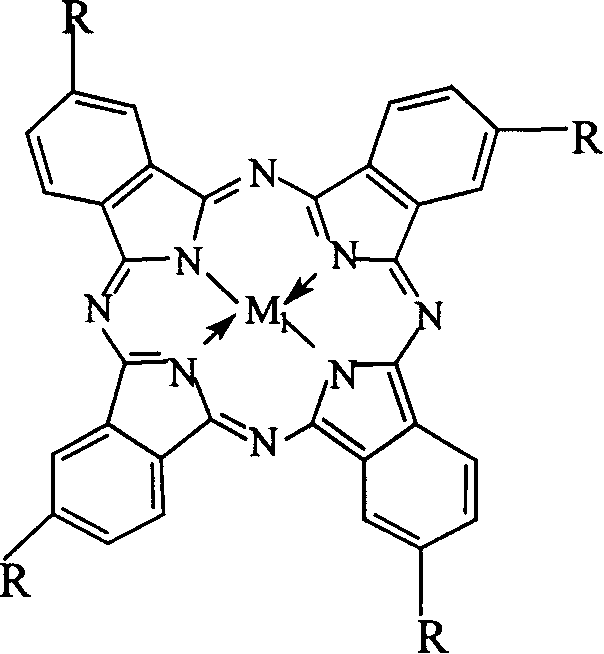
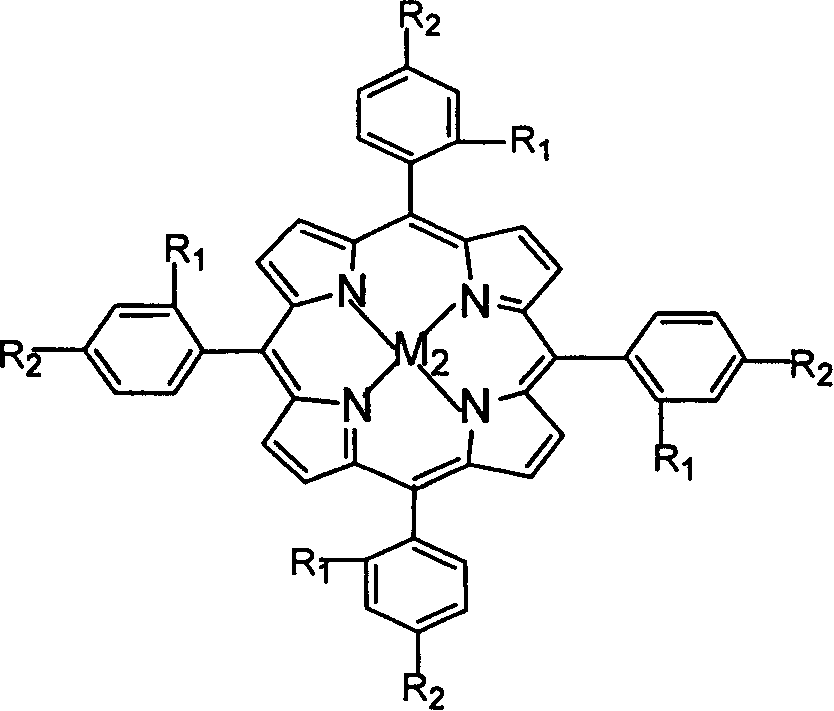
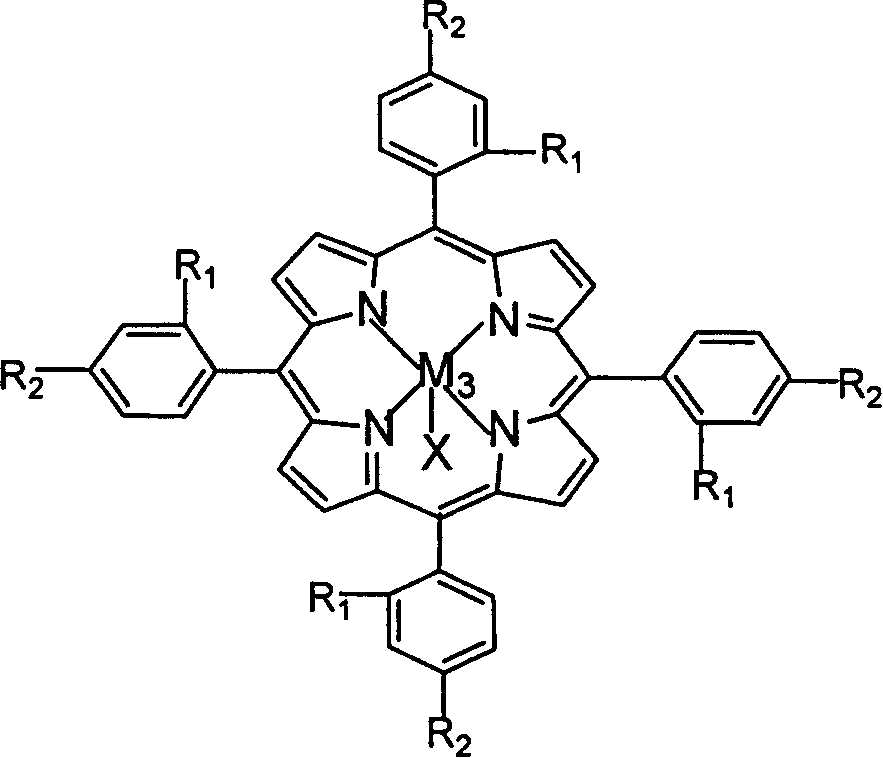
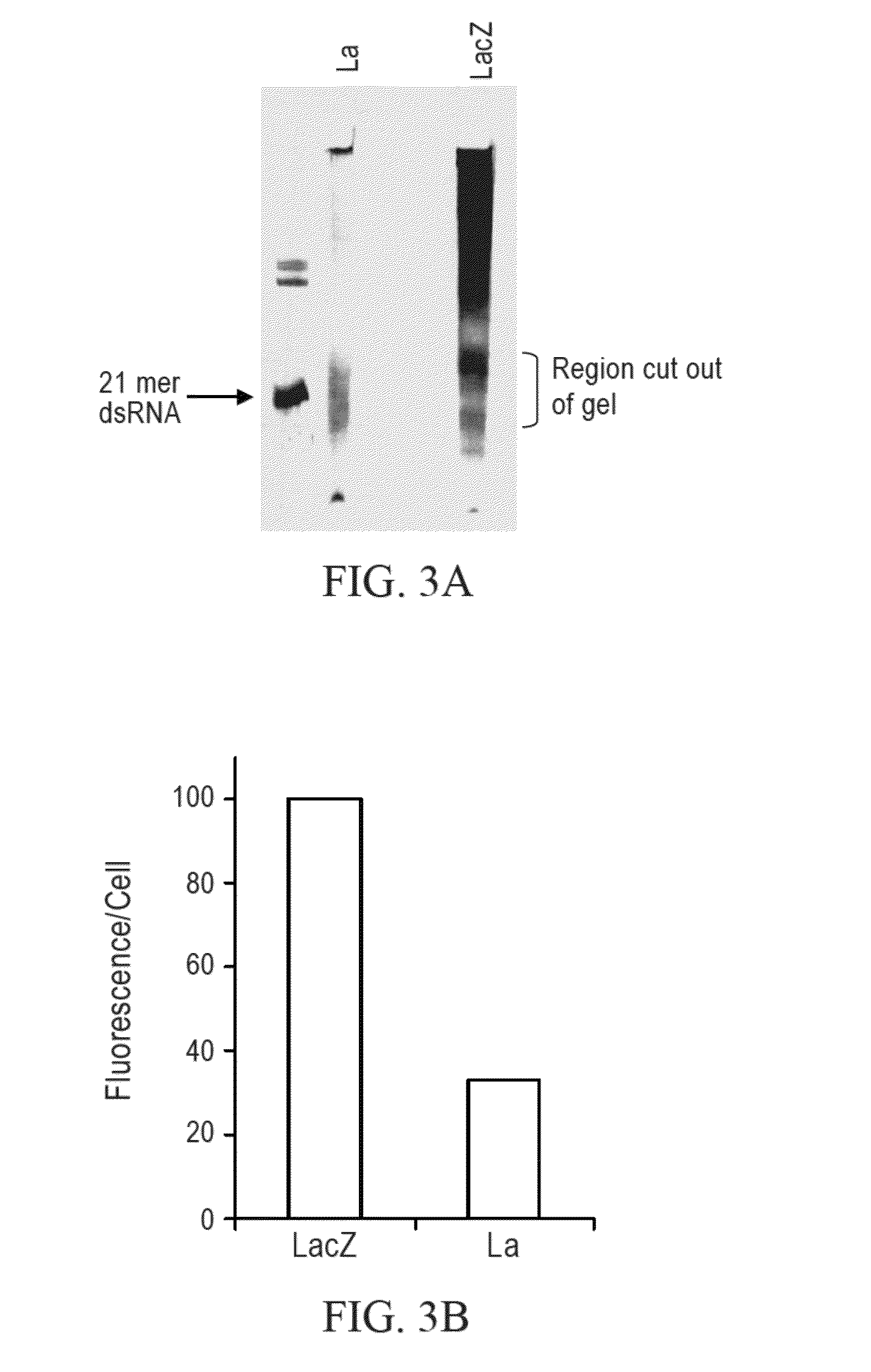
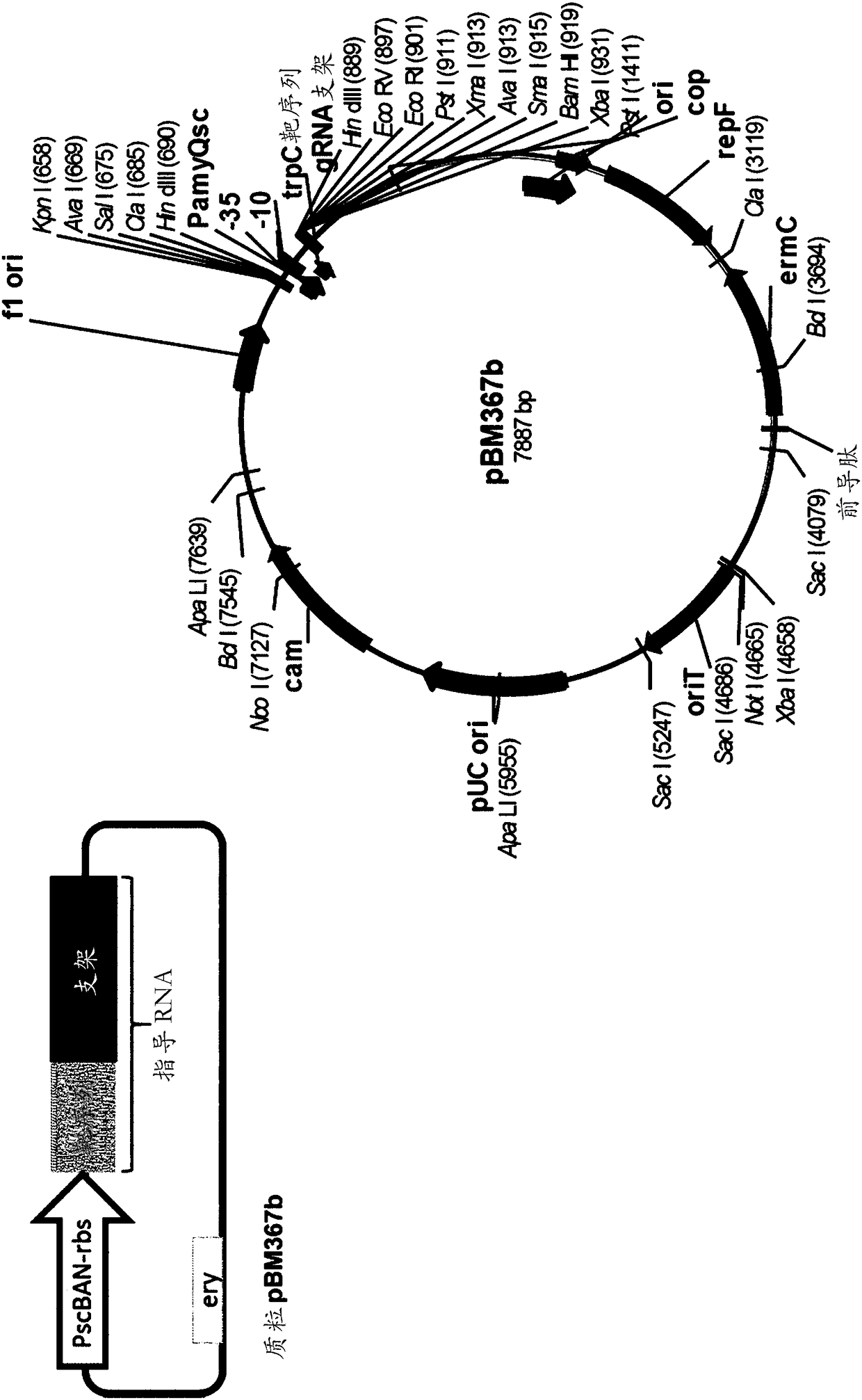
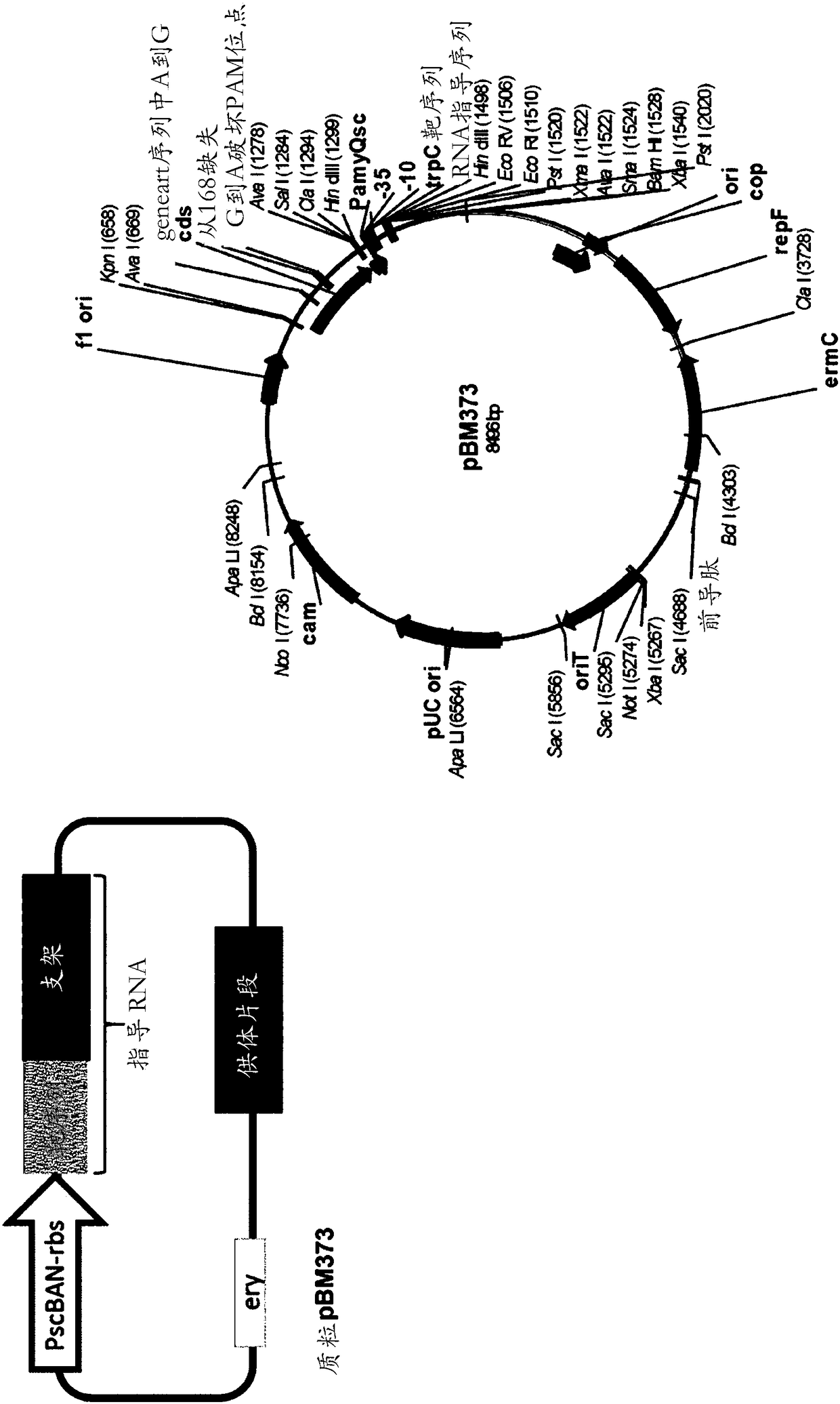
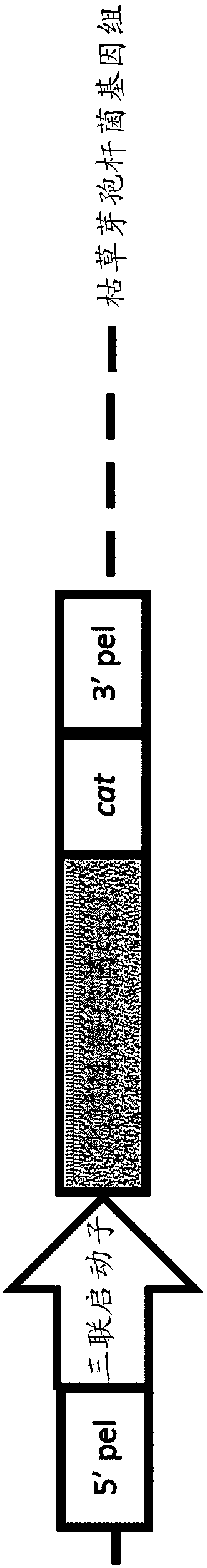
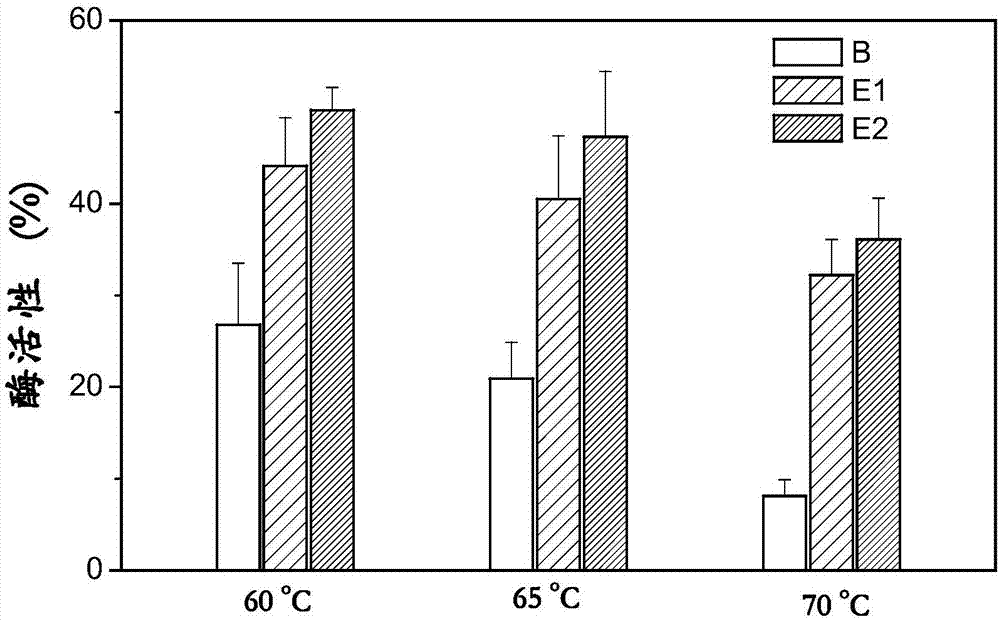
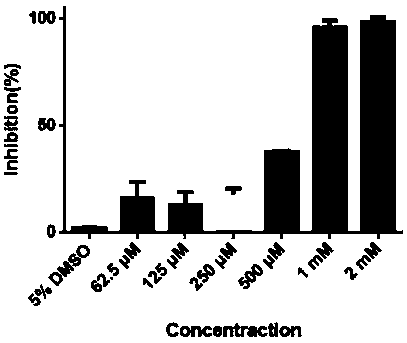
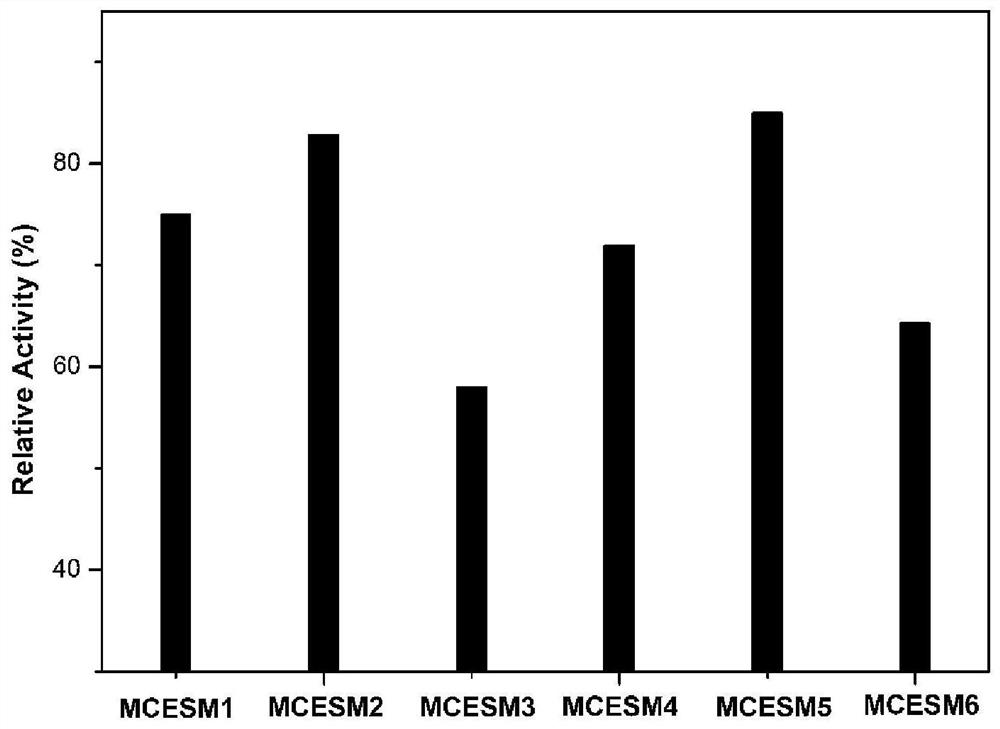
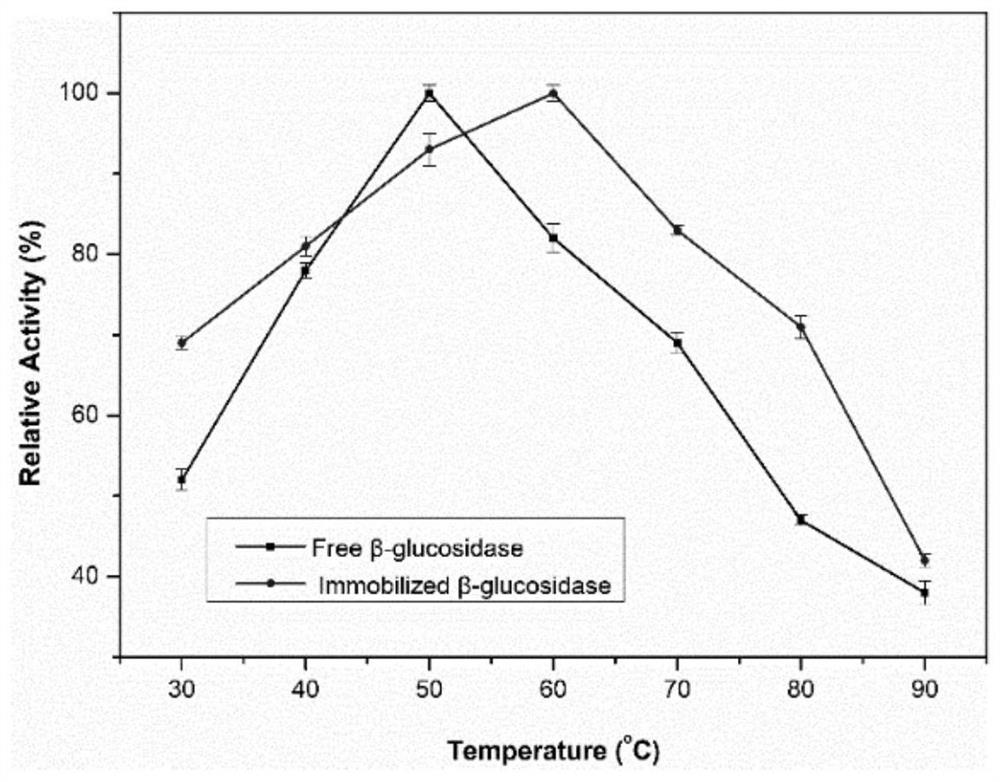
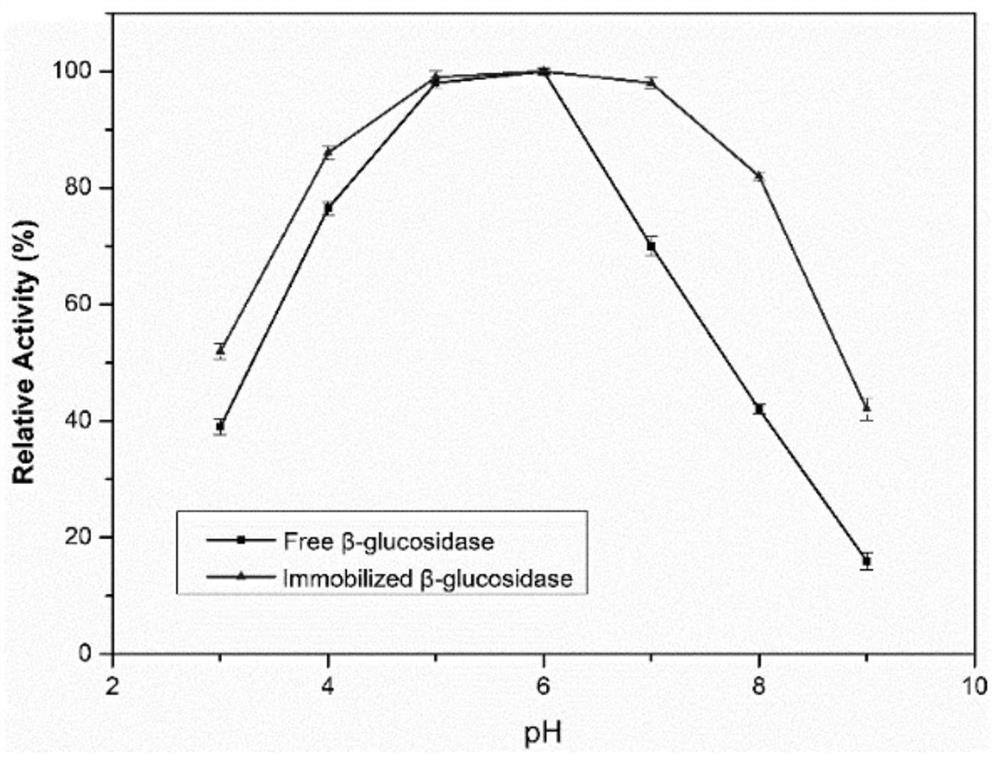
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Enzyme structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
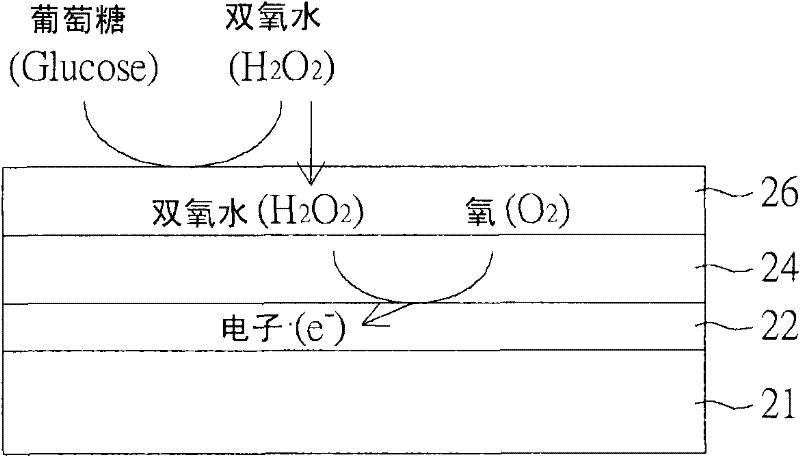
Basic structure of enzyme. Enzymes are globular protein molecules that have three-dimensional shape with atleast one surface region having an area with a crevice or pocket. The crevice occupies only a small portion of the enzyme’s surface and is known as its active site.
