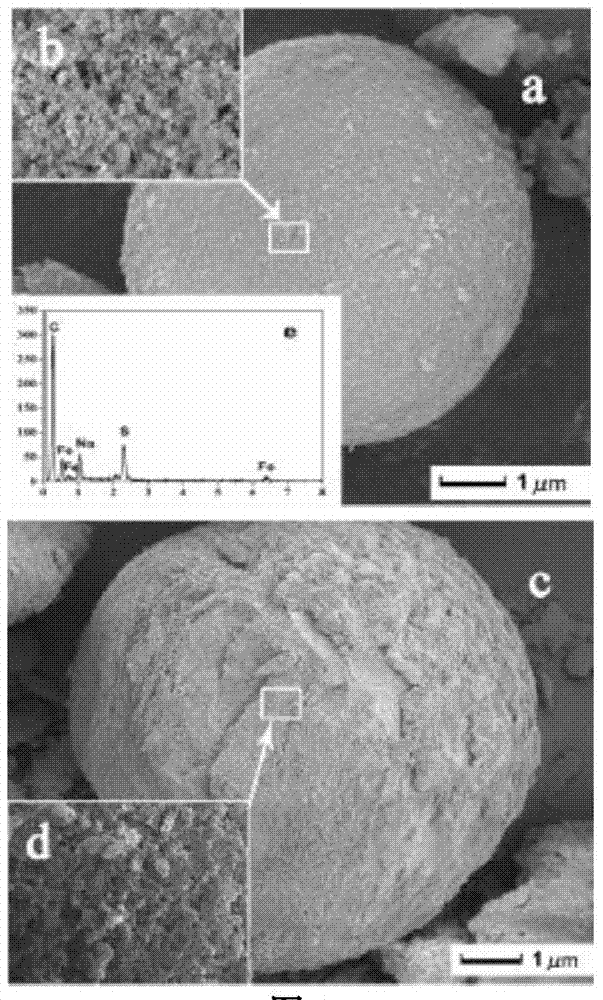
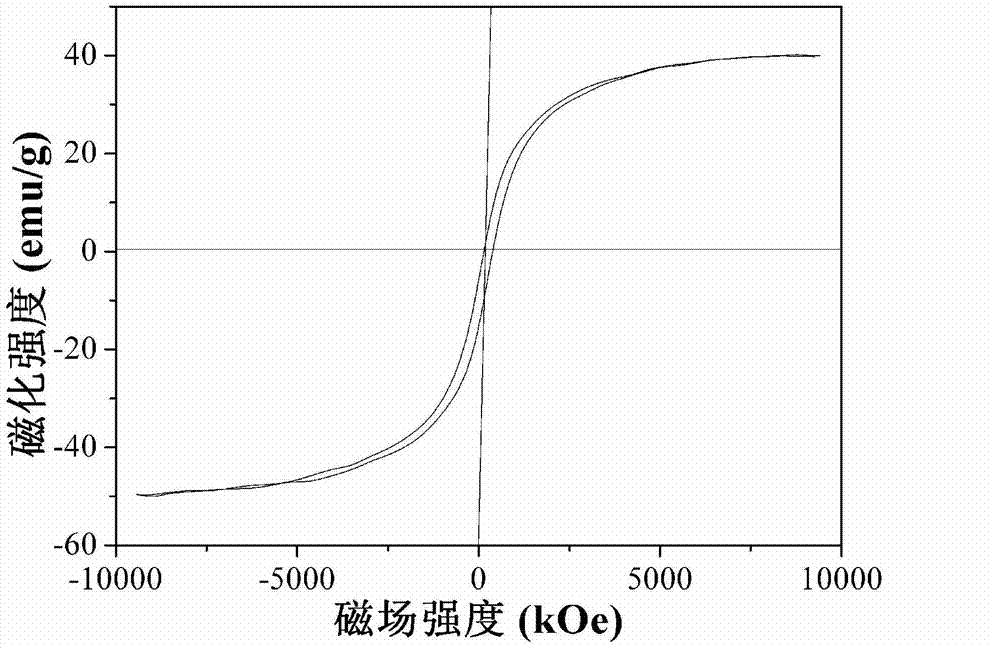
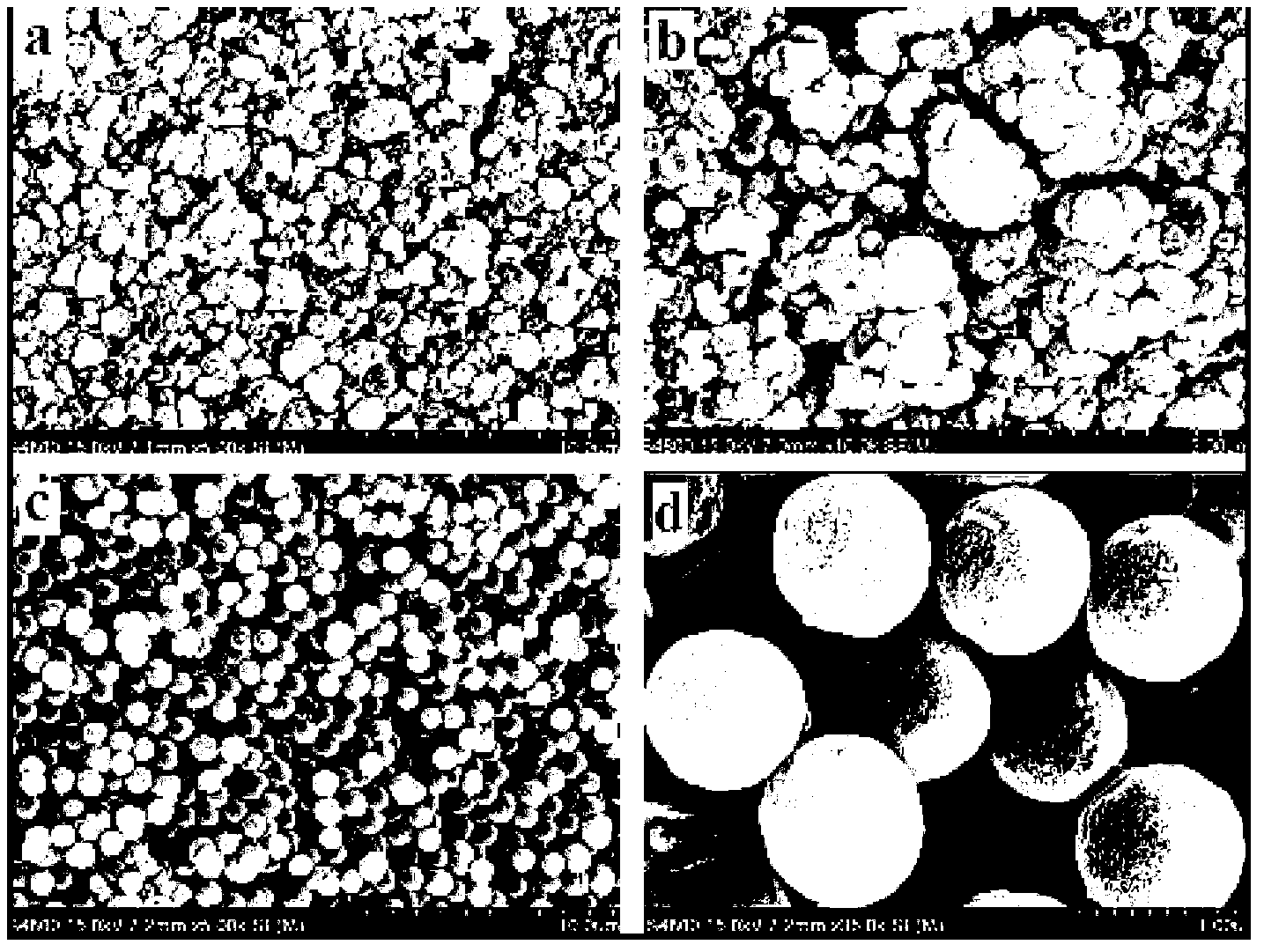
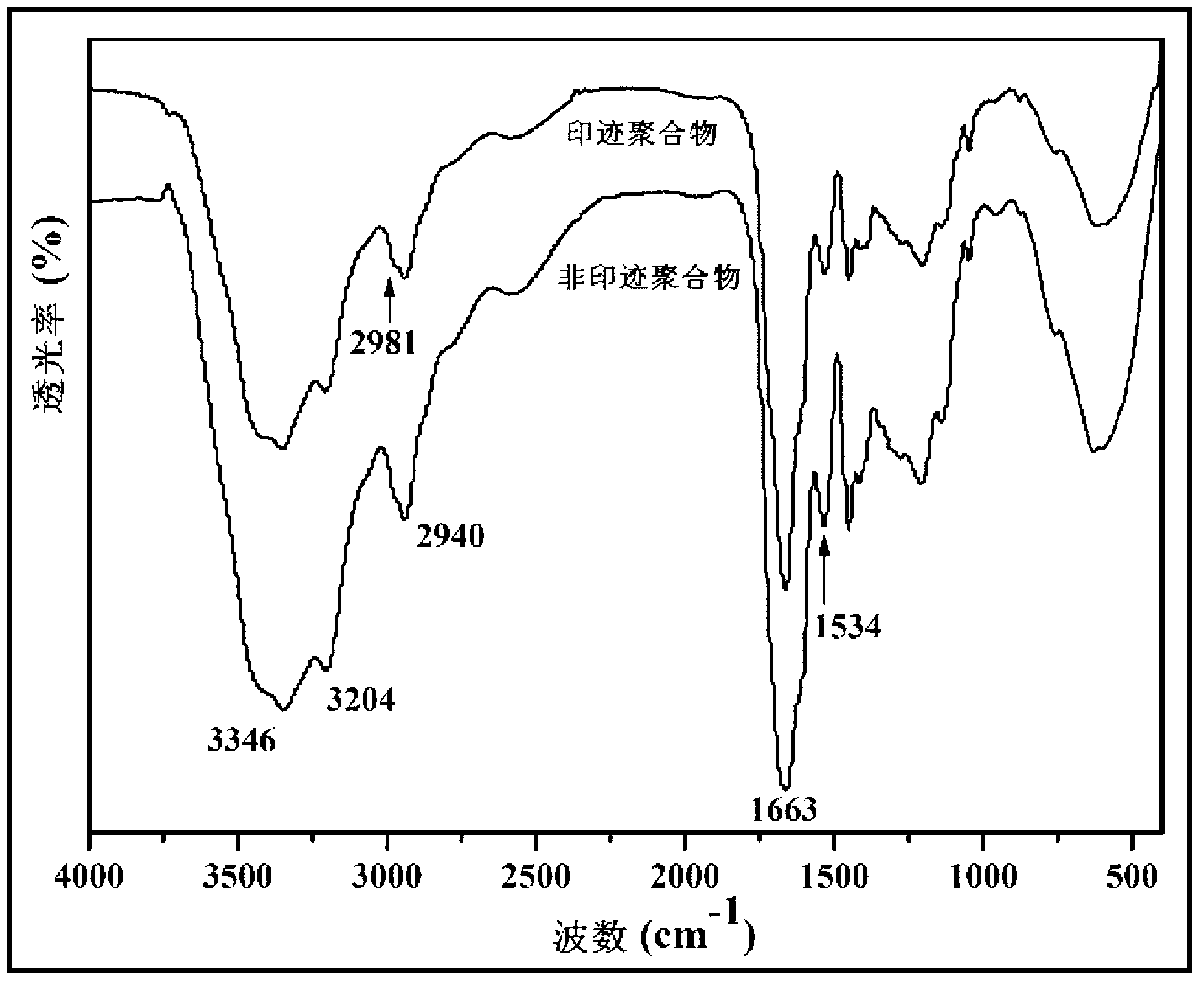
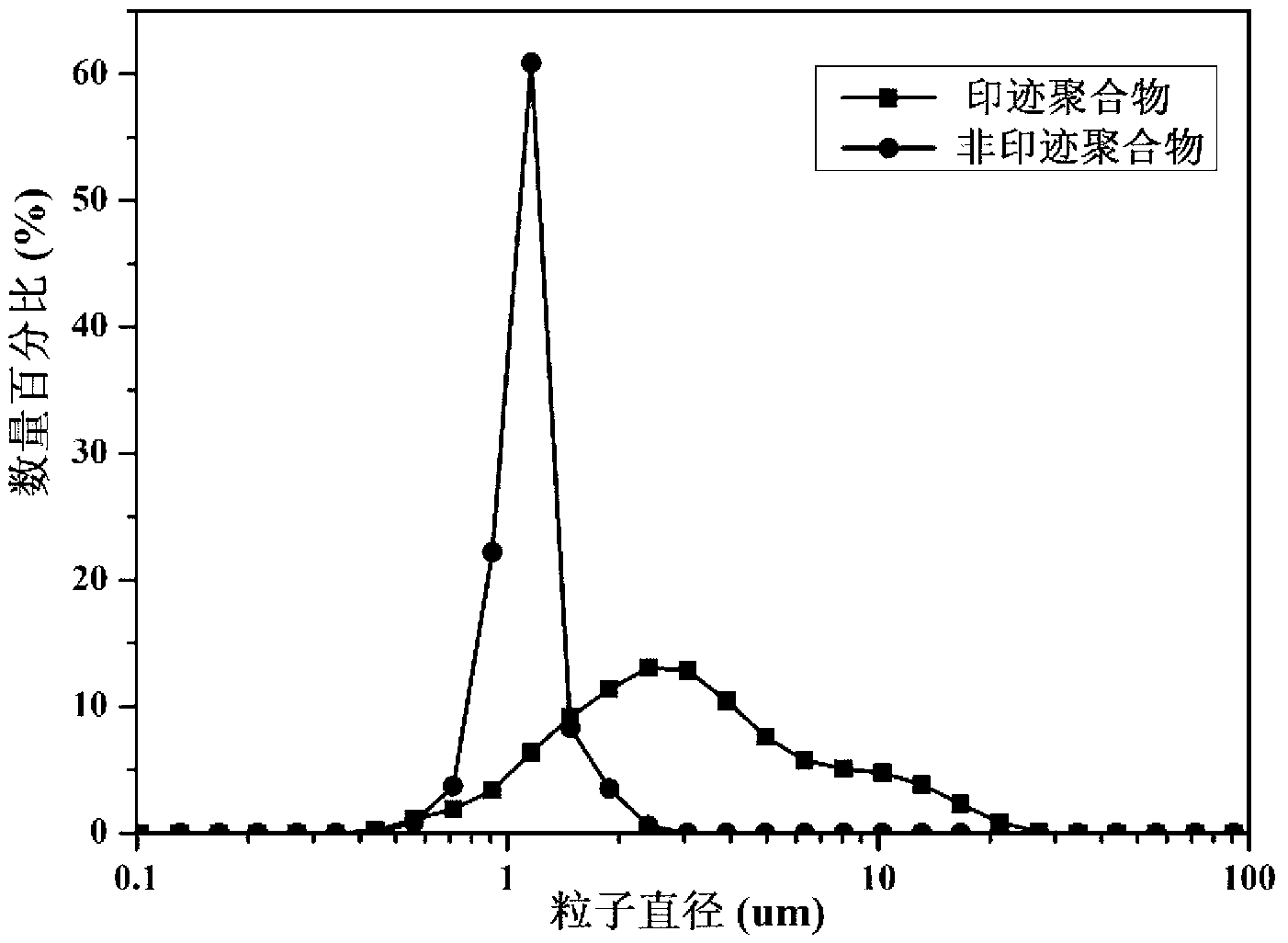
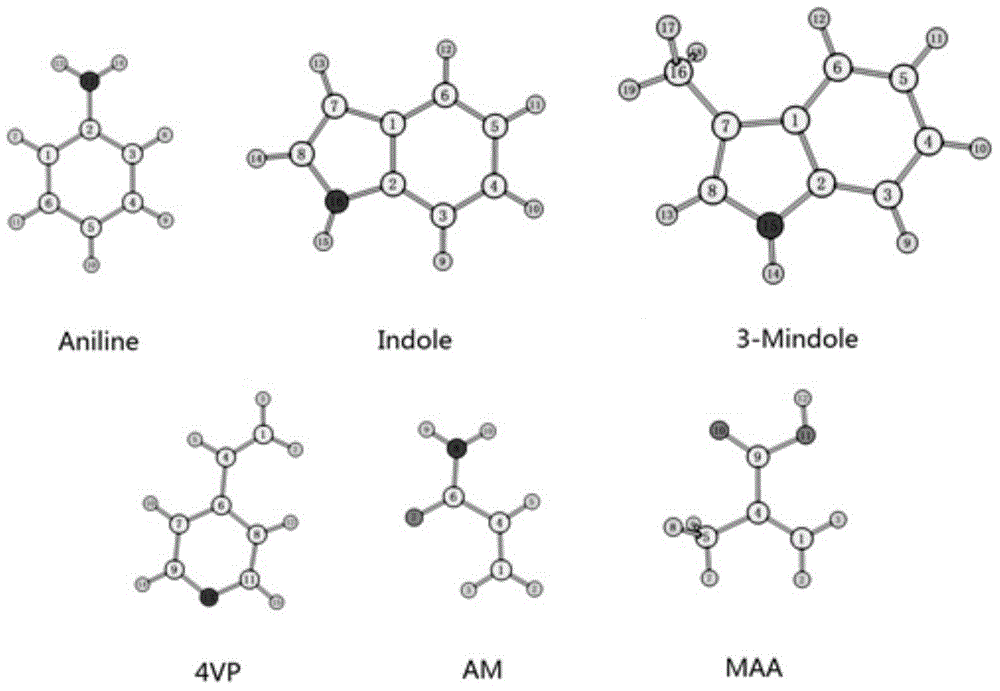
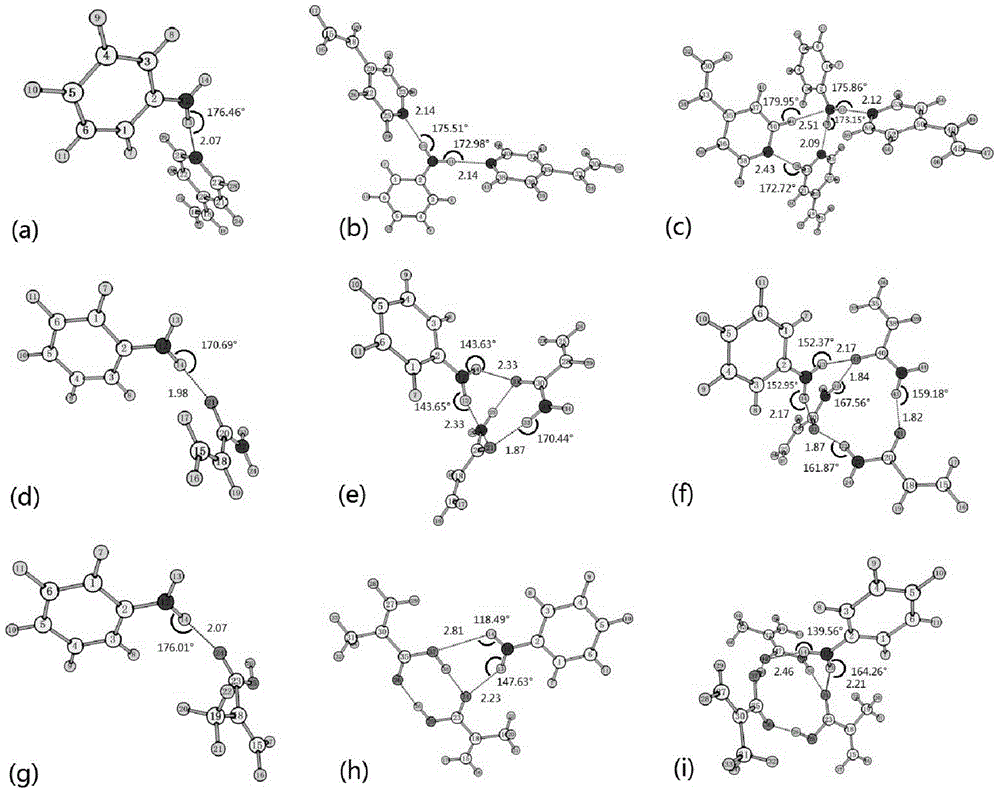
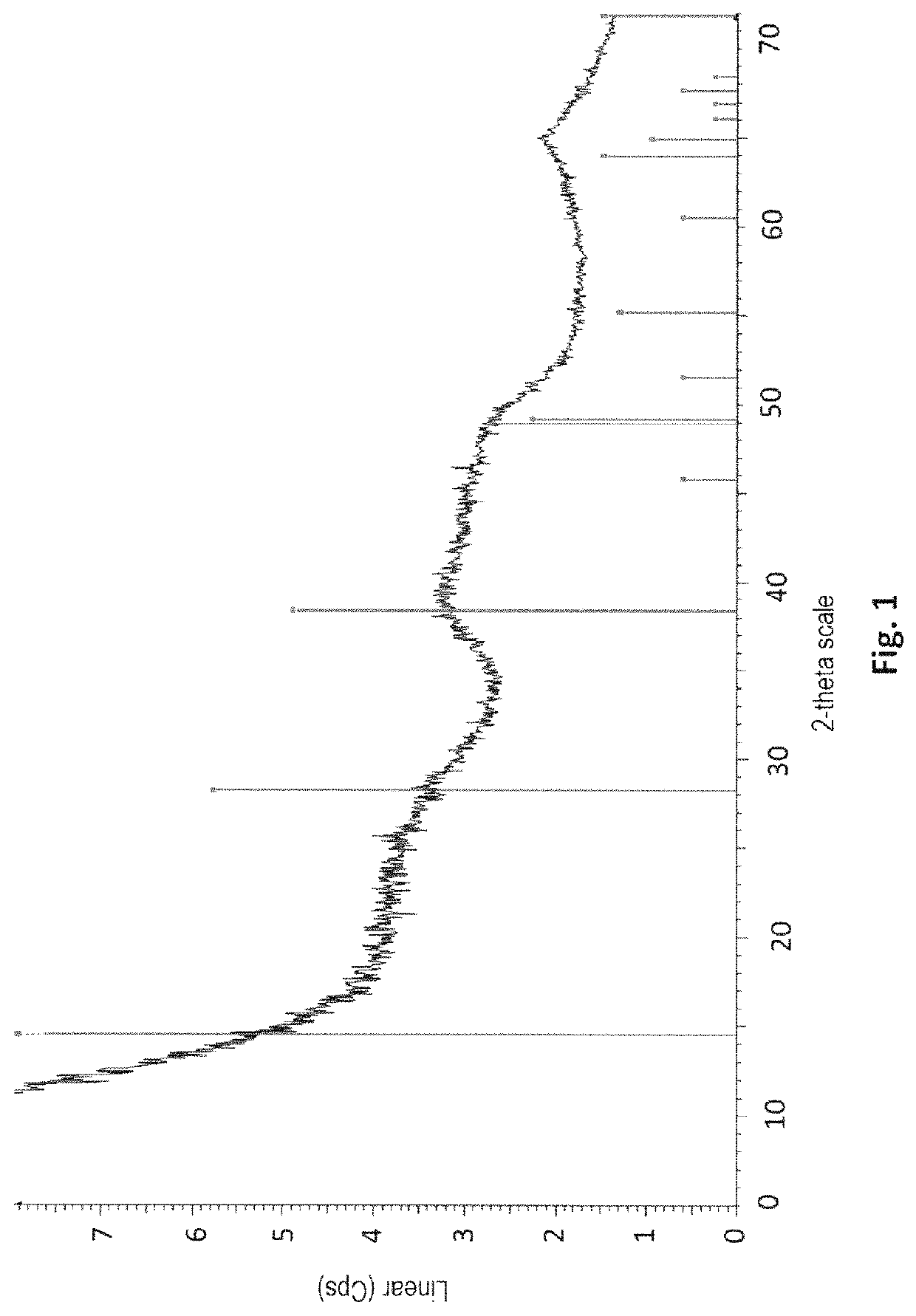
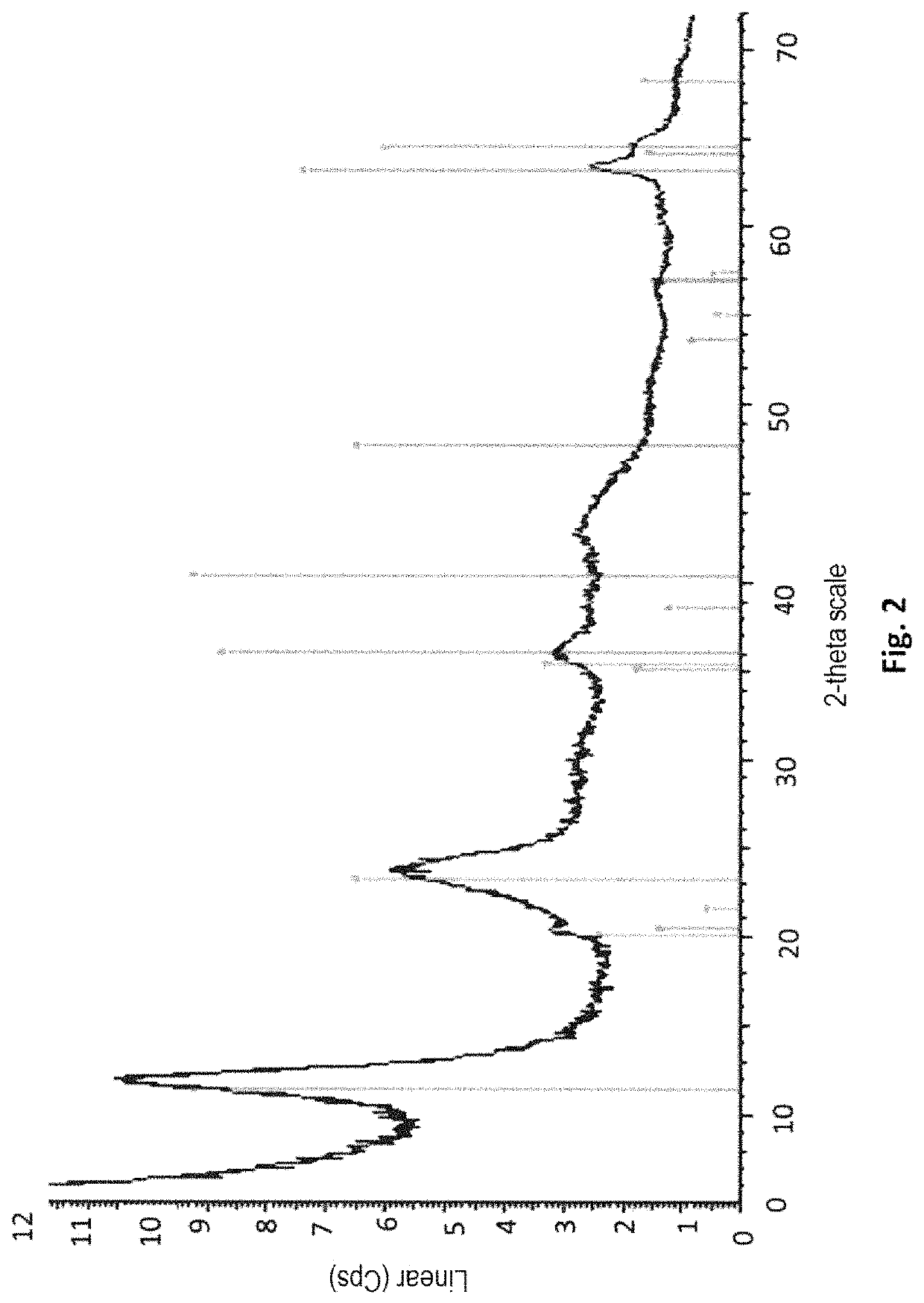
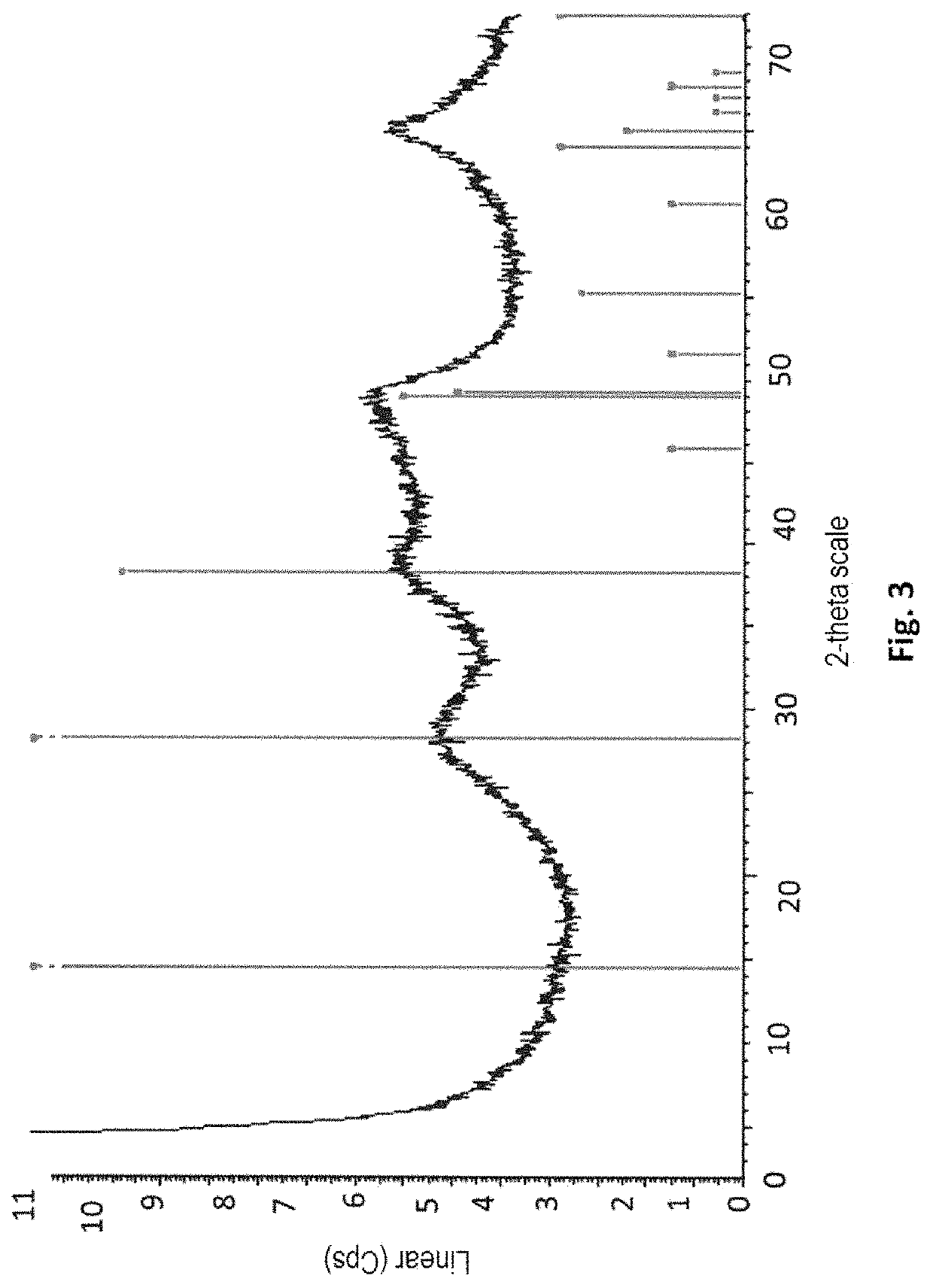
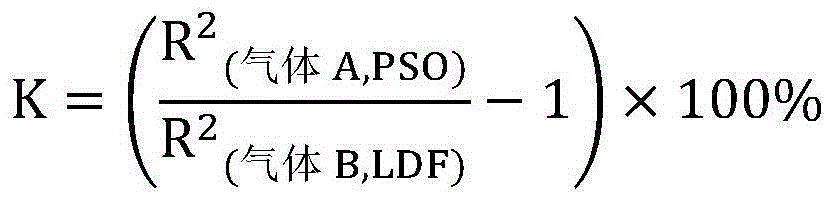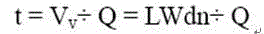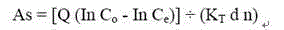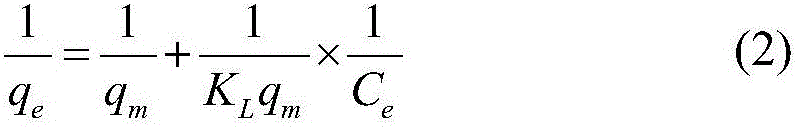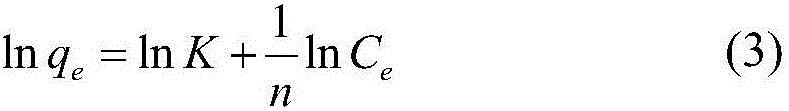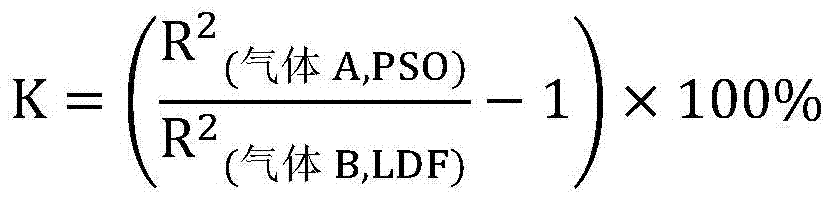Patents
Literature
48 results about "Adsorption kinetic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gold ion imprinting magnetic adsorbent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107376876AGood choiceSimple methodOther chemical processesProcess efficiency improvementCross-linkFunctional monomer
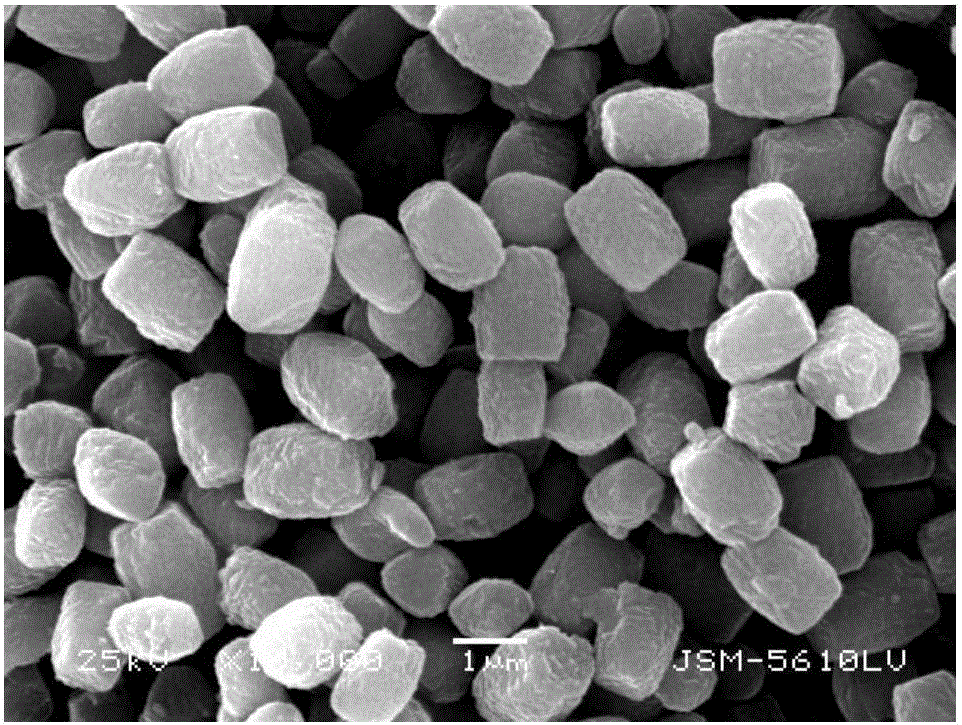
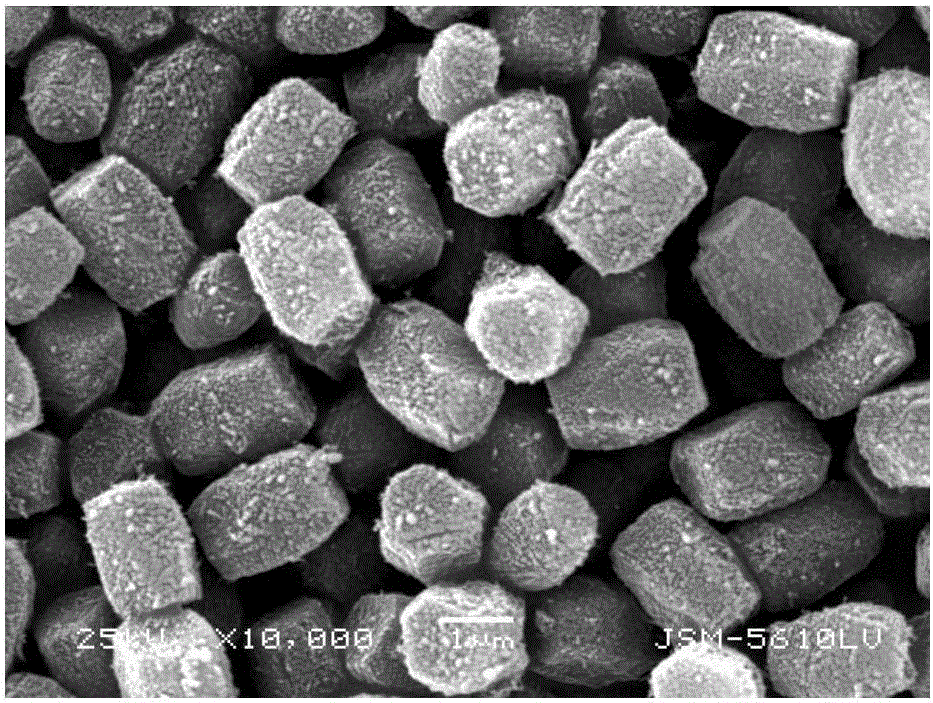
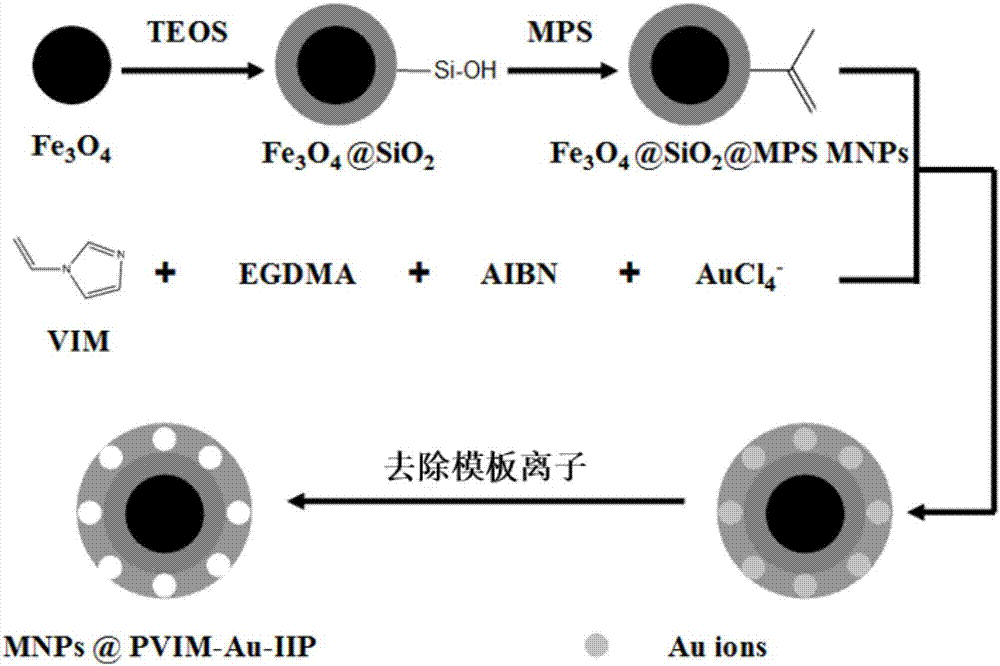
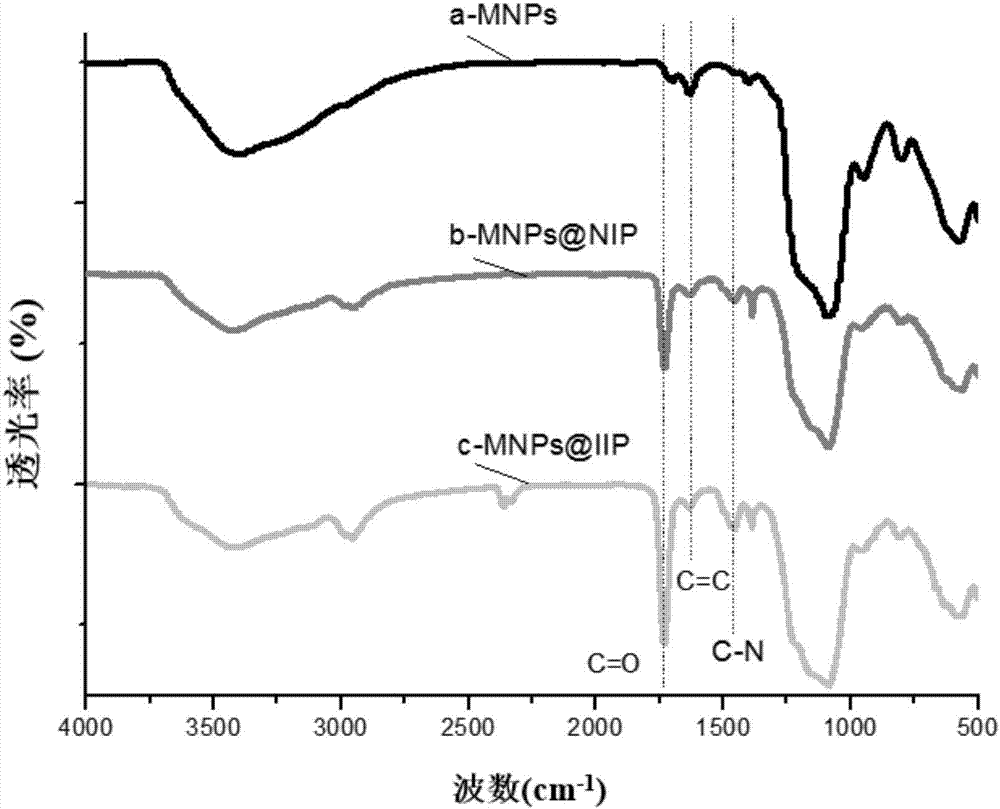
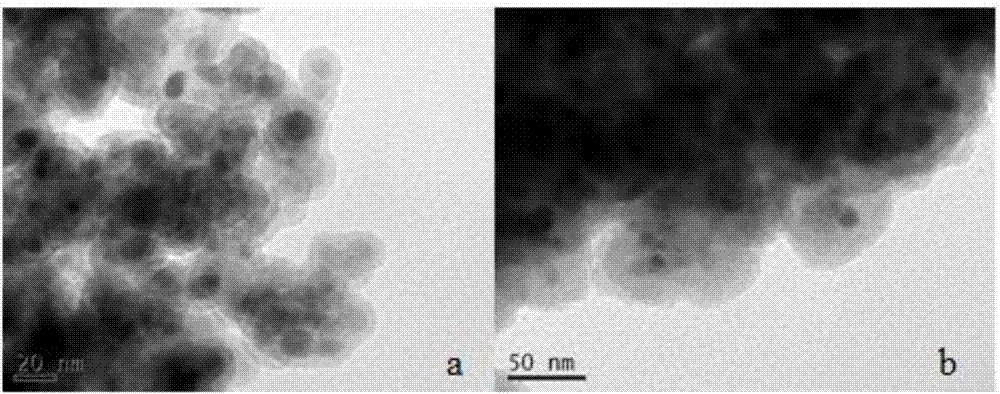
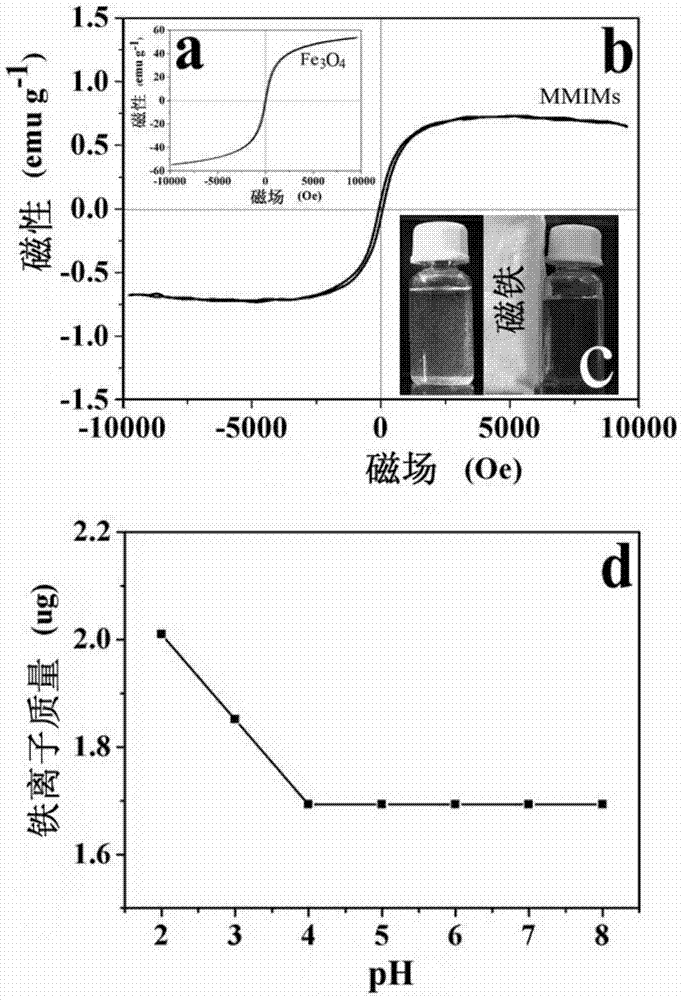
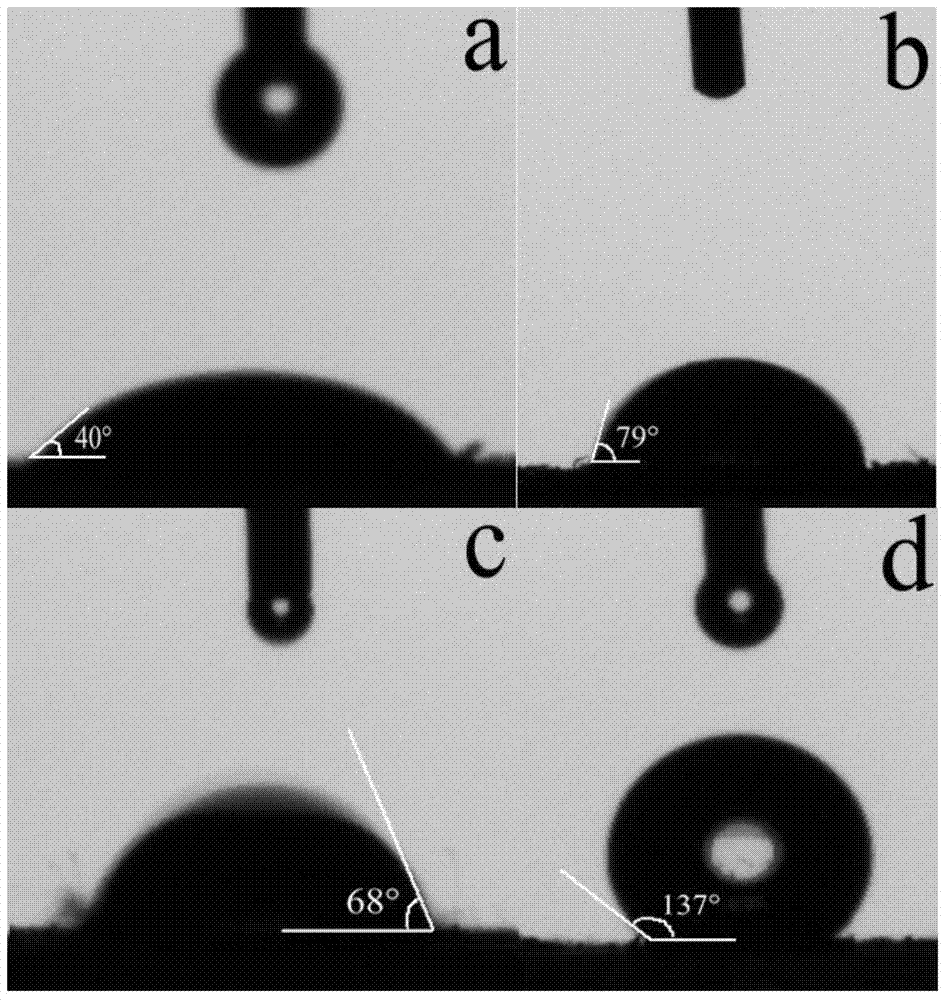
The invention provides a gold ion imprinting magnetic adsorbent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The adsorbent is prepared from a magnetic Fe3O4 core, a SiO2 layer, an MPS coating layer and a PVIM modified IIP coating layer, wherein the outside of the magnetic Fe3O4 core is sequentially wrapped by the SiO2 layer, the MPS coating layer and the PVIM modified IIP coating layer, and the IIP coating layer is in bond connection with imidazolyl. The preparation method of the adsorbent comprises the following steps: utilizing a magnetic Fe3O4 nano particle as the core and preparing Fe3O4SiO2MPS with a core-shell structure by utilizing a silica gel coupling method and utilizing TEOS and MPS as coupling agents; triggering polymerization reaction by utilizing a surface imprinting technology and combining free radical, utilizing Au(III) as a formwork ion, VIM as a functional monomer, EGDMA as a cross-linking agent and AIBN as an initiator, and synthesizing PVIM functionalized PVIM-Au-IIP on the surface of the MNPs to obtain a magnetic material coated with the IIP coating layer; utilizing an HCl solution containing thiourea to clean the material and removing the formwork ion to obtain the gold ion imprinting magnetic adsorbent. The synthesis sketch map of the adsorbent is shown in the description. The method can be used for simply and efficiently preparing the adsorbent which has high selectivity, high adsorption capacity and quick adsorption kinetic performance to Au(III), and the adsorbent has a good application prospect in the field of Au(III) adsorption.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
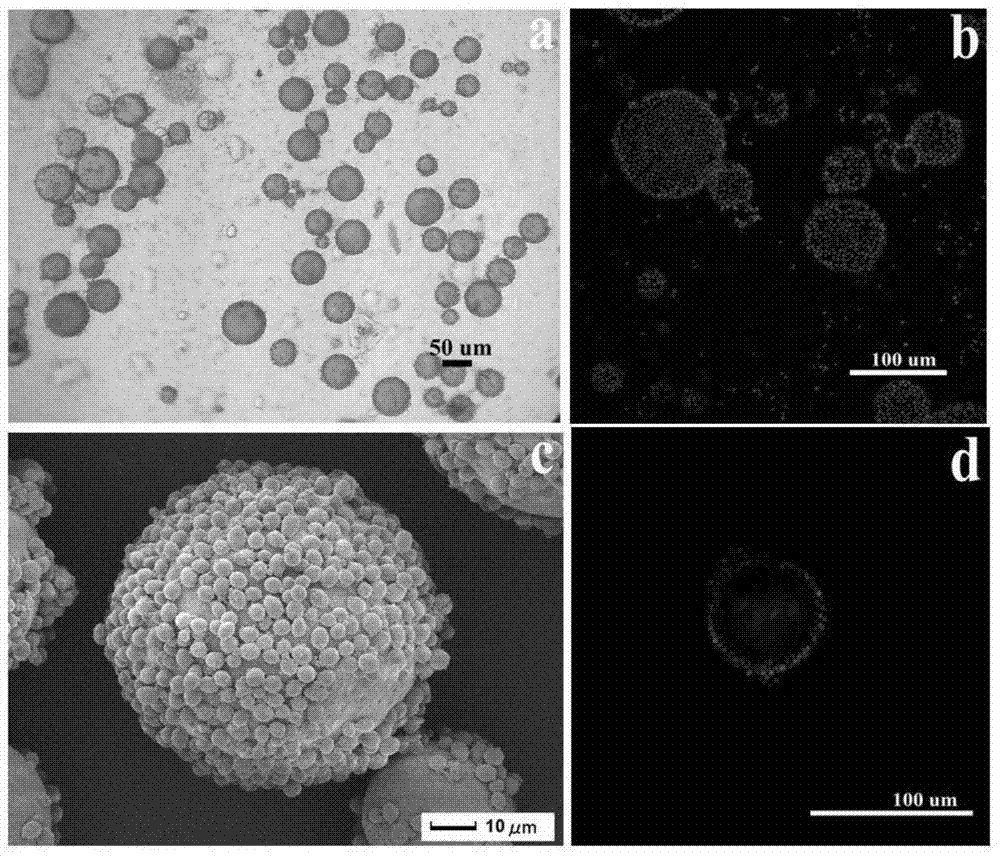
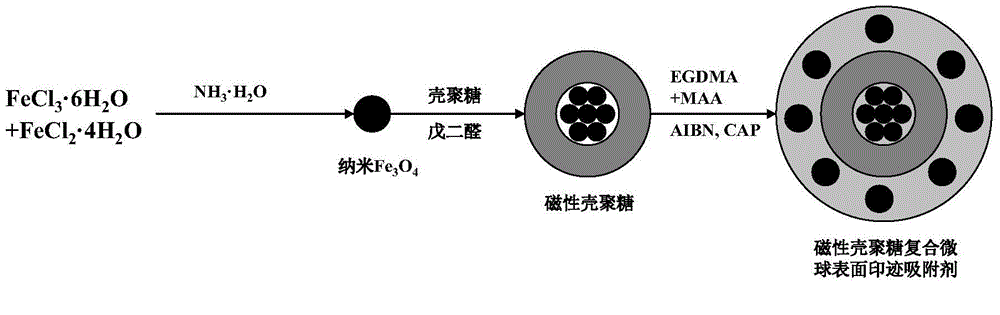
Preparation method of microzyme magnetic blotting composite microsphere adsorbent
InactiveCN103920471AImprove adsorption capacityImprove mechanical propertiesOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesFunctional monomerAdsorption equilibrium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a microzyme magnetic blotting composite microsphere adsorbent, and belongs to the technical field of environmentally-friendly functional material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: preparing ferriferrous oxide nanoparticles through a coprecipitation process, carrying out hydrophobic modification on the surface of the nanoparticles, preparing a stable Pickering emulsion with an oleic acid modified microzyme aqueous solution as a water phase, cyhalothrin as a template molecule, methacrylic acid and 4-vinylpyridine as functional monomers, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a cross-linking agent, dimethyl 2,2'-azobis(2-methylpropionate) as an initiator and hydrophobic Fe3O4 as an oil phase, and carrying out thermal-initiated polymerization to prepare the microzyme magnetic blotting composite microsphere adsorbent. Blotting microspheres obtained in the invention have a good magnetic stability, and the adsorption balance, the dynamics and the selection identification performance of the adsorbent are researched through static state adsorption experiments. Results show that the blotting adsorbent prepared in the invention has a good adsorption capacity, fast adsorption kinetics, and has a selection identification performance on LC.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
