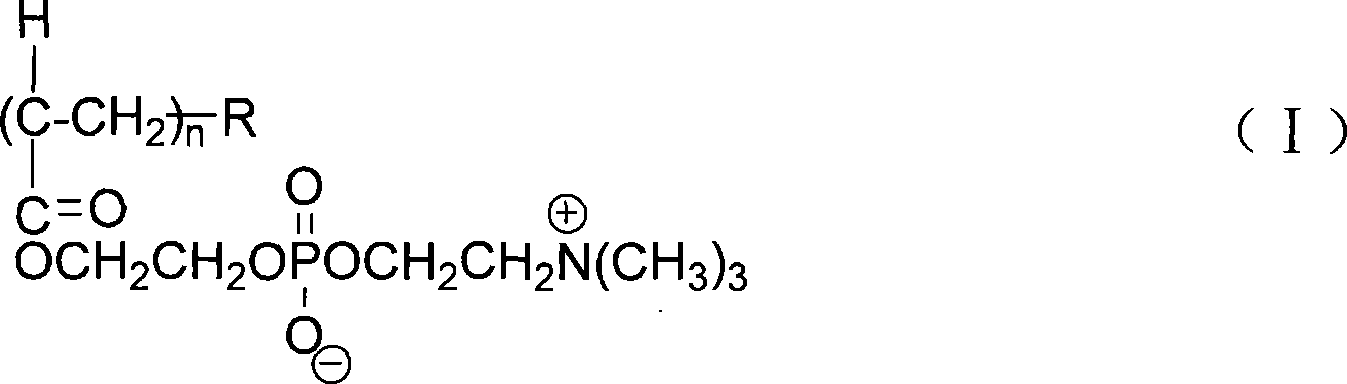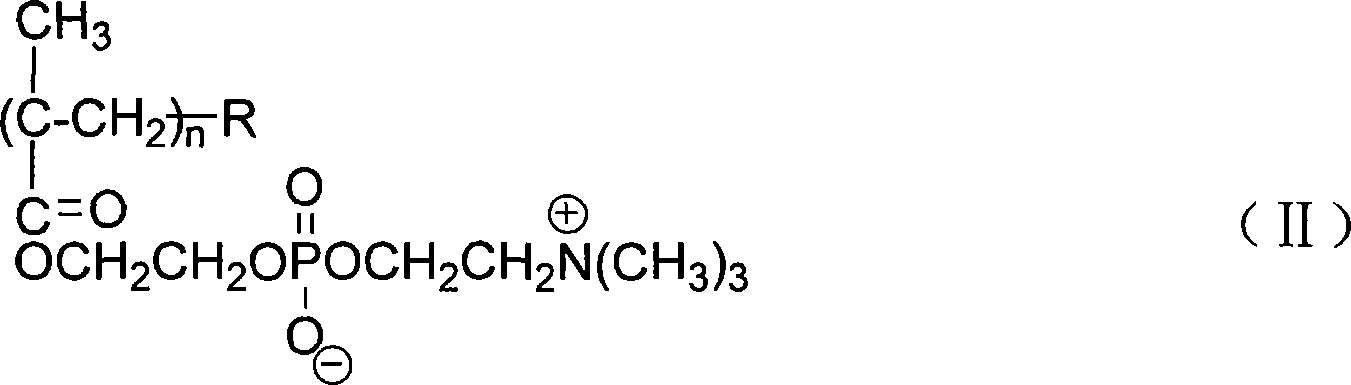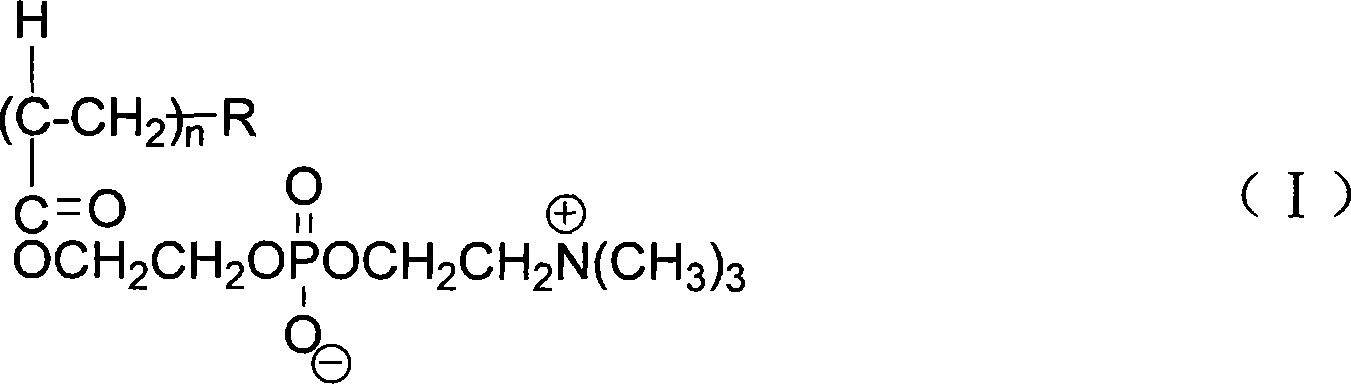Patents
Literature
159 results about "Covalent Interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A physical connection between two atoms or radicals in which a chemical bond is formed by sharing electrons.
Elastic materials
The present invention relates to materials exhibiting the property of rubbery elasticity, consisting of molecules with a mass of between 9 and 9000 g / mol, all or some of the molecules having at least three groups (also referred to as “associative groups”) capable of associating via non-covalent interactions.Although consisting of small non-polymerized molecules that are not chemically crosslinked, this material exhibits properties of rubbery elasticity. According to an embodiment of the invention, this material exhibits rubbery elasticity at ambient temperature. Above a certain temperature, the material flows like a simple liquid. The material is thermoreversible, i.e. after cooling, the material again exhibits the property of rubbery elasticity. This material is self-repairing and potentially recyclable, which is never the case with a chemically crosslinked elastomer.According to an embodiment of the invention, the molecules constituting the material of the invention bear associative groups of formula (1) below:in which A denotes oxygen, sulphur or NH; the carbon atoms of formula (1) can be substituted. Preferably, A denotes oxygen. Advantageously, the material comprises (i) molecules having at least 3 associative groups, and (ii) molecules having a single associative group.Advantageously, the molecules are obtained from fatty acid derivatives.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
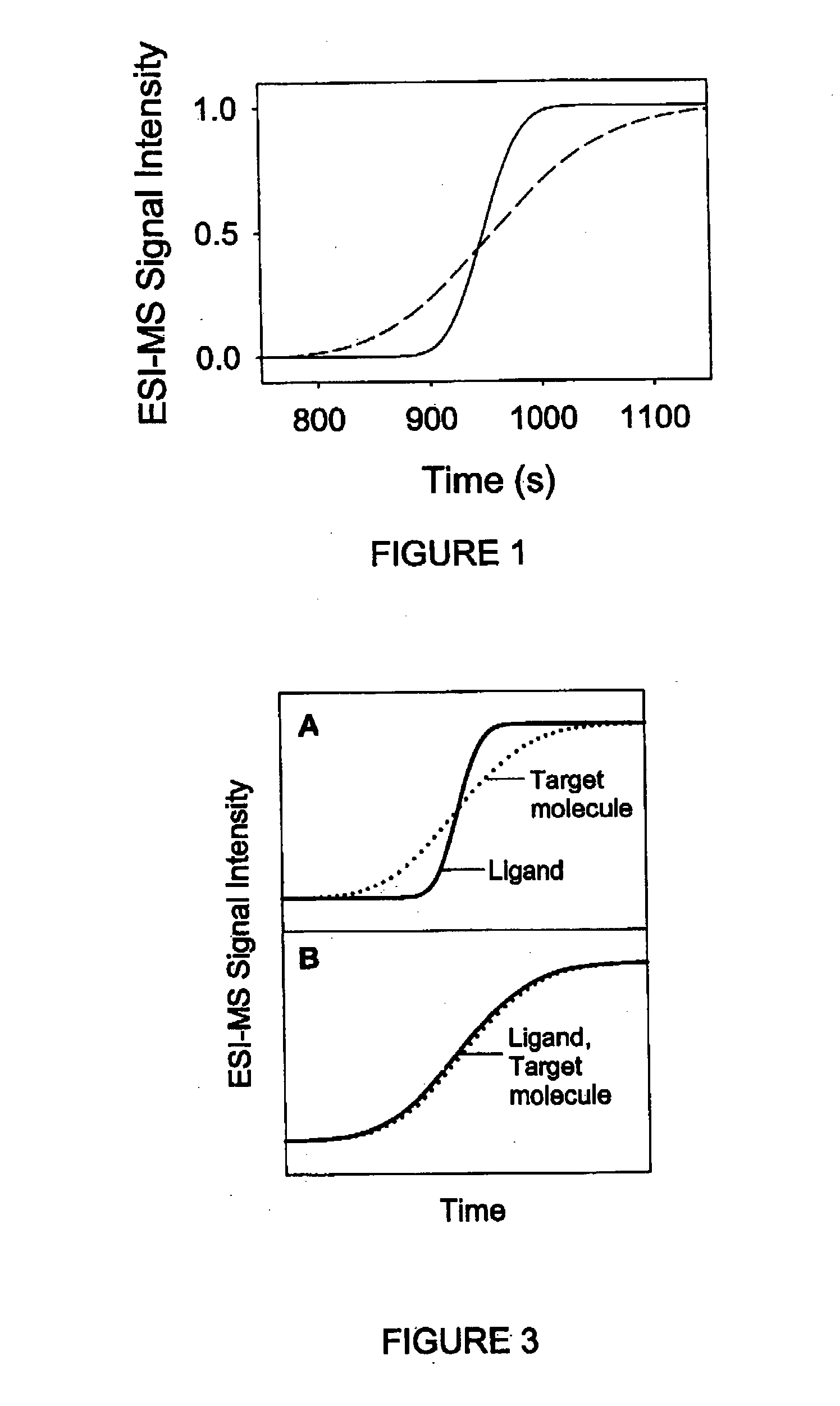
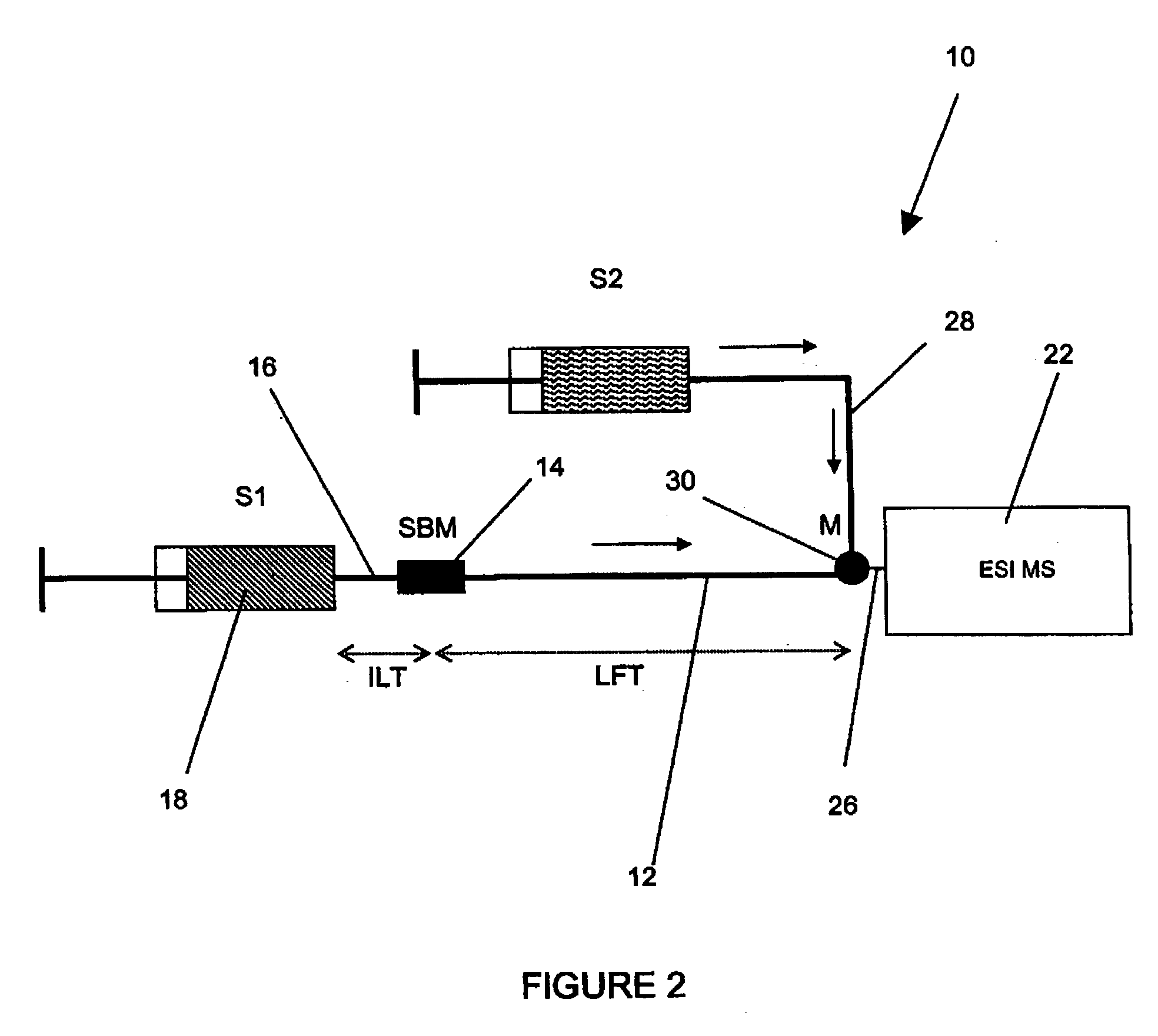
Method and apparatus for the detection of noncovalent interactions by mass spectrometry-based diffusion measurements
InactiveUS20030234356A1Accurate measurementShorten the timeSamples introduction/extractionSurface/boundary effectHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGas phase
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting the noncovalent binding of a potential ligand (such as a drug candidate) to a target, e.g. a biochemical macromolecule such as a protein. The method is based on the Taylor dispersion of an initially sharp boundary between a carrier solution, and an analyte solution that contains the potential ligand(s) and the target. Dispersion profiles of one or more potential ligands are monitored by mass spectrometry at the exit of the laminar flow tube. Potential ligands will usually be relatively small molecules that have large diffusion coefficients. In the absence of any noncovalent interactions in solution, very steep dispersion profiles are expected for these potential ligands. However, a ligand that binds to a large target in solution, will show an apparent diffusion coefficient that is significantly reduced, thus resulting in a more extended dispersion profile. Noncovalent binding can therefore be detected by monitoring dispersion profiles of potential ligands in the presence and in the absence of the target. In contrast to other mass spectrometry-based methods for detecting noncovalent interactions, this method does not rely on the preservation of specific noncovalent interactions in the gas phase. This method has an excellent sensitivity and selectivity, therefore it can be used for testing multiple potential ligands simultaneously. The method is therefore useful for the high throughput screening of compound libraries.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
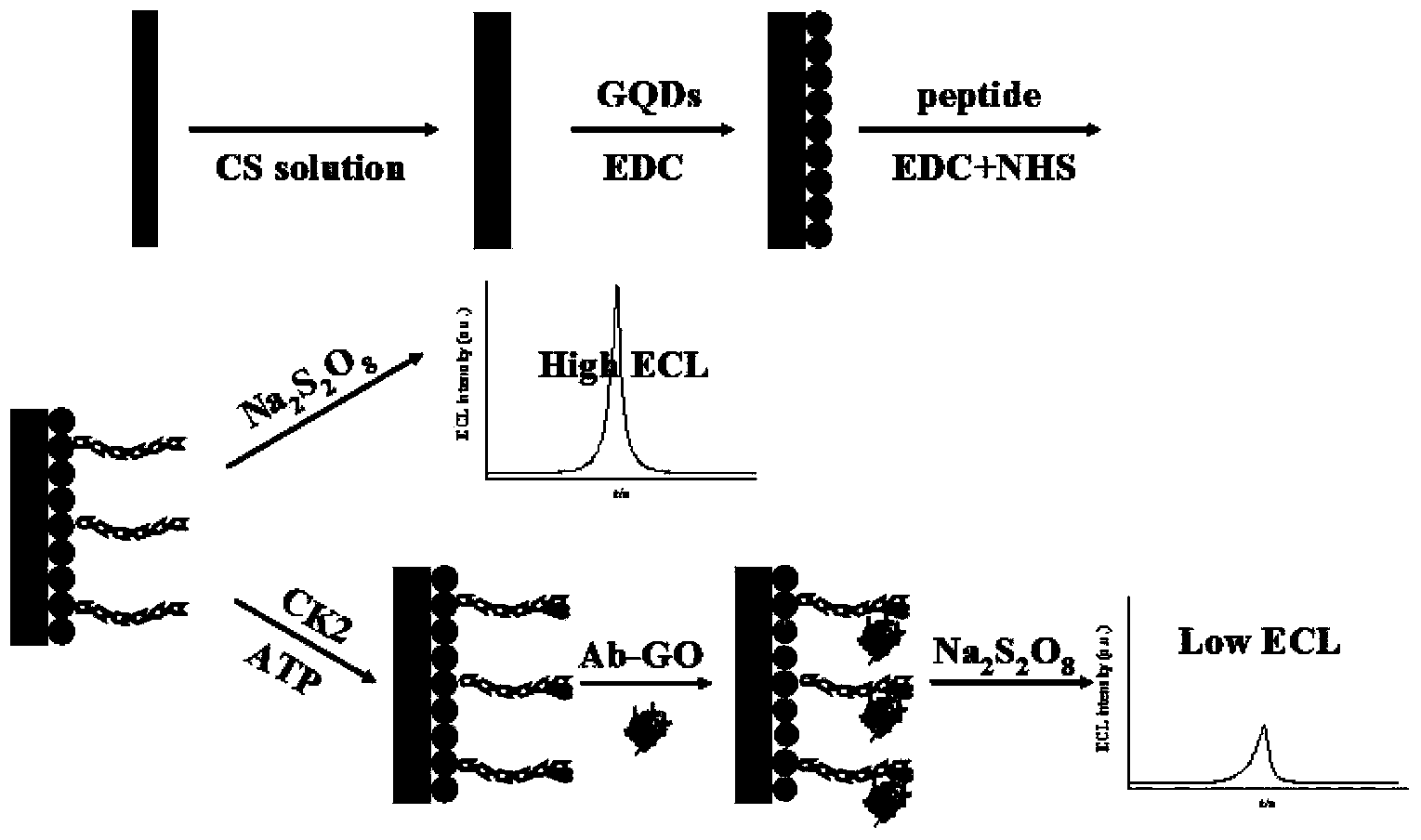
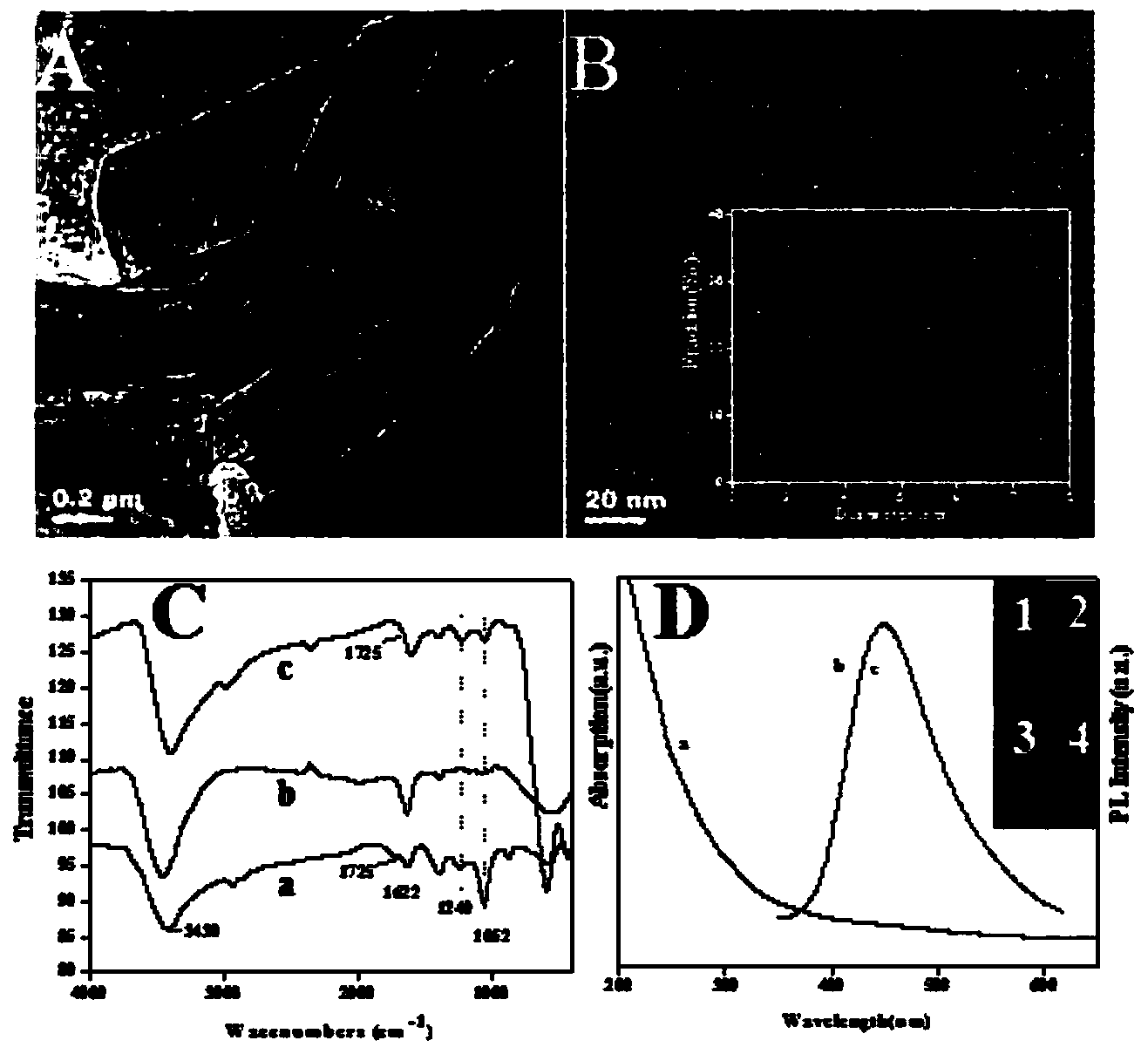
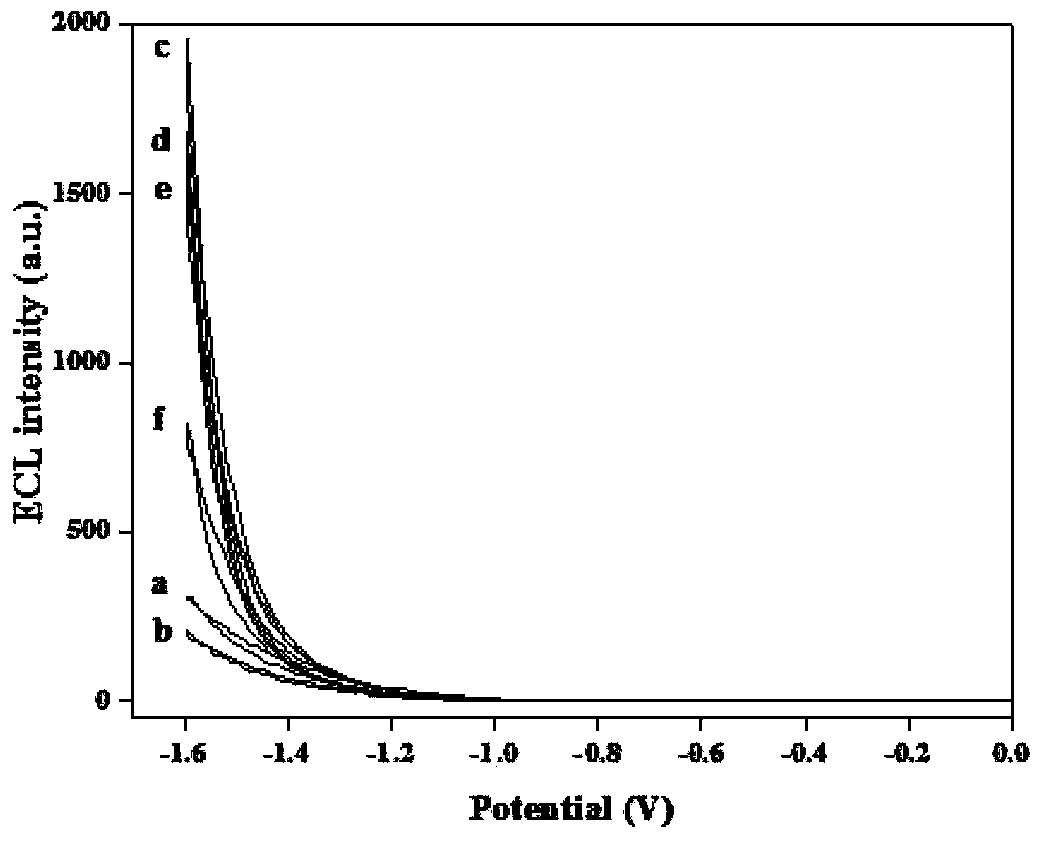