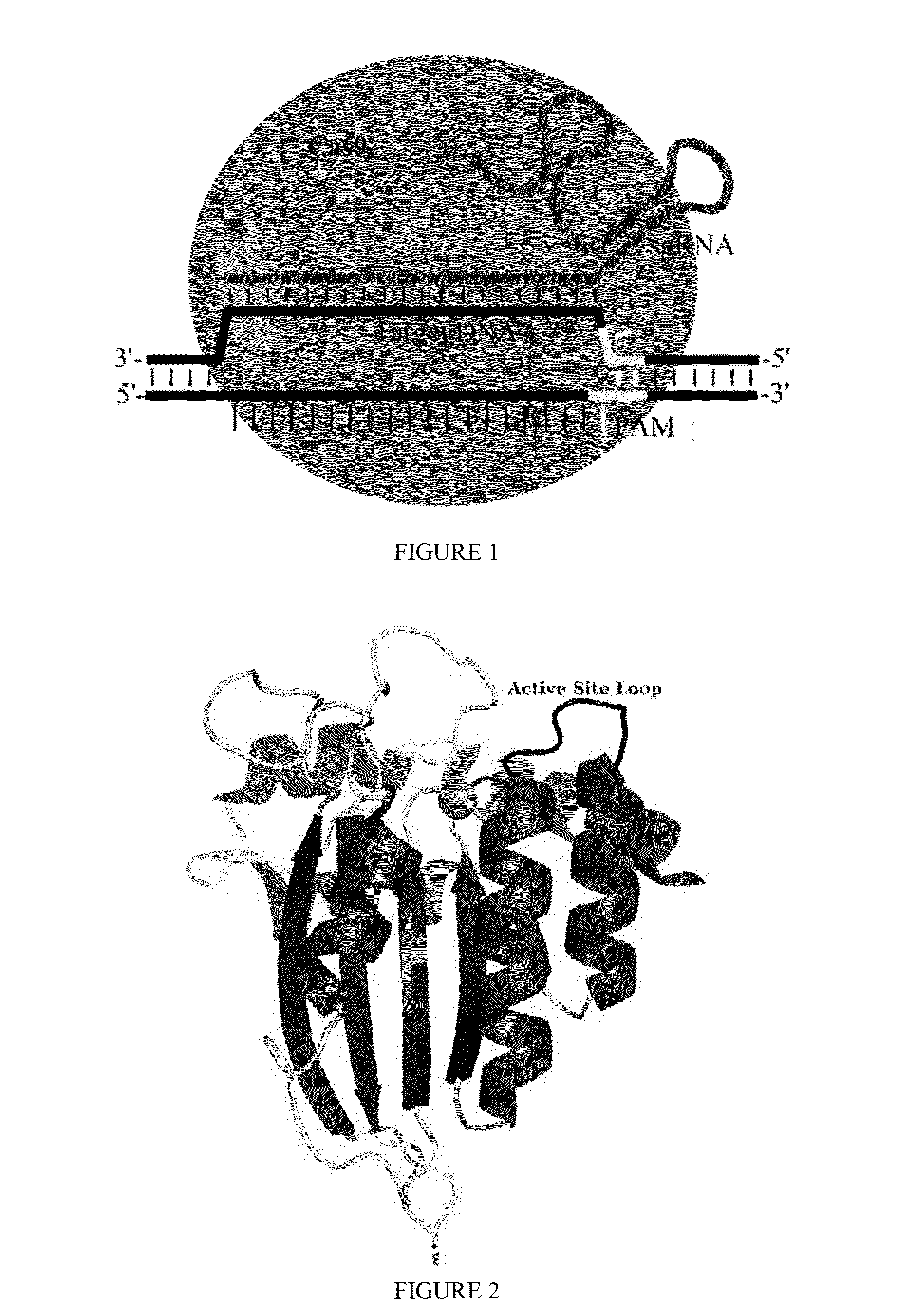
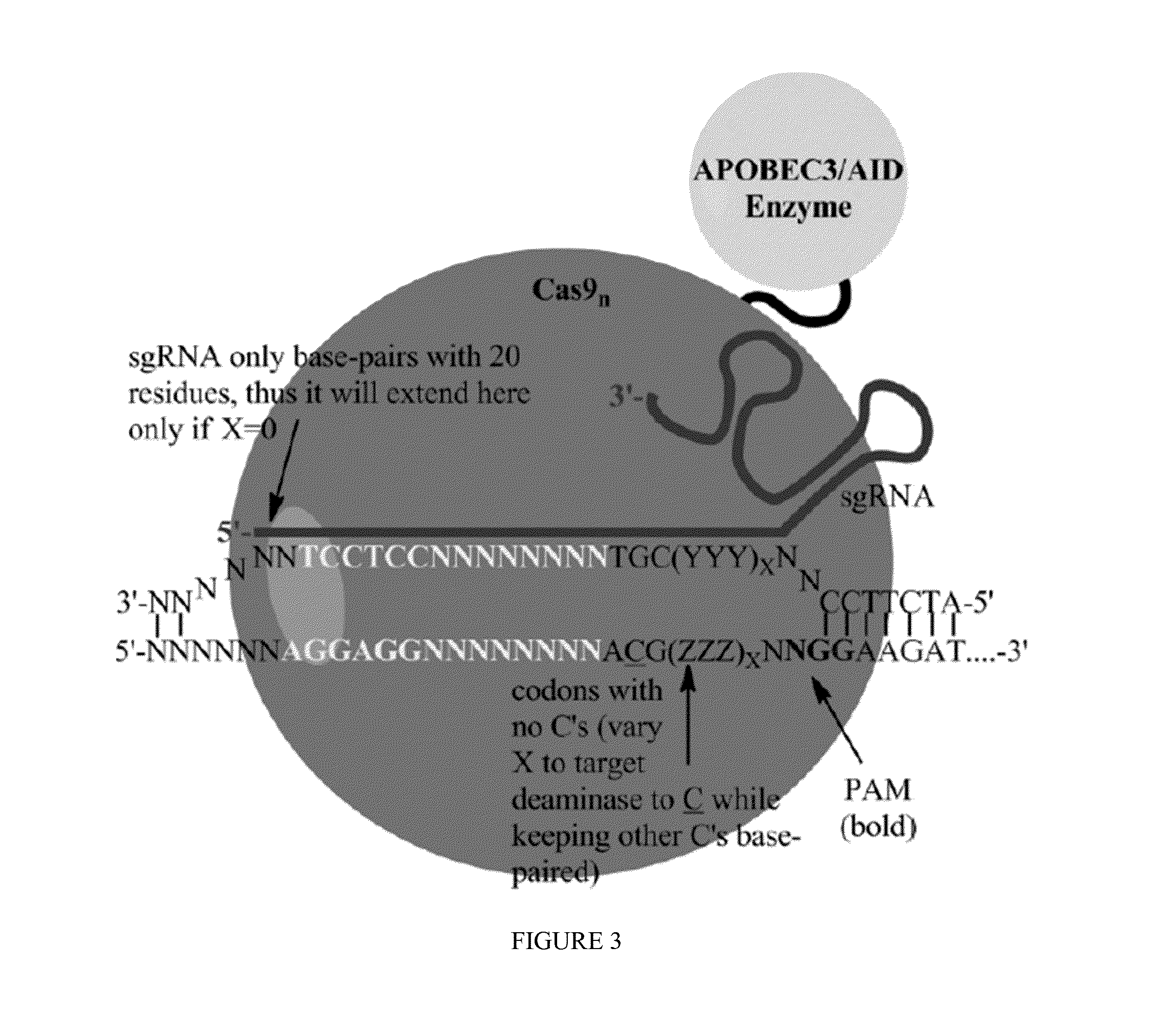
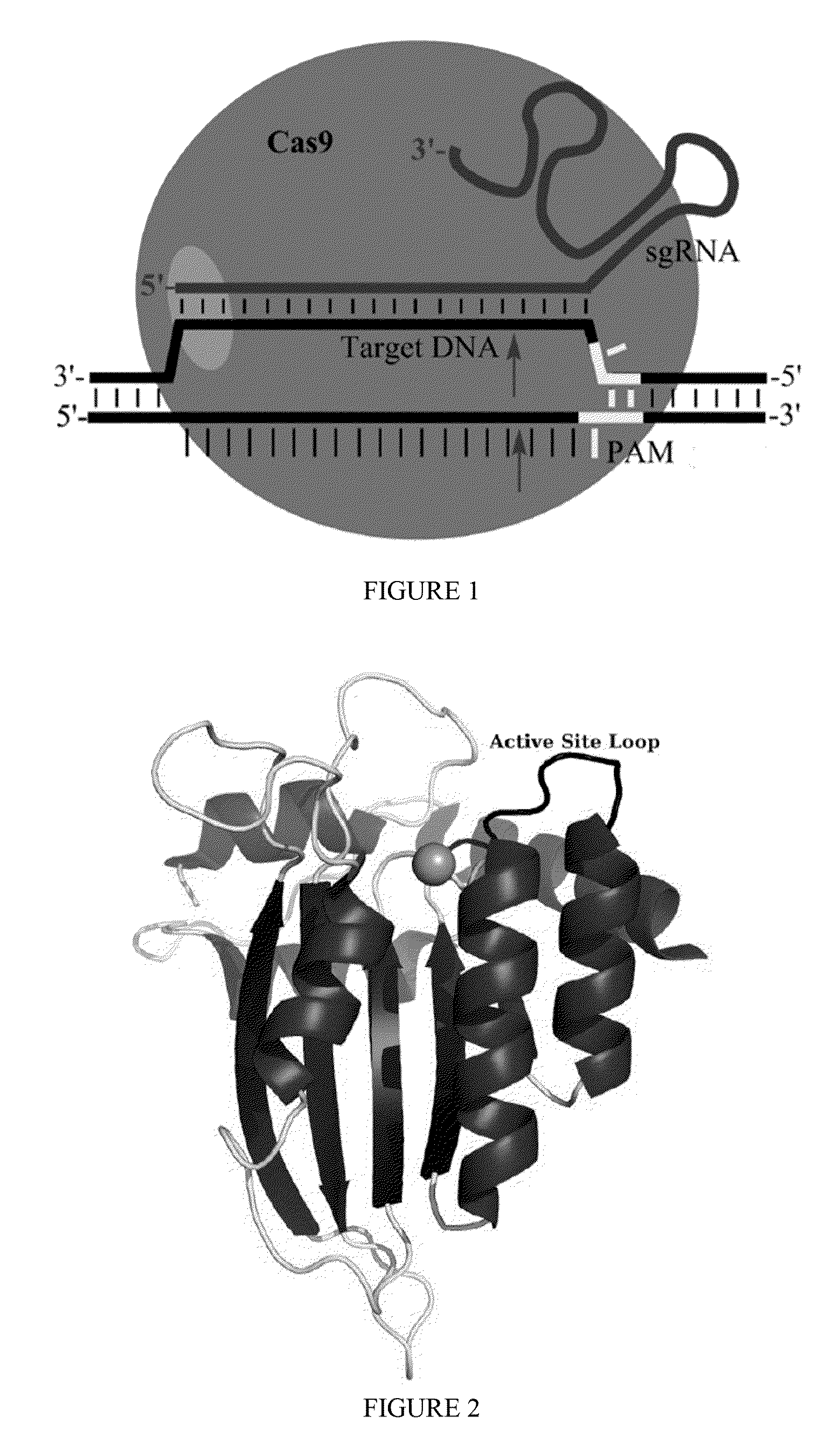
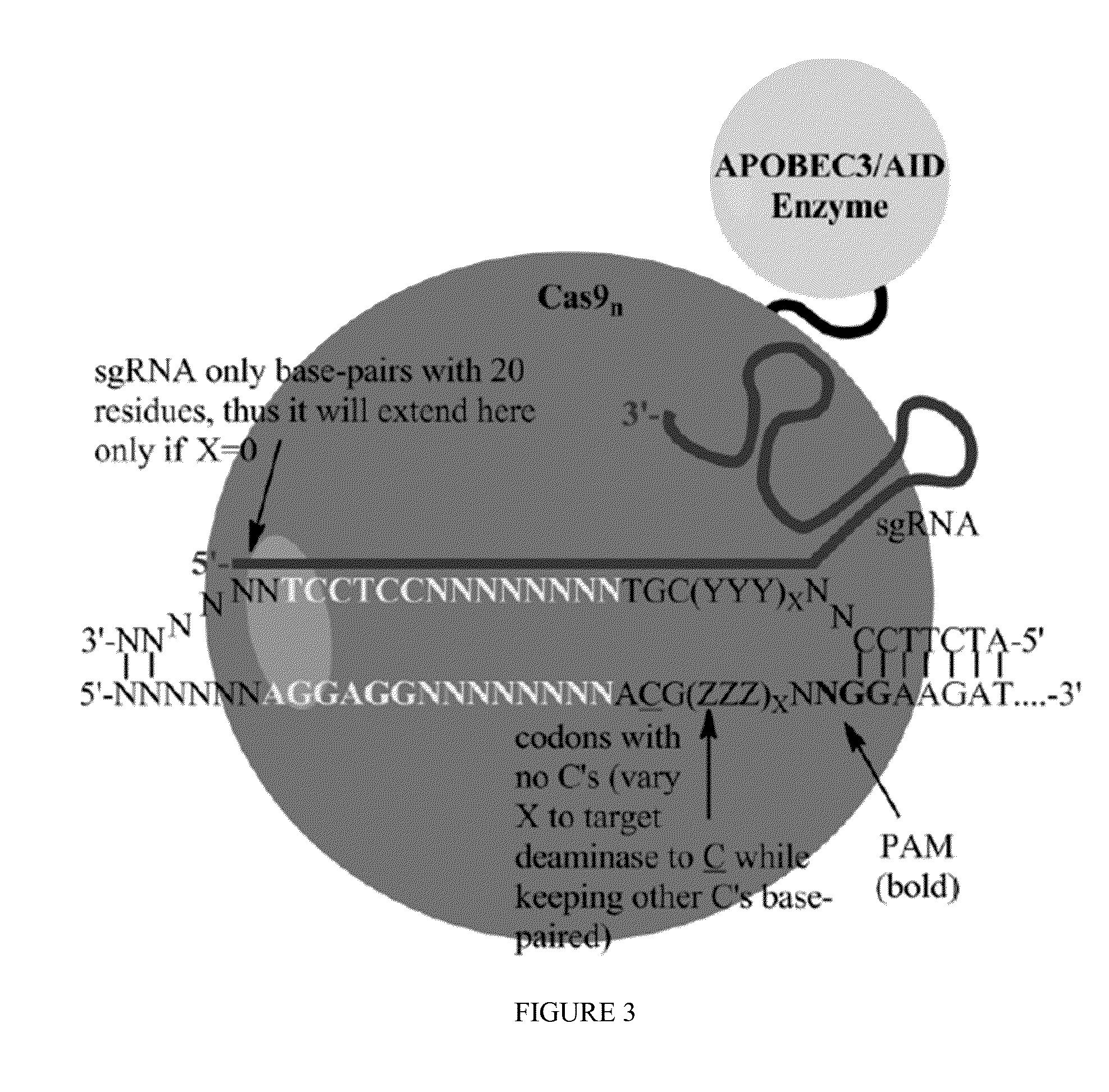
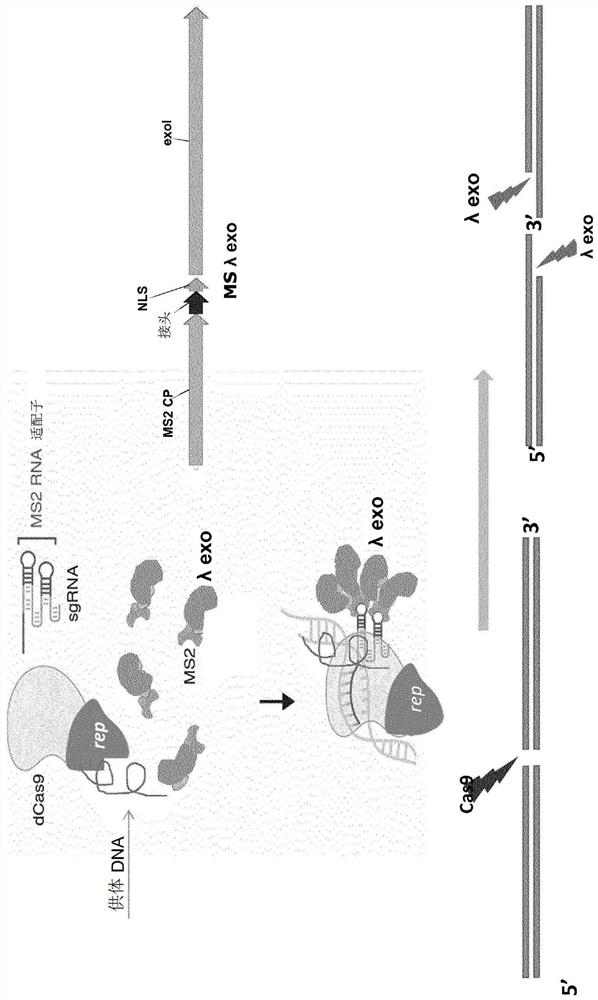
Fusions of cas9 domains and nucleic acid-editing domains
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
InactiveUS20150166984A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant α-antitrypsin protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting an α-antitrypsin point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method of preparing adipinic acid using bionic catalytic oxggen to oxidize cyclohexane
InactiveCN1231449CReduce dosageHigh catalytic activityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationRecyclable catalystEnzyme structure
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
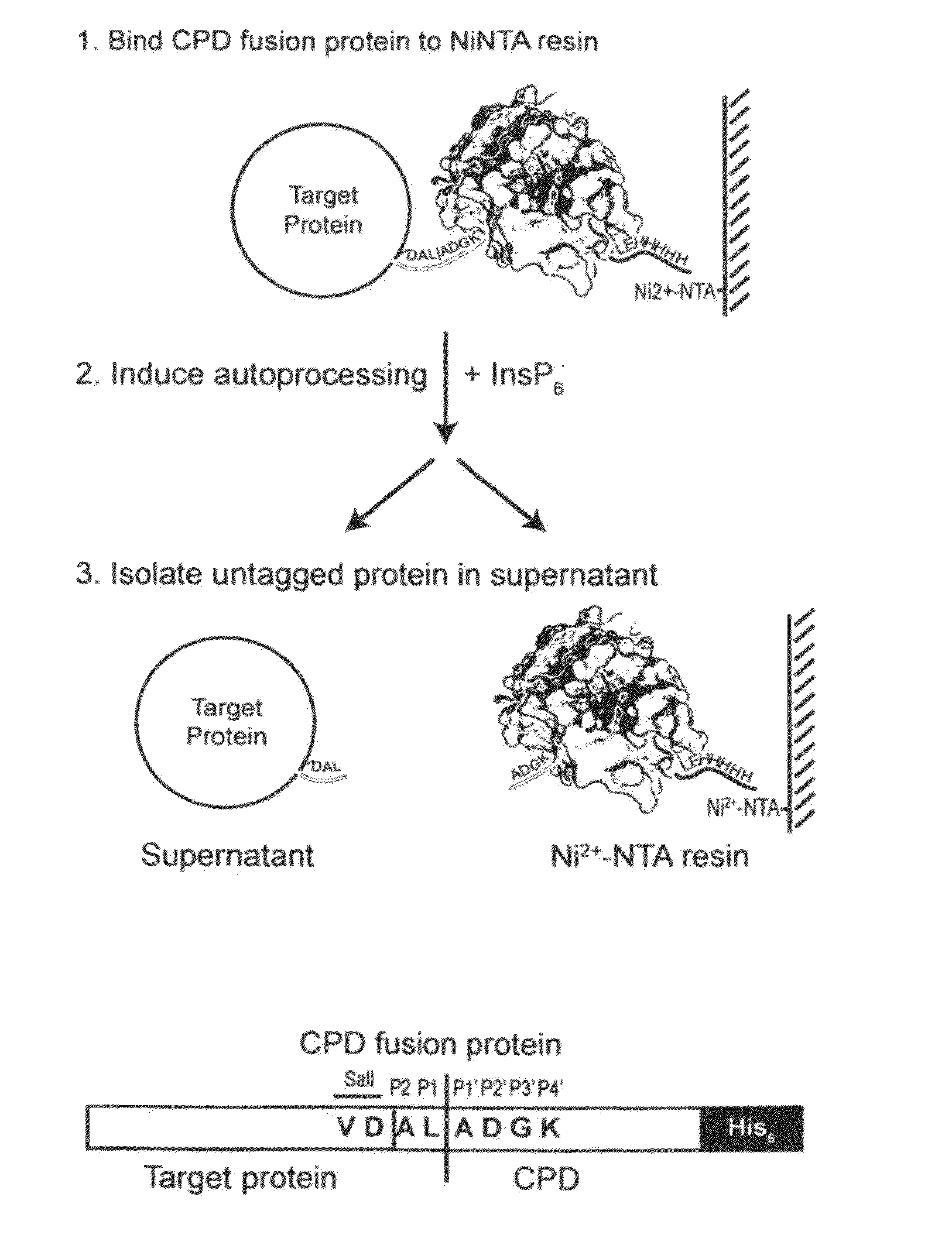
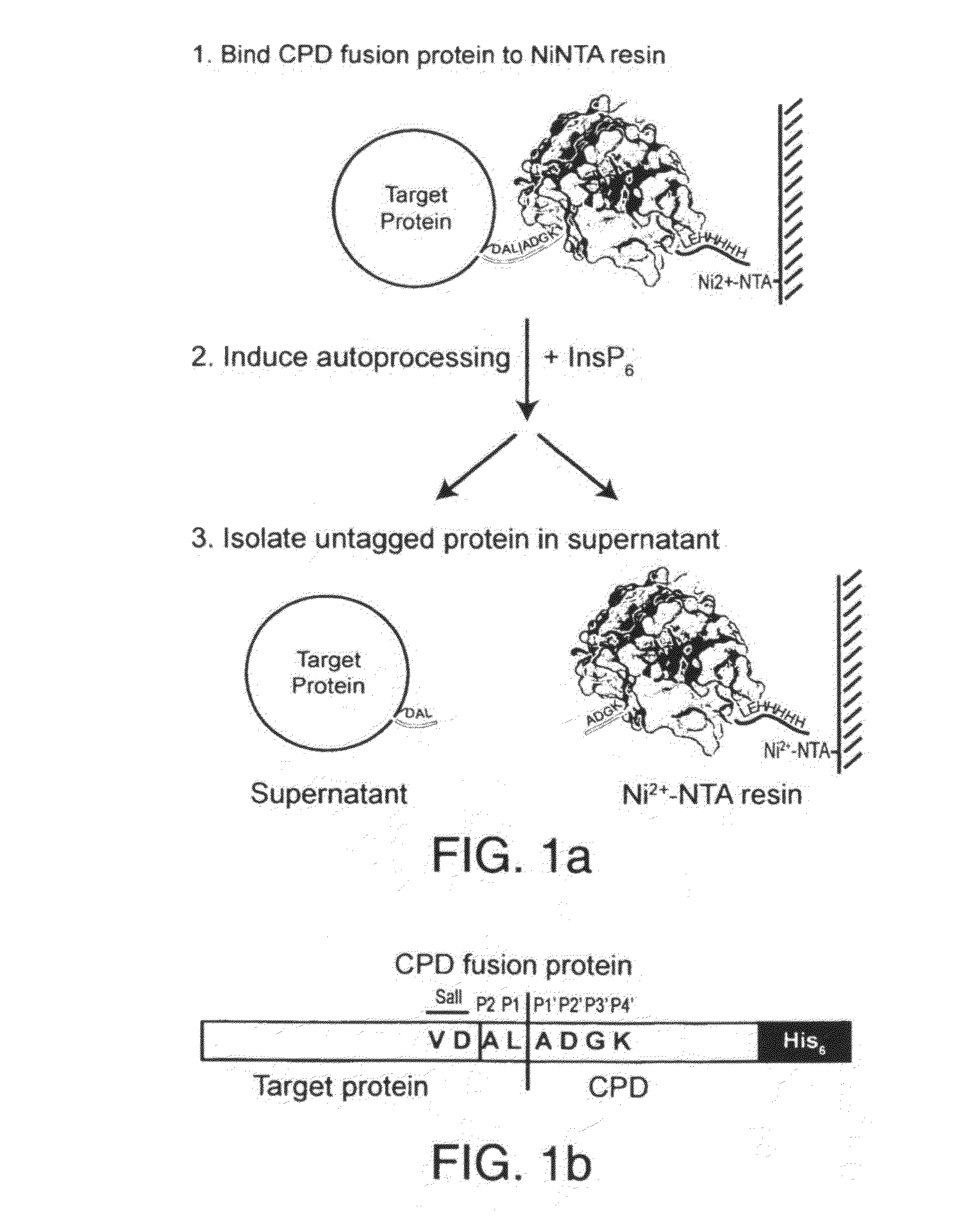
Inducible self-cleaving protease tag and method of purifying recombinant proteins using the same
A method of purifying a protein is disclosed which entails: a) fusing a site-specific affinity-tagged cysteine protease domain to a target protein to form a tagged fusion protein; b) activating the site-specific cysteine protease domain of the tagged fusion protein by subjecting the site-specific affinity-tagged cysteine protease domain to an inducer, which induces autoprocessing at a cleavage site; thereby releasing untagged target protein; and c) isolating the untagged target protein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
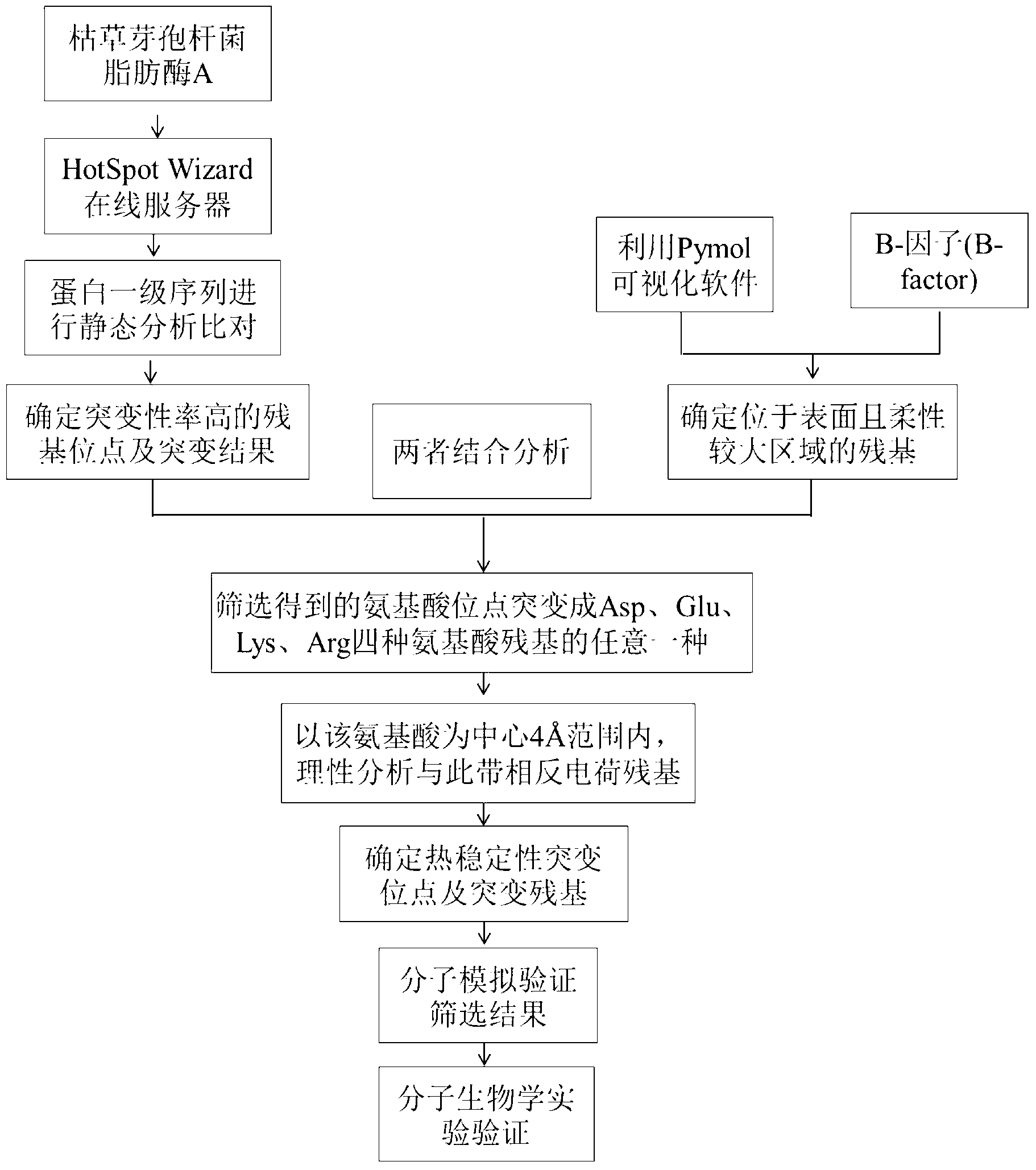
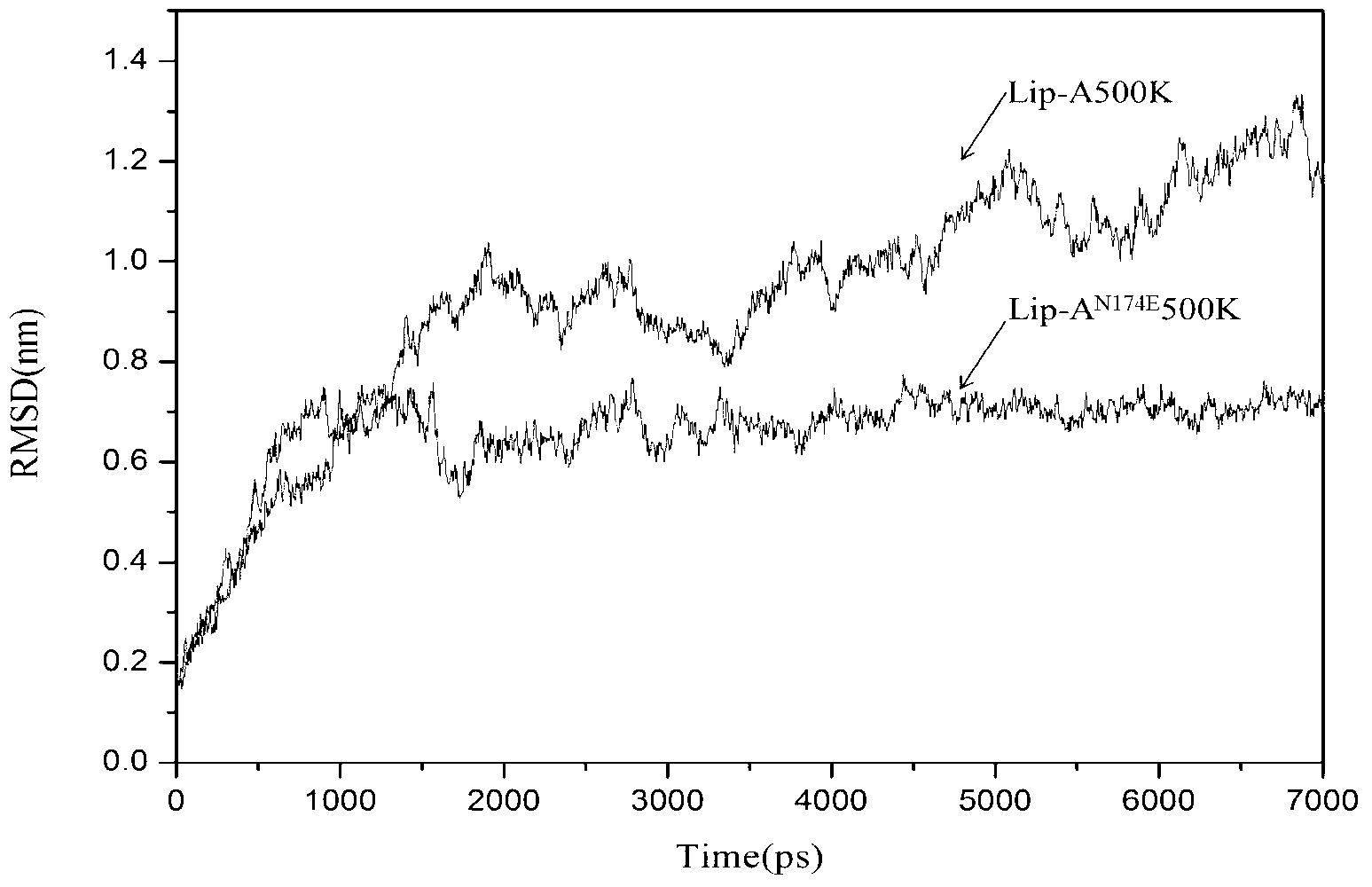
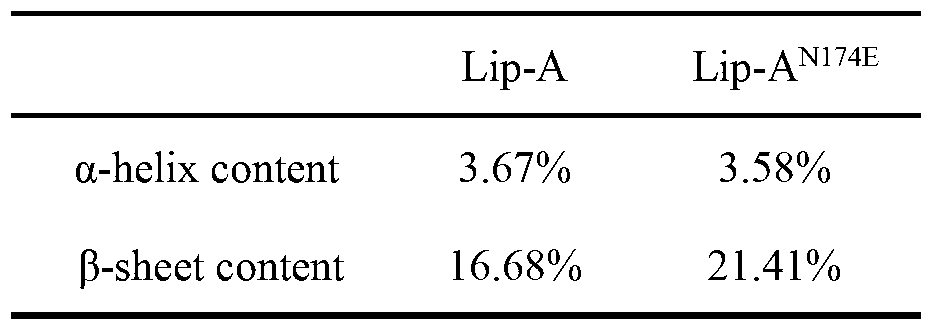
Method for improving heat stability of lipase A of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN103243078AThe method is simple and fastHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEnzyme structureArginine
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and relates to a method for improving the heat stability of lipase A of bacillus subtilis. According to the method, the lipase A of the bacillus subtilis is used as an object of study, and the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, screening mutational hot spot areas; secondly, determining the amino acid site of an area which is positioned on the surface of protein and is higher in flexibility; thirdly, carrying out rational analysis by combining the two steps, mutating the screened amino acid site into any one of four amino acid residues including aspartic acid, glutamic acid, lysine and arginine, taking the amino acid as a center, and searching the amino acid residues with opposite charges in the four amino acids in a range of 4 angstroms to determine a mutation site and a mutation residue; fourthly, on the basis of