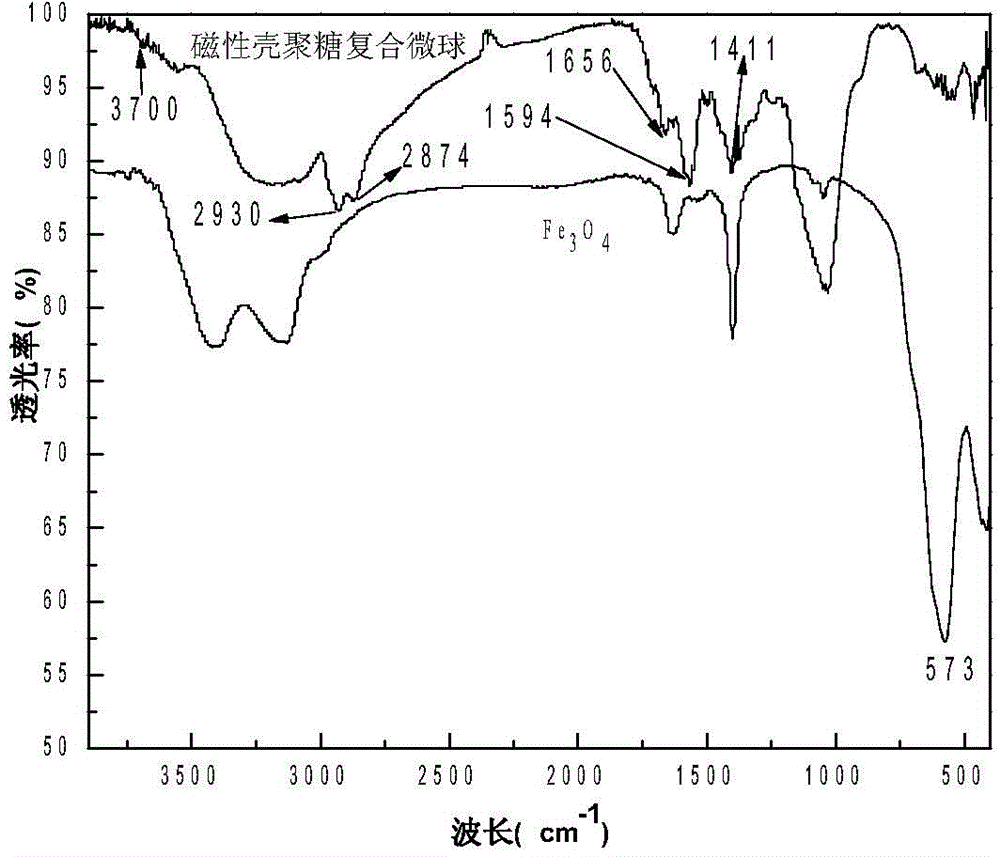
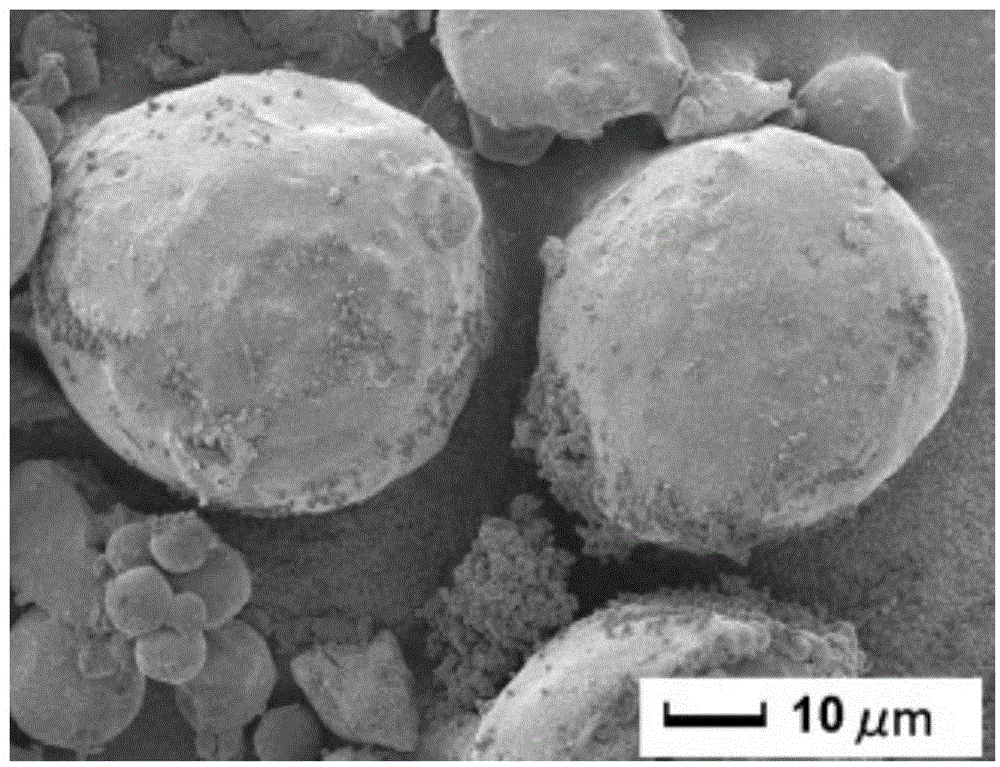
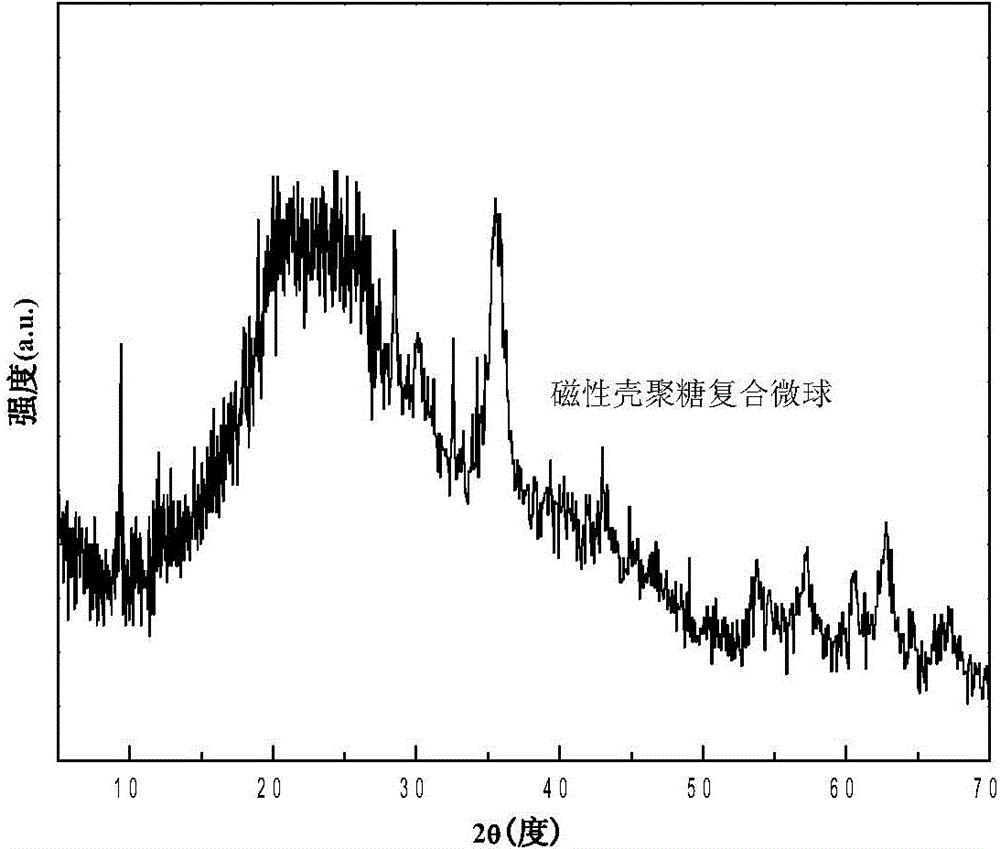
Magnetic chitosan composite microsphere surface imprinted adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104587970AFast Adsorption Kinetic PropertiesImprove adsorption capacityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesEmulsionMicrosphere
The invention provides a magnetic chitosan composite microsphere surface imprinted adsorbent and a preparation method thereof; the imprinted adsorbent contains nanoscale magnetic particles and chitosan physically coating the surface of the magnetic particles; firstly, magnetic chitosan composite microspheres are prepared by an emulsion crosslinking polymerization reaction, the nanoscale magnetic particles are wrapped inside the magnetic chitosan composite microspheres, and then an imprinted polymer is wrapped on the surface of the magnetic chitosan composite microspheres by a precipitation polymerization reaction. The surface imprinted adsorbent has the advantages of fast adsorption kinetics properties, relatively high adsorption capacity, fast magnetic separation efficiency and obvious chloramphenicol molecular recognition properties, and can be used for chloramphenicol selective recognition, separation and enrichment in the environment. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, uniform particle size of the synthetic product, easy controlled temperature, easy separation of the product and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method for molecularly imprinted microsphere surface grafted hydrophilic polymer brush
The invention relates to a preparation method for a molecularly imprinted microsphere surface grafted hydrophilic polymer brush, and belongs to the technical field of environment function material preparation. The method comprises the steps of using sulfamethazine as template molecules, using 4-vinylpyridine as a functional monomer, using ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a cross-linking agent, using methyl alcohol and water as a solvent, using copper bromide / N,N,N',N,'N''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine / azodiisobutyronitrile as an initiating system to initiate reverse atom transfer radical precipitation and polymerization, so as to prepare the molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere with the surface containing active initiators, using the molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere as the macroinitiator, using cuprous bromide / N,N,N',N',N''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine as a catalyst, and polymerizing surface initiated atom transfer radical on a molecularly imprinted microsphere surface grafted hydrophilic hydroxyethylmethacylate brush in the methyl alcohol / water mixed solvent. The molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere prepared through the method has higher adsorption capacity, fast adsorption kinetics property and good selective adsorption performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of magnetic porous adsorbent by suspension polymerization
