Patents
Literature
113 results about "Binding constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
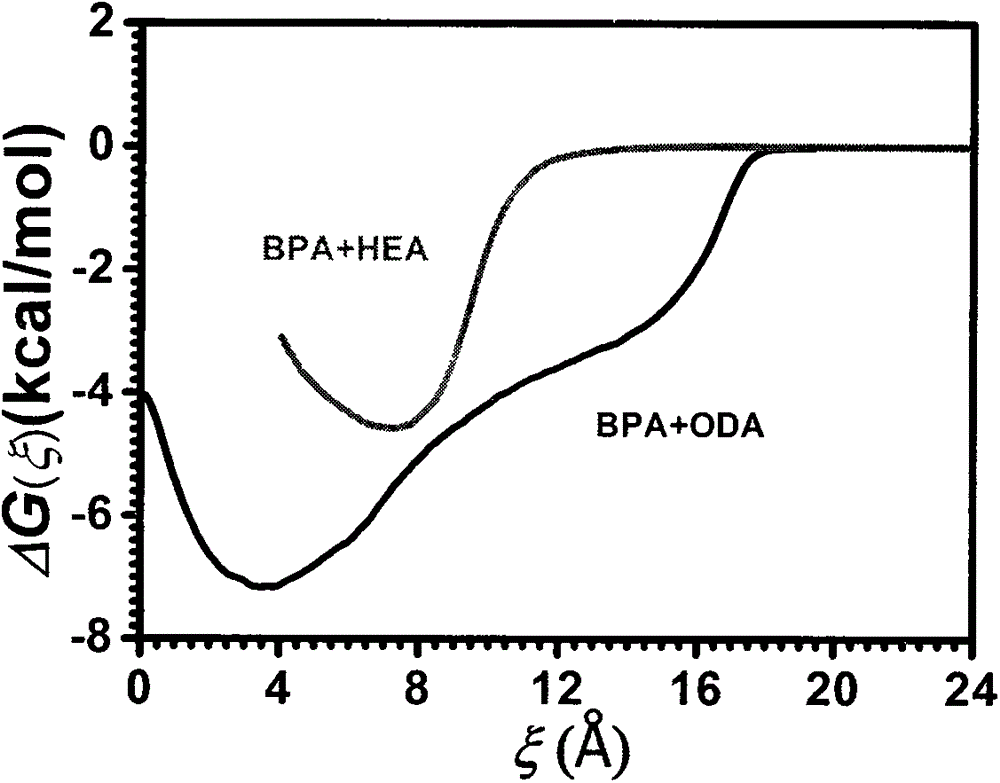
The binding constant, or association constant, is a special case of the equilibrium constant K, and is the inverse of the dissociation constant. It is associated with the binding and unbinding reaction of receptor (R) and ligand (L) molecules, which is formalized as: R + L ⇌ RL The reaction is characterized by the on-rate constant kₒₙ and the off-rate constant koff, which have units of M⁻¹ s⁻¹ and s⁻¹, respectively.
Homogeneous fluorassay methods employing fluorescent background rejection and water-soluble rare earth metal chelates
InactiveUS6242268B1High binding constantNon-metal conductorsGlass making apparatusHalf-lifeMetal chelate
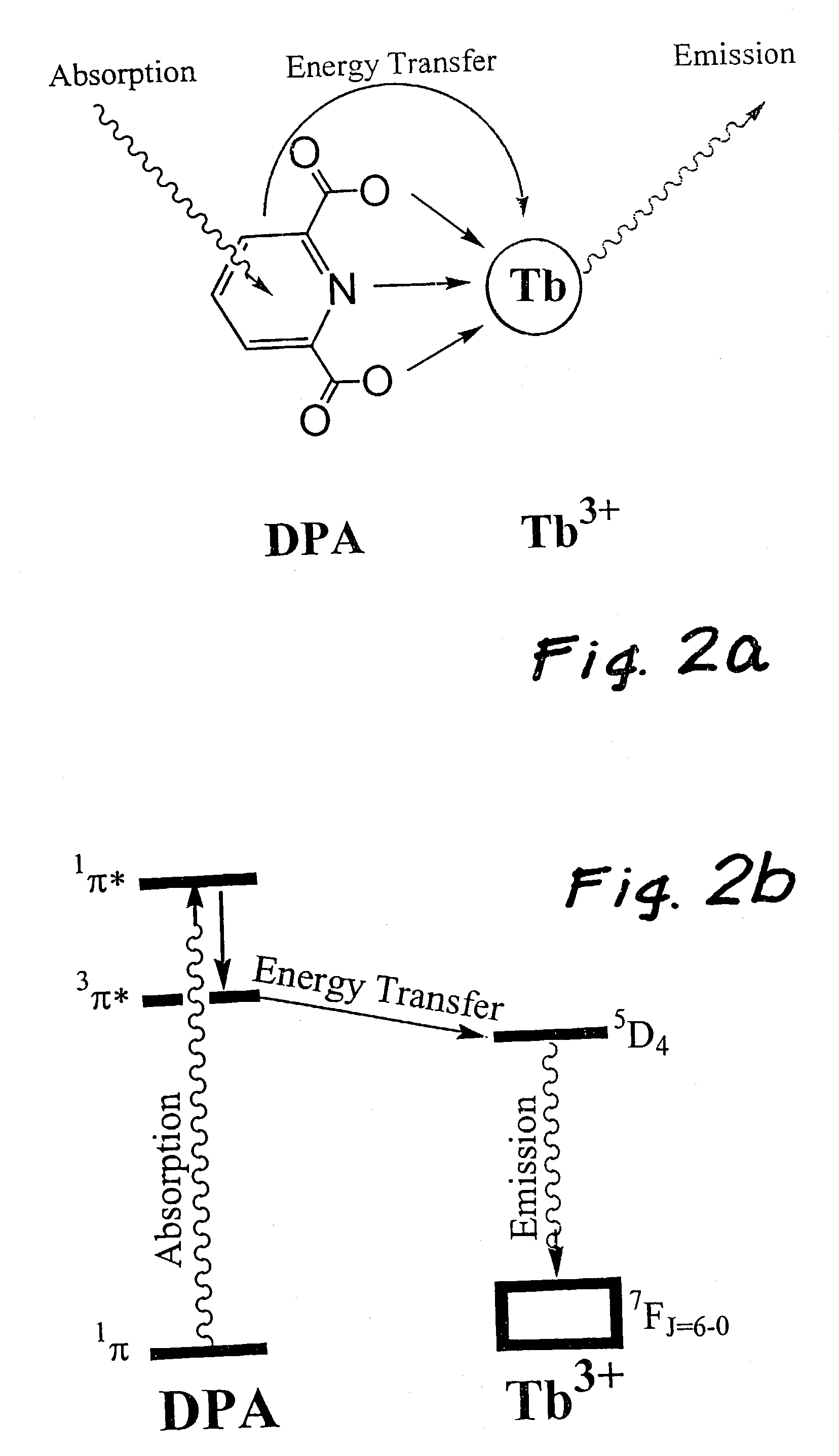
Homogeneous assays for determining quantitatively the extent of a specific binding reaction can be carried out effectively on very dilute solutions using measurements of fluorescence if a fluorescence measurement scheme that is capable of rejecting short-lived background fluorescence is employed and if the fluorescent group being measured has the following properties: a. the group being measured must be a rare earth metal chelate complex combination; b. the chelate must be water-soluble; c. the complex combination must also be stable in extremely dilute aqueous solutions, that is, the measured chelate must have at least one ligand having a metal-to-ligand binding constant of at least about 1013M-1 or greater and it must have a fluorescent emission that is long-lived compared to the longest decay lifetime of ambient substances and have a half life of from 0.01 to 50 msec.
Owner:EG&G WALLAC
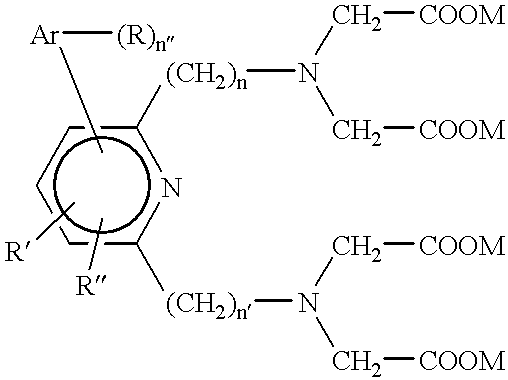
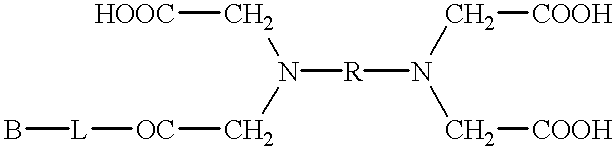
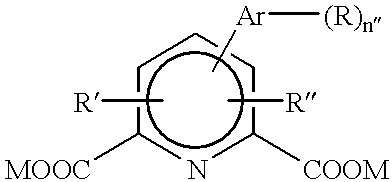
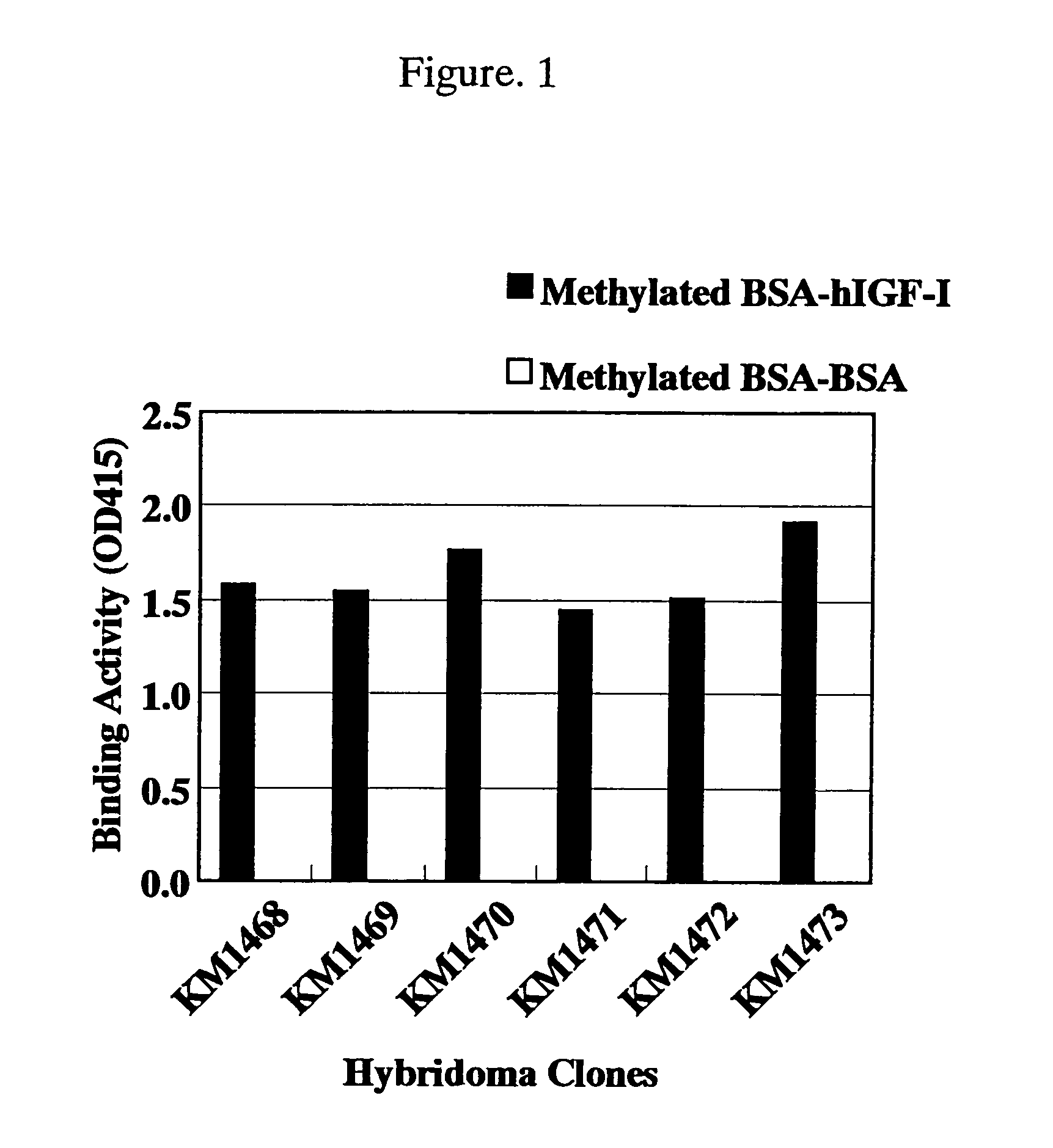
Antibody against human insulin-like growth factor
InactiveUS7438911B2Improve stabilitySuppression problemBacteriaAntipyreticInsulin-like growth factorDisease
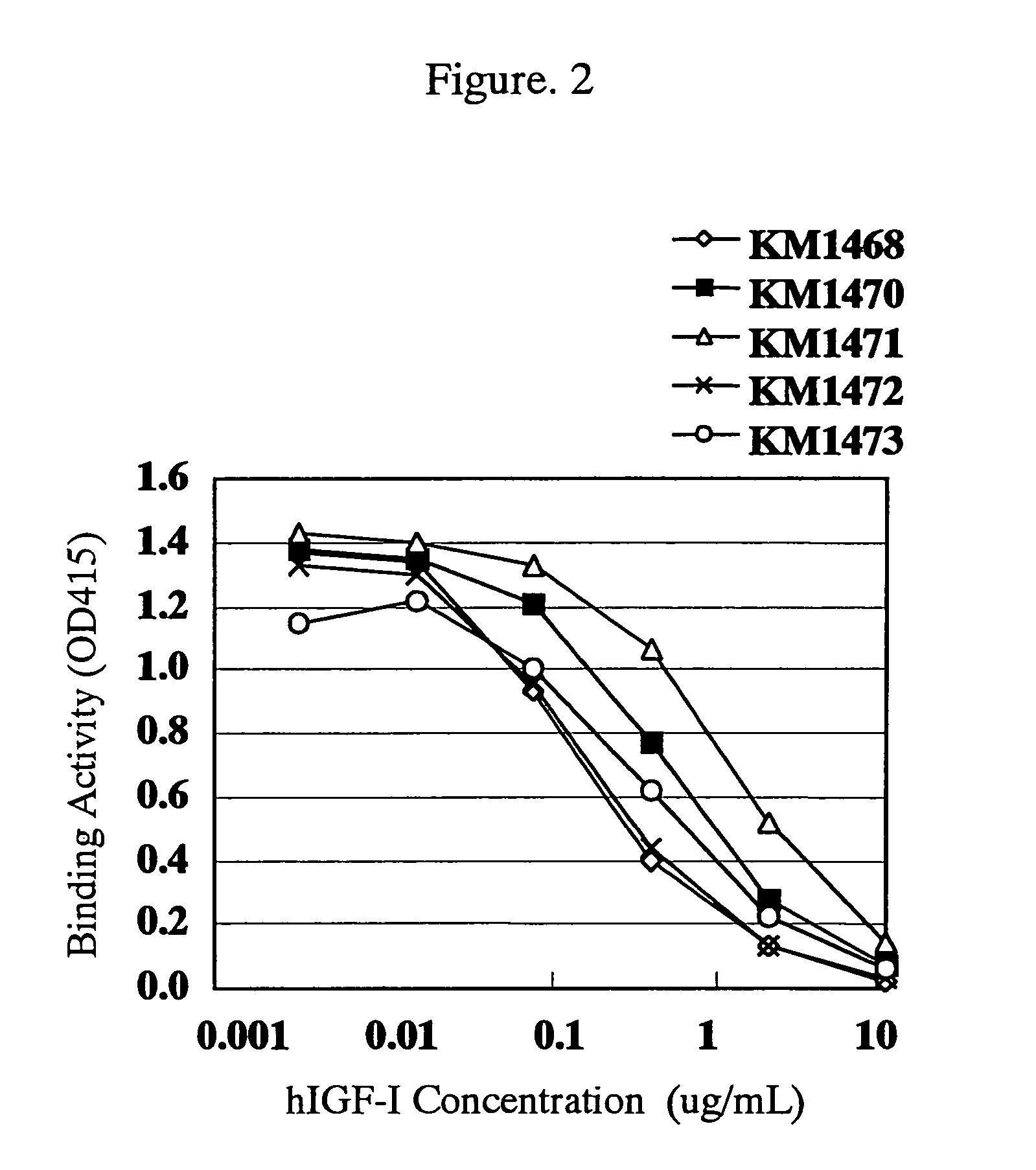
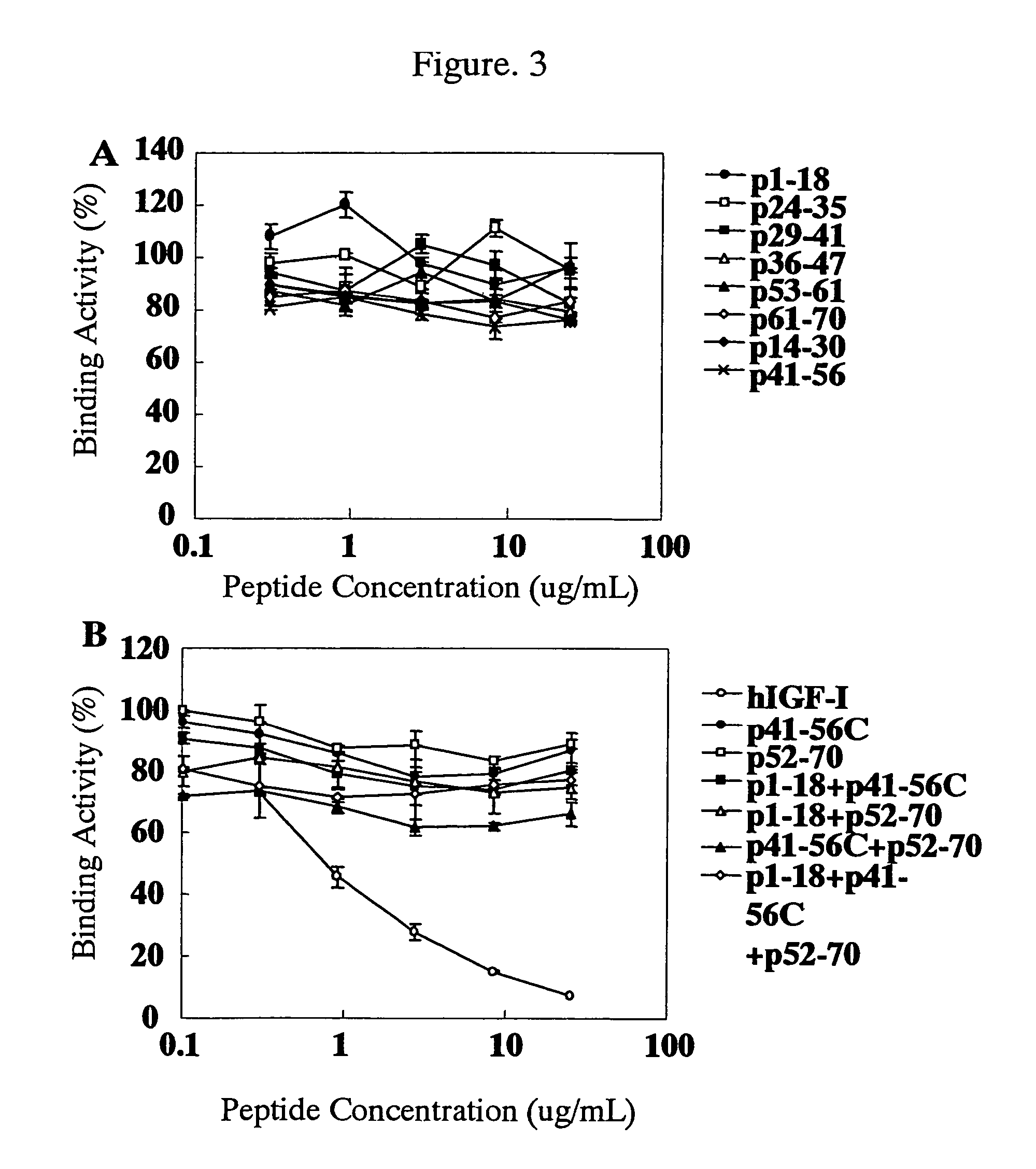
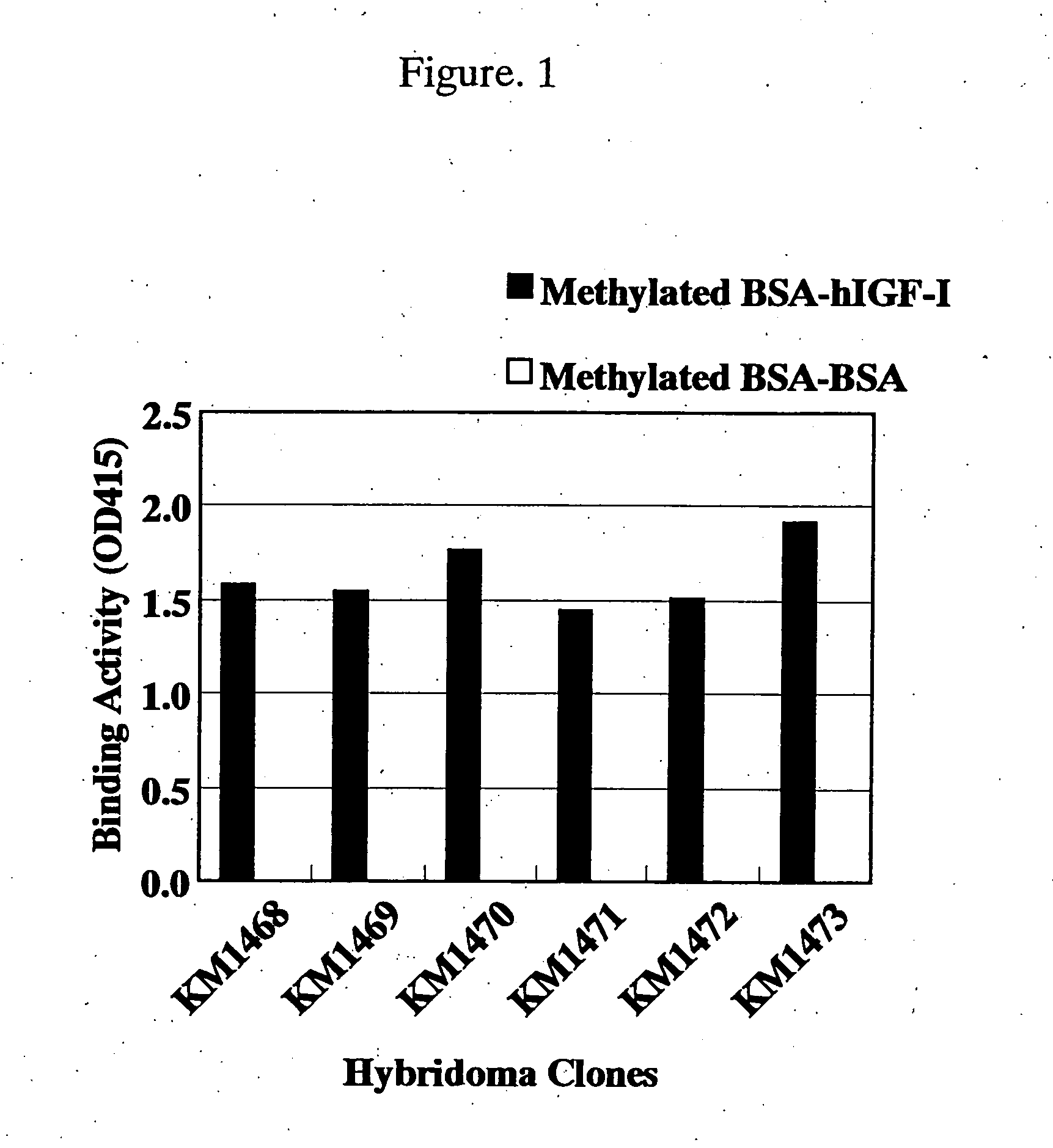
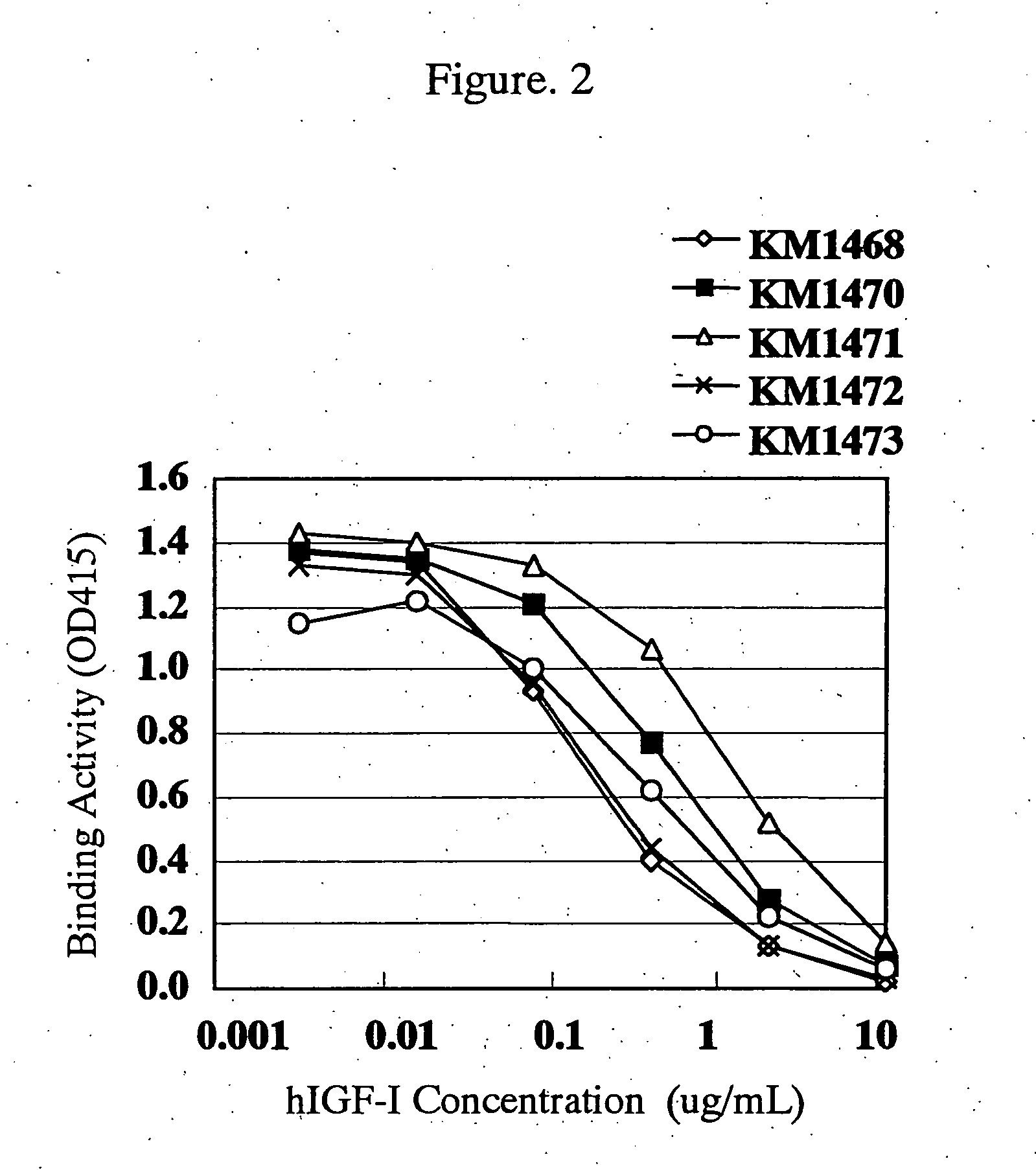
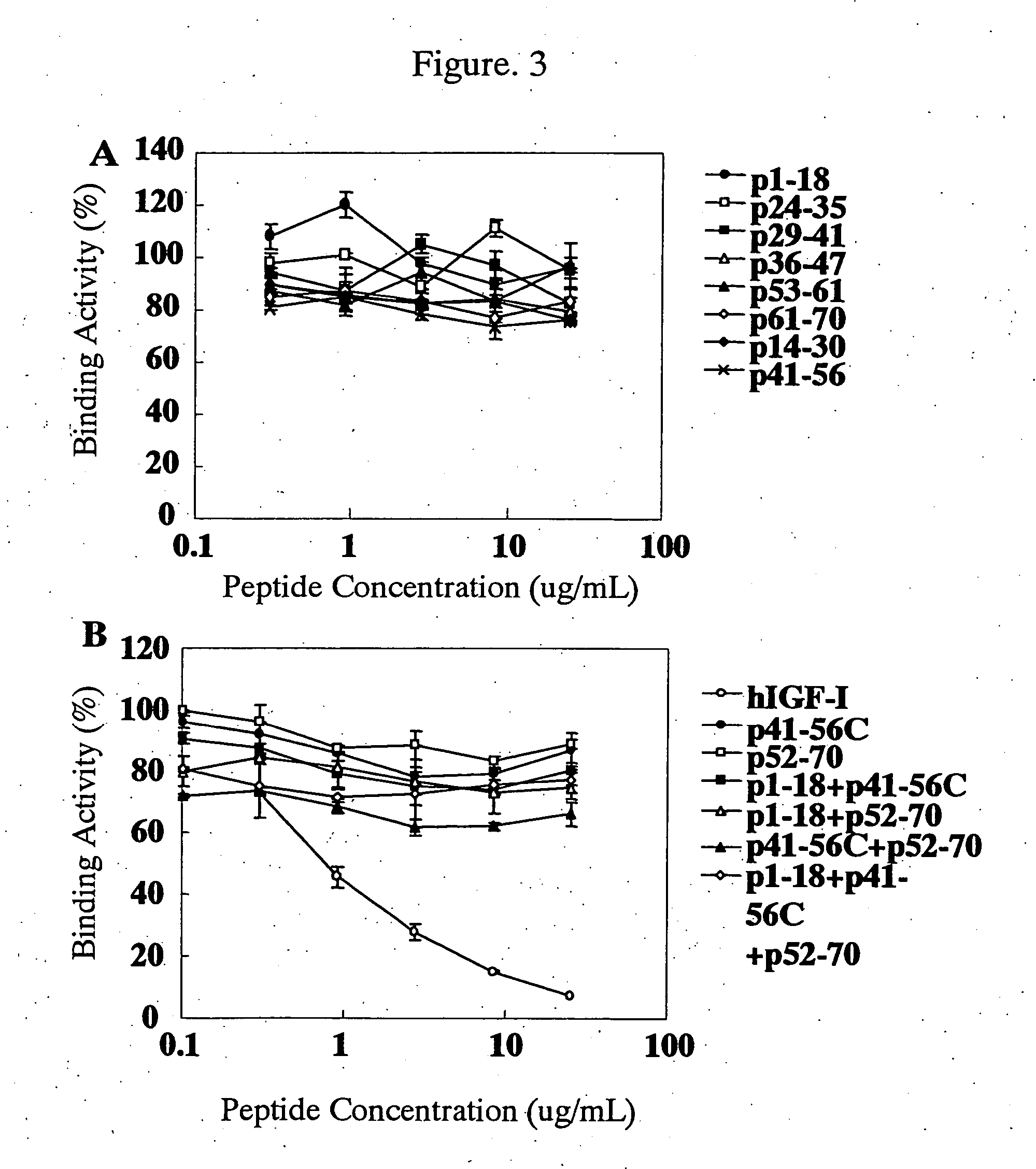
For the effective treatment of diseases such as cancer in which hIGF participates, there have been desired to be developed antibodies which strongly bind to both factors hIGF-I and hIGF-II and inhibit their functions and fragments of these antibodies. The present invention provides antibodies which have the ability to specifically bind to human IGF-I and IGF-II to thereby inhibit the functions of human IGF-I and IGF-II and have binding activity with a binding constant of 5×109 M−1 or more measured with a biosensor BIACORE. In addition, the present invention provides diagnostics, preventives and remedies for an hIGF-mediated disease and a disease showing pathological progressing due to abnormally promoted hIGF production, which use said antibodies.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Antibody against human insulin-like growth factor
