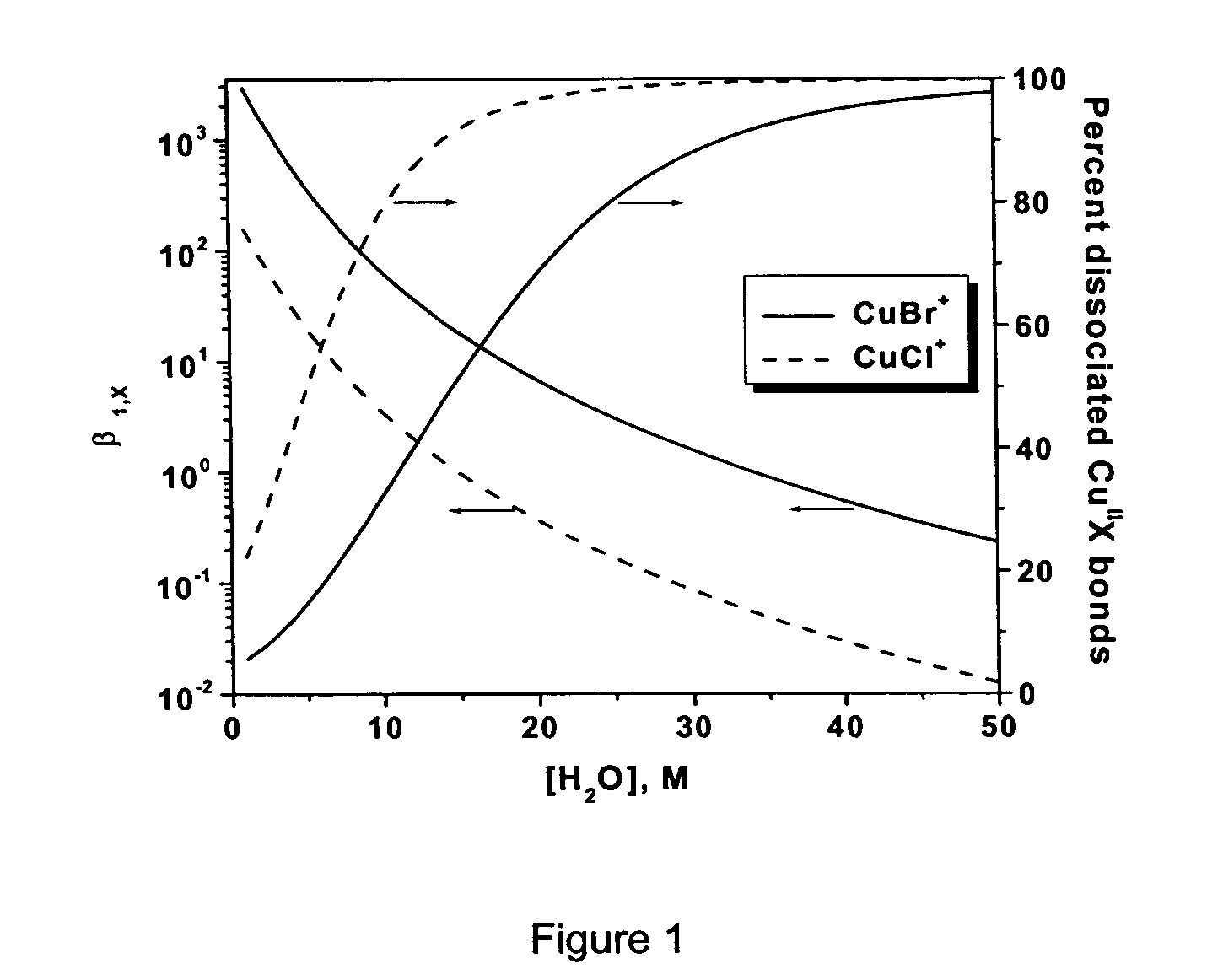
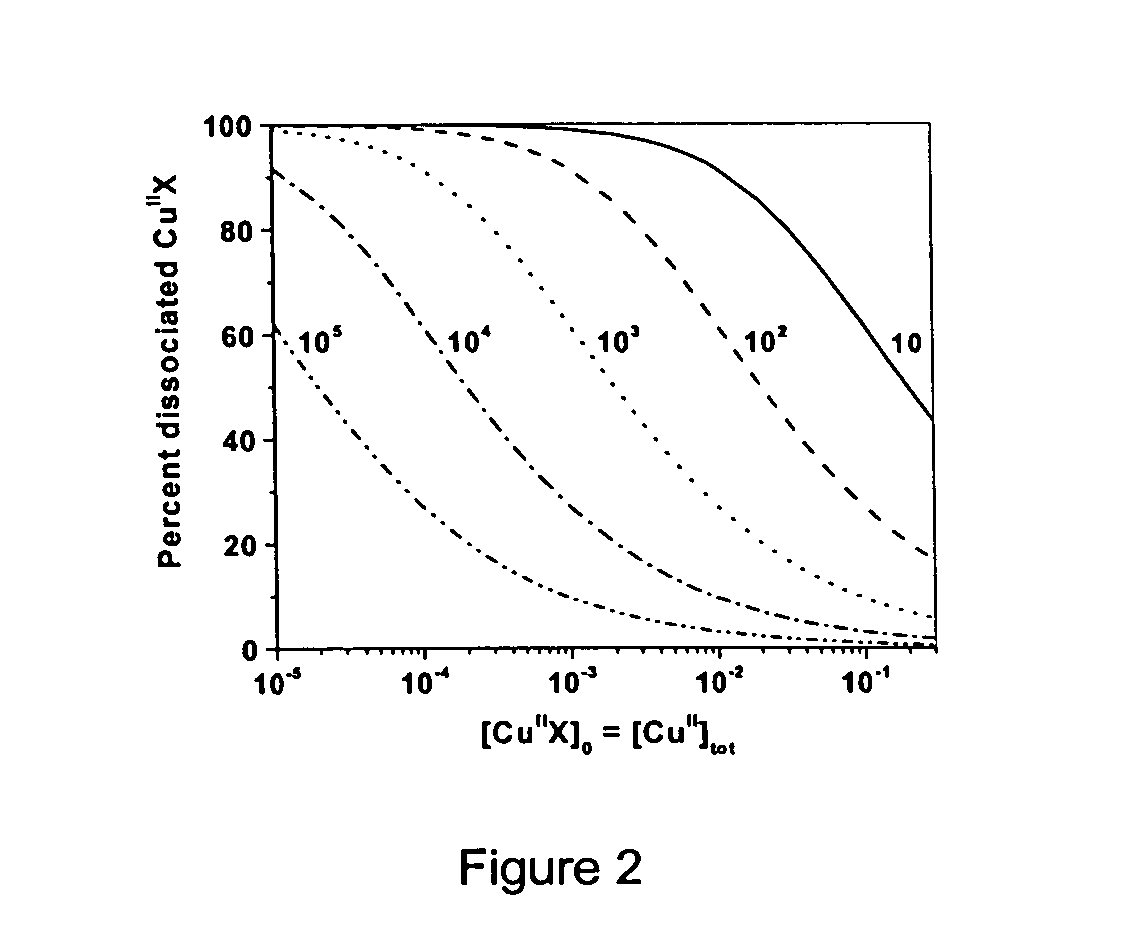
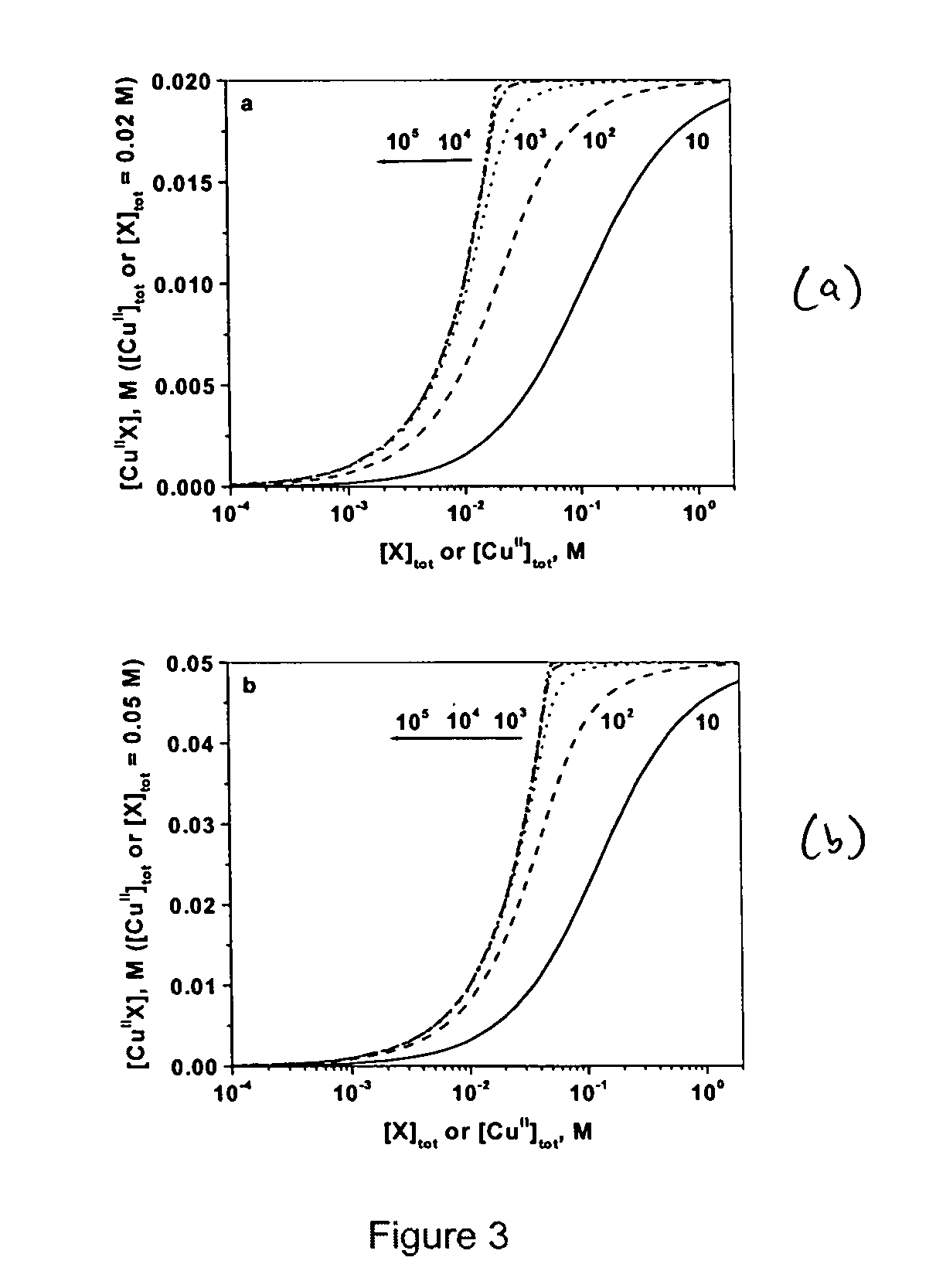
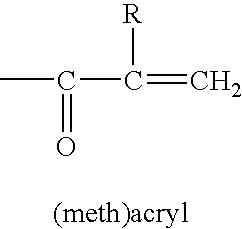
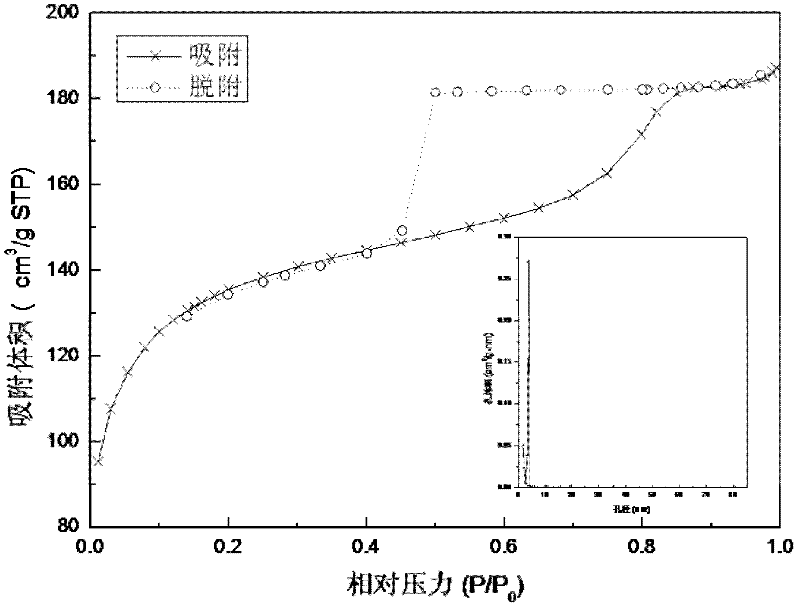
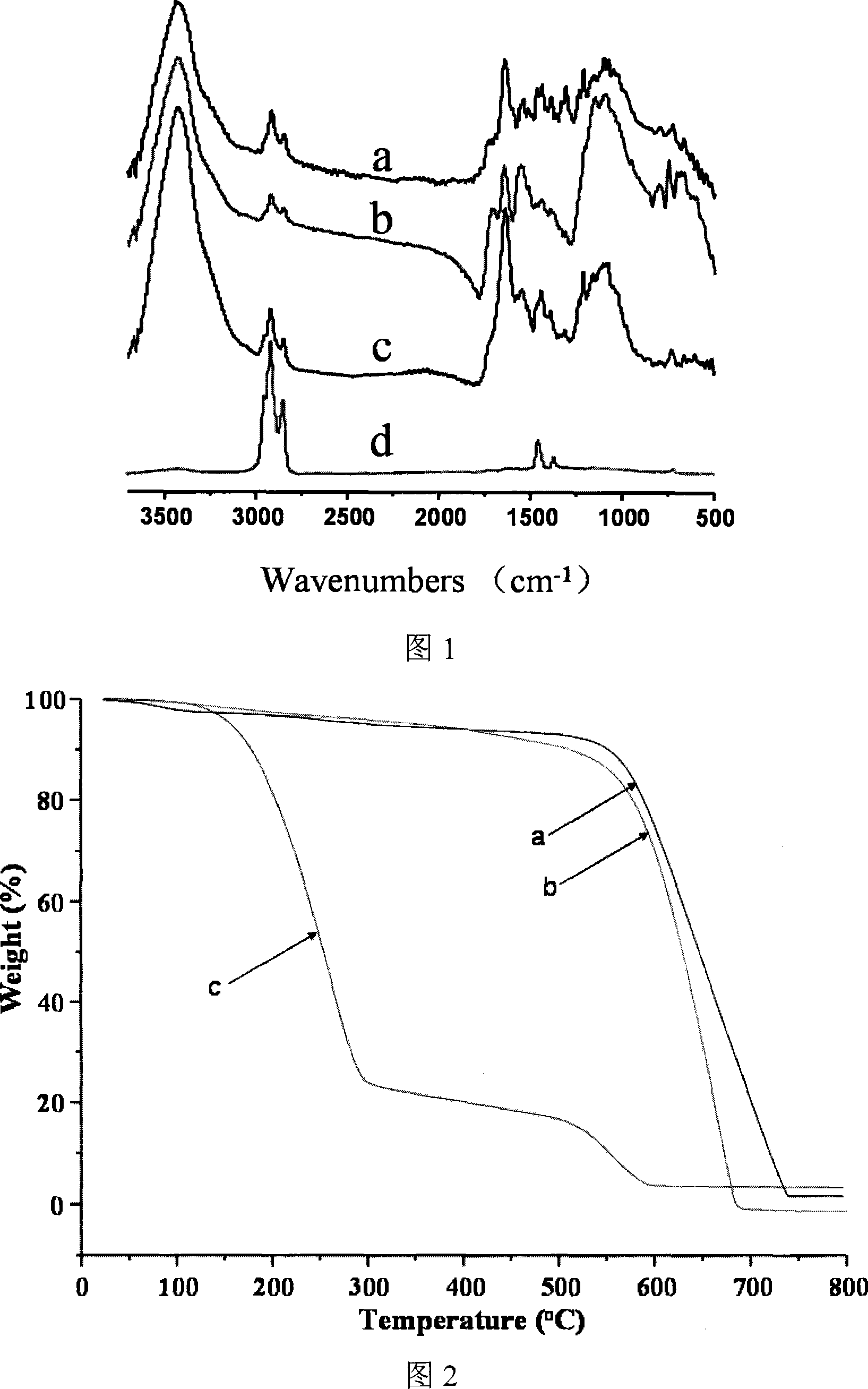
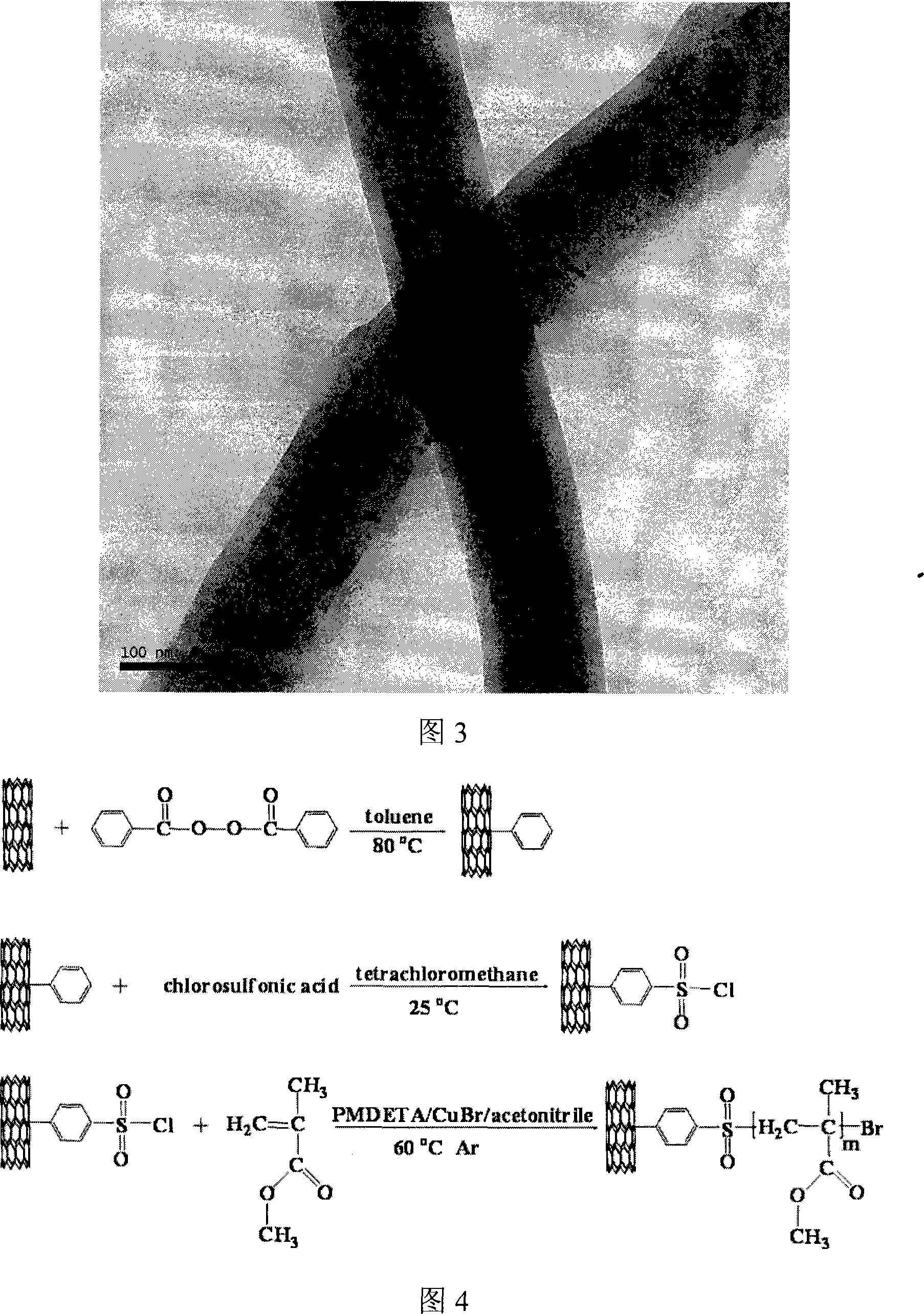
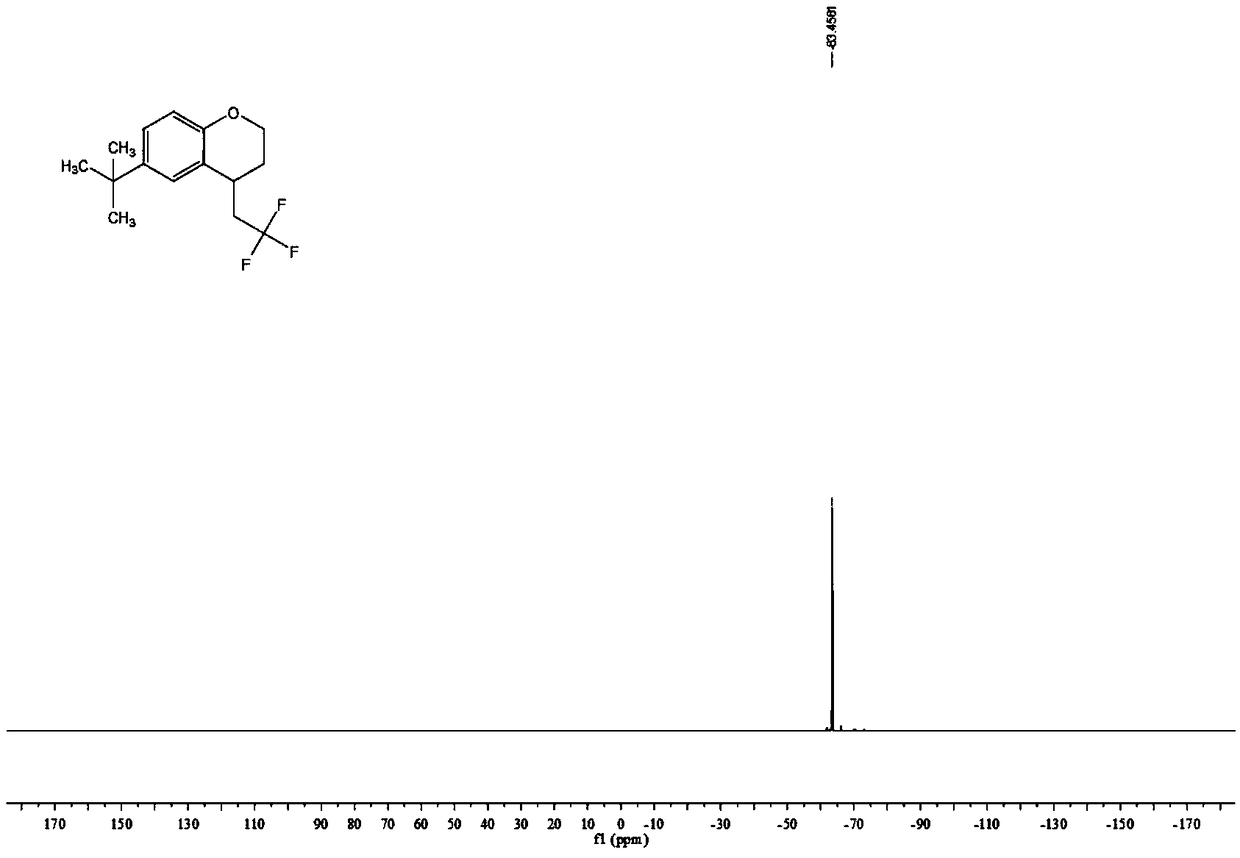
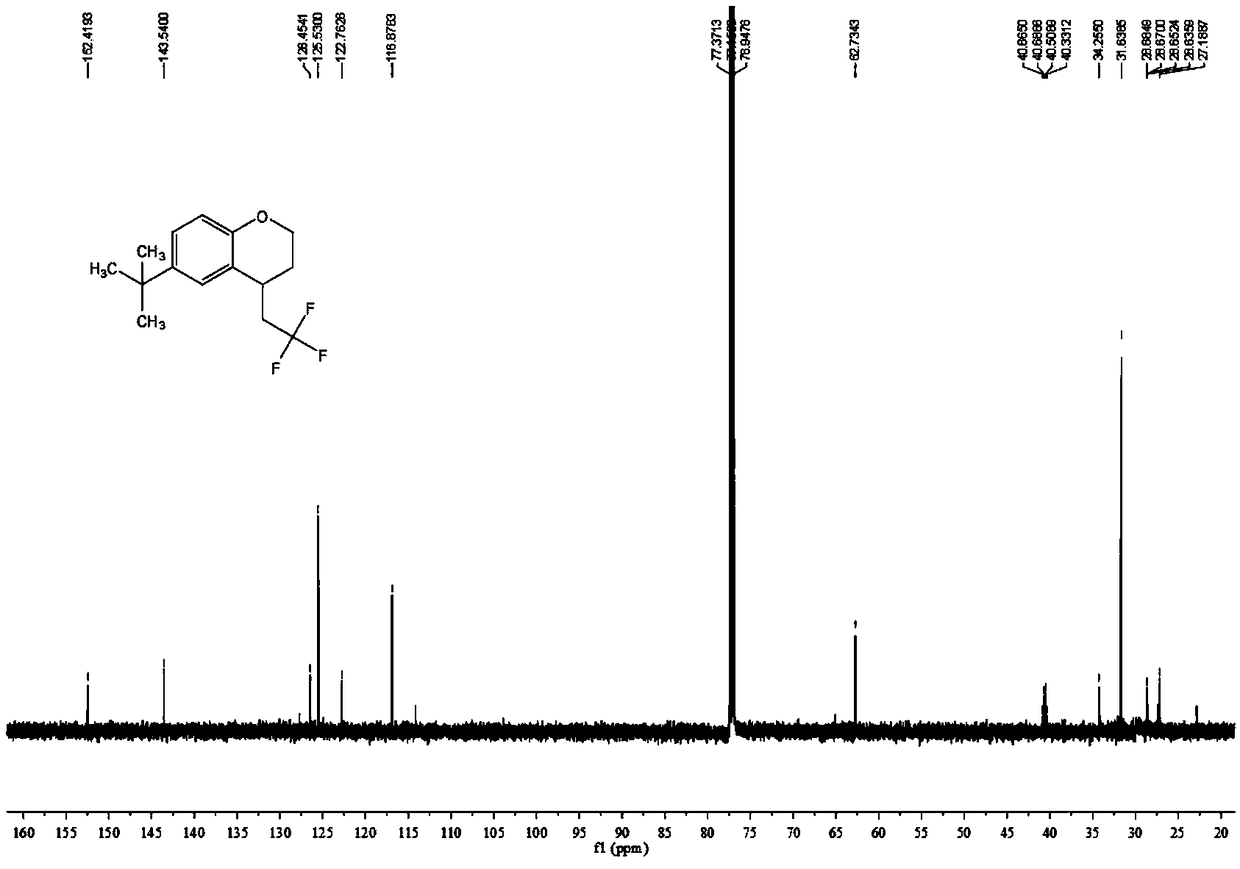
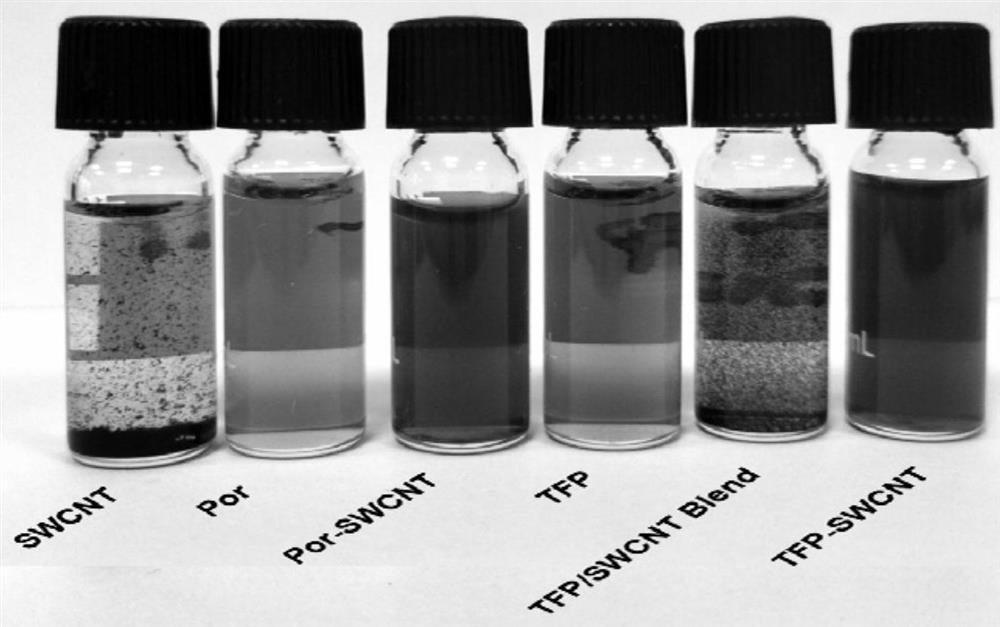
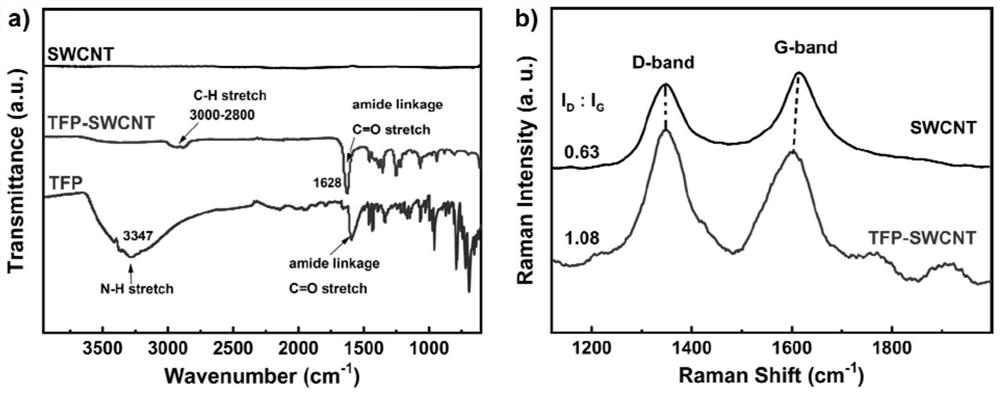
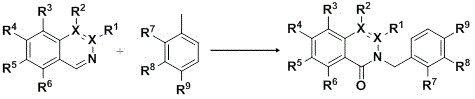
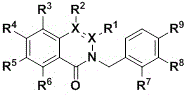