Sensor preparation method based on ECL-RET action between GO and GQDs and application on kinas detection
InactiveCN103512878AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGrapheneAntigenPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a sensor preparation method based on an ECL-RET action between GO and GQDs and an application on kinas detection, and belongs to the field of electrochemiluminescence (ECL). The preparation method comprises the following steps: coating chitosan on the surface of an electrode, and orderly assembling graphene quantum dots and polypeptides onto the surface of the electrode through a covalent interaction. Under the actions of protein kinase and triphosadenine, the polypeptides carry out phosphorylation reactions, through the specific recognition action between an antibody and an antigen, oxidized graphene conjugated with a phosphorylated antibody is assembled to the phosphorylated serine sites of the polypeptide, thus the distance between the oxidized graphene and the graphene quantum dots is narrowed down, so that the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) of graphene quantum dots is quenched. The larger the concentration of protein kinase is, the more phsophorylated sites are generated on the polypeptide modified electrode surface, the more oxidized graphene is assembled on a sensing interface, the stronger the electrochemiluminescence quenching effect of graphene quantum dots will be, and thus the high sensitive detection on protein kinase is achieved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
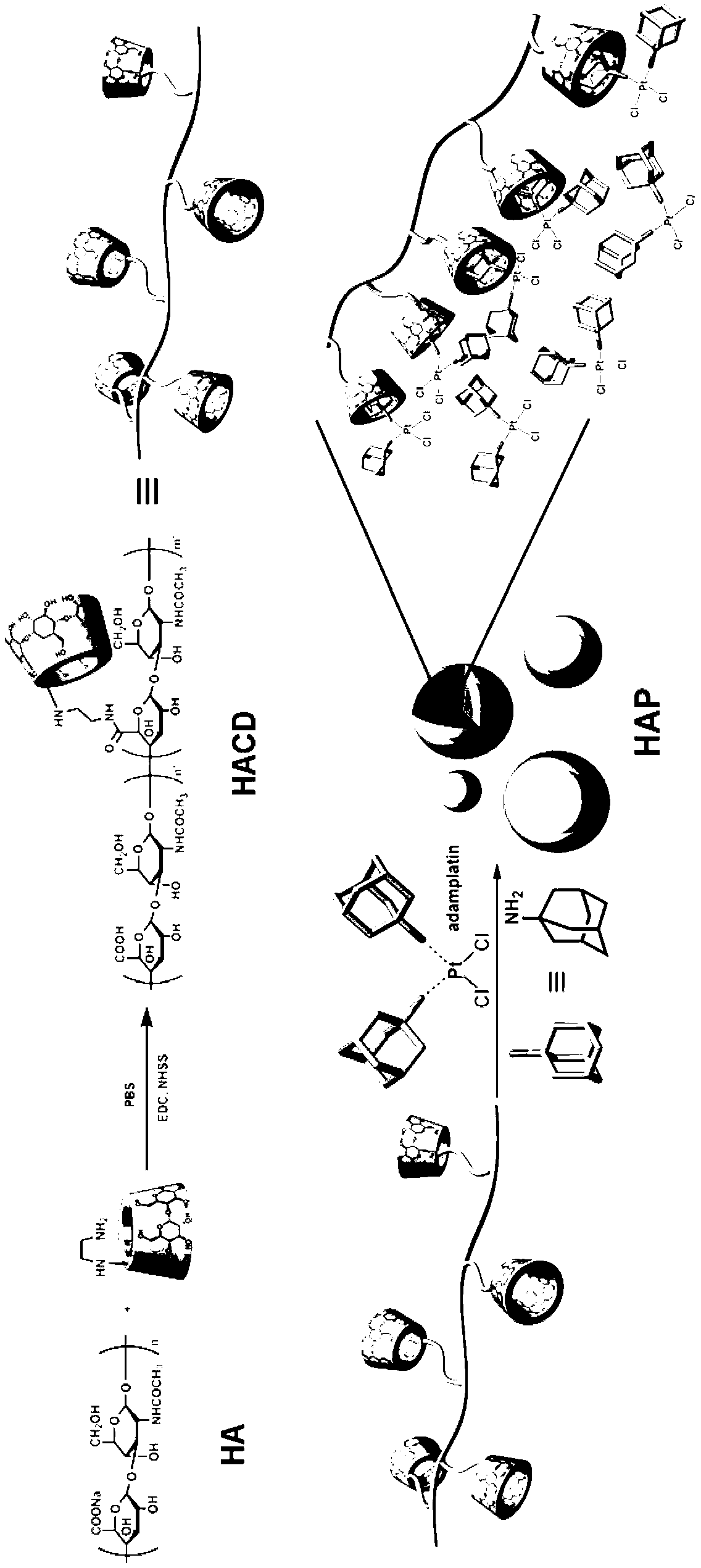
Supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin and preparation of supramolecule assembly
InactiveCN102698286AAchieve selective killingSmall toxicityHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses a supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin. The supramolecule assembly is a binary supramolecule assembly which is synthesized on the basis of cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and adamplatin. A preparation method of the supramolecule assembly is characterized in that the cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and the adamplatin are respectively synthesized, and through the strong non-covalent interaction of cyclodextrin and adamantine and the amphiphilic action of molecules, a supermolecule nano particle which takes the hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as a shell and the adamplatin as a core is formed. The supramolecule assembly disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the supramolecule assembly of the targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin has a simple synthetic route, is low in preparation cost and high in productivity, and is suitable for amplification synthesis and practical production application; and through endocytosis in which a malignant cell surface hyaluronic acid receptor serves as a medium, the supramolecule assembly (HAP) is brought in cancer cells in a target manner, so that the protection of normal cells and the targeting selective killing of cancer cells are realized, the anti-cancer activity is obviously improved, and toxic and side effects are obviously reduced.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
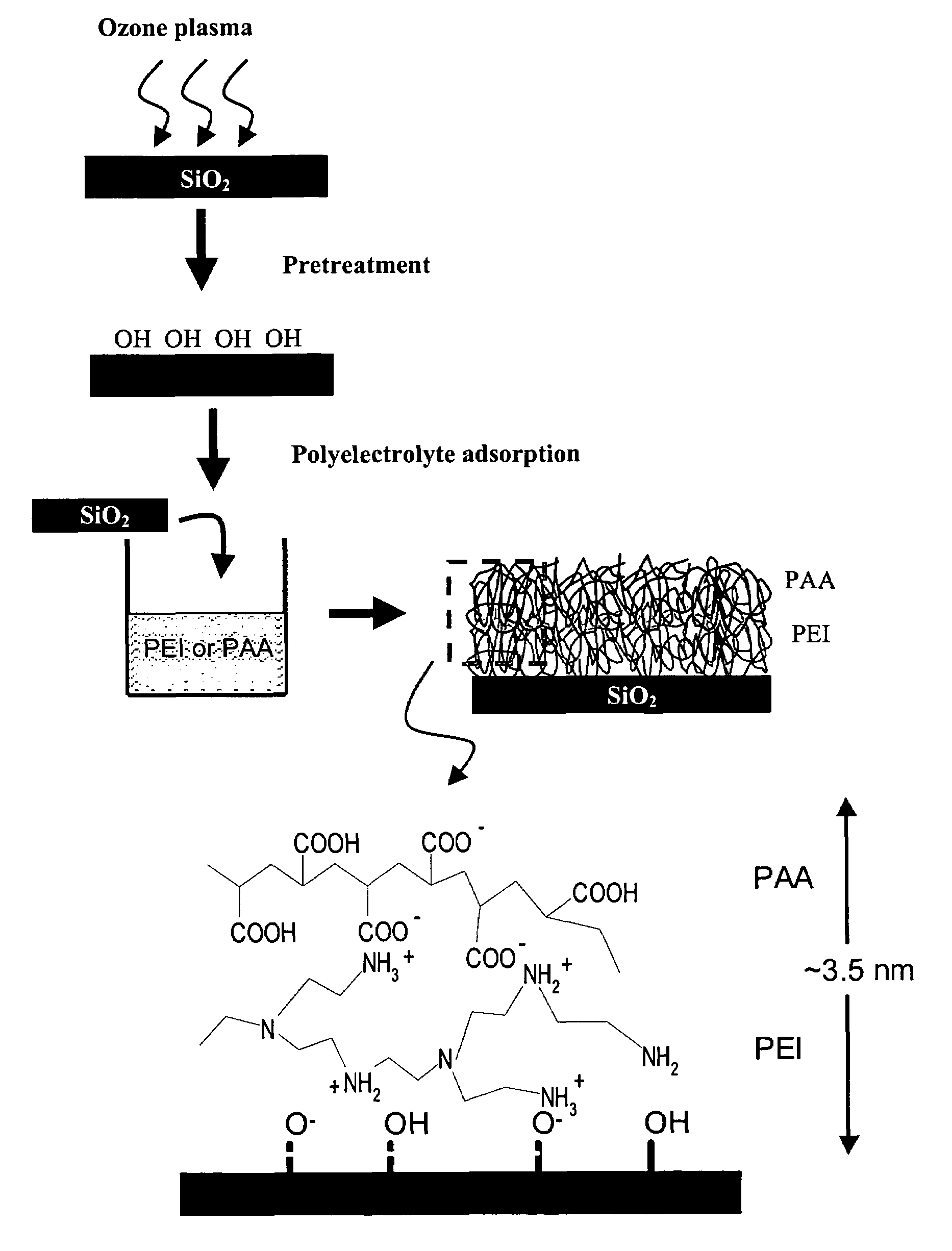
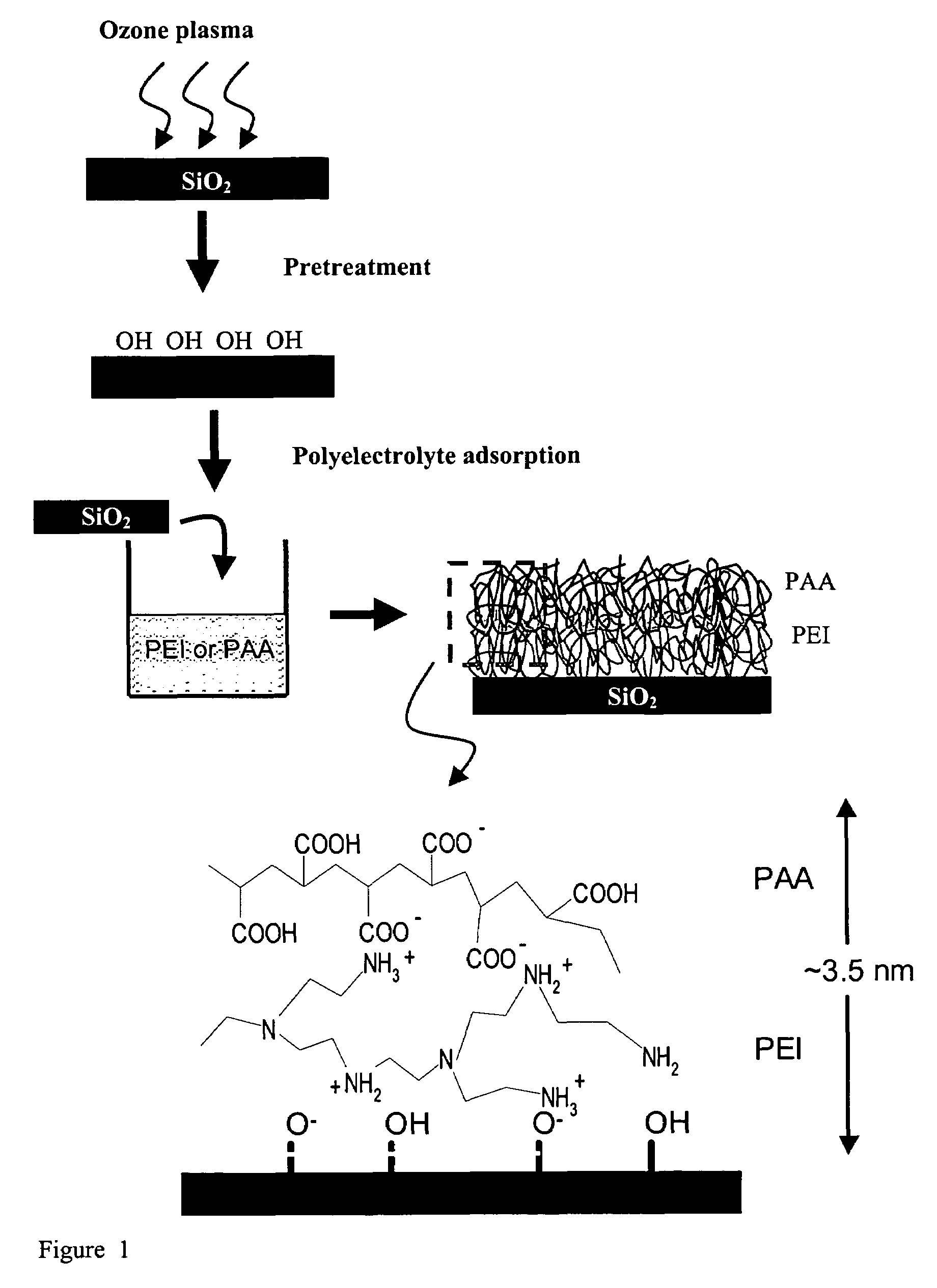
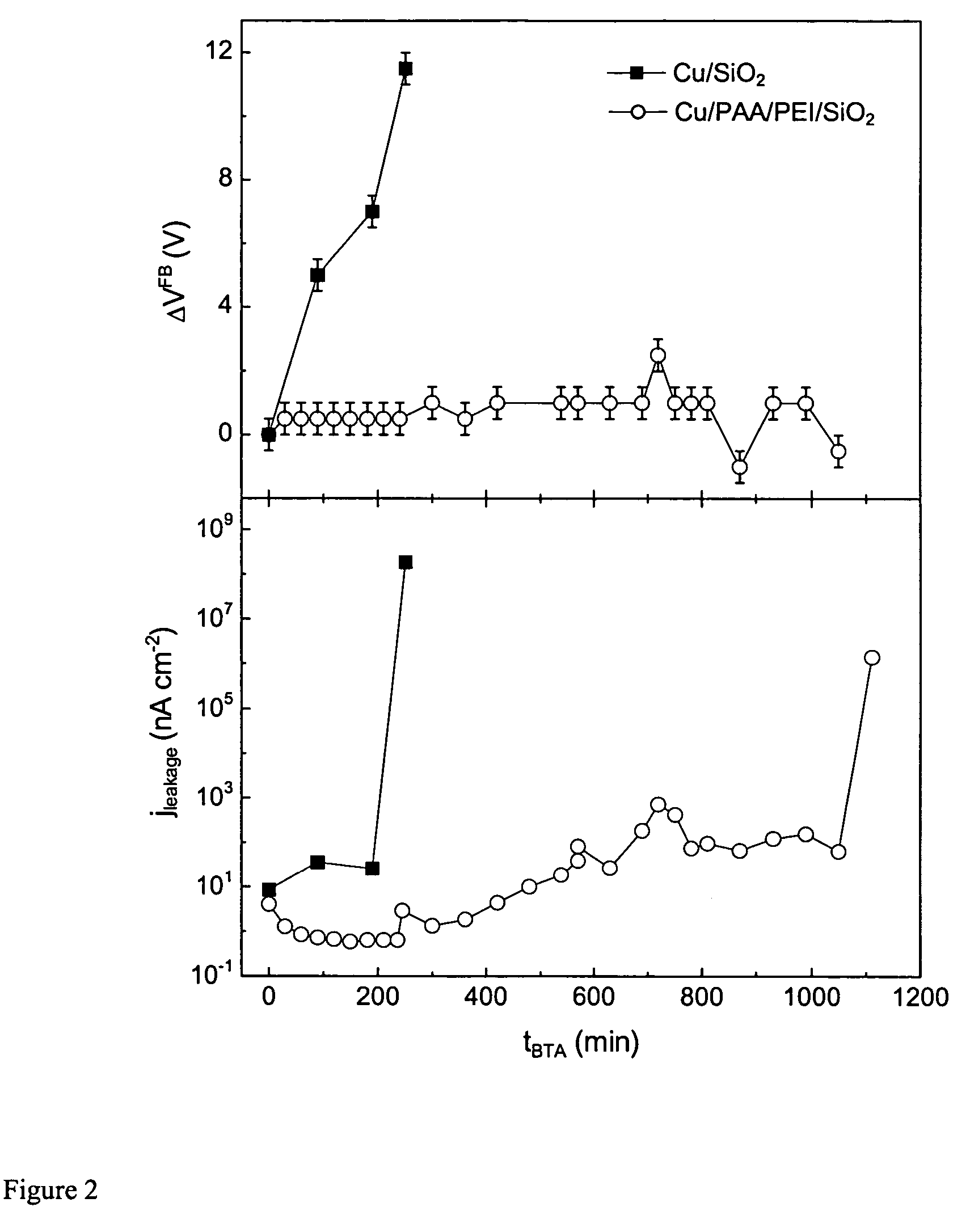
Polyelectrolyte nanolayers as diffusion barriers in semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20050001317A1Improve adhesionInhibit migrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricDevice material
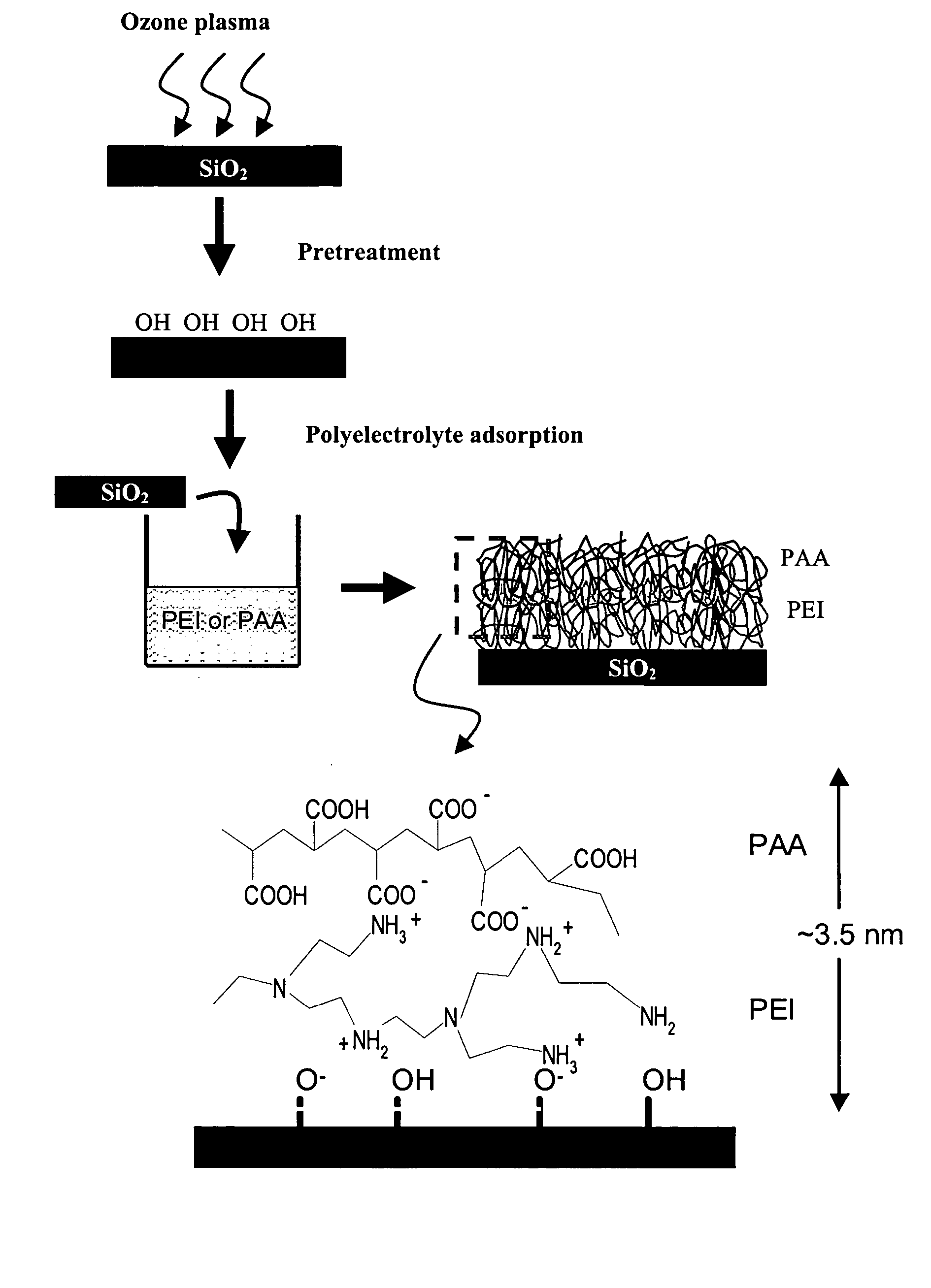
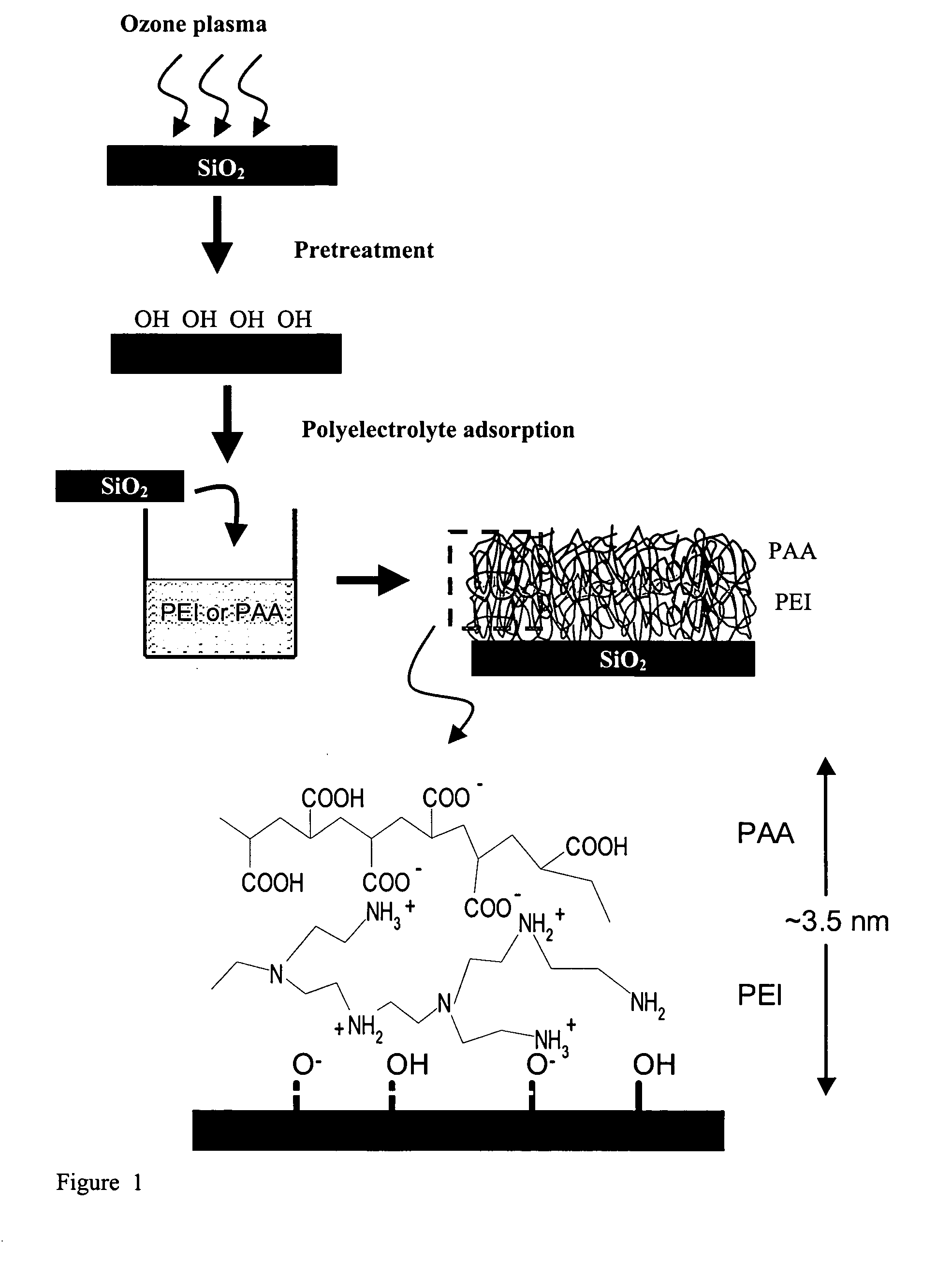
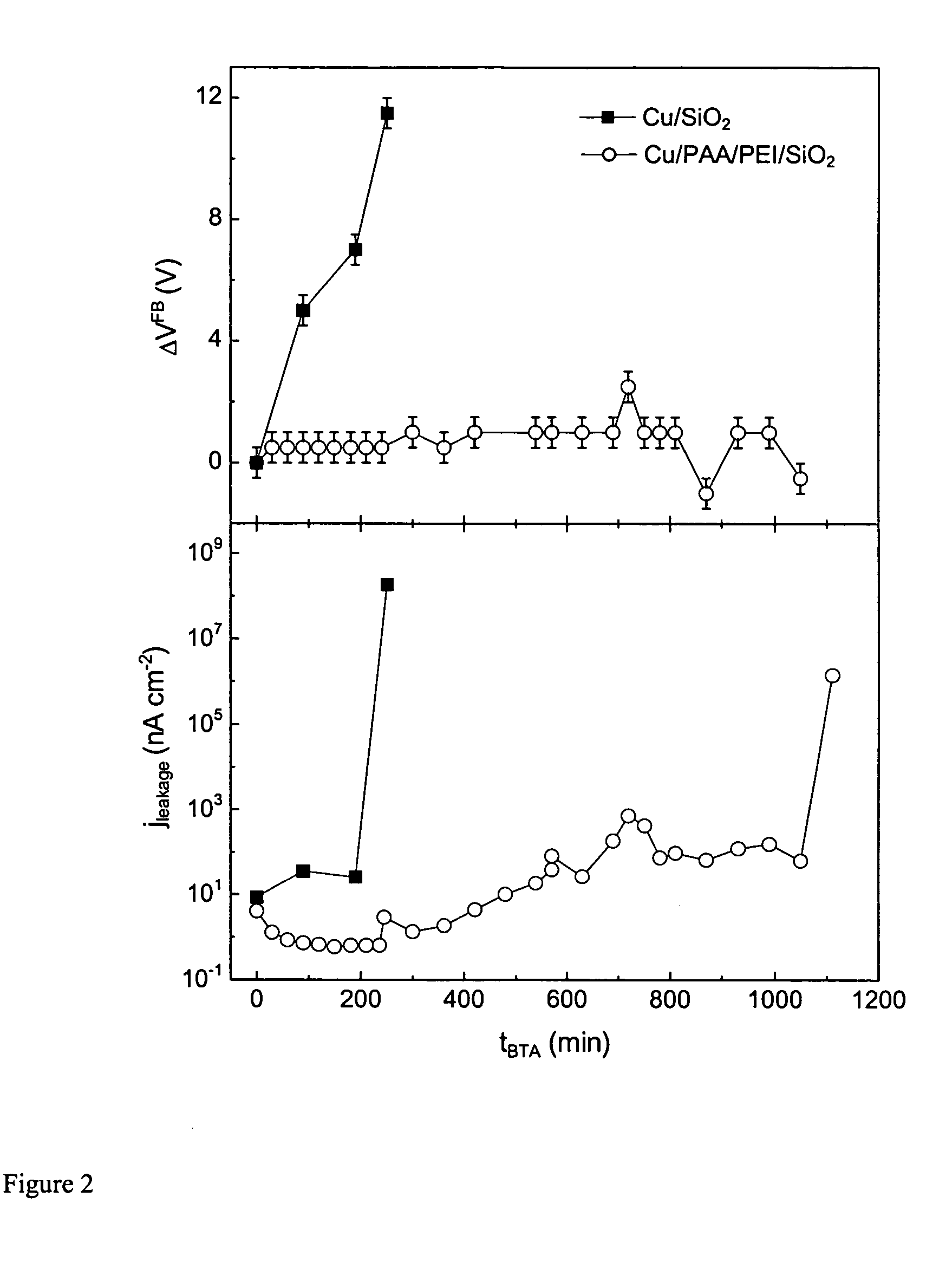