InactiveUS20060165695A1Improve stabilitySuppression problemBacteriaAntipyreticInsulin-like growth factorDisease
For the effective treatment of diseases such as cancer in which hIGF participates, there have been desired to be developed antibodies which strongly bind to both factors hIGF-I and hIGF-II and inhibit their functions and fragments of these antibodies. The present invention provides antibodies which have the ability to specifically bind to human IGF-I and IGF-II to thereby inhibit the functions of human IGF-I and IGF-II and have binding activity with a binding constant of 5×109 M−1 or more measured with a biosensor BIACORE. In addition, the present invention provides diagnostics, preventives and remedies for an hIGF-mediated disease and a disease showing pathological progressing due to abnormally promoted hIGF production, which use said antibodies.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Flavivirus human monoclonal antibody and application
ActiveCN106589116AImprove bindingViral antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesFlaviviridaeMonoclonal antibody
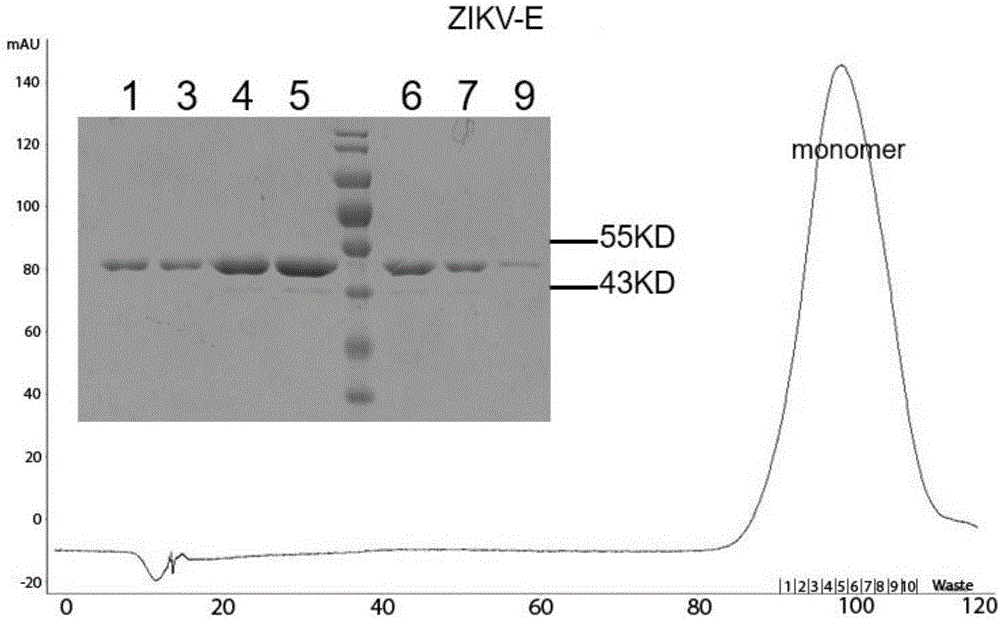
The invention discloses a flavivirus human monoclonal antibody and application, which belong to the technical field of medicine. According to the flavivirus human monoclonal antibody and the application provided by the invention, three antibodies capable of protein-binding with ZIKV-E are acquired, and binding sites of the three antibodies are confirmed. The three antibodies are completely different from a reported ZIKV antibody sequence, and are three new-found antibodies. The binding constants of the three antibodies and the ZIKV-E are 39.9pM (Z5), 44.7pM (Z6) and 200pM (Z7), which show that the three human monoclonal antibodies have a higher ZIKV-E protein-binding capacity. Through competiton experiments, the binding sites of the three antibodies have competitive relationships with 2A10G6, and the phenomenon shows that the binding sites of the three antibodies are near FL, and E protein of flaviviridae is highly conserved at the FL part. The antibody provided by the invention effectively detects the infection of common flaviviridae viruses: ZIKV, dengue 1-4 type and yellow fever viruses, and has huge application values on clinic detection and fundamental research.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for the characterization of the three-dimensional structure of proteins employing mass spectrometric analysis and computational feedback modeling
InactiveUS7047171B1Samples introduction/extractionAnalogue computers for chemical processesESI mass spectrometryProtein-protein complex
