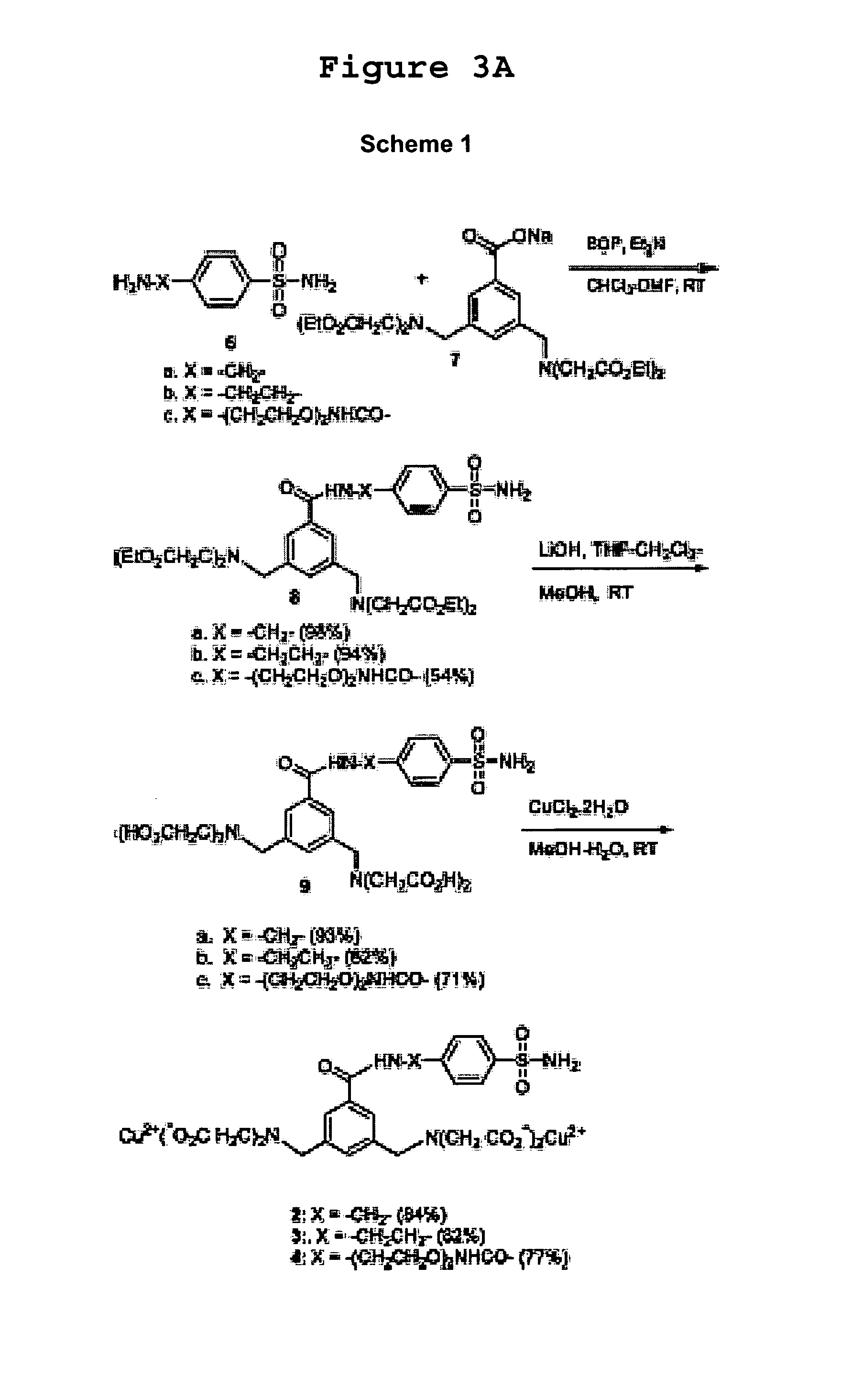
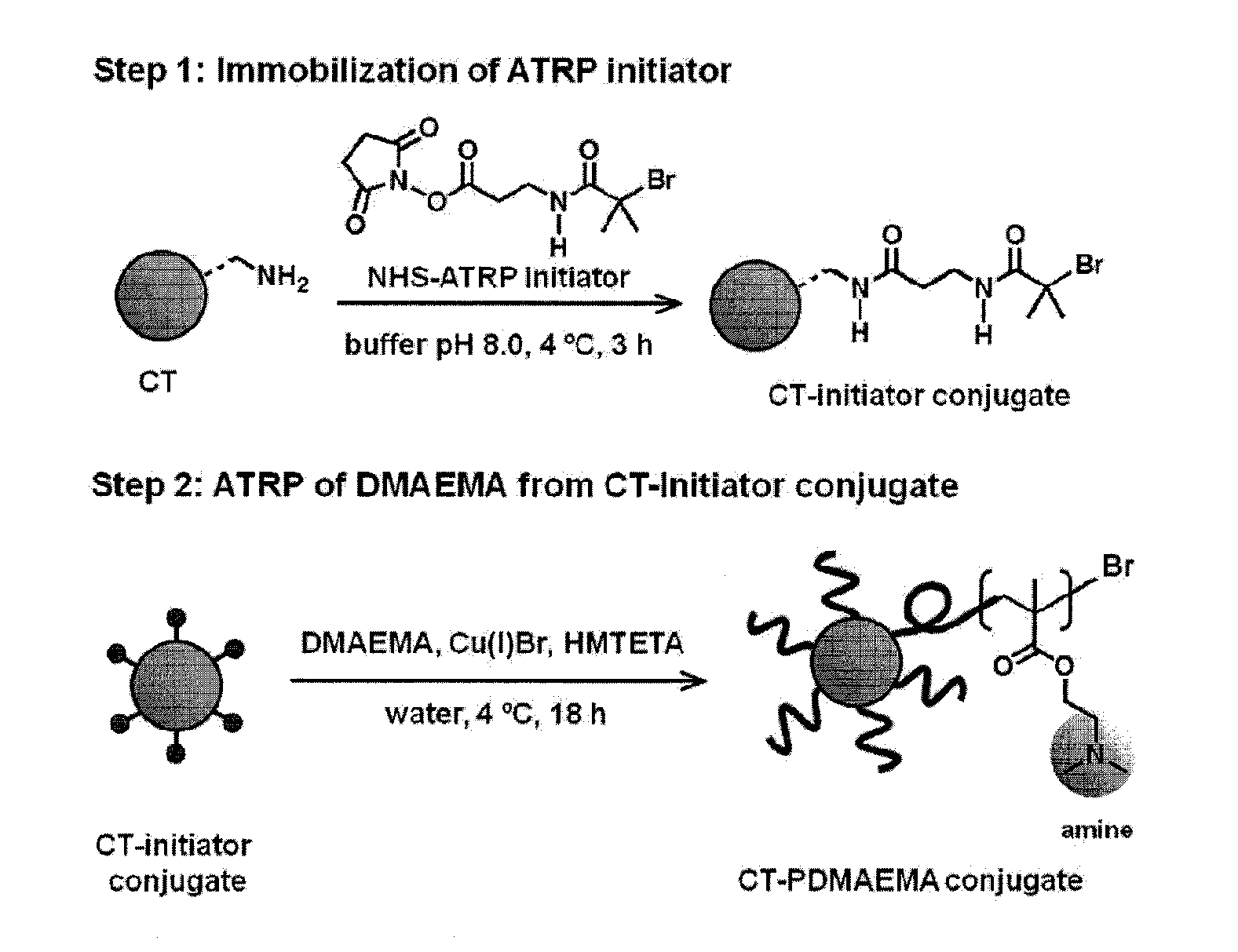
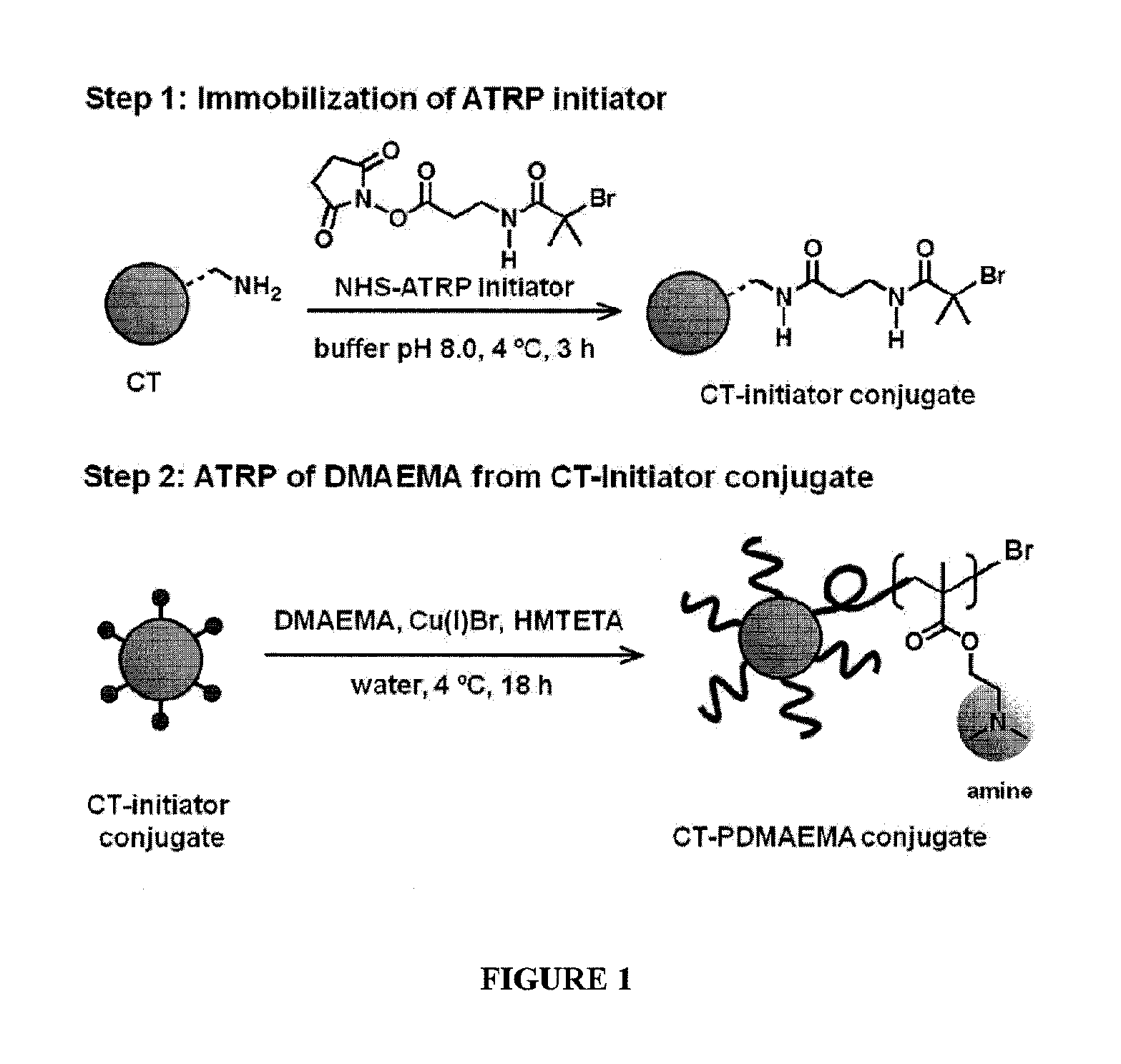
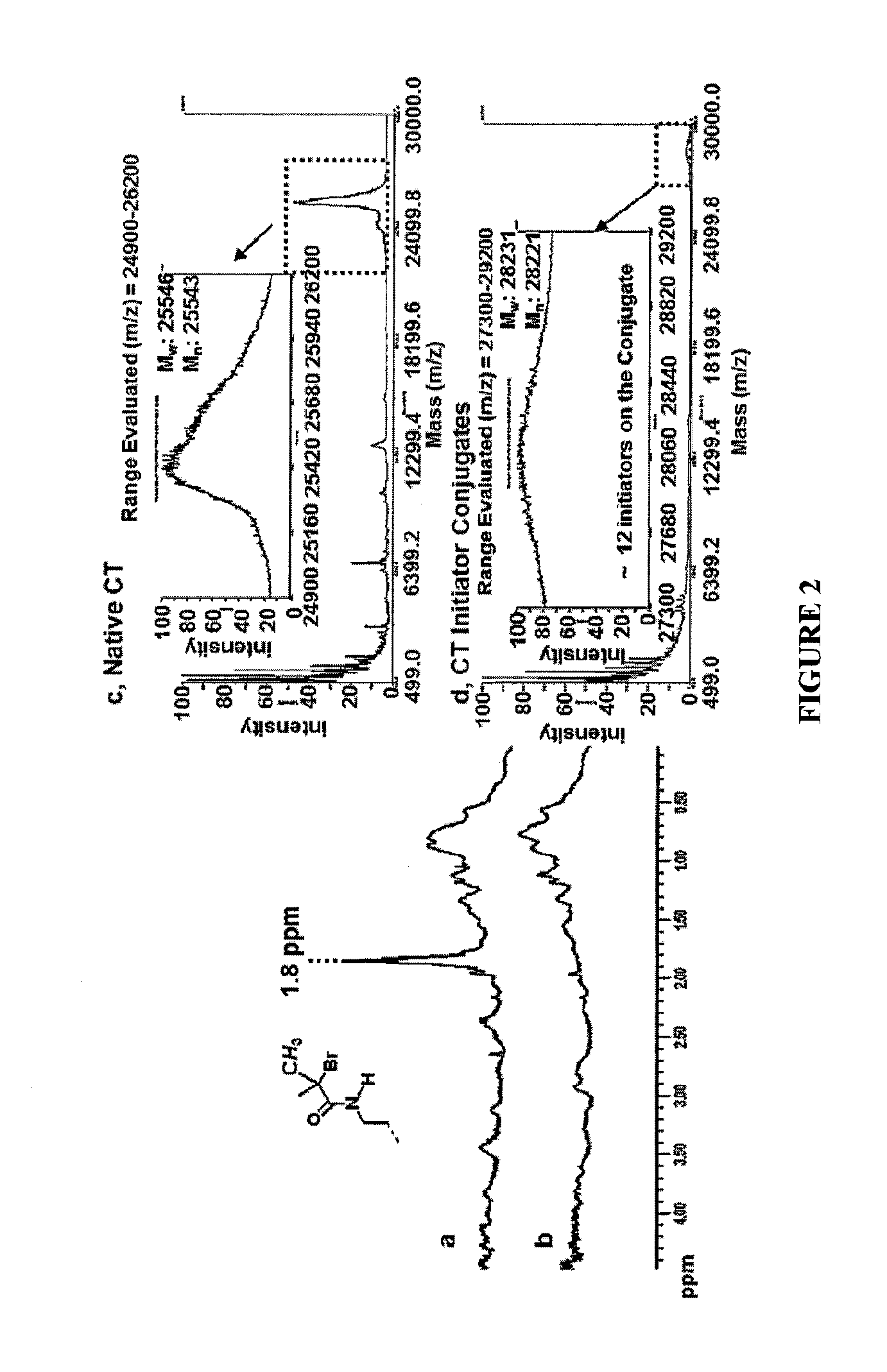
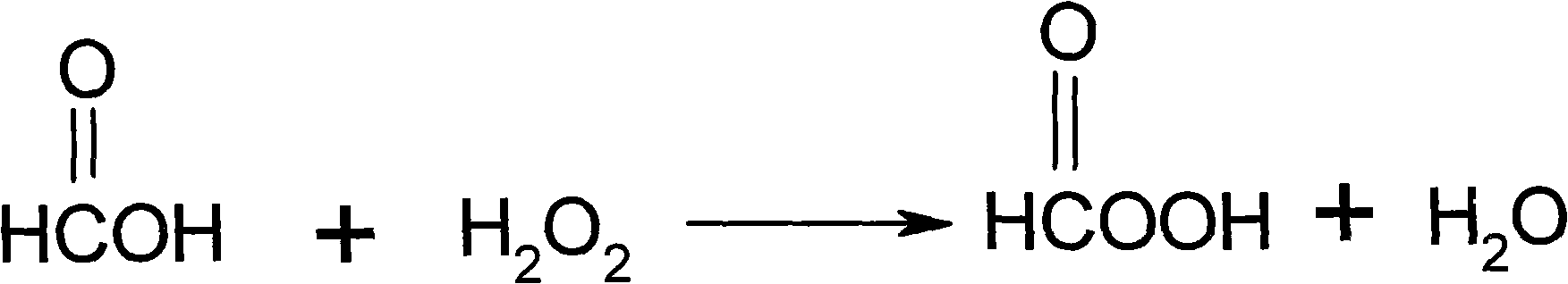
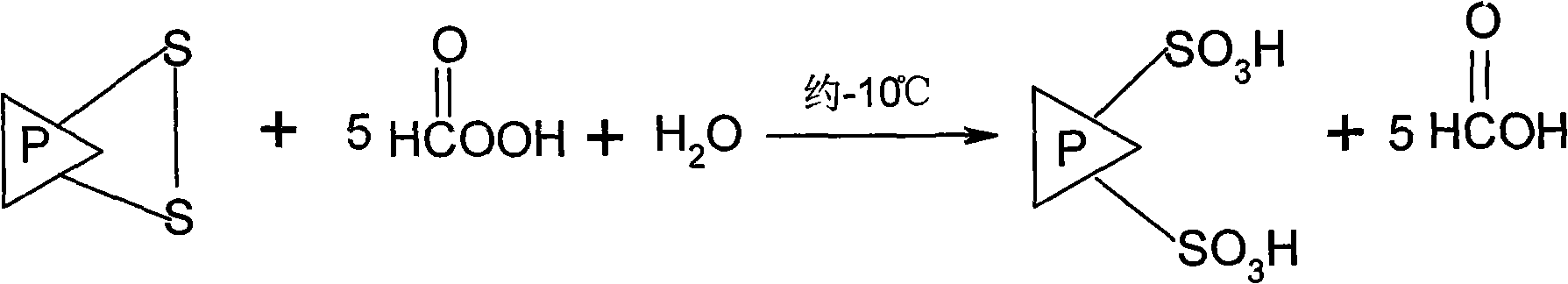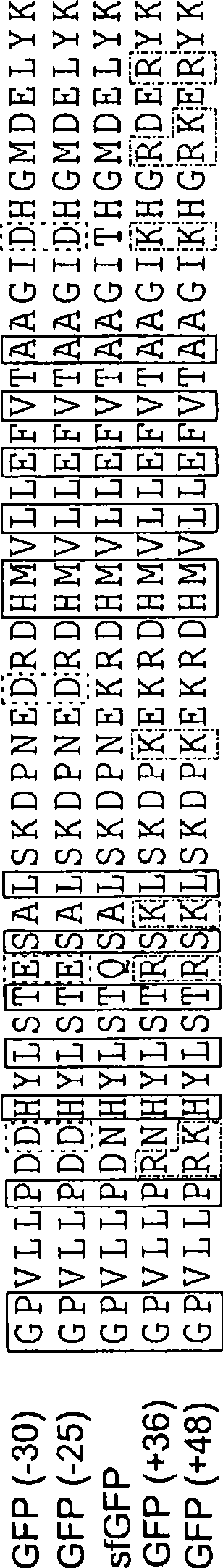Patents
Literature
121 results about "Protein surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein surface remodeling
ActiveUS20120129759A1Improve thermodynamic performanceImprove solubilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesBiotin-streptavidin complexBiochemistry
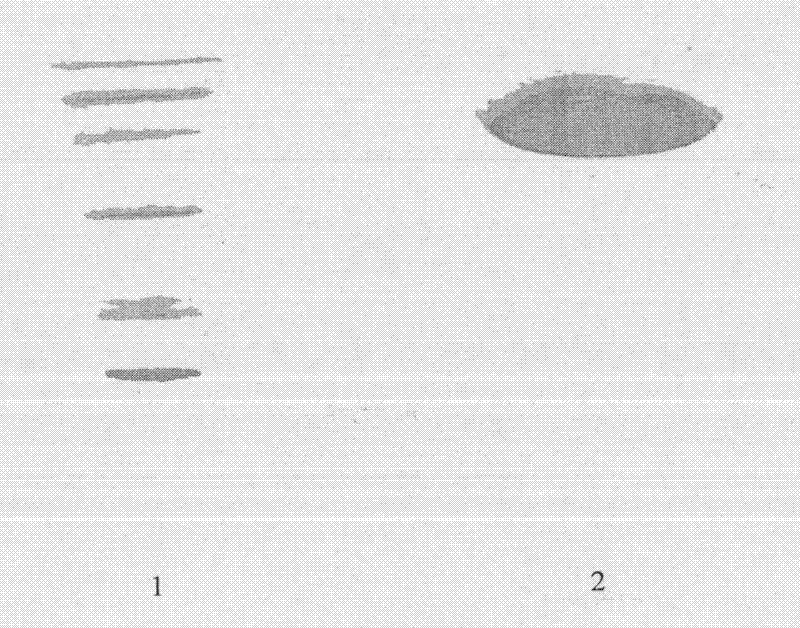
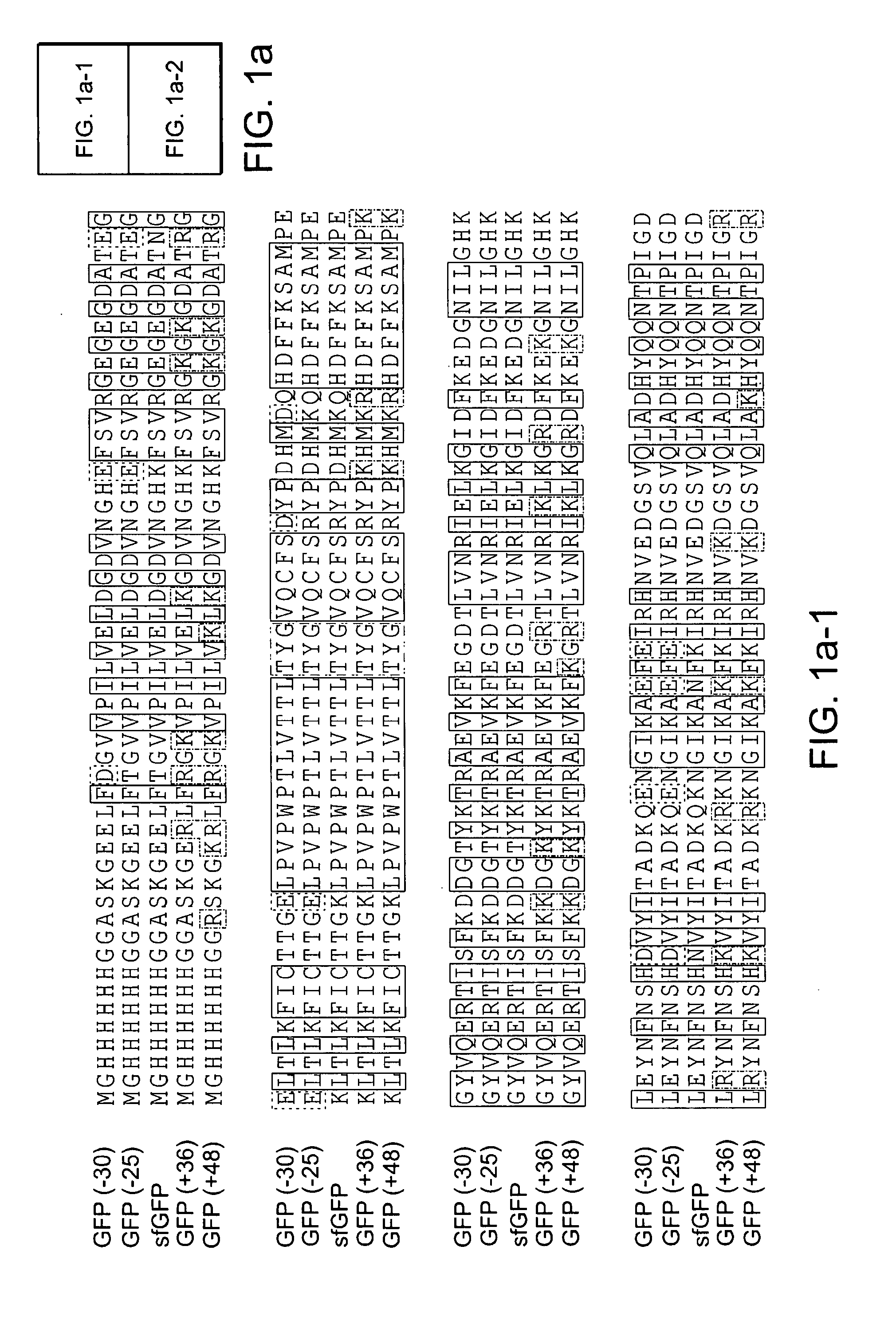
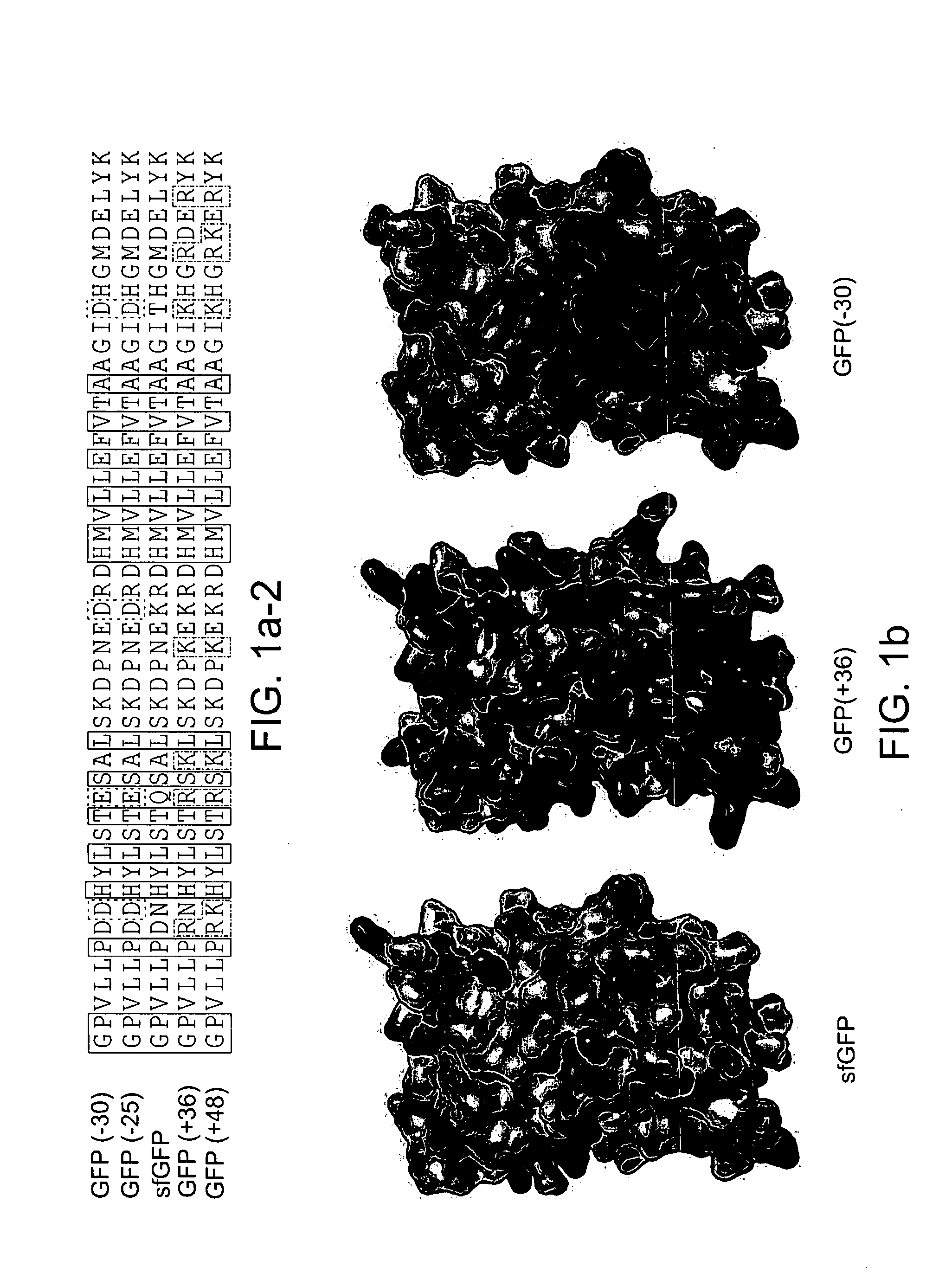
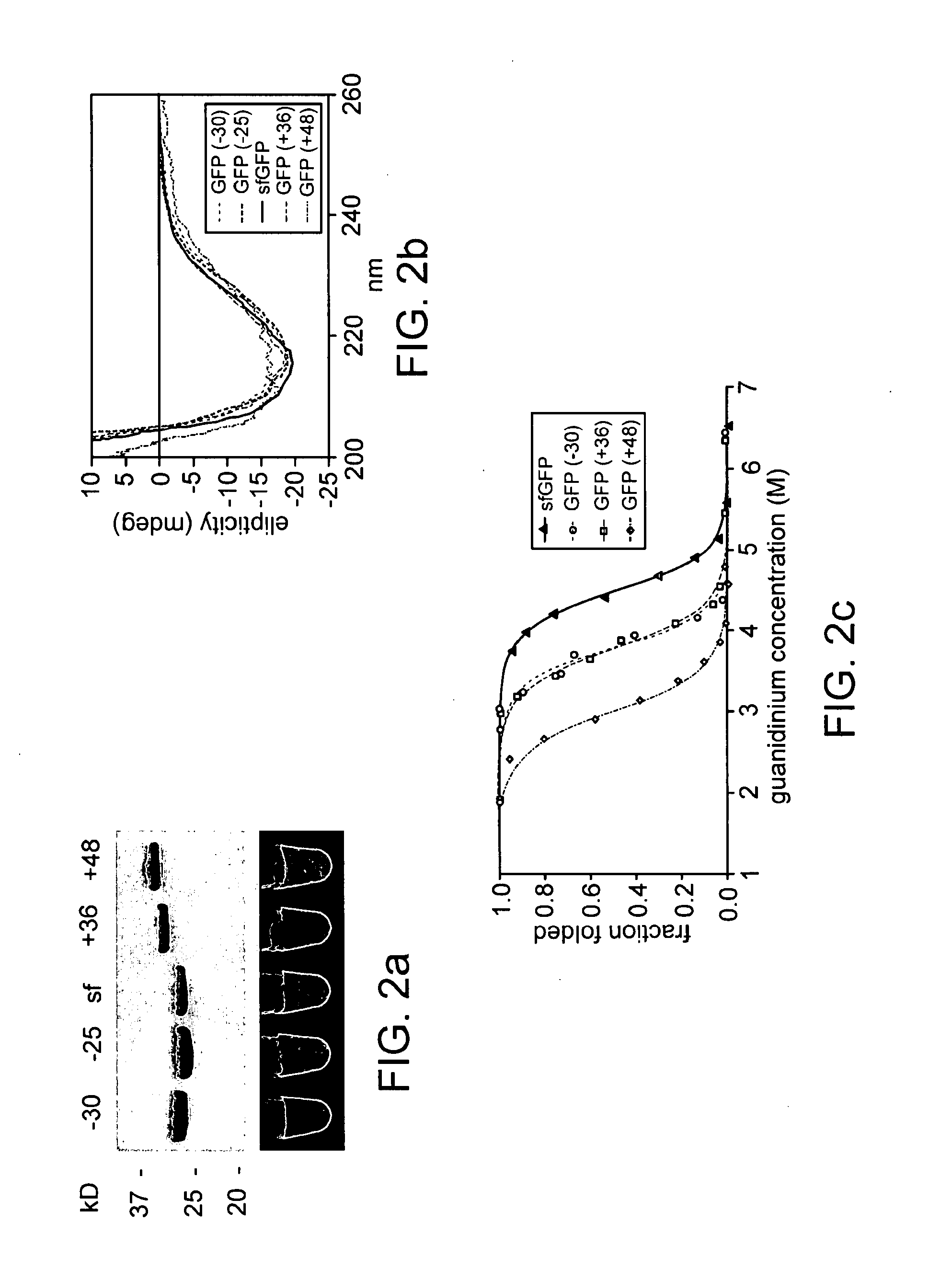
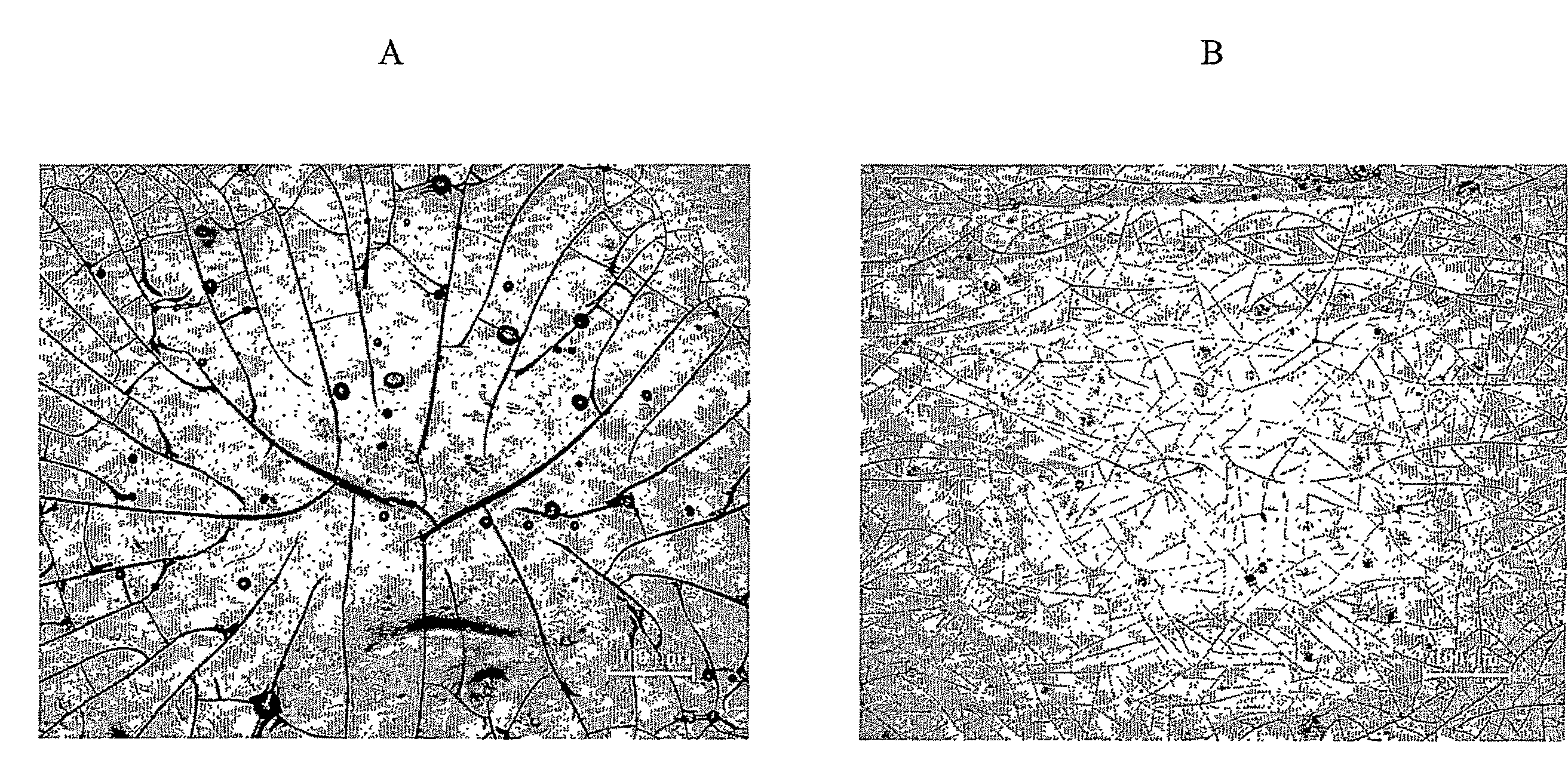
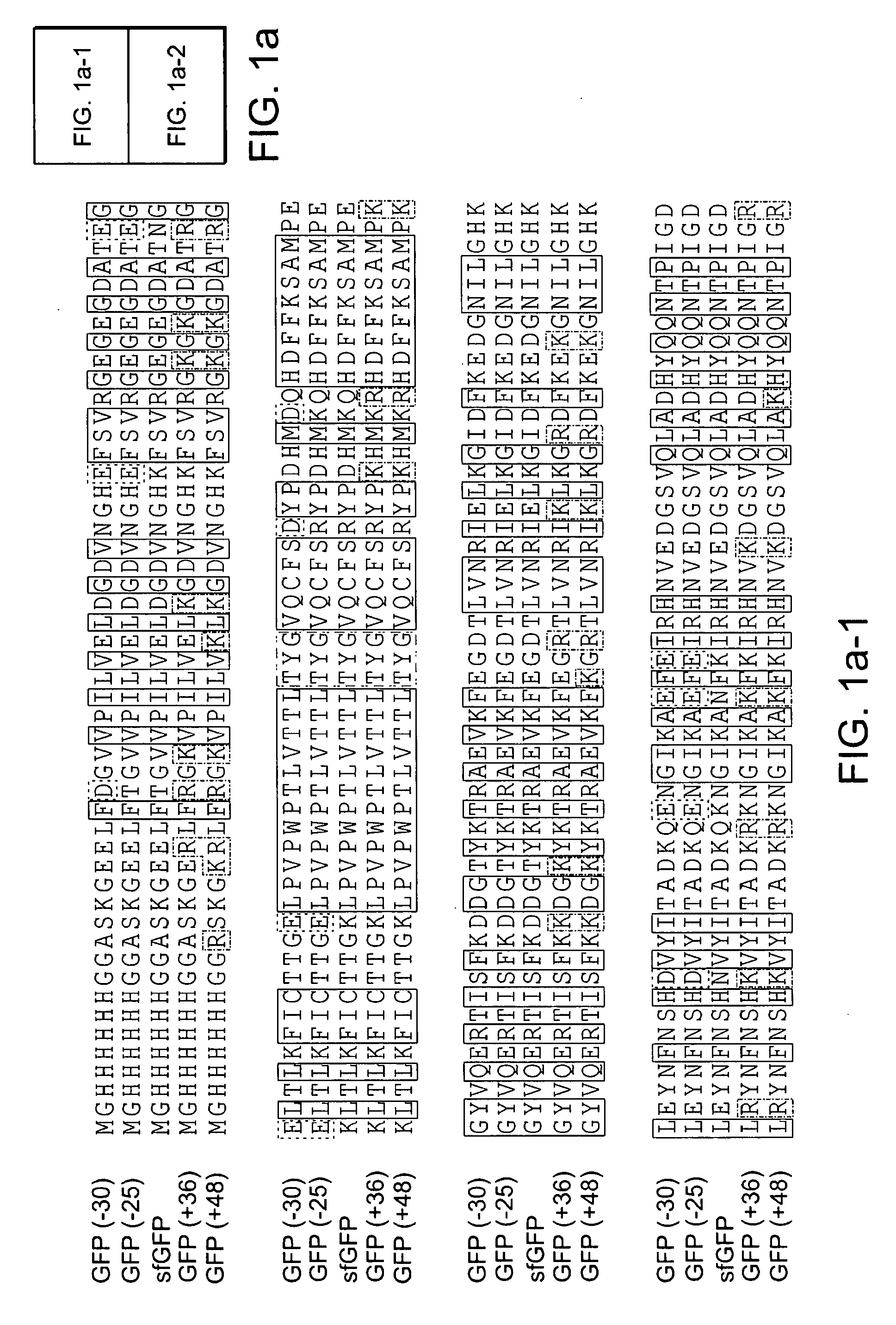
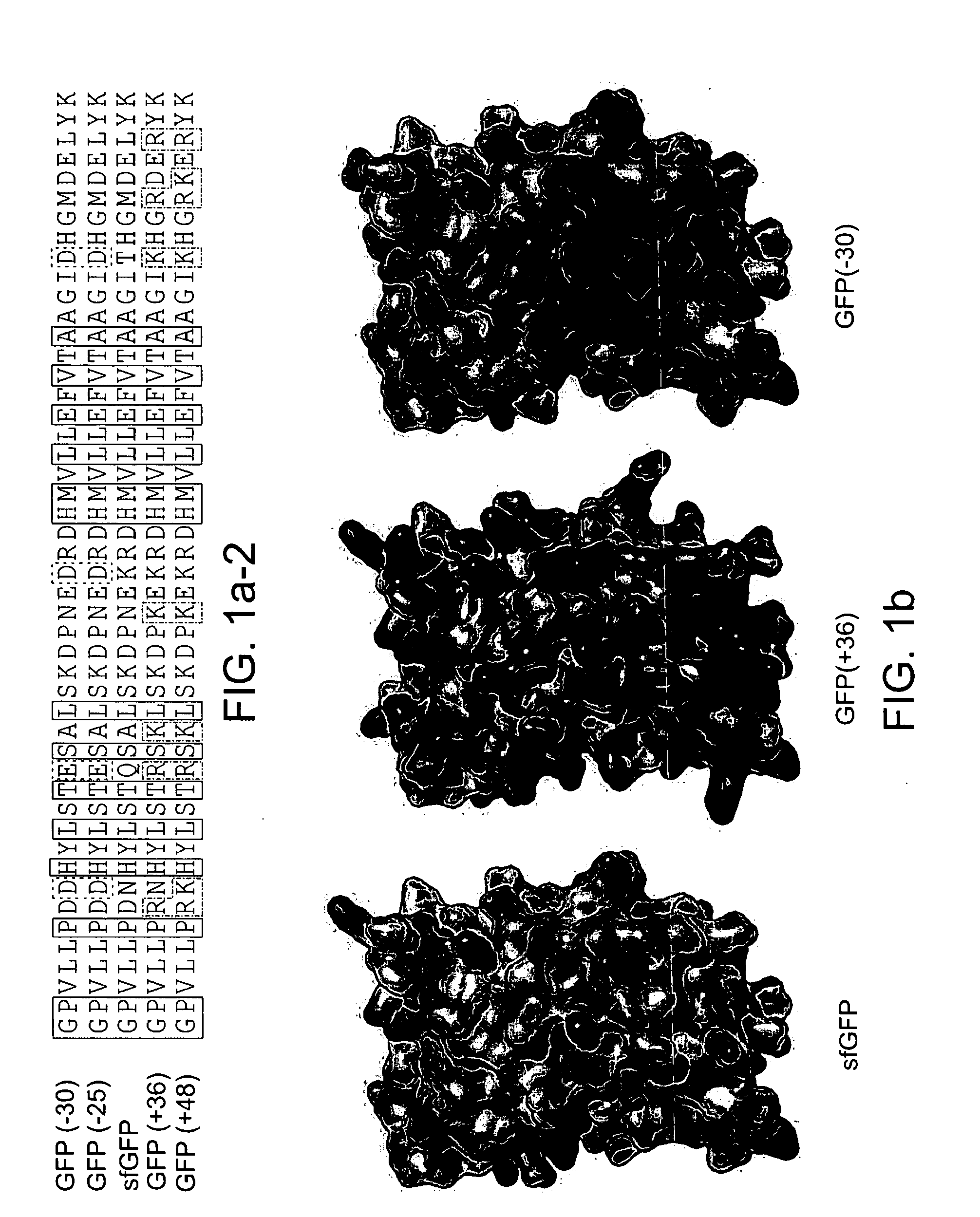
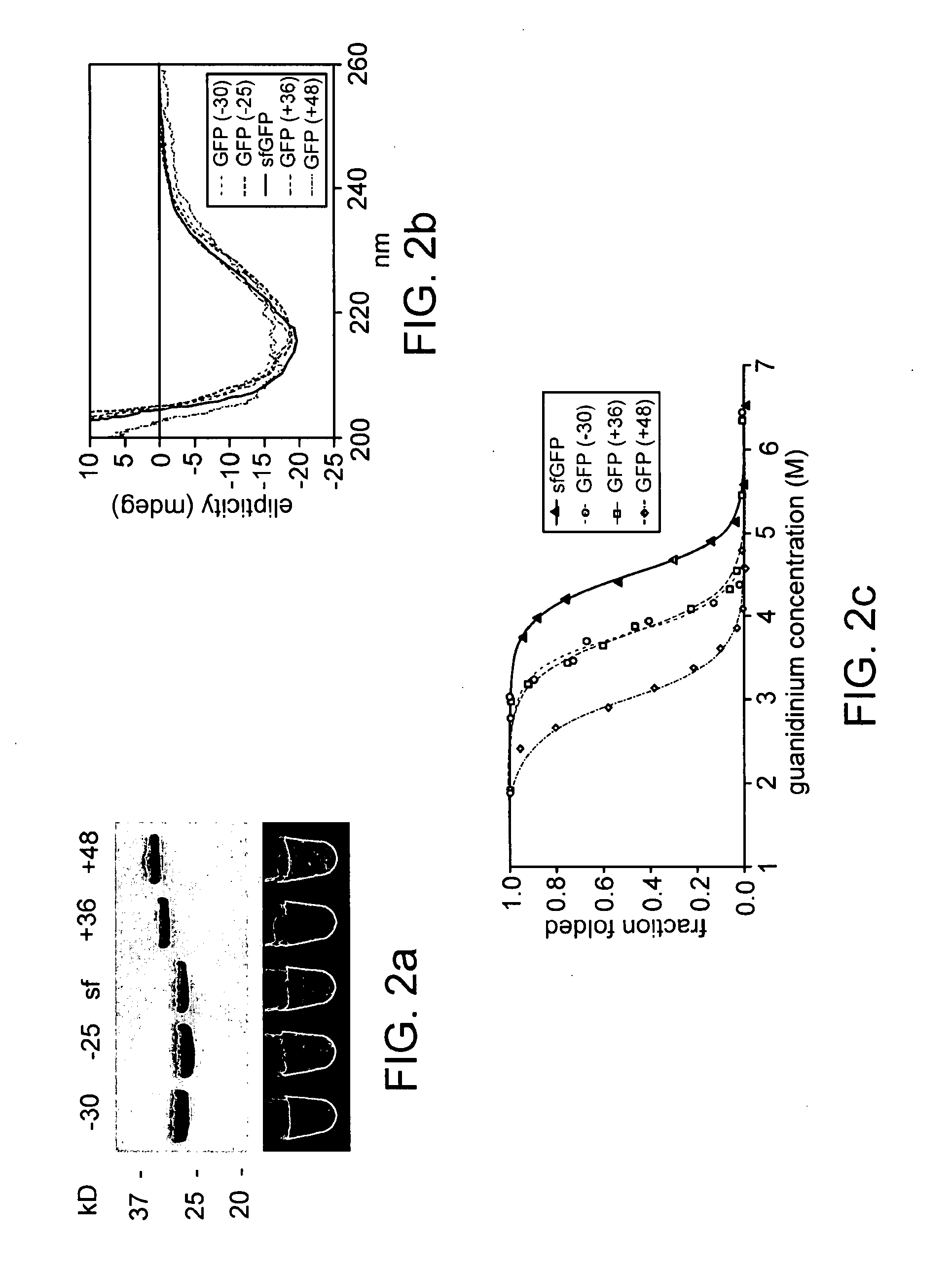
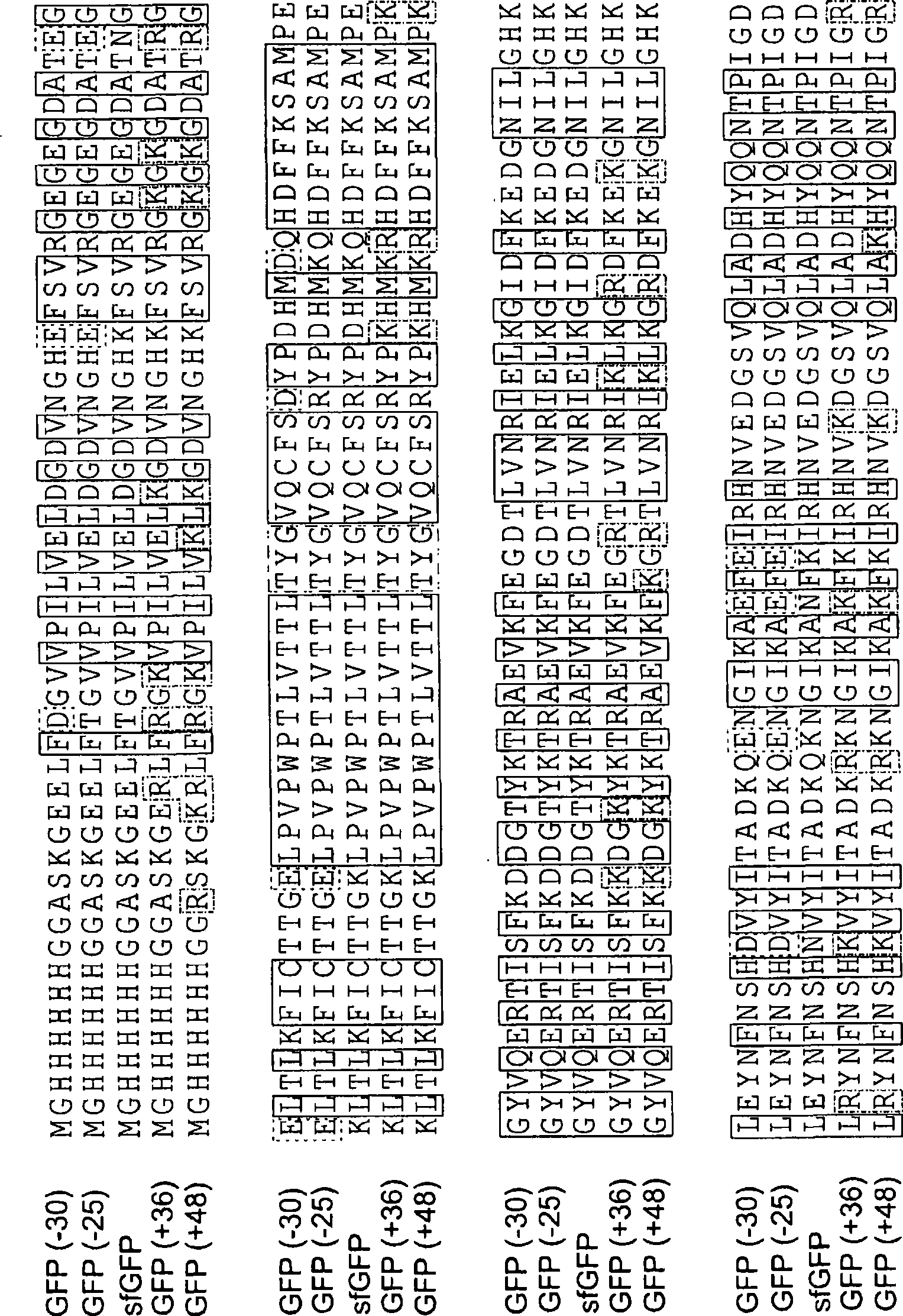
Aggregation is a major cause of the misbehavior of proteins. A system for modifying a protein to create a more stable variant is provided. The method involves identifying non-conserved hydrophobic amino acid residues on the surface of a protein, suitable for mutating to more hydrophilic residues (e.g., charged amino acids). Any number of residues on the surface may be changed to create a variant that is more soluble, resistant to aggregation, has a greater ability to re-fold, and / or is more stable under a variety of conditions. The invention also provides GFP, streptavidin, and GST variants with an increased theoretical net charge created by the inventive technology. Kits are also provided for carrying out such modifications on any protein of interest.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Hair treatment compositions incorporating hair substantive polymers
