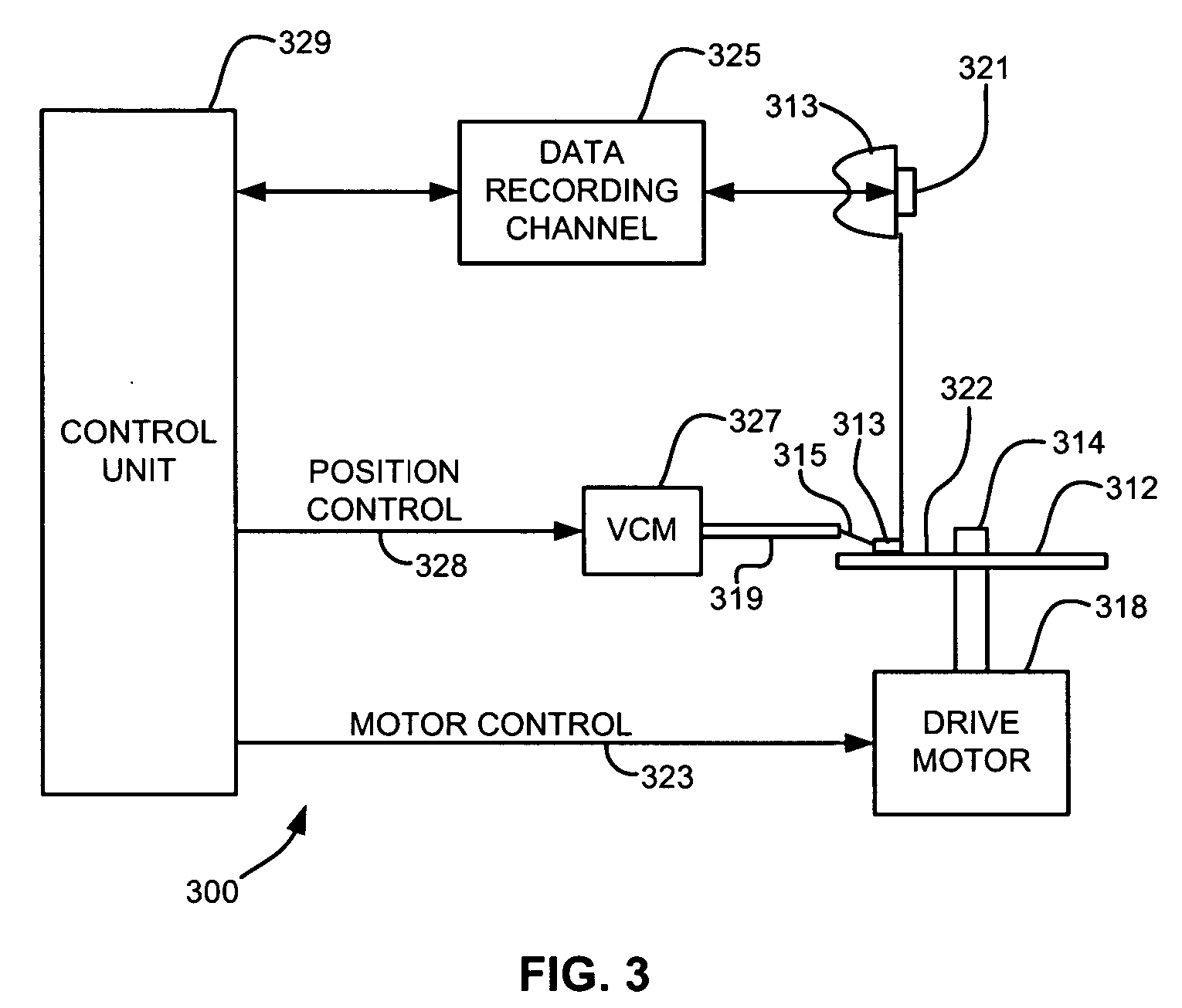
Patents
Literature
121 results about "Magnetic stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetic composite material surface imprinting thermosensitive adsorbent, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102527349AHigh mechanical strengthImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationMethacrylateMagnetic stability
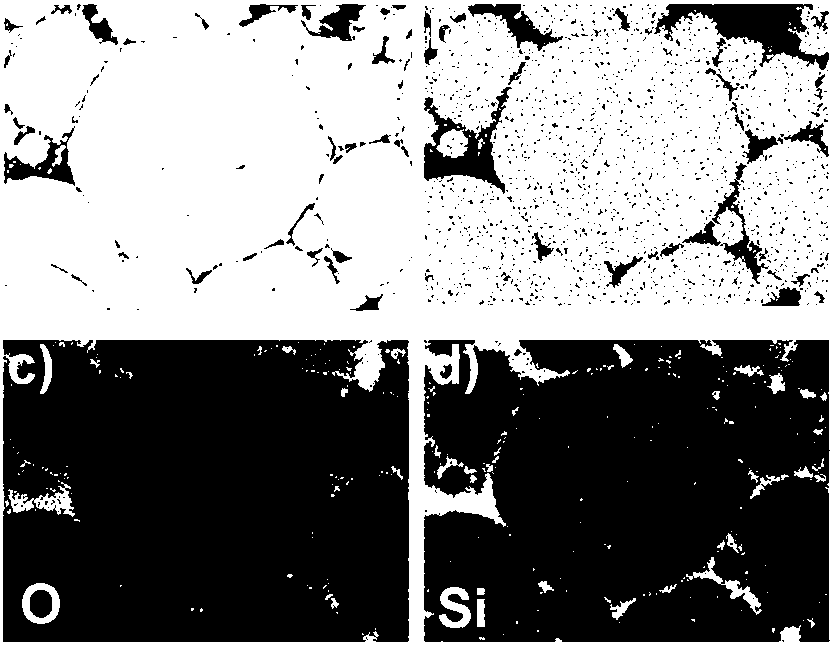
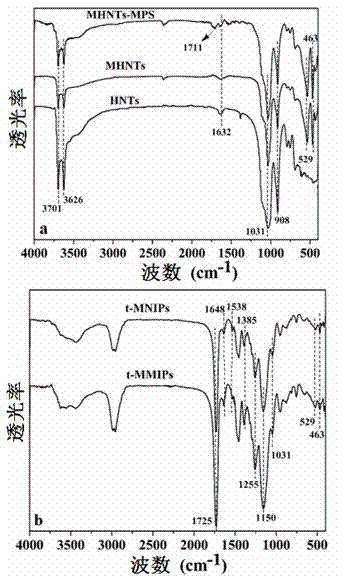
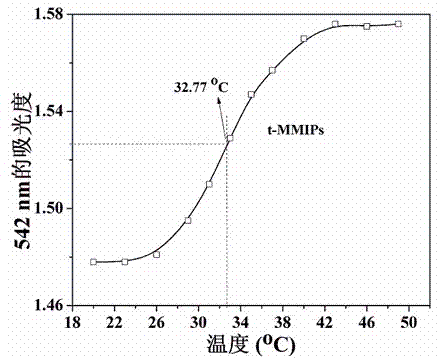
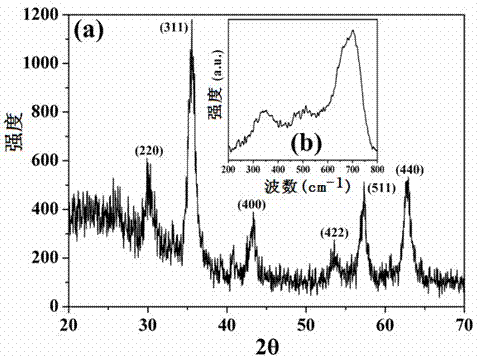
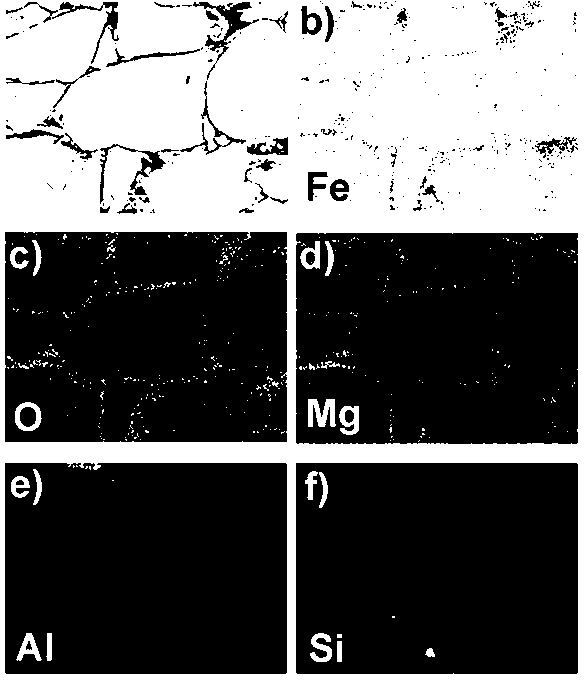
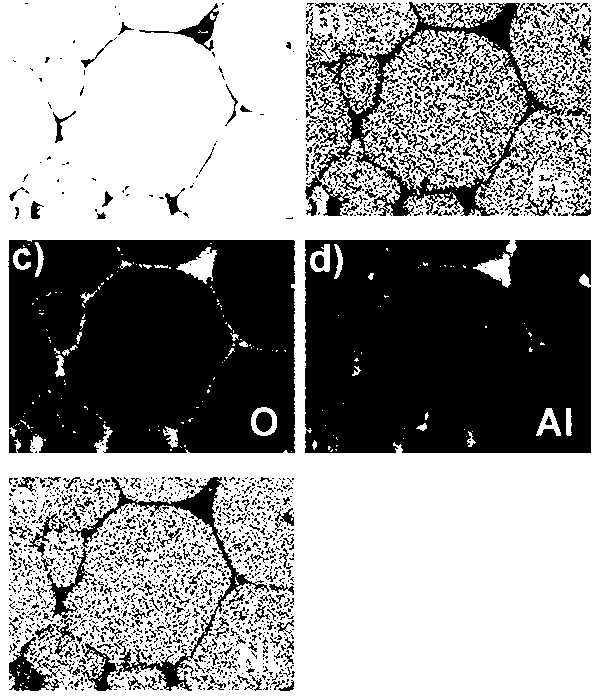
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of environment functional materials, in particular to a magnetic composite material surface imprinting thermosensitive adsorbent, and a preparation method and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, a ferroferric oxide / nerchinskite nanotube magnetic composite material is prepared by a solvent thermal synthesis method; secondly, the magnetic composite material is modified on ethenyl by using 3-(methacrylo) propyltrimethoxyl silane; and finally, the nerchinskite nanotube magnetic composite material is prepared by using the ethenyl-modified magnetic composite material as a substrate material, 2, 4, 5-trichlorophenol as a template molecule, methacrylate as a functional monomer, N-isopropylacrylamide as a thermosensitive functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a cross-linking agent, and 2,2'-azodiisobutyronitrile as an initiator. The prepared thermosensitive imprinting adsorbent is obvious in thermal stability and magnetic stability, sensitive in magnetic effect and thermosensitive effect, relatively high in adsorption capacity, obvious in reversible absorption / release function along with temperature and obvious in tertiary calcium phosphate (TCP) molecule recognition performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of metal soft magnetic powder core
InactiveCN103247403ASimple preparation processEasy to useInorganic material magnetismMagnetic stabilityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal soft magnetic powder core, which aims at solving the technical problems of high pollution, high cost and poor magnetic stability in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of raw material sieving, insulation coating, to-be-formed magnetic powder preparation, pressure forming, heat treatment and surface spraying. The method has the technical benefits that a preparation technique is simple; used equipment is simple; the insulation coating is conducted on magnetic powder with nano oxide dispersion liquid; a using effect is good; an environment is not polluted; the raw material cost is low; an organic solvent and an organic binder are not used in a preparation process; soaking and solidification treatment is not conducted; the method is low in cost and pollution-free; and the metal soft magnetic powder core prepared by the method has good magnetic stability, a higher quality factor and lower magnetic core loss.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH +1
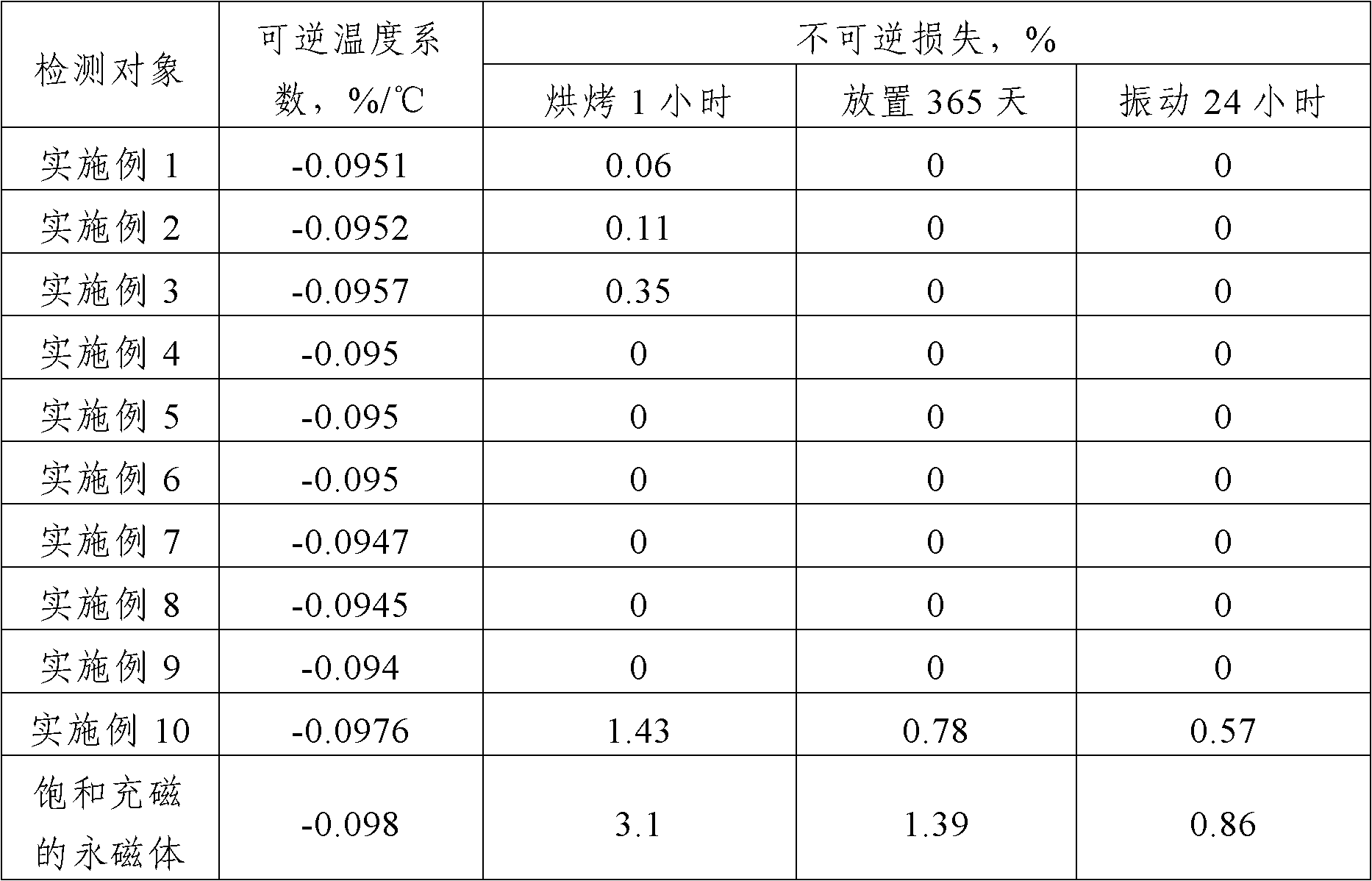
Cold-heat circulation aging treatment method for increasing magnetic stability of permanent magnets
ActiveCN102568808ASimple processEasy to operatePermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic stabilityRadiation resistant
The invention discloses a cold-heat circulation aging treatment method for increasing magnetic stability of permanent magnets. The method comprises the following steps of: putting one or more permanent magnets magnetized in a saturated manner on a non-magnetic bottom plate; then putting in a high-low temperature chamber, and freezing at minus 70 DEG C to minus 20 DEG C for 30-120 min; then, heating the high-low temperature chamber to 60-250 DEG C at the temperature increasing rate of 1-10 DEG C / min, and keeping the temperature for 30-240 min; and finally, naturally cooling to room temperature, and completing cold-heat circulation aging treatment. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, total loss, irreversible loss, reversible loss and reversible temperature coefficients when temperature of the permanent magnets is changed can be effectively eliminated or reduced; and heat stability, time stability, magnetic stability and radiation-resistant magnetic stability of the permanent magnets under a vibration condition can be increased.
