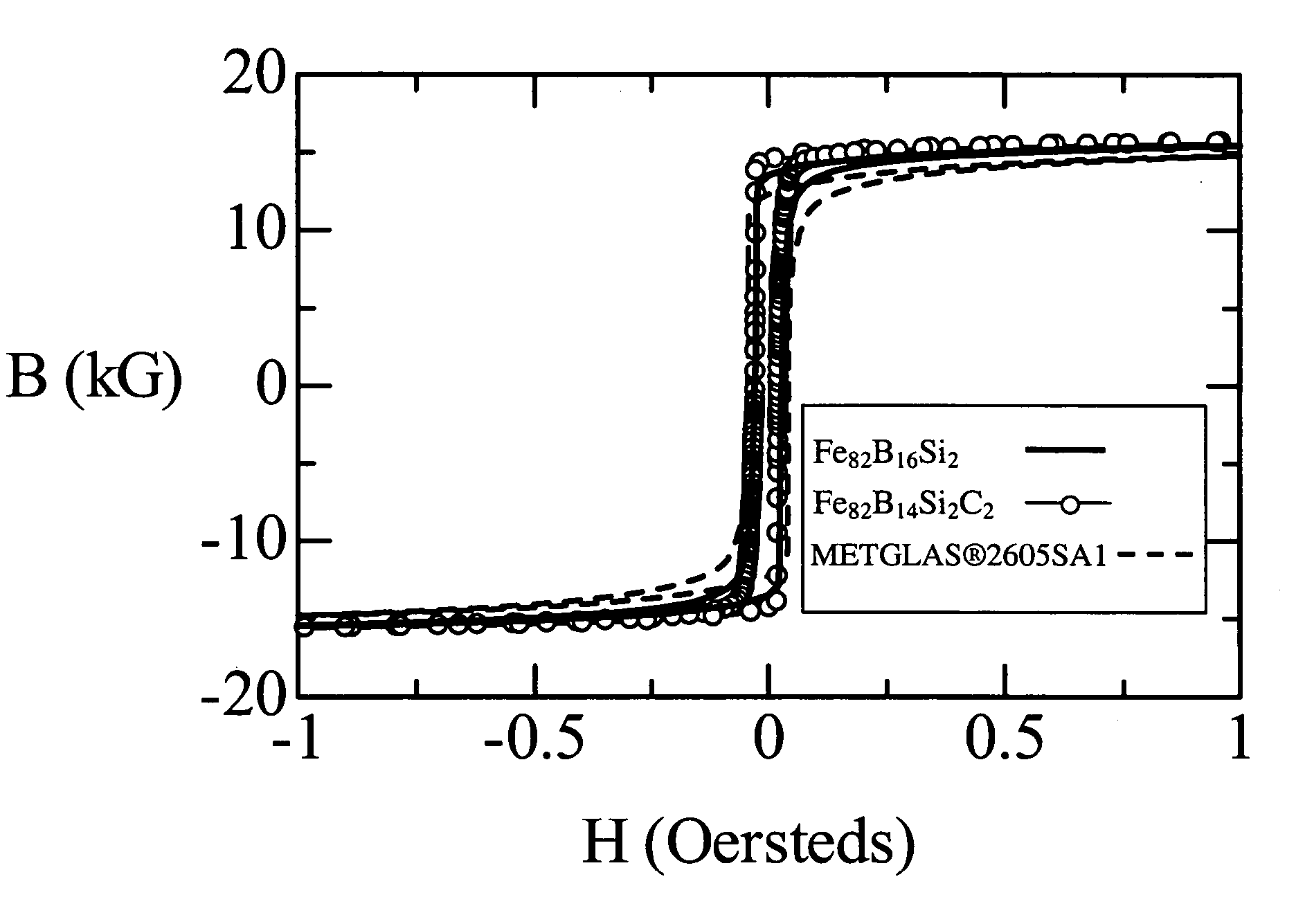
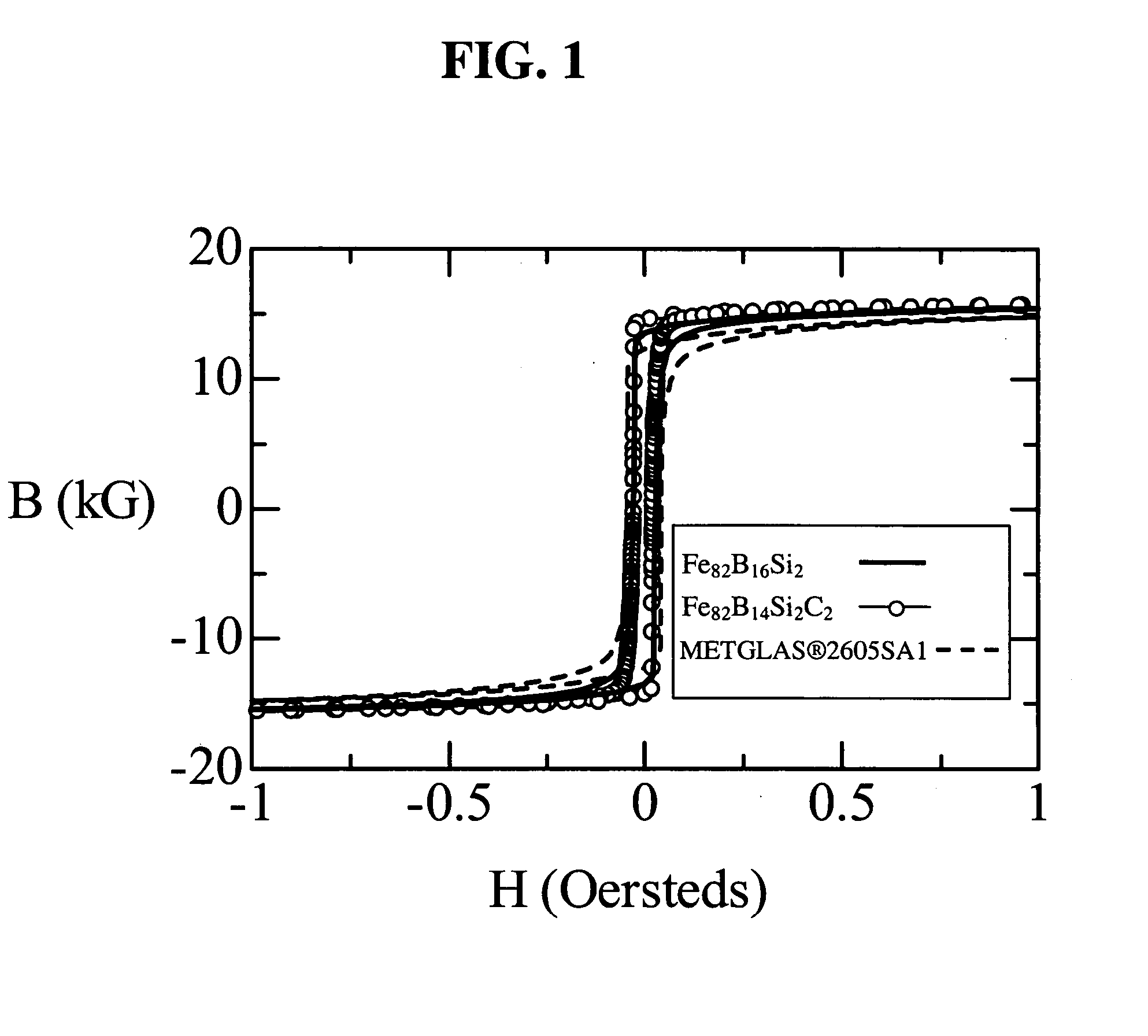
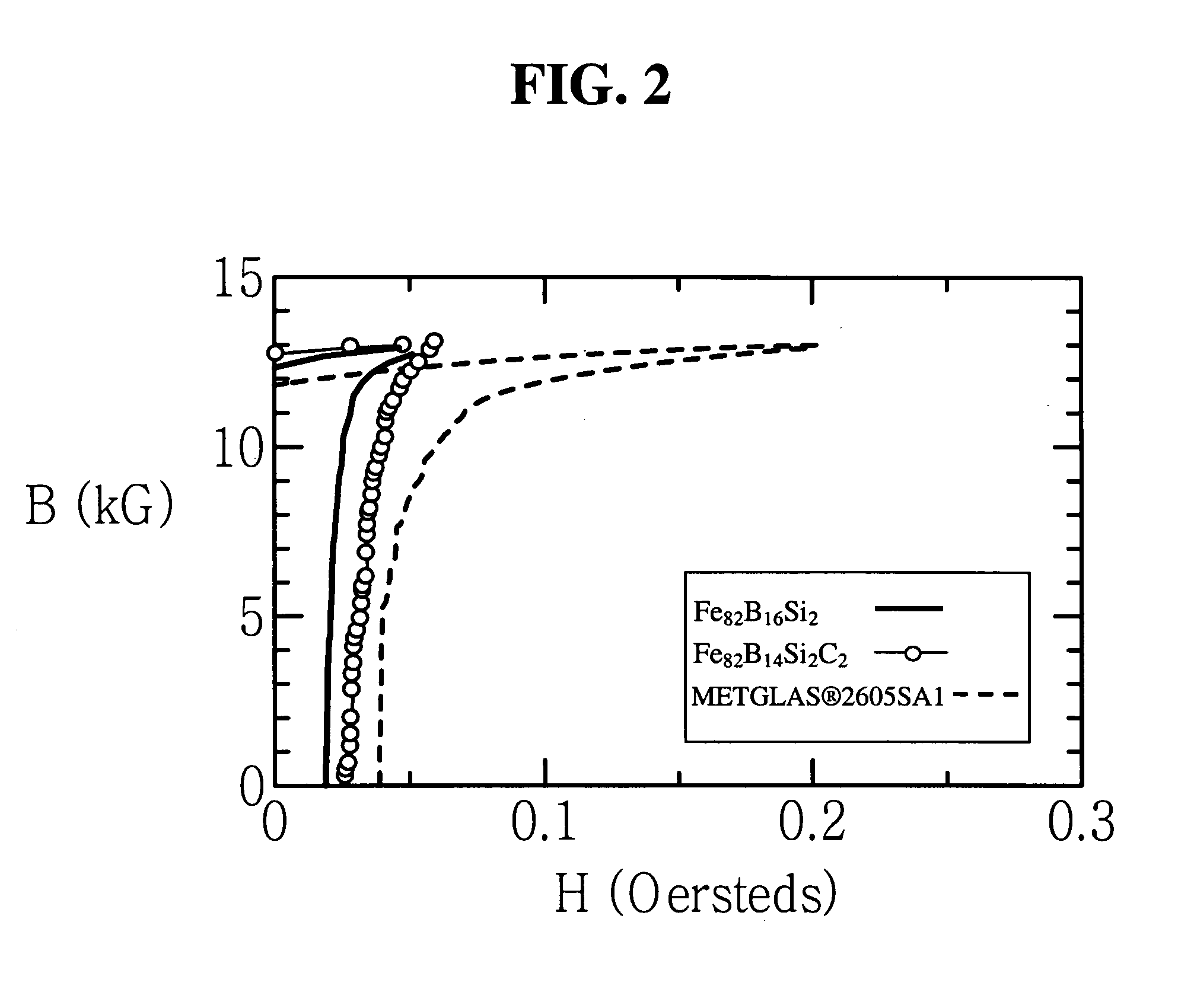
Iron-based high saturation induction amorphous alloy
a high saturation, amorphous alloy technology, applied in the direction of transformer/inductance magnetic core, magnetic material, magnetic body, etc., can solve the problem of high cost, significant loss of magnetic flux or induction in the air gap between the rotor, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of low ac magnetic loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
[0032] About 60 kg of the constituent metals, such as FeB, FeSi, Fe and C, were melted in an crucible and the molten metal was rapidly solidified by the method described in the U.S. Pat. No. 4,142,571. The ribbon formed had a width of about 170 mm and a thickness of about 25 μm and was tested by a conventional differential scanning calorimetry to assure its amorphous structure and determine the Curie and crystallization of the ribbon material. A conventional Archimedes' method was used to determine its mass density, which was needed for material's magnetic characterization. The ribbon was found ductile.
example ii
[0033] The 170 mm wide ribbon was slit into 25 mm wide ribbon which was used to wind toroidally shaped magnetic cores weighing about 60 gram each. The cores were heat-treated at 300-350° C. with a DC magnetic field of about 20 Oe (1600 A / m) applied along the toroid circumference direction. A primary copper wire winding of 10 turns and a secondary winding of 10 turns were applied on the heat-treated cores for magnetic measurements.
example iii
[0034] The magnetic characterizations of the heat-treated magnetic cores with primary and secondary copper windings of Example II were performed by using commercially available BH loop tracers with DC and AC excitation capability. AC magnetic characteristics, such as core loss, were examined by following ASTM A912-93 Standards for 50 / 60 Hz measurements.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com