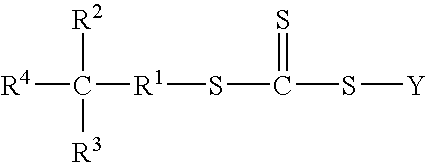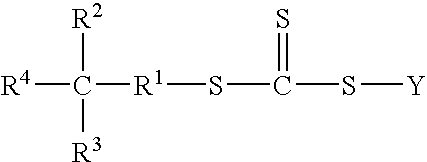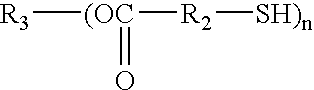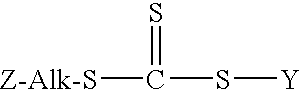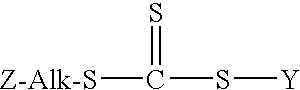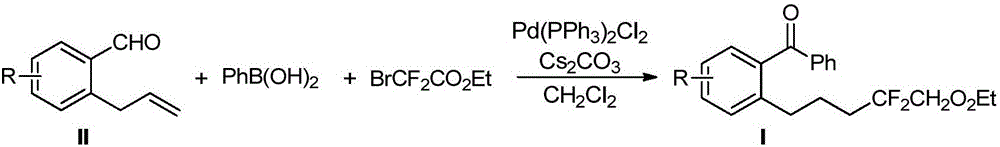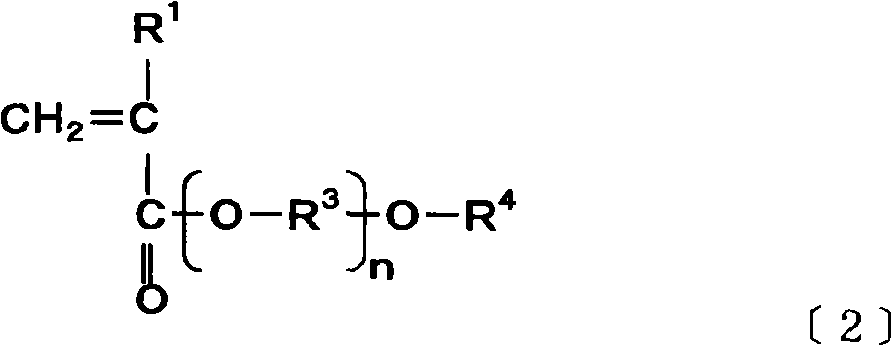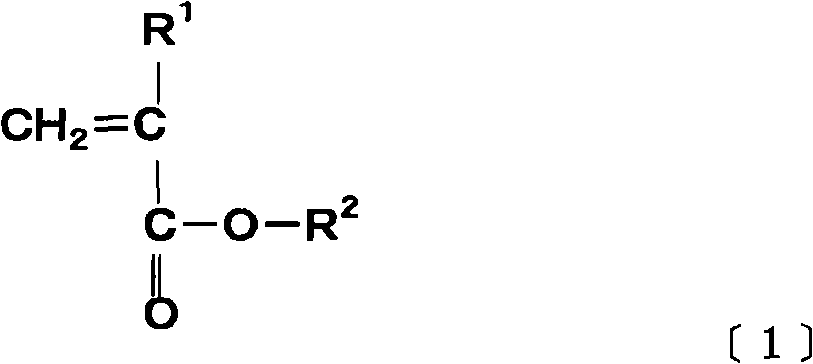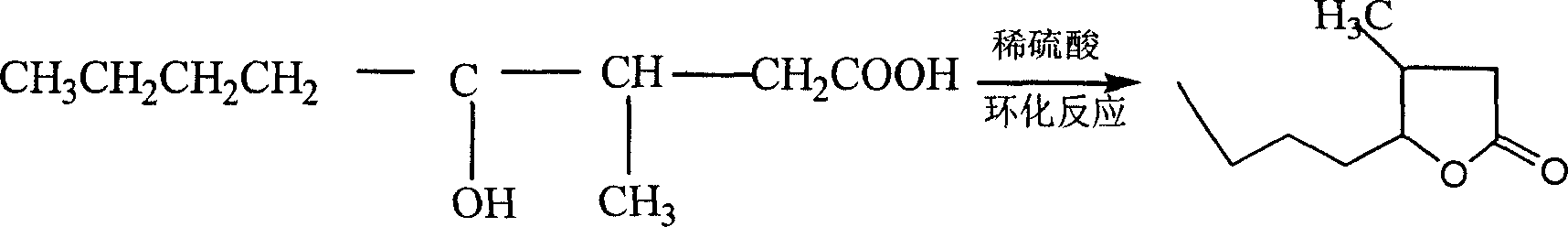Patents
Literature
173 results about "Free-radical addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Free-radical addition is an addition reaction in organic chemistry involving free radicals. The addition may occur between a radical and a non-radical, or between two radicals.