Owner:西安西工大思强科技股份有限公司
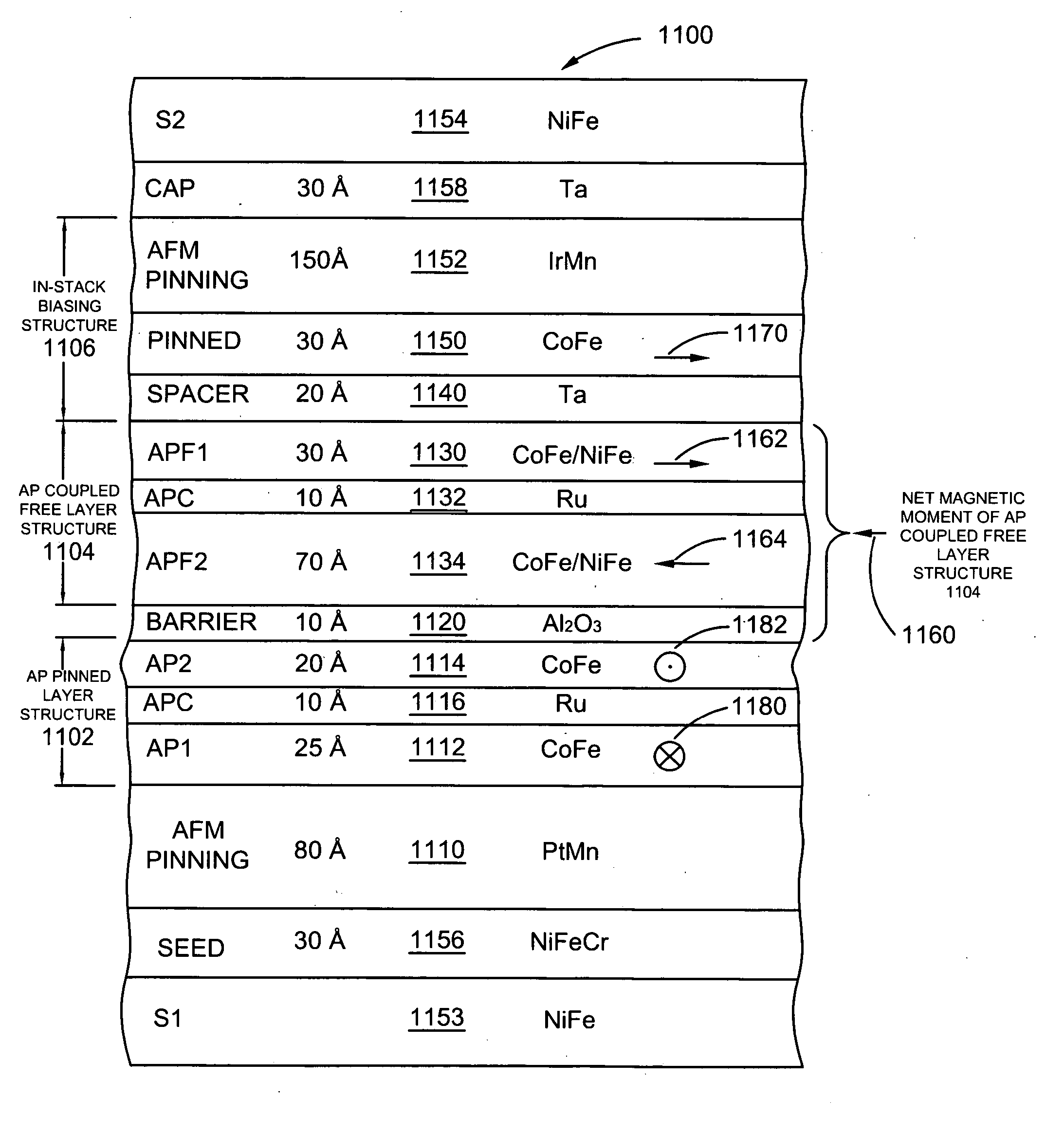
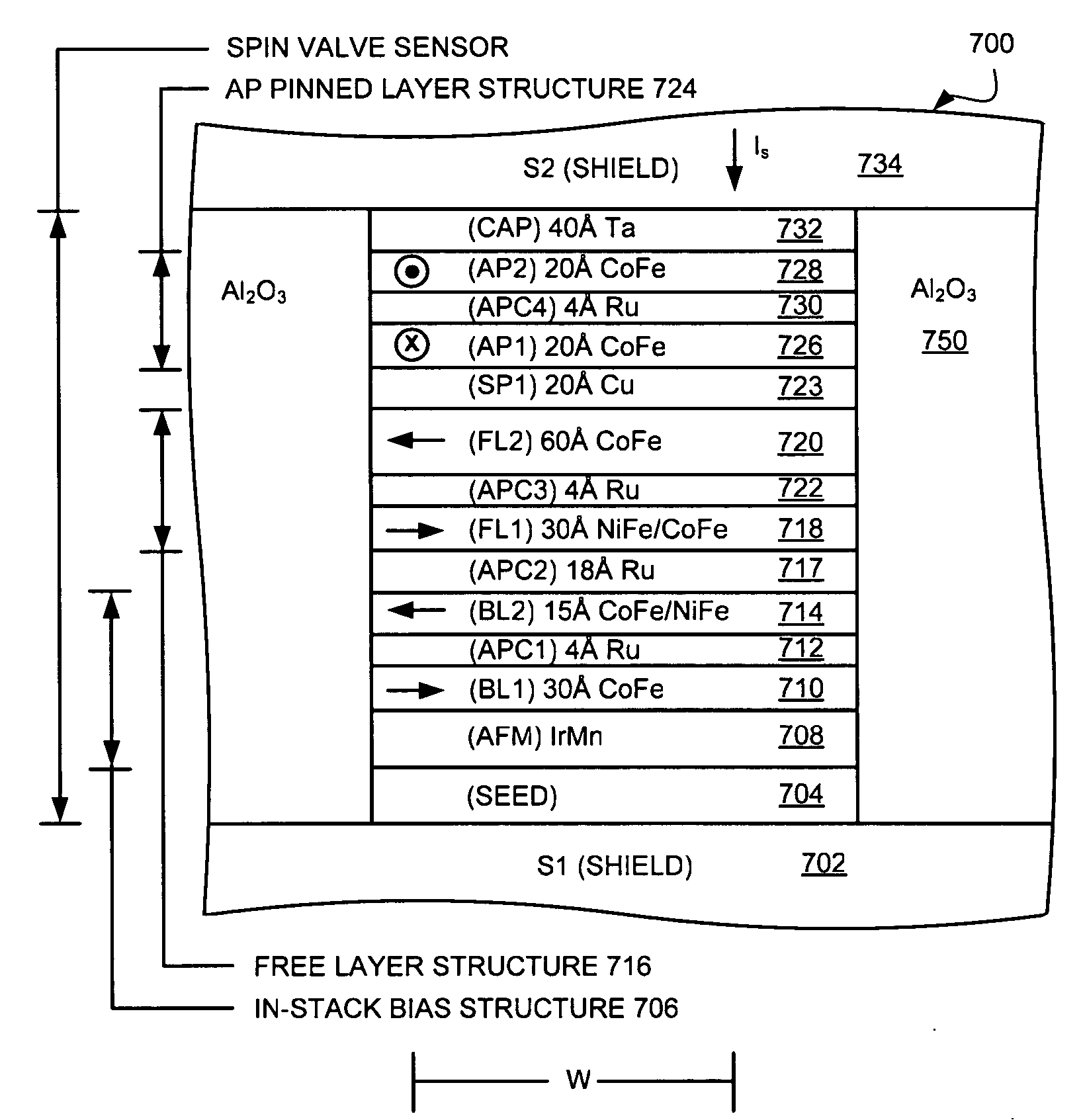
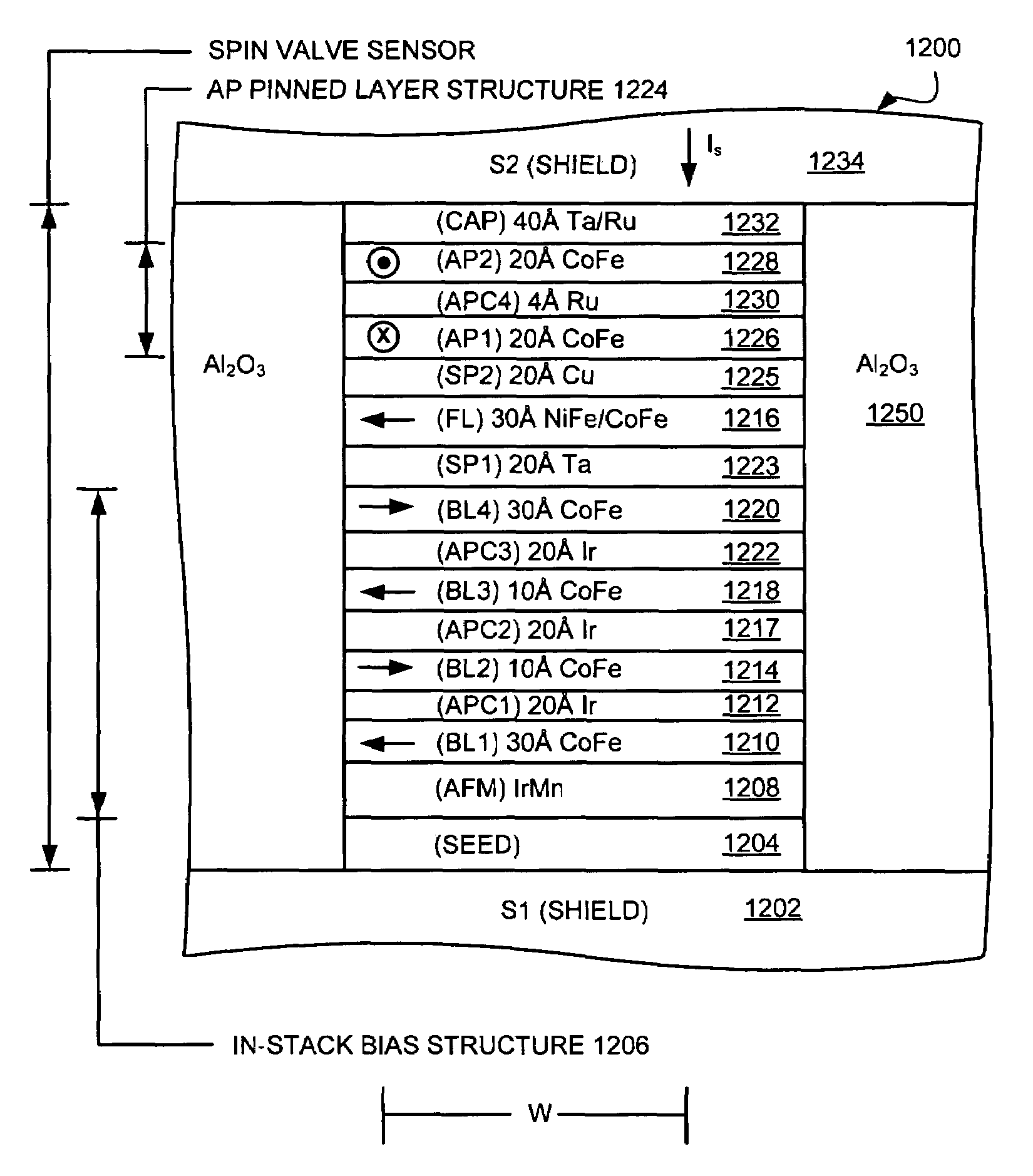
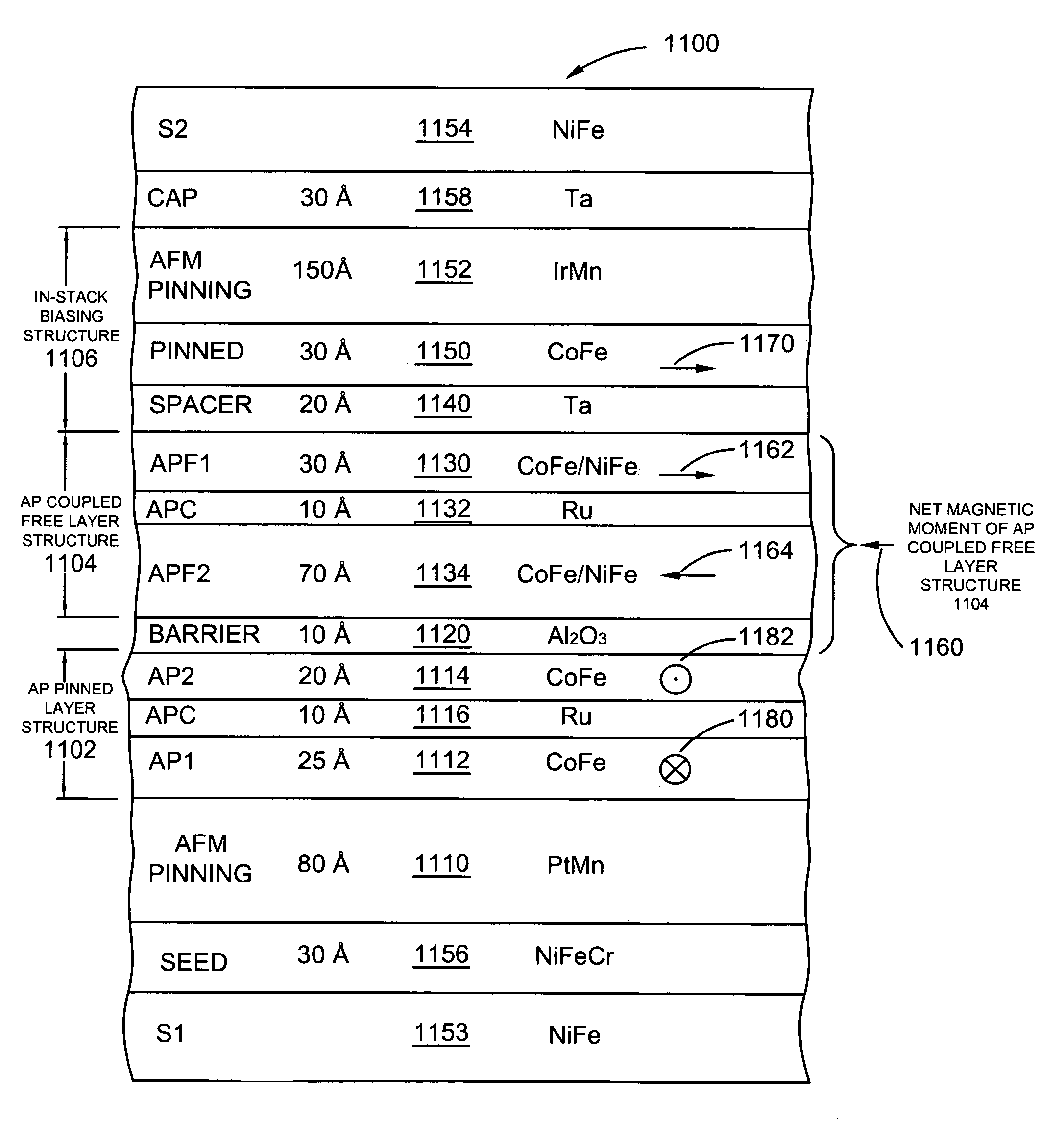
Read sensor having an in-stack biasing structure and an AP coupled free layer structure for increased magnetic stability
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method of contactless magnetic electroporation
This invention provides a novel method of tissue electroporation that eliminates the need for electrodes that conduct electricity to the tissues. This invention creates electric currents and fields sufficient for porating cell membranes for improving the delivery of polynucleotides such as plasmid and linear DNA and RNA constructs, and polypeptides such as antigen protein constructs into mammalian eucaryotic cells purely by magnetic field pulses that does not require the use of contacting electrodes to conduct electric or ionic current. This invention thus provides a method for improving transfection and immunogenicity of pharmaceutical substances without direct contact with a living body, and may be called magnetopermeabilization. A concomitant aspect of the invention is the method by which a drug such as a solution containing DNA is delivered to a targeted tissue bed that is optimal in conjunction with magnetopermeabilization for maximal transgene expression and drug effect.
