Patents
Literature
44 results about "Water proton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
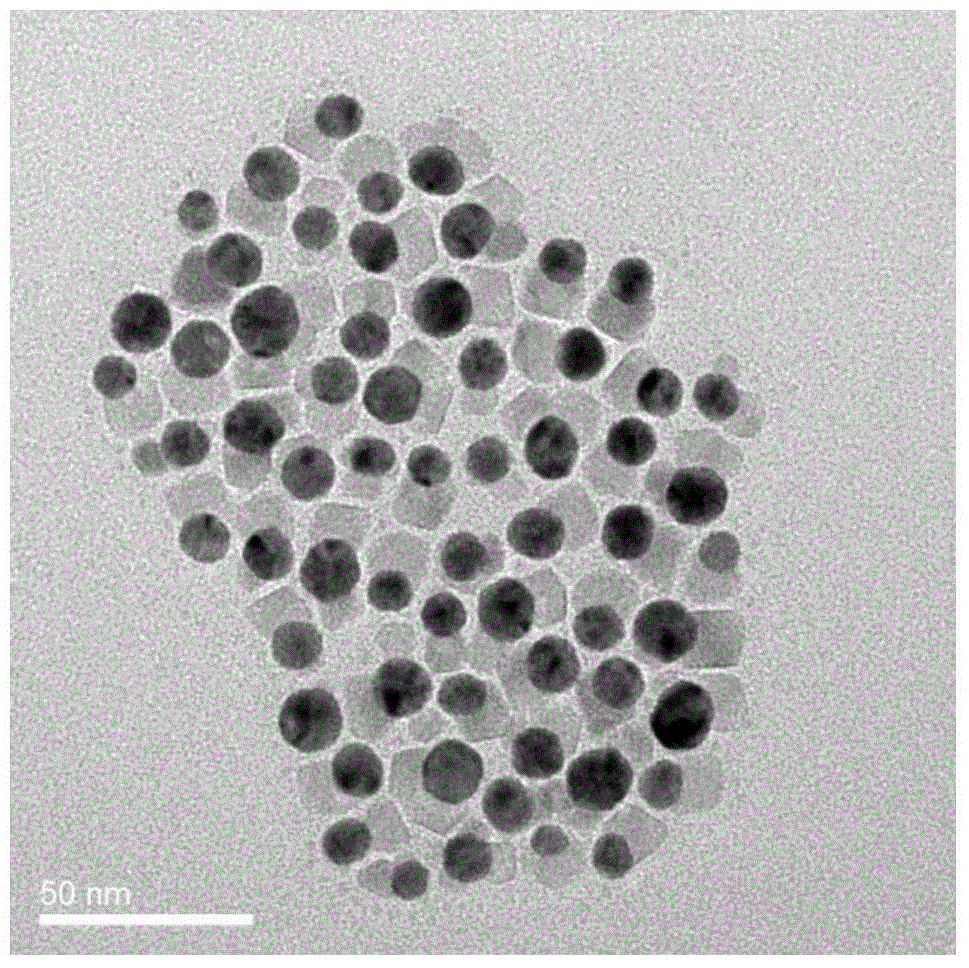
Protons in water are commonly described with the help of two limiting structures. In the Eigen complex (H9O4+) (left), the proton is part of the central H3O+ ion surrounded by three water molecules. In the Zundel cation (H5O2+) (right), the proton forms strong hydrogen bonds with two flanking water molecules.
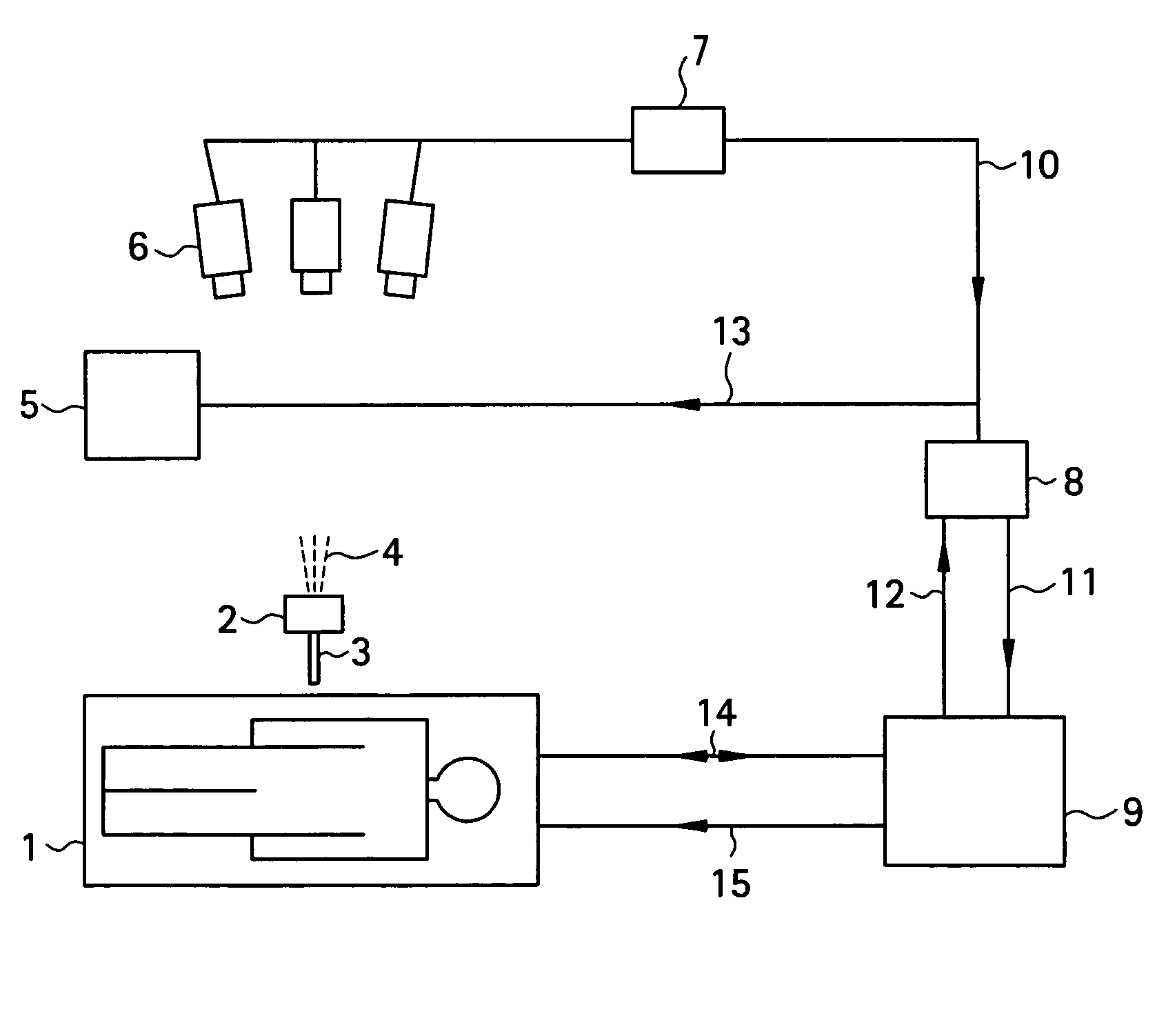
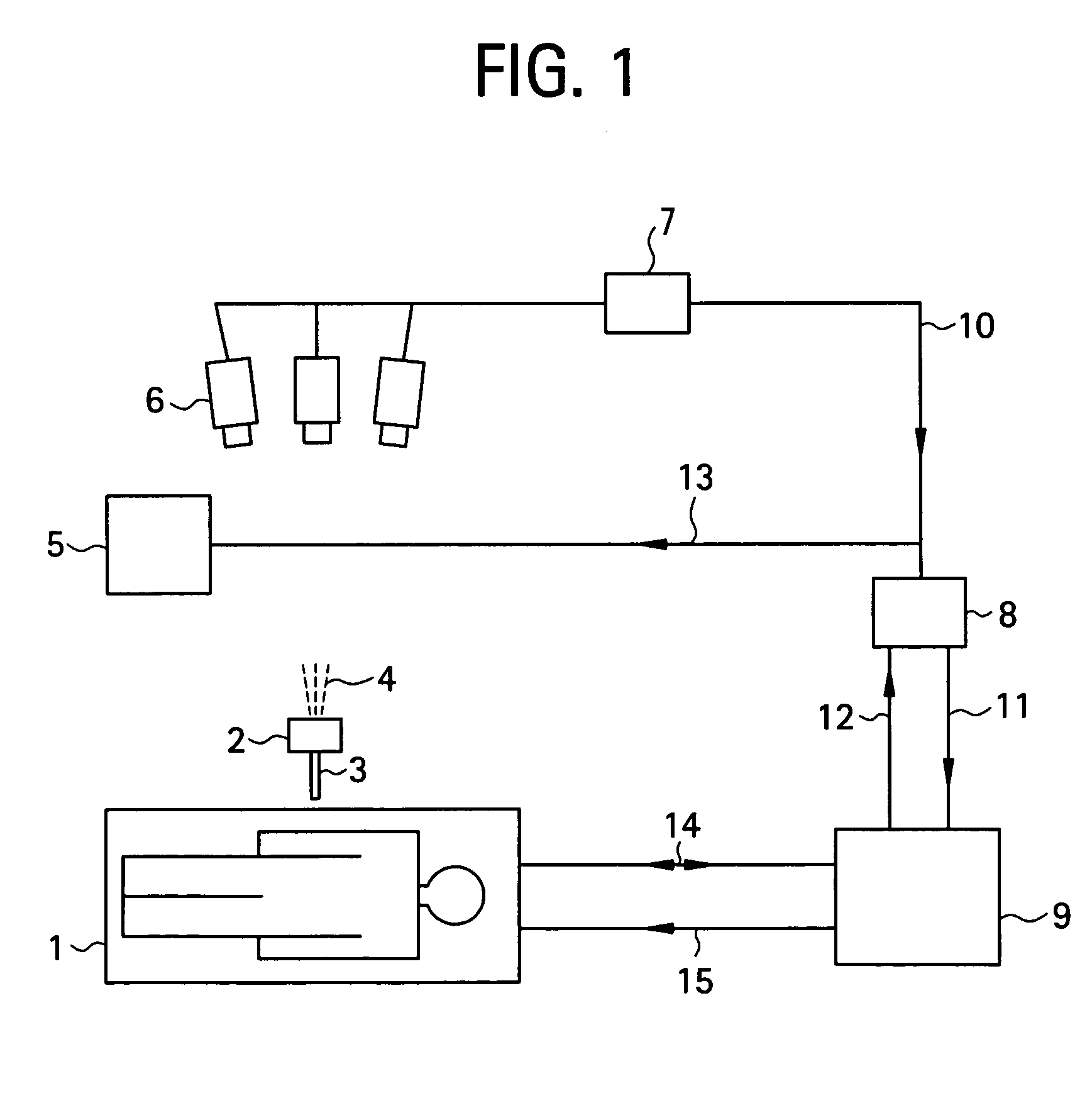
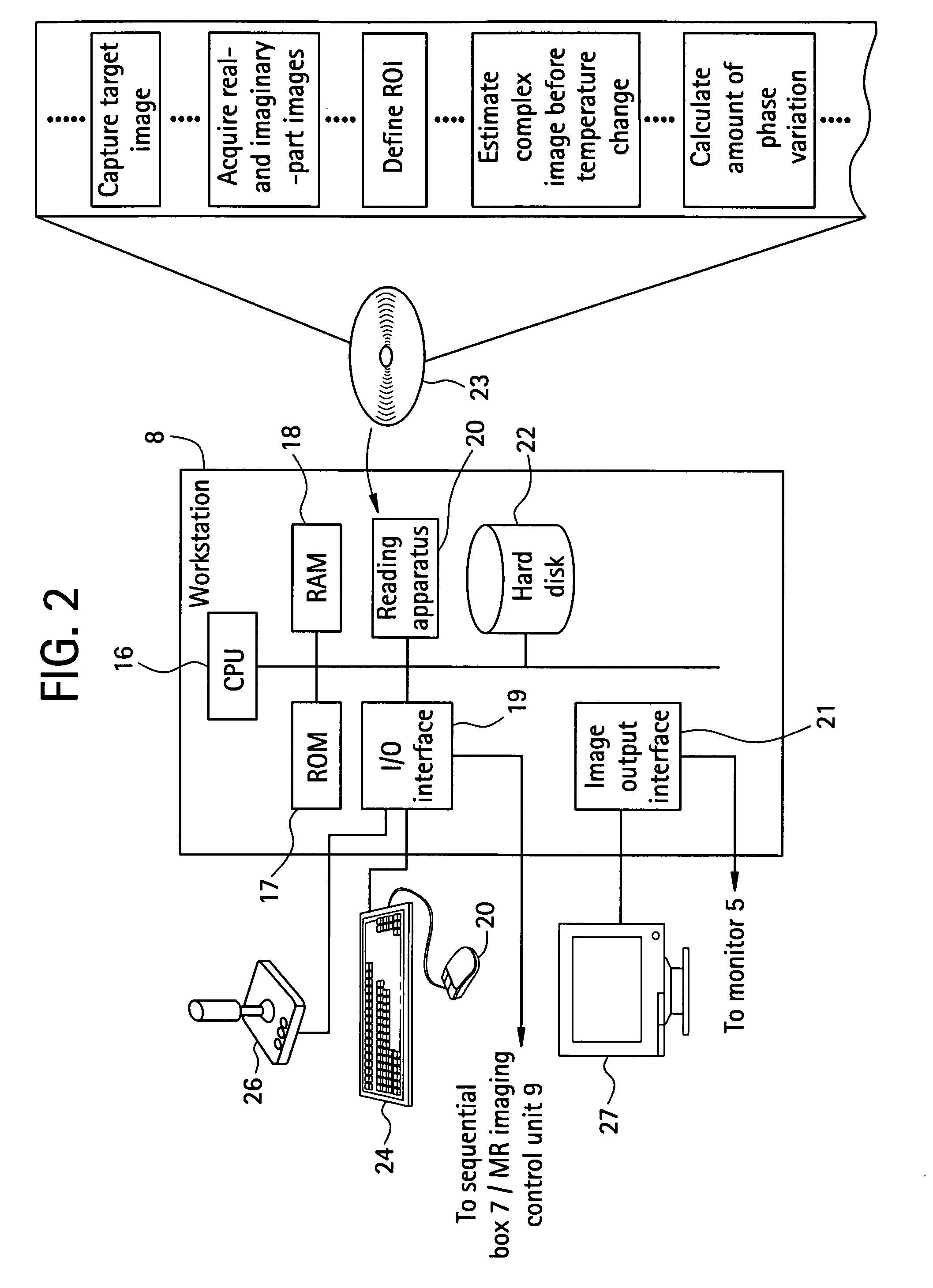
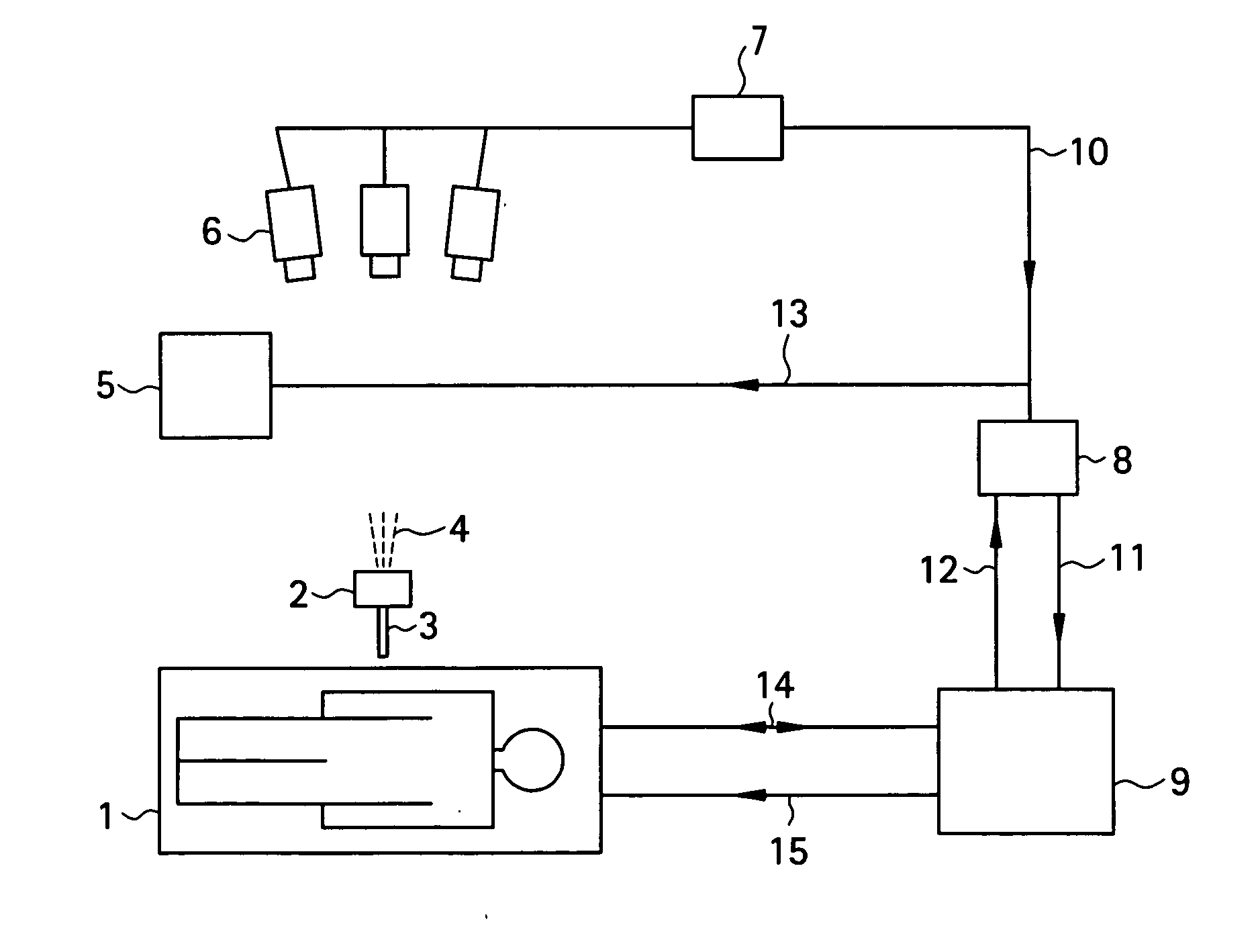
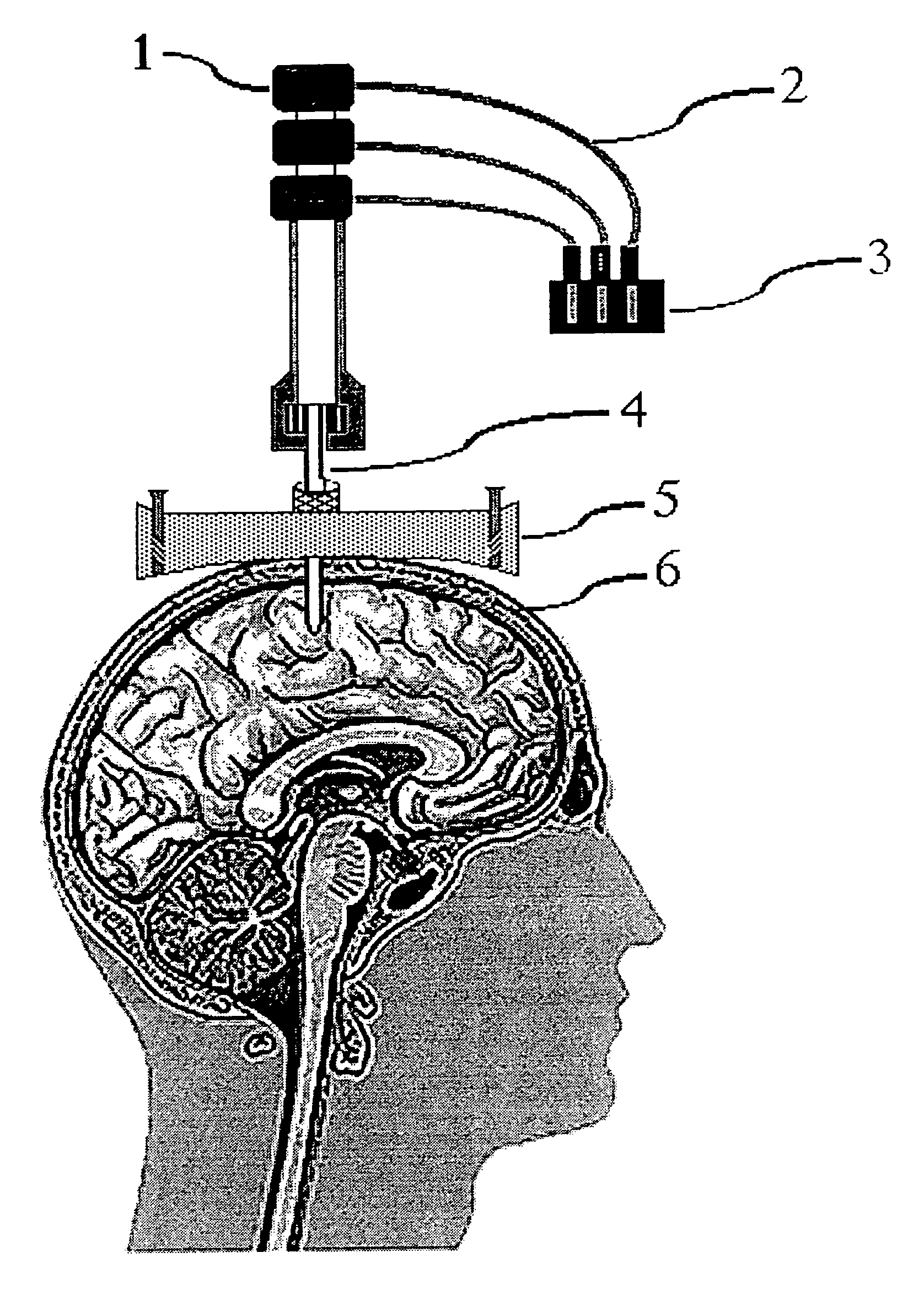
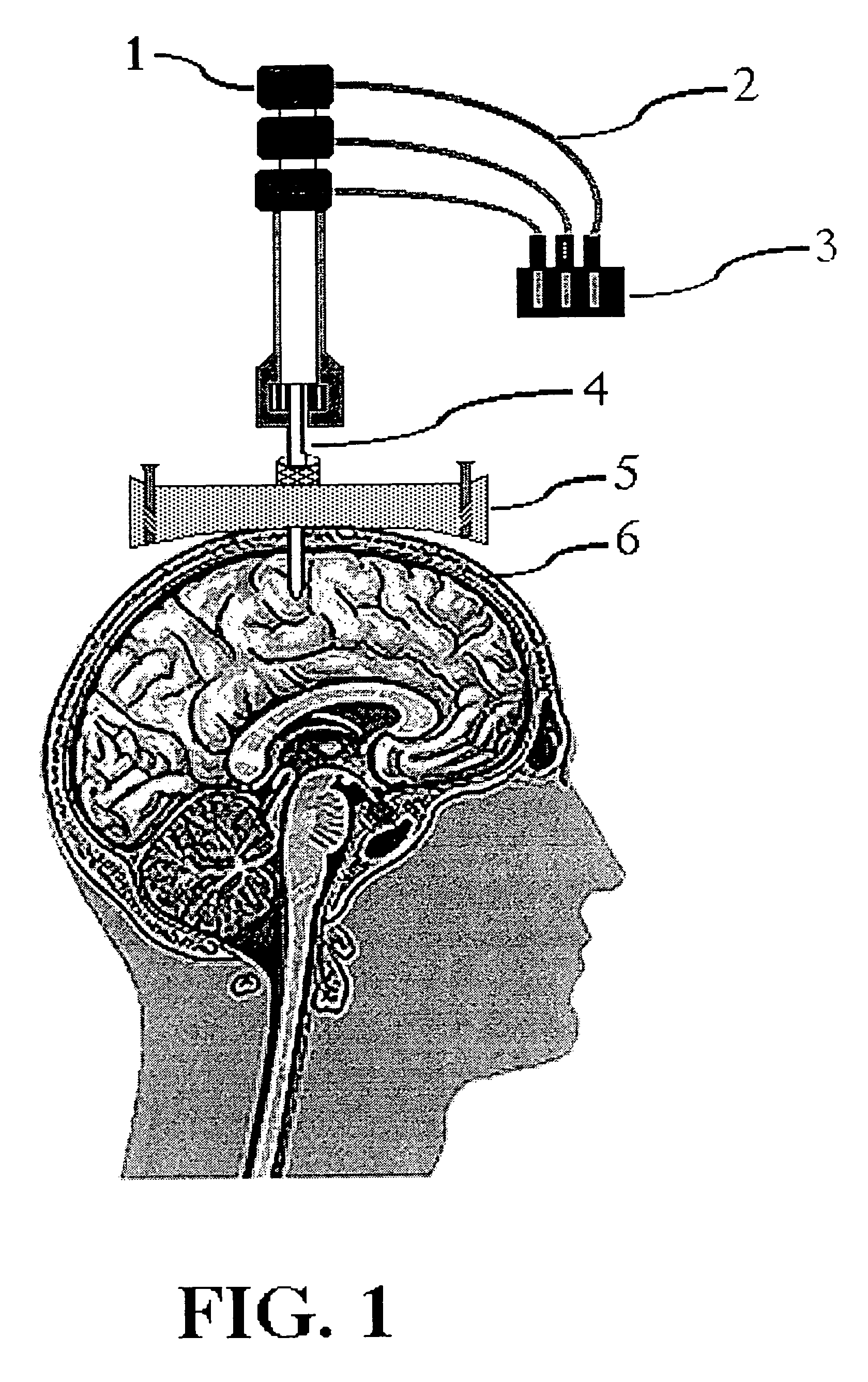
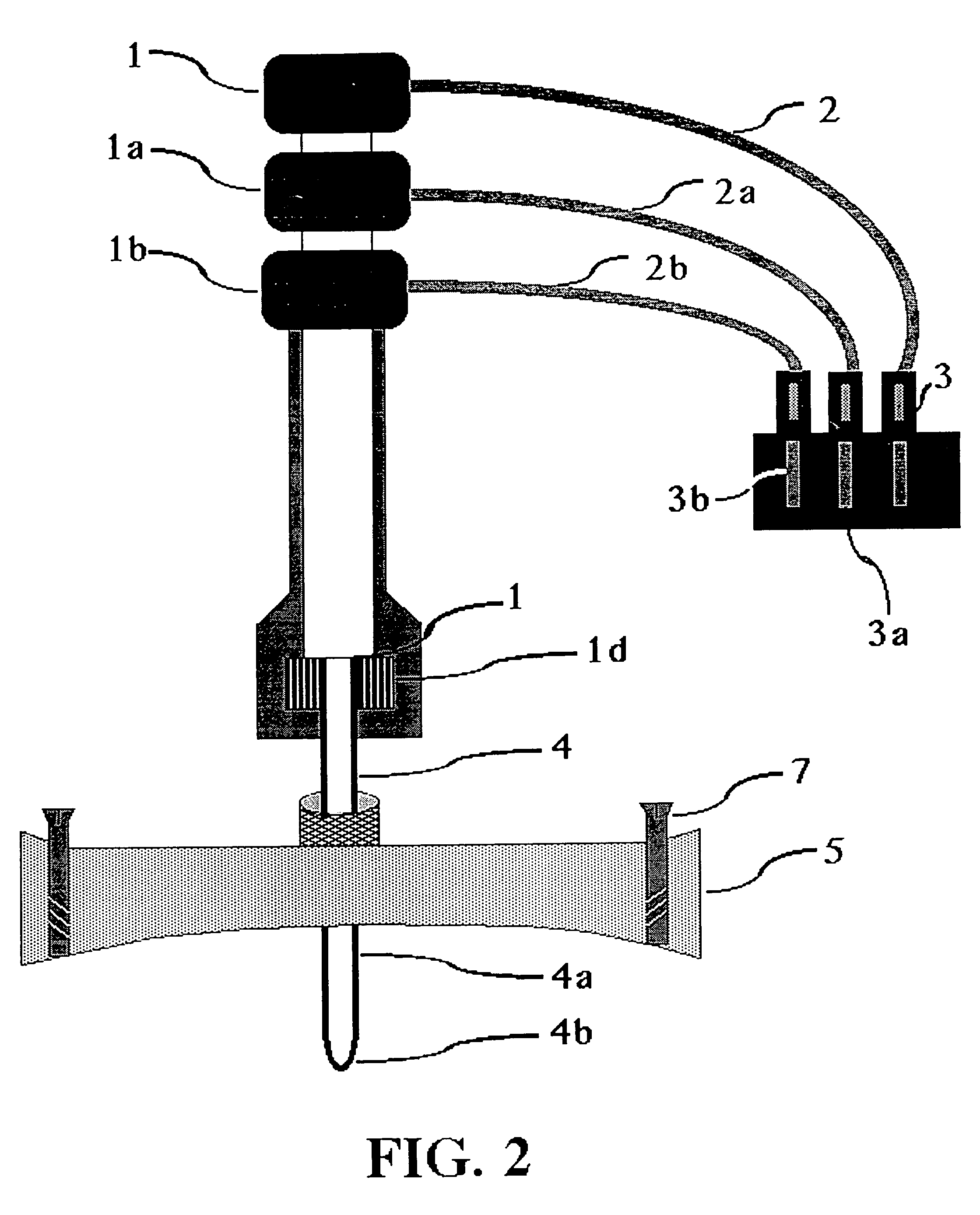
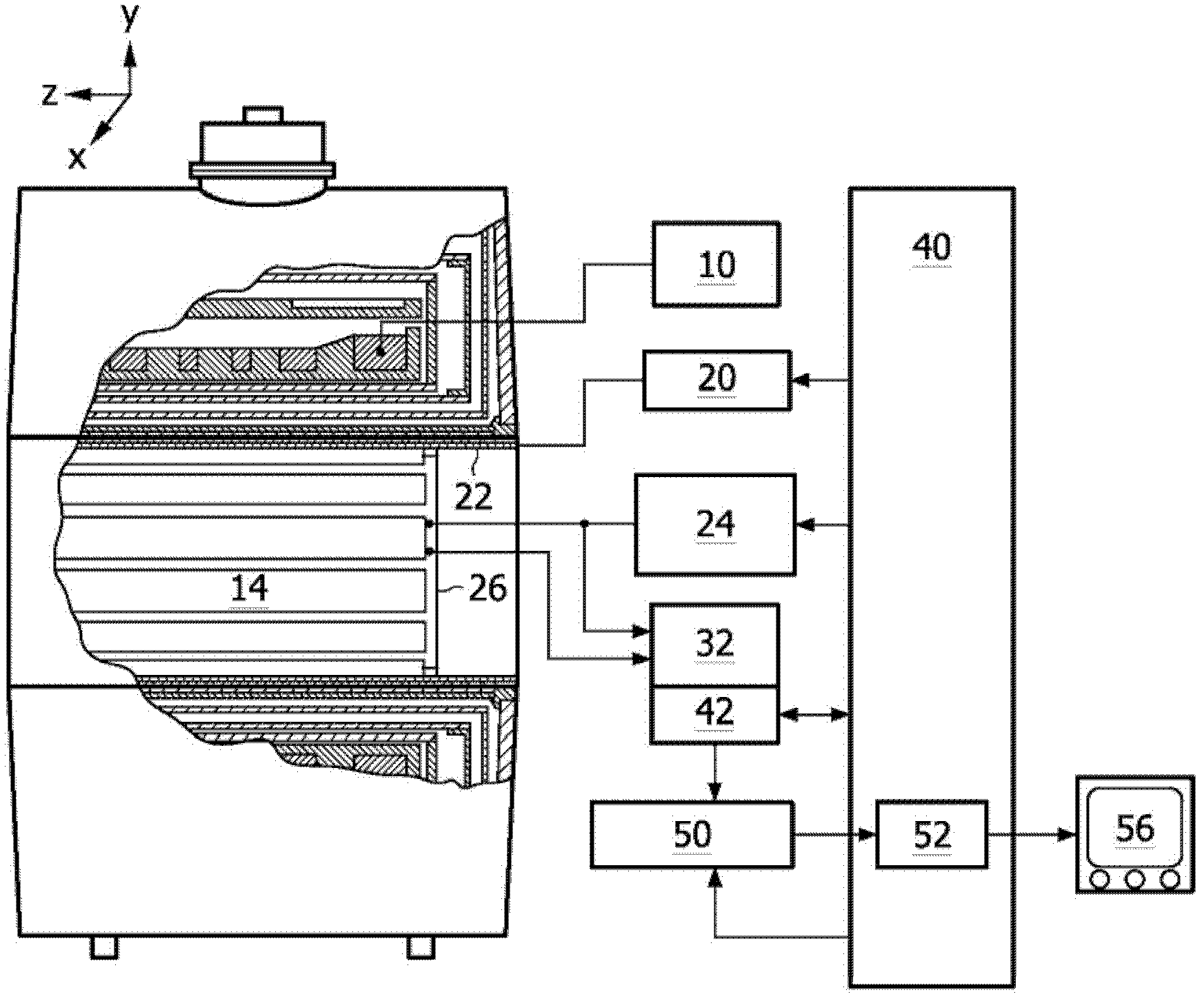
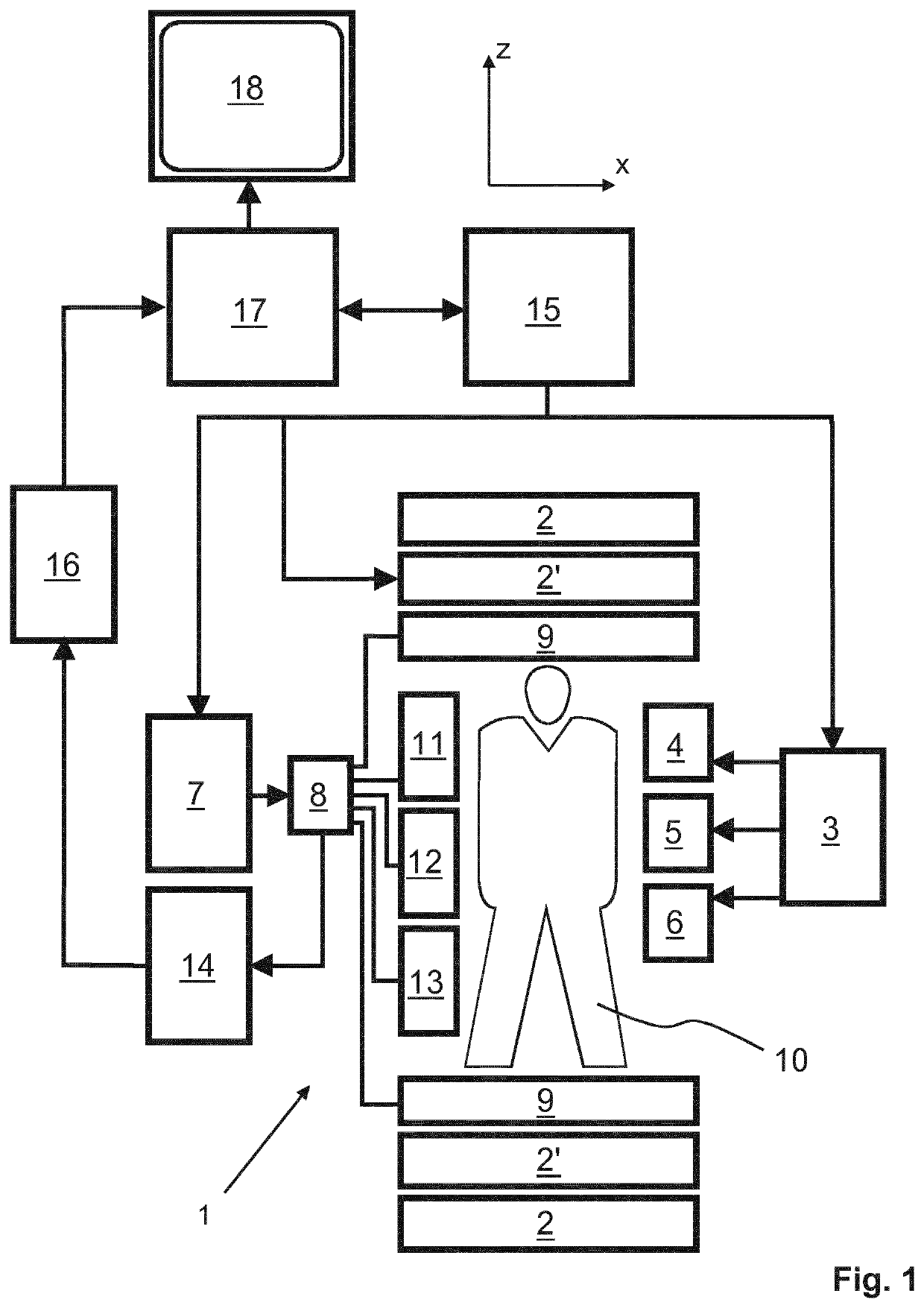
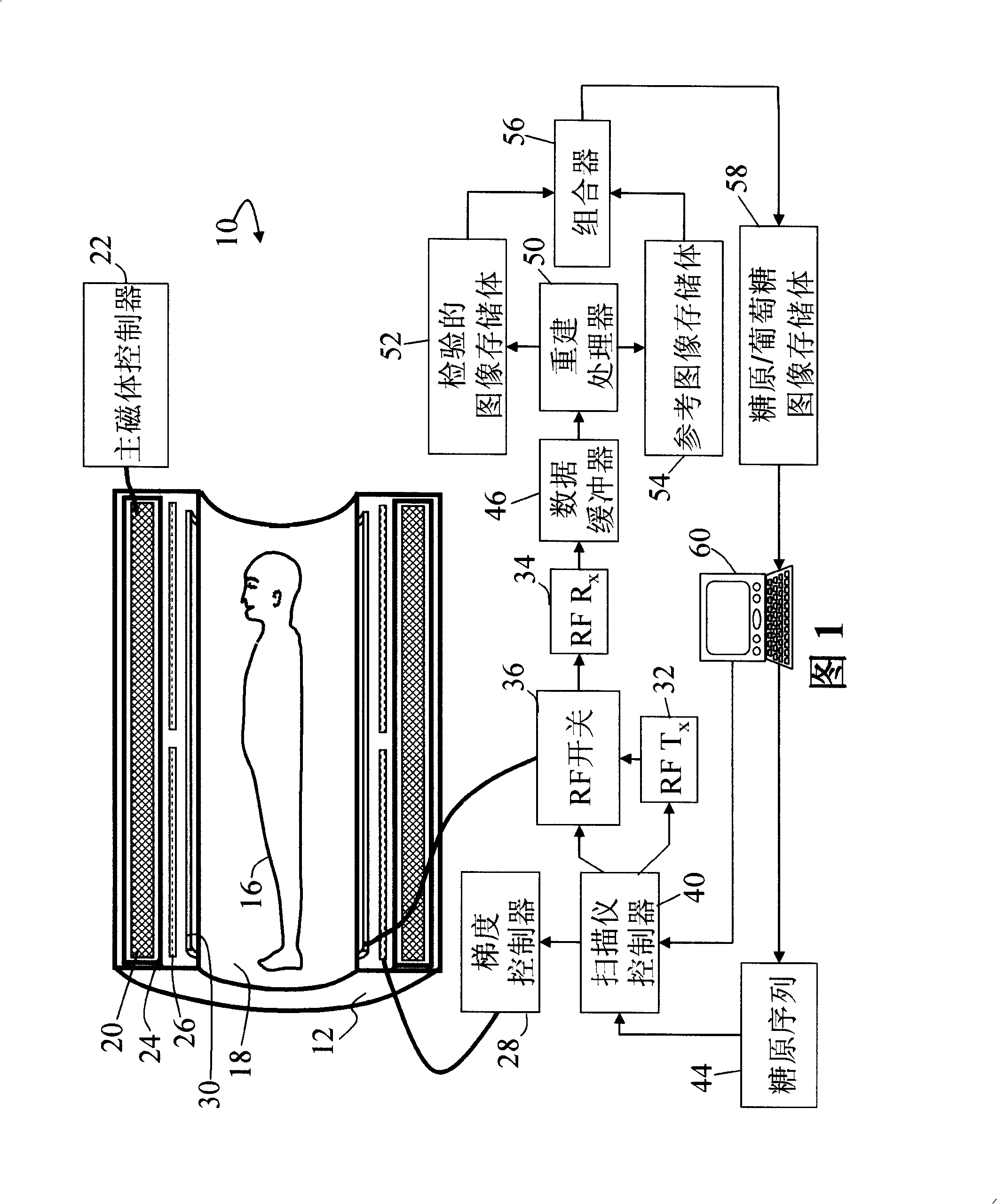
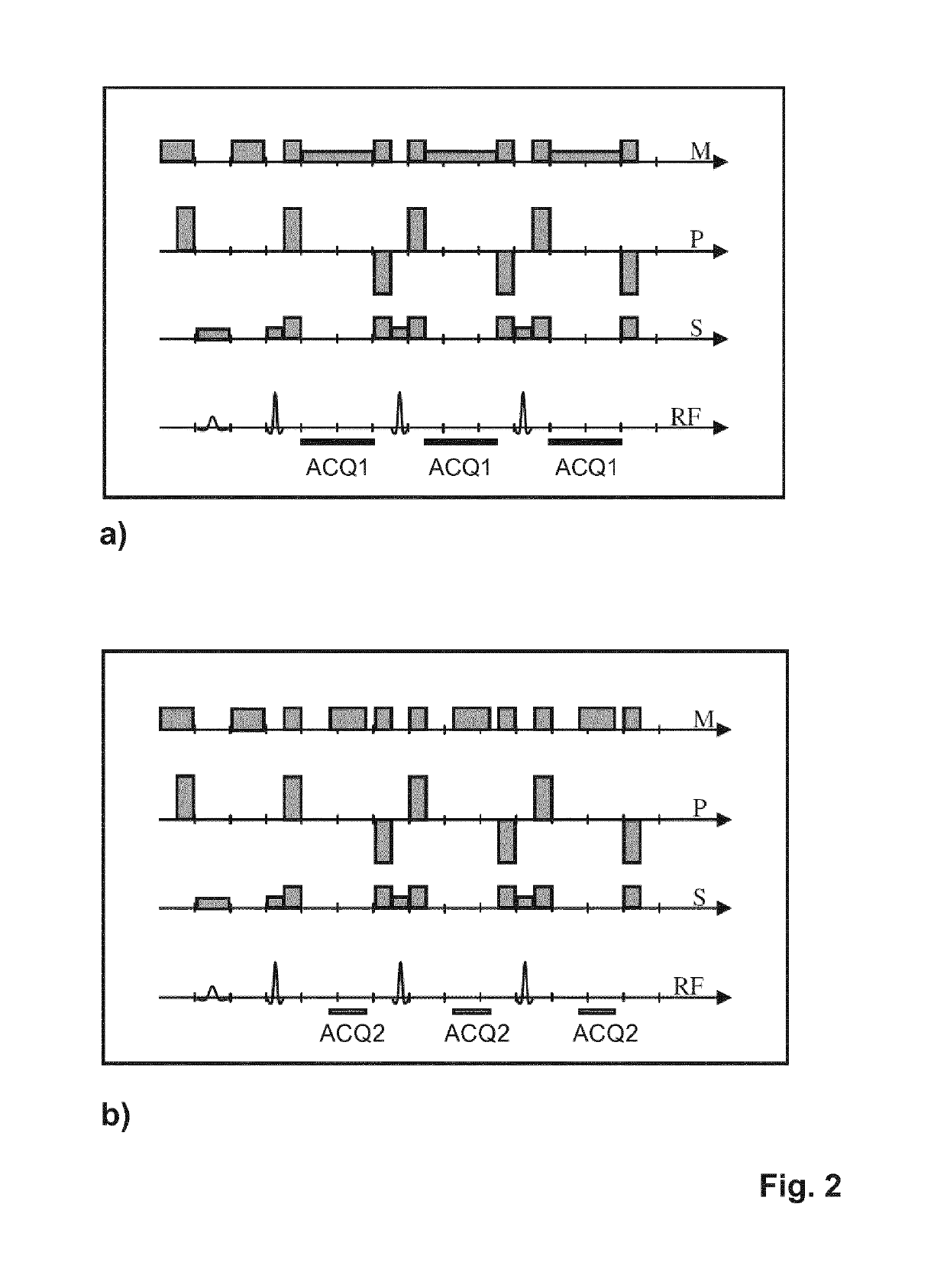
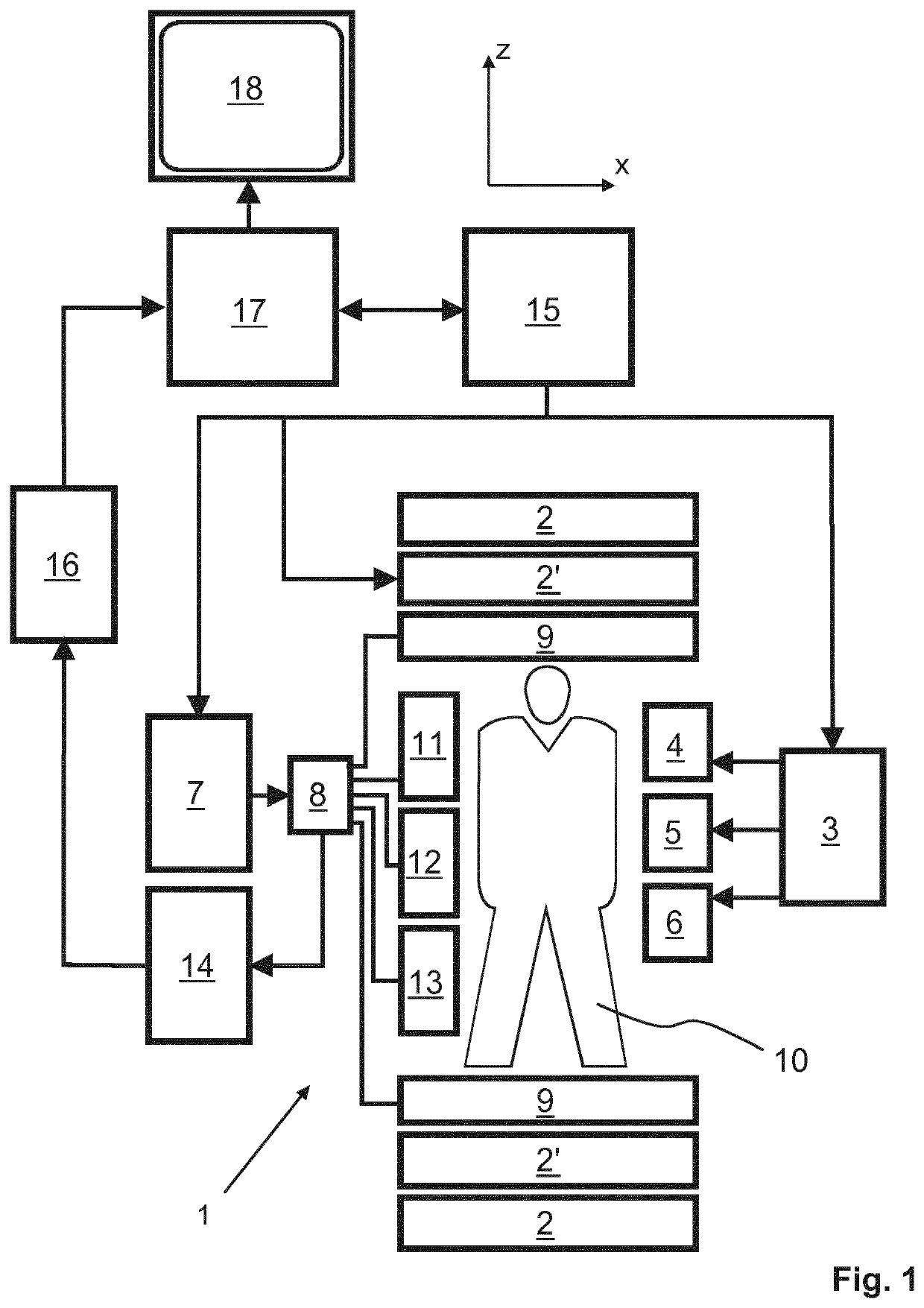
Self-referencing/body motion tracking non-invasive internal temperature distribution measurement method and apparatus using magnetic resonance tomographic imaging technique
InactiveUS7505805B2AdvantageousGood for observationChiropractic devicesEye exercisersObject motionPhase difference
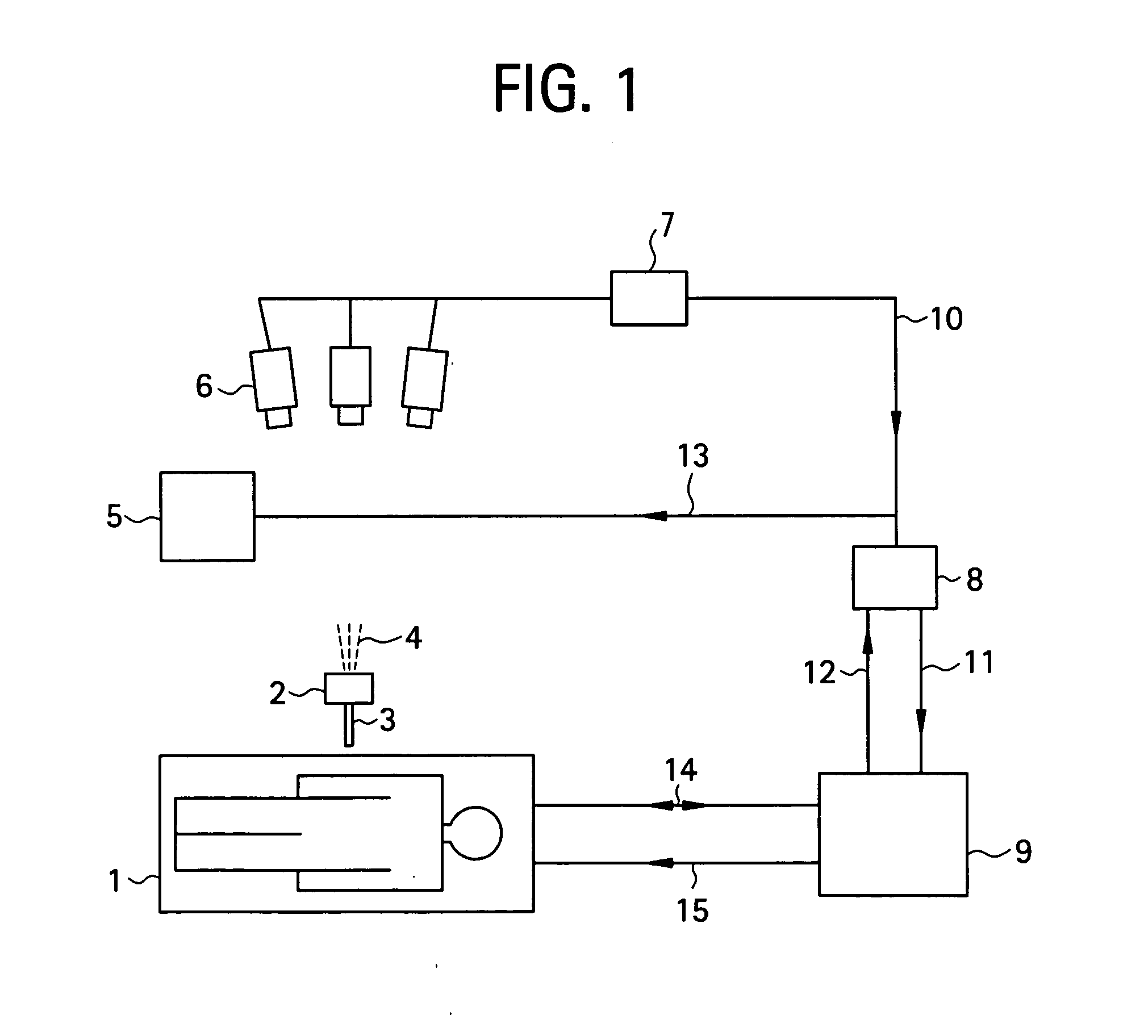
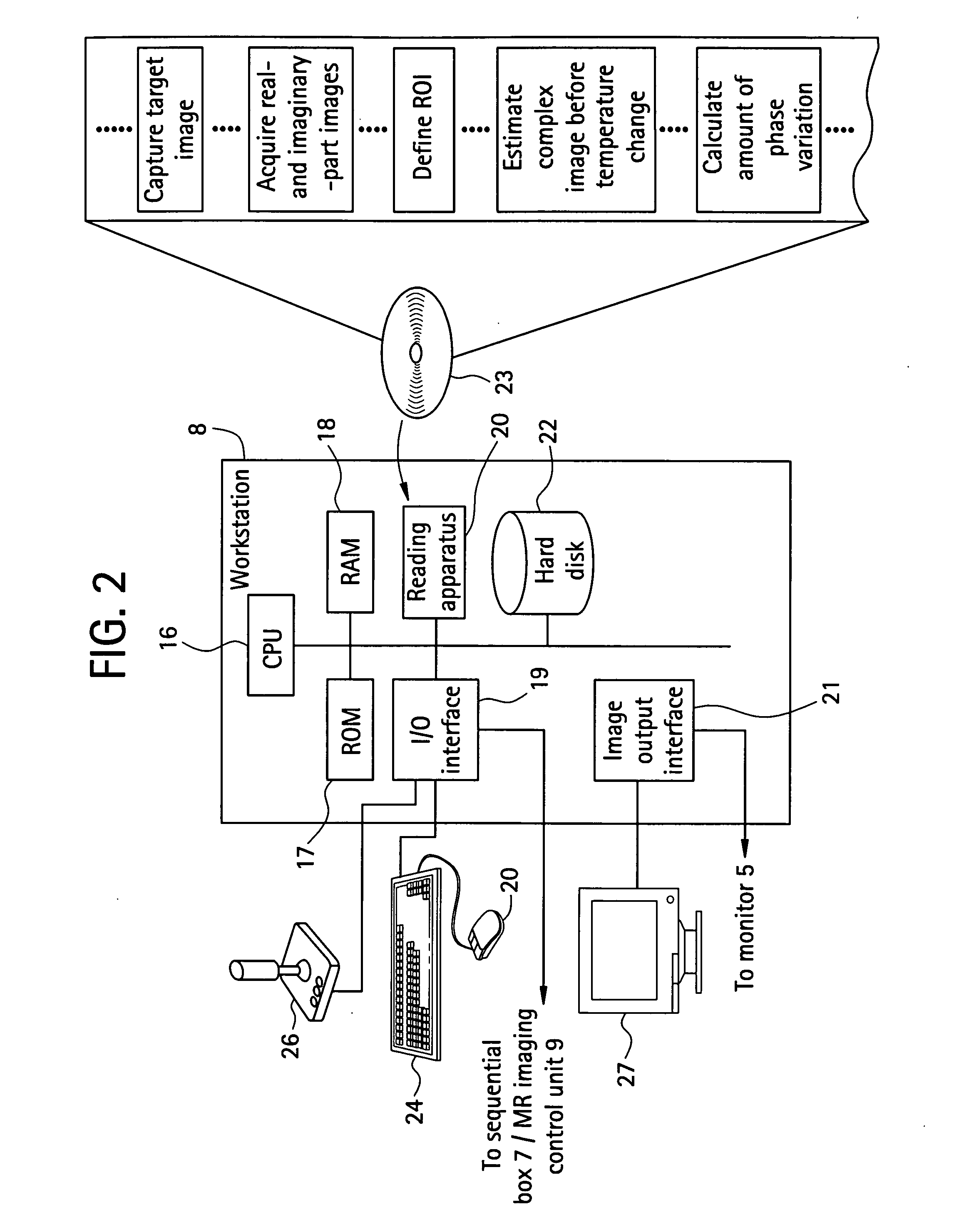
A noninvasive image measuring method of measuring internal organ / tissue temperature using an MRI system. Temperature measurement insusceptible to body motion and spatial variation of magnetic field is realized by utilizing the position and size of a temperature change region as a priori information to determine the phase distribution of the complex magnetic resonance signal of water proton at a given temperature point and by subtracting the phase distribution before the temperature change estimated (self-referred) from the phase distribution in the peripheral region for each pixel of the image, thereby eliminating the subtraction process of image before and after temperature change. The precision of temperature measurement can be enhanced by estimating a complex curved surface formed of the peripheral region in each temperature change region of the real-part and imaginary-part images of the complex magnetic resonance signal, and calculating the phase difference between an actually measured complex signal distribution and the estimated complex signal distribution of the complex signal distribution for each pixel, thereby reducing the estimation error due to phase transition from −π to +π occurring in a phase distribution. Furthermore, temperature can be measured through optimal imaging following up body motion by using an optical positioning system in combination even if the part being measured is shifted.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Self-referencing/body motion tracking non-invasive internal temperature distribution measurement method and apparatus using magnetic resonance tomographic imaging technique
InactiveUS20070055140A1Good treatment effectBetter heat controlDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase differenceNon invasive
A noninvasive image measuring method of measuring internal organ / tissue temperature using an MRI system. Temperature measurement insusceptible to body motion and spatial variation of magnetic field is realized by utilizing the position and size of a temperature change region as a priori information to determine the phase distribution of the complex magnetic resonance signal of water proton at a given temperature point and by subtracting the phase distribution before the temperature change estimated (self-referred) from the phase distribution in the peripheral region for each pixel of the image, thereby eliminating the subtraction process of image before and after temperature change. The precision of temperature measurement can be enhanced by estimating a complex curved surface formed of the peripheral region in each temperature change region of the real-part and imaginary-part images of the complex magnetic resonance signal, and calculating the phase difference between an actually measured complex signal distribution and the estimated complex signal distribution of the complex signal distribution for each pixel, thereby reducing the estimation error due to phase transition from −π to +π occurring in a phase distribution. Furthermore, temperature can be measured through optimal imaging following up body motion by using an optical positioning system in combination even if the part being measured is shifted.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
