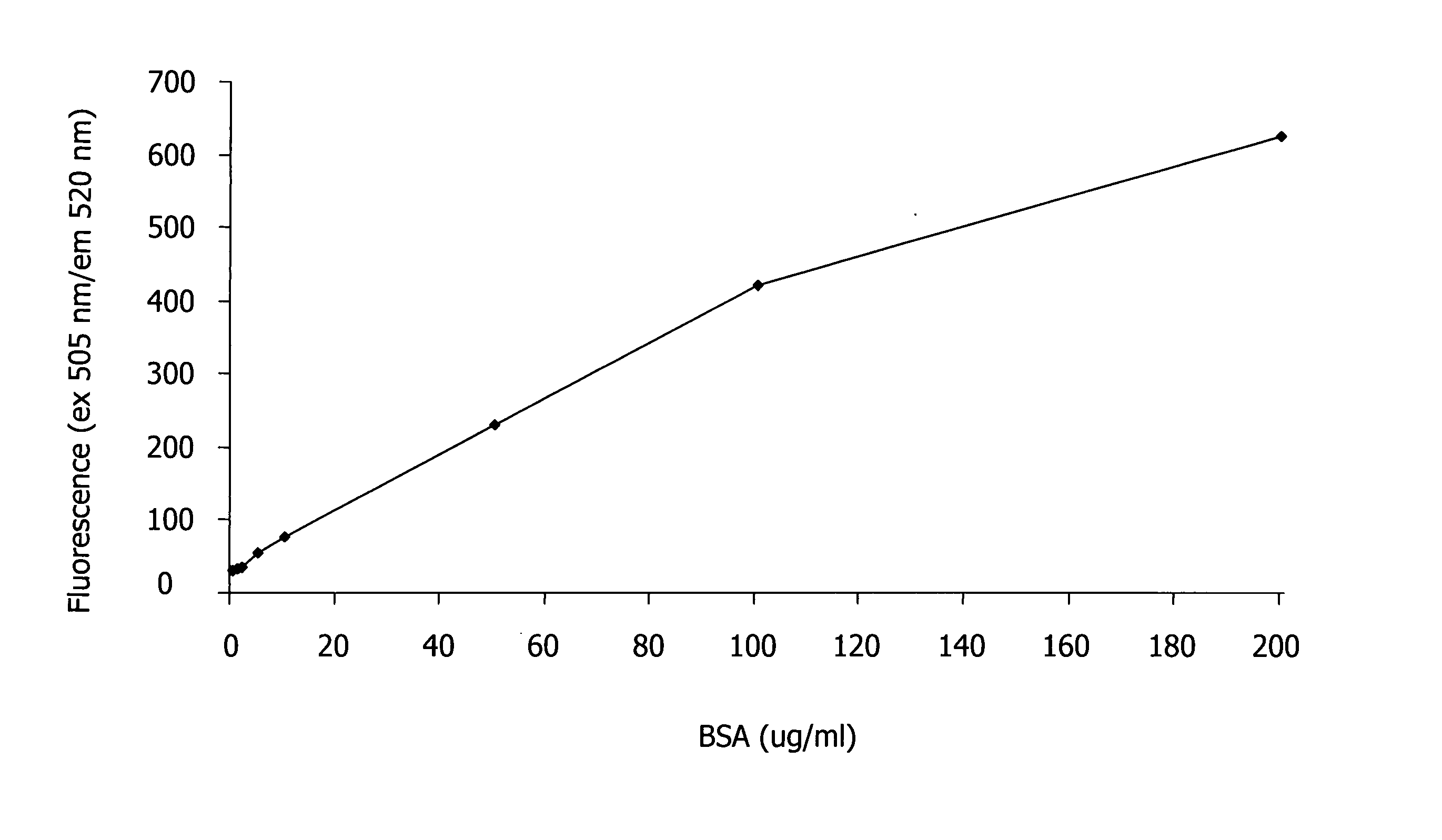
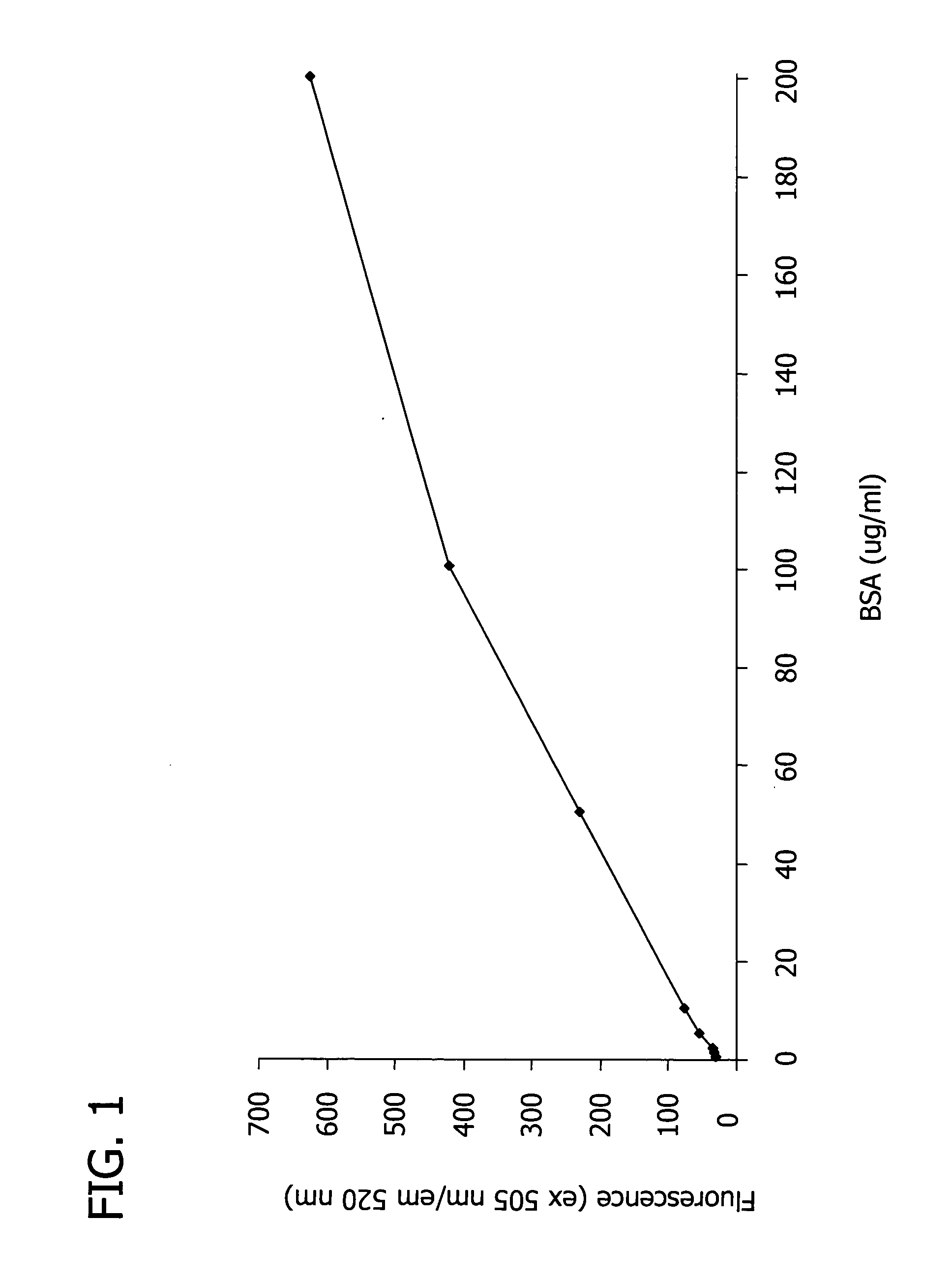
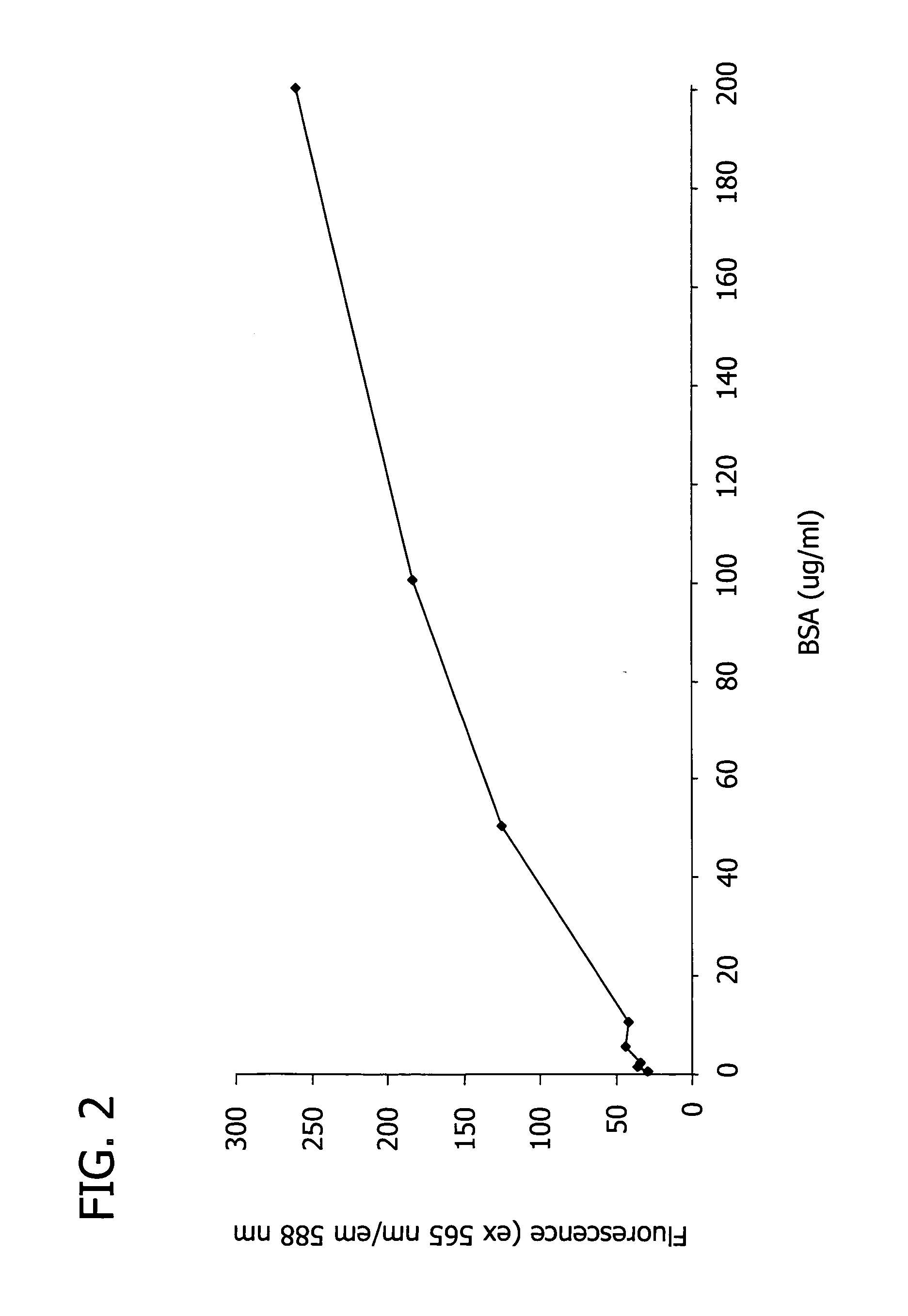
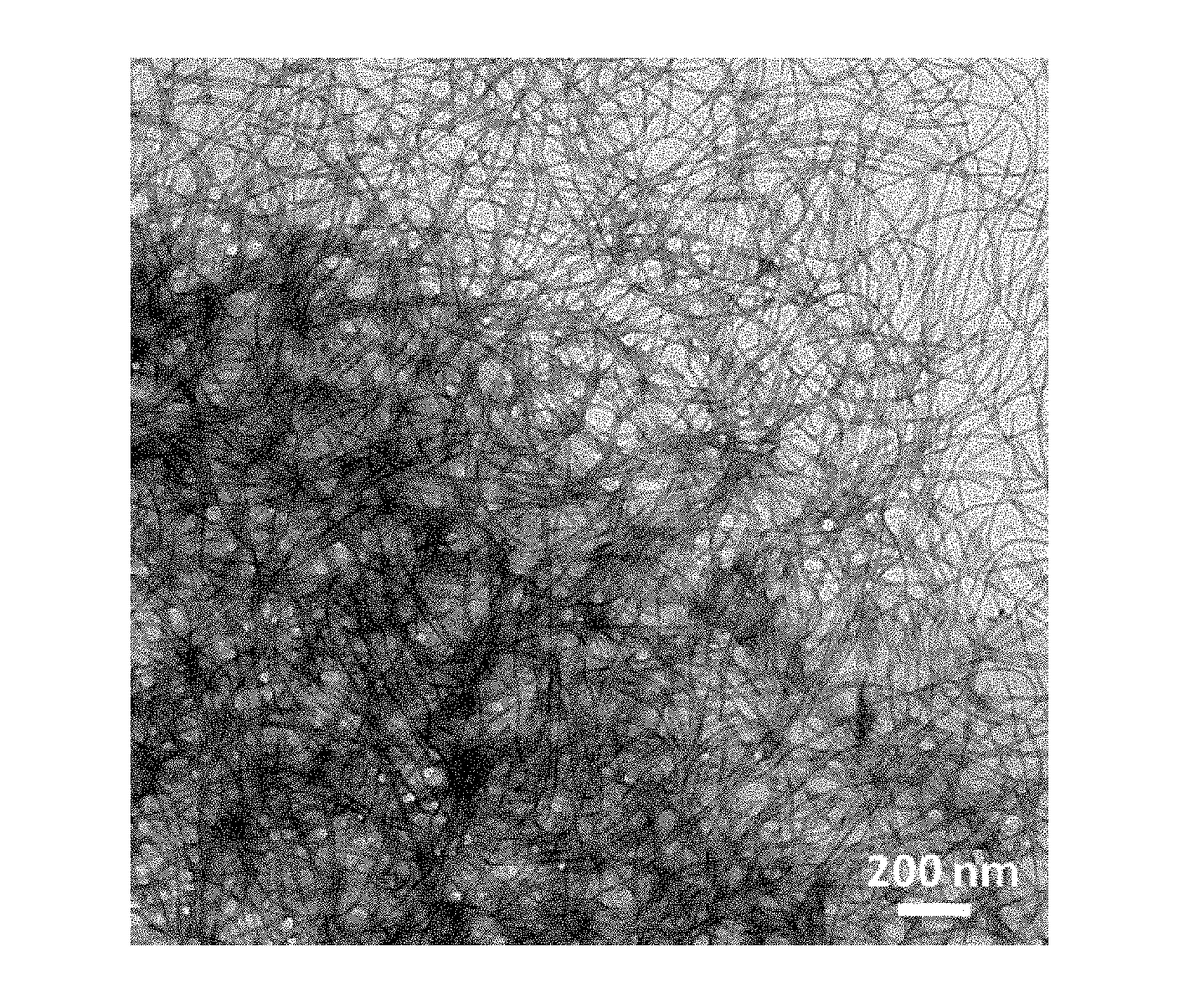
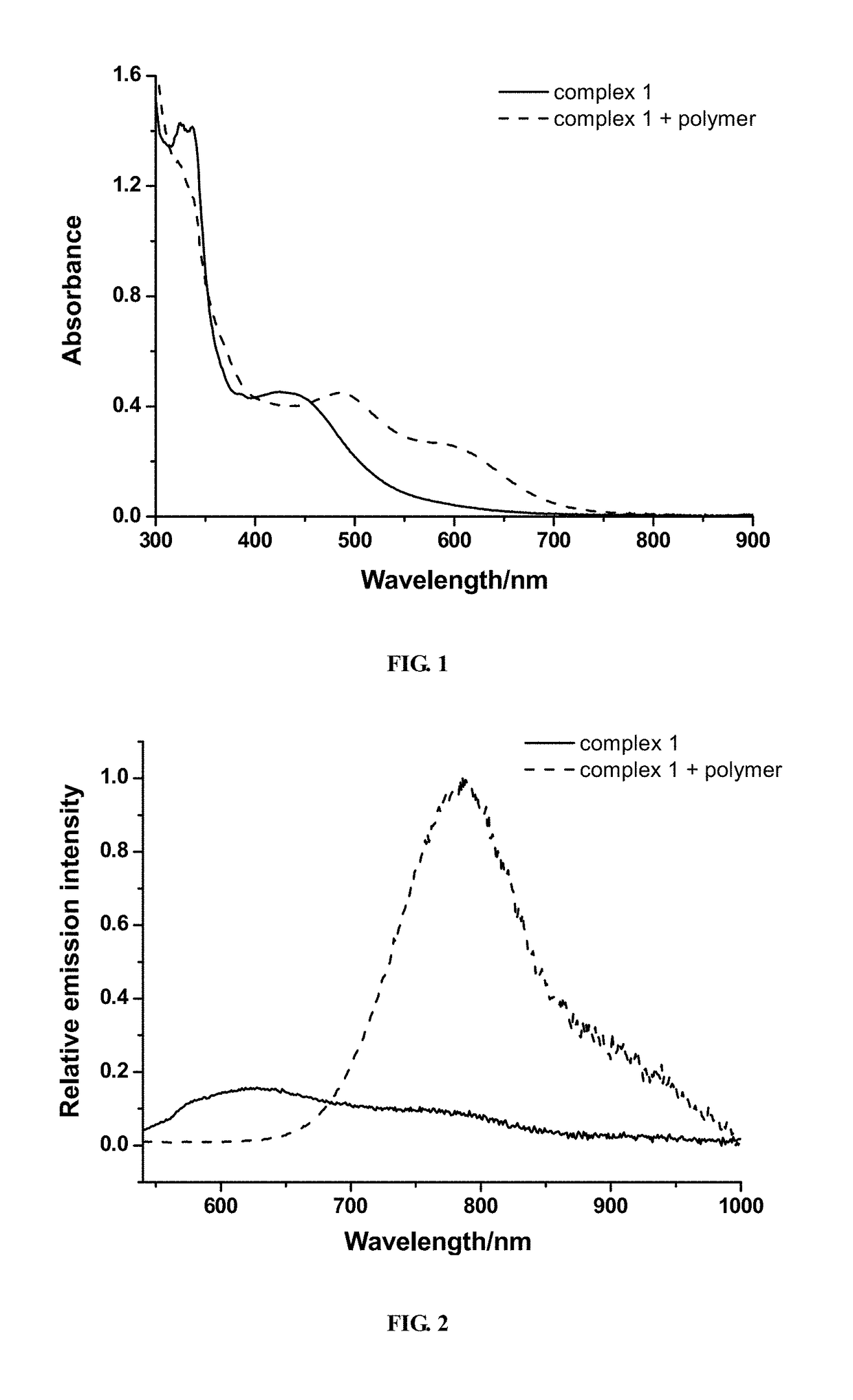
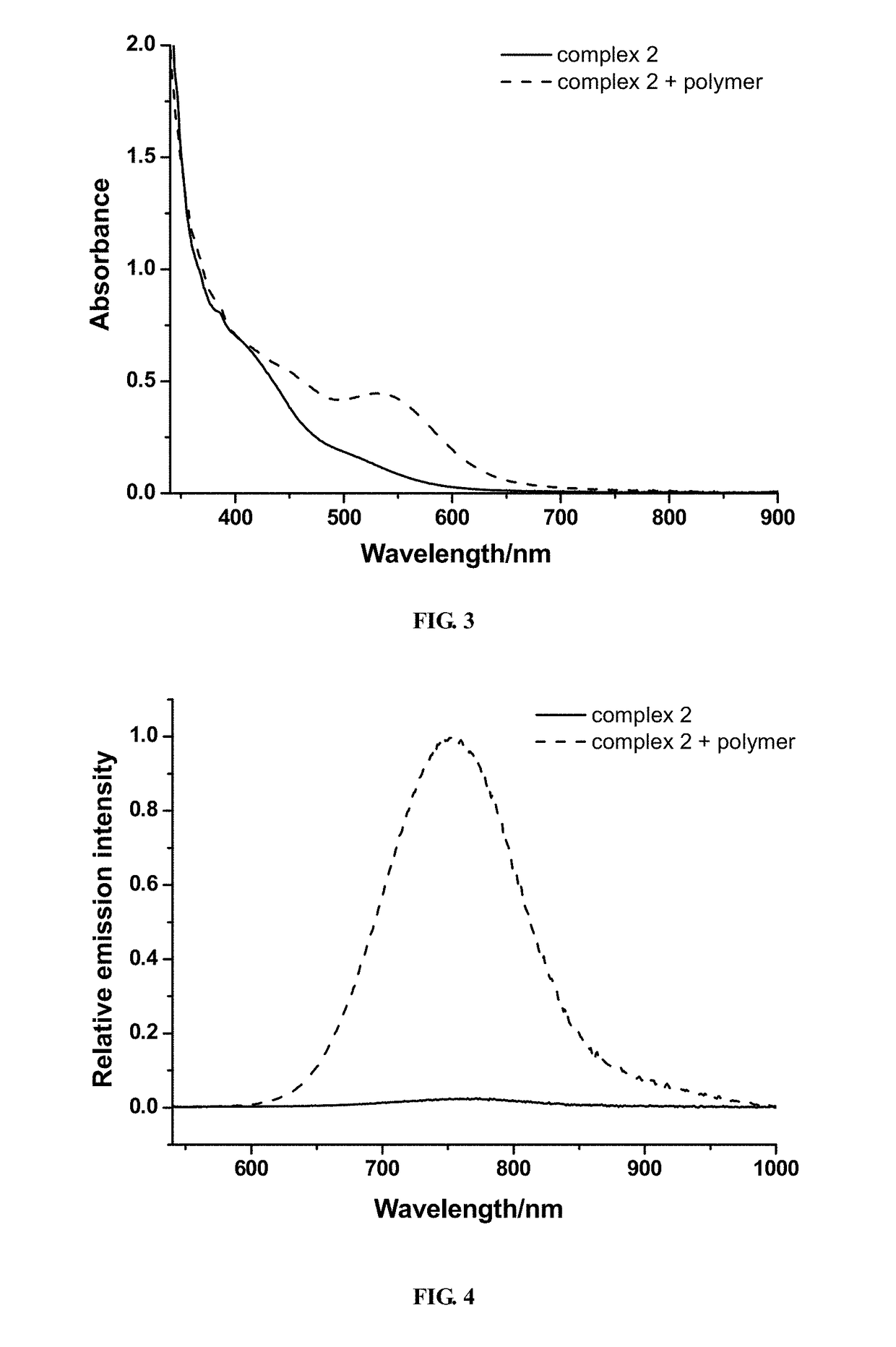
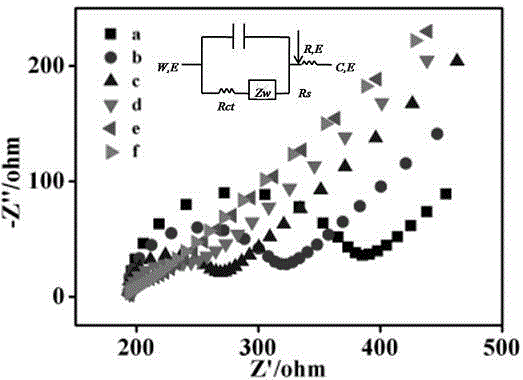
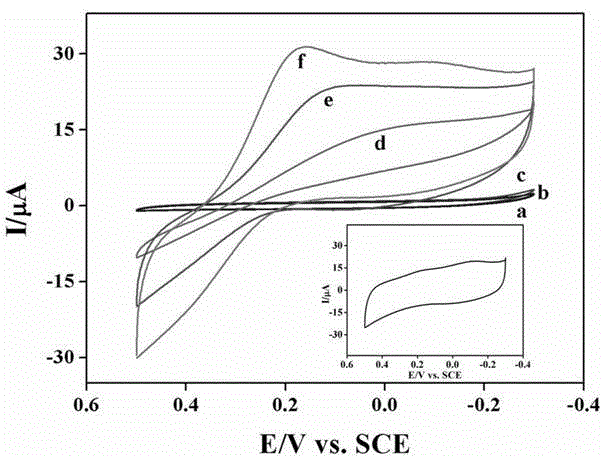
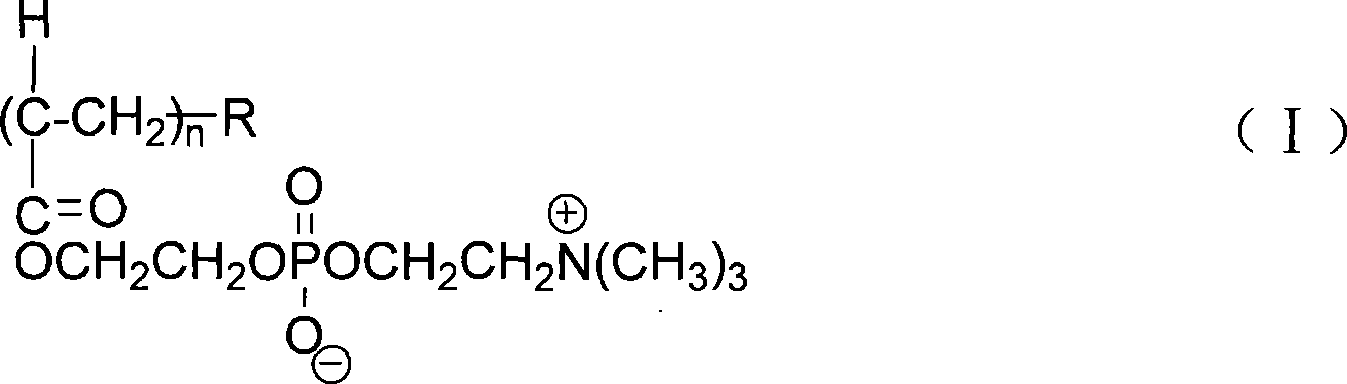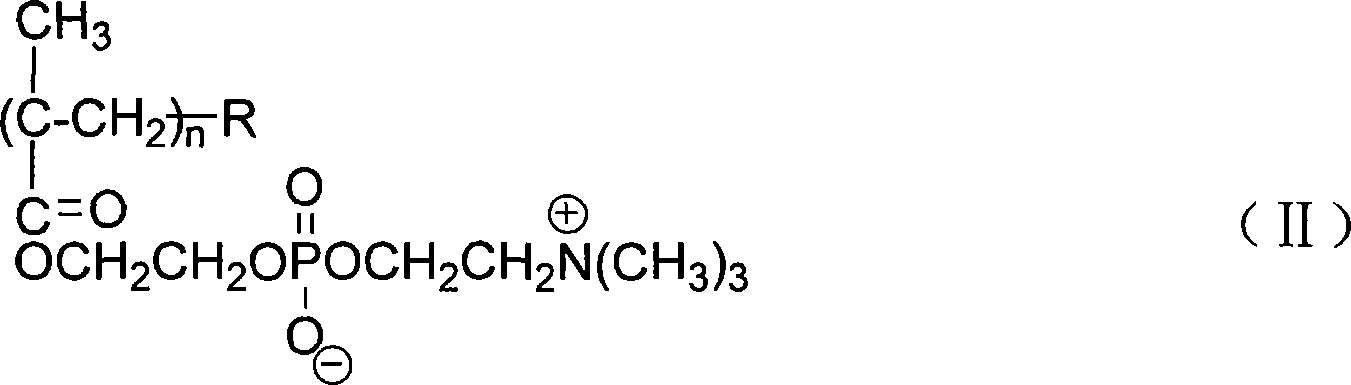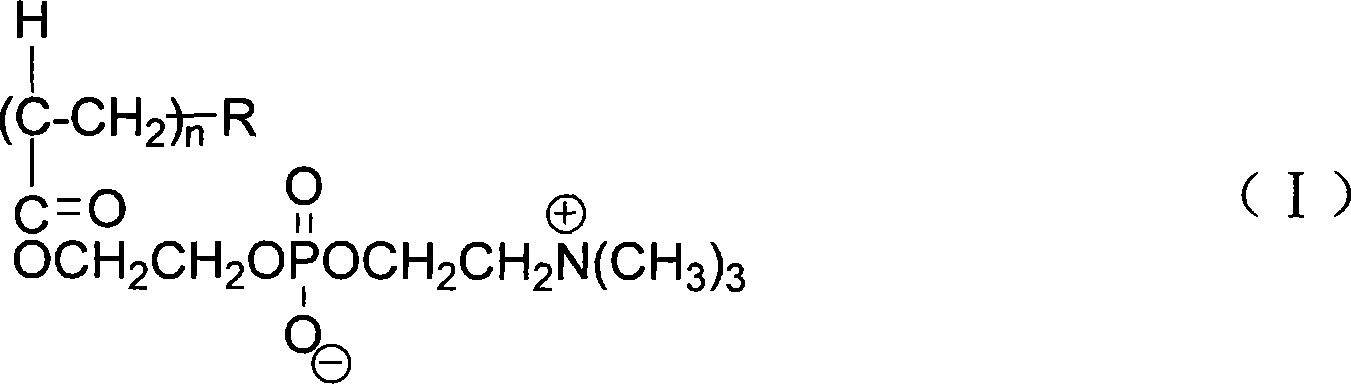Patents
Literature
188 results about "Non-covalent interactions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. The chemical energy released in the formation of non-covalent interactions is typically on the order of 1-5 kcal/mol (1000–5000 calories per 6.02 x 10^23 molecules). Non-covalent interactions can be classified into different categories, such as electrostatic, π-effects, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic effects.