The present invention provides a diffusion barrier useful in an integrated circuit, which serves to prevent the migration of material from a conductive layer to the underlying substrate and further provides improved adhesion of the conductive layer to the substrate. The diffusion barrier comprises a polymer which is a polyelectrolyte, having both cationic and anionic groups along its backbone chain. Preferred polyelectolyte barriers are polyethyleneimine (PEI) and polyacrylic acid (PAA). Other polyelectrolytes may be used, such as those that contain SH— OH— aromatic groups, or those that can interact with either the metal or the adjacent layers via covalent interactions and cross-linking (e.g., POMA, PSMA). The polymeric layer may be applied in two coatings, so that the amine side chains contact the dielectric (e.g. silicon) substrate and the acidic groups are adjacent to the overlying metallic interconnect (e.g. copper). The diffusion barrier may be made thin, preferably less than 5 nm thick, which is advantageous in devices having high aspect ratios.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Hydrophylic phenylboric acid functional porous integral material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102059103AReduce hydrophobicityReduce manufacturing costIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesBoronic acidEngineering
The invention provides a hydrophilic phenylboric acid functional porous integral material, which is a cross-linked framework structured hydrophilic phenylboric acid functional porous integral material with penetrated transparent ducts, is formed by 4-(-3-butenyl sulfone) phenylboric acid and crosslinker N,N-bisacrylamide under initiation of a free radical reaction initiator, and can perform a covalent interaction with dihydroxyl compound under a neutral pH condition. The hydrophilic phenylboric acid functional porous integral material can be used for specifically identifying, separating, enriching or immobilizing the dihydroxyl compounds. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the hydrophilic phenylboric acid functional porous integral material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
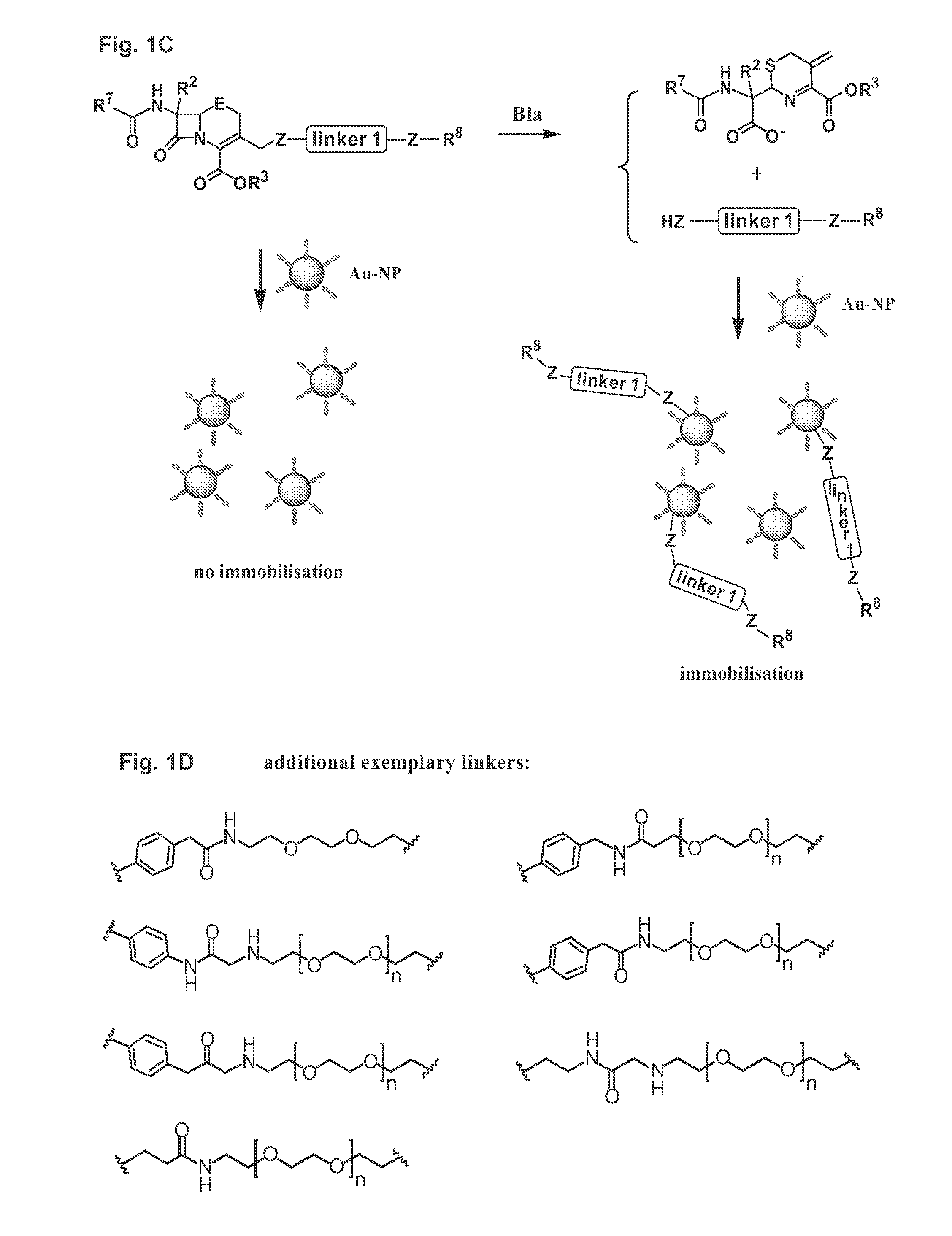
Methods and compounds for detecting beta-lactamase activity
ActiveUS20090275065A1Easy to operateOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementThio-Nanoparticle
The present invention relates to compounds for and a method of detecting beta-lactamase activity in a sample. The sample is contacted with a nanoparticulate tag. The nanoparticulate tag comprises a metal or a combination of metals, or it comprises a nanotube of a metal, boron nitride and / or carbon. The respective metal is capable of forming one of a covalent bond, a coordinative bond and a non-covalent interaction with a thio or a seleno group. The sample is contacted with a compound of one of general formulas (I)-(III) and (VII)-(IX). At least one beta-lactam moiety of the compound is cleaved by the beta-lactamase activity in the sample. As a result a cleavage moiety Z-A-Z, Z-A-Z-R15, Z-A-Z-R16, Z-A-Z-R17, Z-A-Z-R18 or Z-G-N(R8)R9 is released that is immobilised on the surface of the nanoparticulate tag by a covalent bond via a Z atom. The presence of beta-lactamase activity is determined based on the presence of the cleavage moiety immobilized onto the surface of the nanoparticulate tag.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Method for preparing magnetic silica microspheres with surfaces modified by cations
ActiveCN101723389ACause lossLarge amount of extracted nucleic acidSilicaPreparing sample for investigationEpoxyMicrosphere