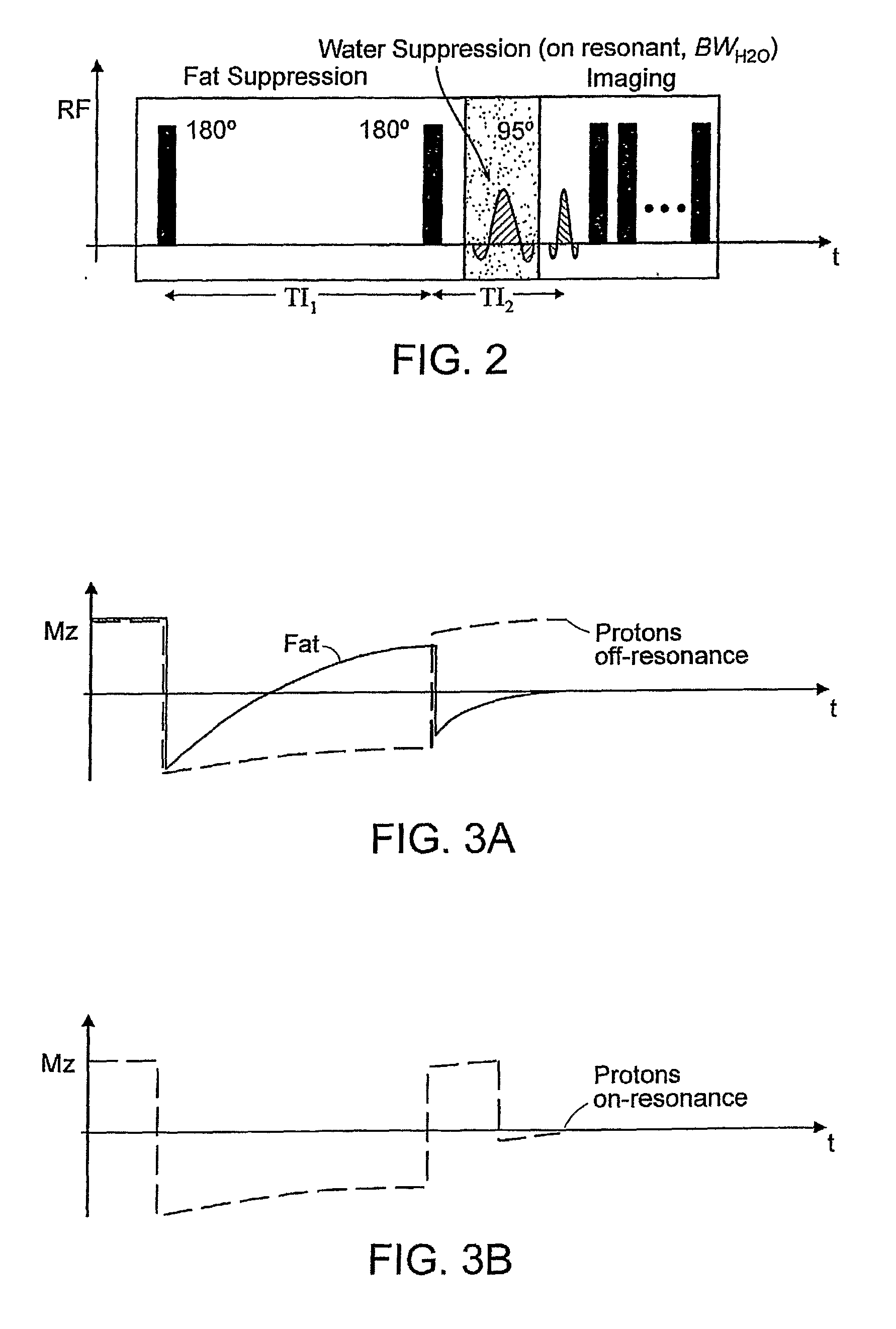
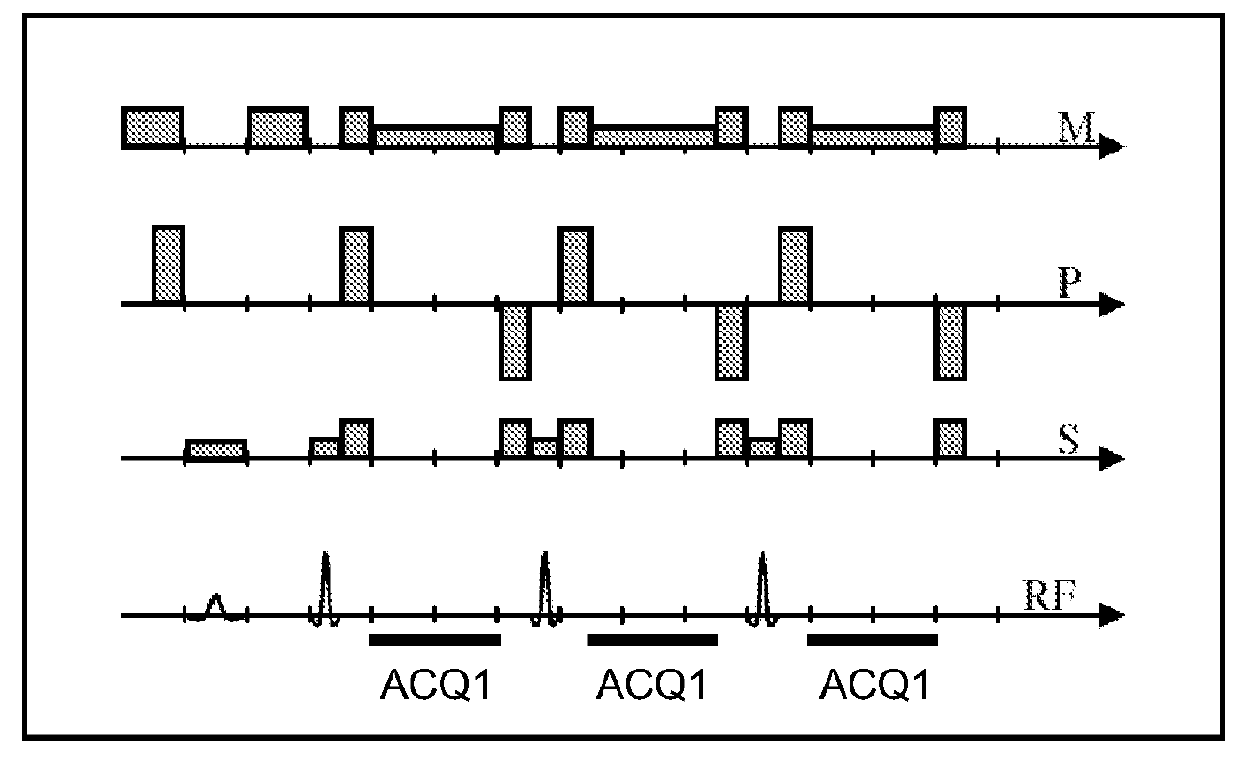
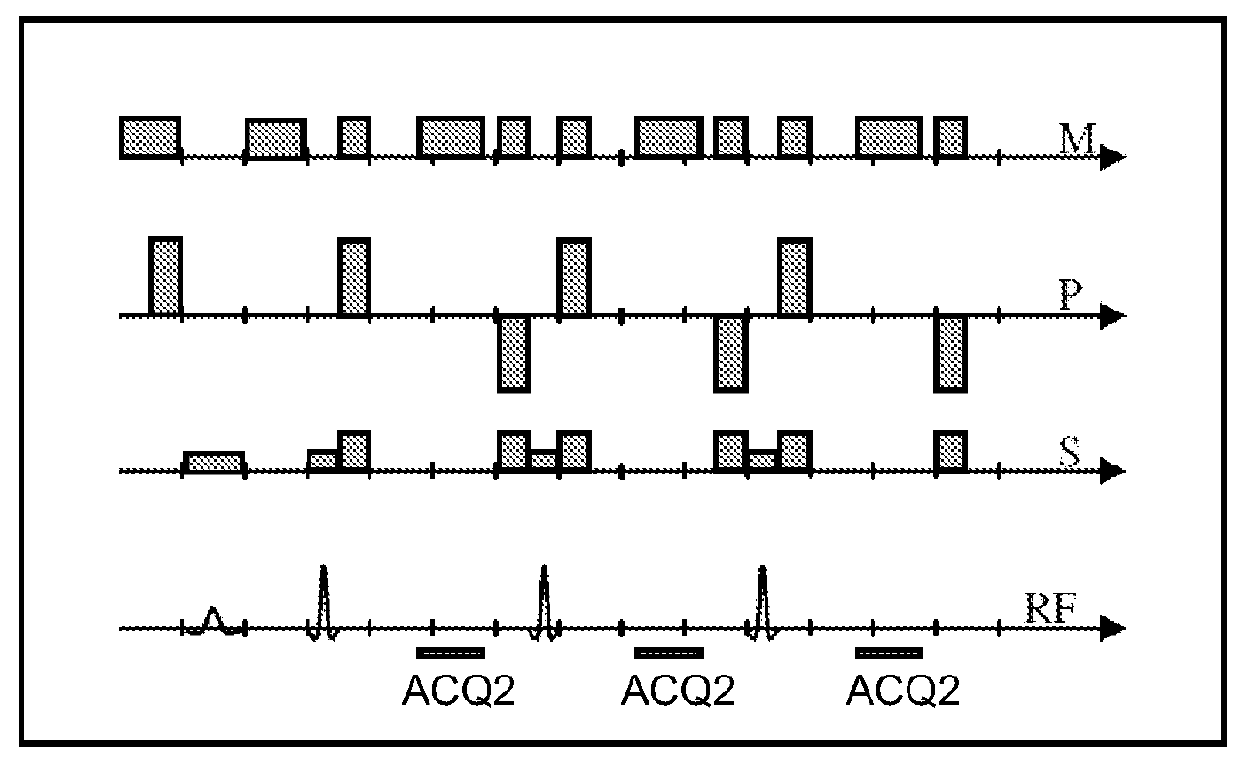
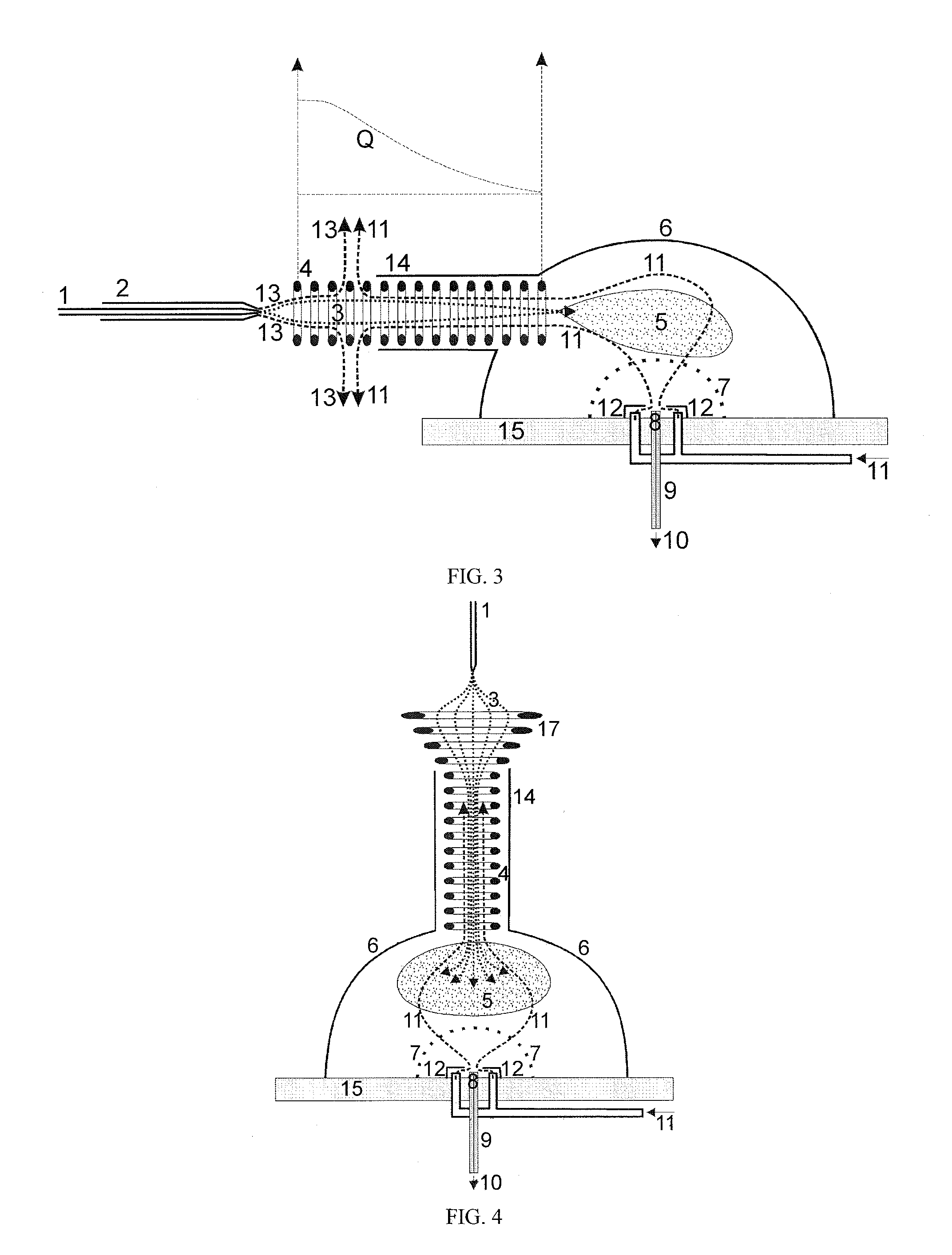
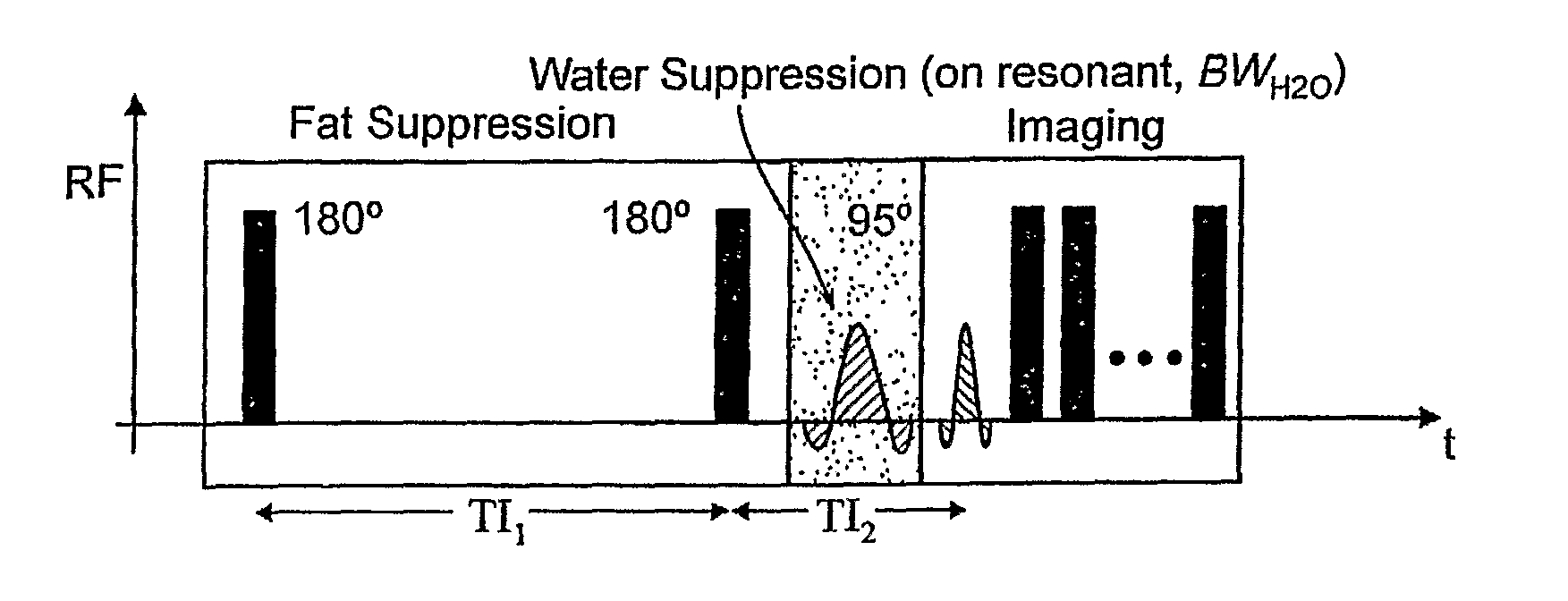
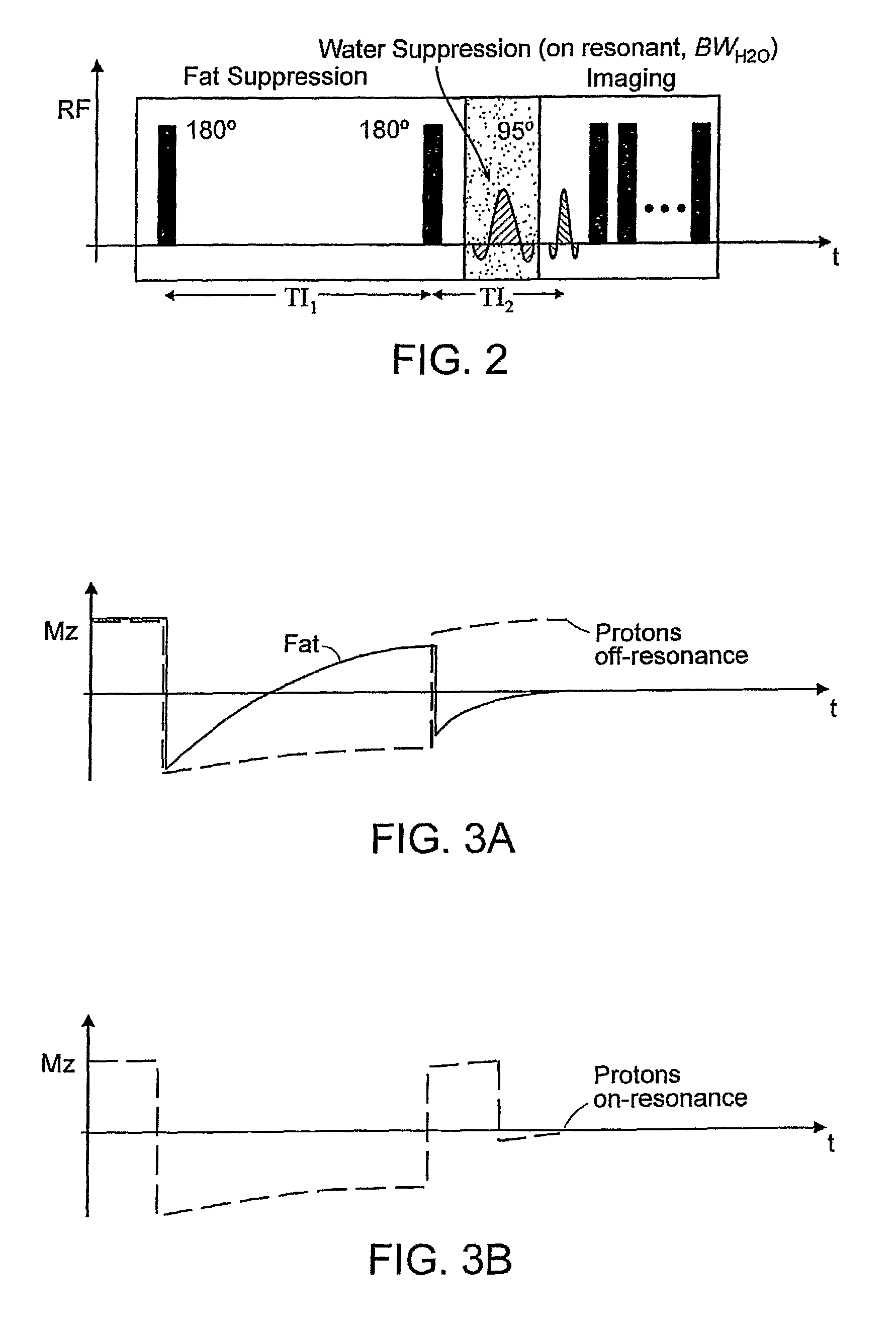
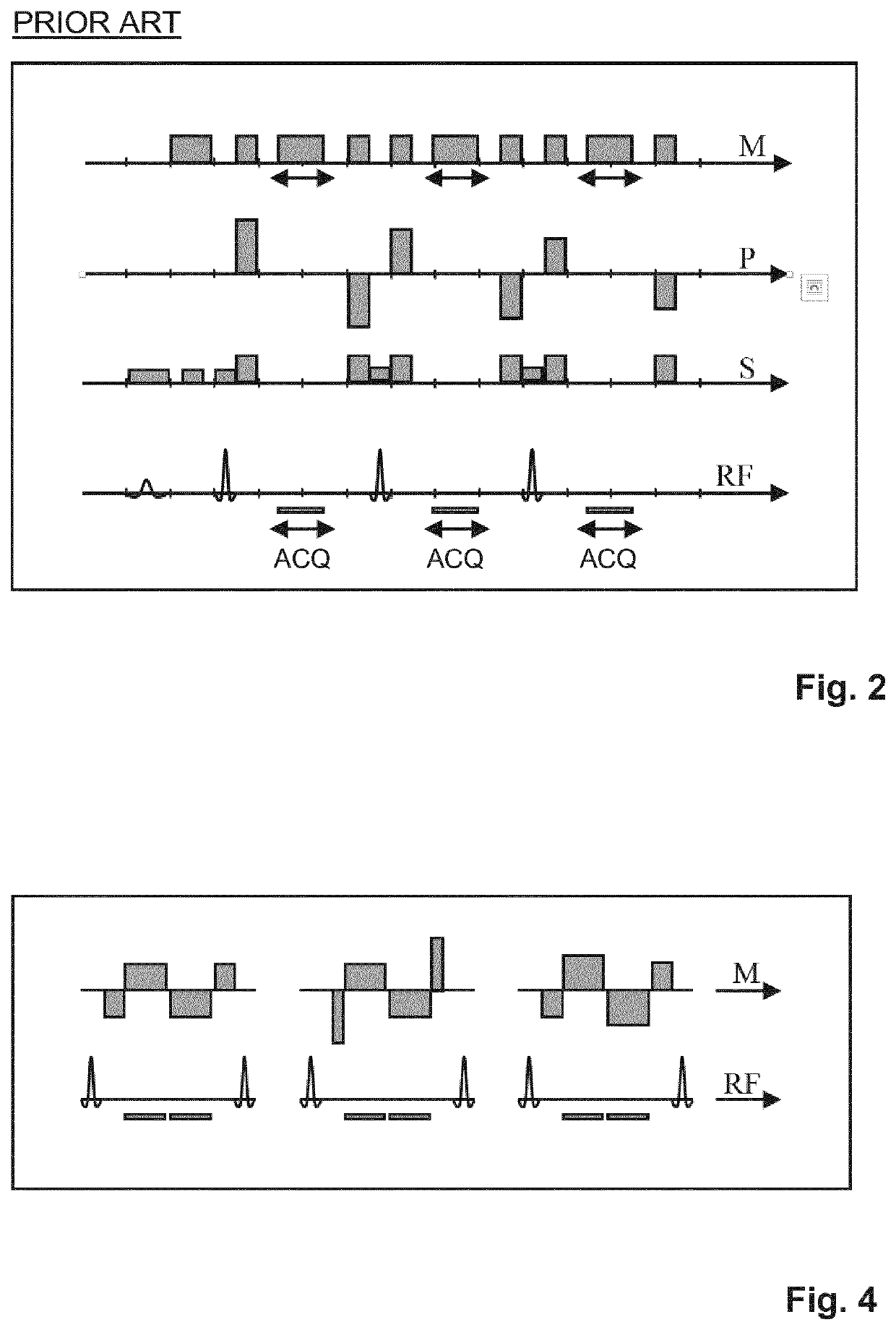
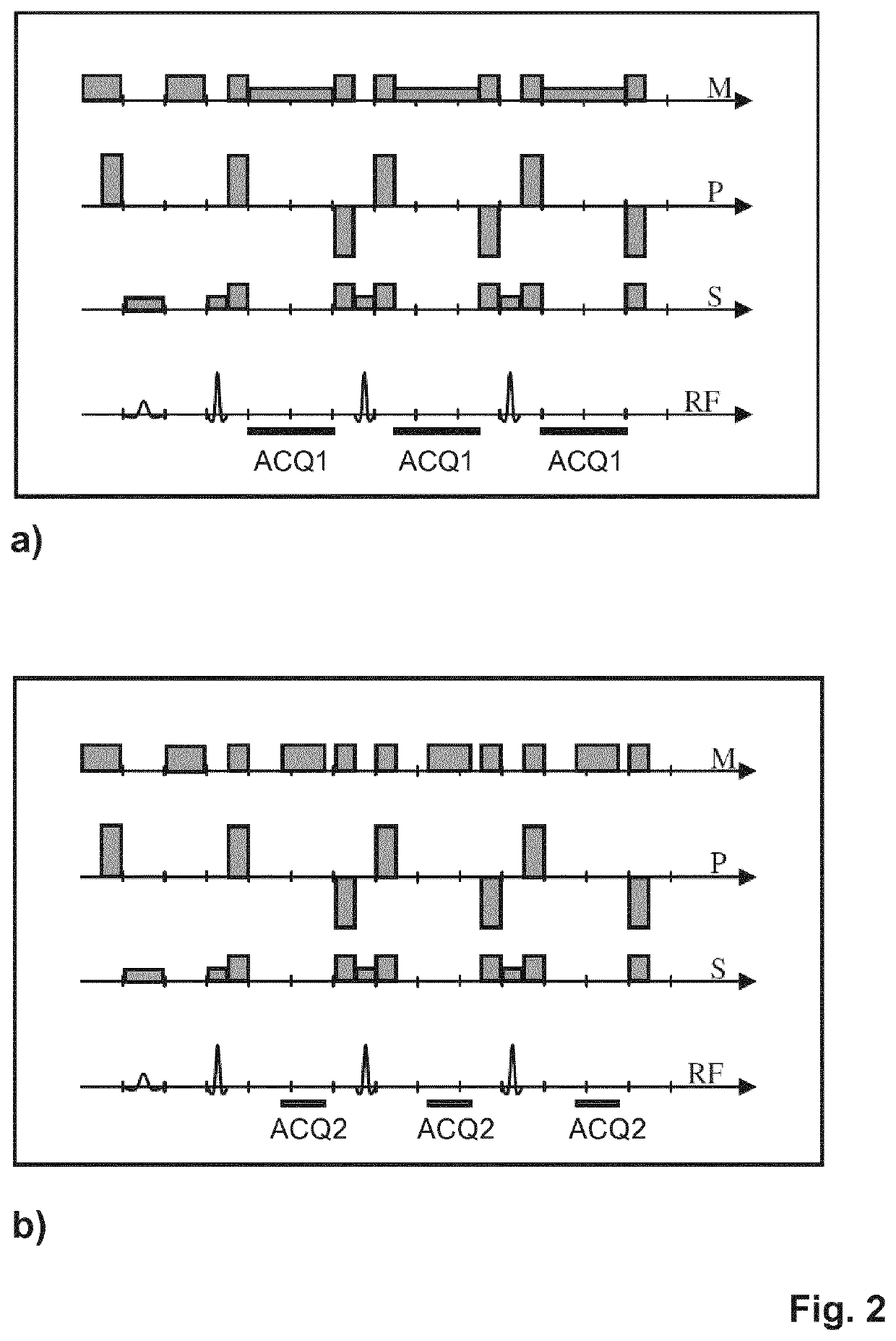
Method for magnetic resonance imaging using inversion recovery with on-resonant water suppression including mri systems and software embodying same
ActiveUS20090027051A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic susceptibilityInversion recovery
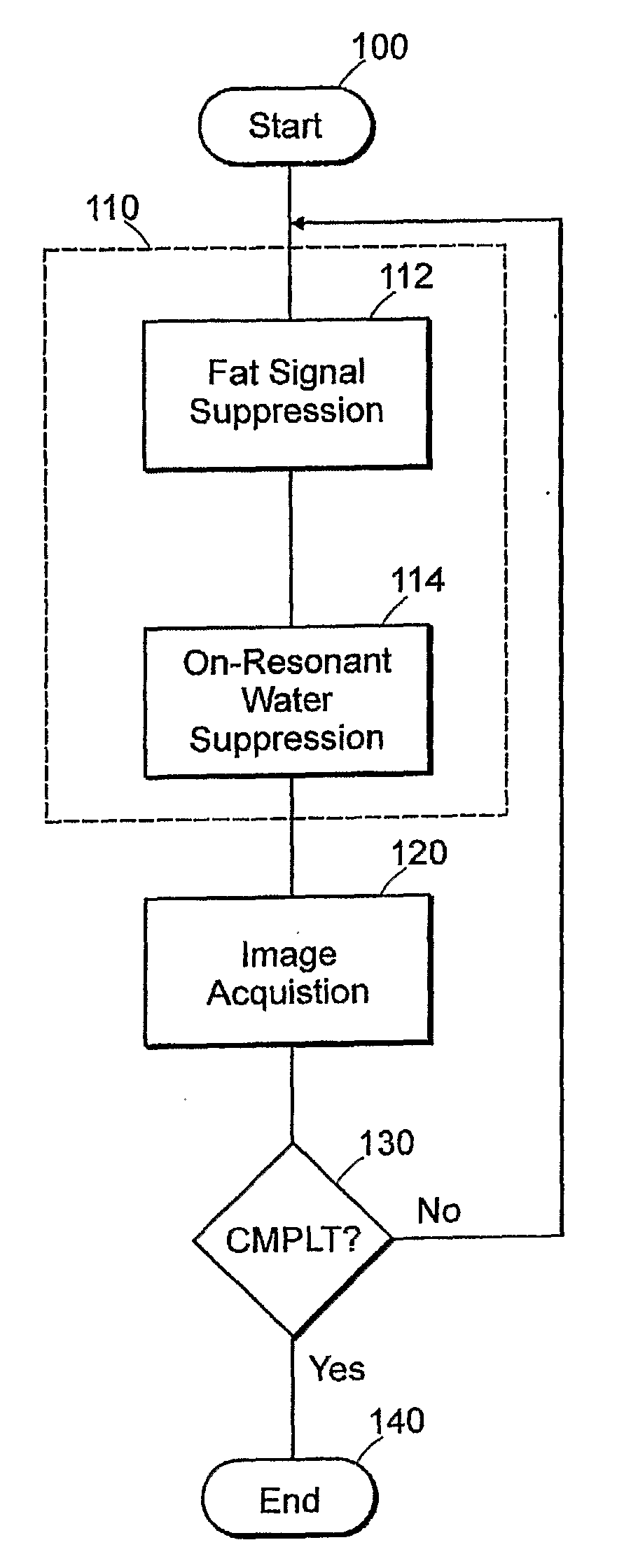
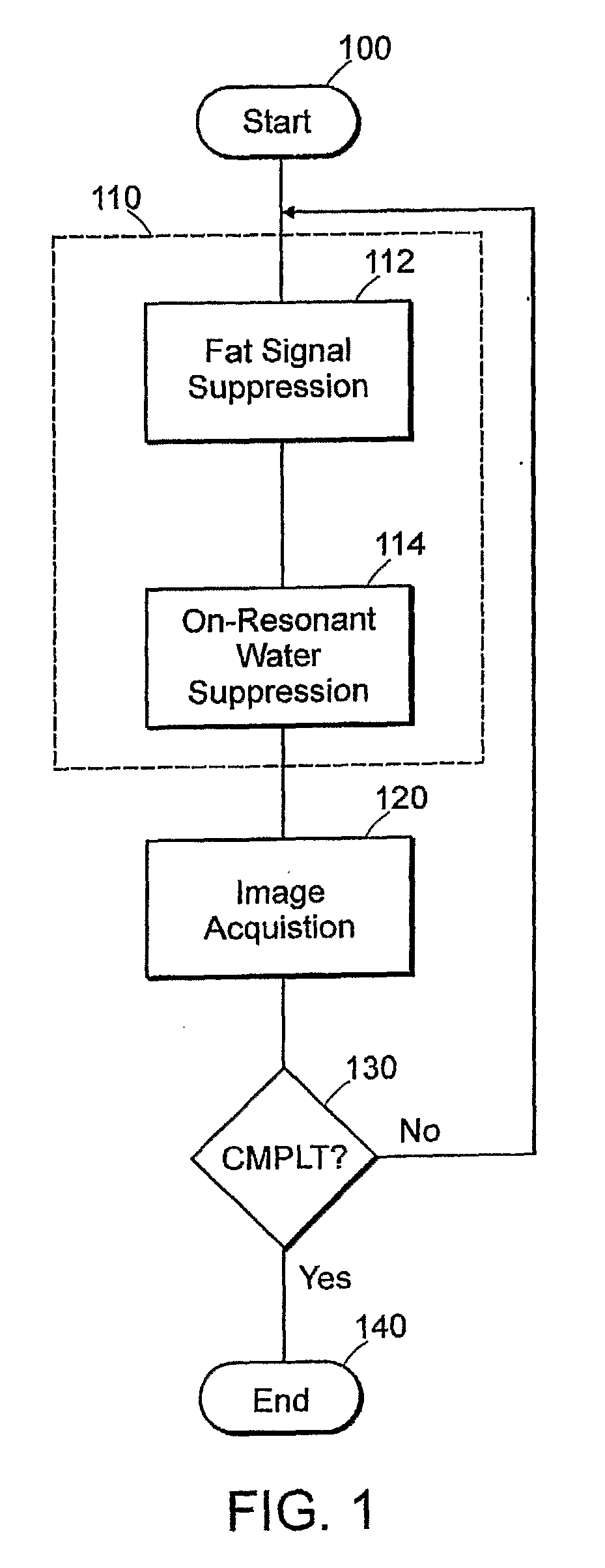
Featured are methods for magnetic resonance imaging of a volume, such a volume having susceptibility-generating objects or interfaces having susceptibility mismatches therein. Such a method includes selectively visualizing one of susceptibility-generating objects or interfaces having susceptibility mismatches as hyperintense signals, where such visualizing includes controlling variable imaging parameters so as to control a geometric extent of a signal enhancing effect, m more particular aspects of the present invention, such selectively visualizing includes attenuating or essentially suppressing signals from fat and / or water, namely on-resonant water protons, so as to thereby enhance a signal(s) associated with magnetic susceptibility gradient(s). Also featured are MRI systems, apparatuses and / or applications programs for execution on a computer system controlling the MRI data acquisition process embodying such methods.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Magnetic resonance apparatus for use with active electrode and drug deliver catheter
InactiveUS7505807B1Altered growthImprove efficacyMagnetic measurementsCannulasDrugs solutionResonance
The invention is an apparatus and method for treatments and targeted drug delivery into a living patient, particularly but not exclusively using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The apparatus and method are useful in delivery to all types of living tissue and uses MR Imaging to track the location of drug delivery and estimating the rate of drug delivery. An MR-visible drug delivery device positioned at a target site (e.g., intracranial delivery) delivers a diagnostic or therapeutic drug solution into the tissue (e.g., the brain). The spinal distribution kinetics of the injected or infused drug agent are monitored quantitatively and non-invasively using water proton directional diffusion MR imaging to establish the efficacy of drug delivery at a targeted location.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
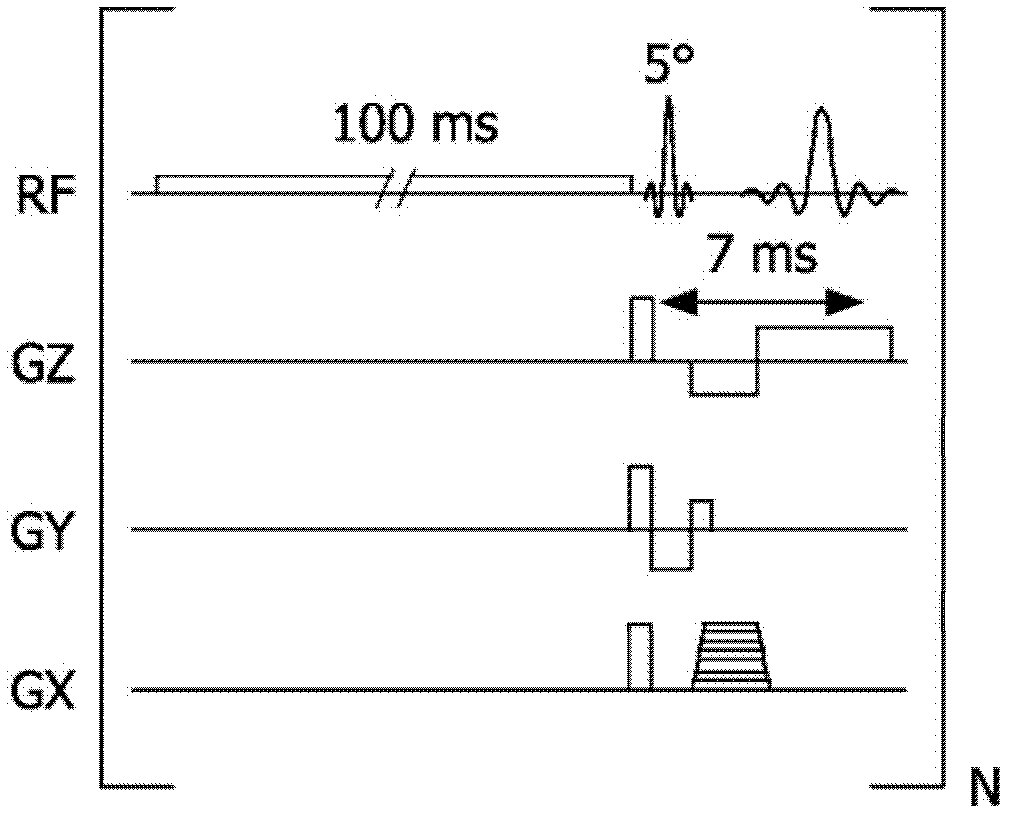
MR imaging using nested pulse sequence involving IR pulse
InactiveUS6850793B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSignificant positive effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCross relaxationImage contrast
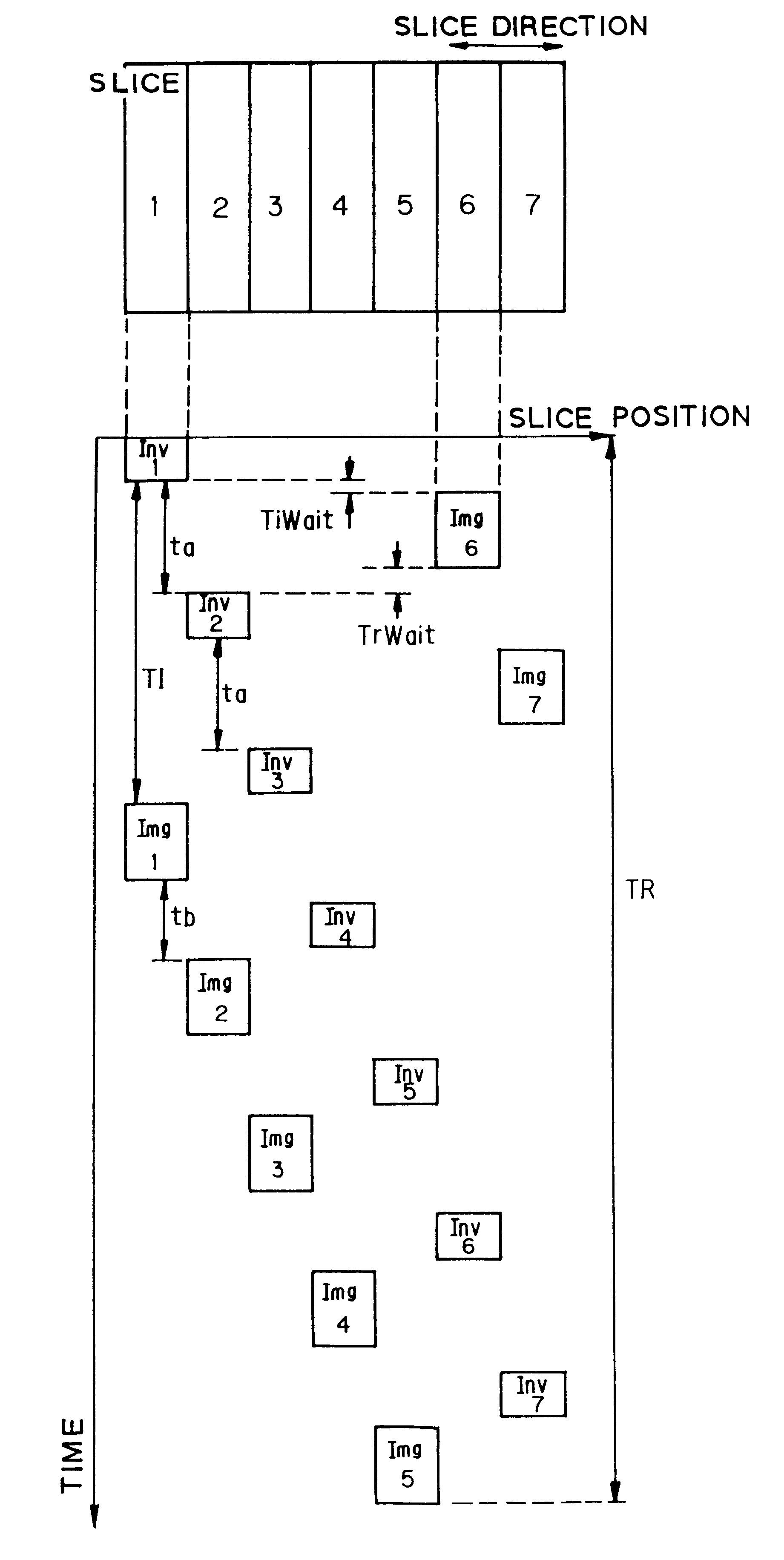
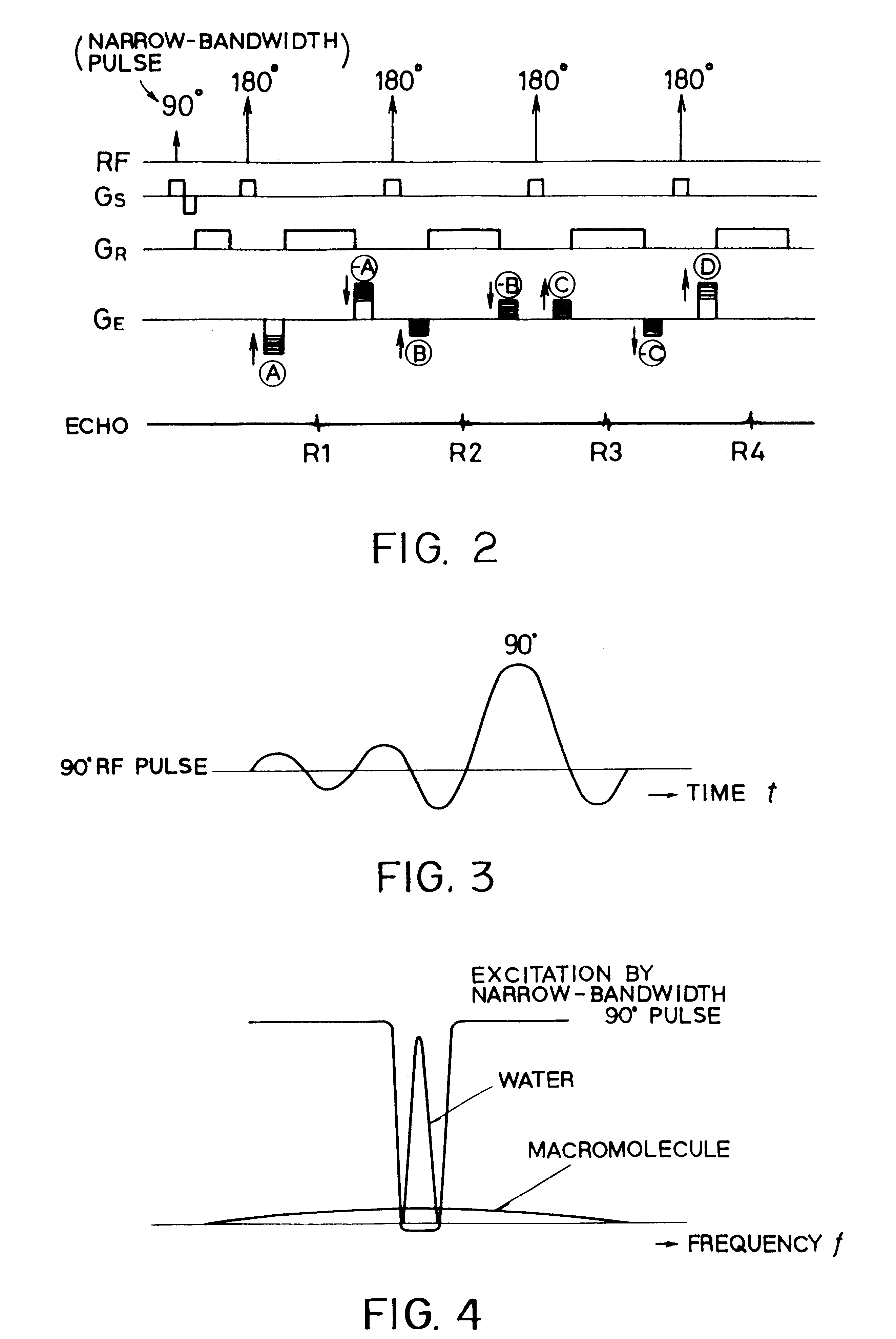
