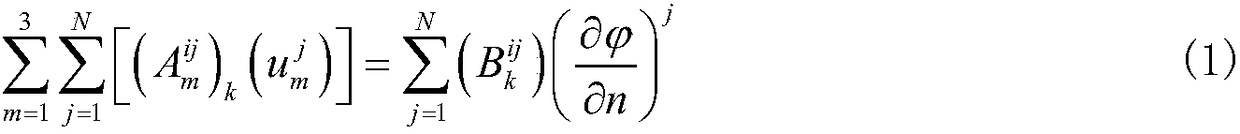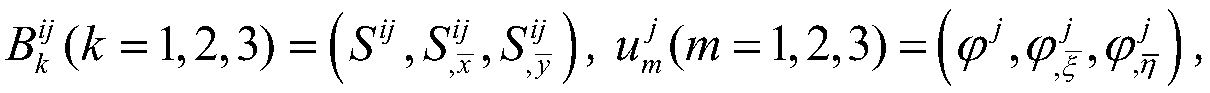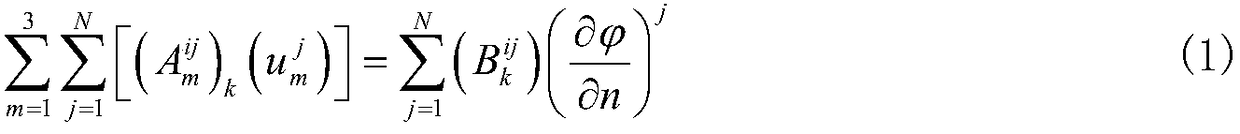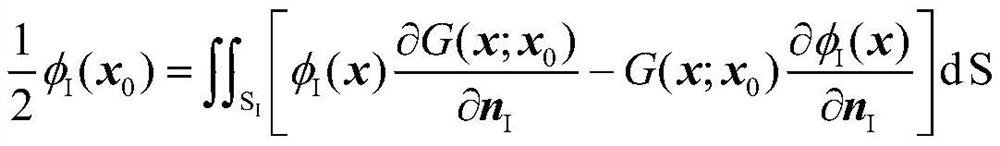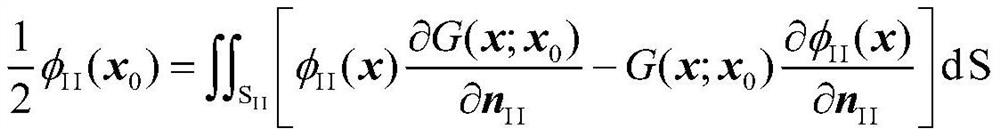Patents
Literature
148 results about "Wave force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
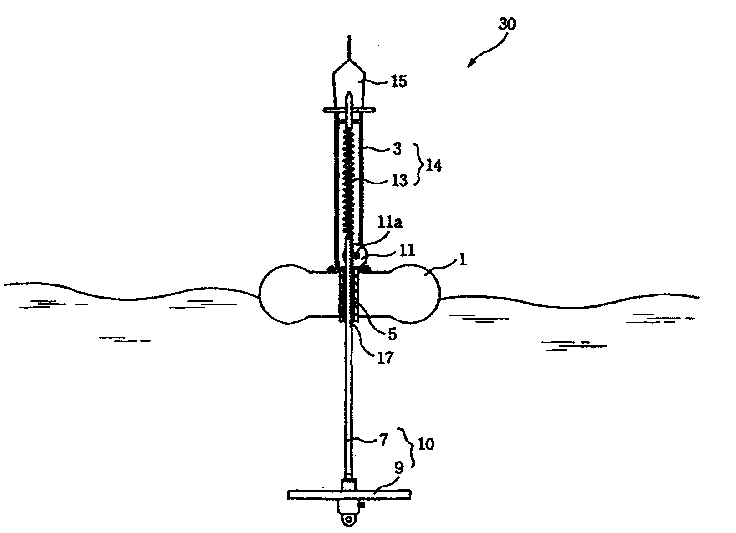
The force of the wave hitting the shore causes an equal and opposite force of the shore hitting the wave in the opposing direction. From Newton’s 2nd law, we can see that the wave accelerates more than the shore as a result of the hit due to the differential in mass of the shore and the wave hitting it.
