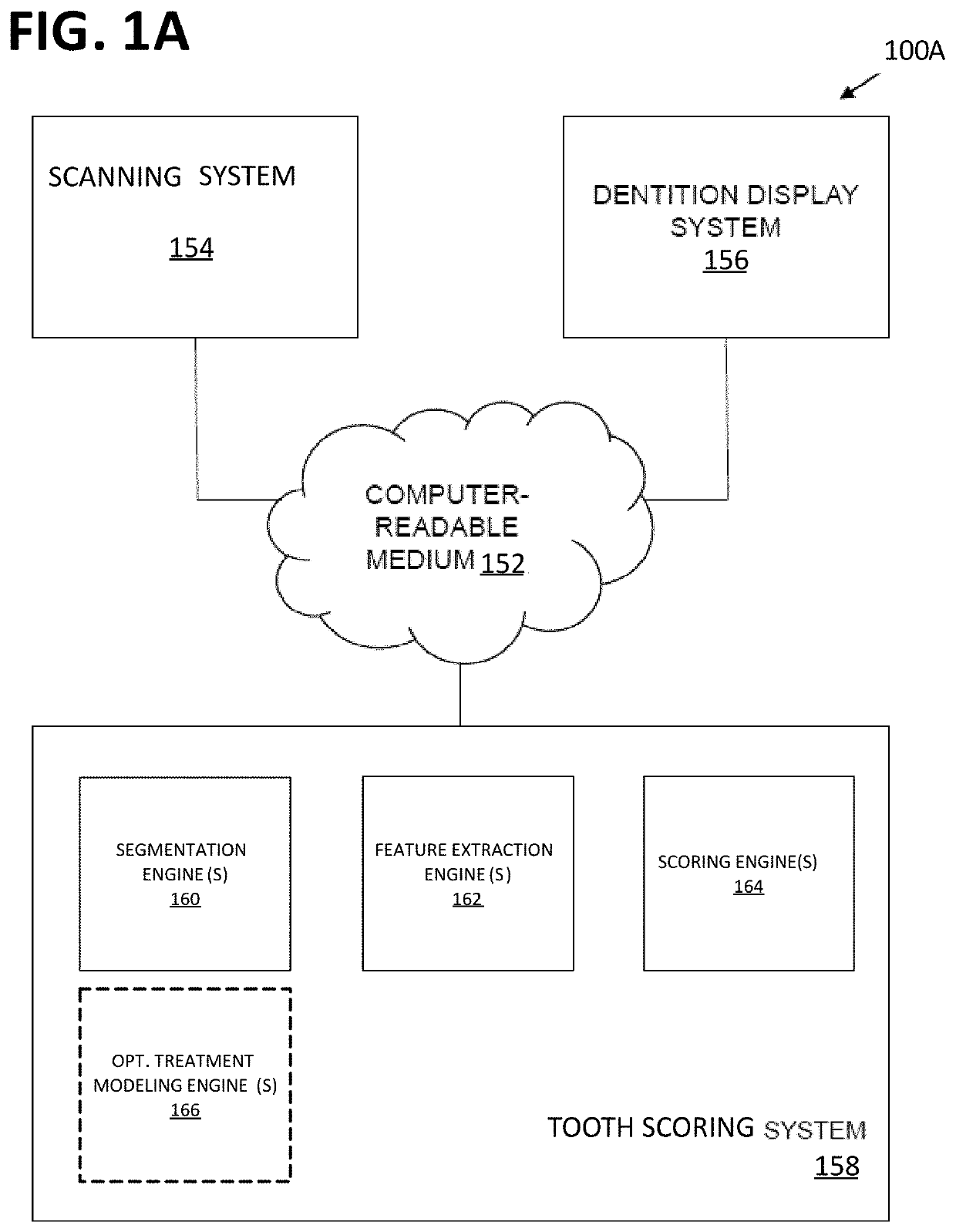
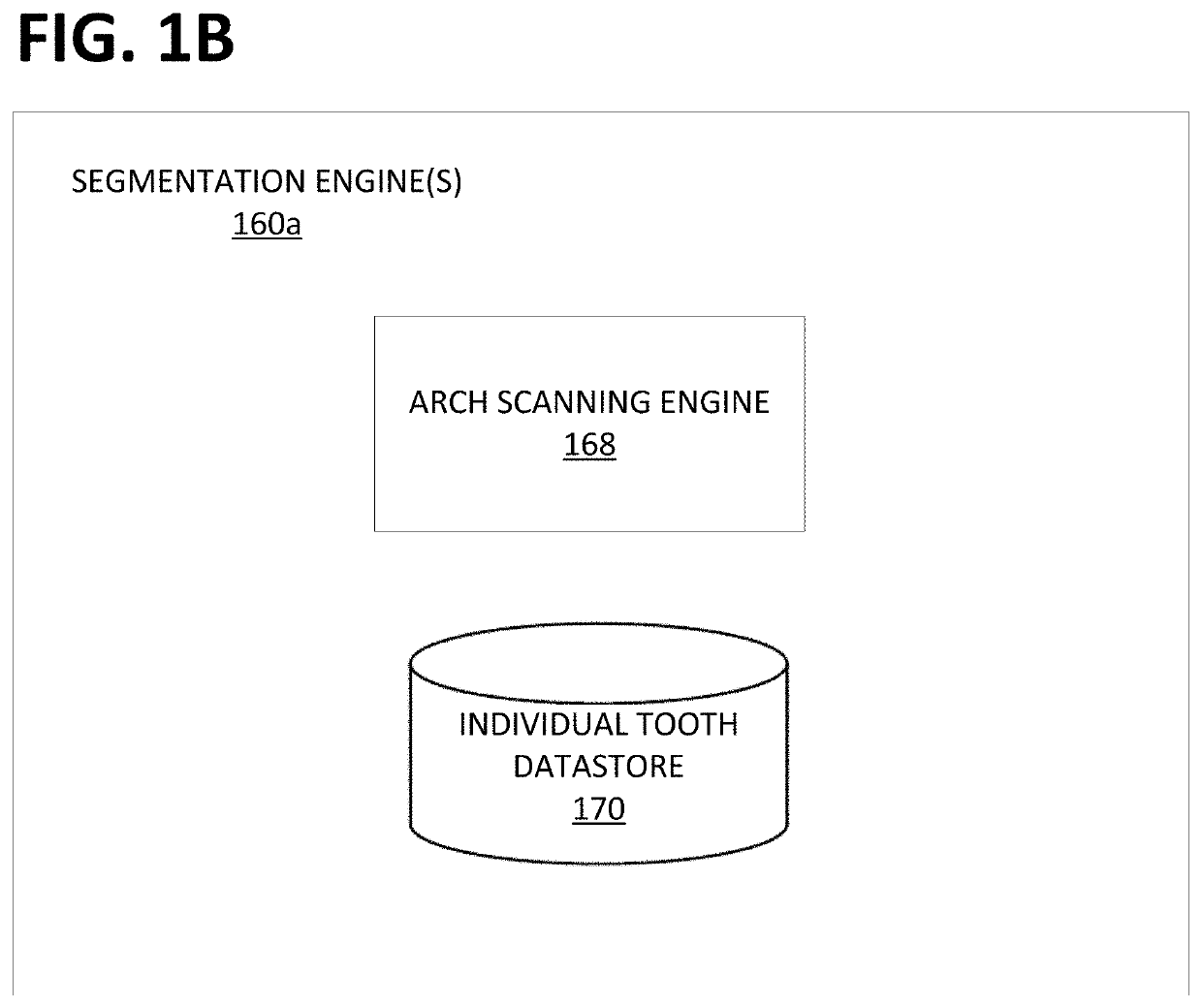
Patents
Literature
529 results about "Tooth position" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
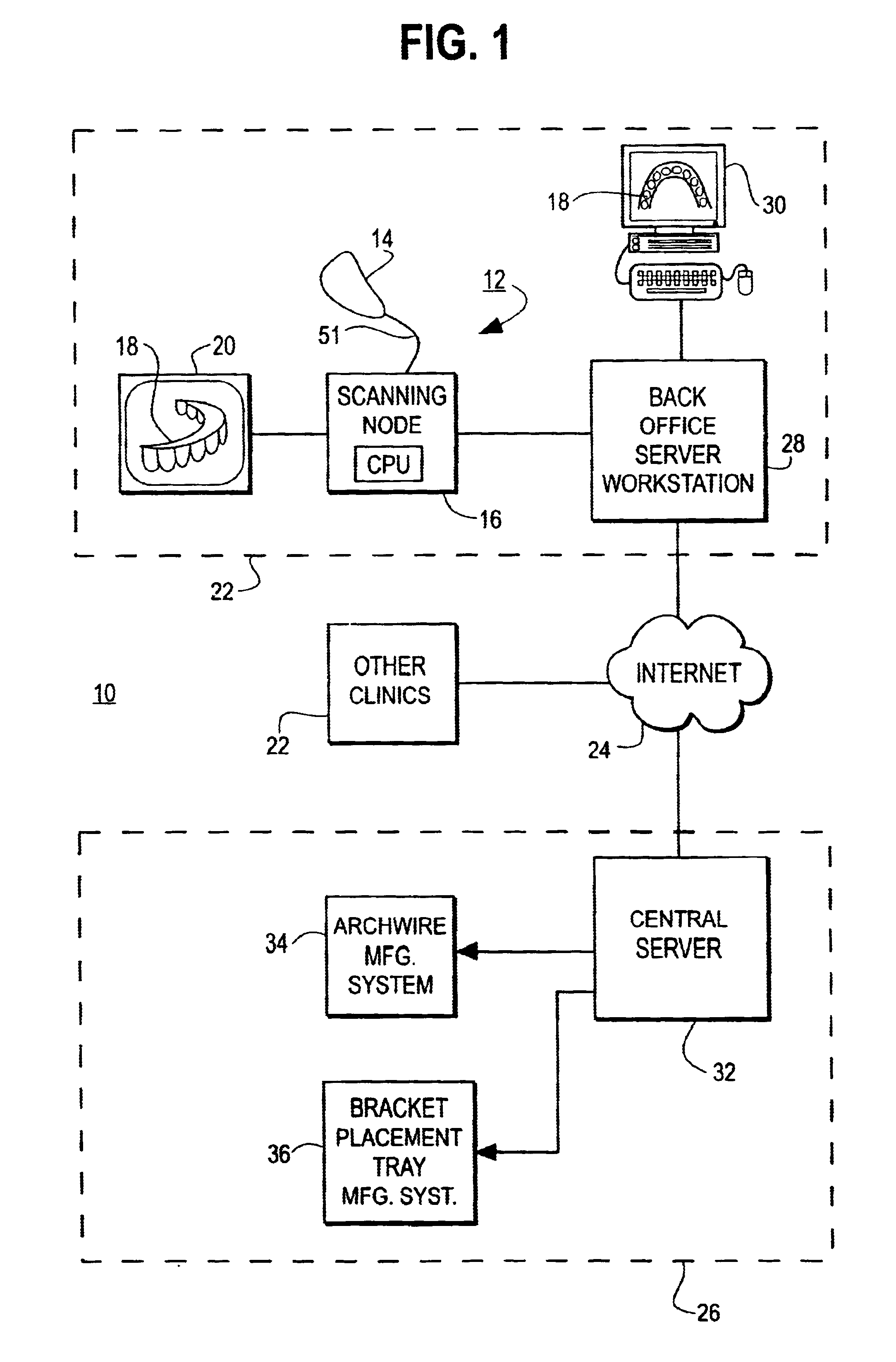
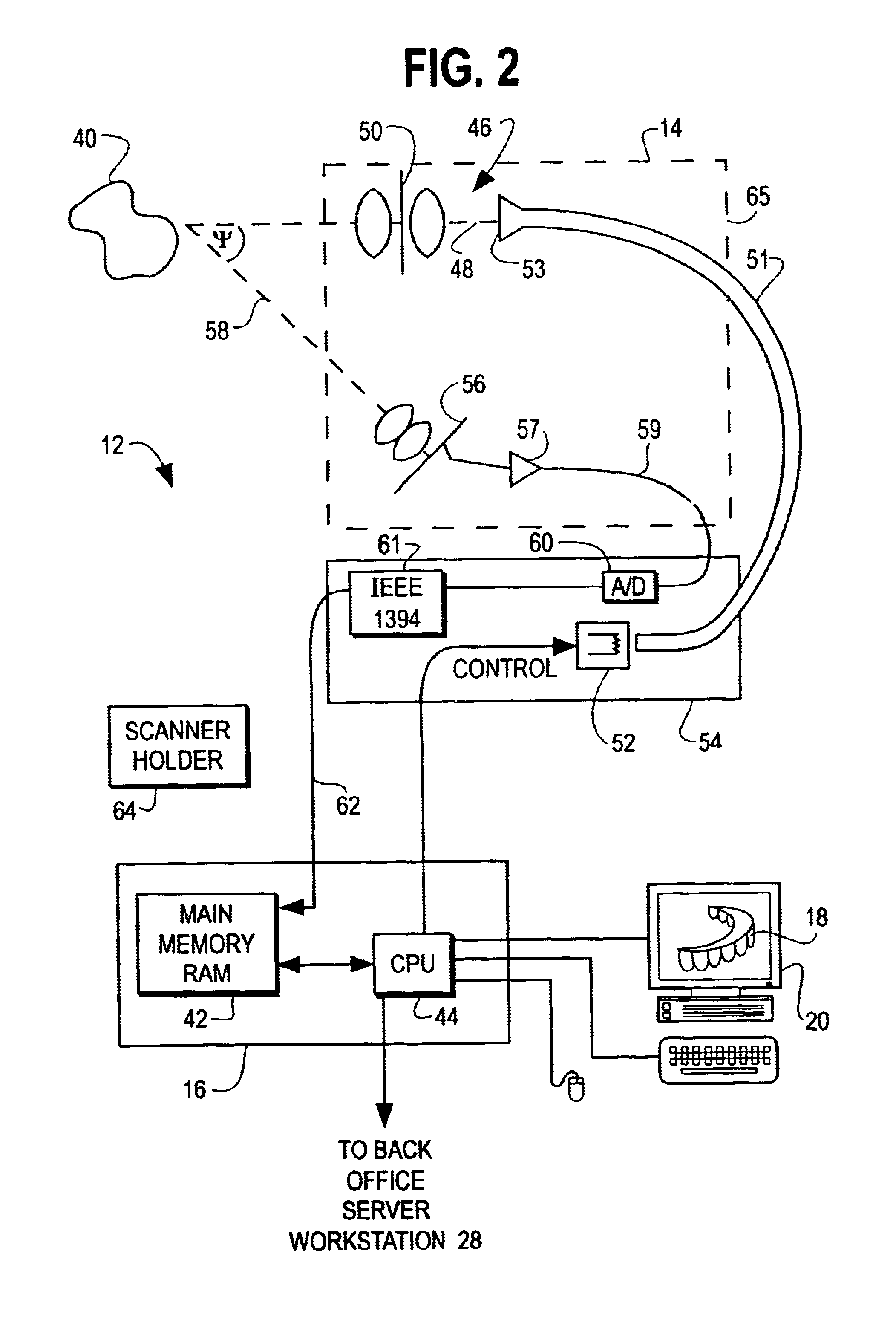
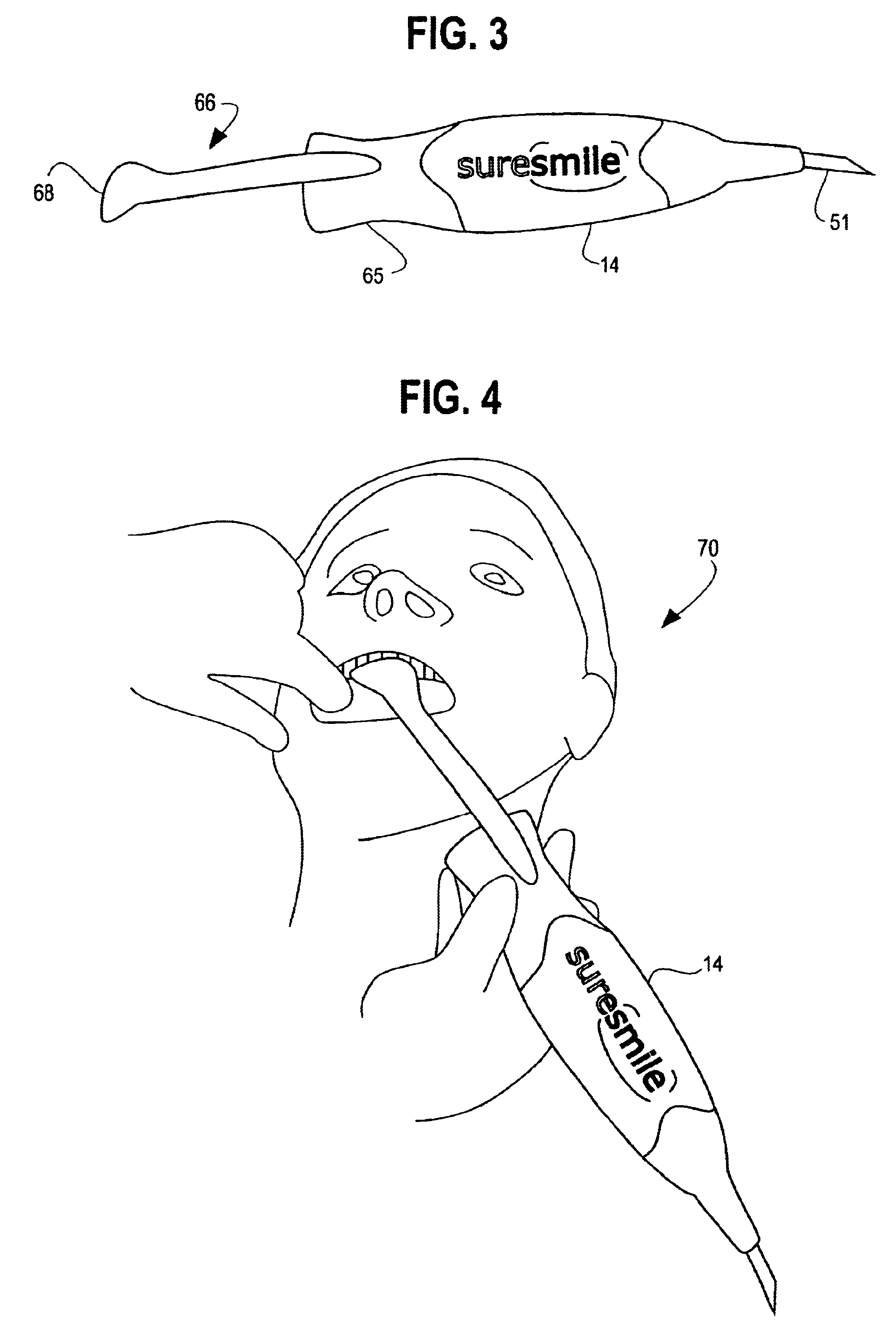
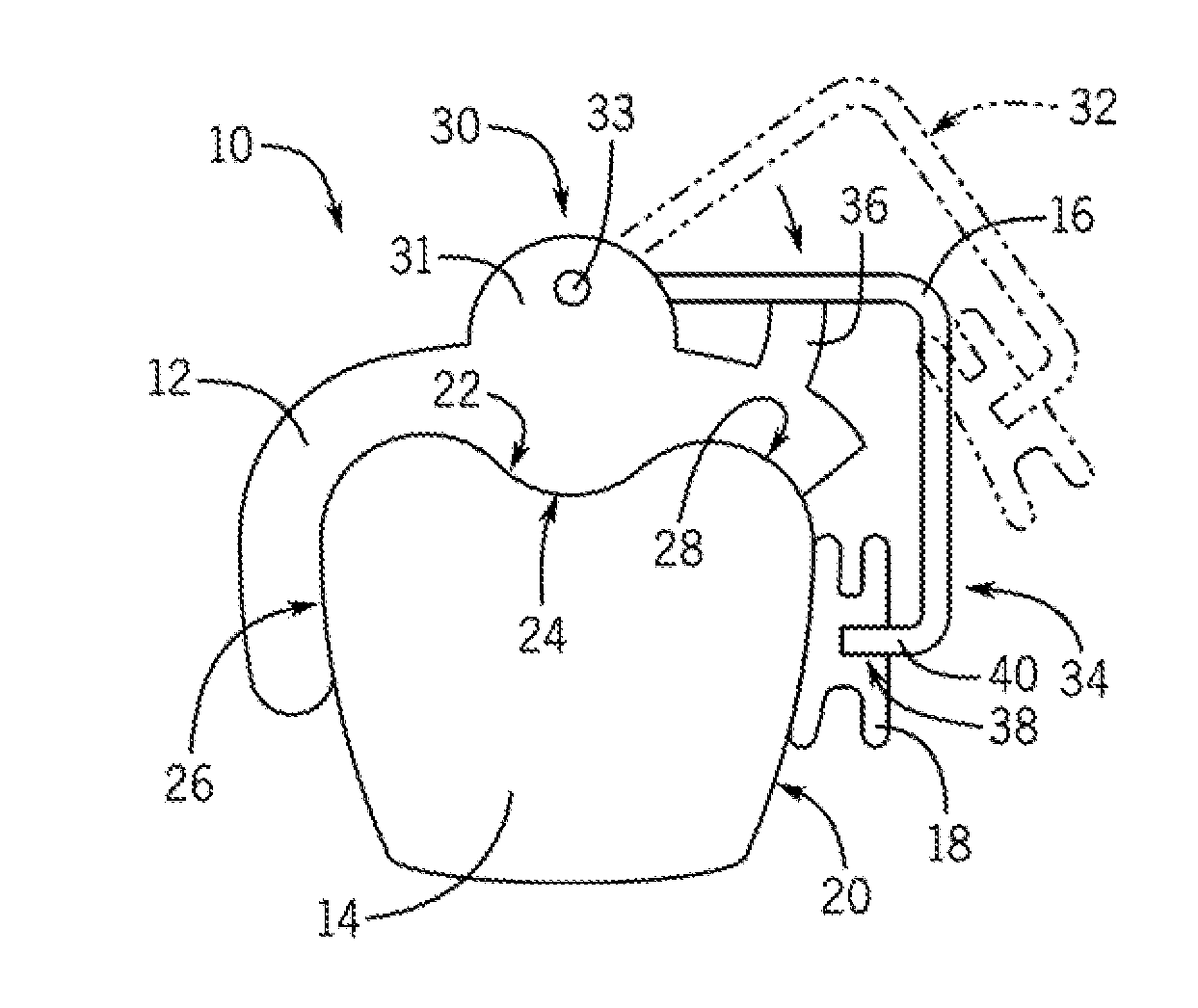
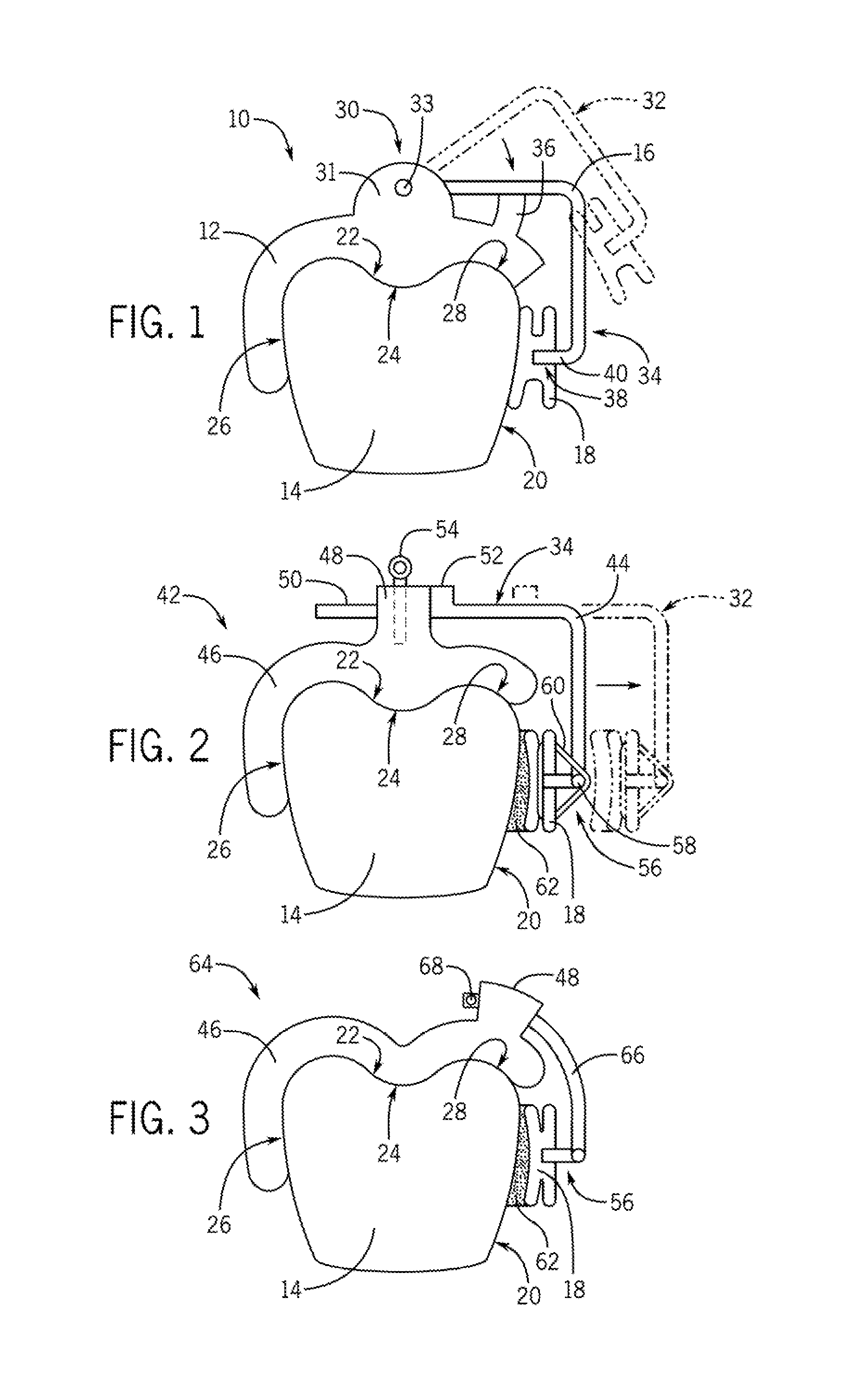
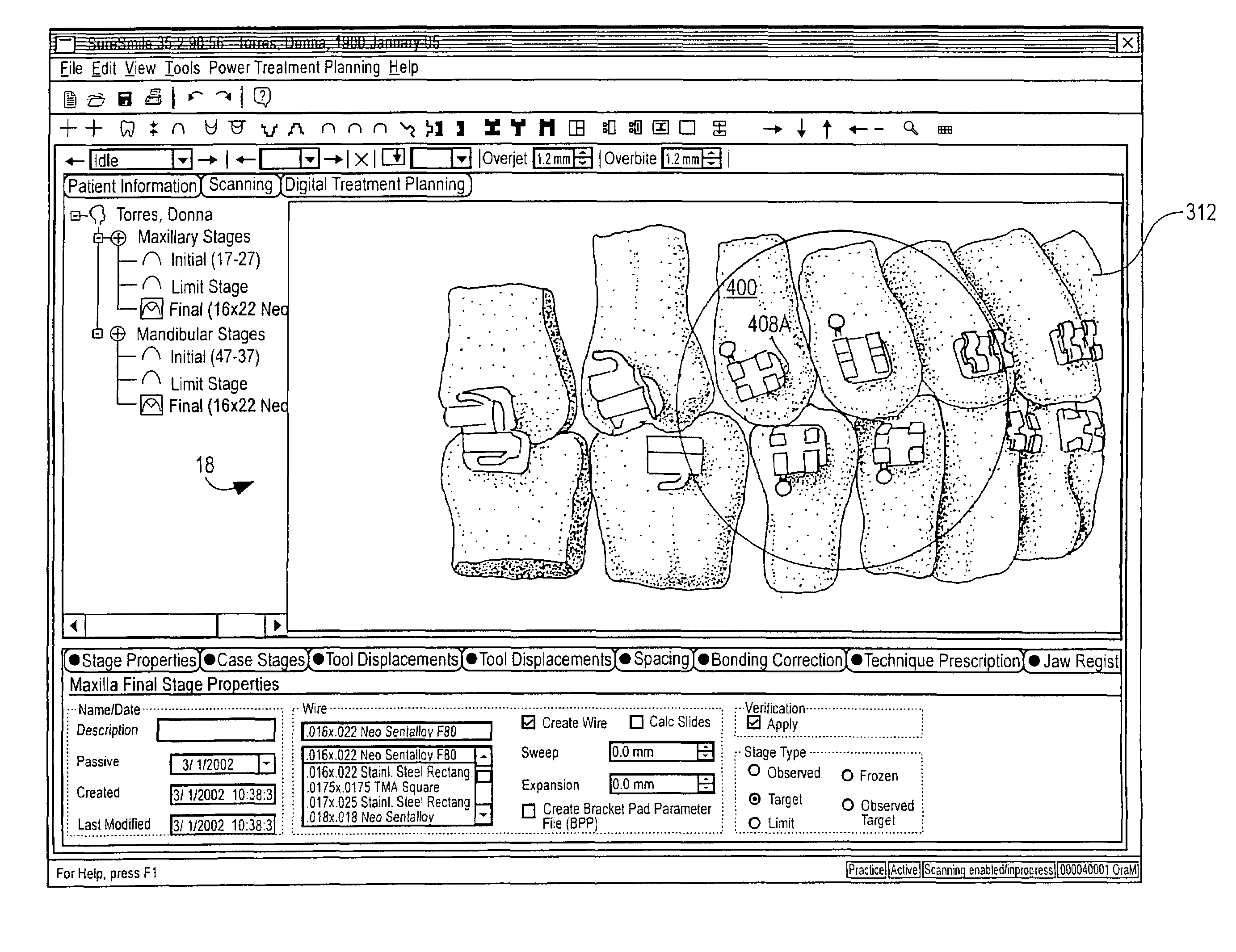
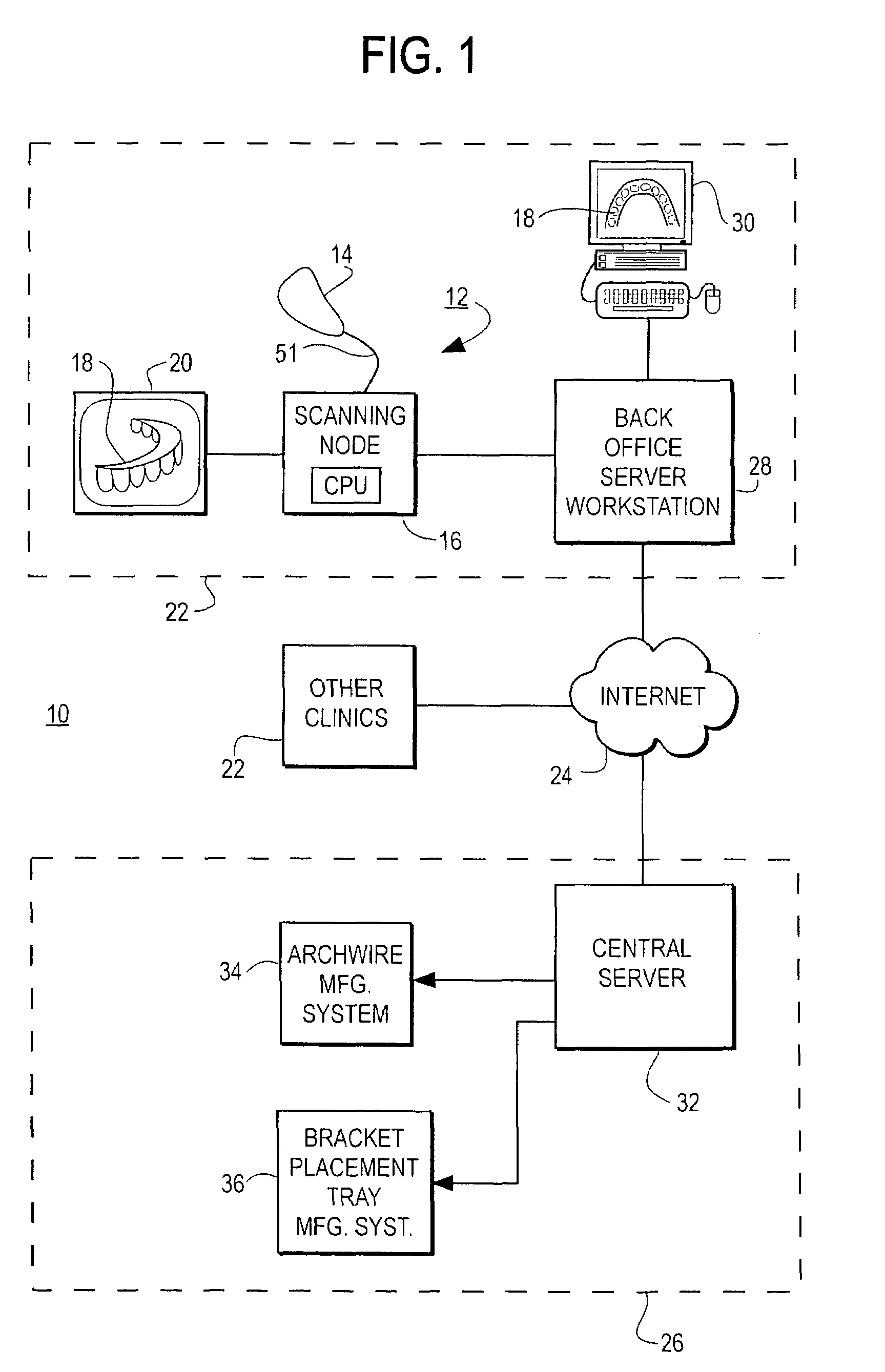
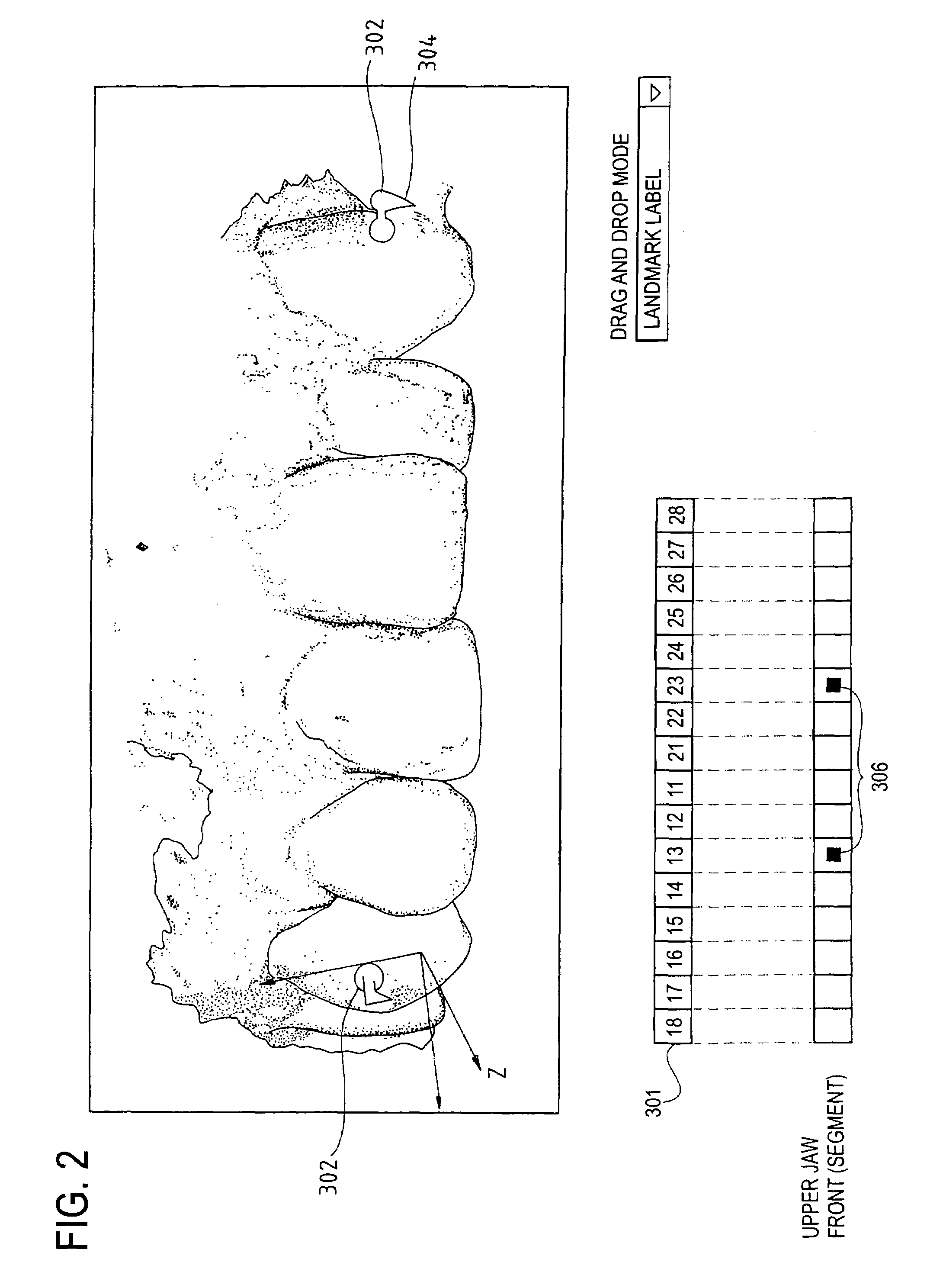
Orthodontic treatment planning with user-specified simulation of tooth movement
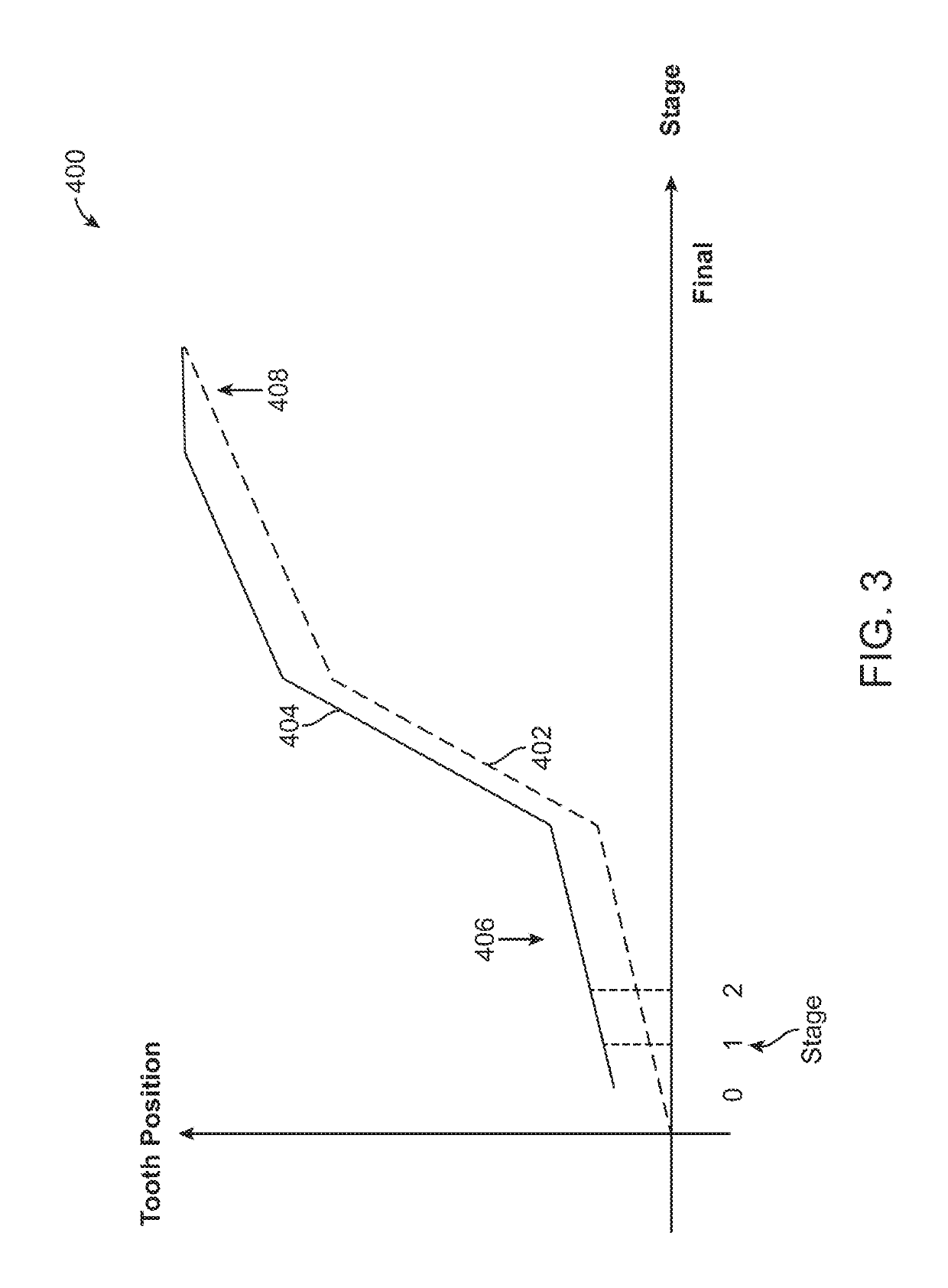
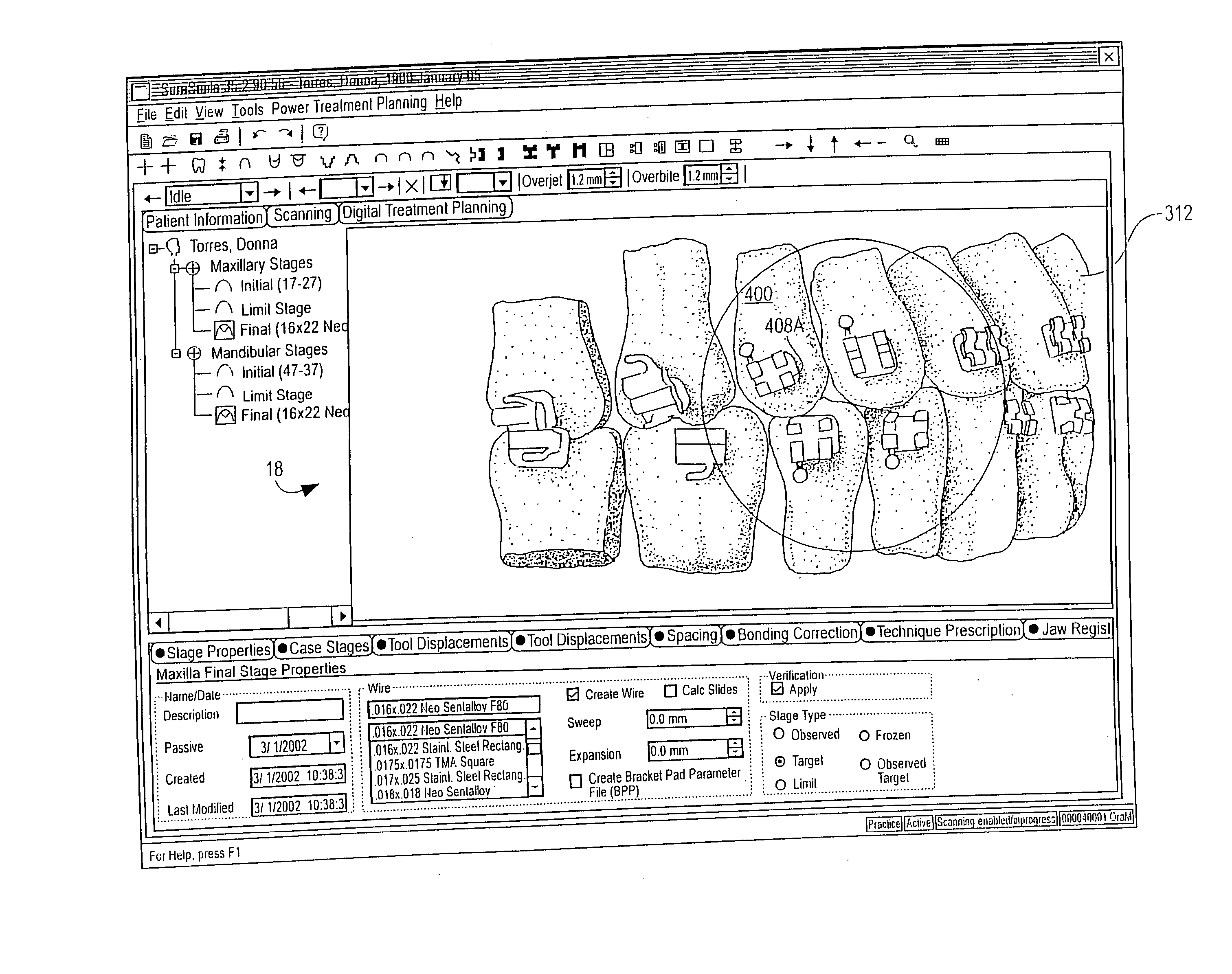
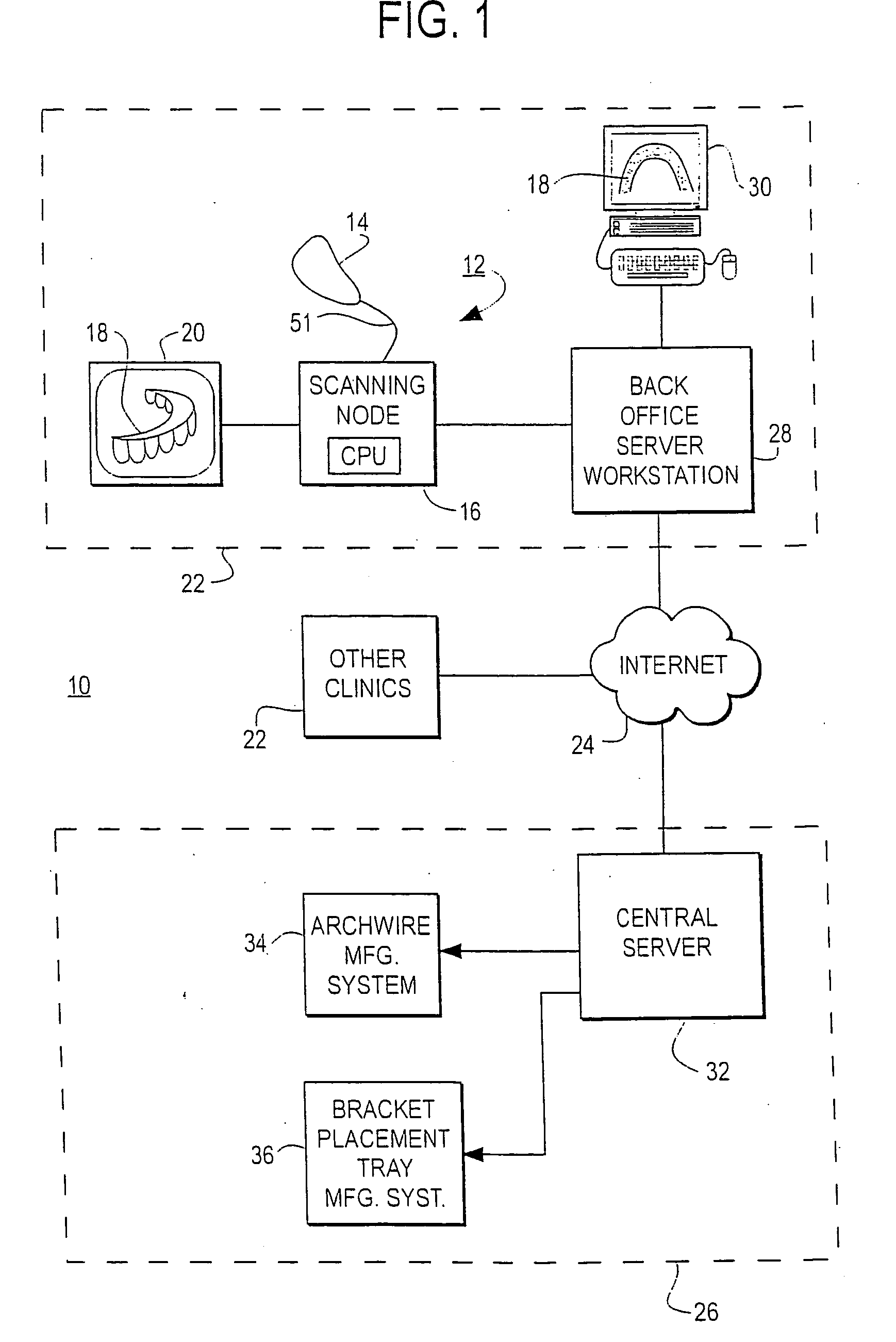
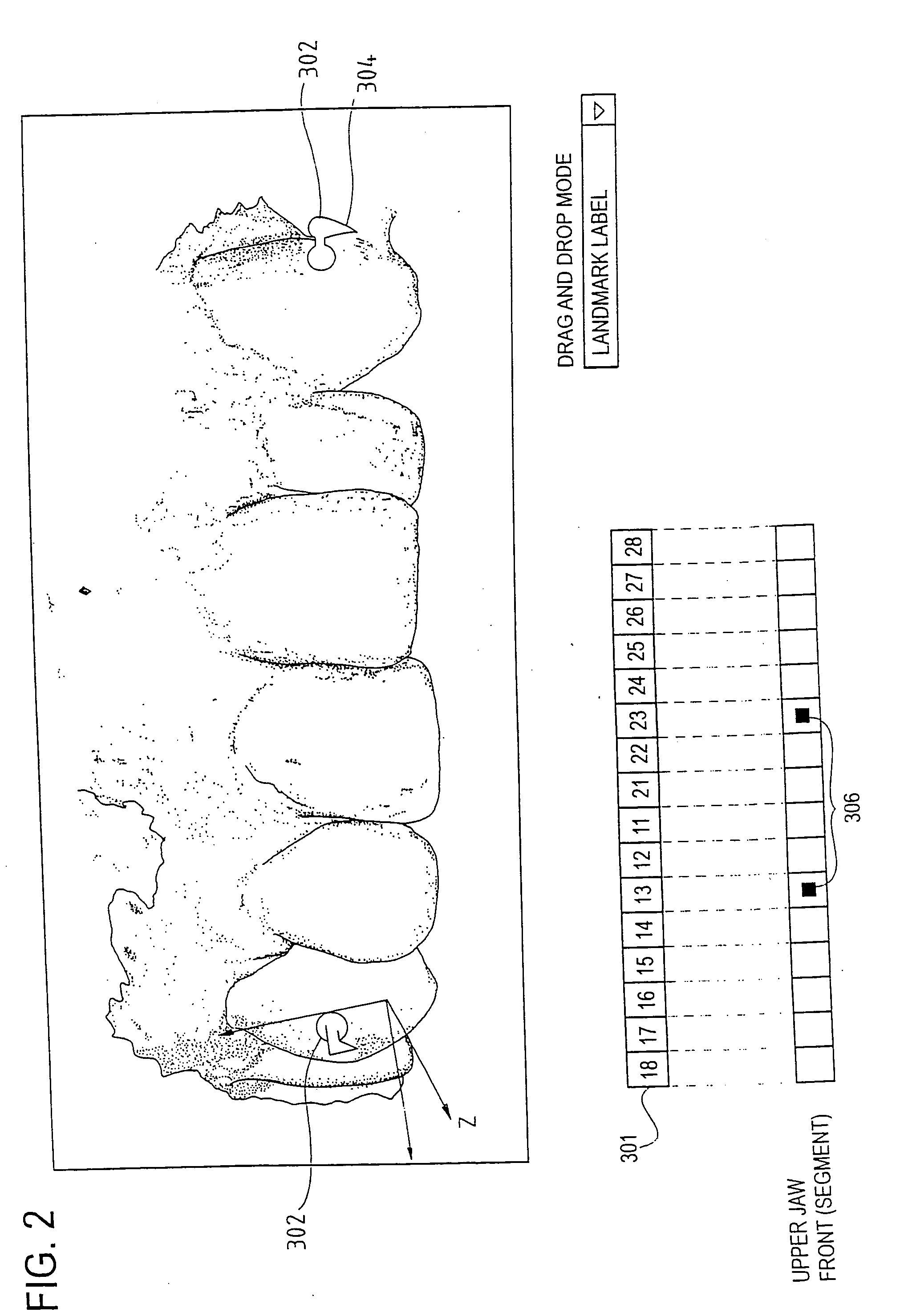
An interactive, software-based treatment planning method to correct a malocclusion is described. The method can be performed on an orthodontic workstation in a clinic or at a remote location such as a lab or precision appliance manufacturing center. The workstation stores a virtual three-dimensional model of the dentition of a patient and patient records. The virtual model is manipulated by the user to define a target situation for the patient, including a target archform and individual tooth positions in the archform. Parameters for an orthodontic appliance, such as the location of orthodontic brackets and resulting shape of an orthodontic archwire, are obtained from the simulation of tooth movement to the target situation and the placement position of virtual brackets. The treatment planning can also be executed remotely by a precision appliance service center having access to the virtual model of the dentition. In the latter situation, the proposed treatment plan is sent to the clinic for review, and modification or approval by the orthodontist. The method is suitable for other orthodontic appliance systems, including removable appliances such as transparent aligning trays.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ORAMETRIX