A method for characterizing the three-dimensional surface structure of molecules, particularly proteins and protein complexes, employing mass spectrometric analysis, an electrospray ionization (ES) source, a novel data interpretation process that utilizes comparisons of particular binding constants (KB) and heats of formation (ΔHf), and computational feedback modeling.
Owner:HV OPS H NU
Chemical Target-Binding Compositions
Herein is described compositions and methods for modulating and regulating the concentration of a chemical target in an organism or in an ecosystem. In one embodiment, the concentration is regulated such that it is maintained below or above a certain threshold, thus avoiding toxic or harmful effects of the chemical target. The described compositions may, for example, be implanted in a human body or placed in the ecosystem. The compositions comprise binding moieties that reversibly bind to a chemical target in the organism or ecosystem. The binding capacity and the binding constants for a chemical target are designed such that the composition maintains the concentration of the chemical target substantially within a beneficial range of concentrations.
Owner:THERABIT
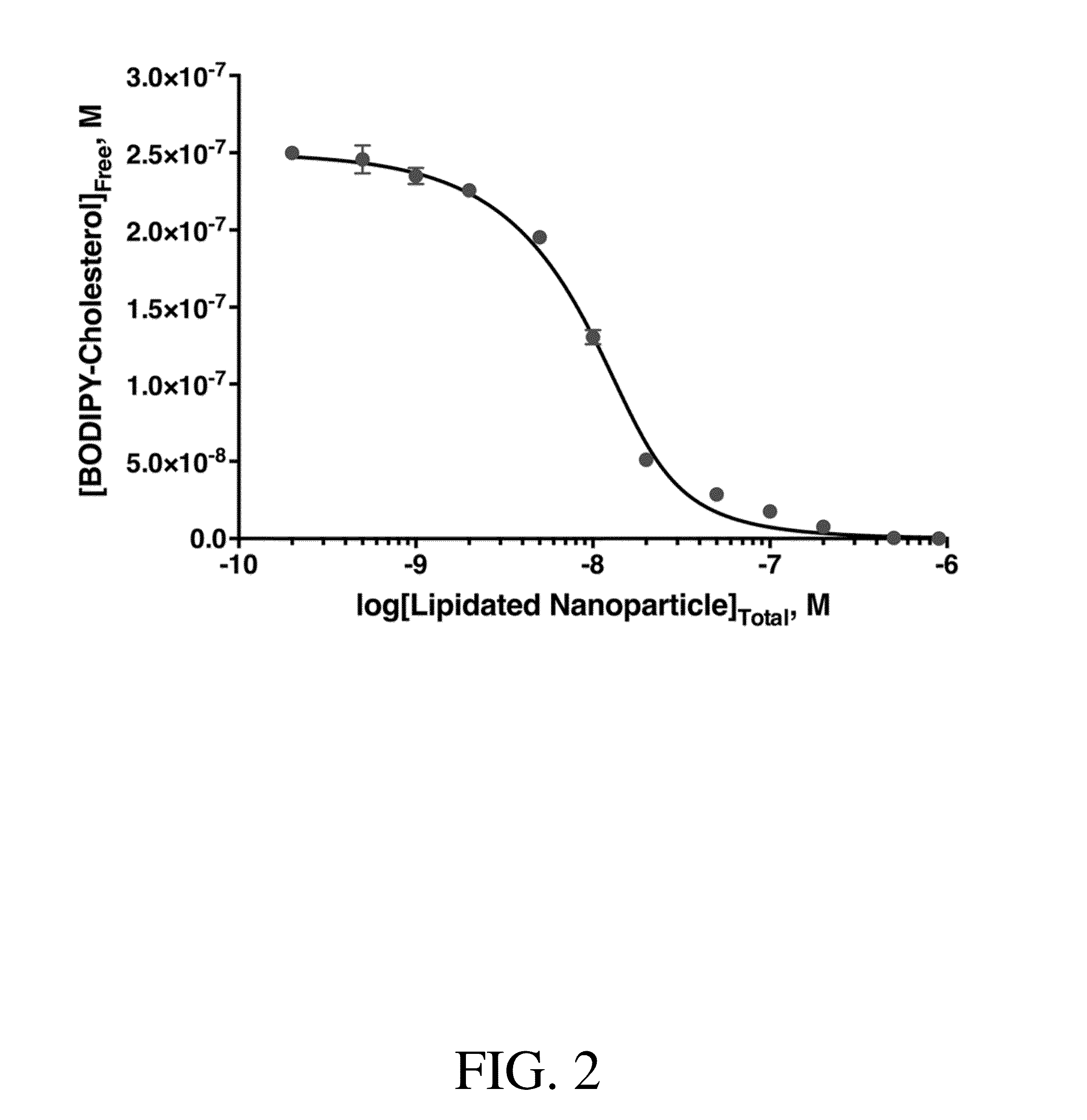
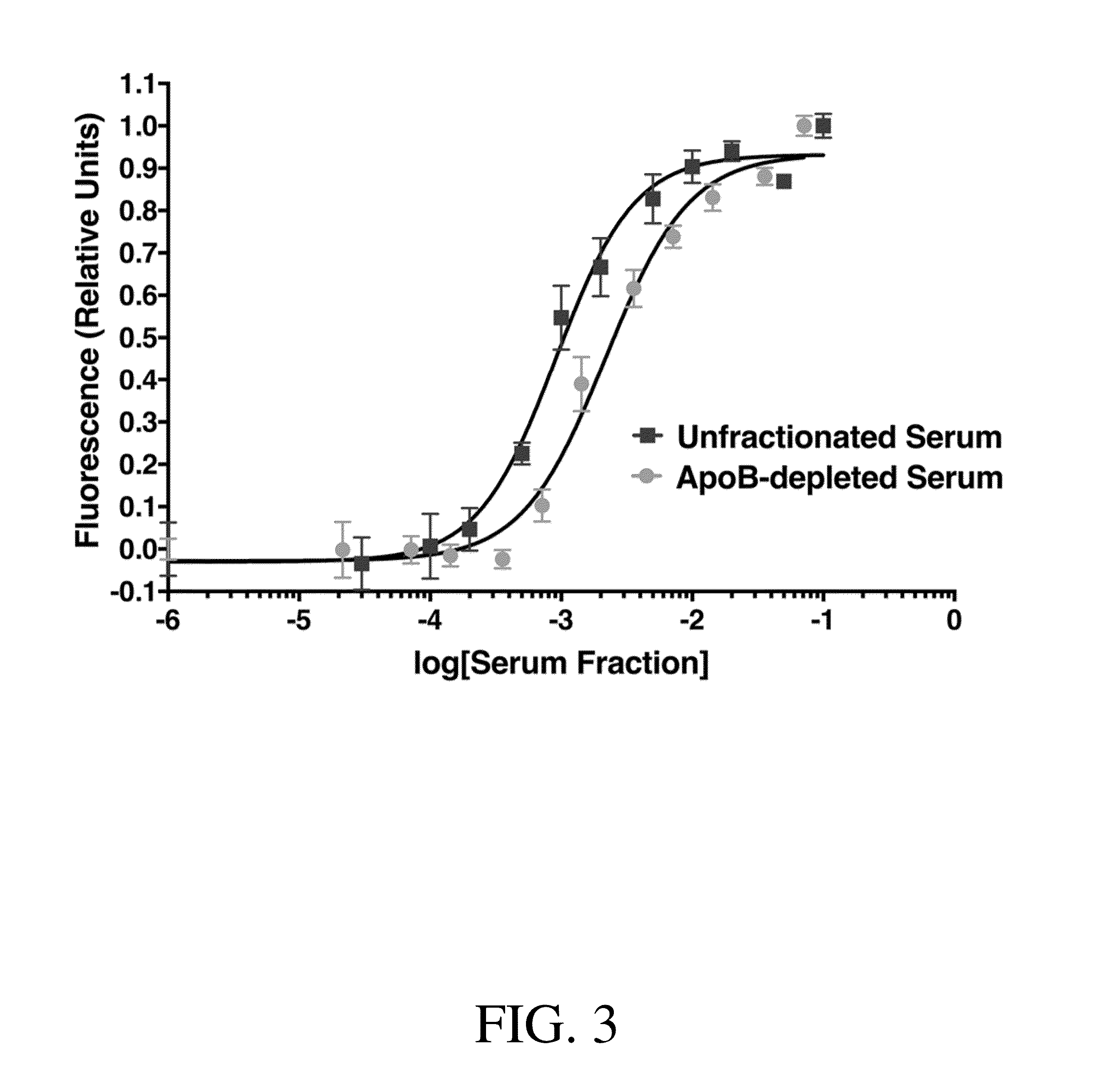
Assays for measuring binding kinetics and binding capacity of acceptors for lipophilic or amphilphilic molecules
ActiveUS20160274134A1Increase volumeEnhanced signalDisease diagnosisBiological testingCell freeNanoparticle
Aspects of the invention relate to methods for measuring the binding constant of a lipophilic or amphiphilic molecule acceptor for a lipophilic or amphiphilic molecule. Methods involve rapid, cell-free competition assays including a labeled lipophilic or amphiphilic molecule and nanoparticle.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
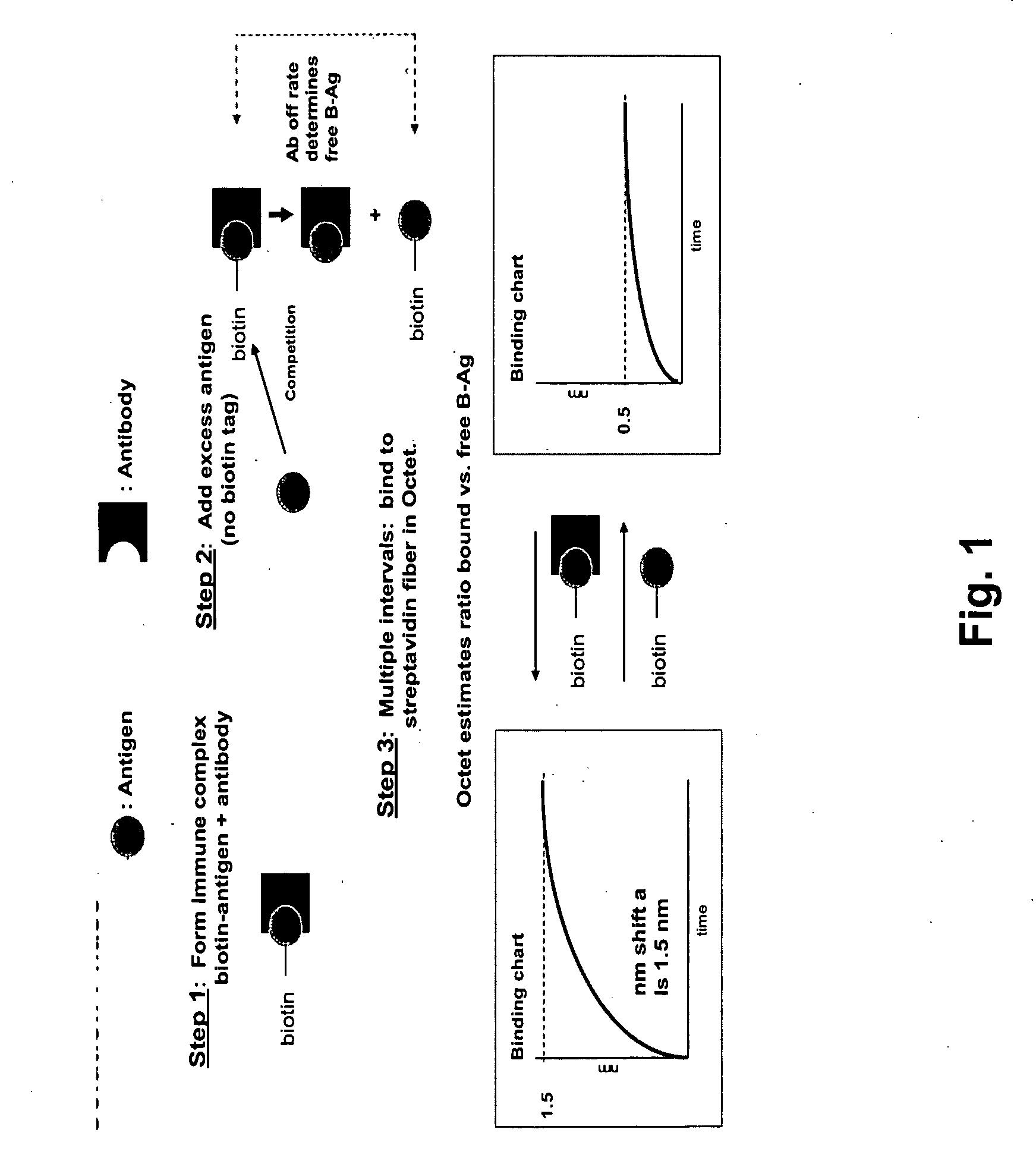
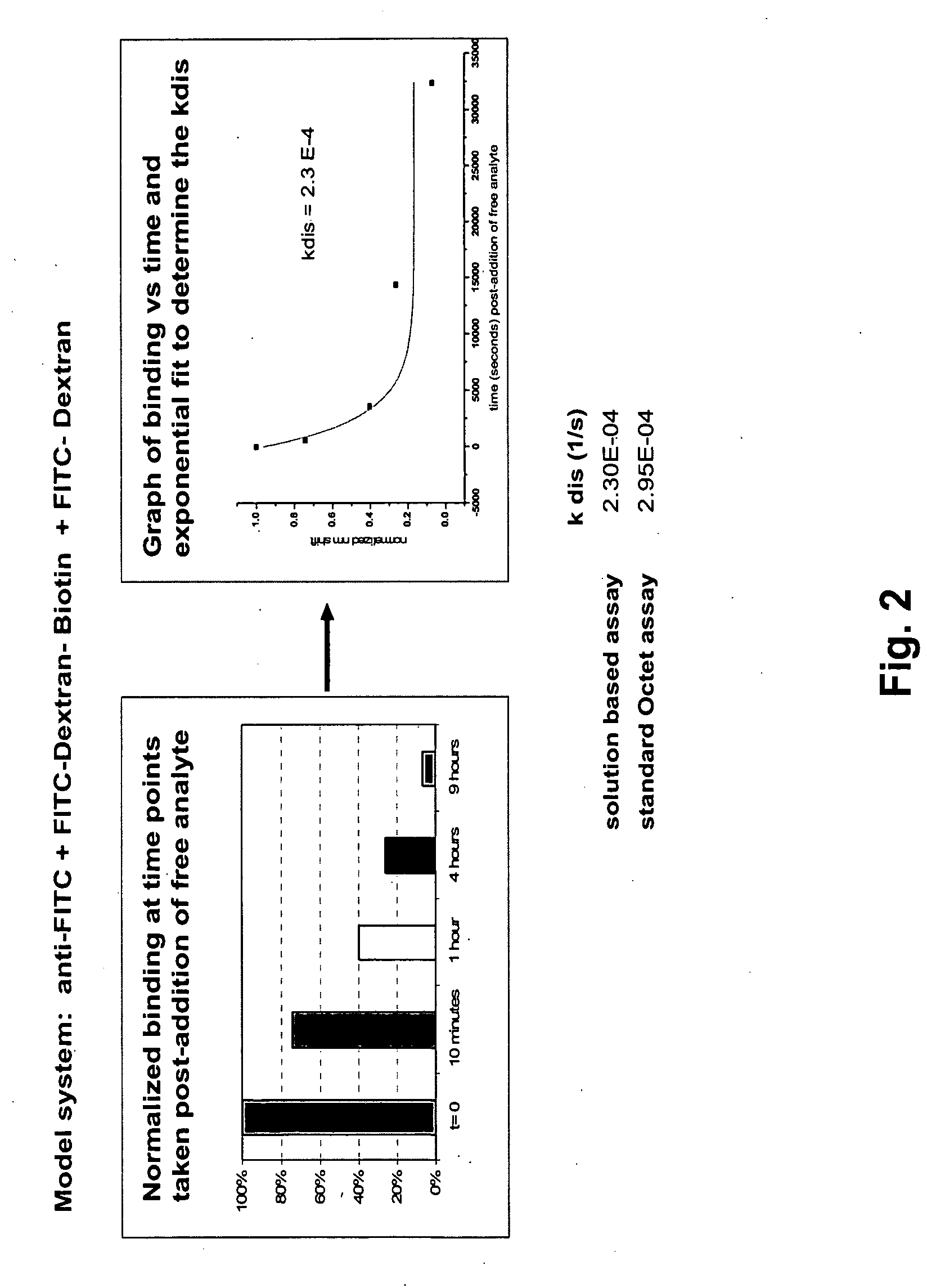
Methods for characterizing molecular interactions
InactiveUS20070161042A1Biological testingChemical methods analysisDissociation rate constantContinuous measurement
Methods are provided for measuring rate constants for high affinity molecular interactions using an assay format for determining dissociation rates in liquid phase. The invention uses a biosensor that at selected time intervals is contacted with a sample solution to estimate the ratio of bound vs. free ligand. Dissociation rate constants determined according to the methods of the invention more closely mimic in vivo binding constants and avoid diffusional barrier artifacts that accompany measurements performed using solid phase devices. The methods of the invention provide further advantage by not requiring continuous measurements be made on a biosensor instrument thus leaving it available to process other samples. The methods permit accurate determination of dissociation rates of reactions for which dissociation slowly occurs over intervals of hours to days or more.
Owner:PALL FORTEBIO
Small molecule inhibitors of autotaxin and methods of use