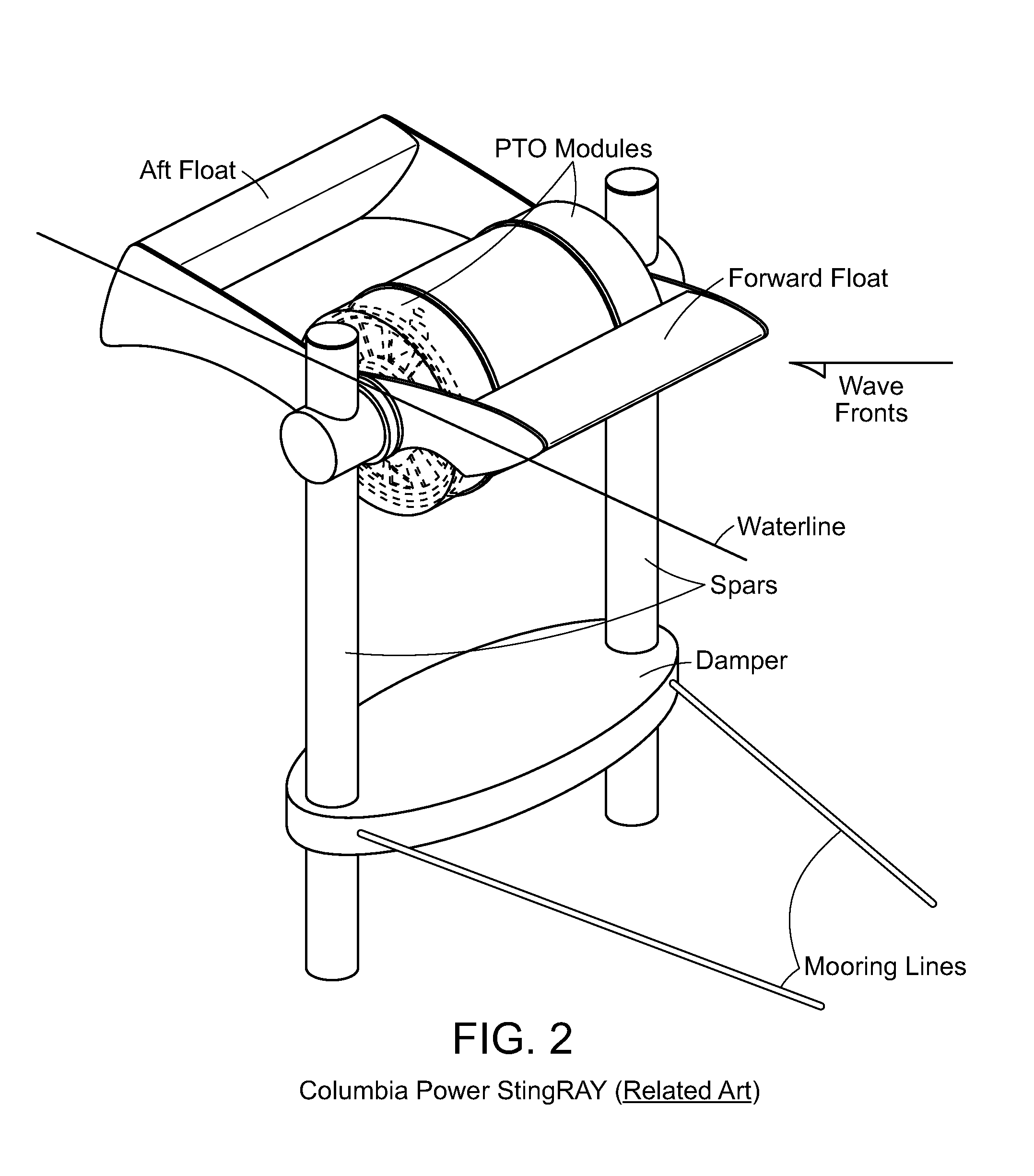
Wave Energy Device
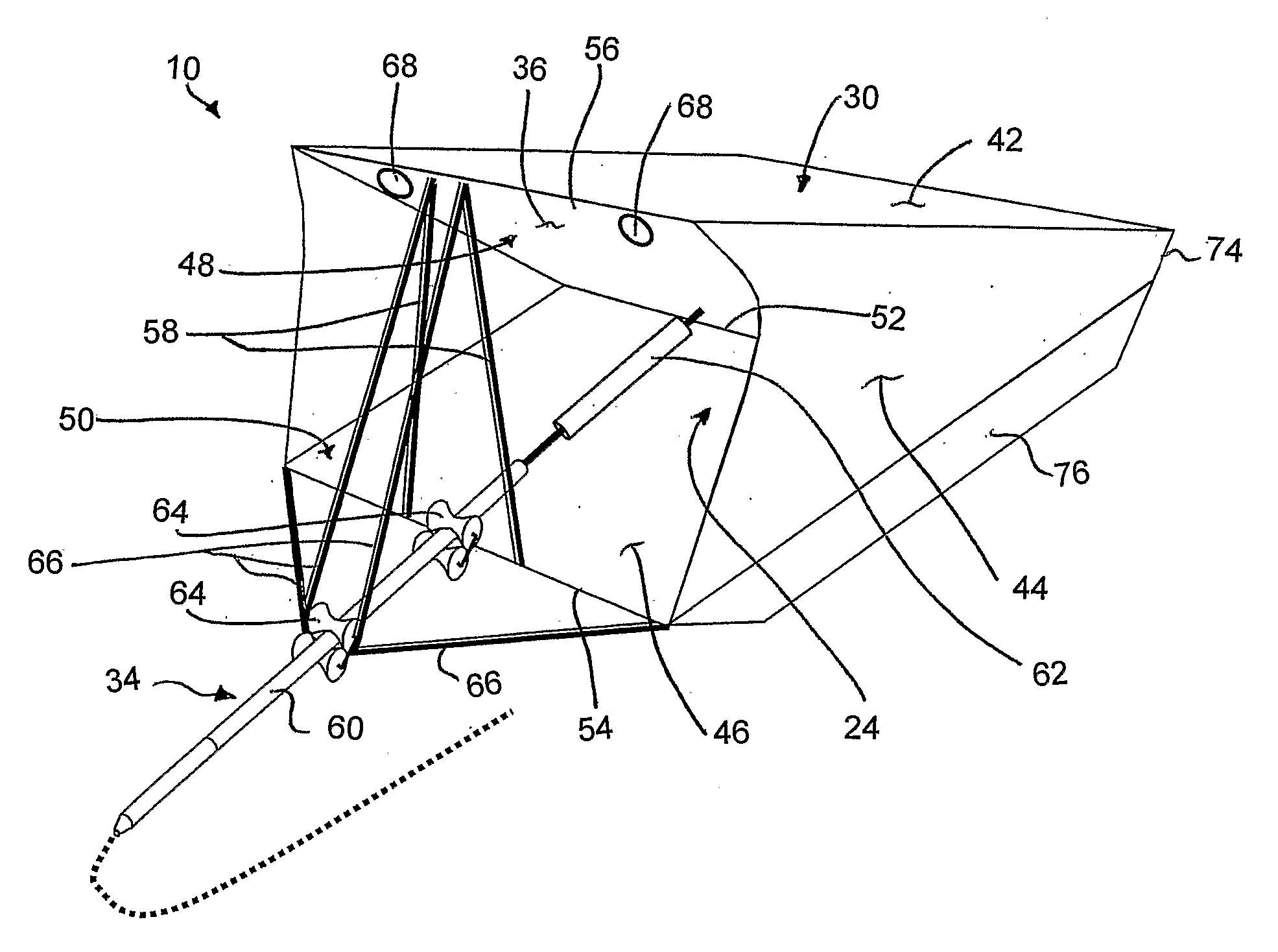
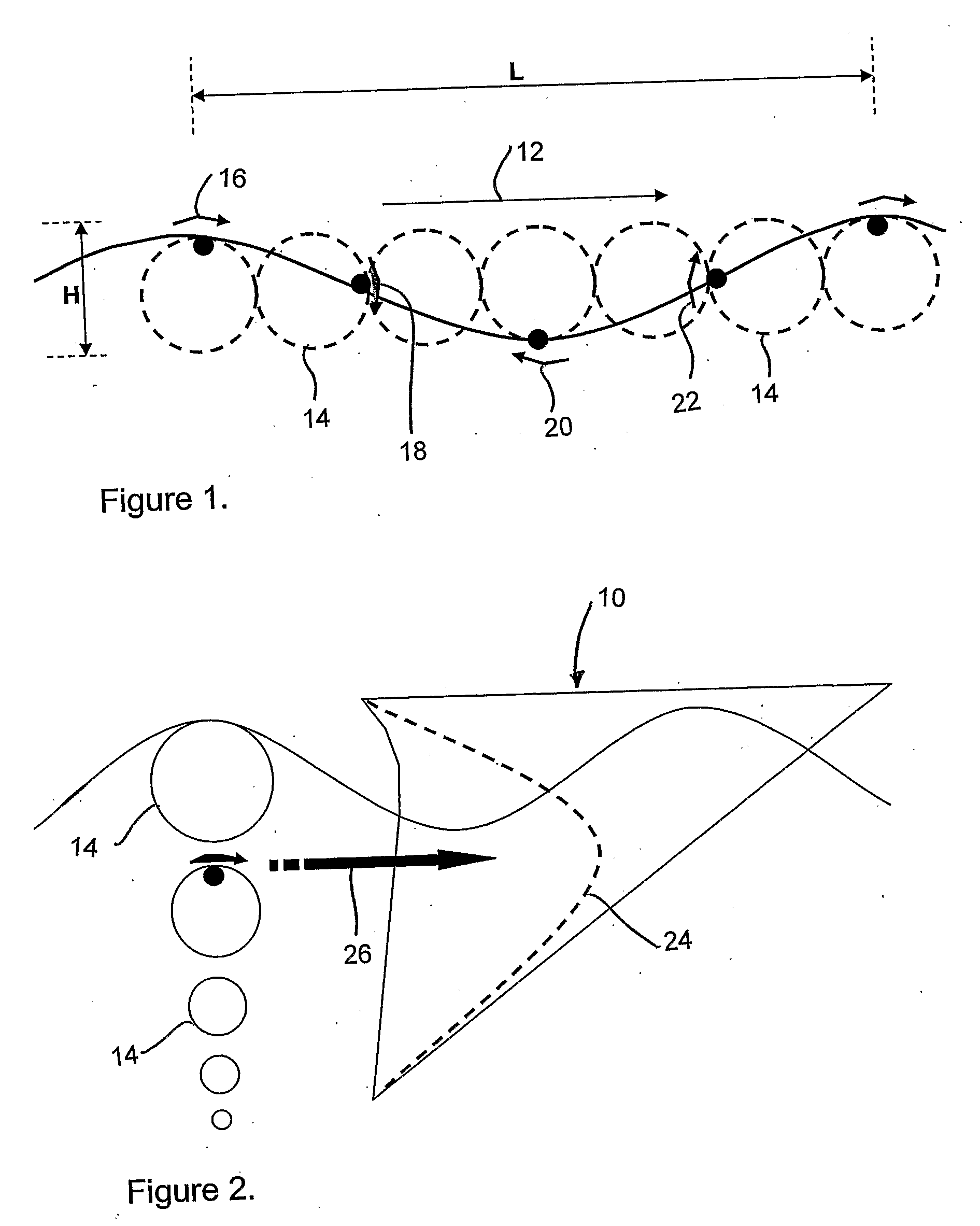
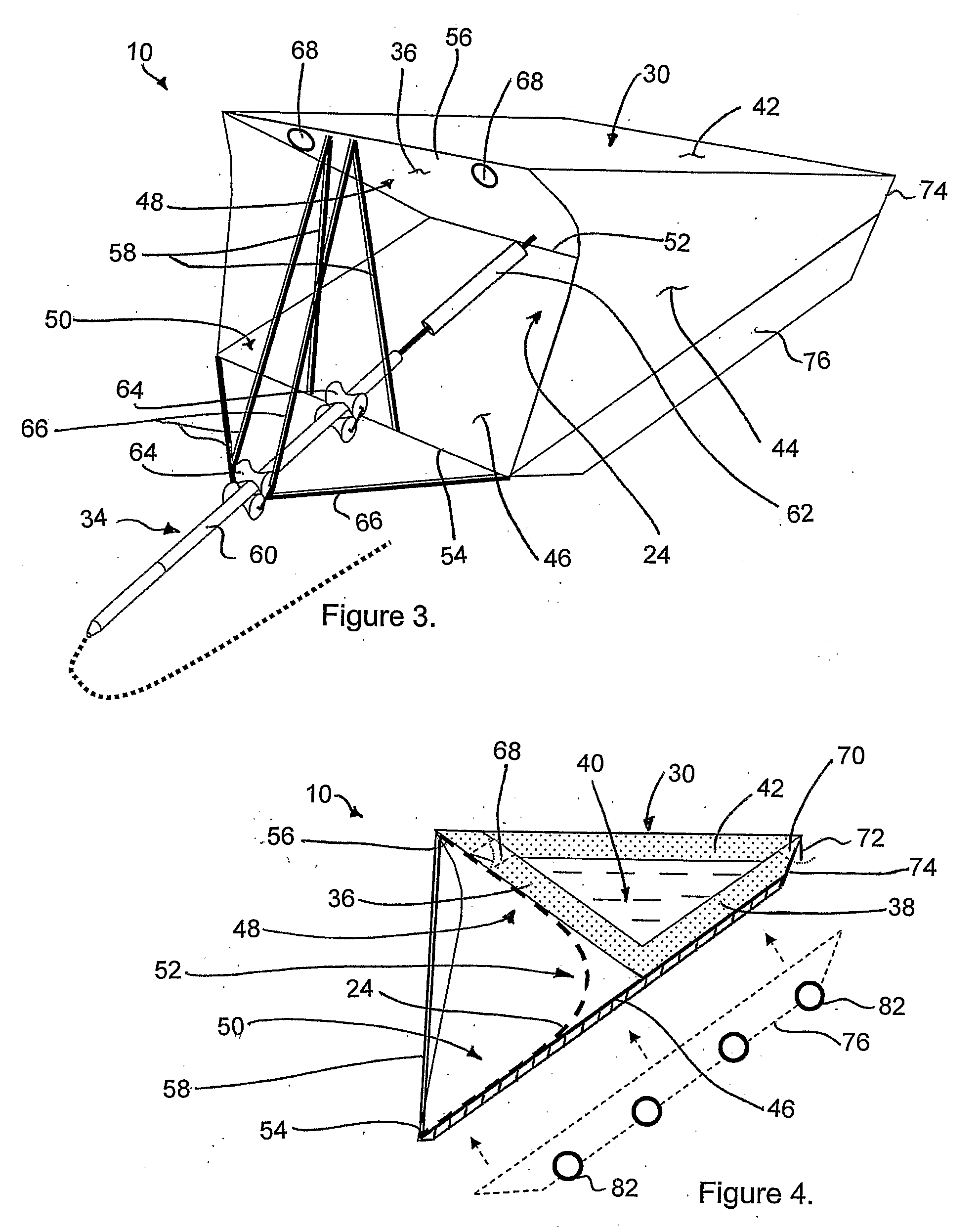
InactiveUS20080093852A1Improve stabilityImprove efficiencyBuoyancy controlMachines/enginesExtreme weatherForms of energy
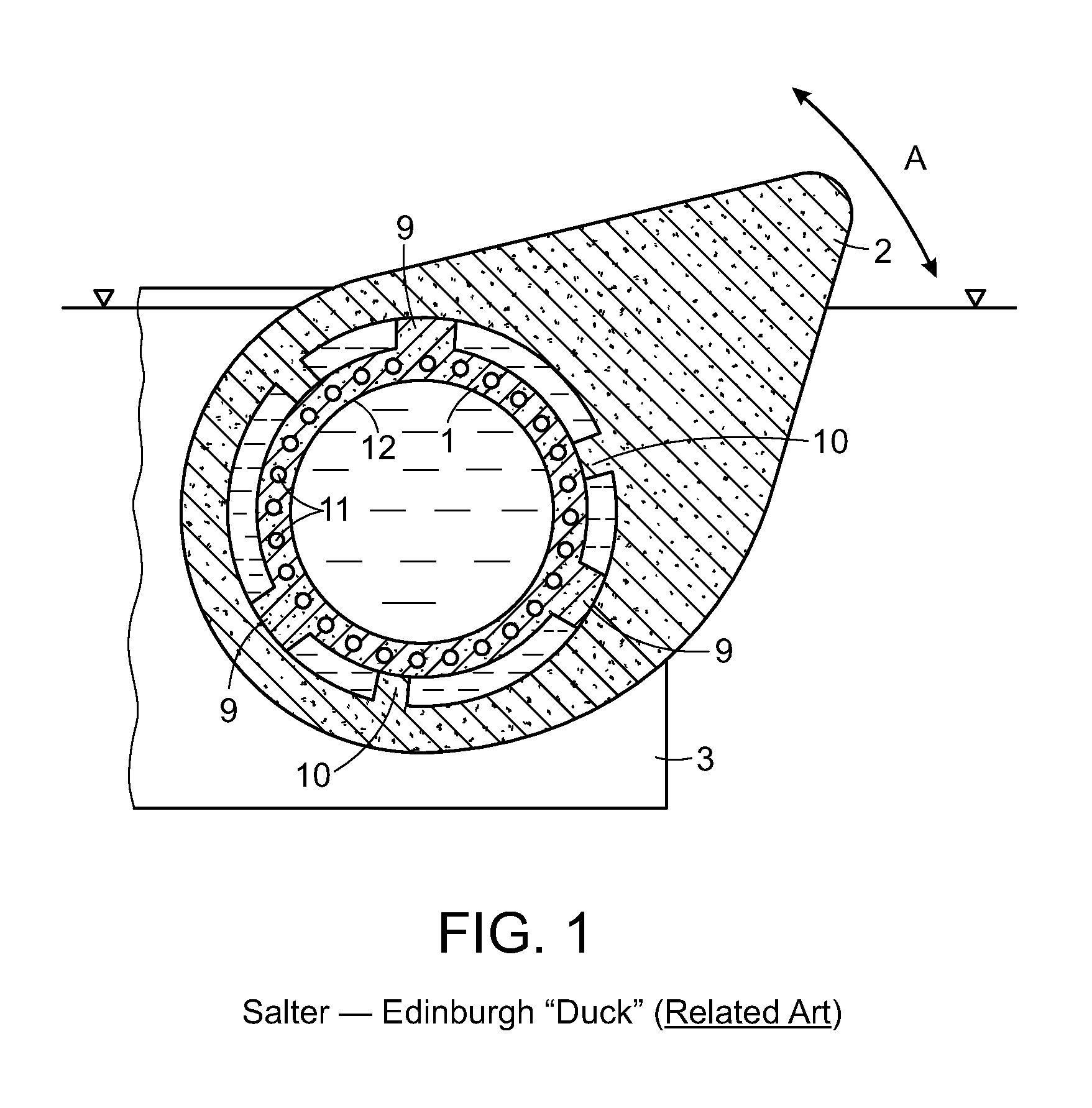
A wave energy device converts the motion of waves on a body of water into a usable form of energy, for example a flow of pressurized water or an electrical current. The device includes a buoyant body for tracking the rise and fall of the wave and a working surface coupled for movement with the buoyant body and which is designed to