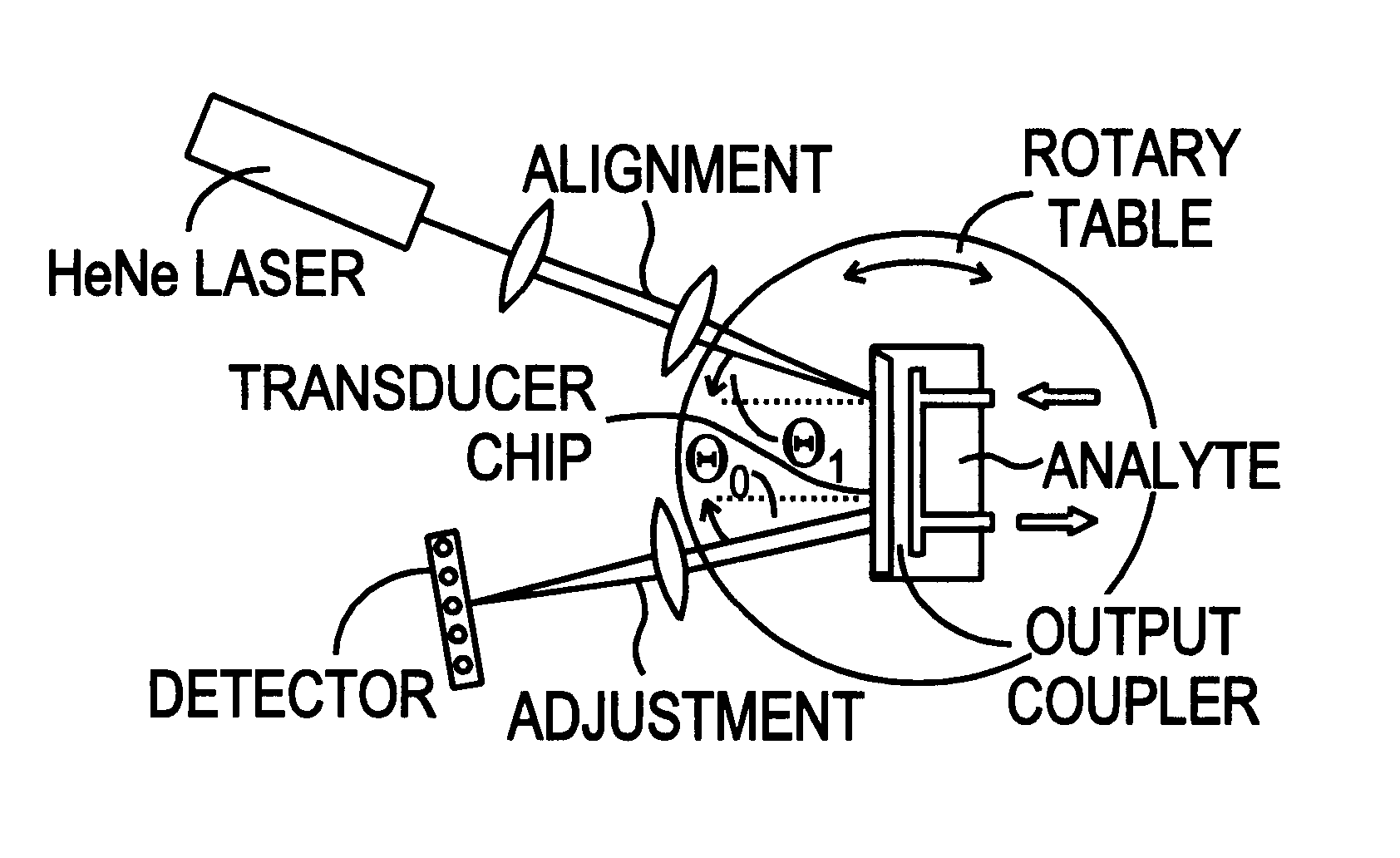
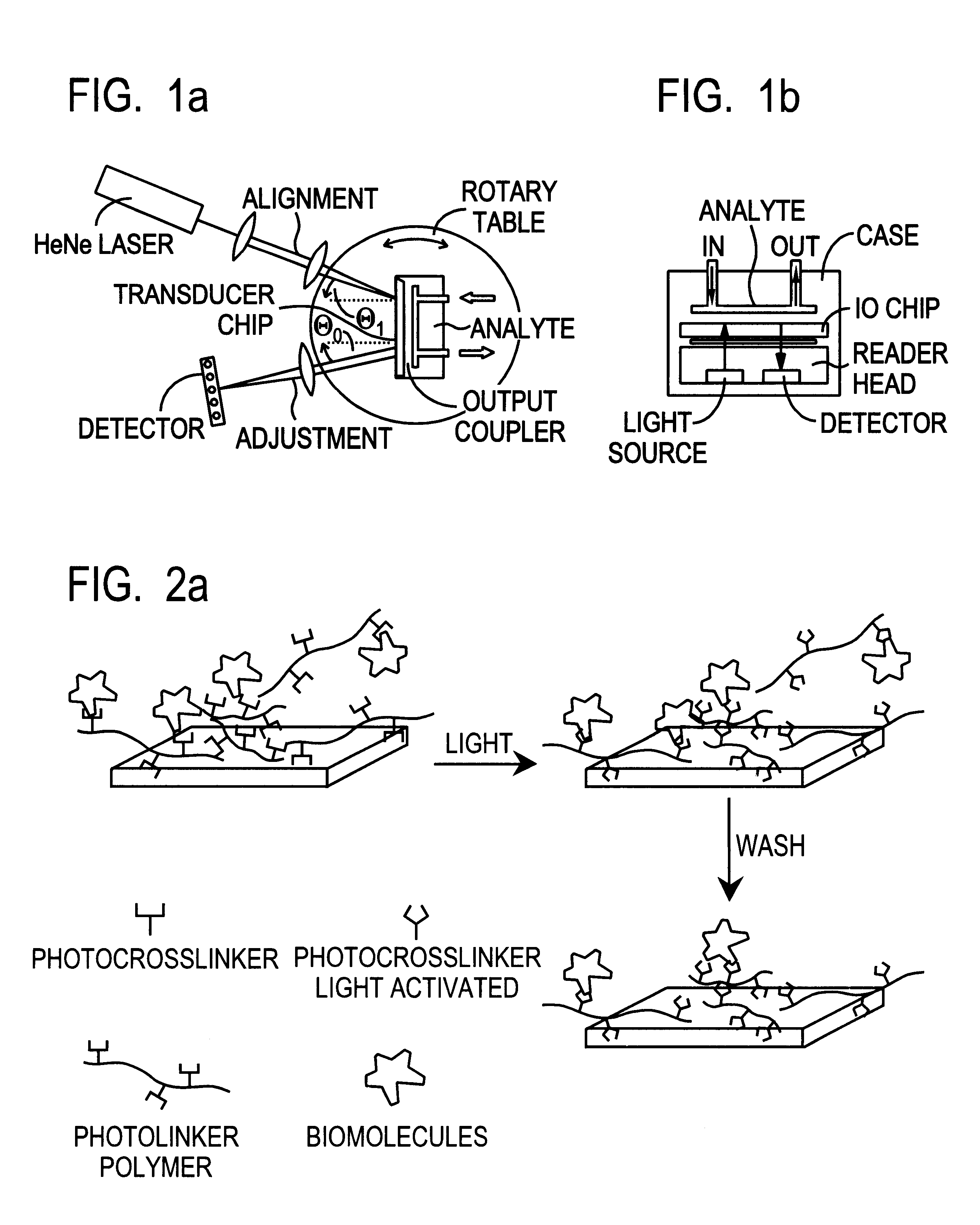
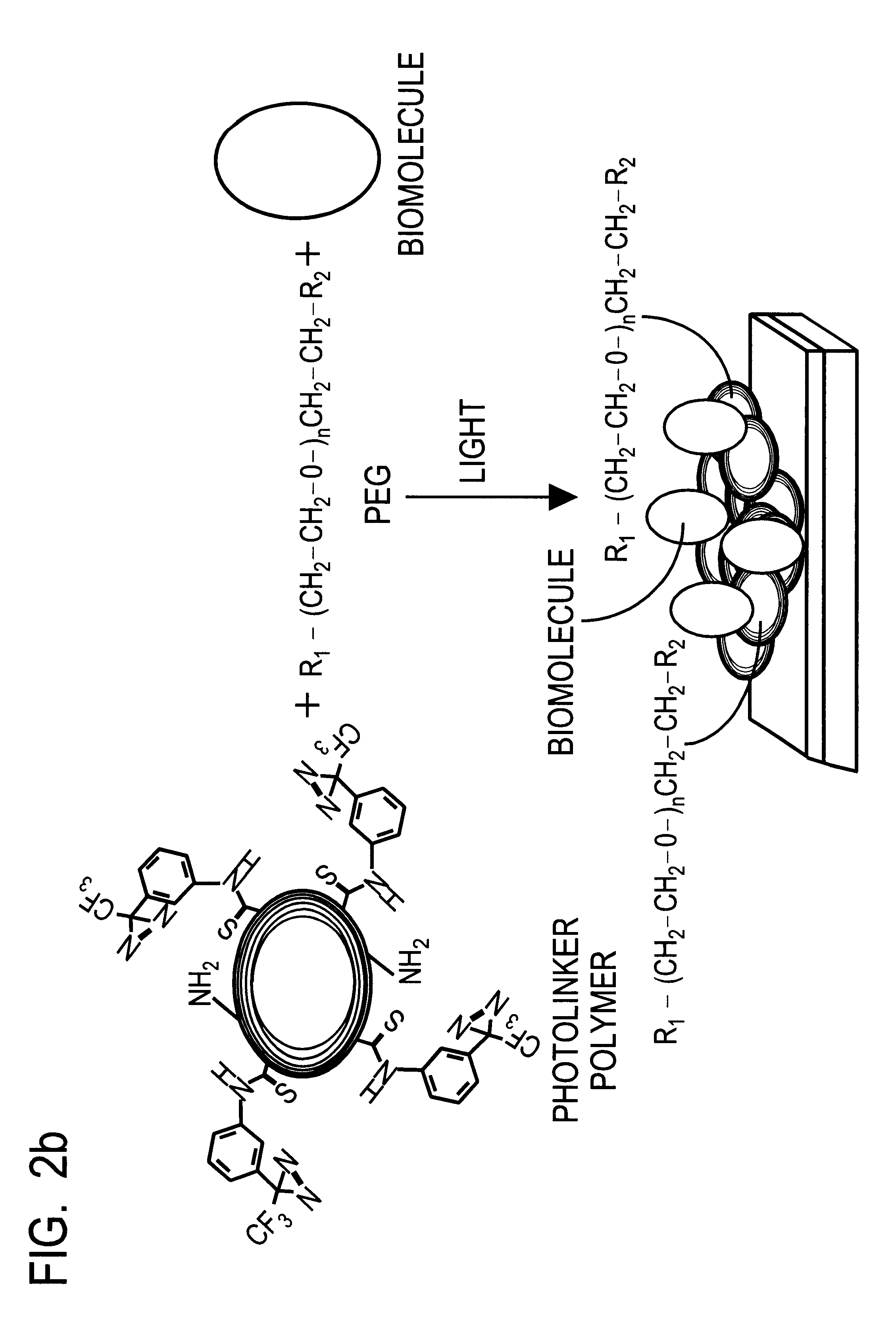
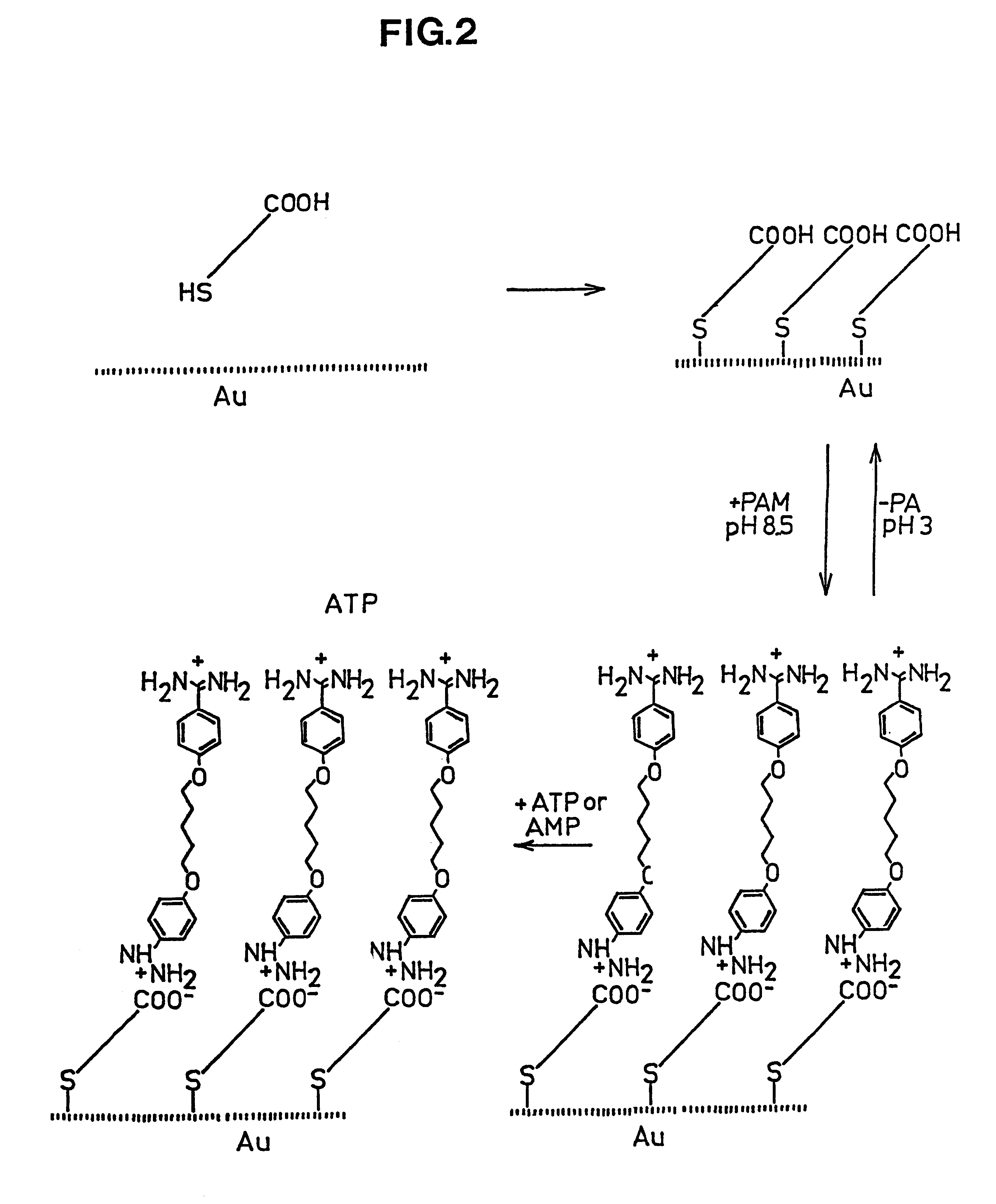
Optical sensor unit and procedure for the ultrasensitive detection of chemical or biochemical analytes
InactiveUS6346376B1High sensitivitySelective retentionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific detectionNon-covalent interactions
This document describes an optical sensor unit and a procedure for the specific detection and identification of biomolecules at high sensitivity in real fluids and tissue homogenates. High detection limits are reached by the combination of i) label-free integrated optical detection of molecular interactions, ii) the use of specific bioconstituents for sensitive detection and iii) planar optical transducer surfaces appropriately engineered for suppression of non-specific binding, internal referencing and calibration. Applications include the detection of prion proteins and identification of those biomolecules which non-covalently interact with surface immobilized prion proteins and are intrinsically involved in the cause of prion related disease.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
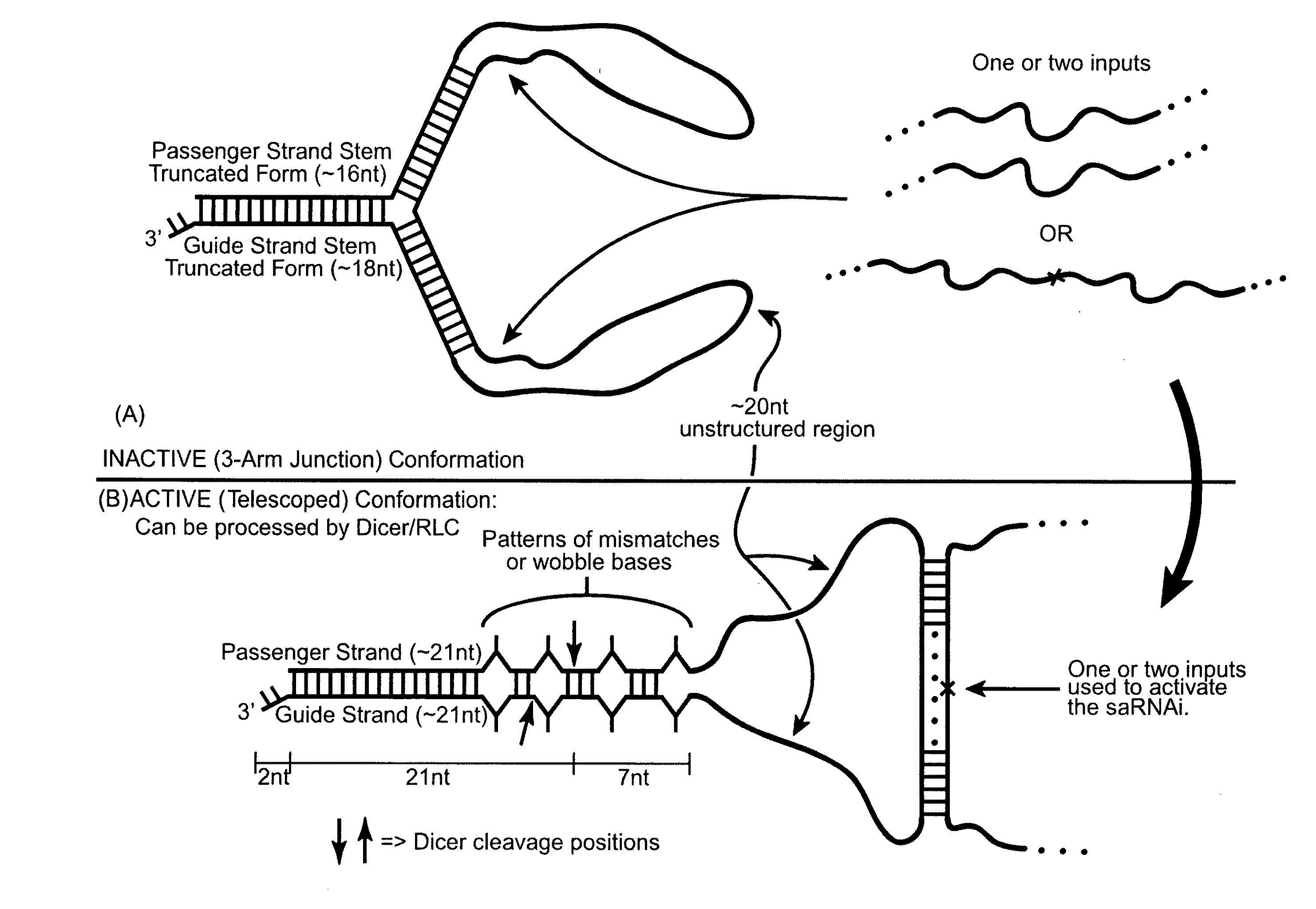
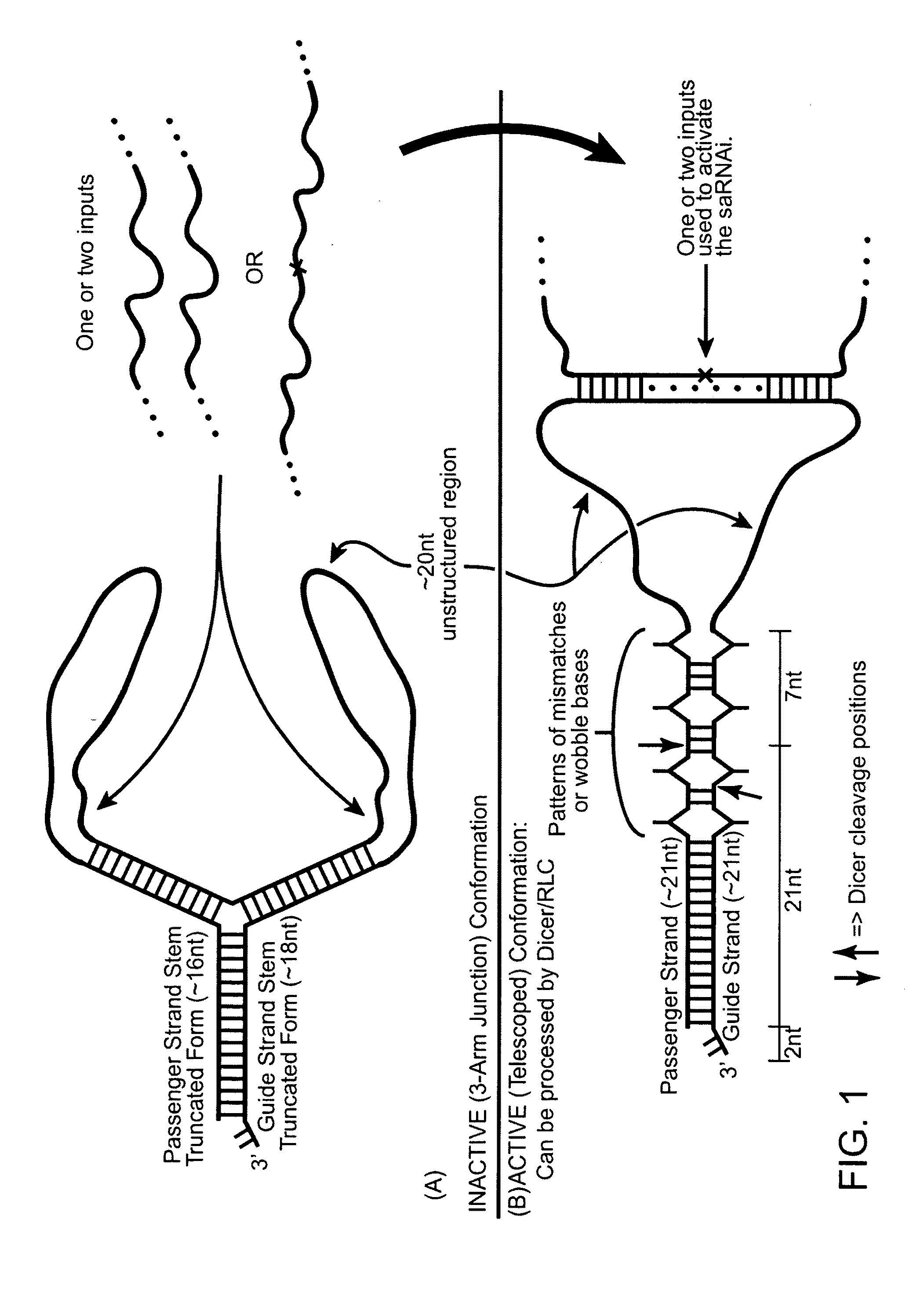
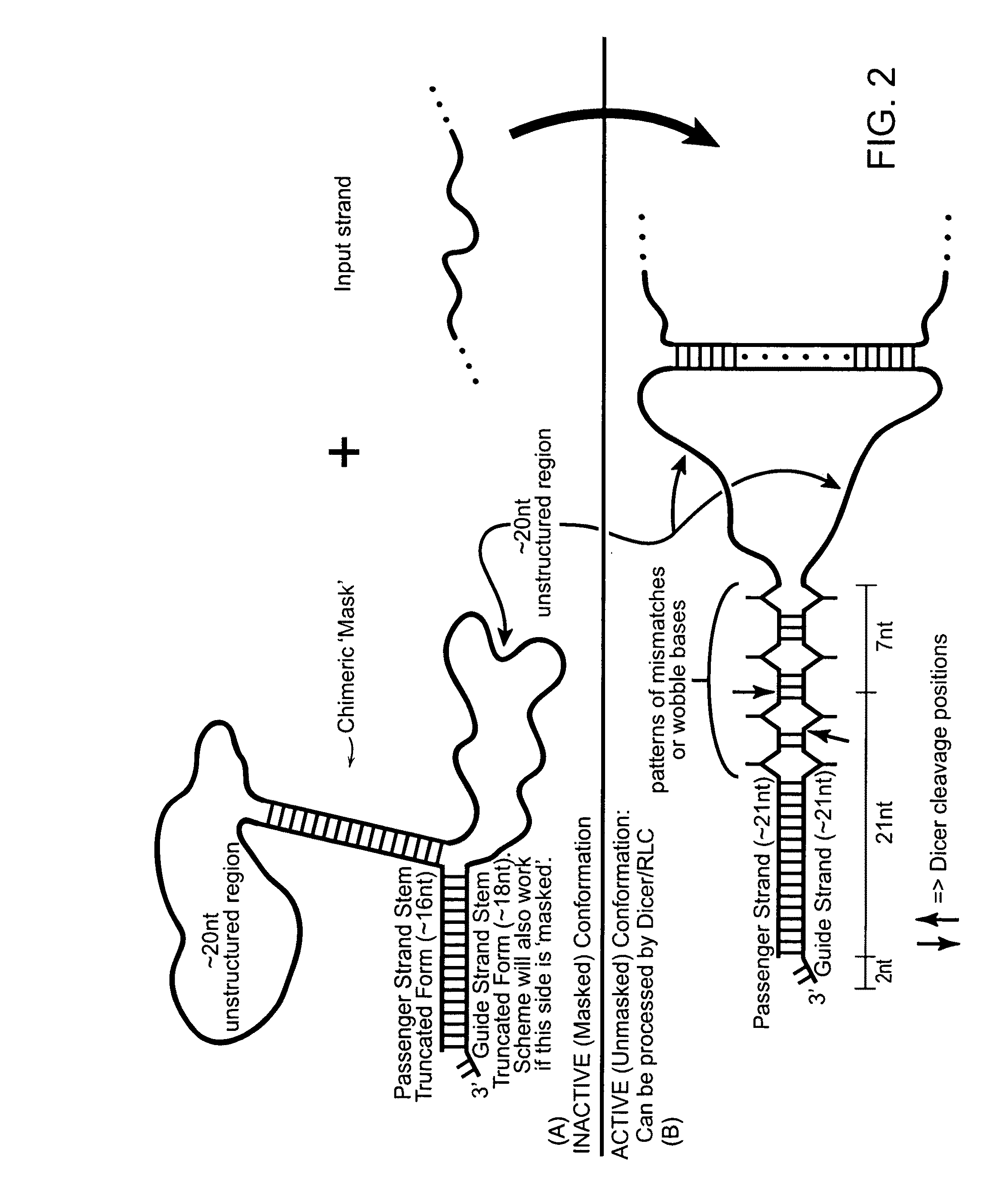
Signal activated RNA interference
ActiveUS20090234109A1Eliminate steric hindranceInhibits the degradation of the blocking sequenceSugar derivativesScreening processHomopolynucleotideDicer
The invention provides compositions and methods for signal activated RNA interference (saRNAi), preferably in vivo. The invention provides polynucleotides that switches between an inactive form and an active form upon covalent or non-covalent interaction with one or more specific chemical signals, such as disease-specific mRNA, miRNA, or other cellular RNA products with sequences that characterize diseased states of the cell. The interaction between the subject polynucleotides and the signals is preferably mediated by hybridization, which exposes, facilitates the formation, and / or allows the formation of a substrate that can be processed by proteins of the RNAi pathway (such as Dicer). The input and output of multiple different polynucleotides of the invention can form an in vivo signaling network. In addition, the multiple input signals can be integrated to modulate the activity of the subject polynucleotides.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
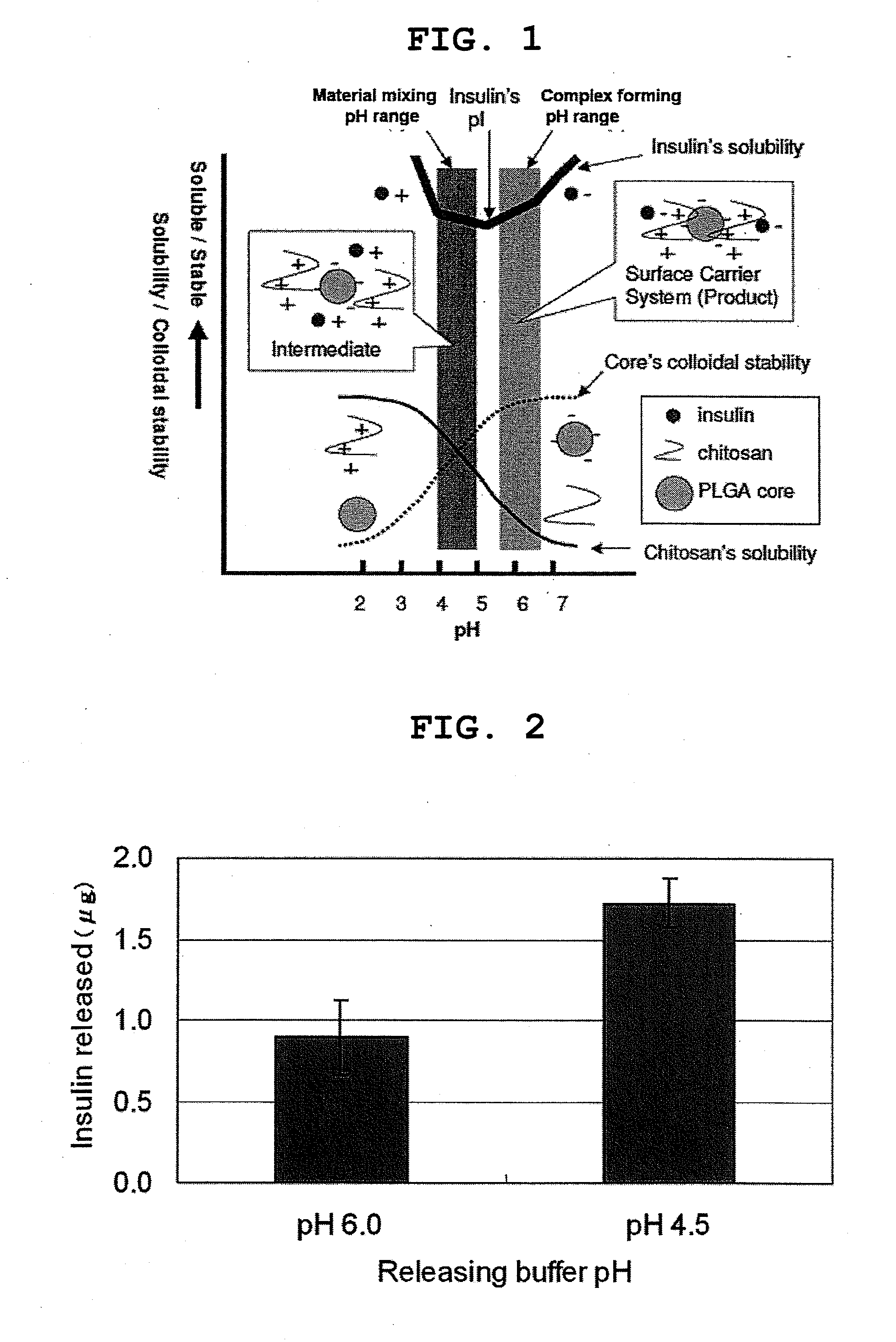
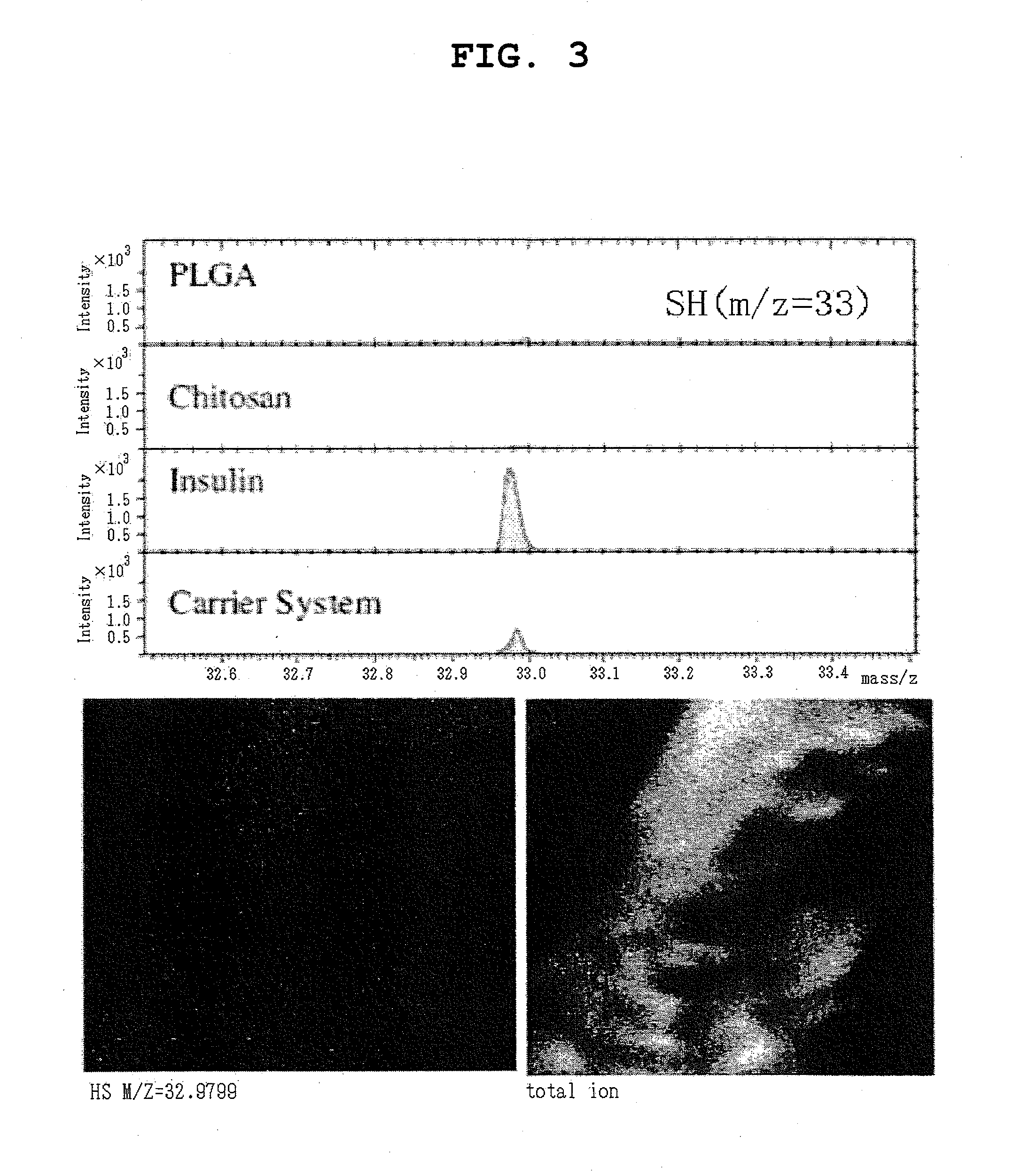
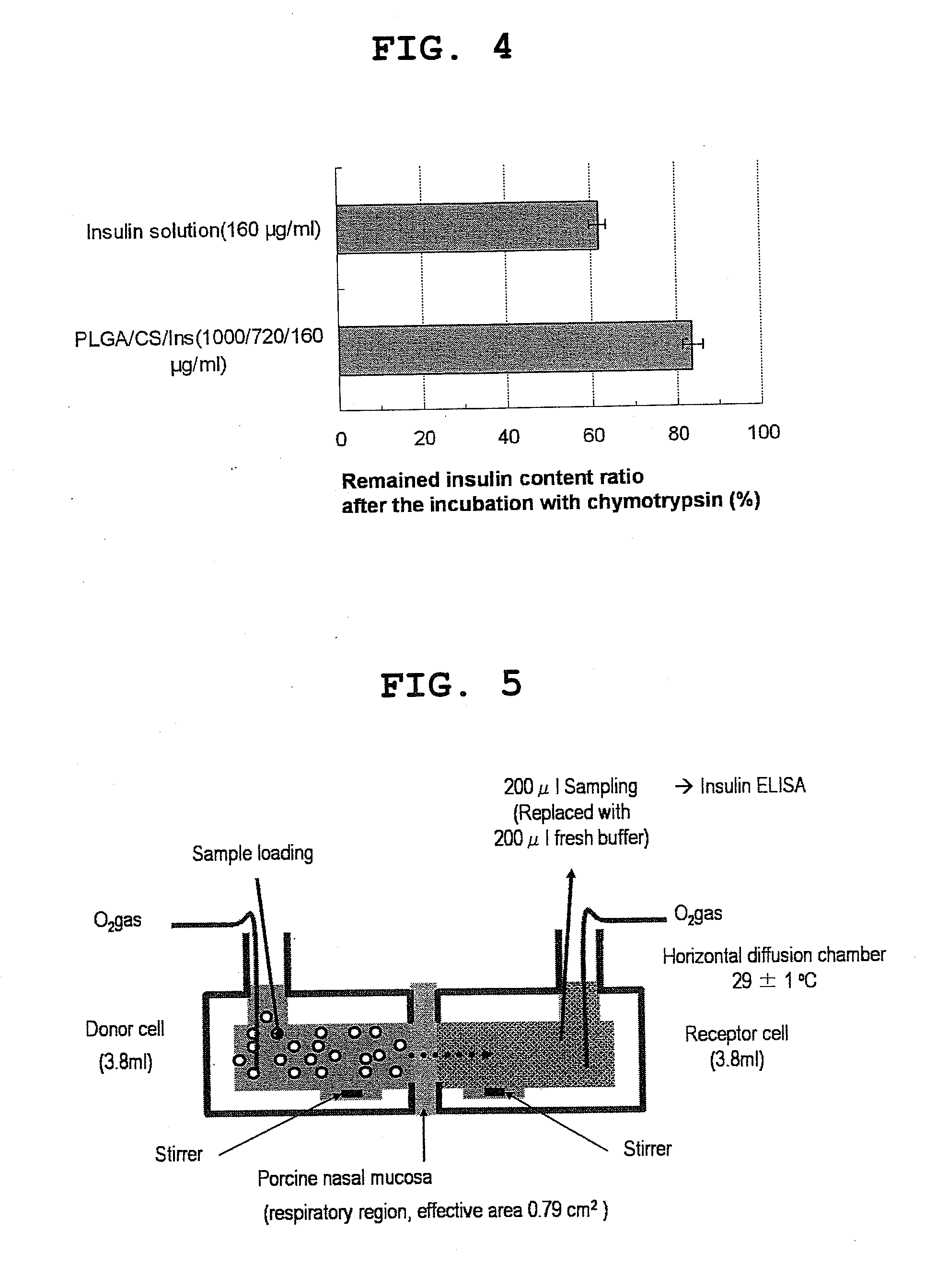
Pharmaceutical composition containing surface-coated microparticles
InactiveUS20110189299A1Increase capacityImprove efficiencyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMedicineMicroparticle
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition that can be used for efficient administration of low-molecular weight drugs and polymeric compounds such as peptides and proteins by methods other than injection, as well as a method for producing the composition. The pharmaceutical composition is for transmucosal administration and comprises (a) a drug having a positive or negative charge at a predetermined pH, (b) a pharmaceutically acceptable small particle and (c) a pharmaceutically acceptable surface-coating polymer capable of being electrically charged at the pH, wherein the surface of the small particle is coated by the surface-coating polymer, the drug is immobilized on the surface of the small particle via the surface-coating polymer, and a complex is formed by a noncovalent interaction between the small particle and the surface-coating polymer and a concurrent electrostatic interaction between the surface-coating polymer and the drug.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