InactiveCN103588919AHigh mechanical strengthGood magnetic responseOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionFunctional monomerAdsorption equilibrium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a magnetic porous adsorbent by suspension polymerization, belongs to the technical field of environmental functional material preparation, and is characterized in that: styrene and divinyl benzene are used as functional monomers, azodiisobutyronitrile is used as an initiator, toluene and cyclohexanol are used as a pore forming agent, a porous adsorbent is prepared by use of a suspension polymerization method, a sulfonation method is used for modification on the surface of the porous adsorbent to generate a magnetic material, and finally the magnetic porous adsorbent is prepared. The prepared magnetic porous adsorbent has a porous structure, is conducive to the adsorption of pollutants, and is also conducive to the rapid separation due to the magnetic property. The prepared magnetic porous adsorbent can be used in water environment for selective adsorption of phenol pollutants. Static adsorption experiments are used to study adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics properties of the adsorbent, and results show that the magnetic porous adsorbent obtained by the preparation method has better adsorption capacity and faster adsorption kinetics properties.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Green preparation method of hydrophilic molecular engram polymer
The invention a green preparation method of a hydrophilic molecular engram polymer, and belongs to the technical field of environment function materials. A hydrophilic molecular engram polymer microsphere is prepared through a one-pot method by taking nontoxic innocuous ethanol as a green solvent, tetracycline as a template molecule, methacrylic acid and acrylamide as a difunctional monomer, N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide as a cross-linking agent and azoisobutyronitrile as a free-radical initiator. According to the invention, higher acting force is proved to exist between the template molecule and the polymerized monomer and influence parameters, namely morphology, size distribution, and the like, of a polymer through multiple representation means; and the adsorption equilibrium, dynamic and selective property of a prepared engram polymer particle on the tetracycline are researched by utilizing a static adsorption experiment, and a result indicates that the hydrophilic molecular engram polymer obtained by utilizing the green preparation method disclosed by the invention has higher adsorption capacity, fast adsorption kinetics property and specific recognition property on tetracycline antibiotics in a water solution.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Cellulose-based phenolic compound molecularly-imprinted adsorbing agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105664882ARealize high-value utilizationLow costOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCelluloseMicrowave
The invention relates to a cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent which has the high-selectivity adsorption capacity on a phenolic pollutant in a solution and a preparation method of the cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent.The cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent is synthesized by adopting an active free radical polymerization method.The method comprises the steps that smashed cellulose is dissolved in a cellulose dissolving agent under the assistance of ultrasonic waves or microwaves, and then homogeneous-phase esterifying modification is performed on the cellulose to prepare a cellulose macroinitiator; the phenolic pollutant is taken as a template, a functional monomer, a hole generating agent, a catalyst and a coordination agent react under a certain condition, and after reacting is finished, template molecules are washed off to obtain the cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent for the phenolic pollutant.A static adsorption test is used for studying the adsorption balance, kinetics and selectivity recognition properties of the imprinted adsorbing agent.A result shows that the obtained cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent has the quick adsorption kinetics property and the superior phenolic pollutant molecule recognition property on the phenolic pollutant.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of molecularly imprinted polymer capable of simultaneously adsorbing multiple nitrides