capture and convert both heave and surge forces of the waves. The device includes a rapid deployment and retrieval capability and a capability to rotate to accommodate changes in wave direction. The device is universally attached to the sea floor, which allows the device to pitch, yaw and roll with the wave forces from any direction, thereby reducing the likelihood of damage due to extreme weather or damage to or from marine traffic in the event of an encounter.
Owner:WAVE ENERGY TECH
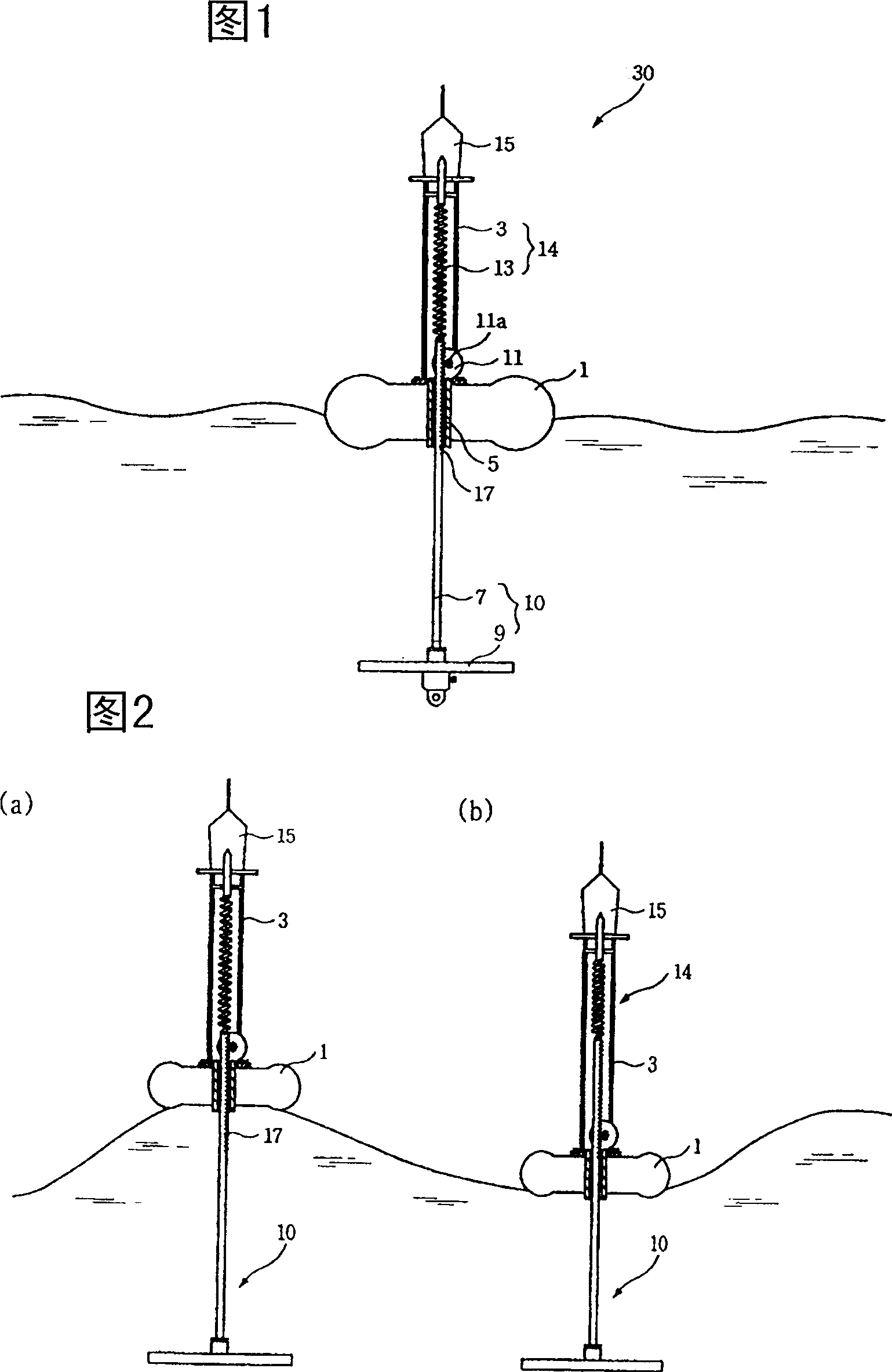
Buoy having waveforce self-generating unit and waveforce generating method
The present invention proposes a buoy with a self-generating device using wave force. The buoy consists of a buoy floating on the sea and a lower feeding part that vertically passes through the guide sleeve at the center of the buoy. Above the floating body, the rack on the upper part of the lower feeding part meshes with the gear on the engine to convert the linear reciprocating motion of the lower feeding part into the rotary motion of the generator, so that the generator generates electricity; the upper support on the floating body is a support It is used for the lower feeding part; a beacon light is set on the buoy, which uses the electric energy generated by the generator to mark the position of the buoy.