The invention provides a hair treatment composition comprising a hair substantive polymer, the hair substantive polymer comprising a polymeric backbone bearing: (a) at least one side chain which is formed from a hair fiber targeting group which is covalently linked to the polymeric backbone, the hair fiber targeting group being a non-cationic species which is capable of specifically interacting with the protein surface of the hair fiber in a non-covalent interaction having a bond energy ranging from 0.5 to 3 Kcal / mol, when the composition is applied to hair; (b) preferably, at least one side chain which is different to side chain (a) and which comprises a hair benefit agent. Compositions of the invention provide for deposition and delivery of benefit agents to hair in a more efficient and targeted manner.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Latex Adhesives Derived From Ionic Strength Induced Soy Protein Complexes
InactiveUS20080287635A1Easy to operateHigh strengthPeptide preparation methodsFiberProtein molecules
Macro hydrophobic clusters and complexes of soybean globular proteins were observed using TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). Upon unfolding, hydrophobic groups of the proteins became exposed toward the surface of the protein and actively interacted with other hydrophobic groups of other protein molecules, thereby forming hydrophobic bonding. The hydrophobic bonding resulted in hydrophobic protein clusters, the formation of which was affected by the degree of protein unfolding, protein structure, and hydrophobic components. Such hydrophobic clusters followed the global minimum free energy theory and formed spherical like structures with diameters ranging from 100 nm to 3000 nm. Such an understanding lends applicability to many uses in adhesives, molding composites, surfactants for oil-water systems, bio-based interior construction paints and paper coatings, fiber production, and metal powder molding applications.
Owner:SUN XIUZHUI +2
Methods and materials for enhancing the effects of protein modulators
InactiveUS20060009918A1Good effectChemical treatment enzyme inactivationSpecial data processing applicationsProtein regulationActive site
