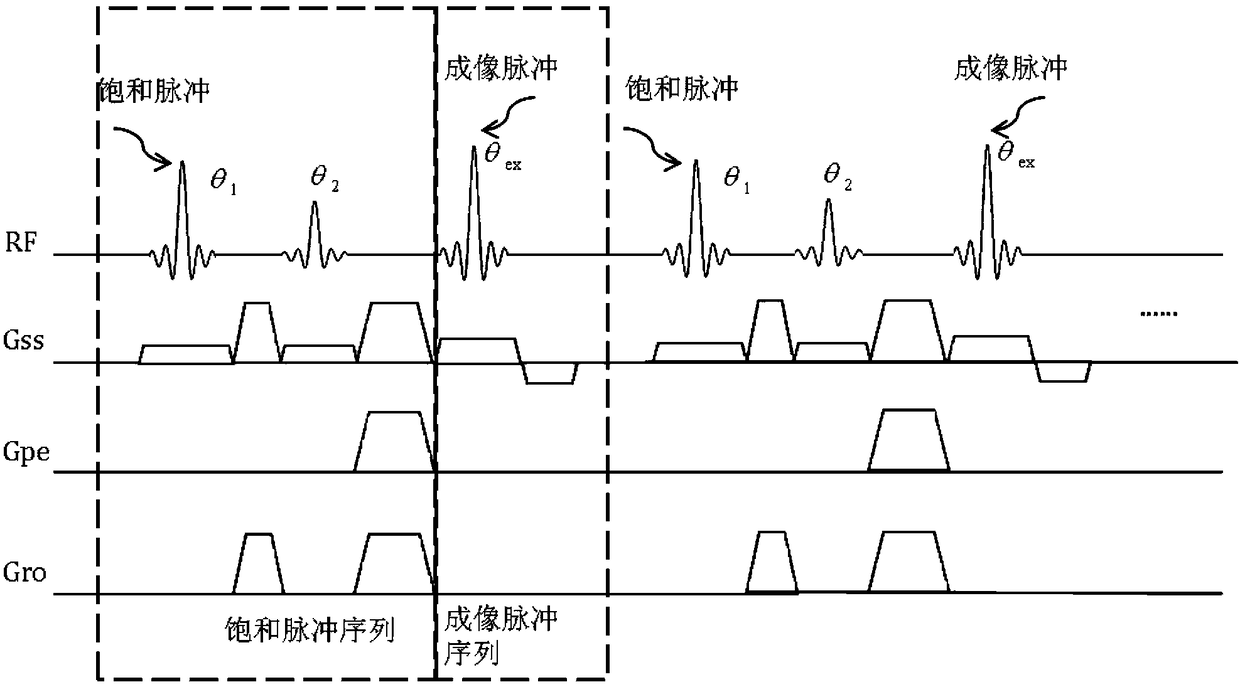
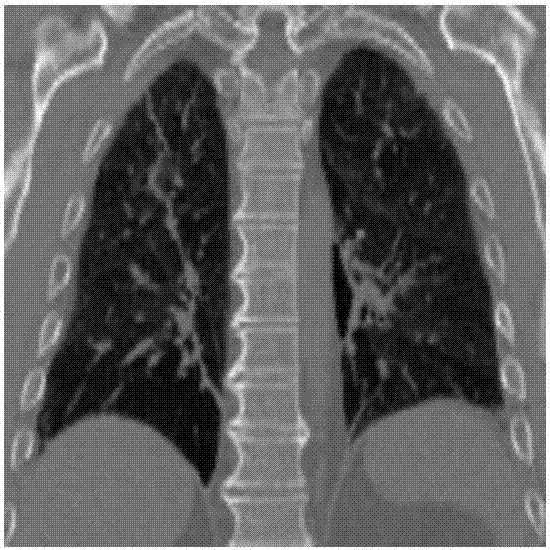
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method and system, wherein the method comprises: before imaging scanning, determining a preset deflection angle of a radio frequency pulse to excite specific tissues; analyzing a corresponding dual-saturated pulse deflection angle according to the preset deflection angle; combining a dual-saturated pulse and a gradient pulse to form a dual-saturated pulse saturation module, wherein the gradient pulse includes a layer-selecting gradient pulse that is used for exciting a corresponding layer of the specific tissues; executing an imaging scanning process, to be specific, applying the dual-saturated pulse saturation module and an imaging pulse sequence sequentially to a scanning area to perform magnetic resonance imaging. By carrying out magnetic resonance imaging through the dual-saturated pulse saturation module and the imaging pulse sequence, saturated band signal inhibition non-uniformity due to non-uniformity of B1 field can be overcome, and motion artifacts due to organ motion, tissue motion and other motions can be inhibited.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Liver three-dimensional multi-modality image registration method based on discontinuous motion
ActiveCN107230223APreserve Boundary DiscontinuityAvoid globally smooth resultsImage enhancementImage analysisFree-form deformationOrgan Motion