Stabilization of transition metal complexes for catalysis in diverse environments
This present invention is directed towards the identification or design, preparation, and use of suitable transition metal complexes for use as catalysts. The transition metal complexes may comprise heterodonor ligands. The present invention is also directed toward a method of determining the suitability of a transition metal complex for use in a catalytic reaction, such as, but not limited to, atom transfer radical polymerization (“ATRP”), atom transfer radical addition (“ATRA”), atom transfer radical cyclization (“ATRC”), and other catalytic redox reactions. The method assists in the approximate determination of the fundamental properties of the transition metal complex in a reaction media, such as, but not limited to, solubility, redox potential, stability towards acidic, basic, or ionic species, conditional radically transferable atom phylicity, and propensity toward disproportionation and therefore, the suitability of the complex to be used as a catalyst in the reaction media. The method provides a basis for prediction and evaluation of the properties of a transition metal complex for a particular selective catalytic reaction in a broad range of reaction environments. An understanding of the principles of the disclosed method allows a transition metal complex to be tuned to specific reaction medium by selecting a transition metal complex and ligand combination having the desired qualities.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
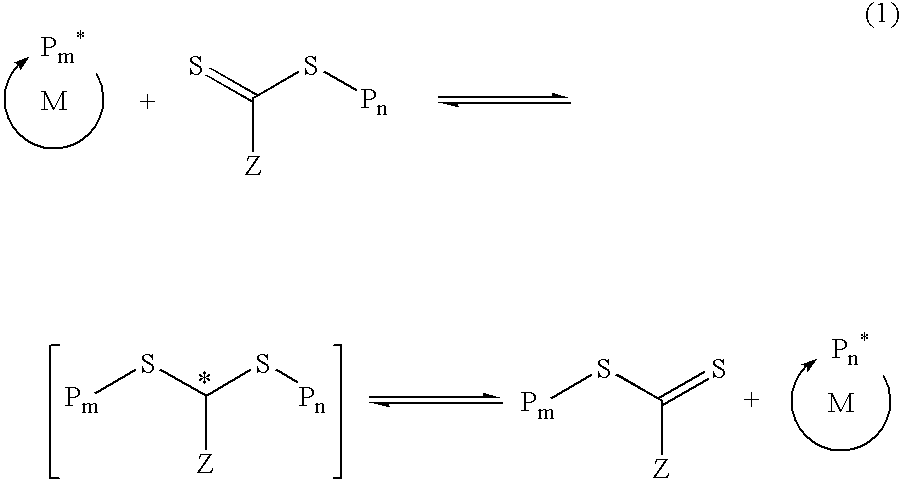
Functional trithiocarbonate RAFT agents
InactiveUS7230063B1Organic chemistryOrganic compound preparationTrithiocarbonic acidFree-radical addition
The present invention is directed to a free radical control agent of the structural formula:wherein R1 is a divalent alkyl group of 1 to 12 carbon atoms, R2 and R3 are each independently hydrogen or an alkyl group of 1 to 12 carbon atoms, and R4 is —OH or —COOH, with the proviso that the total carbon atoms of R1, R2, and R3 is no greater than 12; and wherein Y represents a functional group that is capable of activating a vinylic carbon toward free radical addition.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
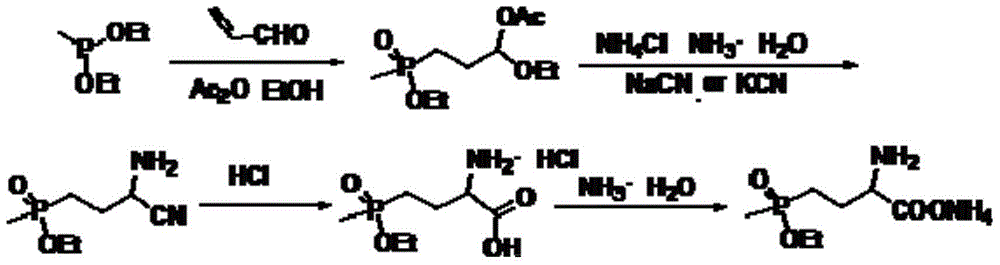
Preparation method of glufosinate and analogue of glufosinate
InactiveCN104892670AHigh yieldHigh purityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphite esterHydrolysis
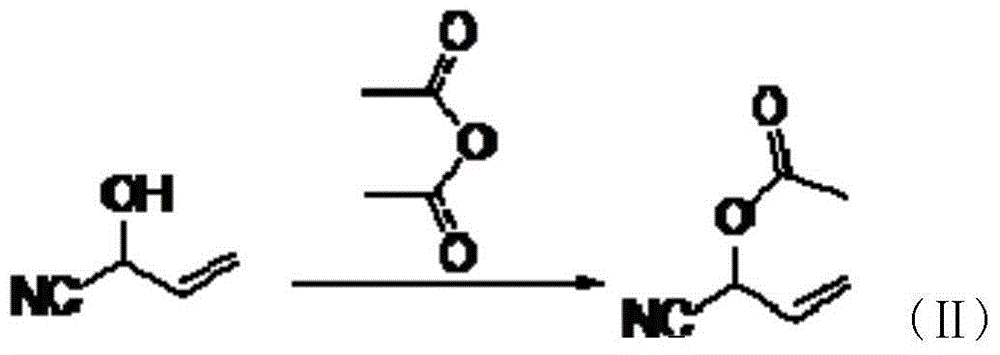
The invention discloses a method used for synthesizing glufosinate and an analogue of glufosinate by taking methylphosphoric dichloride and 2-hydroxy butane-3-nitrile as initial raw materials. According to the method, esterification is carried out so as to obtain methyl phosphite ester (I) and 2-acetyloxy-3-butenenitrile (II), intermediate (3-acetyloxy-3-cyano-propyl)-methylphosphonate (III) is obtained via Michael free radical addition, and glufosinate and the analogue (IV) are obtained via ammoniation and hydrolysis. Synthetic route of the method is short; yield is high; by-product is less; product purity is high; and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
Modified heterophasic polyolefin composition
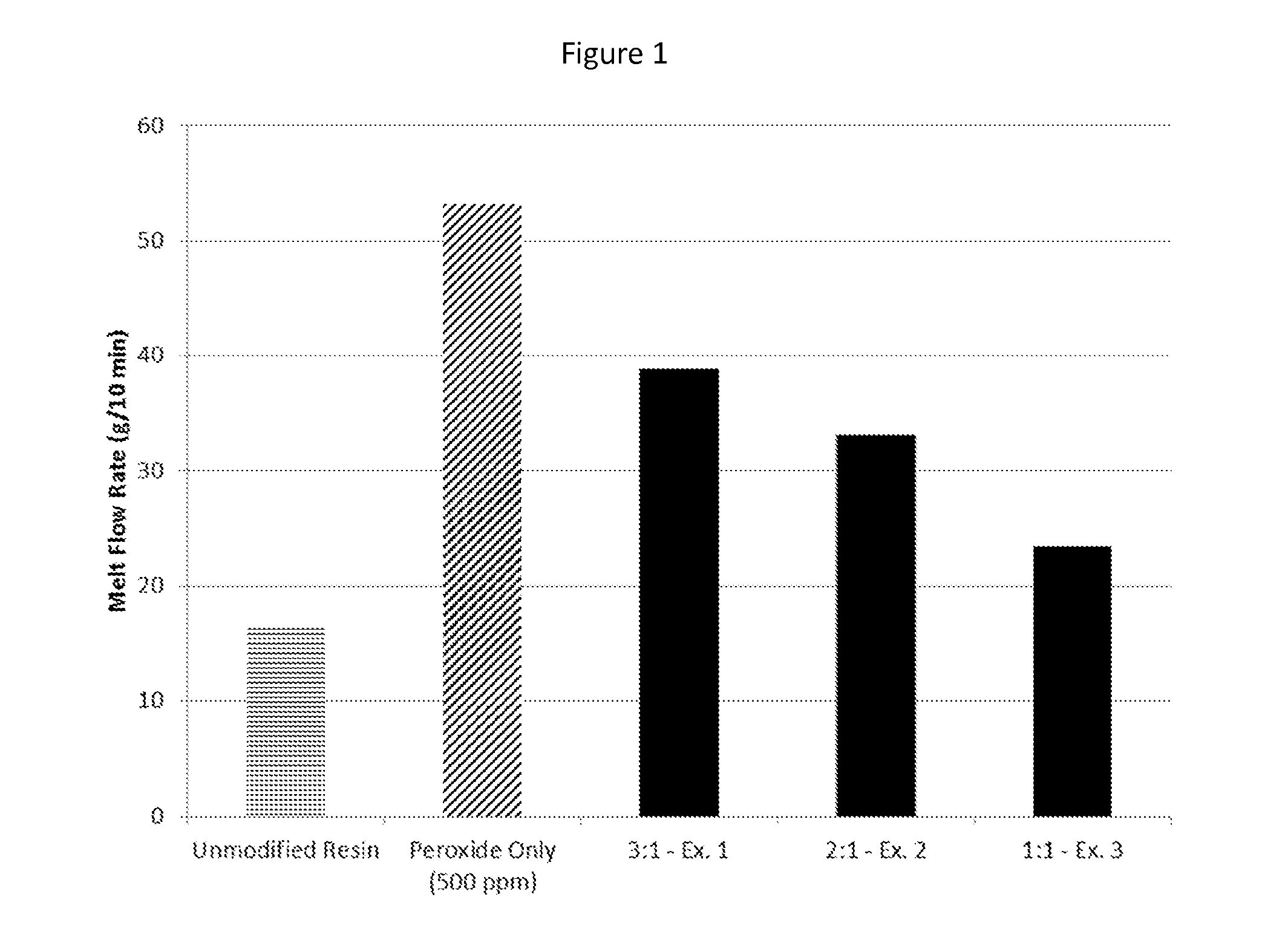
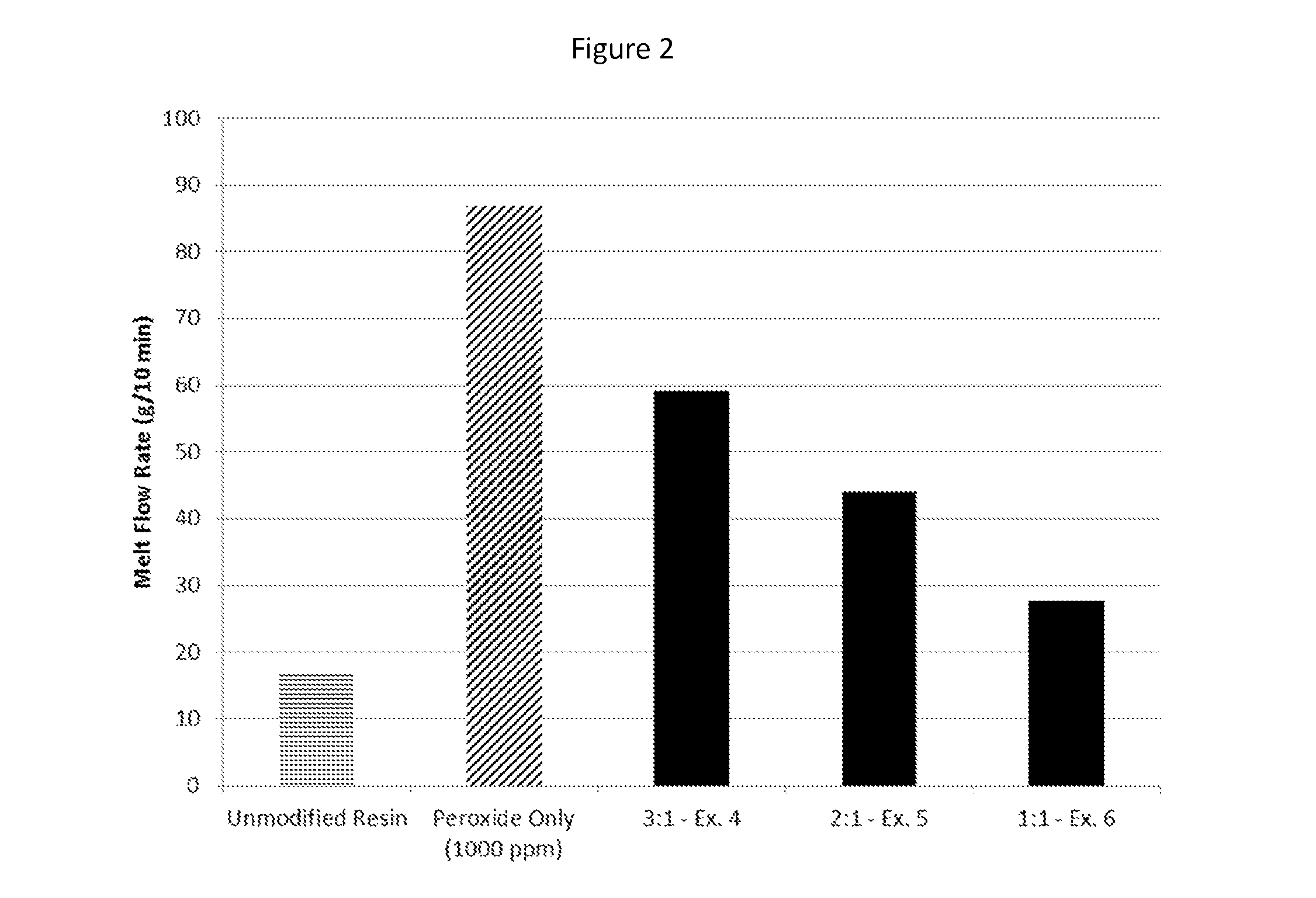
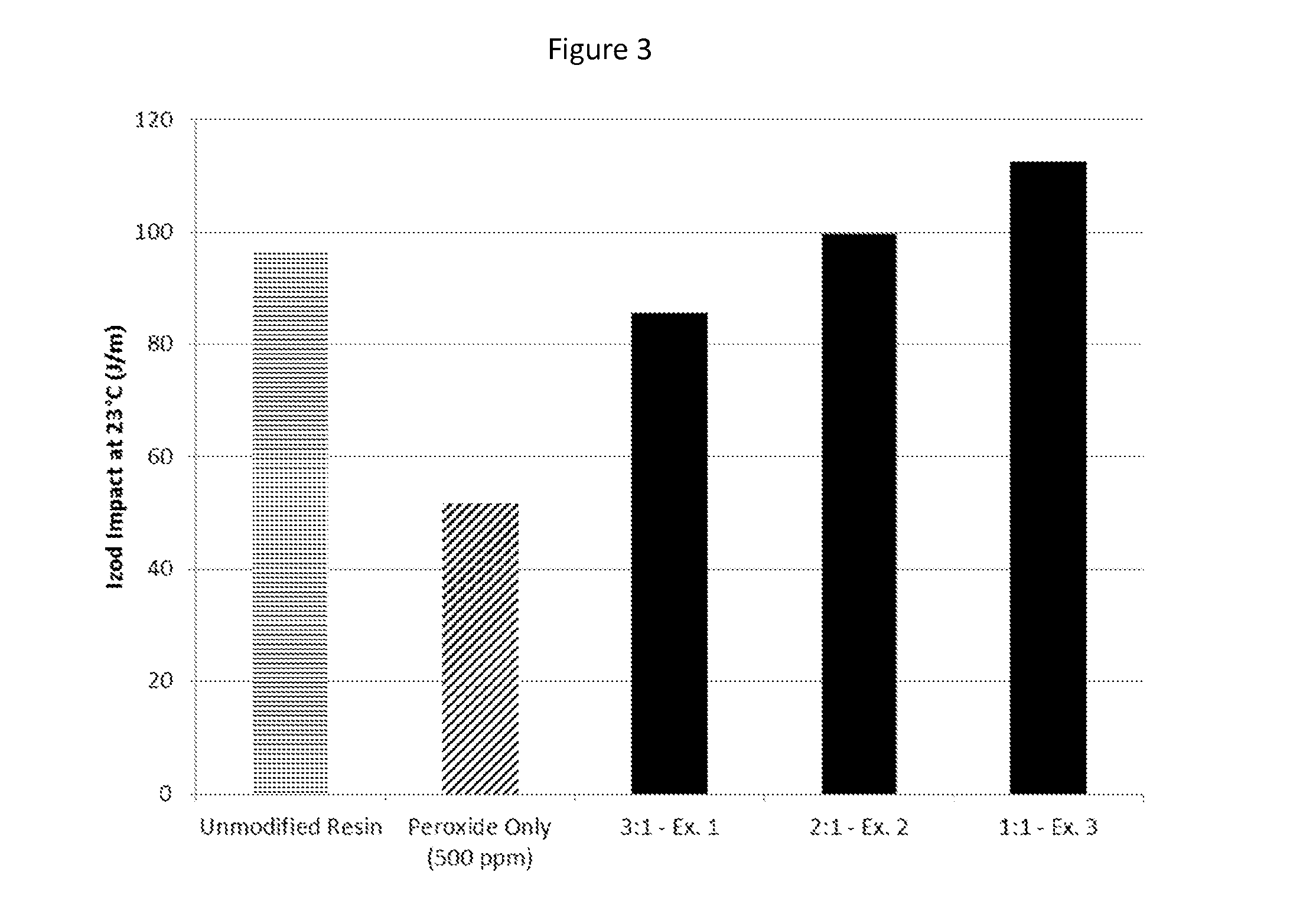
A method of creating a modified heterophasic polyolefin composition is provided, whereby a polyolefin composition having at least two phases is melt mixed with a free radical generator, such as a peroxide, and a compatibilizing agent characterized by at least one nitroxide radical and at least one unsaturated bond capable of undergoing a radical addition reaction. Modified heterophasic polyolefin compositions with increased melt flow rates, impact strength, and clarity, which incorporate the compatibilizing agent, are also included within the scope of the invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Method of coating a substrate with a radiation and chemically curable coating composition
The present invention provides a process for forming a coating on a substrate in which the coating composition comprises a polyene, a polythiol and a Michael addition catalyst. The coating is cured by exposure to ultraviolet radiation resulting in both free radical addition polymerization and Michael addition cure.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Controlled free radical agent for nanocomposite synthesis
InactiveUS6998452B1Increase profitLow densitySilicon organic compoundsSpecial tyresSilanesTrithiocarbonic acid