The invention relates to a method for preparing magnetic silica microspheres with surfaces modified by cations, and the number of electric charges of the modified cations varies with pH of solution. Ethyl orthosilicate is hydrolyzed to generate the magnetic silica microspheres by a sol-gel method in the presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Epoxy silane reagent of 3-Glycidoxypropyltrimethoxy silane (GPTMS) is adopted to activate magnetic silica microparticles, and the cationic modifying agent with the pKa value within 4 to 8 is used as functional group, therefore, the magnetic silica microspheres with surfaces modified by cations are prepared by covalent interaction. The method comprises the preparation of the magnetic silica microspheres, the epoxidation of the magnetic silica microspheres and the cationic modification on the surfaces of the magnetic silica microspheres. The magnetic microspheres prepared by the method are used for separating nucleic acid from biological samples according to the variation of the electric charges on the surfaces.
Owner:XIAN GOLDMAG NANOBIOTECH
Composition for polymer gel, gel prepared from composition and application of gel
ActiveCN112341637AGood anti-swelling performanceExcellent underwater bonding performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusInksPolyelectrolytePolymer science
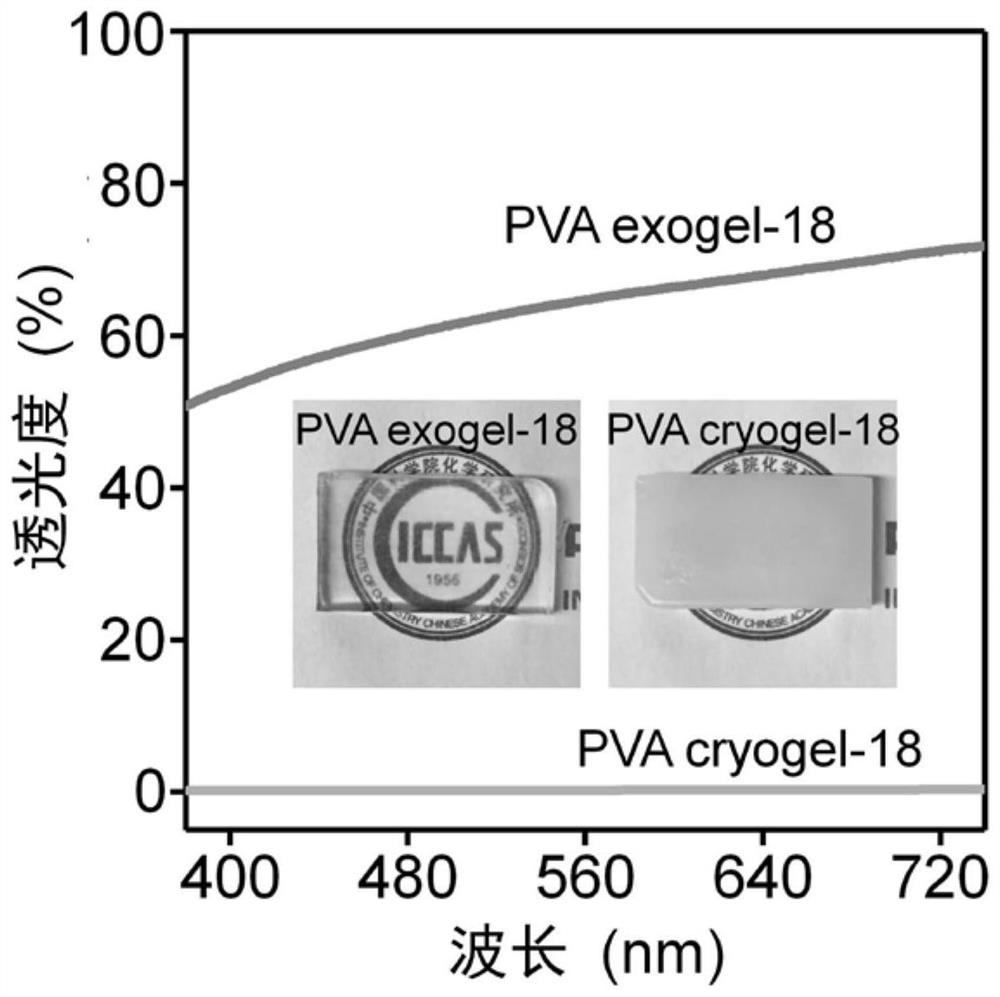
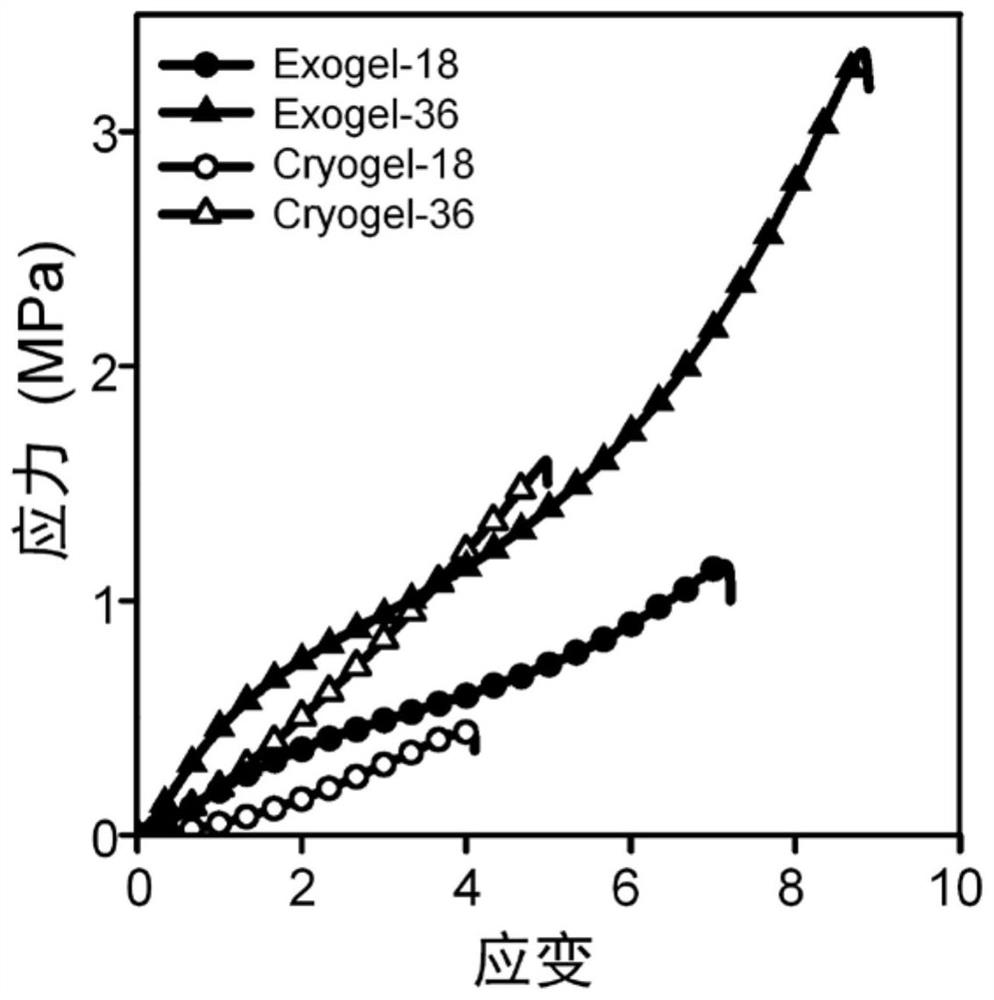
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer gel materials, and provides a composition for polymer gel, gel prepared from the composition and application of the gel. The composition comprises a polymer compound, a first solvent and a second solvent, wherein the polymer compound comprises but is not limited to at least one of the following substances: a polymer with a hydrogen bond effect, a polymer with a hydrophobic effect and a charged polyelectrolyte; in the first solvent, the non-covalent interaction in / among the high-molecular compounds is in a weakening shielding state; in thesecond solvent, the non-covalent interaction between the polymer compounds is activated and enhanced. The polymer gel prepared by the invention has high transparency, excellent mechanical properties,swelling resistance and icing resistance.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Testing device and method utilizing optical waveguide micro-ring resonator for testing methane concentration
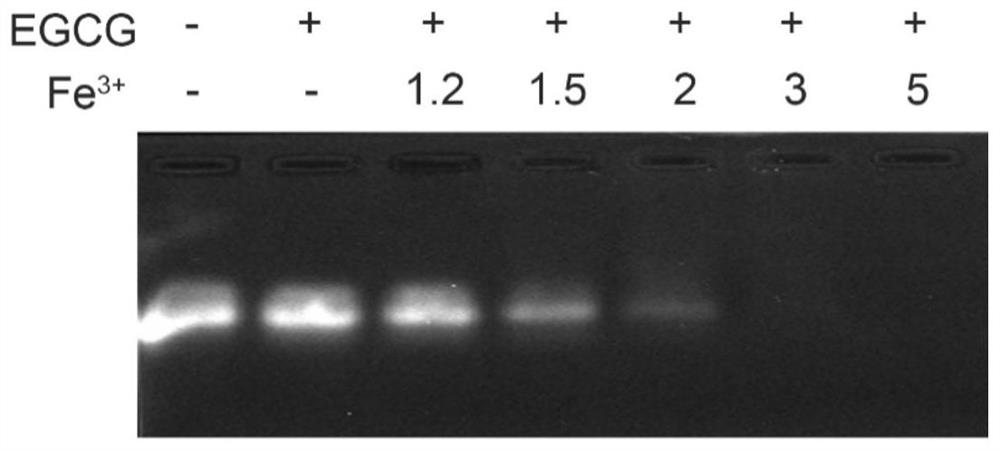
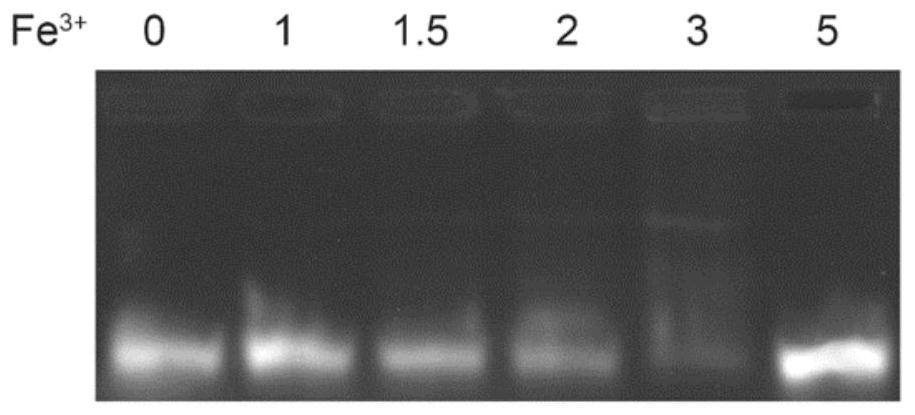
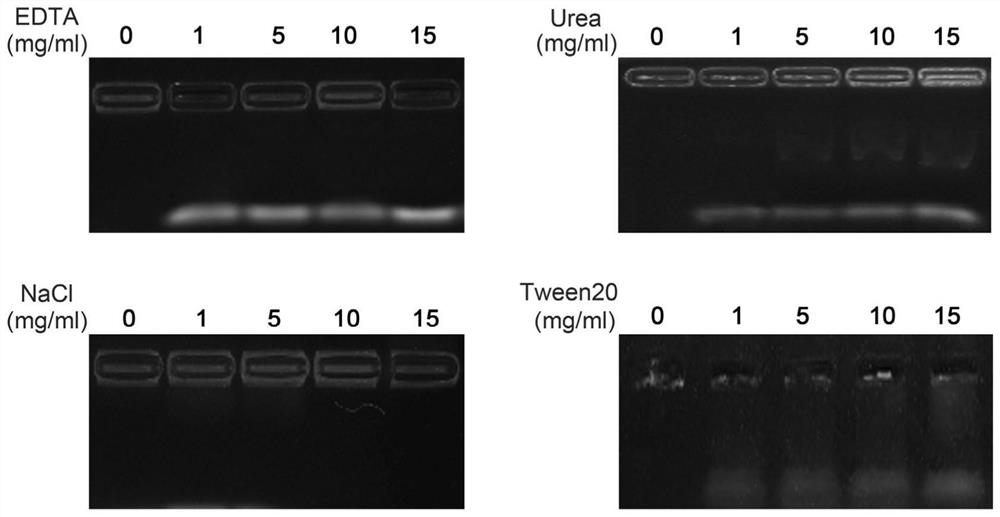
ActiveCN105044031AImprove measurement accuracyReliable resultsPhase-affecting property measurementsUltrasound attenuationCovalent Interaction
The invention provides a testing device and method utilizing an optical waveguide micro-ring resonator for testing methane concentration. The micro-ring resonator in the testing device is composed of two parallel waveguides and an annular waveguide, wherein the annular waveguide comprises a lower cladding, a waveguide core arranged on the lower cladding and a sensitive membrane arranged on the surface of the waveguide core in a coating mode. The sensitive membrane is used for covalent interaction with methane gas so that the effective refractive index of the annular waveguide can be increased along with increase of the methane concentration. Through measuring the central wavelength of an output optical signal, the corresponding methane gas concentration is obtained through calculation. Due to the facts that the central wavelength of the output optical signal is measured through the testing device and method for the methane concentration, and it is unnecessary to measure the light intensity of the output optical signal, the angle of incident light and attenuation on the light intensity by materials have no influences on measurement, the testing device and method utilizing the optical waveguide micro-ring resonator for testing the methane concentration are higher in measurement accuracy and more reliable in result.