Owner:成哲基
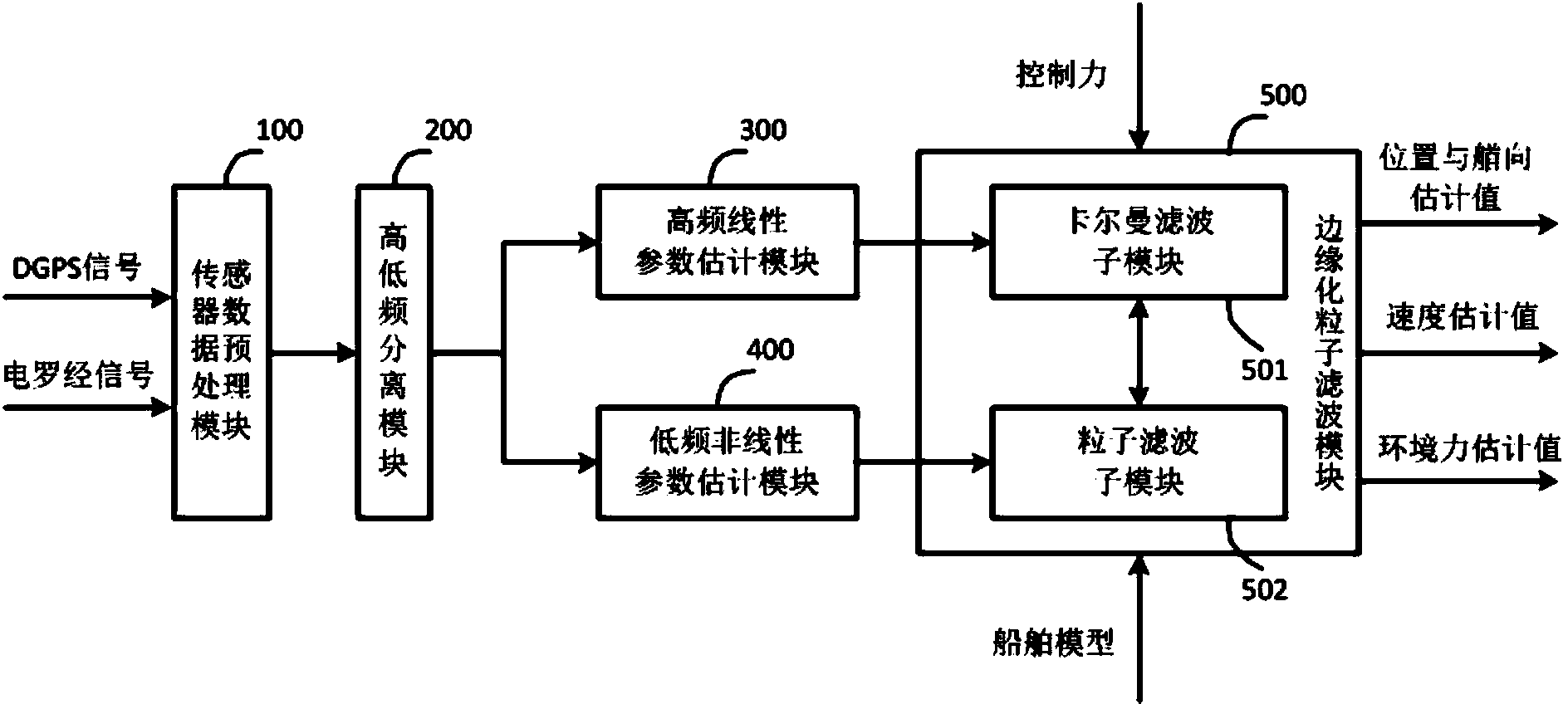
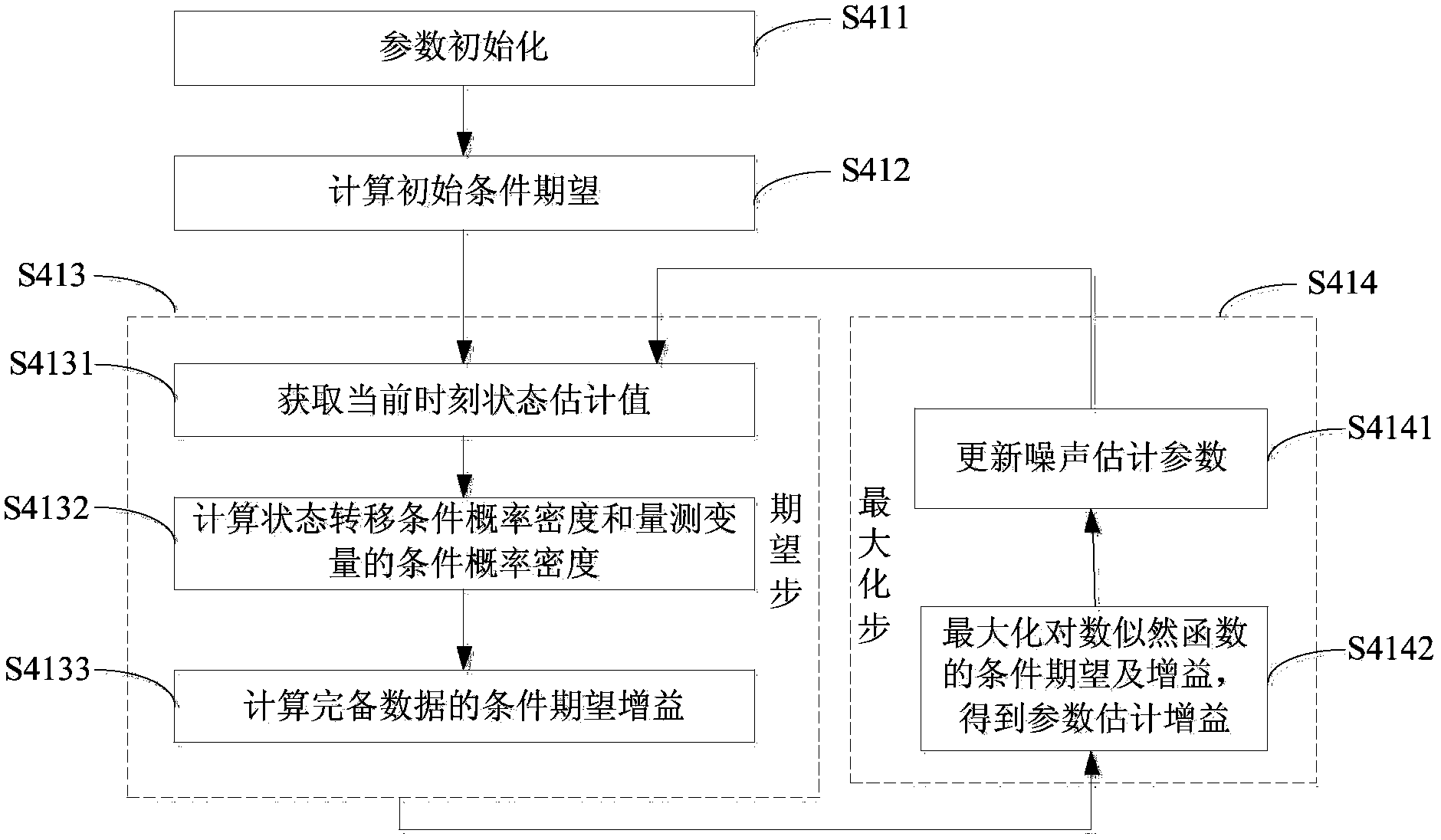
Deep-sea vessel dynamic positioning oriented high-precision real-time state estimation method and system
InactiveCN103838970AImprove State Estimation AccuracyTaking into account real-timeSpecial data processing applicationsLinear motionEstimation methods
The invention relates to a deep-sea vessel dynamic positioning oriented high-precision real-time state estimation method and system. The method includes: separating a high-frequency signal caused by a first-order wave force from a low-frequency vessel motion signal so as to obtain a high-frequency motion component and a low-frequency motion component; in a marginalized particle filter frame, subjecting both the high-frequency motion component the low-frequency motion component to parameter estimation and state estimation; using results of the parameter estimation and state estimation as input of next-cycle parameter estimation and state estimation, and repeating the steps until the end. The deep-sea vessel dynamic positioning oriented high-precision real-time state estimation method and system has the advantages that the difference between high-frequency linear motion and low-frequency linear motion is fully considered, the nose parameter estimation method applicable to both high-frequency and low-frequency motions is provided, the state estimation method based on marginalized particle filter and oriented towards vessel dynamic positioning is therefore provided, and state estimation precision increase and timeliness are balanced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Device for carrying out gas production and gas injection by utilizing wave force to hoist nutritive salt on seabed
InactiveCN103210862ASave energySimple organizationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaForms of energyProcess engineering
The invention relates to an artificial upwelling device and aims to provide a device for carrying out gas production and gas injection by utilizing a wave force to hoist nutritive salt on a seabed. The device carrying out gas production and gas injection to hoist the nutritive salt on the seabed comprises a guide rail mechanism, a floating mechanism, a gas collecting mechanism, a gas conveying pipe and an upwelling mechanism; the floating mechanism is embedded on the guide rail mechanism; the gas collecting mechanism is fixed inside the guide rail mechanism; and the upwelling mechanism is connected with the gas collecting mechanism by the gas conveying pipe. The device directly utilizes fluctuation of waves to carry out gas collection and gas injection and utilizes wave energy to replace other forms of energy supplied by the ground, so that energy is effectively saved; an adopted gas injection hoisting method has high efficiency, a large upwelling ratio (i.e. a ratio of upwelling liquid flow to gas injection flow) and higher efficiency; and moreover, the device adopts the simple mechanisms, is low in cost and is very convenient to install and lay out.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reverse arc-shaped bulwark and computing method for total horizontal wave force of bulwark
InactiveCN104727270AImprove the state of stressReduce wave forceBreakwatersQuaysWave pressureEngineering
The invention discloses a reverse arc-shaped bulwark. The bulwark comprises a front wall and a square caisson structure, wherein the front wall is of a continuous semicircular-cylinder-shaped arc-shaped wave-ward surface structure, and the square caisson structure is arranged behind the front wall. According to a computing method for total horizontal wave force of the reverse arc-shaped bulwark, computing is performed through the following formulas that P=KPPZ, and the correction factor KP=0.91. The reverse arc-shaped bulwark has the advantages that the reverse arc-shaped bulwark is similar to a straight wall type bulwark in vertical pressure distribution, the position nearby the static water level belongs to triangular distribution, and the position below the static water level belongs to parabolic distribution; according to annular pressure distribution of the reverse arc-shaped bulwark, when a wave crest acts, the wave pressure intensity of central section of each arc is the maximum and decreases with the increase of the angle of each arc; when a wave trough acts, the wave pressure intensities are basically equal and are evenly distributed. A revised Goda formula should be adopted for computing the total horizontal wave force of the bulwark, and computing and analysis show that the total horizontal wave force of the reverse arc-shaped bulwark is about 10% smaller than the wave force of the straight wall type bulwark of the same size.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Sea glider driven by wave force