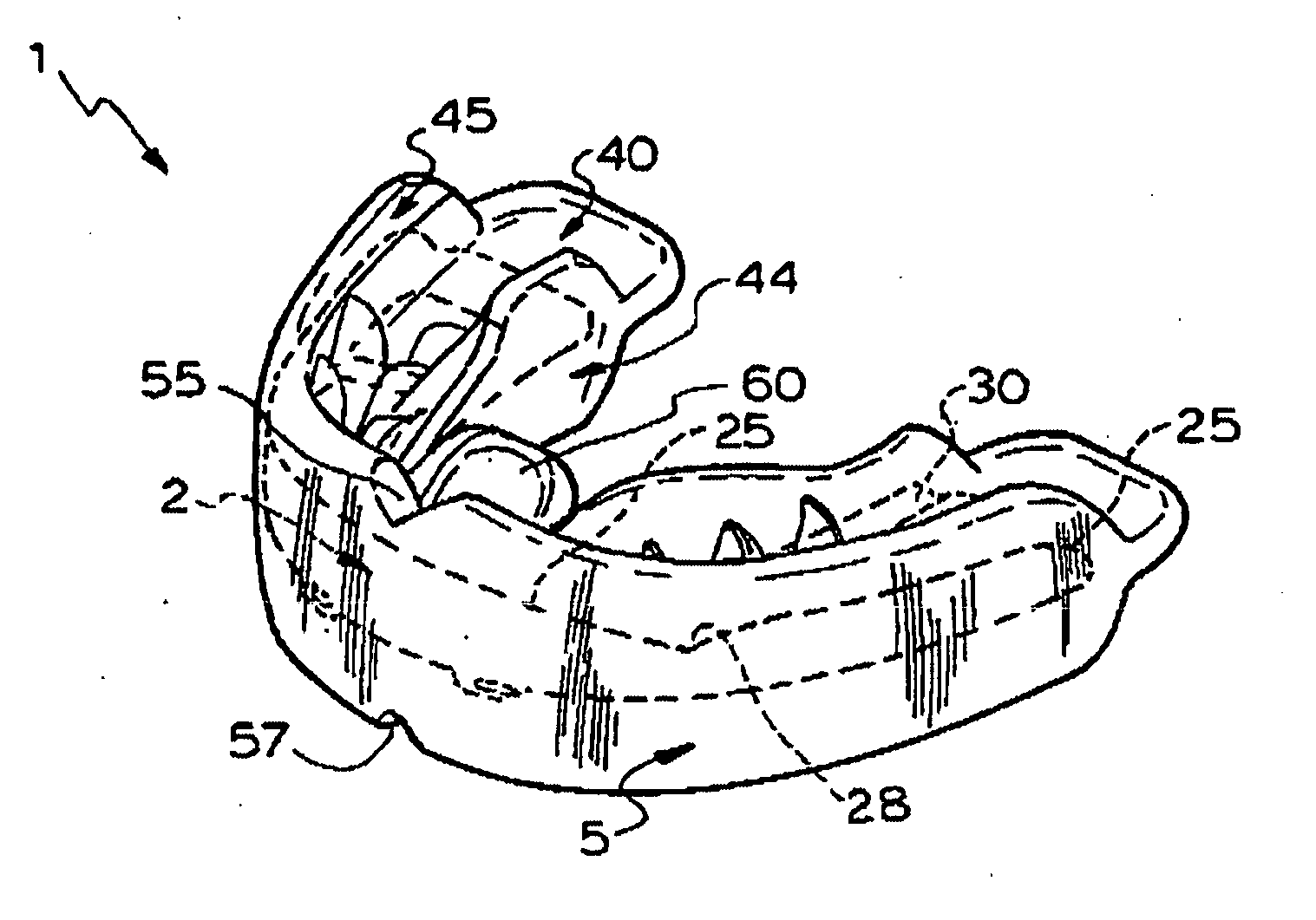
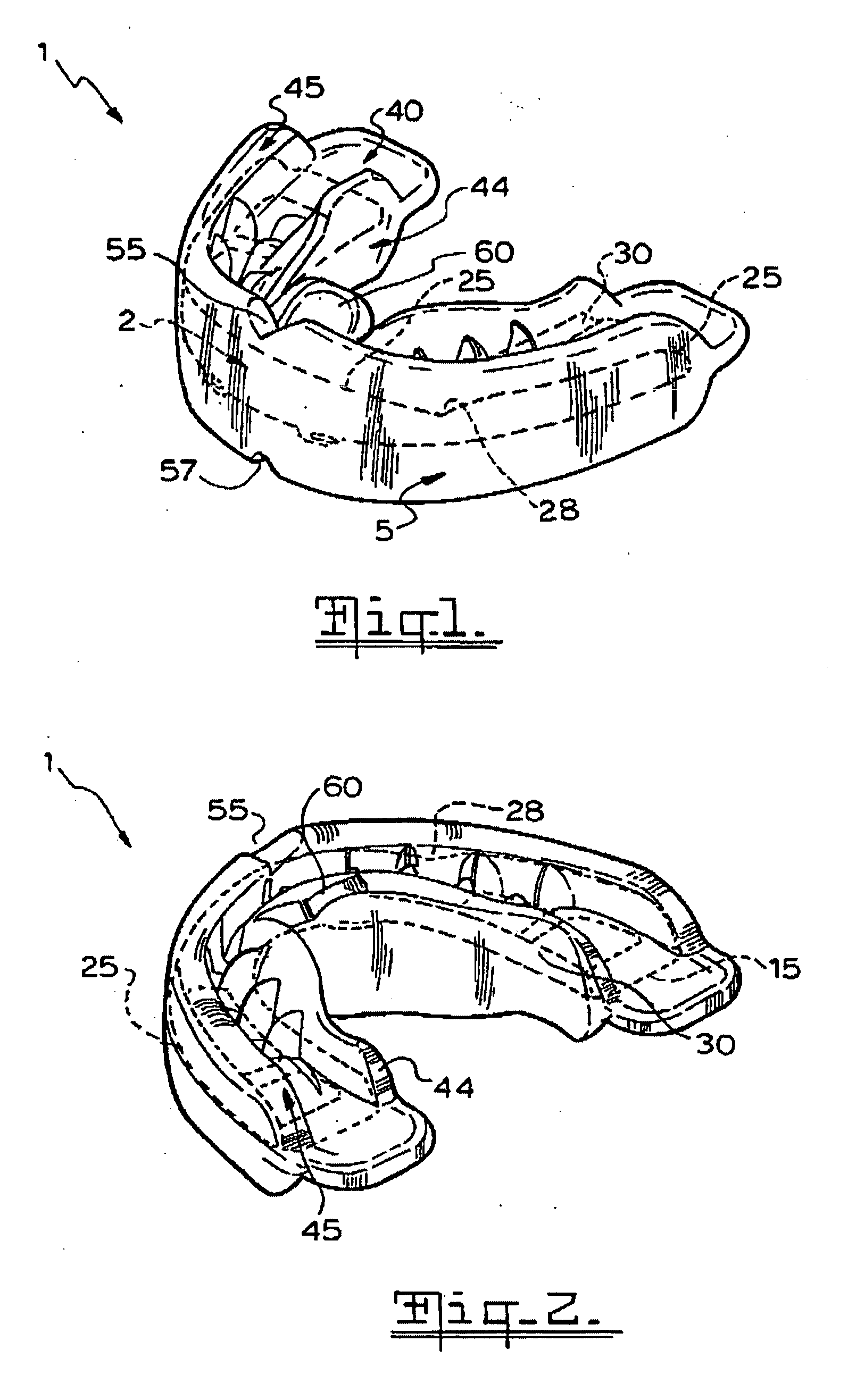
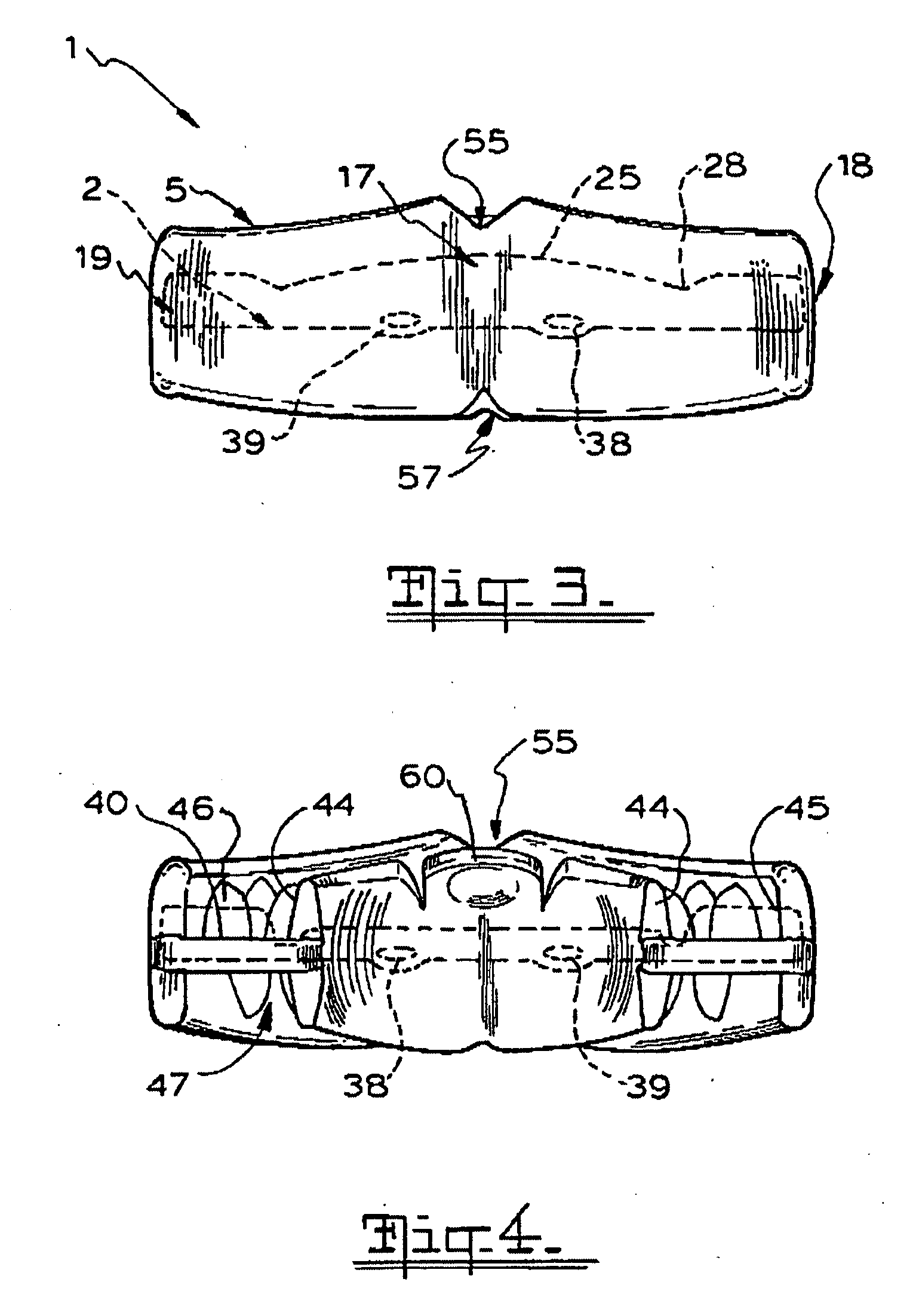
Oral appliance
InactiveUS20060084024A1Resistant to in usePromote muscle relaxationOthrodonticsTeeth fillingOral applianceEngineering
An orthodontic trainer 1 for assisting the correction of the misalignment of teeth is disclosed. The trainer 1 comprises a base member 2 made of nylon having a generally U-shaped form corresponding to the outline of the jaw of a user and a teeth engaging member 5 that encases the base member 2. The base member 2 has an open frame structure with curved inner and outer elongate frame members 12, 10 interconnected at spaced intervals by transverse frame members 15. The trainer 1 includes a outer teeth repositioning formation in the form of an outer flange is positioned on the outer elongate frame member 10. The trainer 1 also includes an inner teeth repositioning formation on the inner elongate frame member 12. The continuous teething engaging member 5 that is made of silicone rubber or PVC comprises a web 40 and inner and outer flanges 44, 45 projecting up and down from both upper and lower faces of the web 40. These flanges 44, 45 and the web 40 define upper and lower channels within which the upper and lower teeth of the user can be received. The trainer 1 also includes teeth positioning formations on the teeth engaging member 5 projecting into the upper and lower channels for encouraging the correct positioning of the teeth of a user.
Owner:FARRELL CHRISTOPHER JOHN
Orthodontic teeth positioning appliances