Owner:BEIJING COAL MINING ELECTRIC EQUIP TECHN DEV +1
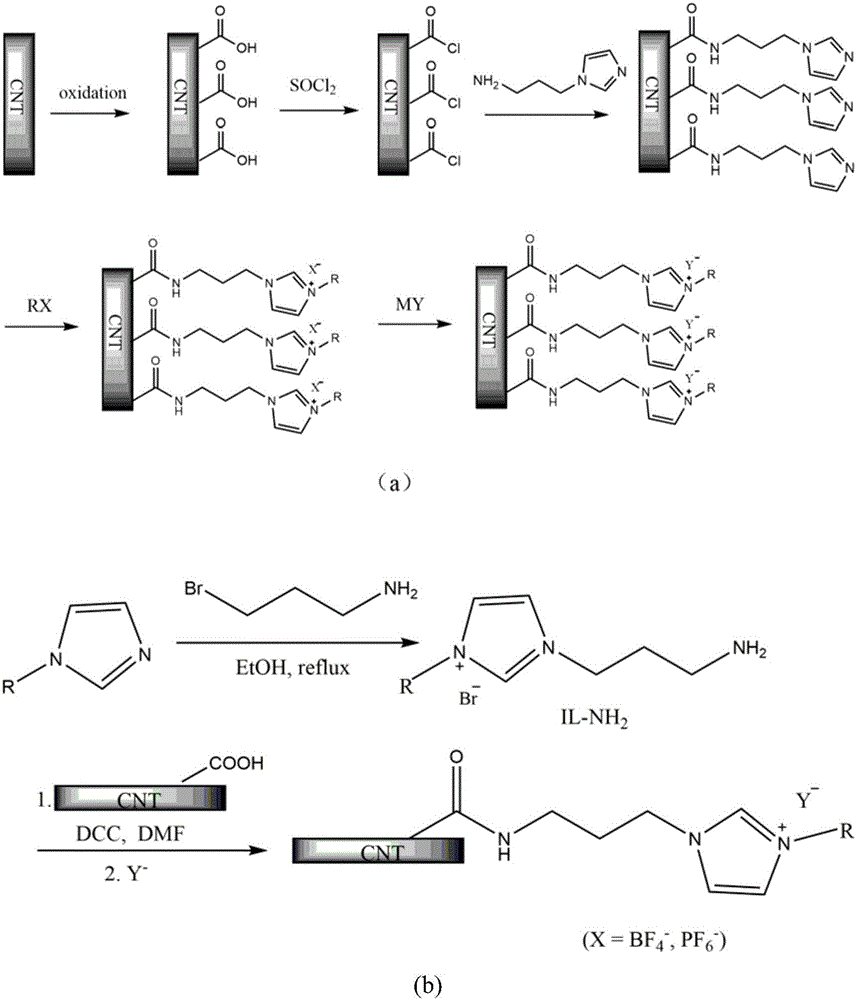
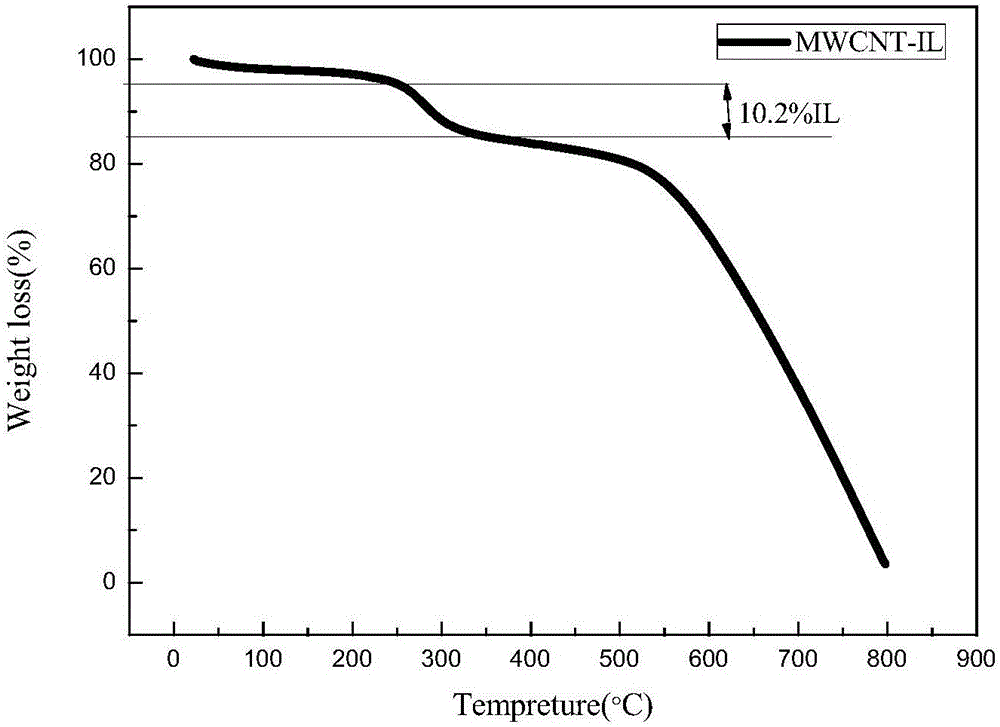
Functionalized ionic liquid-modified carbon nanotube and method for immobilizing lipase through carbon nanotube
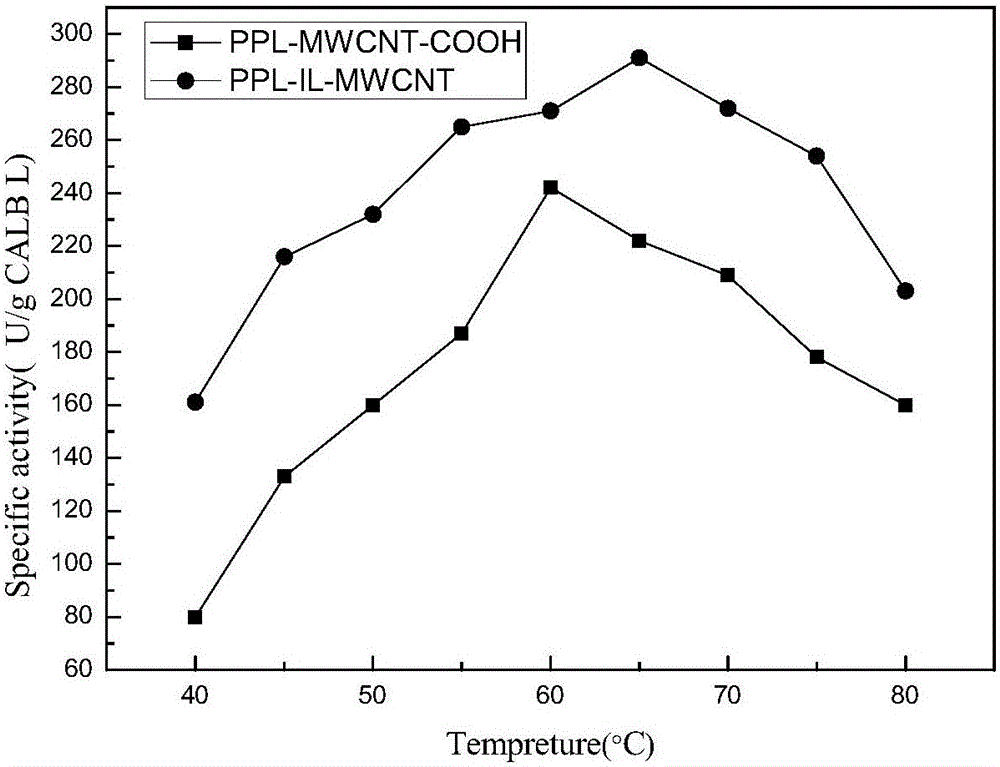
InactiveCN105836731AGood enzymatic propertiesLow priceNanotechnologyOn/in organic carrierModified carbonIonic liquid
The invention provides a functionalized ionic liquid-modified carbon nanotube and a method for immobilizing lipase through the carbon nanotube. According to the method, functionalized ionic liquid with functional groups such as the alkyl group, the carboxyl group, the amino group and the hydroxyl group is introduced to the surface of the carbon nanotube to generate electrostatic interaction, hydrogen-bond interaction, hydrophobic interaction, covalent interaction and the like with amino acid residues of enzyme molecules, the binding force between carriers and enzymes is enhanced, the microenvironment where the enzymes are located is changed, and therefore the catalytic performance of the immobilized enzymes is improved. The functionalized ionic liquid-modified carbon nanotube is used for immobilization of the lipase, and innovation of the lipase immobilization method is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
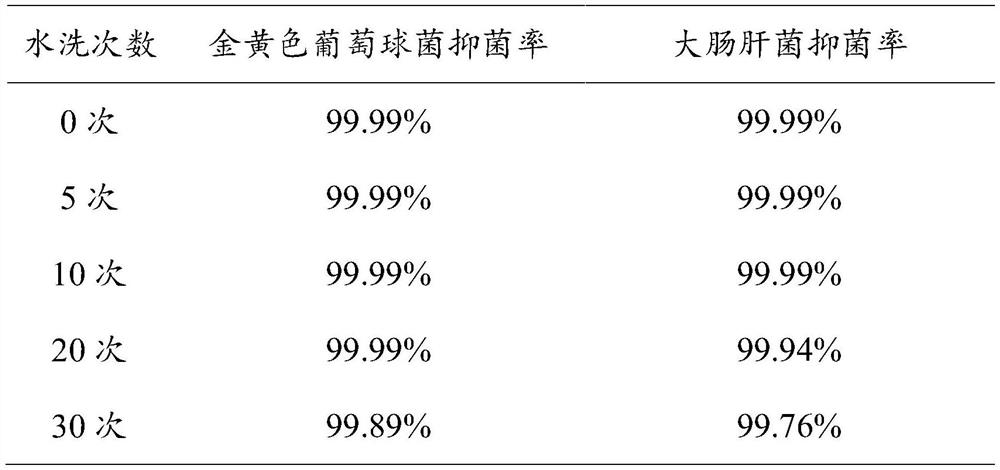
MXenes-AgNPs synergistic antibacterial cotton fabric and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112941899AEasy reunionSustained antibacterial effectBiochemical fibre treatmentLight resistant fibresCovalent InteractionAntibacterial activity
The invention provides an MXenes-AgNPs synergistic antibacterial cotton fabric. Through the synergistic antibacterial effect of MXenes and AgNPs, the cotton fabric has excellent antibacterial activity and lasting antibacterial ability. AgNPs are uniformly loaded on the surface of the MXene two-dimensional nanosheet through covalent interaction, so that the MXenes nanocomposite loaded with AgNPs is formed. The surface of the cotton fabric is uniformly coated with the AgNPs-loaded MXenes nano composite material through covalent interaction. In addition to the antibacterial property, the cotton fabric prepared by the invention further has multiple functions of ultraviolet resistance, electromagnetic radiation resistance, conductivity and the like, the additional value of the cotton fabric is greatly improved, and the application range of the cotton fabric is greatly widened.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF TRADE & COMMERCE
Acid choline biomimetic polymers coated carbon-nano tube and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101181989ANon-covalently stableEasy to operateNanostructure manufactureDispersion stabilityPhosphorylcholine
The invention discloses a carbon nano-tube covered by phosphorylcholine base biomimetic polymer and a preparation method thereof. The invention utilizes phosphorylcholine amphiphilic polymer comprising a hydrophobic segment to carry out non-covalent coverture of the carbon nano-tube, uses the hydrophobic segment to carry out non-covalent interaction with the carbon nano-tube and uses the phosphorylcholine to improve dissolubility, dispersion stability and blood compatibility of the carbon nano-tube in water. The method uses the phosphorylcholine amphiphilic polymer comprising the hydrophobic segment, the carbon nano-tube and water as raw materials and obtains the carbon nano-tube covered by the phosphorylcholine base biominetic polymer by assistance of ultrasonic dispersion and centrifugal method. The invention has simple technique and good stability, and the dissolubility of the prepared water-soluble carbon nano-tube reaches as high as 3mg / mL, thus having considerable application prospect in the field of drug delivery, gene transmission, molecular diagnosis and detection, separation of biomolecules, biosensor, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103205824AImprove thermal stabilitySimplified post-processing stepsConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsFilament/thread formingFiberDesorption
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of functional fiber materials. The cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber is prepared by following compositions, by mass, 10-100 parts of cyclodextrin or cyclodextrin derivatives, 20-200 parts of phase change substances and 20-100 parts of cellulose polymer through the electrostatic spinning technology, and can be applied to fields of biomedical materials, separating adsorption materials, energy-saving heat-insulating materials and the like. A supermolecular composite fiber is formed by cyclodextrin and phase-change work components through hydrogen bond and other non-covalent interaction, and the phase change substances are enabled to be less prone to desorption from the cellulose polymer while the obtained energy-storage superfine fiber does not need posttreatment processes like surface crosslinking, so that improvement of heat stability of the materials and simplification of preparation process are facilitated. The main raw materials are natural or seminatural products, so that the cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber is good in biocompatibility, nontoxic and harmless, easy to degradation, low in cost and environment-friendly.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Rapid melamine determination method using bare gold nanoparticles as developing probe
InactiveCN102706814AEasy to manufactureReduce processing requirementsColor/spectral properties measurementsVisual observationNanoparticle
The invention discloses a rapid melamine determination method using bare gold nanoparticles as a developing probe. The gold nanoparticles are gathered under the action of electrostatic interaction and covalent interaction of AcCl4- / AuC12-ion absorbed on the surface of an exocyclic amino group of melamine and the bare gold nanoparticles, thereby expressing the change of the solution color and the ultraviolet absorption spectrum characteristic. The limit of detection of visual observation is 0.05 mg / L. The detected linear range of the absorbance ratio is 5-200 mu g / L, and the limit of detection is 0.2 mu g / L. After the simple pretreatment, the melamine content in the milk powder sample can be determined by adopting the method.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
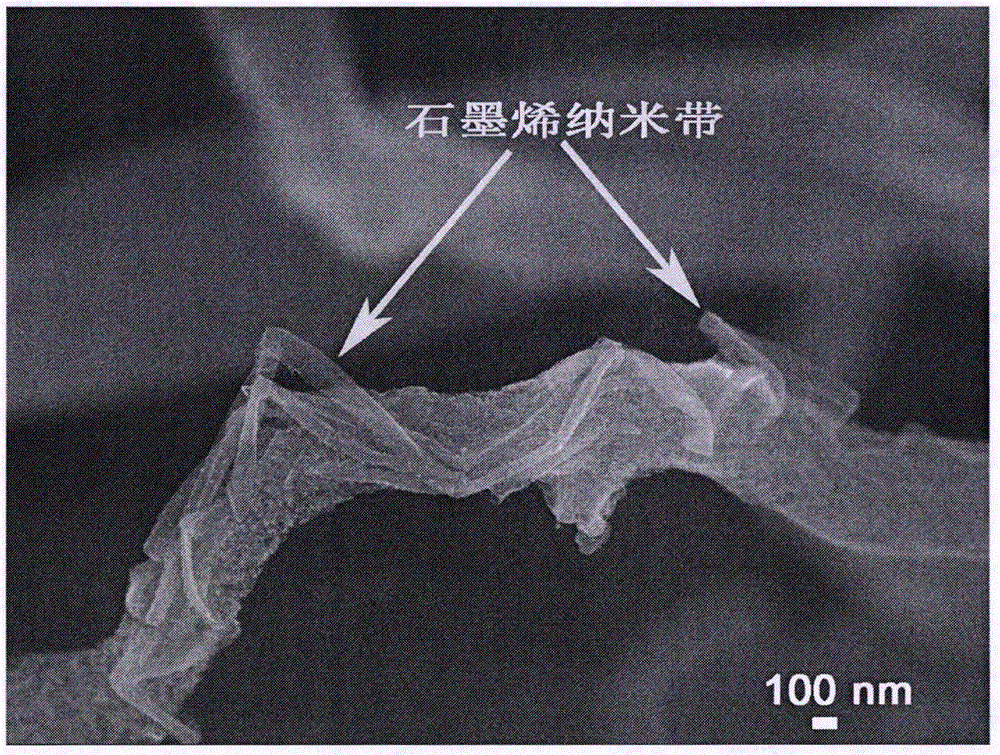
Preparation method of graphene nanoribbon in situ toughened nano carbon fiber
Belonging to the technical field of nano carbon fiber composite materials, the invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene nanoribbon in situ toughened nano carbon fiber. The method includes: firstly preparing an easily dispersible graphene nanoribbon, taking a macromoleclar polymer as the raw material, preparing a nano carbon fiber precursor solution, dispersing the graphene nanoribbon in the nano carbon fiber precursor solution, and conducting stirring dispersion, electrostatic spinning and heat treatment to obtain a graphene nanoribbon in situ toughened nano carbon fiber product. The method has the advantages of simple process, convenient operation, is conducive to realizing large-scale production, is convenient for popularization and application, and is low in cost. As the edge of the graphene nanoribbon and nano carbon fiber have in situ covalent interaction, the graphene nanoribbon in situ toughened nano carbon fiber prepared by the method has good electrical conductivity, good thermal conductivity and high mechanical strength, and can be widely applied to composite materials, conductive agents, heat conduction agents and mechanical enhancers, etc.