InactiveUS20110110886A1Inhibit and reduce and growthInhibit and reduce likelihoodHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMetastatic melanoma
Autotaxin (ATX) is a prometastatic enzyme initially isolated from the conditioned media of human melanoma cells that stimulates a myriad of biological activities including angiogenesis and the promotion of cell growth, survival, and differentiation through the production of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). ATX increases the aggressiveness and invasiveness of transformed cells, and ATX levels directly correlate with tumor stage and grade in several human malignancies. To study the role of ATX in the pathogenesis of malignant melanoma, we developed antibodies and small molecule inhibitors against recombinant human protein. Immunohistochemistry of paraffin embedded human tissue demonstrates that ATX levels are markedly increased in human primary and metastatic melanoma relative to benign nevi. Chemical screens identified several small molecule inhibitors with binding constants ranging from nanomolar to low micromolar. Cell migration and invasion assays with melanoma cell lines demonstrate that ATX markedly stimulates melanoma cell migration and invasion, an effect suppressed by ATX inhibitors. The migratory phenotype can be rescued by the addition of ATX's enzymatic product, LPA, confirming that the observed inhibition is linked to suppression of LPA production by ATX. Chemical analogues of the inhibitors demonstrate structure activity relationships important for ATX inhibition and indicate pathways for their optimization. These studies suggest that ATX is an approachable molecular target for the rational design of chemotherapeutic agents directed against human malignancies driven by the ATX / LPA axis, especially including malignant melanoma, among numerous others including breast and ovarian cancers.
Owner:YALE UNIV
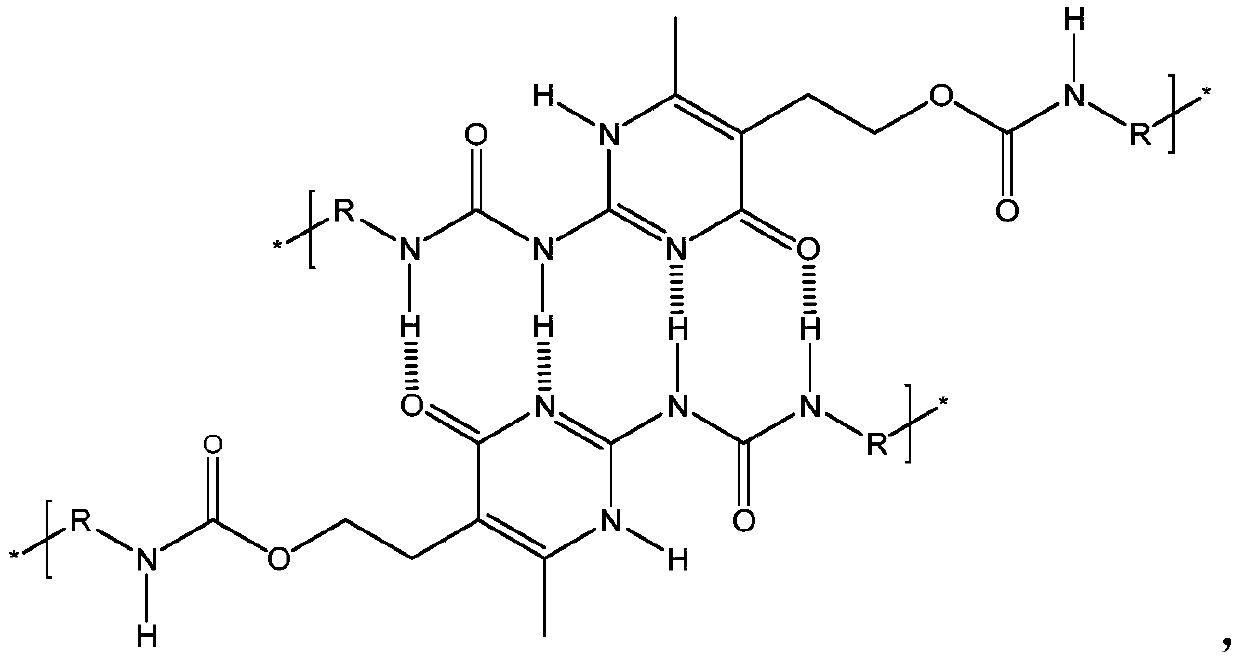
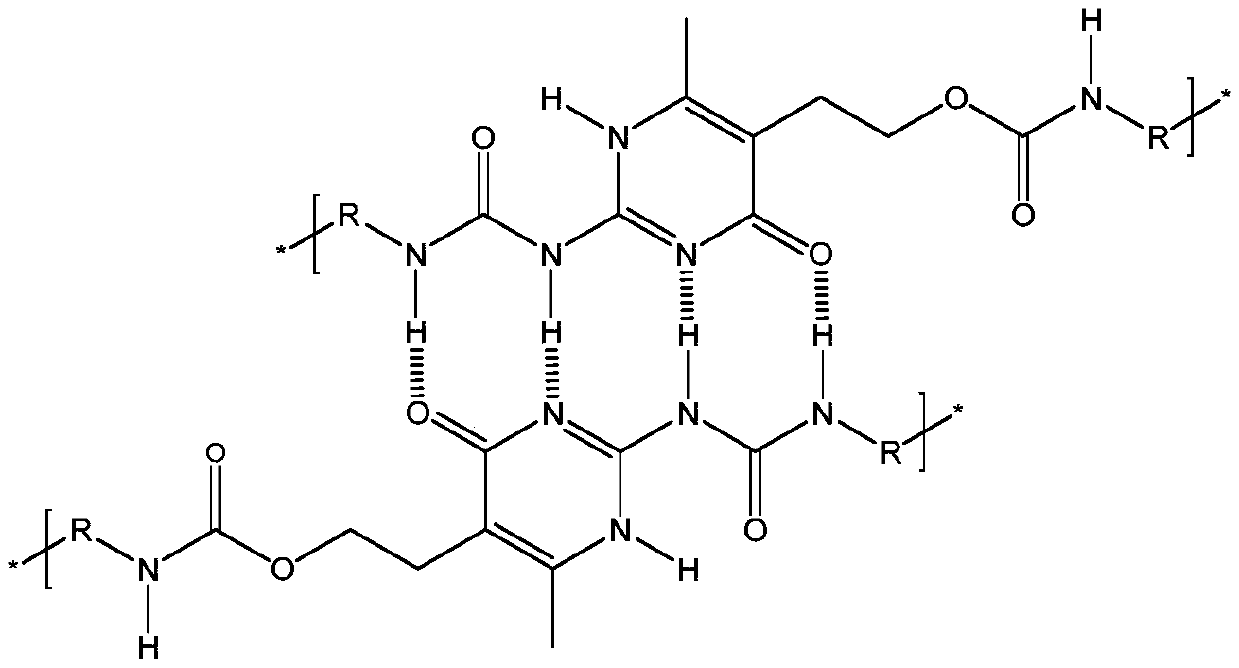
Waterborne polyurethane dispersion with quadrupolar hydrogen bond and preparation method of waterborne polyurethane dispersion
The invention discloses a waterborne polyurethane dispersion with a quadrupolar hydrogen bond and a preparation method of the waterborne polyurethane dispersion. A repeating unit of a polyurethane molecular chain is a quadrupolar hydrogen bond element of a 2-ureido-4[1H]-pyrimidone type, the non covalent bond has a very high binding constant and reversibility, and probability of constructing a complex functional material is provided. As an amino-uracil monomer joins in diisocyanate, the quadrupolar hydrogen bond of the 2-ureido-4[1H]-pyrimidone type is introduced into a green and low-toxicityenvironmental-friendly macromolecule system, namely waterborne polyurethane, in a macromolecule dihydric alcohol prepolymerization mode, and thus a low VOC (volatile organic compound) polymer which isgood in self healing capability and high in tension strength can be prepared. The waterborne polyurethane dispersion has very good research prospects and application values in the field of polyurethane functional coatings.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