the acknowledge of an enzyme structure and a functional relationship, resolving ionic bonds, and introducing a mechanism of action for stabilizing the protein structure of the lipase A of the bacillus subtilis; and finally, proving hot spot residues with modified heat stability through hot stability experiments of mutant strains of the lipase A of the bacillus subtilis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
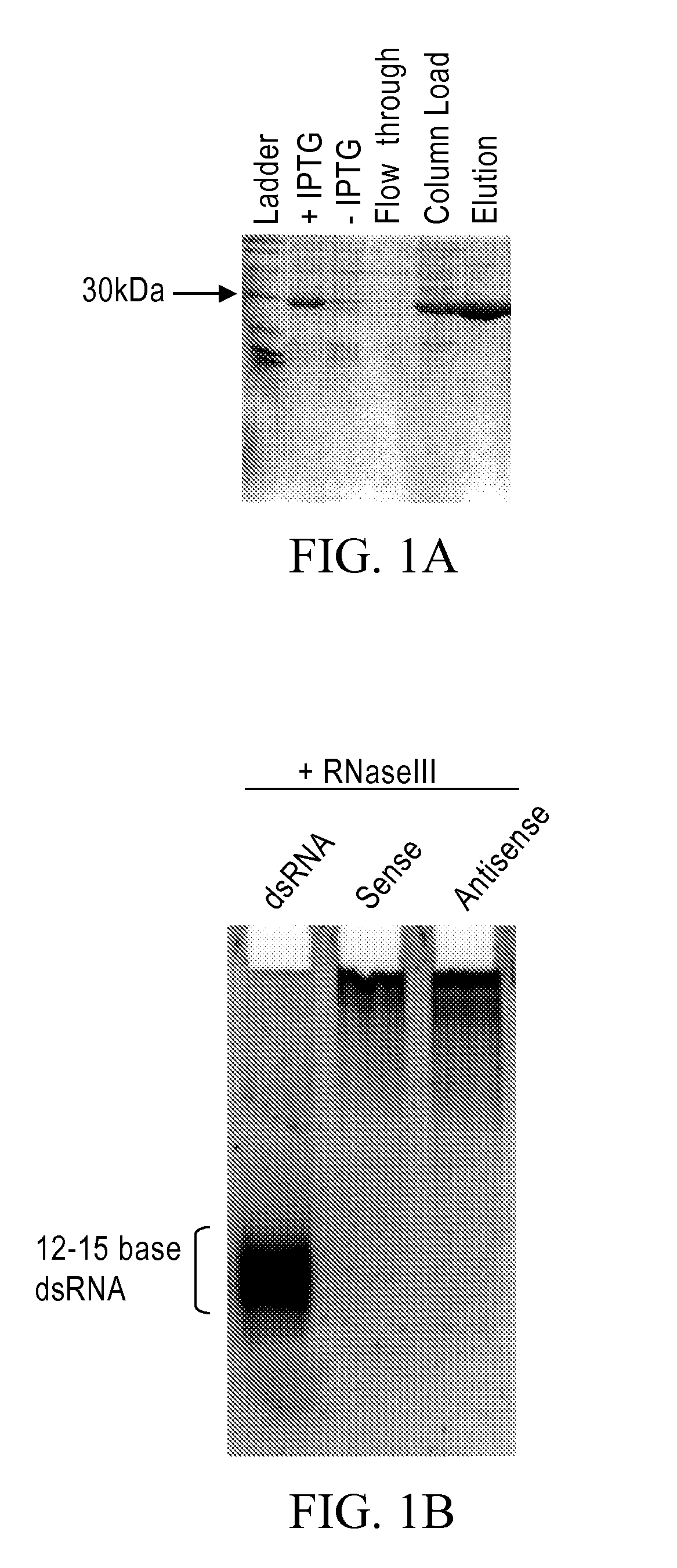
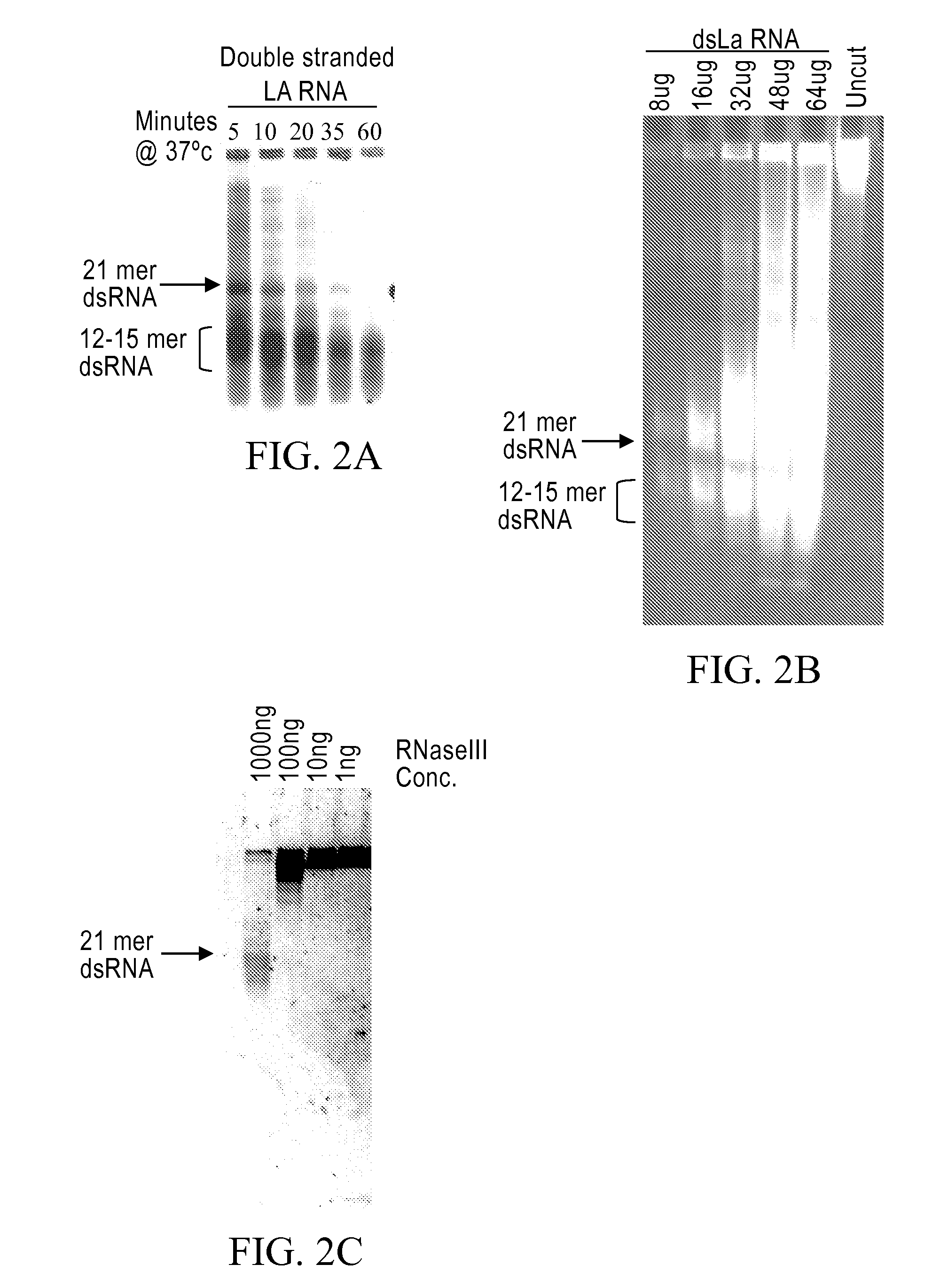
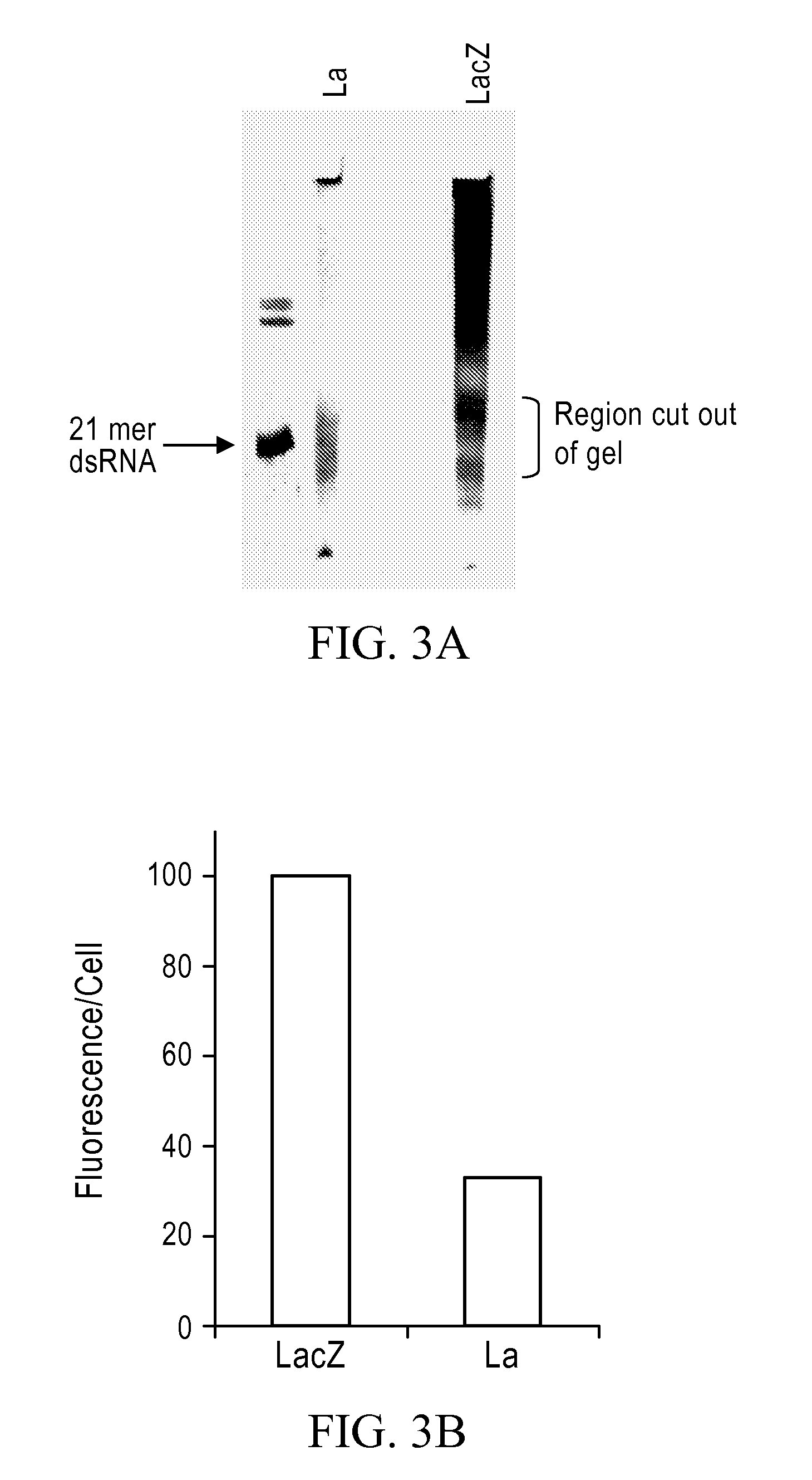
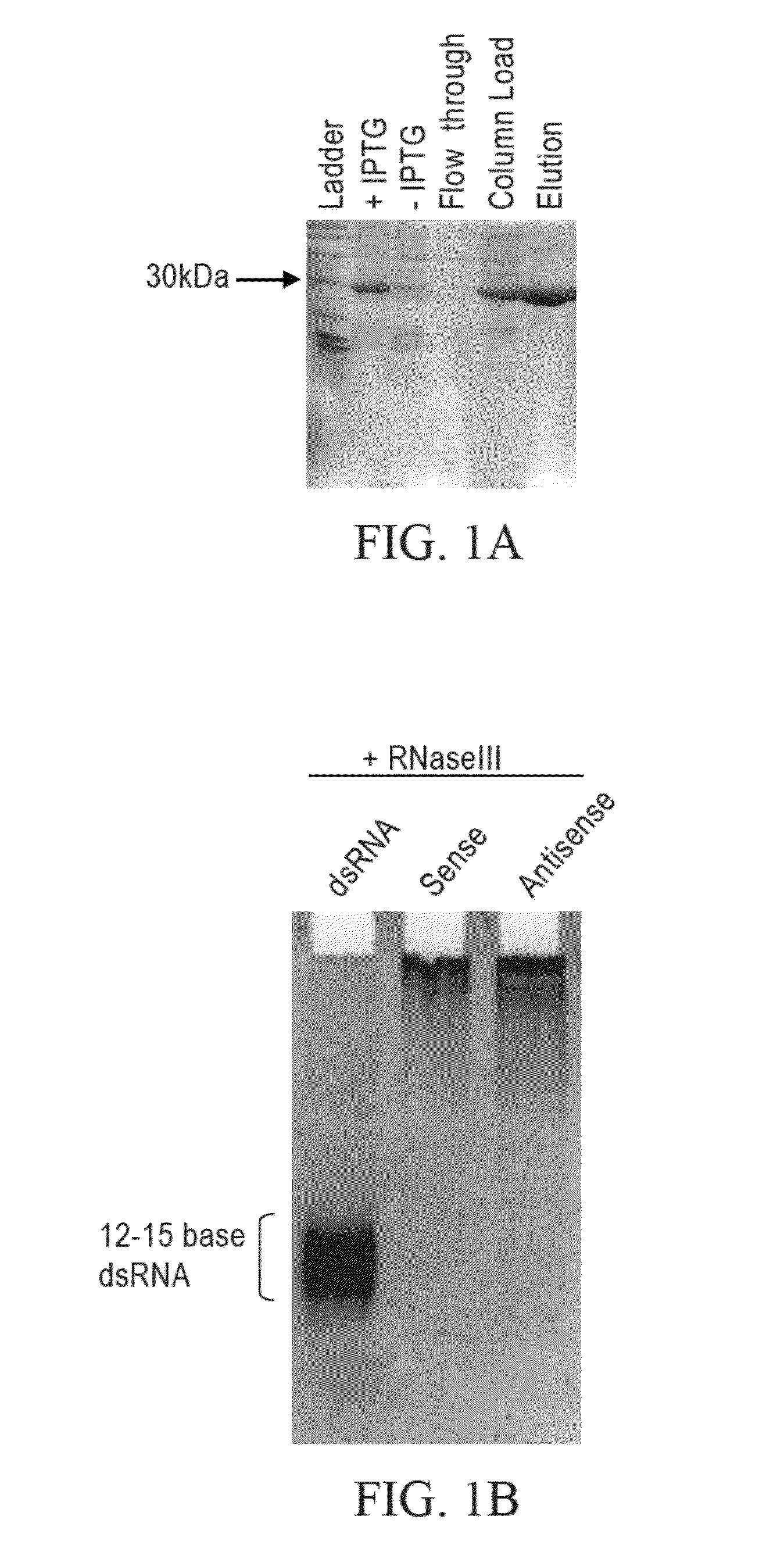
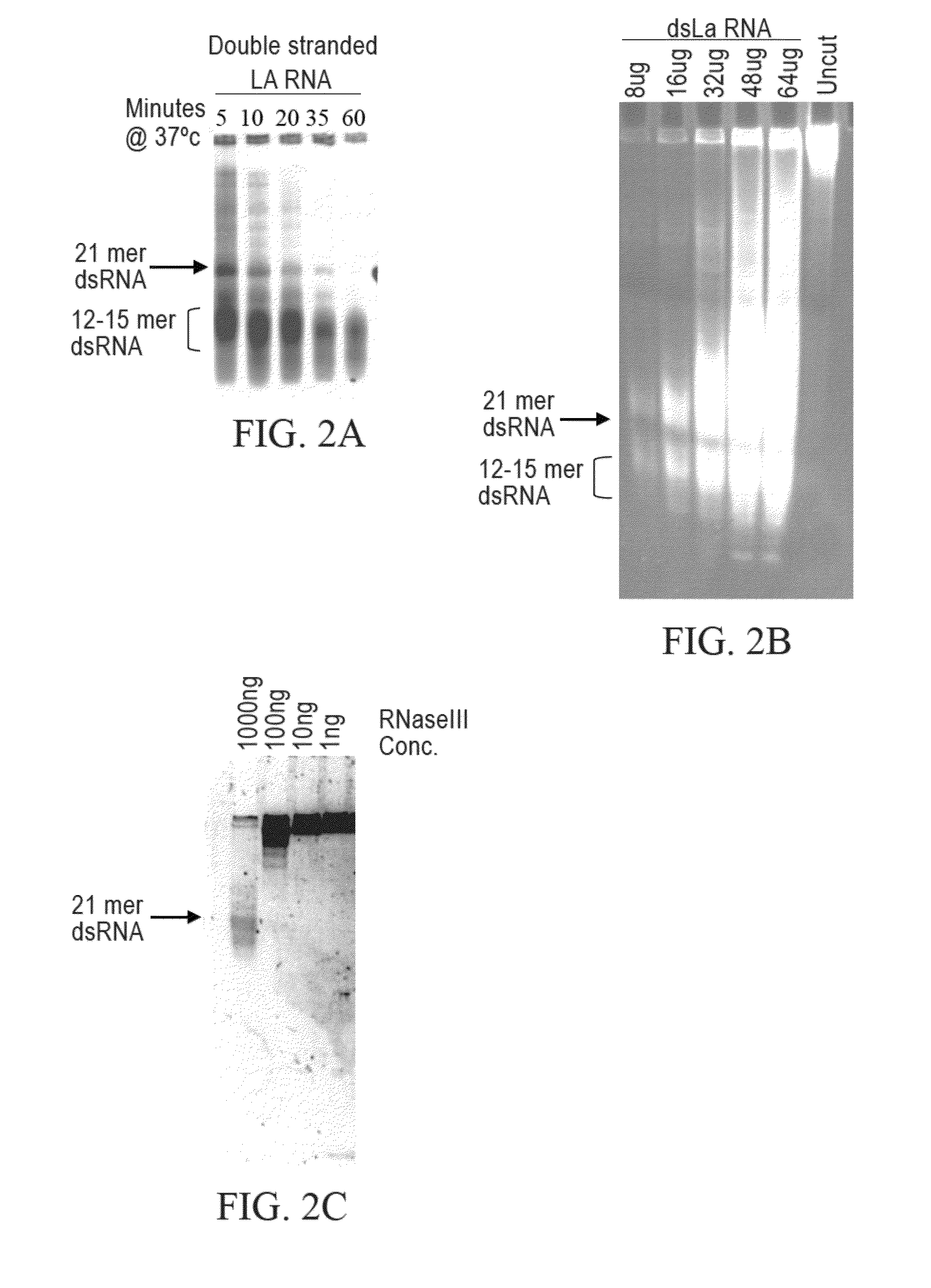
Methods and compositions relating to polypeptides with rnase iii domains that mediate RNA interference
The present invention concerns methods and compositions involving RNase III and polypeptides containing RNase III domains to generate RNA capable of triggering RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) in a cell. In some embodiments, the RNase III is from a prokaryote. RNase III activity will cleave a double-stranded RNA molecule into short RNA molecules that may trigger or mediate RNAi (siRNA). Compositions of the invention include kits that include an RNase III domain-containing polypeptide. The present invention further concerns methods using polypeptides with RNase III activity for generating RNA molecules that effect RNAi, including the generation of a number of RNA molecules to the same target.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Homogeneous compound catalyst/enzyme structure, fabricating method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102192938AGood reproducibilityImprove stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoretic coatingsEnzyme structureElectrophoresis
The invention provides a homogeneous compound catalyst / enzyme structure, a fabricating method thereof and an application thereof. According to the homogeneous compound catalyst / enzyme structure and the fabricating method thereof, an electrophoretic deposition (EPD) is employed. On the proper electrophoretic deposition condition, a plurality of catalyst particles and enzyme molecules are deposited and fixed simultaneously on a substrate, and thus a compound catalyst / enzyme film is form on the surface of the substrate. The compound catalyst / enzyme film contains a plurality of enzyme molecules, which is mixed and distributed homogeneously and used for catalyzing biomolecule reactions, as well as catalyst materials used for catalyzing electrochemical reactions. The compound structure can be used to form a working electrode of a biological recognition element of a microsensor.
Owner:黄炳照
Methods and compositions relating to polypeptides with rnase iii domains that mediate RNA interference
