Method for improving heat stability of lipase A of bacillus subtilis
A Bacillus subtilis, thermostable technology, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of complex process, high price, large screening workload of high-throughput screening methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
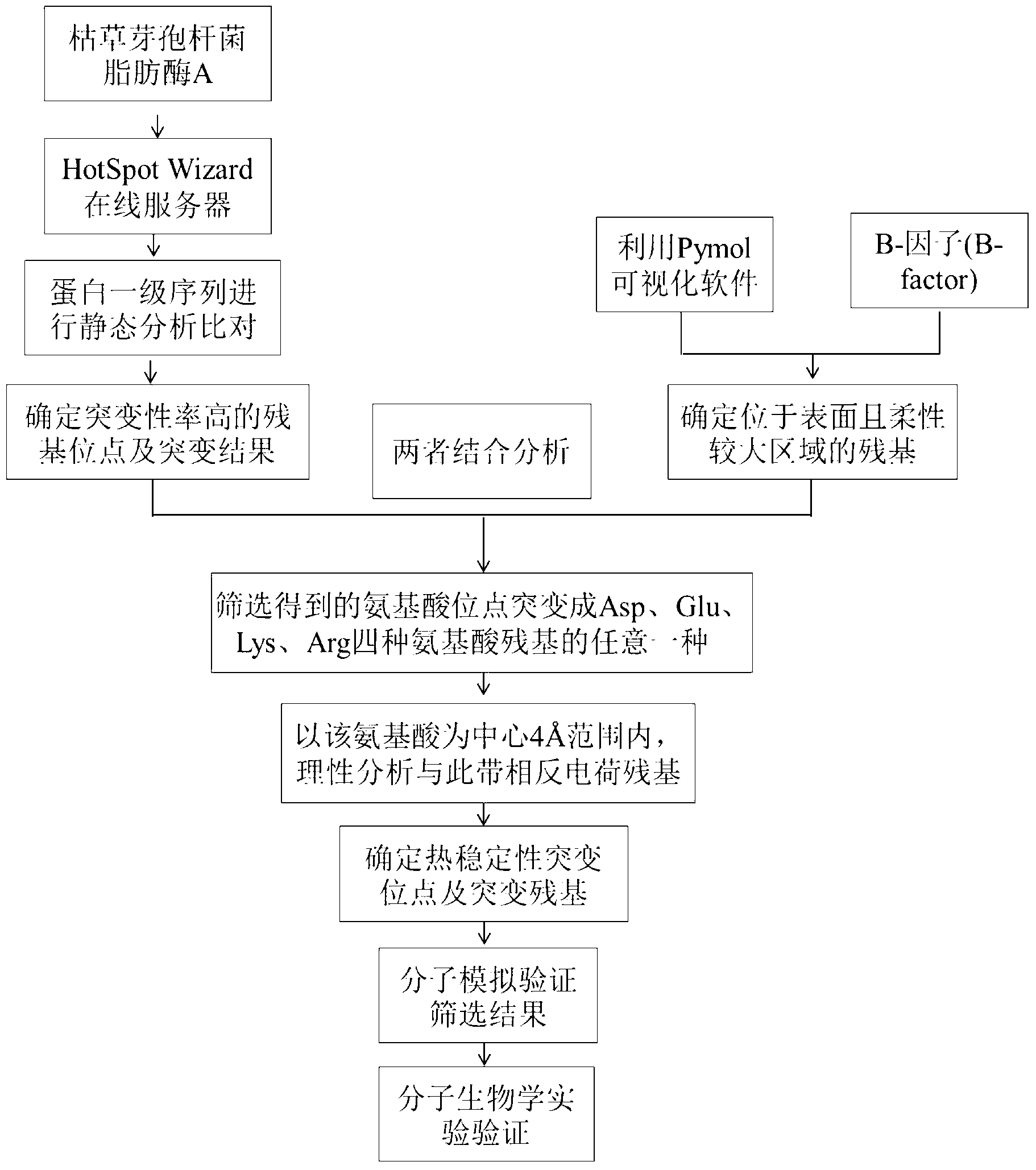
[0024] This example illustrates the method of step 1) of the present invention for predicting hot spots of amino acid mutations in Bacillus subtilis lipase A.