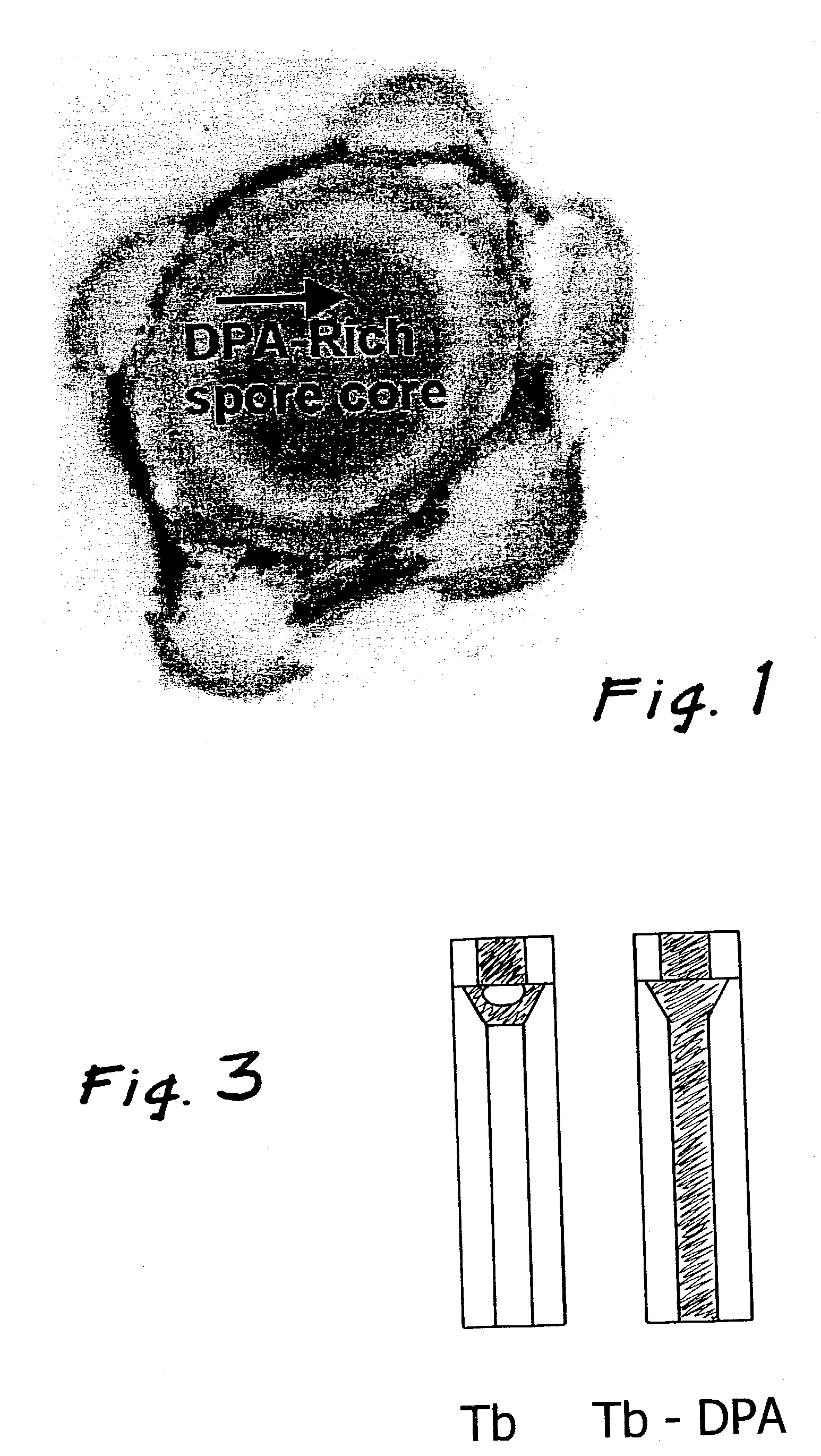
Method bacterial endospore quantification using lanthanide dipicolinate luminescence
ActiveUS7306930B2High sensitivityIncrease dipicolinic acid binding constantMicrobiological testing/measurementPhotoluminescenceLanthanide
A lanthanide is combined with a medium to be tested for endospores. The dipicolinic acid released from the endospores binds the lanthanides, which have distinctive emission (i.e., luminescence) spectra, and are detected using photoluminescence. The concentration of spores is determined by preparing a calibration curve generated from photoluminescence spectra of lanthanide complex mixed with spores of a known concentration. A lanthanide complex is used as the analysis reagent, and is comprised of lanthanide ions bound to multidentate ligands that increase the dipicolinic acid binding constant through a cooperative binding effect with respect to lanthanide chloride. The resulting combined effect of increasing the binding constant and eliminating coordinated water and multiple equilibria increase the sensitivity of the endospore assay by an estimated three to four orders of magnitude over prior art of endospore detection based on lanthanide luminescence.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
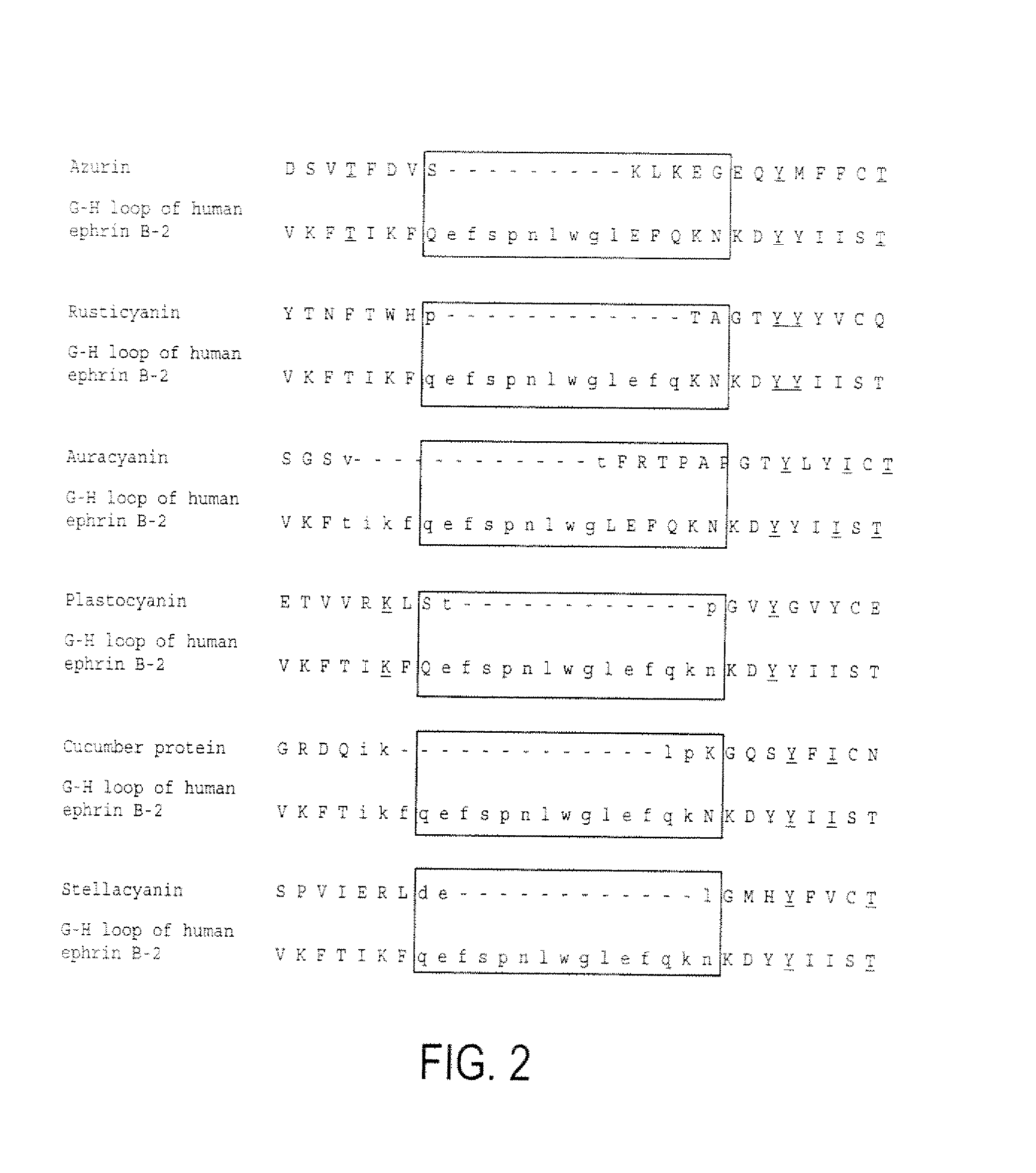
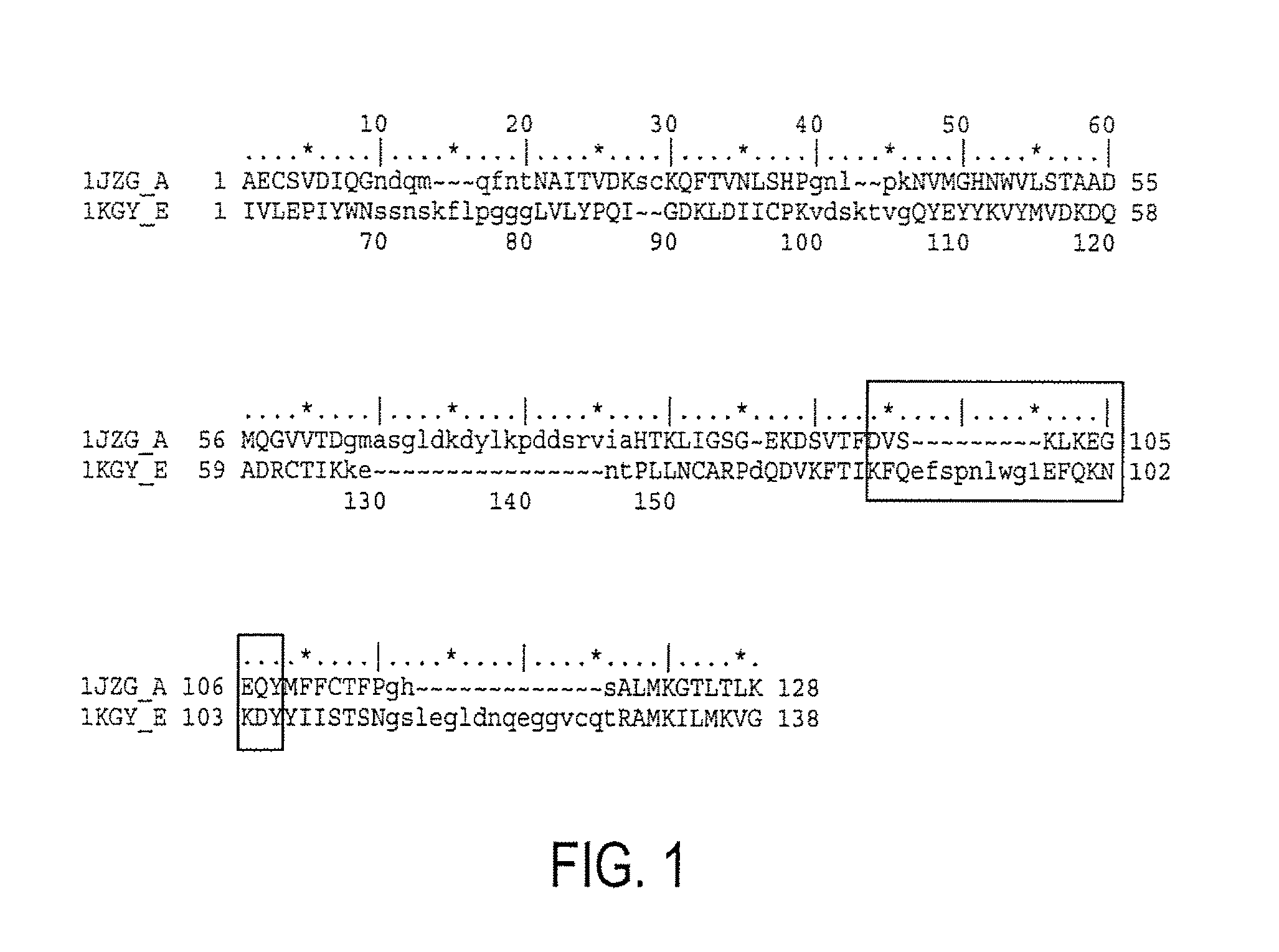
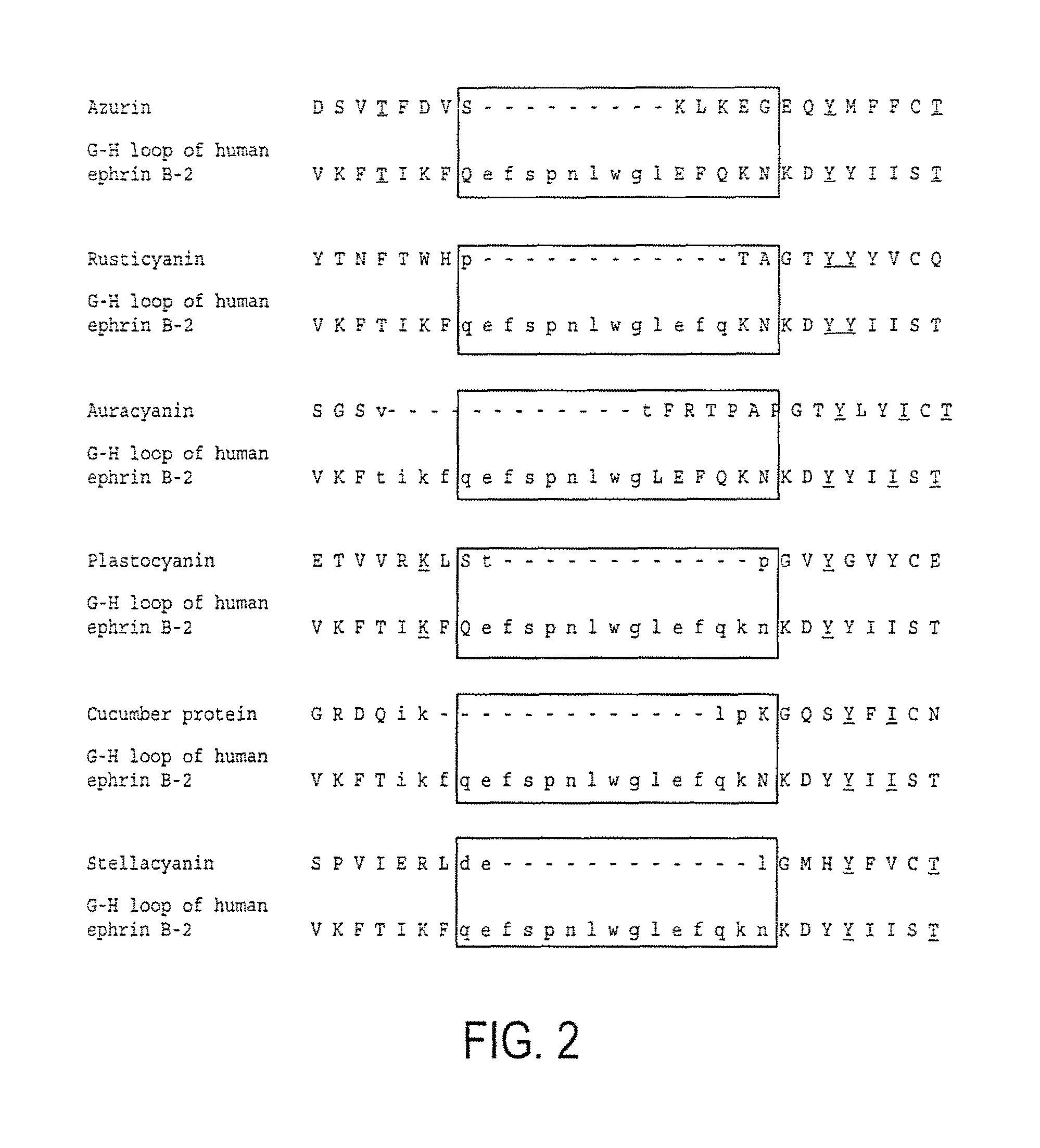
Compositions and methods for treating conditions related to ephrin signaling with cupredoxins and mutants thereof
InactiveUS20080221015A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalEphrin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods of use of cupredoxins, and variants, derivatives and structural equivalents of cupredoxins that interfere with the ephrin signaling system in mammalian cells. Specifically, the invention relates to compositions and methods that use cupredoxins, such as azurin, rusticyanin and plastocyanin, and variants, derivatives and structural equivalents thereof, to treat cancer in mammals. The invention specifically includes mutants with altered Eph binding constants and selectivities.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Targeting of Erb Antigens
A conjugate comprisinga) a trifunctional cross-linking moiety, to which is coupledb) an affinity ligand via a linker 1,c) a cytotoxic agent, optionally via a linker 2, andd) an anti Erb antibody or variants thereof having the ability to bind to Erb antigens expressed on mammalian tumour surfaces with an affinity-binding constant of at least 5×106 M−1,wherein the affinity ligand is biotin, or a biotin derivative having essentially the same binding function to avidin or streptavidin as biotin, wherein stability towards enzymatic cleavage of the biotinamide bond has been introduced in linker 1.