In addition to the known MT (magnetization transfer) effect, an RMT (reverse MT) is newly found, which increases a detected MR signal strength. Both the MT and RMT effects can be explained with mutual interaction, such as phenomena of chemical exchange and / or cross relaxation, acted between a pool of water proton spins and another pool of macromolecule proton spins, for example, within an object. In order to enhance the MT or RMT effect, the frequency bandwidths of RF pulses, such as a 90° RF exciting pulse in a SE or FSE method, an inversion pulse in a FLAIR or fast FLAIR method, and others, are controlled. To enhance the MT effect, the bandwidth is controlled into a wider value (approx. more than 1250 Hz) than the normally (conventionally) used bandwidth, while to obtain the RMT effect, the bandwidth is controlled into a narrower value (approx. less than 1000 Hz) than the normally used bandwidth. Actively controlling the MT or RMT effect permits changed image contrast in MR imaging.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Dixon-type water/fat separation MRI using high-snr in-phse image and lower-snr at least partially out-of-phase image
InactiveUS20160033606A1Low sampling efficiencyImprove sampling efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention relates to a method of Dixon-type MR imaging. The method comprises the steps of—generating a first imaging sequence for producing first MR echo signals at a first echo time, such that contributions from MR signals emanating from water protons and MR signals emanating from fat protons to the first MR echo signals are essentially in phase,—acquiring the first MR echo signals at a first signal-to-noise ratio,—generating a second imaging sequence for producing second MR echo signals at a second echo time, such that contributions from MR signals emanating from water protons and MR signals emanating from fat protons to the second MR echo signals are at least partially out of phase,—acquiring the second MR echo signals at a second signal-to-noise ratio which is different from the first signal-to-noise ratio, and—reconstructing a MR image from the first and second MR echo signals, wherein signal contributions from water protons and fat protons are separated. Moreover the invention relates to a MR device and to a computer program to be run on a MR device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Mr imaging with cest contrast enhancement
InactiveCN102257399AMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic variable regulationMagnetic field gradientMedicine
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic microstructures for magnetic resonance imaging
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance structure with a cavity or a reserved space that provides contrast and the additional ability to frequency-shift the spectral signature of the NMR-susceptible nuclei such as water protons by a discrete and controllable characteristic frequency shift that is unique to each MRS design. The invention also relates to nearly uniform solid magnetic resonance T2* contrast agents that have a significantly higher magnetic moment compared to similarly-sized existing MRI contrast agents.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE COMMERCE +1
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for correction of a b0 map for chemical shifts
ActiveUS20150204955A1Simple and fast to carry-outSimple and fast to carryImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceSpins
In a method for correction of a B0 field map measured with a magnetic resonance device, that describes deviations from a nominal field strength in the homogeneity area of the magnetic resonance device by deviations from a nominal frequency for protons bonded to water, the deviations being represented as Larmor frequency values for different picture elements shifted by chemical shifts, the B0 field map is recorded with spins of the fat and water protons not in phase. The B0 field map is segmented by evaluating the differences of the Larmor frequency values of adjacent picture elements of the B0 field map in at least two contiguous clusters. For each cluster, a decision is made on the basis of a smoothness criterion and a compactness criterion as to whether a cluster containing a majority of protons bonded into fat is involved. Clusters identified as containing a majority of protons bonded into fat are corrected by lowering the Larmor frequency values by the difference between the nominal frequency for protons bonded into water and the corresponding nominal frequency for protons bonded to fat.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