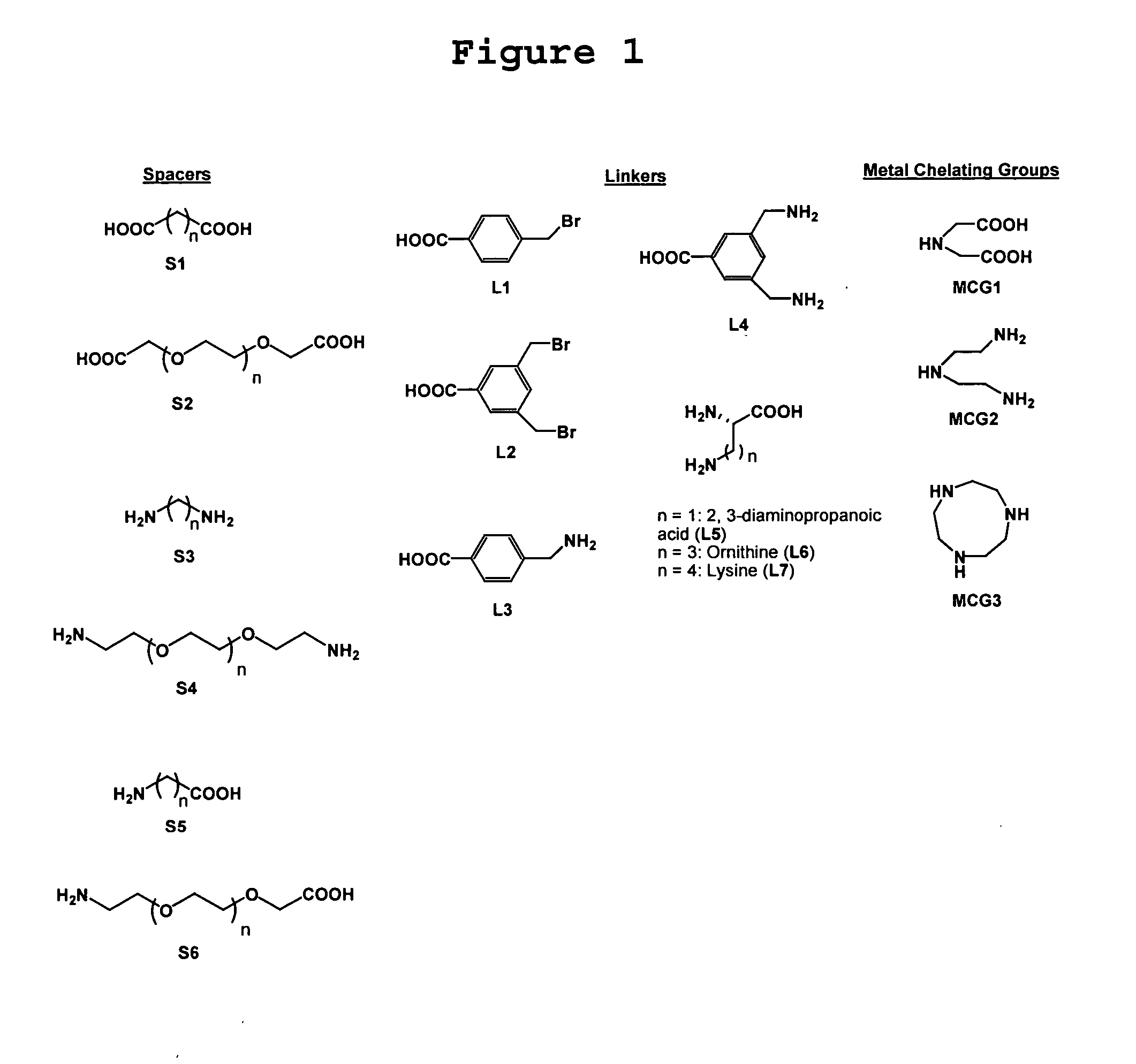
Disclosed is a method for enhancing the effect of a protein modulator on a protein by modifying the protein modulator so that the protein modulator binds with the surface of the protein, along with a method for modulating a protein's biological function by contacting the protein with such a modified protein modulator. Also described are modified protein modulators having the formula PM-SP-(LK)p-MCG-(M)q, where PM is a protein modulator which interacts with an active site or allosteric site of a protein; SP is a spacer; LK is a linker; p is 0 or 1; q is an integer greater than or equal to one; MCG is a metal chelating group; and M is a metal ion.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Fire fighting and fire retardant compositions
Disclosed herein are fire-fighting compositions, and methods thereof, comprising a surfactant and a fraction of a fermentation mixture comprised of yeast exoproteins, where the proteins enhance ability of water to extinguish Class A, Class B and Class K fires, as defined by the National Fire Protection Association. In one embodiment the surfactant is optimized to wet and penetrate into the substrate, for example wood, as in a Class A fire. In a second embodiment, the surfactant is optimized for foaming to provide fire fighting protection in a Class B fire. Further embodiments include methods for using the same protein-surfactant fire fighting composition for both polar (e.g., alcohol) and non-polar combustible liquids. In yet another embodiment, methods are described where the proteins comprise stress shock proteins and where the residual protein-surfactant combination that is not degraded from the fire acts to stimulate resident bacterial populations to accelerate the biodegradation of residual hydrocarbons and surfactants from the composition. In another embodiment, the compositions are free of solvents, fluorine-free as in fluoro surfactants and fluoro-polymers.