Owner:重庆锦添翼新能源科技有限公司
Detection of polyamino acids using trimethincyanine dyes
InactiveUS20060207881A1Easy and safe and economical to synthesizeRapid time periodSludge treatmentMethine/polymethine dyesCovalent InteractionNon-covalent interactions
The present invention is generally directed to a method for detecting polyamino acids. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a method for detecting polyamino acids using trimethincyanine dyes that interact non-covalently with polyamino acids to produce an optically detectable dye / polyamino acid complex.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Pharmaceutical compositions for transmucosal delivery
InactiveCN108697803AHydroxy compound active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrophilic polymersCovalent Interaction
The present application relates to a pharmaceutical composition for transmucosal administration of an active lipophilic compound through the oral mucosa comprising a lipophilic active compound, a polymeric matrix formed by two or more water-soluble polymers and a rapid dissolution agent. At least one of the water-soluble polymers is an amphiphilic polymer and at least one is either a hydrophilic polymer or an amphiphilic polymer with a hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance different from the first amphiphilic polymer. In addition, the polymeric matrix is not crosslinked and no covalent interaction occurs between the two or more polymers and between the polymers and the lipophilic active compound, which is interwoven with the aforesaid polymeric matrix.
Owner:SOLUBEST
Supermolecular assembly for targeted conduction of anticancer taxol prodrug and preparation method thereof
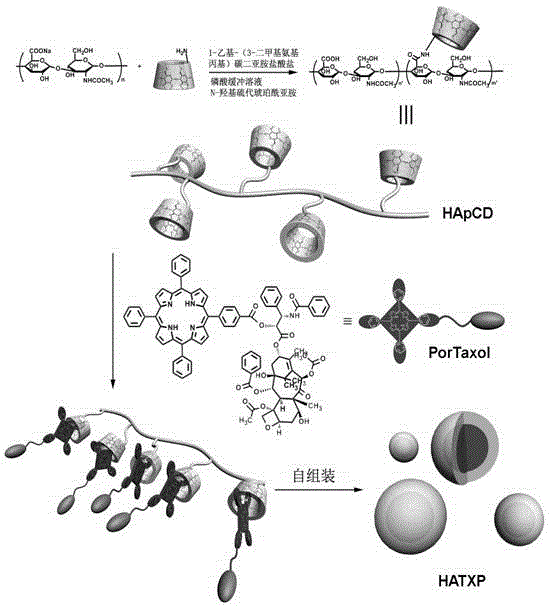
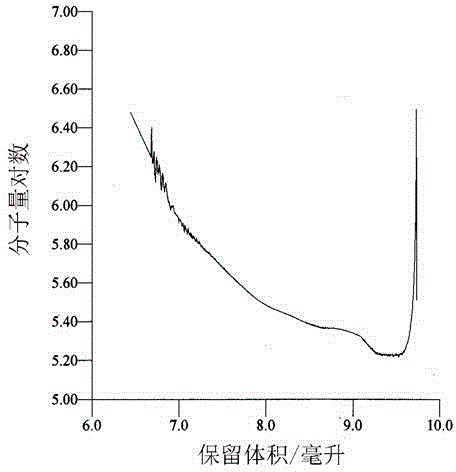
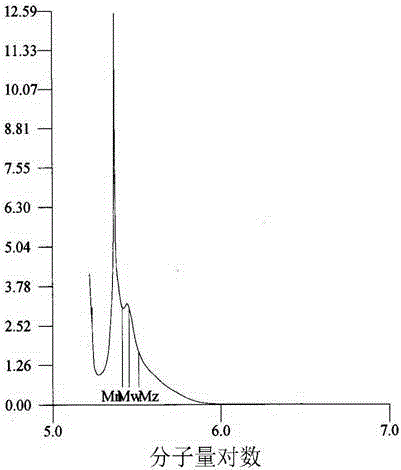
InactiveCN104127882AAchieve selective killingSimple preparation processOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses a supermolecular assembly for targeted conduction of anticancer taxol prodrug. The supermolecular assembly is a binary supermolecular assembly which is synthesized from full-methylated cyclodextrin modified hyaluronic acid and porphyrin modified taxol prodrug, the binary supermolecular assembly is formed into supermolecular nano particles which take hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as shells and hydrophobic porphyrin modified taxol prodrug as kernels based on the strong non-covalent interaction of full-methylated cyclodextrin and porphyrin and the amphiphilic action of molecules, and the particle size of the nano particles is 30-40nm. The supermolecular assembly has the advantages that the supermolecular assembly is simple in synthesis route, low in production cost, relatively high in yield and applicable to amplified synthesis and practical production and application; due to endocytosis which takes an overexpressed hyaluronic acid receptor on the surface of a malignant cell as a medium, the supermolecular assembly (HATXP) is introduced into cancer cells in a targeted manner, protection on normal cells and targeted selective killing of cancer cells are achieved, the anticancer activity is remarkable, and the toxic and side effects are remarkably reduced.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Small molecule printing
InactiveUS20050095639A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical MoietyChemical compound
The present invention provides compositions and methods to facilitate the identification of compounds that are capable of interacting with a biological macromolecule of interest. In one aspect, a composition is provided that comprises an array of one or more types of chemical compounds attached to a solid support, wherein the density of the array of compounds is at least 1000 spots per cm2. In particularly preferred embodiments, these compounds are attached to the solid support through a covalent interaction. In general, these inventive arrays are generated by: (1) providing a solid support, wherein said solid support is functionalized with a selected chemical moiety capable of interacting with a desired chemical compound to form an attachment; (2) providing one or more solutions of one or more types of compounds to be attached to the solid support; and (3) delivering said one or more types of compounds to the solid support, whereby an array is formed and the array of compounds has a density of at least 1000 spots per cm2. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for utilizing these arrays to identify small molecule partners for biological macromolecules of interest comprising: (1) providing an array of compounds, wherein the array has a density of at least 1000 spots per cm2; (2) contacting the array with one of more types of biological macromolecules of interest; and (3) determining the interaction of specific small molecule-biological macromolecule partners.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nanotube wiring
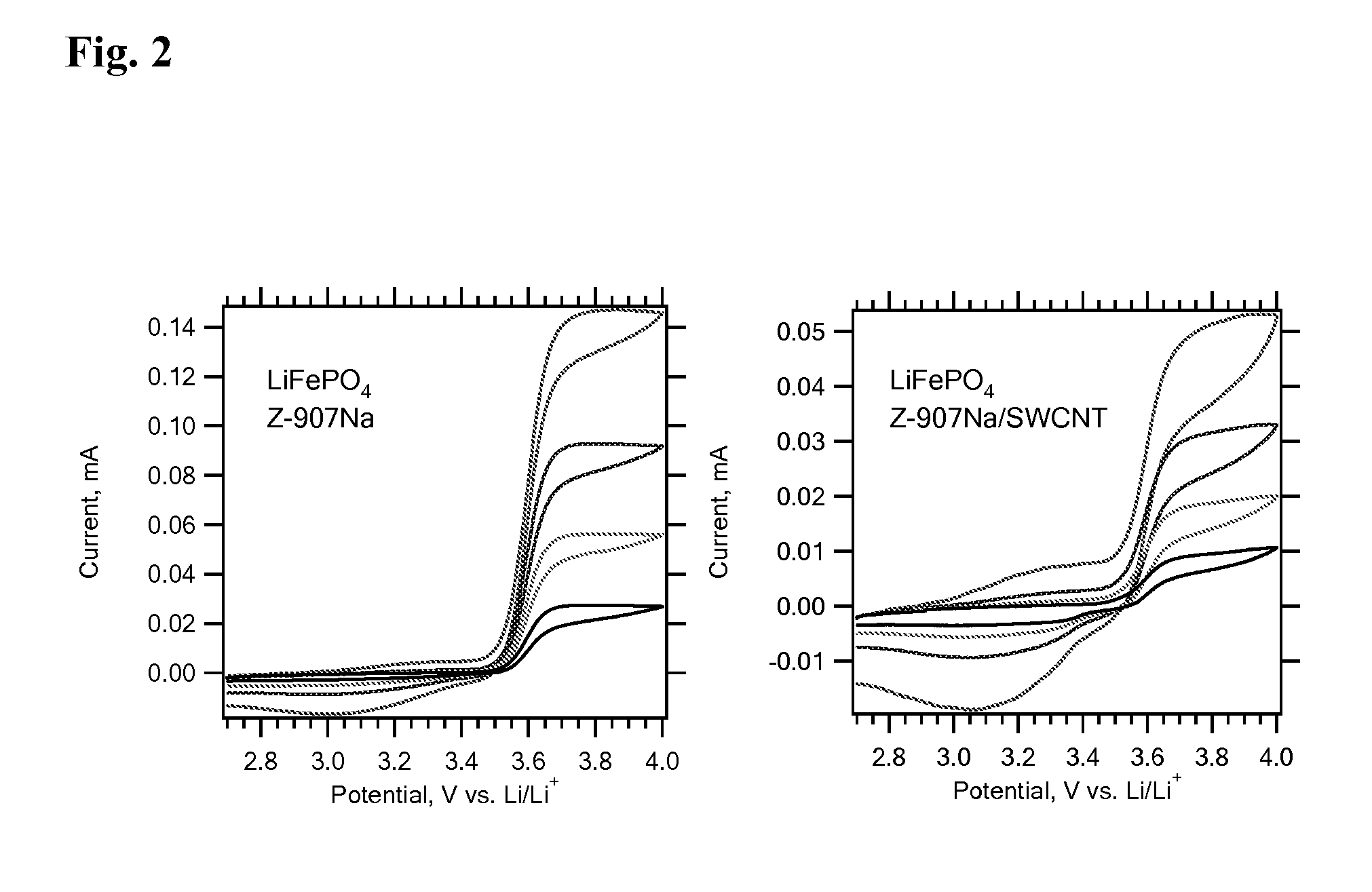
InactiveUS20100068621A1Optimize volumeHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologySecondary cellsOlivineDerivatization