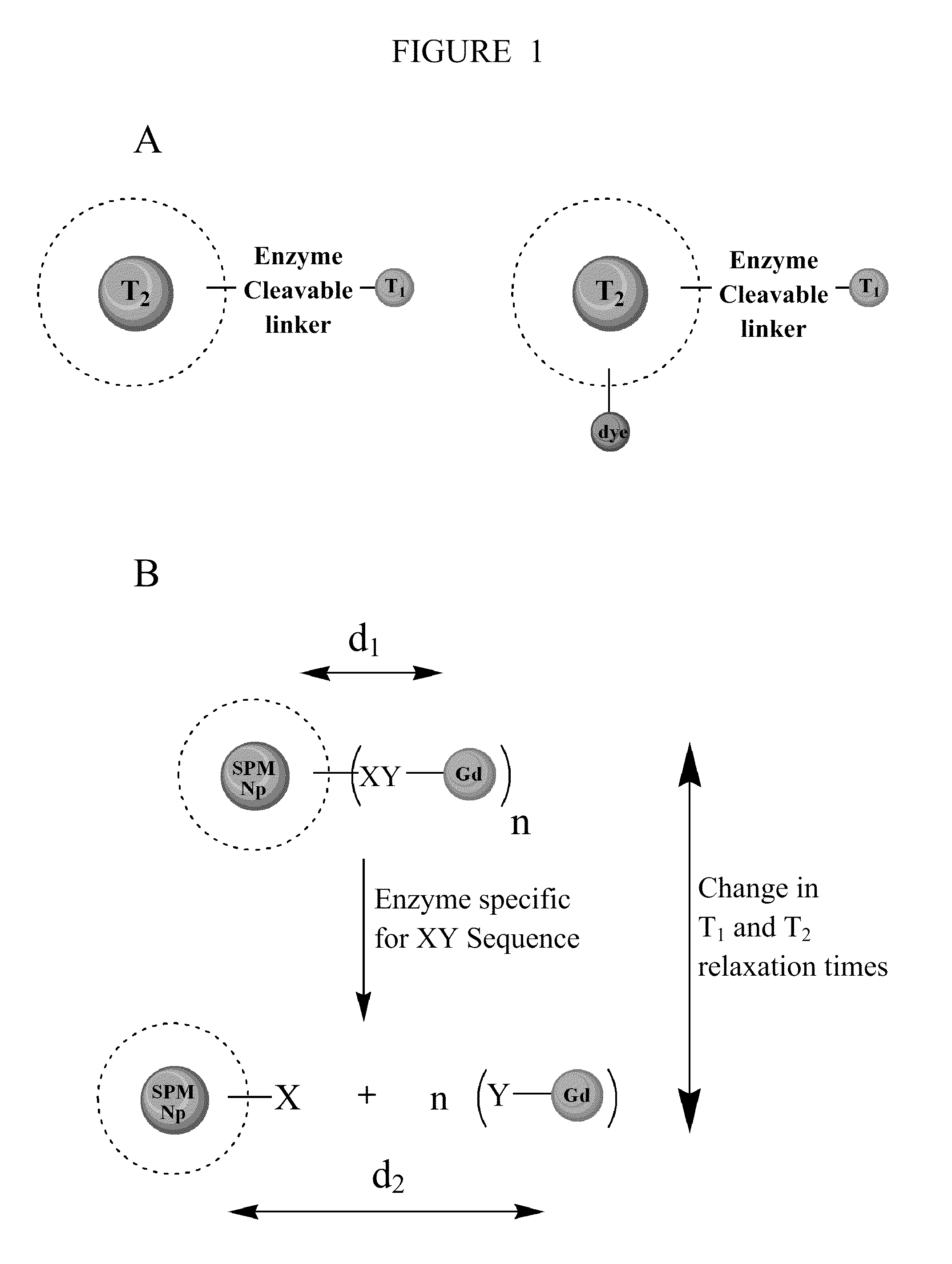
Contrast agents
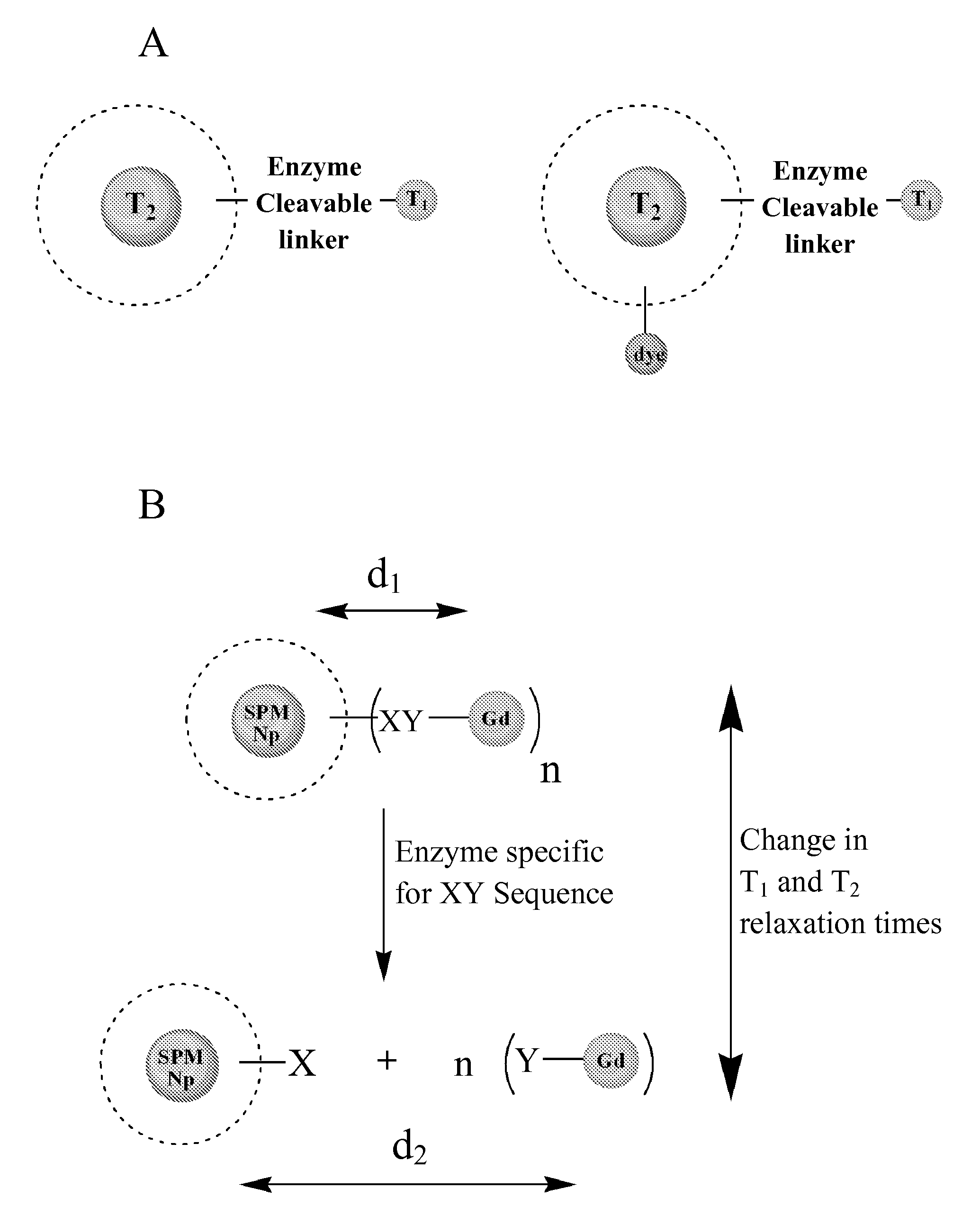
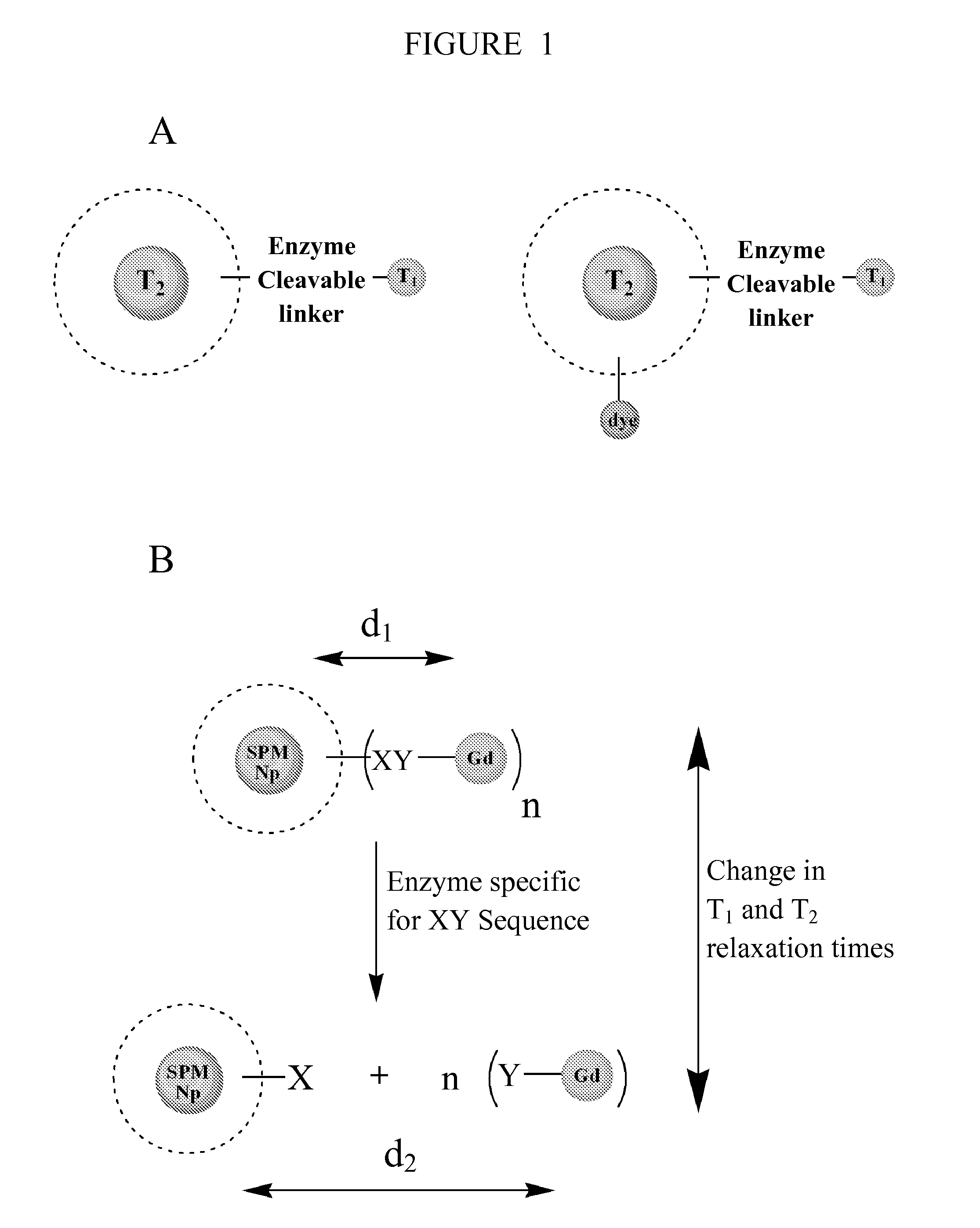
The present invention relates generally to multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. In particular, the present invention provides a MRI contrast agent configured to manipulate both the longitudinal (T1) and transverse (T2) relaxation times of surrounding water proton spins.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Melamine dual-mode sensor based on Au-Fe3O4 composite nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104764706AImplementing Dual Mode DetectionChange in relaxation rateColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceInterference resistance
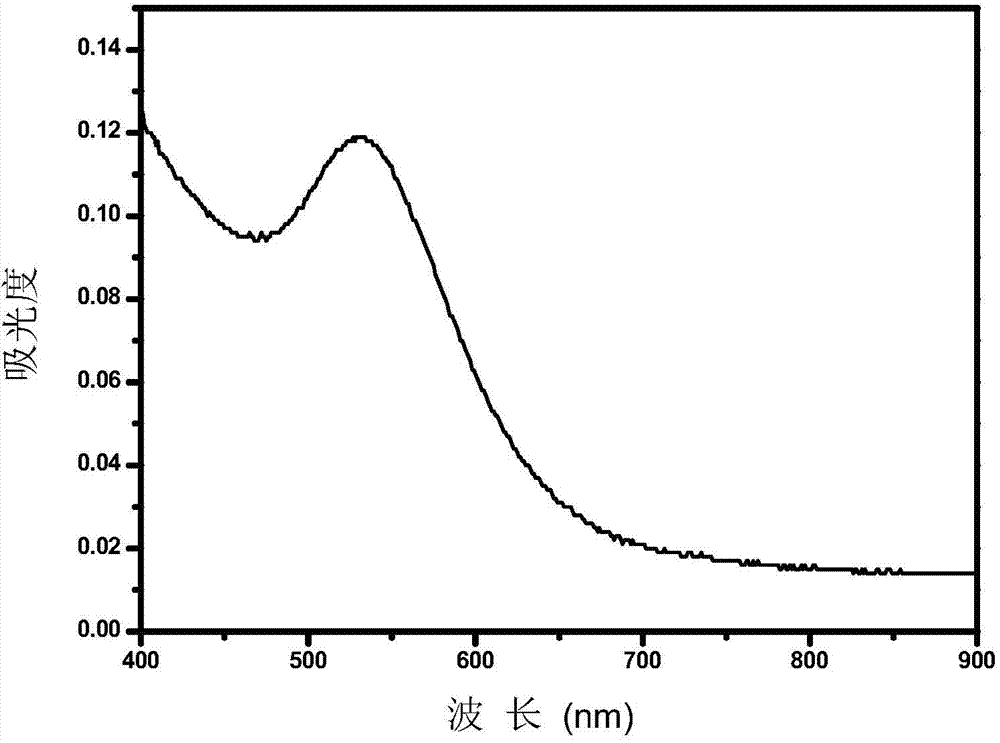
The invention relates to a melamine dual-mode sensor based on Au-Fe3O4 composite nanoparticles and a preparation method thereof. The invention relates to the field of nuclear magnetic resonance sensing. First, oleylamine oleic acid on the surfaces of the Au-Fe3O4 composite nanoparticles is stripped through NOBF4; and a specific receptor unit modifies the surfaces of the composite nanoparticles stripped by NOBF4 under the strong coordination effect of an Au-S bond, thus obtaining target composite nanoparticles which can be used for preparing the melamine dual-mode sensor. Compared with prior art, the dual-mode sensor provided by the invention has the advantages that in the presence of melamine, dispersed-state nanoparticles are induced to aggregate so that the transverse relaxation time of water protons around the nanoparticles and the ultraviolet absorption spectrum of the nanoparticles are changed. According to the sensor, melamine is detected with both an ultraviolet absorption spectrum method and a nuclear magnetic resonance method; therefore, the sensor has the advantages of wide application range, high selectivity and high interference resistance. A method is provided for realizing fast application under different actual situations.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Contrast agents
The present invention relates generally to multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. In particular, the present invention provides a MRI contrast agent configured to manipulate both the longitudinal (T1) and transverse (T2) relaxation times of surrounding water proton spins.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
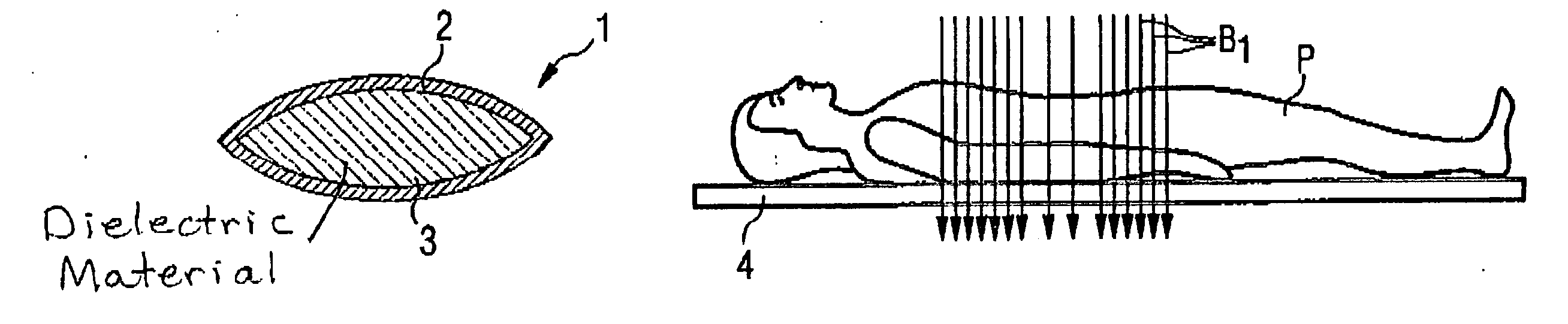
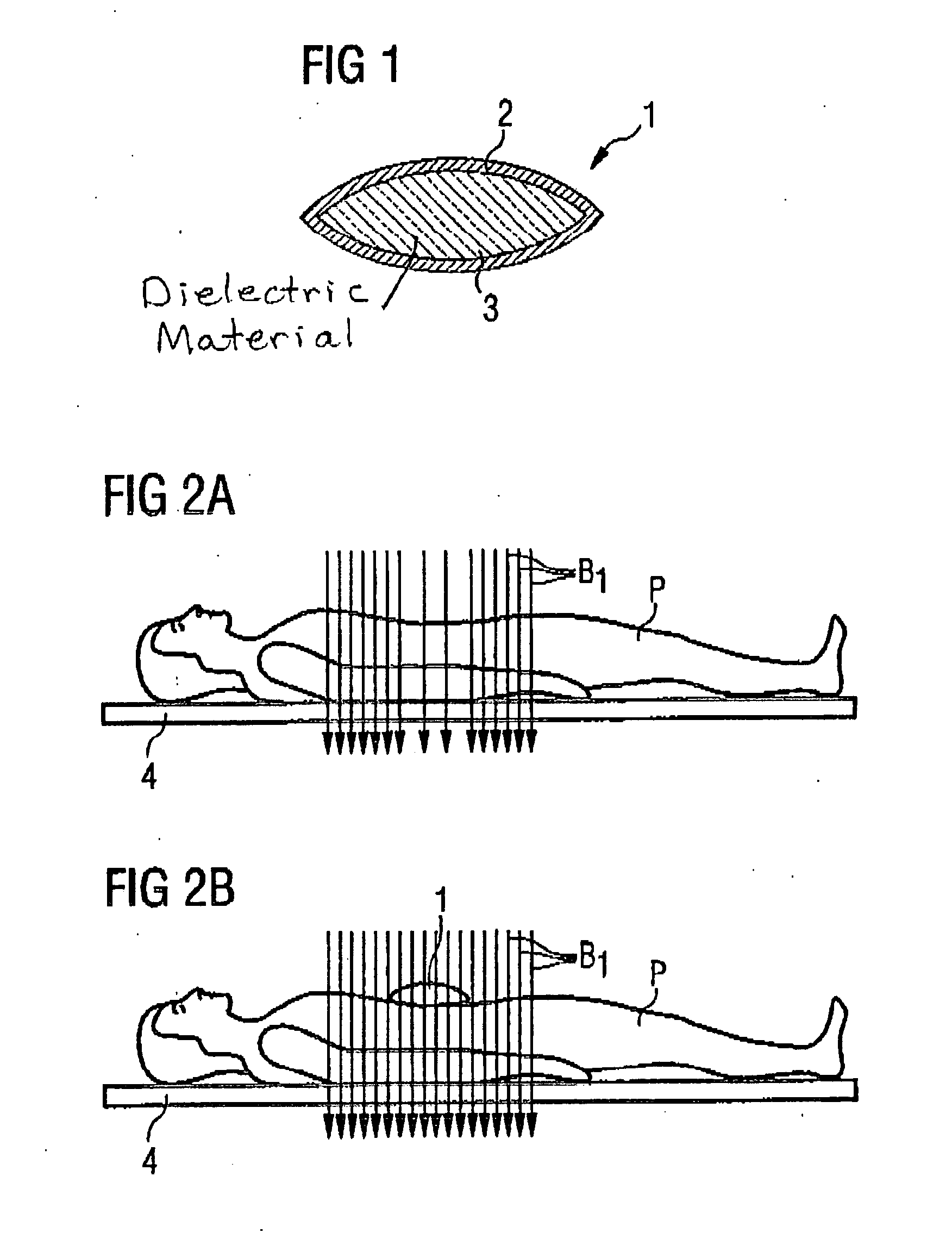
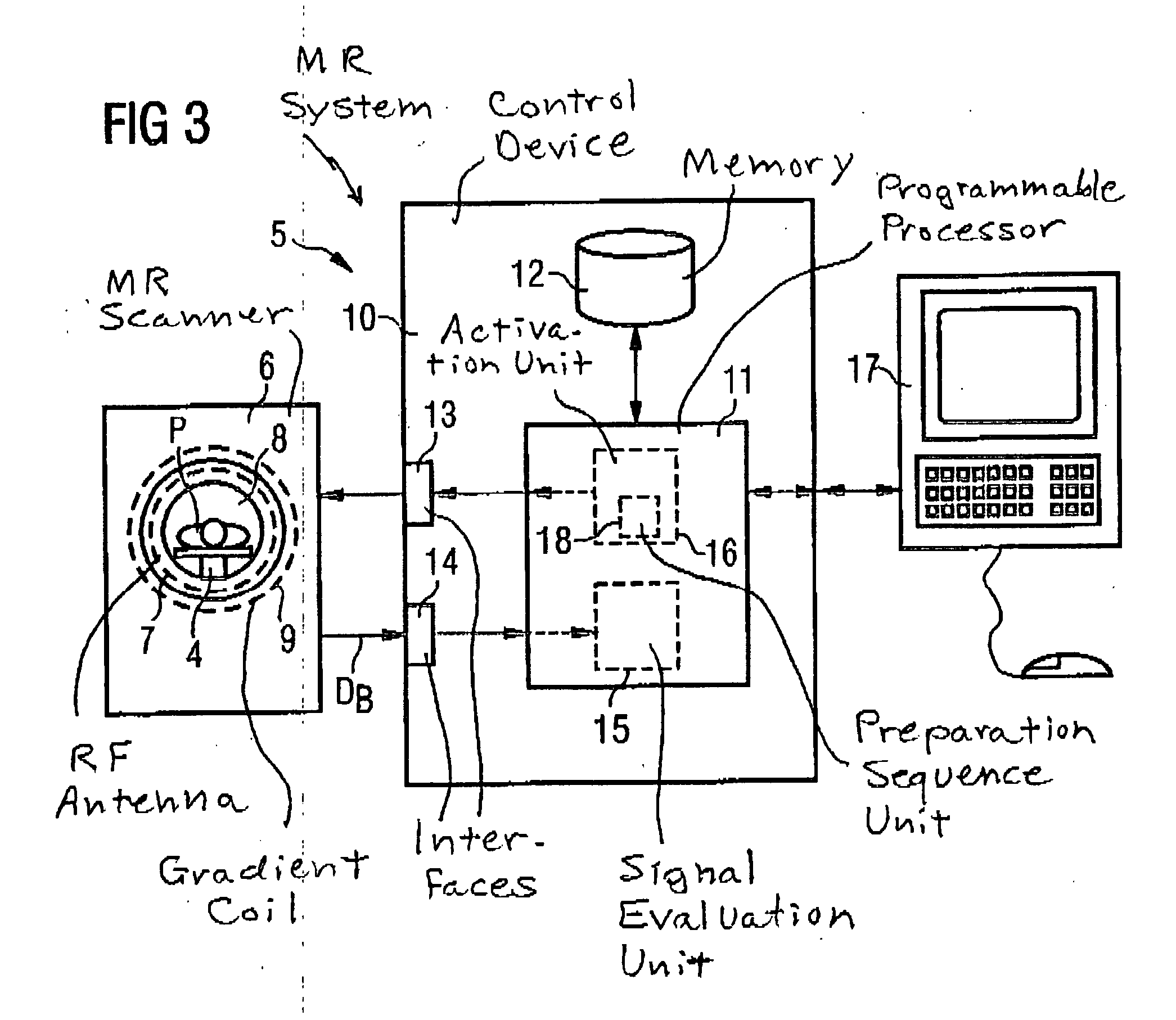
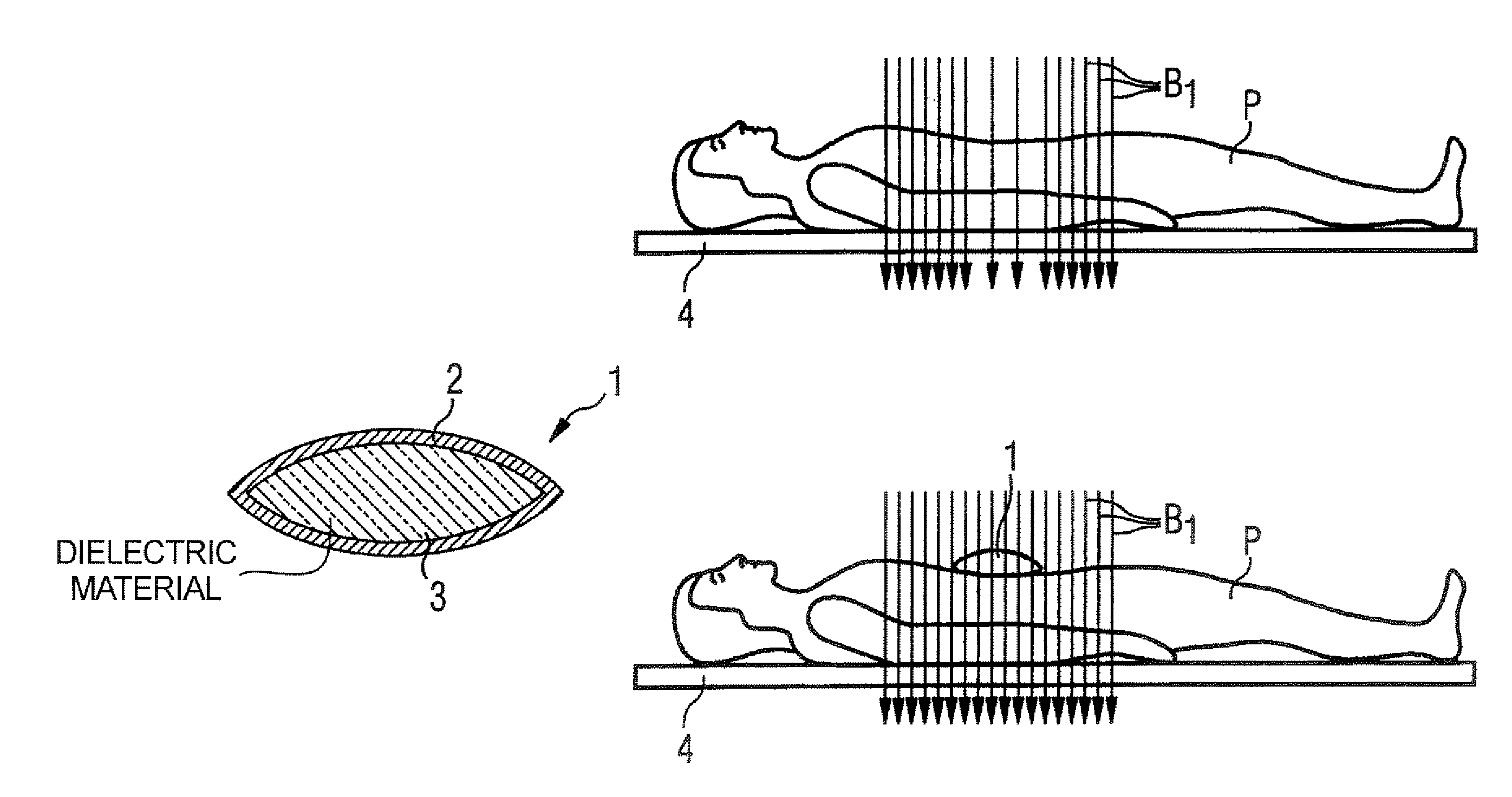
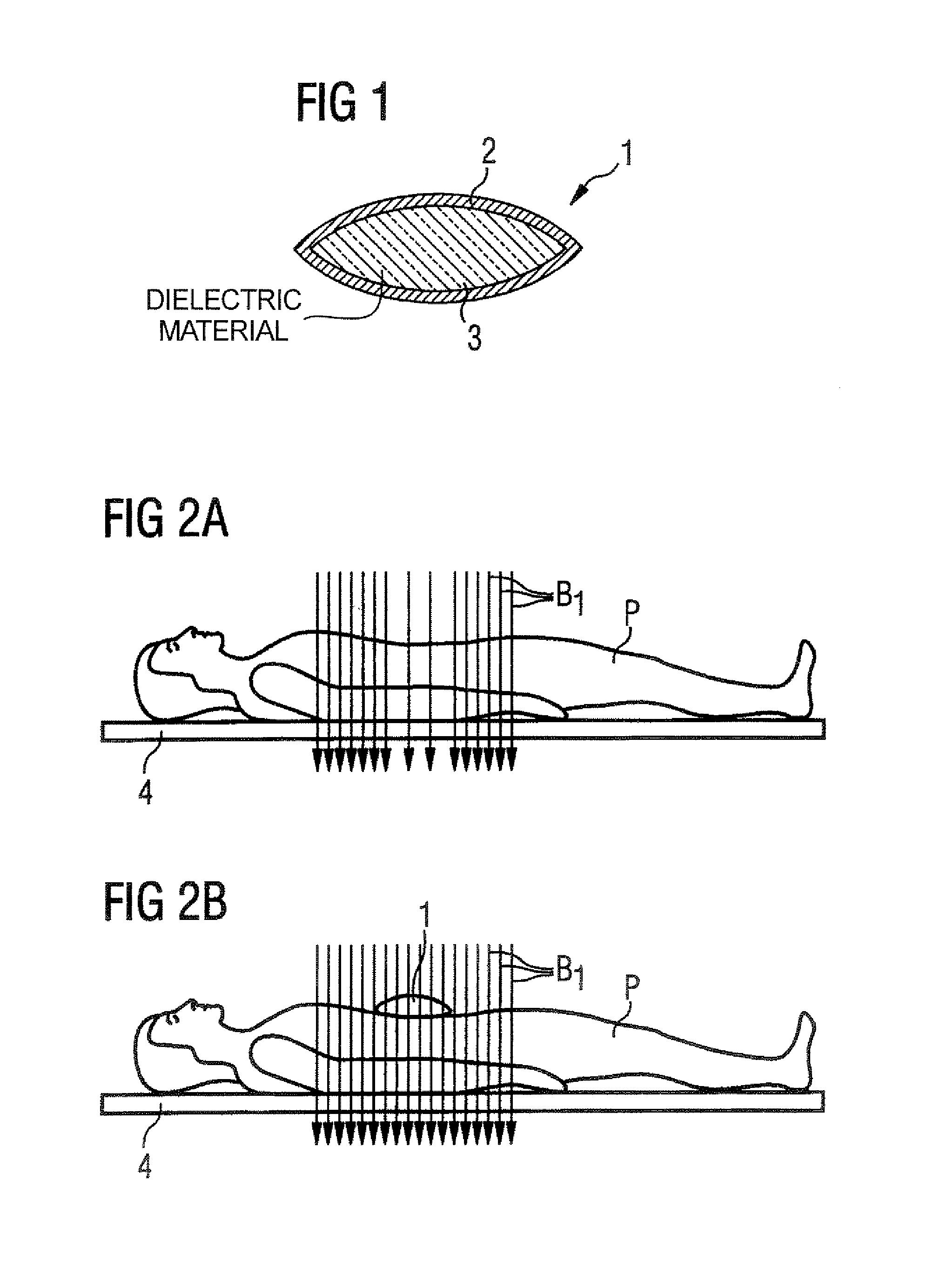
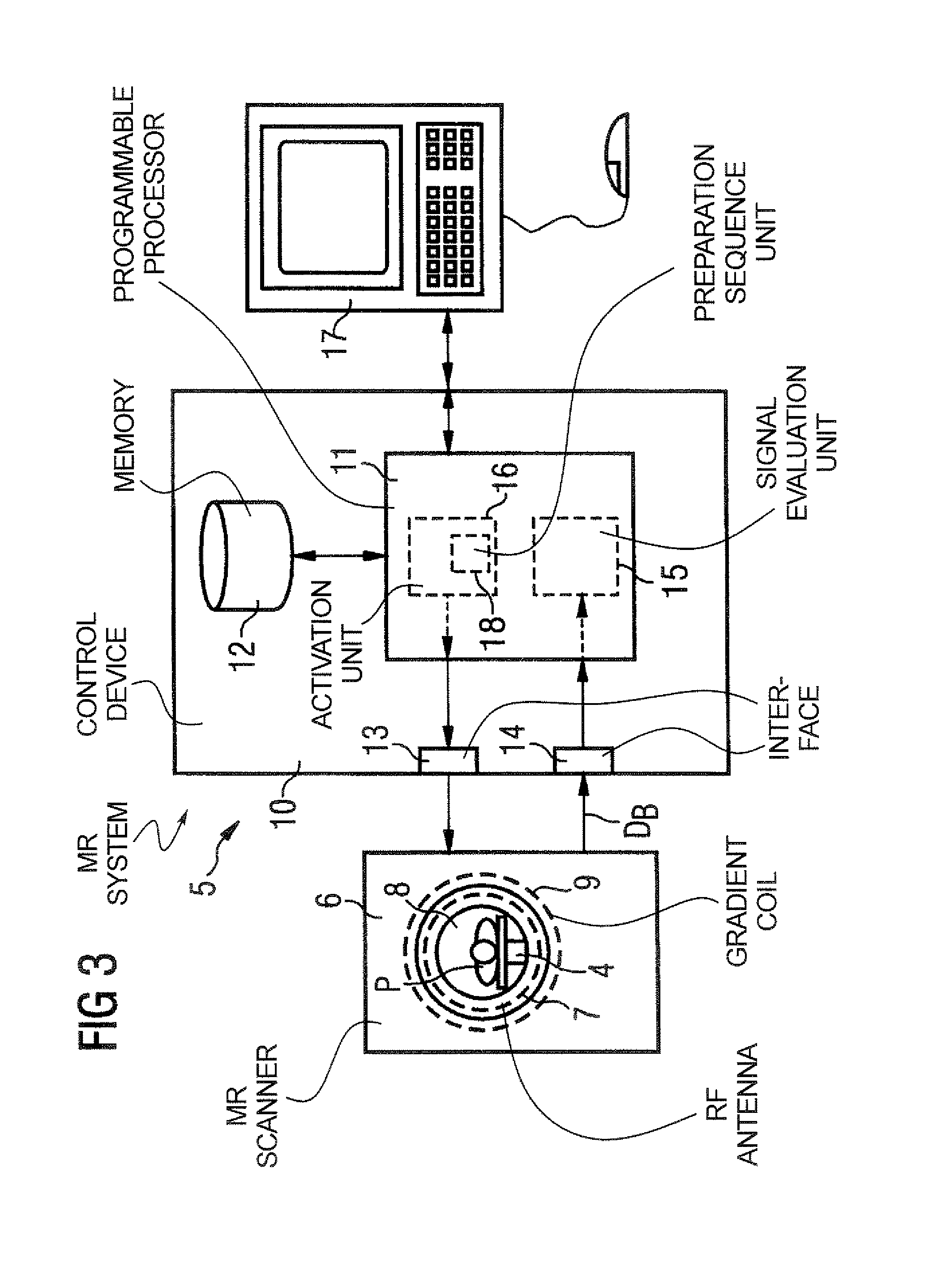
Method, dielectric element, and MR system for generating an MR exposure
ActiveUS20050194974A1Reduce exposureMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDielectricElectricity
For generating of magnetic resonance exposures of an examination subject, a dielectric element with high dielectric constant is positioned on the examination subject to locally influence the B1 field distribution, the dielectric element being formed primarily of material whose magnetic resonance line(s) is / are shifted by at least a specific degree relative to the magnetic resonance line of water protons for a given magnetic field. In a measurement for generation of a magnetic resonance exposure a measurement sequence is used, such in the acquisition of the raw image data the dielectric material of the dielectric element supplies no signal contributions for the image generation and / or the signals caused by the dielectric material of the dielectric element can be separated from the signals caused by the examination subject.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic microstructures for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150377997A1Material nanotechnologyDiagnostic recording/measuringMRI contrast agentResonance