InactiveUS20130230920A1Retain activityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsRNase III activityEnzyme structure
The present invention concerns methods and compositions involving RNase III and polypeptides containing RNase III domains to generate RNA capable of triggering RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) in a cell. In some embodiments, the RNase III is from a prokaryote. RNase III activity will cleave a double-stranded RNA molecule into short RNA molecules that may trigger or mediate RNAi (siRNA). Compositions of the invention include kits that include an RNase III domain-containing polypeptide. The present invention further concerns methods using polypeptides with RNase III activity for generating RNA molecules that effect RNAi, including the generation of a number of RNA molecules to the same target.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
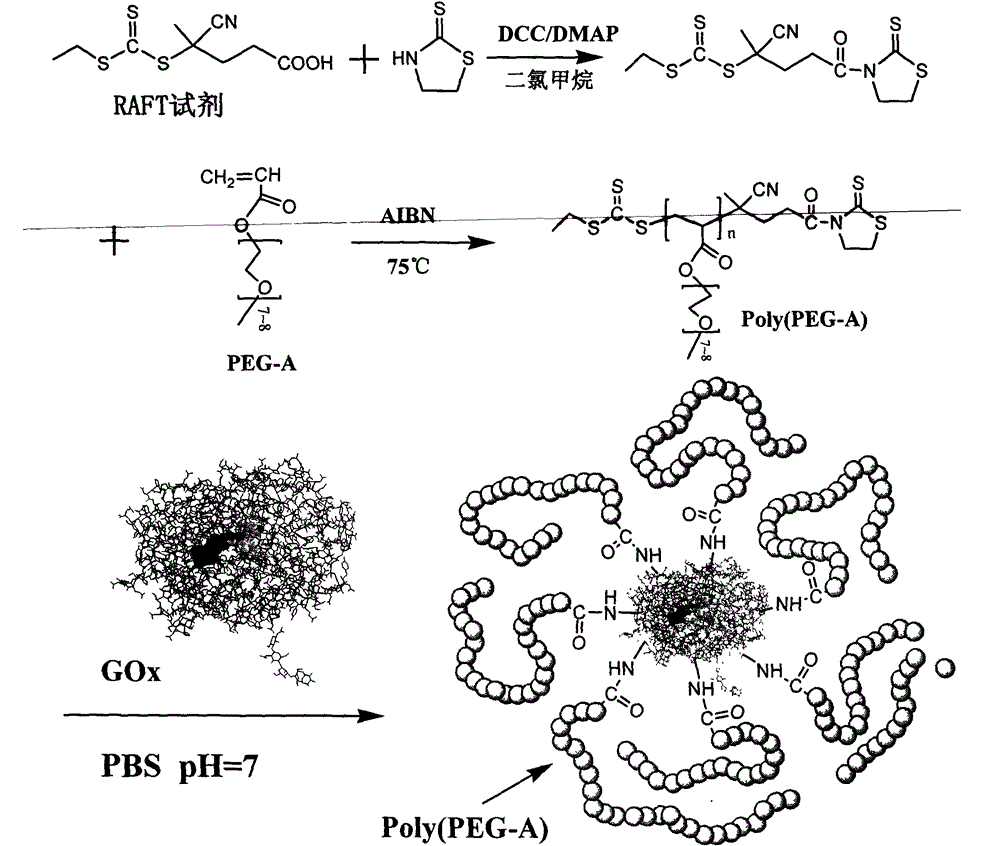
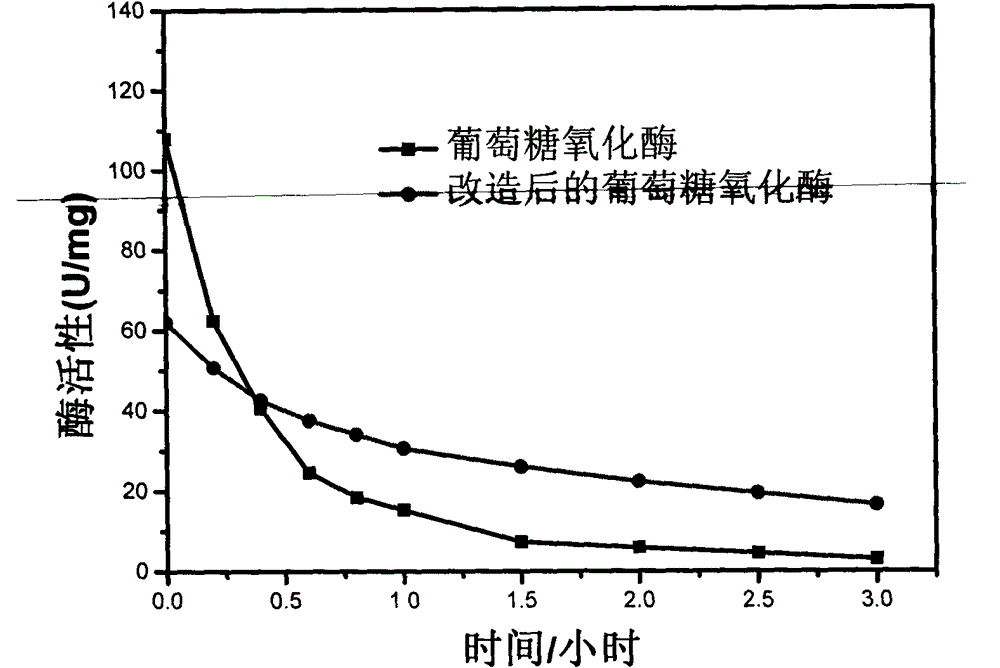
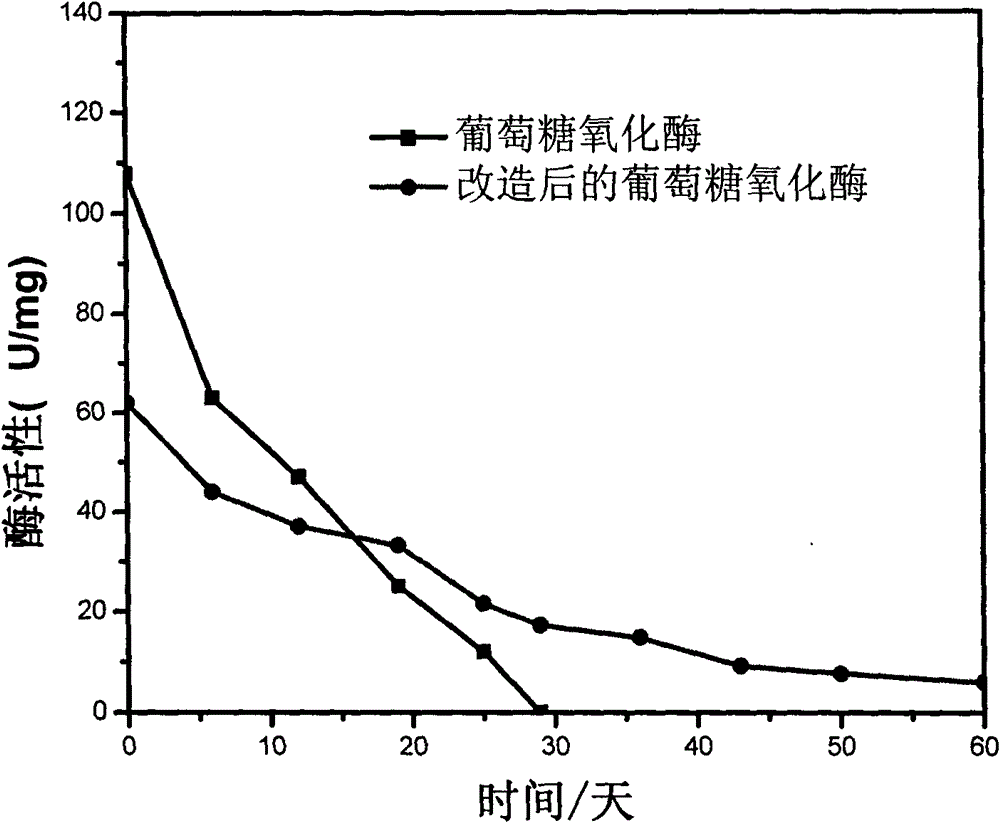
New method for improving life and stability of glucose oxidase by modifying surface of glucose oxidase with biocompatible polymer
The invention provides a new method for modifying surface of glucose oxidase, and aims at improving heat stability and life of glucose oxidase by modifying glucose oxidase utilizing amino group on the surface. The method comprises the steps: synthesizing alpha-(1-oxo-2-propenyl)-omega-methoxyl-poly(ethylene oxide) (PEG-A) high polymer with RAFT (reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer) reagent with mercaptothiazoline terminal group through RAFT polymerization method; and carrying out amidation reaction between mercaptothiazoline group at the terminal of polymer chain and amino group on the surface of glucose oxidase to connect the mercaptothiazoline group to the surface of glucose oxidase. The polymer chain of the modified glucose oxidase partially wrap the activity center (flavin adenine dinucletide: FAD) and other components of the enzyme, so that stabilizing and protective action on the enzyme structure are realized. Therefore, the modified glucose oxidase has excellent heat stability and longer service life.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Genome editing in bacillus host cells
The present invention relates to methods for modifying the genome of a Bacillus host cell by employing a Class II Cas9 enzyme with only one active nuclease domain, e.g. the S. pyogenes Cas9 nickase, together with a suitable guide RNA for each target sequence to generate a site-specific nick in at least one genome target sequence followed by the repair of the nick(s) via integration of one or moremodified modified donor part of the Bacillus host cell genome through classical double homologous recombination on each side of the nick(s).