[0025] Taking Bacillus subtilis lipase A (Bacillus subtilis lipase A, PDB: 1I6W) as the research target, using the HotSpot Wizard online server to virtually screen mutation hotspots, and statically analyze the primary sequences of more than 50 Bacillus subtilis lipase family proteins By comparison, the mutability rate and mutation results of each residue of Bacillus subtilis lipase A are obtained, the amino acid residue sites with high mutation rate are screened, and functional amino acids around the catalytic active center and substrate channel are excluded, thereby predicting amino acid mutations hotspot area.
[0026] This round of screening for thermally stable points was performed on residues with a mutation rate of 9. For example, in the first round, residues with a mutation rate of 9 cannot be screened for reas...
Embodiment 2
[0029]This example illustrates step 2) of the present invention, a method for determining the amino acid sites located on the surface of the protein and in a relatively flexible region.
[0030] Use Pymol visualization software and B-factor (B-factor) to determine the amino acid positions on the surface of the protein and in the more flexible region.
[0031] Use PyMOl to visualize amino acid processes located on protein surfaces:
[0032] PyMOL>load 1I6W.pdb (open the three-dimensional structure of Bacillus subtilis lipase A);
[0033] PyMOL>show surface (protein is expressed in surface form);
[0034] PyMOL>color white (the protein surface is displayed in white);
[0035] PyMOL>select3, resi3 (3 represents the third residue, and the following residues are displayed in this way);
[0036] PyMOL>color red,3 (show the third amino acid in red to determine whether it is on the surface of the protein);
[0037] PyMOL>color white,3 (make the third amino acid epitope white).
...
Embodiment 3
[0042] This example illustrates the method of combining the results obtained in Example 1 and Example 2 to analyze and determine amino acid mutation sites related to thermal stability.
[0043] Combine the results obtained in Examples 1 and 2 to determine the amino acid mutation site related to thermostability, if the mutation becomes aspartic acid (Asp), glutamic acid (Glu), lysine (Lys), arginine (Arg ) Any one of the four amino acid residues can improve the thermostability of the enzyme.
[0044] Using Pymol visualization software, with this amino acid as the center, in 4 The process of searching for the oppositely charged amino acid residues in the above four amino acids within the scope.
[0045] PyMOL>select60, resi60 (select amino acids that can be mutated);
[0046] PyMOL>select near60,60expand4 (select 4 range of residues, determine if it is the oppositely charged residue).