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance structure with a cavity or a reserved space that provides contrast and the additional ability to frequency-shift the spectral signature of the NMR-susceptible nuclei such as water protons by a discrete and controllable characteristic frequency shift that is unique to each MRS design. The invention also relates to nearly uniform solid magnetic resonance T2* contrast agents that have a significantly higher magnetic moment compared to similarly-sized existing MRI contrast agents. The invention also relates to a magnetic resonance sensor that alters it shape in response to a condition of an environment such that the condition may be detected.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Evaluation method for clay and manufacturing method of extrusion molded body
ActiveUS20180304494A1Improve yieldUniform propertyInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationSpinsMixed states
A method performs evaluation of properties of a clay rod, with which a honeycomb structural body is produced. The method mixes raw materials to produce a clay, and extrudes the clay and compresses the extruded clay to produce a clay rod. The method performs NMR to detect at least one of a T1 relaxation time and a T2 relaxation time in each of a normal part and an abnormality part extracted from the clay rod. Each of the T1 relaxation time and the T2 relaxation time corresponds to a relaxation time of nuclear spins of water protons magnetically excited in each of the normal part and the abnormality part. The method performs the evaluation of uniformity of a mixed state and a compression state of the clay rod based on a difference in T1 relaxation time and T2 relaxation time between the normal part and the abnormality part.
Owner:DENSO CORP
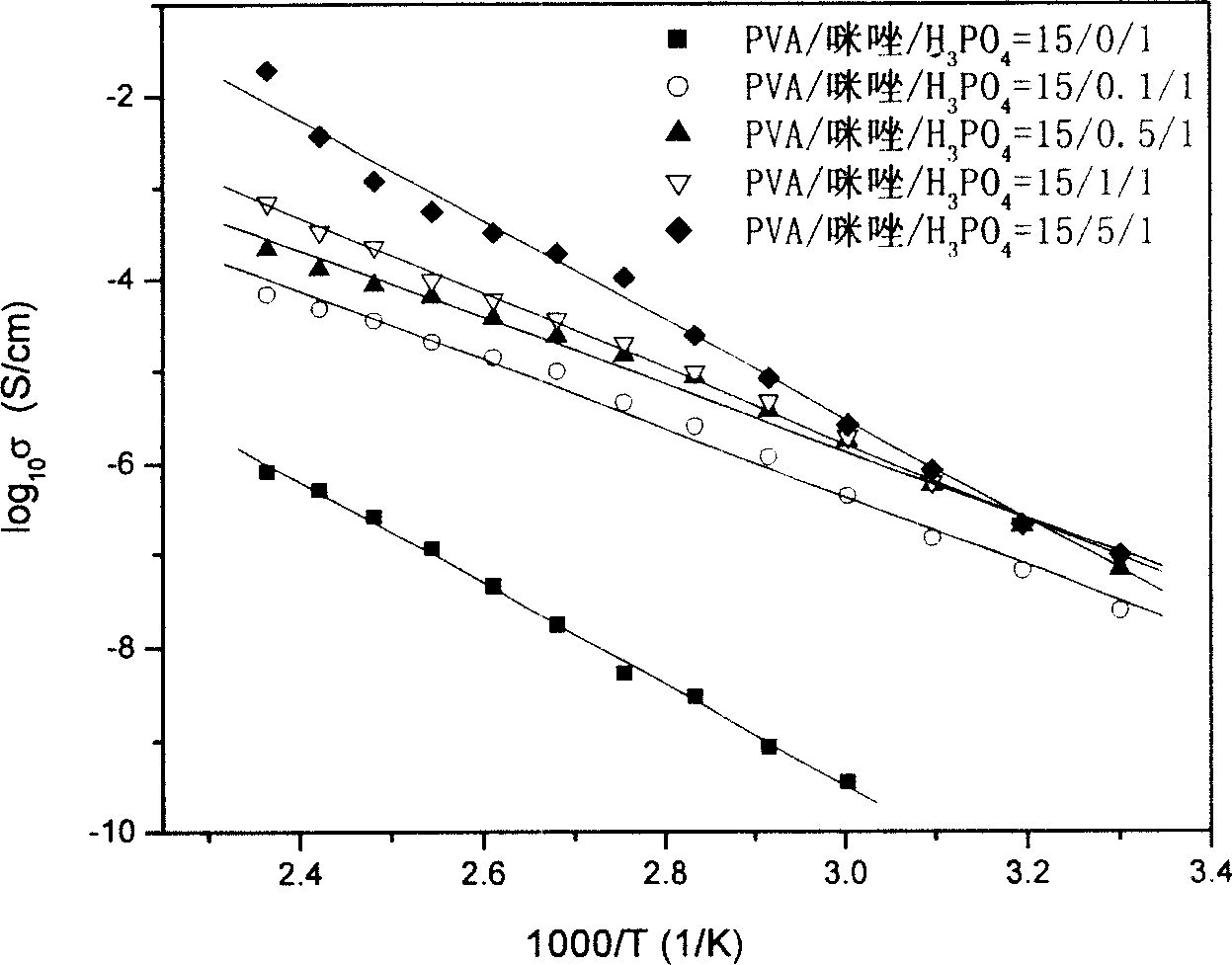
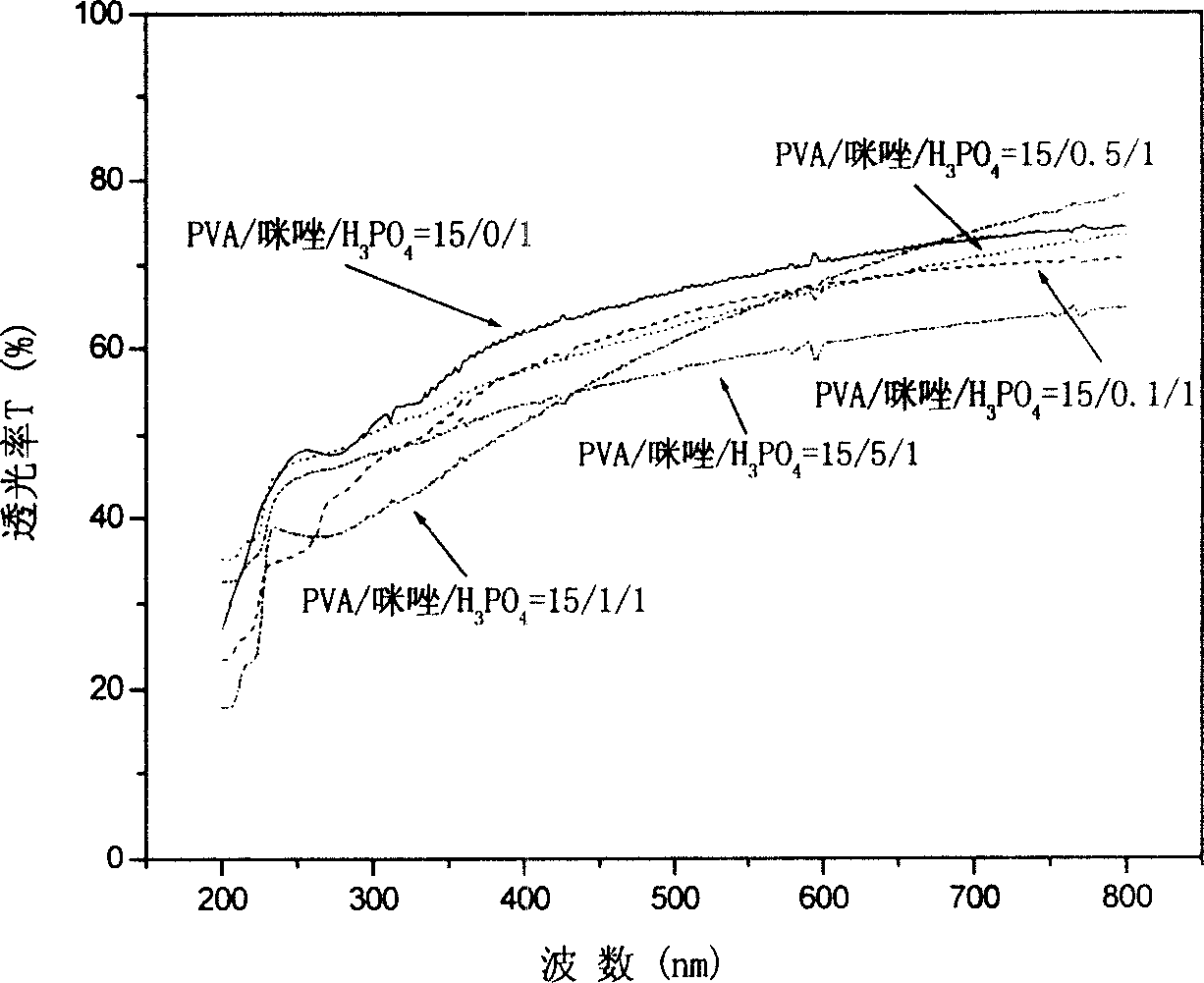
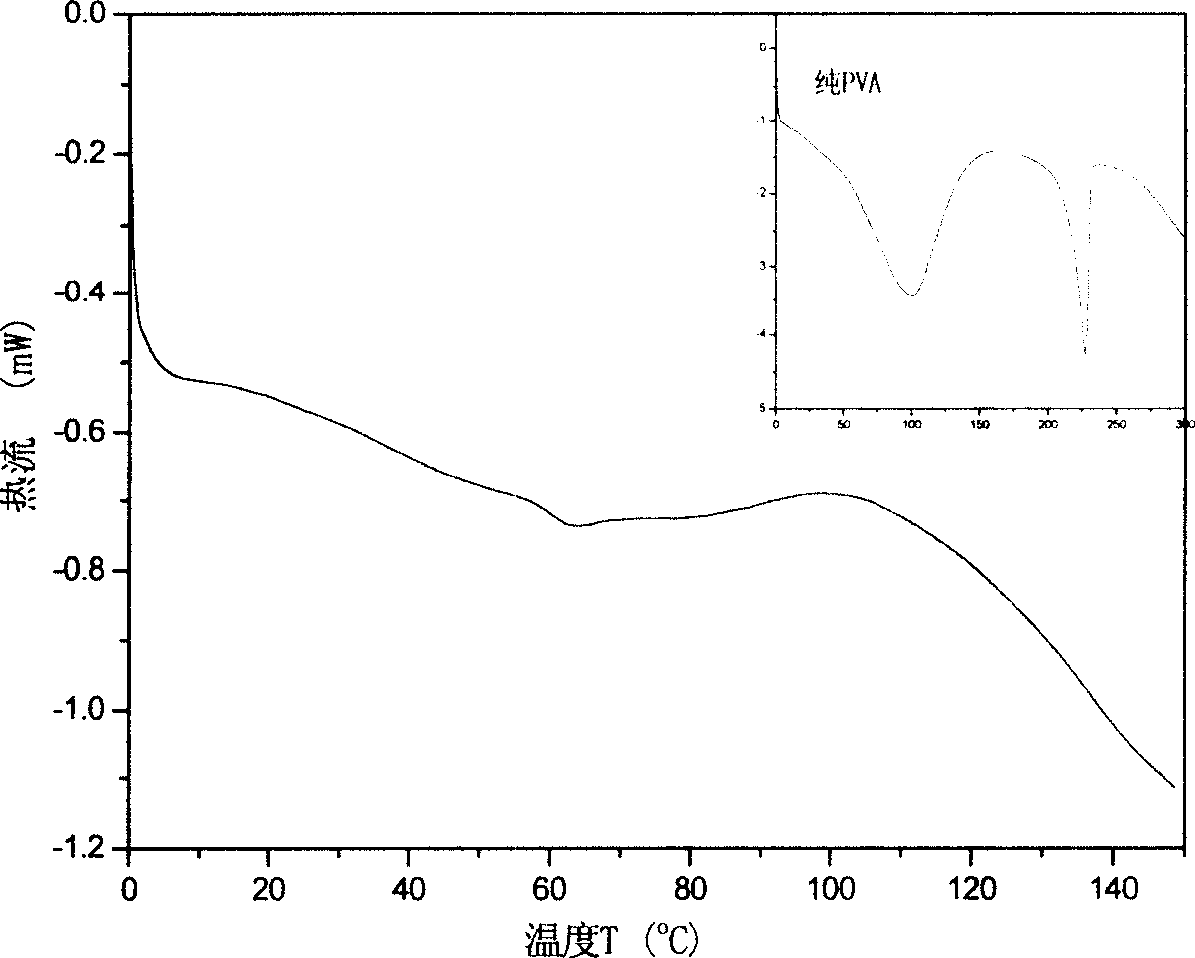
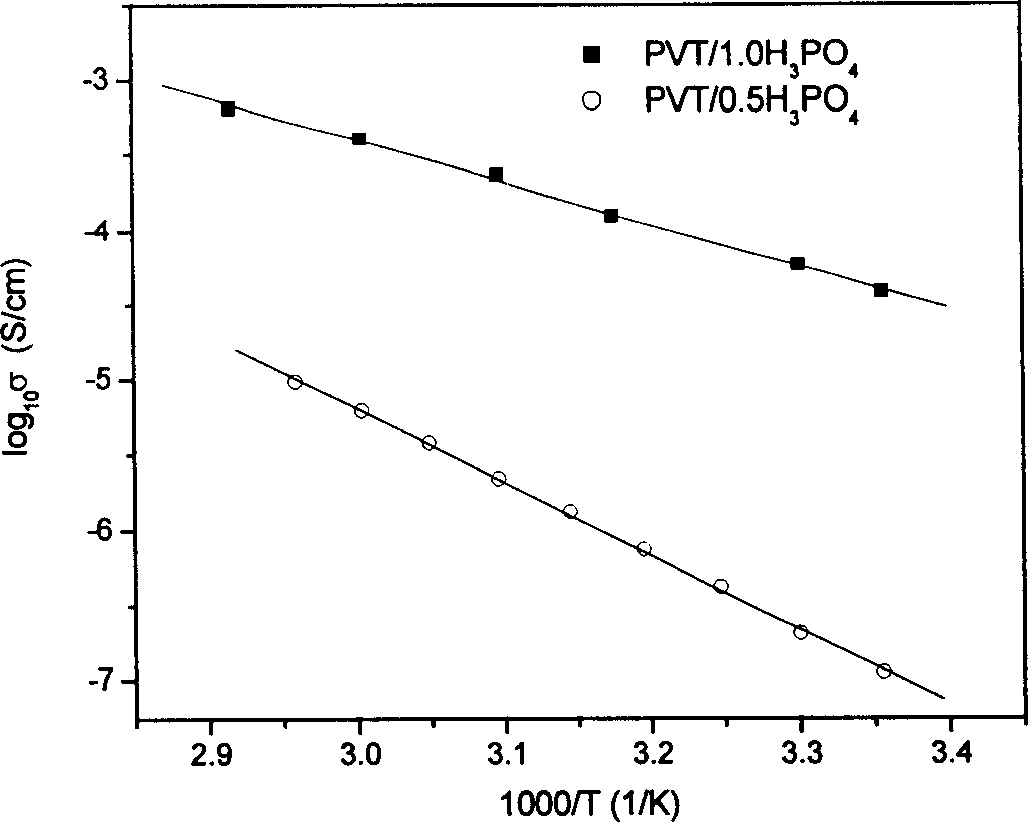
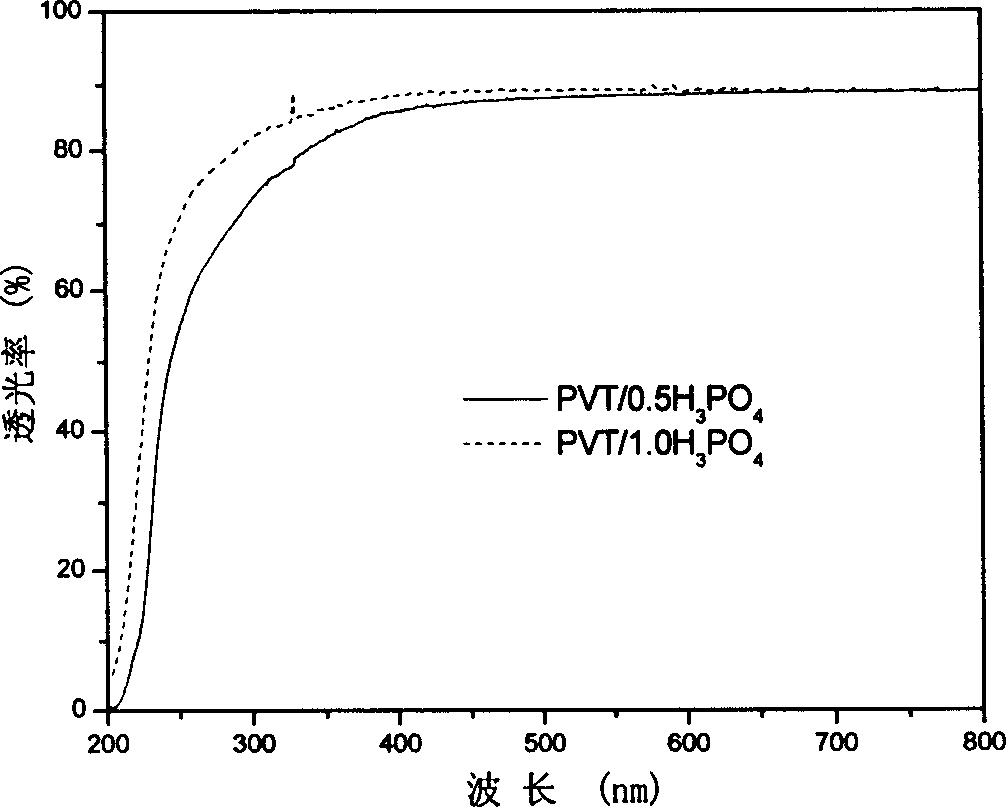
Transparent polymer non-aqueous proton conducting material and its preparing method
The present invention belongs to macromolecule material and electrochemistry technological fields, concretely relating to a kind of transparent polymer non-water proton electric material based on polyvinyl alcohol and nitrogen heterocyclic compound and its producing method. Its characteristic is: add nitrogen heterocyclic compound into normal polyvinyl alcohol / acid compound proton electric system, then its proton conductivity can improve 2 - 4 magnitudes. The light penetrating rate of polyvinyl alcohol / acid / nitrogen heterocyclic compound composite membrane is almost the same as normal polyvinyl alcohol / acid compound proton electric membrane in certain content bound of nitrogen heterocyclic compound. It can be widely used in various entire solid state electrochemistry apparatuses.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
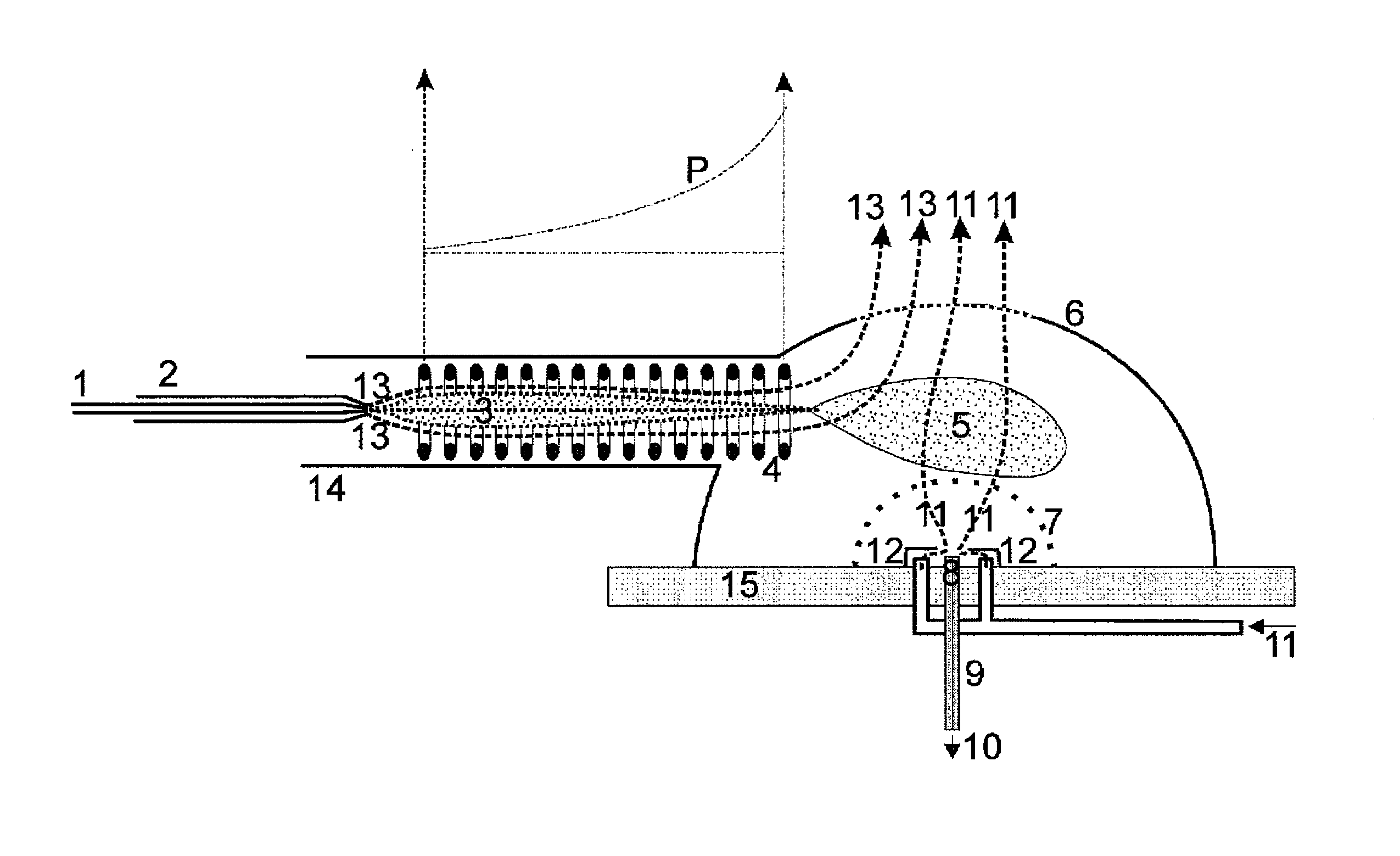
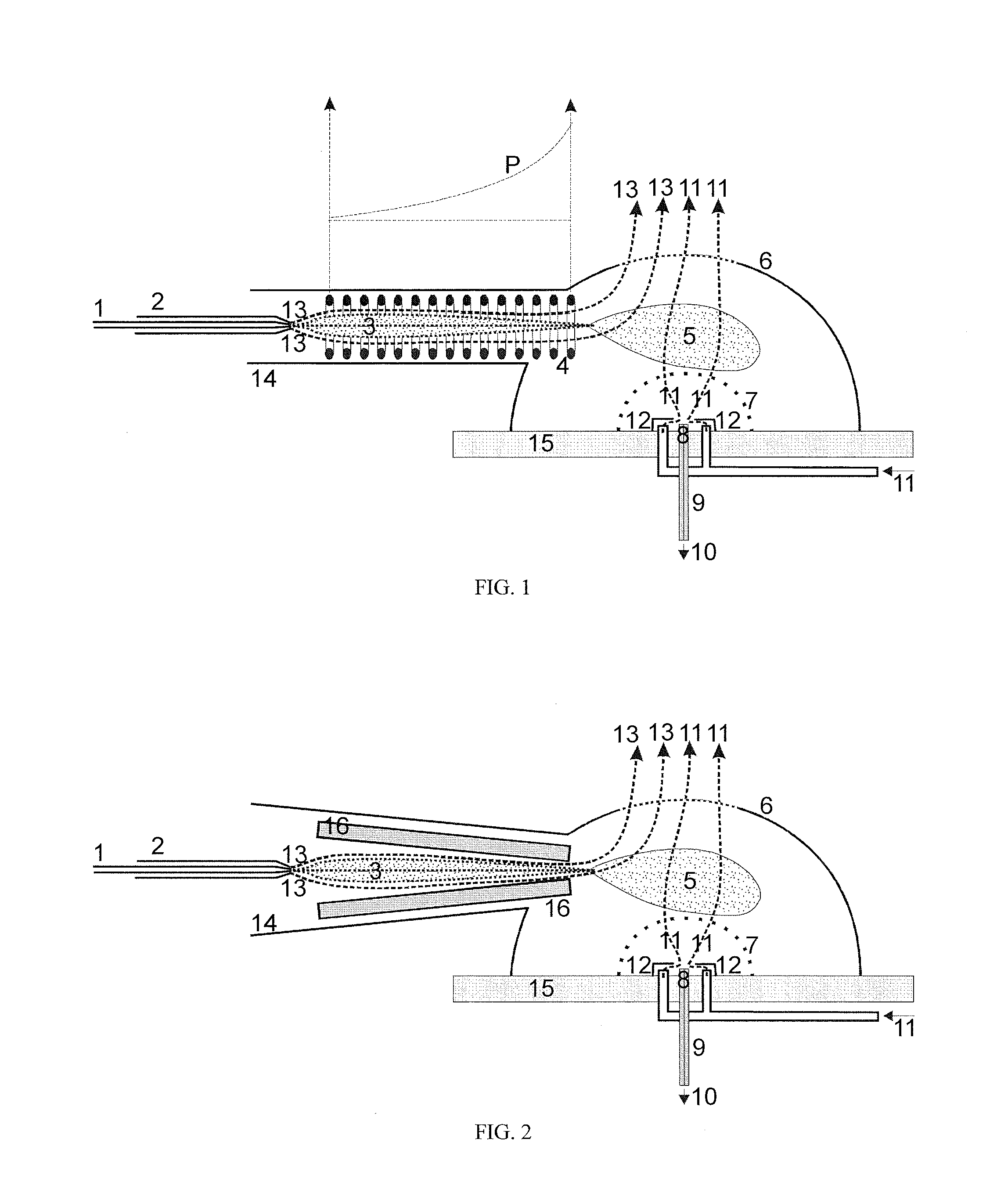
Guiding charged droplets and ions in an electrospray ion source
ActiveUS20100193679A1More time to vaporizeLong retentionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAnalyteWater proton
Charged spray droplets are guided in a pseudopotential distribution generated by audio frequency voltages at electrodes of a guiding device, focusing the spray droplets toward the axis. An axial electric field profile and an axial flow profile of a drying gas in the guiding device allow the drift of different-sized droplets to be controlled in the longitudinal direction of the guiding device, so that the droplets are roughly equal in size when they leave the guiding device and finally dry up shortly after leaving. As a result, the ions are formed in a relatively small spatial region. Electrostatic potentials guide the analyte ions from this small spatial region to the entrance aperture of the inlet capillary; during this process, very light ions, especially protons and water-proton complexes, can be filtered out by a mobility filter.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
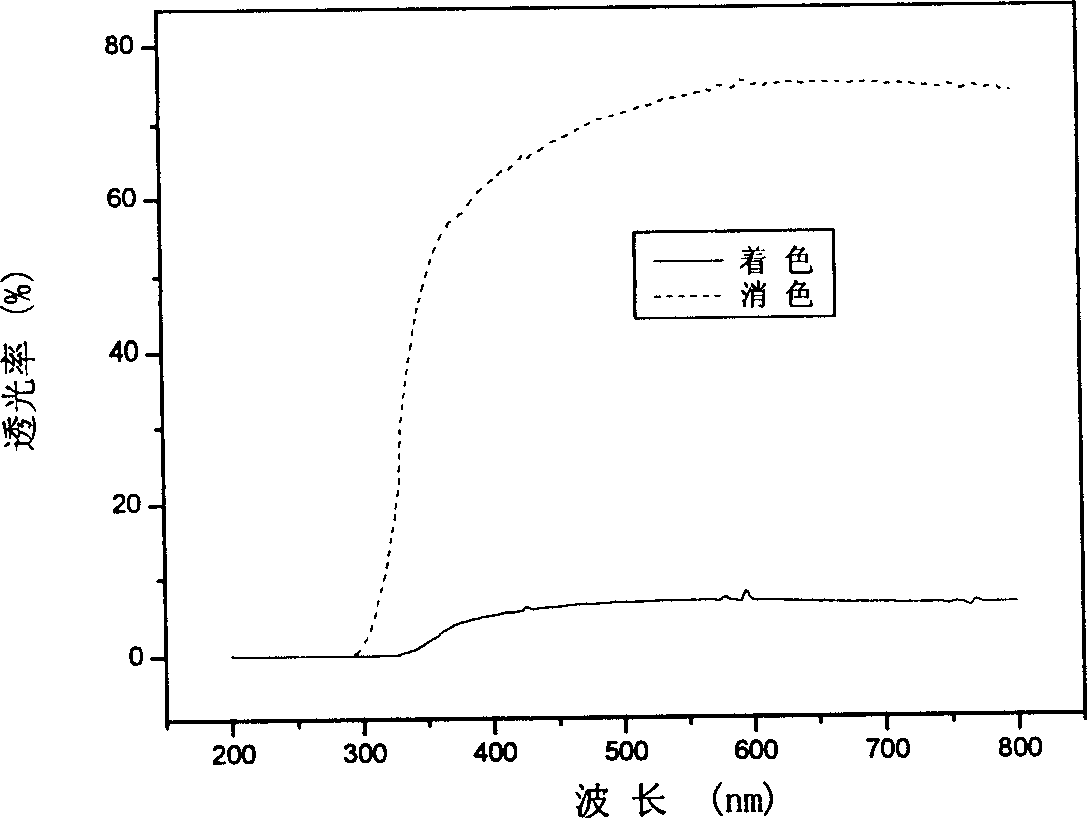
Transparent non-water proton conductive material of side group type azacyclic polymer and its preparing method