InactiveUS20120129117A1Efficient use ofEasy to useOthrodonticsDental toolsTooth positionAnterior teeth
An Orthodontic teeth positioning appliance comprising an anterior positioning component, a posterior component and a resilient means connecting the anterior and posterior components. The anterior positioning component is configured to be in contact with, in order to push against, the lingual faces of a plurality of anterior teeth, when worn by the user and the posterior component is configured to be anchored to at least one posterior tooth, when worn by the user in order that the resilient means urges apart the anterior positioning component from the posterior component. The appliance is preferably removable by the user.
Owner:ORTHO PRO TEKNICA
Software and Methods for Dental Treatment Planning
ActiveUS20090098502A1Easy to movePrecise positioningMedical simulationLocal control/monitoringBody of mandibleAfter treatment
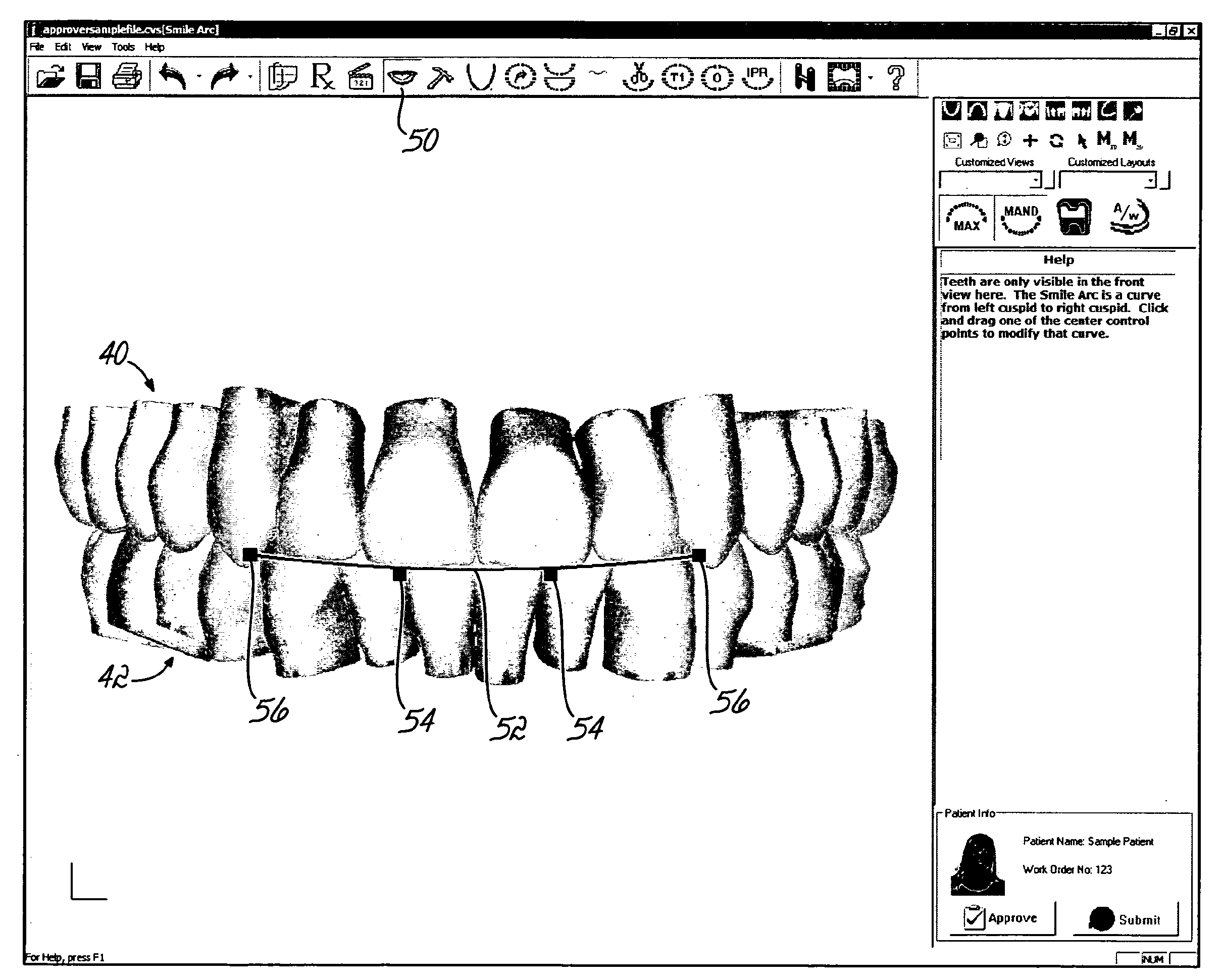
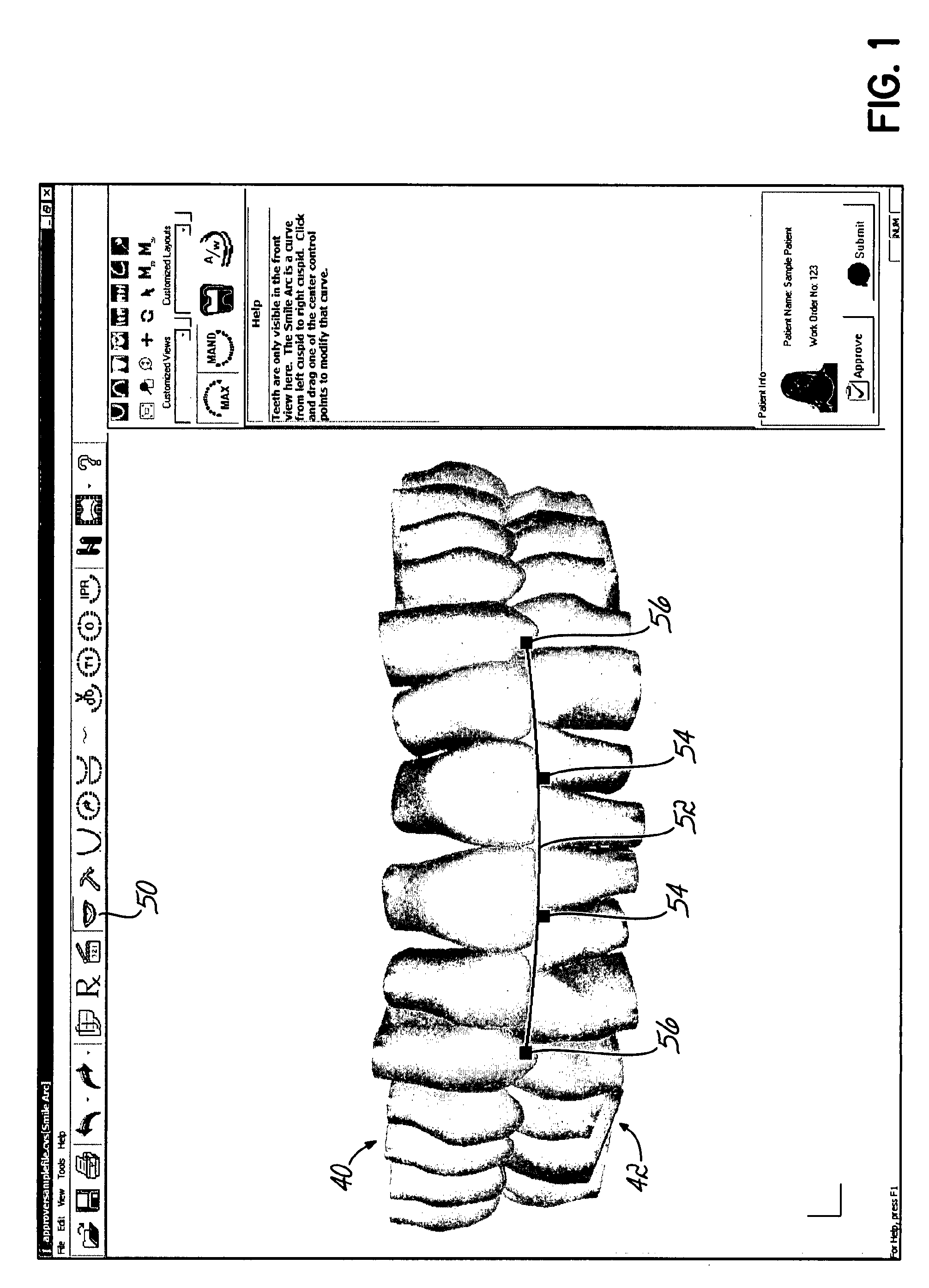
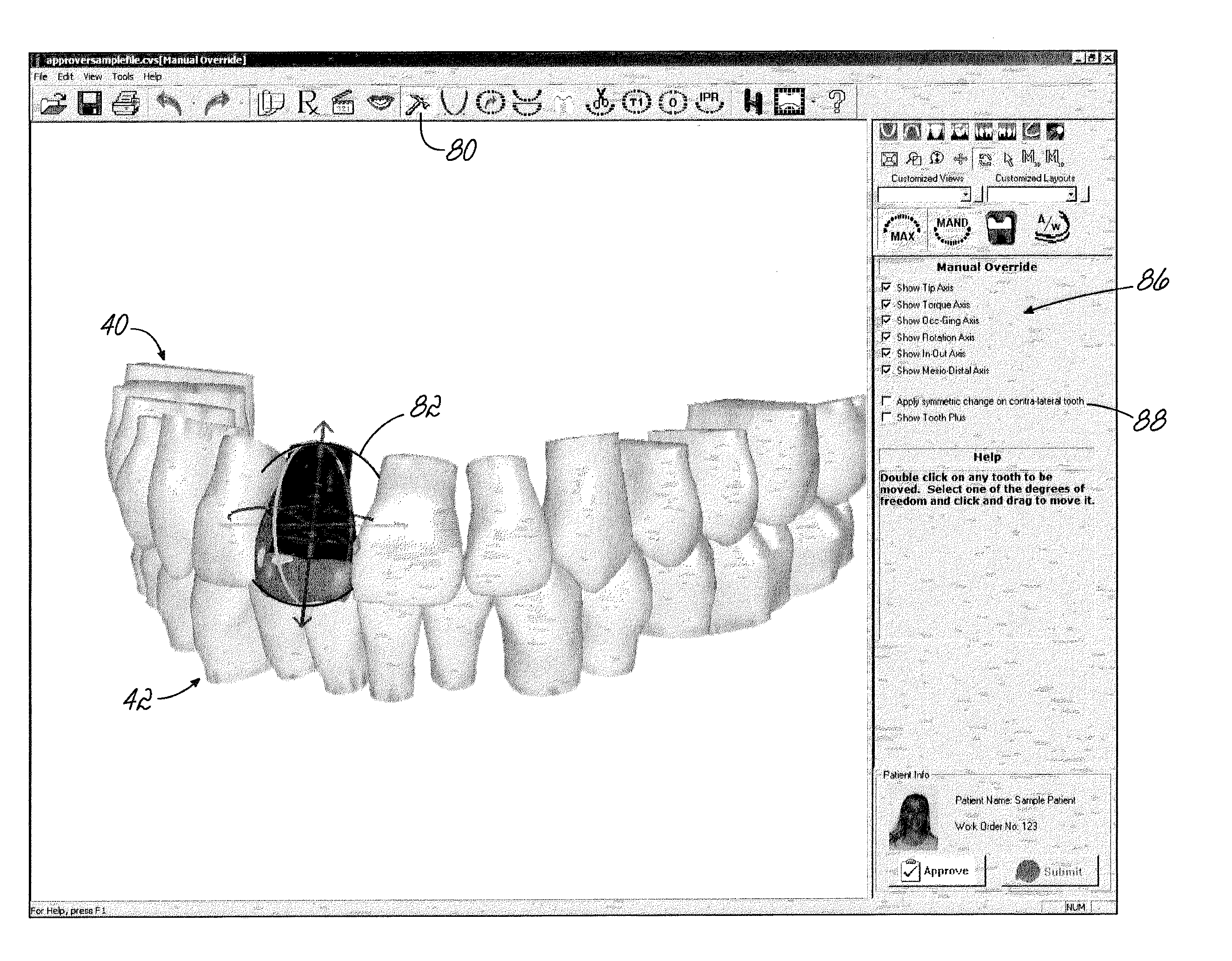
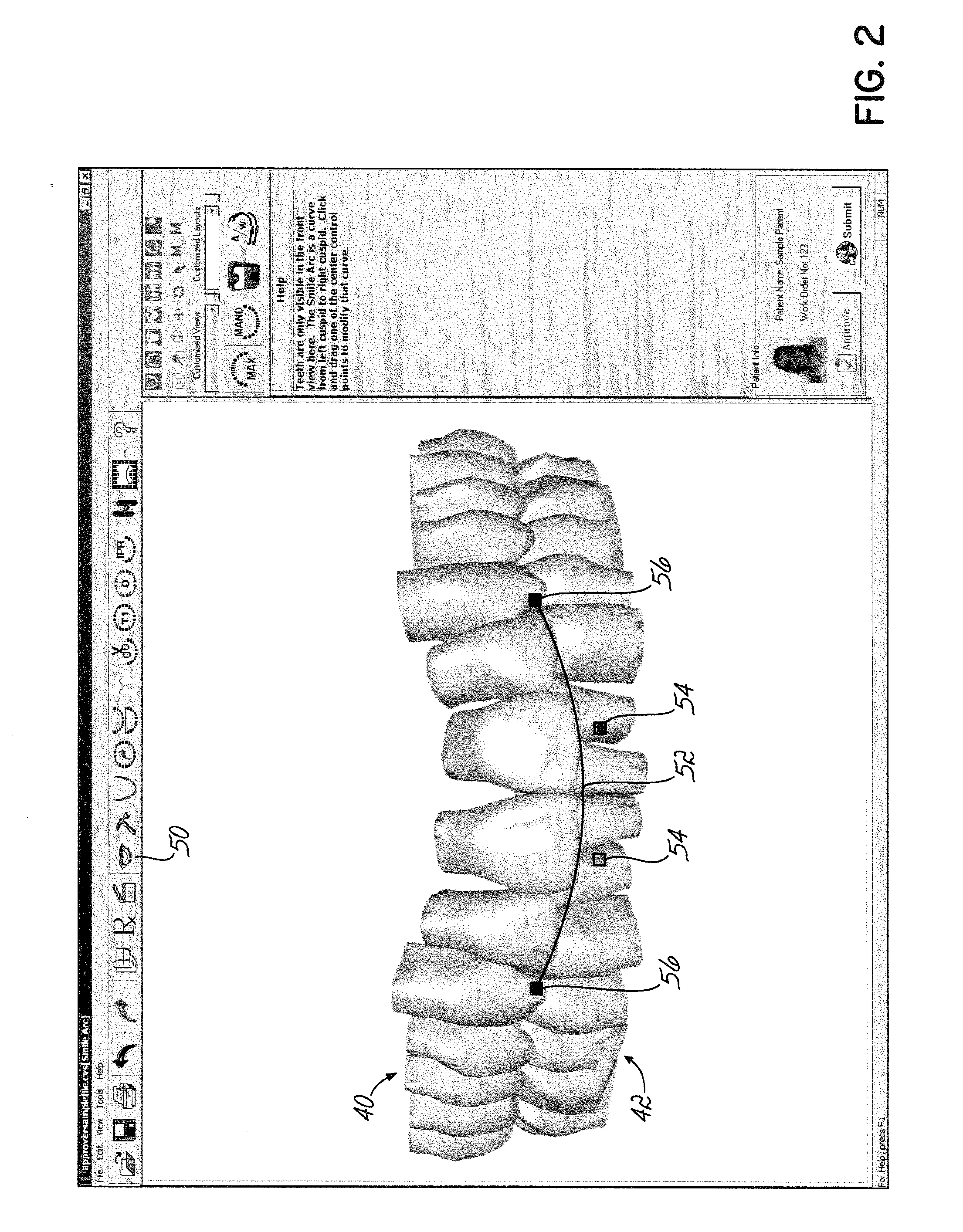
Computer-implemented methods to plan, display and evaluate orthodontic treatment plans. A plurality of teeth in a representation on a computer display may be moved simultaneously in accordance with a mathematically defined pattern. Software tools available to generate the treatment path may include adjusting the smile teeth, moving teeth along a curve fit to points in the mandible, individually moving a tooth, cross sectioning to check for interference and simulations of occlusal points, highlighting teeth that have moved from their original position, making notations on the teeth, and generating and saving animation sequences of before and after treatment tooth positions.