InactiveCN104877071AUniform particlesLarge specific surface areaWaste minimisationFunctional monomer
The invention provides a molecularly imprinted polymer capable of simultaneously adsorbing multiple nitrides and a preparation method of the molecularly imprinted polymer, and belongs to the technical field of environmental pollution control chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly simulating an imprinting preassembly system based on a density functional theory by using a molecular simulation technology, screening out an optimal functional monomer, and preparing a molecularly imprinted adsorption material based on simulation results by virtue of seeded emulsion polymerization. An adsorbing agent synthesized by using the method provided by the invention is uniform in particle, large in specific surface area and good in adsorption kinetics; and compared with a conventional single template imprinting adsorption material, the molecularly imprinted polymer provided by the invention ensures that multiple imprinted binding sites are successfully formed, and has greater practical values.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method of measuring variable-pressure absorption gas separation performance of carbon molecular sieve on basis of liquid absorption gas flooding principle
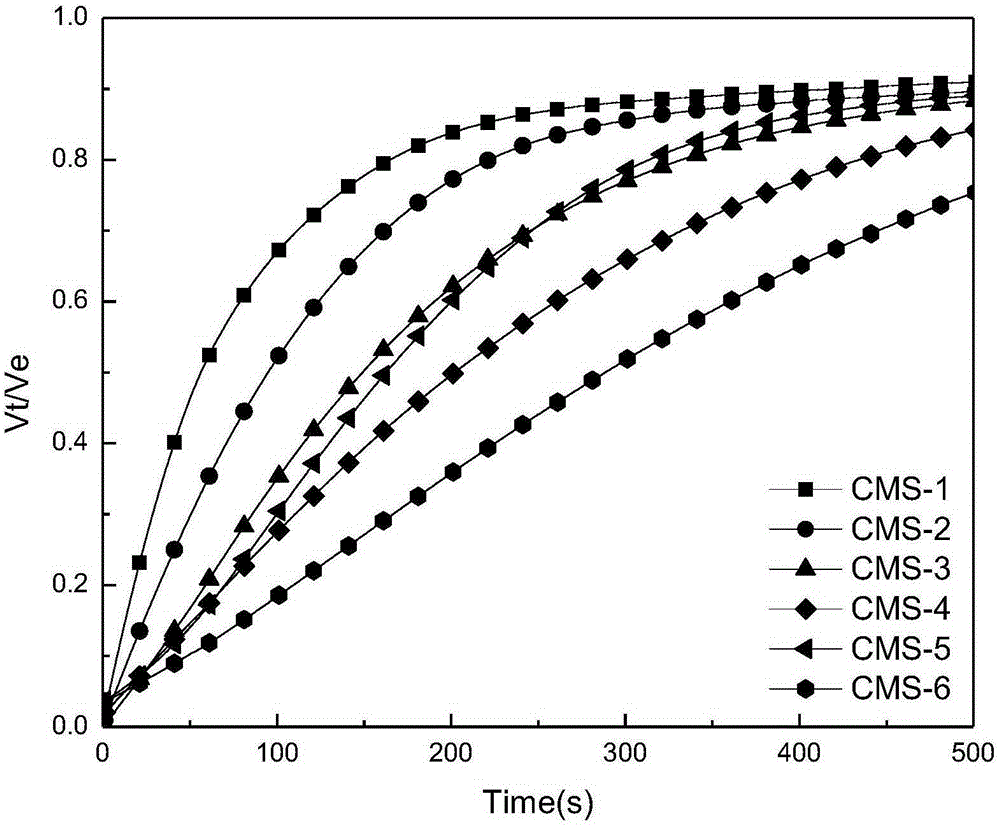
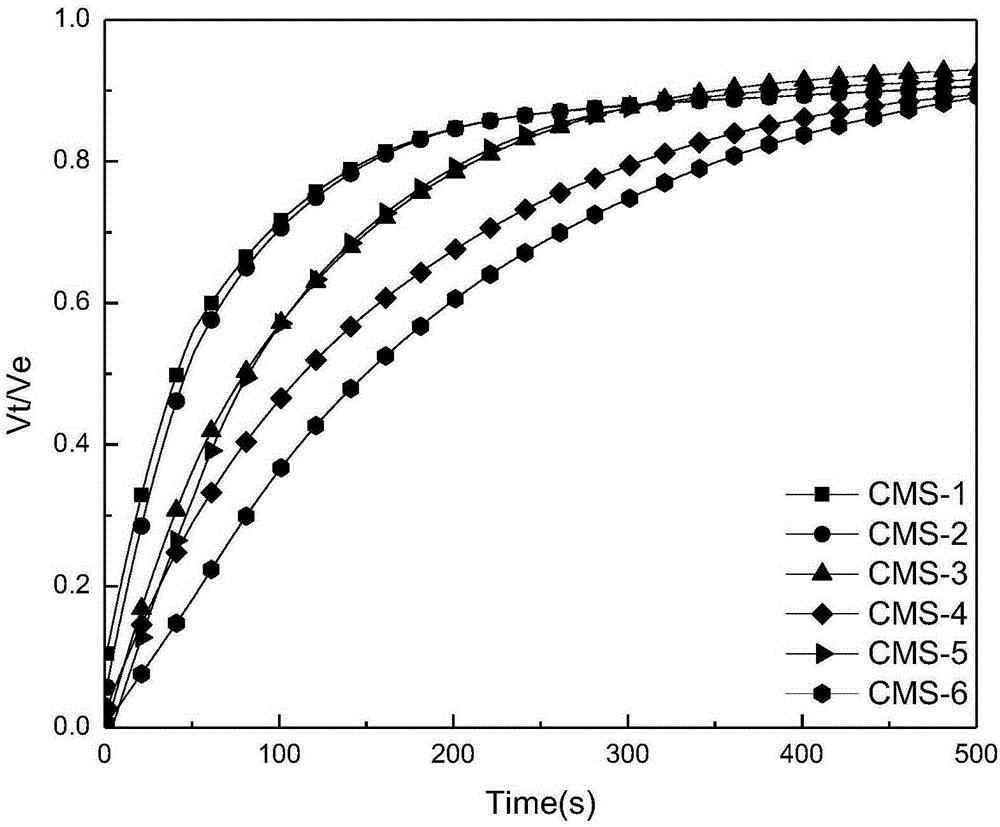
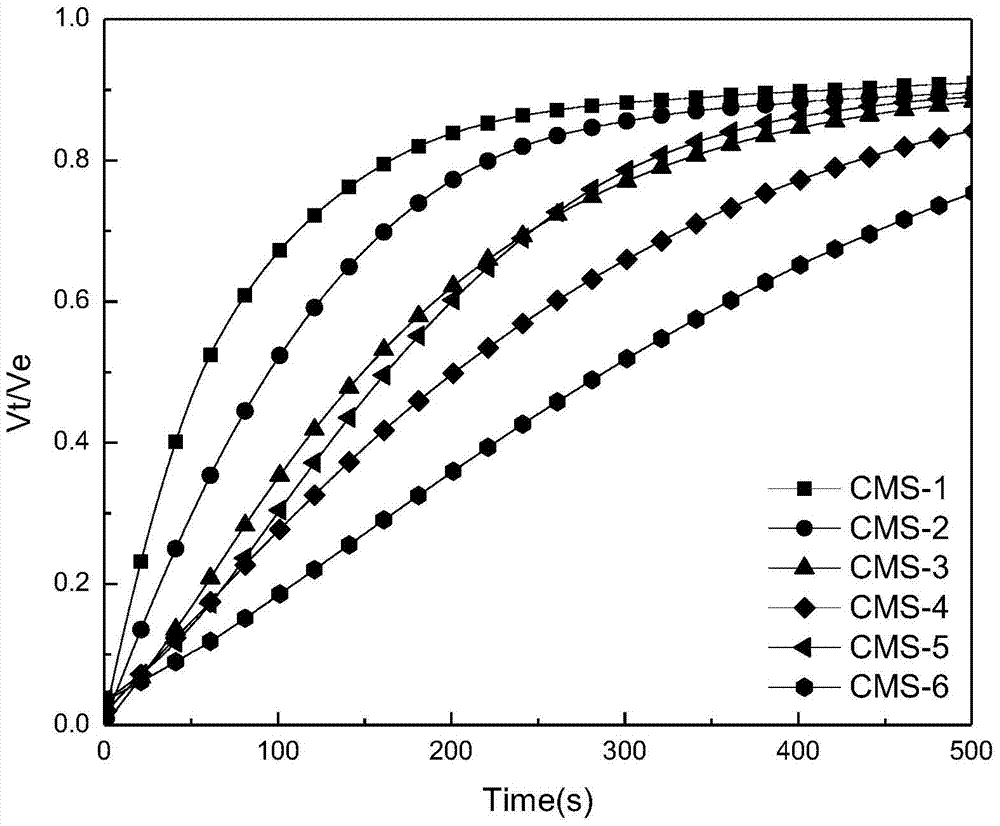
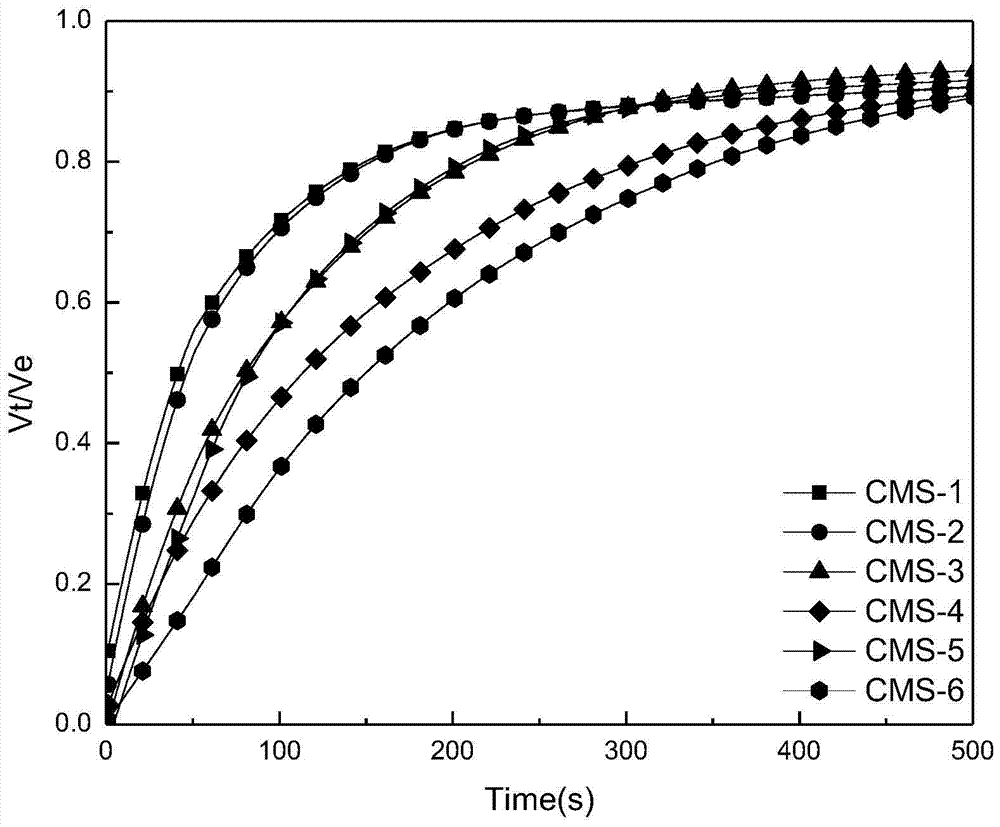
The invention discloses a method of measuring the variable-pressure absorption gas separation performance of a carbon molecular sieve on the basis of a liquid absorption gas flooding principle. According to the method, a carbon molecular sieve of a saturated adsorption gas probe is immersed into a liquid probe; a liquid absorption gas flooding experiment is performed under a constant volume condition; a liquid absorption gas flooding kinetic curve and a balanced gas flooding quantity are obtained. Through the adsorption kinetic model simulation, the dynamic mechanism and the gas selectivity coefficient K are determined, and are used for judging the micropore opening dimension relative dimension rule, the distribution uniformity and the micropore volume relative dimension of the carbon molecular sieve; further, the method for evaluating the variable-pressure adsorption gas separation performance of the carbon molecular sieve is built. The method has the advantages that the carbon molecular sieve with the micropore opening dimension and the micropore volume meeting the gas separation requirement can be accurately judged in the aspects of the adsorption mechanism and the pore structure; high selectivity can be ensured; higher adsorption volume can also be ensured.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
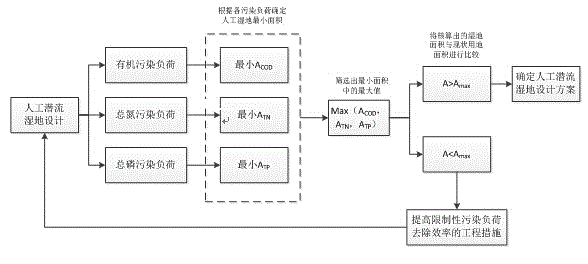
Design method based on three-pollution load for subsurface constructed wetland
InactiveCN104817188AGuaranteed removal effectEnsure water purification effectSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandQuality data
The invention relates to a design method based on three-pollution load for subsurface constructed wetland. The design method is based on a three-pollution load reaction / adsorption kinetic model, the relationship between constructed wetland pollutant treatment load and a required wetland area is mainly taken into account, and three-pollution load-area equation set is established and deduced. The equation set is solved according to designed constructed wetland design operation water amounts and effluent quality data, so that the constructed wetland required area based on organic pollutant, nitrogen and phosphorus load can be obtained, and the maximum value is set as an ideal wetland area; if the area is smaller than a practical available area, intensification facilitates are additionally arranged, and the wetland area is remeasured and calculated. By adopting the design method, purification of water with organic pollutants, nitrogen and phosphorus, of the constructed wetland, is comprehensively considered, and the water purification effect of the wetland can be effectively ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