InactiveCN1749351AHigh transparencyEasy to packOrganic conductorsTenebresent compositionsConductive materialsElectrochemistry
The present invention belongs to the field of functional high molecular material and electrochemical material technology, and is especially a kind of transparent non-water conducting proton material, which is based on side group type azacyclic polymer and used for solid electrochromic device (ECD). Side group type azacyclic polymer is made to compound with Lewis acid component and small molecular azacyclic compound is added to obtain the novel solid polymer as non-water conducting proton material with relatively high proton conductivity and high transparency. The solid ECD with the material as conducting ion layer has easy filming, easy dispersing and easy device packaging, compared with traditional small molecular lithium salt and inorganic proton electrolyte. The solid ECD has excellent chromic effect and high chromic response, and is suitable for making great area electrochromic device.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Guiding charged droplets and ions in an electrospray ion source
ActiveUS8368012B2More time to vaporizeLong retentionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansCapillary TubingWater proton
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method for magnetic resonance imaging using inversion recovery with on-resonant water suppression including MRI systems and software embodying same
InactiveUS8054075B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic susceptibilityInversion recovery
Featured are methods for magnetic resonance imaging of a volume, such a volume having susceptibility-generating objects or interfaces having susceptibility mismatches therein. Such a method includes selectively visualizing one of susceptibility-generating objects or interfaces having susceptibility mismatches as hyperintense signals, where such visualizing includes controlling variable imaging parameters so as to control a geometric extent of a signal enhancing effect, m more particular aspects of the present invention, such selectively visualizing includes attenuating or essentially suppressing signals from fat and / or water, namely on-resonant water protons, so as to thereby enhance a signal(s) associated with magnetic susceptibility gradient(s). Also featured are MRI systems, apparatuses and / or applications programs for execution on a computer system controlling the MRI data acquisition process embodying such methods.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
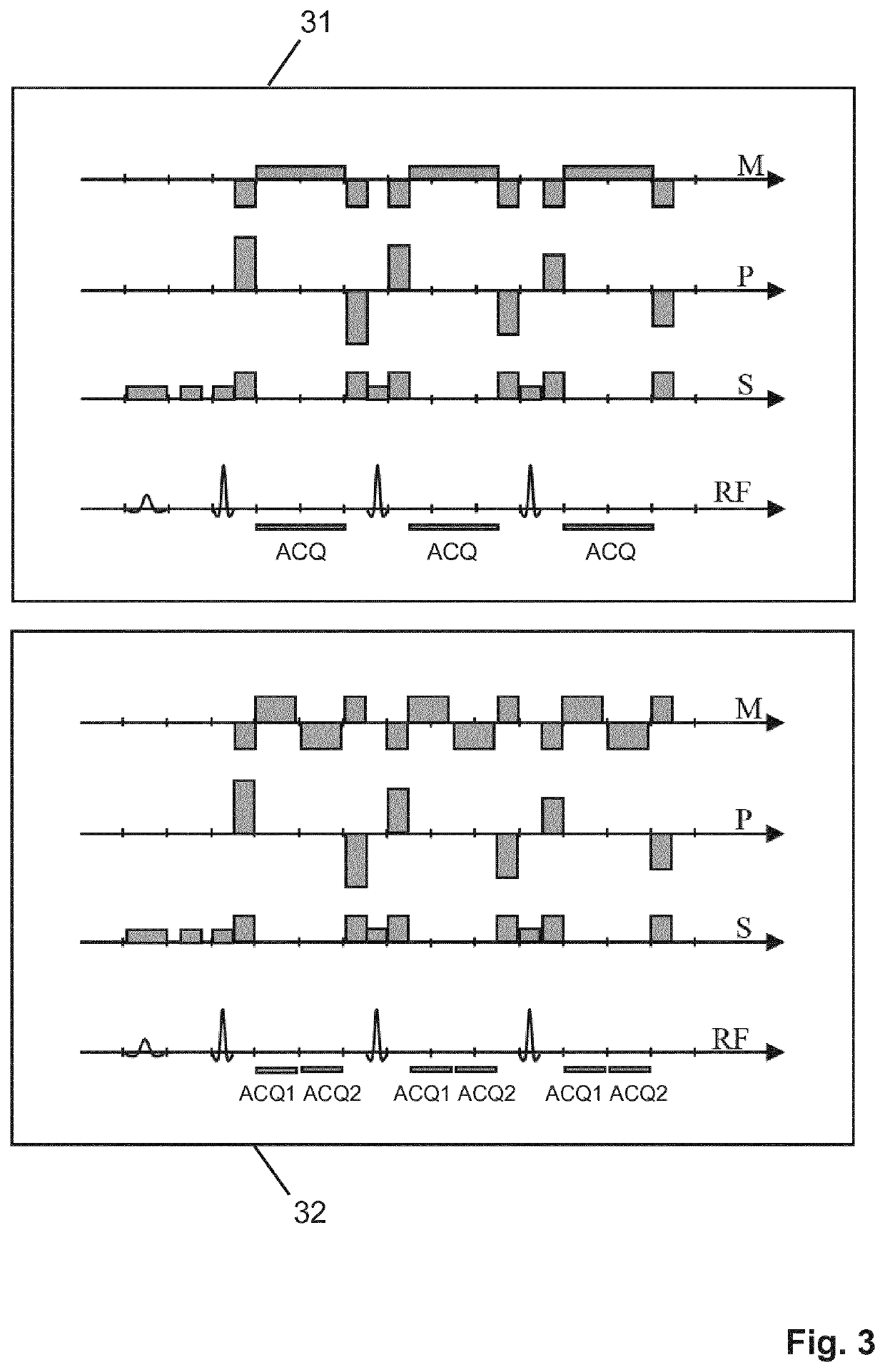
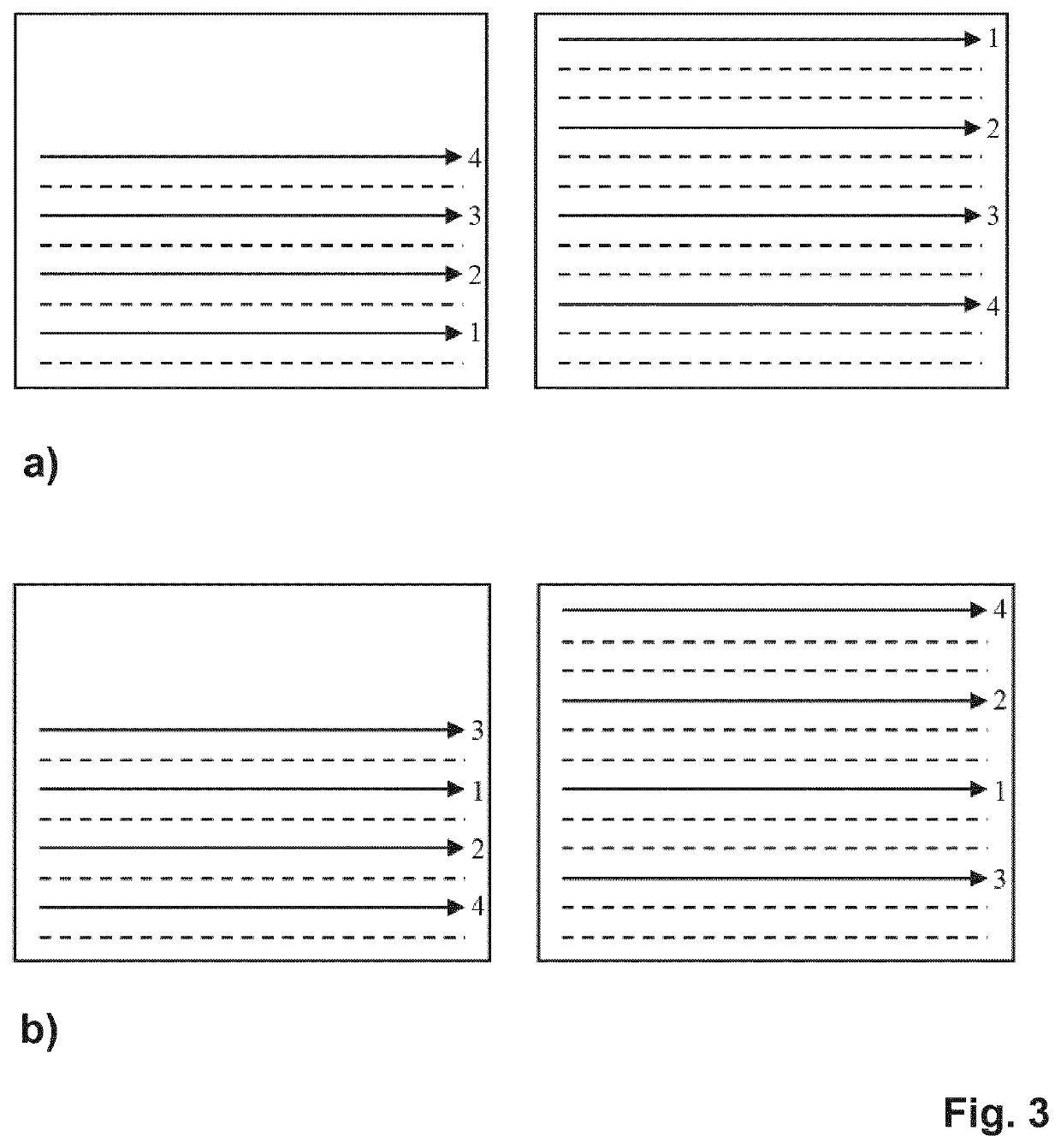
Dixon-type water/fat separation mr imaging
ActiveUS20200319280A1Low sampling efficiencyImprove sampling efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientRadio frequency
The invention relates to a method of Dixon-type MR imaging. The method comprises the steps of:—subjecting the object (10) to a first imaging sequence (31) comprising a series of refocusing RF pulses, wherein a single echo signal is generated in each time interval between two consecutive refocusing RF pulses,—acquiring the echo signals from the object (10) at a first receive bandwidth using unipolar readout magnetic field gradients,—subjecting the object (10) to a second imaging sequence (32), which comprises a series of refocusing RF pulses, wherein a pair of echo signals is generated in each time interval between two consecutive refocusing RF pulses,—acquiring the pairs of echo signals from the object (10) at a second receive bandwidth using bipolar readout magnetic field gradients, wherein the second receive bandwidth is higher than the first receive bandwidth, and—reconstructing a MR image from the acquired echo signals, whereby signal contributions from water protons and fat protons are separated. Moreover the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program to be run on a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dual-mode sensor for detecting Cd<2+> based on magnetic nanoparticles and preparation method of dual-mode sensor
