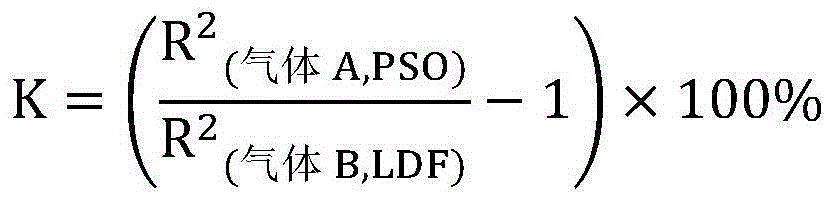Method of measuring variable-pressure absorption gas separation performance of carbon molecular sieve on basis of liquid absorption gas flooding principle
A technology of carbon molecular sieve and pressure swing adsorption, which is applied in suspension and porous material analysis, measurement device, permeability/surface area analysis, etc., can solve the problem that the gas separation performance of the adsorbent is not comparable, the optimal experimental conditions are different, and there is no formation evaluation criteria, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
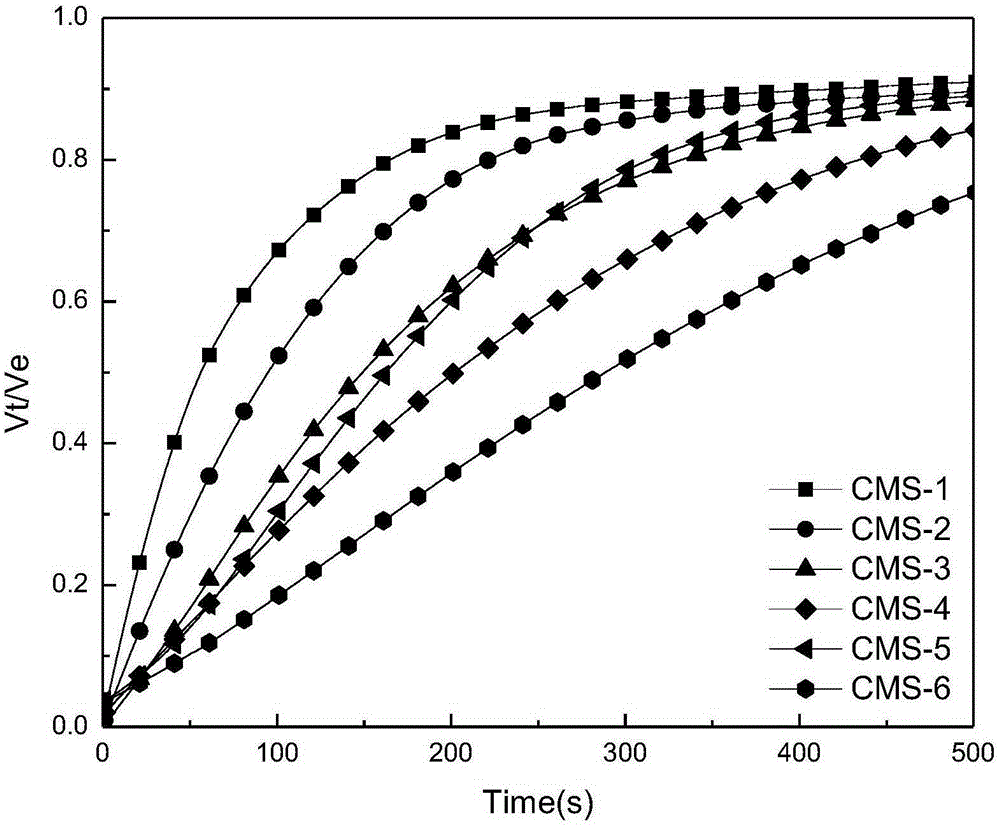
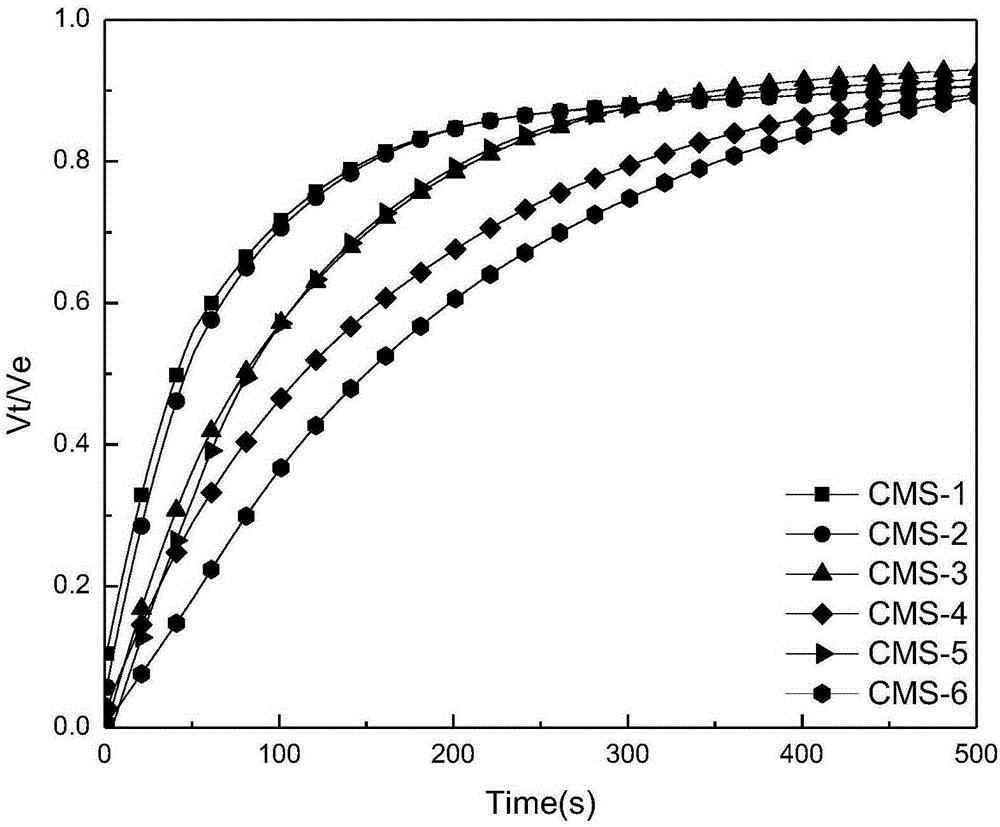
[0029] In this example, six kinds of carbon molecular sieves (CMS-1 to CMS-6) for air separation were used to carry out water absorption and displacement of O 2 / N 2 In the experiment, the kinetic curve of liquid suction and gas displacement and the equilibrium gas displacement volume V e (ml / g), such as figure 1 , 2 shown. With the help of pseudo-second-order kinetic adsorption (PSO) model and linear driving force (LDF) model for linear simulation, analysis and comparison of their linear correlation coefficient R 2 and kinetic parameters (shown in Tables 1 and 2), determine the kinetic speed control step in the process of water absorption and gas drive, and calculate the value of selectivity coefficient K, as shown in Table 3.
[0030] By analyzing the six kinds of carbon molecular sieves in Table 3, water flooding O 2 / N 2 The speed control step and K value of the process, and the nitrogen production performance of pressure swing adsorption air separation are summarize...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this example, four kinds of carbon molecular sieves (CMS-1~CMS-4) were used to carry out water absorption and flooding at 30°C with a constant volume liquid absorption and gas displacement device. 2 / CH 4 In the experiment, the kinetic curve of liquid suction and gas displacement and the equilibrium gas displacement volume V e (ml / g), such as figure 1 , 2 shown. The pseudo-second-order kinetic adsorption (PSO) model and the linear driving force (LDF) model were used to perform linear simulation to determine the kinetic speed control step of the water absorption and gas displacement process, and to calculate the value of the selectivity coefficient K, as shown in Table 6. The law of K value: CMS-1>CMS-2>0>CMS-3>CMS-4, corresponding to the law of gas separation effect: CMS-1 CMS-3>CMS-4. The K value of CMS-2 is closest to 0, so it is most suitable for pressure swing adsorption separation of N 2 / CH 4 craft.
[0037] Table 1 PSO model and LDF model simulate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com