Owner:ORMCO CORP
Apparatus for temporomandibular joint-related corrections of tooth position
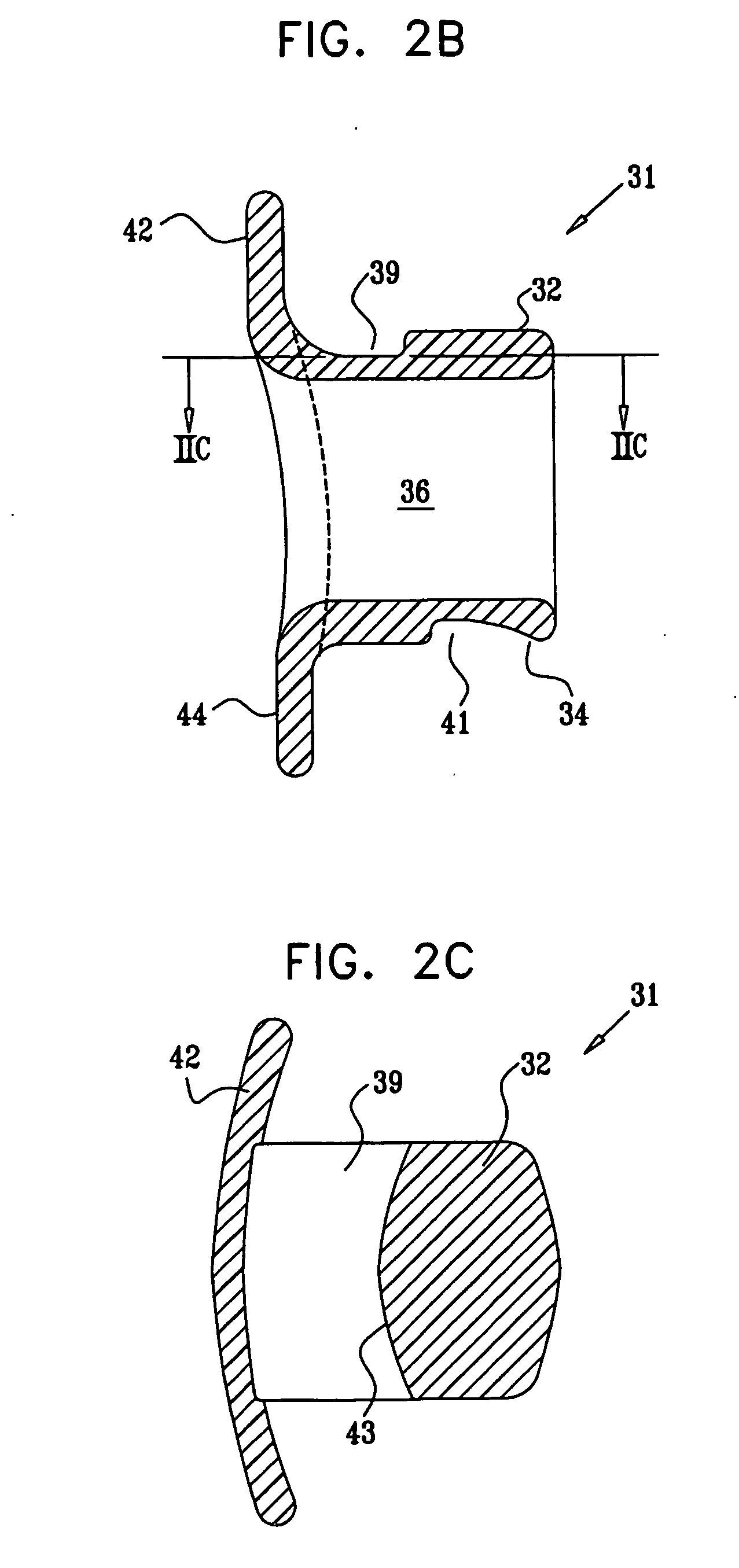
ActiveUS20150079531A1Increase forceAmplify torque effectOthrodonticsDental toolsFilling materialsComputer module
The invention relates to an apparatus for temporomandibular joint-related corrections of tooth position, taking into account a variant of the registration or construction of the bite predetermined by the user.The invention is characterized in that a base module extending at least on the occlusion-bearing part of one side of the jaw is supported in an intermaxillary manner and has cavities formed by a setup technique to accommodate teeth, by means of which the tension forces necessary for tooth movements can act on the teeth, in that the base module has a three-dimensionally defined jaw support designed in accordance with specifications of the user, and in that the jaw support is formed by bite blocks and / or interceptors which have cavities filled with a filling material of predeterminable elasticity.
Owner:HEINE GERNOT
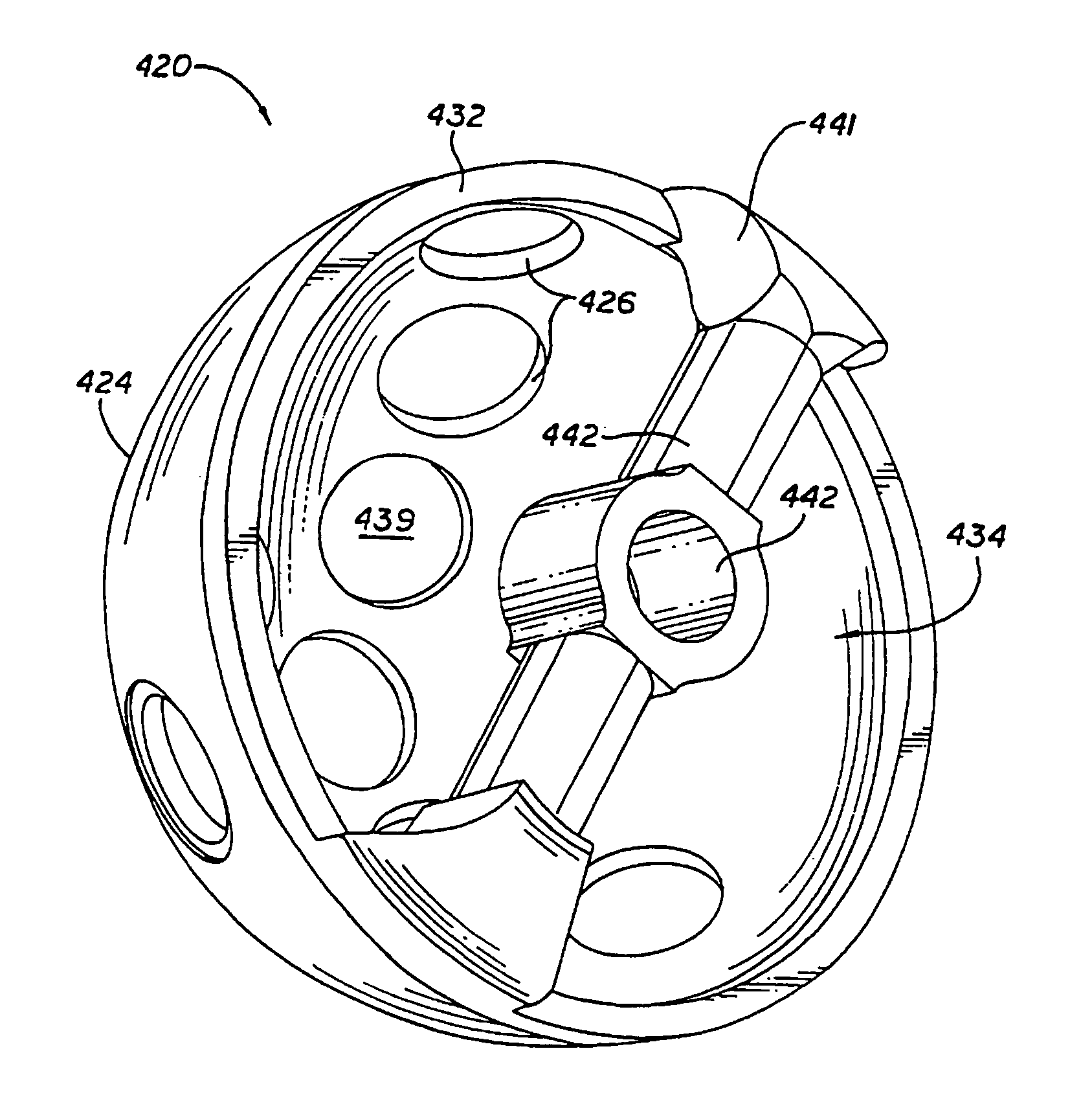
Virtual bracket library and uses thereof in orthodontic treatment planning
InactiveUS20060078842A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationTreatments proceduresTooth position
An orthodontic workstation stores a library of virtual three-dimensional brackets in a memory. Each of the virtual brackets has a unique three-dimensional configuration and prescription. Typically, the library of bracket comprises a library of commercially available, off-the-shelf brackets. The workstation further includes an interactive treatment planning program that permits a user to move teeth from a virtual model of the dentition to a proposed set-up. In one possible embodiment, the treatment planning program provides the ability to display a virtual bracket placed on a virtual tooth and change the prescription or configuration of the virtual bracket. The treatment program automatically compares the modified prescription with the prescription information of the virtual brackets in the library and selects a bracket from the library that most closely matches the virtual bracket displayed on the tooth. Thus, the user does not have to use customized brackets. Any deviation in tooth position resulting from a discrepancy between the off-the-shelf bracket and the user-defined bracket can be corrected for by changing the position of the bracket on the tooth or by changing the shape of the archwire.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
Arthroscopic shaver and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20060212060A1Improve efficiencyCuts bone efficientlyOther manufacturing equipments/toolsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsMilling cutterArthroscopy
An arthroscopic shaver with an inner cutting window having a plurality of teeth positioned along the lateral cutting edges, the teeth being configured for easy penetration into tissue to prevent ejection of tissue from the cutting window during closure. The inner cutting edges are formed in a milling operation using a milling cutter having an end radius equal to that of the surfaces forming the inner surfaces of the cutting edges. The teeth may be symmetrically or asymmetrically placed about the tube axis when viewed in a plan view.
Owner:ARTHREX
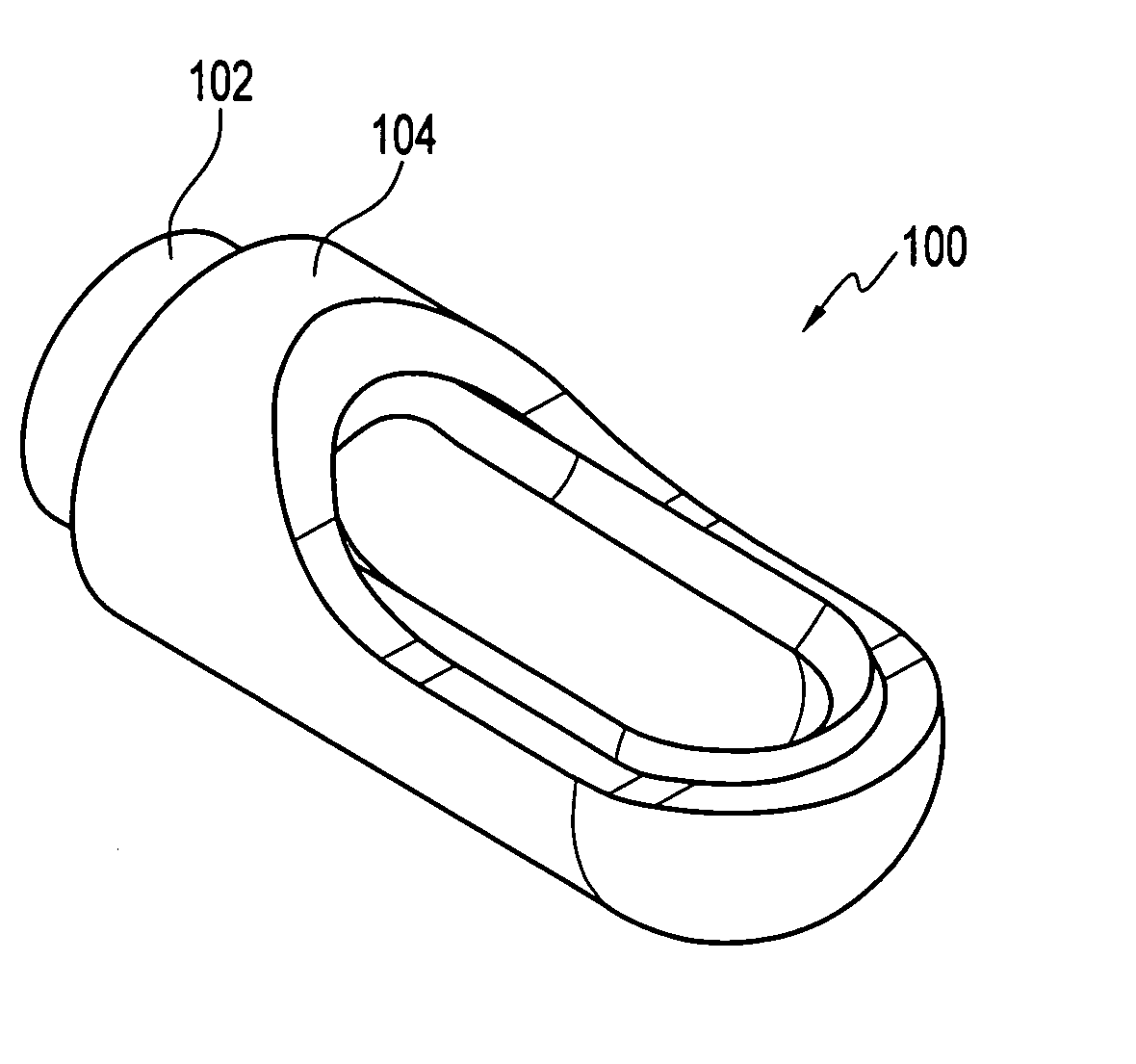
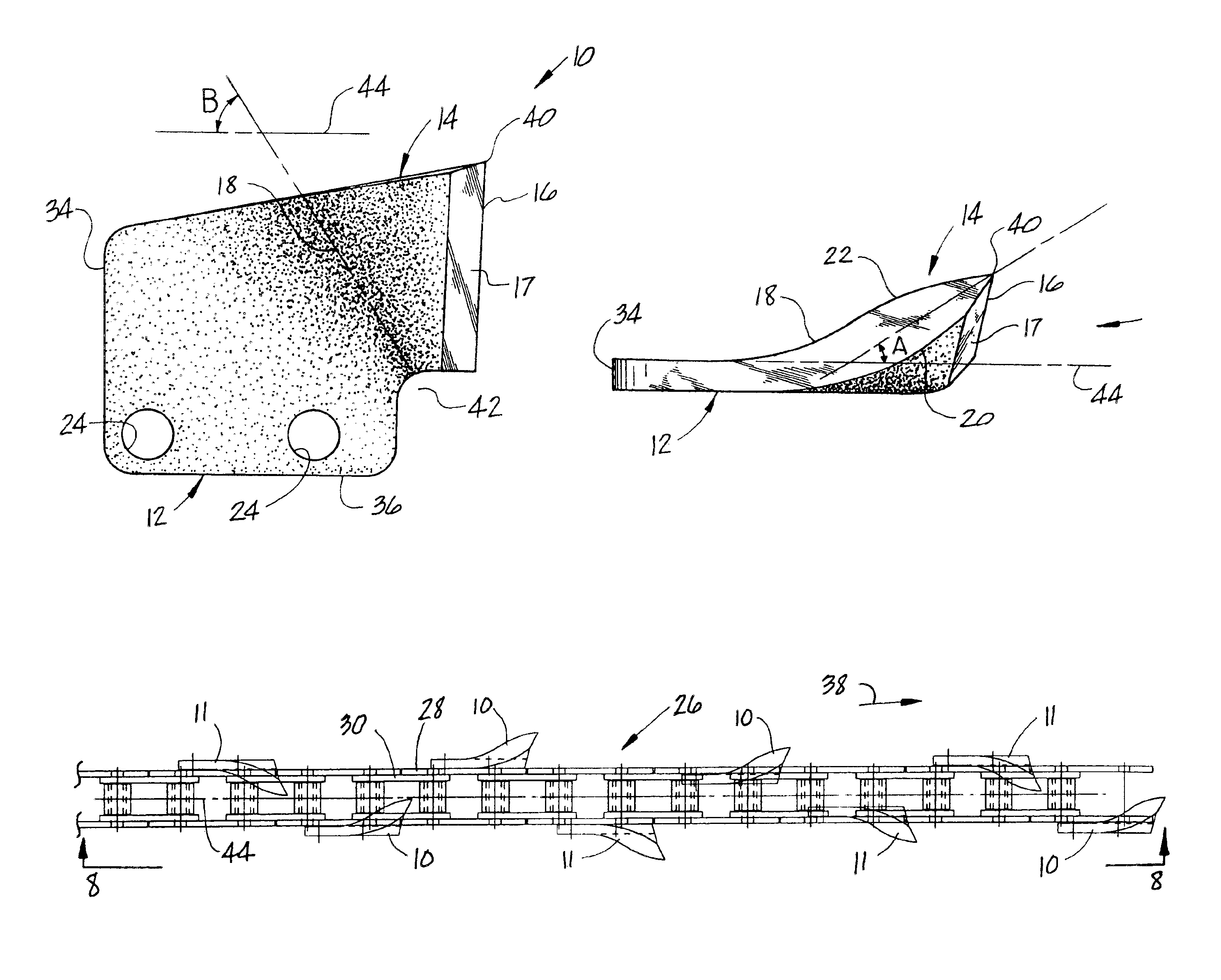
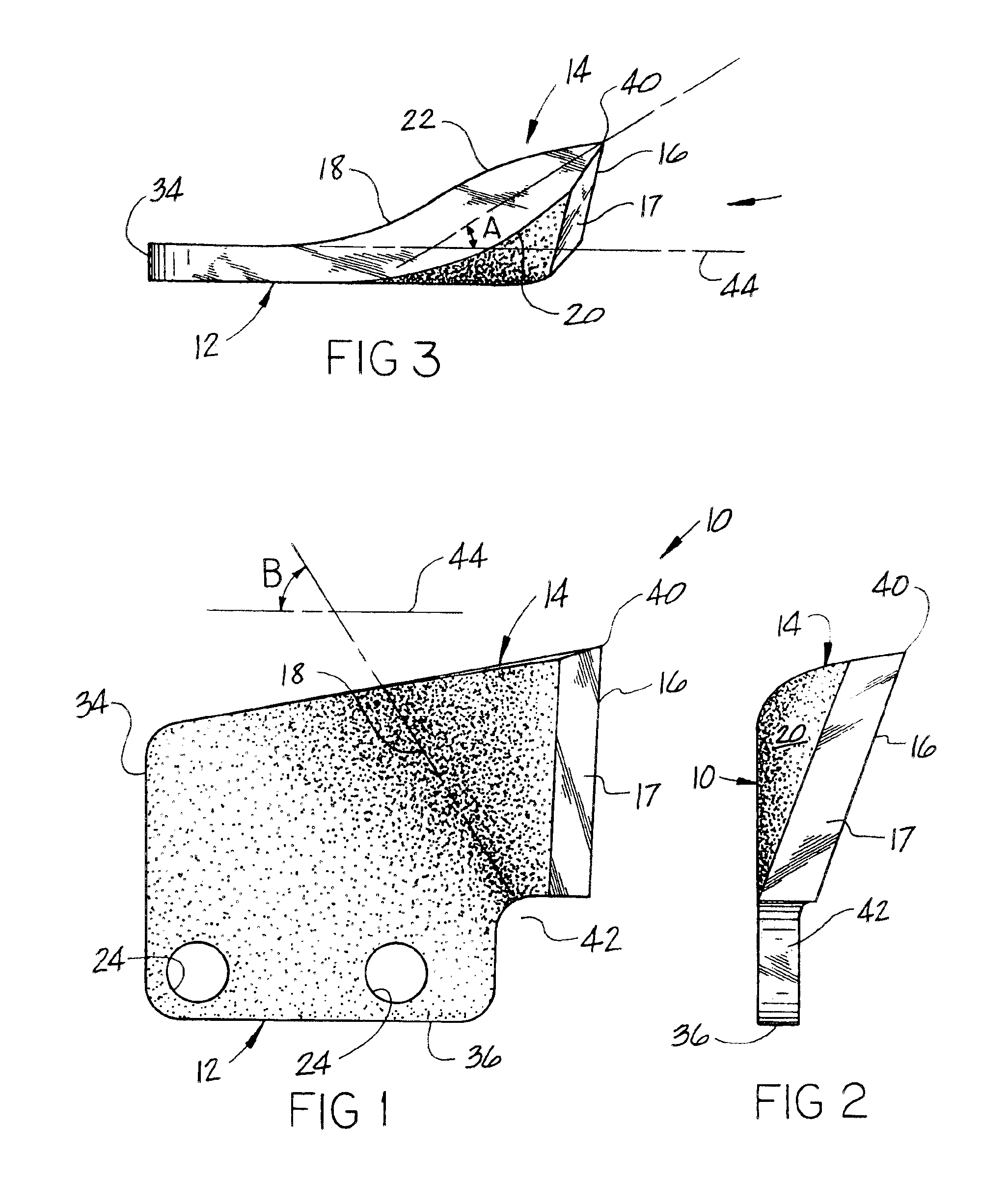
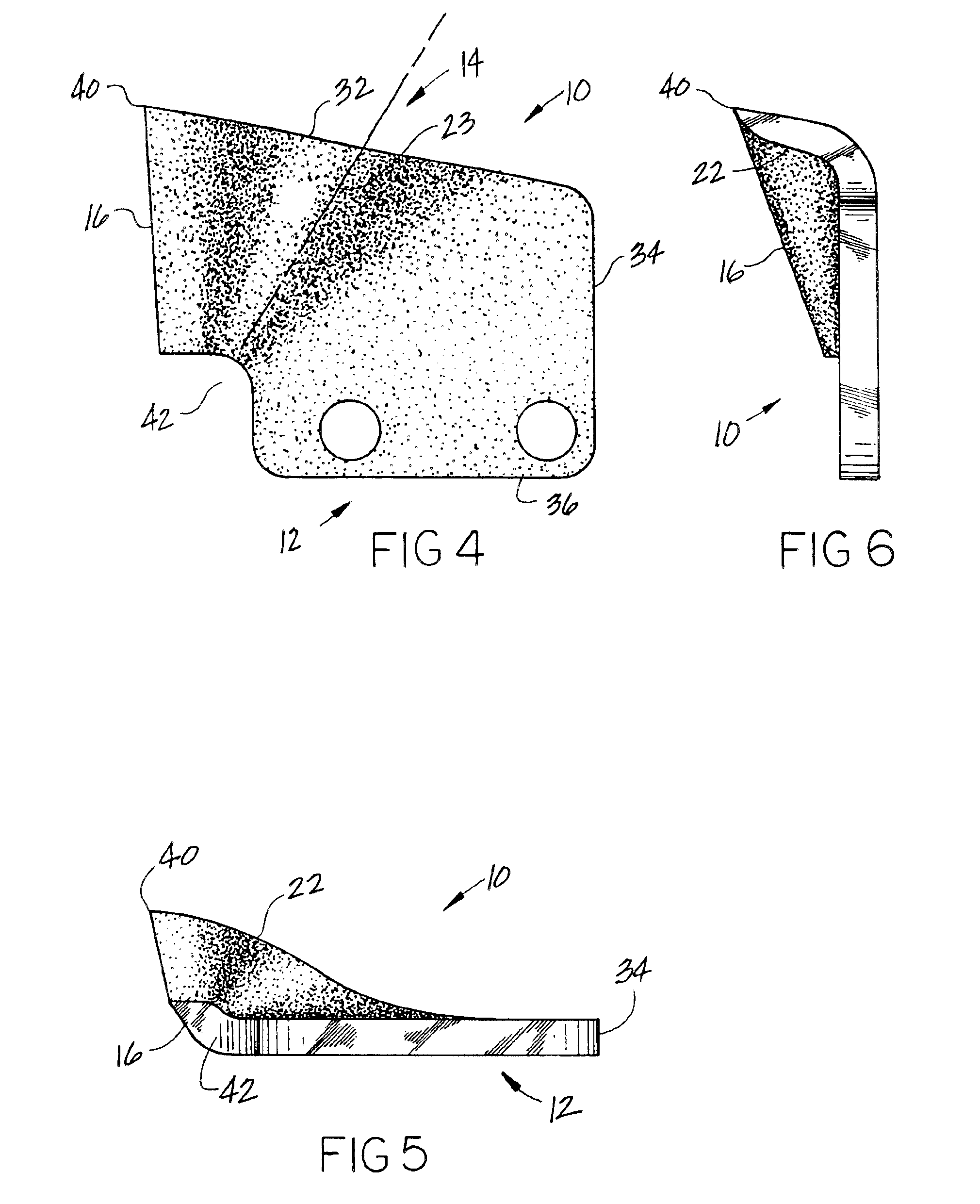
Cutting tooth for trencher chain
InactiveUS6854201B1Efficient productionLess power requirementMechanical machines/dredgersSlitting machinesAcute angleEngineering
A cutting tooth used on an endless chain-trenching machine to fracture and excavate the ground. The tooth includes a mounting portion for attachment to the chain and a cutting portion having a straight cutting edge at the leading end of the tooth positioned normal to the direction movement of the chain. The cutting portion is aligned from the mounting at an acute angle to the plane of the mounting portion and including convex surfaces on both sides of the cutting portion and a juncture line between the mounting portion and the cutting portion forms an acute angle with the direction movement of the chain whereby the cuttings produced by the tooth are lifted away by the chain as the chain is digging.