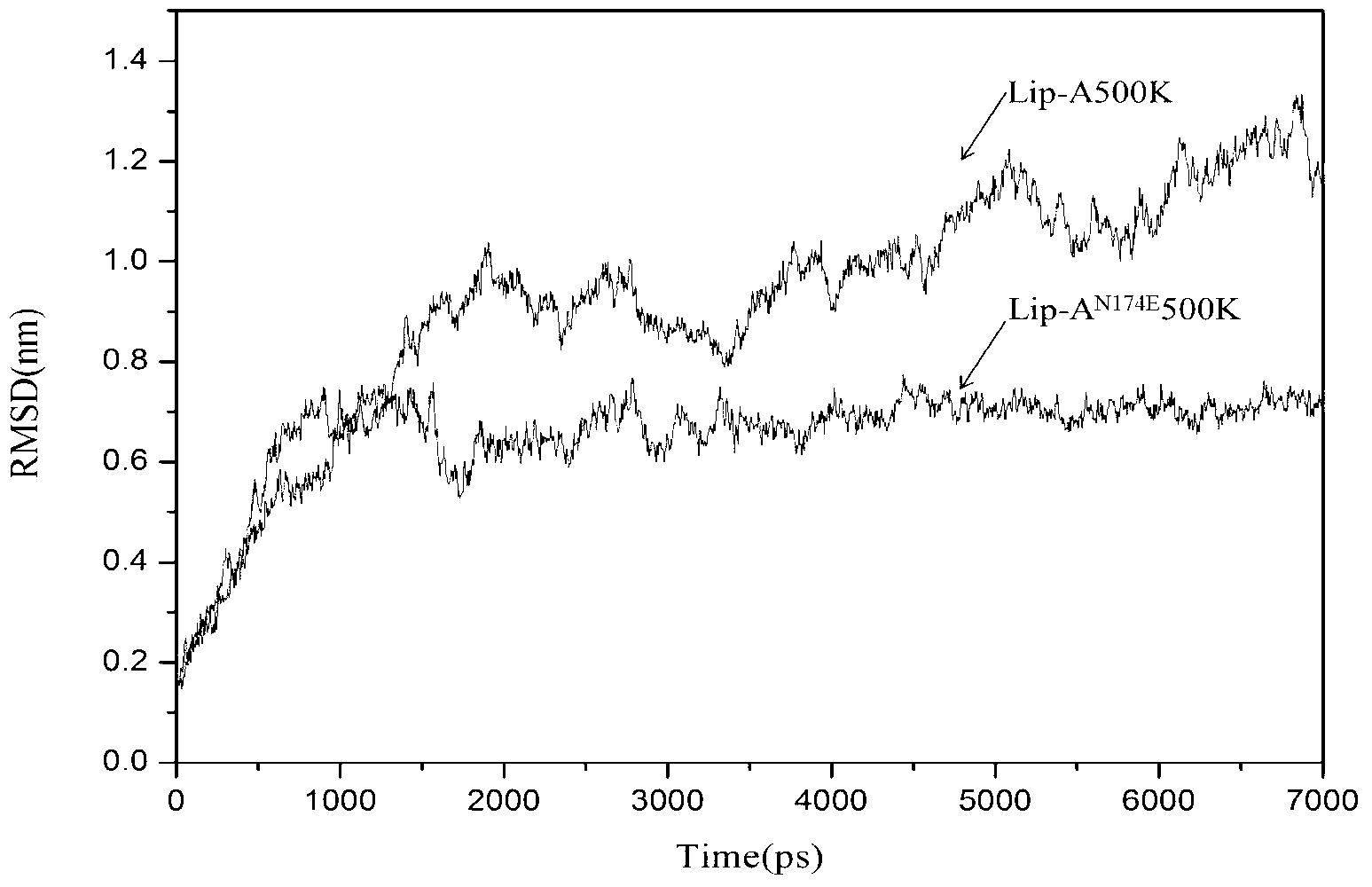
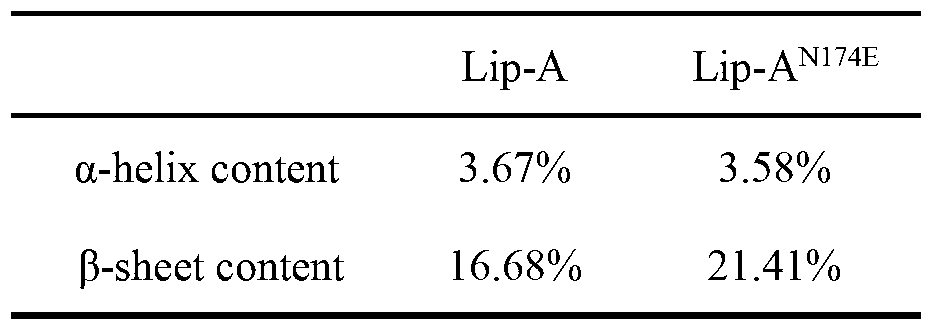
[0047] Through the above analysis, the following high mutation rate residues and result...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com