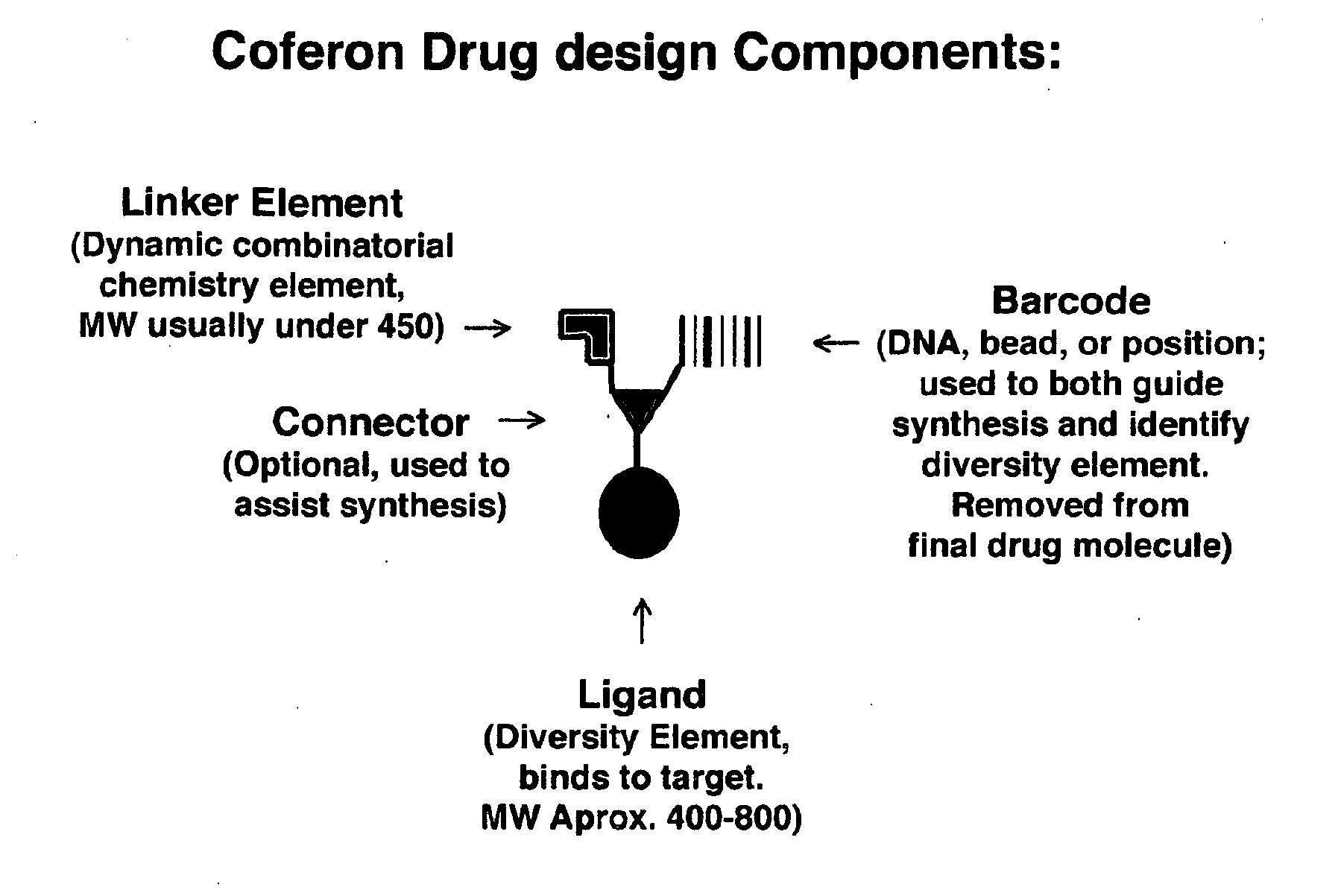
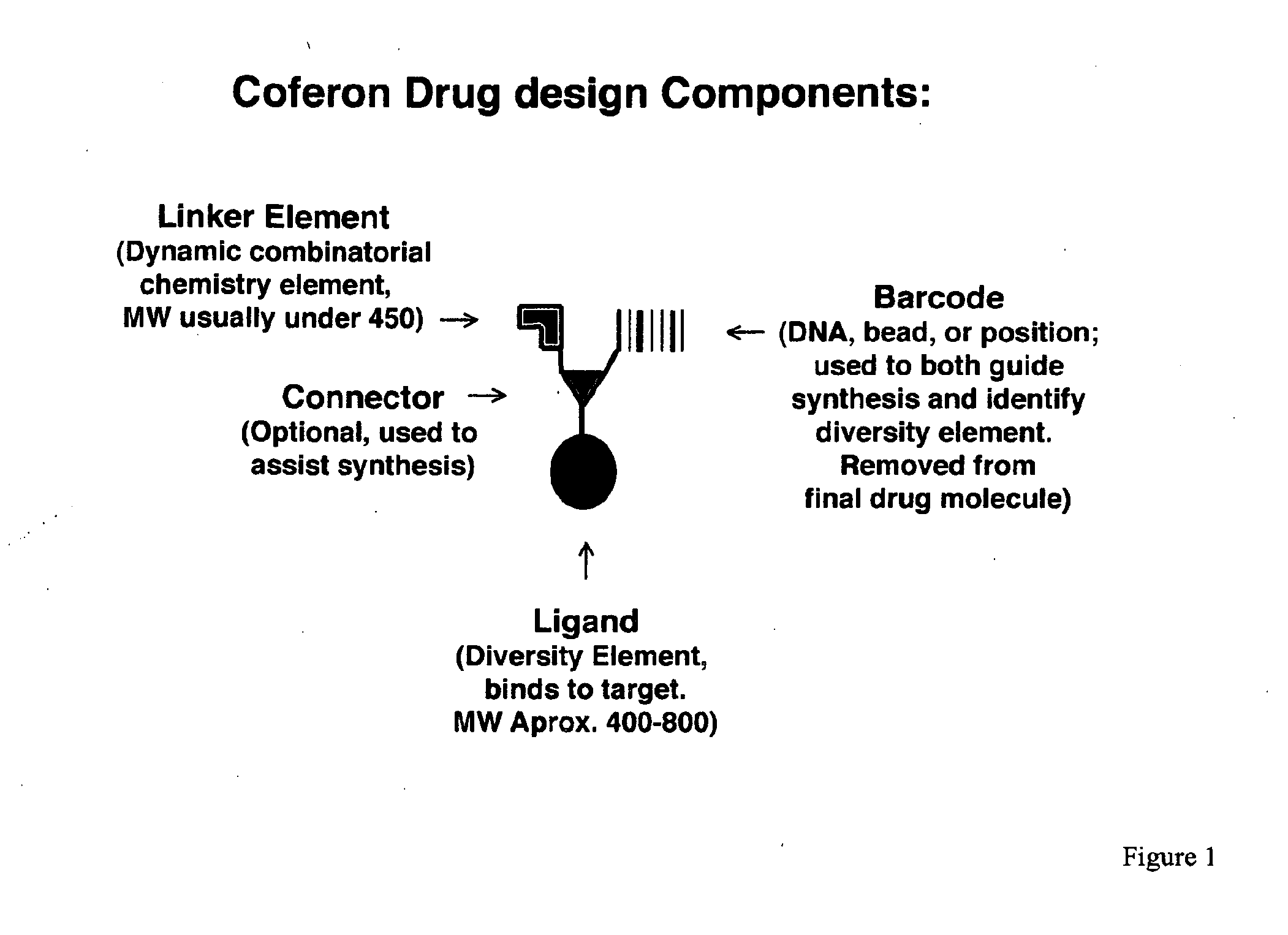
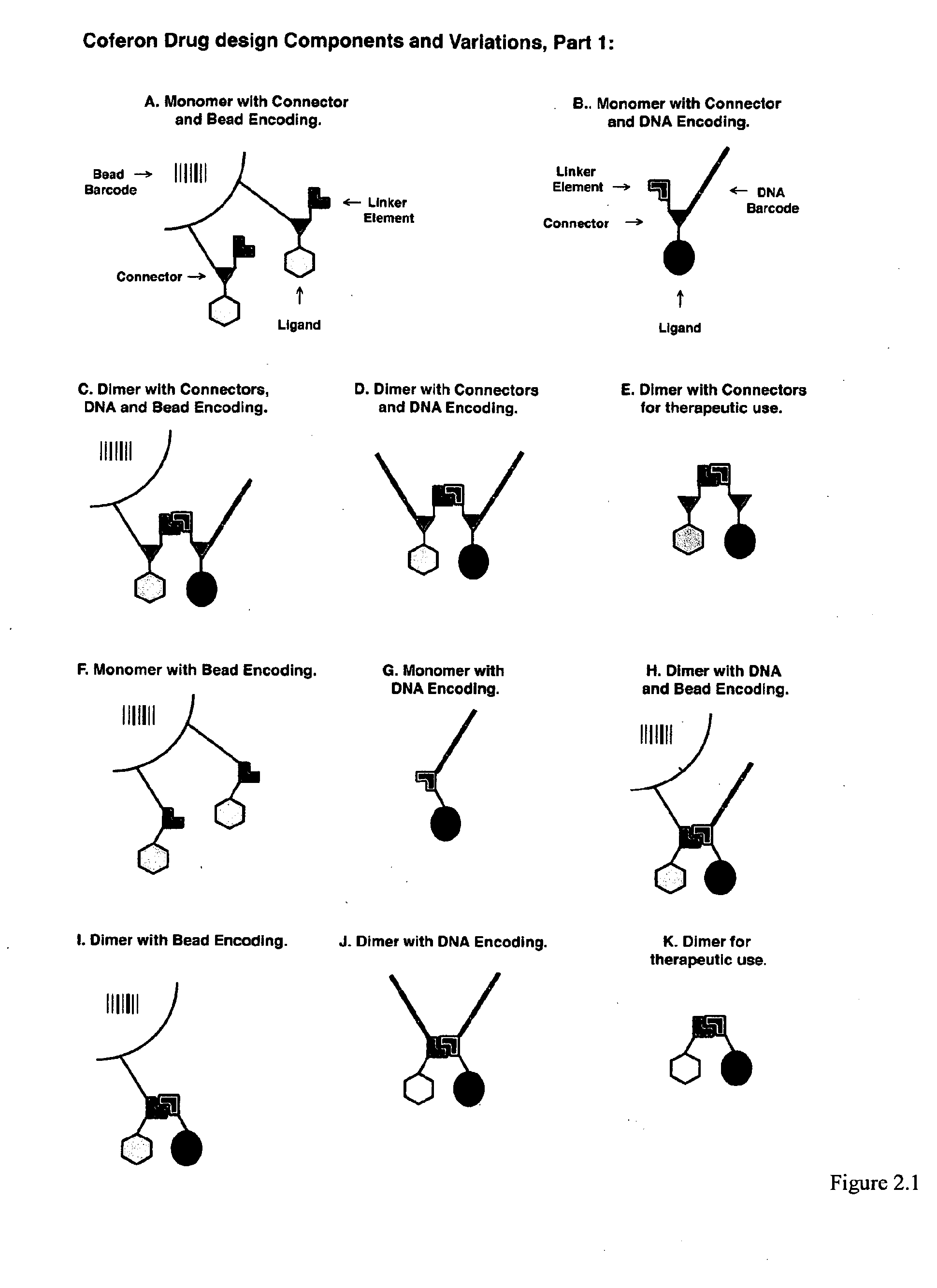
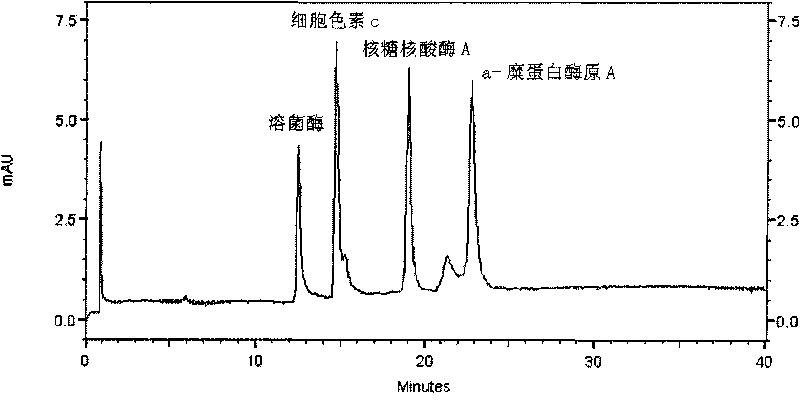
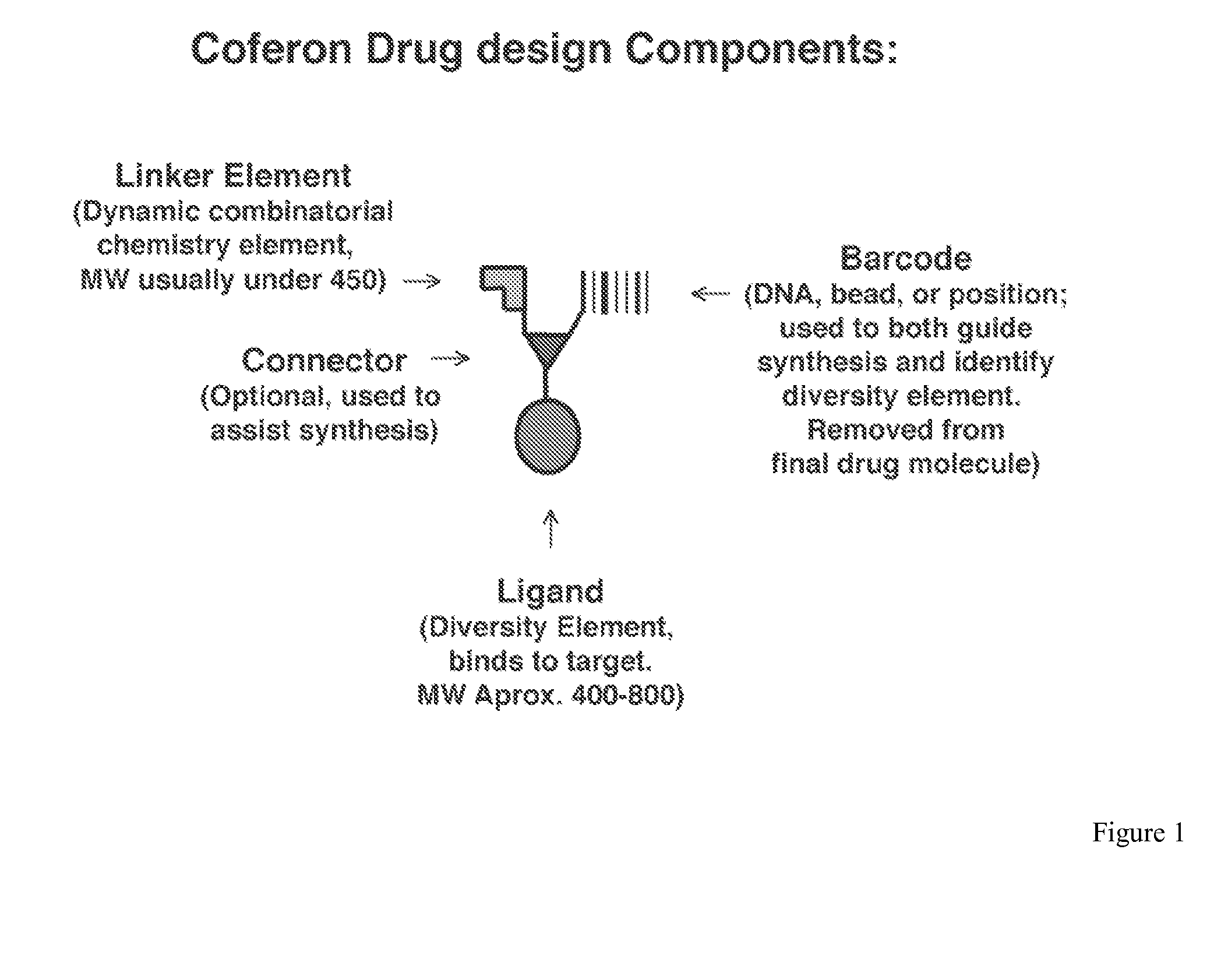
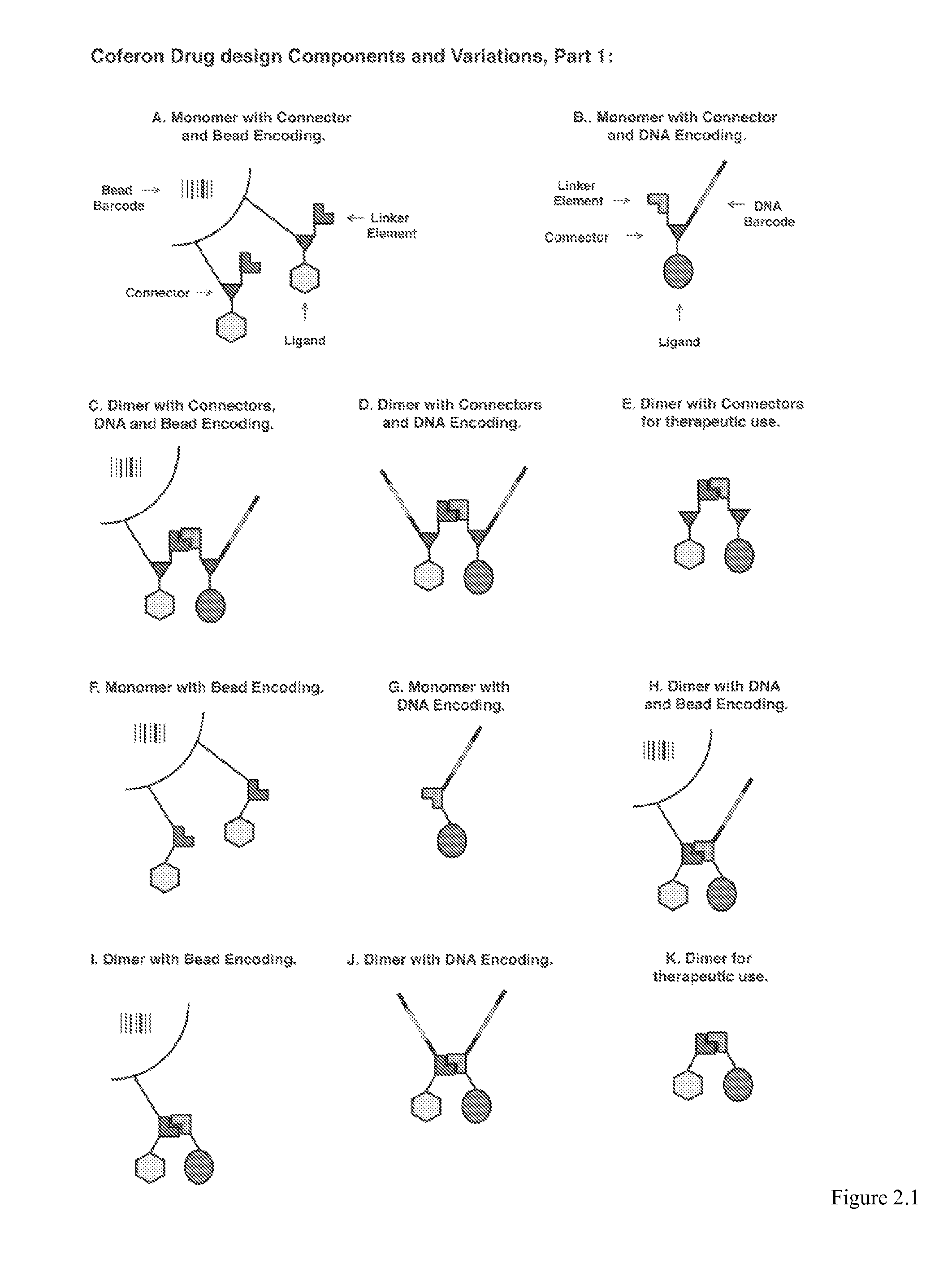
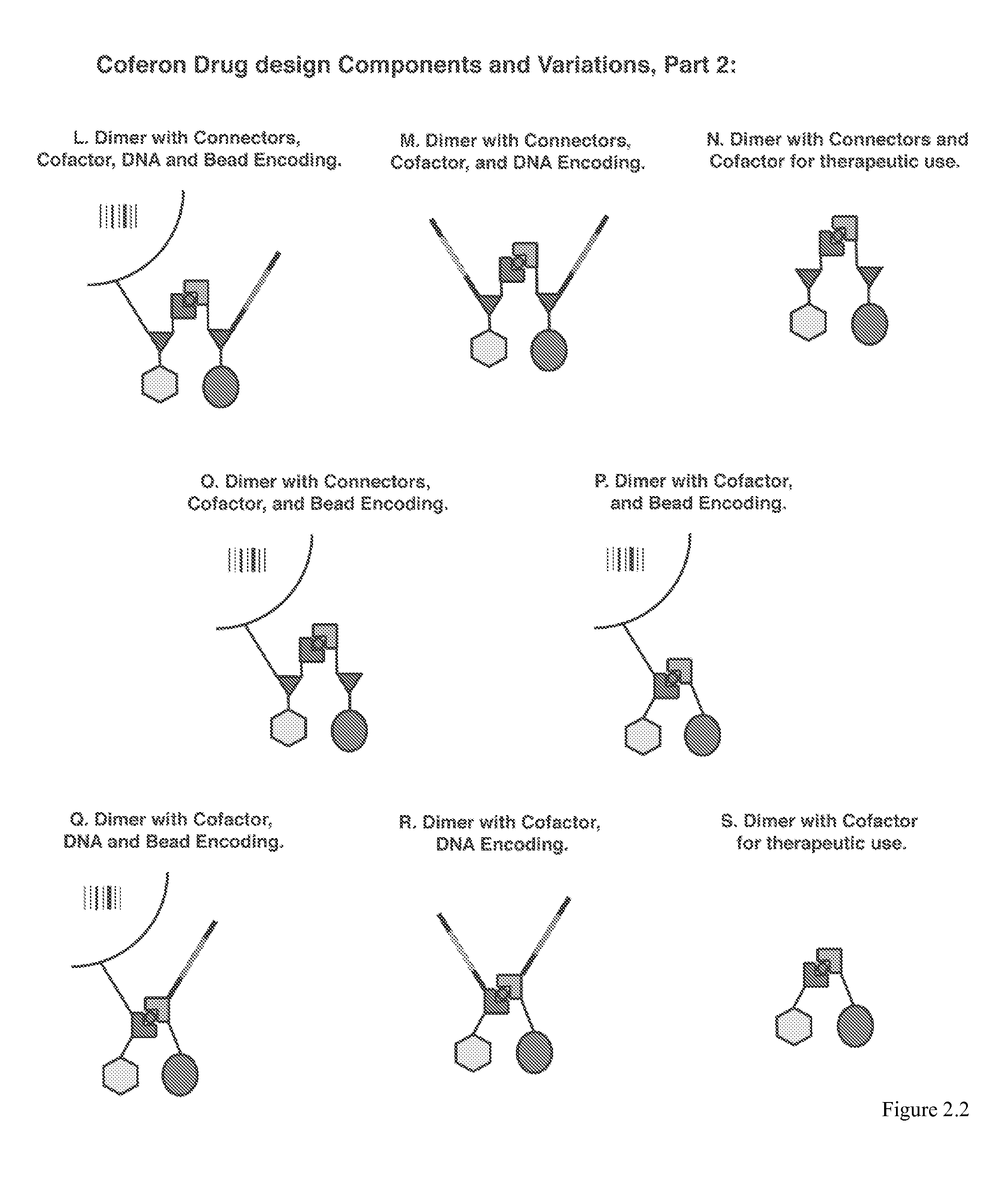
Coferons and methods of making and using them
ActiveUS20110263688A1Easy to modifyDisrupt interactionSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesChemical compoundCombinatorial chemistry
A monomer useful in prepaπng therapeutic compounds includes a diversity element which potentially binds to a target molecule with a dissociation constant of less than 300 11 M and a linker element connected to the diversity element The linker element has a molecular weight less than 500 daltons, is connected, directly or indirectly through a connector, to said diversity element, and is capable of forming a reversible covalent bond or noncovalent interaction with a binding partner of the linker element The monomers can be covalently or non-covalently linked together to form a therapeutic multimer or a precursor thereof
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Hair treatment compositions incorporating hair substantive polymers
The invention provides a hair treatment composition comprising a hair substantive polymer, the hair substantive polymer comprising a polymeric backbone bearing: (a) at least one side chain which is formed from a hair fiber targeting group which is covalently linked to the polymeric backbone, the hair fiber targeting group being a non-cationic species which is capable of specifically interacting with the protein surface of the hair fiber in a non-covalent interaction having a bond energy ranging from 0.5 to 3 Kcal / mol, when the composition is applied to hair; (b) preferably, at least one side chain which is different to side chain (a) and which comprises a hair benefit agent. Compositions of the invention provide for deposition and delivery of benefit agents to hair in a more efficient and targeted manner.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Elastic materials
The present invention relates to materials exhibiting the property of rubbery elasticity, consisting of molecules with a mass of between 9 and 9000 g / mol, all or some of the molecules having at least three groups (also referred to as “associative groups”) capable of associating via non-covalent interactions.Although consisting of small non-polymerized molecules that are not chemically crosslinked, this material exhibits properties of rubbery elasticity. According to an embodiment of the invention, this material exhibits rubbery elasticity at ambient temperature. Above a certain temperature, the material flows like a simple liquid. The material is thermoreversible, i.e. after cooling, the material again exhibits the property of rubbery elasticity. This material is self-repairing and potentially recyclable, which is never the case with a