Protein surface molecular imprinting material based on RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer) strategy as well as preparation method and application thereof
A surface molecular imprinting and protein technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of protein spatial conformation changes, difficult imprinting sites, etc., and achieve excellent selective recognition ability, fast mass transfer rate, The effect of good hydrophilicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] 1. Preparation of lysozyme surface imprinted material based on RAFT method
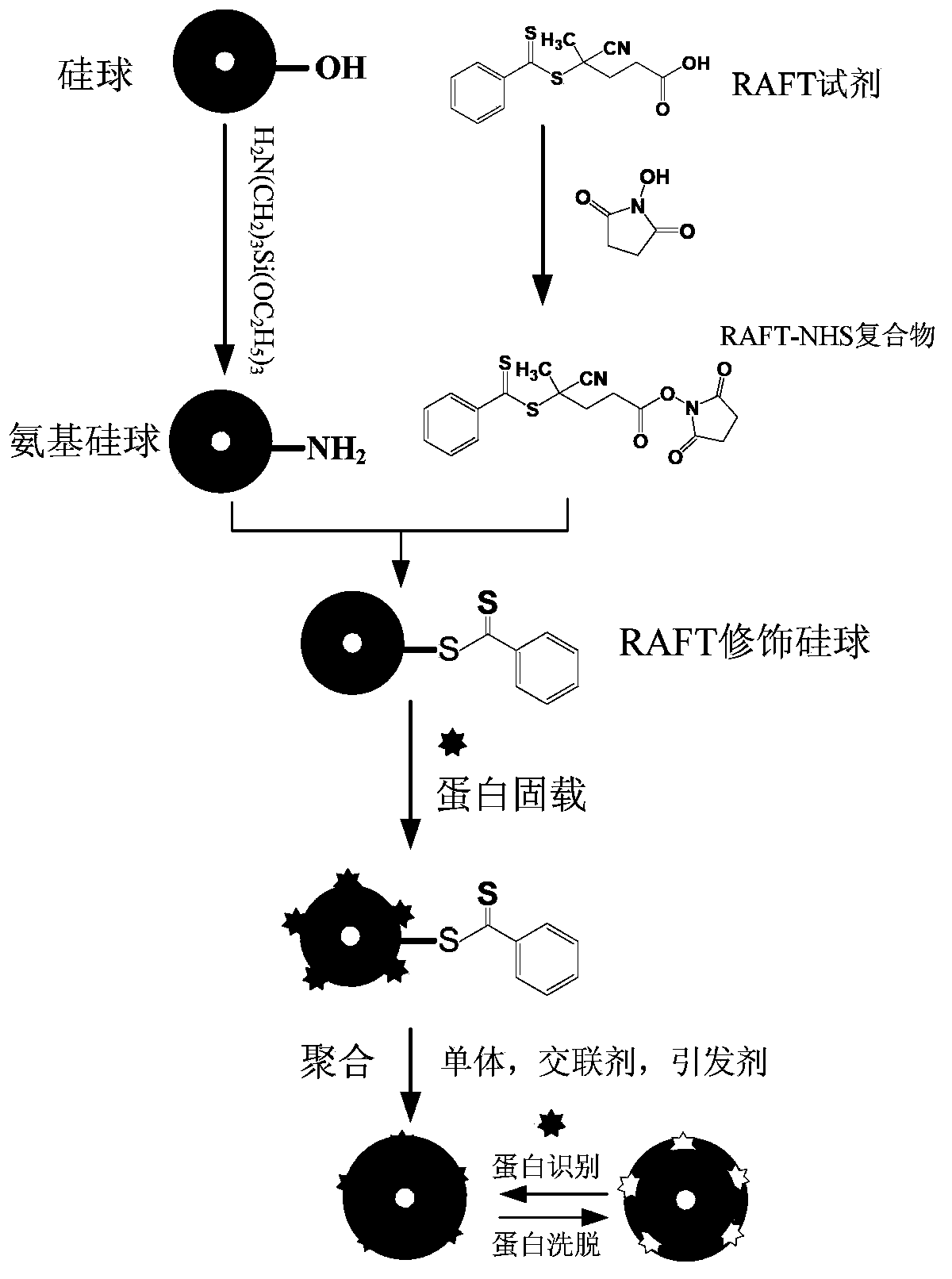
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is prepared according to the following process:
[0046] 1) Preparation of silica gel particles modified by RAFT reagent: firstly, amino groups are modified on the silica gel surface through silanization reaction of aminopropyltriethoxysilane on the surface of silica gel particles, and 100 mg of silica gel particles and 2.0 mL of methanol are added to each batch, and fully homogenized Afterwards, 50 μL of aminopropyltriethoxysilane was added, shaken and mixed, and reacted for 24 hours. Weigh 46.17mg of EDC, 22.60mg of NHS, 45.50mg of dithioester reagent 4-cyano-4-(phenylcarbonothioylthio)pentanoic acid (CPCP), add 30mL of ethanol to fully dissolve, weigh 400mg of dried amino silicon spheres, homogenate For the sealing reaction, the reaction temperature is 25° C., and the reaction time is 18 hours. After the reaction, wash with acetonitrile, ethanol, and w...
Embodiment 2
[0055] In order to investigate the adsorption capacity and kinetic characteristics of the lysozyme surface imprinted materials prepared above based on the RAFT method, the adsorption capacities of MIP1 and NIP1 materials to template proteins were measured at different adsorption times. The protein concentration in the solution was determined by chromatography. The specific measurement steps are as follows: take MIP1 and NIP1 materials respectively, 10 mg each, add 0.50 mL of 0.40 mg / mL lysozyme, and statically adsorb at 4 ° C for 1, 5, 15, 30 and 60 minutes, and then centrifuge to remove the upper Wash the supernatant solution twice with 1.0mL 40% acetonitrile to remove the remaining monomer and cross-linking agent, and then use 0.5mL eluent (20% formic acid + 40% acetonitrile + 40% water, v / v) to elute the template protein After 10 min, the protein concentration in the eluate was determined by HPLC. Its adsorption kinetic curve is given by Figure 4 shown. The adsorption c...
Embodiment 3
[0057] In order to investigate the selectivity and non-specific adsorption of the lysozyme surface imprinting material MIP1 based on the RAFT method and the control material NIP1 prepared above to the target protein and non-specific adsorption, further interference experiments were carried out.
[0058] 1. Preparation of protein mixture solution
[0059] Prepare 5.0mg / mL phosphate solutions of lysozyme, ribonuclease B, porcine serum albumin and myoglobin (pH=7.4) respectively. The four protein solutions were added in equal volumes, and then diluted with phosphate solution (pH=7.4), so that the final concentration of each protein was 0.40 mg / mL.
[0060] 2. Selective recognition of template proteins
[0061] Take 15 mg of lysozyme surface imprinting material based on the RAFT method prepared in Example 1, add 1.0 mL buffer for washing, and then add 0.4 mL of the protein mixed solution described in 1 for each part, mix well and then statically adsorb for 24 hours. Centrifuge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com