ActiveCN104149959AImprove battery lifePropulsion based emission reductionPropulsion power plantsEngineeringUnderwater glider
The invention relates to high-cruise-ability self-propelling systems used for marine environment monitoring and provides a sea glider driven by wave force. The sea glider comprises two floater base bodies, two solar panels, a base body connecting plate, a glider base frame and a cable, wherein the two floater base bodies are connected through the base body connecting plate, the base body connecting plate and each floater base body are fixedly connected through a plurality of fastening screws, a drying box is fixedly connected to the base body connecting plate through a plurality of fastening screws, a sealing cover is installed at the upper end of the drying box, and drying box partition boards are installed in the drying box. The sea glider driven by wave force has the advantages that the whole glider is driven to move forwards through the interaction force between underwater glider wings and water currents, and extra secondary power supply is not needed; electric energy generated by the solar panels is only supplied to all instruments and does not need to serve as a driving energy source, and therefore the cruising ability of the glider is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for predicting movement of FLNG (floating liquefied natural gas) by considering rocking influence of liquid cabin
InactiveCN103984793AAccurate impactImprove design efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsTime domainEngineering
The invention relates to a method for predicting the movement of FLNG (floating liquefied natural gas) by considering the rocking influence of a liquid cabin. The method comprises the following steps of 1) describing non-linear rocking of liquid in the cabin in a time domain based on a potential flow theory and a panel method to obtain the velocity potential of the rocking of the liquid in the cabin and the pressure of the liquid on the cabin wall caused by the rocking; 2) using the pressure obtained in the step 1) as external force input at the right end of an equation of motion of a ship body, considering the influence of external wave force, calculating motion response of the ship body, obtaining the position of the ship body, and updating a free liquid level; 3) using the obtained position of the ship body at the current moment and the updated free liquid level as boundary conditions of the rocking problem of the liquid in the cabin to obtain the rocking problem of the liquid in the cabin at the next moment, circulating continuously, and stopping after time is set. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of shortening computation time, greatly improving the design efficiency of the liquid cabin and the FLNG and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Generation device by using ocean wave buoy
InactiveCN1971031ASimple structureGuaranteed uptimeMachines/enginesEngine componentsSurface oceanShallow sea
The invention discloses a power generation equipment with ocean wave buoy, comprising buoy and cable connected at the top of shell in turn, permanent magnet and spring connected with cable in the shell orderly. The other end of spring is connected with the bottom of shell. Coil is set round the permanent magnet and the coil is connected with the cable towards the outer of shell. Pulley through cable is set at the top of shell and sealing equipment is set between cable and shell. Because of seawater with huge wave energy, the buoy moving continuously under the effect of wave force and connected with magnet, coil set round the magnet, the magnet driven by the movement of buoy cuts the magnetic field line in the shell of power generation equipment so as to generate current in coil and output the current by cable. In the power generation equipment of invention wave energy in ocean is used as the driving energy to move the buoy and the power generation equipment driven by buoy through cable supplies power. The power generation equipment with ocean wave buoy is mainly applied in generating power in shallow sea region.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Mixed wave force power-generating device