This invention relates to a process for producing a free radical control agent of the structural formula: wherein Z is selected from the group consisting of wherein R1 is an alkyl group of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, cyclohexyl or phenyl; wherein R2 is an alkoxy group of 1 to 8 carbon atoms or a cycloalkoxy group of 5 to 8 carbon atoms; wherein Alk is a divalent hydrocarbon of 1 to 18 carbon atoms; and wherein Y represents a functional group that is capable of activating a vinylic carbon toward free radical addition; said process comprising the steps of (1) reacting a mercaptosilane of the structural formula: Z-Alk-SH with carbon disulfide in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst and an alkali metal hydroxide to produce a trithiocarbonate salt; and (2) reacting the trithiocarbonate salt with a halogen containing compound of the structural formula X-Y to produce the free radical control agent, wherein X represents a halogen atom. Such free radical control agents are capable of covalently bonding to silica / silicate surfaces and are of particular benefit in producing rubbery compounds that will be loaded with silica fillers, such as tire tread rubbers.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Dispersant and preparation method thereof, and application of dispersant in anionic polyacrylamide water-dispersible emulsion polymerization
The invention provides a comb-type graft copolymer dispersant and a preparation method thereof, and an application method of the dispersant in anionic polyacrylamide emulsion polymerization. Three monomers are subjected to free radical addition copolymerization reaction to obtain the comb-type graft copolymer. The dispersant provided by the invention has the advantages of low molecular weight, low negative charge density, strong side-chain steric hindrance, low viscosity, high dissolving speed, low brine sensitivity, quick diffusion and adsorption, high stabilization efficiency and adjustable molecular structure, effectively lowers the viscosity of the emulsion polymerization system, and enhances the solid content of the product and the stability of the water-dispersible emulsion.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS +1
Method for preparing 6-difluoro alkyl ketone
ActiveCN106748771AAchieving Structural Diversity SynthesisHigh reaction yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPalladium catalystKetone
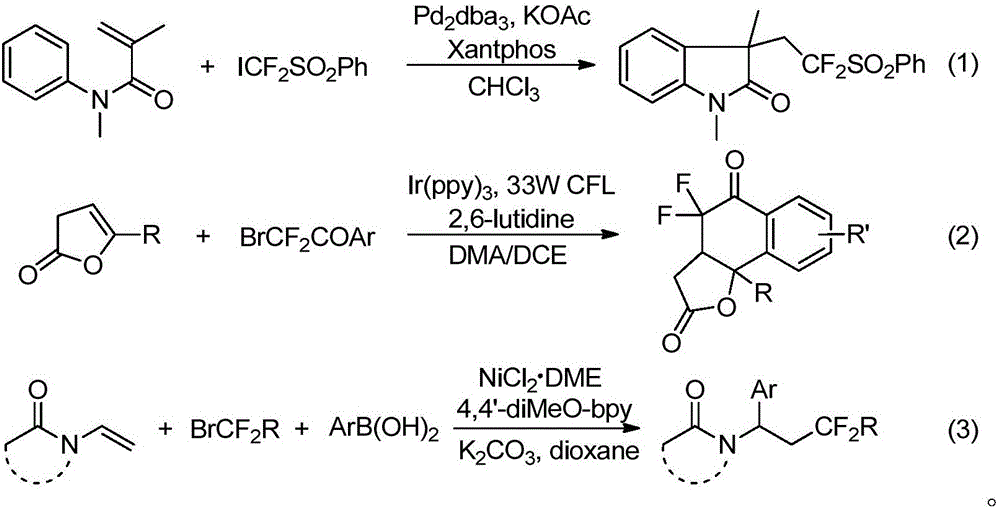
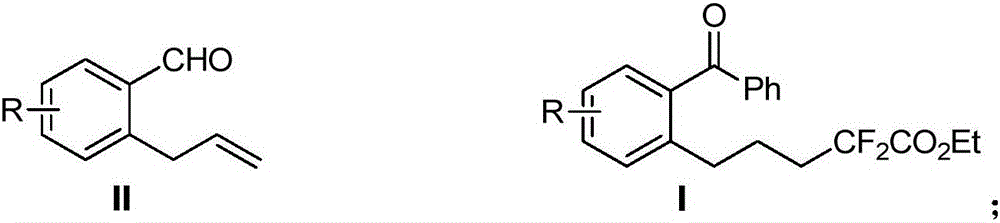
The invention discloses a method for preparing 6-difluoro alkyl ketone. The method includes mixing allylbenzene formaldehyde, phenylboronic acid, monobromo difluoro acetic ester, palladium catalysts, alkali and solvents with one another to form reaction systems; carrying out reaction and then treating reaction products to obtain the 6-difluoro alkyl ketone with the structure shown in a formula I. The structure of the allylbenzene formaldehyde is shown in a formula II. The method has the advantages that 1, n-hydrogen atom transfer radical addition strategies are applied to remote aryl difluoro alkylation for alkene, three-component reaction is completely carried out on monobromo difluoro methyl compounds, the allylbenzene formaldehyde and boric acid by means of palladium catalysis, accordingly, the 6-difluoro alkyl ketone can be synthesized by the aid of one-pot processes, reaction conditions are mild, the method is easy to implement and excellent in yield and has excellent theoretical value and an excellent application prospect, functional groups are good in compatibility, and substrates are wide in applicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Photocurable resin composition
ActiveCN101356204AExcellent fatigue resistanceExcellent durability against vibration fatigueAntioxidantElastic modulus
Disclosed is a photocurable resin composition suitable for photocuring cast molding, particularly a photocurable resin composition having excellent vibration fatigue durability. The photocurable resin composition comprises (A) at least one resin selected from a photoradical-polymerizable resin, photoradical-addition-polymerizable resin and a photocation-polymerizable resin, (B) a photopolymerization initiator, and one or both of (C) an antioxidant and (D) a photostabilizer. When cured, the photocurable resin composition shows a tensile elastic modulus of 1-30 MPa and a tensile elongation at break of 200% or more. The photocurable resin composition may additionally comprise (E) a rubber composition.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Polymer Synthesis
A method of preparing a block copolymer of Formula (B) wherein P1 represents a substantially aqueously soluble polymeric component and P2 represents a substantially aqueously insoluble polymeric component, comprises admixing an aqueously soluble polymer macro-chain transfer agent comprising P1 with a monomer (M2) and initiating an aqueous dispersion-type radical addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerisation. (P1) is derived from a monomer (M1) selected from monomers of the Formulae (M1A), (M1B) and / or (M1C) where R1, R10 and R11 represent a substituent of (M1A) or (M1C) which allows P1 to be at least partially aqueously soluble, R2 represents H, CH3 or CN, RS represents one or more substituents of the aromatic ring effective to allow P1 to be at least partially aqueously soluble, and monomer M2 is selected from: where R3 is a substituent of (M2) which allows P2 to be substantially aqueously insoluble, and R4 and R6 independently represent H or methyl.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD
Compositions and methods for functionalizing or crosslinking ligands on nanoparticle surfaces
This disclosure provides novel ways to modify / functionalize, including crosslink, ligands in the surface coating or molecules in other coatings on a nanoparticle, by using radical addition reactions to add a reactant group onto a ligand / molecule of a nanoparticle. Examples include using a functionalized benzophenone that can be attached or crosslinked to a ligand in the surface coating of a nanocrystal by photochemically-initiated radical addition.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
High molecular weight chelation structure
InactiveUS20070274945A1Less toxicityIncreased vascular retentionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntinoxious agentsSide chainHeme
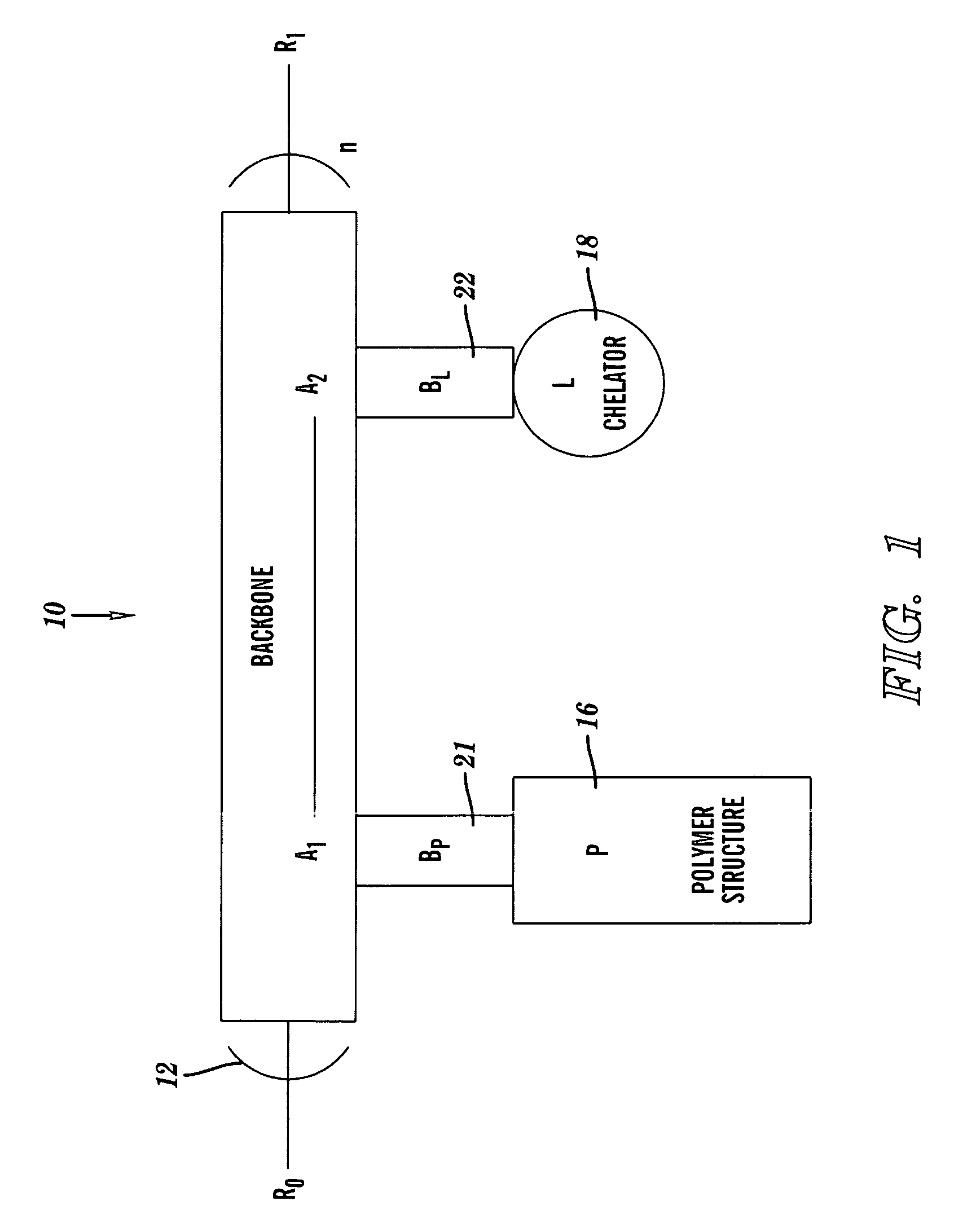
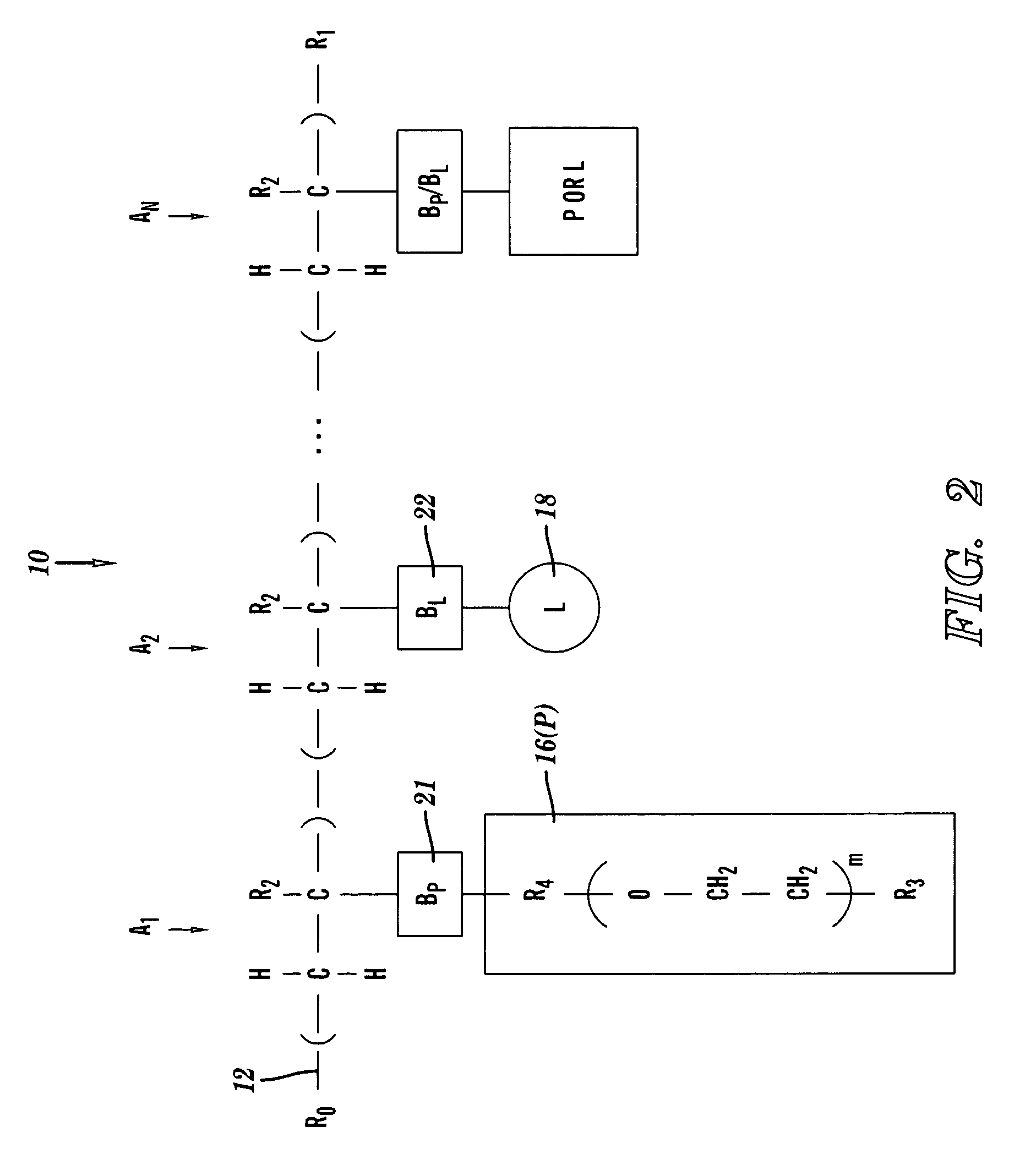
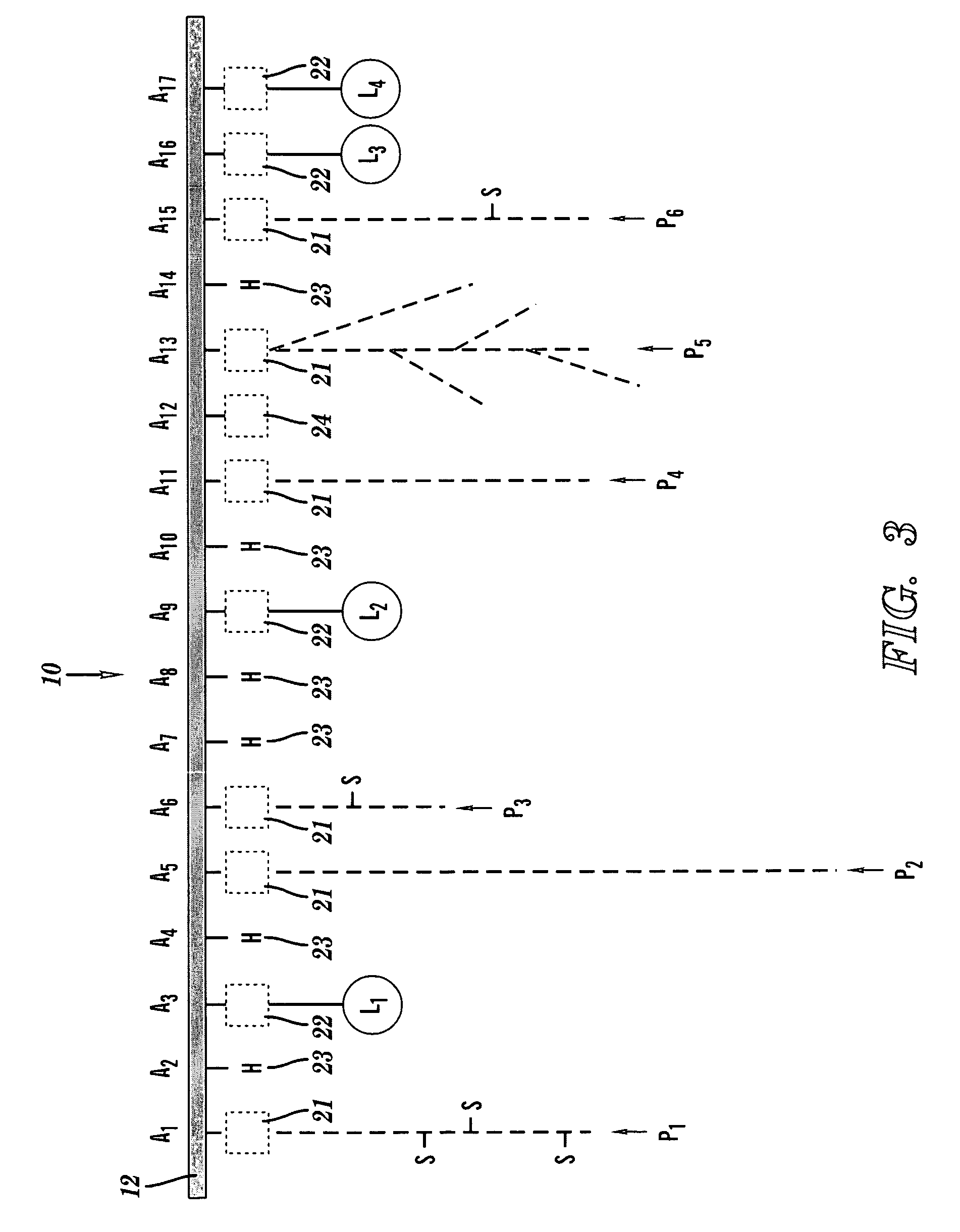
A chelation structure and method of forming and using the chelation structure. The chelation structure has a backbone that includes a linear sequence of monomeric backbone units, at least one polymer side chain, and at least one chelator side chain. The side chains are each covalently coupled to the backbone at one of the monomeric backbone units by a bond that is independently biodegradable or non-biodegradable. The chelation structure is synthesized by Radical Addition Fragmentation Transfer (RAFT), Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (ATRP), or Free Radical Polymerization (FRP). The chelation structure, individually or in combination with a shuttle chelator, may be introduced into a mammal to bind an amount of a substance in a mammal, the substance being at least one of a metal and heme. The chelation structure has a log stability constant exceeding that of the shuttle chelator for binding the substance within cells of the mammal.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
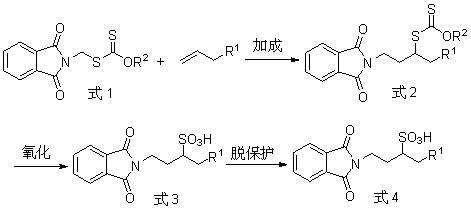
Preparation method of 1-substituted homotaurine
InactiveCN102424665AHas medicinal valueEasy to operateSulfonic acid preparationEnzyme Inhibitor AgentHomotaurine
The invention provides a preparation method of N-phthaloyl protected 1-substituted homotaurine. The method comprises: conducting free radical addition to terminal olefin by dithiocarbonic acid-O-alkyl-S-phthalimidemethyl ester so as to obtain corresponding xanthate, then carrying out oxidation to prepare N-phthaloyl protected 1-substituted homotaurine, then performing acid or base catalyzed hydrolysis or hydrazinolysis, thus obtaining 1-substituted homotaurine. The preparation method of the invention has simple and easily available raw materials, convenient operation, and no need for a tedious desalting and purifying process, thus being especially suitable for large scale industrial production. And the prepared compound can be use as a nutrient, a medicament, an enzyme inhibitor, an antimicrobial agent, a surfactant, a plant growth regulator, and a raw material for preparing sulfono-peptides, etc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
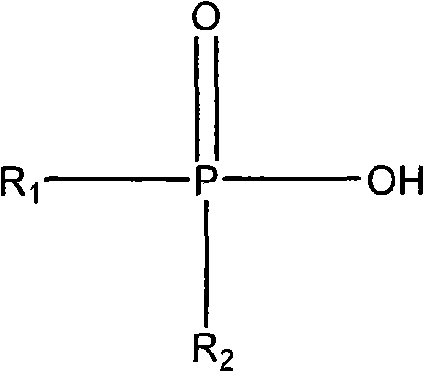
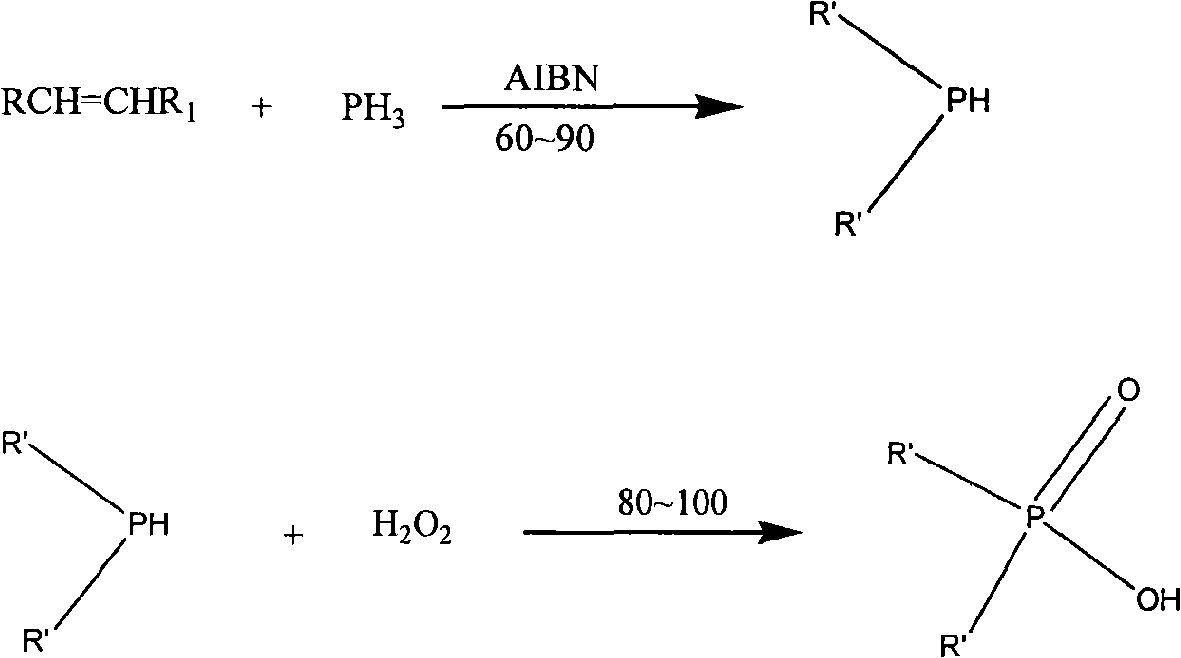
Synthesis method of dialkyl phosphinic acid extractant
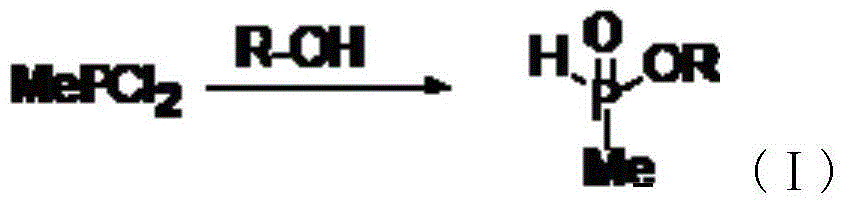
InactiveCN101624401AHigh selectivityEasy extractionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsProcess efficiency improvementMetalloleSynthesis methods
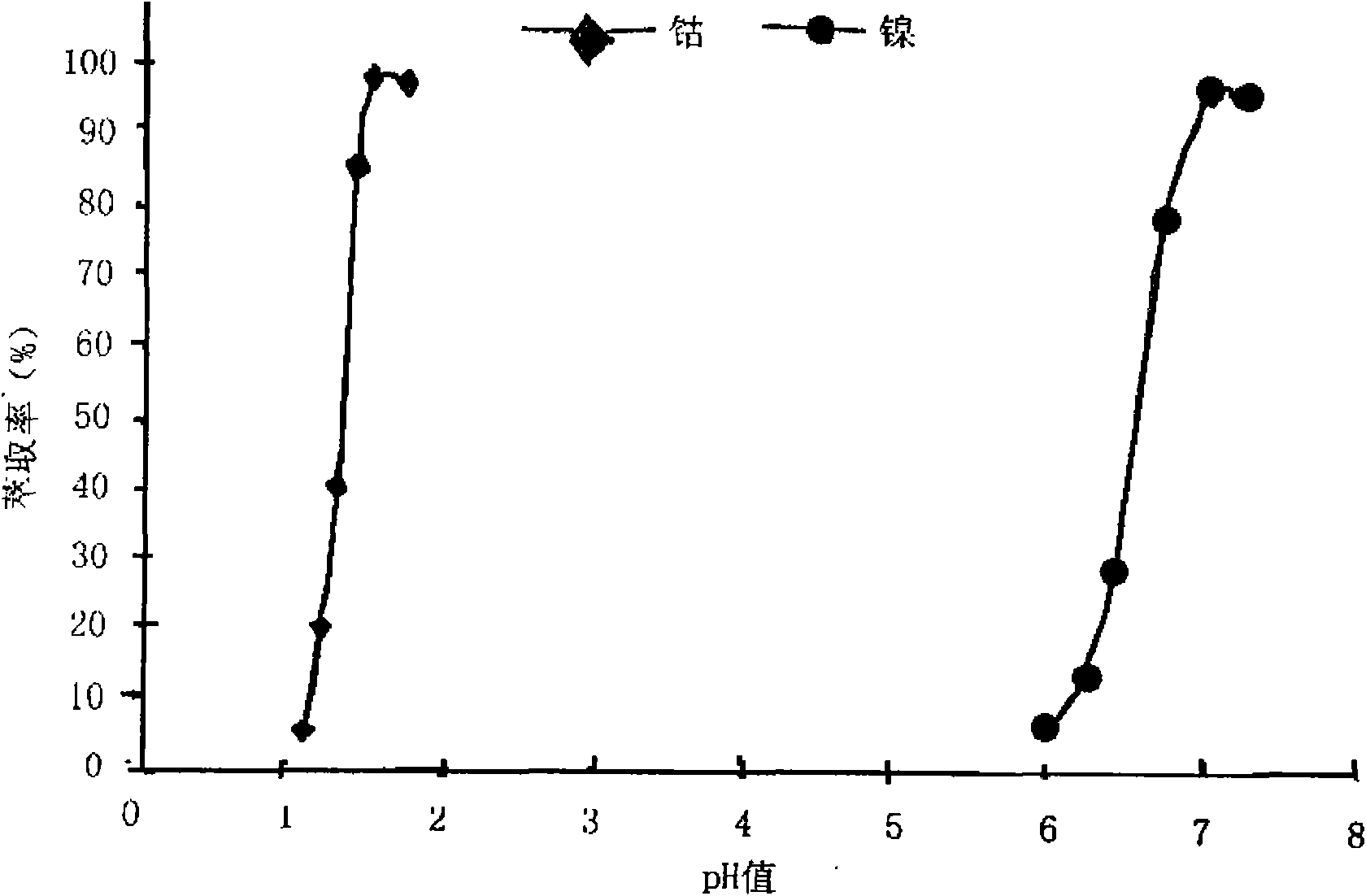
The invention discloses a synthesis method of dialkyl phosphinic acid extractant, belonging to the technical field of organic extractant synthesis and the method adopts phosphine gas high pressure reaction method. The method comprises the following specific steps: step1, using decylene and phosphine to perform free radical addition reaction and obtain dialkylphosphorane; step2, oxidizing dialkylphosphorane with peroxide to oxidize the trivalent phosphorus to pentavalent phosphorus and finally obtaining dialkyl phosphinic acid. The invention has good extraction effect on metal ions such as cobalt and the like in low pH, high selectivity and simple synthesis method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid from hydrogen phosphide as byproduct in sodium hypophosphite production process
ActiveCN103772429AIncrease profitAchieve synthesisGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphinous acidHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for preparing bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid from hydrogen phosphide as a byproduct in a sodium hypophosphite production process. The bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid is prepared by the steps of implementing alkaline cleaning to hydrogen phosphide which is a byproduct in sodium hypophosphite production and freeze-drying the hydrogen phosphide to remove water; pumping the such processed hydrogen phosphide into a high-pressure reaction kettle containing diisobutylene and an initiator through a compressor, wherein the hydrogen phosphide is absorbed by the diisobutylene while hydrogen and little nitrogen in the hydrogen phosphide, instead of being absorbed, enter a combustion furnace along with tail gas, and the purified hydrogen phosphide is subjected to free radical addition reaction with the diisobutylene in the presence of the initiator to generate bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphine; evaporating out residual diisobutylene and monoalkyl substitute; and oxidizing rest materials through hydrogen peroxide to obtain the bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid.