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA
Magnetoresistance effect device, method of manufacturing the same, magnetic memory apparatus, personal digital assistance, and magnetic reproducing head, and magnetic information reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20020130339A1Simple highly productive manufacturing methodControllability lostNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic stabilityRandom access memory
Magnetoresistance effect devices for attaining magnetically stability and for reducing a switching magnetic field. One of the ferromagnetic layers of the magnetoresistance effect device has a plane shape in which a width of an end portions is wider than a center portion sandwiched by two end portions. The end portions are not symmetrical with respect to an easy magnetization axis or longer axis of the plane shape of ferromagnetic material layer, but are substantially rotationally symmetrical with a center of the plane shape as a pivot. The plane shape may have an S-shape where its magnetic domain is stabilized and the switching magnetic field is reduced. The manufacturing method uses two linear mask patterns intersecting with each other to form sharp corners of a ferromagnetic tunnel junction. An electron beam (EB) drawing may be used to form the S-shape plane. The magnetoresistance effect devices may be used in a magnetic memory apparatus, such as a random access memory, a personal digital assistance, a magnetic reproducing head, and a magnetic information reproducing apparatus.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for preparing sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon
ActiveCN103521180AUniform sizeHigh compressive strengthOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMagnetic stabilitySludge
The invention provides a method for preparing sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon. The method comprises the steps as follows: sludge is used as a raw material, an activating agent is added for carbonizing and activating the sludge; nano-sized Fe3O4 is used as a magnetic source for magnetizing the sludge active carbon; and sodium carboxymethylcellulose and aluminum salt are composited to an organic-inorganic binding agent, the binding agent and a p-toluenesulfonhydrazide foaming agent are used for uniformly binding powdery magnetic active carbon into a formed magnetic active carbon precursor with abundant pore structures, and finally, the formed magnetic active carbon precursor is heated to obtain the sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon. According to the method, the sludge is used as a main raw material, the resource utilization of the sludge is achieved, the recycling is convenient, and reutilization can be achieved; and further, the sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon has a stable structure and good magnetic stability, and can be widely used in the fields such as sewage treatment, soil pollution treatment and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
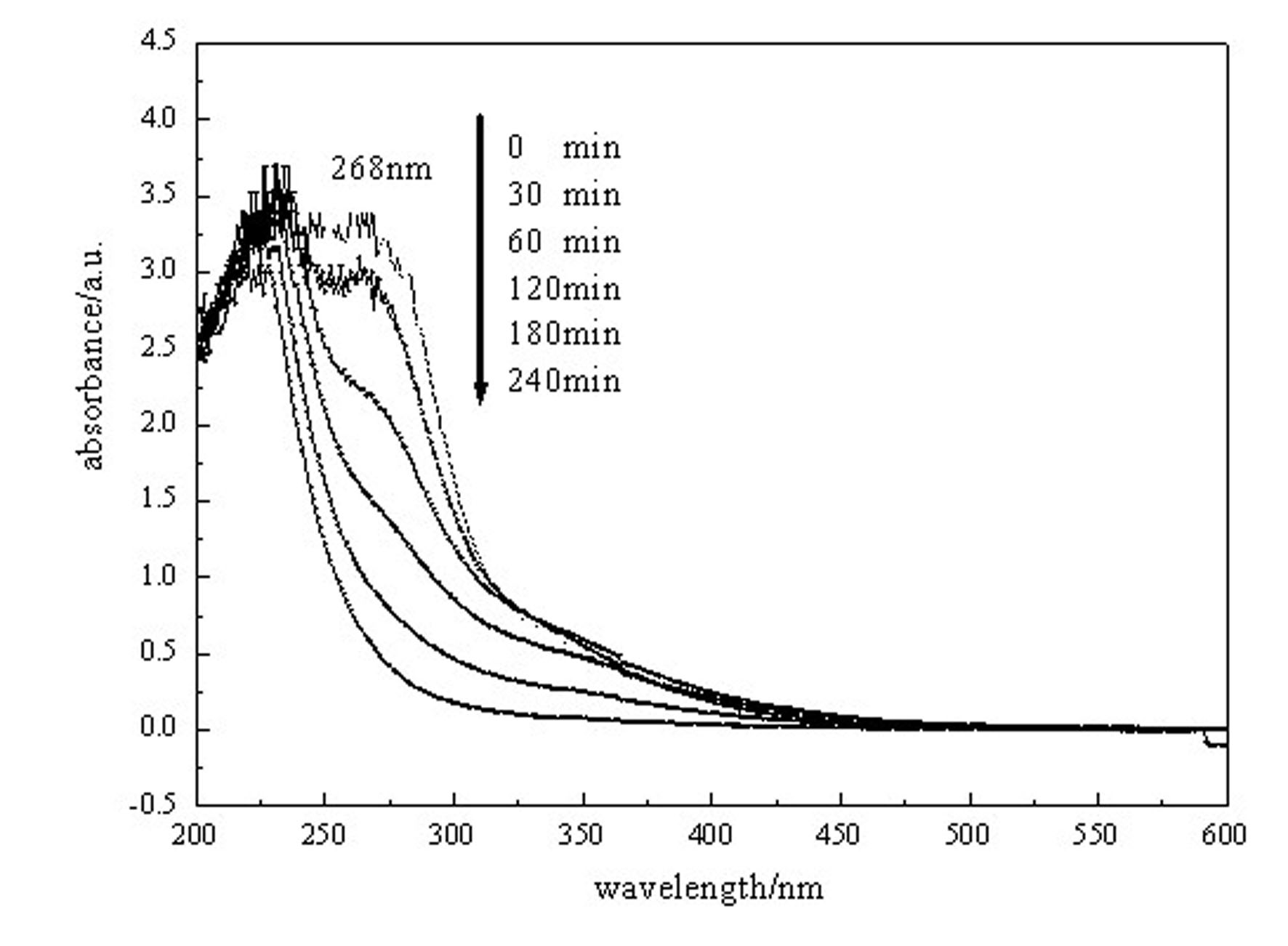
Magnetic-stability fluidized bed photocatalytic reactor and method for treating organic wastewater with difficult degradation thereby
InactiveCN101913680AEasy to separateImprove utilization efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsMagnetic stabilityHelmholtz coil
The invention relates to wastewater treatment method and device, in particular to a magnetic-stability fluidized bed photocatalytic reactor and a method for treating organic wastewater with difficult degradation thereby. The method solves the problems of low photocatalytic quantum, low activity and easy loss of active components existing in the traditional photocatalytic method and comprises the following steps of: feeding the organic wastewater to a reactor through a pump and a liquid inlet, adding a magnetism-loaded photocatalyst to the reactor through a catalyst feeding port, starting a fan to make air pass through a flow buffer and then enter an air distributor and make the magnetism-loaded photocatalyst be in a suspension state; starting Helmholtz coils to generate a magnetic field, opening an ultraviolet lamp when the magnetism-loaded photocatalyst is in the suspension state to degrade the organic wastewater, and then discharging the treated organic wastewater to a second liquid storage tank. The utilization rate of light energy can be improved, and because the magnetism-loaded photocatalyst is in the stable suspension state, the active component loss caused by mutual friction can be reduced; and the device has the advantages of compact structure, mild condition and high utilization rate of the light energy and can operate intermittently and run continuously.
