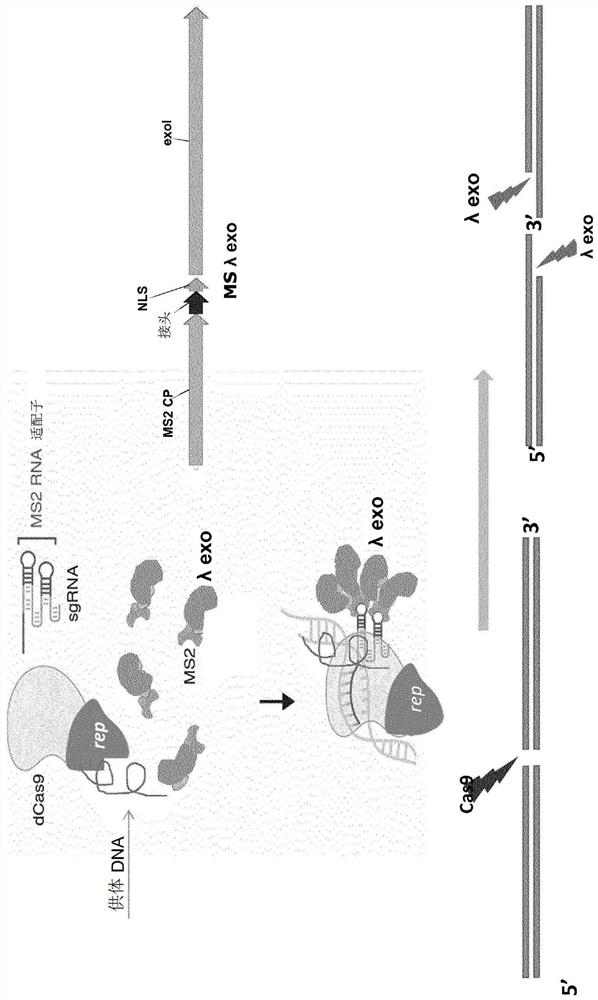
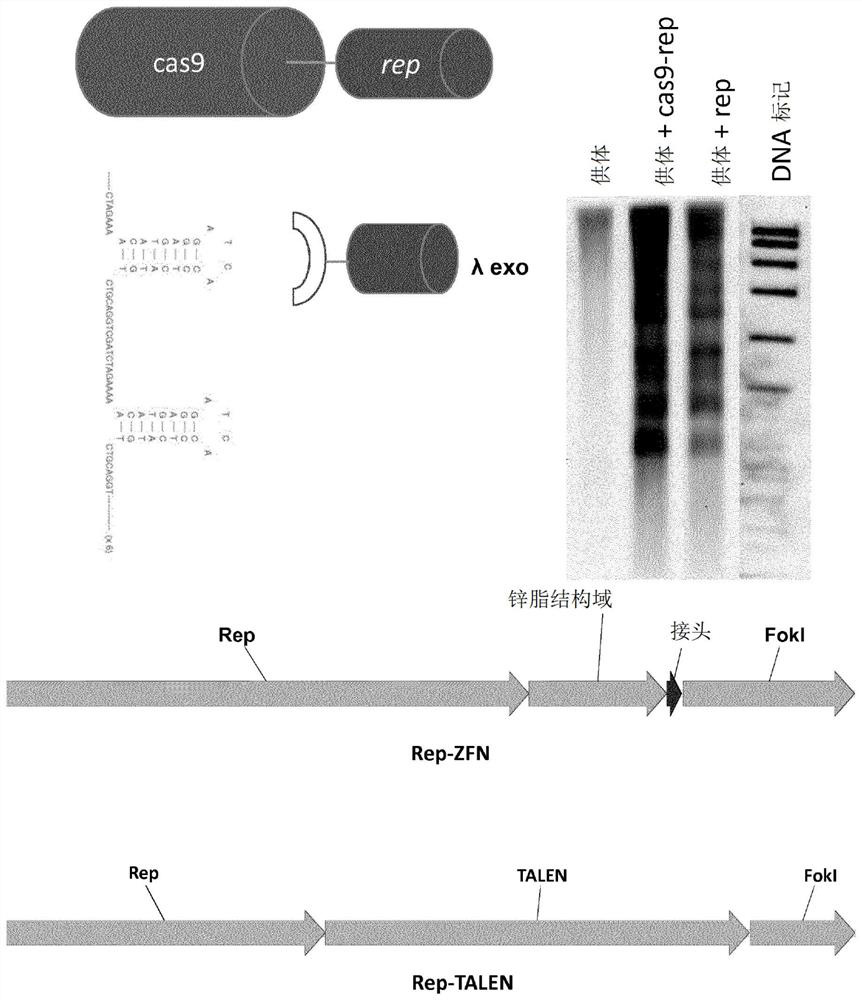
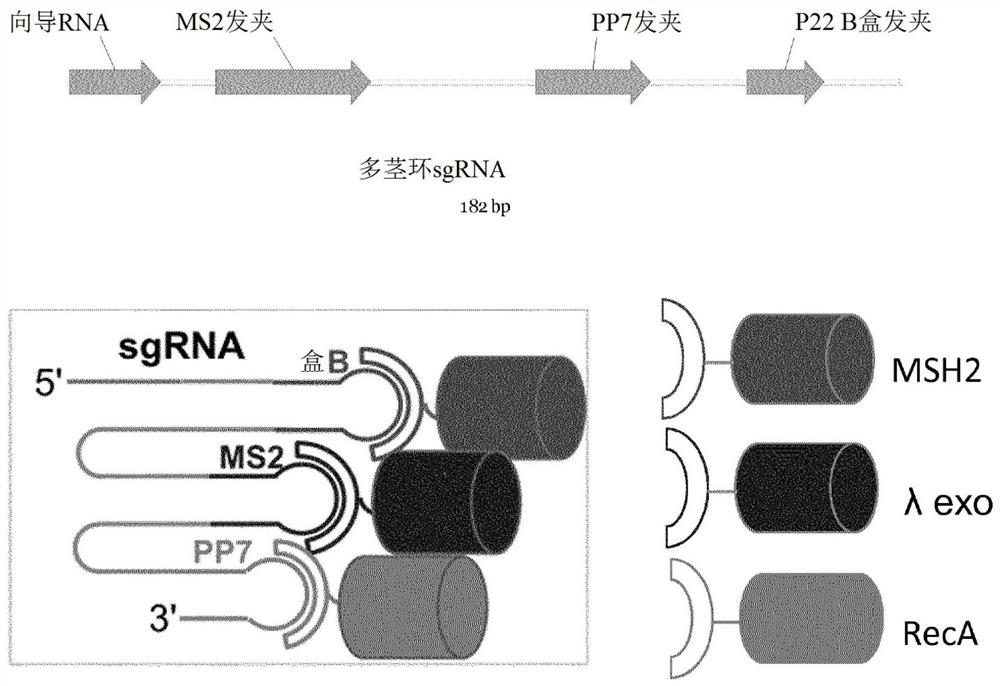
Gene targeting
A genome and fusion protein technology, applied in genetic engineering, polypeptides containing positioning/targeting motifs, enzymes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 3
[0101] Example 3 and Figure 10 An example of a selection vector for introducing knockout mutations in cells and recovering clones or plants on selection medium is given.
[0102] The introduced selection vector usually includes two viral origins of replication flanking the donor DNA fragment and a selectable marker gene fused in whole with respect to product translation, thereby producing a marker effect. The viral origin of replication at the 5' end of the donor DNA contains a eukaryotic promoter fused in-frame with the donor DNA fragment with an ATG translation codon, a linker, a selectable marker gene (e.g. nptII, hygromycin or glufosinate resistance gene ), a terminator (eg, nos terminator), and then the 3' viral origin of replication (SEQ ID NO: 29). All sequences introduced after the ATG codon represent a translation unit, yielding a selectable marker, eg resistance to an antibiotic, in this example: resistance to the kanamycin antibiotic.
[0103] To introduce knocko...
Embodiment 1
[0150] Example 1 Inserting 2 bp into tobacco genome gene.
[0151] To assess the efficiency of gene targeting in tobacco, a set of constructs targeting the exogenous uidA gene of E. coli was prepared.
[0152] Transformation by osmosis (see method below)