InactiveCN104535601AImplementing Dual Mode DetectionChange relaxation timeColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceAnti jammingDual mode
The invention belongs to the technical field of rapid detection, and particularly relates to a dual-mode sensor for detecting Cd<2+> based on magnetic nanoparticles and a preparation method of the dual-mode sensor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a specific receptor unit, preparing Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles, and finally dissolving the specific receptor unit, mPEG-SH and anhydrous sodium carbonate into water; and adding the mixture to an Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticle solution, and carrying out shaking table oscillating reaction for 10-20 hours. According to the dual-mode sensor disclosed by the invention, the disperse state of the nanoparticles changes into an aggregation state from a dispersed state in the presence of Cd<2+> ions. The relaxation time of water protons around the nanoparticles is changed by the change of the state; and due to the presence of gold nanoparticles, ultraviolet absorption spectrums of the nanoparticles change, so that the Cd<2+> is detected by two methods, namely an ultraviolet absorption detection method and a nuclear magnetic resonance method; and the dual-mode sensor has the advantages of high accuracy, high anti-jamming capability and high selectivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Medicinal ultrahigh-field nuclear-magnetism contrast agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104548144AEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsSide effectBiocompatibility Testing
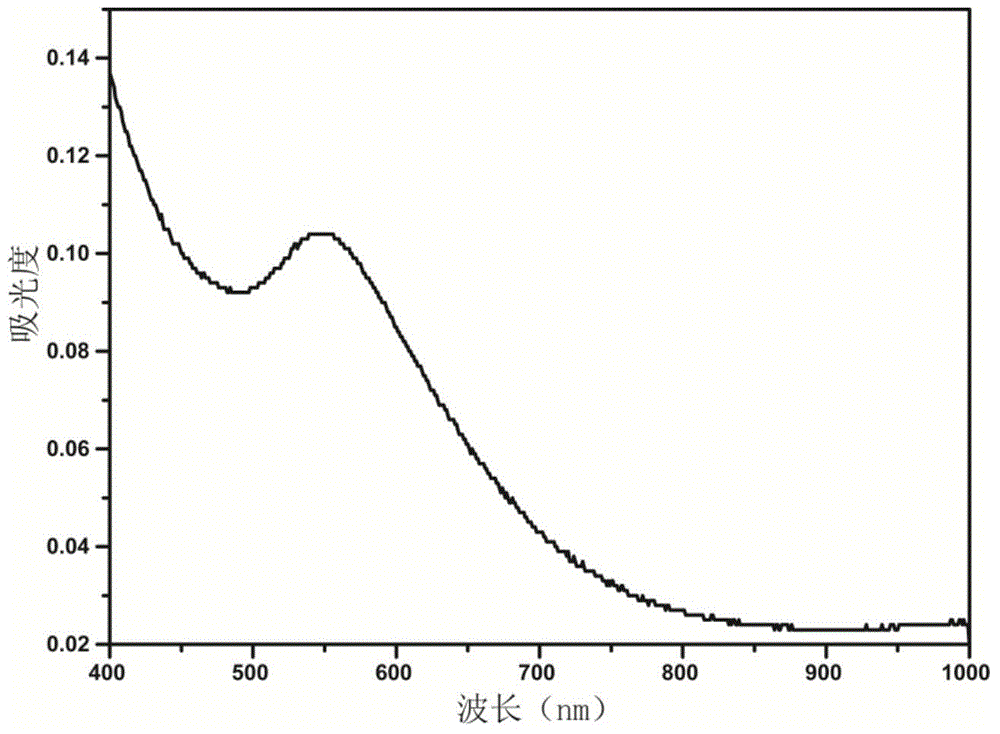
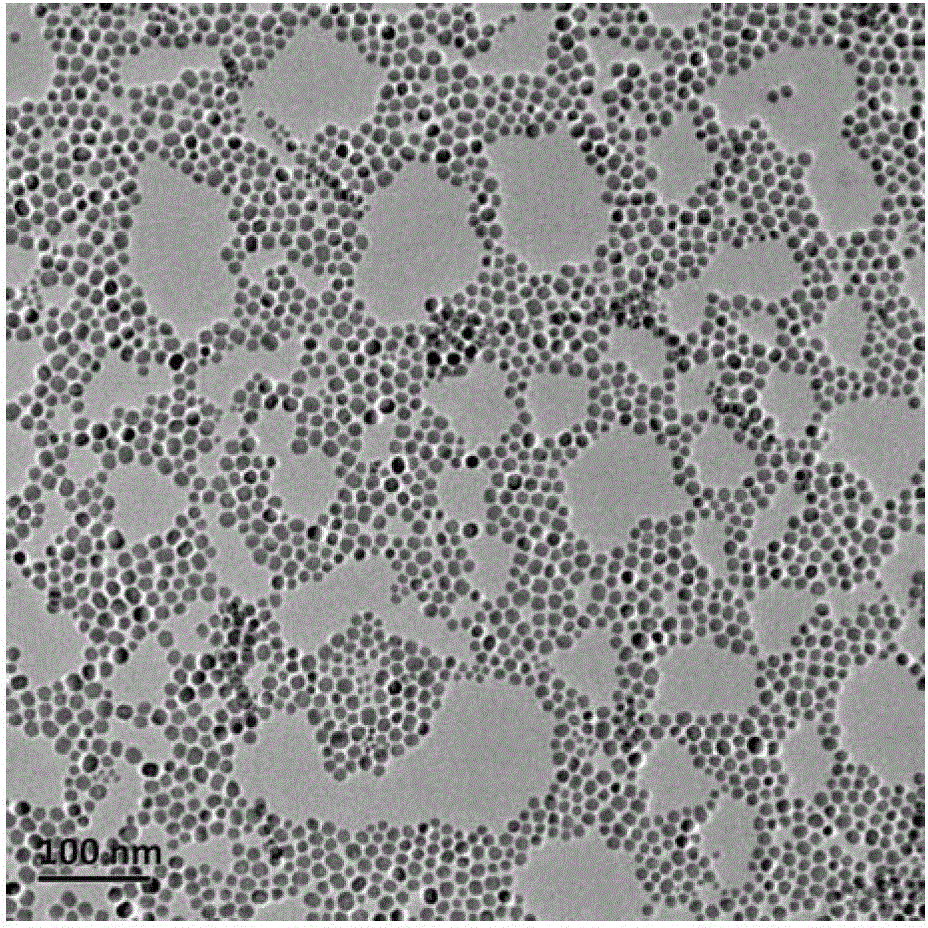
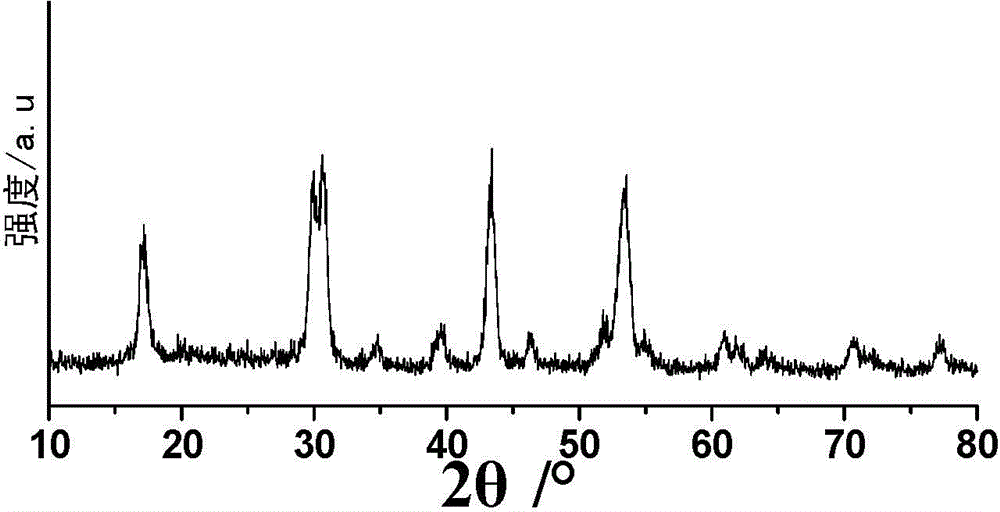
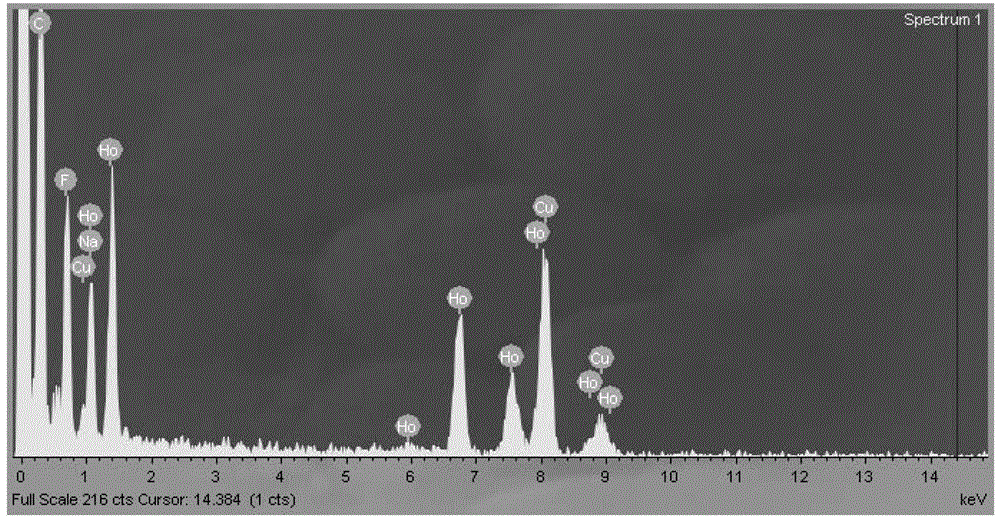
The invention relates to a medicinal ultrahigh-field nuclear-magnetism contrast agent and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal ultrahigh-field nuclear-magnetism contrast agent is NaHoF4 nano-particles modified by phospholipid PEG (polyethylene glycol). A paramagnetic element Ho in NaHoF4 has the maximal effective electron magnetic moment and can be used for effectively changing transverse relaxation time of water protons to produce a T2-weighted imaging effect which is sharply increased with the increase of filed strength and can be used for clinical ultrahigh-field nuclear-magnetism contrast imaging in the future. Moreover, the phospholipid PEG is utilized to perform hydrophilic modification on NaHoF4 particles, so that the biocompatibility is increased, the toxic or side effects are lowered and the blood circulation is promoted. The preparation method is convenient to modify, efficient and beneficial to further grafting biological ligand subsequently.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method, dielectric element, and MR system for generating an MR exposure
ActiveUS7224165B2Reduce exposureMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDielectricElectricity
For generating of magnetic resonance exposures of an examination subject, a dielectric element with high dielectric constant is positioned on the examination subject to locally influence the B1 field distribution, the dielectric element being formed primarily of material whose magnetic resonance line(s) is / are shifted by at least a specific degree relative to the magnetic resonance line of water protons for a given magnetic field. In a measurement for generation of a magnetic resonance exposure a measurement sequence is used, such in the acquisition of the raw image data the dielectric material of the dielectric element supplies no signal contributions for the image generation and / or the signals caused by the dielectric material of the dielectric element can be separated from the signals caused by the examination subject.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic microstructures for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS10215825B2Material nanotechnologyDiagnostic recording/measuringMRI contrast agentFrequency shift