Owner:太原市恒远化工环保科技有限公司
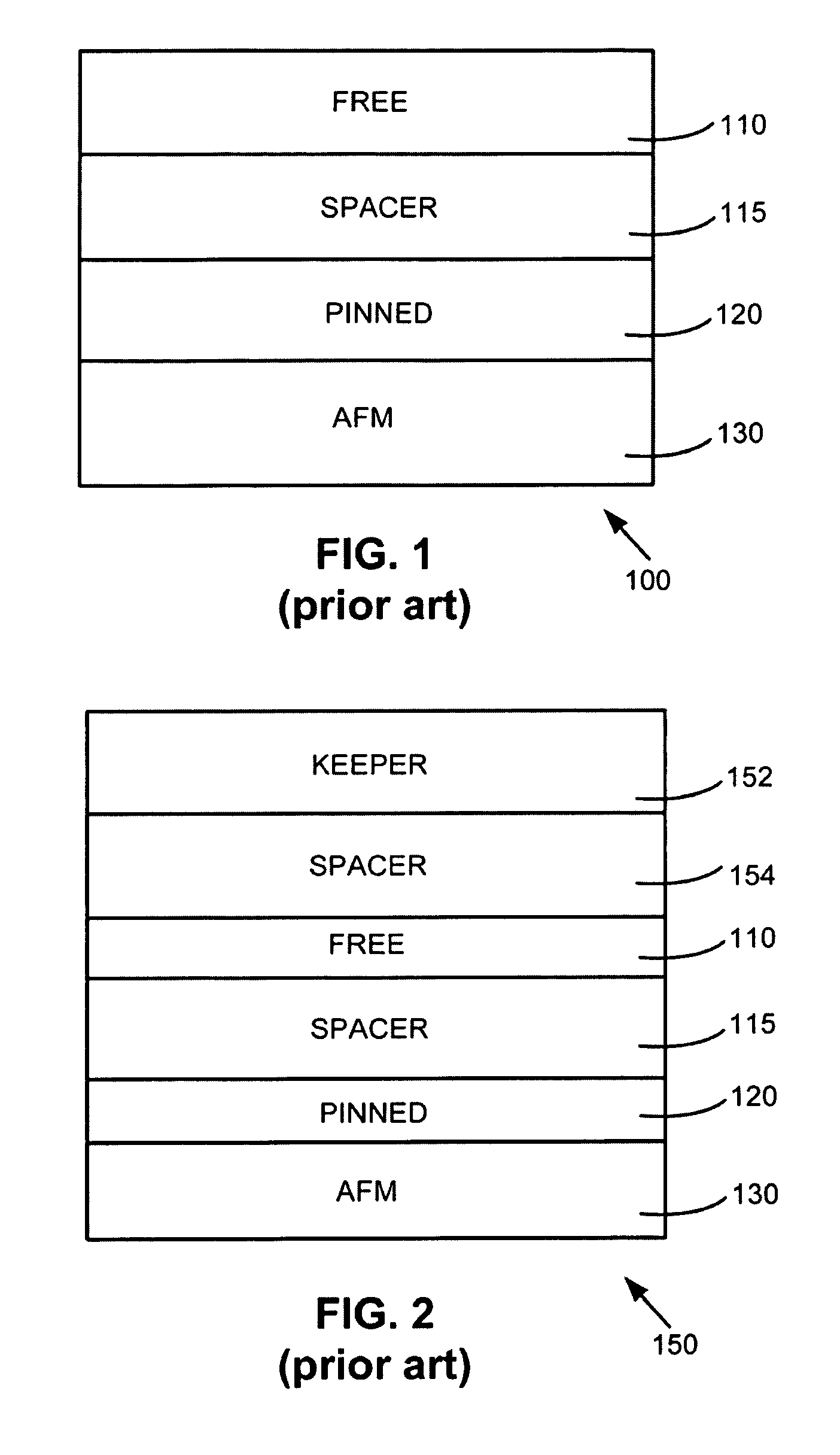
Sensor with in-stack bias structure providing enhanced magnetostatic stabilization
InactiveUS20060044708A1Overcome limitationsEasy to fixNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic stabilityPhysics
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method for preparing magnetic porous polystyrene microspheres on basis of suspension polymerization
InactiveCN103627022AIncrease productionHigh mechanical strengthOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMagnetic stabilityPolymer science
The invention relates to a method for preparing magnetic porous polystyrene microspheres on the basis of suspension polymerization, belonging to the technical field of preparation of environmental functional materials. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing Fe3O4 magnetic particles by a solvothermal process; and preparing magnetic porous polystyrene microspheres by suspension polymerization by using styrene and divinylbenzene as functional monomers, azodiisobutyronitrile as an initiator and toluene and cyclohexanol as pore-forming agents. The obtained microspheres have abundant pores on the surface, thereby being beneficial to enhancing adsorbability; and the Fe3O4 magnetic particles inside the microspheres have magnetic stability, and can be quickly separated under the action of an external magnetic field. The adsorbent is used in a water environment for selectively adsorbing 2,4-dichlorophenol and 2,6-dichlorophenol. The static adsorption experiment result indicates that the magnetic porous microspheres prepared by the method have the advantages of favorable adsorption capacity, quick adsorption kinetic property and favorable regenerability.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Sensor with in-stack bias structure providing enhanced magnetostatic stabilization
InactiveUS7397637B2Easy to fixLarge magnetic thicknessNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic stabilityPhysics
A magnetic head having an in-stack bias structure and a free layer structure. The in-stack bias structure includes an antiferromagnetic layer, and first through fourth antiparallel (AP) pinned bias layers separated by three AP coupling layers. A first spacer layer is positioned above the fourth bias layer of the bias structure. A free layer is positioned above the first spacer layer. The fourth bias layer magnetostatically stabilizes the free layer.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Magnetoresistance effect device, method of manufacturing the same, magnetic memory apparatus, personal digital assistance, and magnetic reproducing head, and magnetic information reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20050078417A1Controllability lostFineness lostNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic stabilityRandom access memory
Magnetoresistance effect devices for attaining magnetically stability and for reducing a switching magnetic field. One of the ferromagnetic layers of the magnetoresistance effect device has a plane shape in which a width of an end portions is wider than a center portion sandwiched by two end portions. The end portions are not symmetrical with respect to an easy magnetization axis or longer axis of the plane shape of ferromagnetic material layer, but are substantially rotationally symmetrical with a center of the plane shape as a pivot. The plane shape may have an S-shape where its magnetic domain is stabilized and the switching magnetic field is reduced. The manufacturing method uses two linear mask patterns intersecting with each other to form sharp corners of a ferromagnetic tunnel junction. An electron beam (EB) drawing may be used to form the S-shape plane. The magnetoresistance effect devices may be used in a magnetic memory apparatus, such as a random access memory, a personal digital assistance, a magnetic reproducing head, and a magnetic information reproducing apparatus.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Ferrite core and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1404076AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismIron compoundsMagnetic stabilityVolumetric Mass Density