Owner:ADVANCED BIOCATALYTICS
POLYMER-BASED PROTEIN ENGINEERING METHODS TO RATIONALLY TUNE ENZYME ACTIVITY, pH-DEPENDENCE AND STABILITY
ActiveUS20160101190A1Improve biological activityHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationStimuli responsiveChymotrypsin
Using a novel water-soluble, active ester amide-containing functionalized controlled radical polymerization initiator, stimuli responsive polymers have been grown from the surface of a protein, exemplified by chymotrypsin or any protein having surface amino acids that will covalently bind to the active ester amide-containing functionalized initiator. It is shown that changes in temperature or pH can change the conformation of the polymer surrounding the enzyme, which in turn enabled the rational tailoring of enzyme activity and stability. This method has afforded an increase in the activity and stability of the enzyme by an order of magnitude at pH's where the enzyme is usually inactive or unstable. Multimodal temperature responsive protein-block copolymer conjugates are described.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Polyethylene glycol modified protein separating and purifying method
The invention relates to a polyethylene glycol modified protein separating and purifying method. The invention discloses a novel cation chromatography media MacroCap Sp which can induct protein surface charge distribution relation sensitively. The more positive charge on a protein surface, the stronger combination capability of the protein with the MacroCap Sp, and the higher ion gradient is needed for elution. By utilizing the above property, polyethylene glycol modified protein molecule can be effectively separated. The method comprises the following steps: (1) after modification of object protein by polyethylene glycol with active reaction group, adjusting pH value of a reaction solution, wherein the pH value should be lower than isoelectric point of the polyethylene glycol modified protein; (2) loading the reaction solution to balanced MacroCap Sp cation exchange columns; (3) adding a sodium salt solution to carry out ion gradient elution based on a balanced buffer solution, and collecting object peak. The method of the present invention is suitable for effective separation of recombinant human granulocyte stimulating factor modified by the polyethylene glycol and exenatide.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIUYUAN GENE ENG
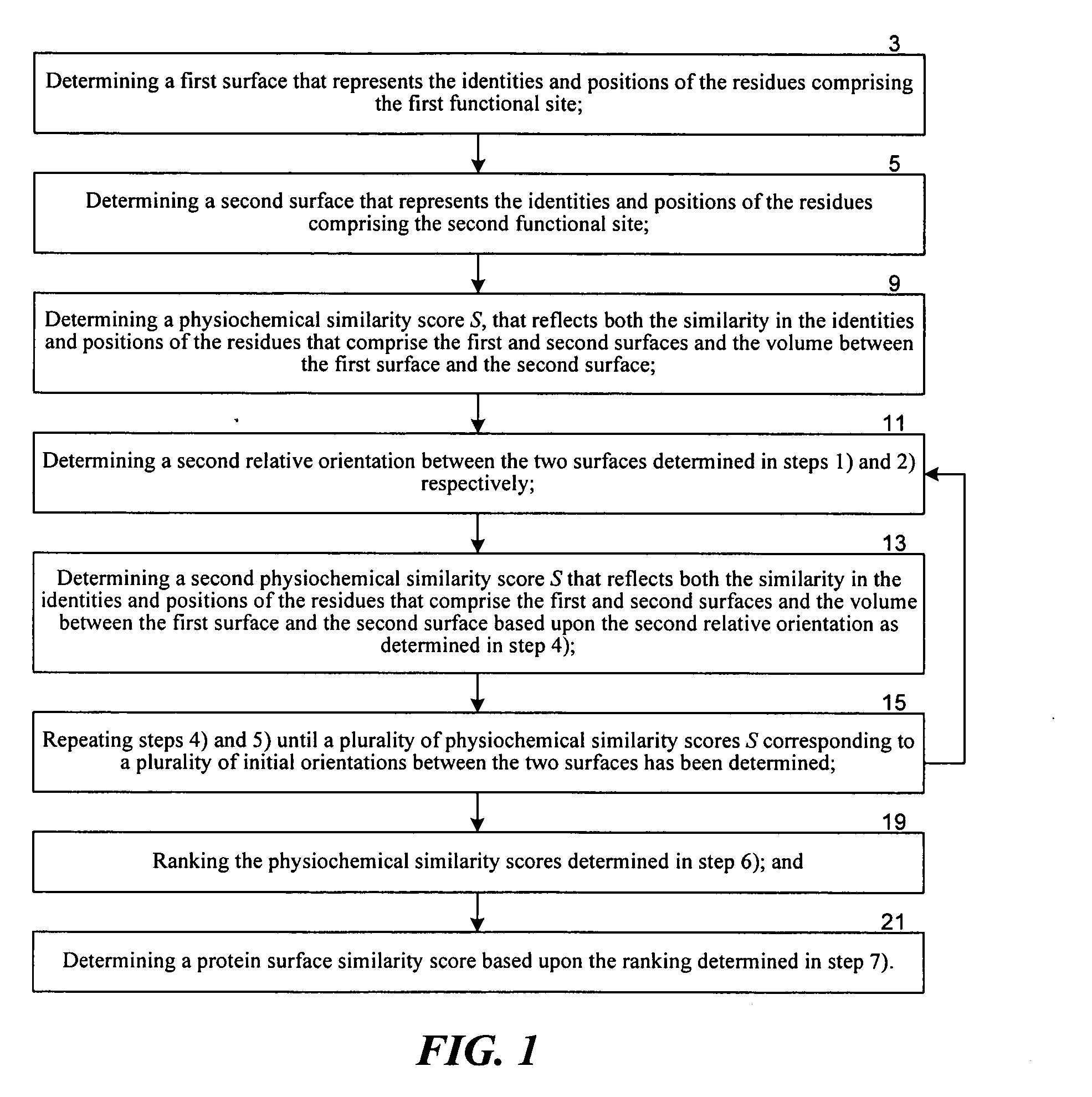
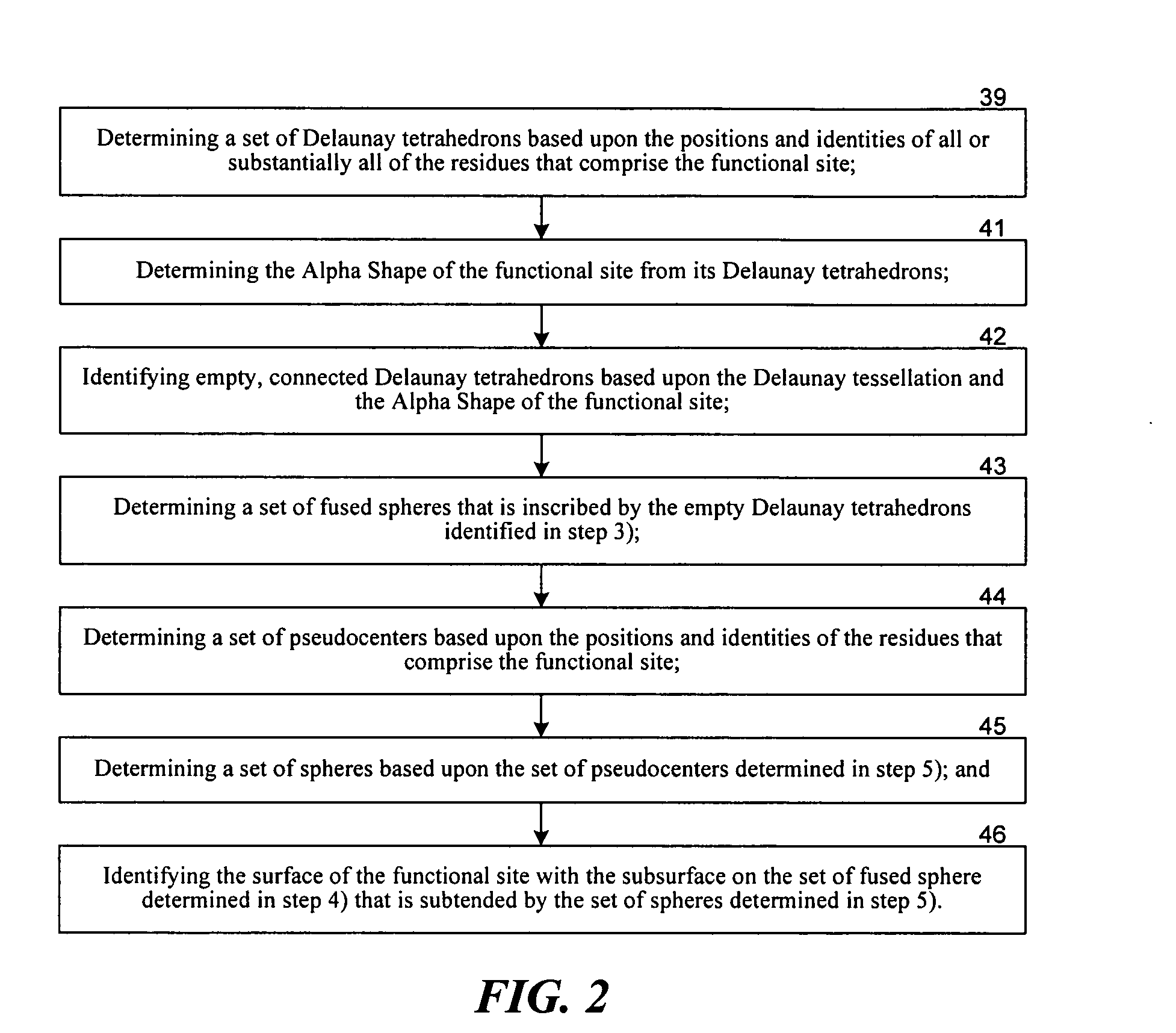
Methods for comparing functional sites in proteins
InactiveUS20050192758A1Effective calculationComputationally efficientProteomicsGenomicsTARP ProteinProtein surface
The present invention relates to methods and systems for representing and scoring the similarity of two protein by iteratively rotating and translating one protein surface representation relative to the other protein surface representation in order to maximize (or minimize) a score that represents both the volume between the two surface representations and the similarity in the identities and positions of the residues comprising the two protein surfaces. In another aspect of the invention, such methods and systems are used to compare and annotate a protein comprising a putative functional site of unknown function with a database of reference proteins of known function.
Owner:EIDOGEN SERTANTY INC
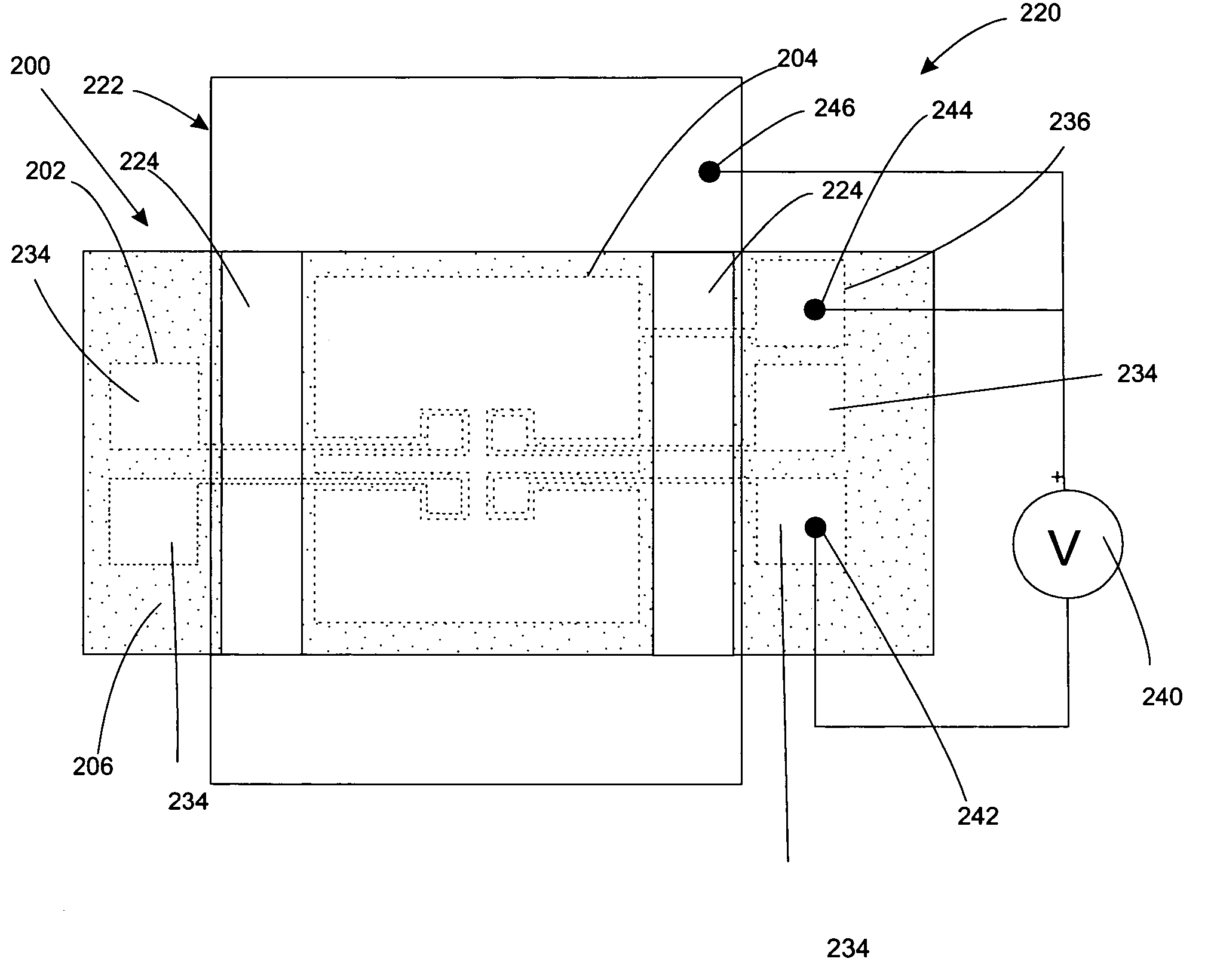
Reconfigurable protein patterning using electrowetting microelectrodes
InactiveUS20060063207A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityMicroelectrode
A protein patterning electrode device consisting of capacitor microelectrode arrays coated with a protein non-adherent layer is provided. Operation of the electrode is based on a phenomenon called “electrowetting,” where surface wettability can dynamically be controlled by varying the voltage across the device electrodes. When an electric field is applied across the electrode layers, the surface accumulates charge and becomes hydrophilic, binding the proteins to the surface via ionic bonding. Electrically controlling the amount of the surface charge permits controlled protein surface affinity. The device provides a means for reconfigurable protein patterning.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
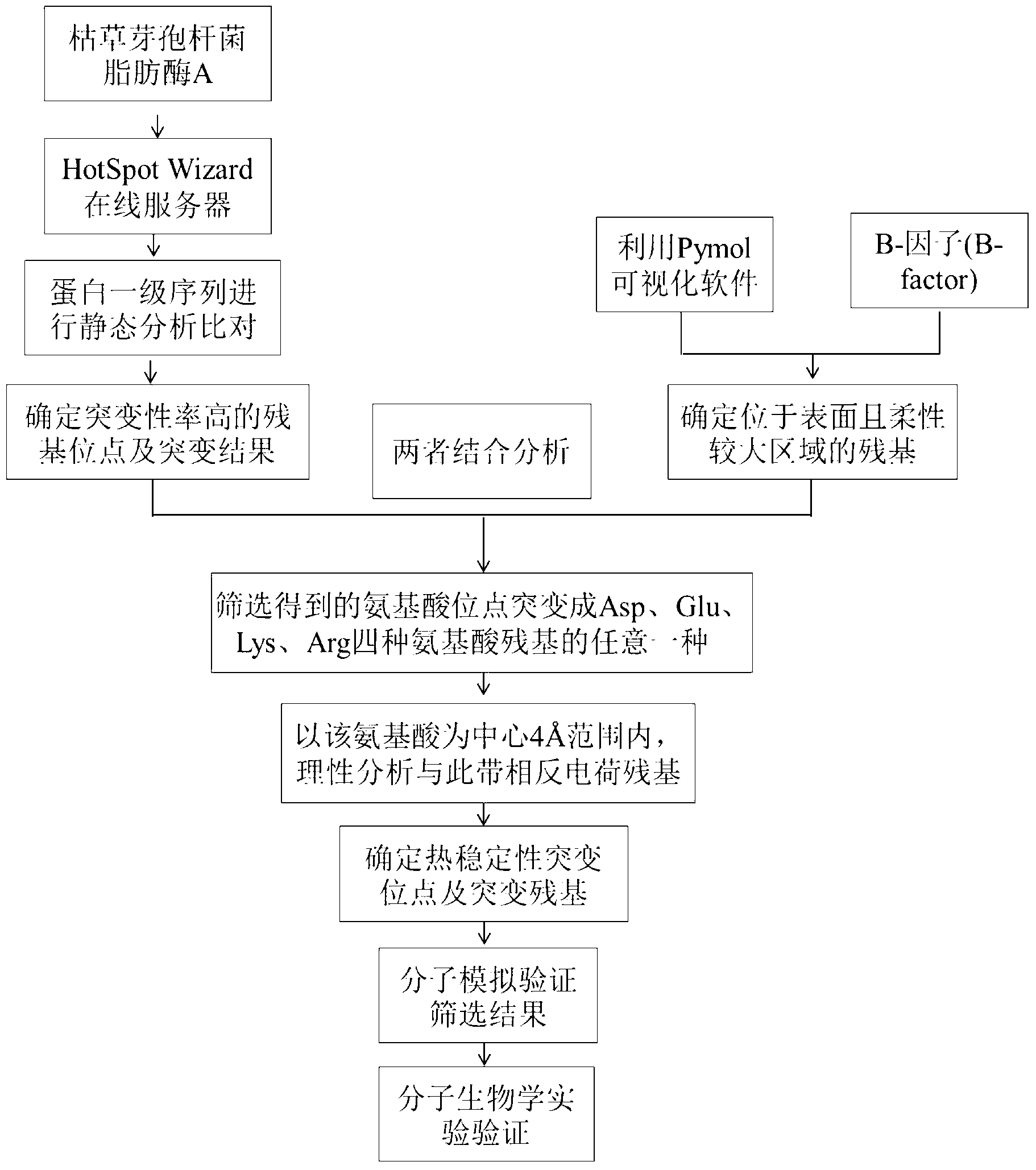
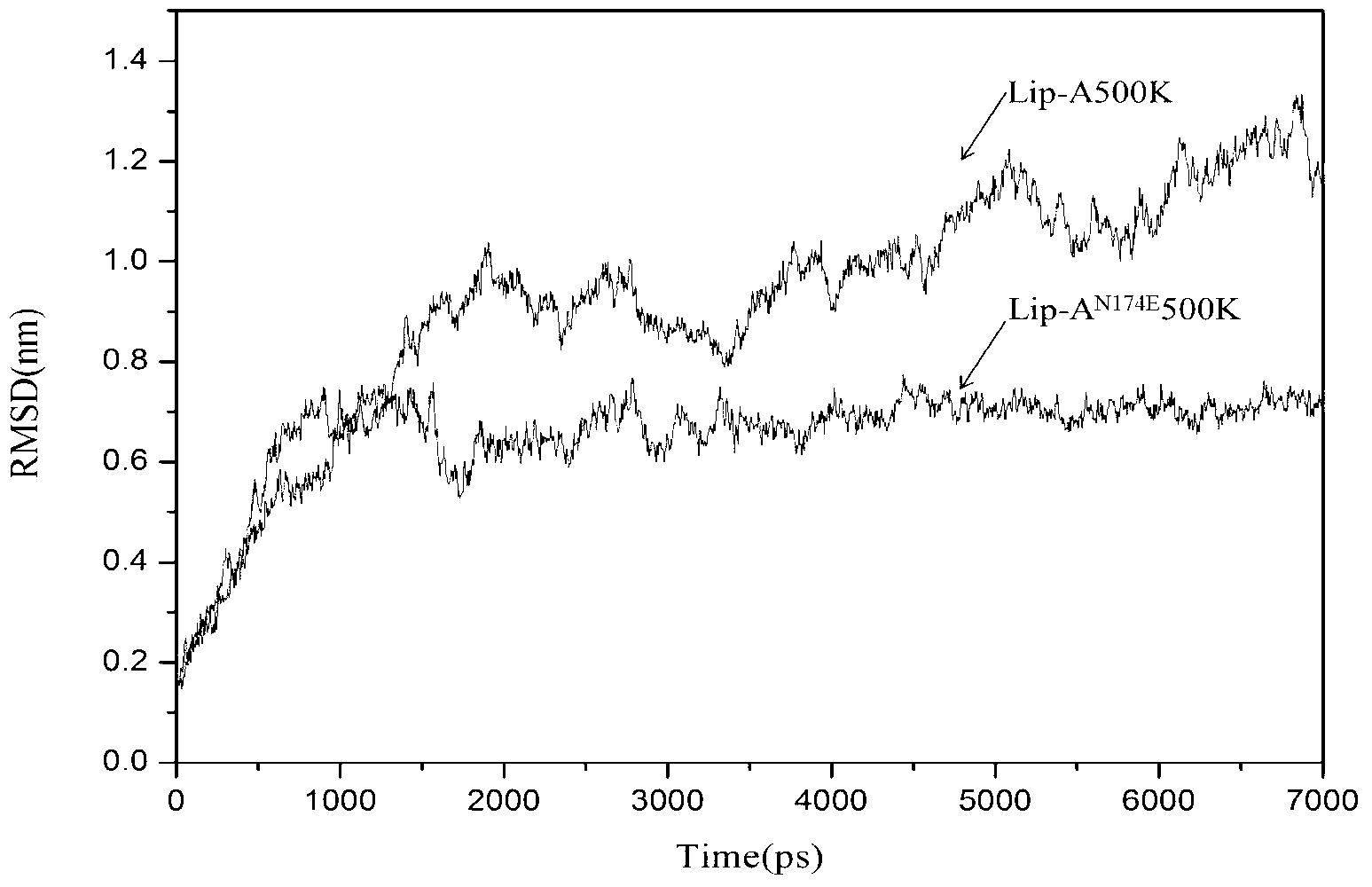
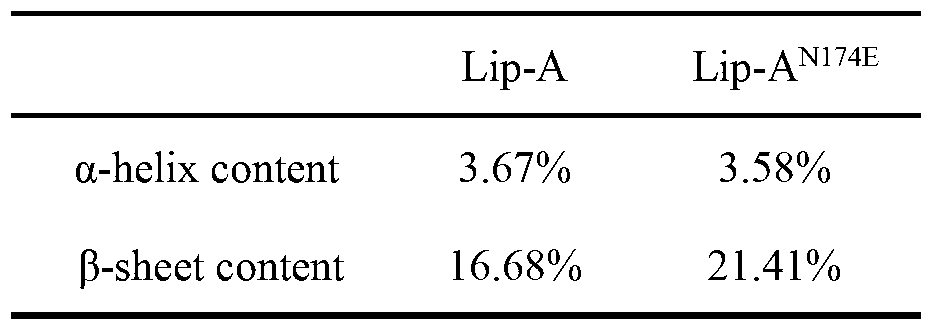
Method for improving heat stability of lipase A of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN103243078AThe method is simple and fastHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEnzyme structureArginine
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and relates to a method for improving the heat stability of lipase A of bacillus subtilis. According to the method, the lipase A of the bacillus subtilis is used as an object of study, and the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, screening mutational hot spot areas; secondly, determining the amino acid site of an area which is positioned on the surface of protein and is higher in flexibility; thirdly, carrying out rational analysis by combining the two steps, mutating the screened amino acid site into any one of four amino acid residues including aspartic acid, glutamic acid, lysine and arginine, taking the amino acid as a center, and searching the amino acid residues with opposite charges in the four amino acids in a range of 4 angstroms to determine a mutation site and a mutation residue; fourthly, on the basis of the acknowledge of an enzyme structure and a functional relationship, resolving ionic bonds, and introducing a mechanism of action for stabilizing the protein structure of the lipase A of the bacillus subtilis; and finally, proving hot spot residues with modified heat stability through hot stability experiments of mutant strains of the lipase A of the bacillus subtilis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
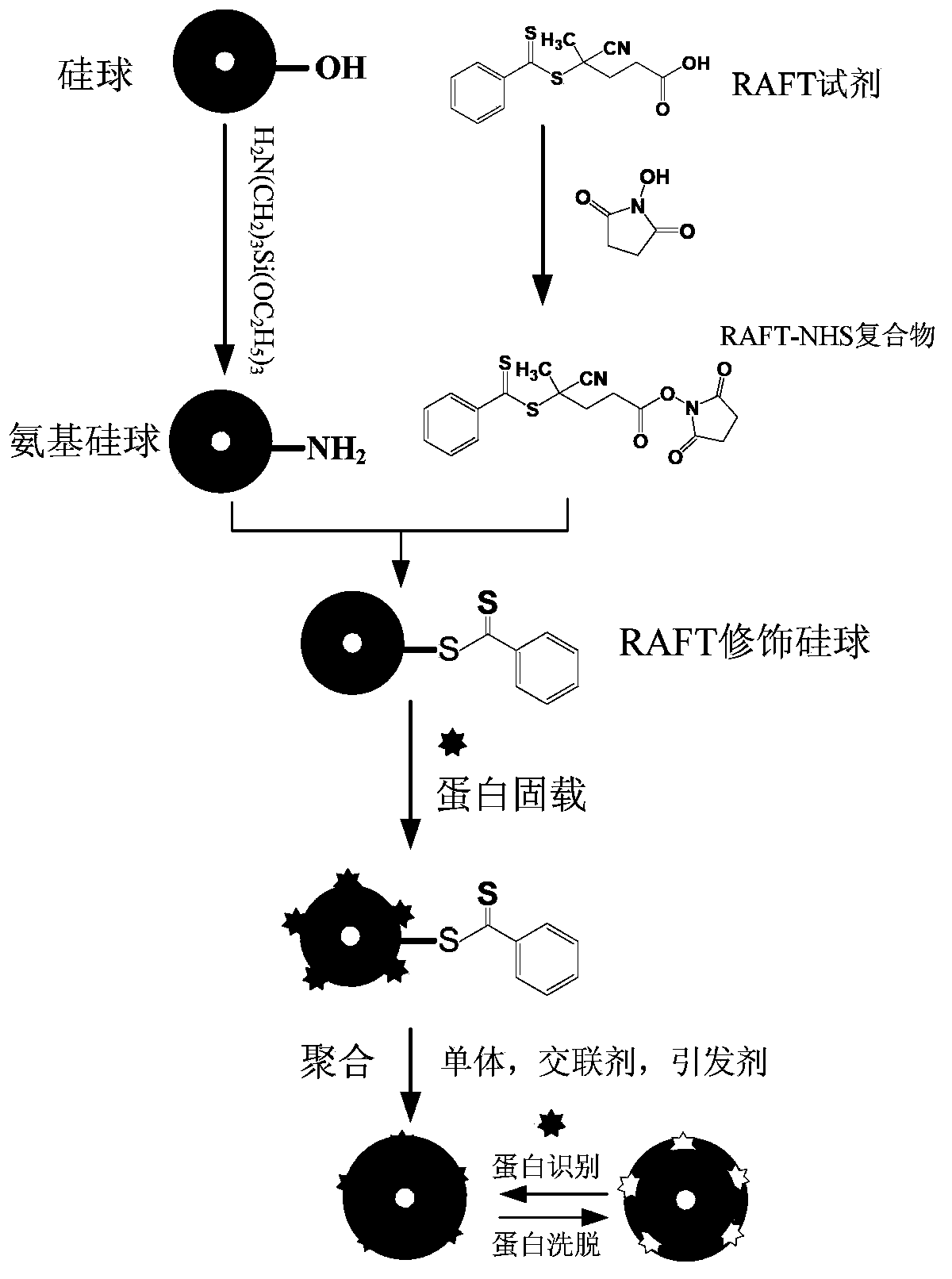