chemically crosslinked elastomer.According to an embodiment of the invention, the molecules constituting the material of the invention bear associative groups of formula (1) below:in which A denotes oxygen, sulphur or NH; the carbon atoms of formula (1) can be substituted. Preferably, A denotes oxygen. Advantageously, the material comprises (i) molecules having at least 3 associative groups, and (ii) molecules having a single associative group.Advantageously, the molecules are obtained from fatty acid derivatives.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
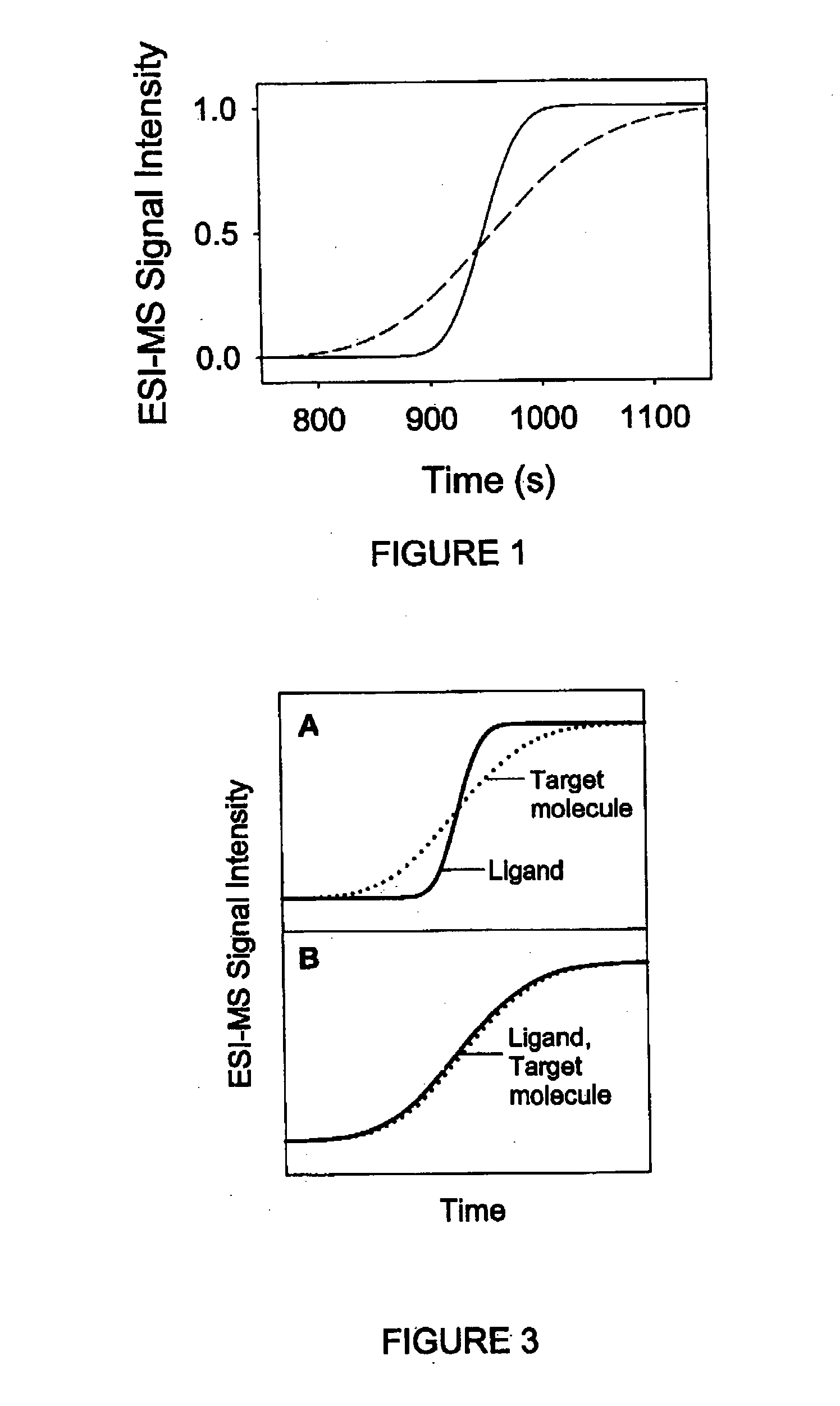
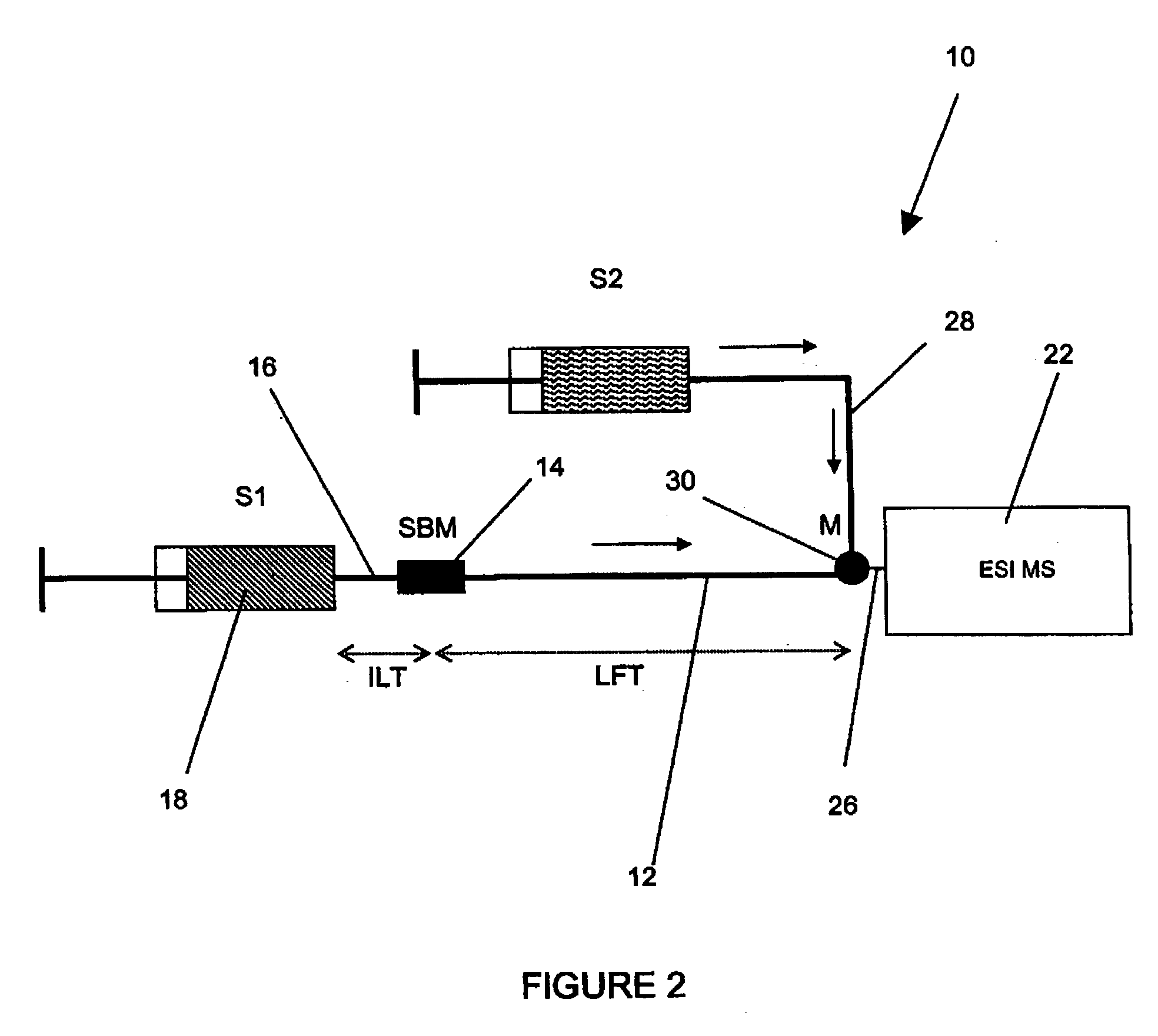
Method and apparatus for the detection of noncovalent interactions by mass spectrometry-based diffusion measurements
InactiveUS20030234356A1Accurate measurementShorten the timeSamples introduction/extractionSurface/boundary effectHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGas phase
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting the noncovalent binding of a potential ligand (such as a drug candidate) to a target, e.g. a biochemical macromolecule such as a protein. The method is based on the Taylor dispersion of an initially sharp boundary between a carrier solution, and an analyte solution that contains the potential ligand(s) and the target. Dispersion profiles of one or more potential ligands are monitored by mass spectrometry at the exit of the laminar flow tube. Potential ligands will usually be relatively small molecules that have large diffusion coefficients. In the absence of any noncovalent interactions in solution, very steep dispersion profiles are expected for these potential ligands. However, a ligand that binds to a large target in solution, will show an apparent diffusion coefficient that is significantly reduced, thus resulting in a more extended dispersion profile. Noncovalent binding can therefore be detected by monitoring dispersion profiles of potential ligands in the presence and in the absence of the target. In contrast to other mass spectrometry-based methods for detecting noncovalent interactions, this method does not rely on the preservation of specific noncovalent interactions in the gas phase. This method has an excellent sensitivity and selectivity, therefore it can be used for testing multiple potential ligands simultaneously. The method is therefore useful for the high throughput screening of compound libraries.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
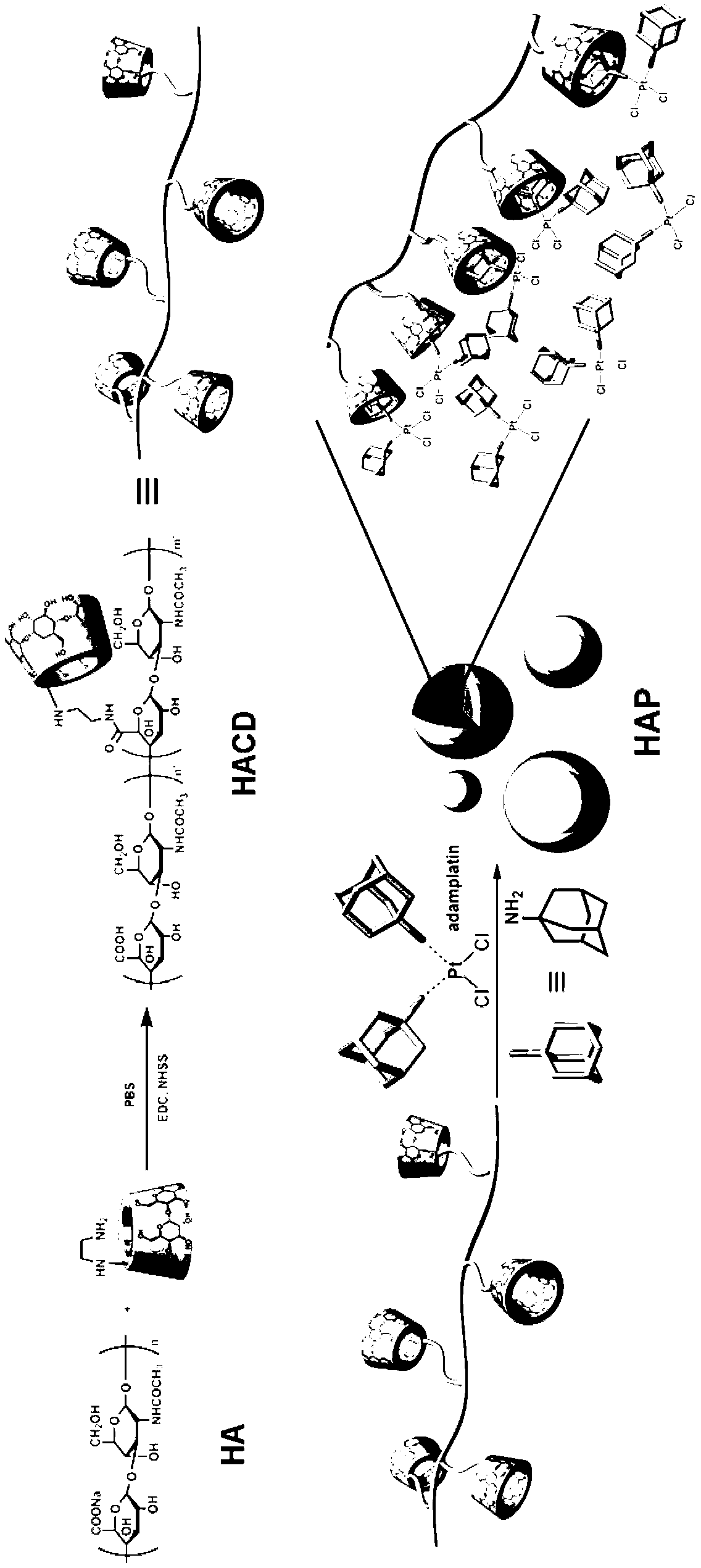
Supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin and preparation of supramolecule assembly
InactiveCN102698286AAchieve selective killingSmall toxicityHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
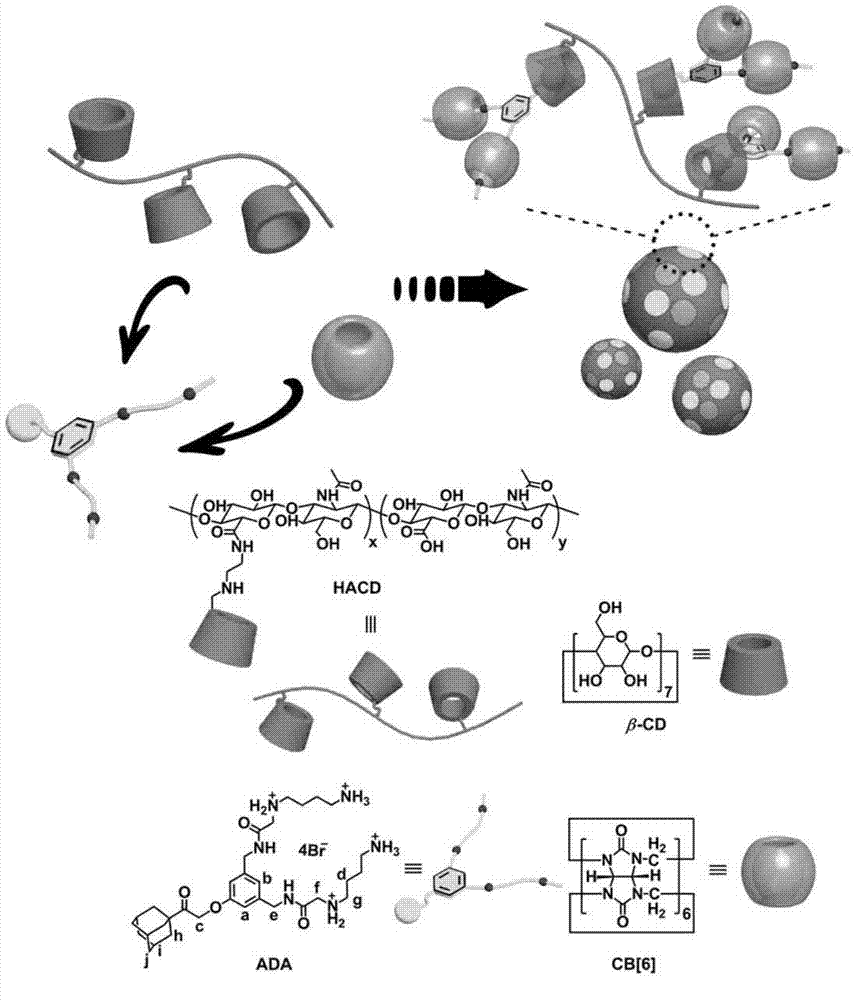
The invention discloses a supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin. The supramolecule assembly is a binary supramolecule assembly which is synthesized on the basis of cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and adamplatin. A preparation method of the supramolecule assembly is characterized in that the cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and the adamplatin are respectively synthesized, and through the strong non-covalent interaction of cyclodextrin and adamantine and the amphiphilic action of molecules, a supermolecule nano particle which takes the hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as a shell and the adamplatin as a core is formed. The supramolecule assembly disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the supramolecule assembly of the targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin has a simple synthetic route, is low in preparation cost and high in productivity, and is suitable for amplification synthesis and practical production application; and through endocytosis in which a malignant cell surface hyaluronic acid receptor serves as a medium, the supramolecule assembly (HAP) is brought in cancer cells in a target manner, so that the protection of normal cells and the targeting selective killing of cancer cells are realized, the anti-cancer activity is obviously improved, and toxic and side effects are obviously reduced.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Electrochromic device including carbon-based material and viologen-based compound, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20160033839A1Improve switching performanceIncreased durabilityTenebresent compositionsNon-linear opticsChemical compoundEngineering
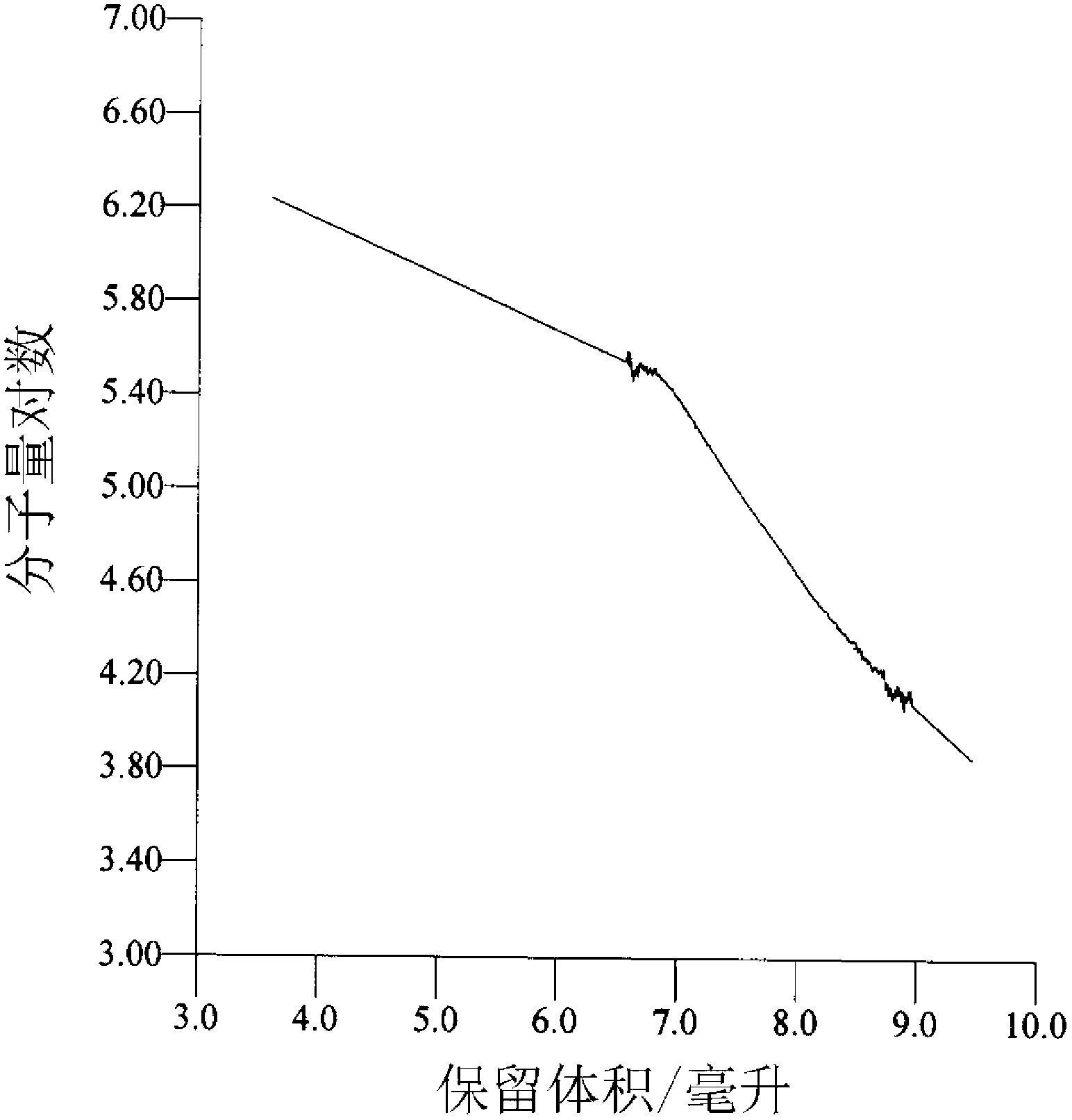
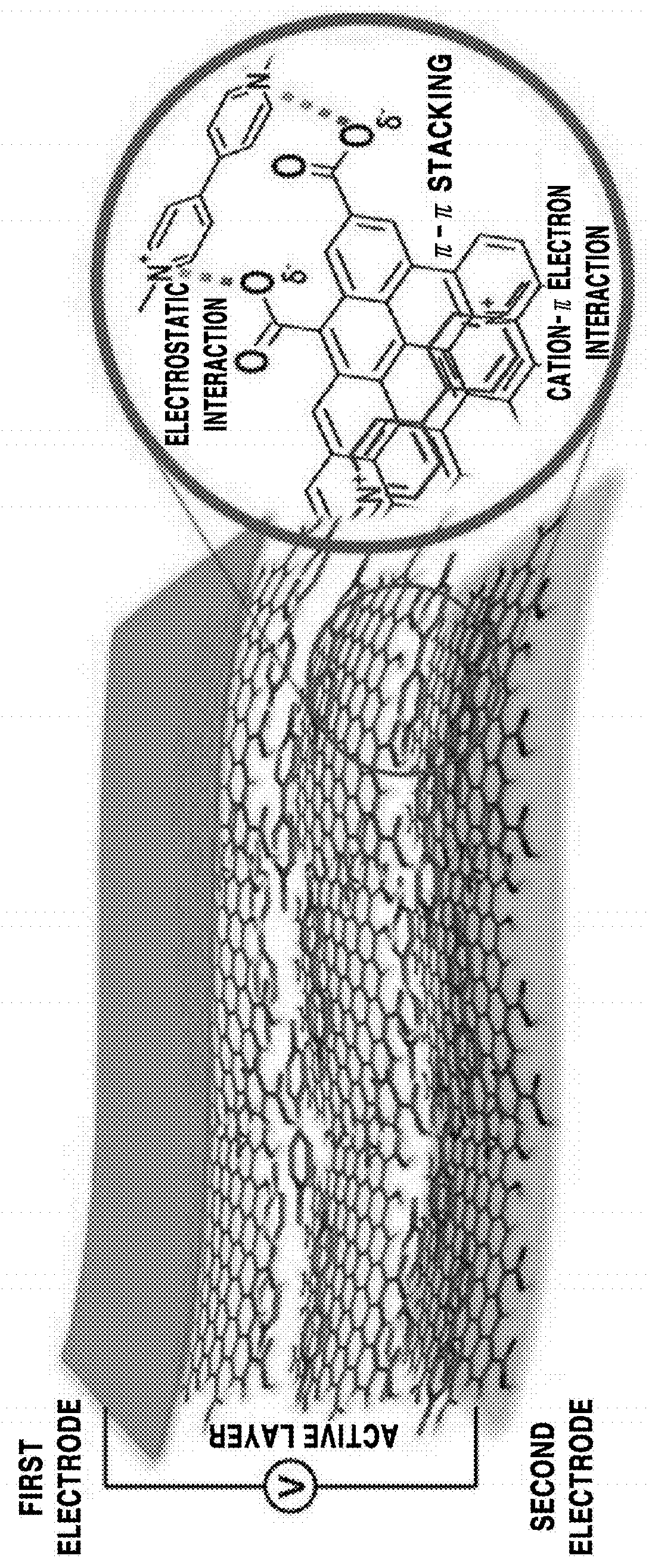
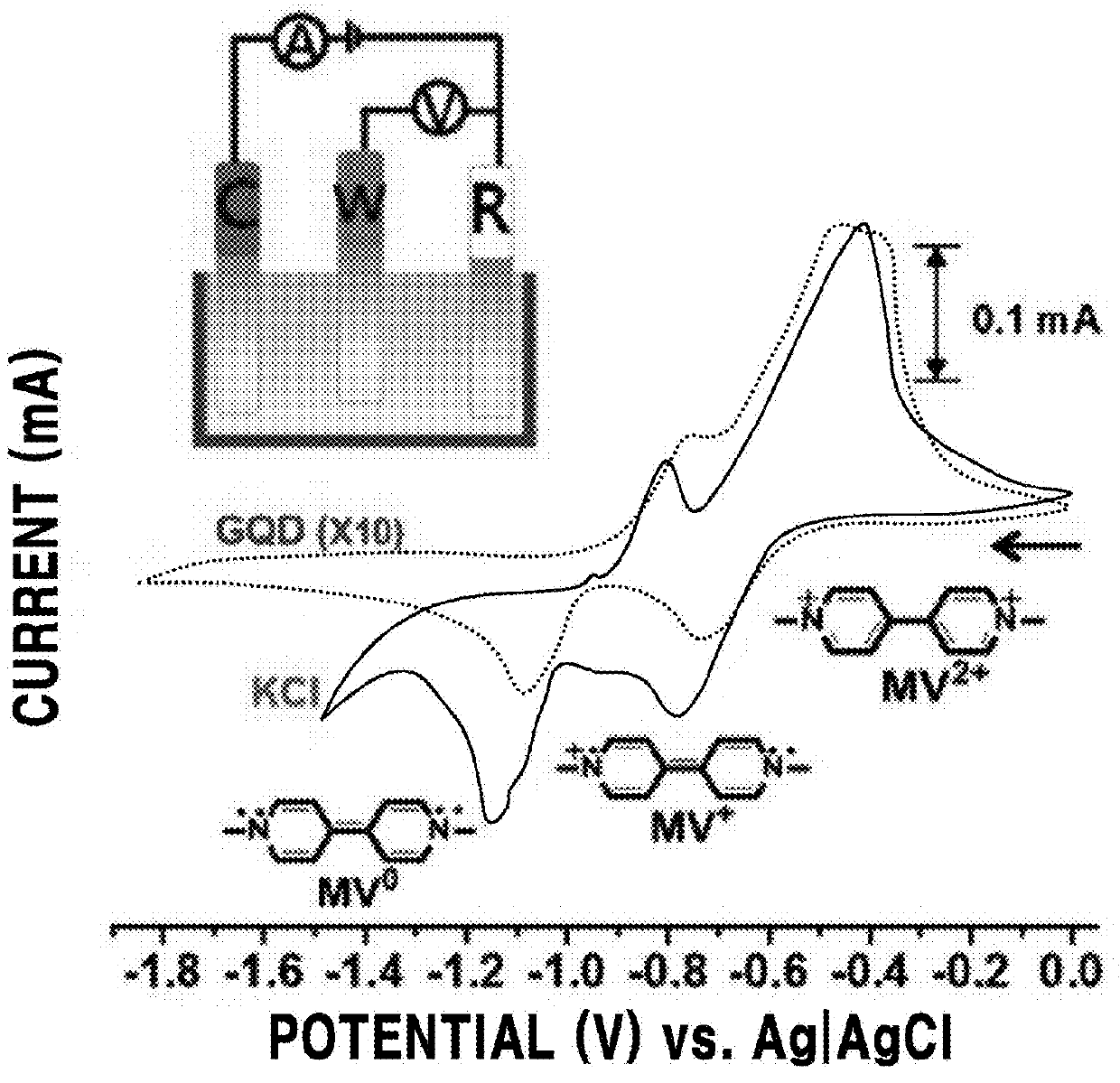
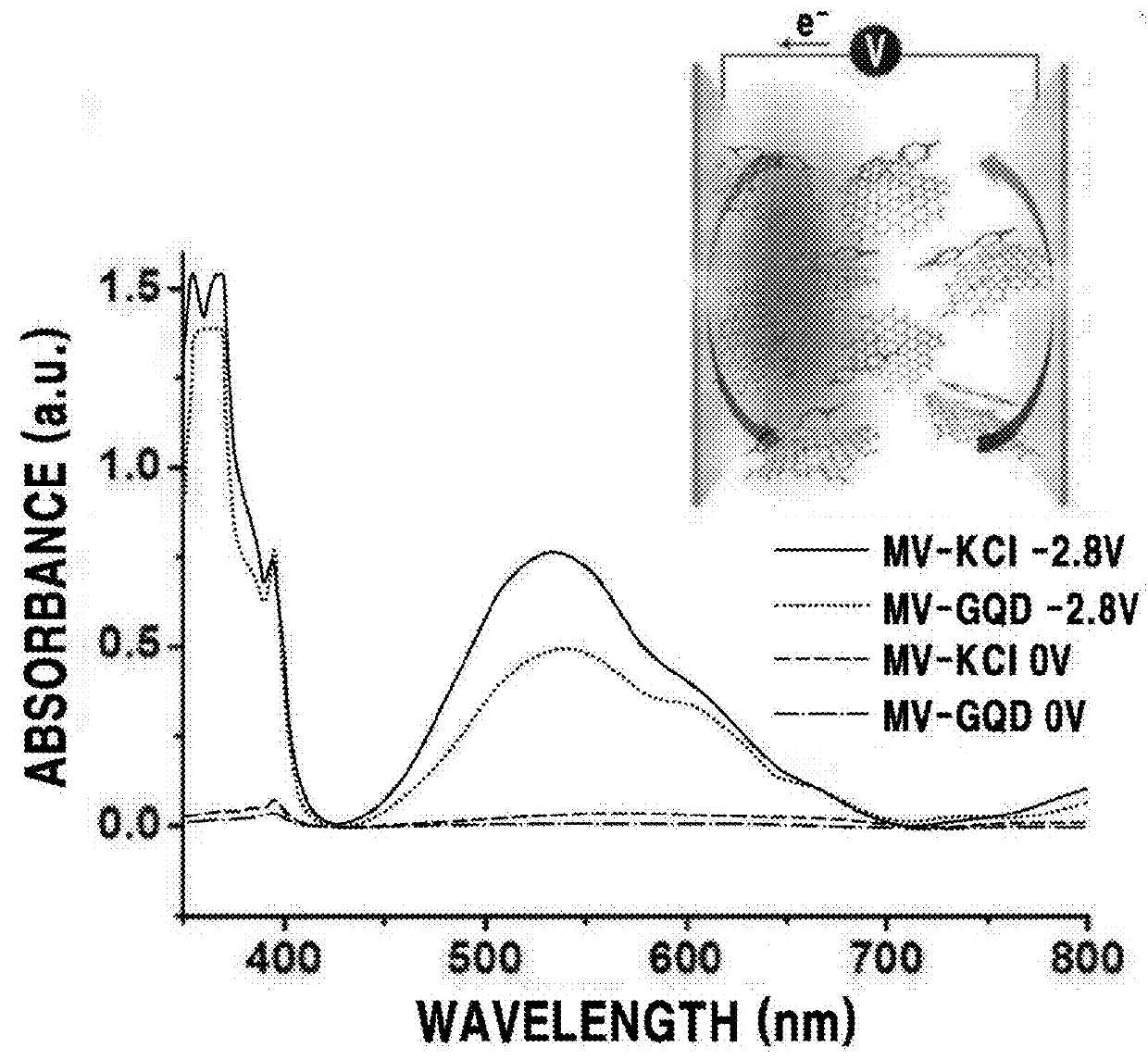
The following description relates to an electrochromic device including a carbon-based material and a viologen-based compound, a method for producing the electrochromic device, and use thereof. There is provided the electrochromic device including an active layer arranged between a first electrode and a second electrode, in which the active layer includes a carbon-based material and a viologen-based compound, and the carbon-based material and the viologen-based compound are bonded to each other through a non-covalent interaction.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
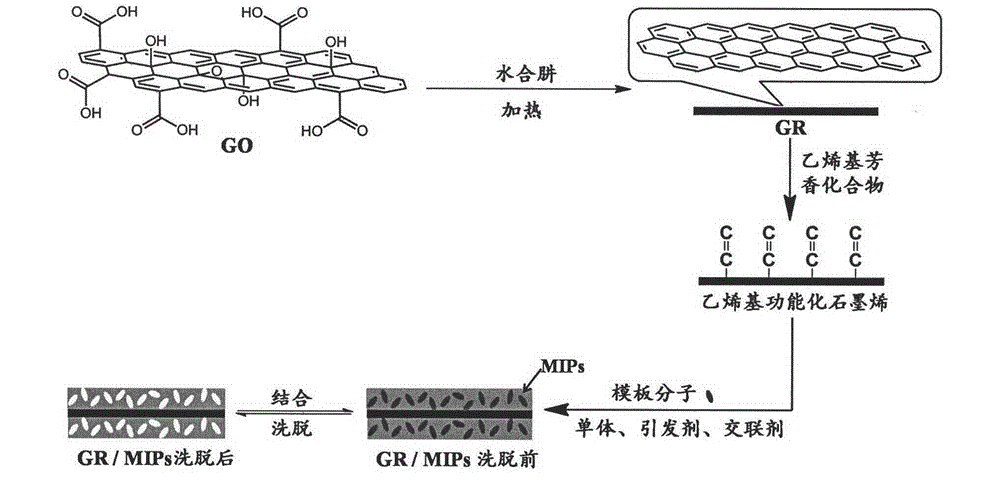
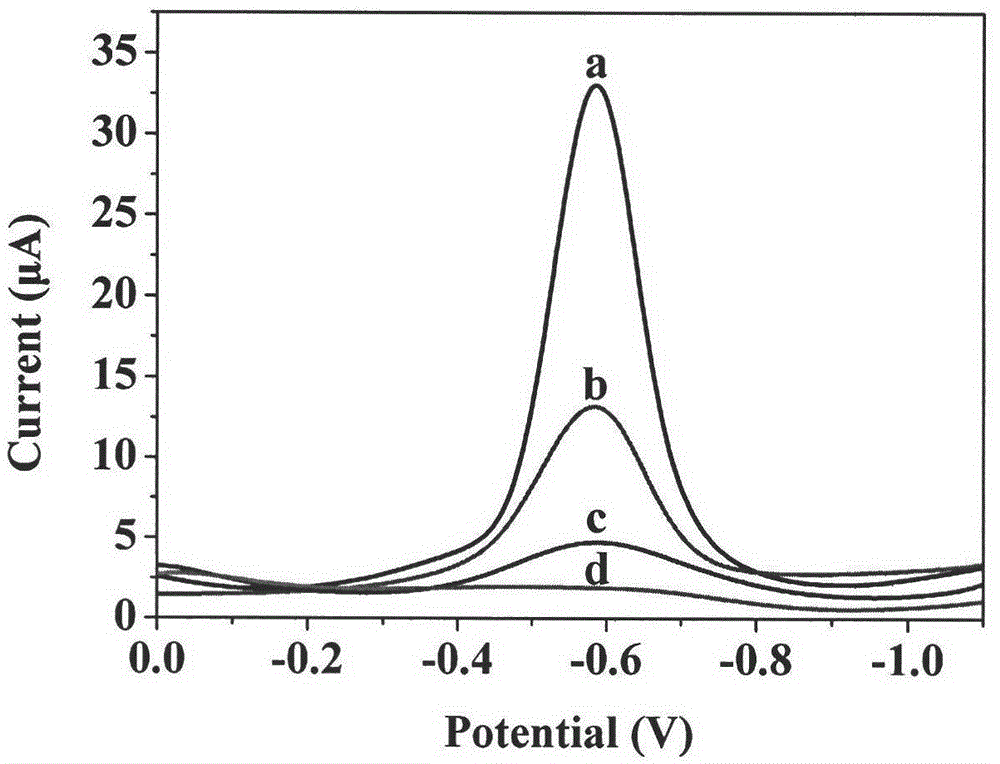
Electrochemical sensor based on graphene molecular imprinting material, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104374815AImprove conductivityLarge specific surface areaMaterial electrochemical variablesDispersityWorkstation
The present invention provides an electrochemical sensor based on a graphene molecular imprinting material, and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of polymer material science and chemistry sensor combination. According to the present invention, graphene and a vinyl aromatic compound form vinyl functionalized graphene through the non-covalent interaction, free radical copolymerization is performed to prepare a graphene molecular imprinting polymer (GR / MIPs), and the GR / MIPs modified electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode are connected on an electrochemical workstation to form the electrochemical sensor of the graphene molecular imprinting material; the graphene and the vinyl aromatic compound are only required to be mixed according to the ratio so as to obtain the vinyl functionalized graphene through the non-covalent interaction, such that the operation is simple, the conditions are mild, the structure of graphene is not destroyed, and the graphene dispersity is improved; and the electrochemical sensor based on the graphene molecular imprinting material has advantages of rapid response, good selectivity, high sensitivity, good stability and the like.