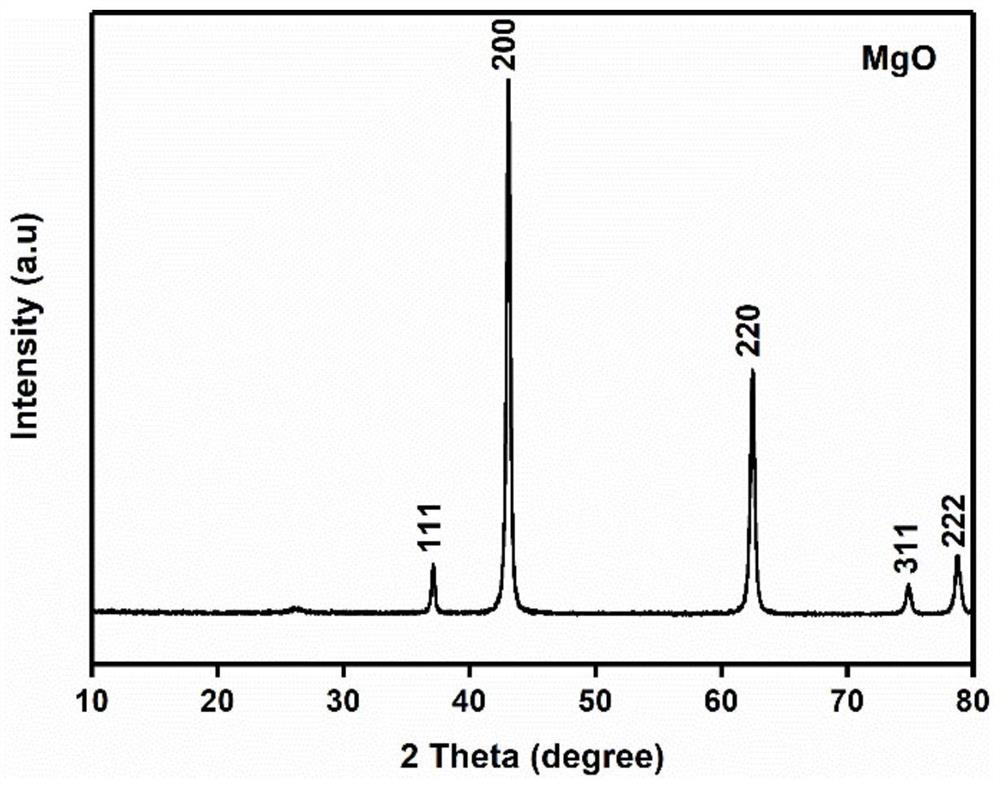
Preparation method of super-efficient sewage dephosphorization adsorbent
ActiveCN111644148AHigh content of nano MgOGood removal effectOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSorbentPollution
The invention relates to a preparation method of a super-efficient sewage dephosphorization adsorbent, and belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment and adsorbents. According to the method, based on a reaction that magnesium metal is combusted in a carbon dioxide atmosphere, MgO crystals and amorphous carbon are generated at the same time simply and quickly in one step; the two substancesare uniformly combined in a nanometer scale, so that the formed magnesium-based nano composite carbon material can be used as the super-efficient sewage dephosphorization adsorbent. The adsorbent hasextremely fast adsorption kinetics, a wide pH application range and relatively strong impurity anion interference resistance, the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent to phosphorus in a solution is higher than 1000mg / g, and the efficient and rapid phosphorus removal effect can be achieved in actual sewage with various complex components. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate,short in preparation period and rich and cheap in raw material source, and the adsorbent has no toxicity to the environment, does not cause secondary pollution during preparation of the adsorbent andphosphorus removal application, and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Composite material for passivating heavy metal nickel in soil as well as preparation and application methods thereof
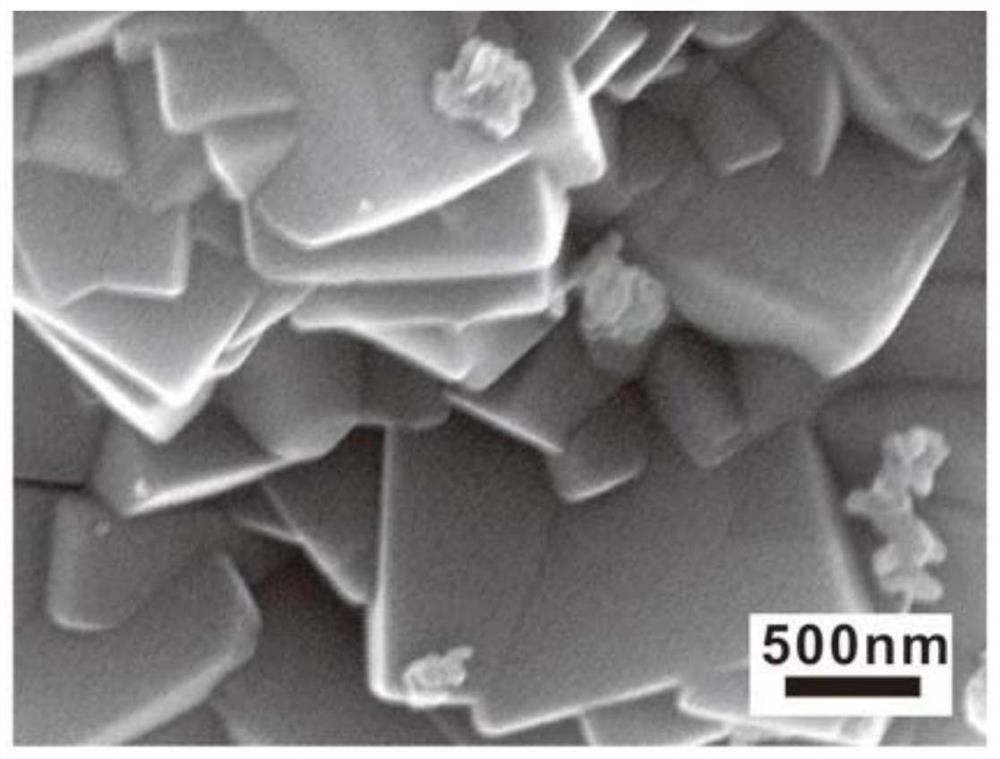
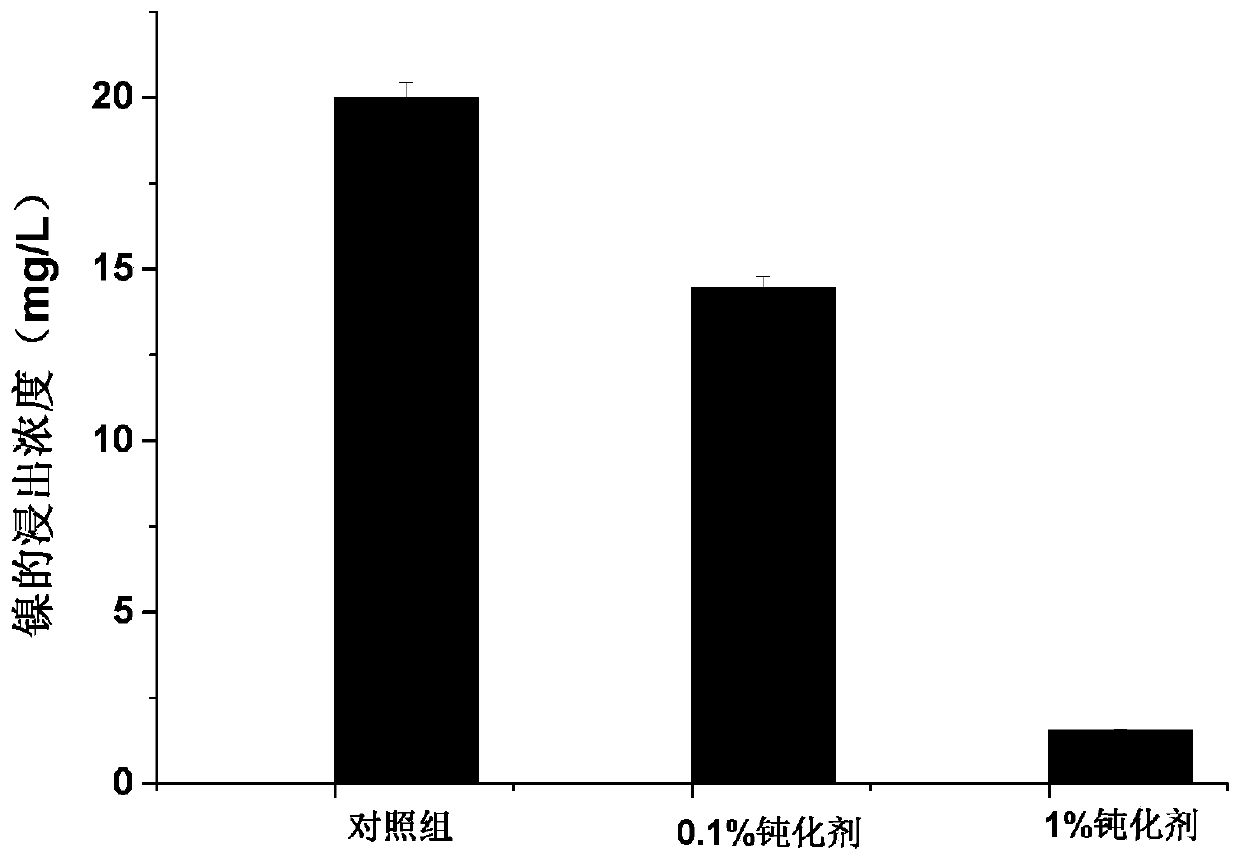
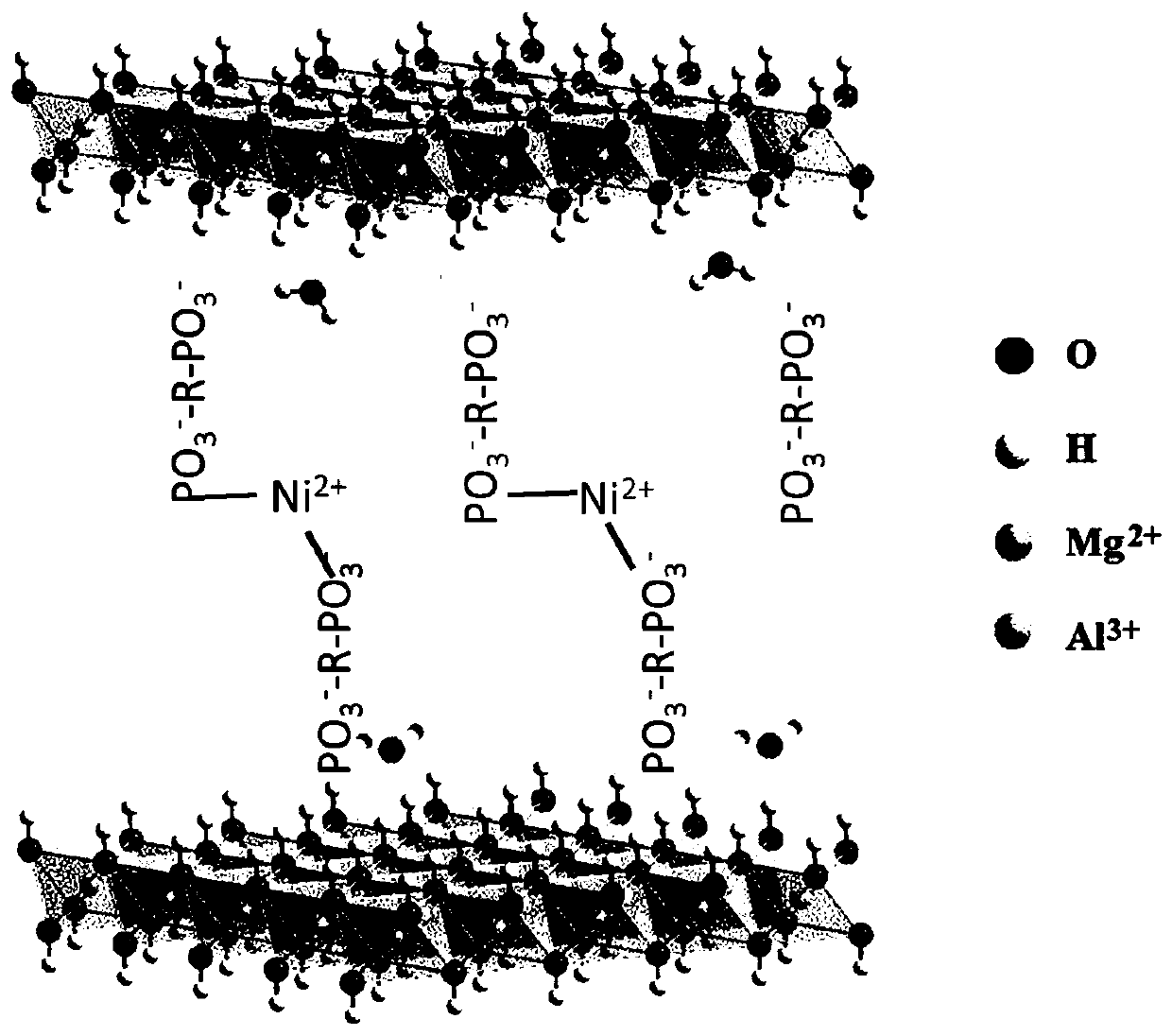
InactiveCN111575012AEasy to operateImprove efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationContaminated soil reclamationComposite materialAdsorption kinetic
The invention discloses a composite material for passivating heavy metal nickel in soil as well as preparation and application methods of the composite material, belongs to the field of soil remediation, and overcomes the defect that the soil heavy metal immobilization effect is realized by changing the pH value of soil in an existing soil remediation method. According to the invention, layered double hydroxide is used as a template, and a novel heavy metal passivator composite material is prepared through organic phosphate modification. Adsorption kinetics results show that the organic phosphate modified layered double hydroxide can quickly adsorb nickel ions to achieve adsorption equilibrium. In addition, leaching toxicity results show that the prepared composite material can significantly reduce the leaching efficiency of heavy metals under acidic conditions.
Owner:苏州市相润土壤修复技术研究院有限公司
Method for reducing methanol content of paper pulp
InactiveCN106053671AEasy to operateFind Methanol ContentComponent separationVapor phase chromatographyFreundlich model
The invention discloses a method for reducing the methanol content of paper pulp. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating a sample; (2) establishing a standard curve; (3) detecting the sample by using a headspace gas chromatograph; (4) calculating a result and establishing an empirical model. The method has the organic effects that the adsorption kinetics of methanol on non-floated eucalypt kraft pulp is checked; after fitting is carried out respectively with Langmuir and Freundlich, fitting results are compared, so that a temperature parameter is introduced into the Freundlich model for least square fitting, to obtain a methanol adsorption amount and empirical models of the concentration and the temperature of methanol; furthermore, the fitting results are objective and accurate for reference during adjustment of a papermaking production procedure (such as pulp washing).