The invention discloses a liver three-dimensional multi-modality image registration method based on discontinuous motion. The liver three-dimensional multi-modality image registration method comprises the steps of: performing preprocessing and rigid registration on an acquired original liver sequence image; adopting a free-form deformation model combined with a three-order B-spline function to simulate elastic deformation of a liver image, adopting a regularization term based on a total variation and hybrid measurement for constructing a cost function, measuring a similarity degree of the two images, and optimizing and solving the cost function by adopting a limited memory quasi-Newton interpolation method. The liver three-dimensional multi-modality image registration method based on discontinuous motion disclosed by the invention avoids the result of global smooth caused by taking two norms as the regularization term in the prior art, can reserve the boundary discontinuity caused by liver organ motion, and is high in registration precision.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
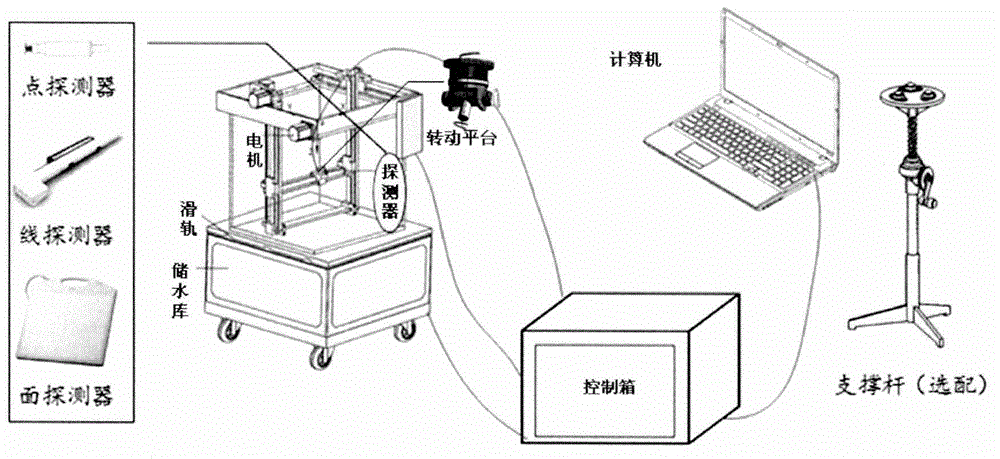
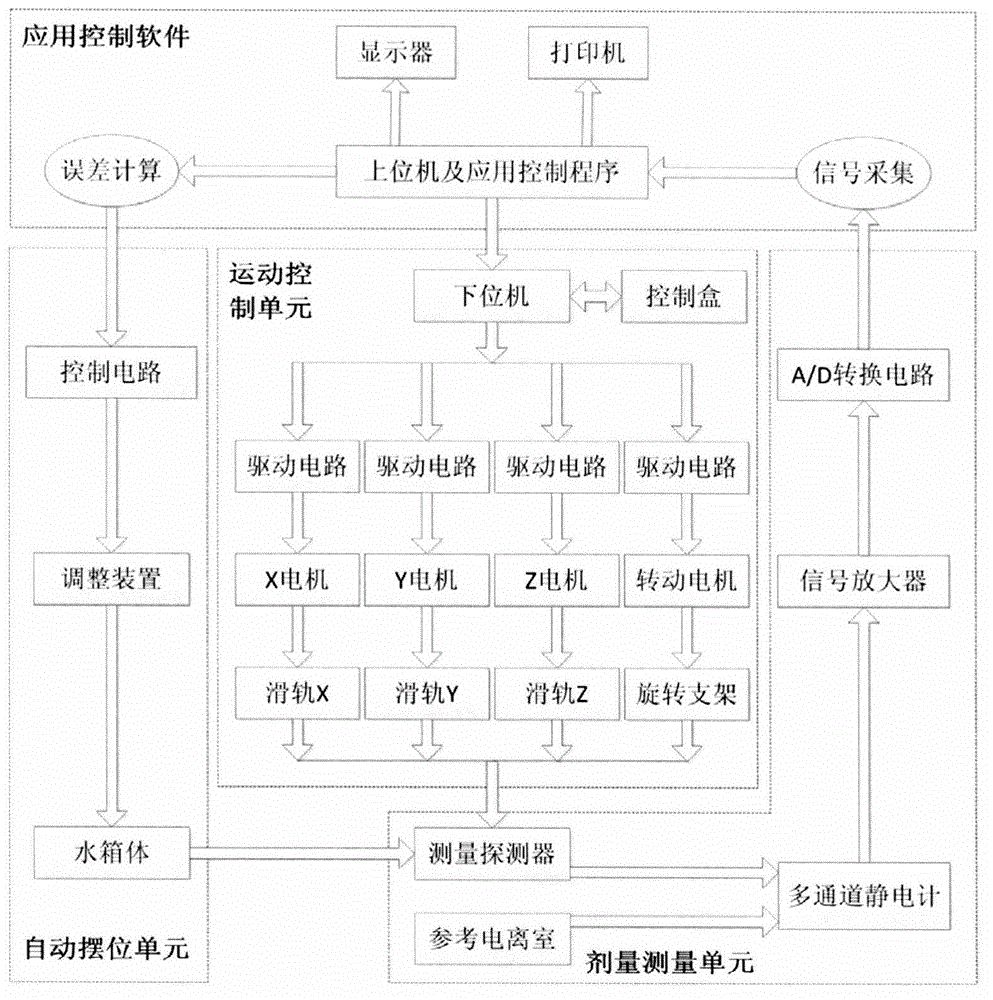
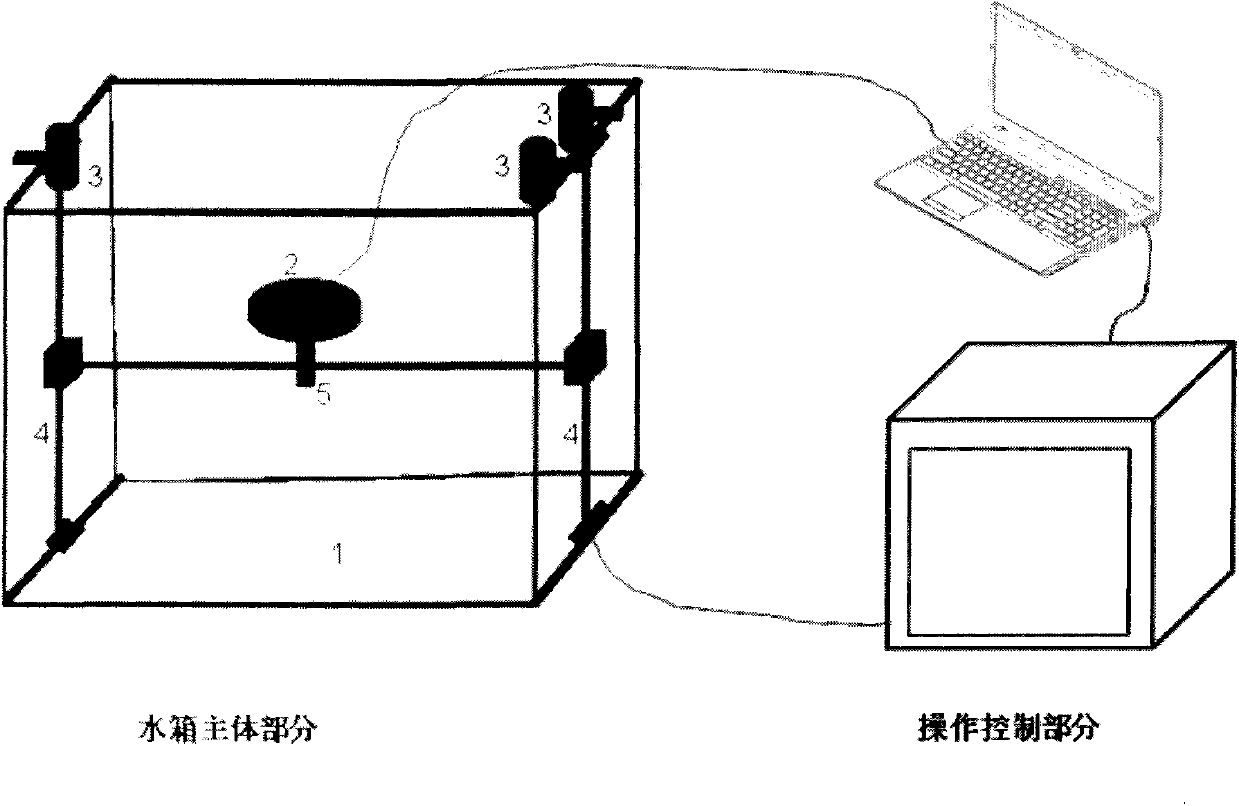
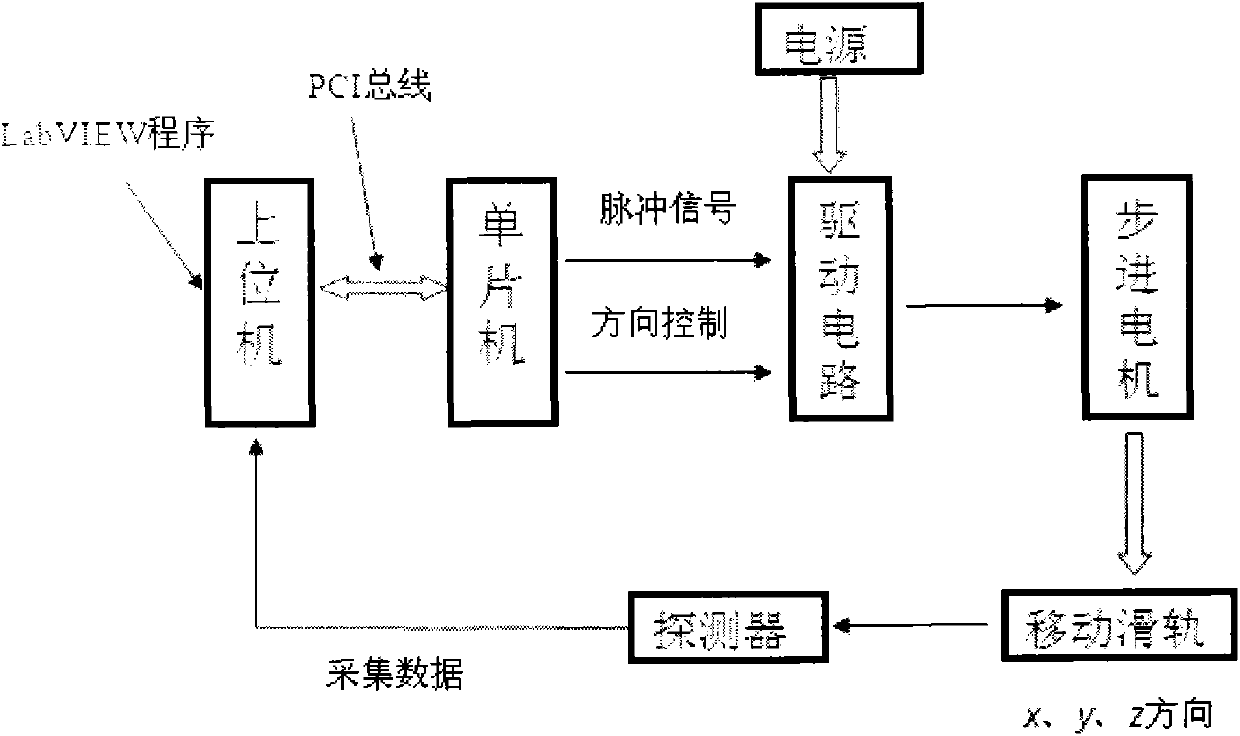
Four-dimensional automatic scan method of measuring complex/dynamic dose field, and four-dimensional automatic scan water tank system
InactiveCN105056407AQuick measurementHigh precisionRadiation intensity measurementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyFlat panel detectorDynamic field