This invention concerns a novel method for surface derivatization of electrode materials for Li-ion batteries. The derivatization is based on adsorption of a composite assembly consisting of amphiphilic redox active molecule attached to single walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT). Its role consists in the enhancement of electronic conductivity of electrode materials, such as phosphate olivines, without requesting any significant increase of the electrode volume and mass. The SWCNT is linked to the redox molecule via non-covalent or covalent interaction with the hydrophobic part of the molecule or electrostatic interaction. The hydrophilic part of the molecule serves as the anchoring site for surface modification of the electrode active material. The redox potential of the molecule is close to the redox potential of the electrode active material. The adsorbed assembly of redox-molecule & SWCNT thus improves the charge transfer from a current collector to the electrode active material.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
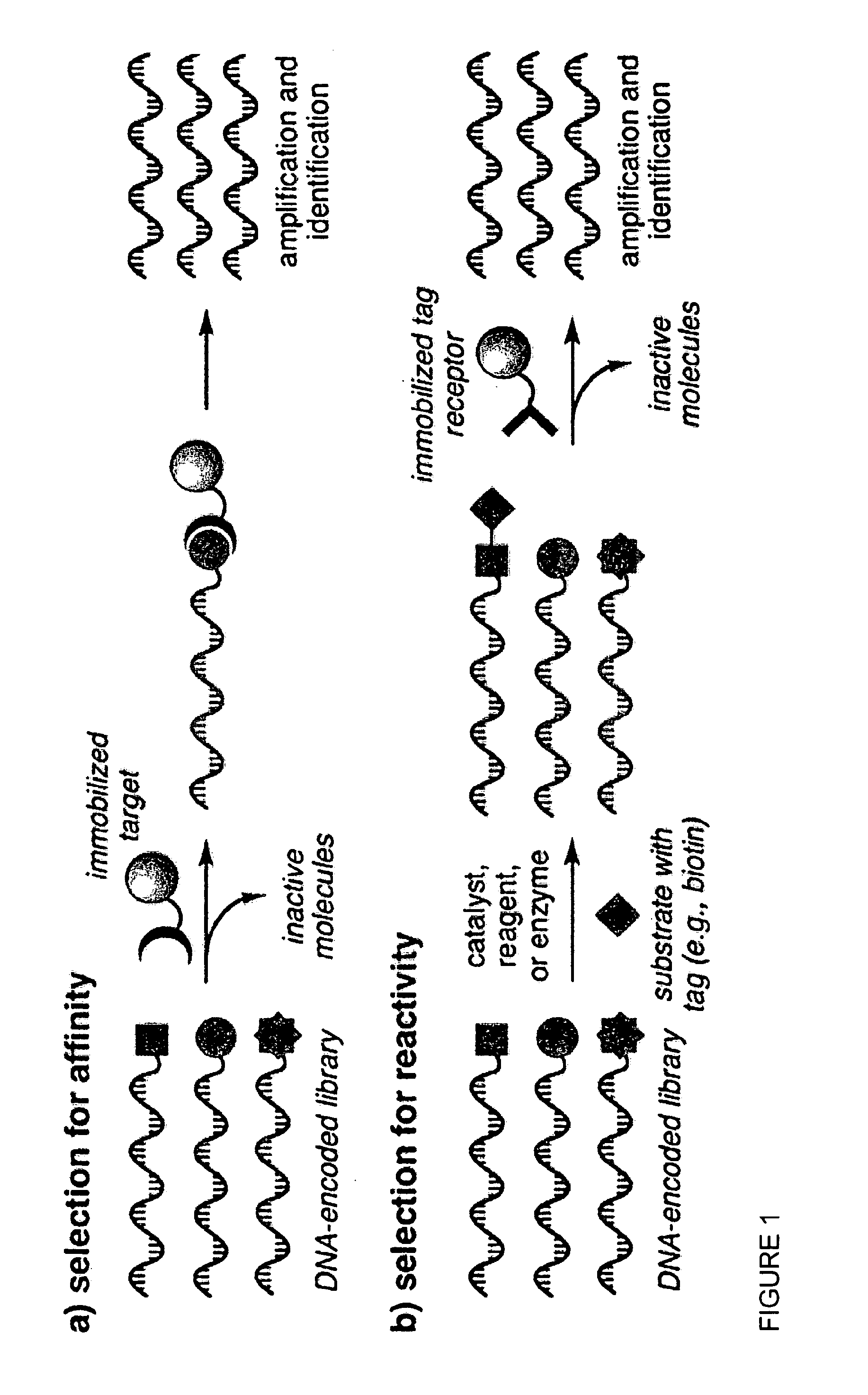
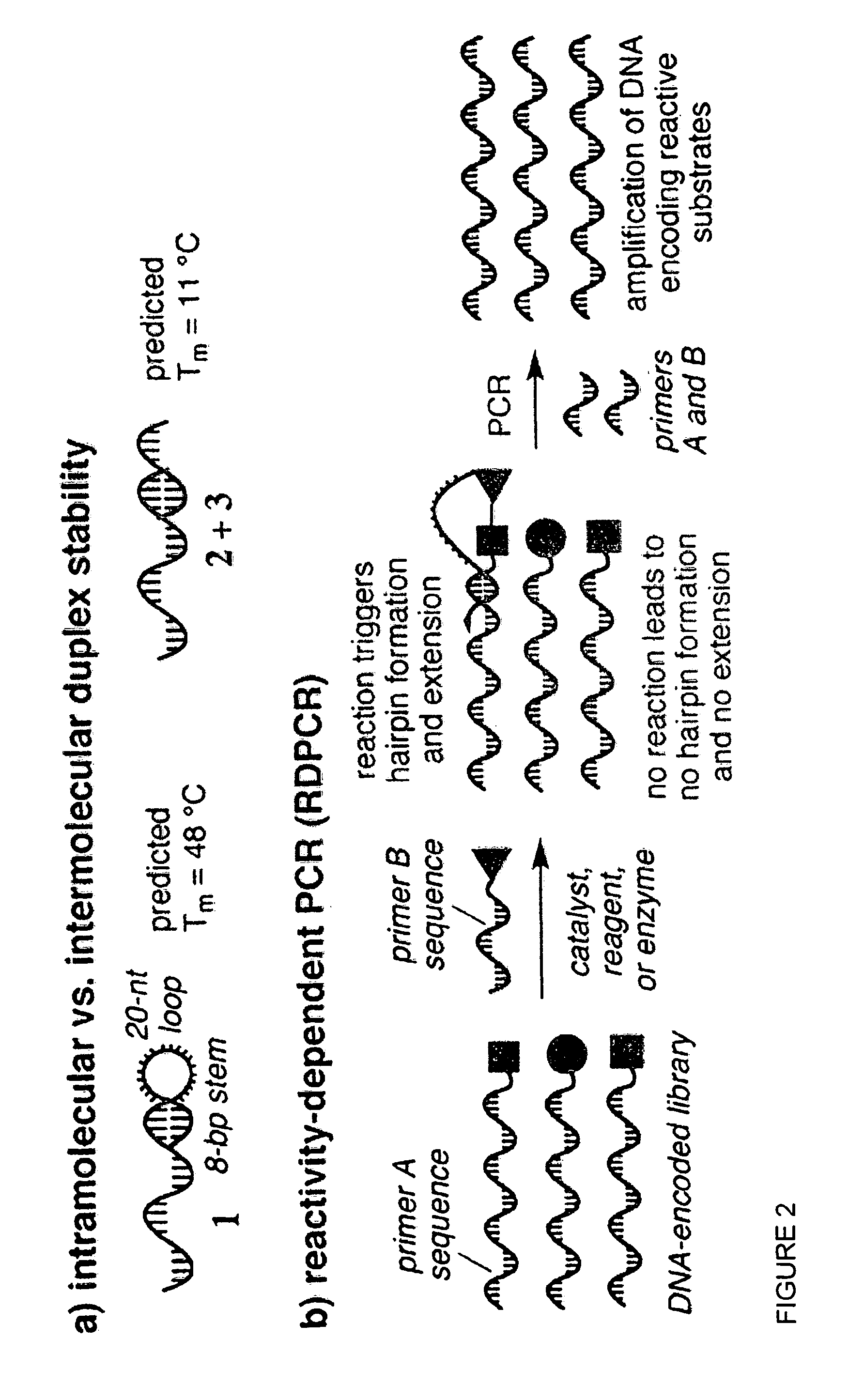
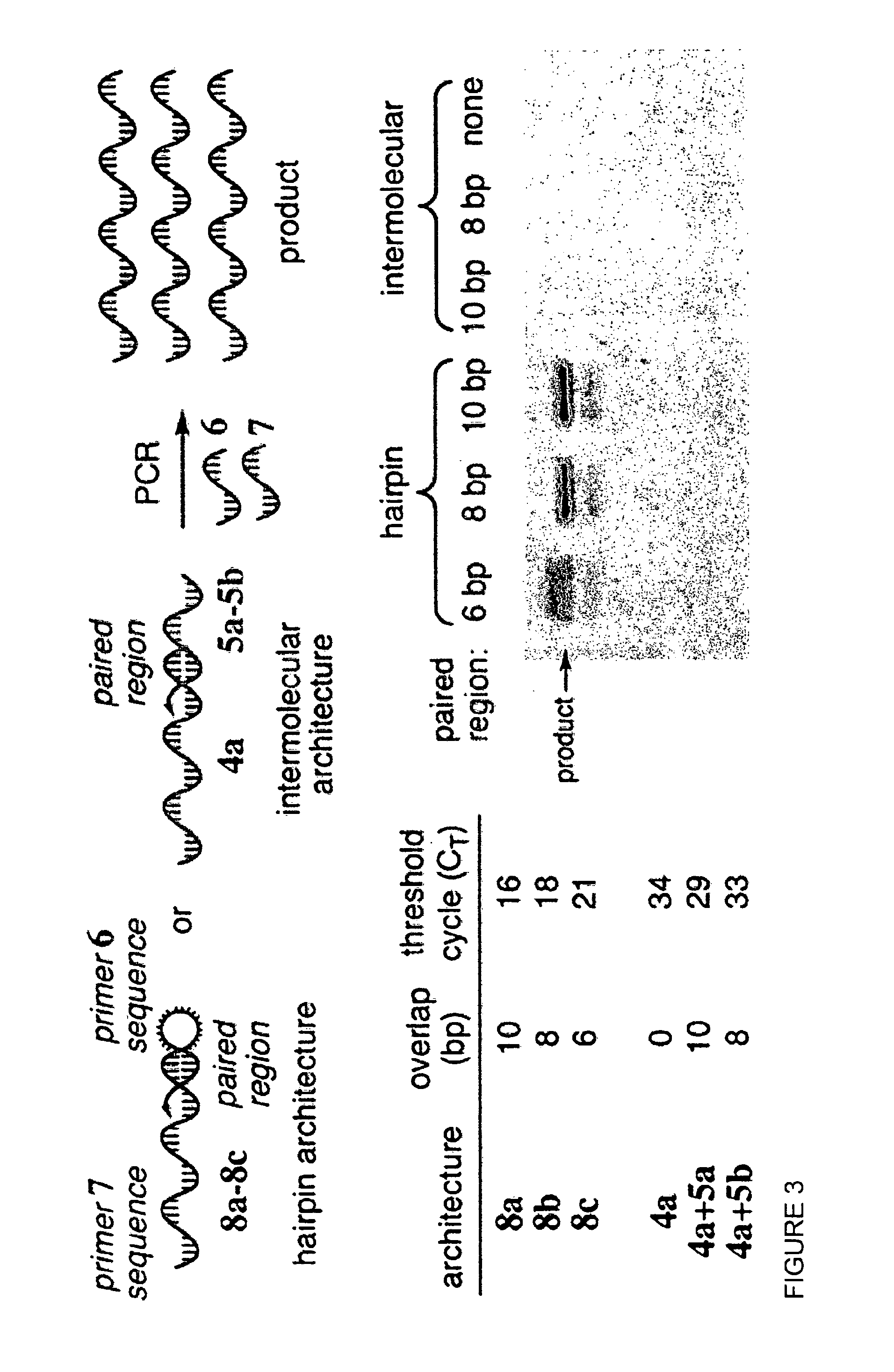
Reactivity-dependent and interaction-dependent PCR
Methods, reagents, compositions, and kits for reactivity-dependent polymerase chain reaction (RD-PCR) and interaction-dependent polymerase chain reaction (ID-PCR) are provided herein. RD-PCR is a technique useful for determining whether a reactive moiety can form a covalent bond to a target reactive moiety, for example, in screening a library of candidate reactive moieties for reactivity with a target reactive moiety, and in identifying an enzyme substrate, for example, in protease substrate profiling. ID-PCR is a technique useful for determining whether a ligand can non-covalently bind to a target molecule, for example, in screening a library of candidate ligands for non-covalent interaction with a target molecule. RD-PCR and ID-PCR are also useful in detecting the presence of an analyte or an environmental condition.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
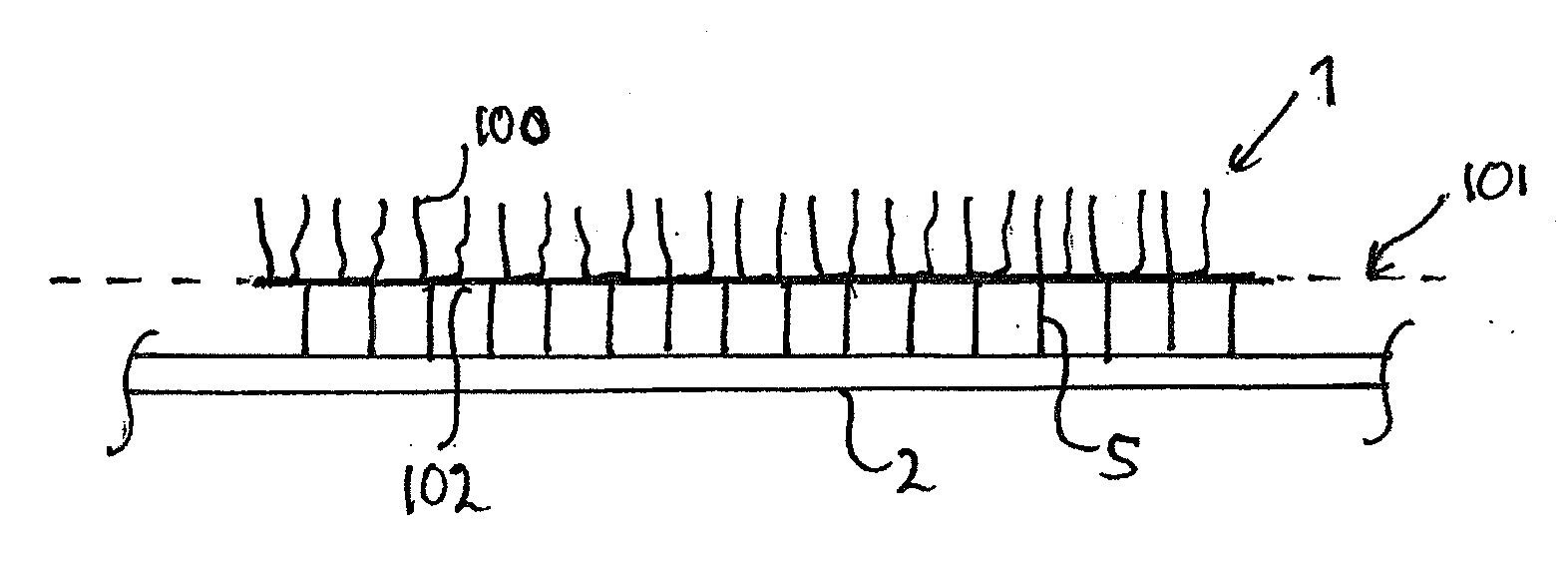
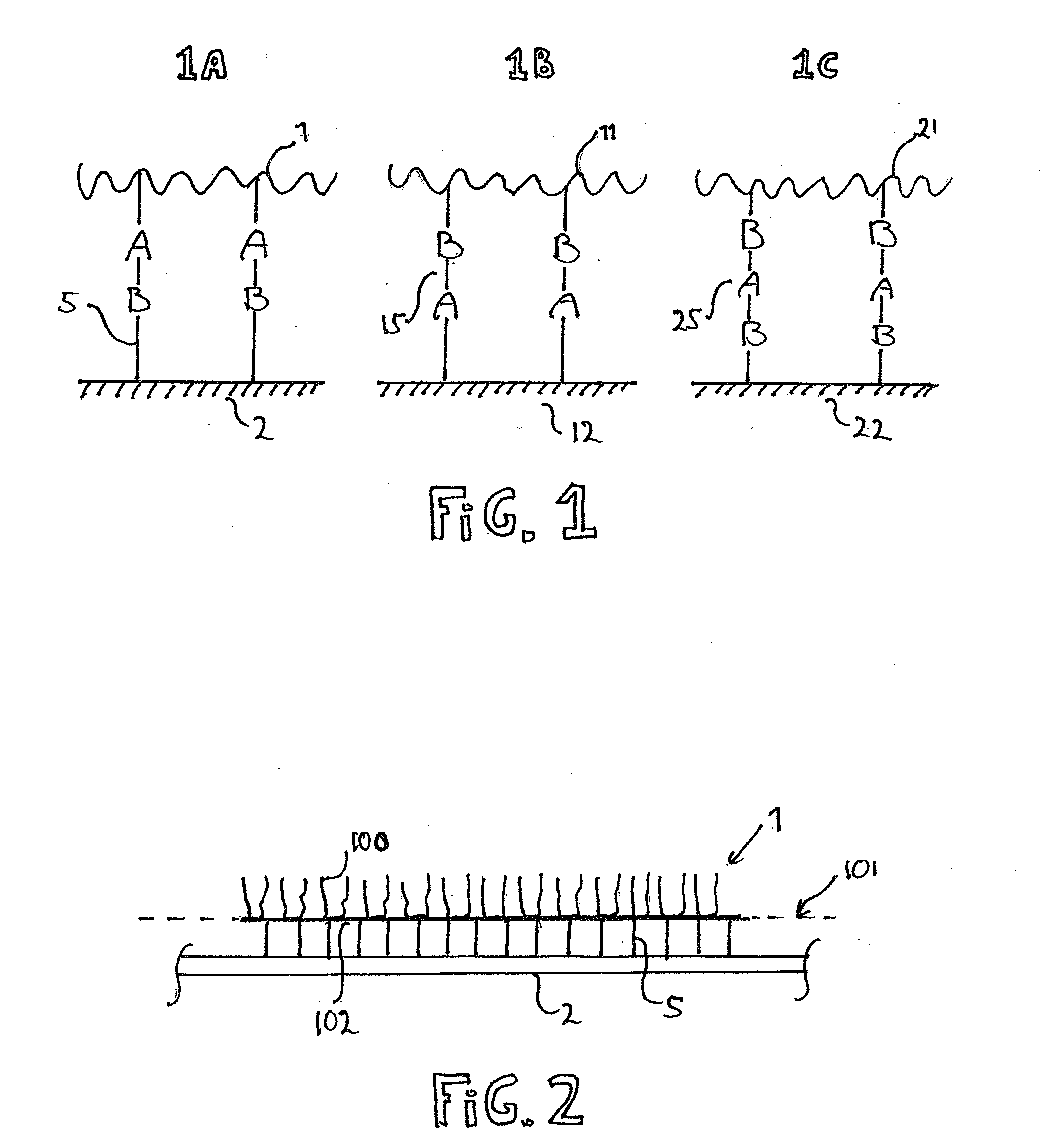
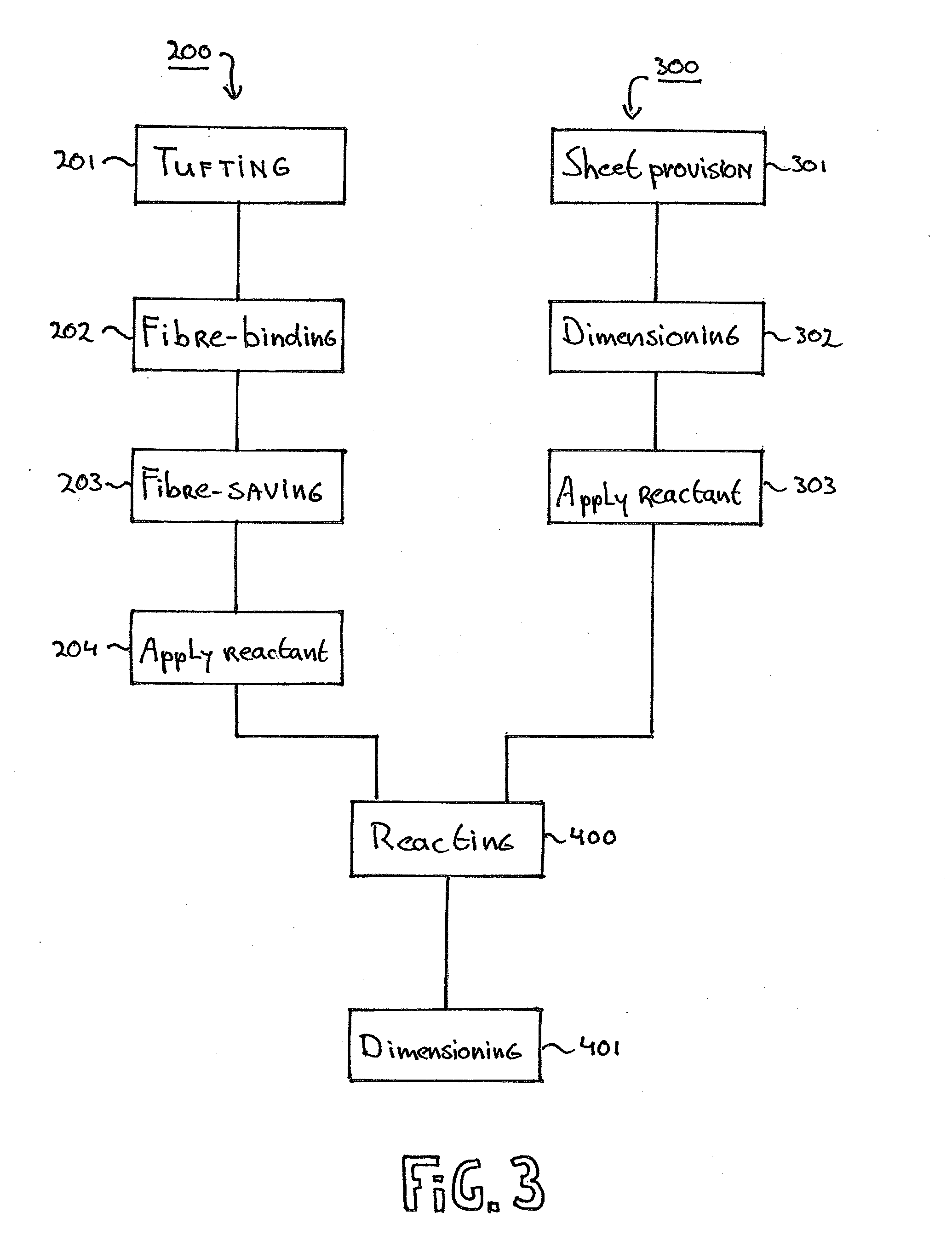
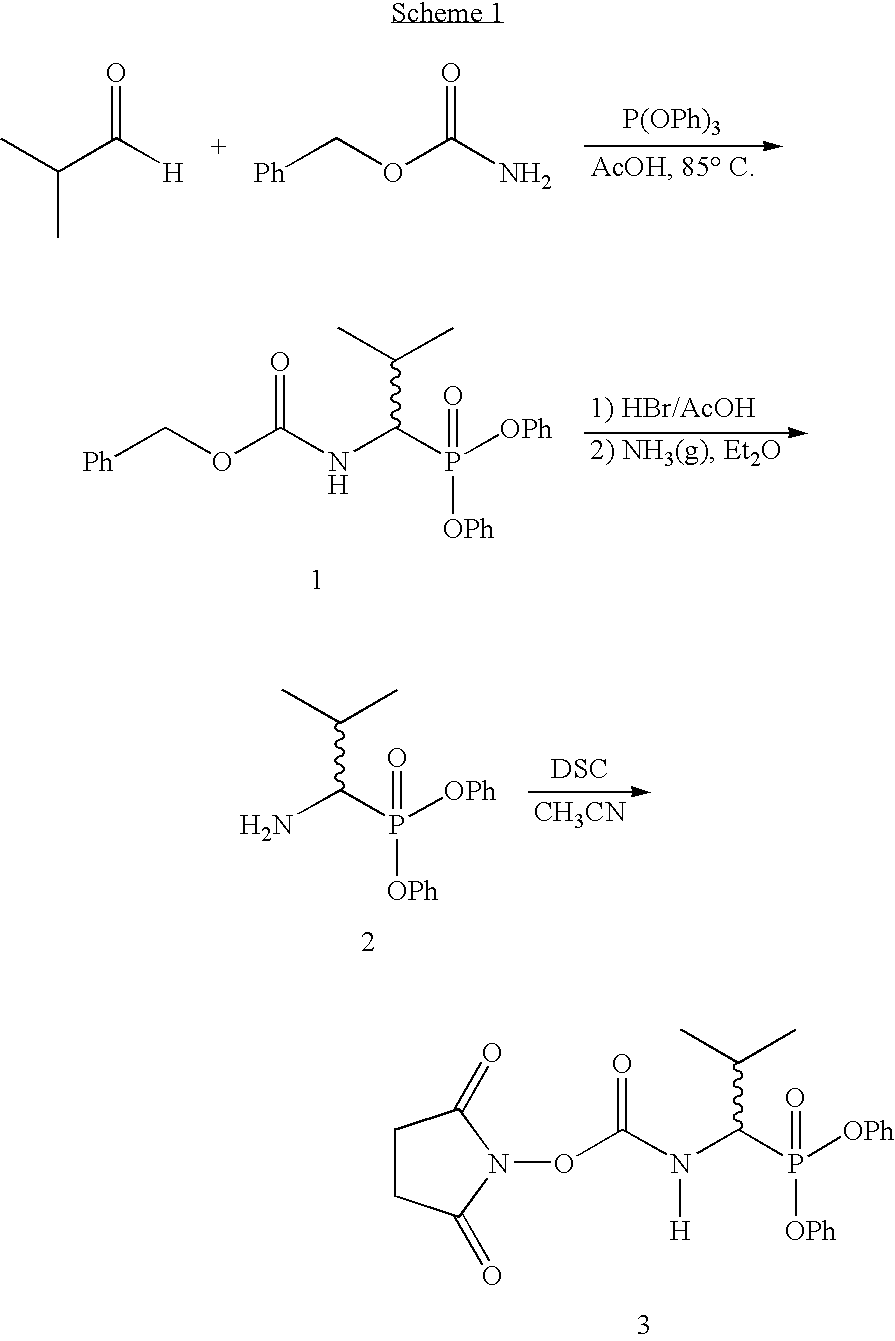
Method to Produce a Textile Product and a Textile Product Resulting from the Same
ActiveUS20130240117A1Reliable and easy connectionInexpensive materialsLiquid surface applicatorsLamination ancillary operationsYarnCovalent Interaction
Owner:COVESTRO NETHERLANDS BV
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: Chemi-SELEX
InactiveUS20060088877A1Less laborReduce labor intensityOrganic chemistry methodsTransferasesCovalent InteractionSystematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment
This application provides methods for identifying nucleic acid ligands capable of covalently interacting with targets of interest. The nucleic acids can be associated with various functional units. The method also allows for the identification of nucleic acids that have facilitating activities as measured by their ability to facilitate formation of a covalent bond between the nucleic acid, including its associated functional unit, and its target.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Nucleic acid drug delivery system, preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and application
PendingCN114099533AHigh encapsulation efficiencyImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticPolyphenolBiology
The invention discloses a nucleic acid drug delivery system, a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition and application, and the drug delivery system is a compound formed by a nucleic acid drug and polyphenol or a polyphenol metal ion complex through non-covalent interaction. Then the surface of the compound is coated with lipid and a biological membrane to form a drug delivery system which is high in encapsulation efficiency, delivery efficiency, stability, safety and preparation simplicity and convenience, and functional requirements on lipid, transfection materials and the like are reduced. The drug delivery system can be prepared into a liquid preparation through a mixing and dispersing technology, and can be further prepared into a freeze-drying preparation by adding a protective agent, so that the drug delivery system is suitable for drugs and diagnostic agents in various administration routes such as oral administration, inhalation, injection, ophthalmic administration, transdermal administration and mucous membrane administration.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for preparing antibacterial titanium material having good biocompatibility and containing silver on surface
InactiveCN108434524AEasy to operateImprove controllabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsCationic polyelectrolytesBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for preparing an antibacterial titanium material having a good biocompatibility and containing silver on the surface. The method comprises the following steps: constructing uniform titanium dioxide nanotubes on the surface of a titanium material by an anodization technology, used as a silver nanoparticle store; and oxidizing sodium alginate by sodium periodate to obtain dialdehyde sodium alginate denoted as ADA and used as an anionic polyelectrolyte, and performing layer-by-layer self-assembling on the anionic polyelectrolyte and cationic polyelectrolyte CHI toform a polyelectrolyte multilayer film. The driving force for forming the multilayer film is derived from the electrostatic interaction between the ADA and the CHI and the covalent interaction between the aldehyde group on the ADA and the amino group on the CHI, so the constructed stable multilayer film can effectively control the release of silver ions, reduce the toxicity of the silver ions toosteoblasts and achieve good biocompatibility, and also can achieve excellent antibacterial properties in order to make a titanium-based implant have good antibacterial and osteogenic properties.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