Owner:HUNTER WILLIAM D +1
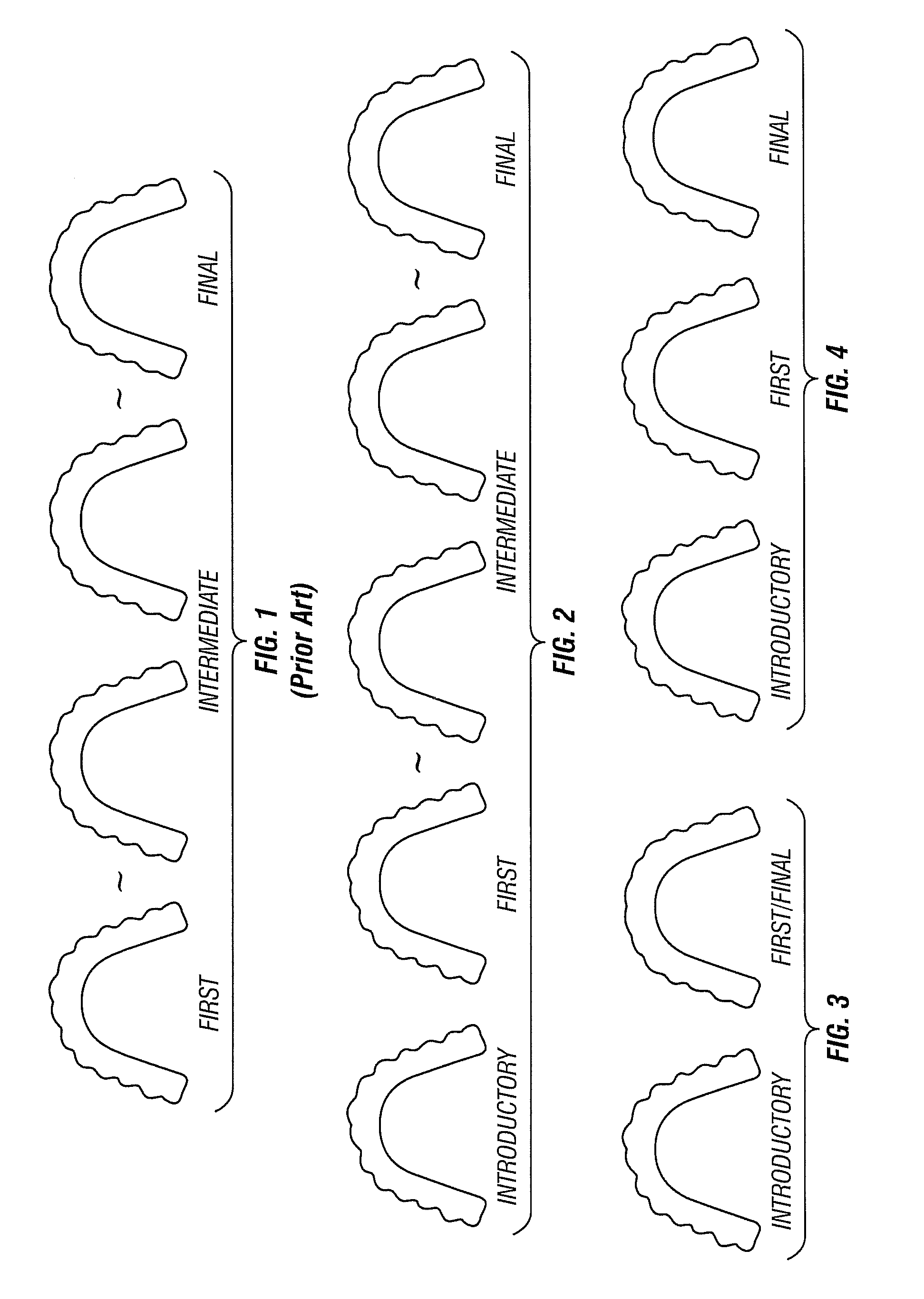
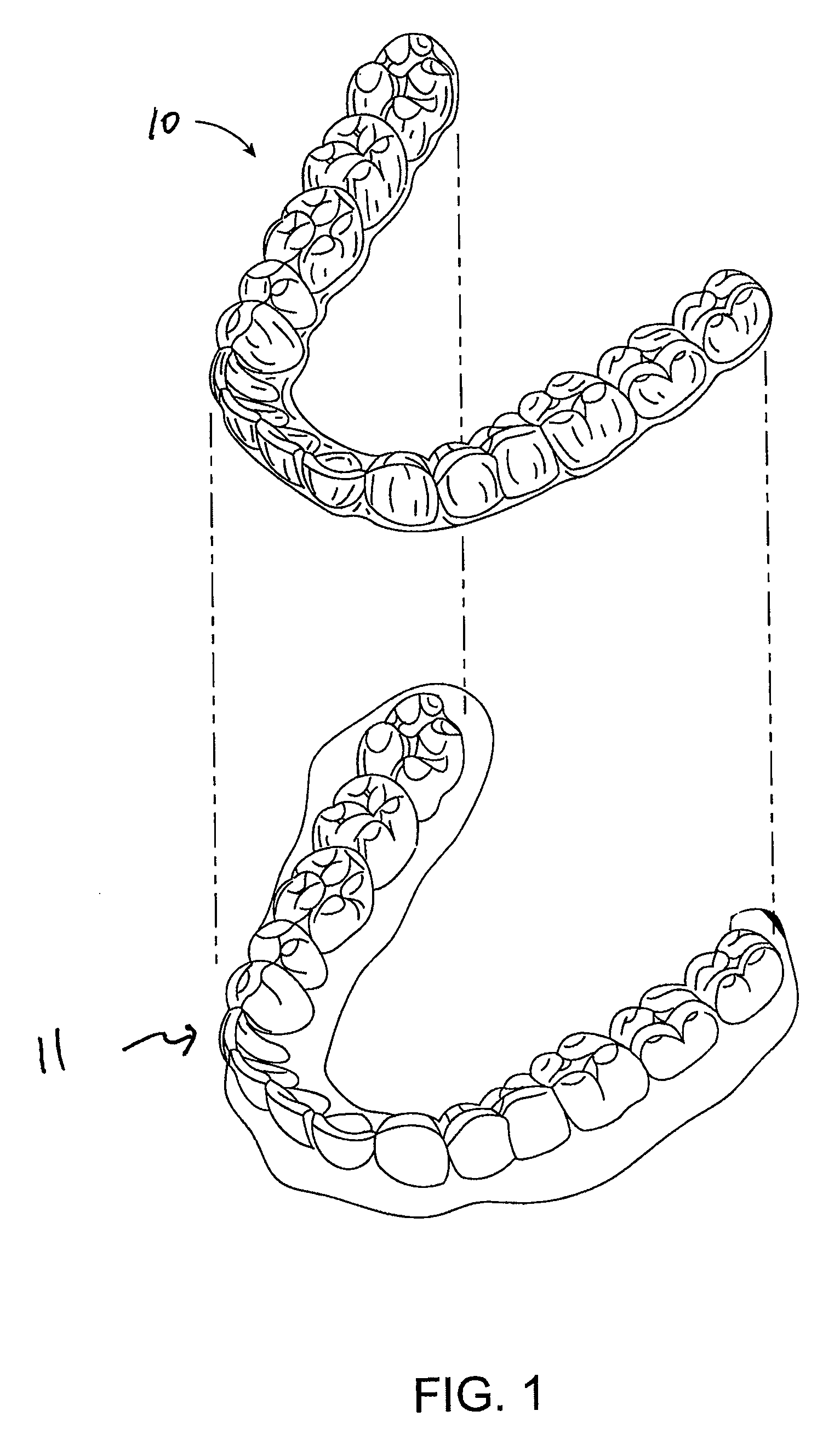
Aligners for incrementally moving teeth, and methods and apparatus of making and using such aligners
Apparatus for repositioning teeth from an initial tooth arrangement to a final tooth arrangement, comprising a series of individual appliances comprising an introductory appliance that conforms to the initial tooth position, and remaining appliances of the series designed to incrementally reposition the teeth from an initial tooth arrangement, through a plurality of intermediate tooth arrangements (if there are any), and to a final tooth arrangement.
Owner:CLEAR CORRECT HLDG
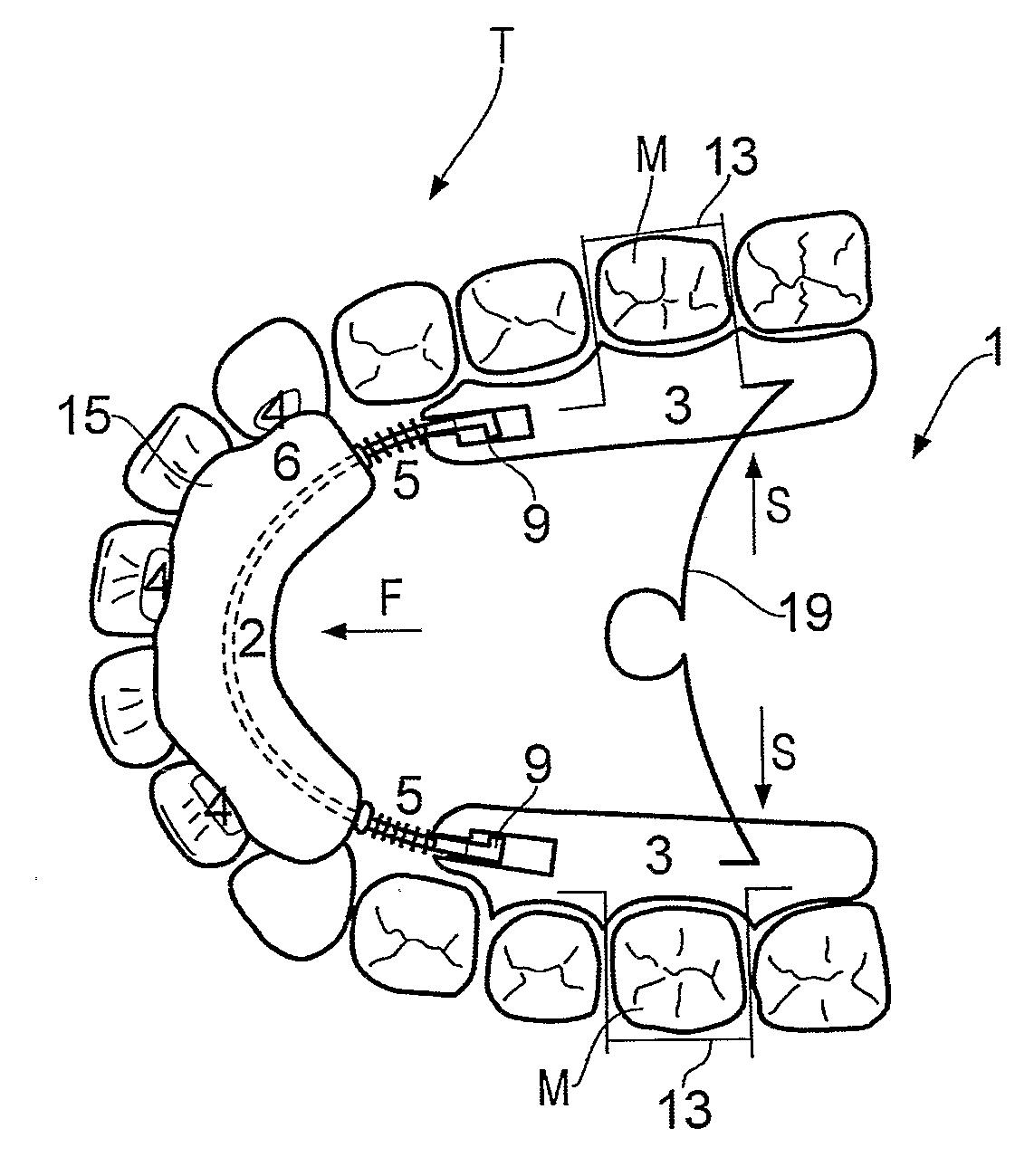
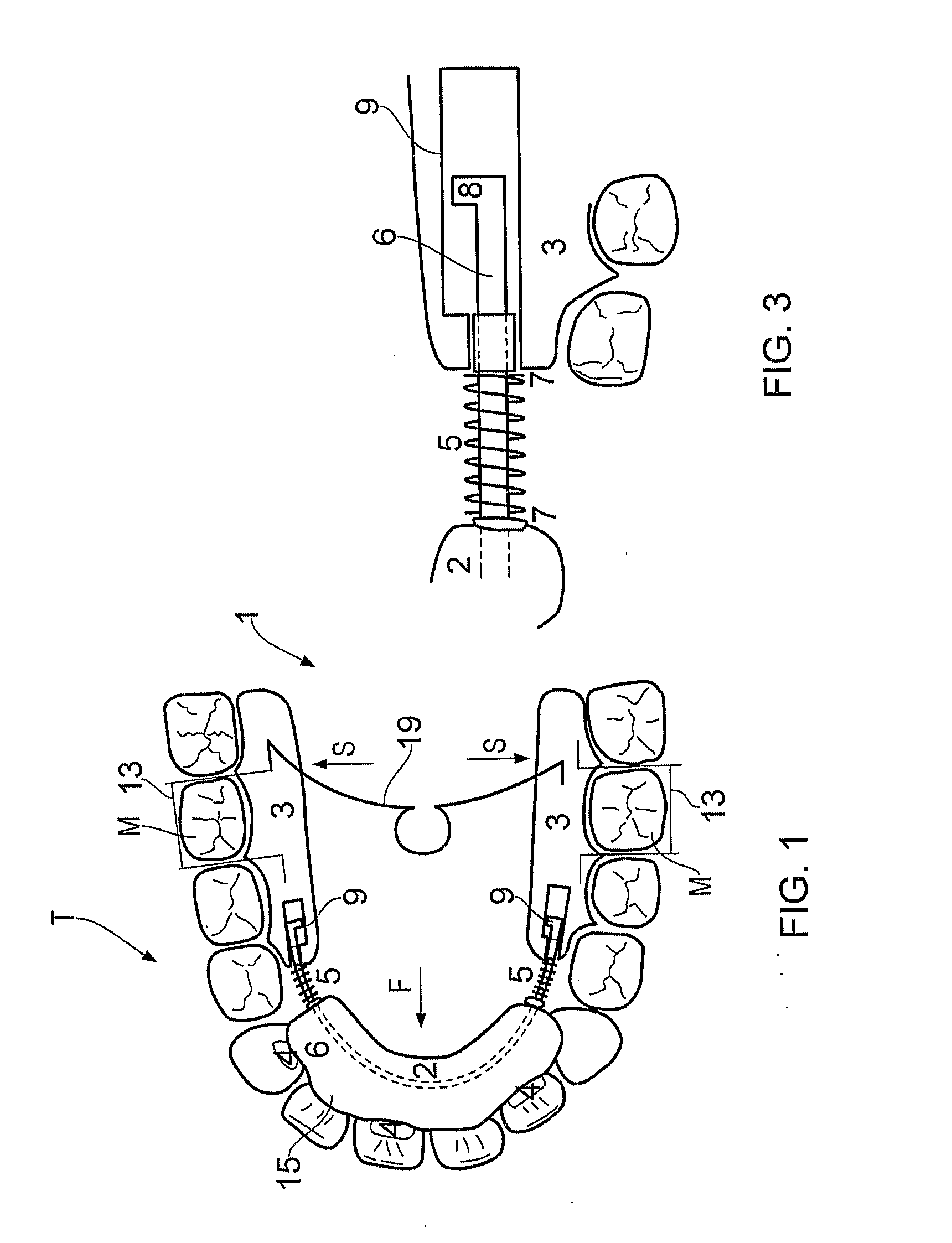
Orthodontic tooth movement device, systems and methods
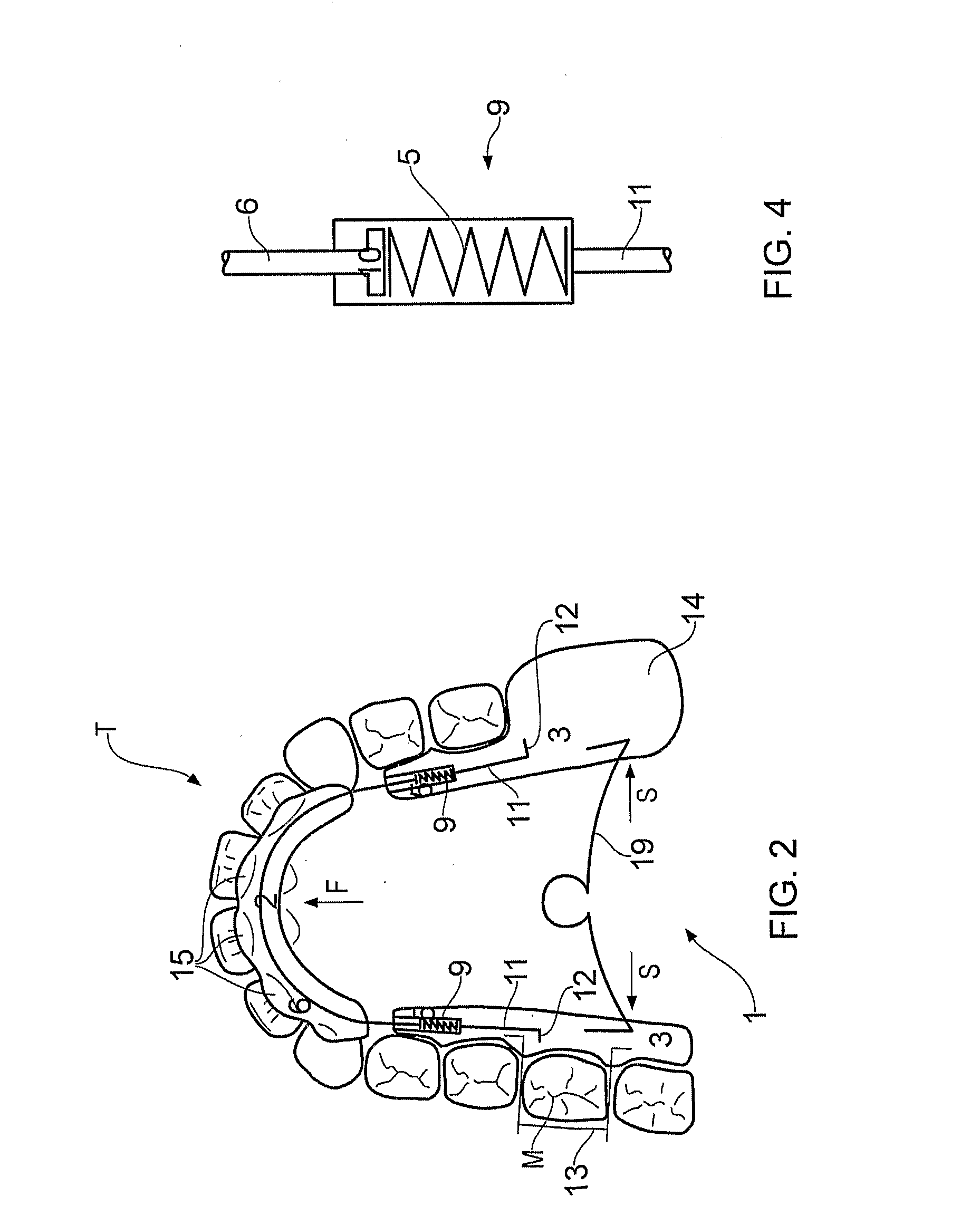
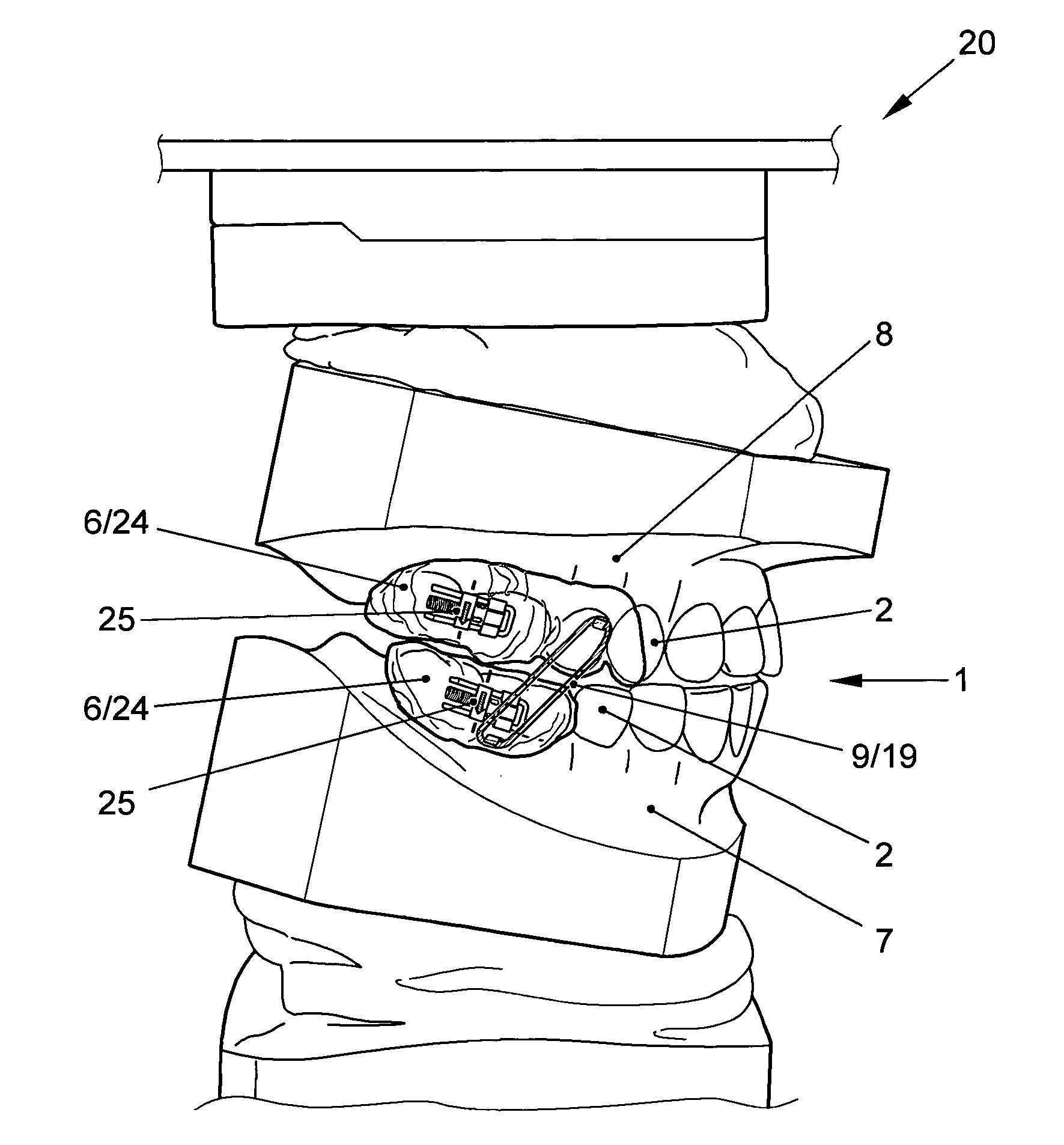
ActiveUS9119691B2Effectively applying tooth movement forcesOthrodonticsDental toolsTooth positionAmbulation Devices
The present invention provides orthodontic appliances and systems, and related methods, for applying a force to a target tooth as an appliances is worn by the patient. One positioning appliance includes a tooth positioning appliance having teeth receiving cavities shaped to apply a positioning force to the patient's teeth. The appliance includes a spring-loaded tooth movement device disposed in the appliance so as to engage an attachment mounted on a surface of a patient's tooth and apply a force to the tooth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Flanged interbody device
InactiveUS20090182428A1Improve stabilityPrevent subsidenceSpinal implantsLamina terminalisEngineering
An interbody implant including a first lateral portion, a second lateral portion positioned opposite to the first lateral portion, a top wall having a plurality of holes, a bottom wall positioned opposite to the top wall, and teeth positioned on the top wall and the bottom wall. The top wall and the bottom wall are attached to the first lateral portion and the second lateral portion. The first lateral portion further includes at least one flange surface and the second lateral portion further includes an opening. The at least one flange surface may be configured to couple to a peripheral wall of the vertebral body and may be adapted to provide at least one of a torsional property, an axial property, and a shear property to the implant. The teeth may be adapted to provide a mechanical interlock between the implant and vertebral endplates of the vertebral body.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
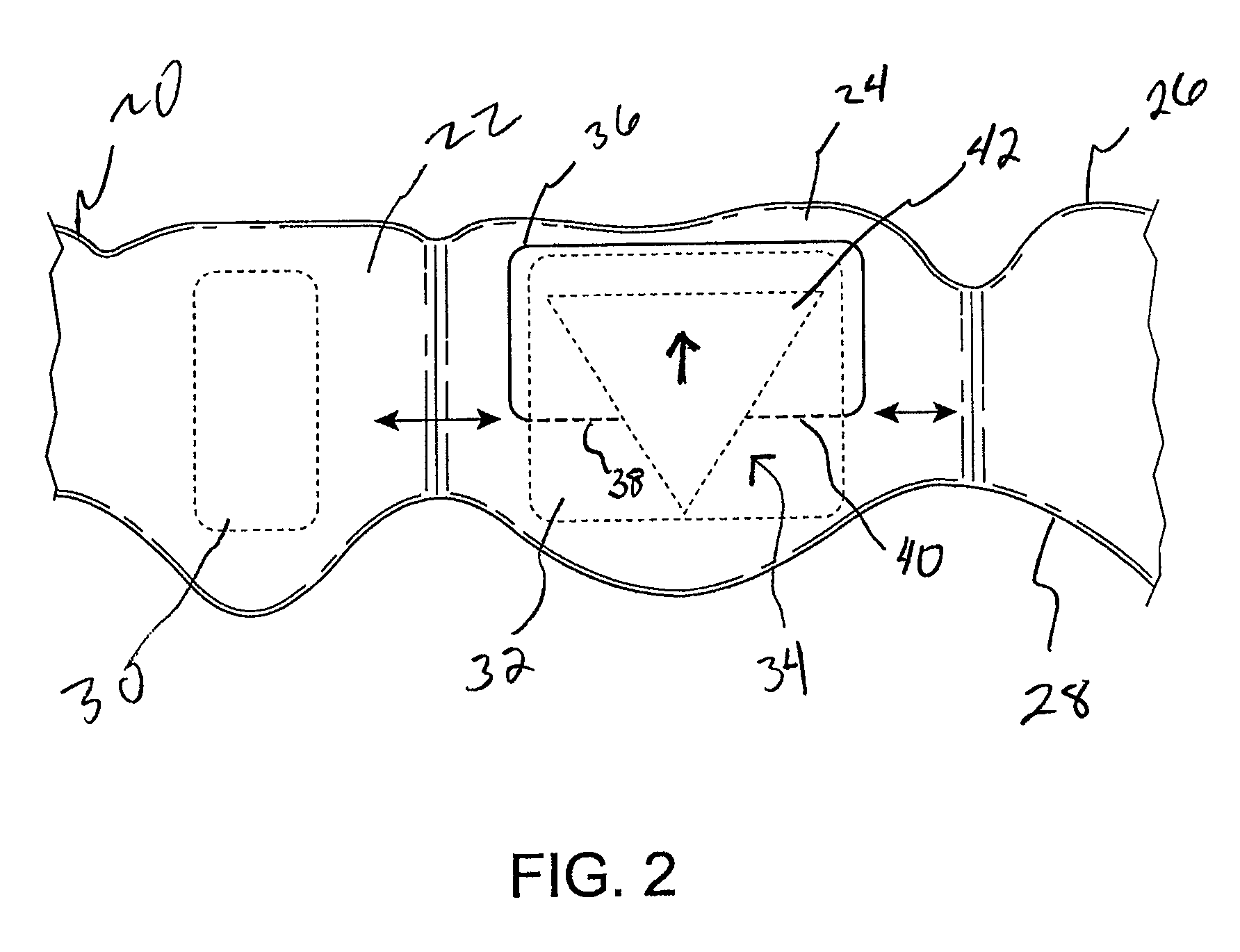
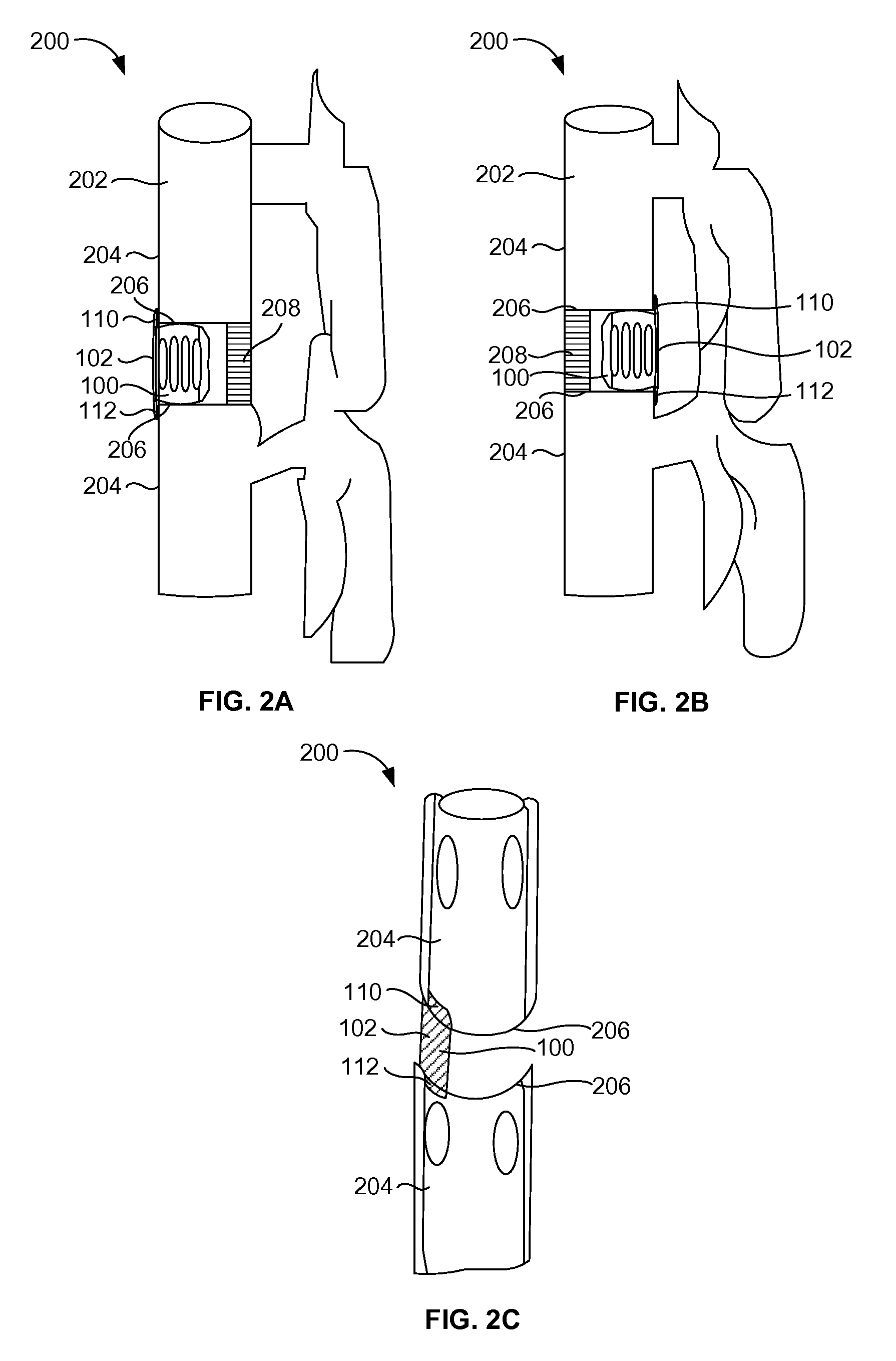
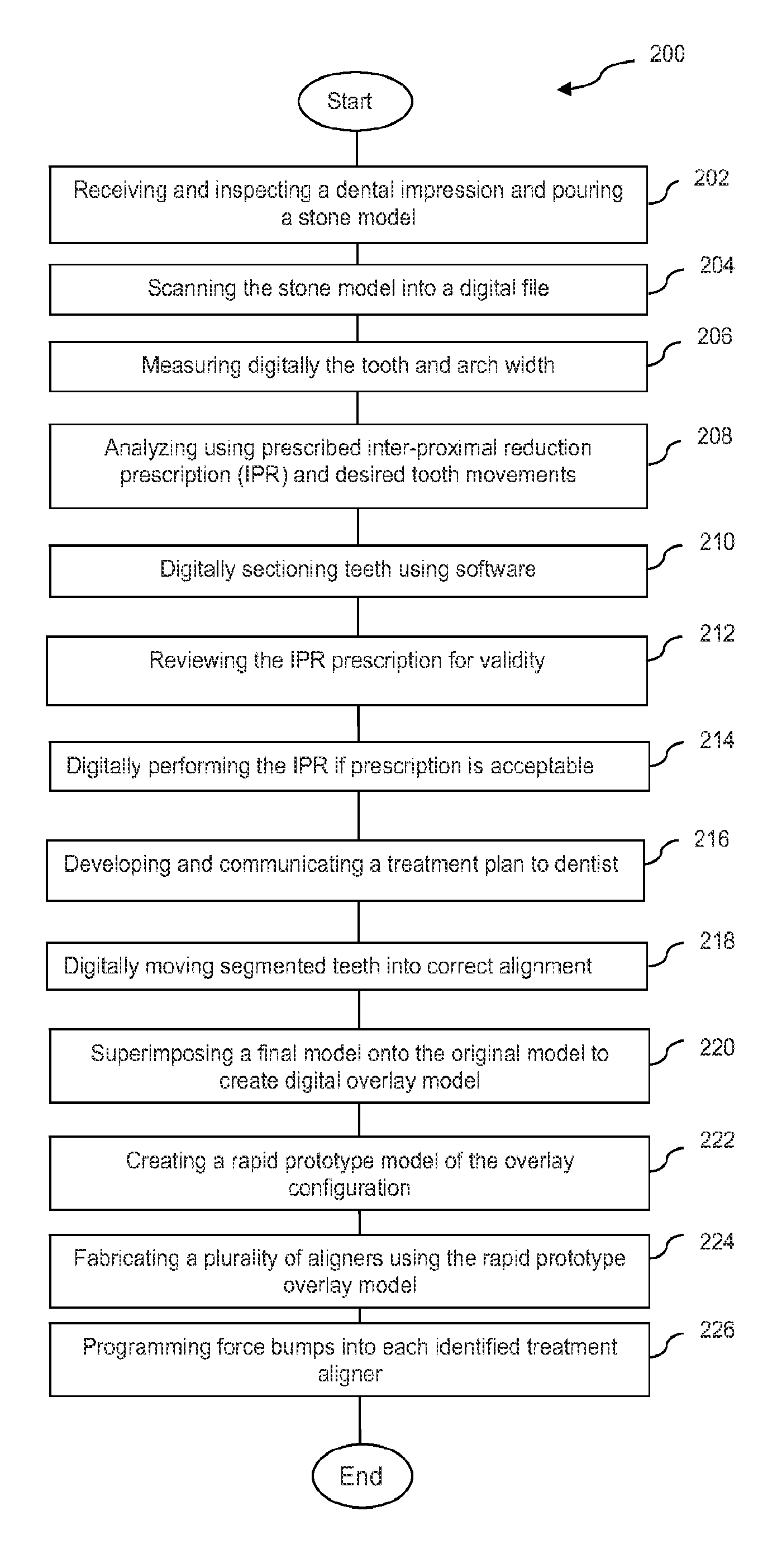
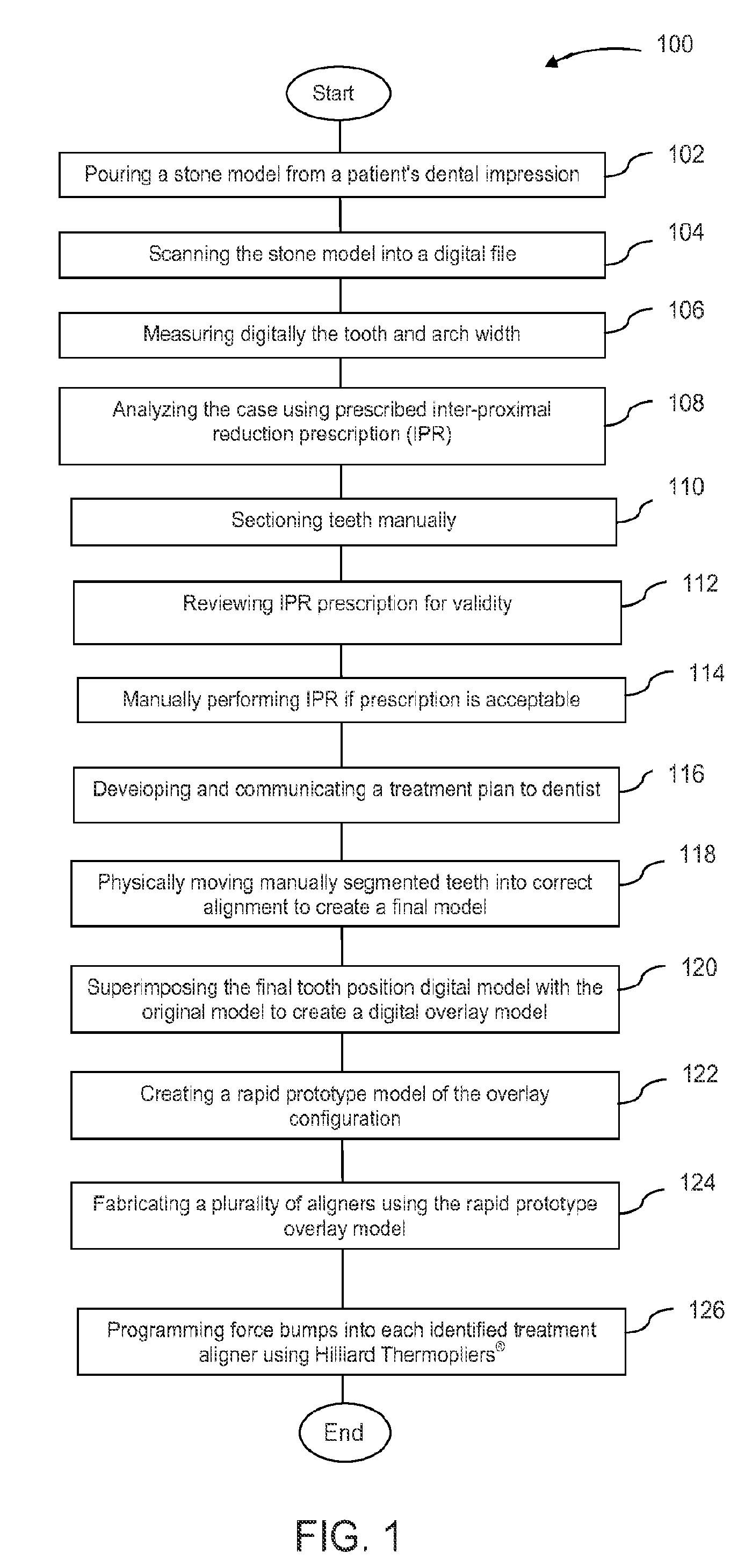
Orthodontic aligner fabrication by overlay method
The orthodontic alignment of misaligned teeth includes preparing a digital and / or physical overlay model which is the superimposed positioning of the patient's original misaligned dentition with the target or final position. The superimposition of one upon the other creates an open space through which teeth may move in a natural manner, allowing for a treatment plan that takes into account the physical interaction of one tooth with another or the differences in tooth movement rates due in part to differences in underlying bone density or the like. An aligner tray fabricated using the model will likewise represent the before and after tooth positions and will also have the open space to allow tooth movement. Force exerting structures are preferably placed into the aligner tray to impinge upon the patient's teeth in a prescribed manner when the aligner tray is inserted into the patient's oral cavity.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Software and methods for dental treatment planning
ActiveUS9529970B2Easy to movePrecise positioningMedical simulationLocal control/monitoringAfter treatmentAnimation
Computer-implemented methods to plan, display and evaluate orthodontic treatment plans. A plurality of teeth in a representation on a computer display may be moved simultaneously in accordance with a mathematically defined pattern. Software tools available to generate the treatment path may include adjusting the smile teeth, moving teeth along a curve fit to points in the mandible, individually moving a tooth, cross sectioning to check for interference and simulations of occlusal points, highlighting teeth that have moved from their original position, making notations on the teeth, and generating and saving animation sequences of before and after treatment tooth positions.
Owner:ORMCO CORP
Endoscopic bite block
