Method for the characterization of the three-dimensional structure of proteins employing mass spectrometric analysis and computational feedback modeling
a three-dimensional structure and protein technology, applied in the field of three-dimensional surface structure characterization of proteins and protein complexes, can solve the problems of reducing sensitivity, reducing the sensitivity of ions, and expensive operation of strong countercurrent gas flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example one
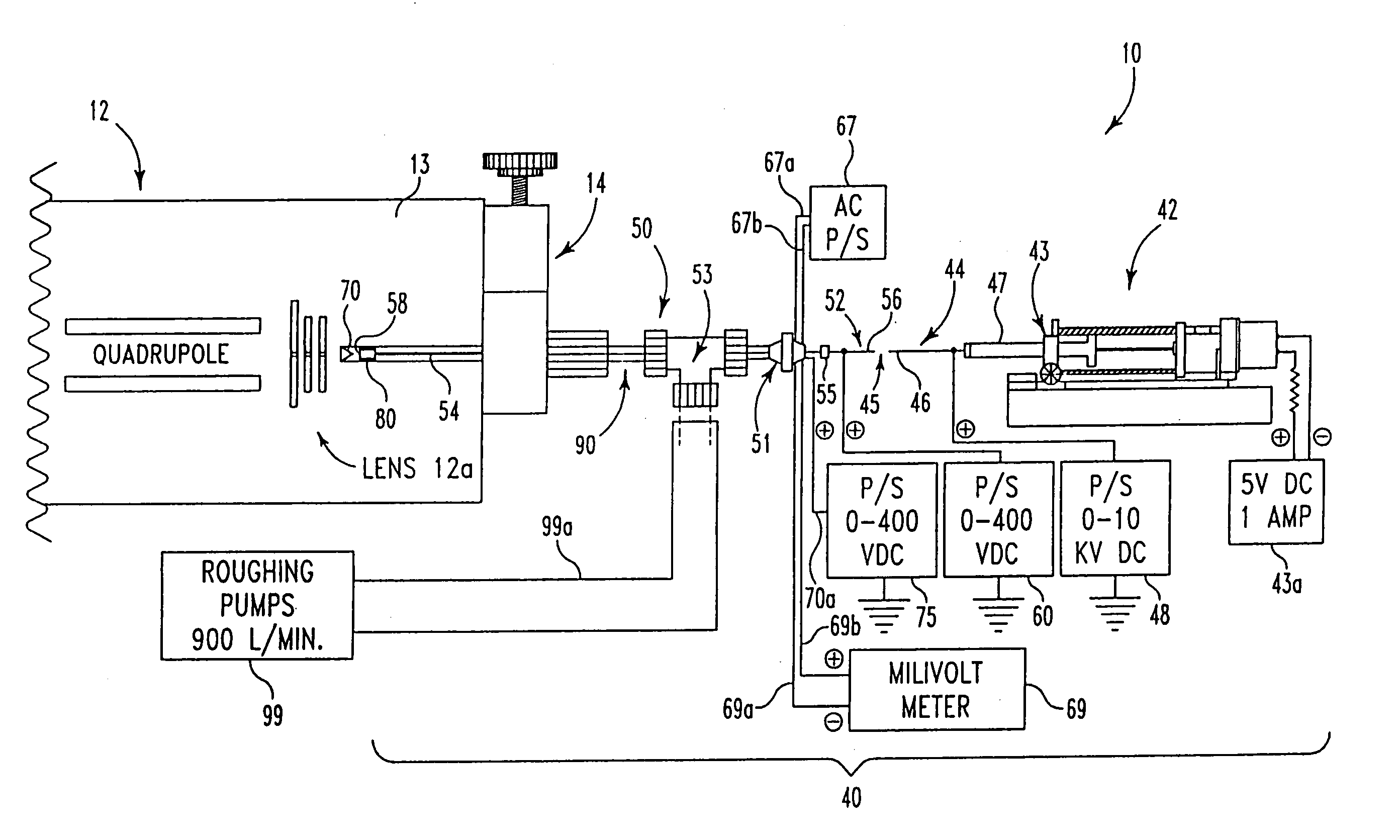
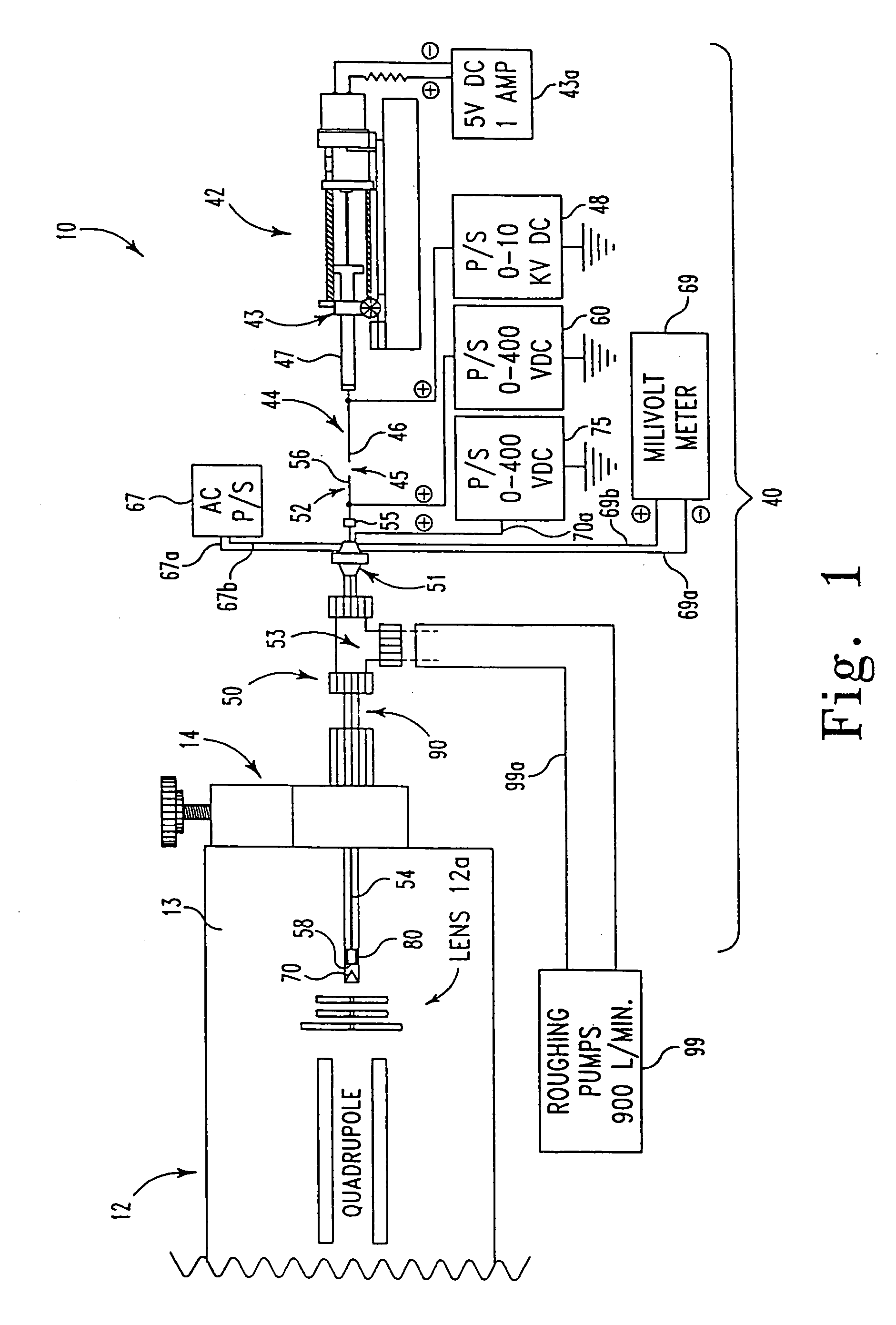
[0070] At least three kinds of quadrupole mass spectrometers have been used with this invention to characterize the ES probe: two single quadrupoles and one custom, double quadrupole instrument. However, any type of mass spectrometer system could accommodate this ES probe interface.
[0071] In this experiment, the following polypeptides were used to optimize the ES probe of this invention: angiotensin III (Sigma #A-0903, 30 pmol / μL, bradykinin (Sigma #B-3259, 47 pmol / μL), renin substrate (Sigma #R-8380, 56 pmol / μL, melittin (Sigma #M-2272, 50 pmol / μL), and glucagon (FIG. 6, Sigma #G-1774, 50 pmol / μL). These polypeptides were prepared with equal parts of methanol and 1% acetic acid / water. Cytochrome c (FIG. 7, horse heart, Sigma #C-2506, 67 pmol / μL) was prepared with 2% acetic acid / water and methanol.
[0072] The ES spectrum of glucagon depicted in FIG. 6 was characterized using a standard EI / CI lens assembly on an Extrel dual quadrupole mass spectrometer (50 in 50:50 MeOH:H2O, 1% acet...
example two
[0074] A study was conducted of the non-covalent interactions of three crown ethers, dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (#1), 18-crown-6 (#2), and dibenzo-18-crown-6 (#3) (FIGS. 17A-17C) with three types of cytochrome c; horse tuna and yeast, utilizing the ES probe 50 and method of this invention. Each of the three different types of cytochrom c displayed different degrees of binding for each of the three crown ethers; however, the binding of the crown ethers was found to increase in the order given above with dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 binding the most tightly and dibenzo-18-crown-6 binding the least tightly.