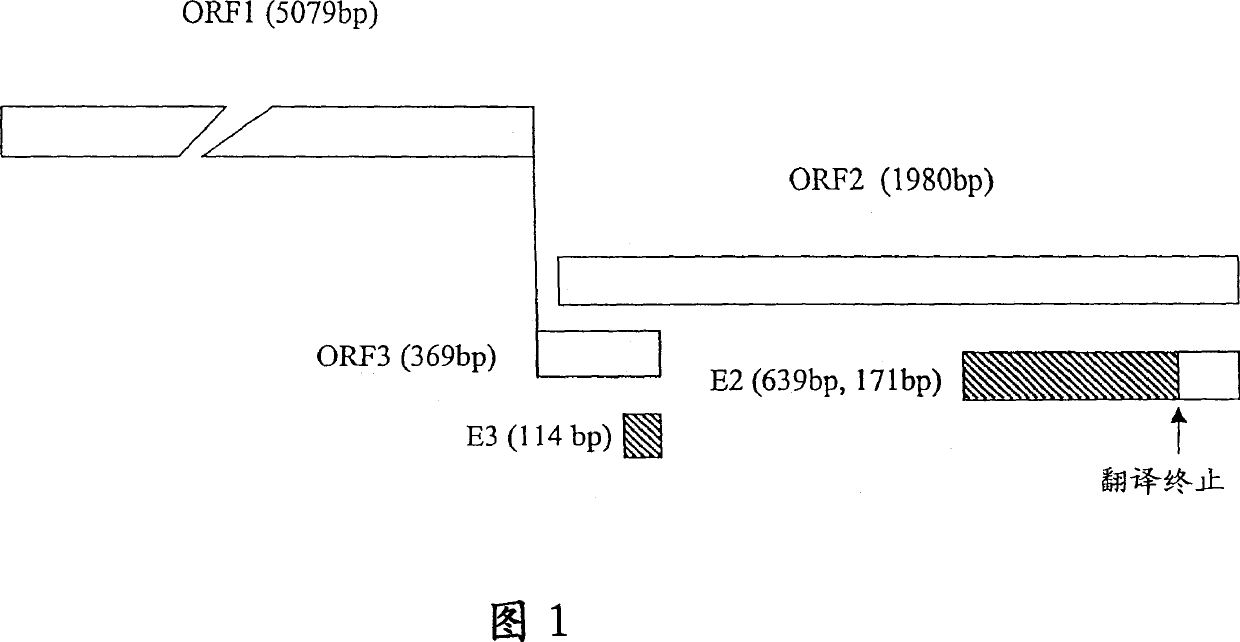
HEV antigenic peptide and its method
A highly immunoreactive viral peptide, pE2, is disclosed which is derived from the carboxy-terminal end region of ORF2 region of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) genome. A unique feature of the novel pE2 peptide is that it possesses conformational antigenic determinants which are only exposed when monomers of the peptide associate with one another through non-covalent interactions to naturally form homodimers. The novel pE2 peptide is proven to be highly reactive with sera from patients having current or past infection with HEV which suggests that the homodimer may mimic certain structural features of the HEV capsid protein. Furthermore, the antigenic activity of the pE2 peptide is strictly conformational in nature and therefore, exhibits immunochemical reactivity only when the peptide exists in a dimeric form. Consequently, the antigenic activity is lost upon dissociation of the dimers, but the activity is restored when the monomers reassociate to form dimers. Moreover, diagnostic methods useful in detecting and diagnosing HEV infection, and the use of a vaccine composition effective in preventing hepatitis E virus infection in which the novel pE2 peptide is utilized are also disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING WANTAI BIOLOGICAL PHARMACY ENTERPRISE
Supramolecular polymer as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111875811AGood luminous propertiesTimely detectionInksMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberCovalent Interaction
The invention discloses a supramolecular polymer as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The supramolecular polymer is specifically a golden yellow luminous host-guest supramolecularpolymer, and is formed by assembling a host compound H and a secondary ammonium salt guest G through host-guest non-covalent interaction. The preparation method comprises the following steps: equivalently mixing a host compound H and a secondary ammonium salt object G according to a molar ratio of 0.9:1-1:1.2, dissolving the raw materials in a mixed solvent of chloroform and acetonitrile, carryingout ultrasonic treatment and standing treatment, and extracting filamentous fibers from the formed viscous fluid, wherein the fibers exhibiting good warm-tone golden yellow luminescence under an ultraviolet lamp. The formed warm-hue light-emitting supramolecular polymer can be applied to fine light-emitting materials, and the supramolecular polymer not only can emit golden yellow light, but alsohas self-repairing capacity due to dynamic reversibility of host-guest interaction and have good application prospects.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Polyelectrolyte nanolayers as diffusion barriers in semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7081674B2Improve adhesionInhibit migrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricDevice material
The present invention provides a diffusion barrier useful in an integrated circuit, which serves to prevent the migration of material from a conductive layer to the underlying substrate and further provides improved adhesion of the conductive layer to the substrate. The diffusion barrier comprises a polymer which is a polyelectrolyte, having both cationic and anionic groups along its backbone chain. Preferred polyelectolyte barriers are polyethyleneimine (PEI) and polyacrylic acid (PAA). Other polyelectrolytes may be used, such as those that contain SH—OH— aromatic groups, or those that can interact with either the metal or the adjacent layers via covalent interactions and cross-linking (e.g., POMA, PSMA). The polymeric layer may be applied in two coatings, so that the amine side chains contact the dielectric (e.g. silicon) substrate and the acidic groups are adjacent to the overlying metallic interconnect (e.g. copper). The diffusion barrier may be made thin, preferably less than 5 nm thick, which is advantageous in devices having high aspect ratios.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
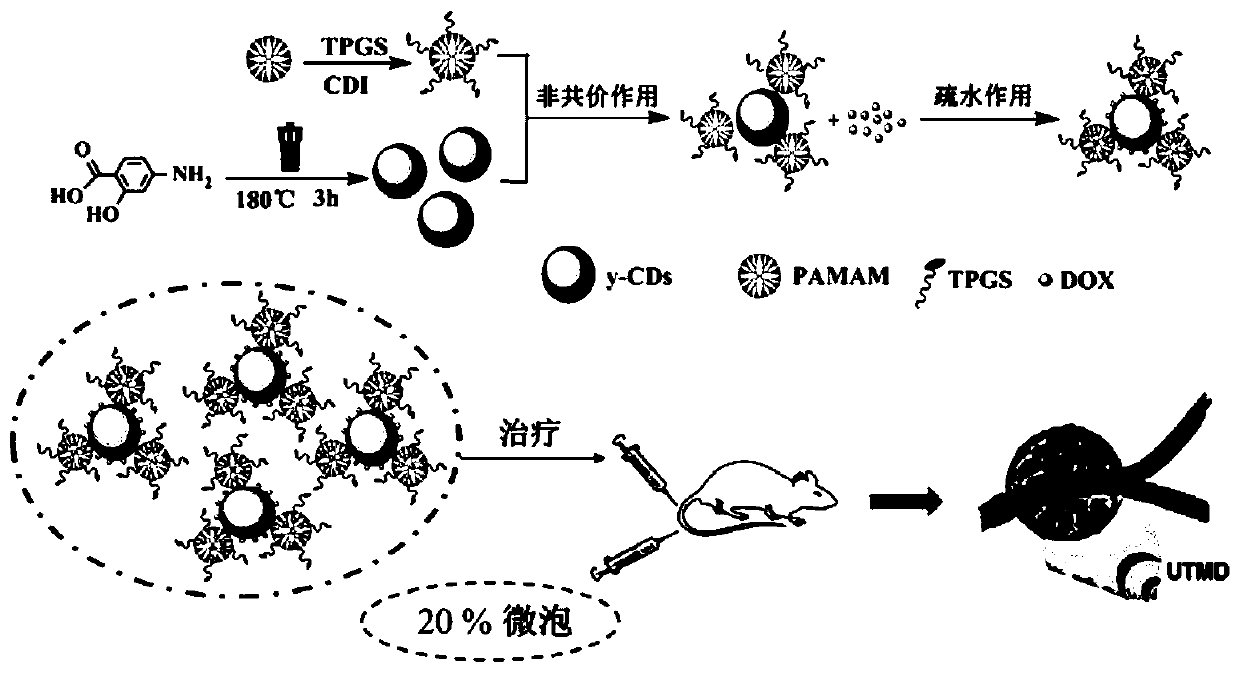
UTMD-based dual drug-loading nano platform and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109821030AEasy to operate and separateLow costOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDendrimerMedicine
The invention relates to a UTMD-based dual drug-loading nano platform and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises synthesizing carbon dots y-CDs by using a one-step hydrothermal method; connecting an anticancer drug TPGS on a dendrimer at the amino terminal to obtain G5-TPGS; combining G5-TPGS with y-CDs by non-covalent interaction to form a nano hybrid material G5-TPGS@y-CDs; loading an anticancer drug doxorubicin DOX to obtain (G5-TPGS@y-CDs)-DOX and then combining the UTMD technology. The platform is simple, easy to operate and separate, low in cost and commercialized in raw material source, and has good development prospects.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com