Owner:GLYCOREX TRANSPLANTATION
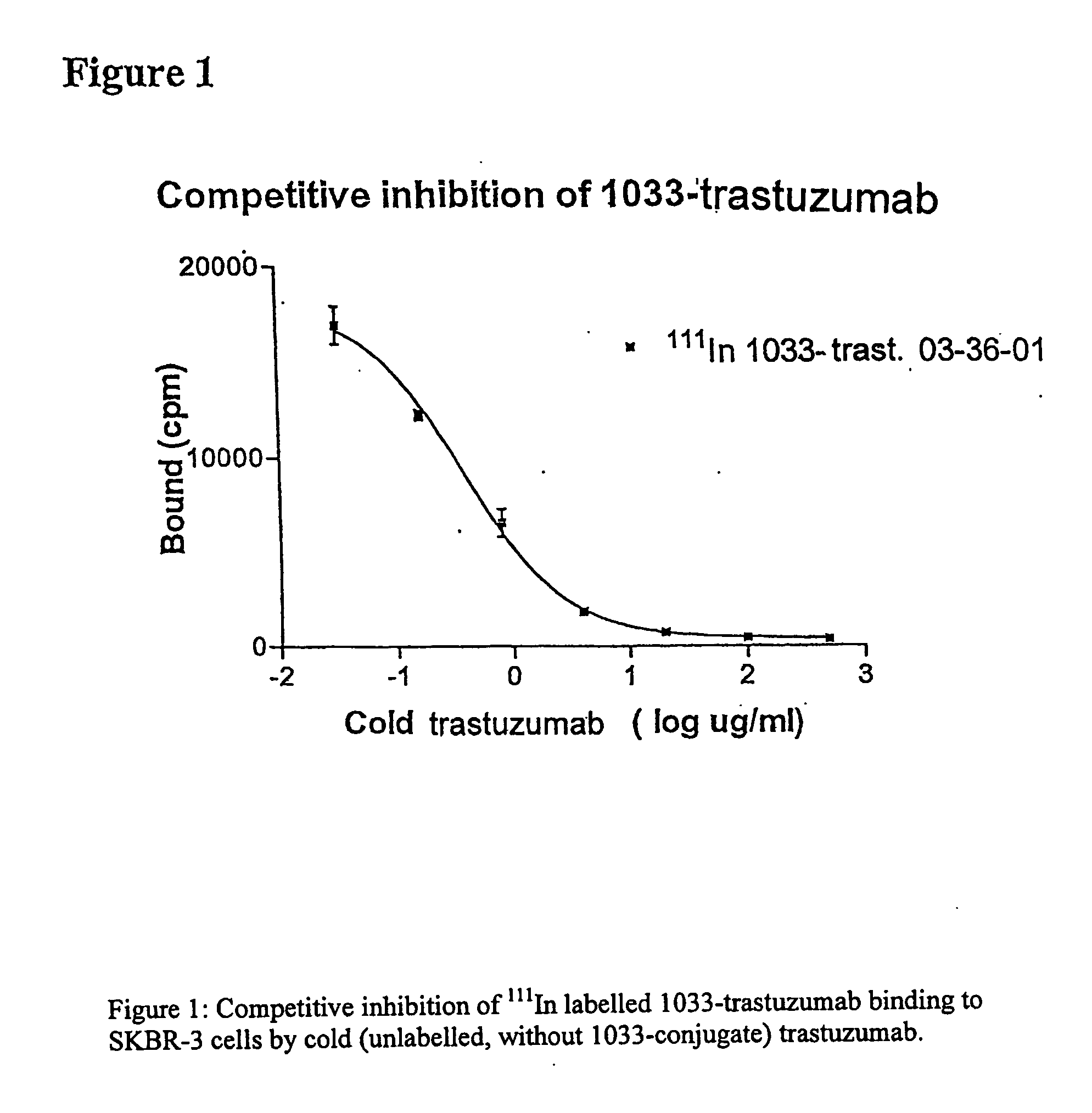
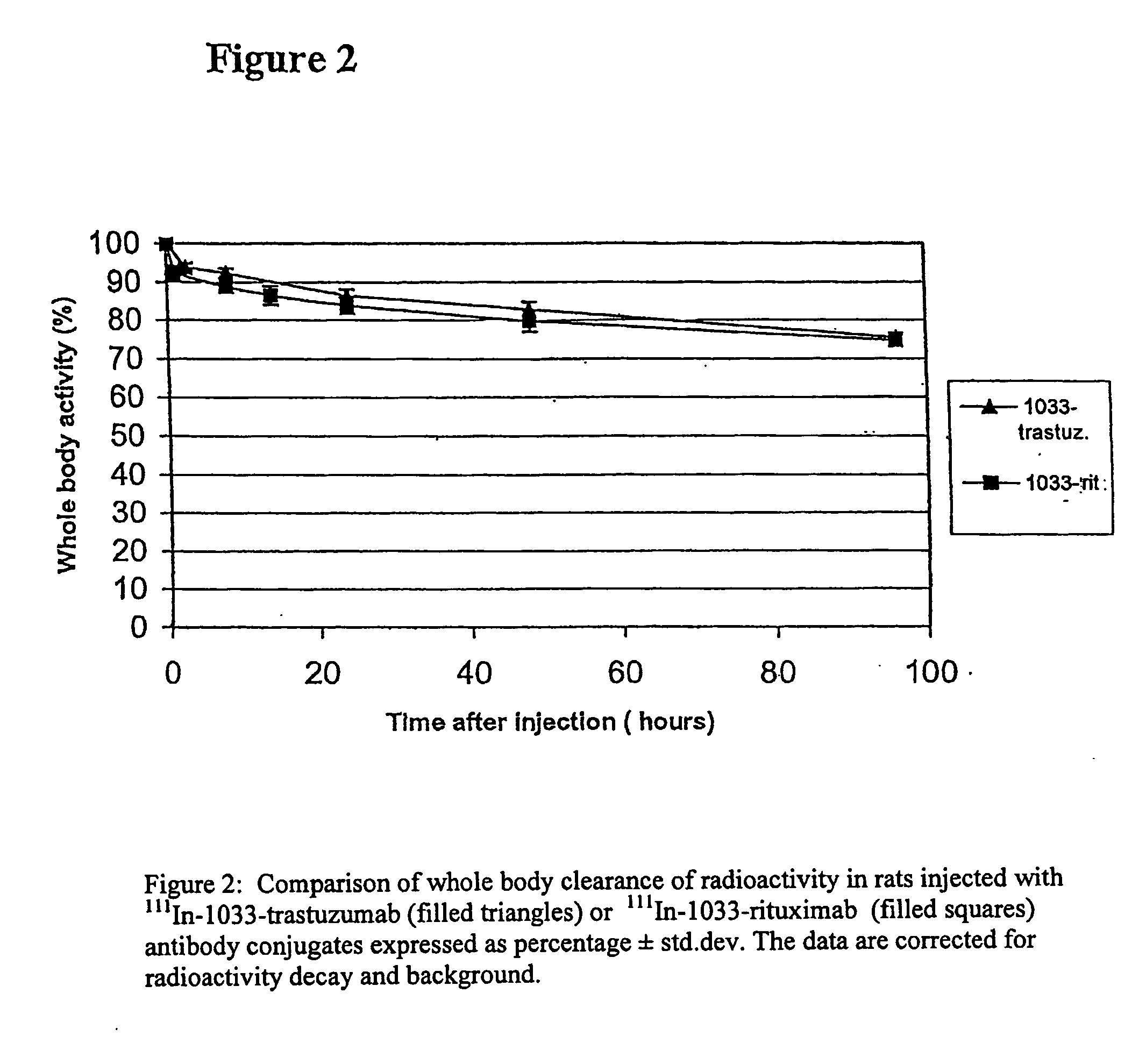
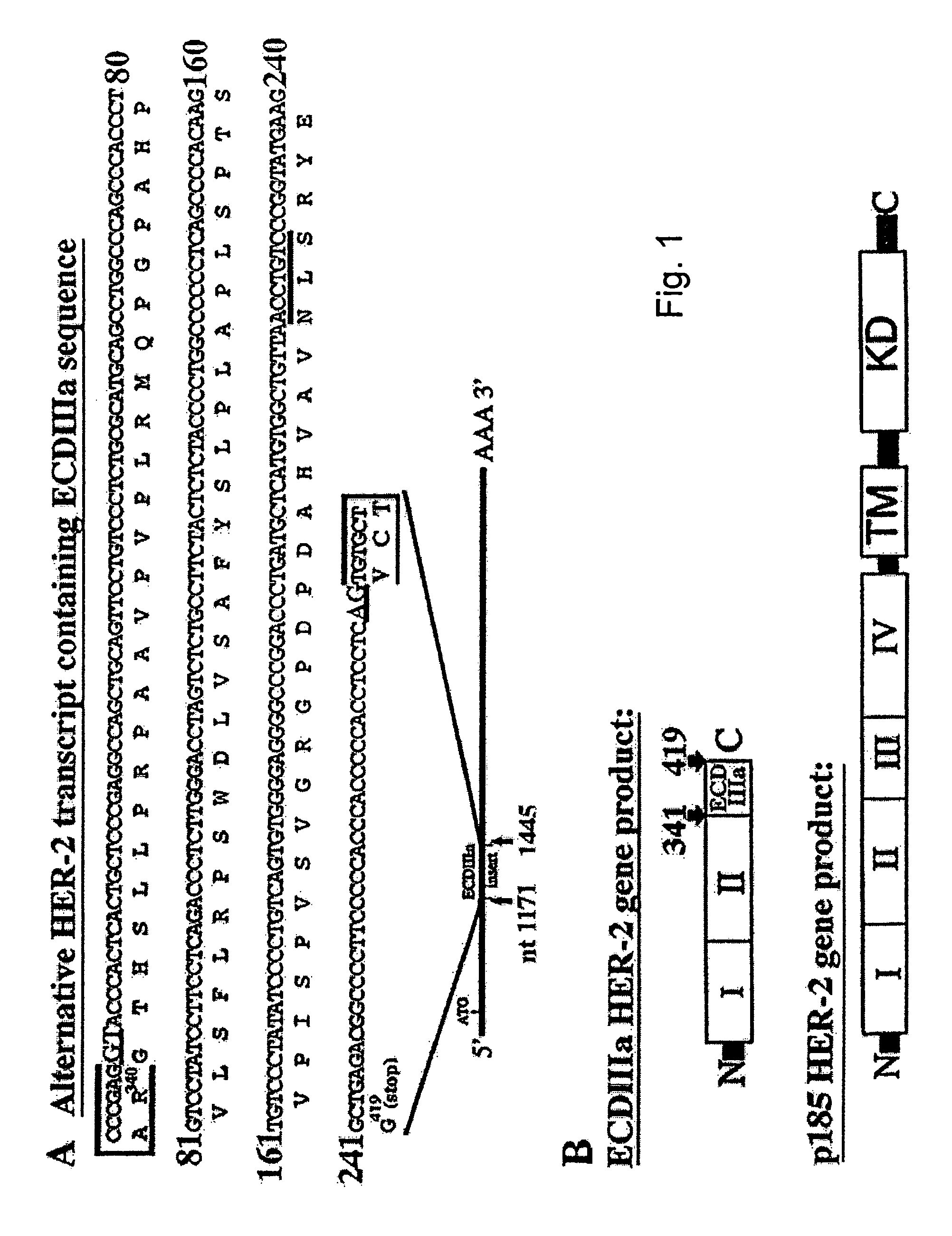
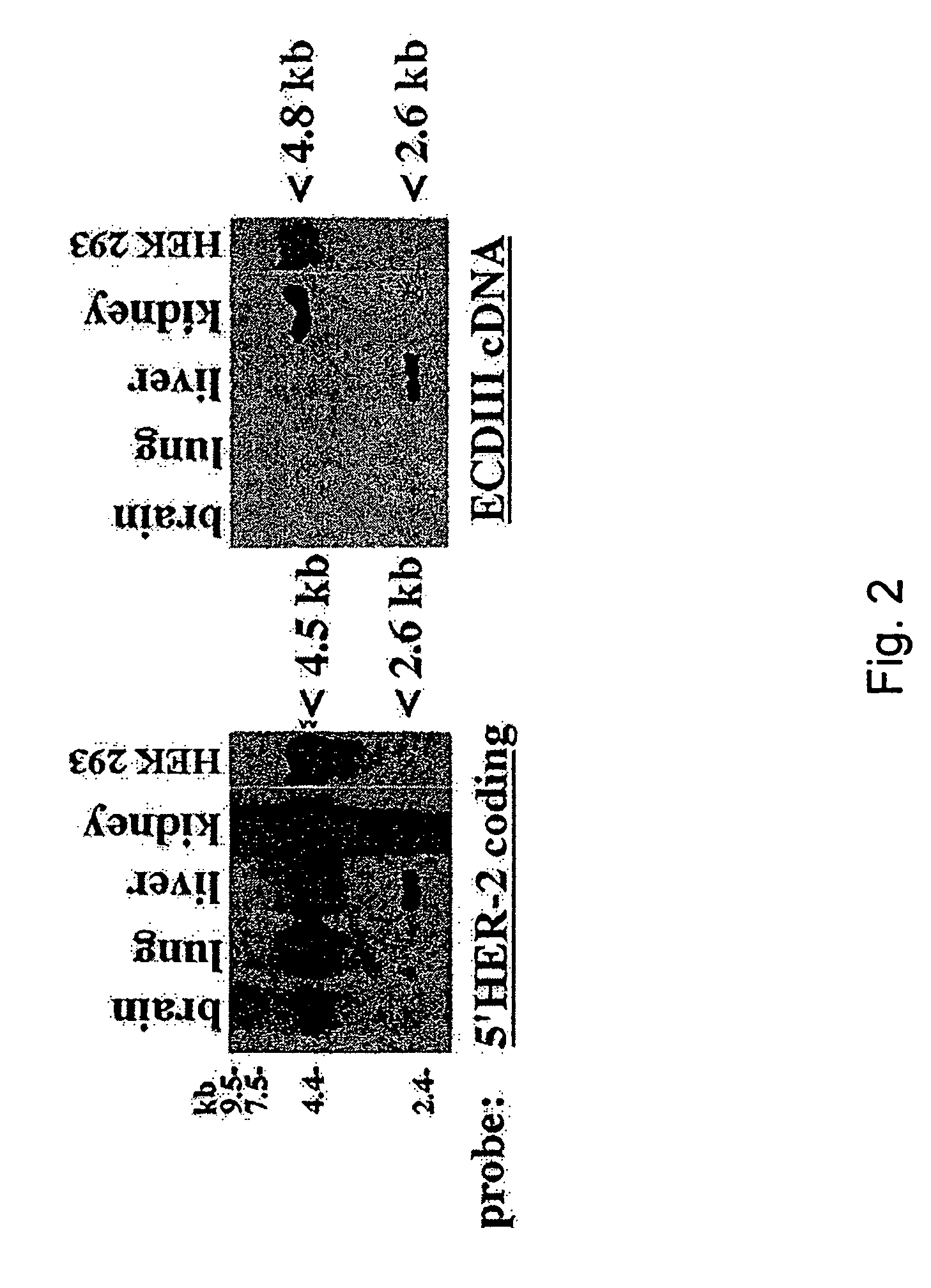
HER-2 binding antagonists
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Preparation method of supramolecular quadruple hydrogen-bond ureido-pyrimidinone (UPy) unit modified polyvinyl chloride (PVC) special resin
The invention relates to a preparation method of supramolecular quadruple hydrogen-bond ureido-pyrimidinone (UPy) unit modified polyvinyl chloride (PVC) special resin. UPy-containing acrylate crosslinking agents are used for modifying PVC, and UPy-containing styrene crosslinking agents are used for modifying the PVC. Compared with the existing crosslinking agents, the crosslinking agents selectedfor use in the method have the beneficial effects that UPy quadruple hydrogen-bond system can form a self-complementary quadruple hydrogen-bond interaction, and is good in stability, strong in self-polymerization ability and very high in binding constant; furthermore, the strong non-covalent cross-linking effect is reversible and has a self-recovery ability; high molecular polymers are formed by means of self-assembly through the interaction of non-covalent hydrogen bonds; the combination of repeating units is based on the interaction of the hydrogen bonds, so that the repeating units can be separated and recombined under appropriate conditions and are reversible; therefore, the PVC polymer not only has the properties of the traditional polymers, but also has the excellent characteristicsof stimulative responsibility, self-repairing property, easy processing and the like, and can be used as special resin for smart materials and self-healing materials.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ENG
Filtration and purification system for pH neutral solutions
InactiveCN1379699ANo loss in complexation efficiencyLow resistance to mass transferMembranesWater contaminantsFiltrationBinding constant
The present invention relates to a method for the removal of metal ions and / or particulate materials from pH neutral solutions using particle removal membranes (e.g., ultra high molecular weight polyethylene) having immobilized ligands capable of removing ions And has a high equilibrium binding constant associated with ion removal. The method is particularly useful for simultaneous filtration / purification of deionized water.