To provide a soft ferrite which has a high saturation magnetic flux density of Bs at a high temperature of 100 DEG C or higher, especially at a temperature of 150 DEG C or so and deteriorates its magnetic properties less (even if sacrificing its low power loss property to some extent) at the above high temperature, especially deteriorates its core loss less, and is superior in magnetic stability. The major composition of ferrite core contains 56 to 57 mol% iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3, 5 to 10 mol% zinc oxide in terms of ZnO, 3 to 6 mol% in terms of NiO, and the residual mol% manganese oxide in terms of (MnO). When the major composition is expressed by: (Zn<2+>a, Ni<2+>b, Mn<2+>c, Mn<3+>d, Fe<2+>e, Fe<3+>f)O4+delta equation (1) (in the equation (1), a+b+c+d+e+f=3, and the relationship delta=a+b+c+(3 / 2)d+e+(3 / 2)f-4) the delta value in the equation (1) is in the range 0 <= delta <= 0.001.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
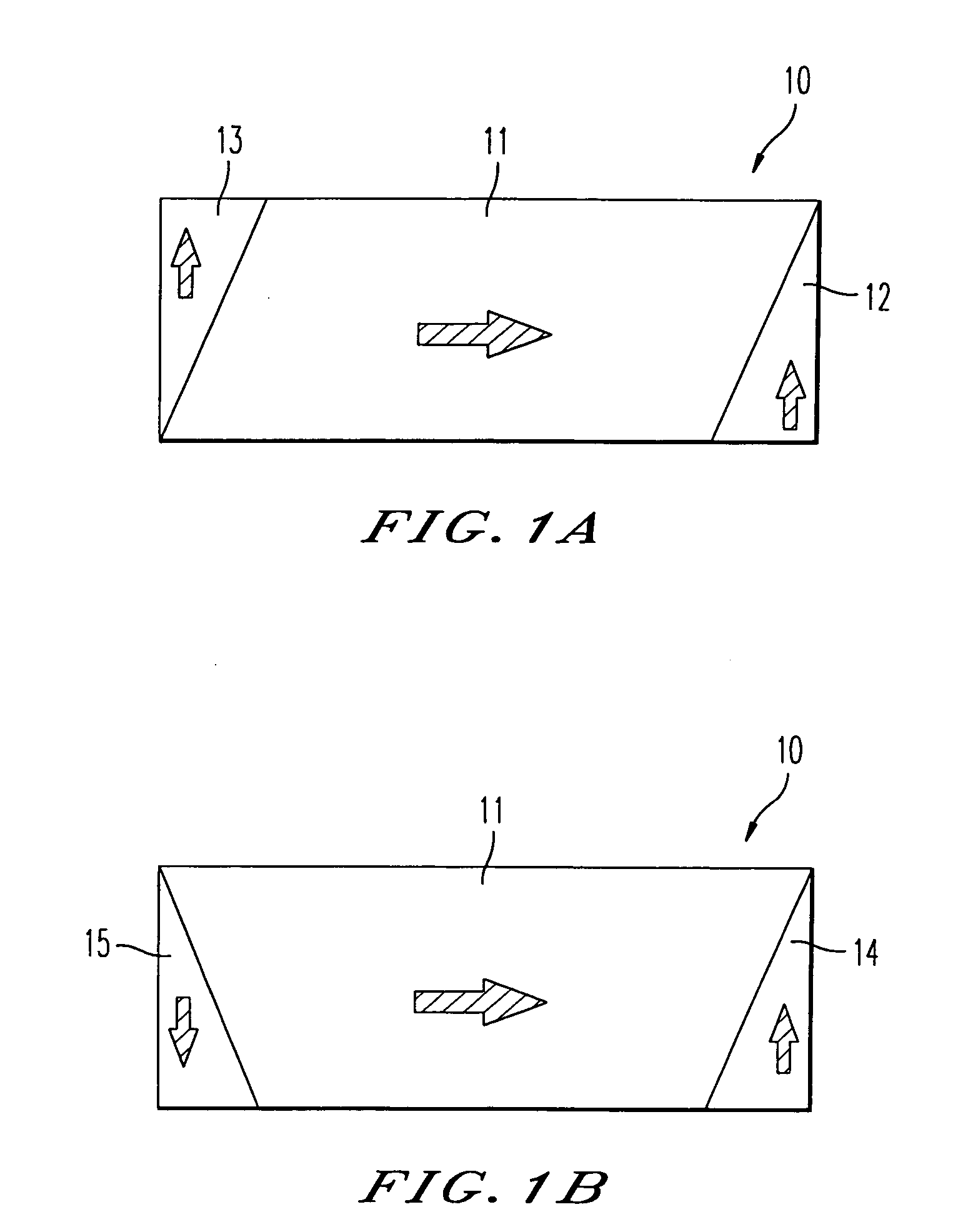
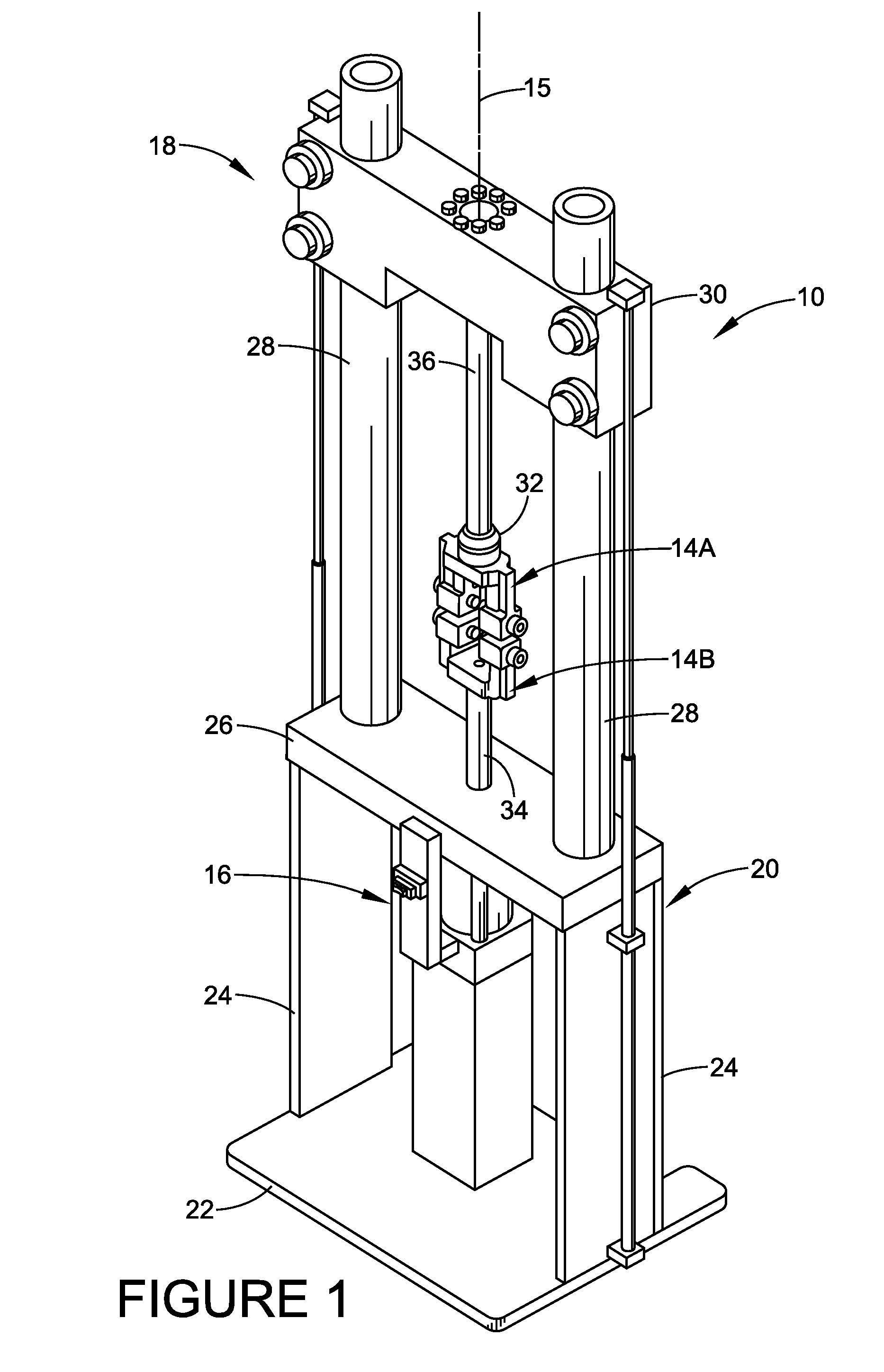
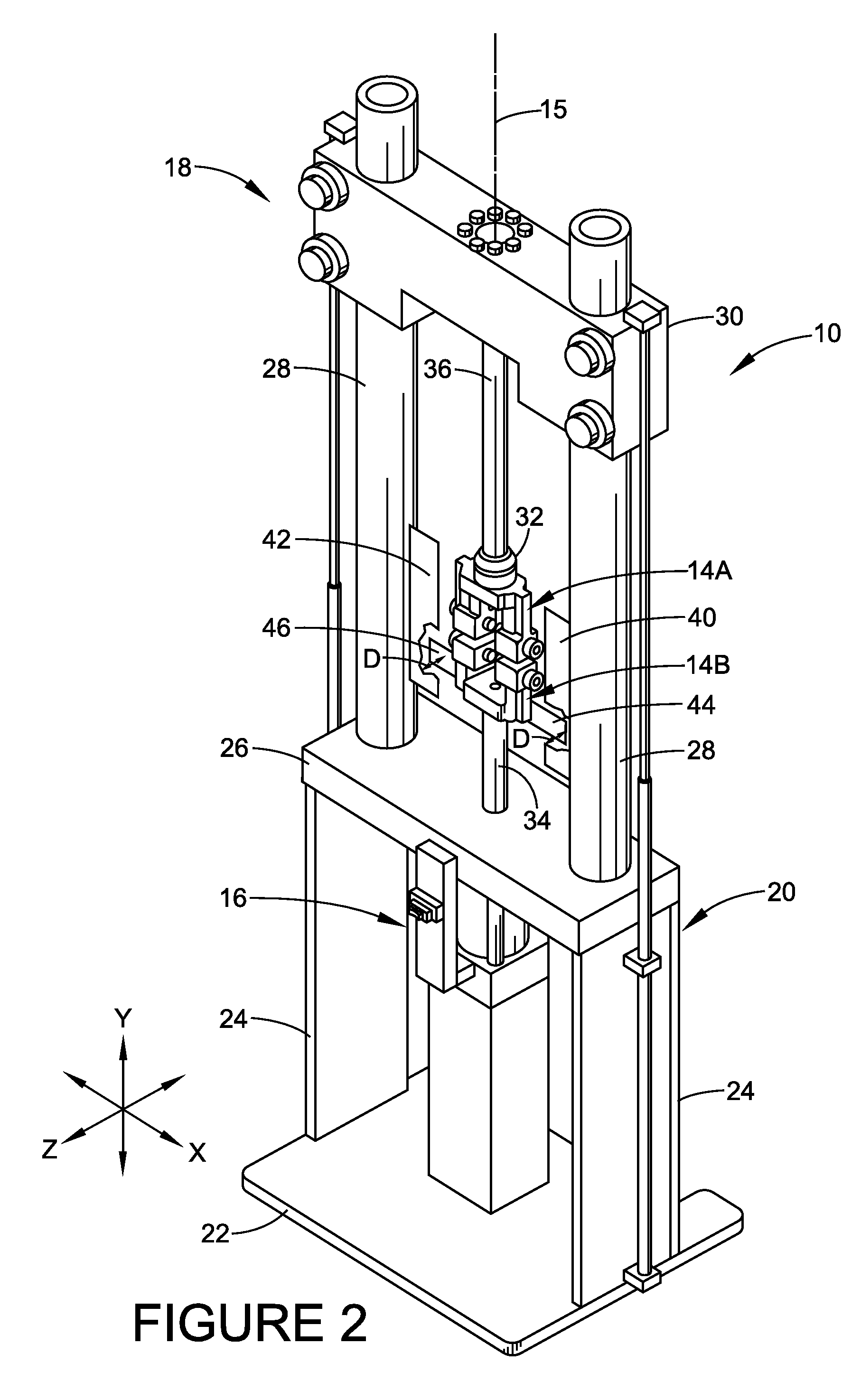
Magnetic stability for test fixture
InactiveUS7568397B2Prevent rotationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMagnetic tension forceMagnetic stability
A test machine for testing the tension or compression properties of a test specimen is provided. The test machine utilizes magnetic force to prevent the fixture of the machine from rotating while placing the test specimen in tension or under compression, which accordingly prevents the test specimen from rotating as well as the source of such rotation. Unintended forces are thereby minimized, enabling a user to obtain more accurate test results.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE FIRESTONE NORTH AMERICAN TIRE
Read sensor having an in-stack biasing structure and an AP coupled free layer structure for increased magnetic stability
Current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP), current-in-to-the-plane (CIP), and tunnel valve type sensors are provided having an antiparallel (AP) coupled free layer structure, an in-stack biasing structure which stabilizes the AP coupled free layer structure and a nonmagnetic spacer layer formed between the in-stack biasing layer and the AP coupled free layer structure. The AP coupled free layer structure has a first AP coupled free layer adjacent to the nonmagnetic spacer layer, a second AP coupled free layer, and an antiparallel coupling (APC) layer formed between the first and the second AP coupled free layers. The net moment of the AP coupled free layer structure has an antiparallel edge magnetostatic coupling with the in-stack biasing structure. At the same time, the first AP coupled free layer has an antiparallel exchange coupling with the second AP coupled free layer. By forming the second AP coupled free layer with a thickness greater than a thickness of the first AP coupled free layer, the AP coupled free layer structure has a net magnetic moment in the direction of the second AP coupled free layer moment. The non-magnetic spacer layer is chosen so that first AP coupled free layer has a parallel interlayer (Neel or Orange-peel or positive exchange) coupling with the in-stack biasing structure, so that the interlayer coupling adds to the edge magnetostatic coupling to increase a stability of the AP coupled free layer structure.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
One-step method for preparing sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon
ActiveCN103521179AUniform sizeHigh compressive strengthOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMagnetic stabilityResource utilization