Owner:湖州度信科技有限公司
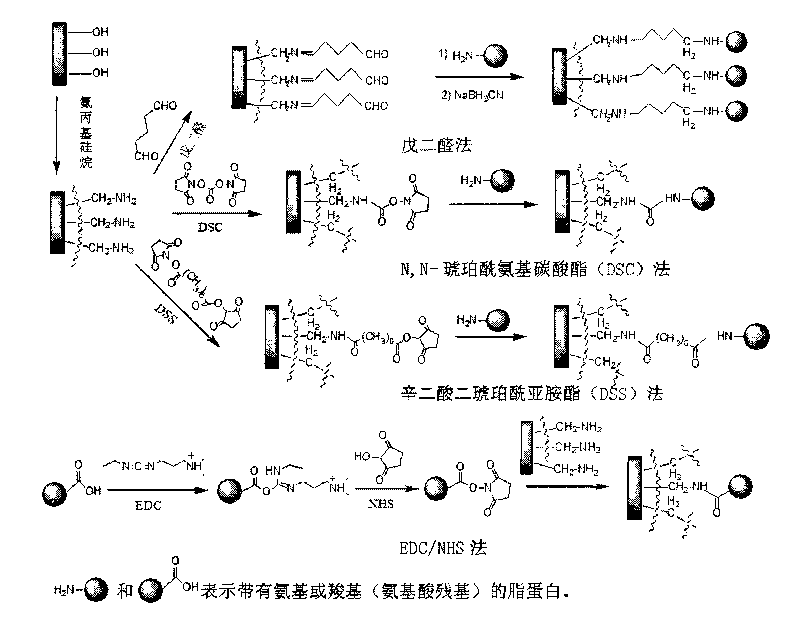
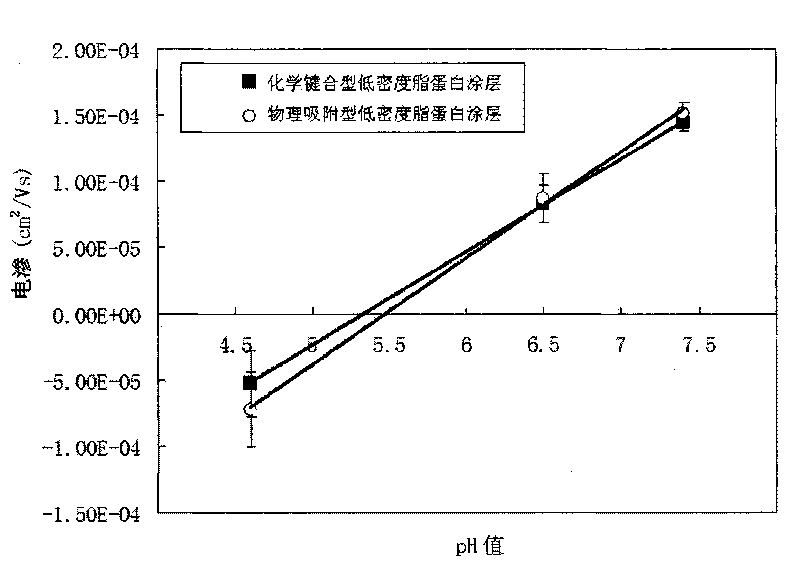
Lipoprotein capillary coating and the preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101750449ARetain activityGood biocompatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEthyl groupNon-covalent interactions
The invention relates to a lipoprotein capillary coating and the preparation method thereof. The coating can be prepared with the physisorphtion and chemical bonding methods. In the physisorphtion, a noncovalent interaction between lipoprotein solution with a concentration ranging from 0.01 to 10mg / ml and the internal wall of a capillary is performed and the lipoprotein solution is self-assembled to the internal surface to form the coating. In the chemical bonding method, the capillary is modified with aminopropyl siloxane and the amino is introduced and then the glutaraldehyde or N, N-DSS or 1-ethide-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)-carbodiimide / N-hydroxysuccinimide is used as the resin acceptor to covalently connect the amino on the capillary wall with the amino acid residues on the lipoprotein on the conditions of buffer solution with a pH ranging from 4 to 9 and lipoprotein with a concentration ranging from 0.1 to 10mg / ml for the purpose of obtain the lipoprotein coating. The coating preserves the biological activity, can be used for suppressing the absorption and electroosmotic adjustment on the surface of the capillary and also can be used for biochemical separation analysis.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coferons and methods of making and using them
ActiveUS20150105553A1Disrupt interactionModulate and inhibit protein-protein signalingSilicon organic compoundsSugar derivativesChemical compoundMolecular binding
The present invention is directed to a monomer useful in preparing therapeutic compounds. The monomer includes a diversity element which potentially binds to a target molecule with a dissociation constant of less than 300 μM and a linker element connected to the diversity element. The linker element has a molecular weight less than 500 daltons, is connected, directly or indirectly through a connector, to said diversity element, and is capable of forming a reversible covalent bond or non-covalent interaction with a binding partner of the linker element. The monomers can be covalently or non-covalently linked together to form a therapeutic multimer or a precursor thereof. Also disclosed is a method of screening for therapeutic multimer precursors which bind to a target molecule associated with a condition and a method of screening for linker elements capable of binding to one another. The present invention additionally relates to a therapeutic multimer, which includes a plurality of covalently or non-covalently linked monomers, therapeutic monomers, and uses of such dimers and monomers.
Owner:BLINKBIO INC
Reversibly, non-covalent bound surface coating
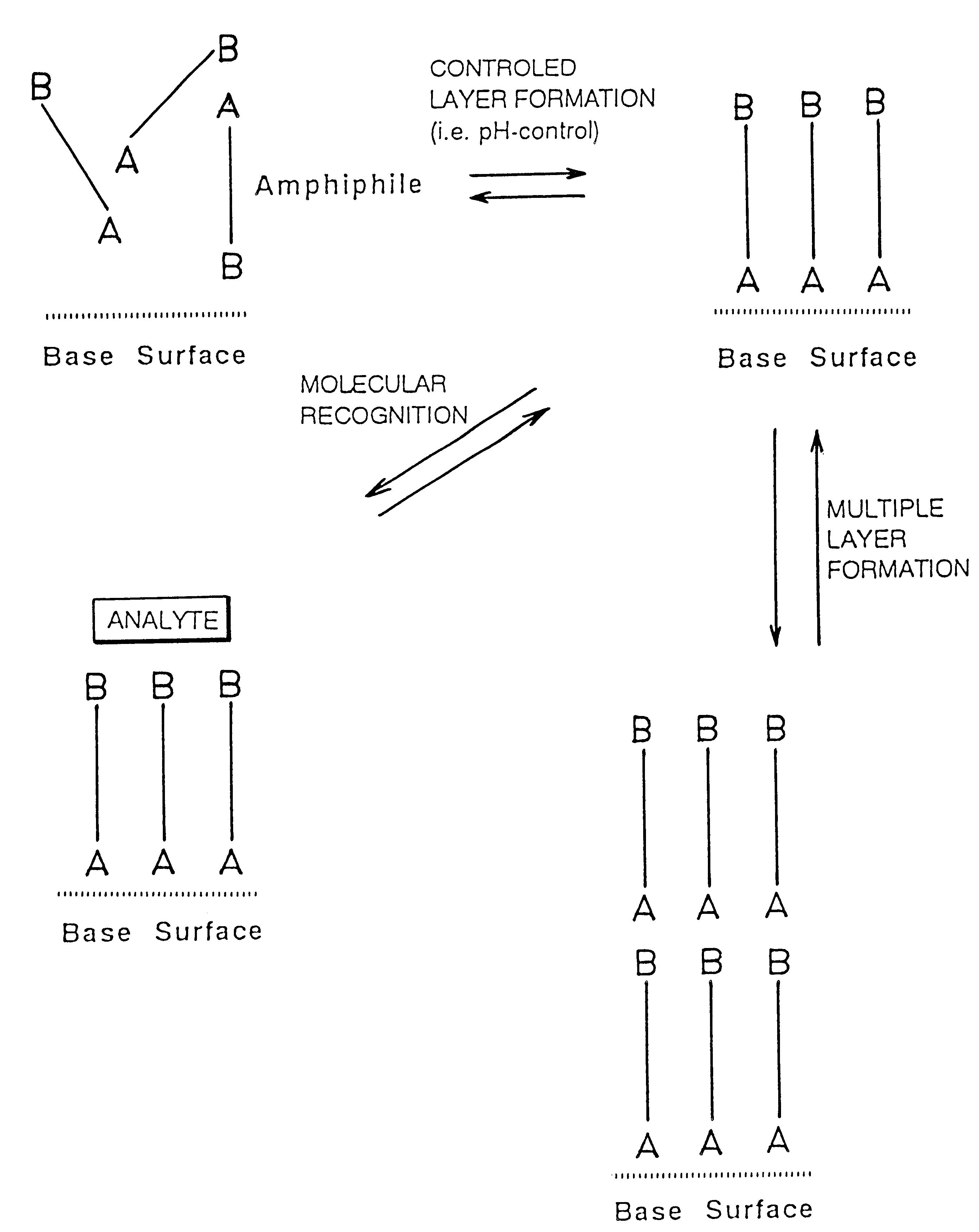
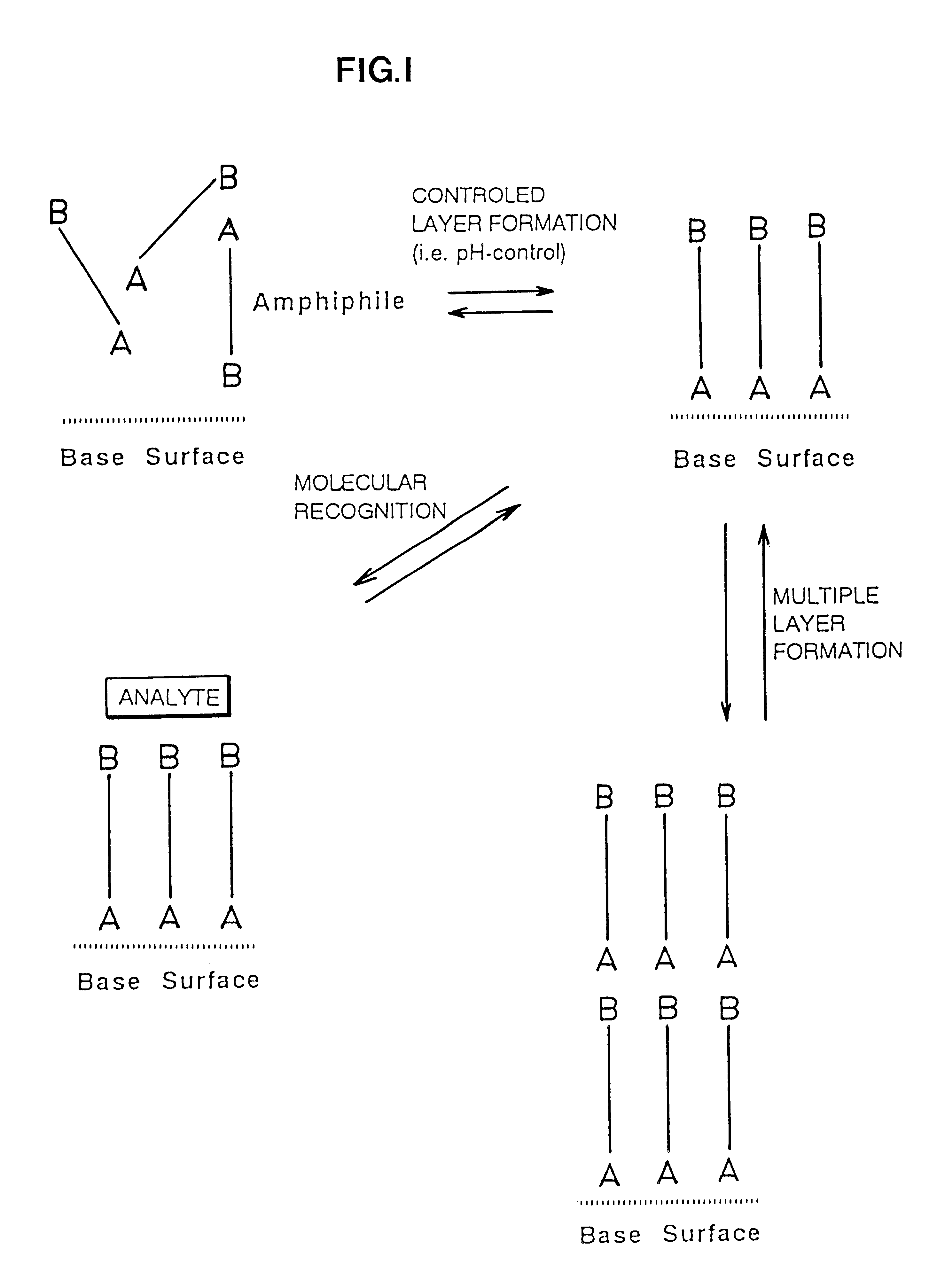
InactiveUS6444321B1Enhancing and inhibiting compatibilityEnhancing ingrowthMaterial nanotechnologyComponent separationAmphiphilePentamidine
A surface coating and its use in chemical analysis, electronics, and optoelectronics is disclosed. The surface coating is characterized in that it comprises an amphiphile reversibly bound to a substrate by non-covalent interaction, preferably by polar interaction. The amphiphile is a bolaamphiphile, such as pentamidine.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Selenium-based biocidal formulations and methods of use thereof
Biocidal formulations that include a selenium compound selected from the group consisting of RSeH, RSeR, RSeR′, RSeSeR, RseSeR′, and RseX, wherein each of R and R′ is an aliphatic or phenolic residue, and wherein X is a protecting group selected from the group consisting of a halogen, an imide, a cyamide, an azide, a phosphate, a sulfate, a nitrate, a carbonate, selenium dioxide, and combinations thereof, are provided. The selenium compounds may be disposed in a mixture or solution or deposited on a surface and non-covalently attached thereto, or the selenium compounds may be present in a suspension and maintained therein through non-covalent interactions. Methods for preventing growth of a species of interest on an object or in a composition are also provided.
Owner:SELENIUM
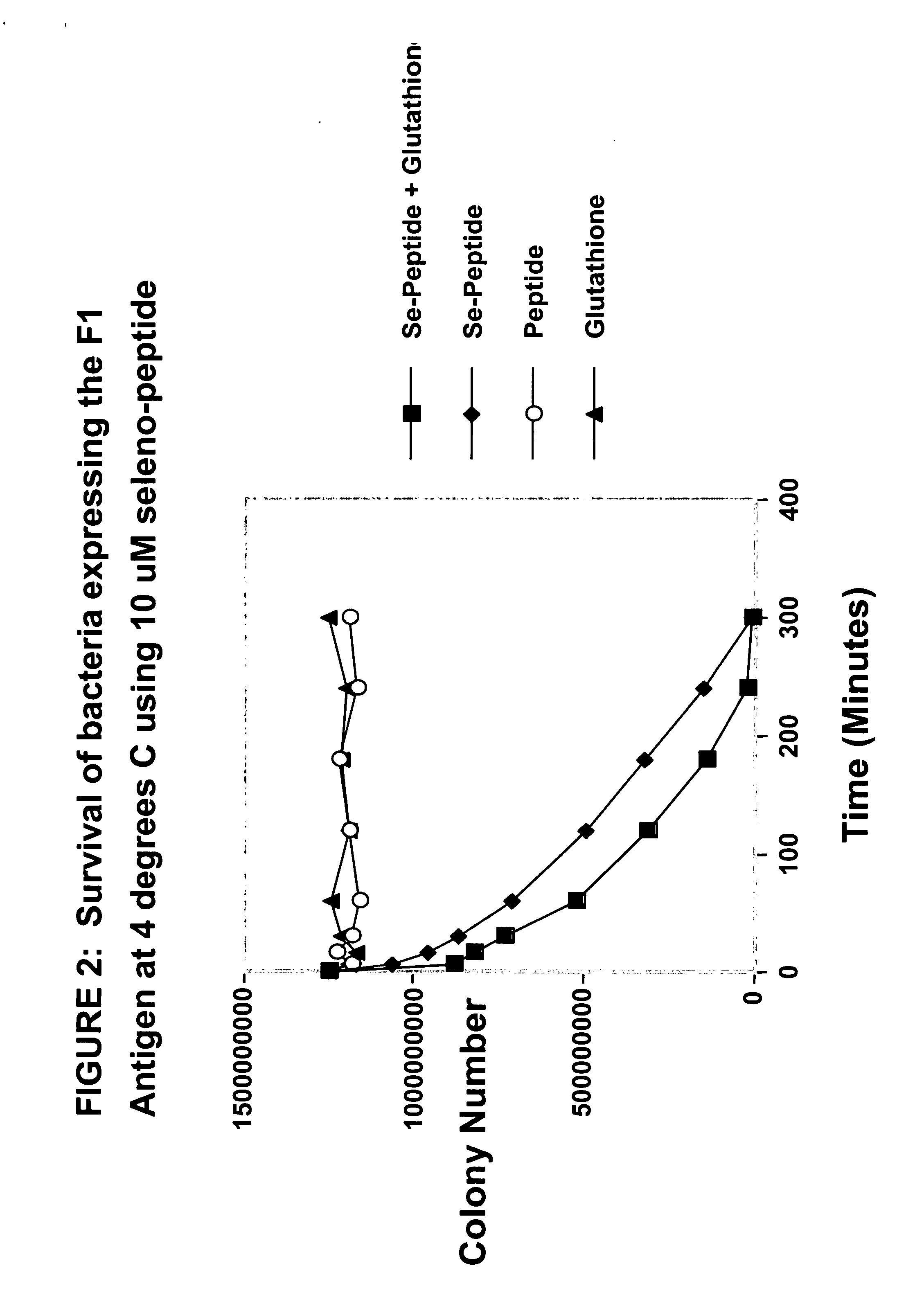
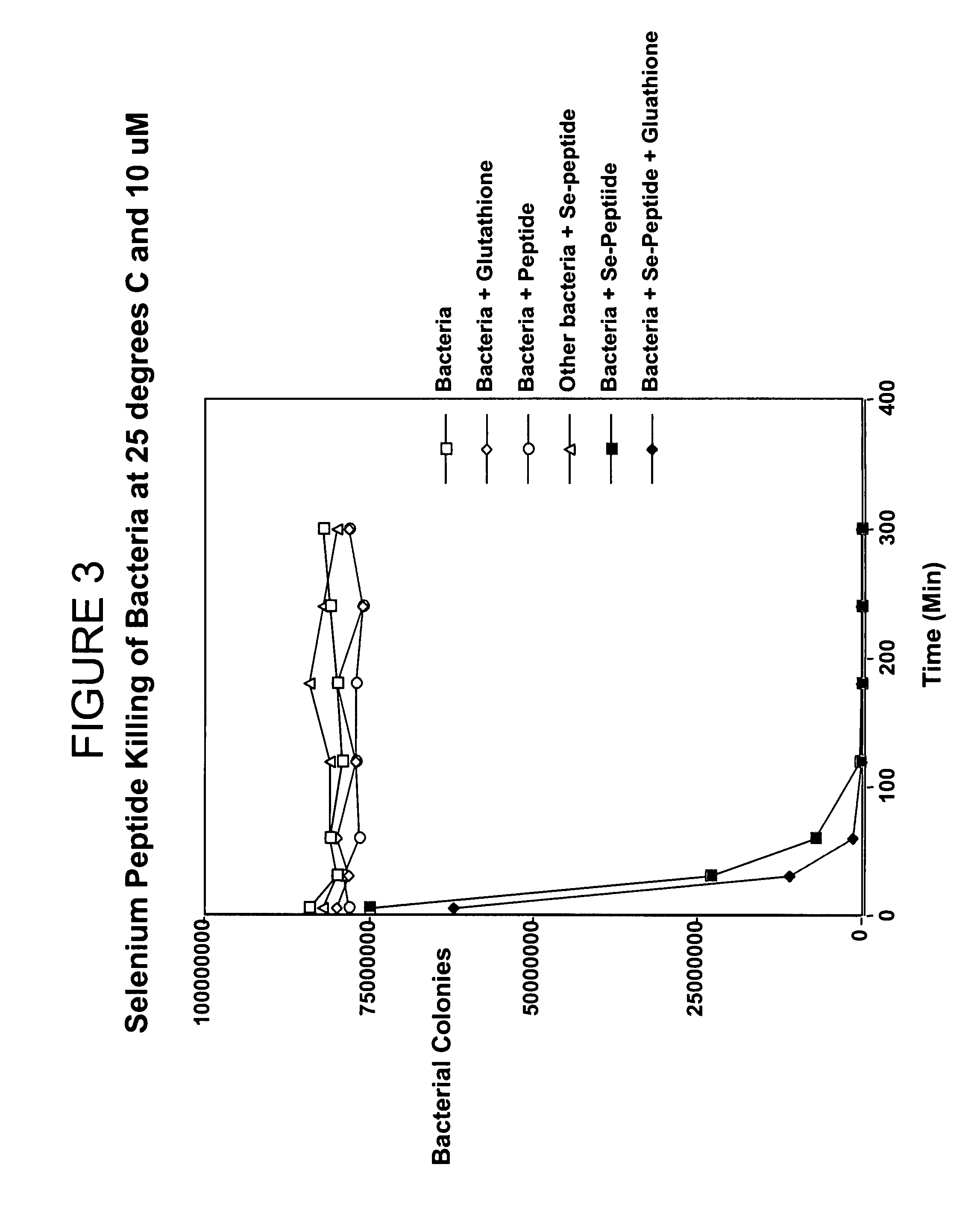
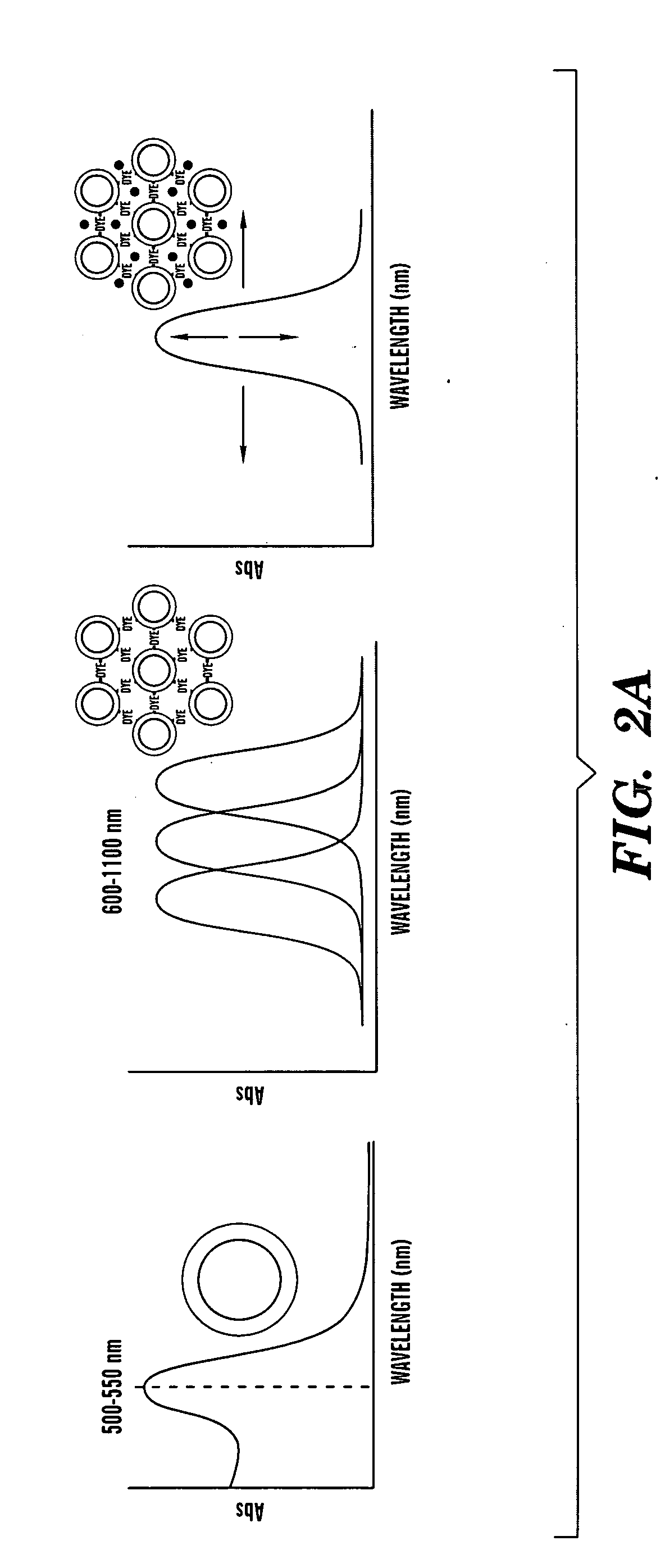
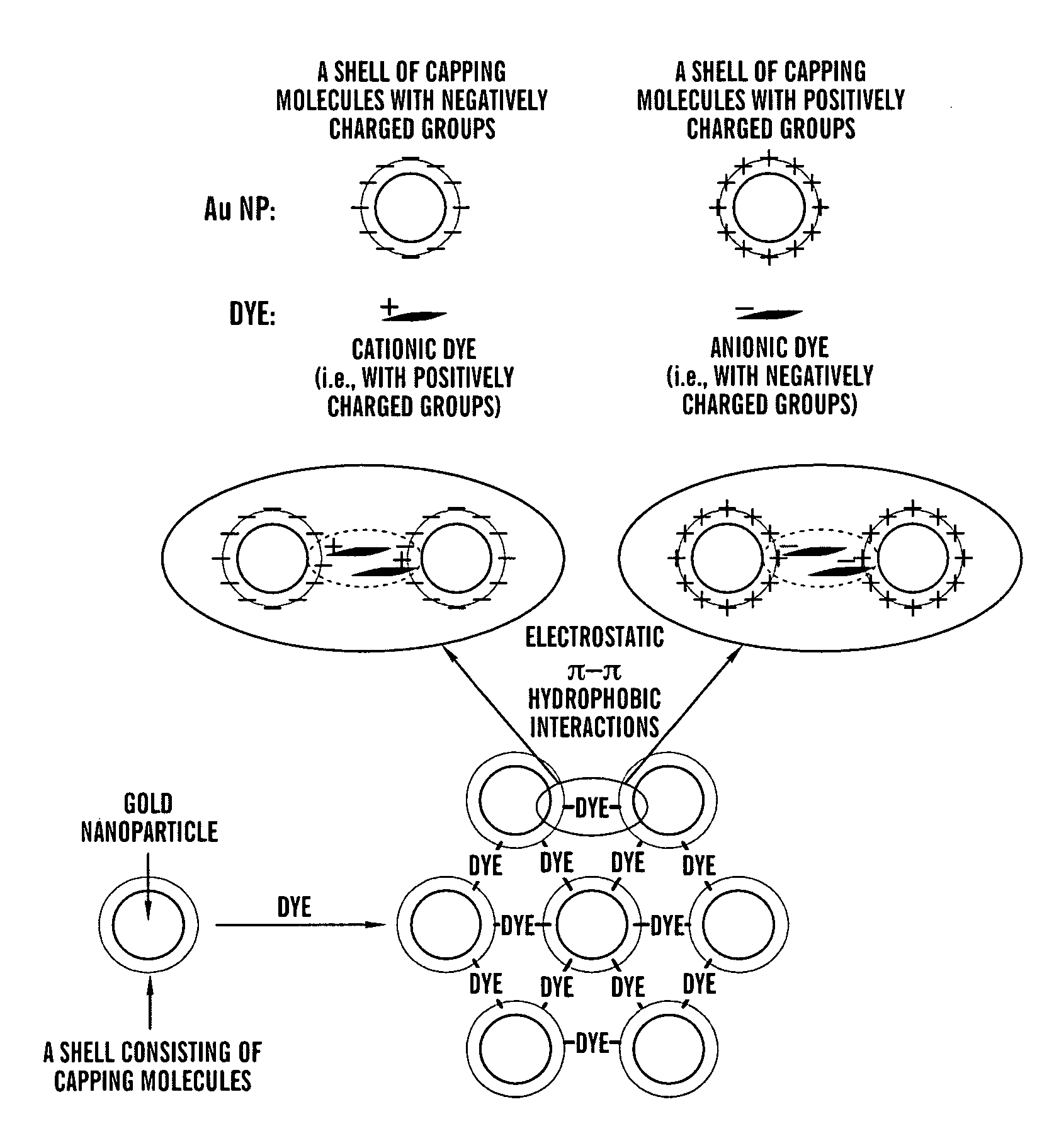
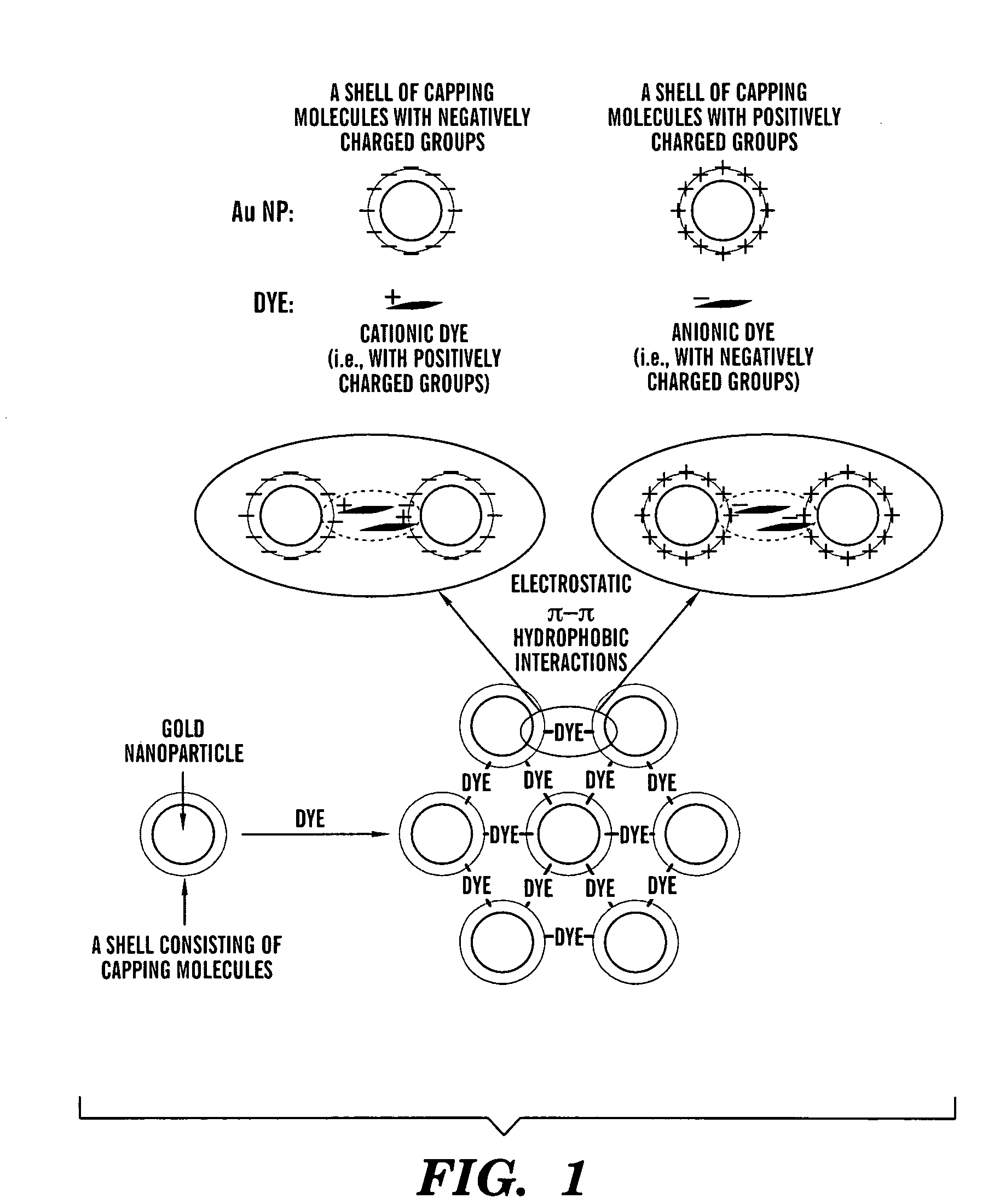
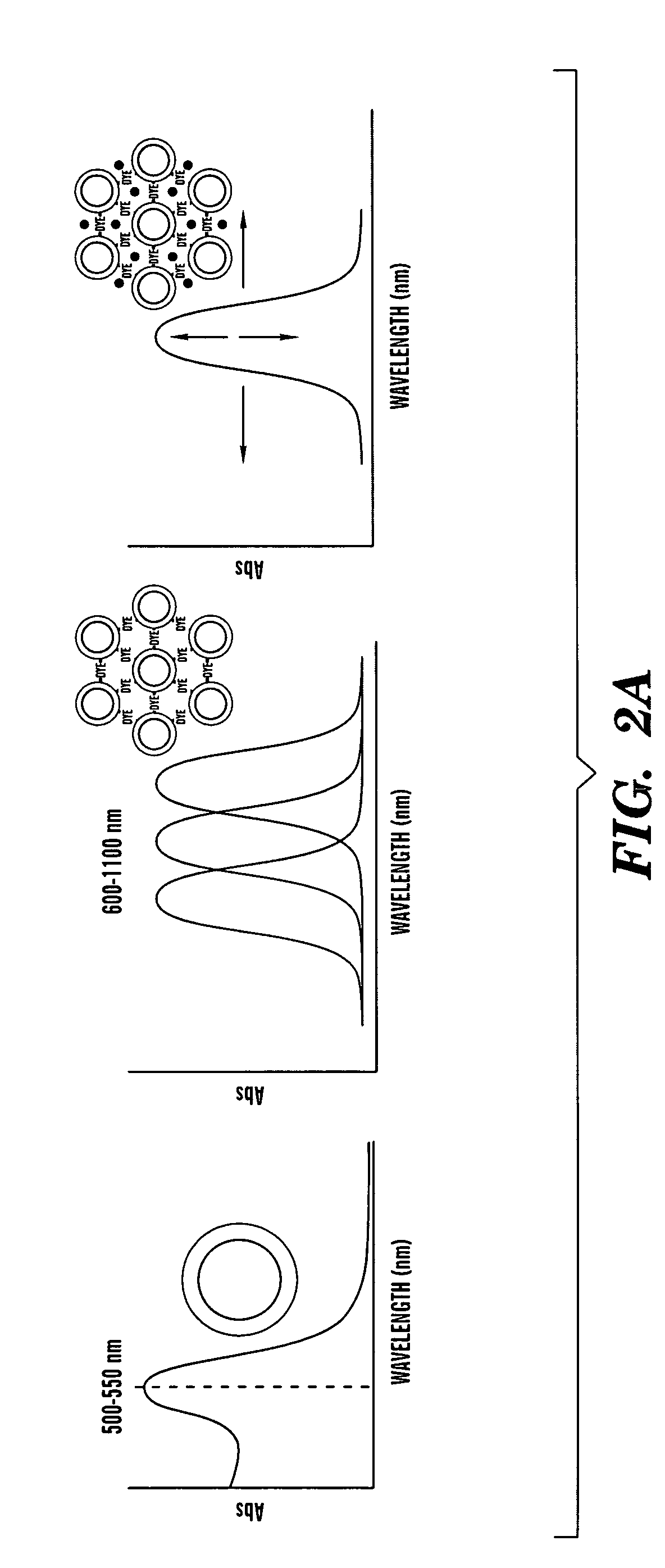
Aggregates of plural transition metal nanoparticles and plural cyanine dye molecules
InactiveUS20080316480A1Improve responseReduce concentrationMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryCyanineAnalyte
The present invention is directed to an aggregate composed of a plurality of nanoparticles of a transition metal and a plurality of cyanine dye molecules that are interacting non-covalently. The nanoparticles are capped with a capping molecule, while the cyanine dye molecule can be cationic, anionic, or neutral cyanine dye. Methods of making such aggregates and for using them in detection of an analyte are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Aggregates of plural transition metal nanoparticles and plural cyanine dye molecules
The present invention is directed to an aggregate composed of a plurality of nanoparticles of a transition metal and a plurality of cyanine dye molecules that are interacting non-covalently. The nanoparticles are capped with a capping molecule, while the cyanine dye molecule can be cationic, anionic, or neutral cyanine dye. Methods of making such aggregates and for using them in detection of an analyte are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Preparation method of membrane for supporting supermolecule ion liquid gel
InactiveCN103657441AImprove permeabilityEasy to separateSemi-permeable membranesDispersed particle separationNon-covalent interactionsTransmembrane pressure
The invention relates to a preparation method for a membrane for supporting supermolecule ion liquid gel, and belongs to the technical field of membrane separation. The membrane consists of porous membrane loaded supermolecule ion liquid gel with the mass accounts for 30%-80% of the total mass of the gel support membrane, wherein the porous membrane is a macromolecule microporous membrane, and has the thickness of 100-200 microns; the supermolecule ion liquid gel is formed by gel factors in an ion liquid by self-assembling and gathering under non-covalent interaction; the mass of the ion liquid accounts for 70%-95% of the total gel mass of the gel. The membrane for supporting the supermolecule ion liquid gel, which is prepared by adopting the method disclosed by the invention, not only has high gas permeation flux and large gas separation factors, but also can prevent the liquid leakage under a relatively high transmembrane pressure, can intensify the performance stability, and prolong the service life. The prepared membrane for supporting the supermolecule ion liquid gel is mainly applied to the fields of acid gas collection of industrial emitted gases, CO2 separation in enclosed cabins of spacecrafts, submarines and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
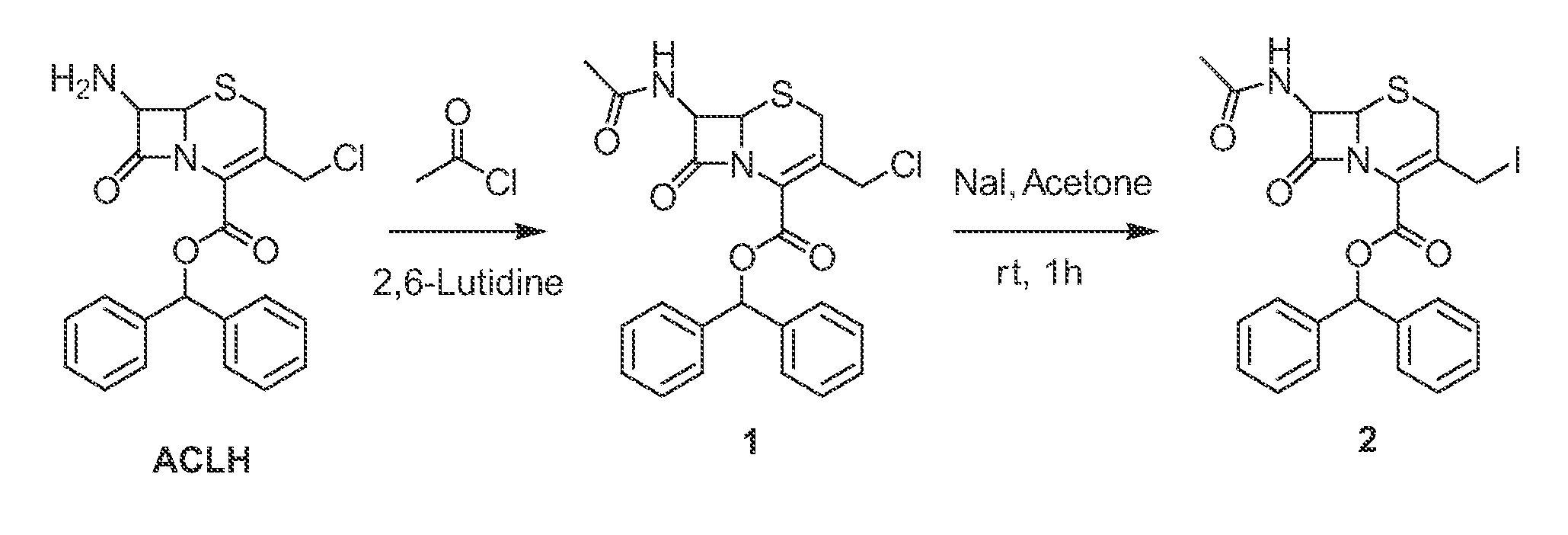
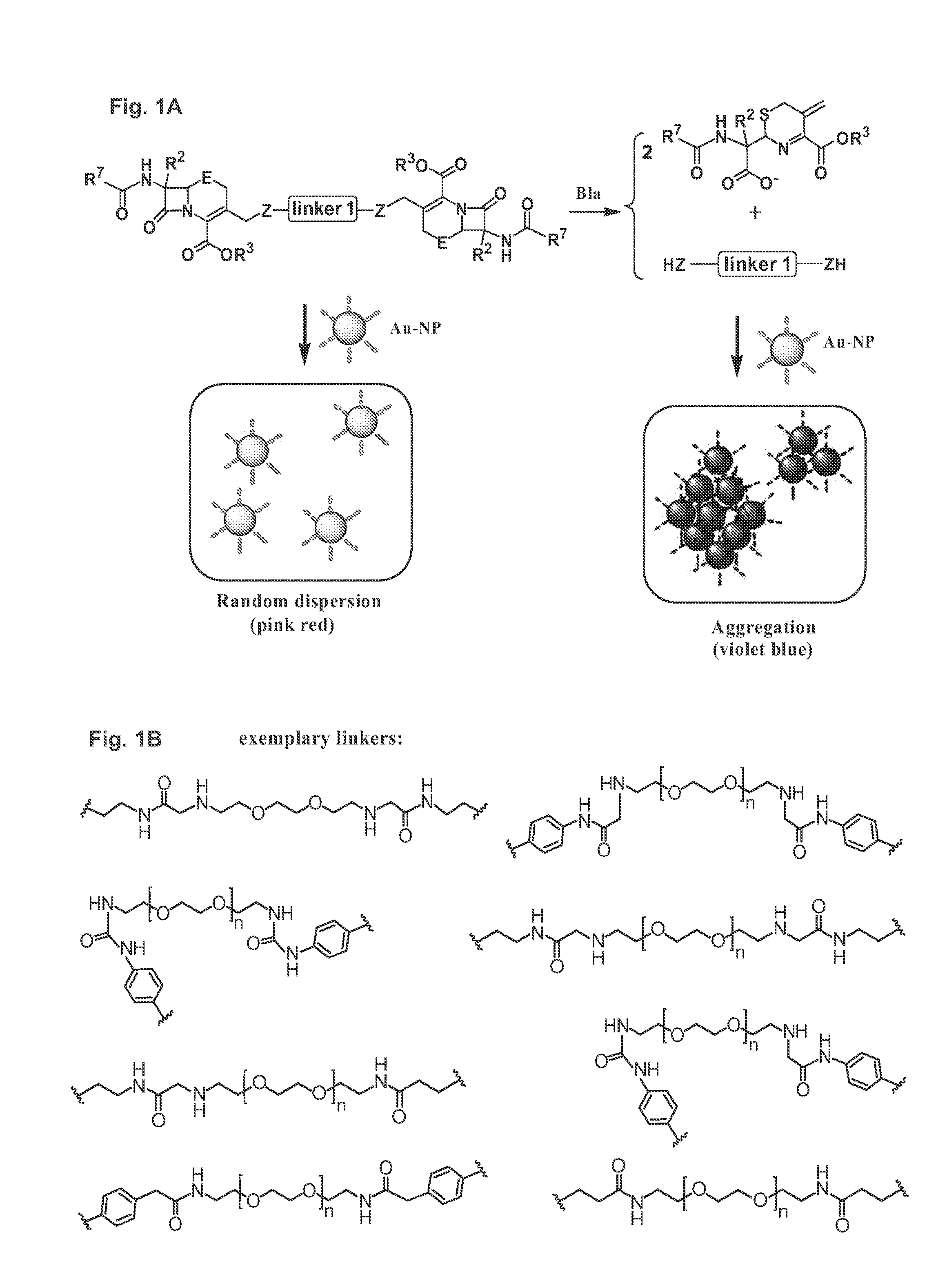
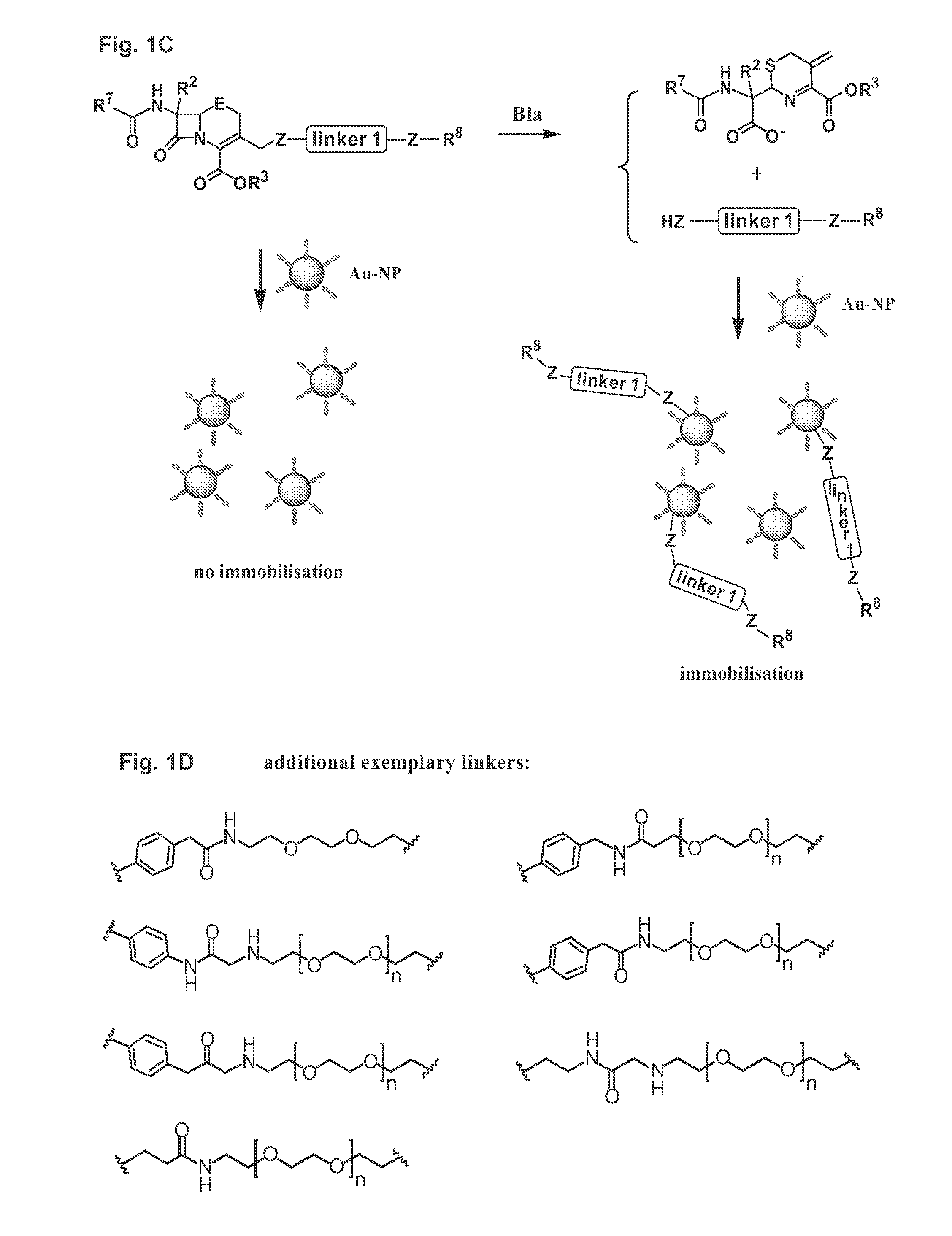
Methods and compounds for detecting beta-lactamase activity
ActiveUS20090275065A1Easy to operateOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementThio-Nanoparticle