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Preparation method of glucose oxidase nanogel with good thermal stability
ActiveCN107164359AAvoid structural changesImprove thermal stabilityOxidoreductasesOn/in organic carrierCross-linkEnzyme structure
The invention relates to a preparation method of glucose oxidase nanogel with good thermal stability. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a monometer, glucose oxidase and a cross-linking agent into a mixed solution which serves as a water phase, and adding a surfactant into a non-polar or weak-polar organic solvent insoluble in water, thus obtaining an oil phase after dissolving; under the stirring condition, dropwise adding the water phase into the oil phase, carrying out continuous stirring to obtain a transparent and stable microemulsion system, adding an initiator into the microemulsion system, so that the monomer is polymerized and crosslinked in situ in the aqueous phase droplets of the microemulsion, and enabling glucose oxidase to be wrapped inside, so that the nanogel is formed, wherein the three-dimensional network structure of the gel can realize multi-point and multi-face immobilization for glucose oxidase, even when the mutual acting force between two subunits of glucose oxidase is weakened at high temperature, the separation still can be avoided, and therefore, the irreversible enzyme structure change caused by subunit dissociation can be effectively prevented.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Stabilization of enzymes
InactiveCN1914316AStable hollow sphere structureIncreased contact surface areaHydrolasesEnzyme stabilisationCross-linkCrystallography
A process for producing enzyme structures includes providing an emulsion of droplets of a first liquid phase dispersed in a second liquid phase. The one liquid phase is a hydrophilic phase, while the other liquid phase is a hydrophobic phase which is immiscible with the hydrophilic phase. Enzyme molecules are located at or within interfacial boundaries of the droplets and the second liquid phase. The enzyme molecules of the respective droplets are cross-linked so that individual enzyme structures, which are stable and in which the enzymes are immobilized with a majority of active sites of the enzymes being orientated either internally or externally, are formed from individual droplets.
Owner:CSIR
Gene mining method combining functional sequence and structural simulation, NADH preference type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application
PendingCN112908417AHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove conversion rateProteomicsGenomicsEnzyme structureProtein structure
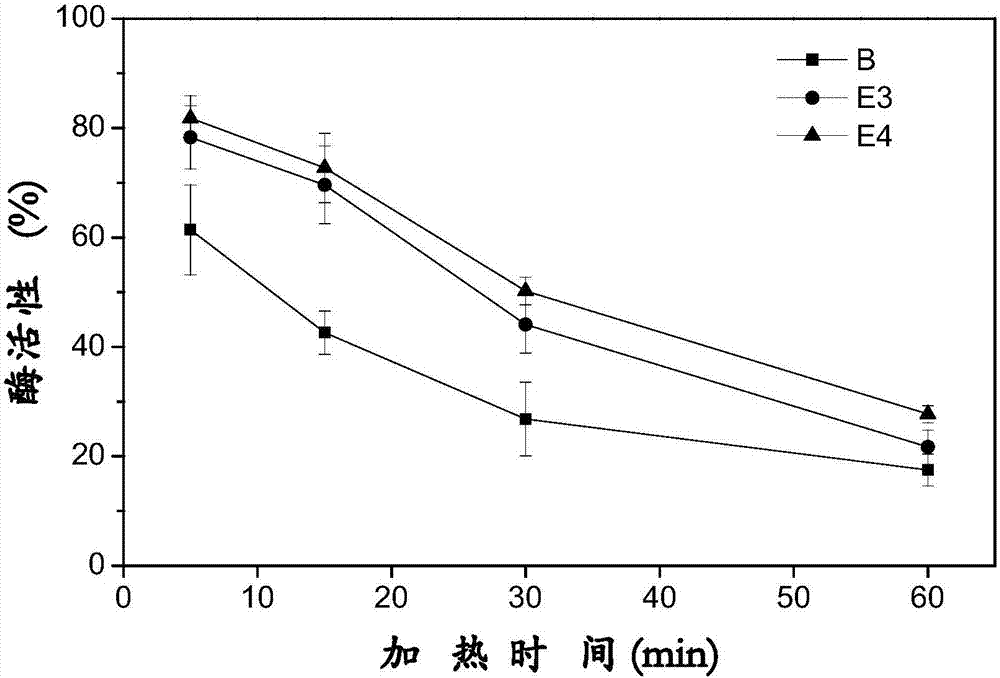
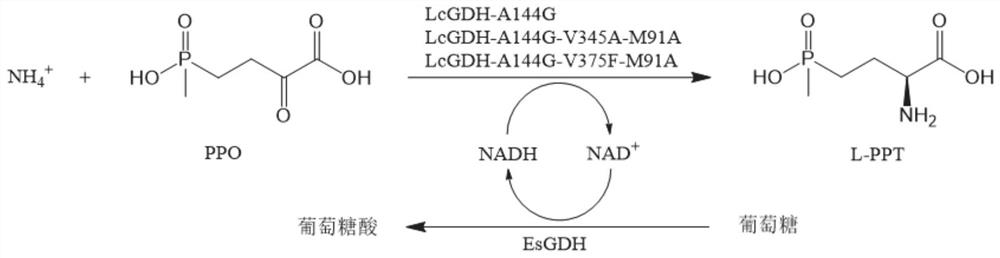
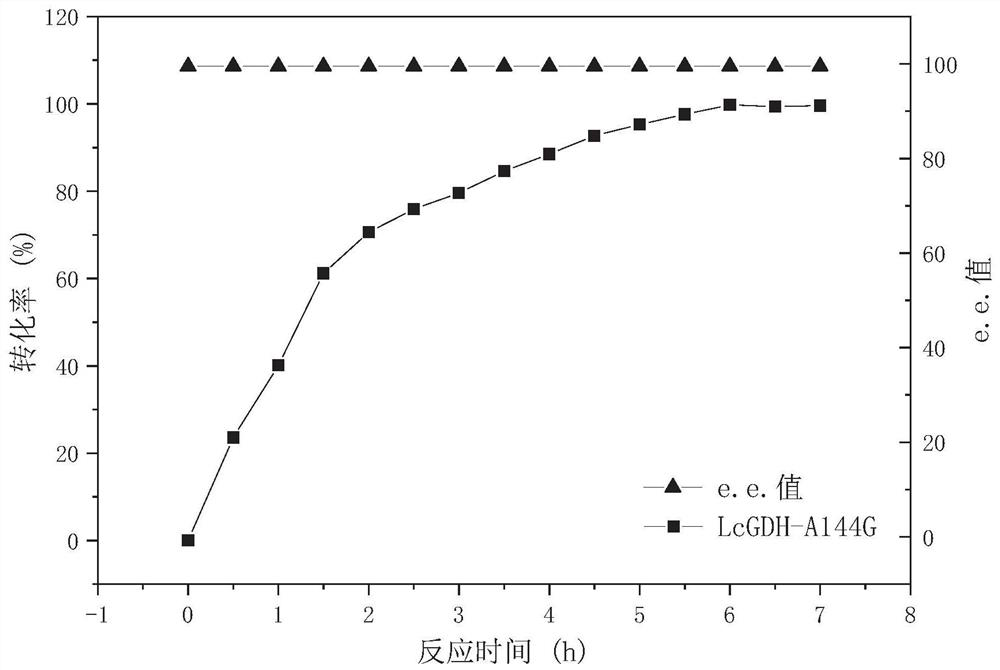
The invention discloses a gene mining method combining a functional sequence and structural simulation, an NADH preference type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and an application. The gene mining method comprises the following steps: (1) analyzing a characteristic sequence of NADH type glutamate dehydrogenase; (2) searching a gene pool according to the characteristic sequence; (3) performing clustering analysis and protein structure simulation on the searched genes; and (4) selecting a gene with high gene polymerization degree and a protein structure similar to that of known glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase as a candidate gene. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out gene mining to obtain wild glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase which is derived from Lysinibacillus composti and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, carrying out mutation screening to obtain an NADH preference type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant, and selecting a mutation site from one of the following: (1) A144G-V375F-M91A; (2) A144G-V345A-M91A; and (3) A144G. The mutant enzyme can be subjected to catalytic reaction by using cheap coenzyme NAD.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for cleaning membrane pollution by utilizing singlet oxygen
ActiveCN105289311AStrong oxidation abilityEasy to cleanSemi-permeable membranesEnzyme structureSinglet oxygen
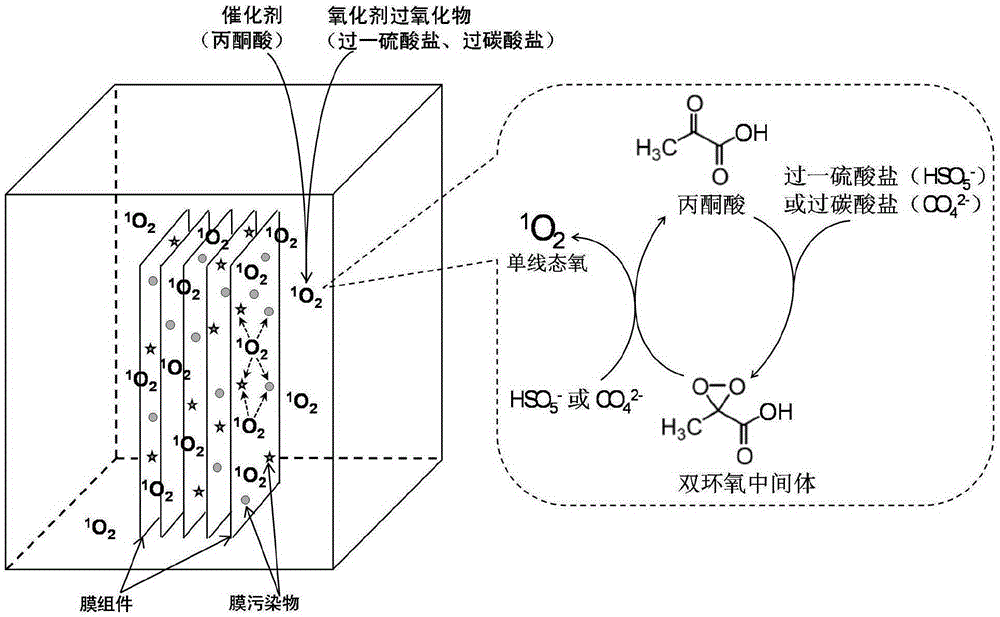
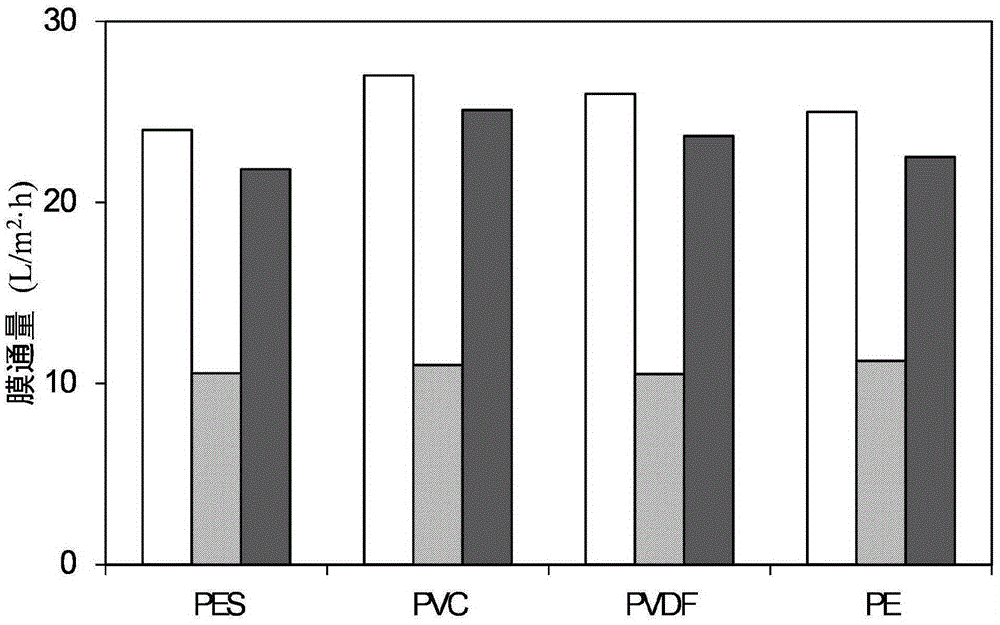
A method for cleaning membrane pollution by utilizing singlet oxygen relates to membrane cleaning methods. The membrane pollution cleaning method comprises adding a catalyst pyruvic acid and an oxidizing agent peroxide (a peroxymonosulfate or a percarbonate) into a pool holding a polluted membrane component, stirring, immersing, and then rinsing, so as to finished the process. A bisepoxy intermediate is generated by using pyruvic acid to catalyze the peroxide, and is further reacted with the peroxide for generating singlet oxygen and pyruvic acid, and the generated pyruvic acid continues to catalyze the peroxide and gives play to cyclic catalysis effect, the generated high-activity singlet oxygen can directly act on membrane-pollution biological cells, rapidly destroy enzyme structure, and reach the purpose of cleaning membrane pollution. The membrane cleaning effect is good, the method does not generate toxic or harmful side products, a waste liquid generated after cleaning can be directly discharged. Pyruvic acid and the peroxide are green, safe and free of toxic and side effects. Operation is simple and practicable.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
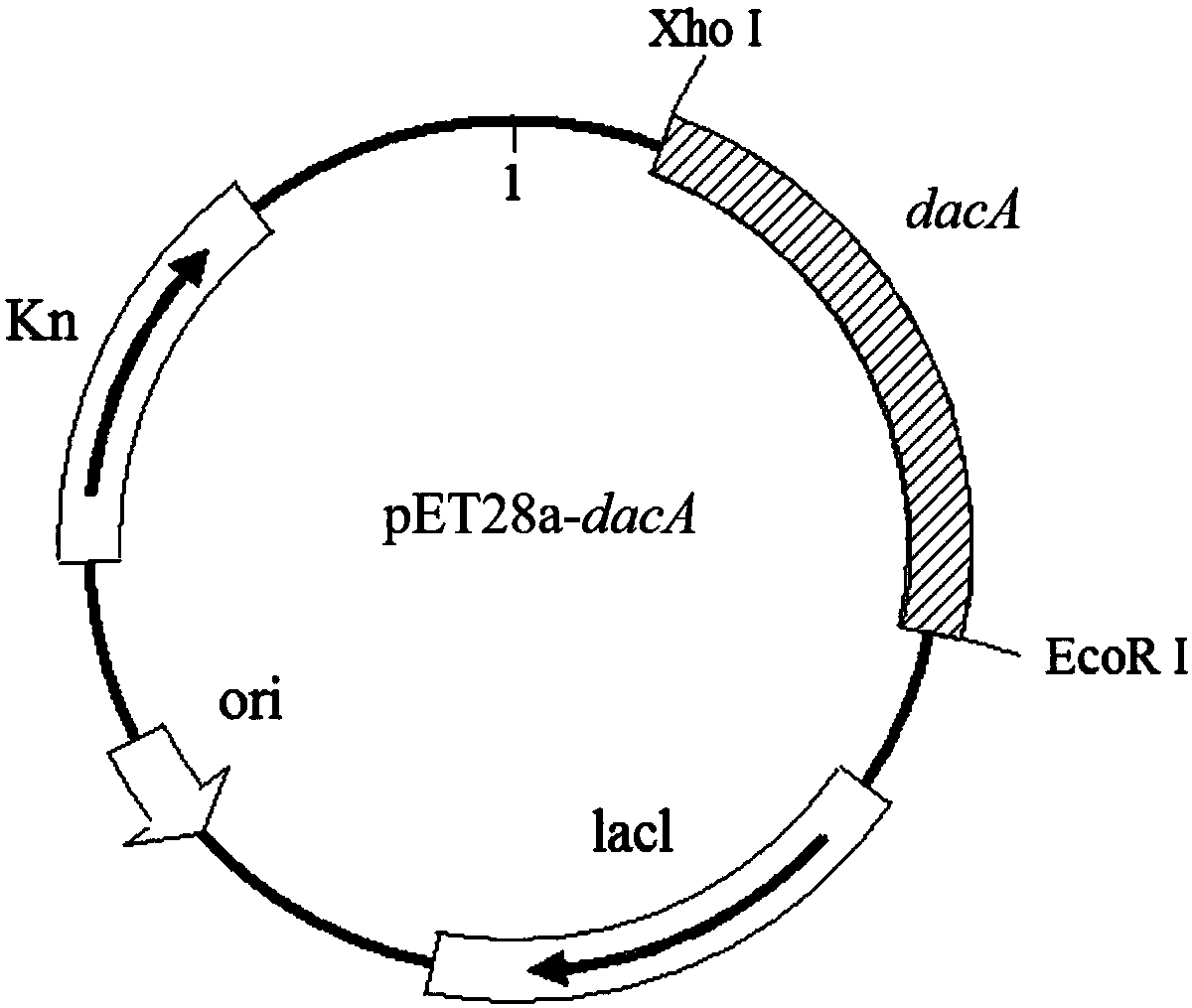
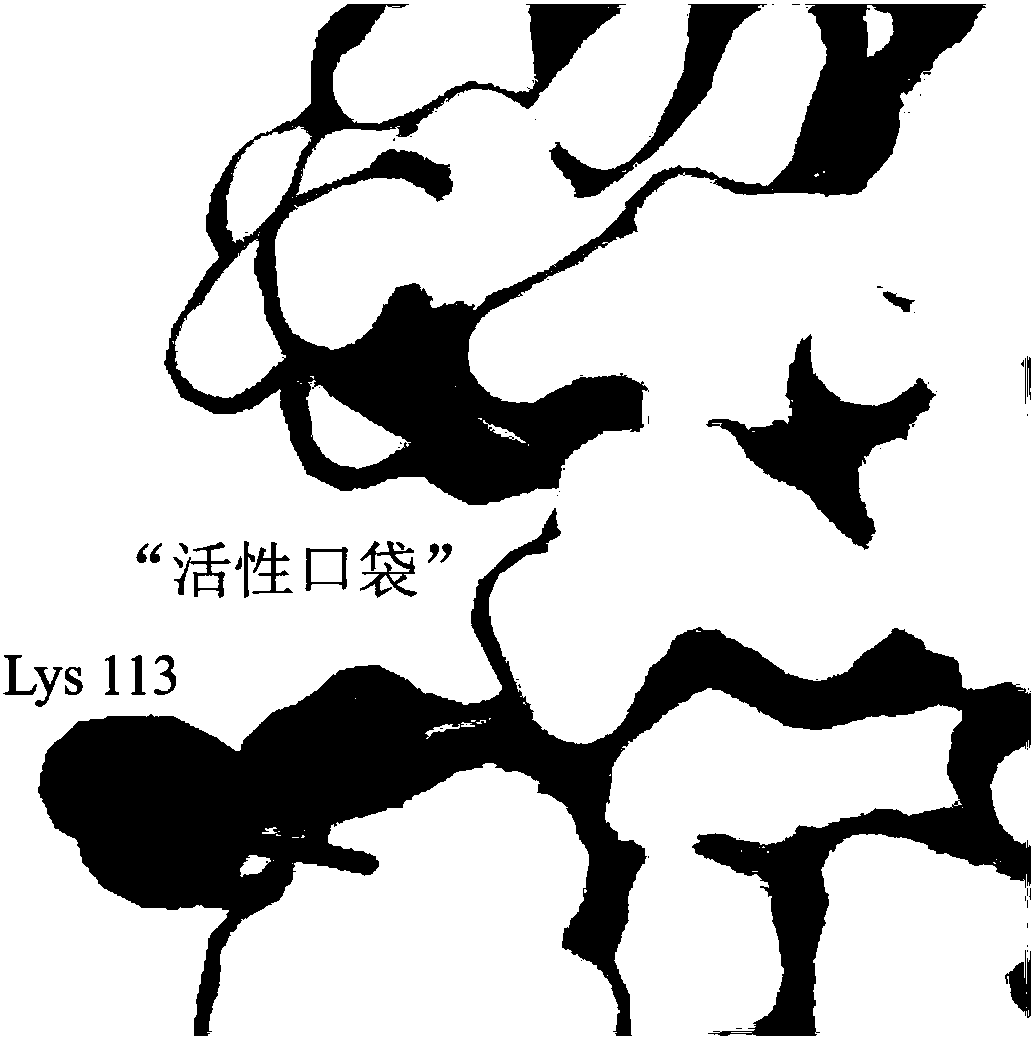
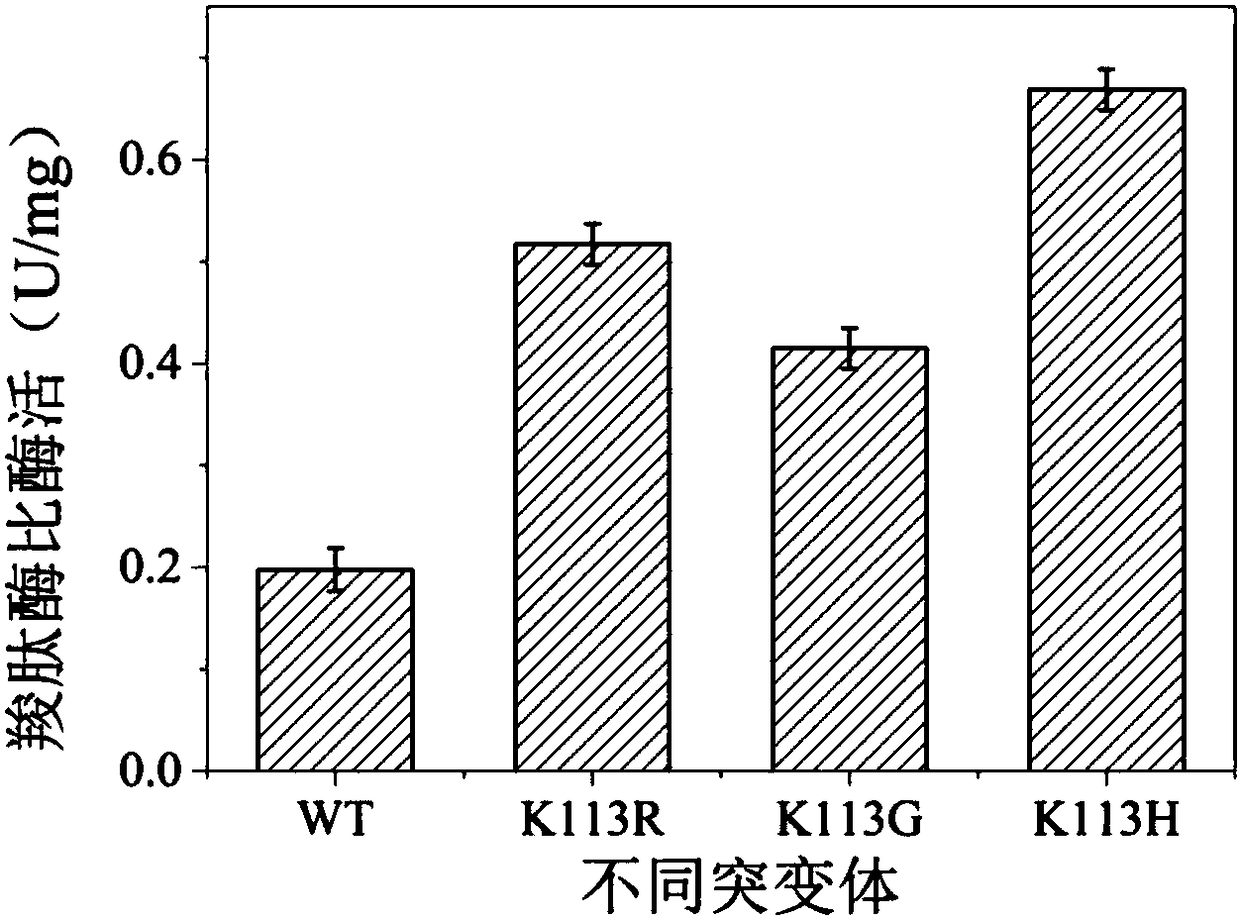
D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108410845AIncreased secretory expression levelsShorten retrofit timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliExocytosis
The invention discloses a D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA from Escherichia coli BL21 is used as a female parent, key sites and a mutation manner are determined based on enzyme structure analysis, and the DacA mutant with improved catalysis efficiency is obtained through fixed point mutation by using a molecular biological technology. Under the modification condition, the catalysis efficiency constant k<cat> of E.coli D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA mutant K113G is improved at most, from 6543.4s<-1> to 9428.1s<-1>. Due to adoption of the method, the catalysis efficiency of the D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA is improved remarkably, layinga foundation for the application of metabolizing and modifying E.coli to improve exocytosis level and the like. The method has an important guiding significance in property modification of other enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Stabilization of Enzymes
InactiveUS20080213858A1Increase enzyme activityImprove emulsion stabilityHydrolasesOther chemical processesCrystallographyCross-link
A process for producing enzymes structures includes providing an emulsion of droplets of a first liquid phase dispersed in a second liquid phase. The one liquid phase is a hydrophilic phase, while the other liquid phase is a hydrophobic phase which is immiscible with the hydrophilic phase. Enzyme molecules are located at or within interfacial boundaries of the droplets and the second liquid phase. The enzyme molecules of the respective droplets are cross-linked so that individual enzyme structures, which are stable and in which the enzymes are immobilized with a majority of active sites of the enzymes being orientated either internally or externally, are formed from individual droplets.