Owner:CHANGSHU NEW TECH CHEM
Method for synthesizing perfluoroalkyl propanol
InactiveCN102633601ALow priceRaw materials are easy to getOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholWeather resistance
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing perfluoroalkyl propanol. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out free radical addition reaction on perfluoroalkyl ethylene and methyl alcohol in the presence of organic peroxide initiator, wherein the molar ratios of perfluoroalkyl ethylene to methyl alcohol and perfluoroalkyl ethylene to the organic peroxide are respectively 1:20-1:40 and 1:0.01-1:0.02, the pressure is 1.2MPa-2.0MPa, the temperature is 90-190 DEG C and the time is 1-3h; and after reacting, purifying through reduced-pressure distillation to obtain perfluoroalkyl propanol. The method has the advantages of easily-obtained materials, low cost, safety and environmental friendliness; methyl alcohol is used as the reactant and solvent, is low in cost and can be recycled; the operation process is simple, safe and stable without generating by-products, the purity of the finished product is 99.1-99.5% and the yield is 95.6-98.1%; and perfluoroalkyl propanol has excellent performance, has the water and oil resistance, corrosion resistance and weather resistance similar to perfluoroalkyl ethanol, and is a good substitute for perfluoroalkyl ethanol.
Owner:锦州恒通氟化学有限公司
Stannum porphyrin axial covalent functionalized reduced graphene oxide nonlinear optical materials, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105254640APromote absorptionImprove solubilityOrganic chemistry methodsNon-linear opticsSolubilityDispersion stability
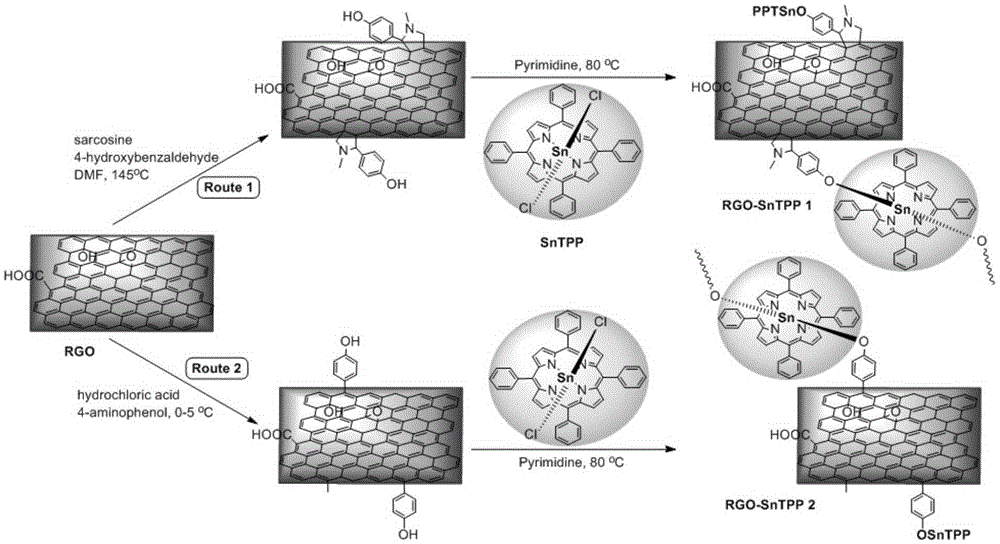
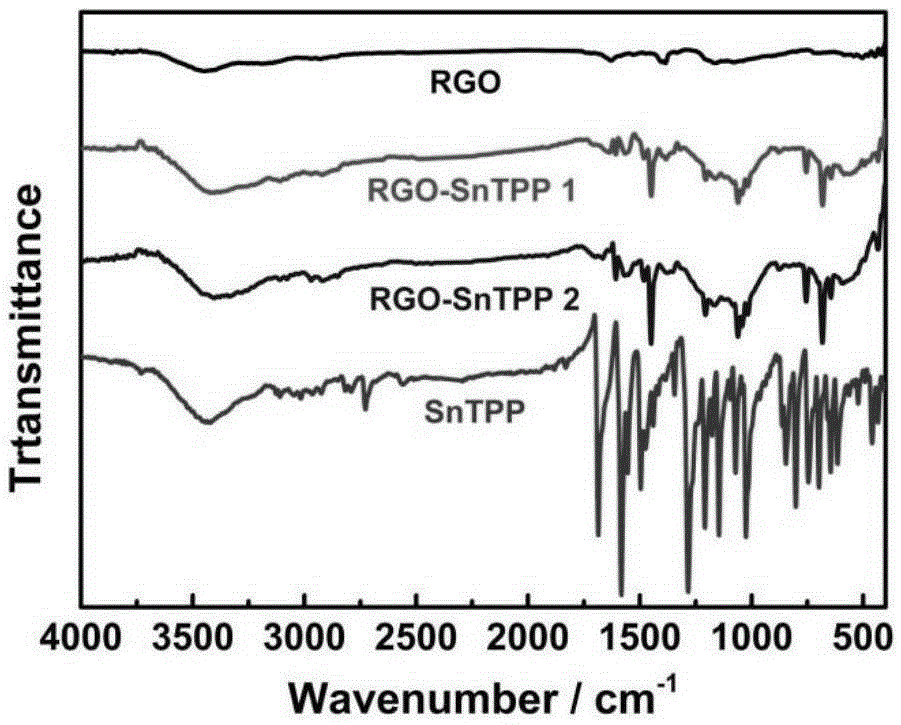
The invention belongs to the field of military industry strong laser protective material, and more specifically discloses organic transition metal stannum porphyrin axial functionalized reduced graphene oxide nano hybrid light-sensitive functional materials with excellent nonlinear absorption performance, and a preparation method of the organic-inorganic covalent functionalized nano materials. Development of the novel porphyrin covalent graphene nonlinear absorption materials with excellent solubility is used for solving problems that graphene is poor in solubility and dispersion stability, and conventional strong laser protective materials are limited. According to the preparation method, organic transition metal stannum porphyrin is connected with the surface of reduced graphene oxide via covalent axial bonds via 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition and free radical addition instead of simple physical mixing of two materials with different optical functions; solubility, dispersion stability, and nonlinear absorption performance of graphene are improved via synergistic effects of organic transition metal stannum porphyrin with reduced graphene oxide; nonlinear optical performance and solubility of the obtained materials are improved greatly; and application prospect is promising.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for synthesizing glufosinate ammonium salt
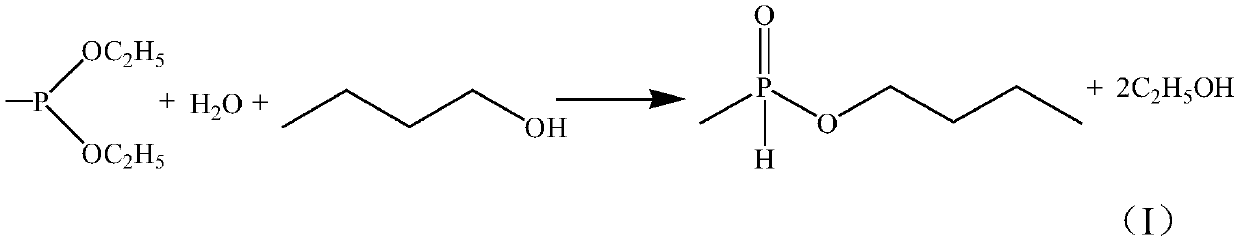
InactiveCN110386950AReduce separation and purification processReduce outputGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiethyl phosphateN-Butanol
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a glufosinate ammonium salt. The method comprises the following steps that (1) methyldiethoxyphosphine and n-butanol are used as raw materials to produce an intermediate I by hydrolysis and transesterification; (2) the intermediate I is subjected to a free radical addition reaction with acrolein cyanohydrin acetate to form an intermediate II; (3) the intermediate II is subjected to an aminolysis reaction with ammonia gas to form a mixture of an intermediate III and an intermediate IV; (4) the intermediate III and the intermediate IV are subjected to acid hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid to form an intermediate V; and (5) the intermediate V is neutralized, purified and crystallized to obtain the glufosinate ammonium salt. The method does not need to use toxic raw materials, avoids the large-scale use of ammonia water and ammonium chloride, not only greatly reduces the safety hazard, but also reduces the quantity of by-products and the amount of waste water generated, and the environmental protection risk is greatly reduced; and the purification process is simple, the product content and the yield coefficient are obviously increased,and the method is suitable for industrial scale production.