The invention provides a one-step method for preparing sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon. The method comprises the steps as follows: sludge is used as a raw material, sludge screened by a 100-200 mesh sieve and self-prepared nano-sized Fe3O4 are uniformly composited in a proportion to form a powdery magnetic active carbon precursor; phenolic resin-silica sol is adopted as a binding agent, the binding agent and an azodicarbonamide foaming agent are used for uniformly binding the powdery magnetic active carbon precursor to form a formed magnetic active carbon precursor with abundant pore structures; and finally, the formed magnetic active carbon precursor is certainly carbonized and activated to obtain the sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon. According to the one-step method, the sludge is used as a main raw material, the resource utilization of the sludge is achieved, the recycling is convenient, and reutilization can be achieved; and further, the sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon has a stable structure and good magnetic stability, and can be widely used in the fields such as sewage treatment, soil pollution treatment and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
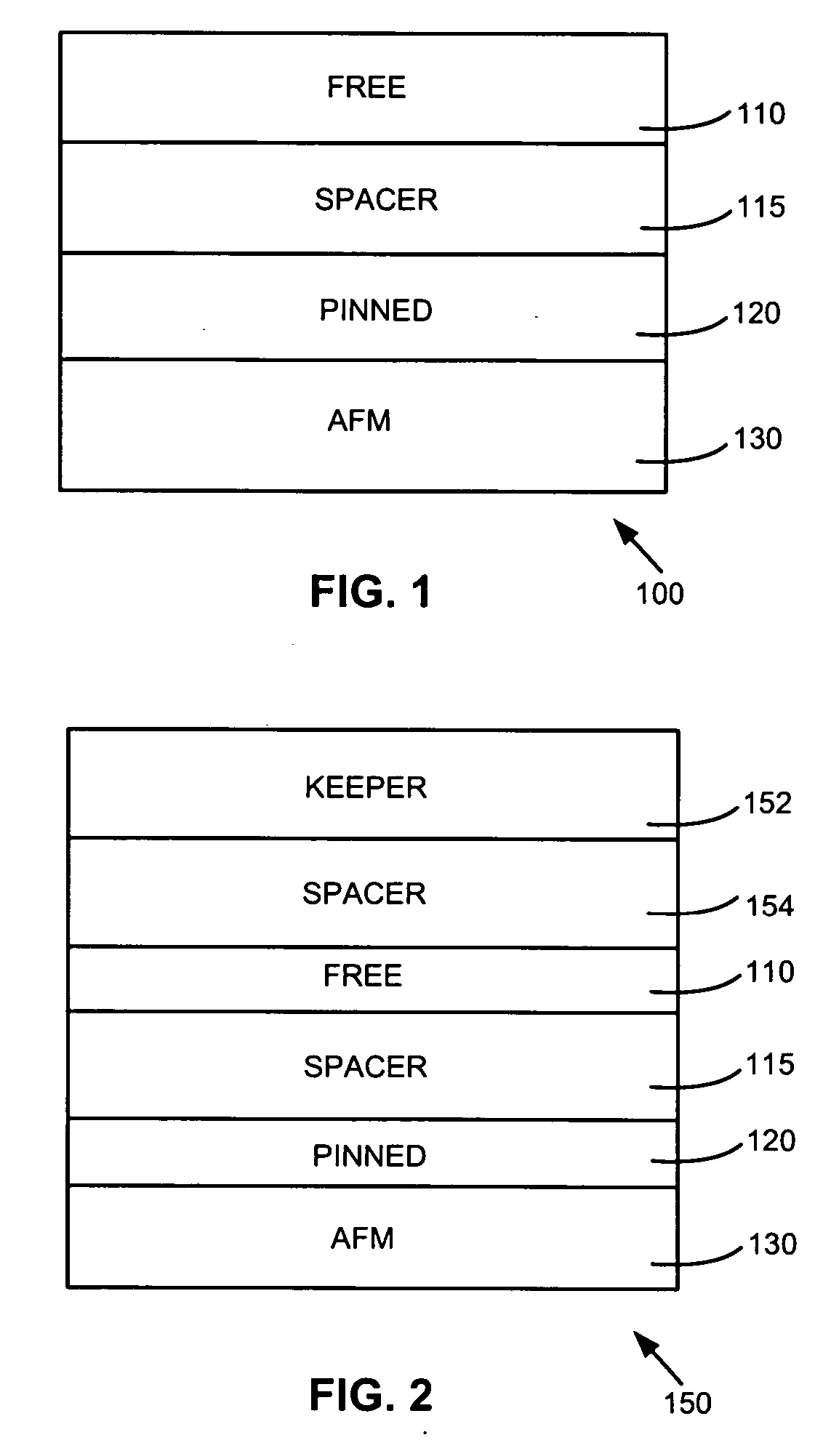
Double layer spacer for antiparallel pinned layer in CIP/CPP GMR and MTJ devices
InactiveUS6870711B1Contribute to of performanceContribute to stabilityElectrical transducersRecord information storageMagnetic stabilityMagnetization
A pinned / pinning layer configuration of the form: AP1 / coupling bilayer / AP2 / AFM, suitable for use in a CIP or CPP GMR sensor, a TMR sensor or an MRAM element, is found to have improved magnetic stability, yield good values of dR / R and have high values of saturation magnetization that can be adjusted to meet the requirements of magnetic field annealing. The coupling bilayer is a layer of Ru / Rh or their alloys, which provides a wide range of coupling strengths by varying either the thickness of the Ru layer or the Rh layer.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
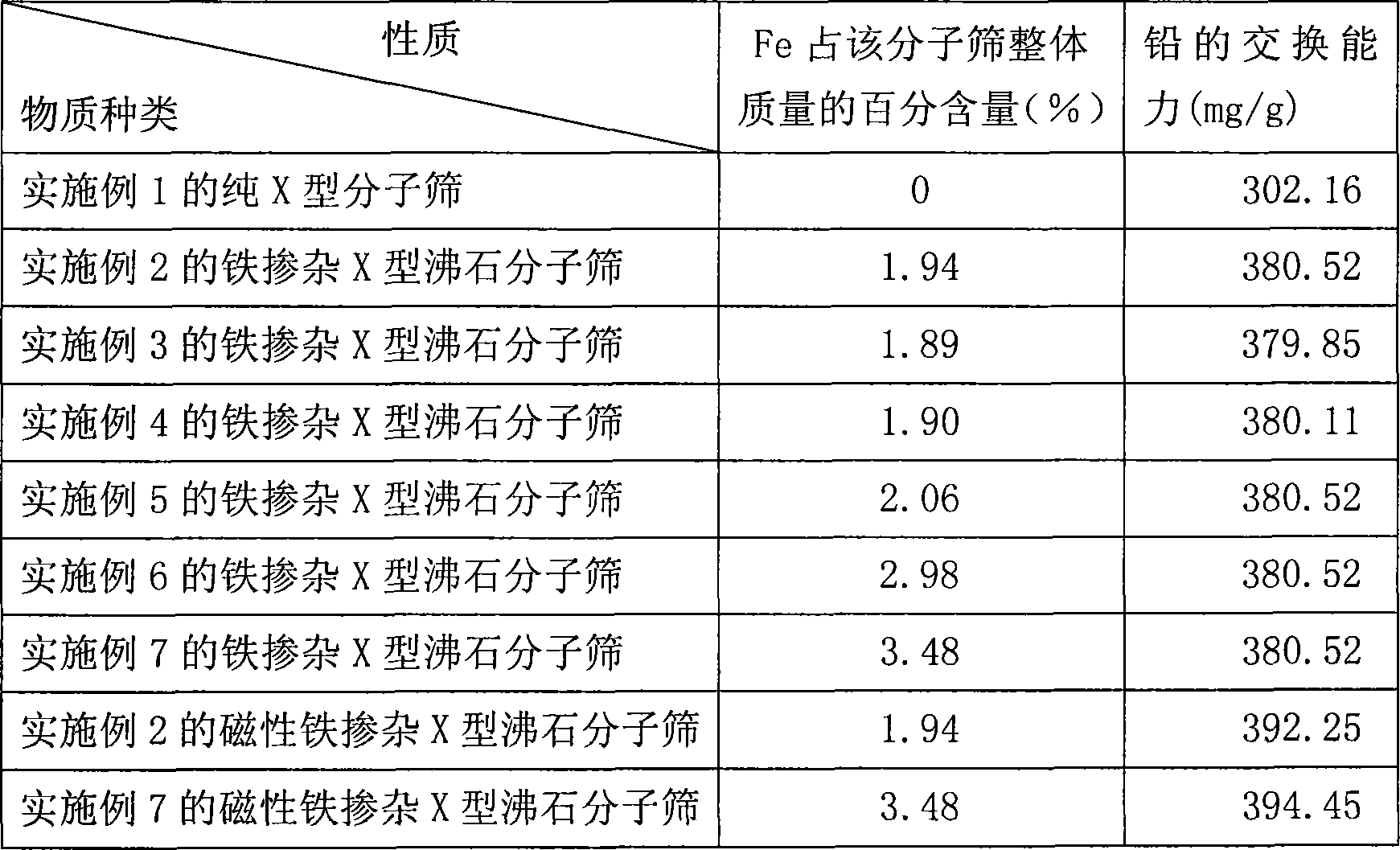
X type zeolite molecular sieve and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101219795AImprove performanceImprove adsorption capacityFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveMagnetic stability
The invention relates to an X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve and a method for preparing thereof, relating to a field of zeolite molecular sieve material; The X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve is a magnetic iron-doped X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve; magnetic ferroferric oxide is formed in the zeolite lattice, wherein, quality percentage of Fe occupying the molecular sieve is 1.89 percent to 3.48 percent. The preparing method comprises the steps that, iron-doped X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve is firstly compounded and then the magnetized magnetic iron-doped X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve is prepared through hydrogen reduction; the method results in a structure of Fe3O4 formed in frame of the iron-doped X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve. The magnetic iron-doped X-shaped zeolite molecular sieve has strong magnetism and magnetic stability, which not only solves the problem that the existing powdery zeolite molecular sieve is difficult to be recycled in reaction solution, and further improves absorption property of the sieve, but also enlarge application range of the zeolite molecular sieve, thereby allowing the zeolite molecular sieve to be applied to catalytic reaction in which iron acts as the catalyst.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
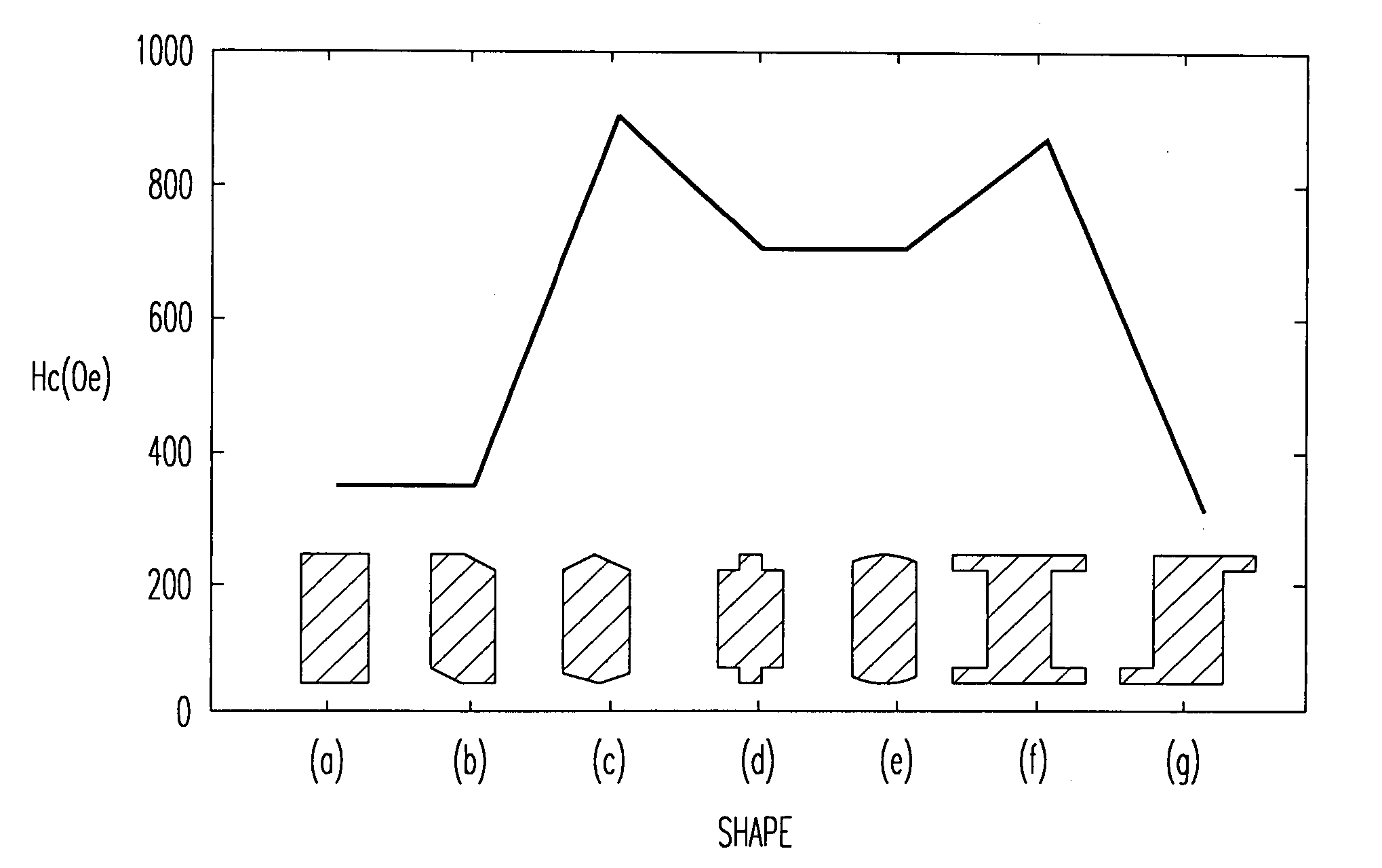
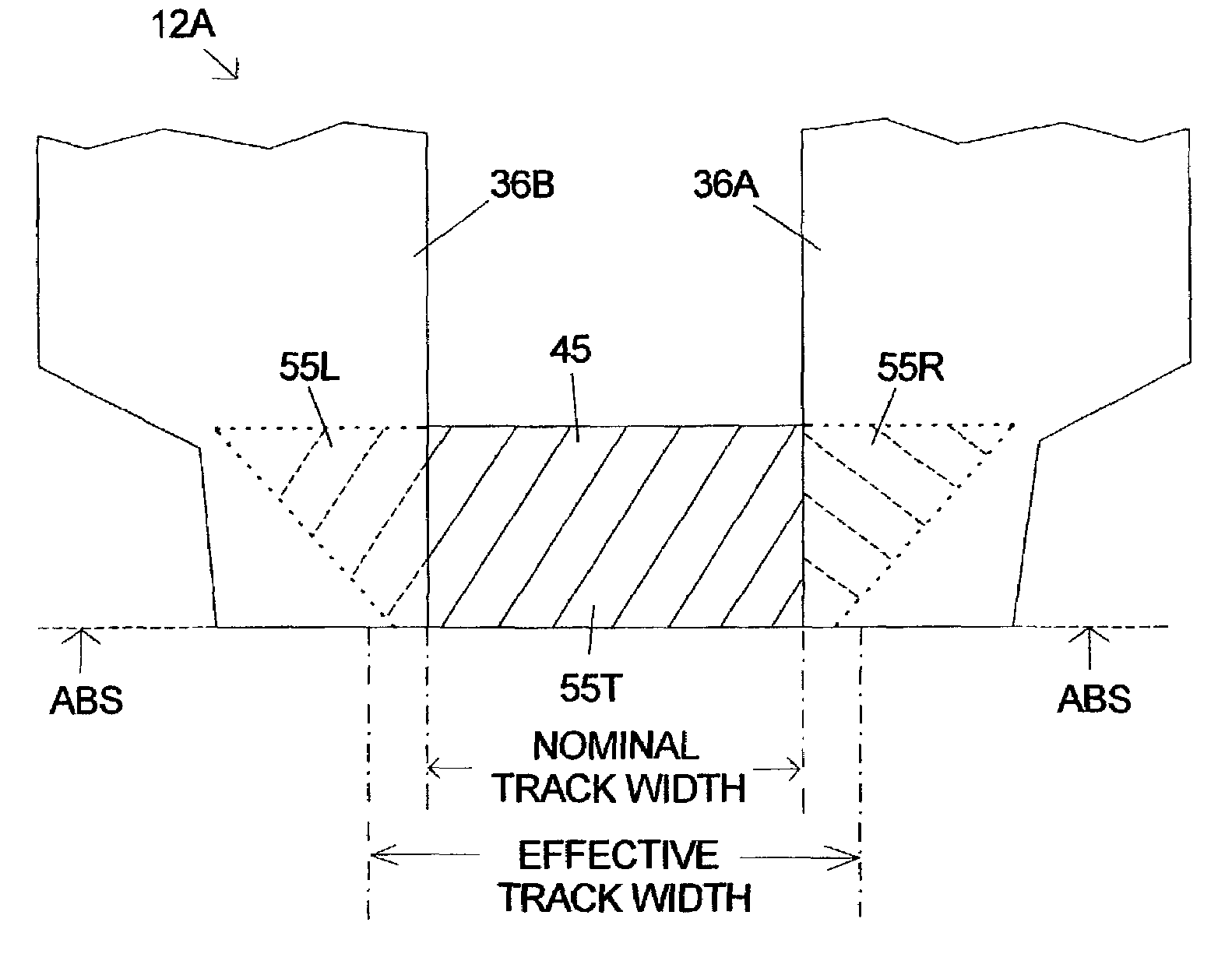
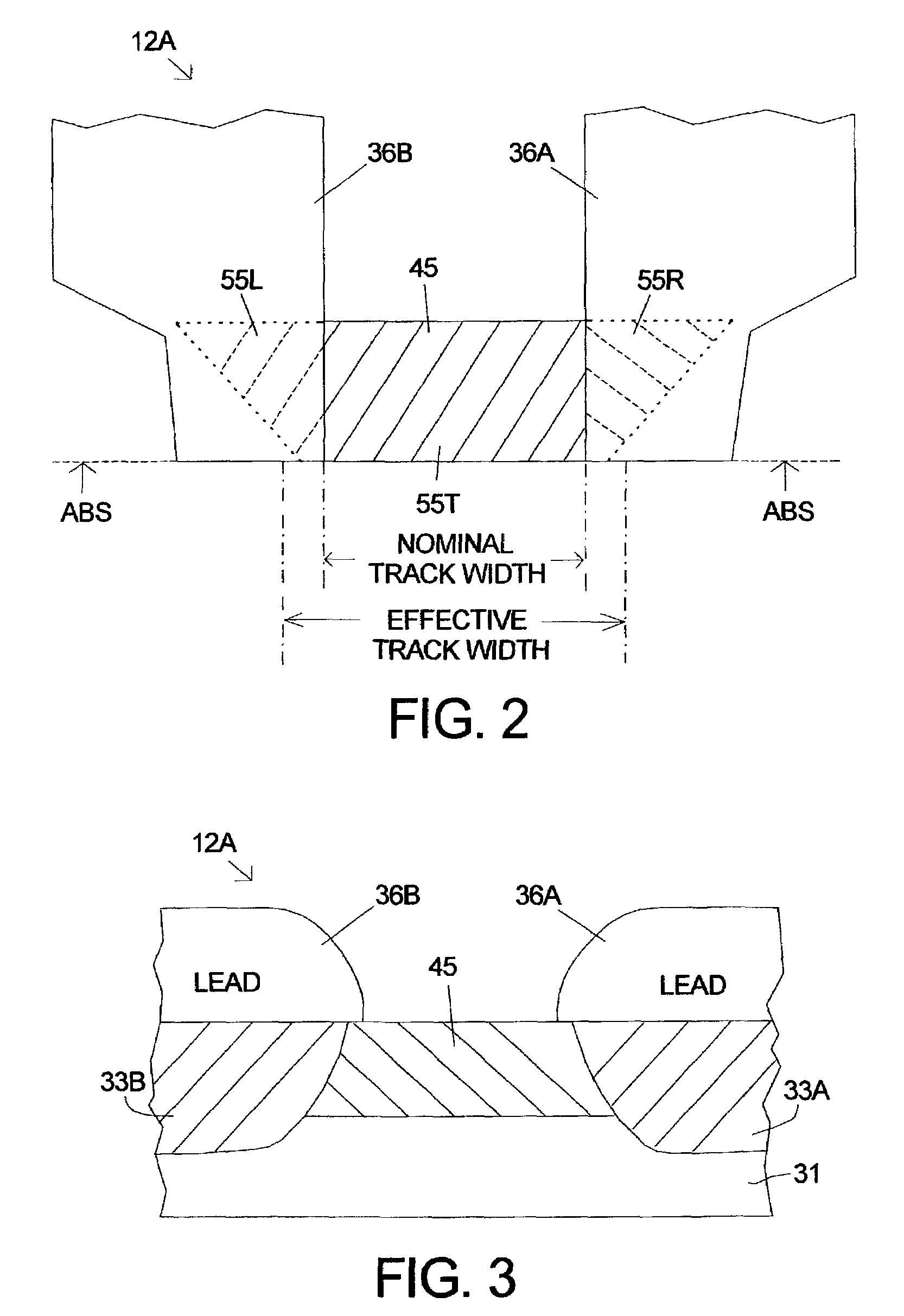
Lead-defined and shaped magnetic sensor