The invention discloses a four-dimensional automatic scan method of measuring a complex / dynamic dose field, and a four-dimensional automatic scan water tank system. The four-dimensional automatic scan water tank system mainly includes a motion control unit, a dose measuring unit, an automatic self-positioning unit, computer application software, a case, a supporting rod, a water tank, etc. Compared with conventional water tanks, the system has the following advantages: 1) four-dimensional measuring control software is designed to achieve a new four-dimensional measuring function; 2) a linear array and a flat-panel detector are utilized to improve the measuring efficiency; 3) the system is provided with a water tank automatic self-positioning auxiliary device, so the self-positioning efficiency is increased; and 4) the water tank and an accelerator interface communicate with each other, so the measuring efficiency is increased. The system is capable of measuring complex and (or) dynamic dose fields, is a significant measuring tool for research and development of novel ray devices and novel irradiation technologies and for applications of the device and technologies, and also provides a more accurate platform for discussion of organ motion influence and other scientific issues.
Owner:戴建荣
Method of imaging
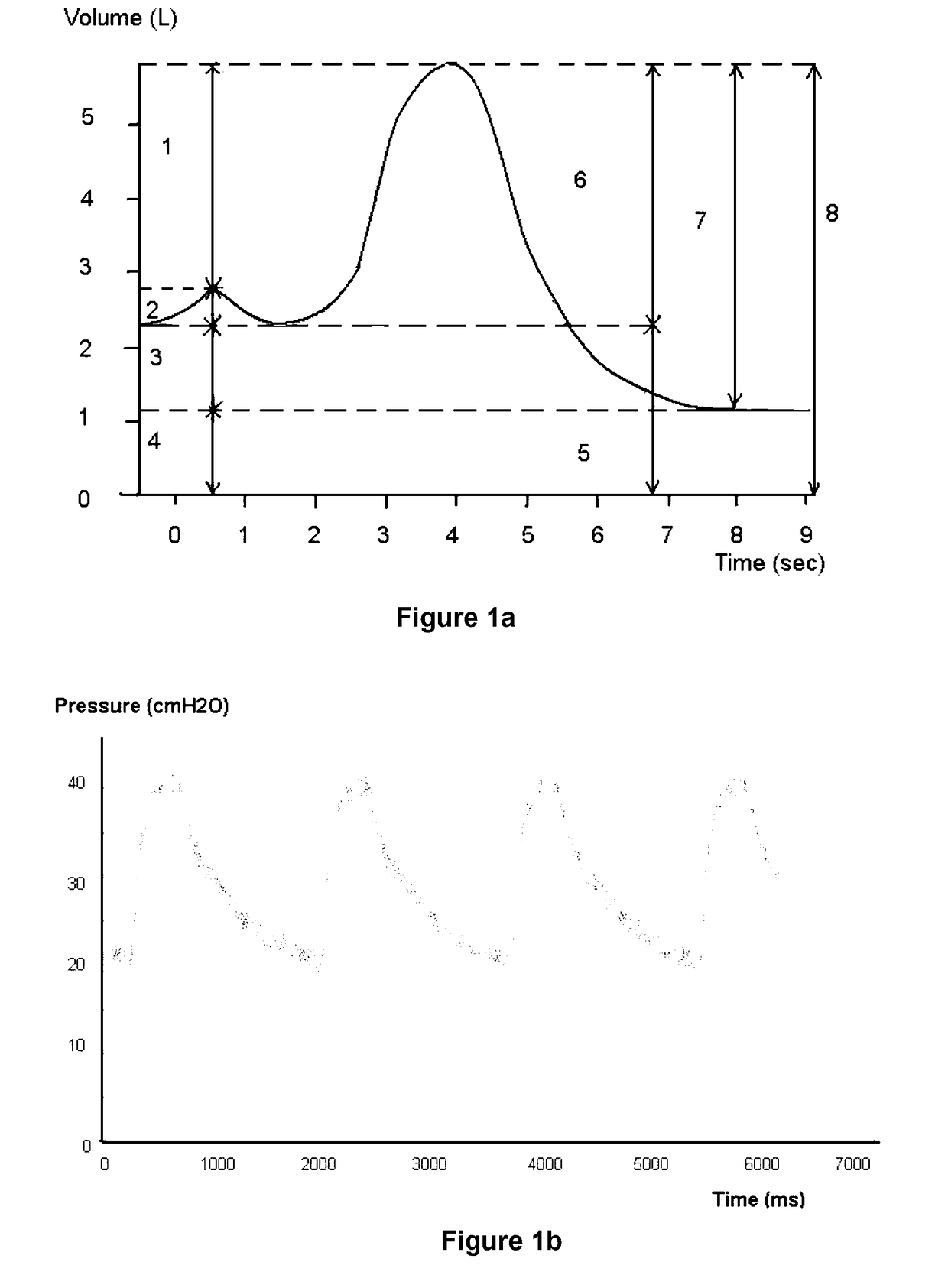
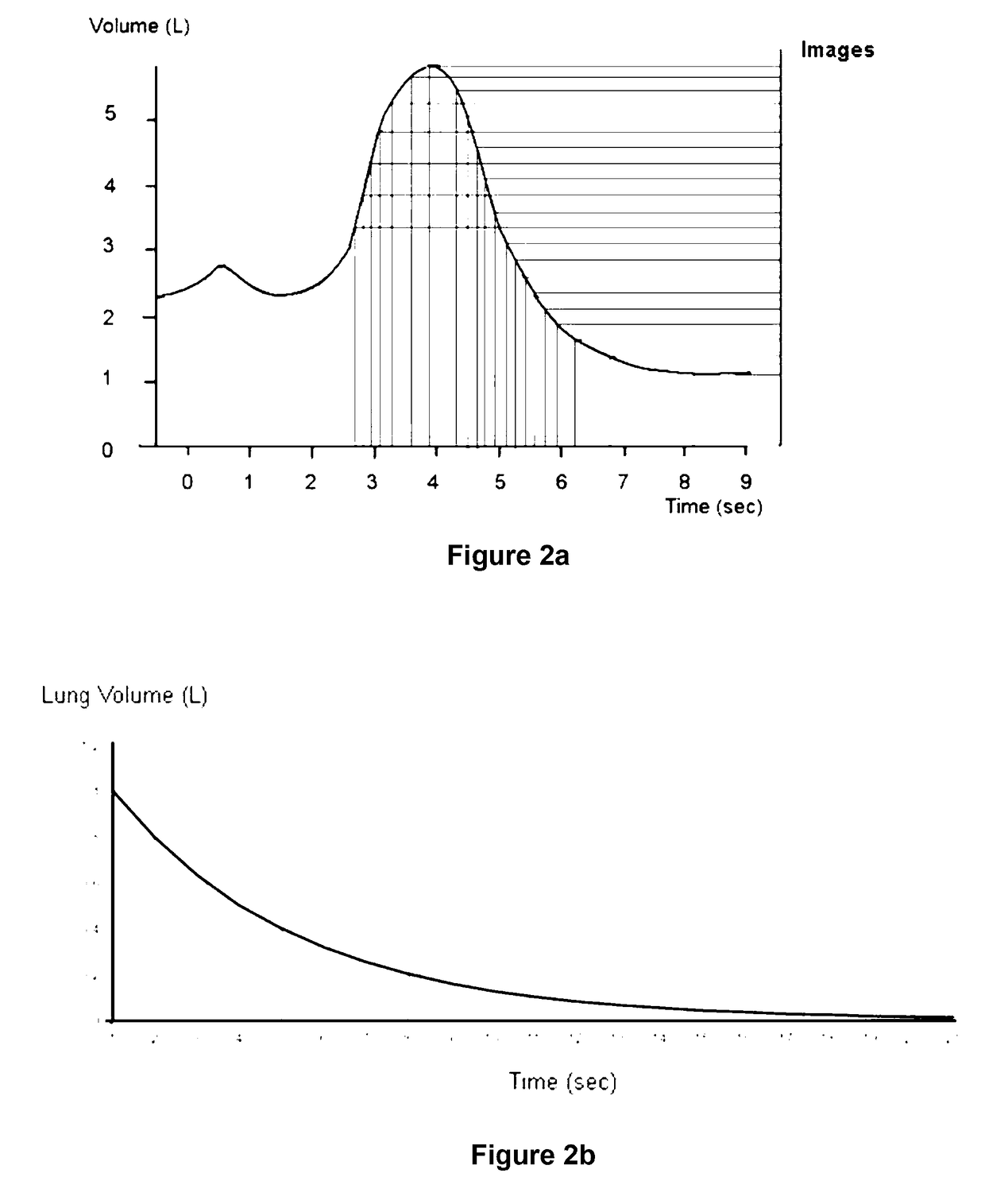
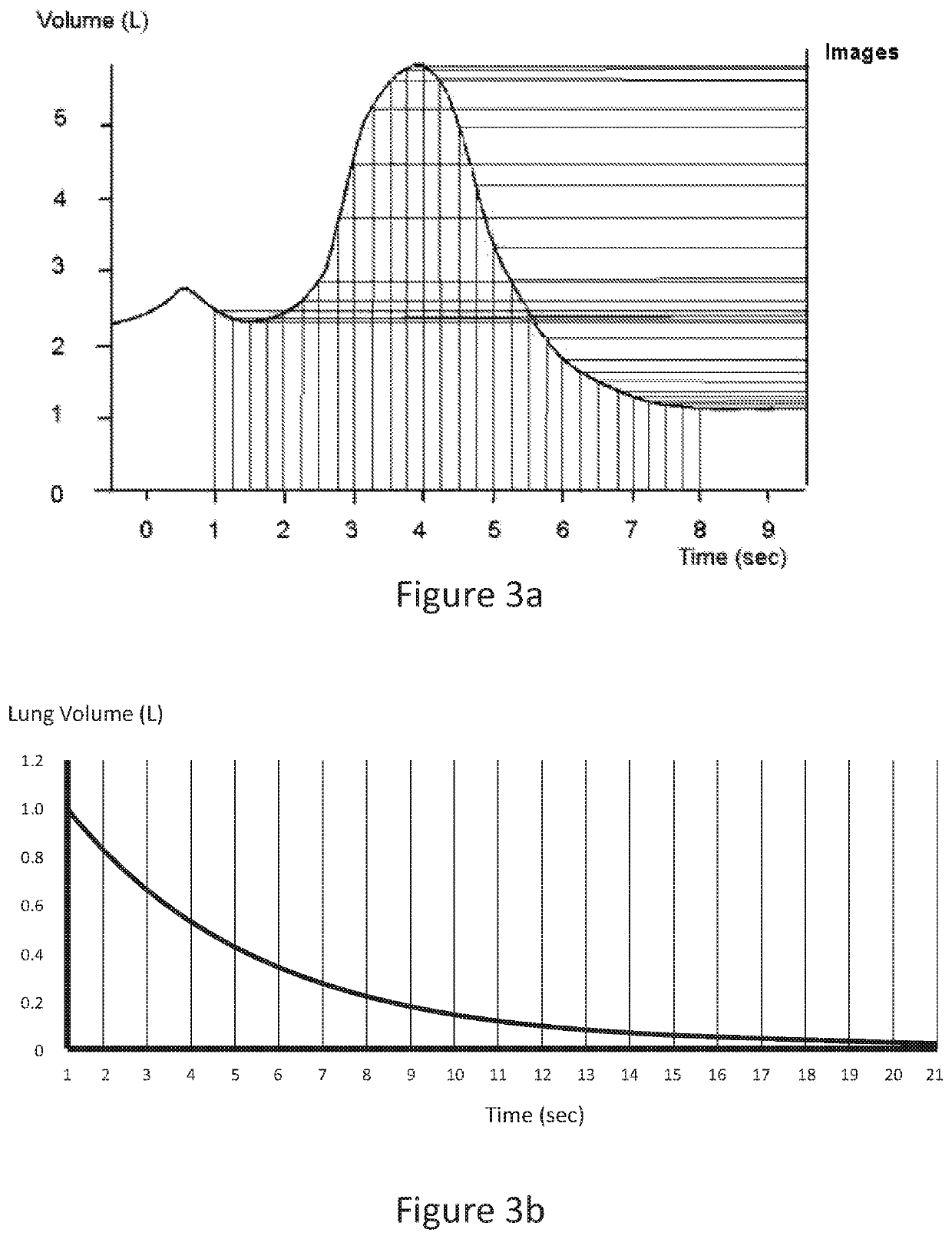
ActiveUS20170143289A1Simple technologyAdvanced technologyHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionOrgan VolumeMethod of images
A method of imaging motion of an organ that changes volume in a patient including the steps of monitoring change in volume of the organ, and recording multiple in vivo images of the organ, wherein the change of organ volume between the images is constant or of some other predetermined value.