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A method for measuring the gas separation performance of carbon molecular sieve pressure swing adsorption based on the principle of liquid suction and gas displacement
The invention discloses a method of measuring the variable-pressure absorption gas separation performance of a carbon molecular sieve on the basis of a liquid absorption gas flooding principle. According to the method, a carbon molecular sieve of a saturated adsorption gas probe is immersed into a liquid probe; a liquid absorption gas flooding experiment is performed under a constant volume condition; a liquid absorption gas flooding kinetic curve and a balanced gas flooding quantity are obtained. Through the adsorption kinetic model simulation, the dynamic mechanism and the gas selectivity coefficient K are determined, and are used for judging the micropore opening dimension relative dimension rule, the distribution uniformity and the micropore volume relative dimension of the carbon molecular sieve; further, the method for evaluating the variable-pressure adsorption gas separation performance of the carbon molecular sieve is built. The method has the advantages that the carbon molecular sieve with the micropore opening dimension and the micropore volume meeting the gas separation requirement can be accurately judged in the aspects of the adsorption mechanism and the pore structure; high selectivity can be ensured; higher adsorption volume can also be ensured.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
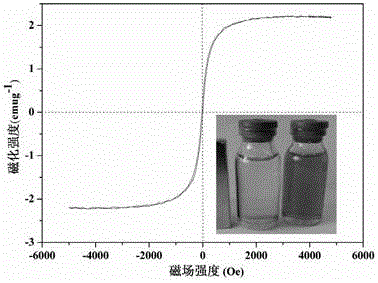
A kind of preparation method of magnetic chitosan composite microsphere adsorbent
InactiveCN103920472BEasy to makeImprove thermal stabilityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMicrosphereSorbent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a magnetic chitosan composite microsphere adsorbent, which belongs to the technical field of environmental material preparation. Using FeCl3 6H2O and FeCl2 4H2O as raw materials, nano-Fe3O4 was prepared by co-precipitation method, then using glutaraldehyde as cross-linking agent, Fe3O4, kaolin and chitosan as raw materials, the magnetic chitosan composite was synthesized by emulsification cross-linking method Microsphere adsorbent, and use it for the separation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride in water environment. Static adsorption experiments were used to study the adsorption and kinetic properties of the prepared adsorbents. The results show that the magnetic chitosan composite microsphere adsorbent obtained by the present invention has fast adsorption kinetic properties, high adsorption capacity and fast magnetic separation efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Cellulose-based phenolic compound molecularly imprinted adsorbent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105664882BRealize high-value utilizationLow costOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCelluloseMicrowave
The invention relates to a cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent which has the high-selectivity adsorption capacity on a phenolic pollutant in a solution and a preparation method of the cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent.The cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent is synthesized by adopting an active free radical polymerization method.The method comprises the steps that smashed cellulose is dissolved in a cellulose dissolving agent under the assistance of ultrasonic waves or microwaves, and then homogeneous-phase esterifying modification is performed on the cellulose to prepare a cellulose macroinitiator; the phenolic pollutant is taken as a template, a functional monomer, a hole generating agent, a catalyst and a coordination agent react under a certain condition, and after reacting is finished, template molecules are washed off to obtain the cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent for the phenolic pollutant.A static adsorption test is used for studying the adsorption balance, kinetics and selectivity recognition properties of the imprinted adsorbing agent.A result shows that the obtained cellulose-based imprinted adsorbing agent has the quick adsorption kinetics property and the superior phenolic pollutant molecule recognition property on the phenolic pollutant.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
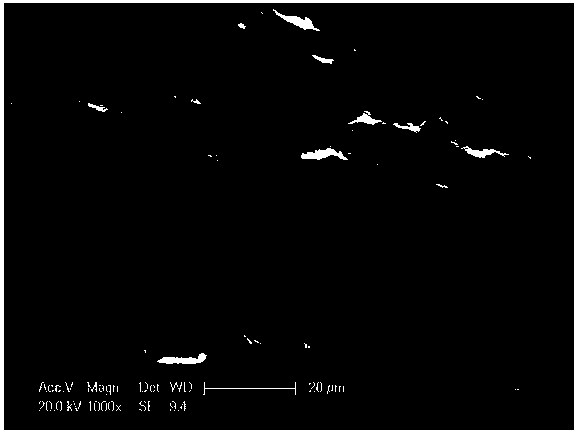
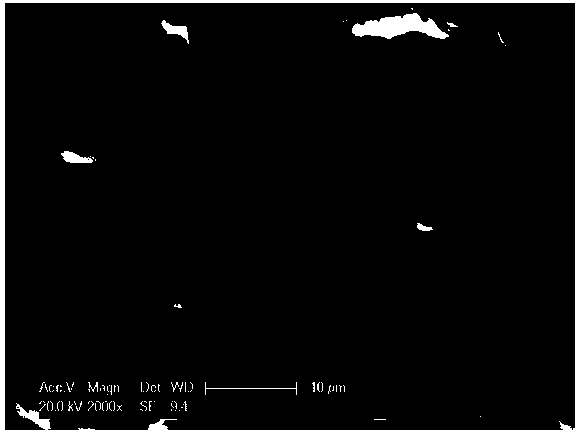
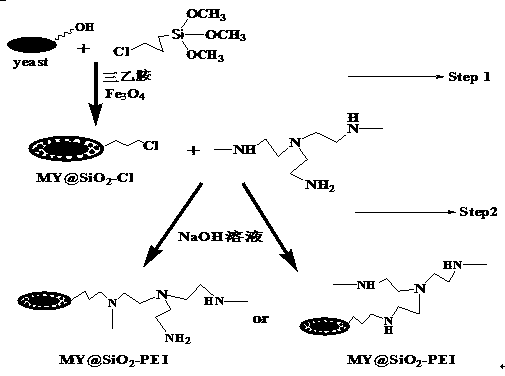
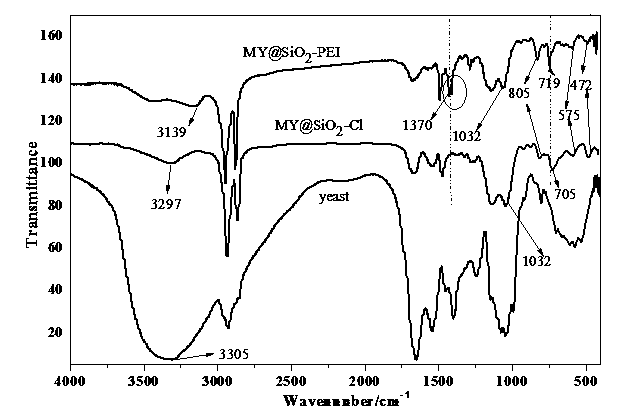
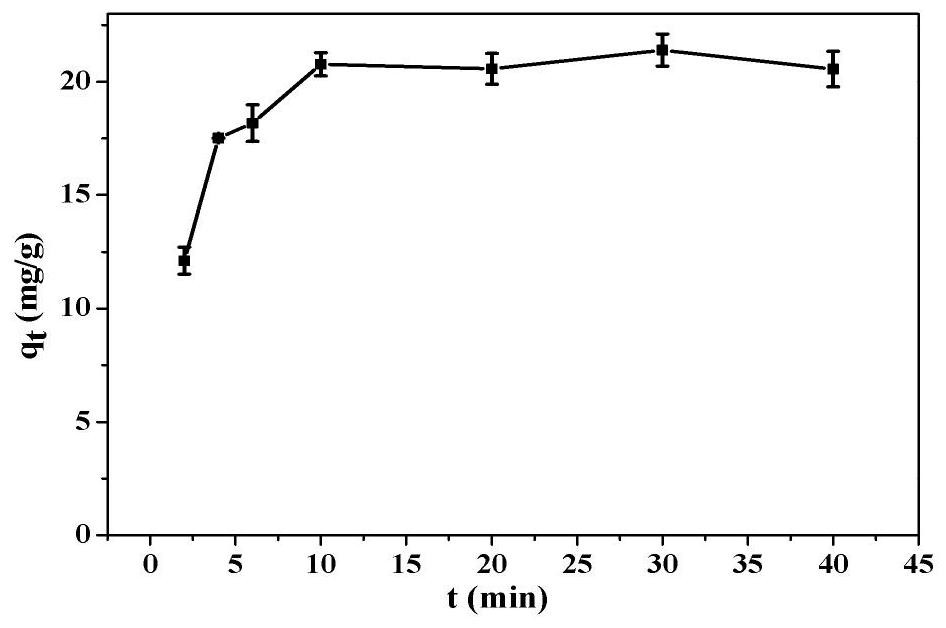
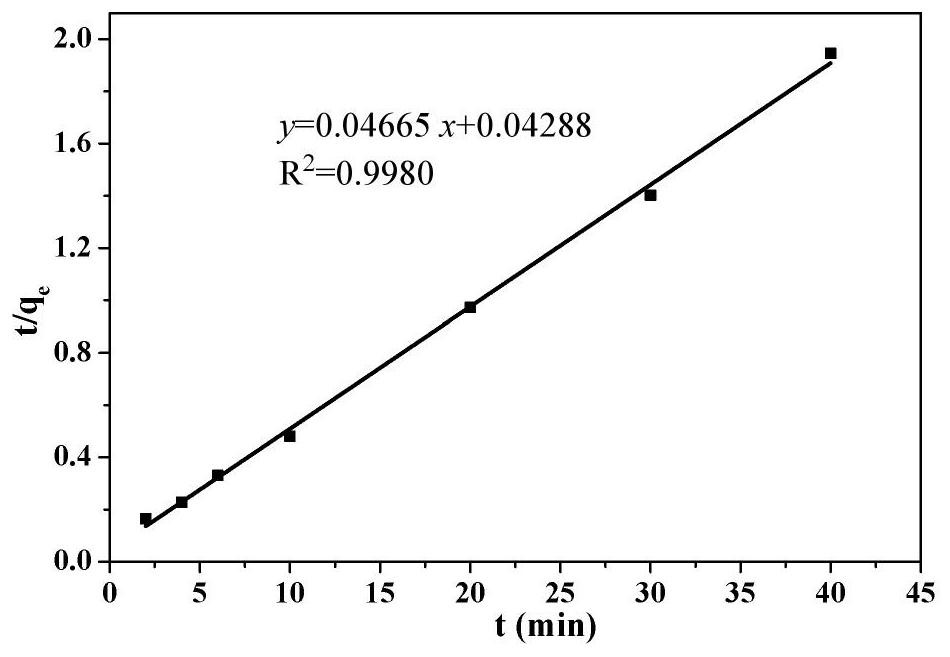
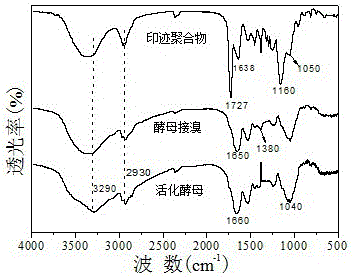
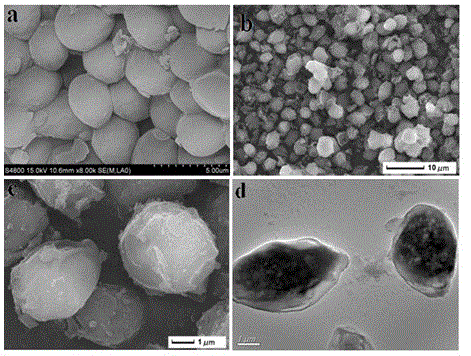
Preparation method and application of magnetic silicon-coated yeast grafted polyethyleneimine biological composite material
InactiveCN103657608AWide variety of sourcesLow costOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesFunctional monomerSorbent
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental function material preparation and relates to a preparation method of a magnetic silicon-coated yeast grafted polyethyleneimine biological composite material for adsorptive separation of cerium ions and strontium ions. According to the technical scheme, the preparation method comprises the following steps: at first, ultrasonically mixing activating yeasts with magnetic nanoparticles, and reacting the mixture with triethylamine and 3-chloropropyl trimethoxysilane in a methylbenzene system to prepare magnetic silicon-coated yeasts; then, adding polyethyleneimine as a functional monomer, producing a substitution reaction of chlorine groups on the surfaces of the magnetic silicon-coated yeasts with a polyethyleneimine solution, and grafting polyethyleneimine onto the surfaces of the magnetic silicon-coated yeasts to prepare the biological composite material. According to the method, the yield of a matrix material is increased; a prepared adsorbent overcomes the deficiency of low mechanical strength of a conventional biological material, is good in magnetic responsibility, can achieve quick separation, is higher in adsorption capacity and adsorption kinetics performance, and can achieve the purpose of quick and efficient adsorptive separation of the cerium ions and the strontium ions.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Water treatment method for adsorbing humic acid in water by metal organic framework HKUST-1
InactiveCN112759026AImprove adsorption capacityPromote regenerationOther chemical processesWater contaminantsDesorptionMetal-organic framework
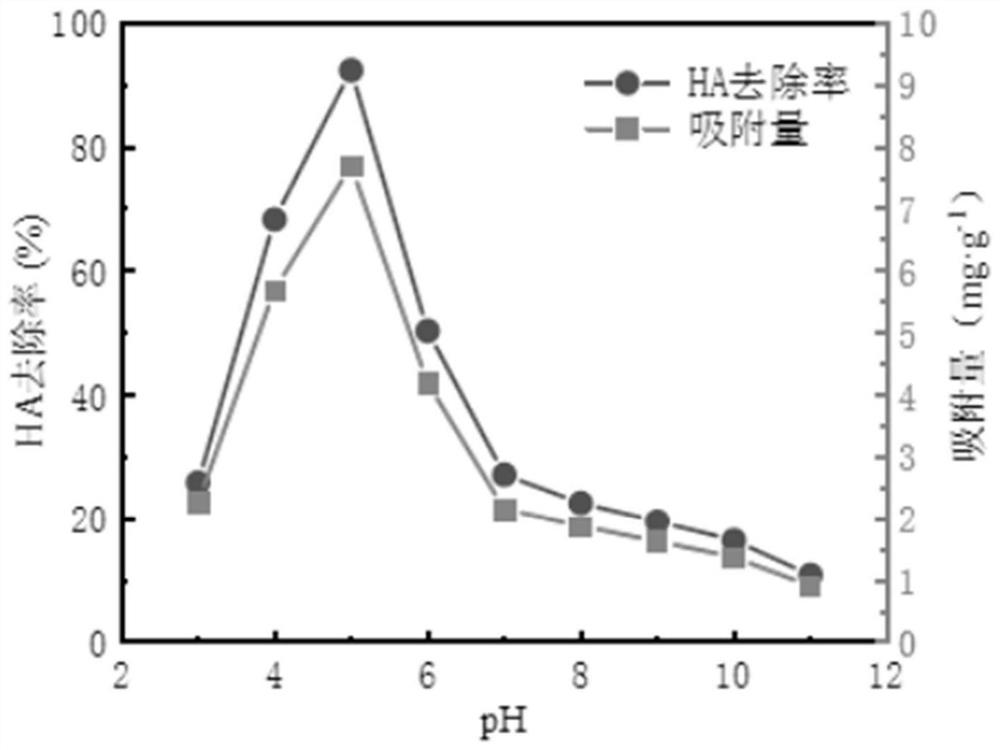
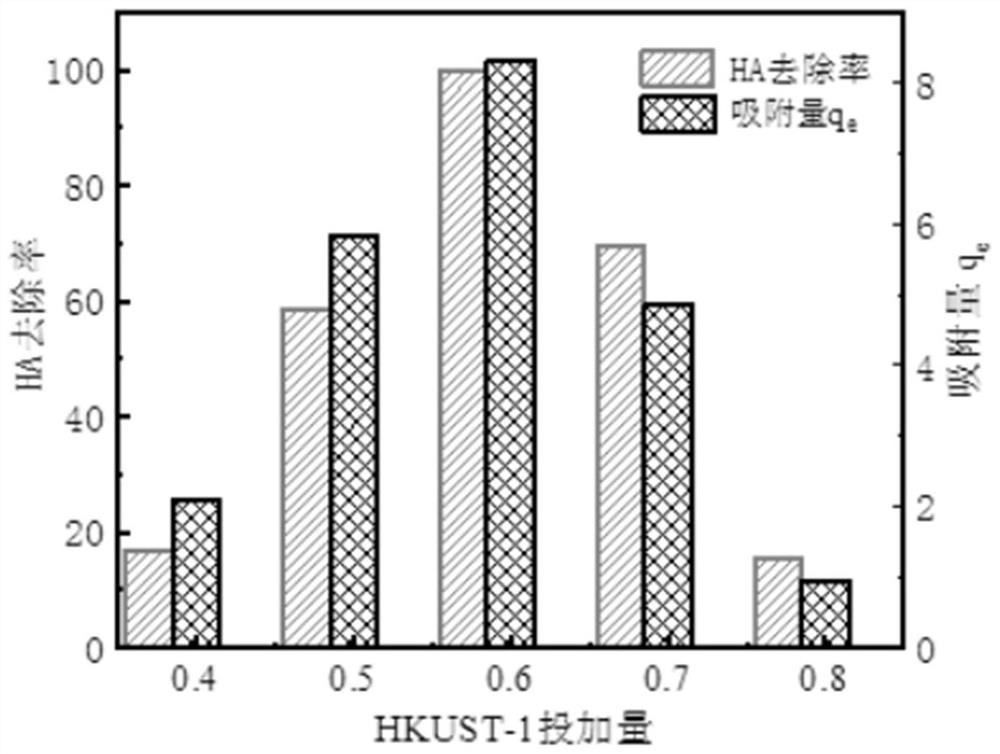
The invention provides a water treatment method for adsorbing humic acid in water by using a metal organic framework material HKUST-1. An adsorption material 1,3,5-trimesic acid copper (HKUST-1) is prepared by adopting a solvothermal method, after the adsorption material HKUST-1 adsorbs a 5mg / L humic acid solution for 120 minutes under the conditions that the tempeature is 298K, the pH value of the solution is 5 and the dosage of the HKUST-1 is 0.6 g / L, the highest removal rate can reach 100%, and the adsorption capacity is 8.33 mg / g. The adsorption of the HKUST-1 on the humic acid accords with a Langmuir adsorption isotherm model, the HKUST-1 is monomolecular layer adsorption, and the theoretical saturated adsorption capacity can reach 16.385 mg / g. A quasi-secondary kinetic model can be used for well describing the adsorption kinetics of the HKUST-1 on the humic acid in the water. Adsorption of the HKUST-1 on humic acid is a spontaneous and disordered heat absorption process. A desorption regeneration result shows that the HKUST-1 has good reproducibility and can be repeatedly used. The application of HKUST-1 in water treatment can develop a new way for micro-pollution treatment of a surface water source with the characteristic of high content of traditional organic matter, and an ideal adsorption application prospect is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Ion selective multi-modified composite electrode material, preparation method and application of composite electrode material in electro-adsorption desalination
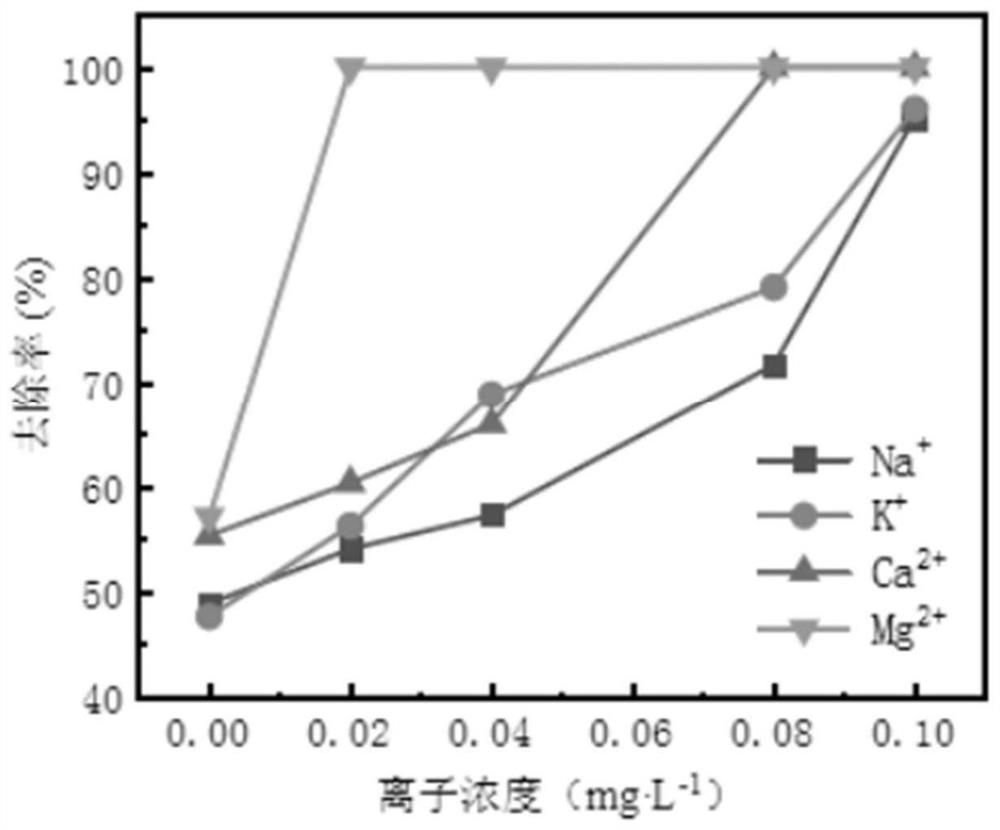
InactiveCN108911058ABig gapImprove adsorption capacityDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatment apparatusComposite electrodeDesalination