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance structure with a cavity or a reserved space that provides contrast and the additional ability to frequency-shift the spectral signature of the NMR-susceptible nuclei such as water protons by a discrete and controllable characteristic frequency shift that is unique to each MRS design. The invention also relates to nearly uniform solid magnetic resonance T2* contrast agents that have a significantly higher magnetic moment compared to similarly-sized existing MRI contrast agents. The invention also relates to a magnetic resonance sensor that alters it shape in response to a condition of an environment such that the condition may be detected.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
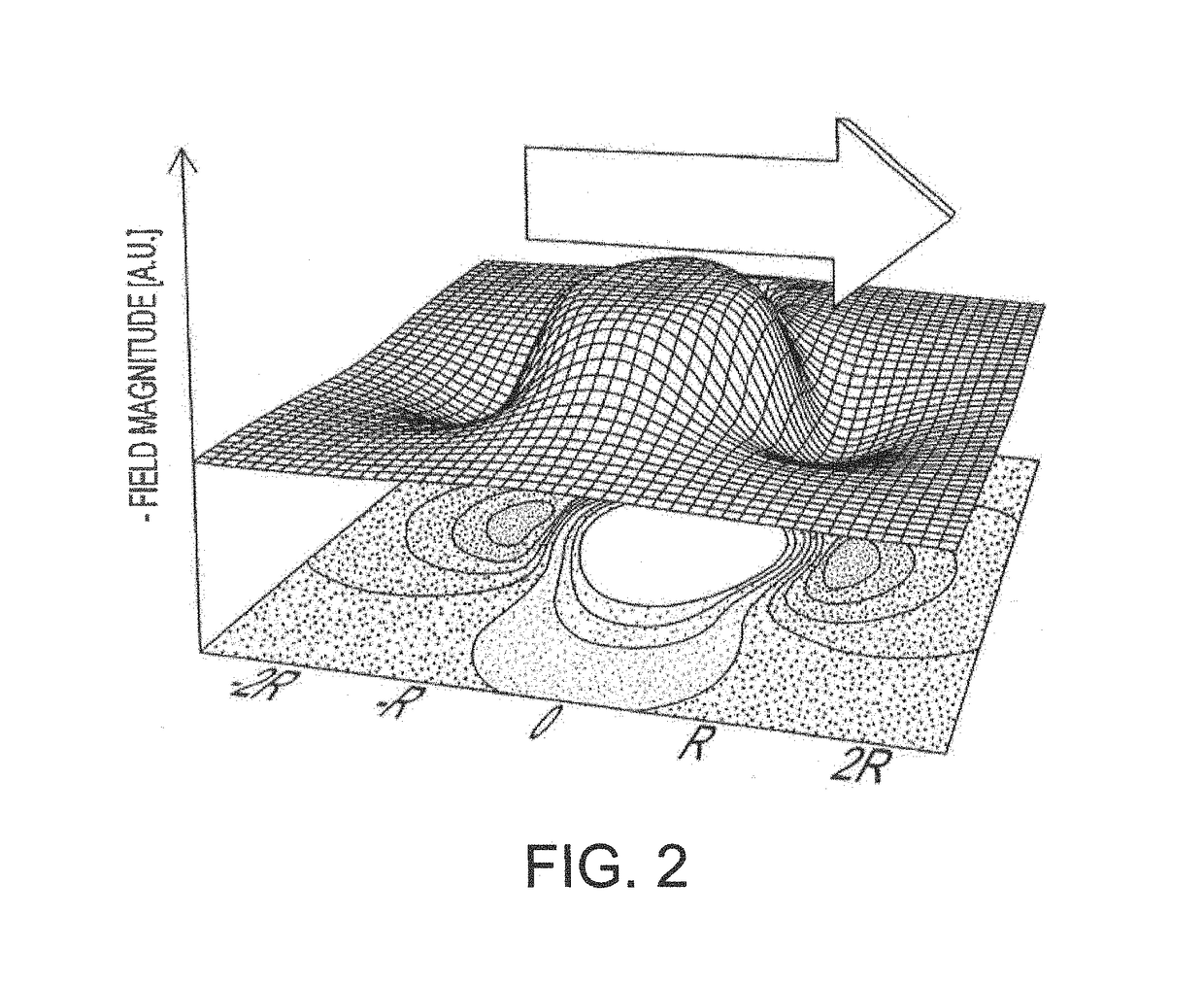
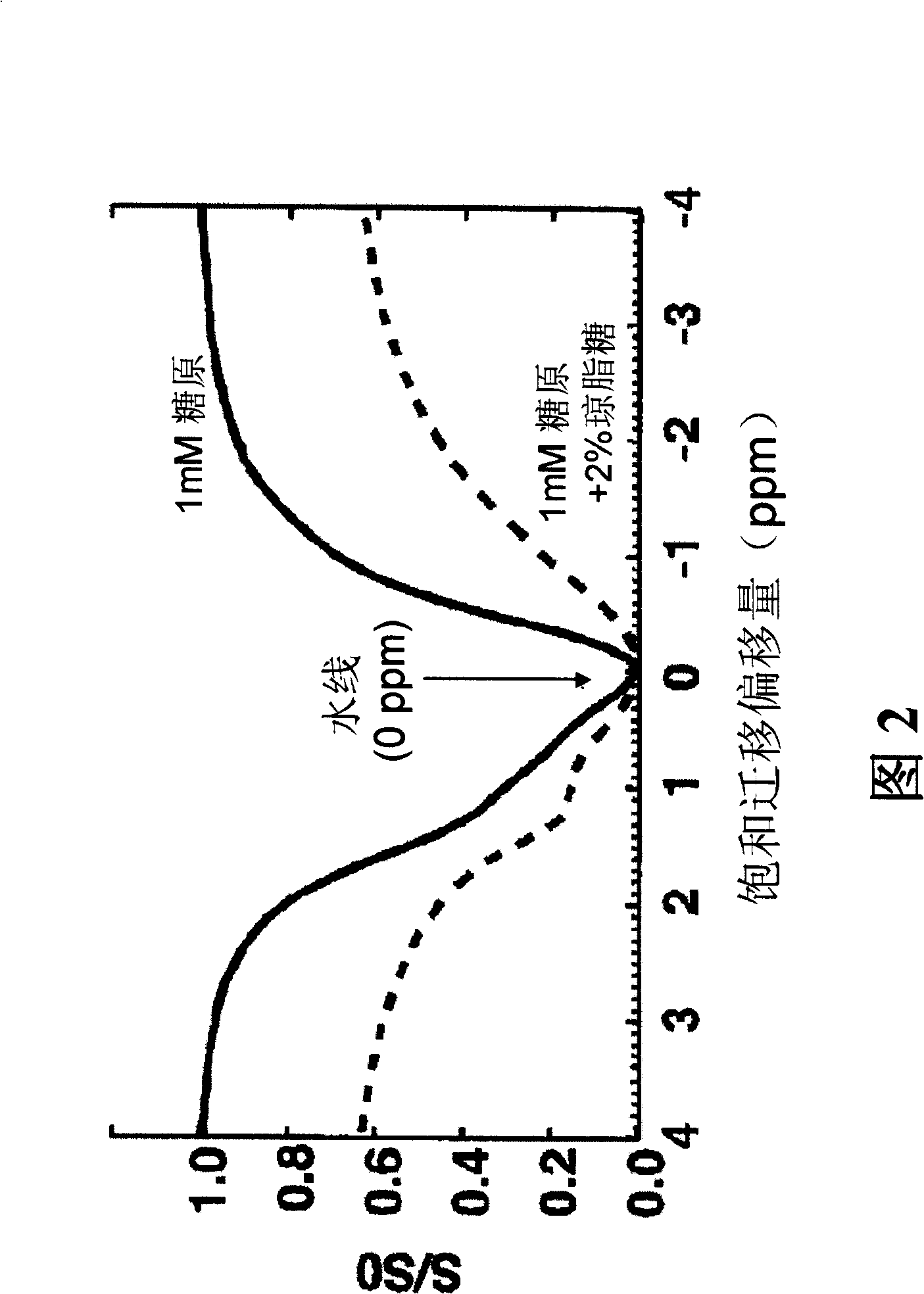
Non-invasive MRI measurement of tissue glycogen
InactiveCN101356447AIncrease signal strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonanceGlucose polymers
In a method for deriving information about a selected monosaccharide or polysaccharide such as glucose or glycogen, a selected modification such as saturation is made of magnetic resonance at a magnetic resonance frequency of protons of hydroxyl groups of the selected monosaccharide or polysaccharide. Probative water proton magnetic resonance data are acquired while the selected modification is substantially in effect. Information is derived about concentration or density of the selected monosaccharide or polysaccharide based at least on the probative water proton magnetic resonance data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Magnetic microstructures for magnetic resonance imaging
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE COMMERCE +1
Mr imaging with dixon-type water/fat separation
ActiveUS20190310336A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproved noise propagationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNoise propagationWater proton
The invention relates to a method of Dixon-type MR imaging. It is an object of the invention to provide a method that enables Dixon water / fat separation with high SNR and with improved noise propagation in the water / fat separation. The method comprises the steps of: —subjecting an object (10) to a first imaging sequence, which generates a number of differently phase encoded first MR echo signals at a first echo time, such that contributions from MR signals emanating from water protons and MR signals emanating from fat protons to the first MR echo signals are essentially in phase, —acquiring the first MR echo signals using a first signal receiving bandwidth, —subjecting the object (10) to a second imaging sequence which generates a number of differently phase encoded second MR echo signals at a second echo time, such that contributions from MR signals emanating from water protons and MR signals emanating from fat protons to the second MR echo signals are at least partially out of phase, —acquiring the second MR echo signals using a second signal receiving bandwidth which is larger than the first receiving bandwidth, wherein the number of phase encodings of the first imaging sequence is smaller than the number of phase encodings of the second imaging sequence, and —reconstructing a MR image from the first and second MR echo signals, whereby signal contributions from water protons and fat protons are separated. Moreover the invention relates to a MR device and to a computer program to be run on a MR device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
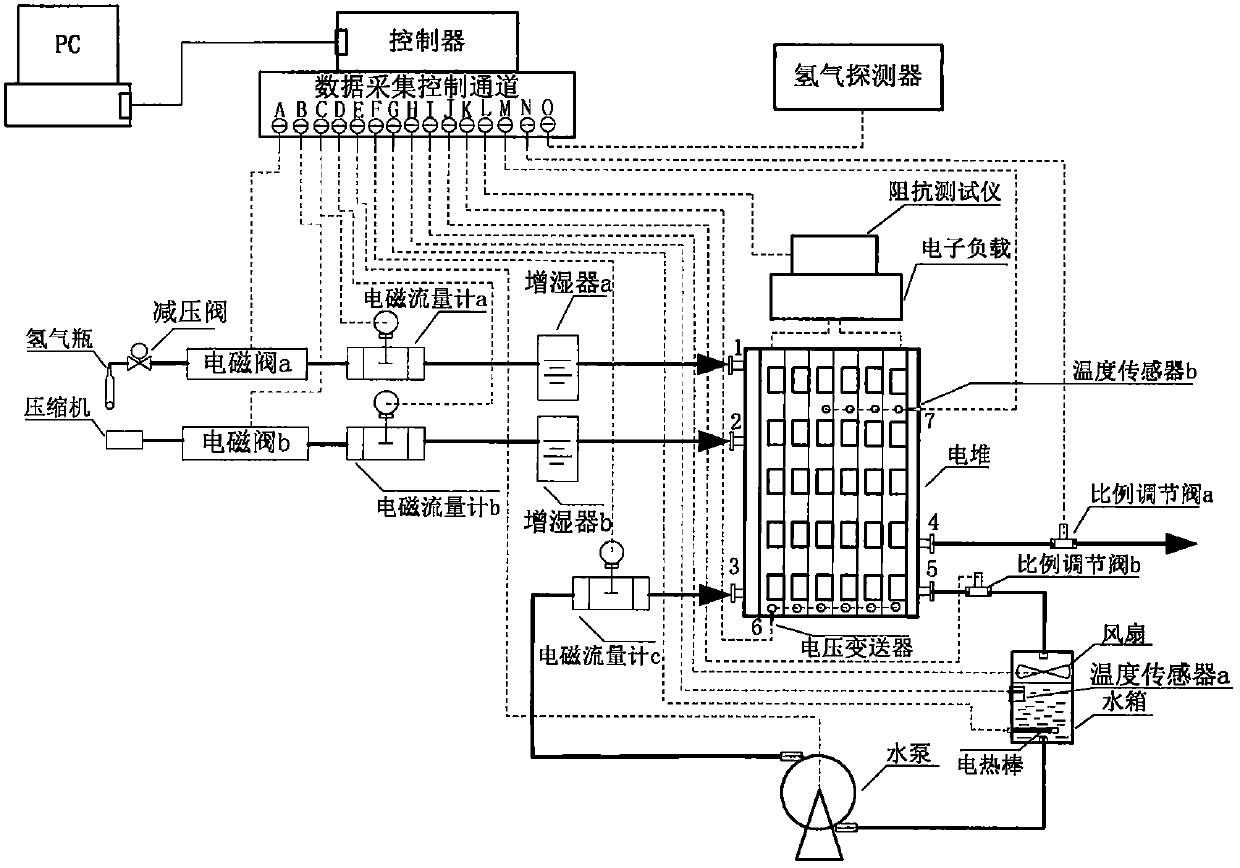
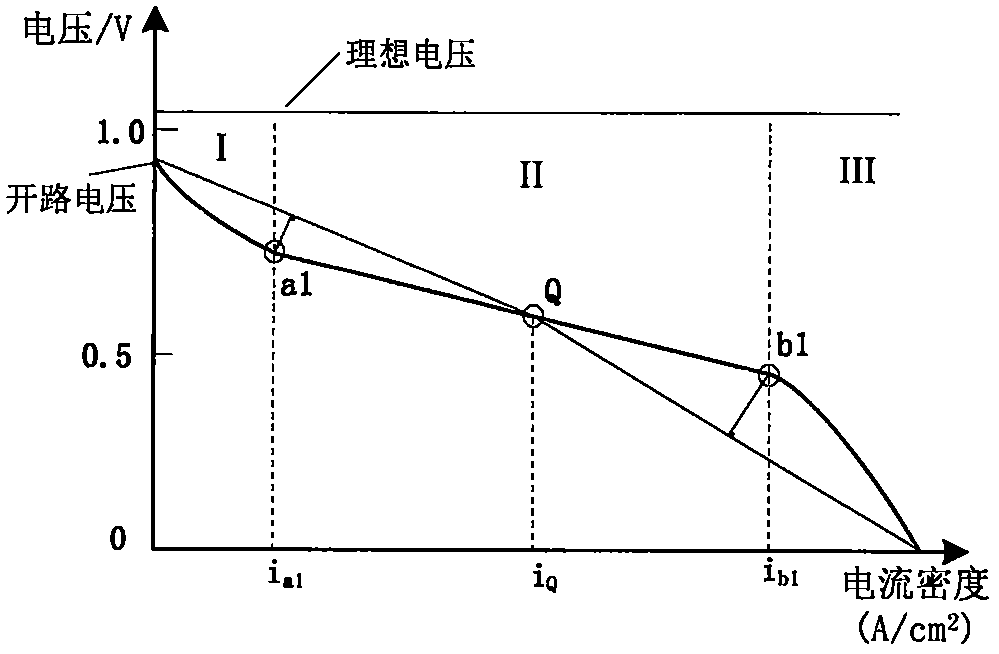
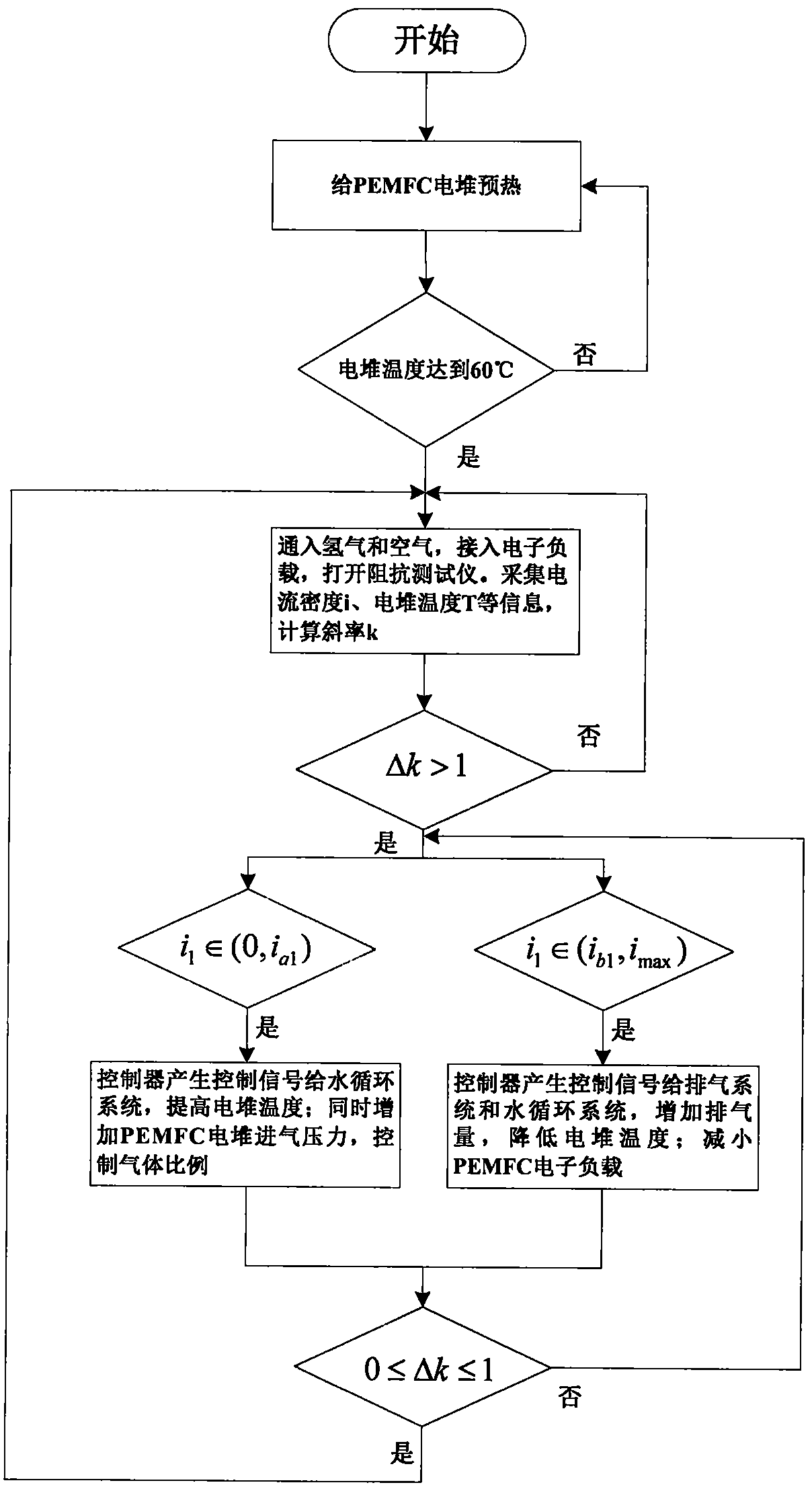
A state monitoring method and system for a water-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
MR imaging with Dixon-type water/fat separation
ActiveUS10895619B2Decreased SNRImproved noise propagationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNoise propagationWater proton
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com