Owner:4DMEDICAL LTD
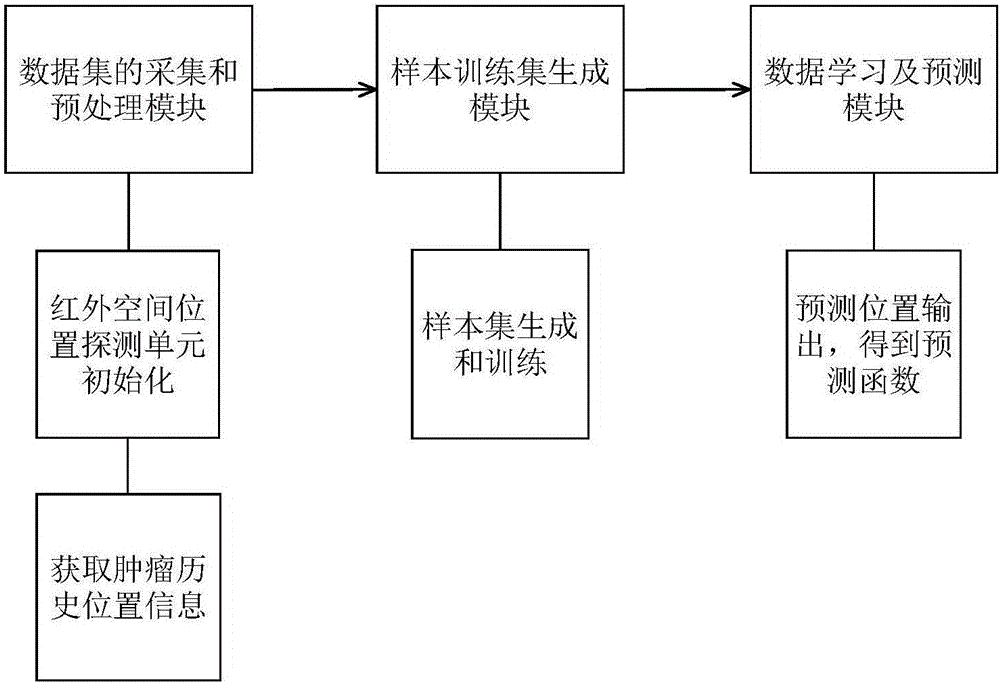
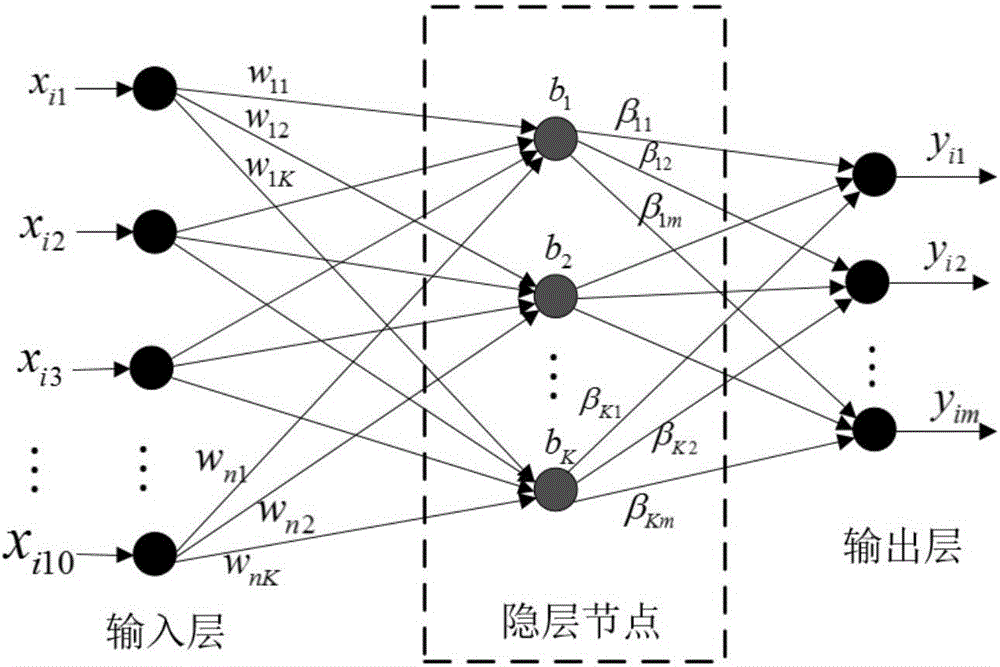
Rapid and accurate tumour position prediction apparatus
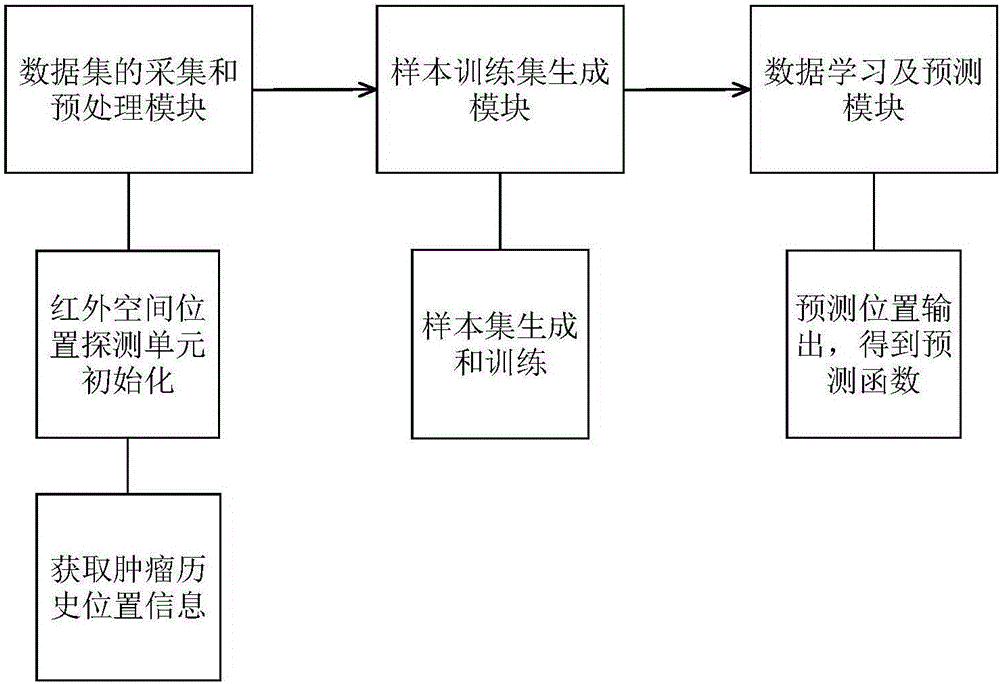
ActiveCN105931262AFast real-time non-invasive acquisitionFast real-time non-invasive processingImage enhancementImage analysisData setOrgan Motion
The invention relates to a rapid and accurate tumour position prediction apparatus. The apparatus includes a data set acquisition and preprocessing module, a sample training set generation module, and a data learning and prediction module, obtains the respiratory movement data and tumour position historical data through the data set acquisition and preprocessing module, and generates the tumour position prediction functions through the sample training set generation module and the data learning and prediction module, thus rapidly and accurately predicting the newly acquired tumour position information of patients by using the tumour position prediction functions. The apparatus improves the accuracy of the real-time tracking and positioning in the tumour target of a patient during the accurate radiation treatment, and corrects the patient's position during the treatment, thereby maximally reducing the error influence caused by target and organ motion.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for quantifying organ motion, apparatus therefor, method for estimating organ position, apparatus therefor, method for irradiating radiation, apparatus therefor, and apparatus for detecting abnormal organ
InactiveUS8457379B2Quantitative precisionImage enhancementImage analysisThree-dimensional spaceThinning
A plurality of CT images of an organ (10) which has undergone a subtle variation or deformation are used as input data, blood vessels and trachea 12 distributed inside the organ are extracted and subjected to thinning, the thus thinned images 14 are used to extract the coordinates of bifurcations 16 and connections, the thus extracted coordinates are used as feature points to track the motion of individual points between a plurality of CT images in a three dimensional space, thereby measuring the movement of the organ (10). Thus, it is possible to realize a local motion tracking at an arbitrary point over an entire region inside an organ, which would be impossible by using a metal marker.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
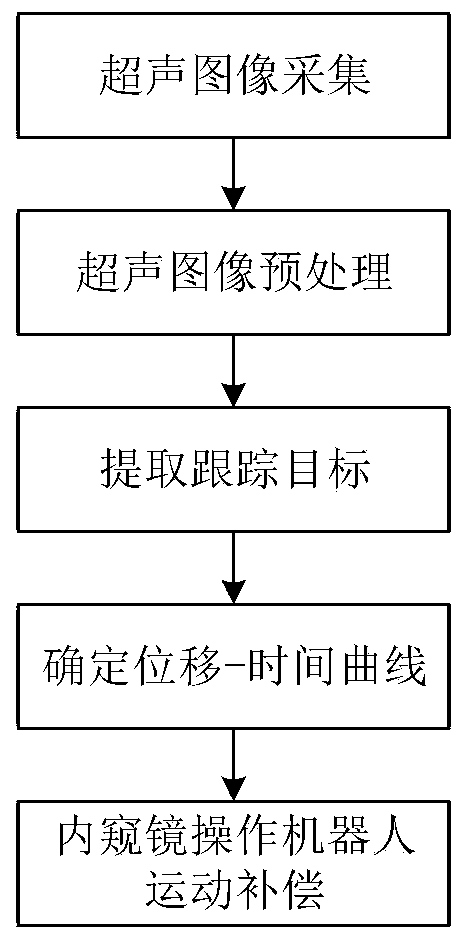
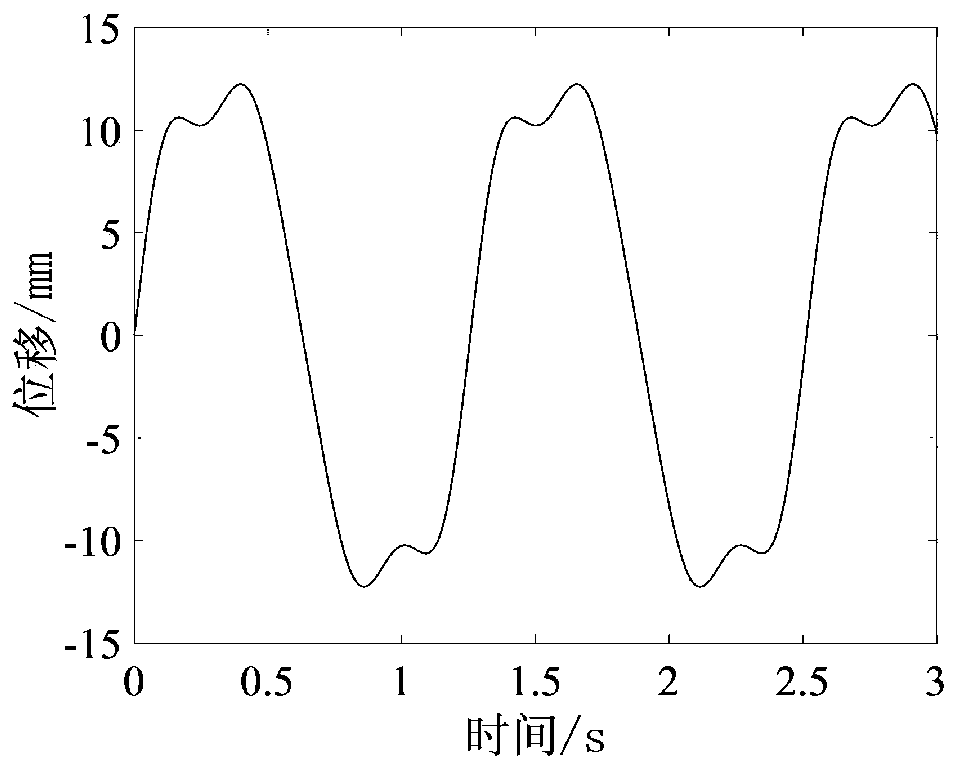
Motion control method for flexible endoscope operation robot
InactiveCN110742691ADisplacement deviation compensationSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingFlexible endoscopyHuman body
The invention relates to a motion control method for a flexible endoscope operation robot. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining image information within a complete respiratory motion cycle of a human body; accurately determining the edge contour of organ tissue by using a medical image wave filtering and partitioning algorithm; determining displacement change condition of the organs along with the time according to the edge contour information, and drawing a displacement-time curve under respiration; and under the condition that the displacement-time curve of the organ is determined, performing motion compensation on the endoscope operation robot by referencing the cycle of the displacement-time curve and a fluctuation amplitude. A real-time ultrasound image is used for directly tracking the motion of the organs, so that the respiratory motion law of different human bodies and the same human body in different time ranges can be directly displayed; the displacement-timecurve of the organs under the breathing state, obtained by collected ultrasonic images and orifical hole images acquired by the endoscope are registered, so that compensation can be performed on displacement deviation between the endoscope and human organs generated by breathing.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Water tank measuring method and system for simulating influence on radiation dose by organ motion
InactiveCN103785111AGuaranteed real-time accuracyGuaranteed flexibilityRadiation therapyEngineeringHigh-motion
The invention discloses a water tank measuring method and system for simulating an influence on a radiation dose by an organ motion. The water tank measuring system comprises a tank body, a detector, a detector motion guiding rack, and a driving device; and the driving device is in transmission connection with the detector, so that the detector is driven to make motion relatively to the tank body under the guidance of the detector motion guiding rack. According to the invention, the water tank measuring system has characteristics of low cost, good universality, high motion precision, fast respond speed, and easy maintenance and the like. Influences on doses by three-dimensional motions of various organs can be simulated and studied precisely; and the planning target and the radiation therapy plan can be corrected, thereby improving precision of the radiation therapy.