Owner:CSIR
Method for improving structural isomerism catalytic activity of CE enzyme and mutant thereof
ActiveCN113564151AImprove catalytic performanceImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme structureA-site
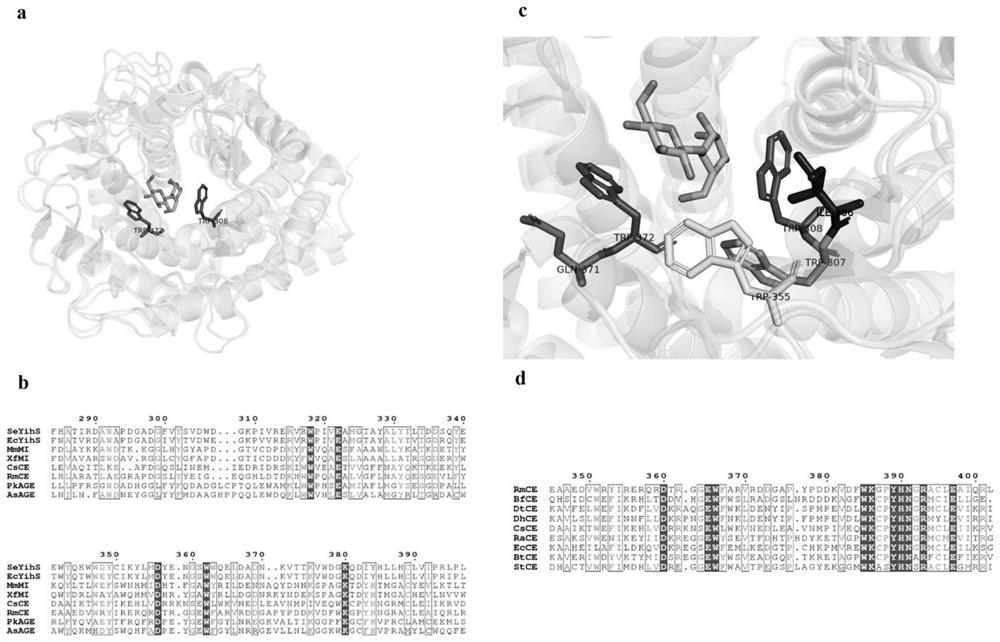
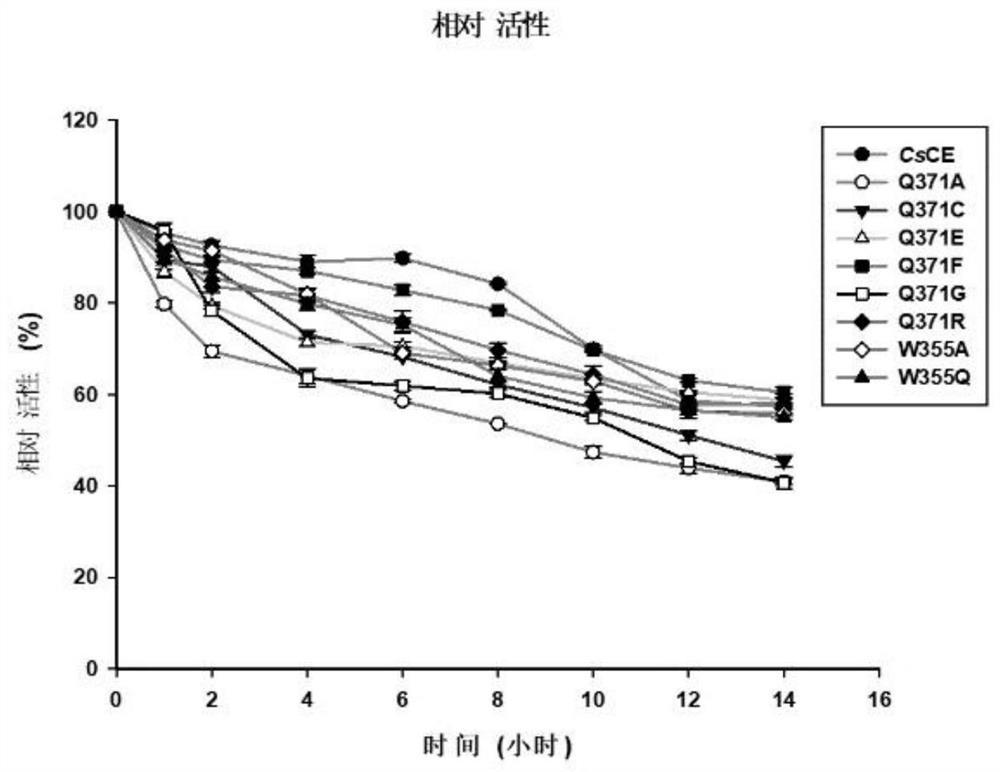
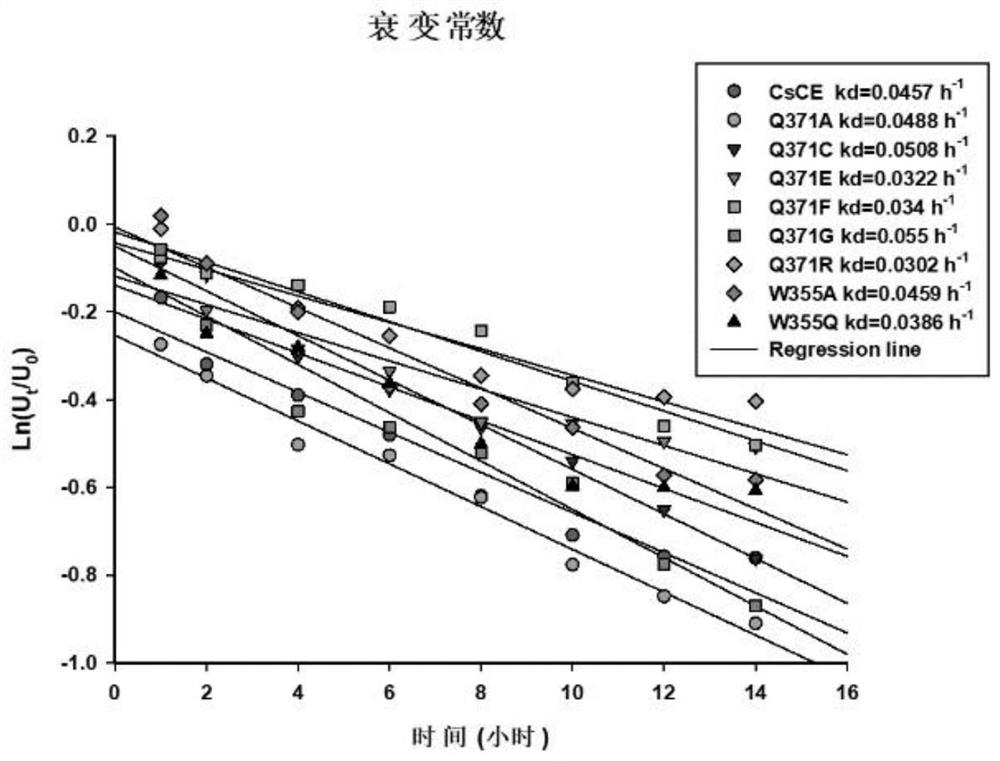
The invention discloses a method for improving the structural isomerism catalytic activity of a CE enzyme and a mutant thereof, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, cellobiose epimerase (CsCE) derived from Caldicellosirutorschcharlyticus is taken as a research object, site-saturation mutagenesis is carried out on a site related to substrate binding based on a semi-rational strategy of sequence alignment and crystal structure analysis, a plurality of mutants with obviously improved structural isomerism catalytic activity are obtained, and the structural isomerism activity of the mutants is improved by about 36-232% than that of a wild type CE enzyme. The invention provides a feasible scheme for CE enzyme improvement, and has important significance for promoting enzymatic industrial synthesis of lactulose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
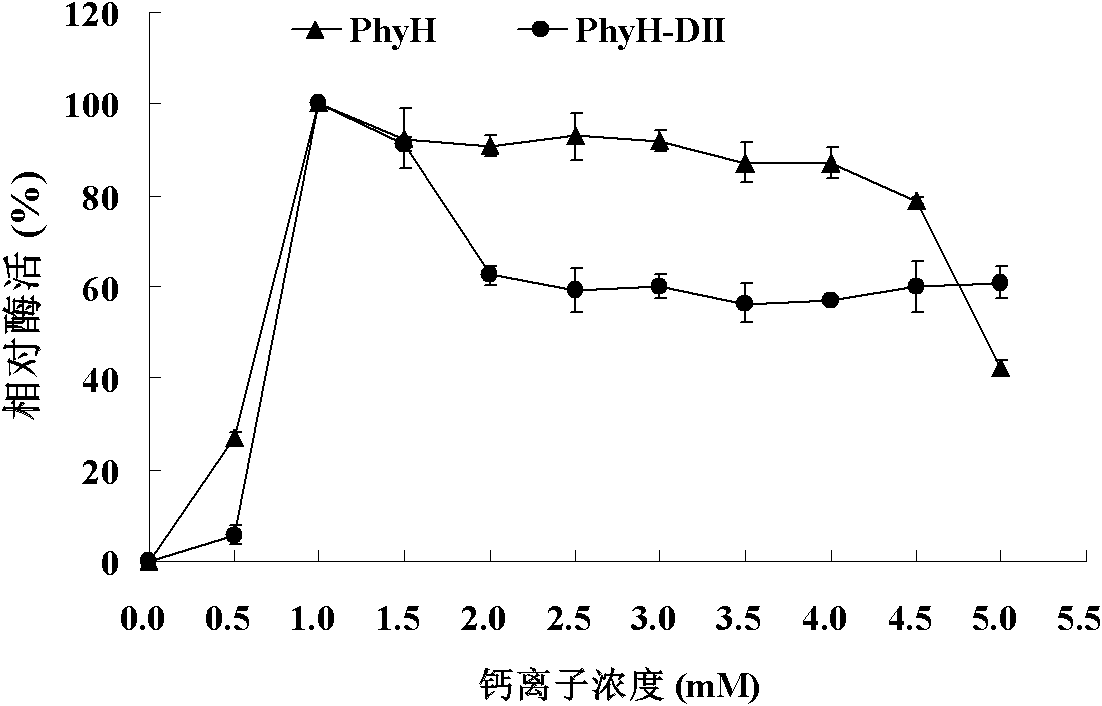
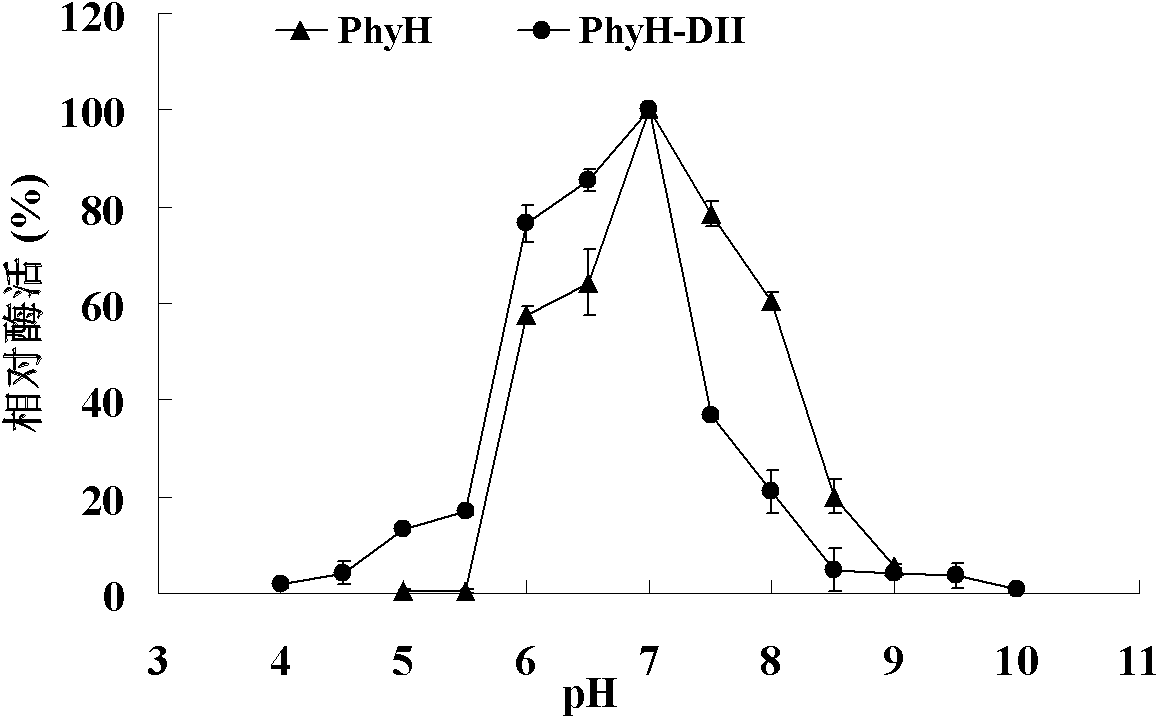
Low-temperature neutral phytase PhyH with double structure domains as well as gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102250853AImprove stabilityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesPhytaseGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a low-temperature neutral phytase PhyH with double structure domains as well as a gene and application thereof. The invention provides the neutral phytase PhyH from Bacillus sp.HJB17, and the amino acid sequence of the neutral phytase PhyH is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; and the invention provides a gene PhyH for coding the neutral phytase. The phytase provided by the invention has good pH stability and still keeps higher enzyme activity in the alkaline range; the phytase has higher relative enzyme activity in a low-temperature range; the phytase has double structure domains, an N terminal is an incomplete BPP (Butyl Pivalate Peroxide) phytase structure domain and a C terminal is a complete phytase structure domain. In short, the PhyH obtained by the invention can be used as the low-temperature neutral phytase which can be applied to cultivation of fish; the PhyH-DI structure domain can increase the catalytic efficiency of other phytases and is good for improving the production and the application of the other phytases.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
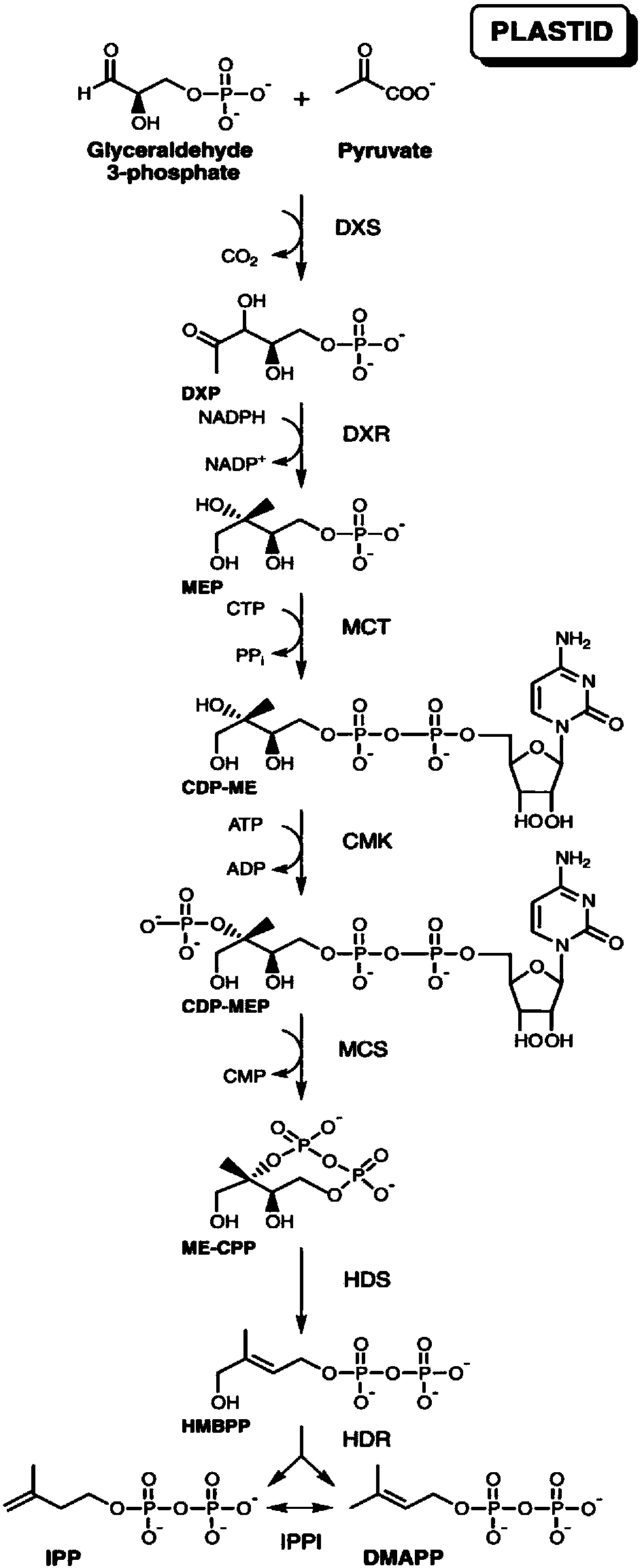
Target for preventing and killing weed-crofton weed and application of target
The invention discloses a target for preventing and killing weed-crofton weed by using key enzyme (2-methyl-D-erythritol-2, 4-cyclic pyrophosphate cyclase, EaispF1) in a biosynthetic pathway of 2-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphoric acid and an application of the target. The target is protein of the following (a) or (b): (a) protein which consists of an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; (b) protein which is formed by substituting and / or missing and / or adding one or more amino acids into the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table, associated with the target and derived from (a). The invention also relates to active compounds A and B designed based on EaispF1 enzyme structure of the crofton weed, and a synthetic method of the active compounds A and B.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Dual-miRNA-initiated master key-drug delivery system and construction method and application thereof
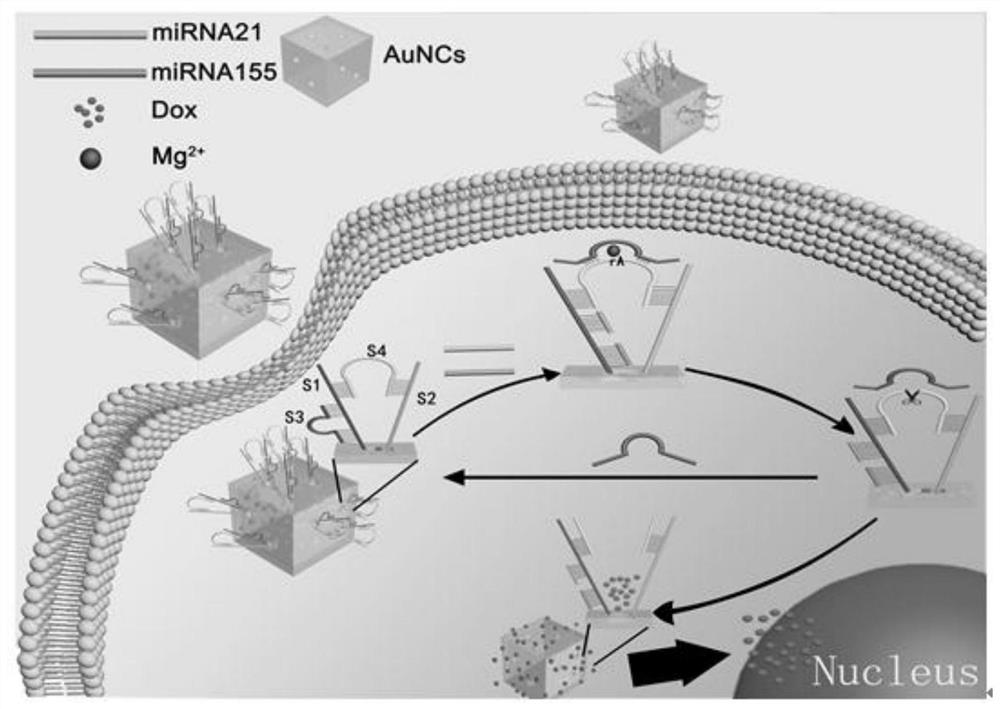
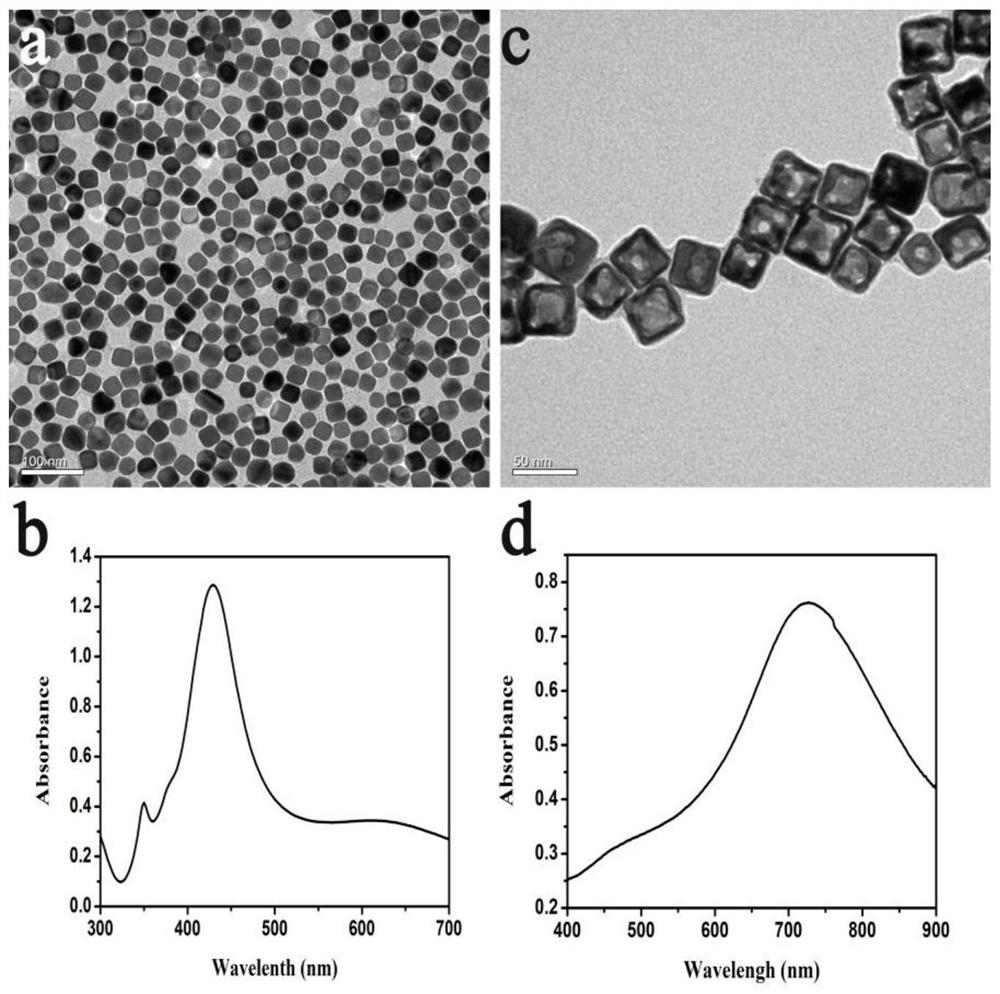
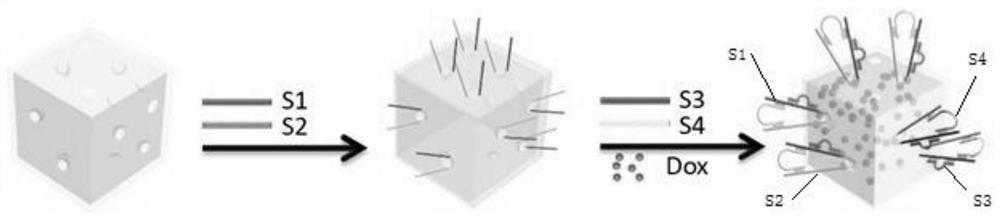
ActiveCN113769111APrecision releaseSmall toxicityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellEnzyme structure
The invention discloses a dual-miRNA-initiated master key-drug delivery system and a construction method and application thereof. The dual-miRNA-initiated master key-drug delivery system comprises a gold nanocage, a fluorescent chemotherapy drug and a DNA bridge-type nanolock, wherein the fluorescent chemotherapy drug is loaded in a hole cavity of the gold nanocage, the DNA bridge-type nanolock is combined with the surface of the gold nanocage to block the hole cavity of the gold nanocage, the DNA bridge-type nanolock is composed of SH-modified long-chain DNA S1, SH-modified long-chain DNA S2, long-chain DNA S3 with a composition sequence of an Mg <2+> enzyme structure and long-chain DNA S4 with an Mg<2+> enzyme recognition sequence, the S1 and the S2 are combined with the surface of the gold nanocage through gold-sulfur bonds, the S3 and the S1 are in partial-base-complementary connection, and the two ends of the S4 are respectively in base-complementary connection with free ends of the S1 and the S2. The function of unlocking a plurality of locks can be executed by a master key by utilizing a cell endogenous substance Mg<2+>-dependent DNA enzyme cyclic shearing reaction, and a drug is released in cancer cells in a targeted and enhanced manner, so that the signal-amplification diagnosis and treatment function of a probe is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
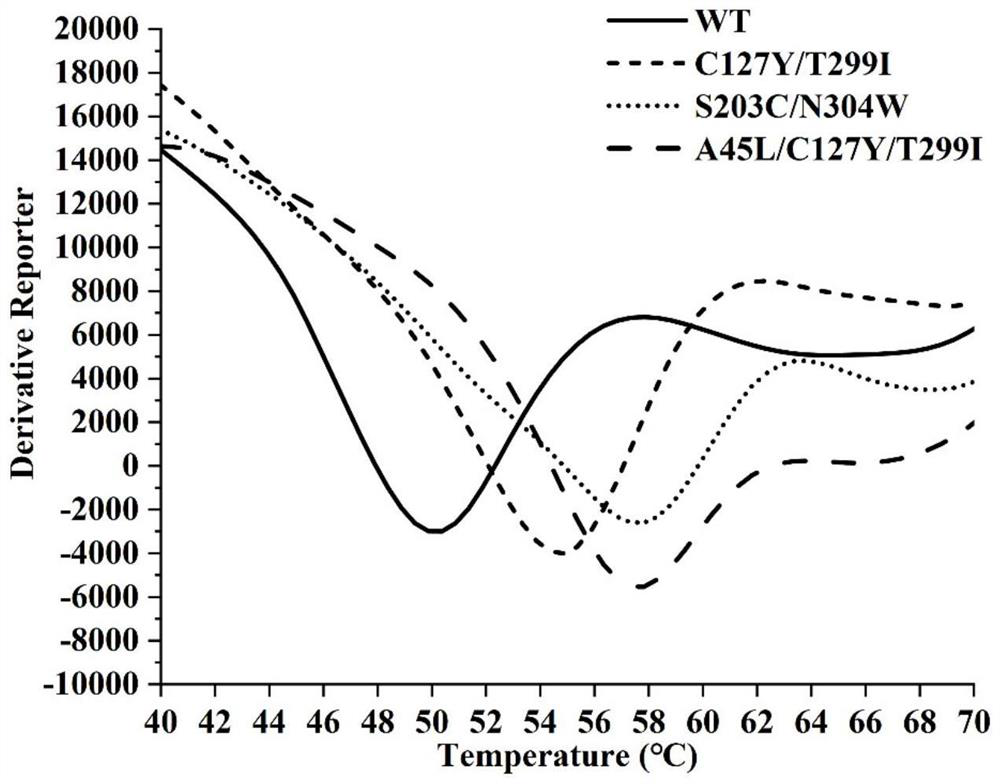
Glycosyl transferase mutant with improved thermal and organic solvent stability
ActiveCN114875007AImprove toleranceHigh practical application valueFermentationGlycosyltransferasesOrganic solventEnzyme structure
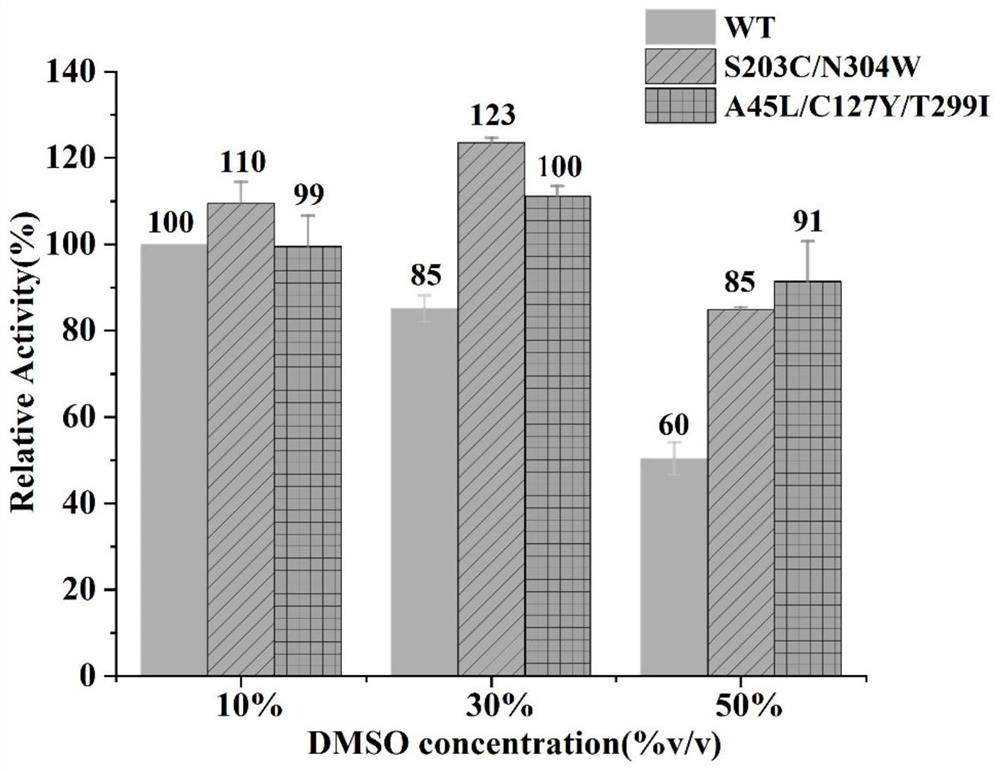