Protein surface molecular imprinting material based on RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer) strategy as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104231143AMass transfer rate is fastImprove recognition efficiencyOther chemical processesCross-link(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The invention relates to a protein surface molecular imprinting material based on an RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer) strategy. The protein surface molecular imprinting material is subjected to polymerization reaction by taking a silica gel granule with a dithioester functional group modified as a matrix, a lysozyme as a template protein, MAA (Methyl Acrylic Acid) and HEMA (Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate) as monomers, MBA (Methylene Diacrylamide) as a cross-linking agent and a phosphate water solution as a solvent and adopting a redox initiate polymerization reaction mode; after the polymerization reaction is completed, the template protein formed in a polymer is eluted, and then the dithioester functional group on a material surface is reduced into sulfhydryl, so that a hydrophilic lysozyme molecular imprinting core-shell structure microsphere can be obtained; and the hydrophilic lysozyme molecular imprinting core-shell structure microsphere is applied to the specific identification of the lysozyme. The protein surface molecular imprinting material disclosed by the invention can be used for realizing the controllability of the polymerization reaction and polymer chain growth by virtue of the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer strategy, and realizing narrow polymer distribution, controllable chain length and uniform polymer layer distribution so as to form sufficient surface imprinting sites.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dilute of alkaline phosphatase maker and application thereof
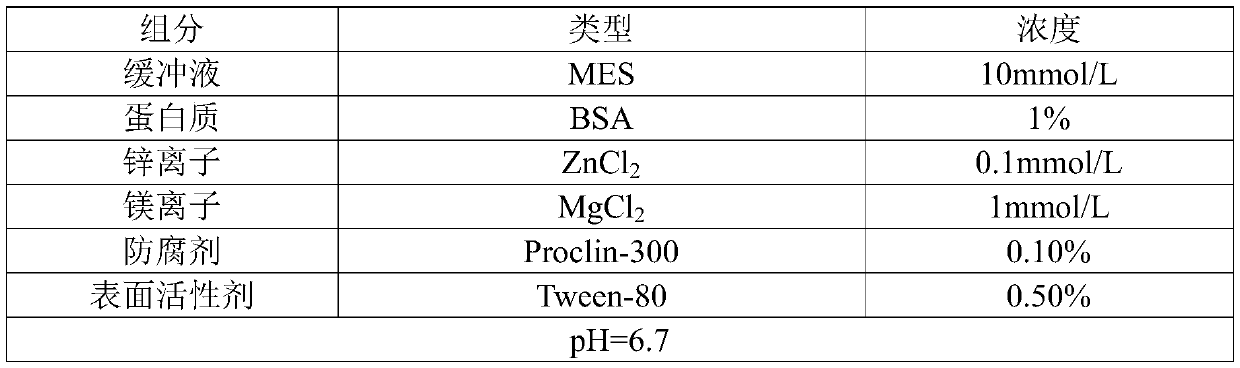
PendingCN110824159AReduce the probability of false positive resultsReduce the probability of detecting false positive resultsMaterial analysisActive agentZinc ion
The invention relates to a dilute of an alkaline phosphatase maker and application thereof. The diluent comprises a buffer, a protein, a surfactant, a zinc ion, a magnesium ion, a preservative and anadditive, wherein the additive comprises a blocking agent and / or alkaline phosphatase; and the alkaline phosphatase is a low-active alkaline phosphatase and / or inactive alkaline phosphatase. The invention creatively adds the blocking agent and / or alkaline phosphatase to the traditional diluent for diluting alkaline phosphatase markers, and can well reduce non-specific reactions and ultimately reduce the probability of false positive results in clinical samples to improve the accuracy of detection and analysis results.
Owner:AILEX TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Beta-mannase heat-resisting mutant, application thereof, recombinant strain and application thereof
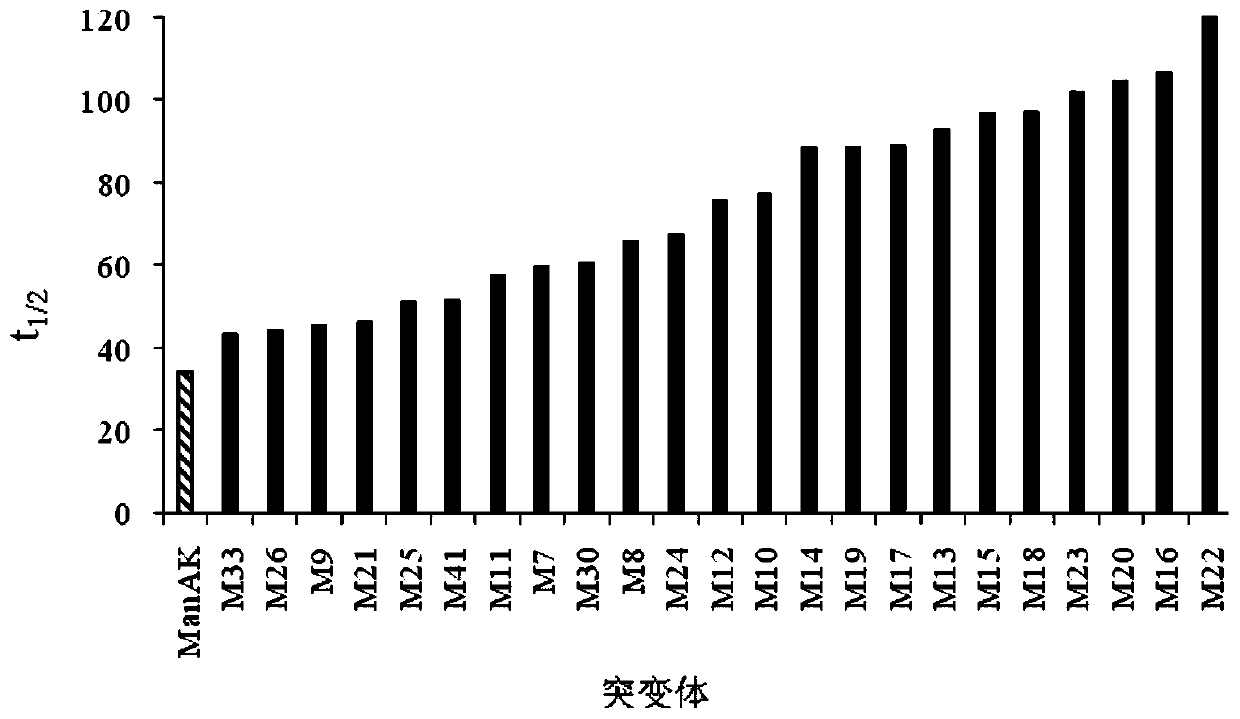
ActiveCN111363735AImprove heat resistanceReasonable optimization of surface charge distributionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a beta-mannase heat-resisting mutant, an application thereof, a recombinant strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. A protein surface charge optimization strategy is adopted, mutation sites are reasonably designed and screened, beta-mannase ManAK from aspergillus candidus is improved, then through a high throughput screening method, forward mutation is sorted, and finally, 23 beta-mannase mutants with improved heat stability are obtained. The heat resistance of the obtained beta-mannase mutant is 1.2-3.5 times of that of original genes, the heat resistance is notably improved, the application of the beta-mannase mutant to business is facilitated, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Manufacturing method of protein modified fiber in acrylic fiber surface ingrafted bean juice
InactiveCN101831806AImproved compatibility with human bodyGood hygroscopicityFibre typesAqueous solutionModified method
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of protein modified fiber in acrylic fiber surface ingrafted bean juice, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) firstly, putting acrylic fiber into alkaline aqueous solution at certain bath ratio, certain mass ratio density and temperature, and hydrolyzing for a certain time; (2) cleaning and drying to obtain hydrolyzed fiber, and causing the hydrolyzed fiber to react with thionyl chloride to obtain chlorination fiber; and (3) putting the chlorination fiber into the bean juice to be ingrafted into fiber of which the surface is covered with a bean juice protein layer. The invention utilizes the ingrafted and modified method of protein on the acrylic fiber surface in the bean juice to realize protein surface modified efficacy of the acrylic fiber in the bean juice, and the human body affinity, hygroscopicity and antistatic property of fiber can be improved. The method of the invention is simple and feasible, can realize industrial production only by simple fiber aftertreatment equipment and has the characteristics of small production investment, low production cost and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method of Surface Modification by Proteins for Analyte Preconcentration for Desorption-Ionization Mass Spectrometry Techniques and for Immunochemical Assays
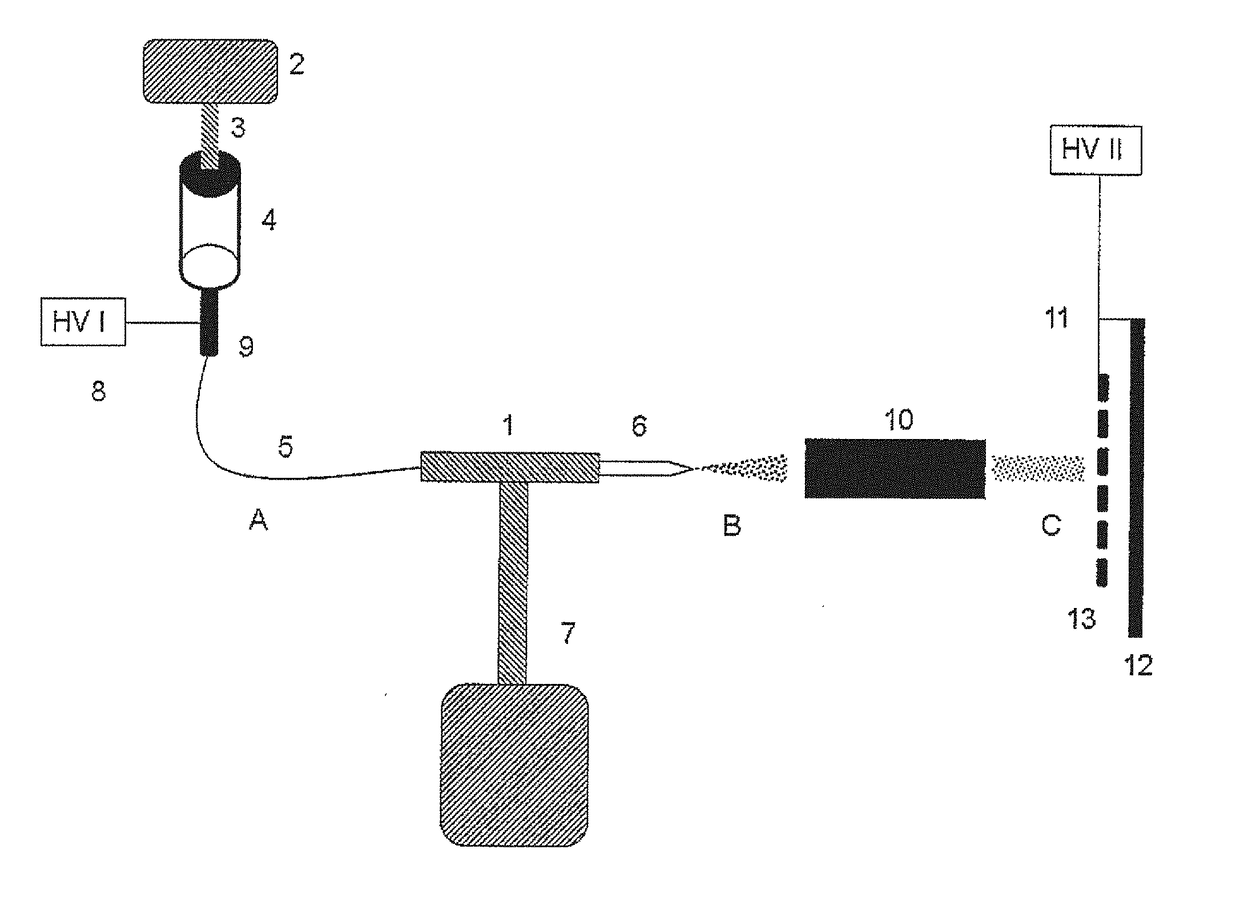
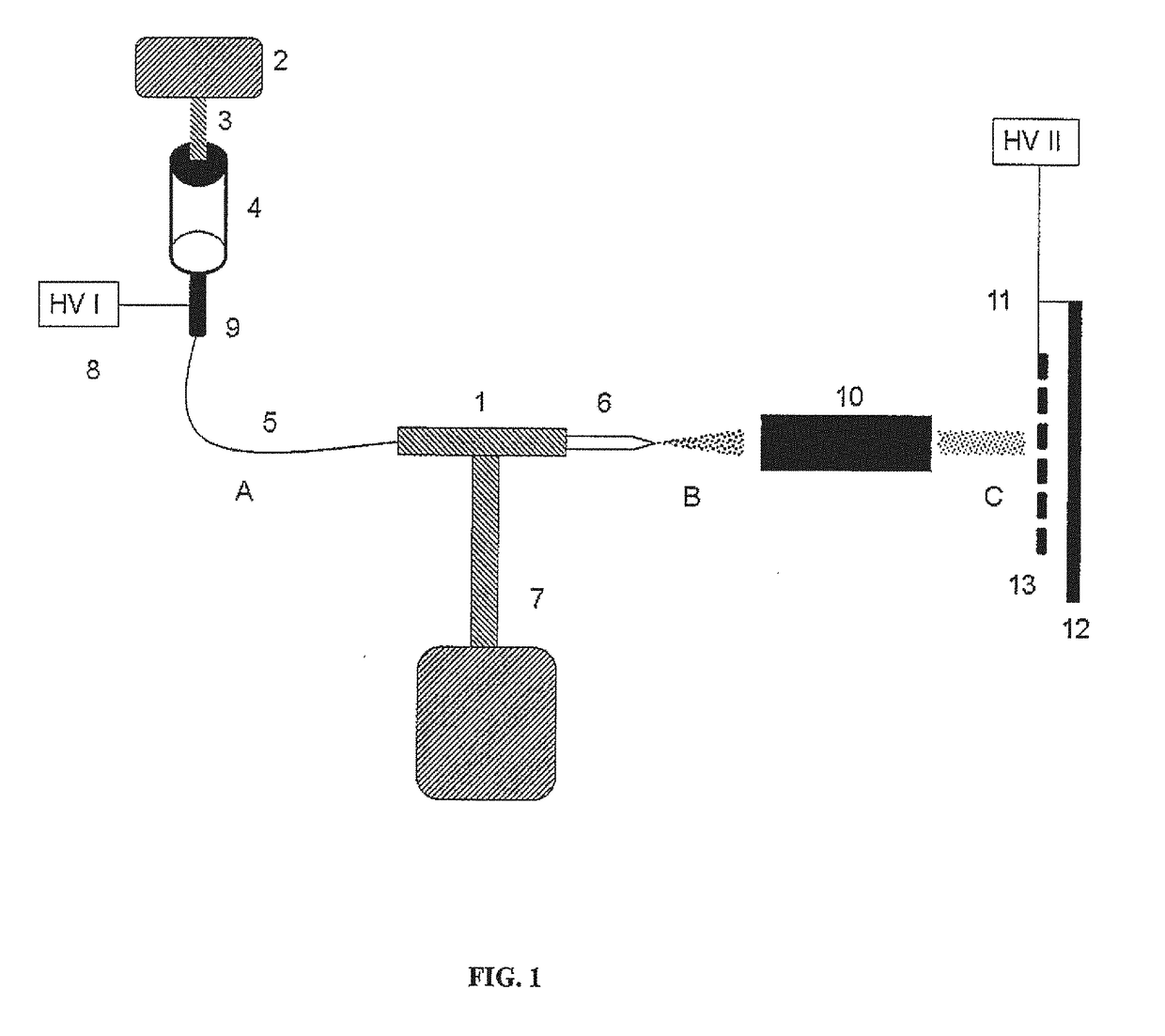
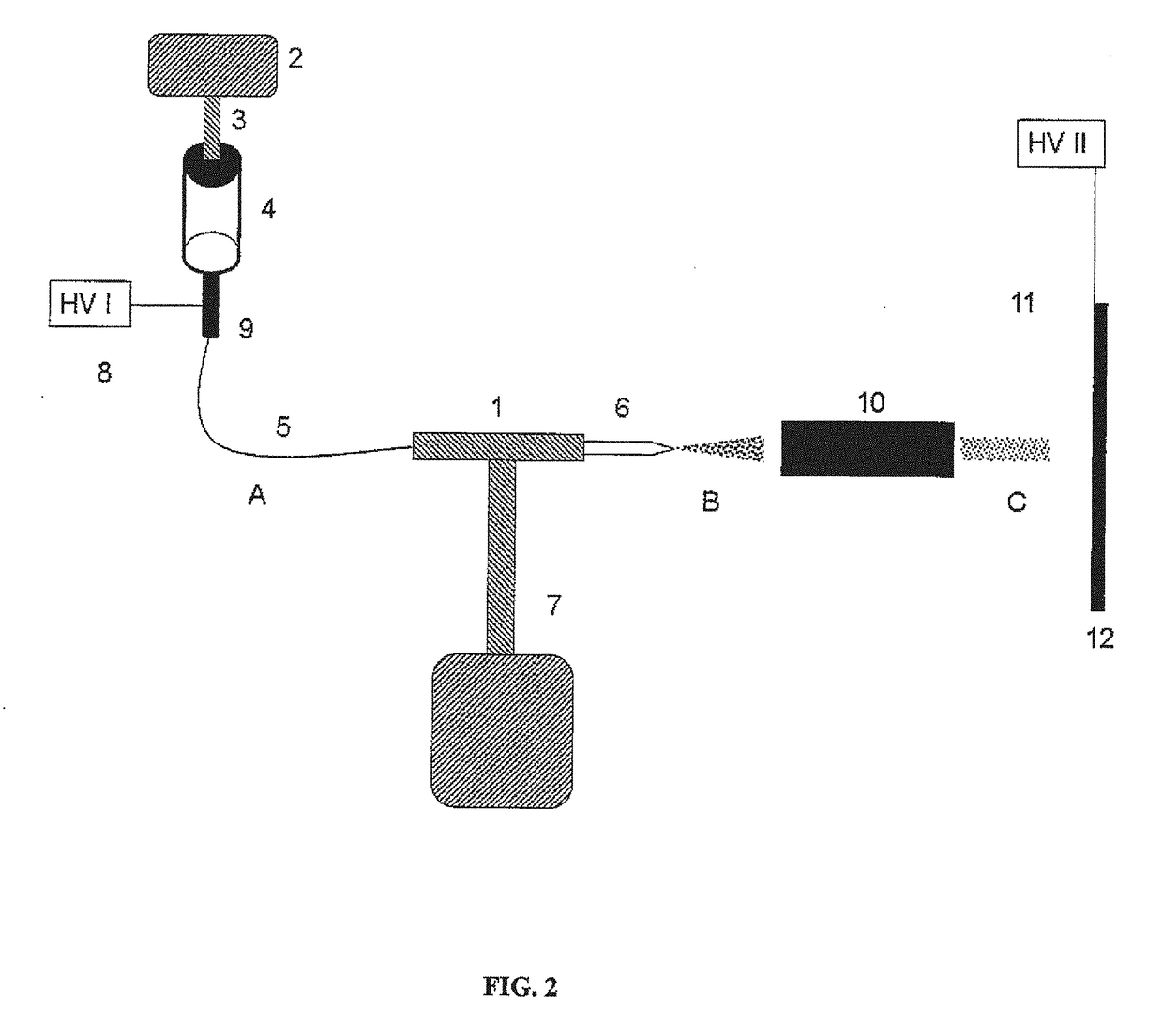
ActiveUS20170242030A1High-quality surfaceOvercome disadvantagesSamples introduction/extractionPreparing sample for investigationProtein solutionEvaporation
A method for modification of solid substrates with proteins for efficient surface preconcentration of an analyte from multi-component samples before the detection based on desorption-ionization mass spectrometry and immunochemical assays. The claimed subject is a method of modification of surfaces used as substrates for desorption-ionization mass spectrometry and immuno-chemical assays. The method is based on electronebulization (electrospraying) of protein solution, depending on the intended application either enzymes, lectins, or antibodies. The formed charged electrospray is dried in real time by its passing through an evaporation compartment and the resulting beam of desolvated ions impacts onto the surface and binds to it firmly. Such modified surface can be then used for a selective interaction with an affinity partner of the deposited protein, its preconcentration or enzymatic modification followed by an analysis by means of desorption-ionization mass spectrometry or immunochemical assays.