Owner:戴建荣 +1
Organ motion compensation
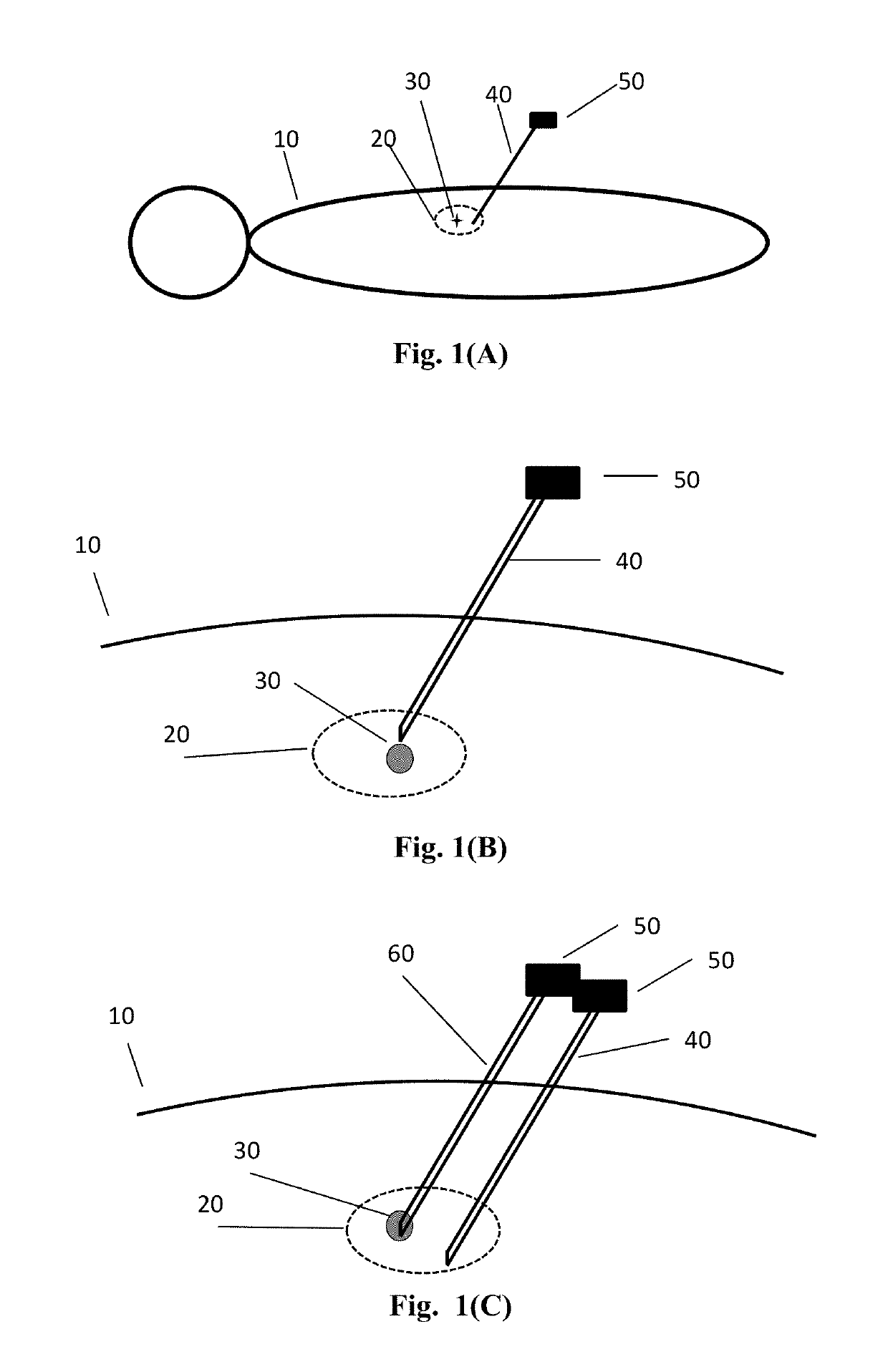
A method and system for motion tracking of a target organ are provided. A tracking needle is partially inserted into an organ. The needle has a sensor element for obtaining continuous needle orientation information which can be used to determine organ motion due to respiration during percutaneous needle insertion.
Owner:CANON USA +1
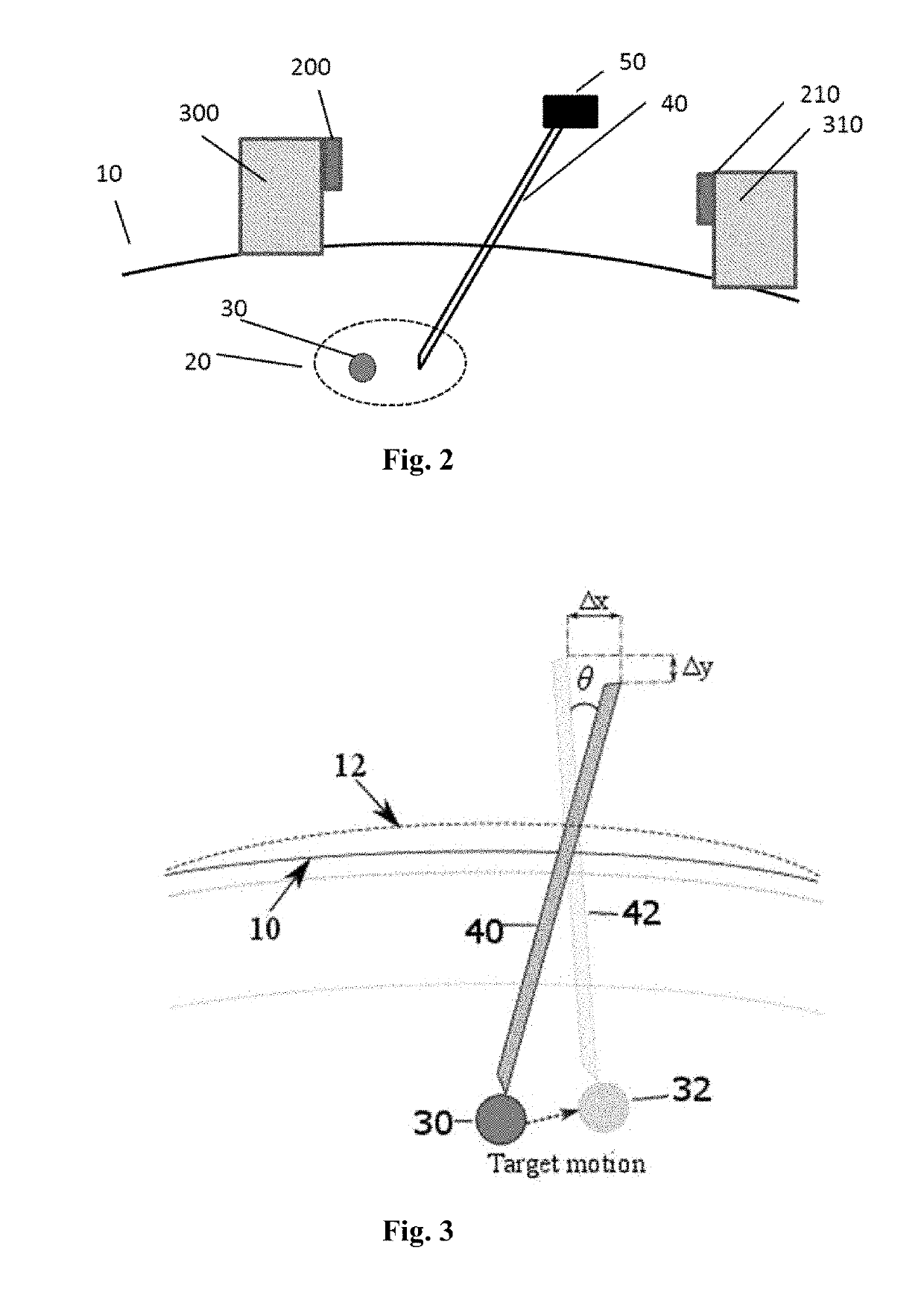
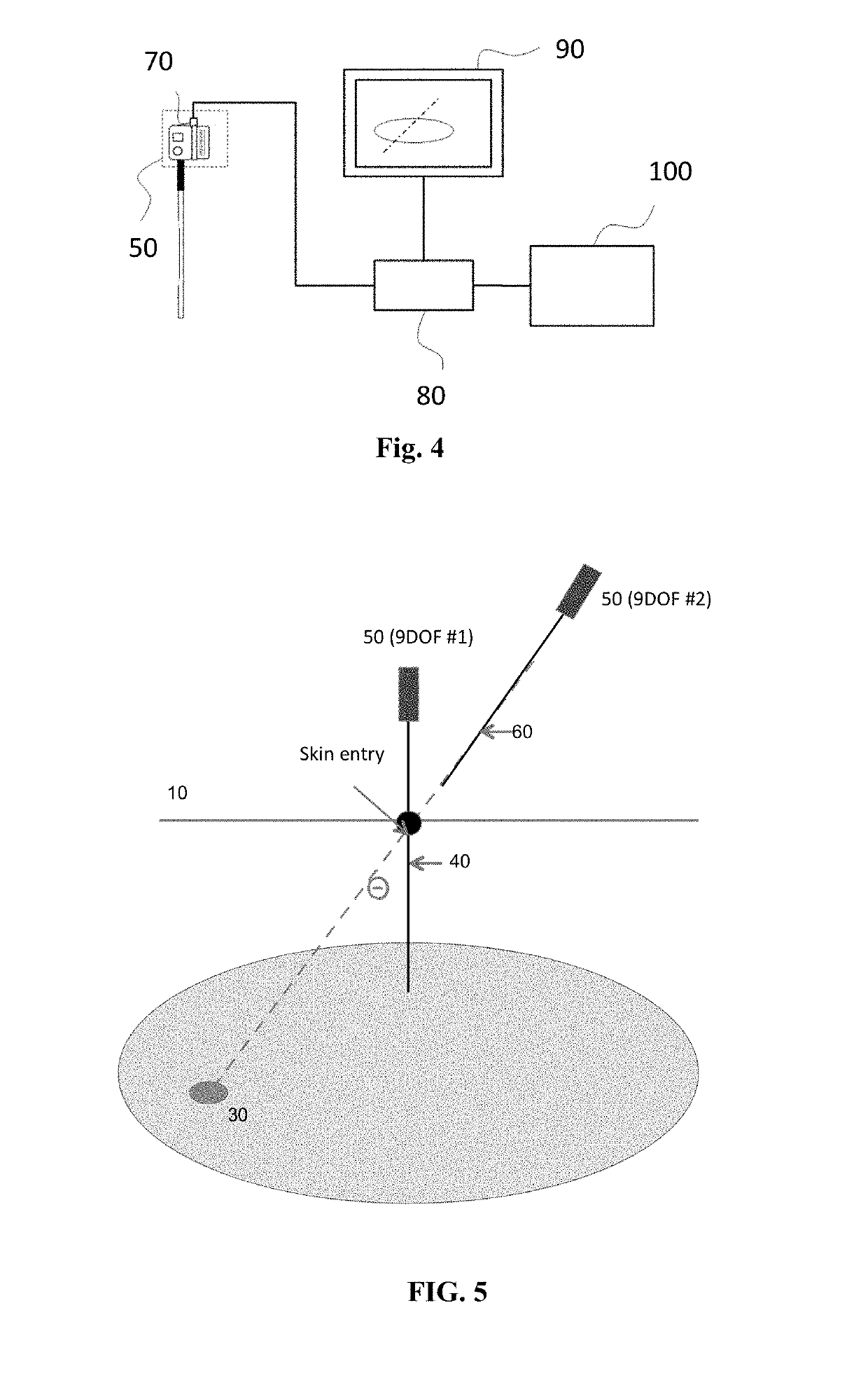
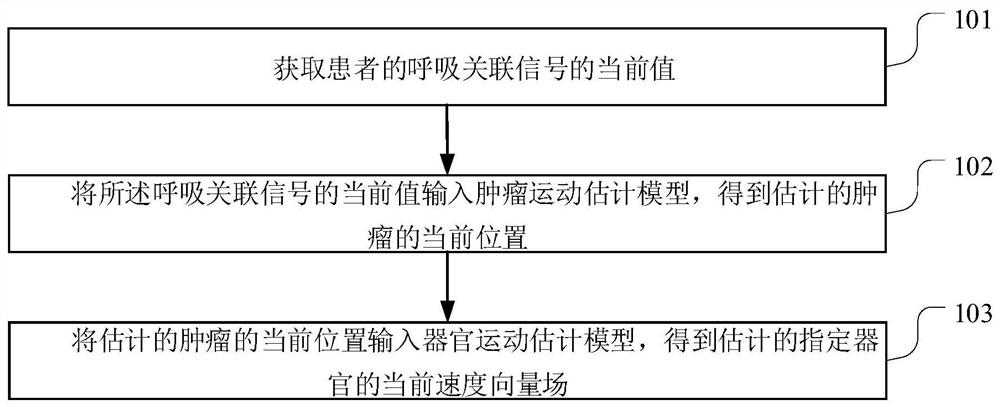
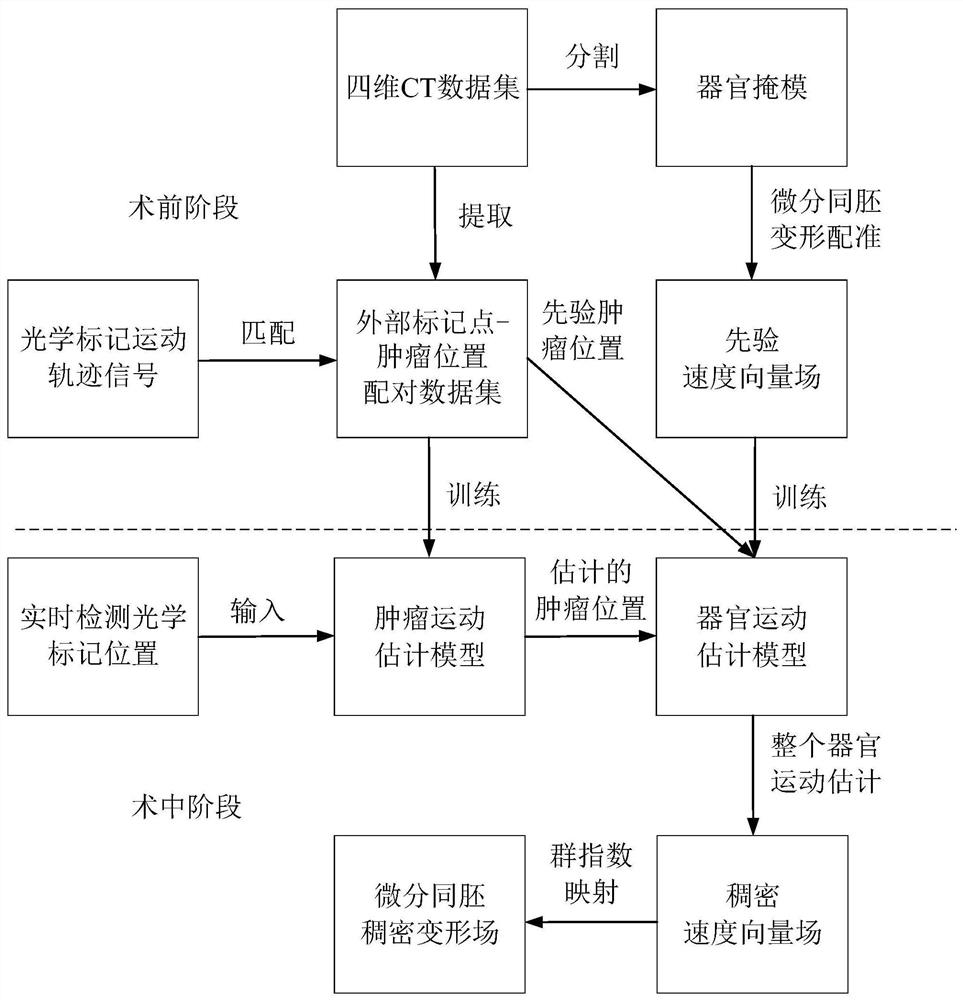
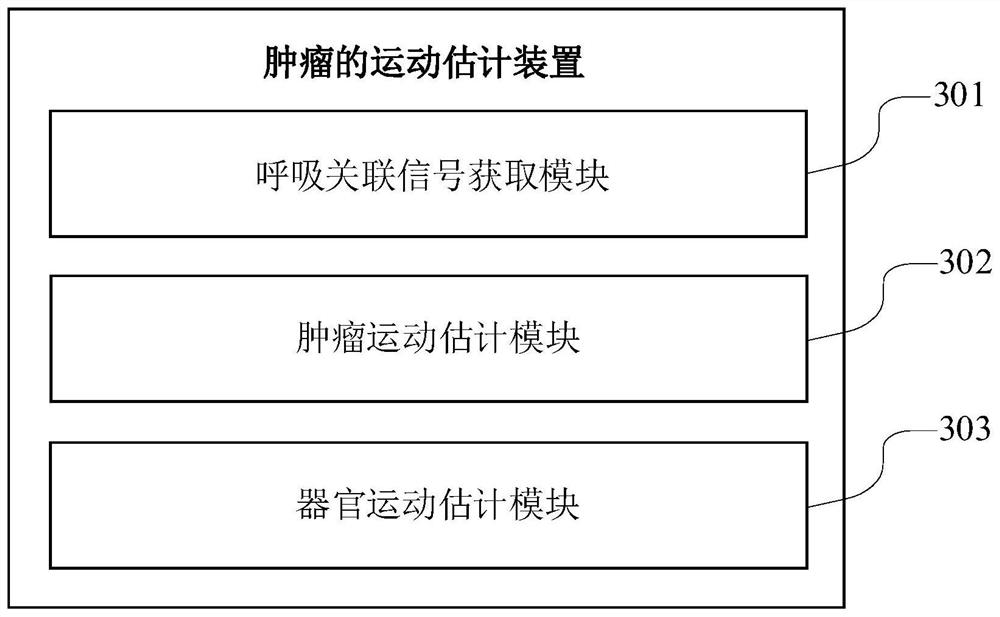
Tumor motion estimation method and device, terminal equipment and storage medium
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, and provides a tumor motion estimation method and device, terminal equipment and a storage medium. The motion estimation method comprises the following steps: acquiring a current value of a breathing-related signal of a patient, wherein the breathing-related signal reflects motion track characteristics of a specified organ with a tumor of the patient in different breathing states; inputting the current value of the respiration-related signal into a tumor motion estimation model to obtain an estimated current position of the tumor; and inputting the estimated current position of the tumor into an organ motion estimation model to obtain an estimated current velocity vector field of the specified organ. By adopting the motion estimation method, the respiratory motion estimation of the whole organ can be realized, and the accuracy of positioning the tumor and important anatomical structures around the tumor is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
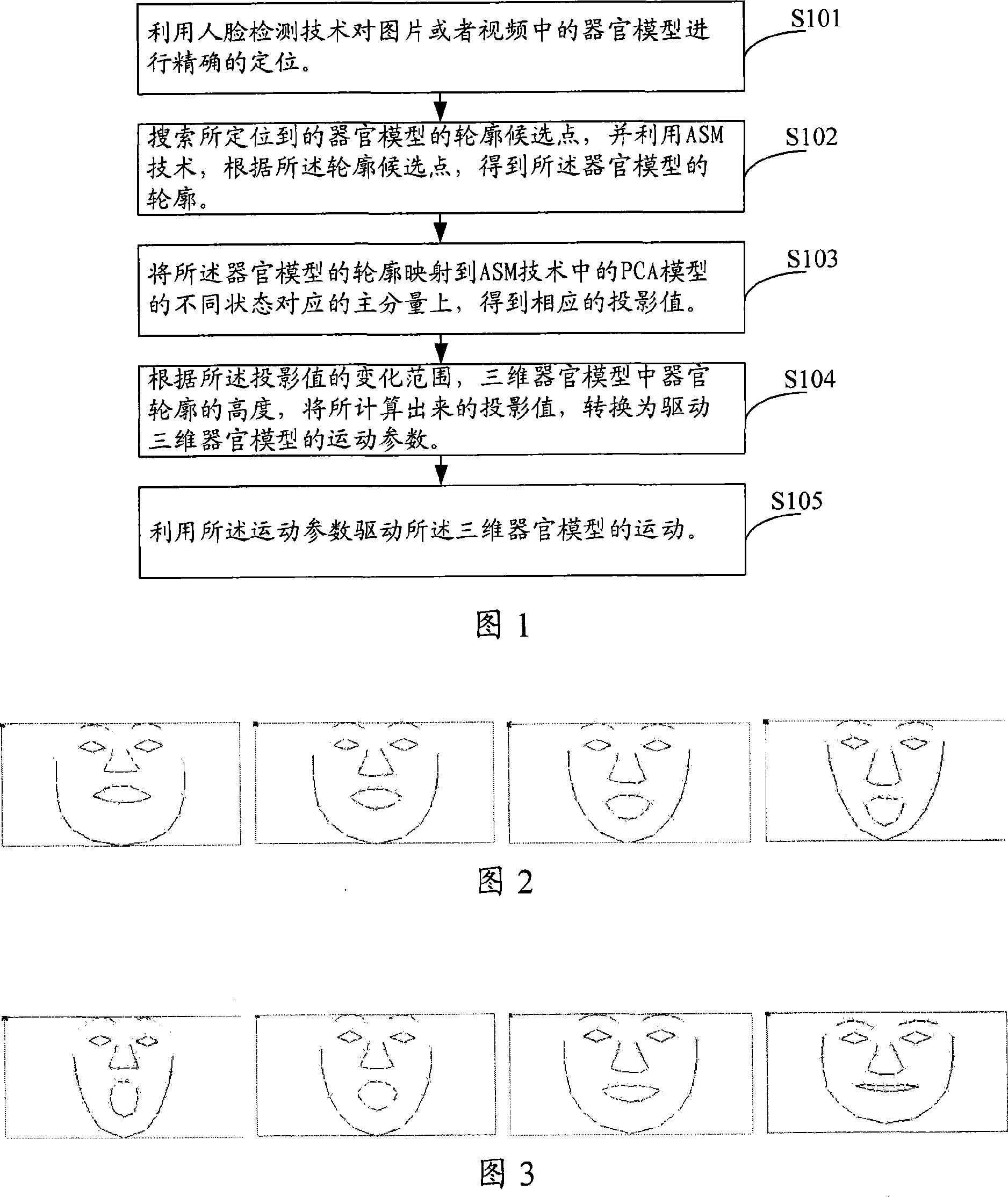
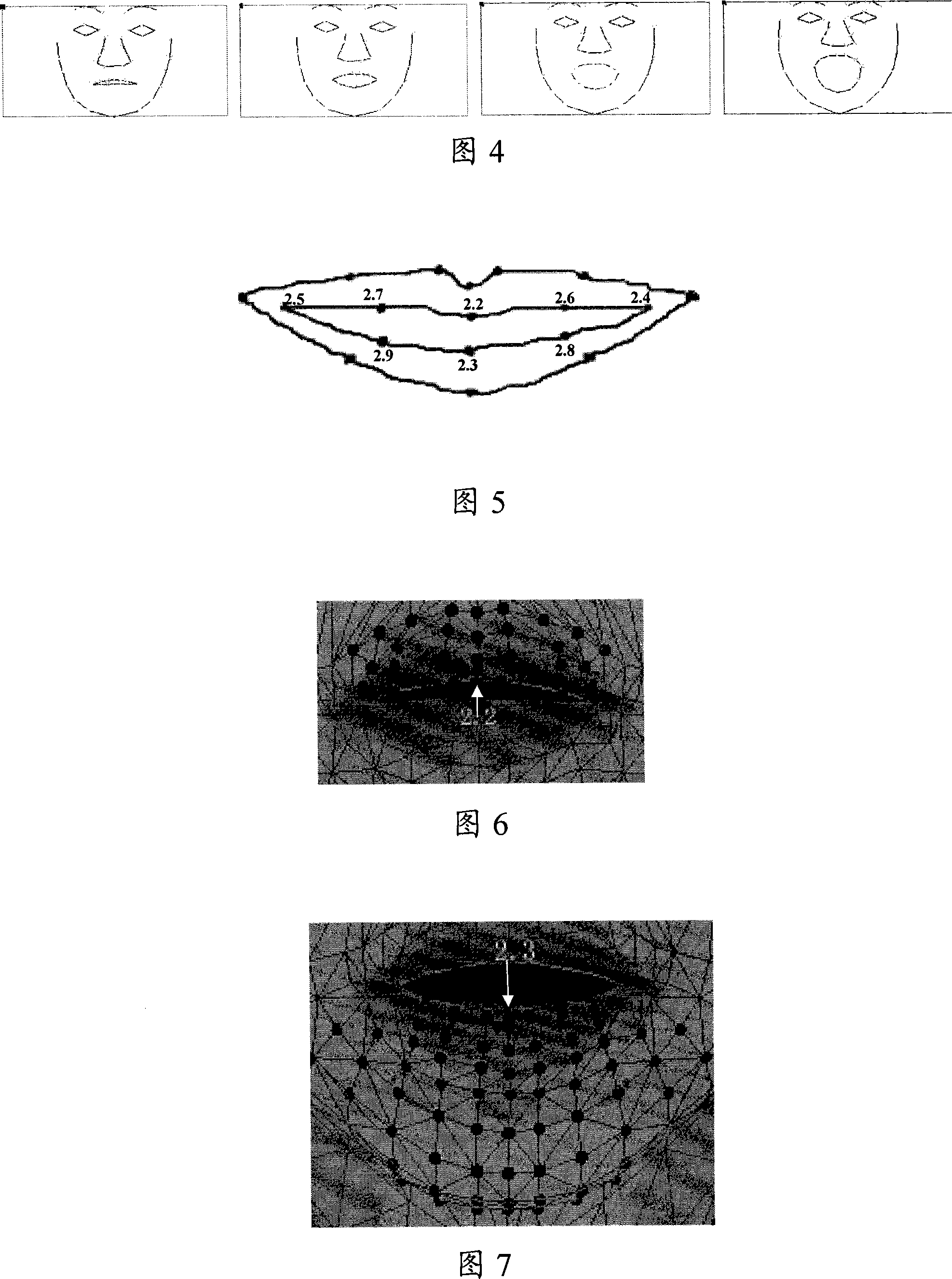
Method and system for realizing organ animation
This invention discloses a realization organ animation methods and systems, its use of technology identified ASM organ profile, contour mapping and organ referred to the PCA model corresponding to the different state of the main characteristics of components, the corresponding projection value; then, in accordance with access to value-driven 3-D projection of organ motion parameters; referred to the use of organ-driven motion parameters campaign Thus, when the implementation of the present invention can drive mouth organ; addition of the invention described in the implementation of control points also can be identified the movement direction; use of organ-driven model of motion parameters, drivers mentioned above control points along the direction of movement sport, it can reflect mouth smile, anger, surprise and fear, and other expressions, therefore use this method to drive the mouth mouth can be shaped and coincide more closely with actual results.