InactiveCN102003330AImprove absorption efficiencyImprove energy conversion efficiencyWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesEngineeringEnergy conversion efficiency
The invention discloses a mixed wave force power-generating device. The device is characterized by containing two parts, namely an upper floating body and a lower floating body, wherein the upper floating body is hollow, one side of the upper floating body is provided with an opening, the hollow part of the upper floating body is provided with a float which is used to heave with waves; the inside of the lower floating body is provided with a conductive coil, a hydraulic cylinder, a hydraulic motor, a generator and a storage battery; the hydraulic cylinder is connected with the hydraulic motor through a hydraulic pipeline, the output shaft of the hydraulic motor is connected with the input shaft of the generator through a coupling; the float in the upper floating body is connected with the piston of the hydraulic cylinder through a connecting rod; the conductive coil which encircles the connecting rod and has multiple turns is arranged on the upper part of the hydraulic cylinder and is fixed relatively to the hydraulic cylinder; a magnet is fixed on the connecting rod and corresponds to the conductive coil; the output end of the conductive coil and the current output electrode of the generator pass through a rectifying unit to be connected with the storage battery. By adopting the device, the wave energy conversion efficiency of the system can be increased and power can be generated more stably; and the influence of marine organism on the device is small and the device has low cost and is suitable to be widely popularized.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Self-propelled wave force power generation platform and moving and berthing method thereof
InactiveCN105197189AStrong ability to absorb wavesEasy to operatePropulsion power plantsMachines/enginesSpace environmentMooring system
The invention relates to a self-propelled wave force power generation platform and a moving and berthing method thereof. The self-propelled wave force power generation platform comprises a rear elbow and a buoyancy compartment arranged on the rear elbow, the rear end of the rear elbow is located below the sea surface, and the front end of the rear elbow is located above the sea surface and is connected with an air turbine. A wave force generator is connected to the air turbine, a deck covers the buoyancy compartment, extends all the way to the upper portion of a rear end opening of the rear elbow, and is supported by supporting columns, the four corners of the deck are each provided with an anchor windlass, and an electric propeller and an electric rudder are arranged below the rear end of the rear elbow. Through the combined application of the electric propeller, the electric rudder and the electric anchor windlasses, anchoring, anchor housing and moving operation of the wave force generator can be quickly achieved, the self-propelled wave force power generation platform is simple and easy to achieve, oceaneering cost is low, a self-cleaning effect on the underwater space environment is achieved, and a mooring system can be conveniently maintained. Meanwhile, energy generated by the self-propelled wave force power generation platform is effectively utilized, energy is saved, and environment friendliness is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wave energy device
InactiveUS7737568B2Improve efficiencyImprove abilitiesBuoyancy controlMachines/enginesExtreme weatherForms of energy
A wave energy device converts the motion of waves on a body of water into a usable form of energy, for example a flow of pressurized water or an electrical current. The device includes a buoyant body for tracking the rise and fall of the waves and a working surface coupled for movement with the buoyant body and which is designed to capture and convert both heave and surge forces of the waves. The invention also involves a rapid deployment and retrieval capability and a capability to rotate to accommodate changes in wave direction. The device is universally attached to the seafloor, which allows the device to safely pitch, yaw and roll with the wave forces from any direction thereby reducing the likelihood of damage due to extreme weather or marine traffic. The universal attachment also allows the device to automatically adjust for varying water elevation due to tides.