The invention provides a glycosyl transferase mutant with improved comprehensive stability of heat and organic solvents. On the basis of enzyme structure analysis and protein stability calculation aided design, amino acids coded by a glycosyl transferase UGT109A3 wild type gene sequence are replaced with Ser203Cys, Asn304Trp, Ala45Leu, Cys127Tyr and Thr229Ile to obtain a glycosyl transferase UGT109A3m (S203C / N304W) double-site mutant and a UGT109A3m (A45L / C127Y / T229I) three-site mutant, the thermal stability Tm value of the obtained optimal mutant is increased by 7.1 DEG C, and in a 50% (v / v) DMSO reaction system, the thermal stability Tm value of the optimal mutant is increased by 7.1 DEG C, and the thermal stability Tm value of the optimal the relative catalytic activity is improved from 60% to 91%, and the actual application value of the glycosyl transferase is improved through the result.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods of targeted genetic alteration in plant cells
The current invention relates to methods of targeted genetic alteration in cells, preferably plant cells, as well as to plant cells and plants thus obtained using at least a fusion protein comprising a site-specific nuclease domain and a deaminase domain, or a construct encoding the same. The method also provides for a composition and a kit comprising a combination of a first fusion protein comprising a cytosine deaminase domain and a second fusion protein comprising an adenine deaminase domain, preferably for use in the method of the invention. The method provides for targeted alteration of a DNA duplex in plant cells with increased efficacy.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
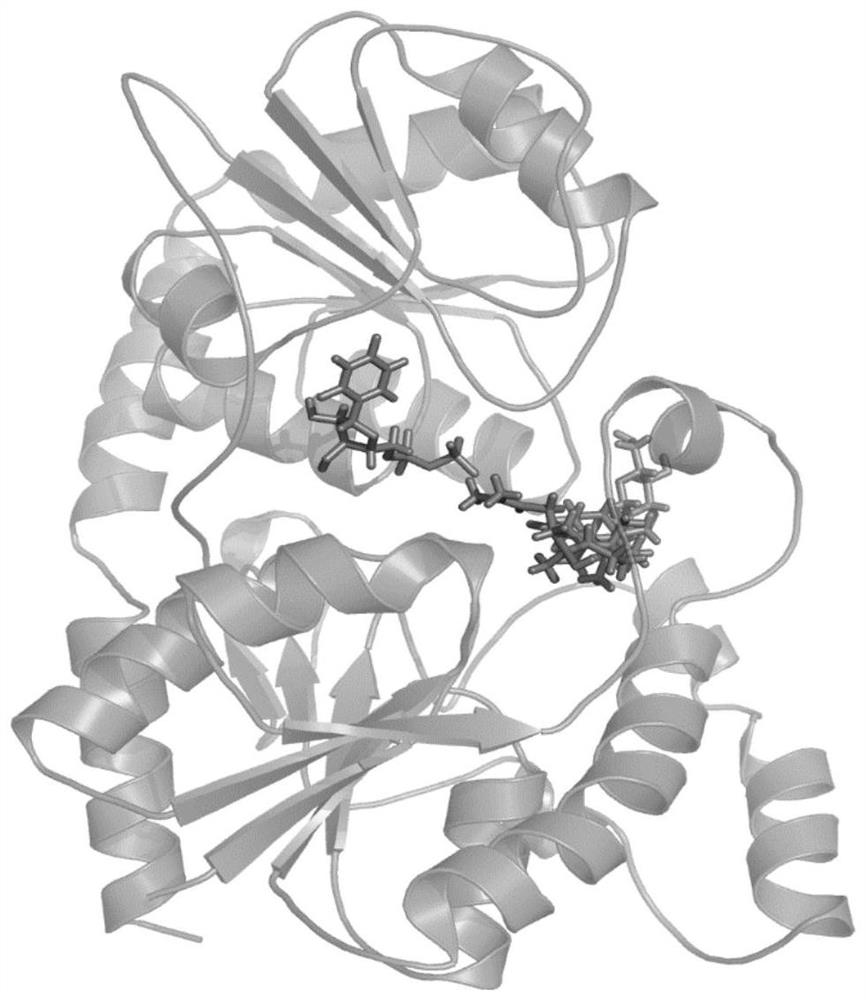
Medicine binding pocket of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) gyrase and application thereof
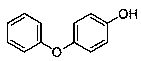
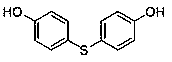
The invention discloses a medicine binding pocket of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) gyrase. The medicine binding pocket is characterized in that an ATP (adenosine triphosphate) enzyme structure domain ofa B subunit of the DNA gyrase is used as a study object, a compound segment is used as a probe, and the protein heat stability transfer experiment, an ATP enzyme hydrolysis activity experiment and anX-ray crystallography diffraction method are performed, so as to find that a novel medical ligand binding pocket exists on the B subunit of the DNA gyrase of the bacteria; the medicine binding pocketis induced by the screened segment probe 4-phenoxyphenol or 4,4'-dyhydroxy diphenyl sulfide. The novel ligand binding pocket has the advantages that an inhibitor for the DNA gyrase with a novel binding mode is designed and screened; the screened compound segment provides basis elements for the segment growth, integration and connection for the design of novel antibacterial medicines; by using thenovel medical pocket as a starting point, the screened segment is spliced with the existing inhibitor to obtain the inhibitor for the DNA gyrase with high affinity and high selectivity, and the problem of medicine resistance property of the existing inhibitor is expected to be solved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Immobilized enzyme carrier, immobilized enzyme and preparation method
PendingCN113652415AImprove structural rigidityEasy to separate and collectOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierEnzyme structureGenipin
The invention discloses an immobilized enzyme carrier, an immobilized enzyme and a preparation method. According to the method, macromolecular particles of chitosan are attached to the surface of an egg shell membrane, magnetic Fe3O4 is uniformly precipitated and distributed on the egg shell membrane in a co-precipitation mode, the prepared magnetic Fe3O4 / CS / ESMP serves as an enzyme carrier of immobilized beta-glucosidase, the rigidity and tolerance of an enzyme structure are improved, and good operation stability is achieved; in addition, the prepared Fe3O4 / CS / ESM@BG can be repeatedly used, and the operation is simple and convenient. The Fe3O4 / CS / ESMP@BG is easy to separate and collect under the action of a magnetic field so as to be recycled, the use efficiency of enzyme is improved, and the prepared Fe3O4 / CS / ESMP@BG can be applied to biosynthesis of genipin.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Stabilization of enzymes in an emulsion by cross-linking
InactiveUS7700335B2Easy to separateIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesOther chemical processesPolymer scienceFluid phase
A process for producing enzymes structures includes providing an emulsion of droplets of a first liquid phase dispersed in a second liquid phase. The one liquid phase is a hydrophilic phase, while the other liquid phase is a hydrophobic phase which is immiscible with the hydrophilic phase. Enzyme molecules are located at or within interfacial boundaries of the droplets and the second liquid phase. The enzyme molecules of the respective droplets are cross-linked so that individual enzyme structures, which are stable and in which the enzymes are immobilized with a majority of active sites of the enzymes being orientated either internally or externally, are formed from individual droplets.
Owner:CSIR
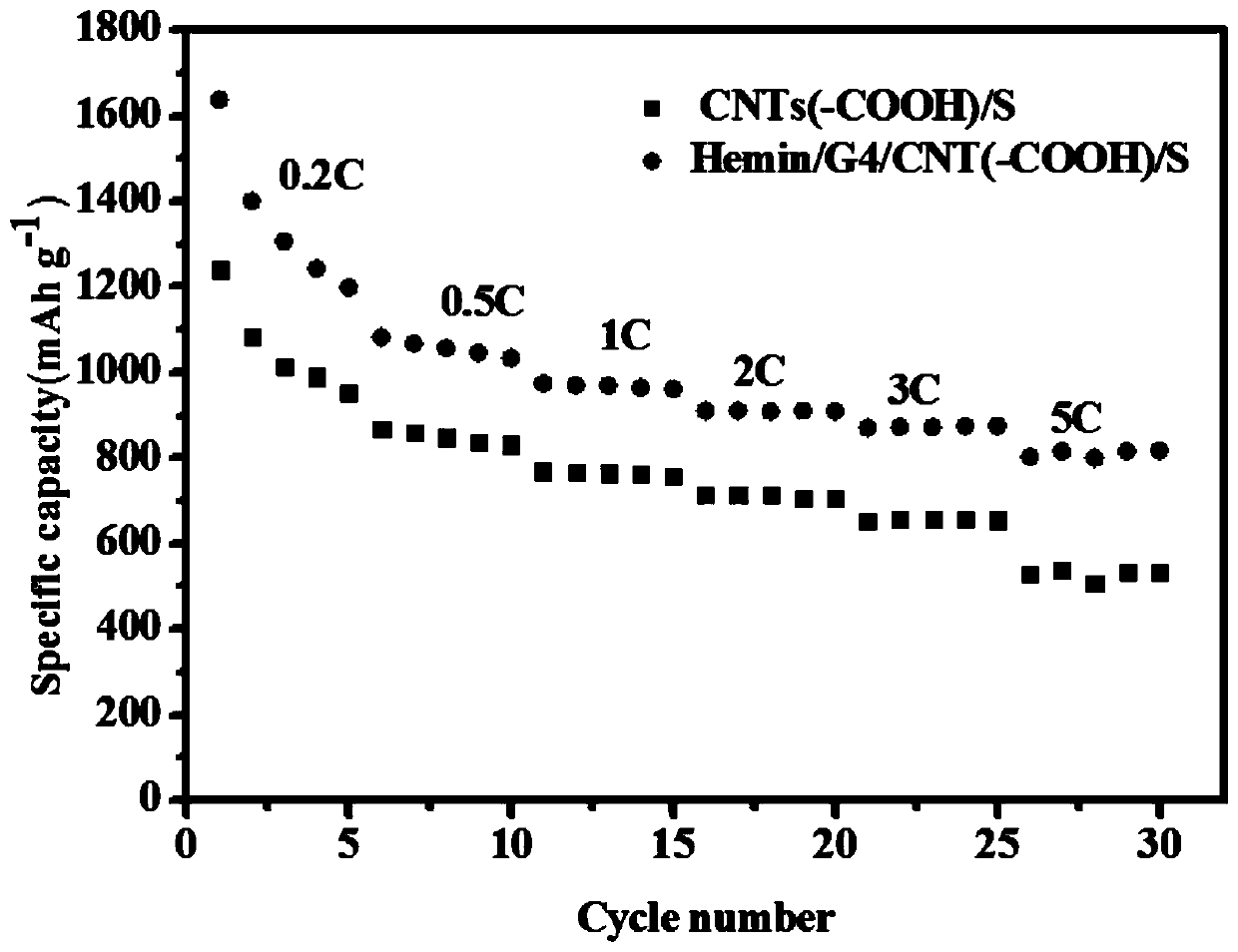
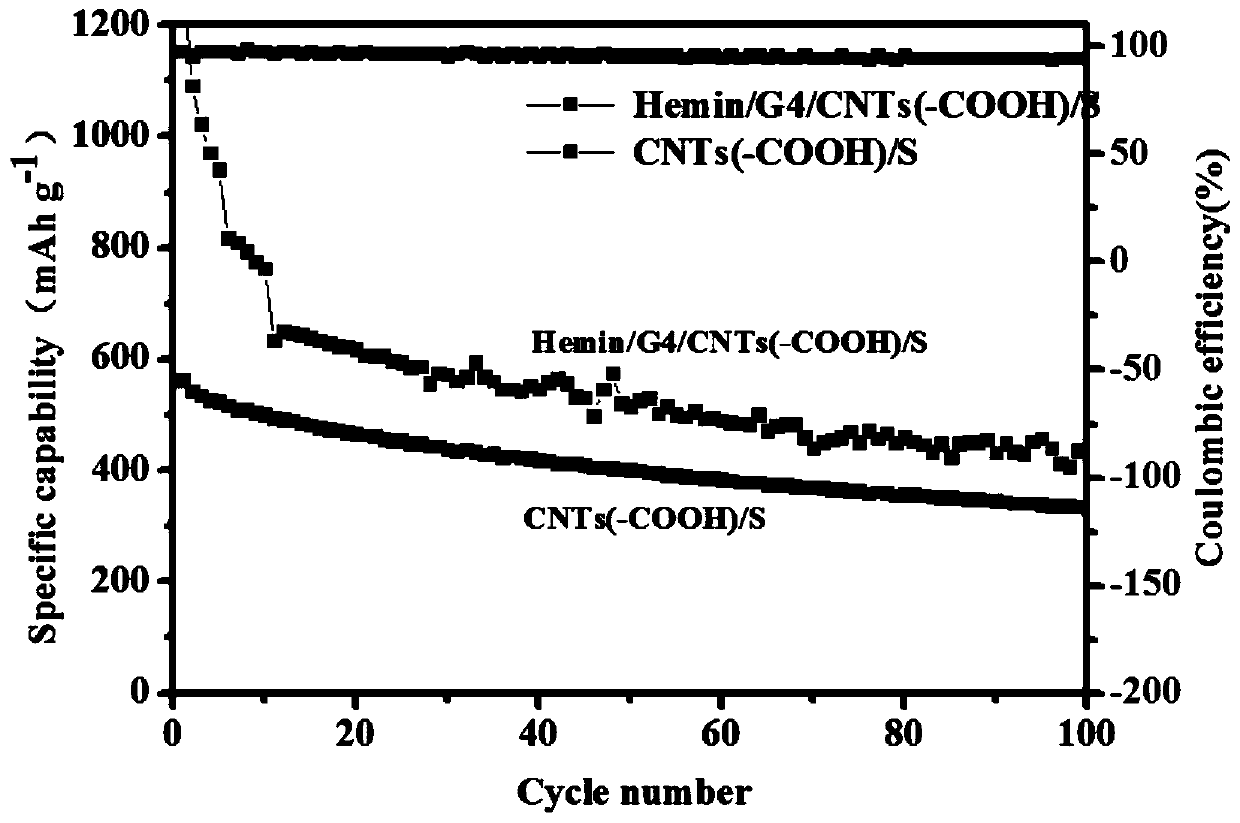
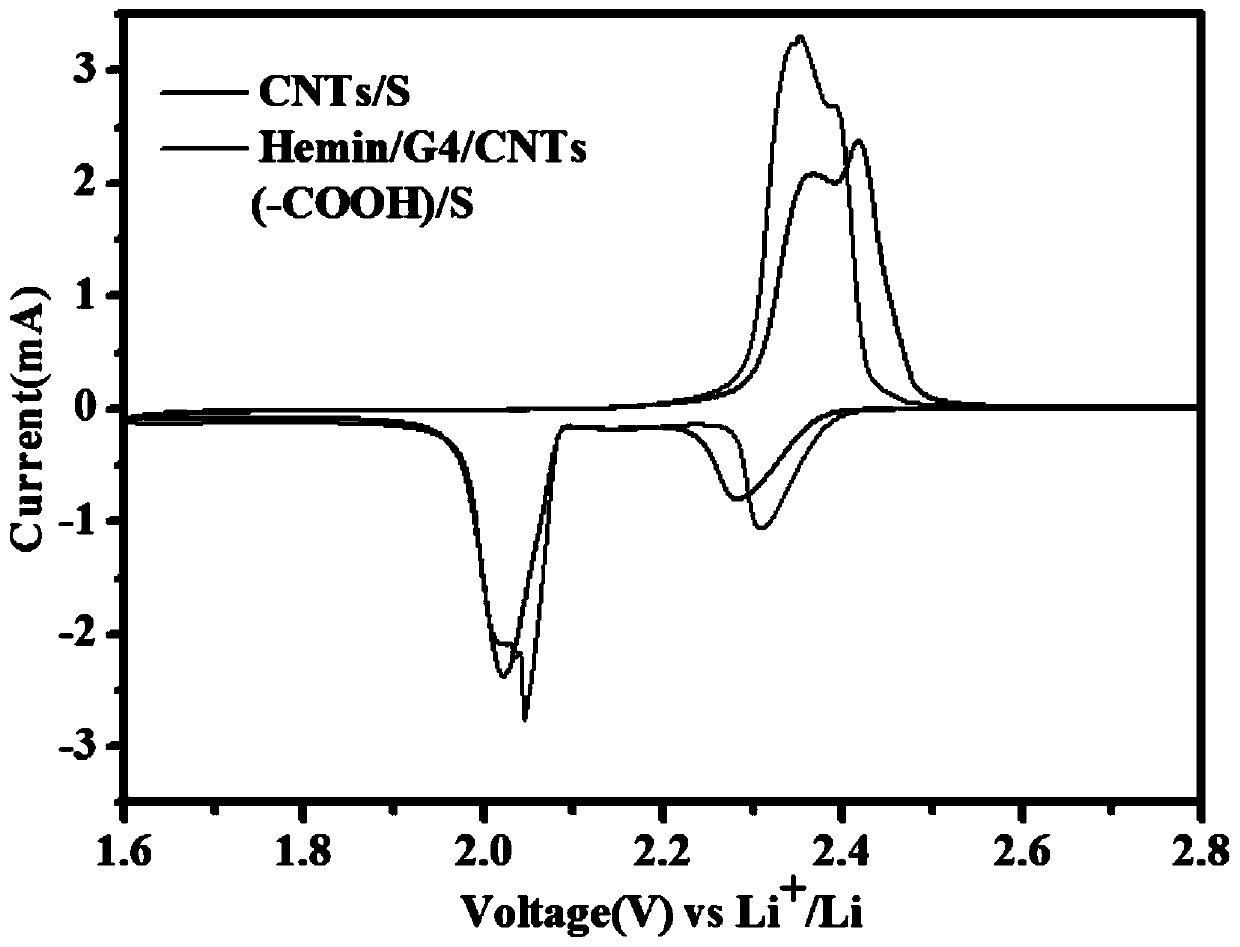
Preparation method of G-quadruplex/heme enzyme/carbon nanotube composite and application of G-quadruplex/heme enzyme/carbon nanotube composite to lithium-sulfur battery
ActiveCN109742338AEasy to operateLower internal resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesEnzyme structureLithium–sulfur battery