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Image reconstruction incorporating organ motion
InactiveUS8824756B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioPromote lowerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionImaging modalitiesSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Systems and methods which implement an image reconstruction framework to incorporate complex motion of structure, such as complex deformation of an object or objects being imaged, in image reconstruction techniques are shown. For example, techniques are provided for tracking organ motion which uses raw time-stamped data provided by any of a number of imaging modalities and simultaneously reconstructs images and estimates deformations in anatomy. Operation according to embodiments reduces artifacts, increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and facilitates reduced image modality energy dosing to patients. The technology also facilitates the incorporation of physical properties of organ motion, such as the conservation of local tissue volume. This approach is accurate and robust against noise and irregular breathing for tracking organ motion.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
System and method for scanned ion beam interplay effect mitigation using random repainting
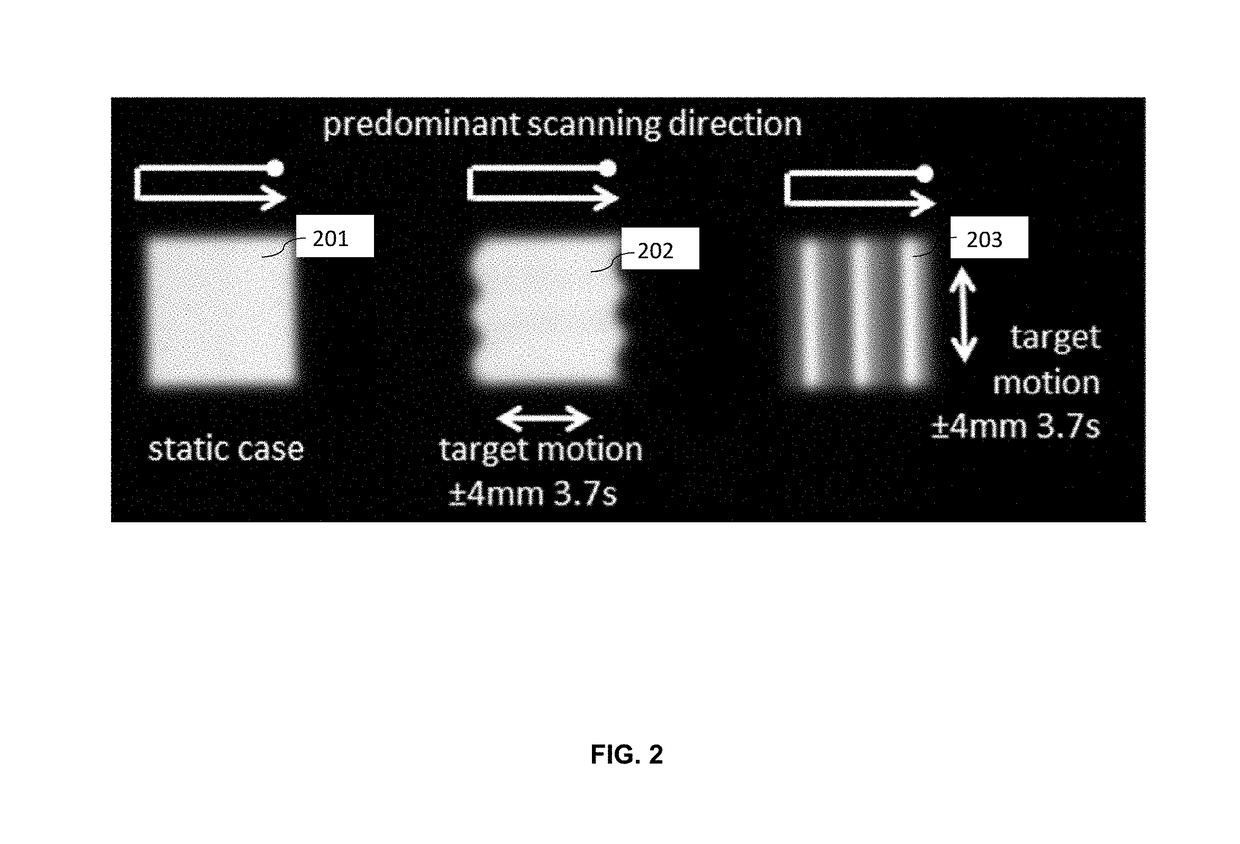
Interference of dose application in scanned ion beam therapy and organ motion, also called interplay effect, may lead to dose deviations at target volumes. Current repainting methods are susceptible to artifacts due to a predominant scanning direction, ranging from fringed field edges to under and overdosed regions (hot and cold spots). To overcome the difficulties inherent in the repainting techniques of conventional proton therapy systems, new random repainting techniques are described herein for mitigating the under-dose and / or over-dose pattern inherent in existing repainting techniques using a random repainting approach that randomly selects spot locations within the target area.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST PARTICLE THERAPY GMBH & CO KG