An endoscopic bite block, with teeth position defining regions which guide the subject's teeth to grip the bite block in their natural position, with the teeth of the upper jaw positioned further out than the lower jaw teeth. These teeth position defining regions are also preferably curved to match the curved shape of the jaw. The upper and lower parts of the front plate of the bite block may also be positioned at different distances out, so that upper and lower lip regions both contact the front plate snuggly. The bite block may be used with separate oral / nasal cannulae, or may incorporate breath sampling or gas supply cannulae. A flexible flapped curtain at the outer end of the bite block may be provided to largely enclose the inner volume of the bite block to enable more accurate capnographic sampling under conditions of wide-open mouth breathing.
Owner:ORIDION MEDICAL 1987
Indirect Bonding Tray and Method of Manufacture Thereof
An indirect bonding tray includes a least on tooth position each tooth portion includes an occlusal surface that conforms to an occlusal surface of an associated tooth of a patient's dentition. At least one of bracket arm includes a bracket arm tip configured to engage an orthodontic bracket. The at least one bracket arm movably attached to at least one tooth portion to move between a first position and second position relative to a bonding surface of the associated tooth. In the second position, the bracket arm is in a position configured to hold an orthodontic bracket in a predetermined treatment position relative to the bonding surface of the associated tooth.
Owner:AMERICAN ORTHODONTICS
Arthroscopic shaver with two pass inner blade and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20060196038A1Improve resection efficiencyImprove efficiencyOther manufacturing equipments/toolsGrinding machinesMulti axisKnife blades
An arthroscopic shaver with an inner cutting window having a plurality of teeth positioned along the lateral cutting edges, the teeth being configured for easy penetration into tissue to prevent ejection of tissue from the cutting window during closure. The inner cutting edges are formed complete by a predetermined sequence of positioning moves and grinding passes on a multi-axis grinding machine. The teeth may be symmetrically or asymmetrically placed about the tube axis when viewed in a plan view.
Owner:ARTHREX
System and method for producing tooth movement
InactiveUS7063533B2Sufficient levelAddressing Insufficient ControlOthrodonticsDental toolsEngineeringDental crowns
The present invention provides methods and systems of repositioning teeth for use in orthodontic treatment, with particular applicability to removable elastic repositioning appliances. Such appliances may be challenged by traditional tooth movements which intrude the crown of the tooth or present tooth positions which reduce available points of purchase. These challenges may be overcome with a series of tooth movements in which a tooth is translated in a “root-first” position. The movements may take advantage of the inherent characteristics of elastic repositioning appliances in translating a tooth from a first position to a desired position along a gingival plane.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
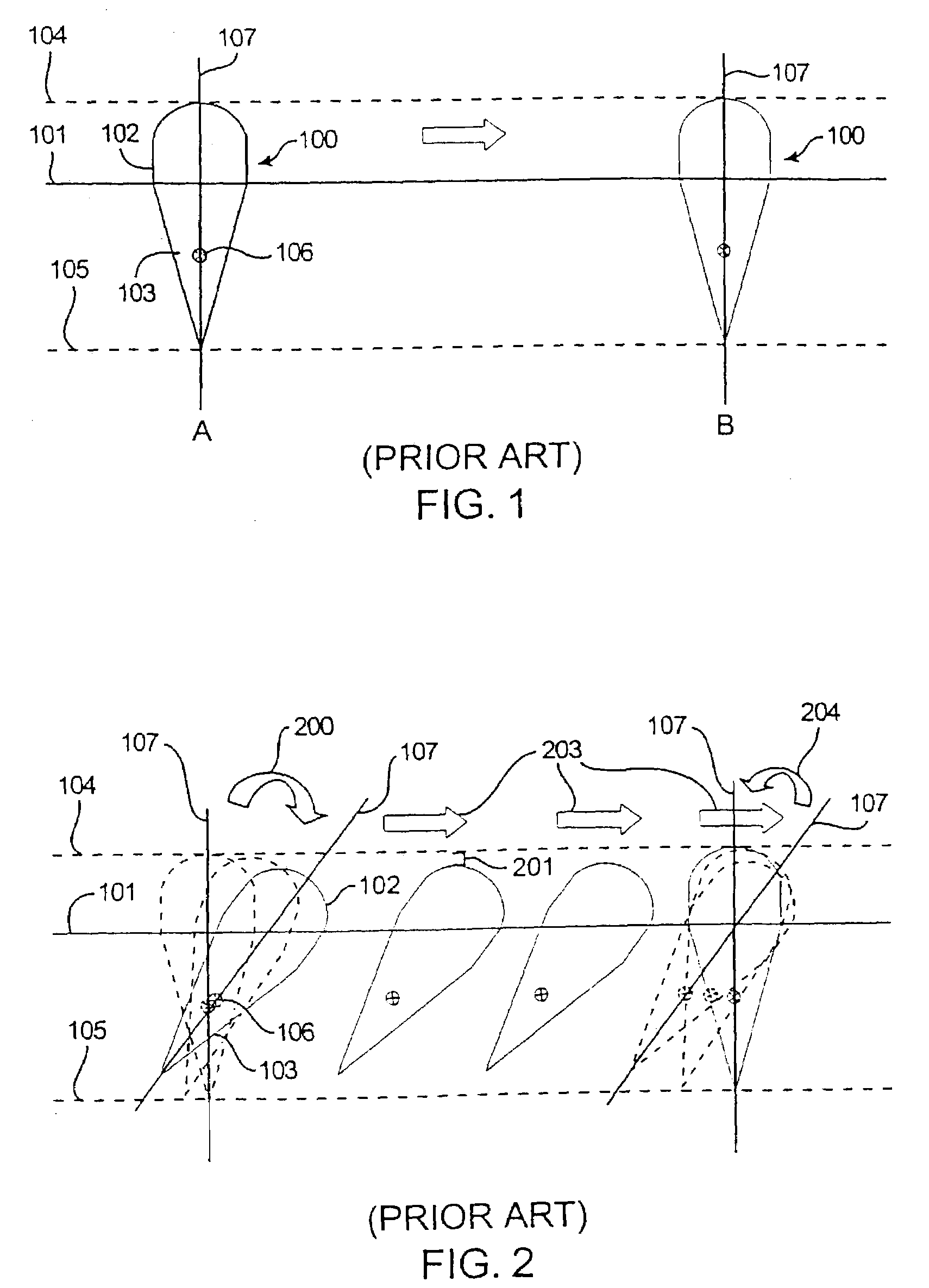
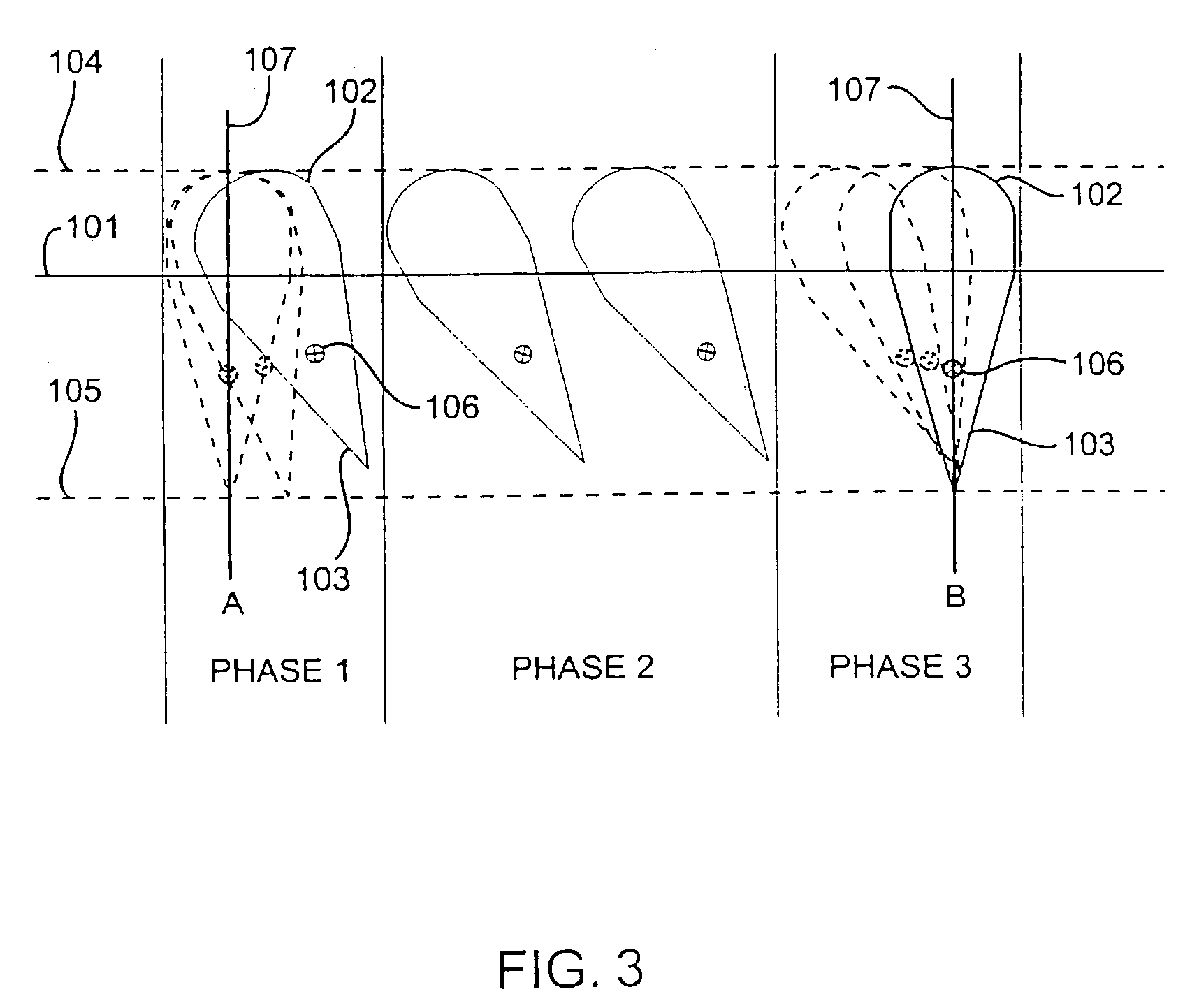
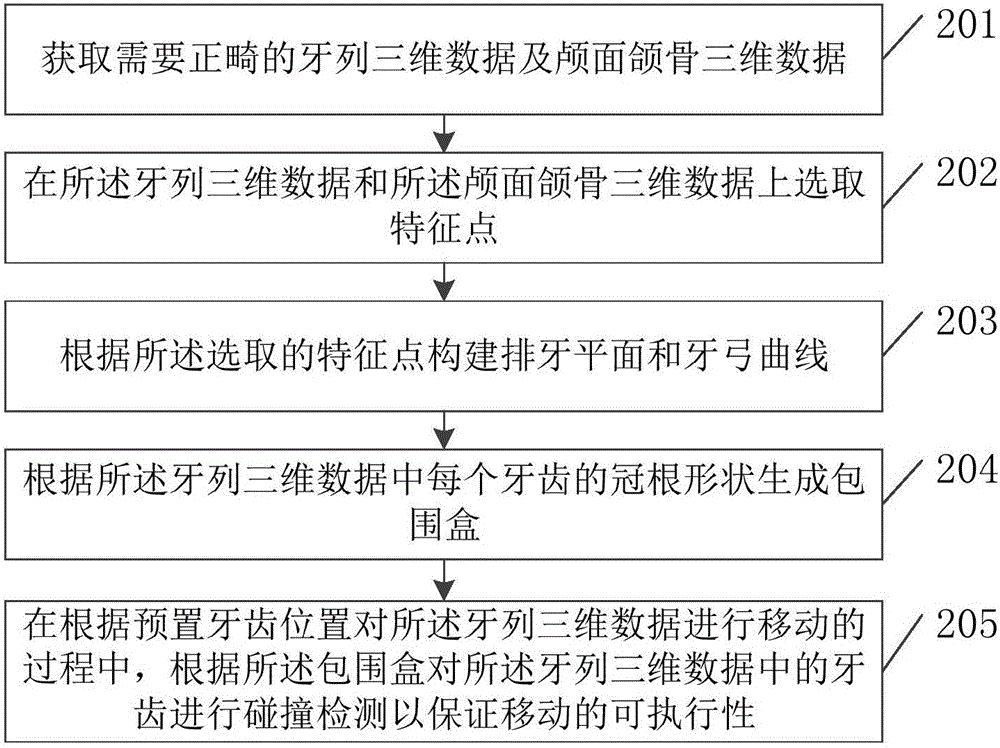
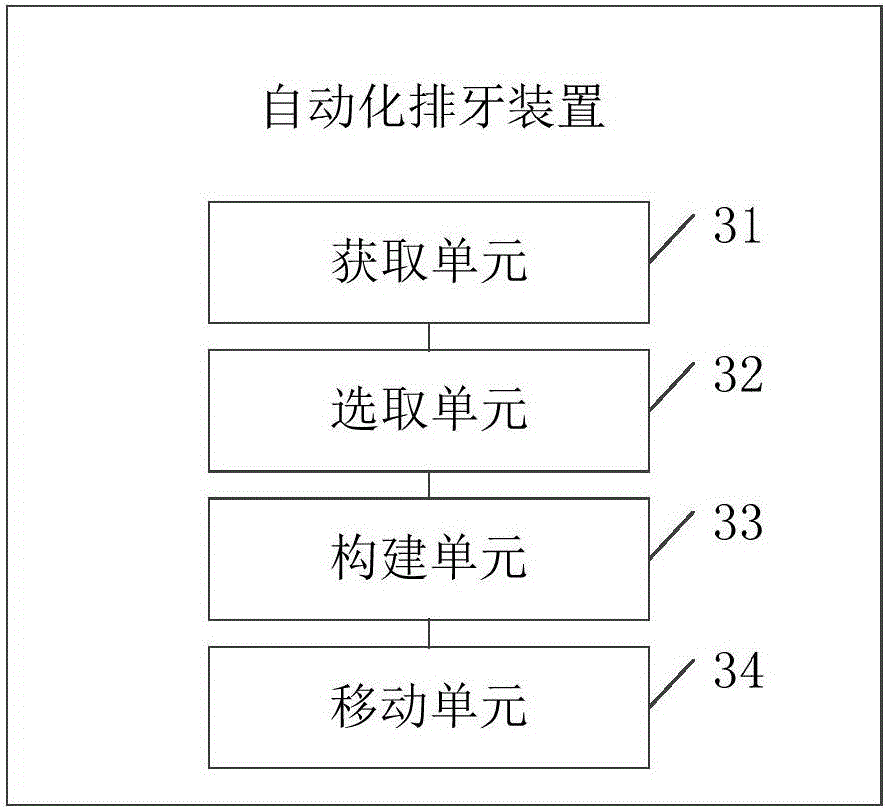
Automatic tooth arrangement method and device
ActiveCN105769353AImprove accuracyConform to the structural characteristicsOthrodonticsSpecial data processing applicationsLower dentitionLower Jaw Tooth
The invention discloses an automatic tooth arrangement method and an automatic tooth arrangement device, relating to the medical field of digital orthodontics, and solving the problem that the automatic tooth arrangement is poor in accuracy. The main technical scheme is as follows: the automatic tooth arrangement method comprises the following steps: acquiring three-dimensional data of dentition needing orthodontics and three-dimensional data of craniofacial jaw bone; selecting feature points on the three-dimensional data of the dentition and the three-dimensional data of the craniofacial jaw bone; constructing tooth arrangement planes and dental arch curves according to the selected feature points, wherein the tooth arrangement planes comprise a median sagittal plane, a horizontal plane and a tooth arrangement occlusal plane, and the dental arch curves comprise an upper jaw tooth arrangement curve and a lower jaw tooth arrangement curve; moving teeth in the three-dimensional data of the dentition according to the preset tooth positions, so that a target dentition after orthodontics is formed, and the preset tooth positions comprise the target upper and lower dentition sagittal position, the target upper and lower dentition vertical position, and the target upper jaw and lower jaw among-dentition position. The automatic tooth arrangement method and the automatic tooth arrangement device are mainly used for the tooth arrangement in the orthodontics.