The present invention relates to compounds for and a method of detecting beta-lactamase activity in a sample. The sample is contacted with a nanoparticulate tag. The nanoparticulate tag comprises a metal or a combination of metals, or it comprises a nanotube of a metal, boron nitride and / or carbon. The respective metal is capable of forming one of a covalent bond, a coordinative bond and a non-covalent interaction with a thio or a seleno group. The sample is contacted with a compound of one of general formulas (I)-(III) and (VII)-(IX). At least one beta-lactam moiety of the compound is cleaved by the beta-lactamase activity in the sample. As a result a cleavage moiety Z-A-Z, Z-A-Z-R15, Z-A-Z-R16, Z-A-Z-R17, Z-A-Z-R18 or Z-G-N(R8)R9 is released that is immobilised on the surface of the nanoparticulate tag by a covalent bond via a Z atom. The presence of beta-lactamase activity is determined based on the presence of the cleavage moiety immobilized onto the surface of the nanoparticulate tag.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Graphene loaded Co-N-C super-molecule hybrid aerogel composite material, preparation method thereof and application
The invention discloses a graphene loaded Co-N-C super-molecule hybrid aerogel composite material which is provided with a three-dimensional porous network-like structure. According to the composite material, the graphene serves as a base, and a Co-N-C active catalysis center is loaded on the graphene base and formed by assembling pyridine-tryptophan gelators, cobalt ions and the graphene base through non-covalent interaction. The composite material is remarkable in oxygen reduction reaction catalysis function and good in stability, electrical property and methanol toxicity resistance. The current density of the composite material can reach 4mA / cm<2>, oxygen reduction take-off potential is about -0.07V, peak potential is about -0.175V, and catalysis effects are comparable with commercial platinized carbon. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the composite material. The pyridine-tryptophan gelators, soluble cobalt salt and the graphene serve as raw materials, the composite material is prepared by hydrothermal reaction, vacuum freeze drying and carbonization treatment, and the preparation method is simple and low in production cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composition for polymer gel, gel prepared from composition and application of gel
ActiveCN112341637AGood anti-swelling performanceExcellent underwater bonding performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusInksPolyelectrolytePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer gel materials, and provides a composition for polymer gel, gel prepared from the composition and application of the gel. The composition comprises a polymer compound, a first solvent and a second solvent, wherein the polymer compound comprises but is not limited to at least one of the following substances: a polymer with a hydrogen bond effect, a polymer with a hydrophobic effect and a charged polyelectrolyte; in the first solvent, the non-covalent interaction in / among the high-molecular compounds is in a weakening shielding state; in thesecond solvent, the non-covalent interaction between the polymer compounds is activated and enhanced. The polymer gel prepared by the invention has high transparency, excellent mechanical properties,swelling resistance and icing resistance.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Supermolecular assembly for small interfering RNA targeting delivery and preparation method
InactiveCN104840975AAvoid decomposition and inactivationImprove gene transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
The invention relates to a supermolecular assembly for small interfering RNA targeting delivery. The supermolecular assembly is a four-element supermolecular assembly synthesized on the basis of beta-cyclodextrin modified hyaluronic acid, an adamantine polyamine compound, cucurbituril [6] and small interfering RNA. The four-element supermolecular assembly is based on the strong non-covalent interaction between beta-cyclodextrin and adamantine and between adamantine polyamine chain and cucurbituril [6], and the electrostatic interaction between the adamantine polyamine chain and small interfering RNA, and forms supermolecular nanoparticles with hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as the shell. The supermolecular assembly provided by the invention has the advantages of simple synthesis and construction route, low production cost and high yield, and is suitable for amplified synthesis and actual production application. Through the endocytosis of a malignant tumor cell surface overexpressed hyaluronic acid receptor as a medium, the four-element supermolecular assembly can be brought into cancer cells targetedly, thus realizing effective silencing to exogenous gene expression and significantly reducing the toxic and side effect at the same time.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Modular aptametric sensors without covalently attached fluorophores
InactiveUS20060172320A1Improve abilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processAptamerAnalyte
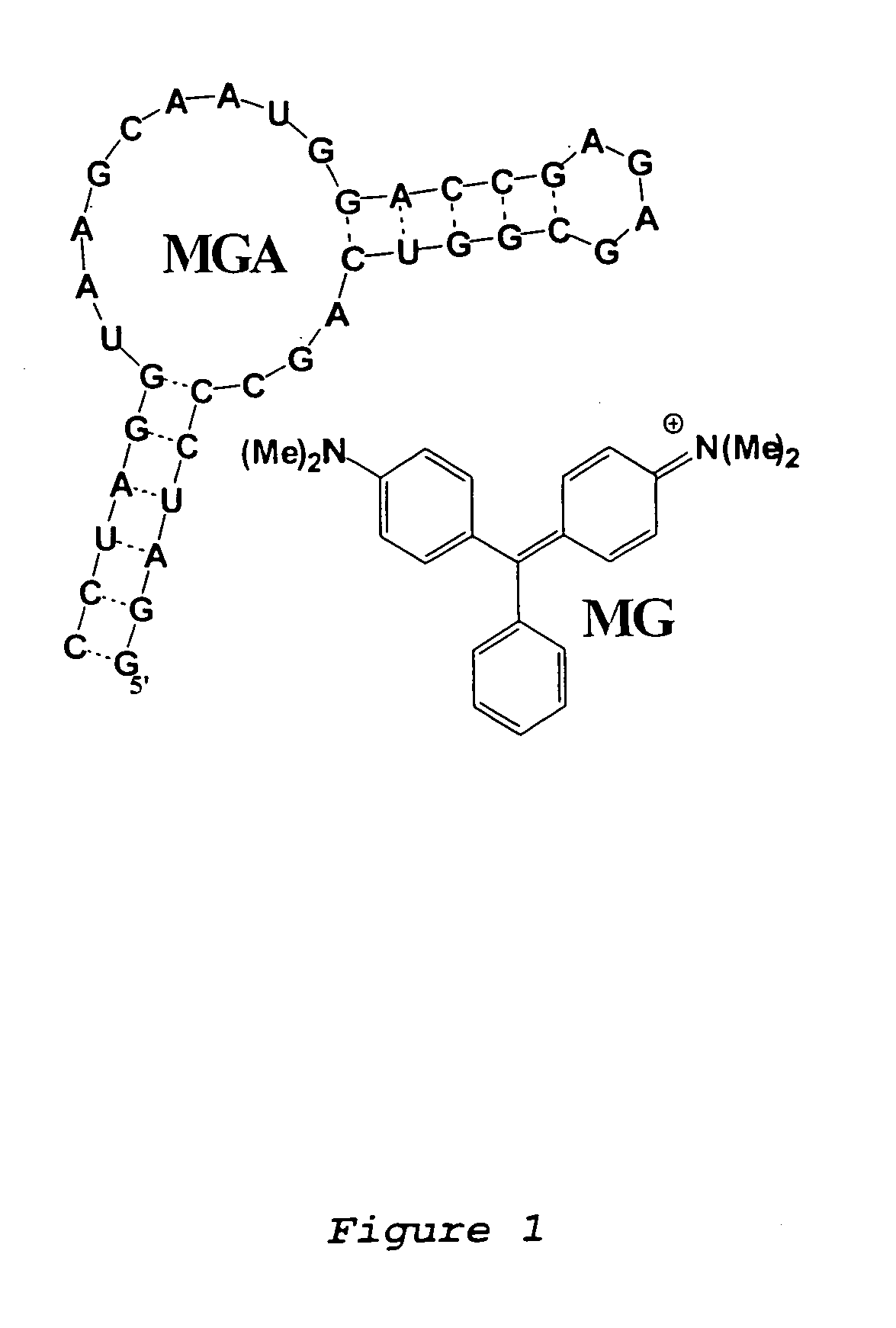
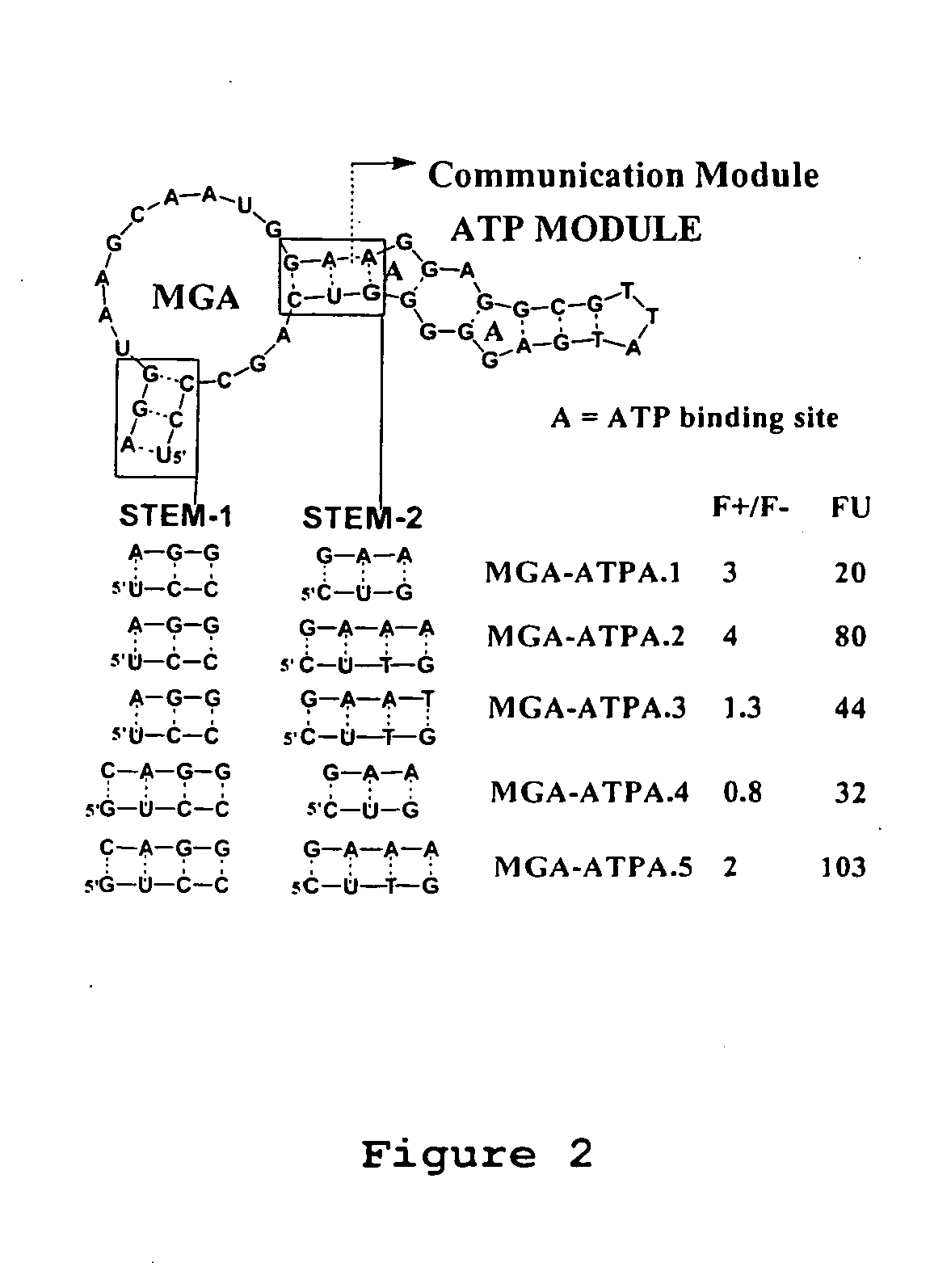
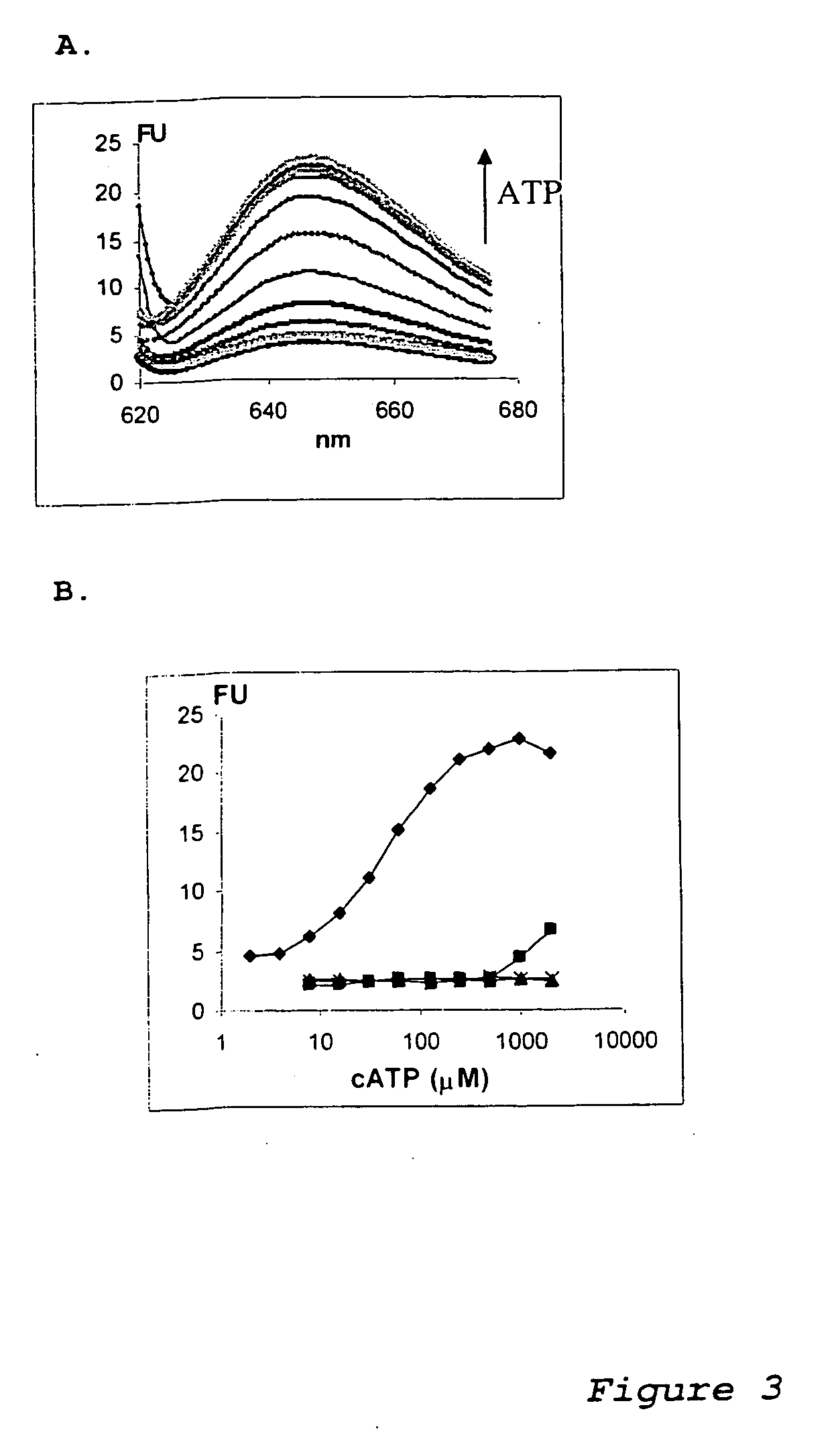
Modular aptameric sensors, transduce recognition events into fluorescence changes through allosteric regulation of non-covalent interactions with a fluorophore. These sensors consist of: (a) a reporting domain, which signals the binding event of an analyte through binding to a fluorophore; (b) a recognition domain, which binds the analyte; and (c) a communication module, which serves as a conduit between recognition and signaling domains. We tested recognition regions specific for ATP, FMN and theophylline in combinations with malachite green binding aptamer as a signaling domain. In each case, we obtained a functional sensor capable of responding to an increase in analyte concentration with an increase in fluorescence. Similar constructs that consist only of natural RNA could be expressed in cells and used as sensors for intracellular imaging.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Active supramolecular polymer and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a supramolecular polymer with an active characteristic. The supramolecular polymer is prepared by the polymerization of two-component supramolecules consisting of planar or linear small-molecular components and a polymer component. The small-molecular components are solvophobic, and can be connected with each other through non-covalent interactions such as metal-metal action, pi-pi action, hydrogen bonds, mutual interaction of solvophobic agents (hydrophobicity), and the like under the regulation and control of the polymer component to form the supramolecular polymer. The polymer component is a hydrophilic solvent and is combined with the small-molecule components through non-covalent interactions such as electrostatic attraction and the like, so that an effect of stabilizing the supramolecular polymer is achieved. The chemical composition, the nanostructure and the size of the supramolecular polymer can be modulated through the chemical component of the small-molecular components, the chemical component and structural parameters of the polymer, the formula, the interaction between the small-molecular components and the polymer component, and the like. The formed two-component or multi-component supramolecular polymer has active terminals, and the newly added planar or linear small-molecular components can continue growing at the active terminals. The invention also provides a method for the polymerization of active supramolecules of a two-component or multi-component system.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
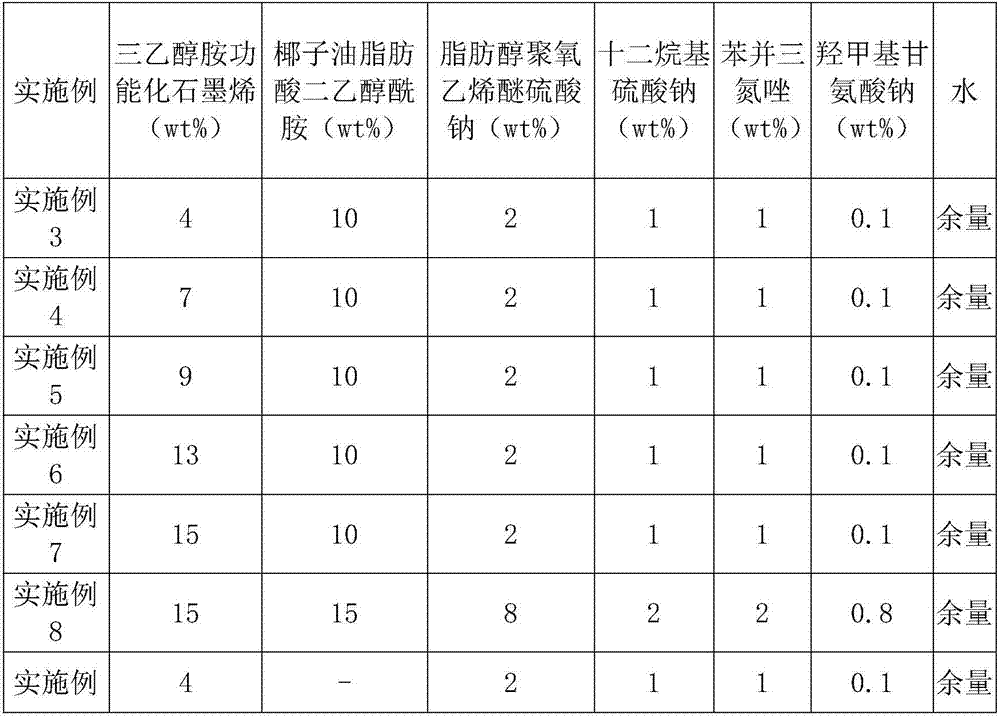
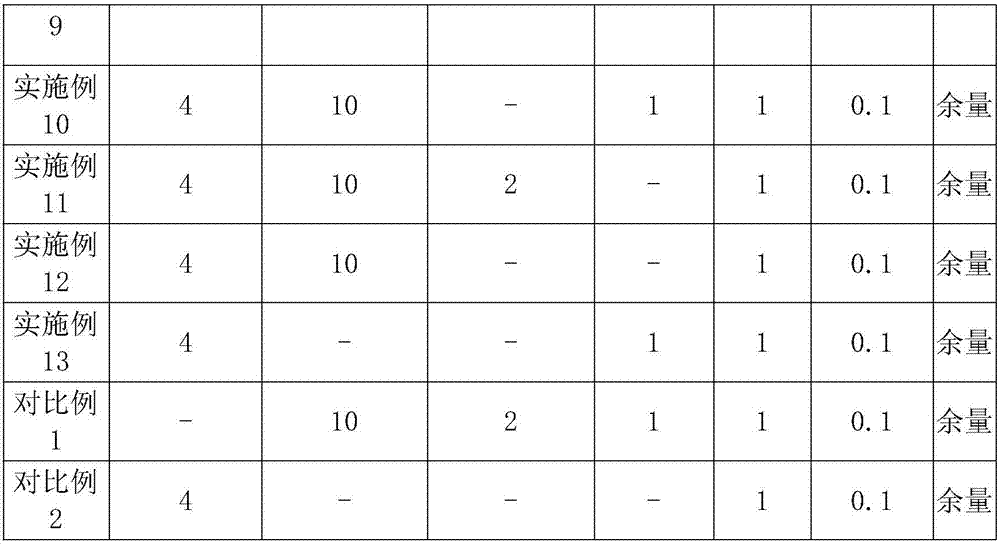
Metal cleaning agent added with functional modified graphene and preparing method of metal cleaning agent