Owner:迈克里斯公司
Molecular synthesis method acrylic acid type functional monomer containing supermolecule quadrupolar hydrogen bond structure
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing an acrylic functional monomer containing a supramolecular quadruple hydrogen bond structure. The optimization of reaction solvent and reaction time can obtain acrylate functional monomers with supramolecular quadruple hydrogen bond structure. The synthesized acrylate functional monomer molecule containing supramolecular quadruple hydrogen bond structure contains terminal double bonds substituted by acrylic acid methyl group in the structure, so that the functional monomer molecule has high activity and is easy to polymerize. The molecular structure also contains a supramolecular quadruple hydrogen bond unit that can form a self-complementary structure, which can reduce the generation of non-specific recognition sites. The molecular structure contains ureido-pyrimidinone supramolecular quadruple hydrogen bond structure units, which can form multiple hydrogen bond structures with high multi-site binding constants with template molecules, which can significantly improve the recognition efficiency of template molecules and the effect of molecular imprinting. The method has the advantages of simple operation, short reaction time and simple post-processing.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ENG
Targeting of ERB antigens
A conjugate comprising a) a trifunctional cross-linking moiety, to which is coupled b) an affinity ligand via a linker 1, c) a cytotoxic agent, optionally via a linker 2, and d) an anti Erb antibody or variants thereof having the ability to bind to Erb antigens expressed on mammalian tumour surfaces with an affinity-binding constant of at least 5x10<6>M<-1>, wherein the affinity ligand is biotin, or a biotin derivative having essentially the same binding function to avidin or streptavidin as biotin, wherein stability towards enzymatic cleavage of the biotinamide bond has been introduced in linker 1.
Owner:米特拉医药股份公司
Method for the characterization of the three-dimensional structure of proteins employing mass spectrometric analysis and computational feedback modeling
InactiveUS20060277017A1Particle separator tubesAnalogue computers for chemical processesESI mass spectrometryProtein-protein complex
A method for characterizing the three-dimensional surface structure of molecules, particularly proteins and protein complexes, employing mass spectrometric analysis, an electrospray ionization (ES) source, a novel data interpretation process that utilizes comparisons of particular binding constants (KB) and heats of formation (ΔHf), and computational feedback modeling.
Owner:HV OPS H NU
Construction method and application of three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model of bcl-2 protein inhibitor
InactiveCN102262715APredicted binding constantFast Prediction of Binding ConstantsSpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a method for constructing a three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship model of a B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein inhibitor and application of the method and belongs to the technical field of biological information. The method comprises the following steps of: according to the known small molecule inhibitor, establishing the three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship model of the Bcl-2 protein inhibitor by using a three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship technology; and further improving the accuracy of the model by using technologies for analyzing molecular similarity, optimizing molecular conformation, optimizing parameters and the like. By the invention, the Bcl-2 protein binding constants of an active unknown compound can be quickly predicted, and clues of the active compound are acquired within short time. Compared with the conventional high-throughput screening technology, the invention has the advantages of greatly improving screening efficiency and reducing cost.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Hyperpolarization <129>Xe switch type magnetic resonance molecular probe for identifying diamine oxidase
InactiveCN109082457AImprove targetingNot immune to fluorescence quenching effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisResonanceMolecular probe
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical analysis and particularly relates to a hyperpolarization <129>Xe switch type magnetic resonance molecular probe for identifying diamine oxidase. The hyperpolarization <129>Xe switch type magnetic resonance molecular probe comprises cucurbit[6]uril and putrescine hydrochloride. The principle of the molecular probe is characterized in thata substrate (putrescine hydrochloride) with high cucurbit[6]uril binding force is converted by diamine oxidase into a product (1-pyrroline) which does not combine with cucurbit[6]uril; before enzymatic reaction, a <129>Xe hyperpolarization chemical exchange saturation transfer signal in the cucurbit[6]uril is inhibited by strong cucurbit[6]uril conjugate until the enzymatic reaction oxidizes the substrate into the product; due to the fact that the binding constant of putrescine hydrochloride@cucurbit[6]uril is several magnitude orders larger than that of <129>Xe@cucurbit[6]uril and (1-pyrroline)@cucurbit[6]uril cannot combine, the <129>Xe hyperpolarization chemical exchange saturation transfer signal in the cucurbit[6]uril appears after the enzymatic reaction through enhanced <129>Xe cucurbit[6]uril interaction, and diamine oxidase identification is achieved through the <129>Xe hyperpolarization chemical exchange saturation transfer signal in the cucurbit[6]uril.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Laundry detergent and/or fabric care compositions
The present invention relates to chemical entities comprising more than one chemical moiety linked to a cellulose binding domain. The present invention also relates to laundry detergent and / or fabric care compositions containing one or more of these chemical entities. The laundry detergent and / or fabric care compositions of the present invention, when containing these chemical entities, can provide a more efficient concentration of the chemical ingredients on the surface of the fabric and thus provide improved benefits.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for detecting pancreatic cancer
InactiveCN103348247AAccurate detectionEasy to detectBiological material analysisBiological testingSpecific lectinHaptoglobin
To provide a method of accurately detecting pathological haptoglobin using a lectin having strong affinity and high specificity for fucose. The method of the present invention for detecting pancreatic cancer is characterized in that a fucose ±1†’6 specific lectin is allowed to act on pathological haptoglobin contained in a sample obtained from a living body, said lectin: (1) being extractede from basidiomycetes, (2) having a molecular weight of 4,000 to 40,000 as determined by the SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and (3) having affinity for a fucose ±1†’6 sugar chain with a binding constant of 1.0 × 10 4 M -1 or more at 25°C.
Owner:J OIL MILLS INC
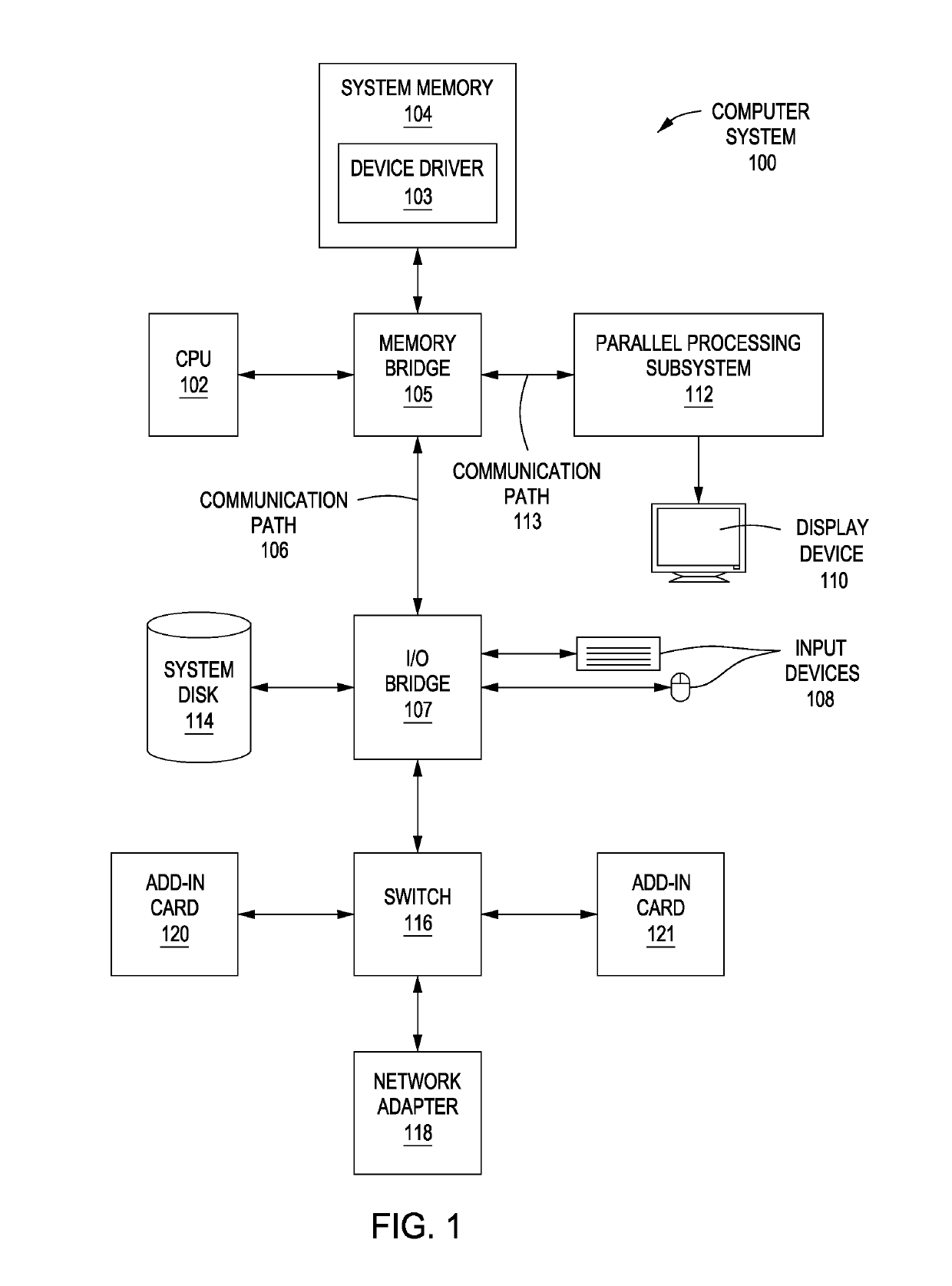
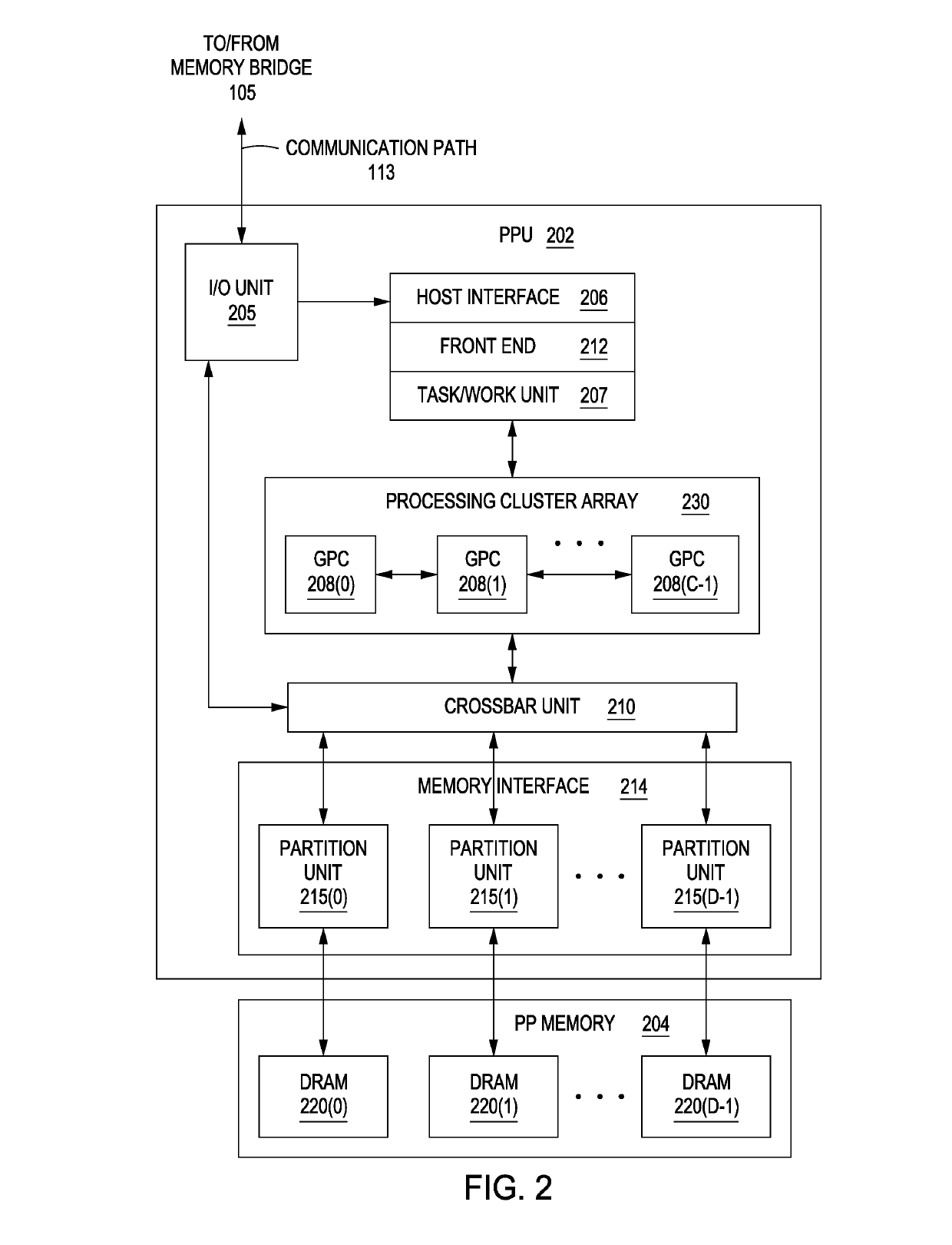
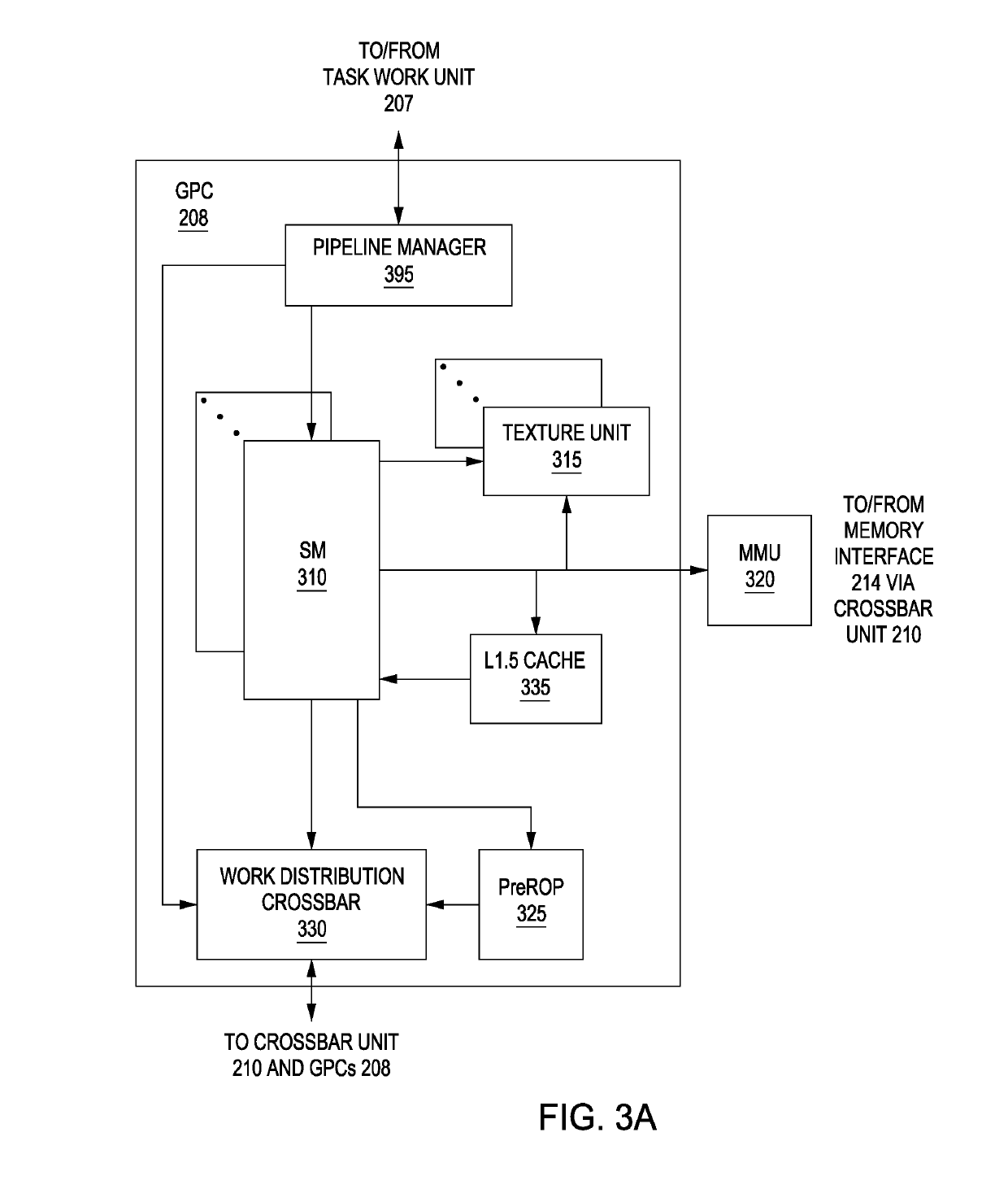
Binding constants at runtime for improved resource utilization
ActiveUS20190146817A1Limited amountRegister arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionResource utilizationApplication software