The nvention discloses an ion selective multi-modified composite electrode material, a preparation method and application of the composite electrode material in electro-adsorption desalination. According to the electrode material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, an electro-adsorption desalination module with the composite electrode material serving as electrodes is used fortreating salt-contained wastewater mainly contains landfill leachate effluent, and the desalting rate is 42.6%, the desalting speed is 90 mg / (L*h), wherein the removal rate of Cl<-> is 66.7%, the removal rate of Ca<2+> is 80.2%, and the removal rate of Mg<2+> is 73.3%; and internal diffusion equation adsorption kinetics fitting is carried out on different ion adsorption processes, the adsorptionconstant of the Cl<-> is 2.78, and after adsorption kinetics fitting, the adsorption constant of the Ca<2+> and the Mg<2+> is 2.06 times or more of the adsorption constant of the Cl<->. The electrodematerial prepared through the preparation method has the advantages of being large in adsorption capacity, strong in conductivity and capable of realizing selective adsorption of cations, especially the Ca<2+> and the Mg<2+>, the electro-adsorption desalination module with the composite electrode material serving as the electrodes can be used for processing the salt-contained industrial wastewaterwith high hardness and complex components in a targeted mode, so that the salt-contained wastewater is effectively desalinated, industrial regeneration and reuse are carried out, and a wide prospectin the field of environmental protection and salt-contained wastewater treatment is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of gamma-Al2O3 adsorbent
InactiveCN105879831ASave raw materialsSimple processOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAluminium chlorideMicron scale
The invention relates to a preparation method of a gamma-Al2O3 adsorbent, in particular to a preparation method of a hexagonal columnar micron-scale gamma-Al2O3 adsorbent with controllable particle size. The preparation method comprises the following steps: one of PSS, PEG 2000 or a Pluronic block copolymer, one of aluminum potassium sulfate and aluminum chloride as well as potassium acetate are dissolved in distilled water sequentially, uniformly and sufficiently stirred and subjected to hydro-thermal treatment, a hydro-thermal product is cooled naturally, separated, washed, dried in vacuum and roasted, hexagonal columnar micron-scale gamma-Al2O3 particles with remarkably accelerated adsorption kinetics on azo dye Congo red and excellent adsorption property are prepared, and the particle size of the hexagonal columnar micron-scale gamma-Al2O3 particles is changed in the length range of 1-2 mu m and in the height range of 2-3 mu m. The preparation method has the remarkable advantages that the raw materials are cheap, the preparation process is simple, reaction conditions are mild, the particle size of the product is controllable in a certain range, the adsorption of Congo red is excellent and the like, and the absorbent can be recycled.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis of a Novel Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Using COK-19 Template for Water and Wastewater Treatment
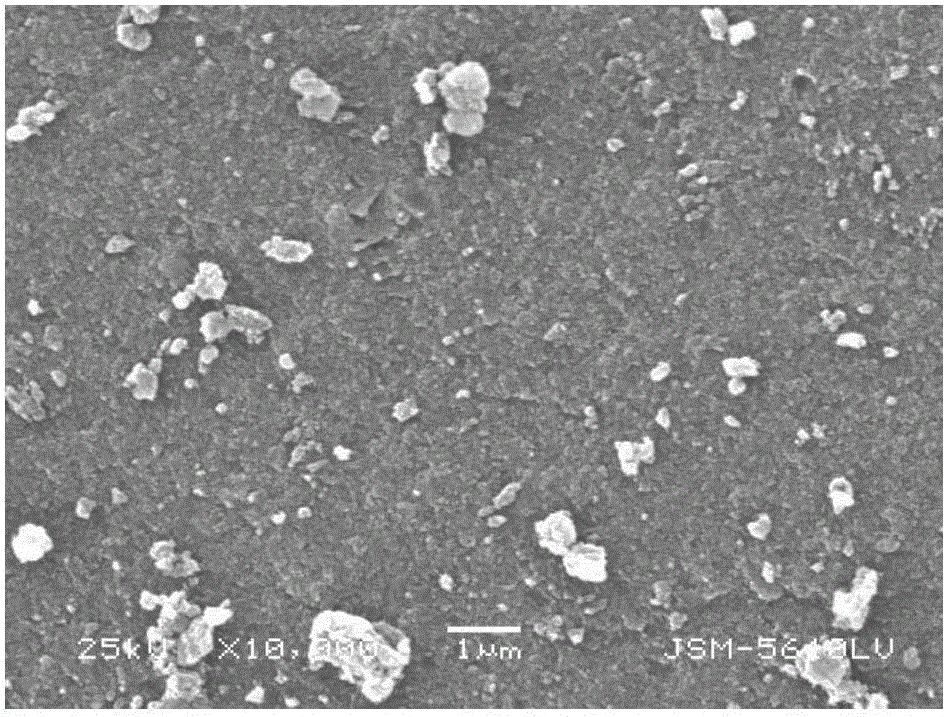
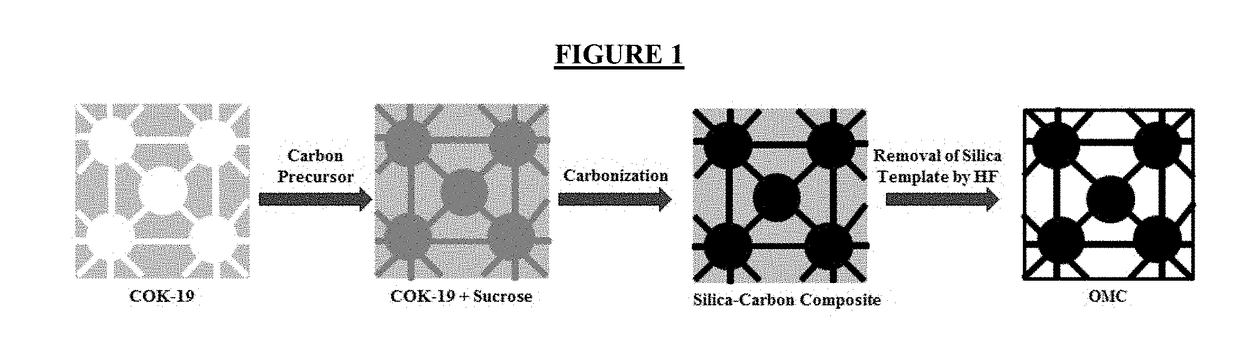
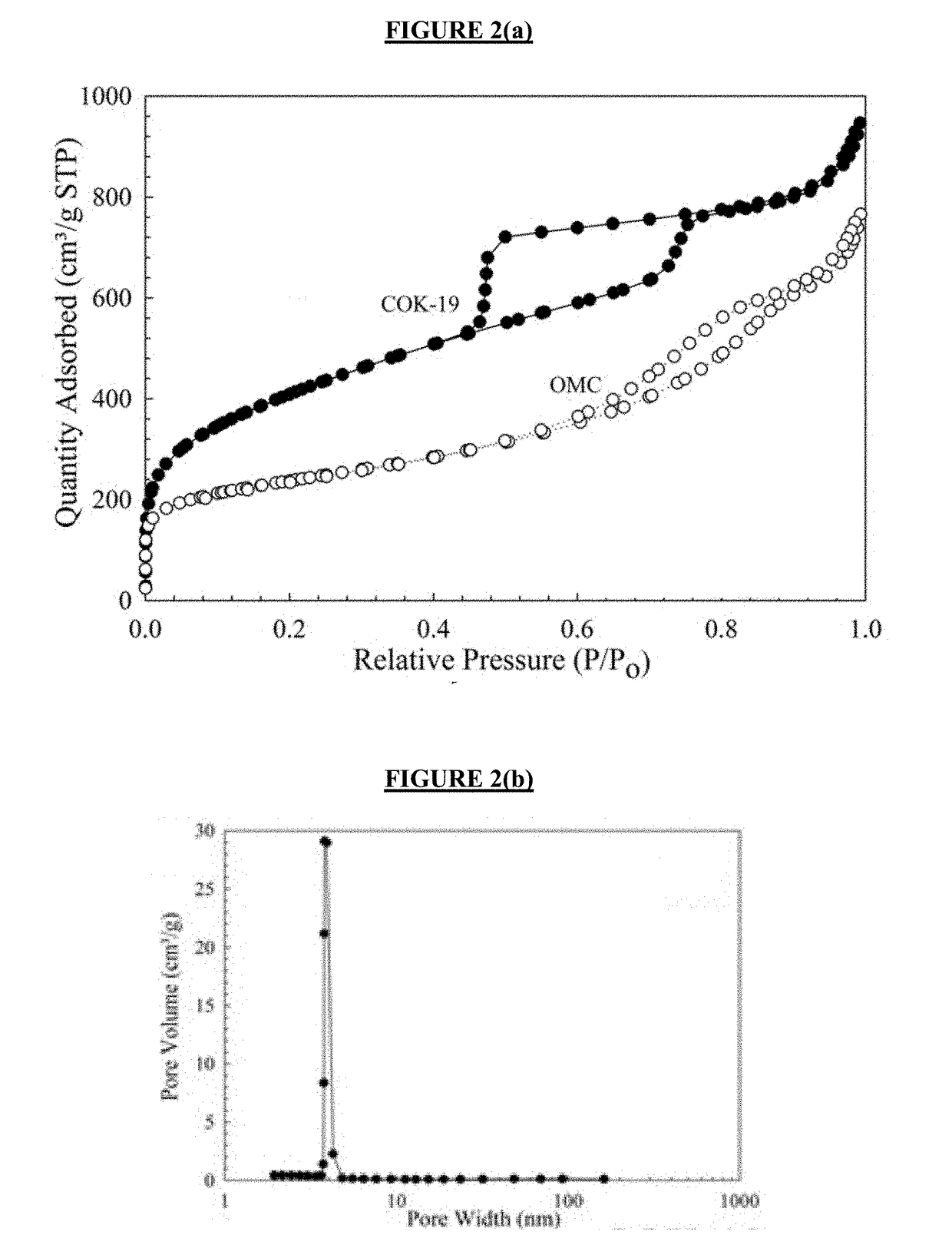
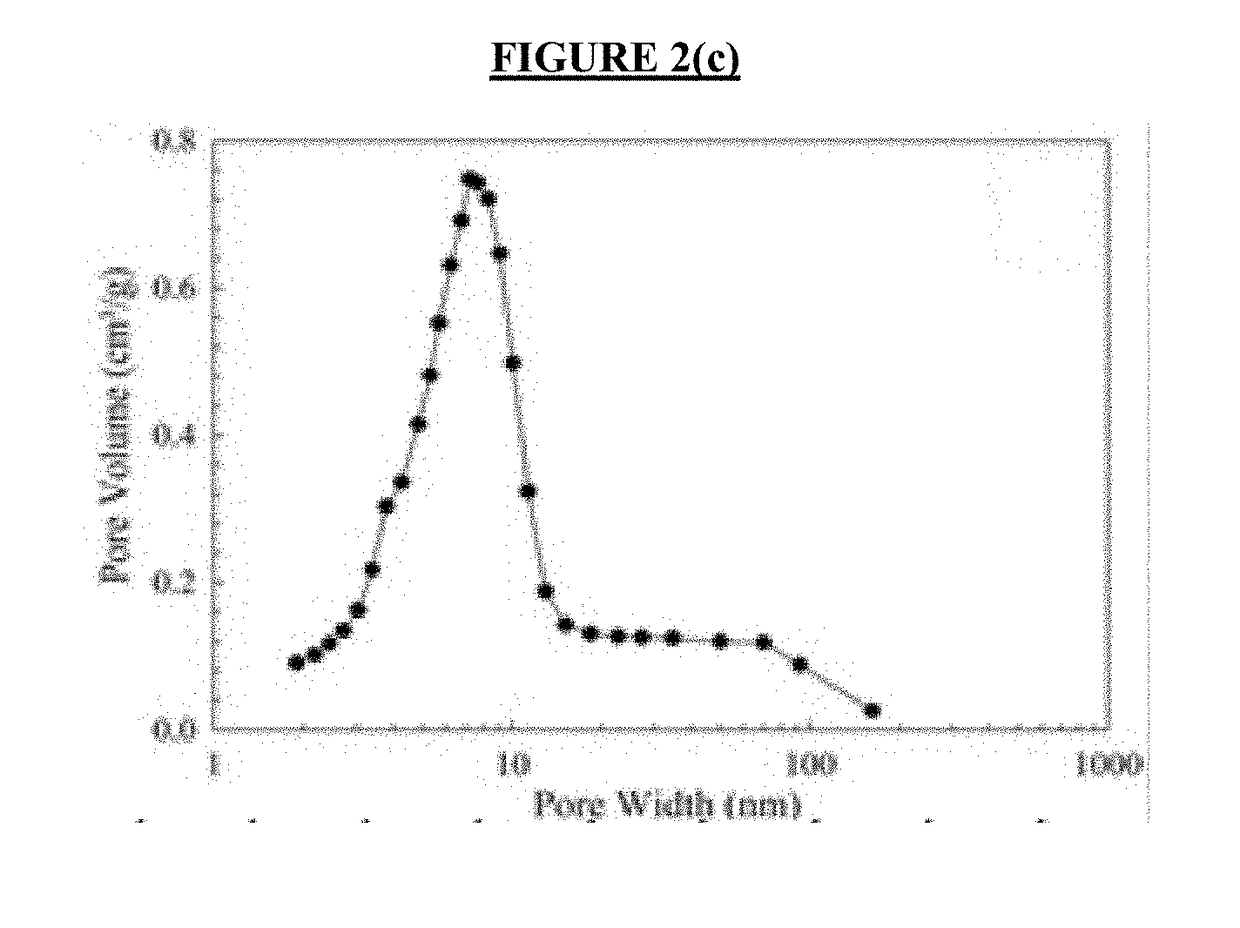
InactiveUS20190046953A1Large specific surface areaLarge average pore sizeGas treatmentOther chemical processesDesorptionCarbonization
Ordered mesoporous carbon was prepared using COK-19 silica template. Ordered mesoporous silica COK-19 was synthesized with cubic Fm3m structure. Sucrose as the carbon precursor was impregnated into the mesopores of silica and converted to carbon through carbonization process using sulfuric acid as a catalyst. Ordered mesoporous carbon was obtained after the removal of silica framework using hydrofluoric acid. Several characterization techniques such as nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms, transmission electron microscope (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and elemental analysis were employed to characterize the OMC. The pore size analysis and TEM images confirmed that OMC has replicated the mesostructure of the COK-19. Results obtained from adsorption kinetics and isotherms suggest that the Pseudo-Second-Order Model and Langmuir Isotherm well described the experimental data. The adsorption study showed that the synthesized OMC has an adsorption capacity of 40.5 mg / g for resorcinol removal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA AT LAFAYETTE
Process for preparing an adsorbing material comprising a precipitating step of boehmite according to specific conditions and process for extracting lithium from saline solutions using this material
ActiveUS10786802B2Improve adsorption capacityImproved adsorption kineticsOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationNitrate anionSulfate radicals
Owner:ERAMET +1
Detection method of rhodamine B
PendingCN114062332AFast adsorptionWide linear rangePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolid phase extractionAdsorption separation
Owner:南宁兴科净医疗科技有限公司
A kind of preparation method of adsorbent for selective separation of ciprofloxacin in water environment
InactiveCN103599759BEasy to retouchSolve the difficulty of synthesisOther chemical processesPtru catalyst(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a novel adsorbent for selectively separating ciprofloxacin in water environment, belonging to the technical field of environmental material preparation. The present invention utilizes commercialized dry yeast as a matrix material, first modifies it into a composite material with an initiating agent, then uses ciprofloxacin as a template, and methacrylic acid and hydroxyethyl methacrylate as functional monomers , ethylene glycol di(methacrylate) ester as cross-linking agent, cuprous bromide as catalyst, using surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization method, synthesized molecularly imprinted adsorption on the surface of yeast in a green and environment-friendly emulsion system agent. Static adsorption experiments were used to study the adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and selective recognition performance of the prepared imprinted adsorbent. The results show that the yeast surface imprinted adsorbent obtained by the present invention has fast adsorption kinetic properties and superior recognition performance for ciprofloxacin in water environment.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for analyzing influence of humic acid in water body on lead adsorption process and mechanism
PendingCN113820400AEasy to operateComponent separationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSoil scienceAnalysis water
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental analysis, and particularly relates to a method for analyzing the influence of humic acid in a water body on the lead adsorption process and the mechanism, the influence behaviors of humic acid on Pb < 2 + > adsorption of micro-plastic under different conditions are elaborated through adsorption kinetics and adsorption isothermal research, and the adsorption mechanism of the micro-plastic on Pb < 2 + > is disclosed by combining the energy distribution characteristics of the sites; the influence of humic acid on the combination process of the micro-plastic and Pb < 2 + > is analyzed and discussed through fluorescence quenching of humic acid, and the process and mechanism of humic acid for promoting the micro-plastic to adsorb Pb < 2 + > are disclosed; the method is simple in operation steps, can systematically analyze the Pb < 2 + > adsorption behavior of the micro-plastic from different angles, provides a scientific basis for effective control of the micro-plastic and lead (Pb (II)) in a water body environment, and has a relatively great application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
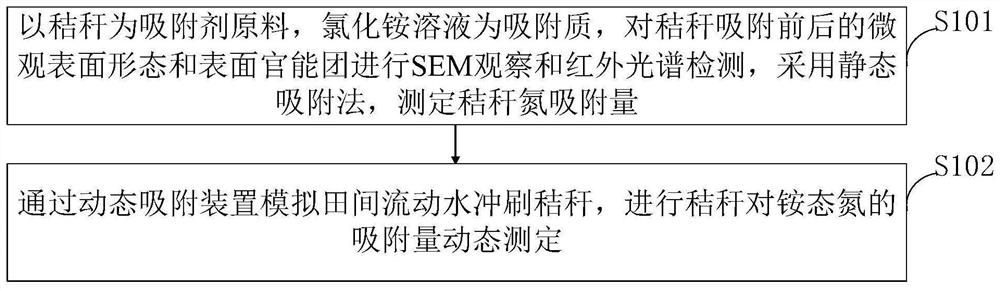
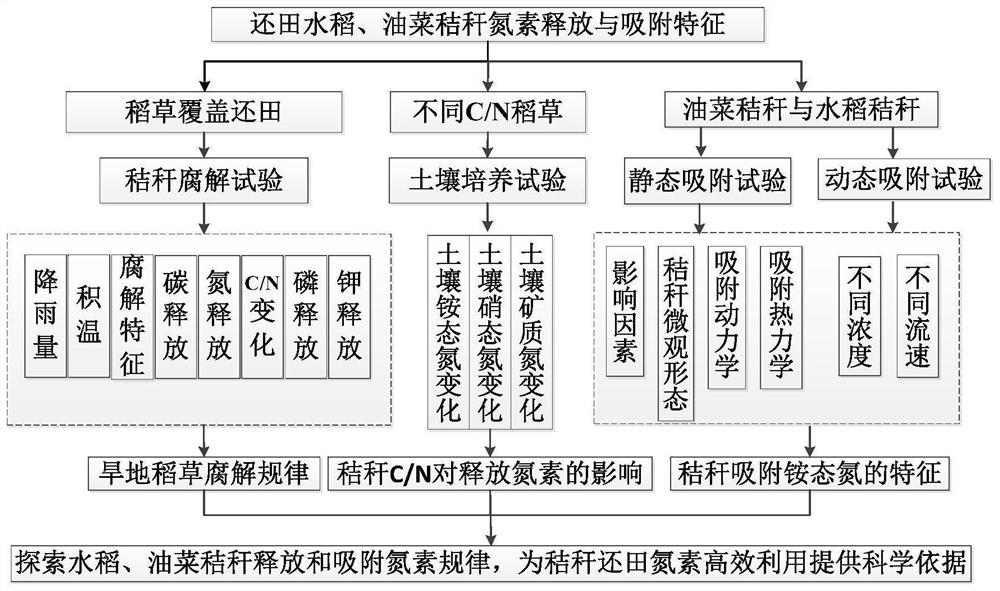
Straw nitrogen adsorption determination method and determination device
PendingCN111982853AFit the actual situationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansSoil scienceStraw