Owner:北京正齐口腔医疗技术有限公司
Virtual bracket library and uses thereof in orthodontic treatment planning
InactiveUS6971873B2Medical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesOff the shelfMedical prescription
An orthodontic workstation stores a library of virtual three-dimensional brackets in a memory. Each of the virtual brackets has a unique three-dimensional configuration and prescription. Typically, the library of bracket comprises a library of commercially available, off-the-shelf brackets. The workstation further includes an interactive treatment planning program that permits a user to move teeth from a virtual model of the dentition to a proposed set-up. In one possible embodiment, the treatment planning program provides the ability to display a virtual bracket placed on a virtual tooth and change the prescription or configuration of the virtual bracket. The treatment program automatically compares the modified prescription with the prescription information of the virtual brackets in the library and selects a bracket from the library that most closely matches the virtual bracket displayed on the tooth. Thus, the user does not have to use customized brackets. Any deviation in tooth position resulting from a discrepancy between the off-the-shelf bracket and the user-defined bracket can be corrected for by changing the position of the bracket on the tooth or by changing the shape of the archwire.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
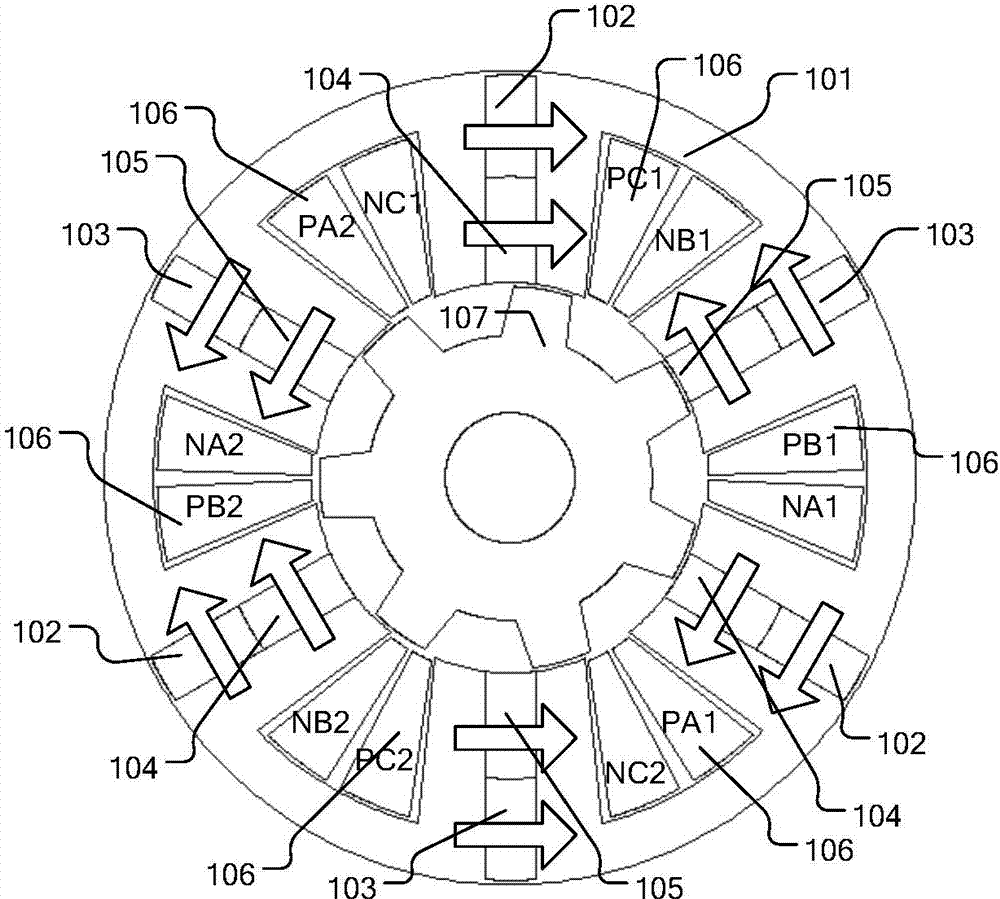
Application method of mixed permanent magnets in flux-switching permanent magnet motor
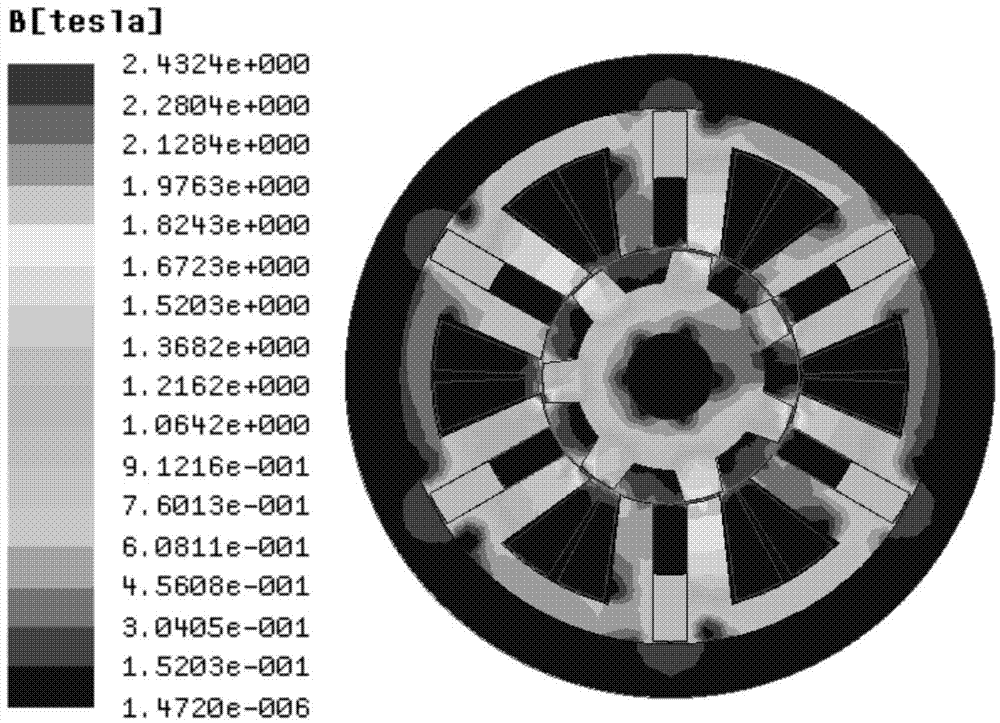
InactiveCN104242501ASignificant progressHighlight substantiveMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsRare earthPermanent magnet motor
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Machine learning scoring system and methods for tooth position assessment
ActiveUS20200085546A1High precisionPrecise positioningImpression capsOthrodonticsPrincipal component analysisComputer vision
Provided herein are systems and methods for scoring a post-treatment tooth position of a patient's teeth. A patient's dentition may be scanned and / or segmented. Raw dental features, principal component analysis (PCA) features, and / or other features may be extracted and compared to those of other teeth, such as those obtained through automated machine learning systems. A classifier can identify and / or output the post-treatment tooth position of the patient's teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Rotary electrical machine
ActiveUS20060152104A1Easy to controlImprove efficiencySynchronous generatorsWindingsElectric machineEngineering
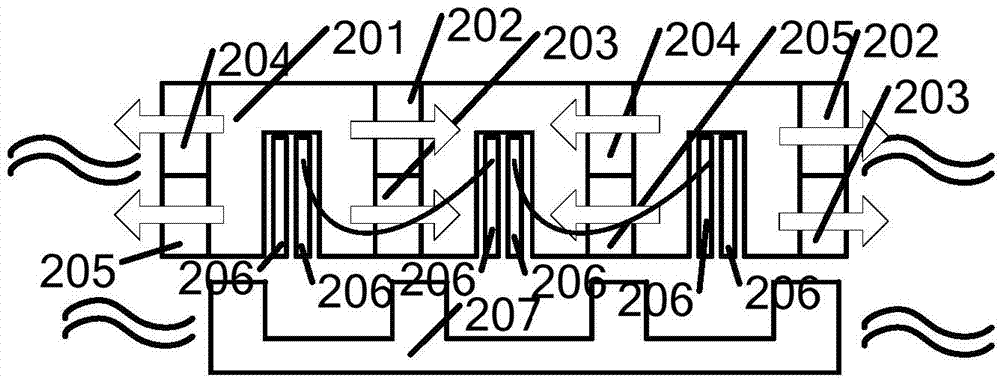
A rotary electrical machine has a mechanism capable of varying an output characteristic, without increasing mechanical loss, or without consuming the electric power that does not contribute to increasing torque. The rotary electrical machine has a rotor with N pole and S pole magnets alternately and fixedly disposed thereon. An end surface, (which opposes the rotor), of each of a plurality of first teeth positioned on a first stator section is broader than that of the opposite surface thereof, and a winding is wound around a portion between both of the end surfaces. A second stator section has second teeth, corresponding the number of the first teeth, and which has no winding. The second teeth are disposed to oppose the end surfaces of the respective first teeth, and each second tooth is reciprocally movable between a reference position at which the second tooth directly opposes the respective first tooth and a maximum movable position located at the right center position between the respective end surfaces. At the reference position, a strong magnetic flux flows into the entire first tooth from each magnet. At the maximum movable position, a weak magnetic flux flows over the end surface of each first tooth. A middle amount of the magnetic flux flow occurs at a middle moved position.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Connector for domed cutting tool
The surgical reamer has a hollow dome with apertures spaced apart arranged in arcs extending from an apex of the dome to the base portion of the dome, and removable teeth positioned in the apertures. Each cutting tooth has a flange that is aligned flush with the external surface of the dome, and a raised cutting edge extending above the flange and the external surface of the dome, and an interior passageway communicating between the outside and inside of the dome. In one embodiment, a base plate is removably secured on the base portion of the dome to provide closure of the central cavity of the dome.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Systems, methods, and apparatus for correcting malocclusions of teeth
ActiveUS20190053876A1Additive manufacturing apparatusOthrodonticsInitial treatmentDental malocclusion