Owner:石家庄瑞凯化工有限公司
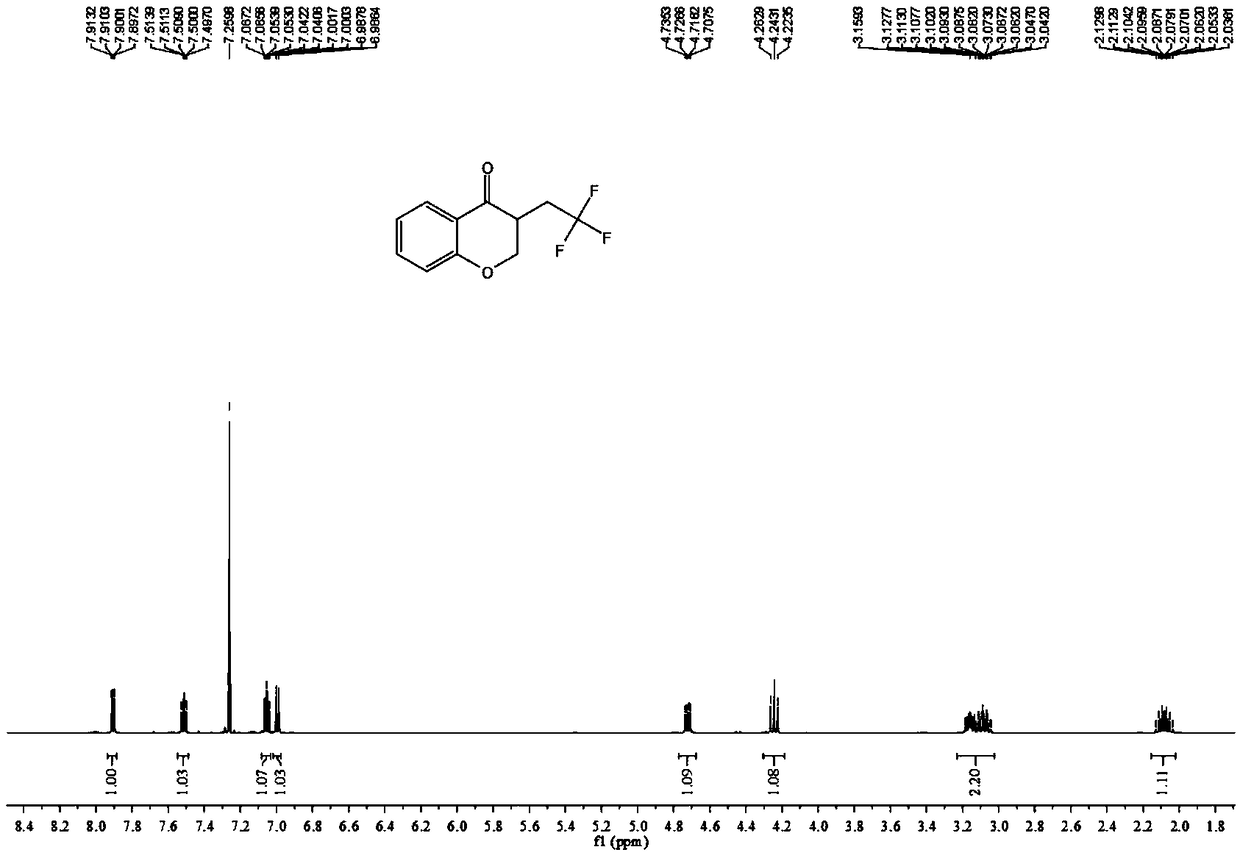
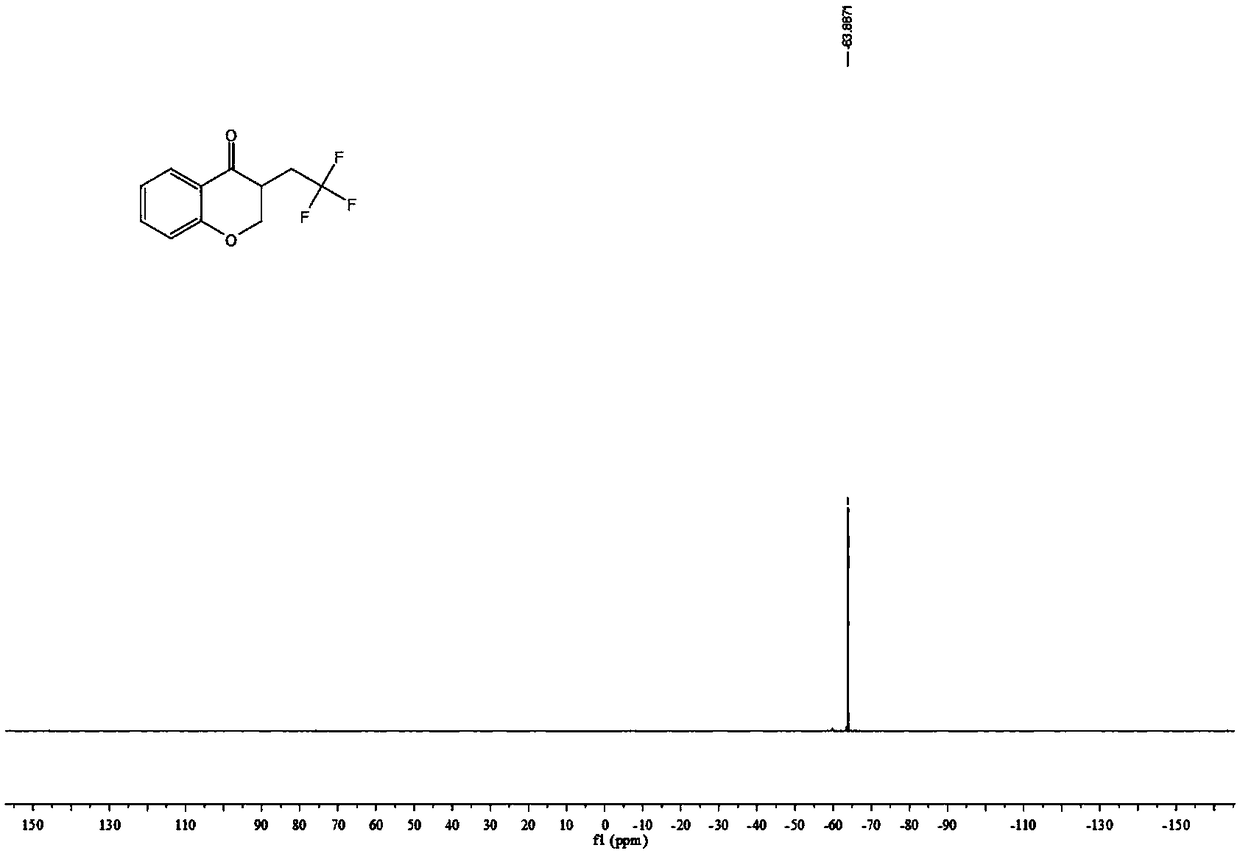
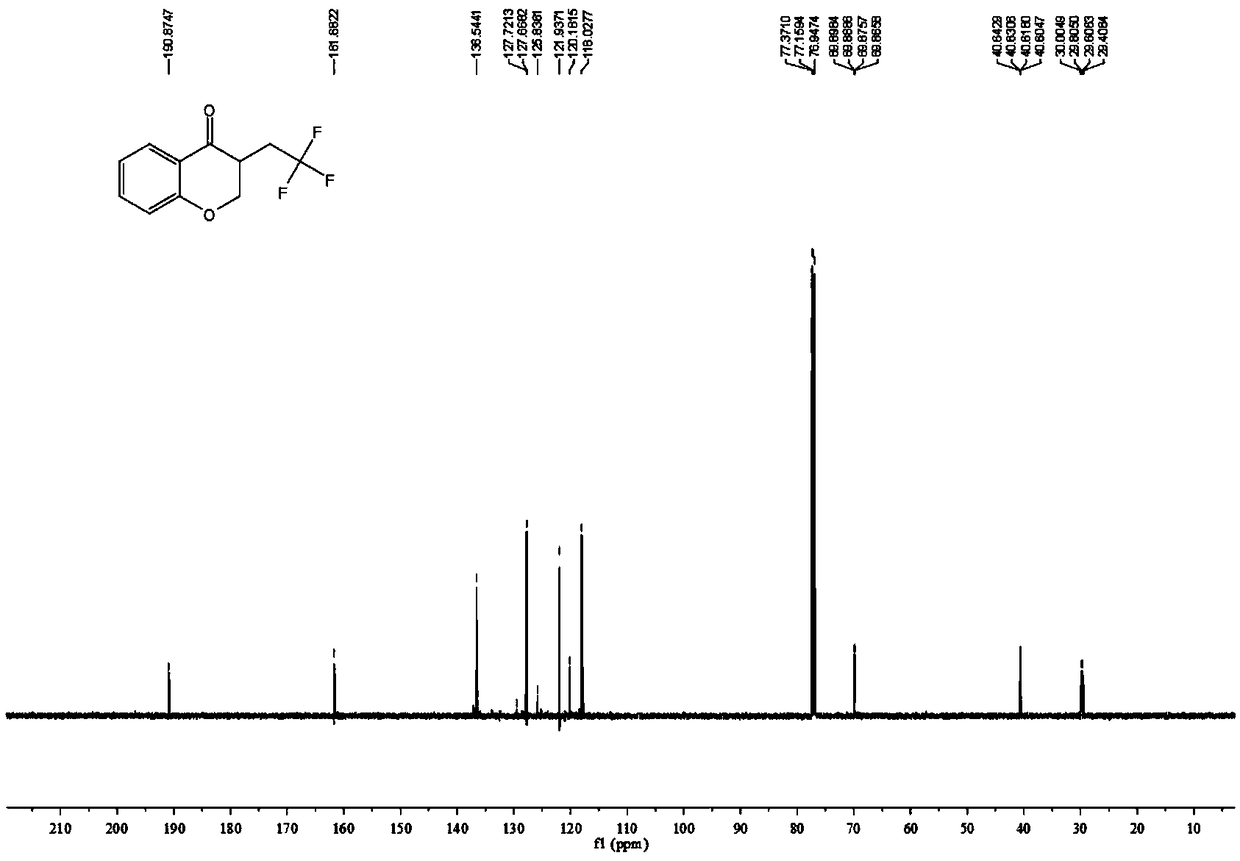
4-Chromanone compound containing trifluoromethyl and preparation method of 4-Chromanone compound
ActiveCN109400564AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateOrganic chemistry4-chromanoneOxidizing agent
The invention provides a 4-Chromanone target compound (III) containing trifluoromethyl and a preparation method of the 4-Chromanone target compound (III), wherein the 4-Chromanone target compound (III) is obtained in the modes that an allylsalicylaldehyde (I) compound serves as a reaction starting raw material, sodium triflate (II) serves as a trifluoromethyl source, persulfate serves as an oxidant, and the trifluoromethyl and allylsalicylaldehyde generate free radical addition, free radical cyclization and an oxidation reaction. The reaction condition involved in the method is mild, operationis easy, product diversity is achieved, and gram-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of method for preparing mesoporous silica
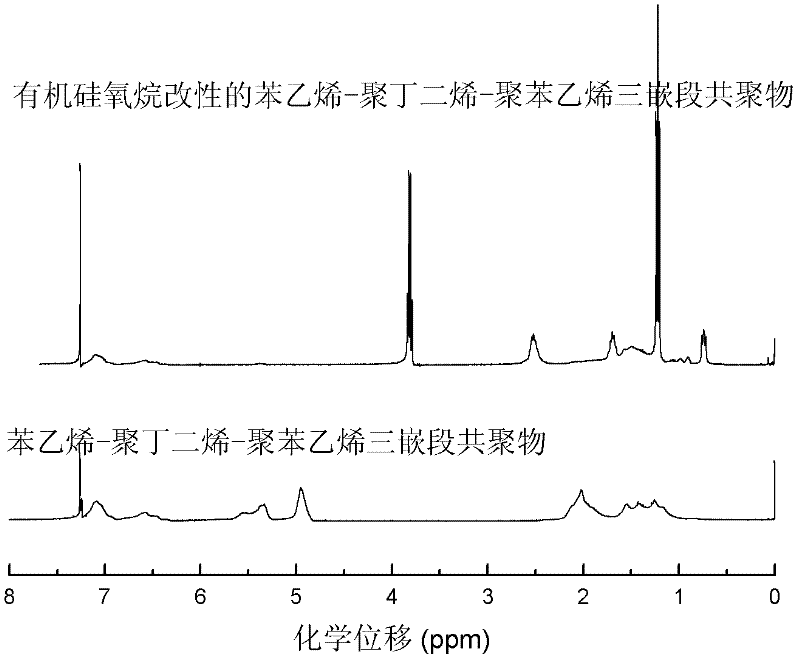
InactiveCN102295291ALow reaction temperatureEasy to manufactureSilicaMesoporous silicaSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing mesoporous silicon dioxide, the method is characterized in that mercapto-vinyl can be used for a free radical addition reaction, organo-silicone containing a mercapto group and polybutadiene block of triblock copolymer of styrene-butadiene-styrene are reacted, an organo-siloxane modified styrene-butadiene-styrene triblock copolymer can be obtained, then the organo-siloxane modified styrene-butadiene-styrene triblock copolymer is carried out a sol-gel reaction with a silicon source under the acidic or alkaline condition to form gel, the mesoporous silicon dioxide is obtained after cracking the gel. Compared with the prior art, the mesoporous silicon dioxide material has the average pore diameter of 5-18nm, the pore volume of 0.24-0.30 cm<3> / g, the specific surface area of 418-480 cm<2> / g, and has the advantages of cheap raw material and easy raw material acquisition, mild reaction condition, simple and high efficient preparation process, safety and environmental protection, and is convenient for large scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Process for preparing silicone-containing addition polymers
InactiveCN101175772ASolving crosslinking problems in polymerization reactionsCoatingsAddition polymerCopper
The invention provides a process for preparing silicone-containing addition polymers by means of free-radical addition polymerization of one or more ethylenically unsaturated organic monomers in the presence of copper-free free-radical initiator and of one or more polymerization regulators, characterized in that the polymerization regulators used comprise silicones containing at least one aldehyde group.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Preparation method of benzene sulfochloride substituted carbon nano-tube and grafting modification method initiated thereby
The invention relates to a method for processing a carbon nanometer tube so that a special initiation functional group can be formed on the surface, which is utilized to initiate and form graft decoration on the tube surface. The method provided by this invention is that purification treatment is carried out on the carbon tube, the attached catalyst and other impurities on the carbon tube surface, then the purified carbon tube is prepared into a benzene-substituted carbon tube, then substitution reaction for a benzene ring of the benzene-substituted carbon tube is carried out, thus producing benzene sulfonyl chloride-substituted carbon tube. In the invention, the carbon tube used for preparing the benzene sulfonyl chloride substitution can adopt free radical addition reaction.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Chromane compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109320489AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateOrganic chemistryTrifluoromethylationSolvent
The invention discloses a chromane compound and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: dispersing olefin shown as a structure (I), a trifluoromethyl reagent shown as a structure (II) and an oxidizing agent in a solvent; heating and stirring the mixture to obtain the chromane compound shown as a structure (III), wherein the structure (III) is shown in the description. The invention further provides a novel method for building a trifluoromethylation chromane compound by taking an olefin compound (I) as a starting raw material of a reaction and sodium trifluoromethanesulfonate (II) as a trifluoromethyl source, and persulfate as an oxidizing agent, and performing free radical addition, free radical arylation cyclization and oxidization on trifluoromethyl and the olefin. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easiness in operation, diverse products, and the capability of realizing scale production.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
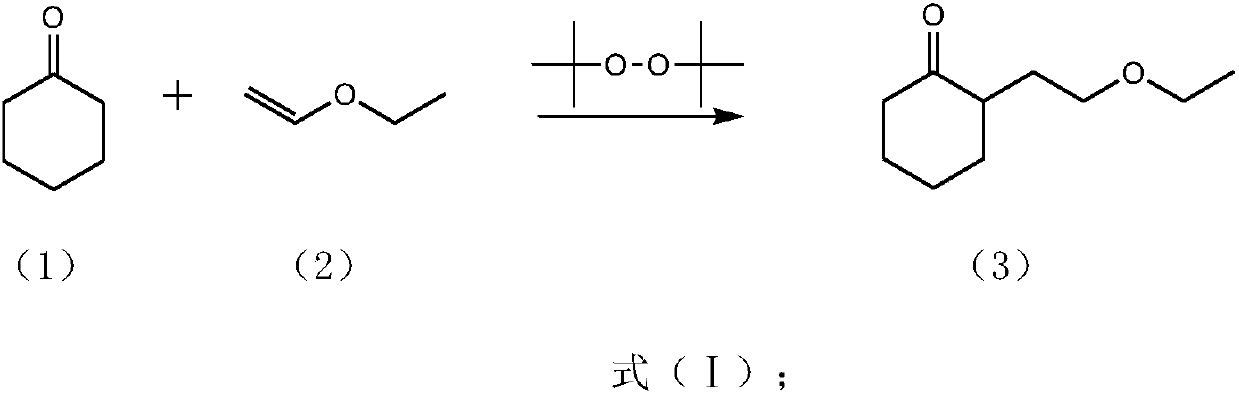
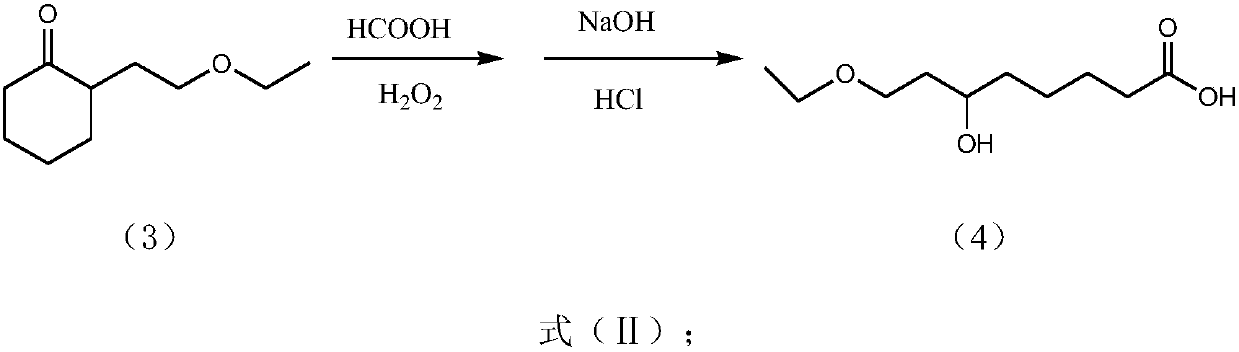
Preparation method of ethyl 6,8-dichlorocaprylate
InactiveCN107673972ALow priceThe synthesis method is simplePreparation from carboxylic acid saltsPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesCyclohexanoneVinyl ether
The invention discloses a preparation method of ethyl 6,8-dichlorocaprylate. The preparation method is characterized in that cyclohexanone and vinyl ether which are cheap in price are mainly taken asbasic raw materials; the basic raw materials are then subjected to free-radical addition, so that 2-(2'-ethoxyethyl)cyclohexanone is obtained; secondly, the 2-(2'-ethoxyethyl)clohexanone is subjectedto oxidation, hydrolysis and acidification reaction, so that 8-ethoxyl-6-hydroxyl-octanoic acid is obtained. The synthetic raw materials adopted by the preparation method are low in whole price, and the synthesis method is simple; the step of chlorination can be effectively omitted at the same time, so that pollution is reduced; furthermore, the overall synthetic route is safe, and major safety accidents are avoided; therefore, the preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of being economical, reasonable, safe and free from pollution.