The invention belongs to the technical field of measurement, and discloses a straw nitrogen adsorption measurement method and device. The straw nitrogen adsorption measurement method comprises the steps of simulating field flowing water to scour straws through a dynamic adsorption device, and carrying out the dynamic measurement of the adsorption capacity of the straws for ammonium nitrogen. According to the invention, the nitrogen adsorption performance of the straws is used as a starting material; a method of combining static adsorption and dynamic adsorption is adopted; microcosmic surfacemorphology and surface functional group changes of the straws before and after nitrogen adsorption are analyzed, influence factors of the two kinds of straws on ammonium nitrogen adsorption and adsorption thermodynamics and adsorption kinetics research of the straws on nitrogen are discussed, an adsorption thermodynamics model and an appropriate kinetic model are established, and an adsorption mechanism of the adsorption thermodynamics model and the appropriate kinetic model is speculated. The adsorption characteristics of the straws to the ammonium nitrogen are determined, the fertilizer retention capacities of the two straws to the ammonium nitrogen fertilizer in the early stage of water and fertilizer combination are evaluated, and the mechanism of adsorbing the ammonium nitrogen by thetwo straws is preliminarily revealed.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Repairing method for acid goaf water
InactiveCN109574125AReasonable designWaste water treatment from quariesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSoil columnQuartz
The invention discloses a repairing method for acid goaf water. The repairing method includes 1, applying an adsorption kinetics method, to be more specific, placing air-dried loess in an oven at thetemperature of 105 DEG C for 24 hours until a constant weight is achieved, sieving the loess by a 200-mesh sieve, and storing the sieved loess for standby use; adding 25-200g of the loess per liter ofthe acid goaf water, and oscillating the acid goaf water at the temperature of 25-45 DEG C and at the speed of 200r / min for 10-60 minutes to treat the acid goaf water; 2, selecting a soil column, laying 2cm-thick quartz sand at the bottom of the soil column, filling the soil column with an air-dried soil sample section by section before compacting, laying 2cm-thick quartz sand on the soil sampleafter filling, and leaching the acid goaf water. The repairing method has the advantages that the adsorption characteristics of the loess on typical pollutants in the acid goaf water are studied, andthe repairing function of a PRB system synergistic material on the goaf water is defined.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
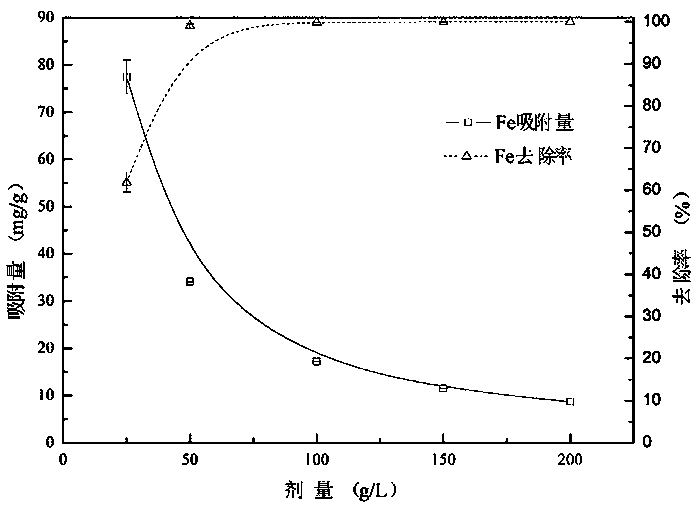
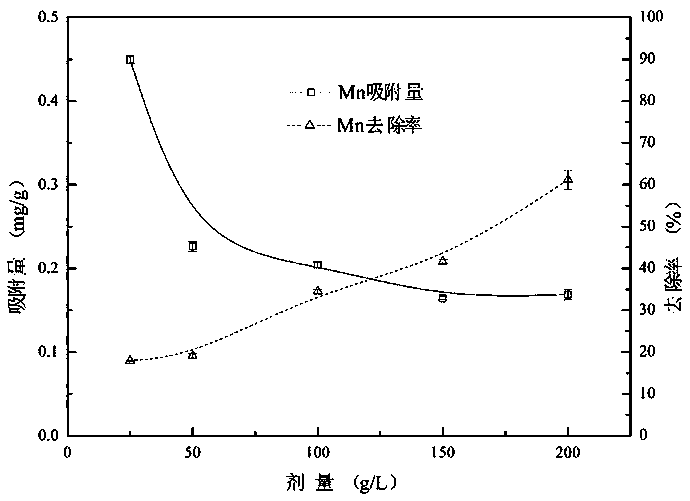
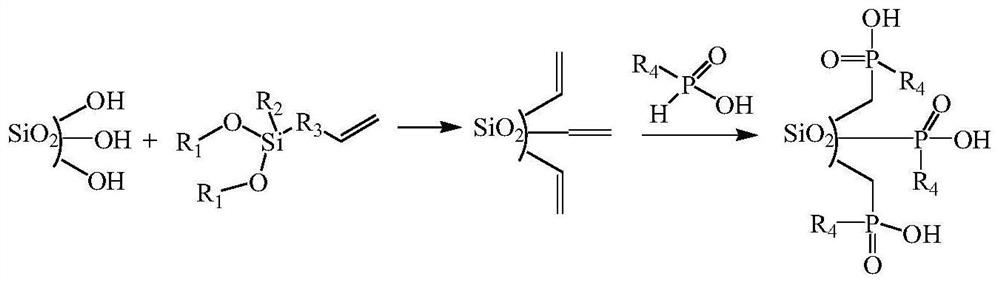
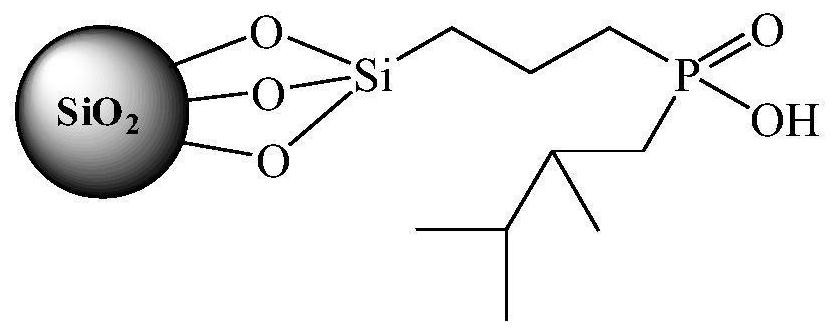
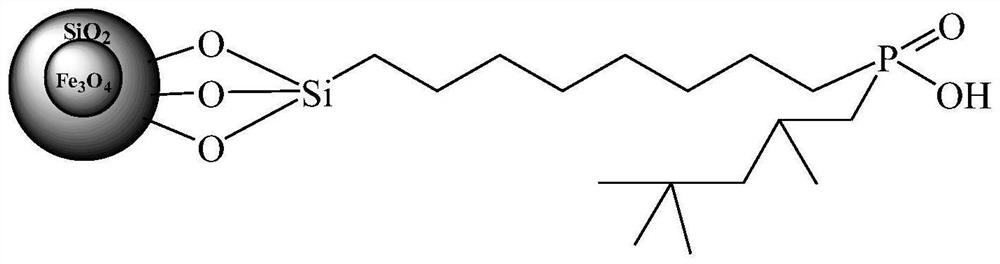
Preparation method of organic phosphinic acid functional group modified silicon-based adsorption material
ActiveCN113522243AHigh grafting rateImprove mechanical propertiesOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSilanesEthyl group
The invention relates to a preparation method of an organic phosphinic acid functional group modified silicon-based adsorption material. An organic phosphinic acid functional group is grafted on the surface of the silicon-based material, wherein R4 is an aliphatic substituent with the carbon atom number of 4-12. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, enabling a silicon-based material to react with a silane cross-linking agent with unsaturated carbon-carbon double bonds, grafting the carbon-carbon double bonds on the surface of the silicon-based material, and then grafting an organic phosphinic acid functional group to the surface of the silicon-based material by utilizing free radical addition reaction of the carbon-carbon double bonds and monoalkyl phosphinic acid, wherein R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group or a beta-methoxyethyl group; R2 is a methyl group, a methoxy group, an ethyoxyl group or a beta-methoxy ethyoxyl group; and R3 is (CH2)n, n= 0-10, or is gamma-methacryloyloxy propyl. The prepared adsorption material is good in mechanical property, stable in chemical property, fast in adsorption kinetics and good in selectivity; the preparation method is simple and easy to implement, large-scale production is easy to achieve, and the grafting rate of organic phosphinic acid functional groups is high. The method can be used in the fields of low-concentration rare earth enrichment, rare earth separation, nuclear-grade zirconium and hafnium separation and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
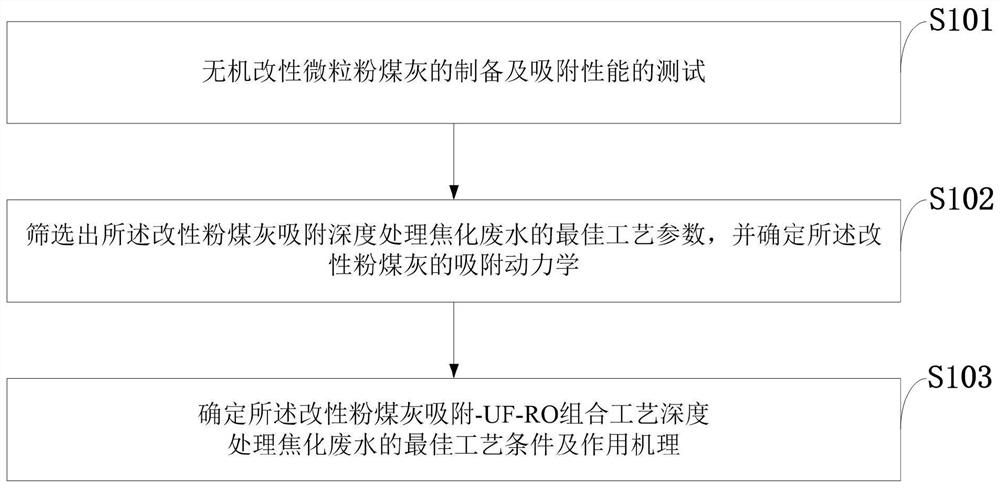
Modified fly ash adsorption-UF-RO advanced treatment coking wastewater detection method
InactiveCN113358839AStrong academicOther chemical processesScattering properties measurementsMembrane foulingFine particulate
The invention belongs to the technical field of coking wastewater evaluation, and discloses a modified fly ash adsorption-UF-RO advanced treatment coking wastewater detection method, which comprises: preparing inorganic modified particle fly ash, and testing the adsorption performance; screening out the optimal process parameters of the modified fly ash for adsorbing and deeply treating the coking wastewater, and determining the adsorption kinetics of the modified fly ash; and determining the optimal process conditions and action mechanism of the modified fly ash adsorption-UF-RO combined process for advanced treatment of the coking wastewater. By utilizing the porous structure and the adsorption characteristic of the modified fly ash, the adsorption removal of phenol, soluble organic matters and fine particulate matters in the coking wastewater is realized, so that the membrane pollution problem in the membrane separation process is reduced, the current national requirements on coking wastewater treatment are met, the operation cost is reduced, theoretical and technical bases are provided for ensuring that the coking wastewater meets stricter environmental protection standards and recycling, and the method has great significance in resource utilization and production cost reduction.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
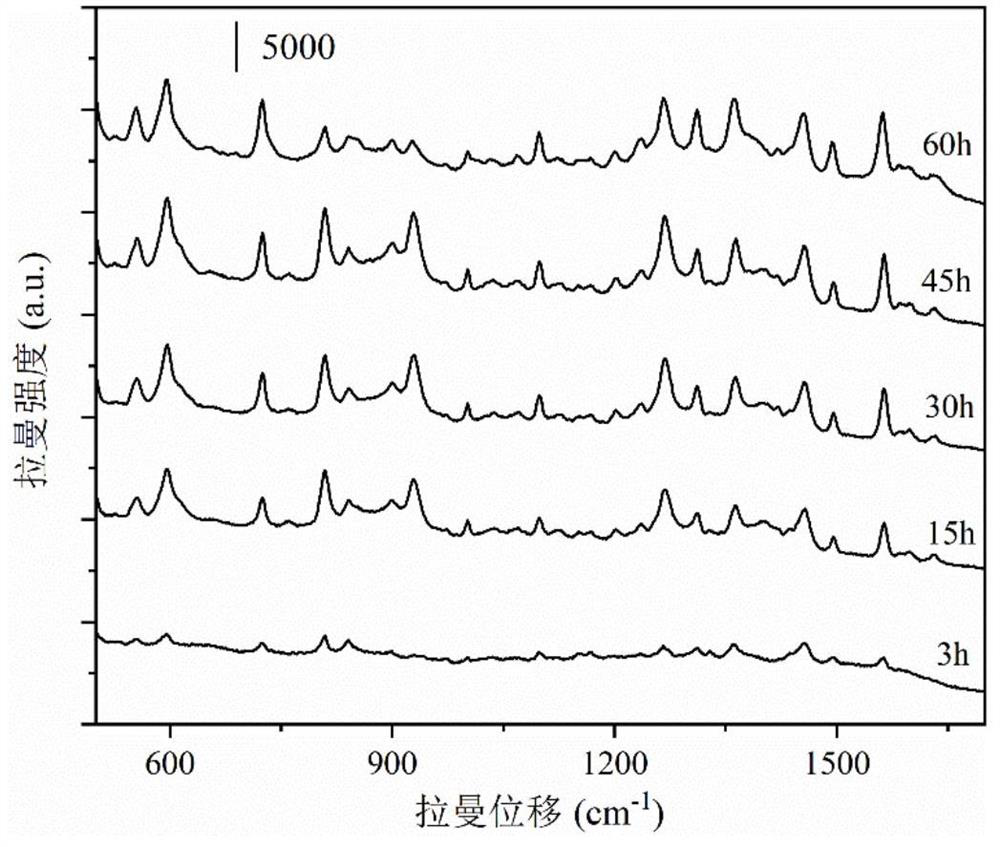
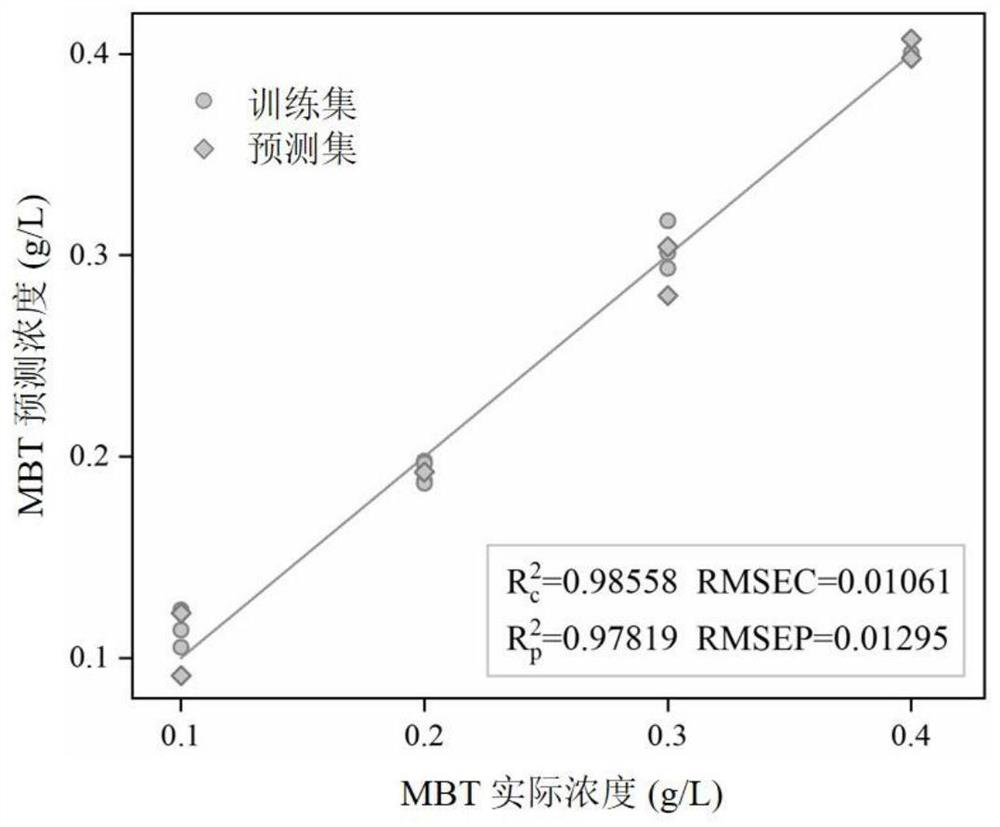
Method for representing adsorption and desorption processes of corrosion inhibitor
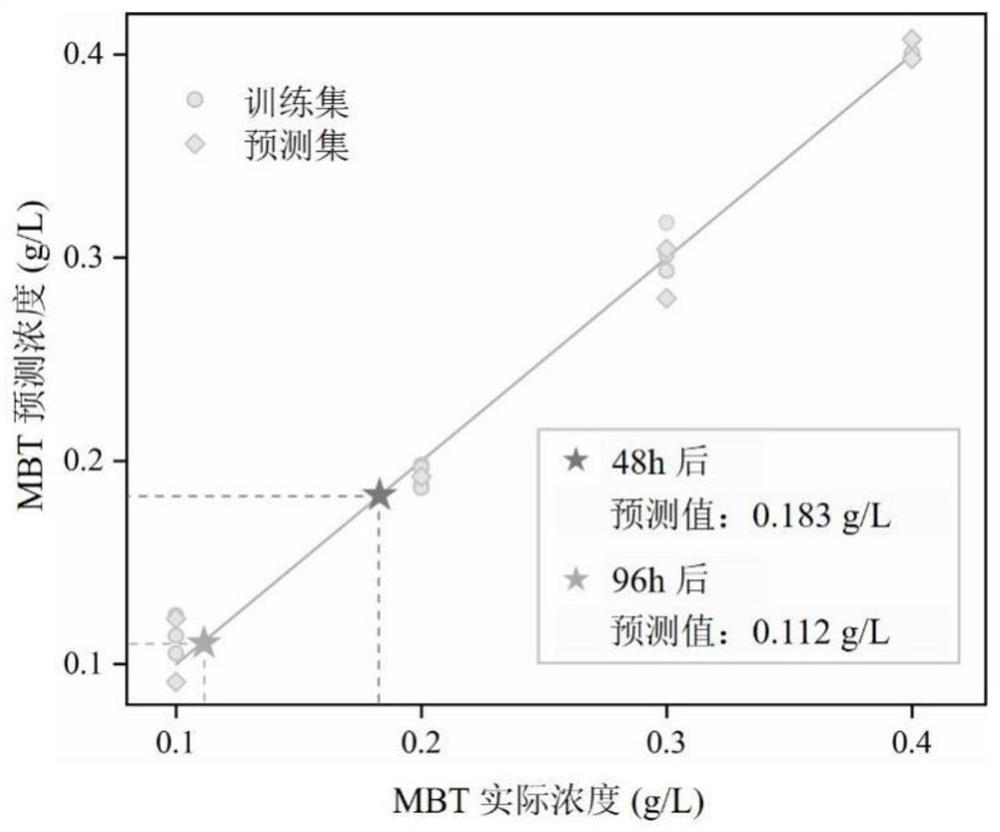
PendingCN113640276AHelps analyze adsorption kineticsClarification of Corrosion Protection EffectsRaman scatteringSpectral bandsMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for representing adsorption and desorption processes of a corrosion inhibitor. According to the method, the enhanced Raman spectrum technology and the least square regression method are combined, and the adsorption and desorption processes of the corrosion inhibitor are reflected by establishing a quantitative mathematical model of the concentration of the corrosion inhibitor and the Raman spectrum intensity. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, measuring an enhanced Raman spectrum of the corrosion inhibitor adsorbed on the surface of metal and alloy thereof to obtain saturated adsorption spectrum intensity; dividing the saturated adsorption Raman spectrums of the corrosion inhibitors with different concentrations into a training set and a prediction set, establishing a mathematical model of the corrosion inhibitor concentration and the spectral intensity by using a least square regression method, and improving the accuracy of the model by reasonably selecting a characteristic spectrum; and substituting the Raman spectrum of the corrosion inhibitor with unknown concentration into the model, and calculating the actual adsorption concentration of the corrosion inhibitor. The method can be used for representing the adsorption and desorption processes of the corrosion inhibitor along with time and concentration changes, facilitates the analysis of the adsorption kinetics law of the corrosion inhibitor, and is of great significance to clarification of the corrosion protection effect of the corrosion inhibitor.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com