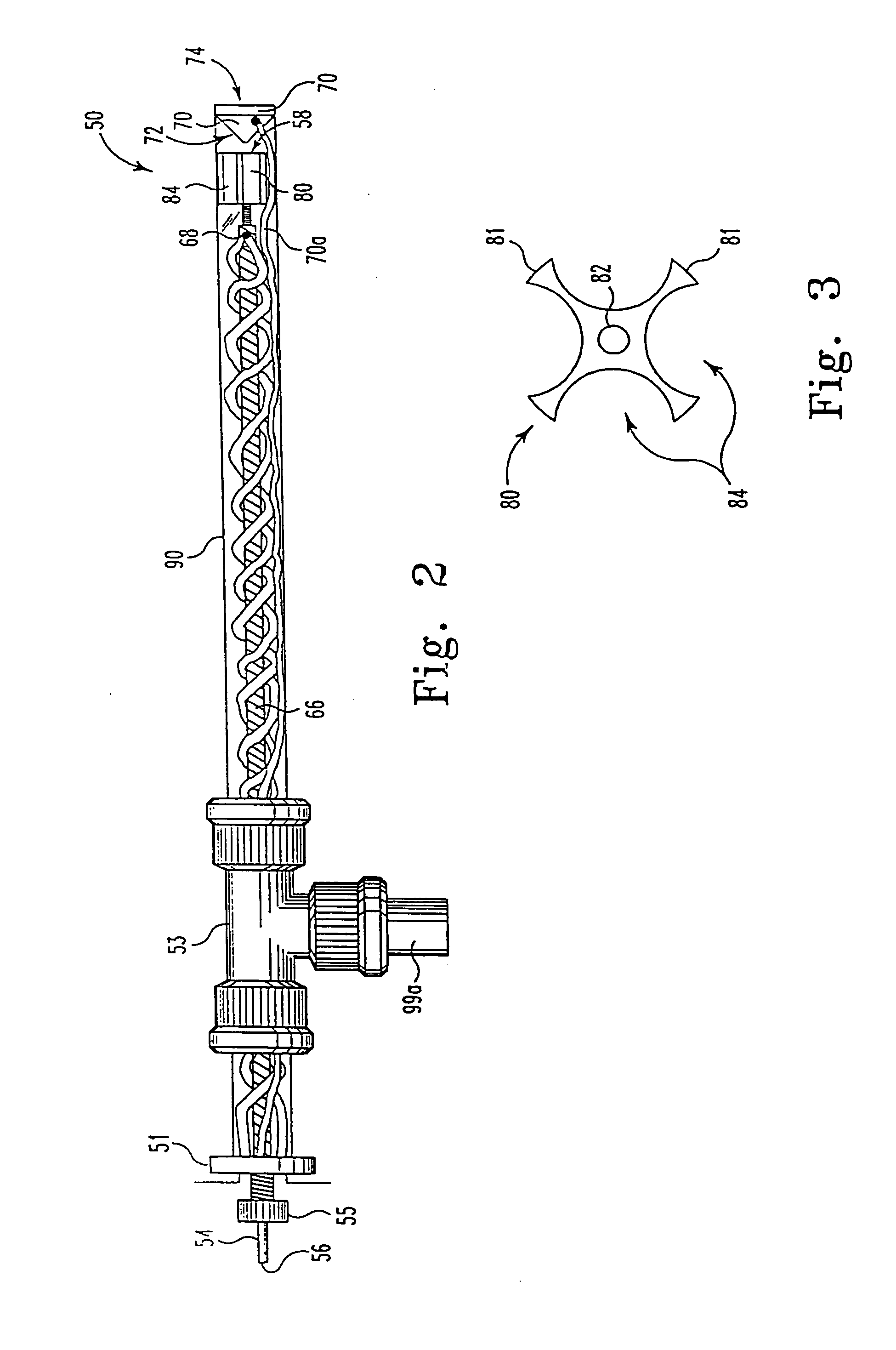
[0075] More particularly, the experiments showing binding of crowns to cytochrome c were done by adding 1, 2, and 3 mol ratios to a 70 pmol / μL mixture of the three different cytochrome c's. The solutions were prepared with equal parts of methanol / water with 1% acetic acid. Typical sample conditions were, 95° C., 2 μL / min, 4000 VDC on the syringe, 170 VDC on the capillary tube, and 60 VDC ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com