Methods and systems are provided for manufacturing an appliance for correcting malocclusions of a patient's teeth. The method may include measuring the positions of a patient's teeth and receiving tooth movement constraints. The method may also include generating an initial treatment plan based on the measured tooth positions and the tooth movement constraints and measuring the malocclusions of the patient's teeth for one or more types of dental malocclusions. The method may also include generating a plurality of treatment plans from the initial treatment plan based on the measured malocclusion and generating a model of an appliance for each stage of the treatment plan. The method may also include generating instructions for fabricating the appliance for each stage of the treatment plan based on the model of the appliance for each stage of the treatment plan.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
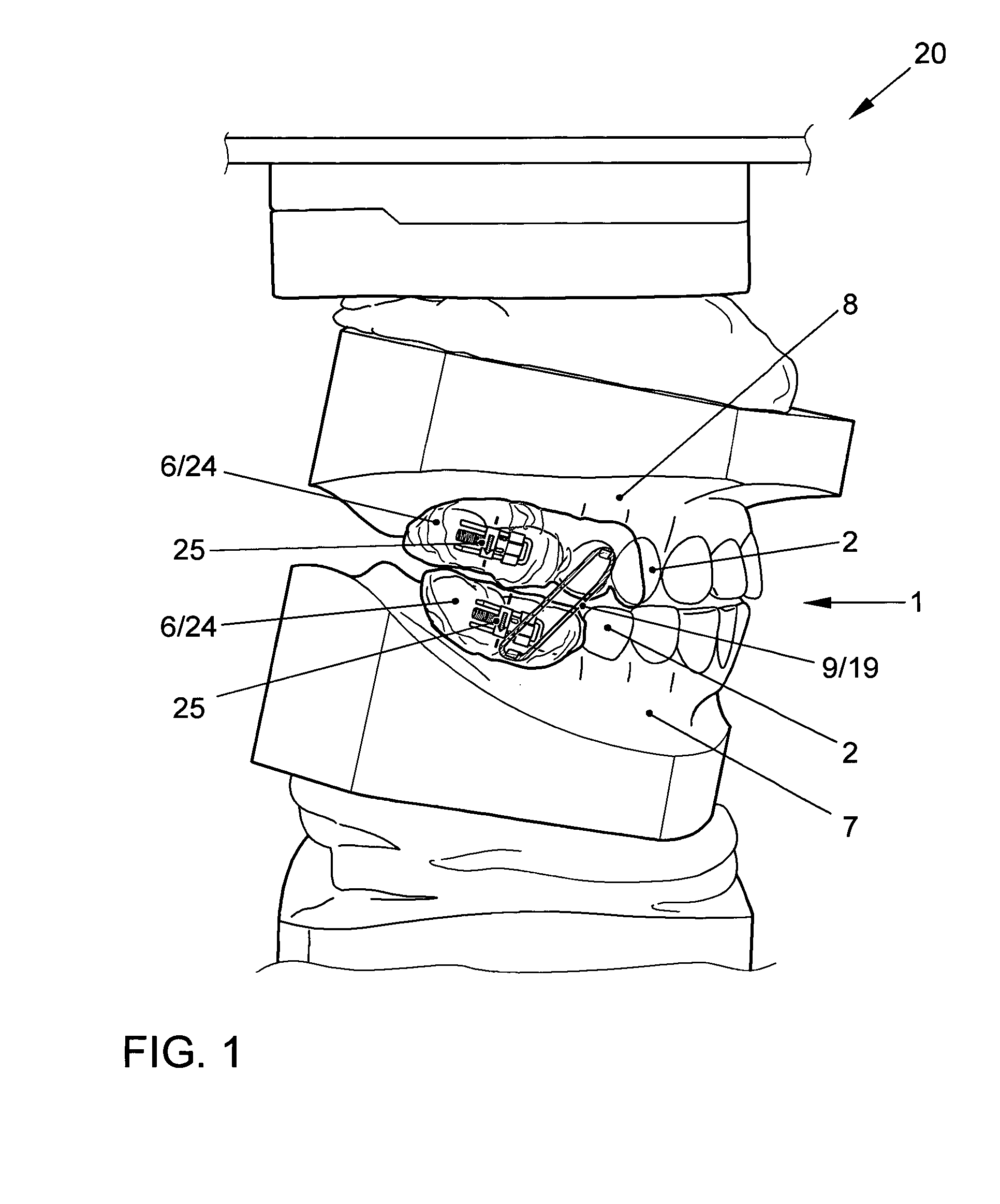
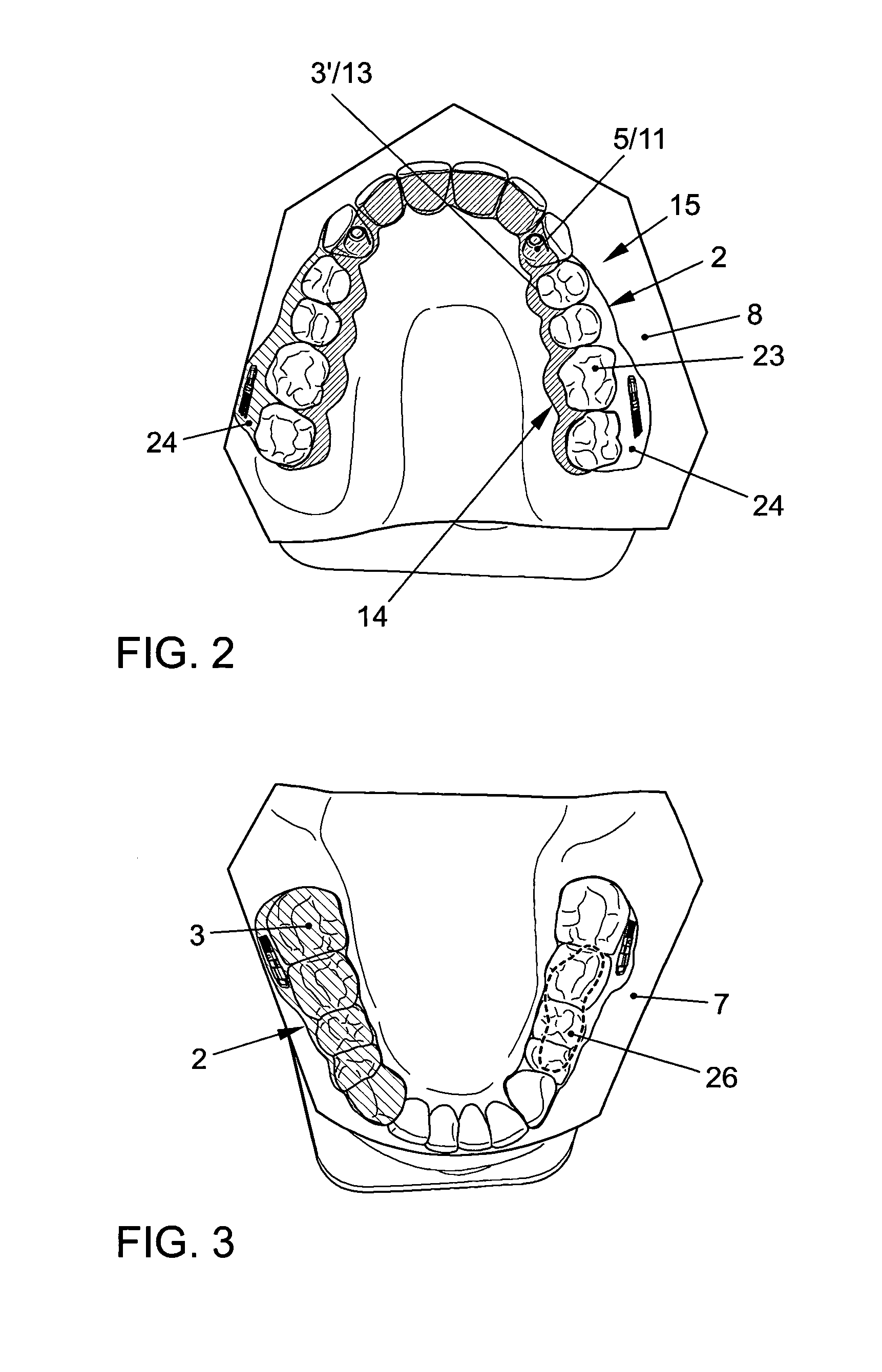
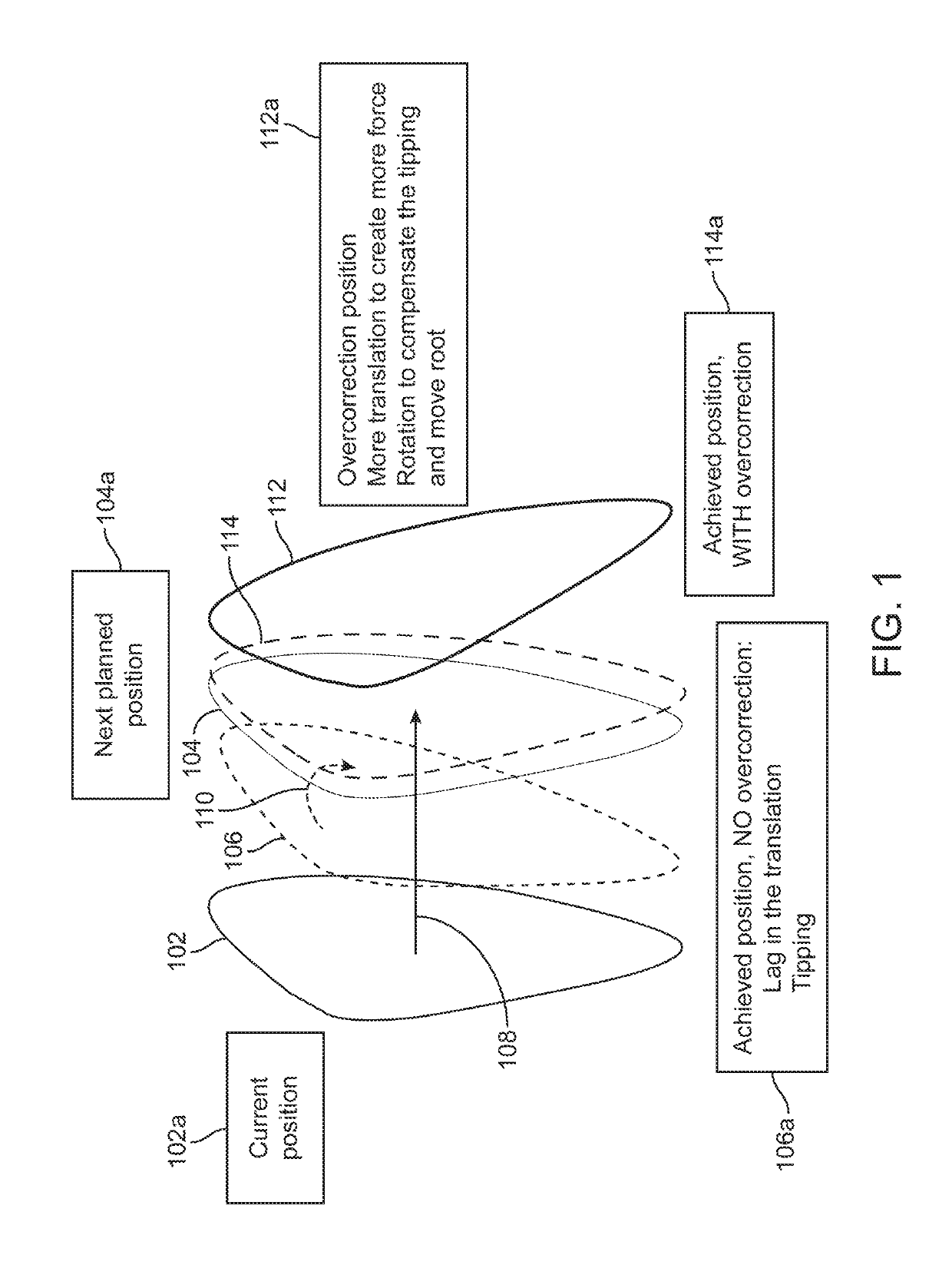
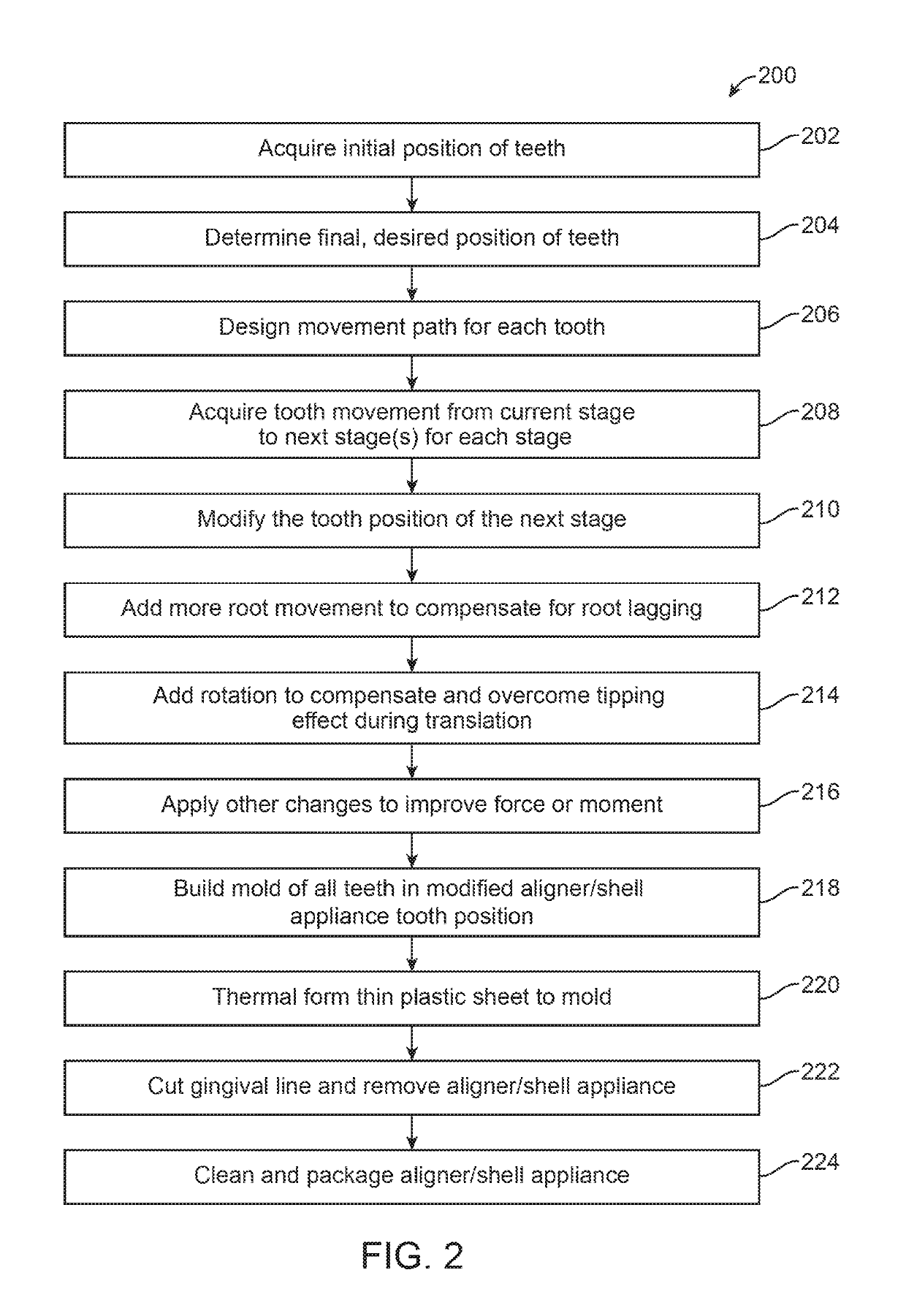
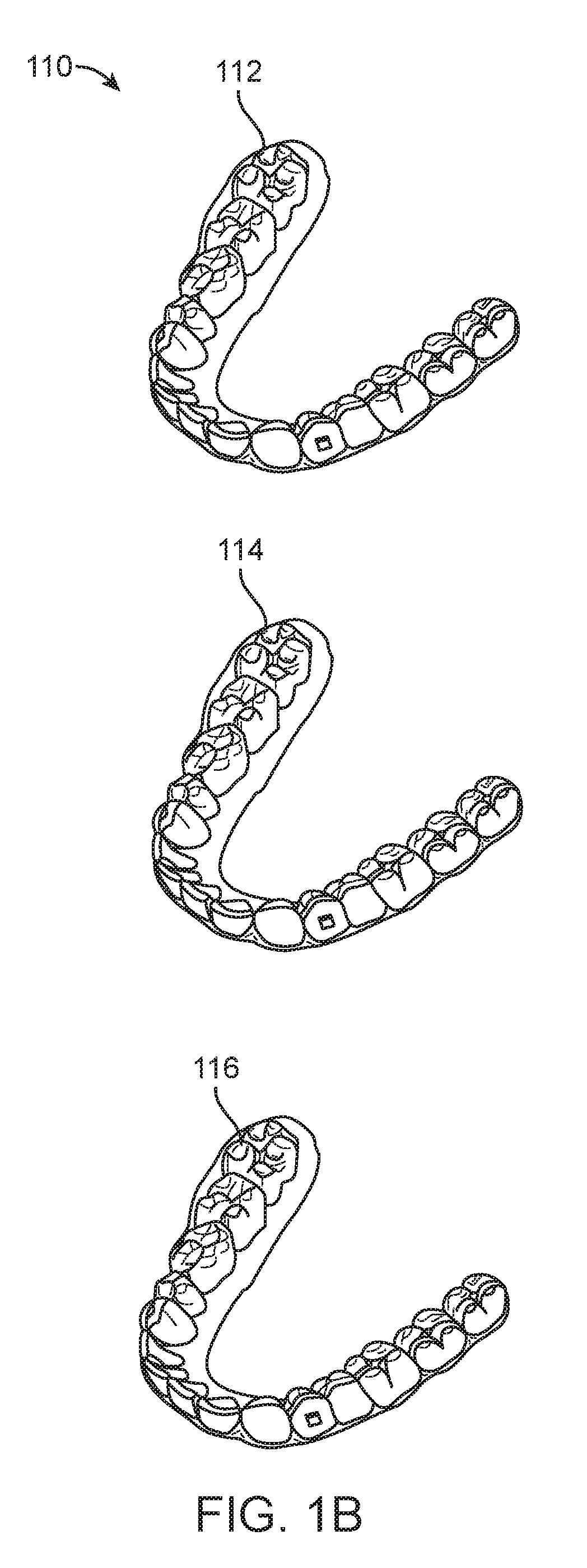
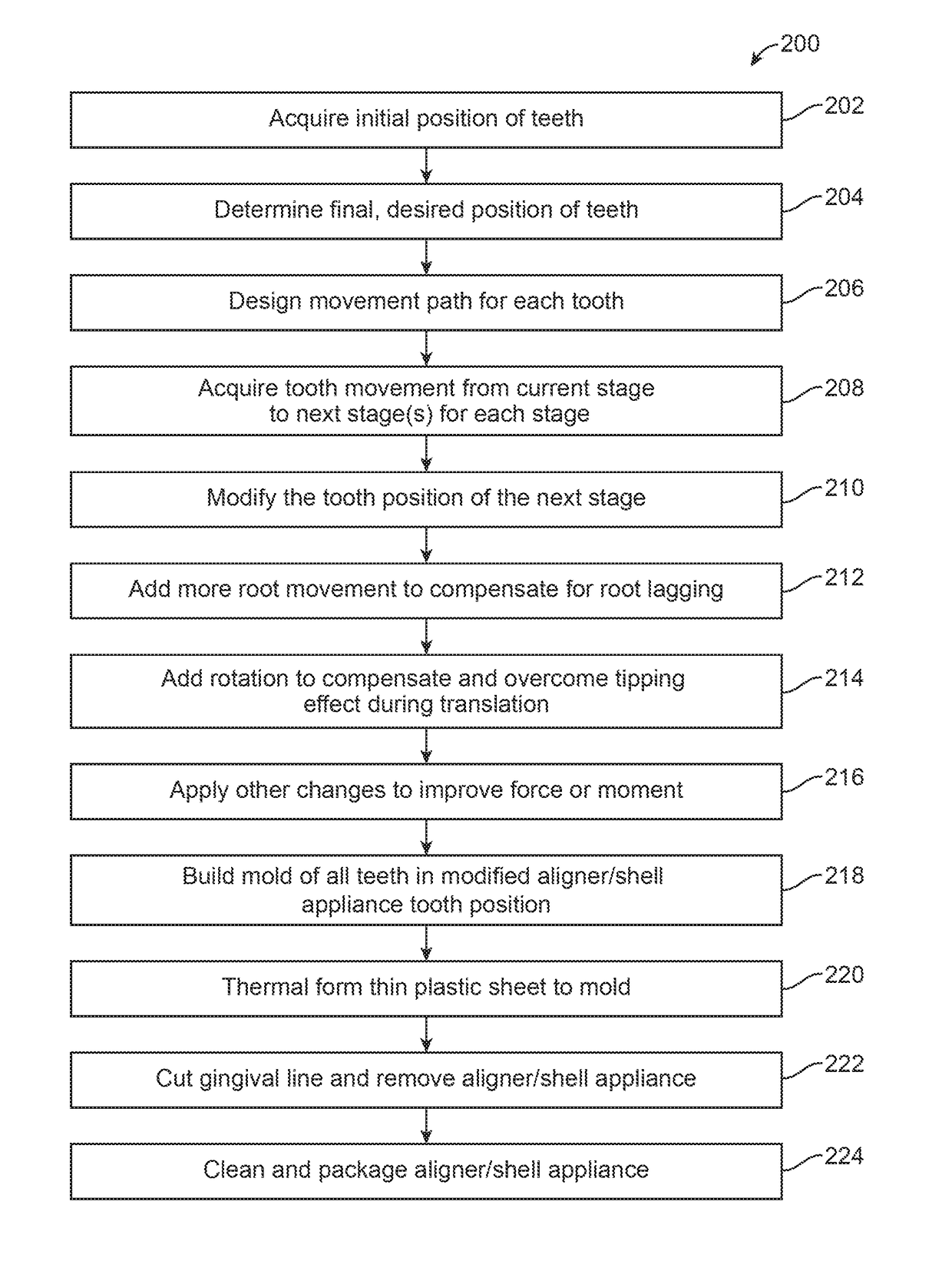
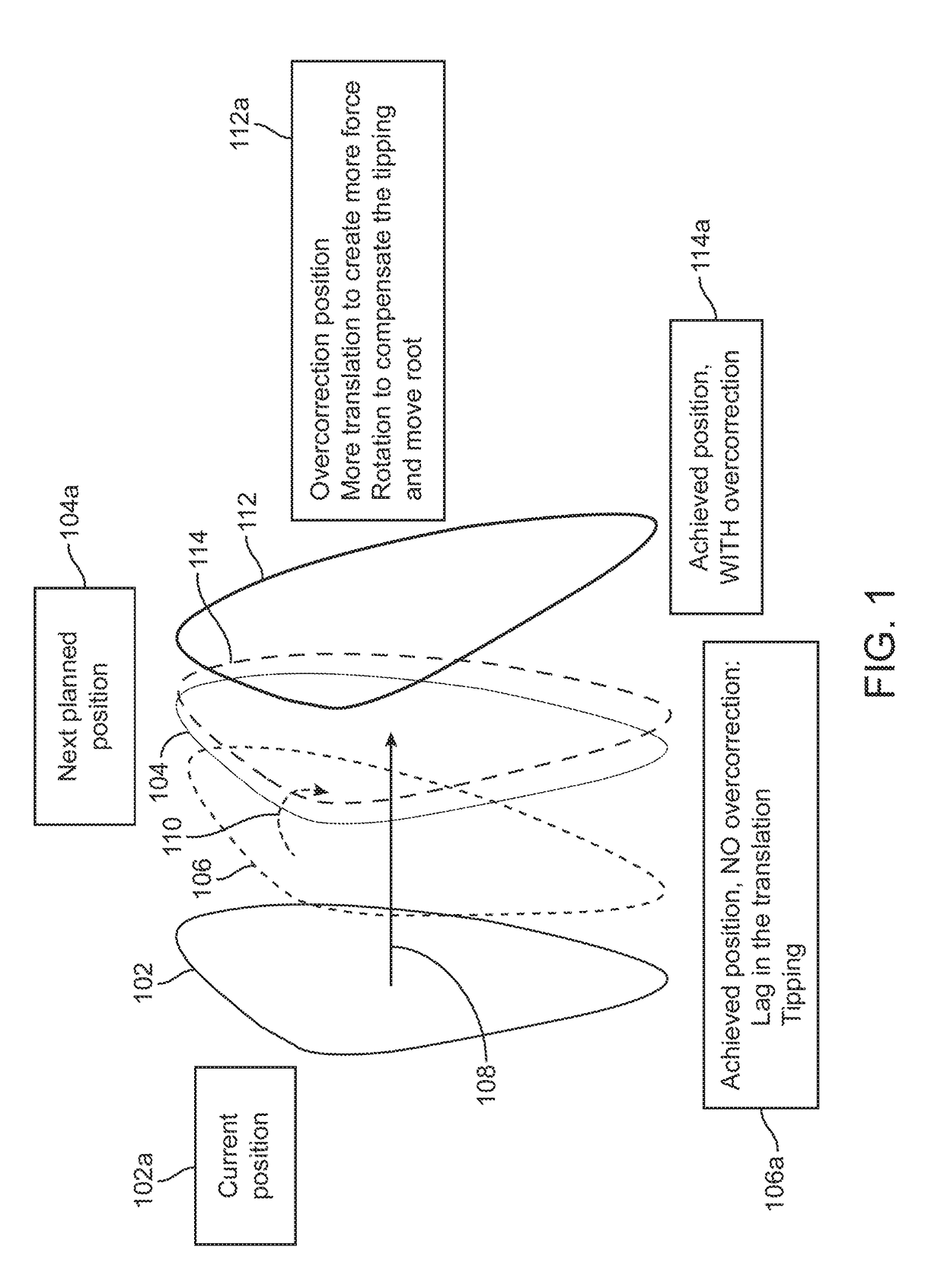
Method to visualize and manufacture aligner by modifying tooth position
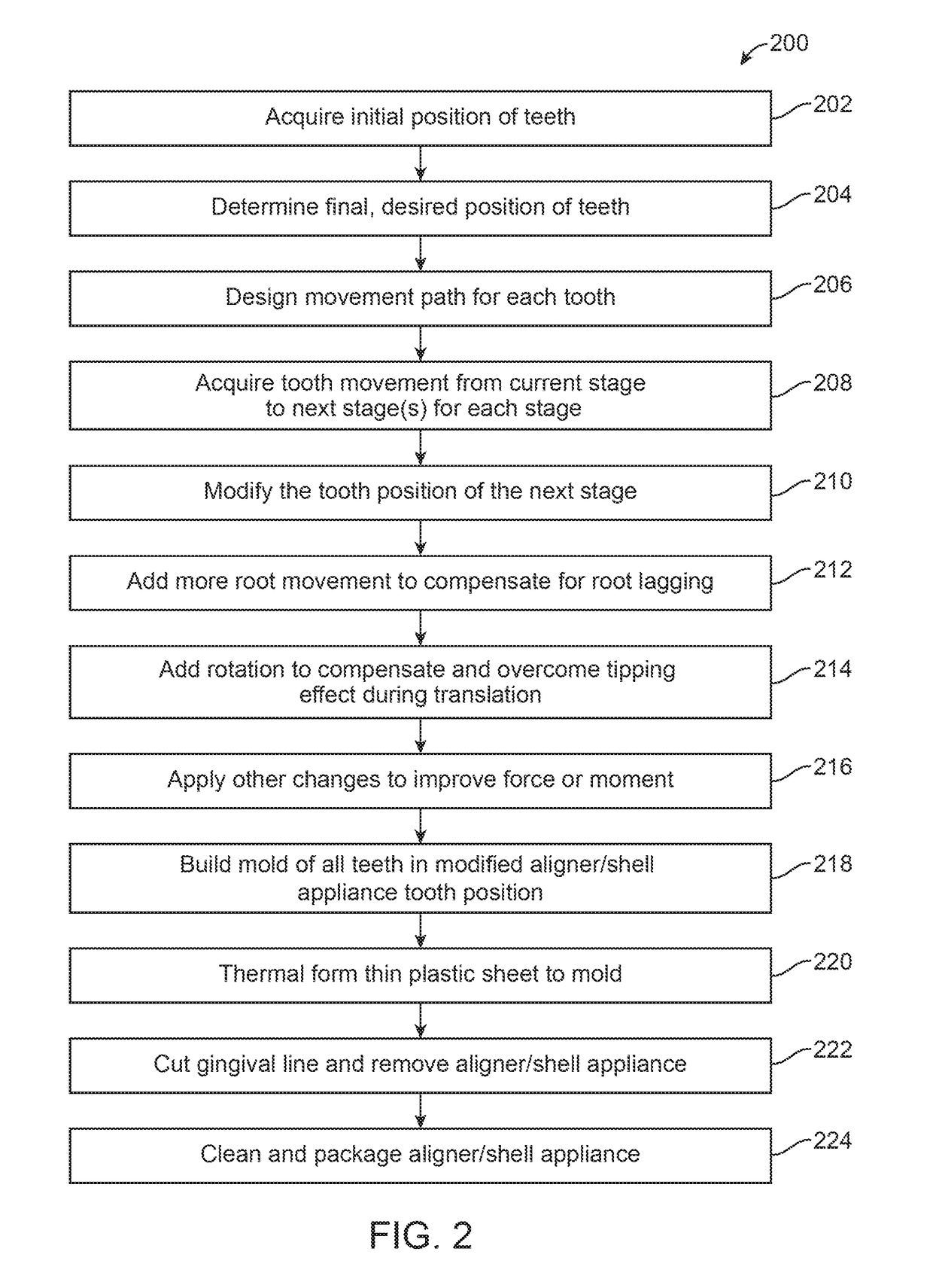
Orthodontic systems and related methods are disclosed for designing and providing improved or more effective tooth moving systems for eliciting a desired tooth movement and / or repositioning teeth into a desired arrangement. Methods and orthodontic systems include the generation of an overcorrection in the tooth-receiving cavities of an appliance worn in the dentition. The overcorrection may provide an improved and more accurately applied force or moment applied to a tooth. The overcorrected force or moment can move a tooth closer to a desired position than if not overcorrected as sufficient force can still applied to the tooth as it gets closer to the desired position. The overcorrected force or moment may also better target the root of the tooth where the biological response to tooth movement occurs. The overcorrection may be calculated in various ways as described herein.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Turbine bucket angel wing compression seal
ActiveUS8083475B2Reducing turbine bucket cooling air lossesPropellersEngine manufactureTooth positionAngel wing
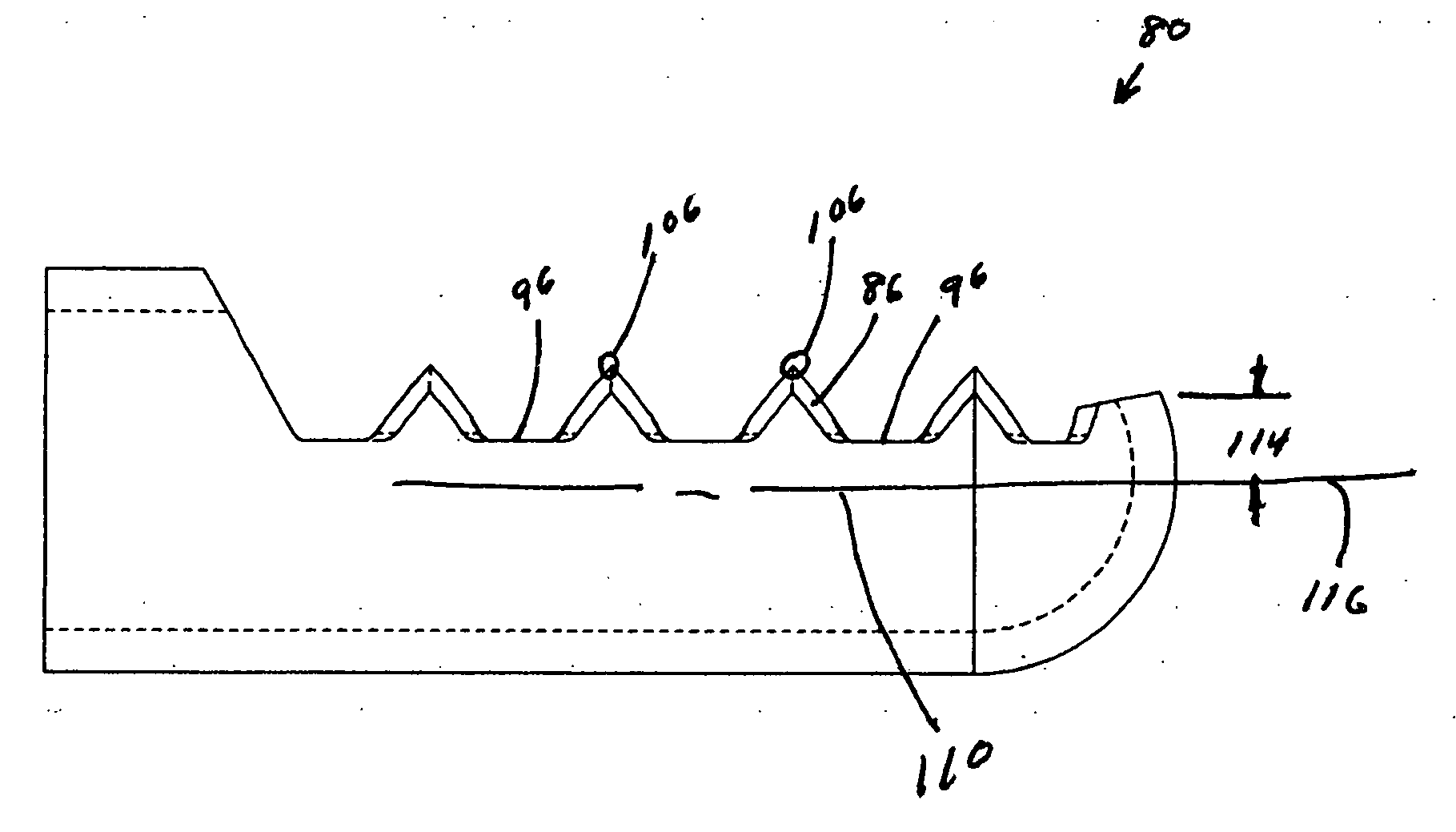
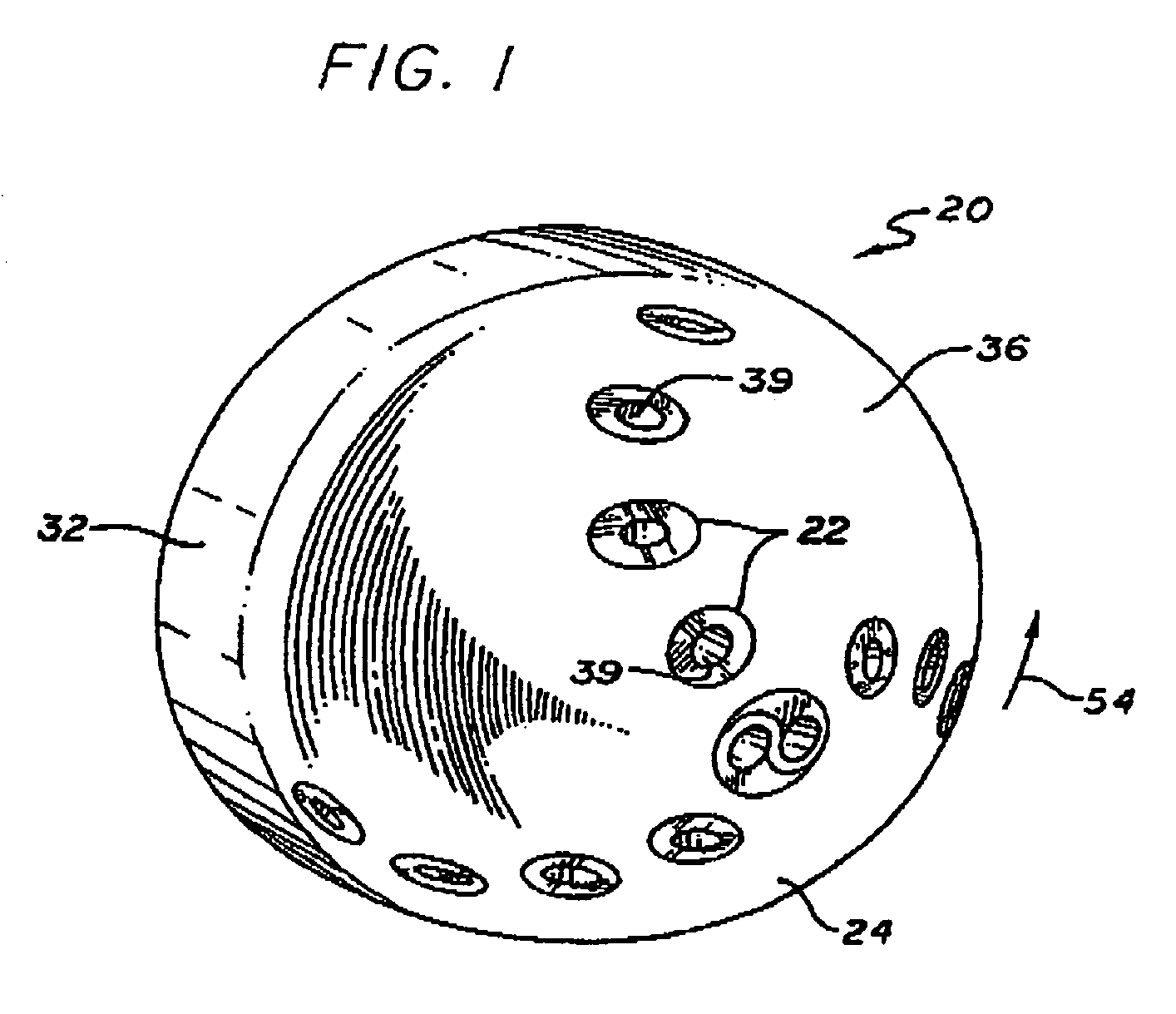
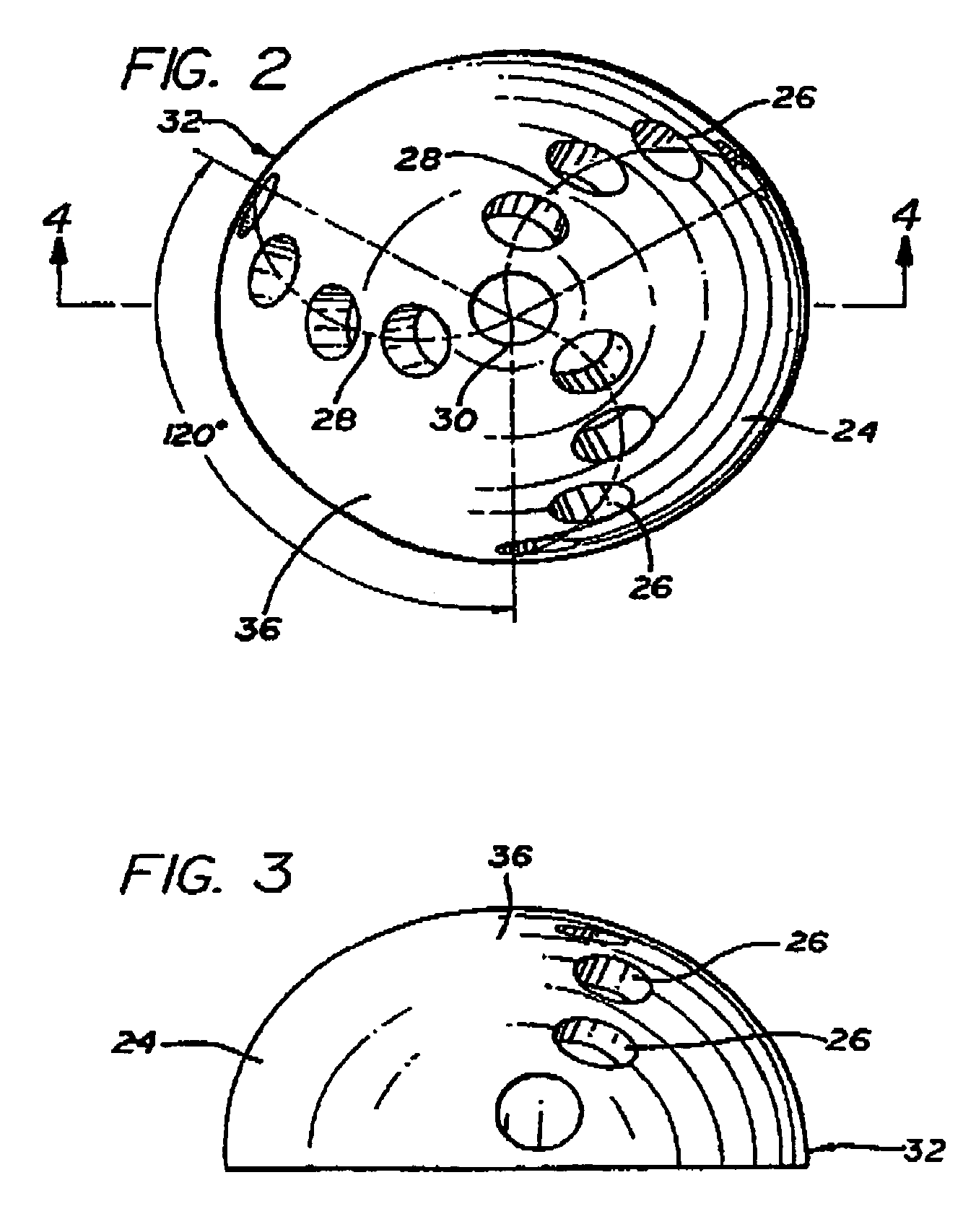
The present application provides an angel wing seal for a turbine bucket. The angel wing seal may include a first wing with a sinusoidally-shaped outer edge and a number of wing teeth positioned thereon.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Dental Retainer
An orthodontic device for retaining teeth in position, or for making minor adjustments to tooth position. The dental retainer includes a rigid lingual portion or arch, and a more flexible and comfortable labial portion or arch, arranged so as to allow the cutting surfaces of the upper and lower molar teeth to meet. Small protrusions of harder material may be located on the inner surface of the labial portion to fit between the teeth in order to prevent relapse of tooth position.
Owner:CLEARRETAIN
Connector for domed cutting tool
InactiveUS7048740B2Easy to remove and replaceImprove cutting accuracySurgeryPaving detailsEngineeringReamer
The surgical reamer has a hollow dome with apertures spaced apart arranged in arcs extending from an apex of the dome to the base portion of the dome, and removable teeth positioned in the apertures. Each cutting tooth has a flange that is aligned flush with the external surface of the dome, and a raised cutting edge extending above the flange and the external surface of the dome, and an interior passageway communicating between the outside and inside of the dome. In one embodiment, a base plate is removably secured on the base portion of the dome to provide closure of the central cavity of the dome.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
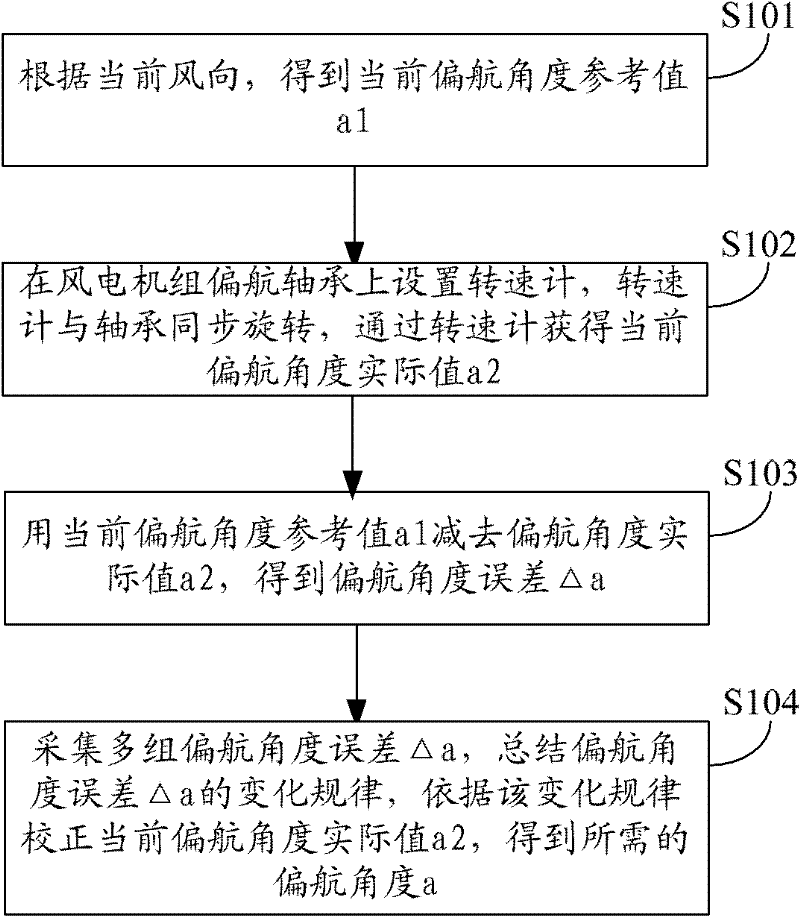
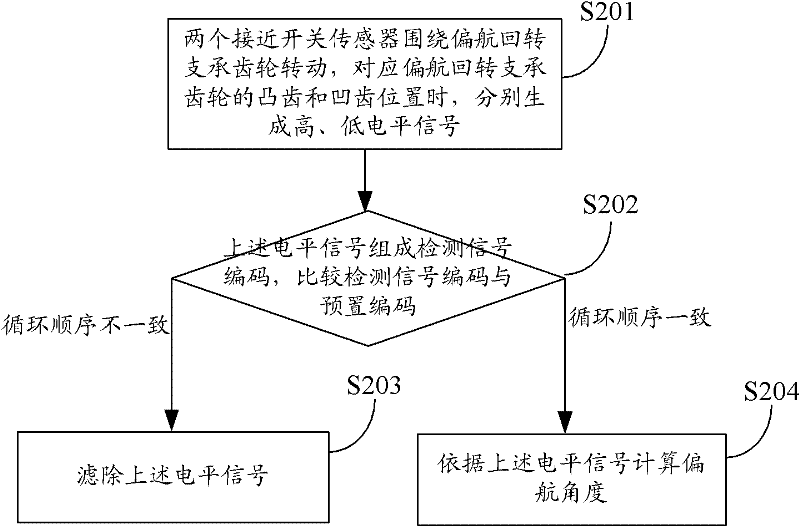
Method and system for computing yaw angle of fan
The invention relates to a method for computing a yaw angle of a fan. In a cabin of the fan, at least two approach switch sensors are arranged at a position adjacent to a yaw rotary supporting gear. The method comprises the following steps of: when the fan yaws and the approach switch sensors rotate around the yaw rotary supporting gear and correspond to convex teeth and concave teeth positions of the yaw rotary supporting gear, generating different level signals; combining the level signals into a detection signal code, comparing the detection signal code with a preset code, and if cyclic sequences are not accordant, filtering out the level signals; and if the cyclic sequences are accordant, computing the yaw angle according to the level signals. The invention also discloses a system forcomputing the yaw angle of the fan. By the invention, high and low level signals for computation of the yaw angle are normal signals; inaccurate computation of the yaw angle, caused by a fault signal, is effectively avoided; and the computation accuracy of the yaw angle is guaranteed.
Owner:SANY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com