Owner:NOVAK +3
Method for preparing protein-based surfactant by opening protein disulfide bond
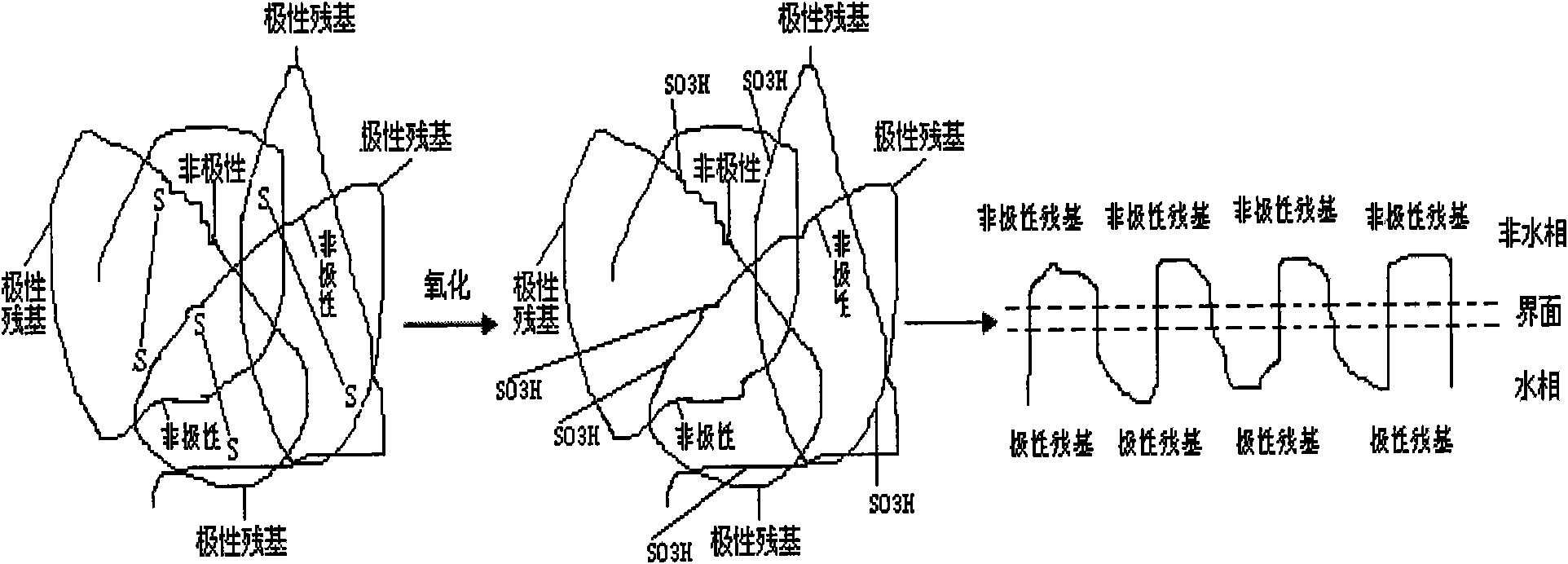
InactiveCN101590382AImprove surface activityIntegrity guaranteedTransportation and packagingMixingPhosphorylationSide chain
The invention relates to a method for preparing protein-based surfactant by opening protein disulfide linkage. The method is characterized by converting disulfide linkage into sulfonic group by oxidizing disulfide bond in protein of peroxide, and opening the folded coiling structure of the protein to represent the surface activity properties so as to prepare the protein-based surfactant which has the functions of emulsification, foaming, defoaming, washing, decontamination, soakage, and the like; by introducing polar group or nonpolar group into a protein side chain with opened disulfide bond, the surface activity properties of peptide fragments can be further improved or increased; moreover, by adopting treatments including acetylization, succinylation, acylation or phosphorylation, protein surface activity properties such as surface tension, emulsification, foaming, defoaming, washing, decontamination and soakage can be changed further. The method furthest prevents protein polar group and nonpolar group from being damaged, and maintains the structural integrity and property naturalness of protein molecules, thereby converting the protein into natural high-performance surfactant.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Recombinant self-assembling protein comprising target-oriented peptide and use thereof
ActiveUS20160074511A1Improve structural stabilityImprovement in photothermal therapyPowder deliveryElectrotherapyTarget tissueStructural stability
The present invention relates to a recombinant self-assembled protein comprising a target-oriented peptide and a use thereof. The recombinant self-assembled protein according to the present invention, comprising a target-oriented peptide, does not require an additional process for providing target-orientedness, and is thus capable of delivering a desired drug to a target tissue or target cell without using additives, such as chemical binders or stabilizers; therefore, the protein can be used for photothermal therapy, drug delivery, imaging, or the like. In particular, according to the present invention, it is to possible to prepare gold-protein nanoparticle fusions in which uniform high-density gold nanoparticles having target-orientedness are bound to protein surfaces, without an additional process of surface stabilization or process for providing target-orientedness. Compared with conventional gold nanoparticles, the gold-protein nanoparticle fusions according to the present invention show structural stability against pH variation and concentration variation, and also have excellent target-orientedness; therefore, the fusions can bring a dramatic enhancement to the utilization of gold nanoparticles in photothermal therapy.
Owner:CELLEMEDY CO LTD
Preparation method of biological protein-based water-tolerant wood adhesive
InactiveCN106634818ARaw materials are easy to getSimple preparation stepsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMicroorganismsProtein moleculesAdhesion strength
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biological protein-based water-tolerant wood adhesive, and belongs to the technical field of adhesive preparation. Fat and oil layer substances contained in protein-rich beancurd skin and spider silk which are taken as raw materials are used for degrading grease under the action of enzyme and microorganisms, the number of hydrophobic ester groups on the surface of protein is increased, and accordingly, the water tolerance of the protein is improved; then the protein is modified with lye, polar compact protein molecules are dispersed, and more protein subunits and hydrophobic groups in the protein are exposed, so that the contact area of the protein with wood surface is increased while the protein is water-tolerant, and the adhesion capacity of the protein is increased; then the chemical bonding force is generated between colloid and a wood substrate through the doping of wood tar, the adhesion strength of the adhesive is further improved, concentration is performed finally, and the adhesive is prepared. The prepared wood adhesive has good water tolerance, high adhesion strength and excellent application prospect.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of asymmetric virus nanoparticles
InactiveCN102321590AHave diversityControllableInactivation/attenuationDepsipeptidesProtein moleculesFunctionalized nanoparticles
The invention discloses a preparation method of asymmetric virus nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out gene modification on the virus capsid protein surface, so that the virus capsid protein simultaneously has coupled functional group and separate group; thoroughly mixing the modified virus capsid protein and wild type virus capsid protein while controlling the proportion of the two virus capsid proteins; and meanwhile, adding corresponding inorganic nanoparticles according to the total amount of the virus capsid protein to implement controllable assembly of the virus nanoparticles, thereby obtaining the asymmetric functionalized nanoparticles which are the goal product. The invention adopts biomacromolecule-protein as the nano material, and the biomacromolecule-protein can be easily modified and manually operated, and can be conveniently obtained massively. On the basis of the structural symmetry of the self-assemblable virus capsid protein, the two different protein molecules can be assembled in an oriented mode according to the previous design, and therefore, the assembly body has diversity and controllability; and the invention has the advantage of manageable reaction conditions, and can implement large-scale production.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
SERS detection method based on adsorption of protein by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles
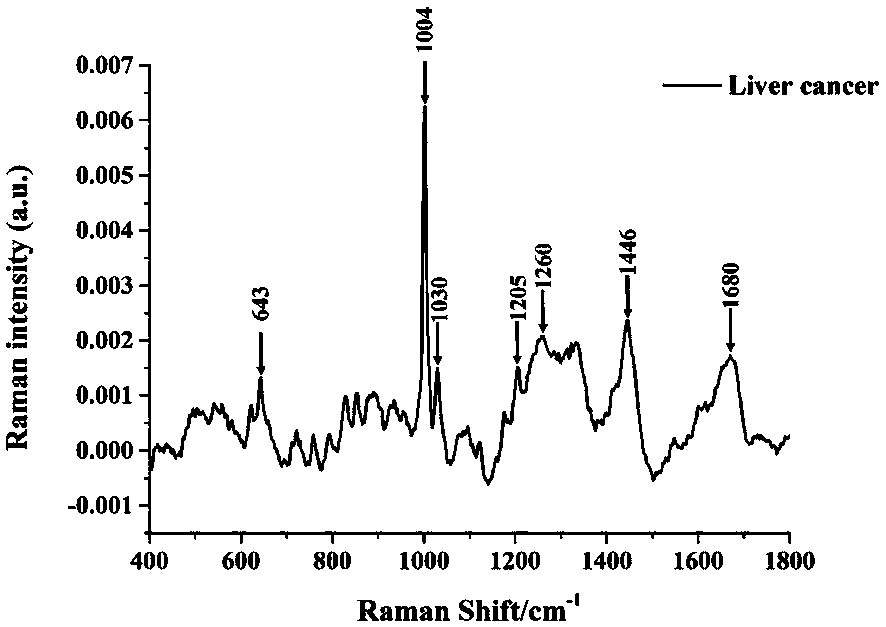
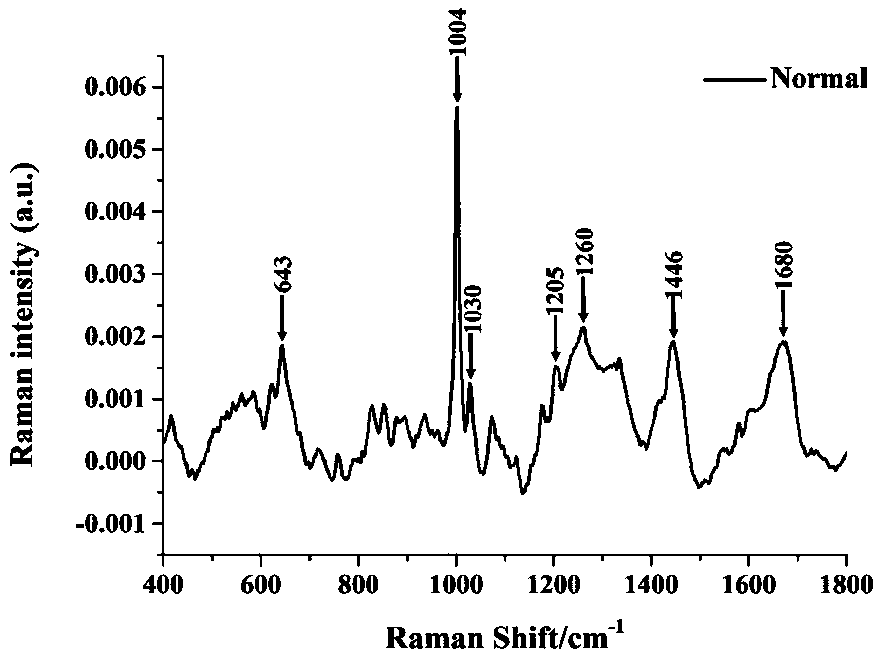
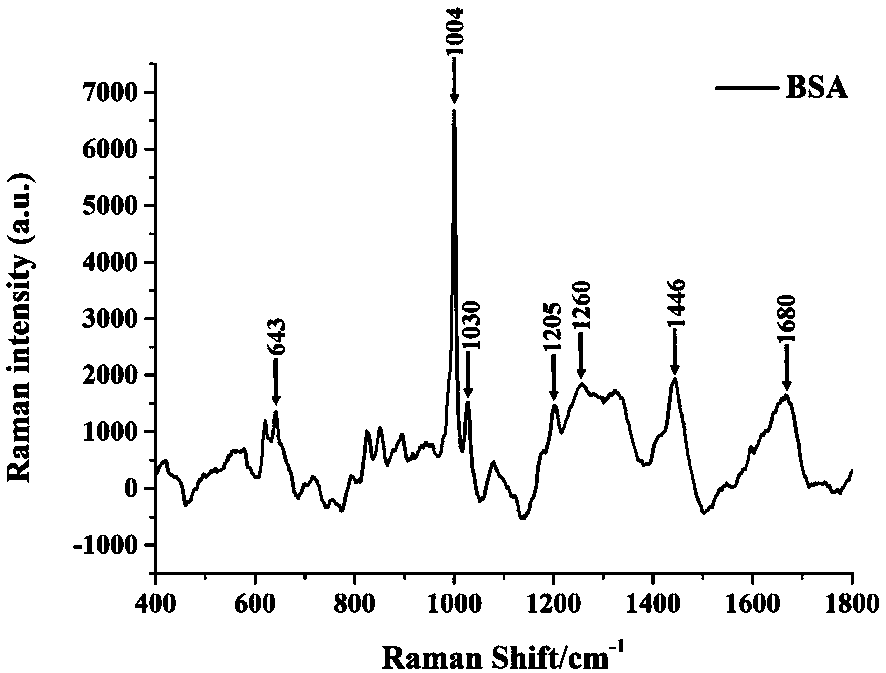