The invention provides a preparation method of a G-quadruplex / heme enzyme / carbon nanotube composite and application of the G-quadruplex / heme enzyme / carbon nanotube composite to a lithium-sulfur battery. The preparation method of the G-quadruplex / heme enzyme / carbon nanotube composite comprises the steps that a heme enzyme and a G-quadrant are added into deionized water containing K<+>, still standing is conducted for 1-3 hours, thus the heme enzyme and the G-quadrant are self-assembled to form a stable G-quadruplex / heme enzyme structure, then G-quadruplex / heme enzyme and a carbon nanotube are added into an N-methyl pyrrolidone solvent, stirring and even ultrasonic dispersion are conducted, in obtained paste, the obtained composite paste is evenly brushed on the surface of a cathode materialof the lithium-sulfur battery by a coater, then drying is conducted, and thus the G-quadruplex / heme enzyme / carbon nanotube composite is obtained (directly used for follow-up assembling and testing ofthe battery). The preparation method is easy to operate, the condition is mild, and mass production is easy; and polysulfide ions can be dissolved in a liquid electrolyte in the charging and discharging processes of the lithium sulfur battery, the shuttle effect is effectively inhibited, and the coulombic efficiency and cycle stability of the lithium sulfur battery are improved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
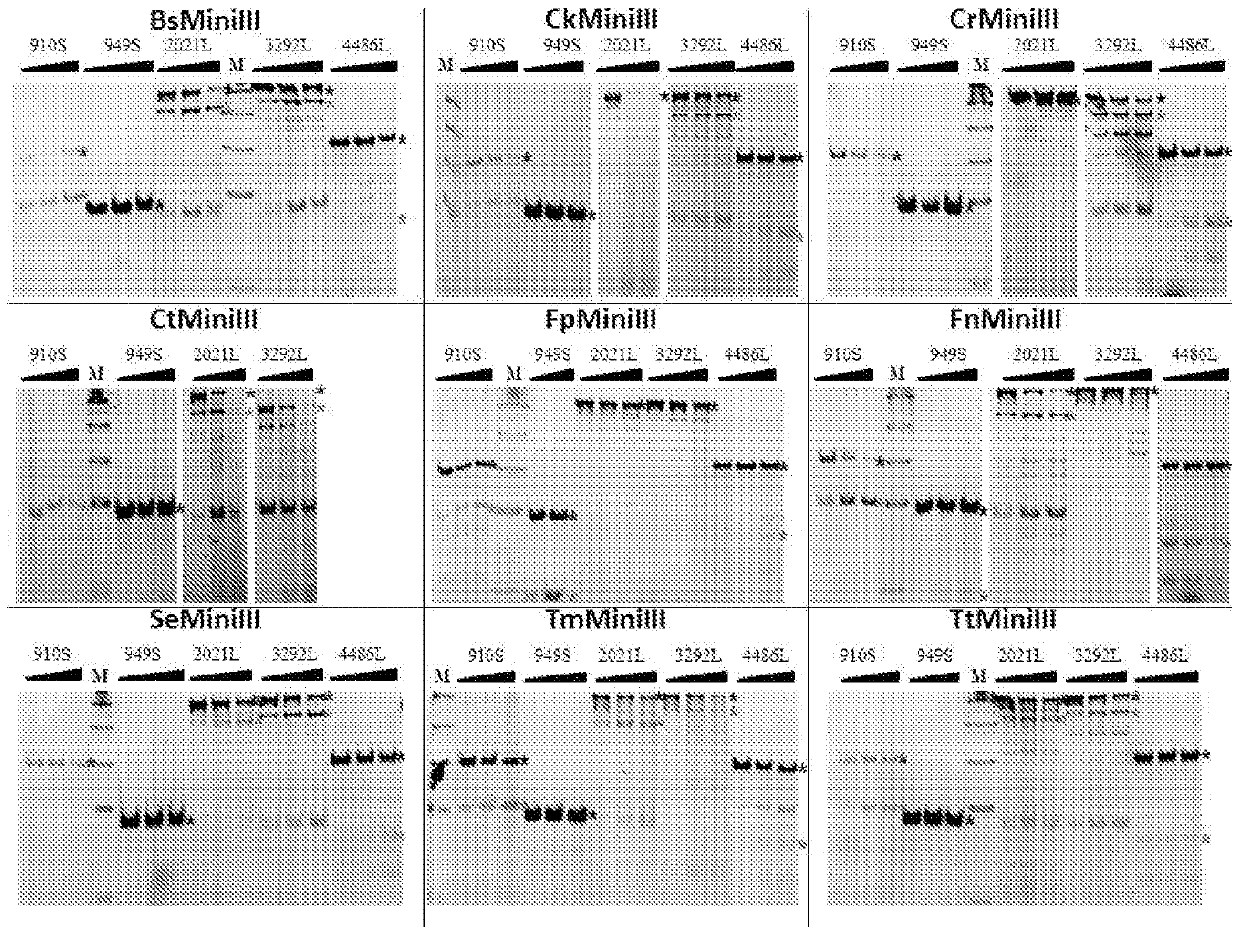
Mini-ILL RNASES, methods for changing specificity of RNA sequence cleavage by Mini-ILL RNASES, and uses thereof
InactiveCN108884450AEasy diagnosisPrevent copyingHydrolasesDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme structureChimeric enzyme
The object of the invention is a Mini-Ill RNase with amino acid sequence comprising an acceptor part, and a transplantable a4 helix, and a transplantable a5b-a6 loop, which form structures of a4 helixand a5b-a6 loop, respectively, in the Mini-Ill RNase structure, wherein the fragments which form structures of a4 helix and a5b-a6 loop, respectively, correspond structurally to respective structuresof a4 helix and a5b-a6 loop formed by amino acid sequence fragments 46-52 and 85-98, respectively, of Mini-Ill RNase from Bacillus subtilis shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein the said Mini- Ill RNase exhibits sequence specificity in dsRNA cleavage being dependent only on a ribonucleotide sequence of the substrate, and independent from an occurrence of secondary structures in the substrate's structure, and independent from a presence of other assisting proteins, and wherein the Mini-Ill RNase is not the Mini-Ill protein from Bacillus subtilis of SEQ ID NO: 1, nor SEQ ID NO: 1 with D94R mutation. The invention also relates to a method of obtaining a chimeric Mini-Ill RNase, a Mini-Ill RNase encoding construct, a cell with a Mini-Ill RNase encoding gene, use of Mini-Ill RNase for dsRNA cleavage,as well as a method of dsRNA cleavage depending only on a ribonucleotide sequence.
Owner:BIOTECH INNOVATIONS SP ZOO
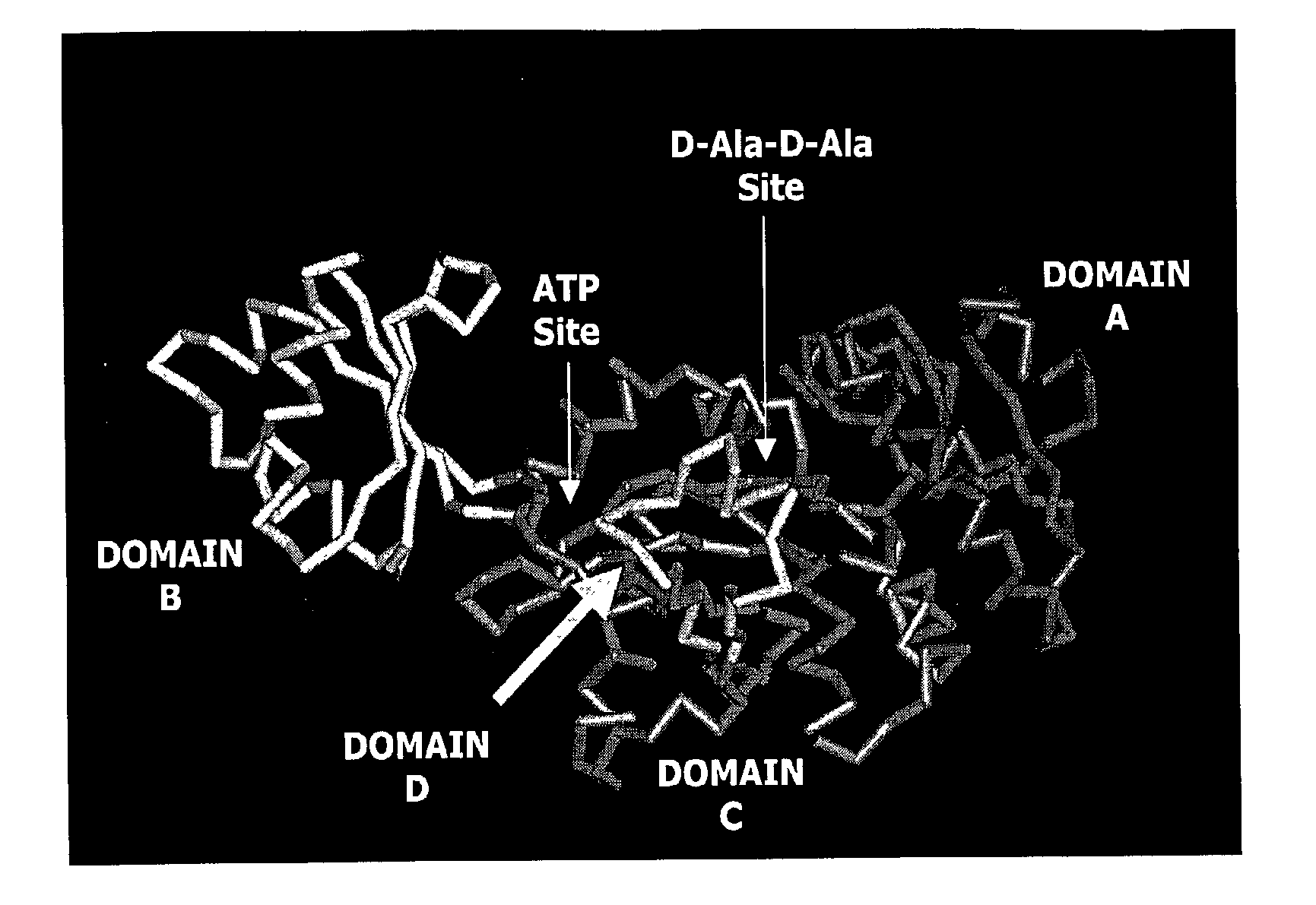
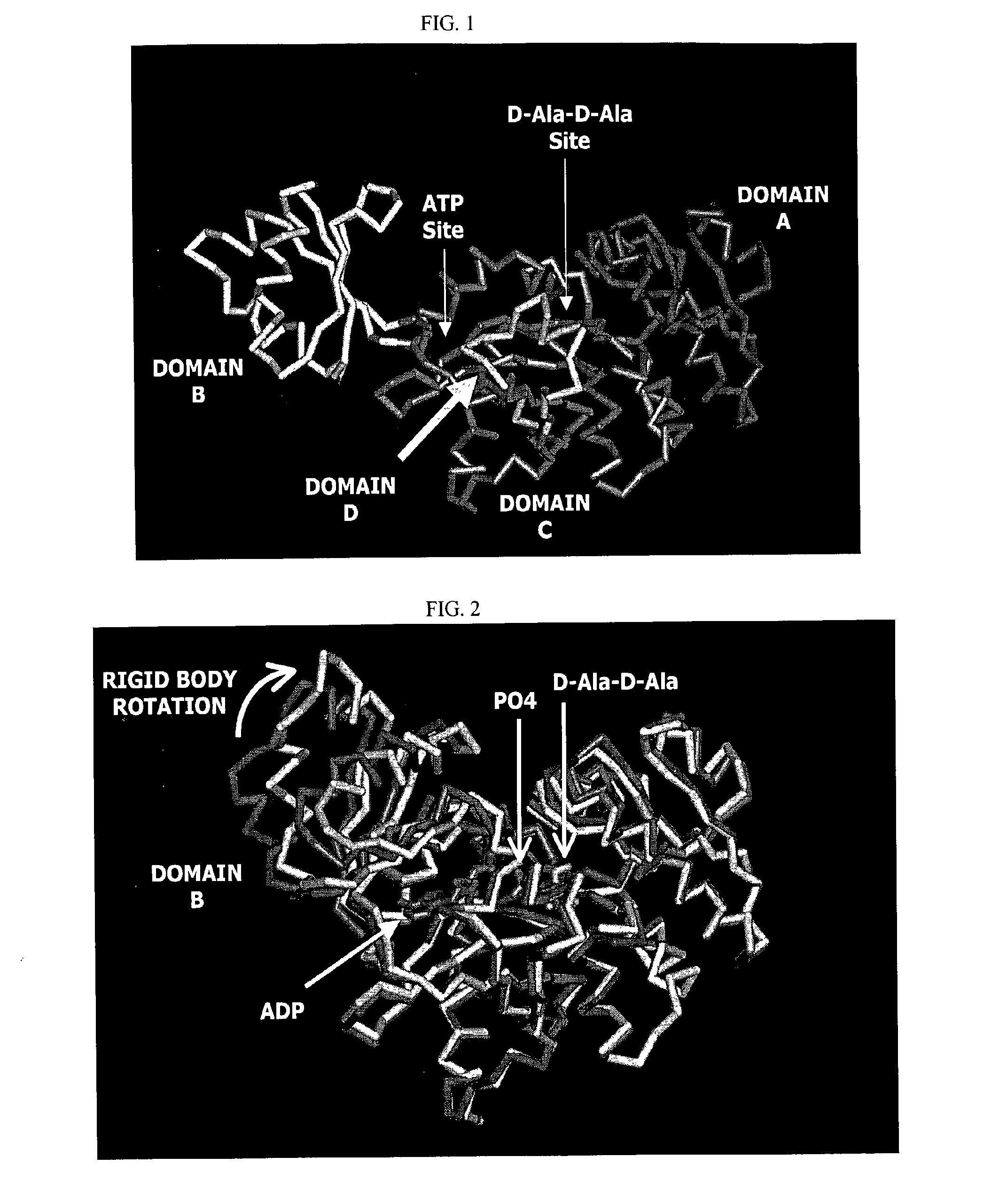
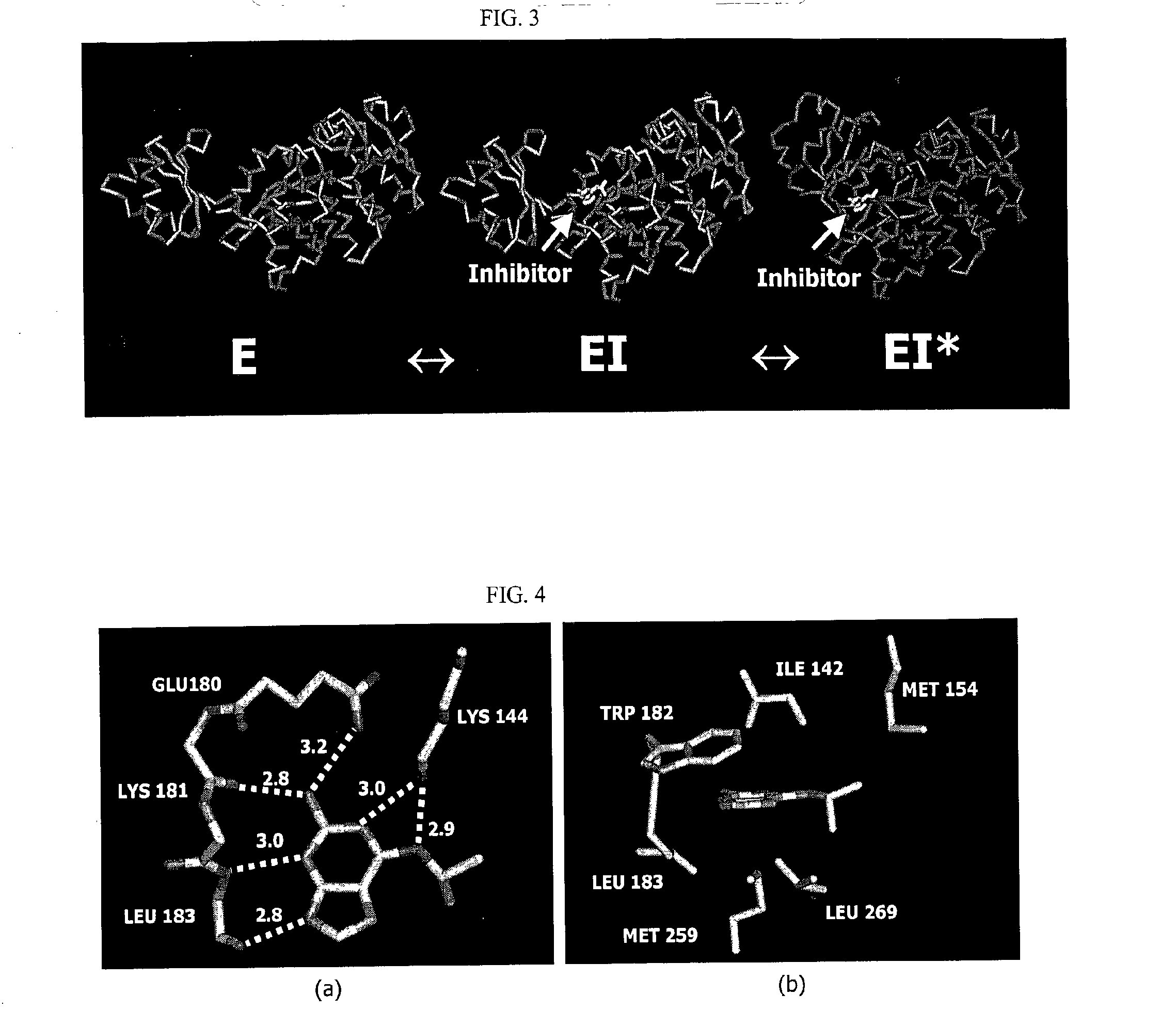
Structure-based drug design methods for identifying d-ala-d-ala ligase inhibitors as antibacterial drugs
The invention is based on the discovery that certain small molecules can bind to the ATP binding site of D-Ala-D-Ala ligase, even in the absence of the enzyme's substrate, and can cause a conformational change in the enzyme structure similar to that which occurs upon binding of ATP and substrate to the enzyme. Without wishing to be bound by any theory, it is believed that such a conformational change is required for either activation or inhibition of the enzyme. The information obtained from this discovery has enabled identification of key interactions in the active site of the enzyme, as well as the design and opimization of inhibitors.
Owner:PLIVA D D
Gene targeting
PendingCN112585272AReliable genetic modificationEffective genetic modificationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainOrigin of replicationEnzyme structure
Methods, reagents and compositions for providing more accurate and reliable genetic modification are provided. In particular a nucleic acid encoding a fusion protein comprising an endonuclease domainand a binding domain for an origin of replication is described. Also provided are methods, reagents and compositions for in vivo genetic modification of the genome of a non-animal cell or organism. Furthermore, the present application relates to uses of the said methods, reagents and compositions for introducing desirable traits to non-animal organisms or ameliorating or removing non-desirable traits in these organisms including in the treatment of disease.
Owner:阿尔根技术有限公司
Constitutively active pyr/pyl receptor proteins for improving plant stress tolerance
The invention relates to constitutively active PYR / PYL receptor proteins for improving plant stress tolerance. The invention provides an expression box, an expression vector comprising the expression box, and a method of using the expression box to enhance the plant resistance. The expression box comprises a heterologous promoter that is operably connected to polynucleotide that encodes PYR / PYL acceptor polypeptides, wherein the PYR / PYL acceptor polypeptides comprise one or more of polyketone cyclase structural domain 2 (PF10604) and polyketone cyclase structural domain 1 (PF03364). By introducing the expression box into plants, the stress resistance of the plants is enhanced, compared with plants without the expression box.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com