[0153] A two base pair deletion was introduced in the uidA gene (SEQ ID NO: 2) of E. coli. The modified uidA gene was introduced into tobacco (ALG 492, Figure 5 ). Transgenic lines were assayed for GUS activity as described by McCabe et al. (Nature Biotechnology, 1988, 6, 923-926). Due to the frameshift of the open reading frame of the uidA gene, no GUS activity was detected in the transgenic lines.
[0154] The tobacco plants carrying the mutated uidA gene were then co-transformed with a repair donor comprising SEQ ID NO: 4 as construct FVLR ( Figure 6 ), said construct expresses (i) Cas9 (construct FVLW; Figure 7b ), (ii) Cas9-Rep fusion protein (construct FVLN; Figure 8 ) (SEQ ID NO: 14) or (iii) the Cas9-Rep f...
Embodiment 2
[0159] Example 2 Insert the DNA fragment into the desired site of the tobacco genome.
[0160] Insertion of long DNA sequences into double-strand breaks represents a challenge for genome modification in different organisms. Here we present a method for increasing insertion efficiency into the tobacco genome using the molecular combination of the present invention.
[0161] Two targets were selected for the experiment, the acetolactate synthase (ALS) gene and the protoporphyrinogen oxidase 1 (PPOX1) gene. Using the translational fusion of the nptII gene (SEQ ID NO: 32), two vectors were designed for insertion into the ends of the ALS (SEQ ID NO: 30) and PPOX1 (SEQ ID NO: 31) genes ( Figure 11 ). The left-flank sequence (LRF), which is translationally fused to the nptII gene, is specifically mutated to confer chlorsulfuron herbicide resistance in ALS and aciflufen herbicide resistance in the PPOX1 gene. The right flanking sequence (RFS) is indicated with the non-coding regio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com