ActiveCN110646401ALow cost of experimentsEasy to operateRaman scatteringSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection method based on adsorption of proteins by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. The SERS detection method comprises the steps of:carrying out mixed incubation on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and a biological sample and absorbing proteins in the sample, adding acid into the mixture to adjust a pH value so as to enable the proteins to fall off from the surfaces of the hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, extracting supernate containing the fallen proteins, uniformly mixing the supernate with an SERS nano active material, detectingto obtain a biological sample protein surface enhanced Raman spectrum by utilizing an SERS technology, and establishing a biological sample protein surface enhanced Raman spectrum database; and acquiring characteristic spectral peaks of surface enhanced Raman spectra corresponding to different biological sample proteins through post-processing and analysis of the data. The SERS detection method has the advantages of quickness, simplicity in operation, low cost and the like, and can be used for effectively detecting the surface enhanced Raman spectra of the proteins in different biological samples.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
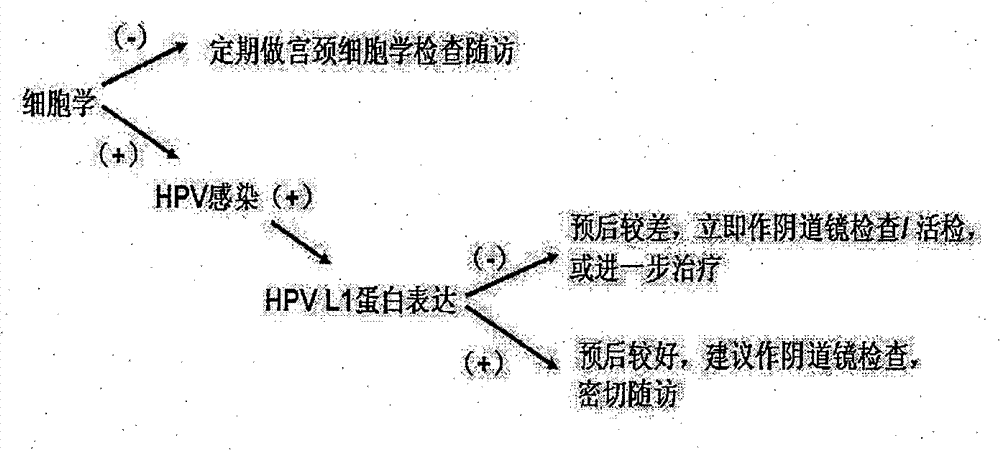
Human papilloma virus (HPV) capsid protein L1 polypeptide and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101914139BSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesPrecancerous conditionMonoclonal antibody agent
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Methods and systems for analyzing and determining ligand-residue interaction
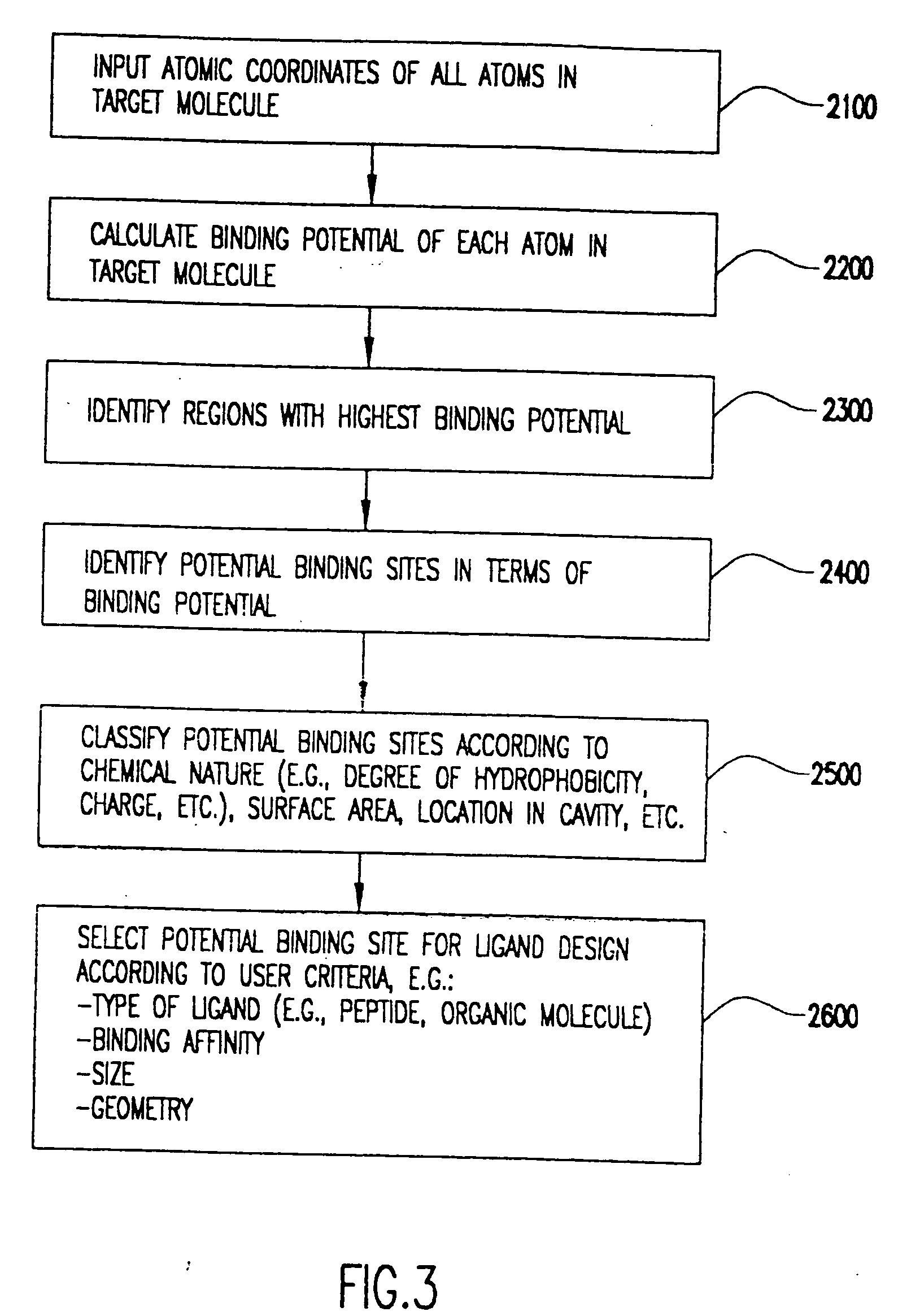
InactiveUS20050123995A1Molecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteComputational physics
A method implemented in the form of a computer simulation code for evaluating the free energy of binding between polypeptide amino acid residues and one or more molecular fragment types is presented. The basis of the method is a novel weighted Metropolis Monte Carlo approach for sampling the grand canonical ensemble. By making use of the properties of the grand canonical ensemble, the affinity of fragments for binding in the vicinity of each protein residue can be efficiently computed. The binding volume associated to each fragment-residue pair is estimated on the basis of a simple proximity criteria, and a useful affinity mapping of the protein surface can be obtained in this way. The analysis of such data for various fragment types provides valuable information to help identify protein binding sites, as well as to identify key fragments used for building potential drug leads.
Owner:LOCUS PHARMA INC
Protein Surface Remodeling
ActiveUS20100209994A1Improve thermal stabilityMore to aggregationSugar derivativesTransferasesProtein formationProtein surface
Aggregation is a major cause of the misbehavior of proteins. A system for modifying a protein to create a more stable variant is provided. The method involves identifying non-conserved hydrophobic amino acid residues on the surface of a protein, suitable for mutating to more hydrophilic residues (e.g., charged amino acids). Any number of residues on the surface may be changed to create a variant that is more soluble, resistant to aggregation, has a greater ability to re-fold, and / or is more stable under a variety of conditions. The invention also provides GFP, streptavidin, and GST variants with an increased theoretical net charge created by the inventive technology. Kits are also provided for carrying out such modifications on any protein of interest.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Fixed-point immobilization method for recombinant protein A affinity ligands
ActiveCN104356238AReduce manufacturing costLow priceSolid sorbent liquid separationCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesEscherichia coliProtein target
The invention provides a fixed-point immobilization method for recombinant protein A affinity ligands. According to the method, an FGE (formylglycine generating enzyme) identification gene sequence is inserted at the tail end of a gene sequence of coding target protein with a genetic engineering means, an expression vector of the target protein is constructed, then the target protein and FGE are co-expressed in escherichia coli, and intracellular aldehyde catalytic conversion of the target protein is realized; then fixed-point immobilization is realized through selective reactions of hydrazide groups on the surface of a medium and aldehyde groups on the surface of the protein. With the adoption of the method, the target recombinant protein can be directly fixed in a broken supernatant of a cell, conditions are mild, steps are simple, the immobilization time is greatly shortened, and the immobilization cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
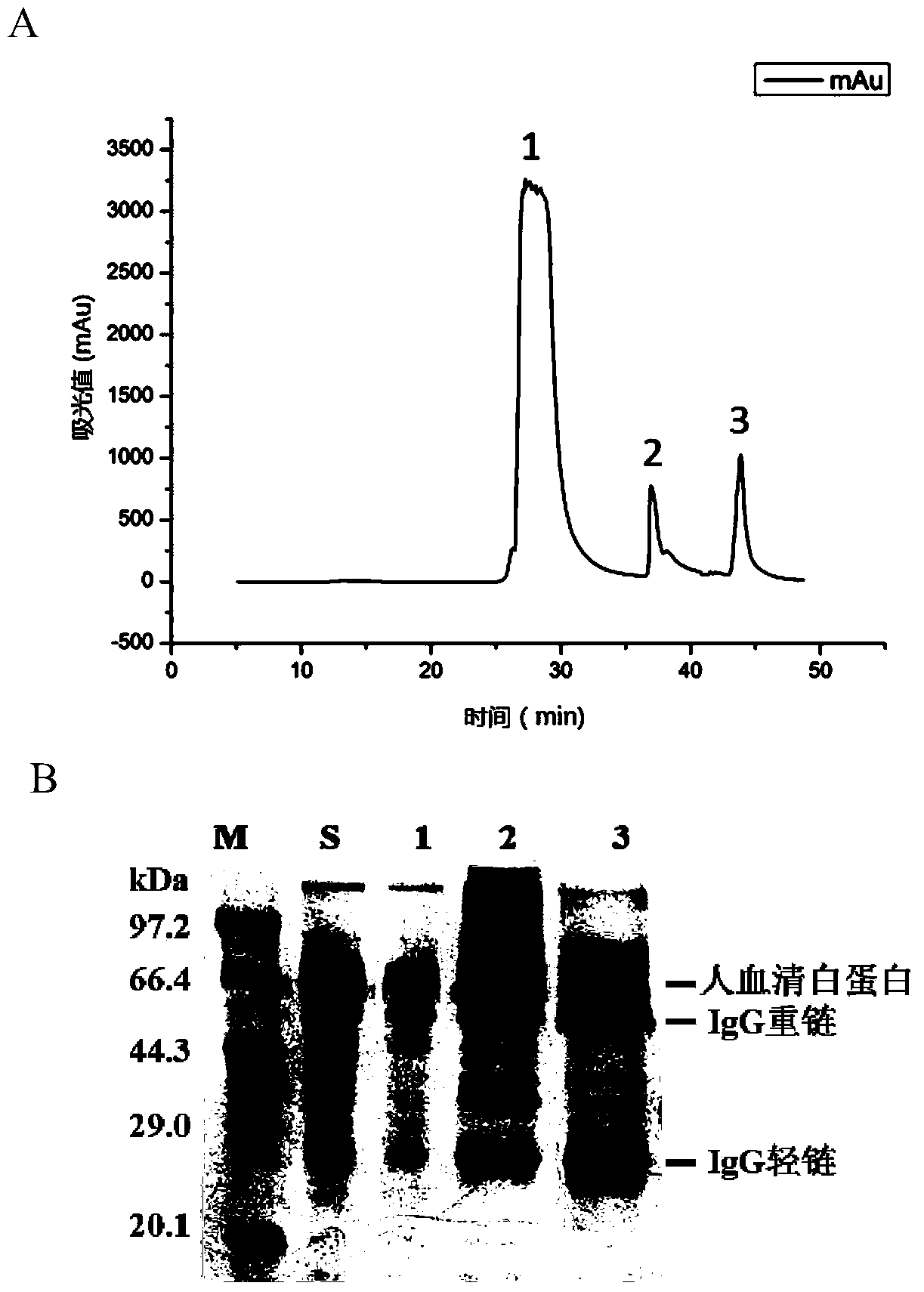
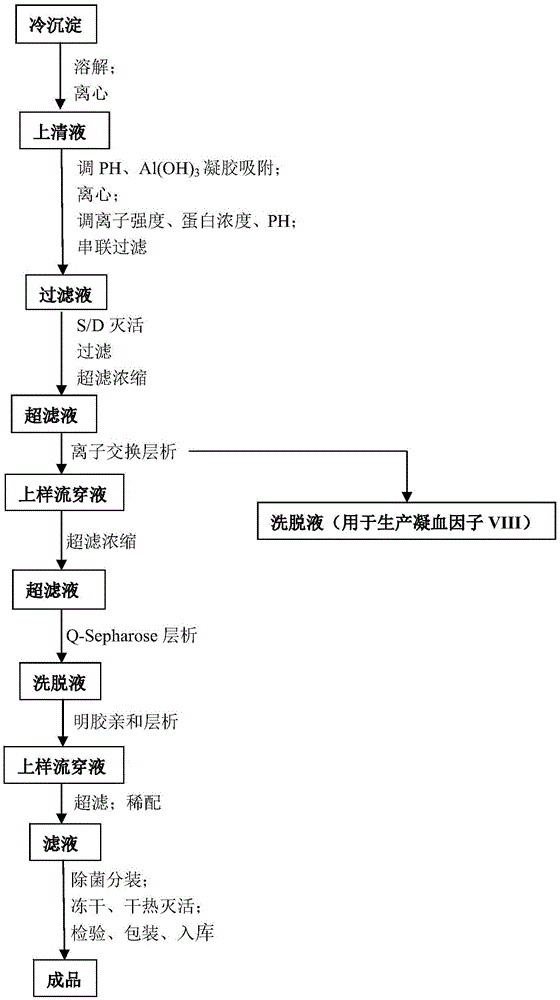
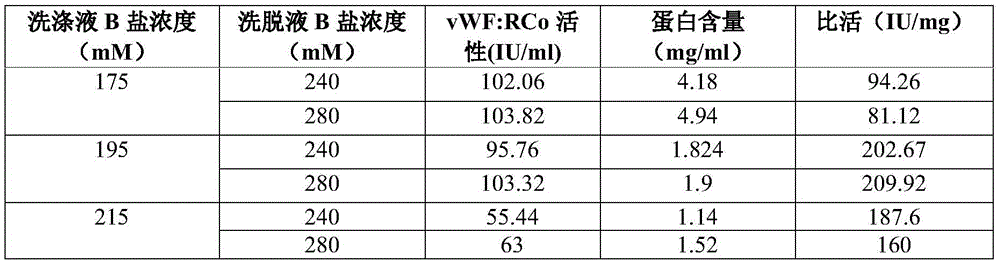
vWF (von willebrand factor) activity protection fluid
InactiveCN105622747AIncrease profitGuaranteed purityFactor VIIPeptide preparation methodsChromatographic separationBlood coagulation factor VIII
The invention discloses a vWF (von Willebrand factor) activity protection fluid. The vWF activity protection fluid is used in preparation for extracting von Willebrand factors from cryoprecipitated blood coagulation factor VIII waste. In a preparation technology of the von Willebrand factors, glycine is added into a chromatographic buffer solution, and lysine, glycine and albumin are added into protein fluid before freeze drying after chromatography to protect vWF activity. The vWF activity protection fluid has the advantages that by means of adding the glycine into the chromatographic buffer solution, vWF activity loss can be reduced in a chromatographic separation and purification process; the albumin, the lysine and the glycine are added into protein dialysate to serve as freeze-drying protectants, so that von Willebrand factor molecules can be stabilized; the albumin serving as an excellent protein stabilizer is capable of effectively adsorbing protein surfaces; the lysine and the glycine, serving as micromolecular amino acids, are capable of protecting a protein structure, increasing collapse temperature of a finished product and stopping protein damage caused by collapse during freeze-drying, so that biological activity is kept.