Owner:福安药业集团烟台只楚药业有限公司
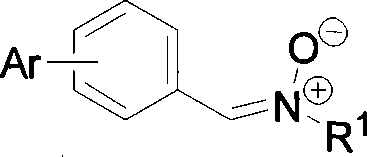
Alpha-biphenyl-N-alkyl nitrone compound and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101225056AIncrease steric hindranceIncrease fat solubilityOximes preparationBenzaldehydeStructural formula
The invention discloses an alpha-xenyl-N-alkyl nitro ketones compound of which the structural formula is as shown in formula (I). The synthetic method is: first adding the benzene boric acid and the bromo benzaldehyde into the toluene which carry on the Suzuki coupling reaction to produce biphenyl formaldehyde under the existence of the potassium phosphate hydrate and the palladium catalyst. Then mixing the biphenyl formaldehyde, 2-nitryl-2- alkyl propane and zinc powder together in the ethyl alcohol, adding ethanoic acid, and put into the refrigerator for refrigeration, then separated for depuration. The alpha-xenyl-N-alkyl niter ketones compound connects aromatic group on the PBN benzene ring, and can increase the steric hindrance of the free radical addition atom and weaken the disproportionation extinguishment of the free radical addition compound or the enzyme catalyzed extinguishment inside the organism thus to increase the life of the free radical addition compound. The nitro alkone compound can be effective reagent for examining the free radicals in the lipin system like cell membrane.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Binder compositions and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS20140275360A1Improved binder compositionAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesLignin adhesivesCarbon–carbon bondAromatic moiety
Binder compositions and methods for making and using same are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the binder composition can include at least one polyphenolic compound, at least one unsaturated compound, and at least one free radical precursor. The unsaturated compound can have two or more unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds. At least one of the unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds can be a pi-bond that is not conjugated with an aromatic moiety and is capable of free radical addition.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Functionalized, absorbable, segmented copolyesters and related copolymers
Absorbable heterochain polymers carrying acid or basic groups, capable of ionic conjugation with basic or acidic bioactive agents, respectively, are produced by free-radical addition of unsaturated functional monomers onto absorbable liquid polymers and subsequent generation of reactive functionality or by direct copolymerization of a carboxylic initiator with cyclic monomers to produce liquid carboxyl-bearing copolyesters or polyester carbonates.
Owner:POLY MED
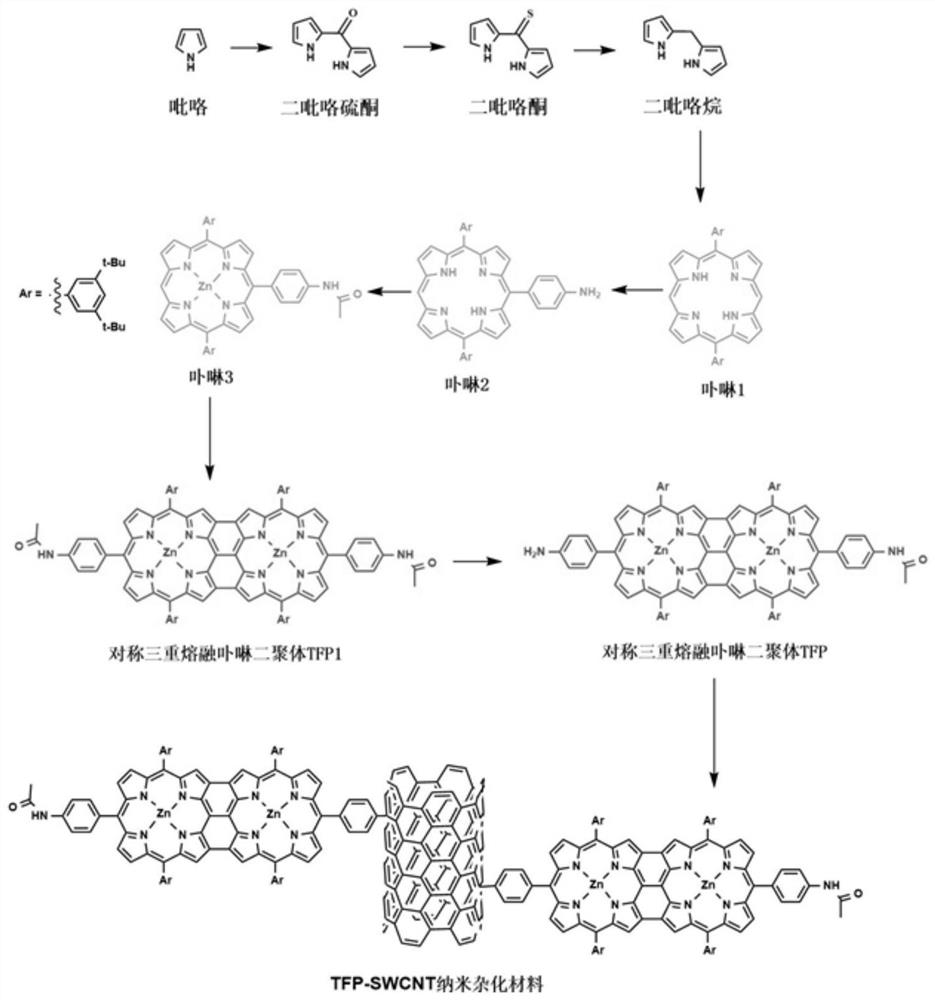
Triple molten porphyrin dimer covalent functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube nonlinear nano hybrid material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112094277AEasy to retouchEasy to operateOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesDimerPorphyrin
The invention relates to a triple molten porphyrin dimer covalent functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube non-linear nano hybrid material and a preparation method thereof. The non-linear nano hybrid material is formed by connecting a triple molten porphyrin dimer TFP to the surface of SWCNT through covalent bonds. Compared with the prior art, the organic-inorganic covalent functionalized nanofunctional material is prepared by connecting TFP to the surface of SWCNT through covalent bonds and the azo salt free radical addition reaction instead of simply and physically mixing the two different optical functional materials, and compared with a traditional material, the prepared material not only has enhanced nonlinear optical properties in the nanosecond visible light field, but also canconvert saturated absorption of a traditional material into anti-saturated absorption in the femtosecond near-infrared field, and has a very wide application prospect.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method of polysubstituted 2-benzyl-1-isoquinolone compound
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polysubstituted 2-benzyl-1 (2H)-isoquinolone compound. In the presence of an iodine catalyst and tert-butyl hydroperoxide serving as an oxidizing agent, an isoquinoline compound experiences a benzyl free radical addition and amidation reaction to generate an isoquinolone compound, wherein the reaction temperature is 60-150 DEG C, and the reaction time is 0.5-72 hours. The reaction overcomes the shortcomings of metal catalyst use and complicated synthesis technology, the reaction raw materials and catalyst are cheap and easily available, the reaction conditions are mild, the reaction is insensitive to light, air and moisture, the yield is very high, and the product is easy to separate and purify and has a perfect application prospect.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
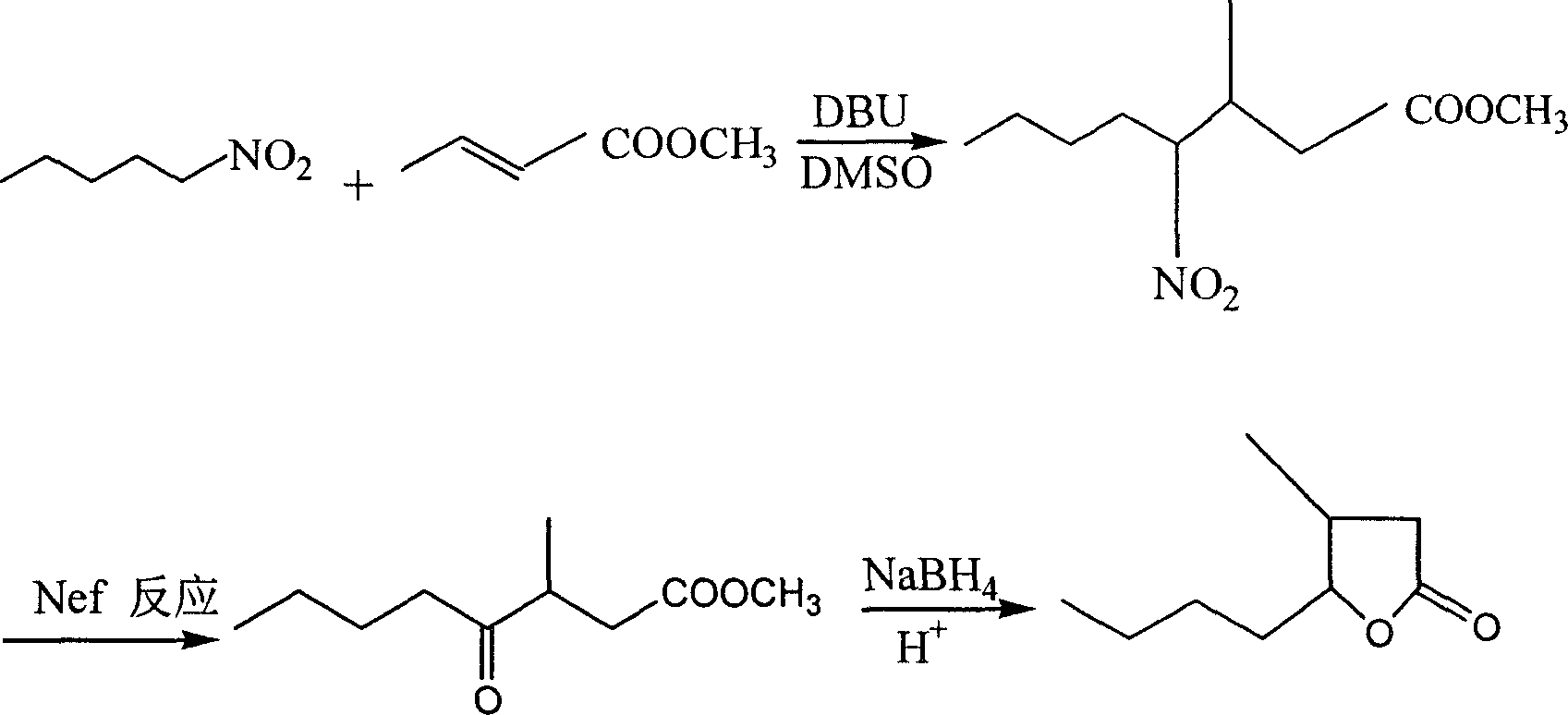
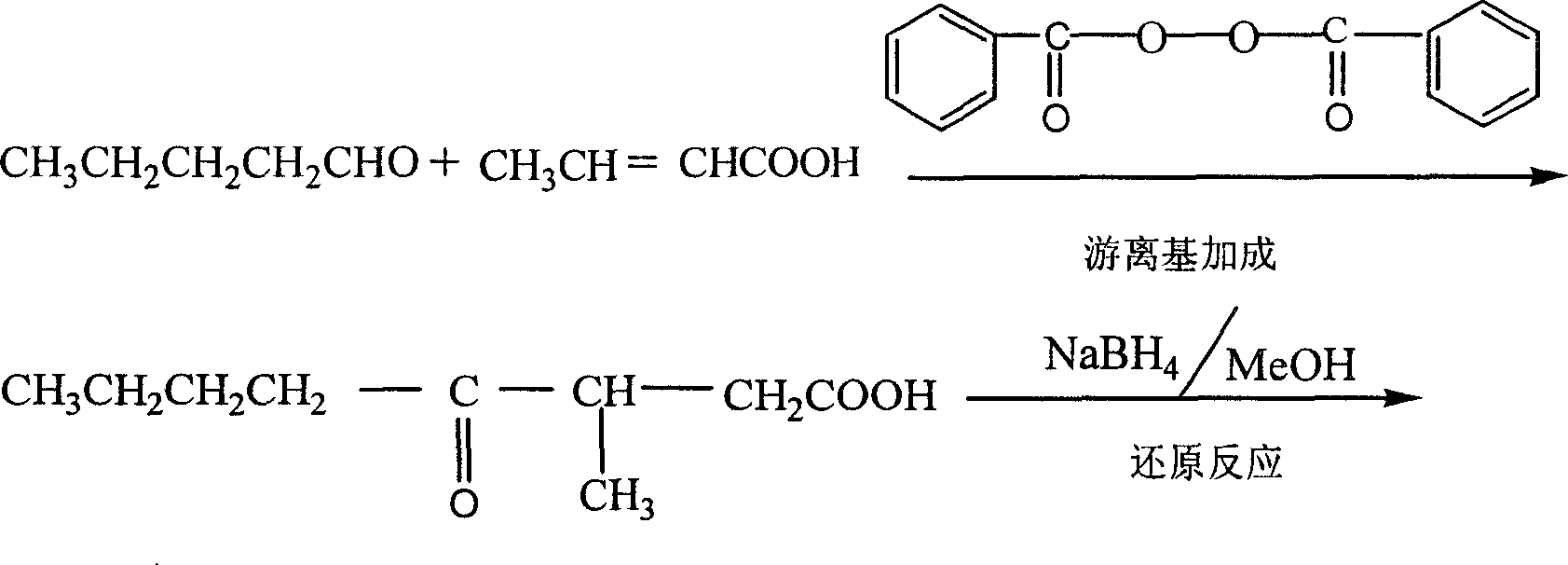
Method for preparing whisky lactone
ActiveCN1915984AEmission reductionAvoid it happening againOrganic chemistryKetonic acidsRefractive index
This invention provides a method for preparing whiskey lactone. The method comprises: (1) reacting n-valeraldehyde and crotonic acid by free radical addition under N2 protection in the presence of initiator and catalyst to obtain a mixture containing ketonic acid; (2) cooling, washing, drying and distilling to obtain ketonic acid; (3) hydrogenating in the presence of Raney Ni catalyst, filtering, heating for vaporizing, dehydrating and cyclizing to obtain whiskey lactone with a yield of 87% and a refractive index ND20 of 1.441-1.447. Determined by a combination of chromatography and mass spectrometry, the whiskey lactone comprises 98% cis-isomer, as well as 2% trans-isomer. The method has such advantages as high yield, simple process, reduced wastewater discharge and is good for environmental protection.
Owner:DALIAN LAIKE FINE CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com