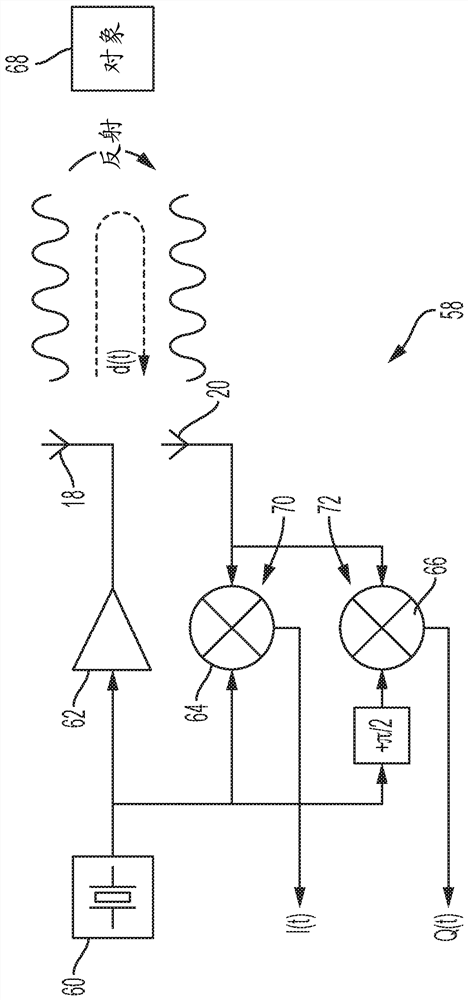
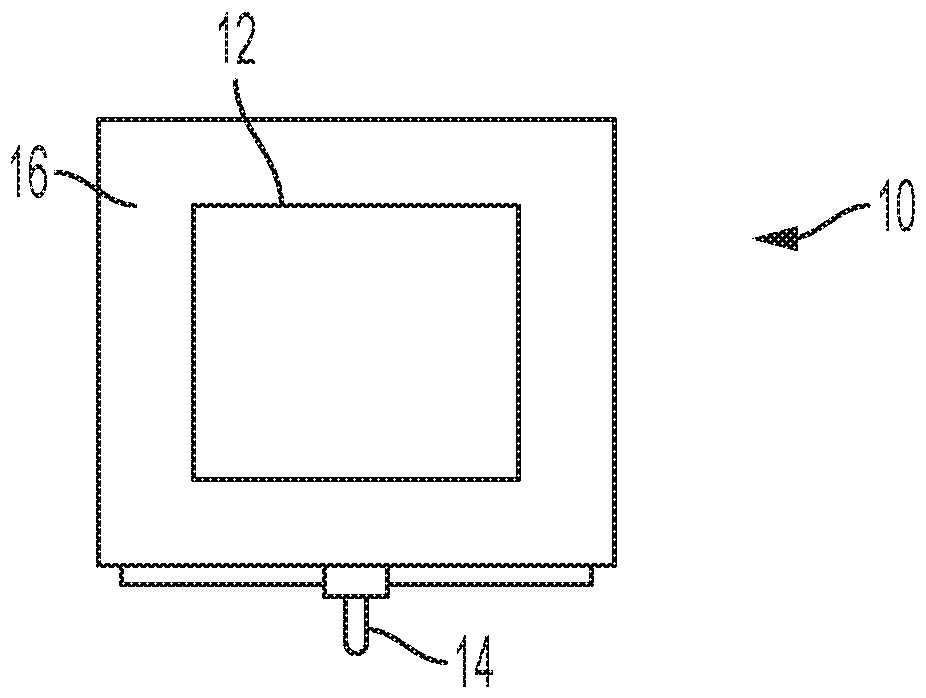
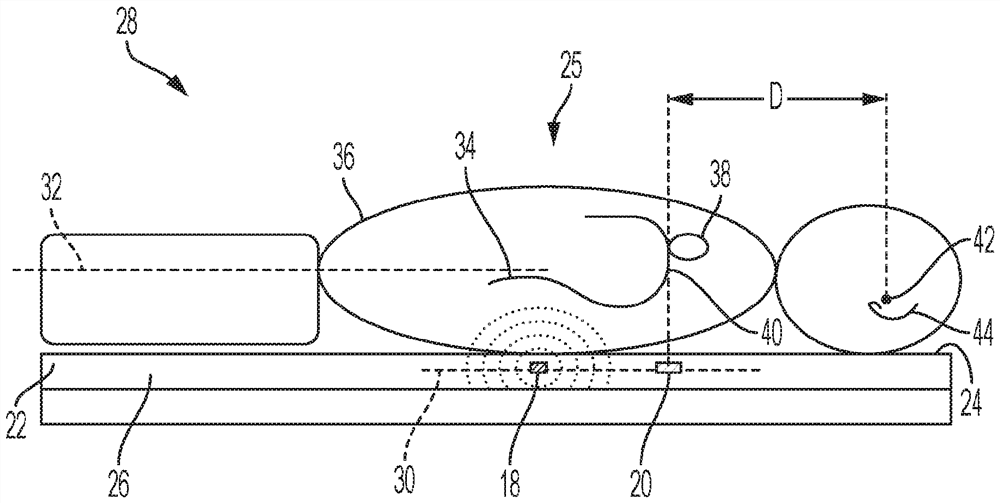
Compact antenna arrangement of radar system for detecting internal organ motion
A compact radar system for detecting displacement of an internal organ of a patient in a medical scanner. The system includes at least one transmitting antenna and at least one receiving antenna located in a bed arrangement that supports the patient. In particular, the receiving antenna is located a predetermined distance from a patient reference location to enable detection of electromagnetic energy reflected from a region of the internal organ undergoing asymmetric displacement. The system further includes a radar energizing system that energizes the transmitting and receiving antennas wherein the transmitting antenna irradiates a volume of the patient's body that includes the internal organ. In addition, the receiving antenna detects the reflected electromagnetic energy from the region of the internal organ undergoing asymmetric displacement to enable determination of inhalation and exhalation by the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Registration and motion compensation for patient-mounted needle guide
Exemplary methods, apparatus, and systems are disclosed for automated registration and motion compensation of patient-mounted needle guide medical devices using fiducial markers, and processing algorithms where a re-registration step is provided. These methods, apparati, and systems adaptively compensate for the displacement of the medical device and / or target location due to the patient movement or internal organ motion.
Owner:CANON USA +1
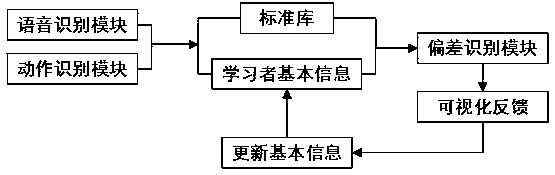
Pronunciation correction method based on vocal organ form and behavior deviation visualization
InactiveCN108877319AForeign language learning is convenient and smartIncrease interest in learningSpeech recognitionElectrical appliancesVocal organCorrection method
The invention discloses a pronunciation correction method based on vocal organ form and behavior deviation visualization. The method comprises the steps: performing the foreign language learning modeling for a learner, acquiring the voice content of the learner and the organ motion corresponding to the pronunciation, and then calling a corresponding pronunciation module in a standard library according