Owner:华润博雅生物制药集团股份有限公司
Protein surface remodeling
InactiveCN101490548AInappropriate folding resistanceStrong recovery abilityBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexProtein insertion
Aggregation is a major cause of the misbehavior of proteins. A system for modifying a protein to create a more stable variant is provided. The method involves identifying non-conserved hydrophobic amino acid residues on the surface of a protein, suitable for mutating to more hydrophilic residues (e.g., charged amino acids). Any number of residues on the surface may be changed to create a variant that is more soluble, resistant to aggregation, has a greater ability to re-fold, and / or is more stable under a variety of conditions. The invention also provides GFP, streptavidin, and GST variants with an increased theoretical net charge created by the inventive technology. Kits are also provided for carrying out such modifications on any protein of interest.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
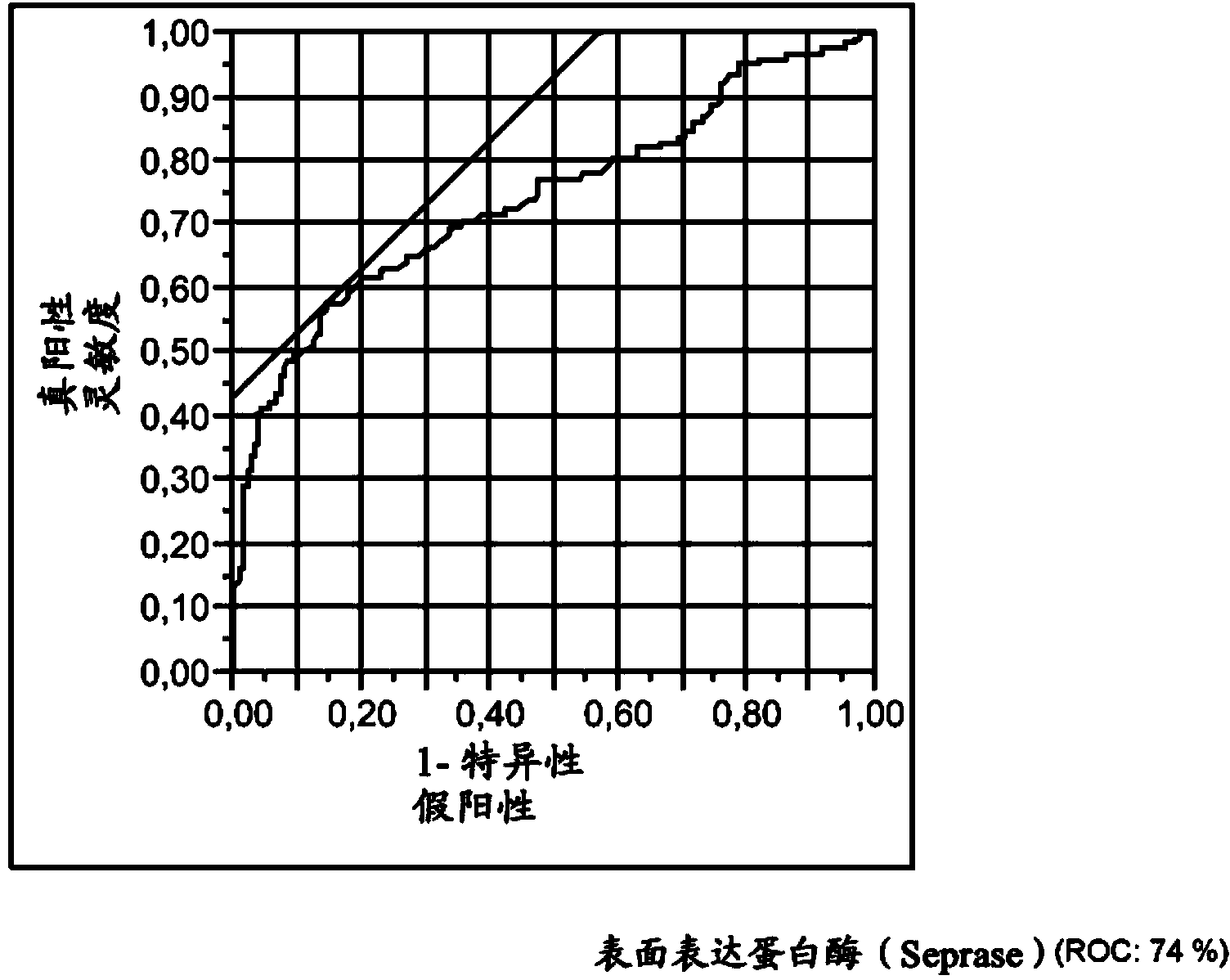
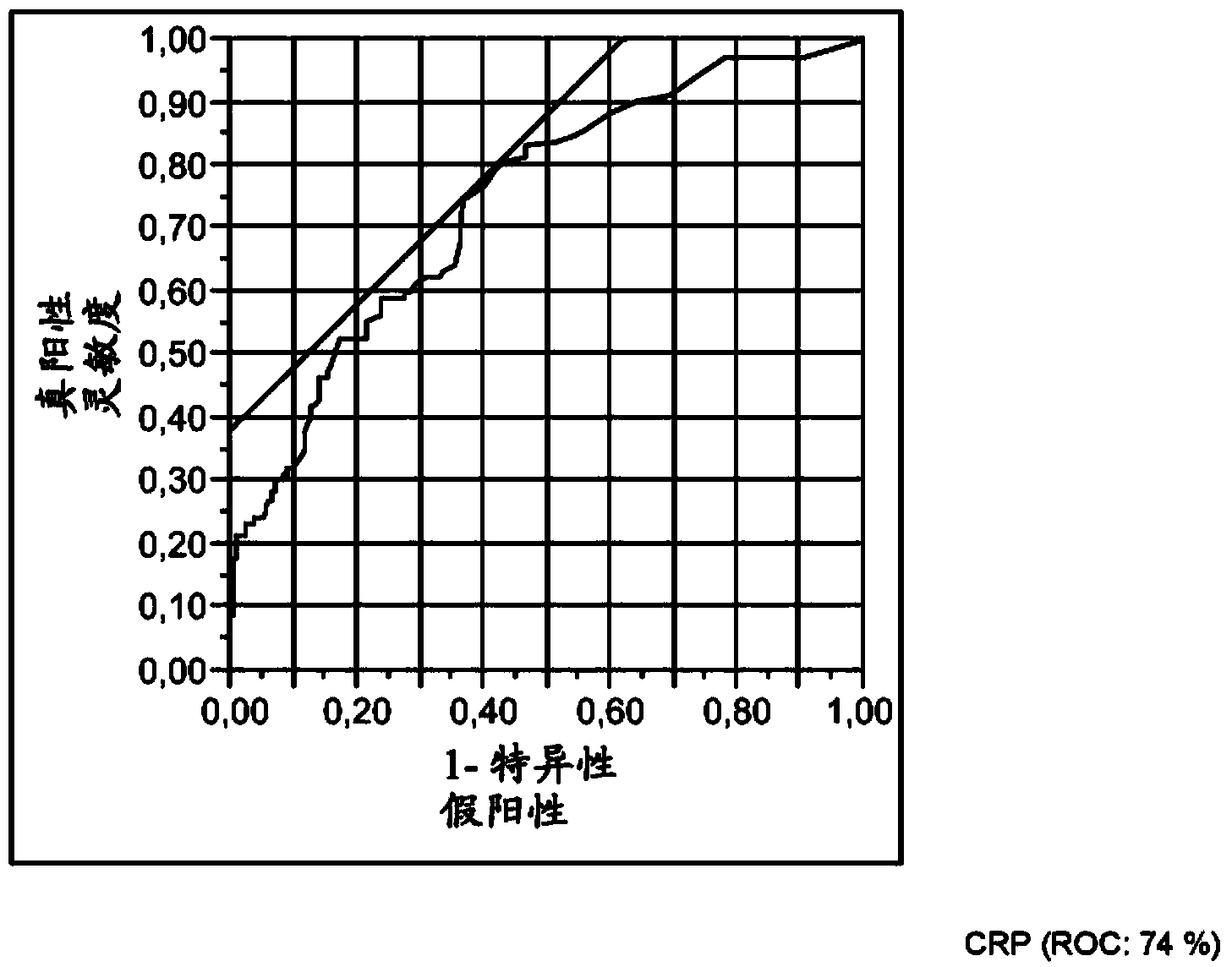
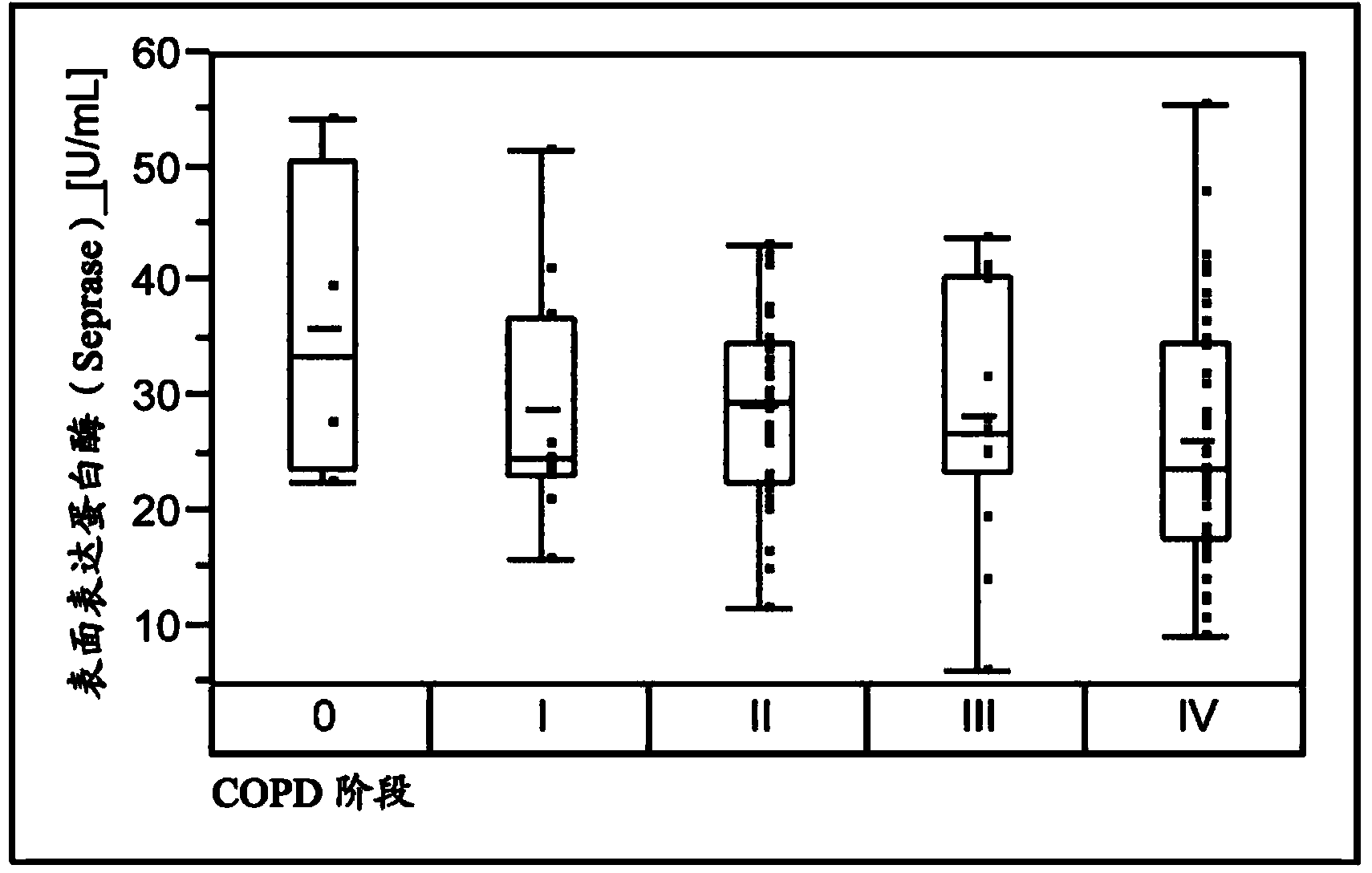
Seprase as marker for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd)
InactiveCN103415772ADisease diagnosisBiological testingObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesChronic obstruction
The present invention relates to an in vitro method aiding in the assessment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (= COPD). It discloses the use of the protein Seprase as a marker of COPD. Furthermore, it especially relates to a method for assessing COPD from a sample, derived from an individual by measuring the protein Seprase in said sample in vitro.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Products containing charged polymer complex microcapsules and method of use
In one aspect, the invention provides a method for treating a protein-containing surface, including applying to the surface a microcapsule suspension including droplets of a dispersed water-immiscible core phase, an aqueous continuous phase, and a wall surrounding each core phase droplet, the wall including the salt formed from at least one amphiphilic Lewis acid reactant or amphiphilic Lewis base reactant, and at least one corresponding Lewis base reactant or Lewis acid reactant.
Owner:CAPSULENT
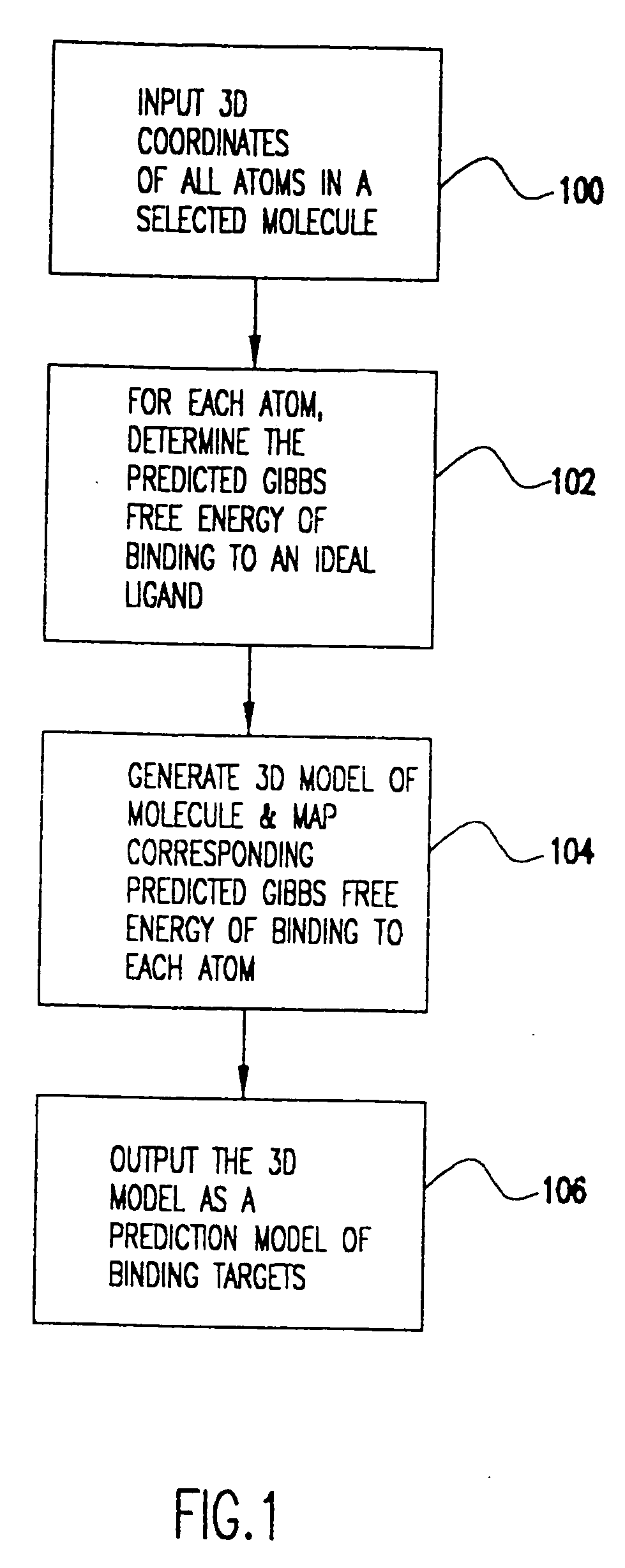
Method for the prediction of binding targets and the design of ligands
A computer-based method for the identification of binding targets in proteins and other macromolecules. More particularly, the invention includes an algorithm aimed at predicting binding targets in proteins. This algorithm, named Woolford, requires knowledge of the high resolution structure of the protein but no knowledge of the location or identity of natural binding sites or ligands. Binding targets in the protein are identified and classified according to their expected optimal affinities. Binding targets can be located at the protein surface or at internal surfaces that become exposed as a result of partial unfolding, conformational changes, subunit dissociation, or other events. The entire protein is mapped according to the binding potential of its constituent atoms. Once binding targets are identified, optimal ligands are designed and progressively built by the addition of individual atoms that complement structurally and energetically the selected target. This algorithm is expected to have significant applications in structure-based drug design since it allows: 1) identification of binding targets in proteins; 2) identification of additional targets if the primary target is known; 3) design of ligand molecules with optimal binding affinities for the selected target; and 4) refinement of lead compounds by defining the location and nature of chemical groups for optimal binding affinity.
Owner:FREIRE ERNESTO +1
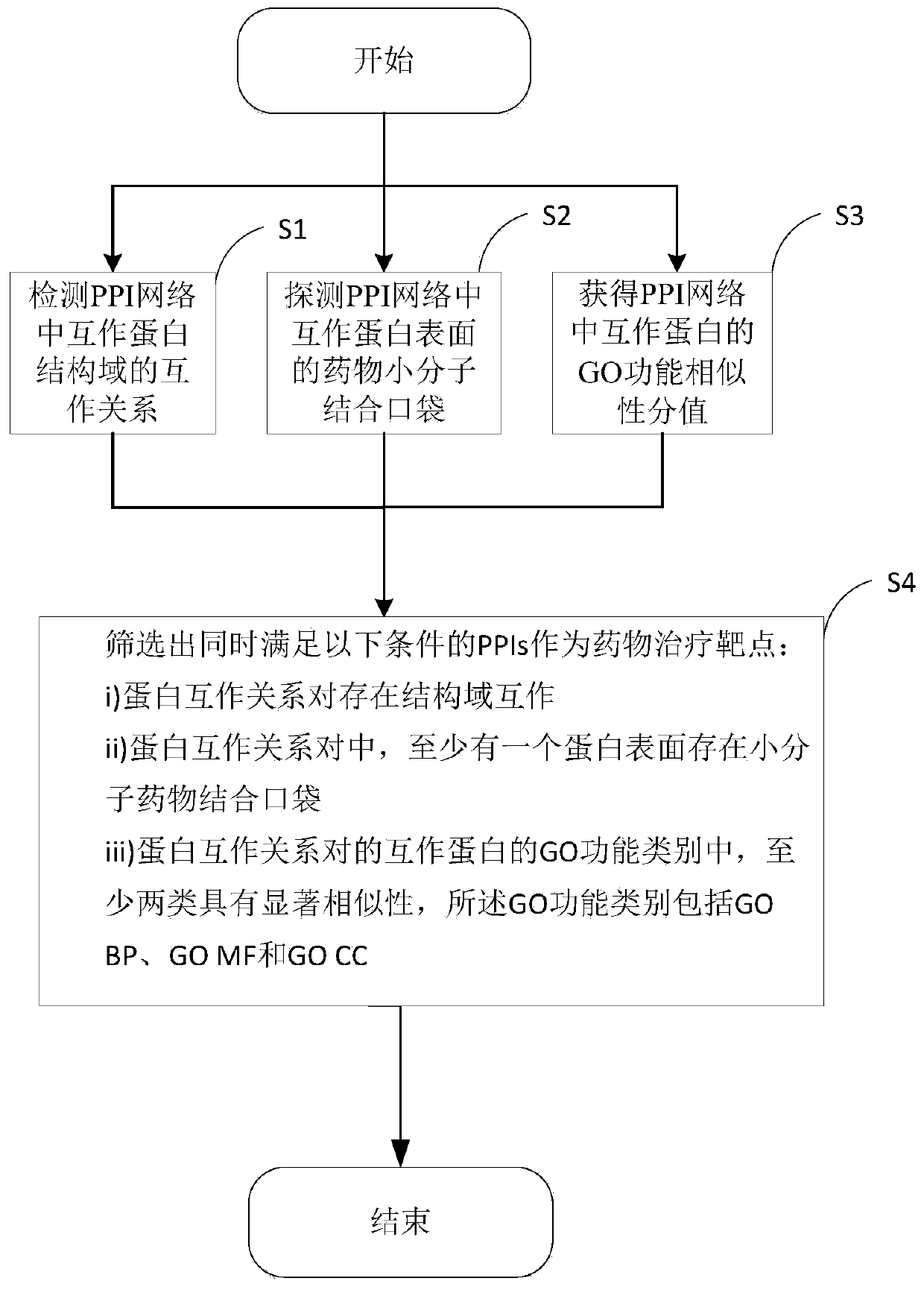
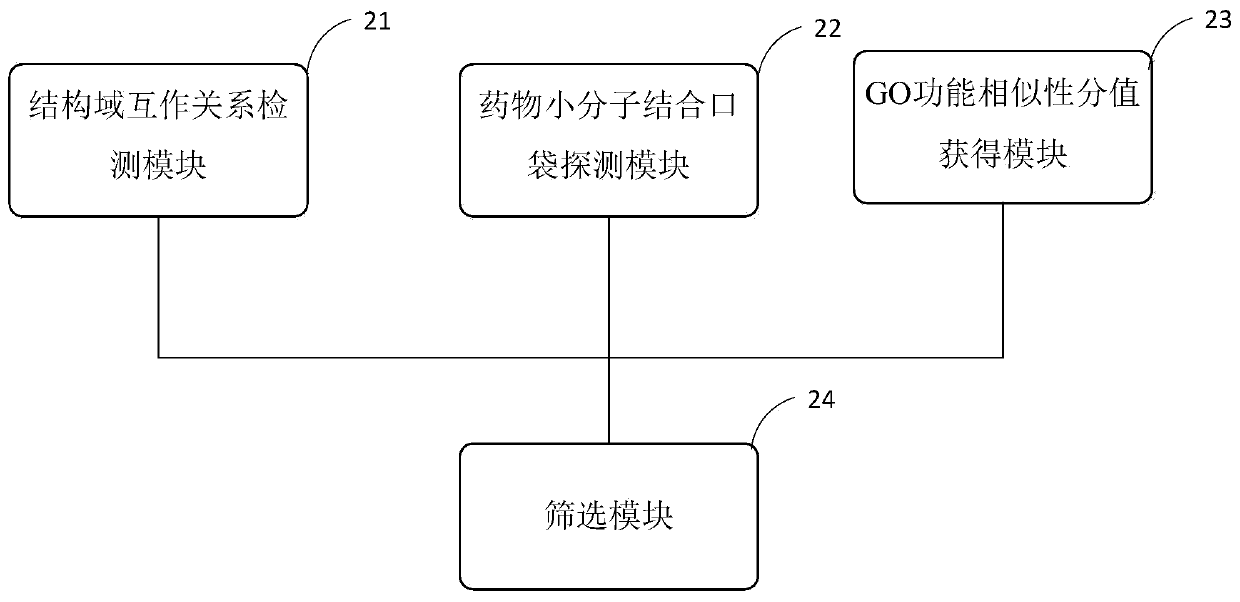
Target PPIs drug property prediction method and device based on protein interaction network
ActiveCN110544506AReliable interactionReduce false positivesProteomicsGenomicsPositive interactionInteractions protein
The invention provides a target PPIs drug property prediction method based on a protein interaction network. The method at least comprises the following steps: S1, detecting the interaction relationship of interaction protein structural domains in the PPI network; S2, detecting a drug small molecule binding pocket on the surface of interaction protein in the PPI network; S3, obtaining a GO function similarity score of the interactive protein in the PPI network; S4, screening out PPIs meeting the following conditions at the same time to serve as drug therapy targets: protein interaction relationship pairs have structural domain interaction; in the protein interaction relationship pair, at least one protein surface has a small molecule drug binding pocket; at least two of the GO function categories of the interaction proteins of the protein interaction relationship pair have significant similarity, and the GO function categories comprise GO BP, GO MF and GO CC. According to the method, three strict mutually independent standards are adopted to comprehensively explore and discover the target PPI, false positive interaction is systematically eliminated, more reliable PPIs are selectedas drug targets, and the calculation result better conforms to objective reality.
Owner:上海源兹生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com