The invention relates to a metal cleaning agent, and discloses a metal cleaning agent added with functional modified graphene and a preparing method of the metal cleaning agent. The metal cleaning agent is composed of 4-15wt% of triethanolamine functional graphene, 13-25wt% of surfactant, 1-2wt% of metal corrosion inhibitor, 0.1-0.8wt% preservative and the balance water. According to the metal cleaning agent, the triethanolamine functional graphene is creatively used to be added into the metal cleaning agent, triethanolamine of the triethanolamine functional graphene and the graphene are bonded as covalent bond, and the surface of the metal cleaning agent contains a large amount of tertiary amine nitrogen and hydroxyl active functional groups; and amino ionic liquid functional graphene achieves graphene modification through the non-covalent interaction between imidazole rings and graphite rings, the graphene has the super large specific surface area, the strong complexing effect is achieved after the grapheme and the triethanolamine are functionalized, so that the strong adsorption capacity is achieved, the hydrophilic and lipophilicity of the triethanolamine are retained, the strong adsorption capacity also can be achieved, and the metal cleaning agent is used without matching of an additional complexing agent.
Owner:郴州国盛新材科技有限公司
Acid choline biomimetic polymers coated carbon-nano tube and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101181989ANon-covalently stableEasy to operateNanostructure manufactureDispersion stabilityPhosphorylcholine
The invention discloses a carbon nano-tube covered by phosphorylcholine base biomimetic polymer and a preparation method thereof. The invention utilizes phosphorylcholine amphiphilic polymer comprising a hydrophobic segment to carry out non-covalent coverture of the carbon nano-tube, uses the hydrophobic segment to carry out non-covalent interaction with the carbon nano-tube and uses the phosphorylcholine to improve dissolubility, dispersion stability and blood compatibility of the carbon nano-tube in water. The method uses the phosphorylcholine amphiphilic polymer comprising the hydrophobic segment, the carbon nano-tube and water as raw materials and obtains the carbon nano-tube covered by the phosphorylcholine base biominetic polymer by assistance of ultrasonic dispersion and centrifugal method. The invention has simple technique and good stability, and the dissolubility of the prepared water-soluble carbon nano-tube reaches as high as 3mg / mL, thus having considerable application prospect in the field of drug delivery, gene transmission, molecular diagnosis and detection, separation of biomolecules, biosensor, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103205824AImprove thermal stabilitySimplified post-processing stepsConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsFilament/thread formingFiberDesorption
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of functional fiber materials. The cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber is prepared by following compositions, by mass, 10-100 parts of cyclodextrin or cyclodextrin derivatives, 20-200 parts of phase change substances and 20-100 parts of cellulose polymer through the electrostatic spinning technology, and can be applied to fields of biomedical materials, separating adsorption materials, energy-saving heat-insulating materials and the like. A supermolecular composite fiber is formed by cyclodextrin and phase-change work components through hydrogen bond and other non-covalent interaction, and the phase change substances are enabled to be less prone to desorption from the cellulose polymer while the obtained energy-storage superfine fiber does not need posttreatment processes like surface crosslinking, so that improvement of heat stability of the materials and simplification of preparation process are facilitated. The main raw materials are natural or seminatural products, so that the cyclodextrin supermolecular composite phase-change energy-storage superfine fiber is good in biocompatibility, nontoxic and harmless, easy to degradation, low in cost and environment-friendly.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Ordered polymer system and intraocular lens
An intraocular lens with an ordered polymer system contained within a lens capsule or a membrane in the lens capsule. The ordered polymer system includes at least one negatively charged copolymer comprising hydrophilic groups, anionic groups and hydrophobic groups, and at least one positively charged copolymer comprising hydrophilic groups, cationic groups and hydrophobic groups. The at least one negatively charged copolymer and the at least one positively charged copolymer are associatively arranged through non-covalent interactions in the lens capsule or the membrane.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Detection of polyamino acids using trimethincyanine dyes
InactiveUS20060207881A1Easy and safe and economical to synthesizeRapid time periodSludge treatmentMethine/polymethine dyesCovalent InteractionNon-covalent interactions
The present invention is generally directed to a method for detecting polyamino acids. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a method for detecting polyamino acids using trimethincyanine dyes that interact non-covalently with polyamino acids to produce an optically detectable dye / polyamino acid complex.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Compositions and methods relating to living supramolecular polymerization and polymers
ActiveUS20170267837A1Good flexibilityMaterial nanotechnologyMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentHydrogenSolvent
A supramolecular polymer with living characteristics is provided based on small molecules or metal complexes of a planar or linear geometry and a polymer. The small molecules are solvophobic and can associate or assemble with each other through non-covalent interactions such as but not limited to metal-metal, π-π, hydrogen-bonding, and / or solvophobic-solvophobic interactions, in the modulation of the polymer. The polymer has affinity to the medium (e.g., solvent) and still interacts with the small molecules via non-covalent interactions such as electrostatic attractions to stabilize the associated / assembled small molecules. Varying the composition and / or length of the polymer can modulate the dimensions of the supramolecular polymer and the nanostructures therefrom. The two- or multi-component supramolecular polymer has active ends to support further supramolecular polymerization upon addition of small molecules of a planar or linear geometry. A process of two-component living supramolecular polymerization is also provided.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Preparation method for PtAuNPs-CTAB-GR modified glassy carbon electrode
InactiveCN104535633ASensitive detectionEasy to makeMaterial electrochemical variablesDispersityNon-covalent interactions
The invention provides a preparation method for a PtAuNPs-CTAB-GR modified glassy carbon electrode. The preparation method comprises: firstly preparing functionalized graphene oxide from graphene oxide and cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) under the non-covalent interaction, then directly adding chloroplatinic acid and chloroauric acid into the solution, and using NaBH4 to perform reduction to obtain the bimetallic PtAuNPs-CTAB-GR nanometer composite material. The net-structure graphene oxide provides more active sites for supporting a platinum-gold nanoparticle, and enables the platinum-gold nanoparticle to have relatively small dimension and relatively good dispersity. By combining advantages of graphene and PtAuNPs, the obtained modified glassy carbon electrode has extremely good electric catalytic activity on H2O2, and has the characteristics of high sensitivity, low detection limit and wide linearity scope.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com