to the target foreign language selected by the learner; searching the deviations of the lip position, tongue position, tooth position, expiratory volume and jaw height of the learner and the corresponding data in the standard library by comparing the same pronunciation contents and organ movement patterns of the learner and the standard library, and visually feeding back the difference of the organ forms between the learner and the organ of the standard sound and the deviation between the two to the learner, and then updating the basic information of the learner. The method achieves therecording of the learning ability of the learner at any time to provide the learner with a coherent executable way of learning foreign languages.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Method of imaging motion of an organ
ActiveUS10674987B2Advanced technologyEqually distributedHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionOrgan VolumeRadiology
A method of imaging motion of an organ that changes volume in a patient including the steps of monitoring change in volume of the organ, and recording multiple in vivo images of the organ, wherein the change of organ volume between the images is constant or of some other predetermined value.
Owner:4DMEDICAL LTD
A tumor location prediction device
ActiveCN105931262BImprove processing speedImprove processing precisionImage enhancementImage analysisData setData acquisition
The invention relates to a rapid and accurate tumour position prediction apparatus. The apparatus includes a data set acquisition and preprocessing module, a sample training set generation module, and a data learning and prediction module, obtains the respiratory movement data and tumour position historical data through the data set acquisition and preprocessing module, and generates the tumour position prediction functions through the sample training set generation module and the data learning and prediction module, thus rapidly and accurately predicting the newly acquired tumour position information of patients by using the tumour position prediction functions. The apparatus improves the accuracy of the real-time tracking and positioning in the tumour target of a patient during the accurate radiation treatment, and corrects the patient's position during the treatment, thereby maximally reducing the error influence caused by target and organ motion.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com