A magnetic recording transducer, useful in a magnetic data storage device, having a read element with improved magnetic stability and a narrow track width is described. An MR stripe according to the invention has a magnetic-stability inducing (MSI) shape selected from an essentially trapezoidal shape, an essentially hexagonal shape, an essentially race-track shape, and an essentially half race track shape. These MSI shapes are oriented in a plane perpendicular to the air-bearing surface (ABS). The MSI shapes are used to encourage the formation of a single magnetic domain state with magnetization direction parallel to the ABS in the absence of a magnetic bias. In one embodiment according to the invention the sensor structure is overlaid on the sides of the top surface with layers of electrically conductive material (overlaid leads) to define an approximately rectangular active region of the larger MSI shape. A sensor structure according to the invention with overlaid leads will have a narrower track width with improved magnetic stability than a sensor which has a comparable volume of magnetoresistive material in a rectangular MR stripe. In another embodiment of the invention the sensor structure has edge-butt leads that make contact at the outer edges of the sensor without substantially overlaying the top surface.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP) magnetoresistive (MR) sensor having an antiparallel free (APF) structure with improved magnetic stability
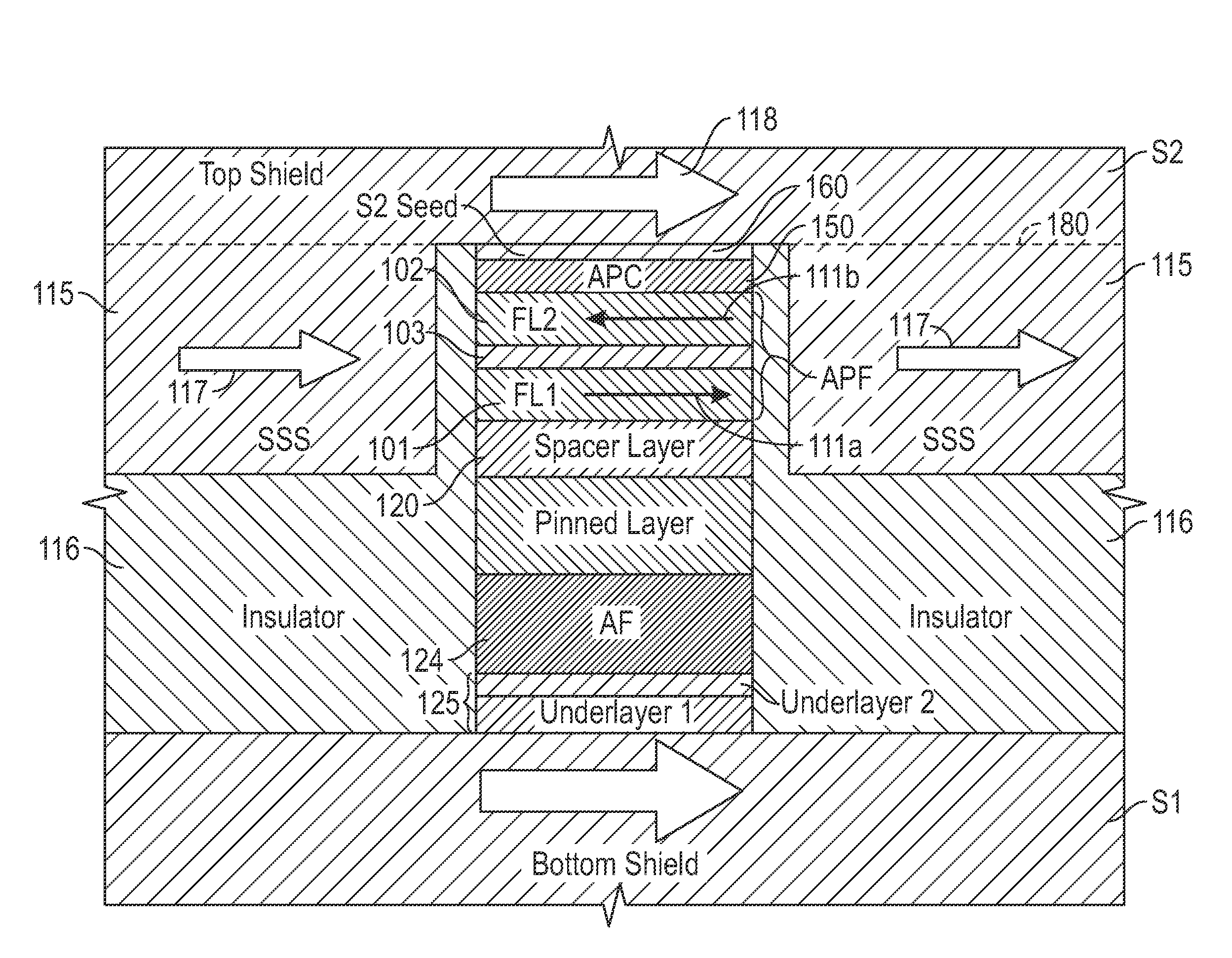
ActiveUS20150116867A1Good magnetic stabilityRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetic stabilityPower flow
A current-perpendicular-to-the-plane magnetoresistive sensor has an antiparallel free (APF) structure and soft side shields wherein the upper free layer (FL2) of the APF structure is magnetically coupled antiparallel to the top shield and a top shield seed layer via a nonmagnetic antiparallel coupling (APC) layer. In one embodiment the antiparallel coupling is through an antiferromagnetic-coupling (AFC) layer that provides a dominant antiferromagnetic indirect exchange coupling of FL2 to the top shield. In another embodiment the antiparallel coupling is by an APC layer that decouples FL2 and the top shield and causes the edge-induced magnetostatic coupling between FL2 and the seed layer to dominate. The degree of coupling is controlled by the composition and thickness of the nonmagnetic APC layer between FL2 and the seed layer, and by the thickness of the seed layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for makinga magnetic random access memory element with small dimension and high qulity
ActiveUS20160163970A1Improve device performanceGood magnetic stabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic stabilityIon bombardment
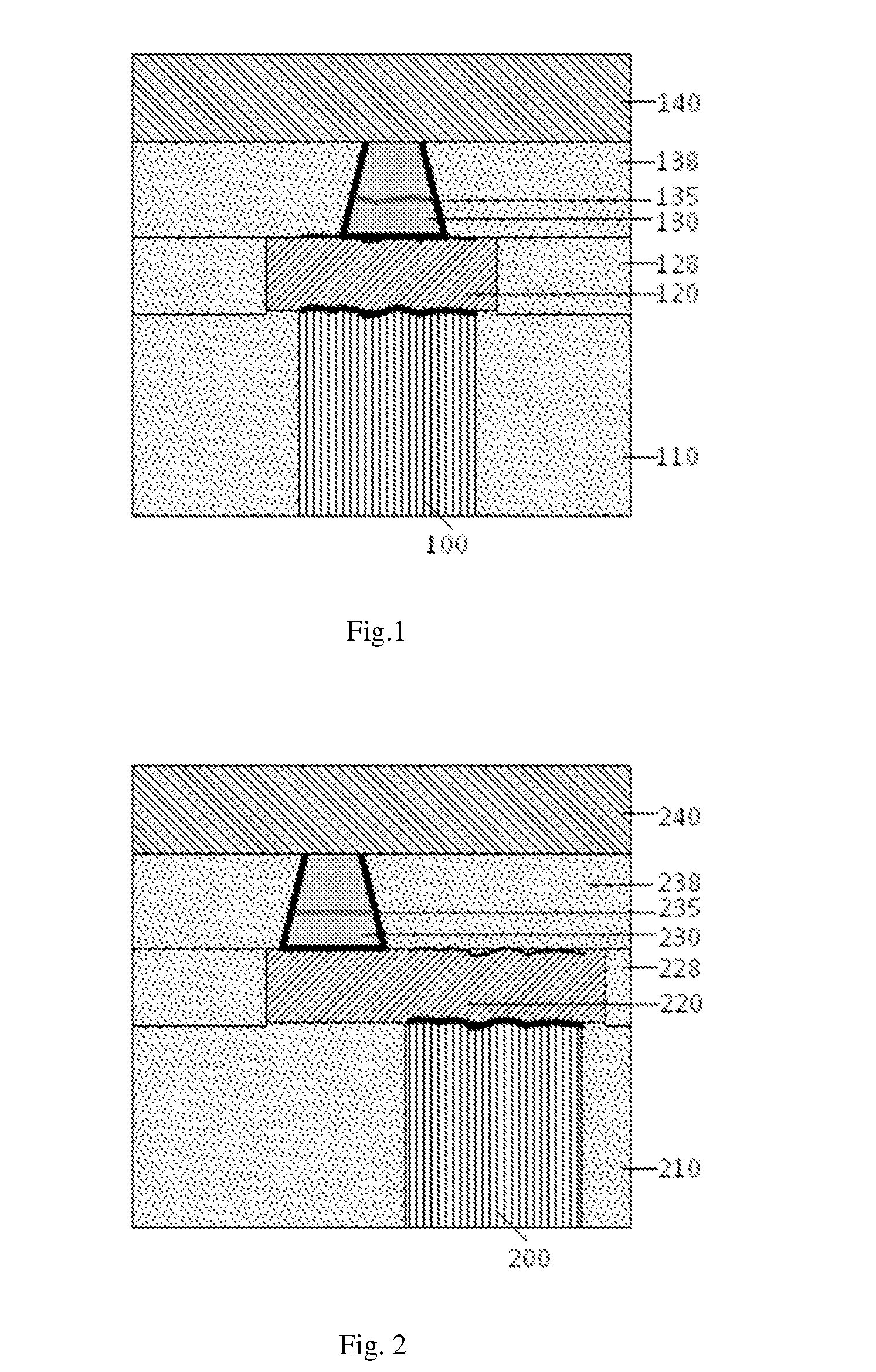
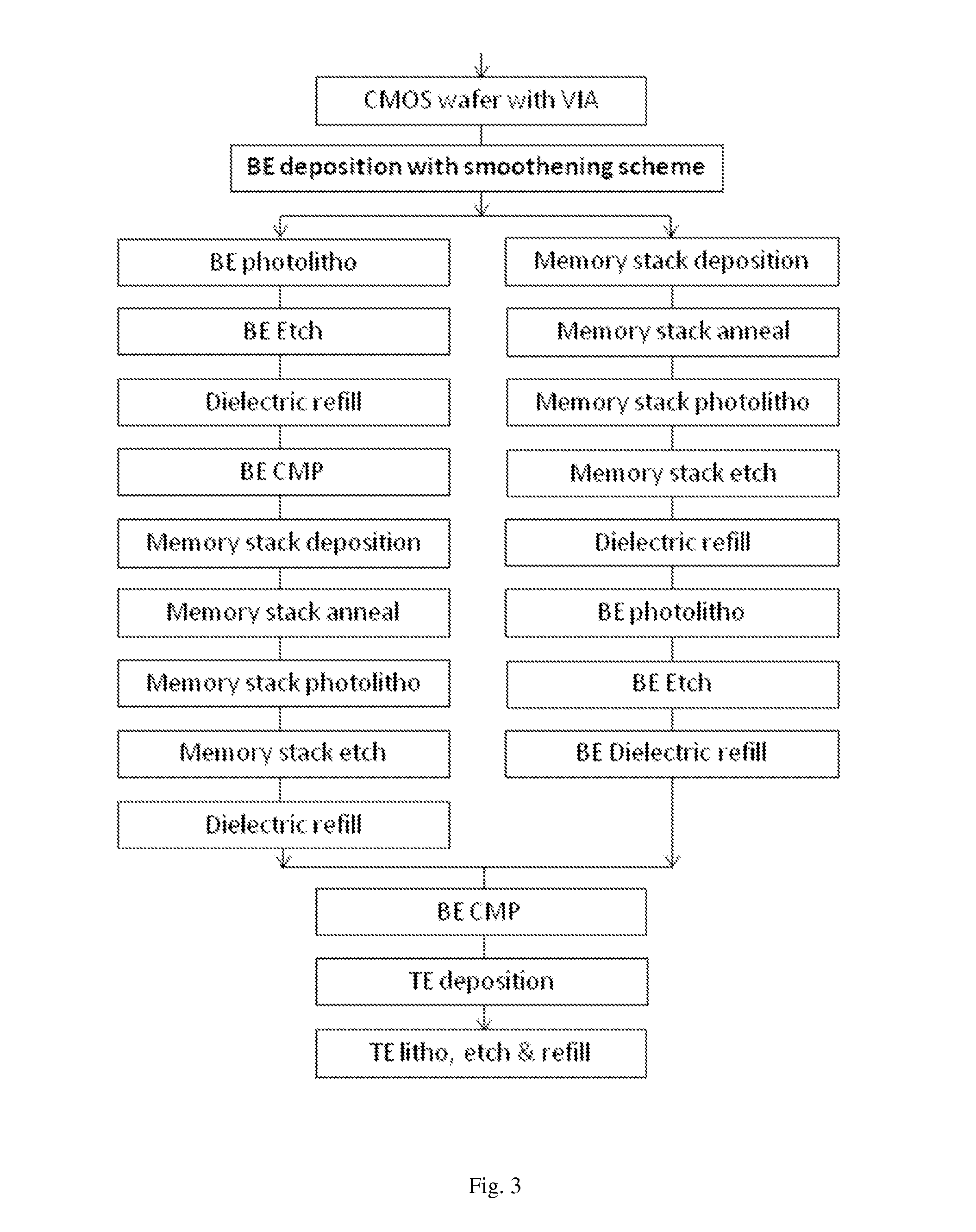
This invention is about a method to make an MRAM element with small dimension, by building an MTJ as close as possible to an associated via connecting an associated circuitry in a semiconductor wafer. The invention provides a process scheme to flatten the interface of bottom electrode during film deposition, which ensures a good deposition of atomically smooth MTJ multilayer as close as possible to an associated via which otherwise might be atomically rough. The flattening scheme is first to deposit a thin amorphous conducting layer in the middle of BE deposition and immediately to bombard the amorphous layer by low energy ions to provide kinetic energy for surface atom diffusion to move from high point to low kinks. With such surface flattening scheme, not only the MRAM element can be made extremely small, but its device performance and magnetic stability can also be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIYU INFORMATION TECH
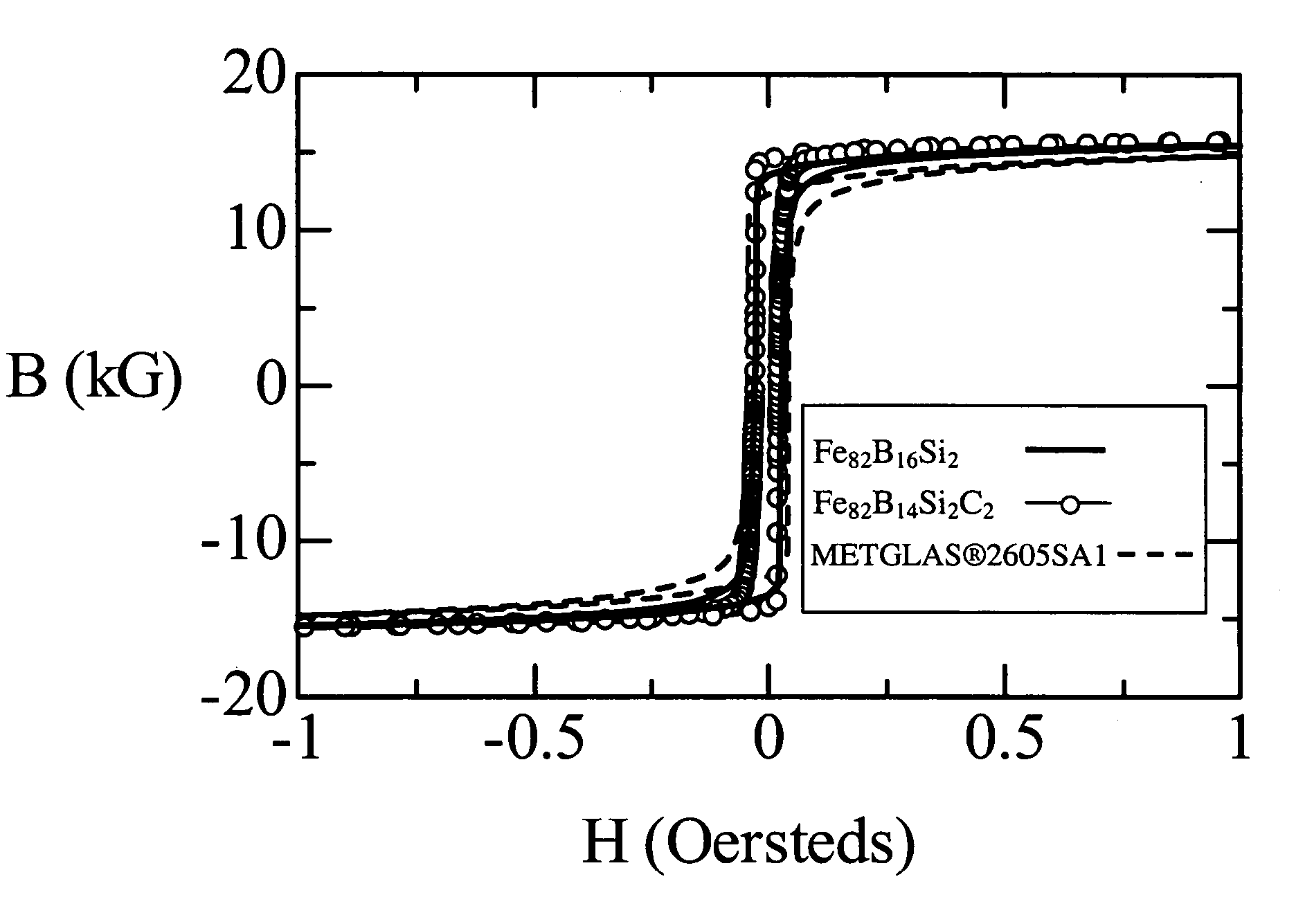
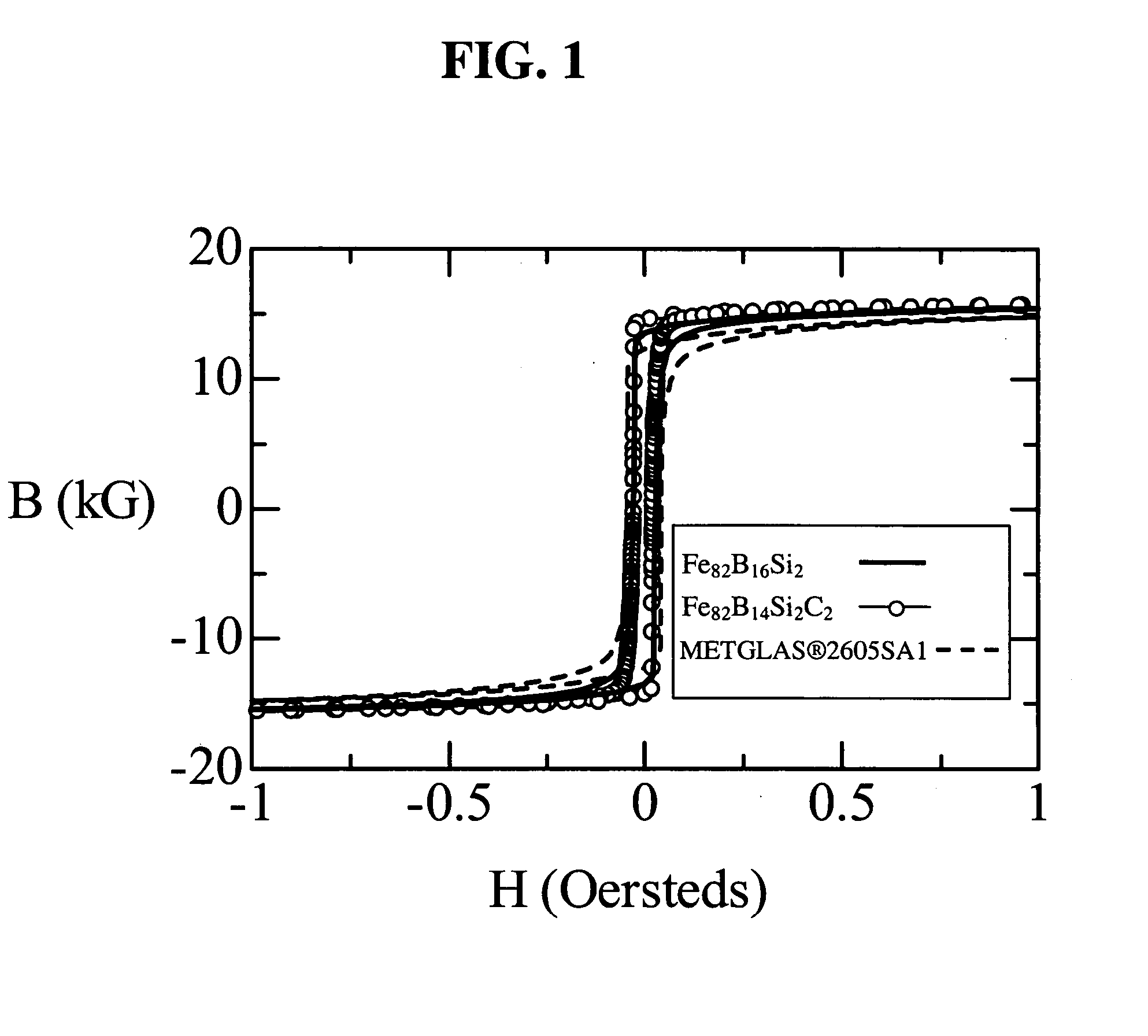
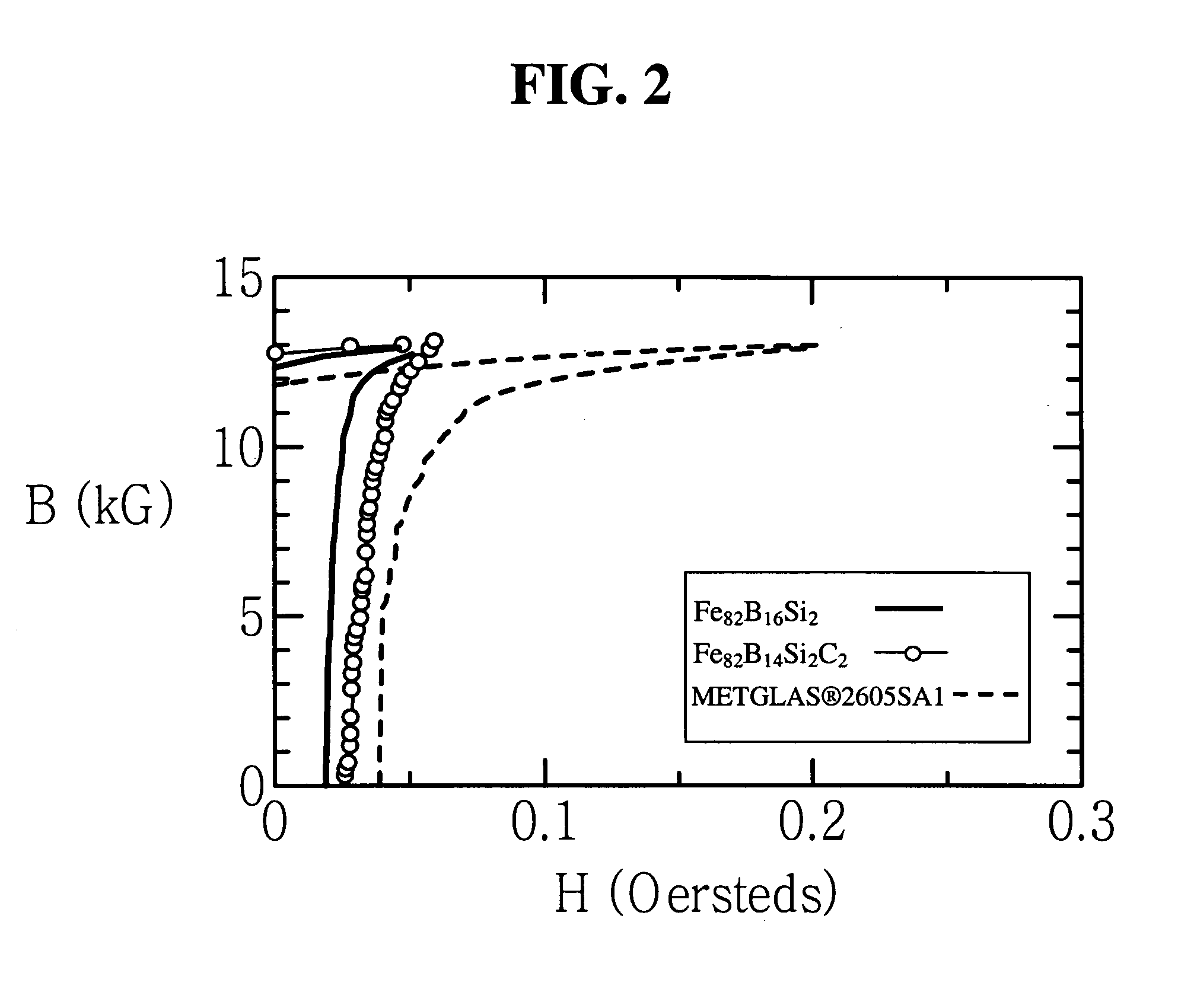
Iron-based high saturation induction amorphous alloy
ActiveUS20060191602A1Low AC magnetic lossTransformers/inductances noise dampingTransformers/inductances magnetic coresMagnetic stabilityChemical composition
An iron-based amorphous alloy and magnetic core with an iron-based amorphous alloy having a chemical composition with a formula FeaBbSicCd, where 81<a≦84, 10≦b≦18, 0<c≦5 and 0<d<1.5, numbers being in atomic percent, with incidental impurities, simultaneously have a value of a saturation magnetic induction exceeding 1.6 tesla, a Curie temperature of at least 300° C. and a crystallization temperature of at least 400° C. When cast in a ribbon form, such an amorphous metal alloy is ductile and thermally stable, and is suitable for various electric devices because of high magnetic stability at such devices' operating temperatures.