A just-in-time (JIT) compiler binds constants to specific memory locations at runtime. The JIT compiler parses program code derived from a multithreaded application and identifies an instruction that references a uniform constant. The JIT compiler then determines a chain of pointers that originates within a root table specified in the multithreaded application and terminates at the uniform constant. The JIT compiler generates additional instructions for traversing the chain of pointers and inserts these instructions into the program code. A parallel processor executes this compiled code and, in doing so, causes a thread to traverse the chain of pointers and bind the uniform constant to a uniform register at runtime. Each thread in a group of threads executing on the parallel processor may then access the uniform constant.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method
The invention discloses a tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method comprises the following processes of collecting tea geometrid antenna total RNA, acquiring total length of a tea geometrid odorant binding protein by RT-PCR, constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the tea geometrid odorant binding protein, inducing the expression of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein by IPTG, carrying out the purification of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein by nickel sepharose gel affinity column, acquiring a binding reaction spectrum of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein and tea leaf smell volatiles by a competitive fluorescent combination method, and determining that the tea leaf smell volatile reducing relative fluorescence intensity of 1-NPN to less than 50% and having the binding constant of 13-45 micromoles per liter is the plant attractant of tea geometrid. The tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method provides a novel means for screening and designing a formula of a plant tea geometrid smell information attractant.
Owner:HANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Compositions and methods for treating conditions related to ephrin signaling with cupredoxins and mutants thereof
InactiveUS9096663B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalEphrin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods of use of cupredoxins, and variants, derivatives and structural equivalents of cupredoxins that interfere with the ephrin signaling system in mammalian cells. Specifically, the invention relates to compositions and methods that use cupredoxins, such as azurin, rusticyanin and plastocyanin, and variants, derivatives and structural equivalents thereof, to treat cancer in mammals. The invention specifically includes mutants with altered Eph binding constants and selectivities.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Compound and preparation method, fluorescent dye and fluorescent probe thereof
InactiveCN107586292AEnhanced fluorescence emission intensityHigh strengthOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesSolubilityDouble bond
The invention provides a compound. The compound is shown in a formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 are selected from H or groups shown in a formula (II) independently, and at least one of the R1 and R2 is agroup selected from the formula (II); R3 is selected from groups consisting of H, F, Cl, Br, OH, OCH3, N(CH3)2 or C1-C6 alkyl groups, and R4 is selected from the C1-C6 alkyl groups. Compared with anexisting embedded fluorescent probe, since a fluorescent probe provided by the invention is provided with a large electron conjugated system and a large plane, the fluorescence emission intensity of the molecule of the fluorescent probe can be influenced by the intensity of a charge transfer effect in the molecule of the fluorescent probe, and when the fluorescent probe combines with G-quadruplexRNA specifically, the flexibility of rotary intramolecular double bonds is limited, so that the effect of intramolecular charge transfer is enhanced, and thus the fluorescence intensity is increased;the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has no biological toxicity, no phototoxicity and no fluorescence quenching, meanwhile, the solubility in water and the cellular permeability are greatlyimproved, and the fluorescent probe has a high binding constant in detection and an extremely low limit of detection.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for rapidly evaluating binding strength of ultrafiltration membrane and small organic molecular pollutant
The invention relates to a method for predicting the binding strength of an ultrafiltration membrane surface adsorption unit and a small molecular pollutant. The method particularly comprises the steps of firstly, constructing a structure of a system; then calculating a binding free energy curve of a small molecule and the ultrafiltration membrane surface adsorption unit, and on this basis, figuring out a binding constant. A binding mechanism is obtained by analyzing a binding process, and a theoretical direction is provided for the optimization of the adsorption unit. Results indicate that the calculating result obtained by using the method is accurate, the design cost can be effectively reduced, and the design efficiency is remarkably improved. Thus the theoretical method provided by the invention can be used for predicting the binding strength of the ultrafiltration membrane surface adsorption unit and the small molecular pollutant.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Laundry detergent and/or fabric care composition comprising modified cellulase
InactiveCN1307634AInhibit transferBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsDetergent compounding agentsCelluloseCellulose binding
The present invention relates to a modified enzyme which comprises a catalytically active amino acid sequence of a cellulolytic enzyme linked to an amino acid sequence comprising a Cellulose Binding Domain (CBD) having a relative binding constant (Kr-a) for binding to amorphous cellulose higher than 2.4l / gcellulose, preferably higher than 3.5l / gcellulose, more preferably higher than 4l / gcellulose, for selective binding and hydrolysis of amorphous cellulose of cotton containing fabrics in a laundry and / or fabric care application. The present invention further relates to laundry detergent and / or fabric care compositions comprising this modified enzyme.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
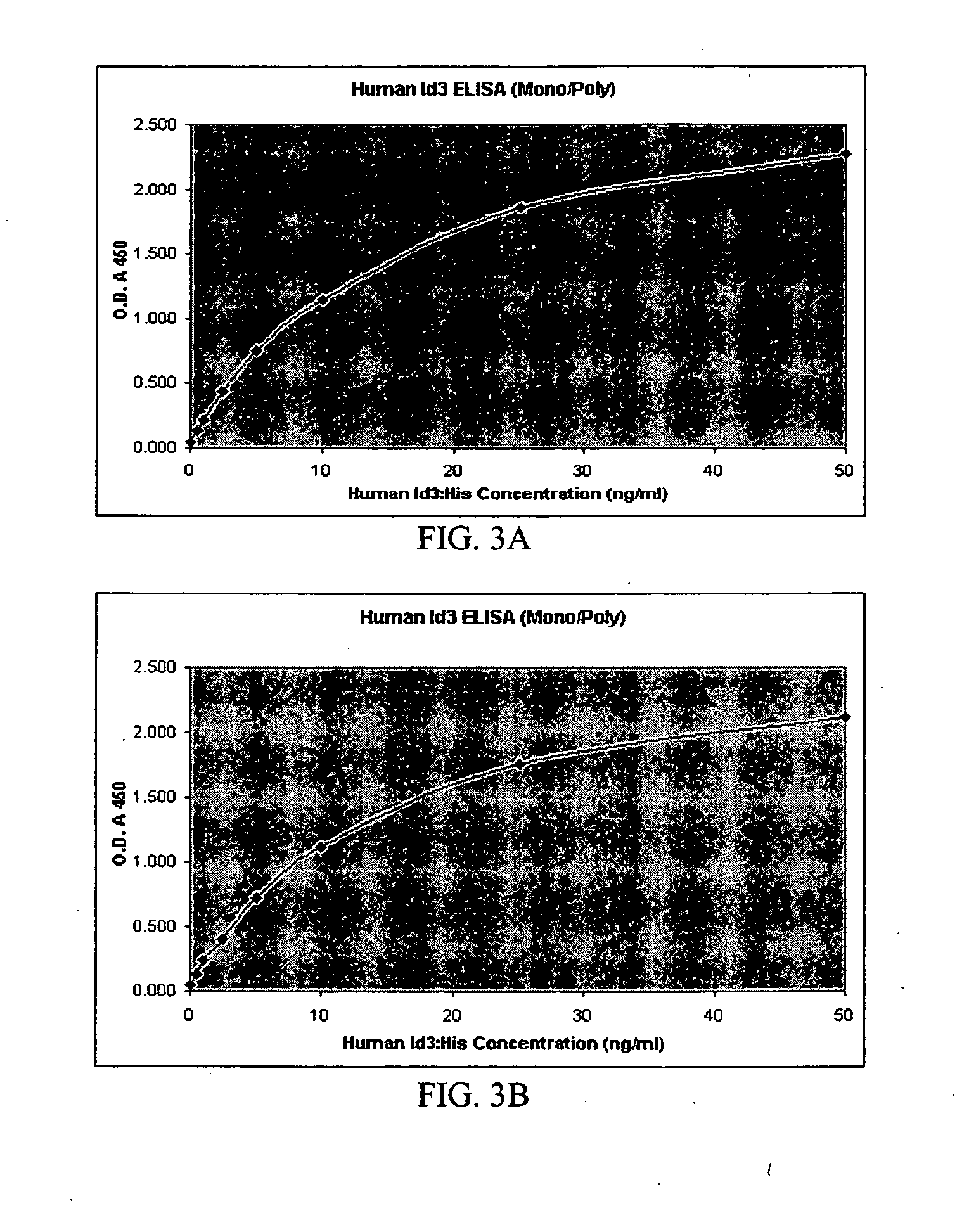
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies against mouse/human Id3 proteins
InactiveUS20070178531A1SensitiveImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisStainingSpecific detection
The present invention relates to a rabbit monoclonal antibody that binds to human Id3 protein and / or mouse Id3 protein with high specificity and high affinity. The antibody has a binding constant, measured with respect to human Id3 protein or mouse Id3, of greater than 1×108 / molar. The antibody has no substantial cross-reactivity to other family Id proteins such as Id1, Id2, or Id4, or other endogenous proteins present in the cells that express Id3 protein. The specificity and high affinity of the rabbit monoclonal antibodies of the present invention allows sensitive and specific detection and / or quantitation of human or mouse Id3 protein in biological samples. The antibodies are useful in immunochemical-based assays such as ELISA, western blot, and immunohistochemical staining.
Owner:BIOCHECK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com