Owner:METGLAS INC +1
Preparation method for magnetic lignin-based activated carbon
InactiveCN103585956AWell-developed poresImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMagnetic stabilityActivated carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method for magnetic lignin-based activated carbon. The method comprises the following specific steps: stirring lignin, a chemical activating agent and a magnetic additive with water into paste, and uniformly mixing; after drying, performing carbonization and activation at the temperature of 650-850 DEG C, and then quenching and cooling, wherein the activation time is 0.5-3 hours; washing by sequentially using diluted acid and water until the pH value is 6-8, drying, and finely grinding, so that the magnetic lignin-based activated carbon is obtained. According to the invention, the combination of a oriented preparation technology and a magnetic functionalization technology for the activated carbon can be realized through a simple and convenient one-step preparation process, the used activating agent is environment-friendly, and the obtained magnetic activated carbon is large in specific area and excellent in adsorptive property, and has sufficient magnetic intensity and magnetic stability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of manufacturing a magnetic head using a magneto-resistive effect
InactiveUS7243412B2High sensitivityReduce widthNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic stabilityMagnetization
A method of manufacturing a magnetic head including a magnetic sensing portion formed of a magnetoresistive effect element, a magnetoresistive effect magnetic head manufacturing method depositing, via a film deposition process, a lamination layer having a free layer comprised of a soft magnetic material of which the magnetization is rotated in response to an external magnetic field, a fixed layer comprised of a ferromagnetic material, an antiferromagnetic layer for fixing the magnetization of said fixed layer, a magnetic flux introducing layer with a tip end of which is opposed to a surface which is brought in contact with or opposed to a magnetic recording medium, and a spacer layer interposed between said free layer and said fixed layer; patterning at least said free layer and said fixed layer with a mask such that opposing side surfaces of said free layer and said fixed layer are formed of one continuous surface; and forming hard magnetic layers having high or low resistance for maintaining a magnetic stability of said free layer in contact with said opposing side surfaces.
Owner:SONY CORP
500 KW magnetic stability non-transferred arc plasma generator
InactiveCN105282952AAblation reliefExtend your lifePlasma techniqueMagnetic stabilityPlasma generator
The invention provides a 500 KW magnetic stability non-transferred arc plasma generator which is provided with a cathode with a cavity, an insulating cylinder, a gap, a first anode, an adjustable insulation seat, a main gas ring, a second anode, a seal, a third anode, a blasting opening and a fourth anode in a spray direction sequentially. Center holes and cooling water ways are formed in all anodes. Auxiliary gas enters the cathode cavity through an auxiliary gas hole in the center of the top of the cathode cavity; main gas is screwed into the top of the second anode through the main gas ring; protection gas is screwed into the top of the fourth anode through the blasting opening; magnetic stability coils are arranged on the outside of the cathode and the and fourth anode. The negative pole of a direct current power supply is connected with the cathode; four anodes on which transfer arc switches are mounted are connected to the positive pole of the direct current power supply. The arc voltage is improved by a four-anode structure, and the power is as high as 500KW. The auxiliary gas, the main gas and the protection gas guarantee dynamic contact of gas and electrodes. The magnetic stability coils enable the arc to be stable and uniform. The service life of the cathode can be prolonged by the aid of the cathode cavity structure. The 500 KW magnetic stability non-transferred arc plasma generator can be used for rubbish and industrial waste virus-free and energy regeneration treatment, radioactive waste disposal, new nano material preparation and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU JINCHUANGLI SCI & TECH
Iron-based high saturation induction amorphous alloy
InactiveUS20060180248A1Low AC magnetic lossTransformers/inductances noise dampingTransformers/inductances magnetic coresMagnetic stabilityChemical composition
An iron-based amorphous alloy and magnetic core with an iron-based amorphous alloy having a chemical composition with a formula FeaBbSicCd, where 80<a<=84, 8<=b<=18, 0<c<=5 and 0<d<=3, numbers being in atomic percent, with incidental impurities, simultaneously having a value of a saturation magnetic induction exceeding 1.6 tesla, a Curie temperature of at least 300° C. and a crystallization temperature of at least 350 ° C. When cast in a ribbon form, such an amorphous metal alloy is ductile and thermally stable, and is suitable for various electric devices because of high magnetic stability at such devices' operating temperatures.
Owner:METGLAS INC +1
Method for preparing magnetic 4A molecular sieve by using kaolin
InactiveCN102936019AWide variety of sourcesLow priceSolid waste disposalAluminosilicate zeolite type-AChemical industryMagnetic stability
The invention discloses a method for preparing a magnetic 4A molecular sieve by using the kaolin. The kaolin serves as main materials, aluminum hydroxide serves as a supplementary aluminum source, deionized water serves as a solvent, Fe3O4 serves as a magnetic carrier, and the magnetic 4A molecular sieve which is low in price, high in performance and recyclable is prepared by a hydrothermal synthesis method. According to the method, the preparation process is simple, materials are easy to obtain, and the operation is simple and convenient; and the synthesized 4A zeolite molecular sieve has the advantages of being high in crystallinity, fine in granularity and good in dispersibility and magnetic stability, a static water adsorption rate of an obtained adsorbent achieves 21.66%, the calcium ion exchange capacity achieves 303.45 mg CaCO3 / g, simultaneously a high removal rate for ammonia nitrogen and heavy metal pollutants is provided, and standards achieve those of the ministry of chemical industry.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Six-parameter quantum inertial sensor and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN105674982ACompact structureSimple structureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMagnetic stabilityQuantum sensor
The present invention belongs to the technical field of rotation speed, acceleration speed measurement and inertial navigation, and relates to a quantum inertial sensor capable of measuring six-parameter inertial parameters and a measuring method thereof. The quantum sensor capable of measuring the six-parameter inertial parameters comprises two-dimensional microcrystalline glass vacuum chambers, a three-dimensional microcrystalline glass vacuum chamber, differential pumping tubes and alkali metal sources, the two two-dimensional microcrystalline glass vacuum chambers are connected with three-dimensional microcrystalline glass vacuum chamber by the differential pumping tubes, and respectively with the alkali metal sources, in addition, and the differential pumping tubes are prepared from microcrystalline glass same as the material of microcrystalline glass of the two-dimensional microcrystalline glass vacuum chambers and the three-dimensional microcrystalline glass vacuum chamber. By use of a scheme of counter-throwing of cold atomic groups and combination of manipulation of the cold atomic groups by Raman beams in different directions, and measurement of six-axis-space inertial parameters can be achieved. Based on low-temperature bonding technique, microcrystalline glass is used for constructing the vacuum chambers, so that the quantum inertial sensor has better light transmitting property, is more compact in structure, higher in thermal and magnetic stability and impact resistance, and more conducive to miniaturization.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Design Method of High Magnetic Field Superconducting Magnet
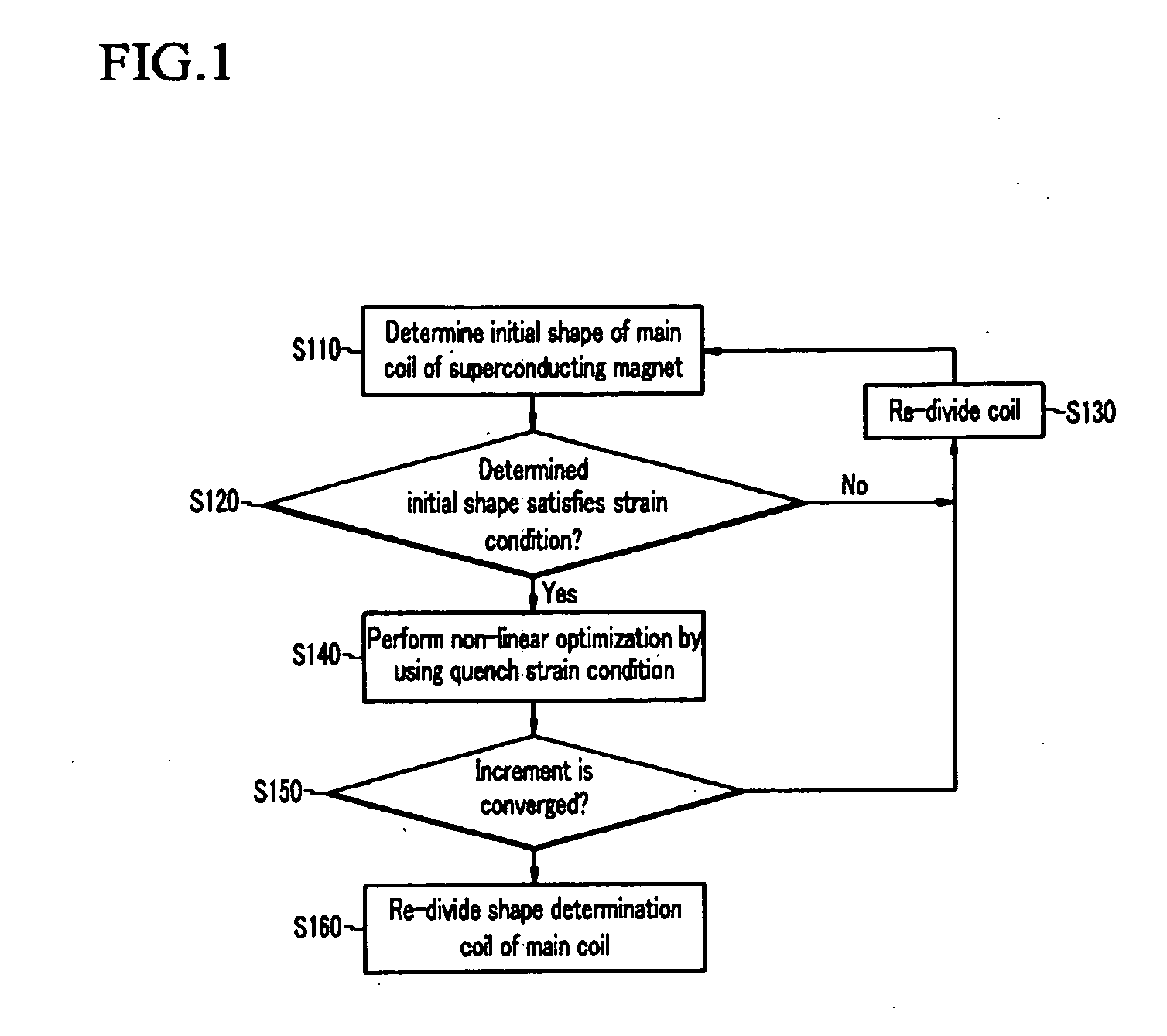
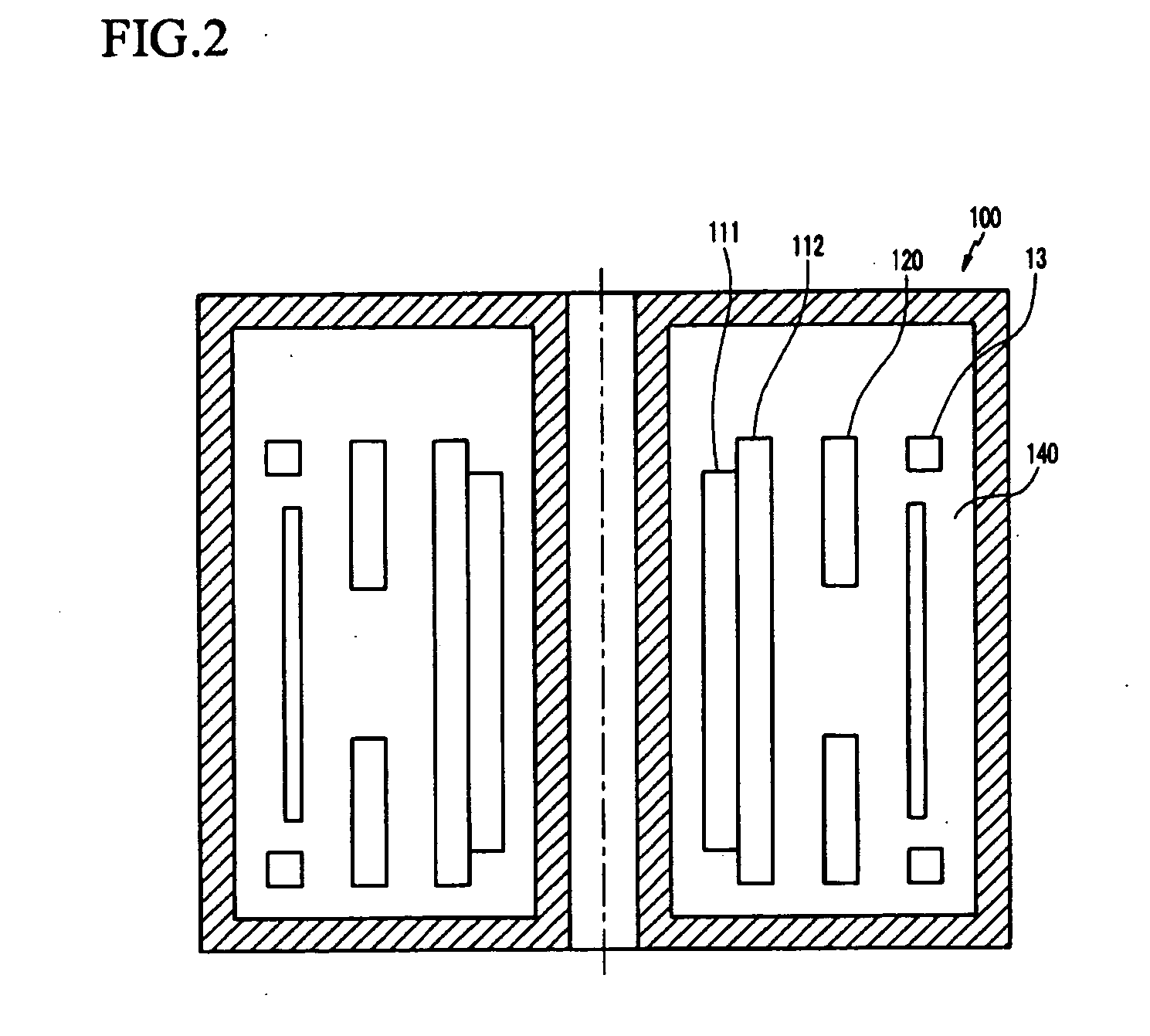
InactiveUS20090322457A1Stable structureImprove uniformityMagnetic measurementsMagnetsMagnetic stabilitySuperconducting Coils
Disclosed is a method for designing a superconducting magnet for generating high magnetic fields with high uniformity for controlling a stray field to be within an allowable range and acquiring structural and magnetic stability by optimizing the arrangement of positions and shapes of coils configuring the superconducting magnet. Volumes of a main coil and a shielding coil are set to be variables, and the critical value of a wires related on the current and magnetic field, the heat transfer depth, and the quench strain are defined to be restriction conditions so that linear programming is applied to determine an initial shape of the shielding coil and division of the main coil based on the sum of total volumes, that is, an objective function. The initial shapes of the main coil and the shielding coil determined through the linear programming are revised and the shape of a shimming coil is determined by using non-linear programming based on the objective function.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Microcrystalline-glass-cavity-based gravity measurement apparatus and measurement method
ActiveCN105652335AHigh transparencyCompact structureGravitational wave measurementMagnetic stabilityVacuum chamber
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of acceleration measurement, relates to a microcrystalline-glass-cavity-based movable gravity measurement apparatus. The movable gravity measurement apparatus comprises a two-dimensional microcrystalline-glass vacuum cavity, a three-dimensional microcrystalline-glass vacuum cavity, an alkali metal source, and a differential pump tube. The two-dimensional microcrystalline-glass vacuum cavity is connected to one side of a three-dimensional cooling vacuum cavity of the three-dimensional microcrystalline-glass vacuum cavity by the differential pump tube; a suction device is connected to the other side of the three-dimensional cooling vacuum cavity; and the alkali metal source is connected to the two-dimensional microcrystalline-glass vacuum cavity. Besides, the differential pump tube is made of the same microcrystalline-glass material as those of the two cavities. According to the gravity measurement apparatus, the vacuum cavities are constructed by using the microcrystalline-glass materials based on the low-temperature bonding technology, so that the light transmission property is good, the structure is compact, the thermal and magnetic stability and the anti-impact capability are high. The engineering practicability of the high-precision and high-reliability movable gravity measurement apparatus can be realized conveniently.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com