Owner:WAVE ENERGY TECH
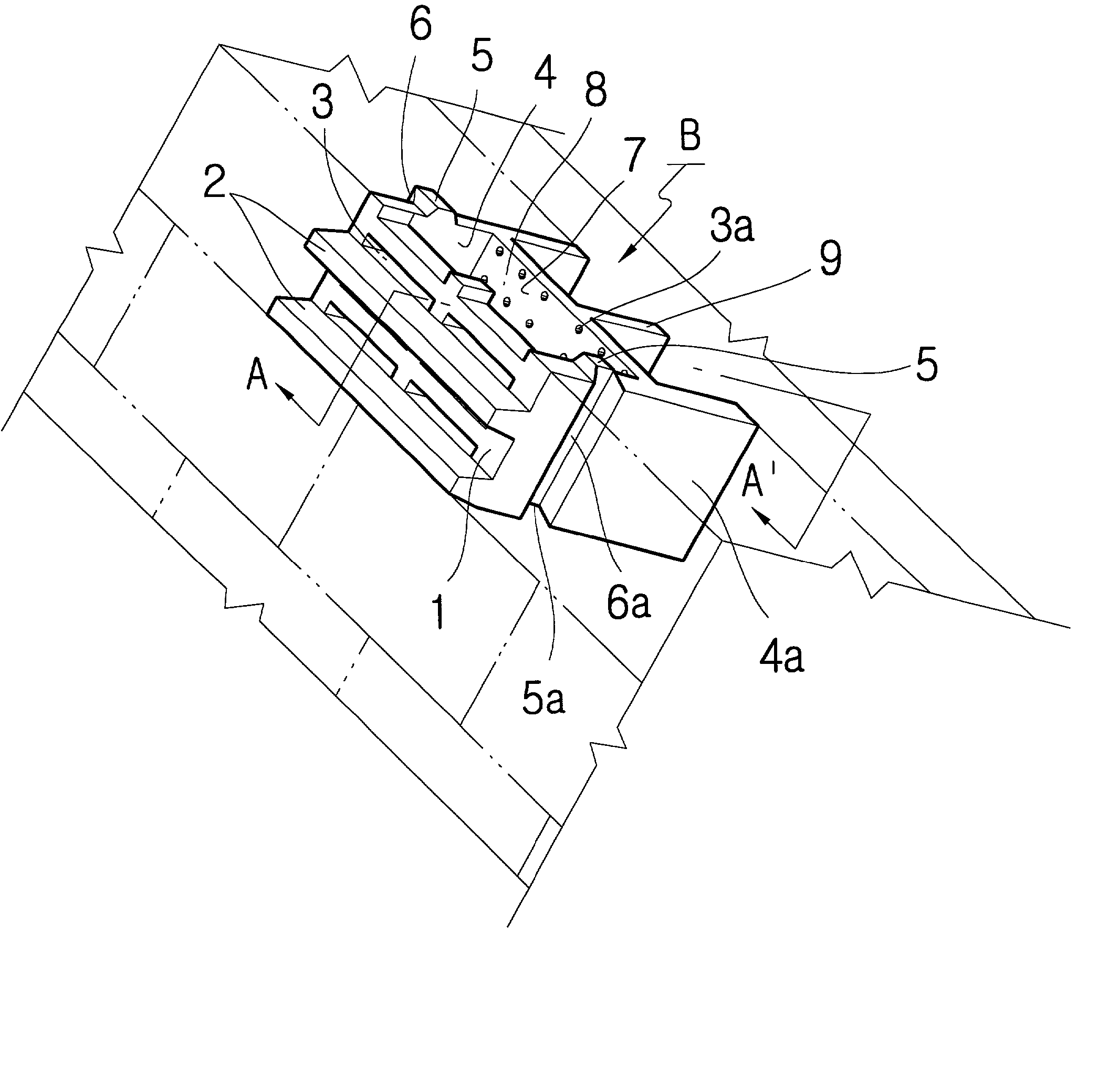
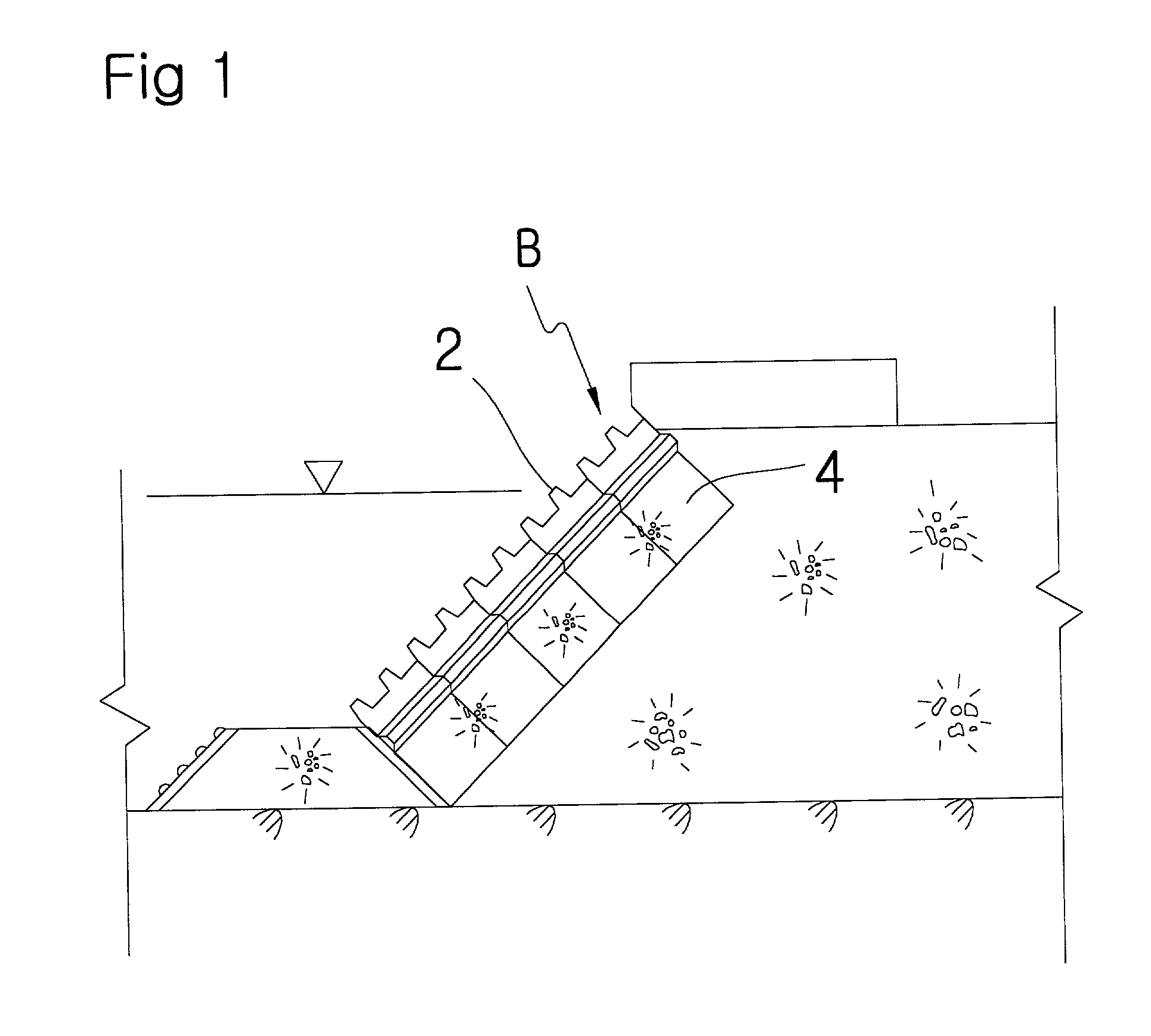
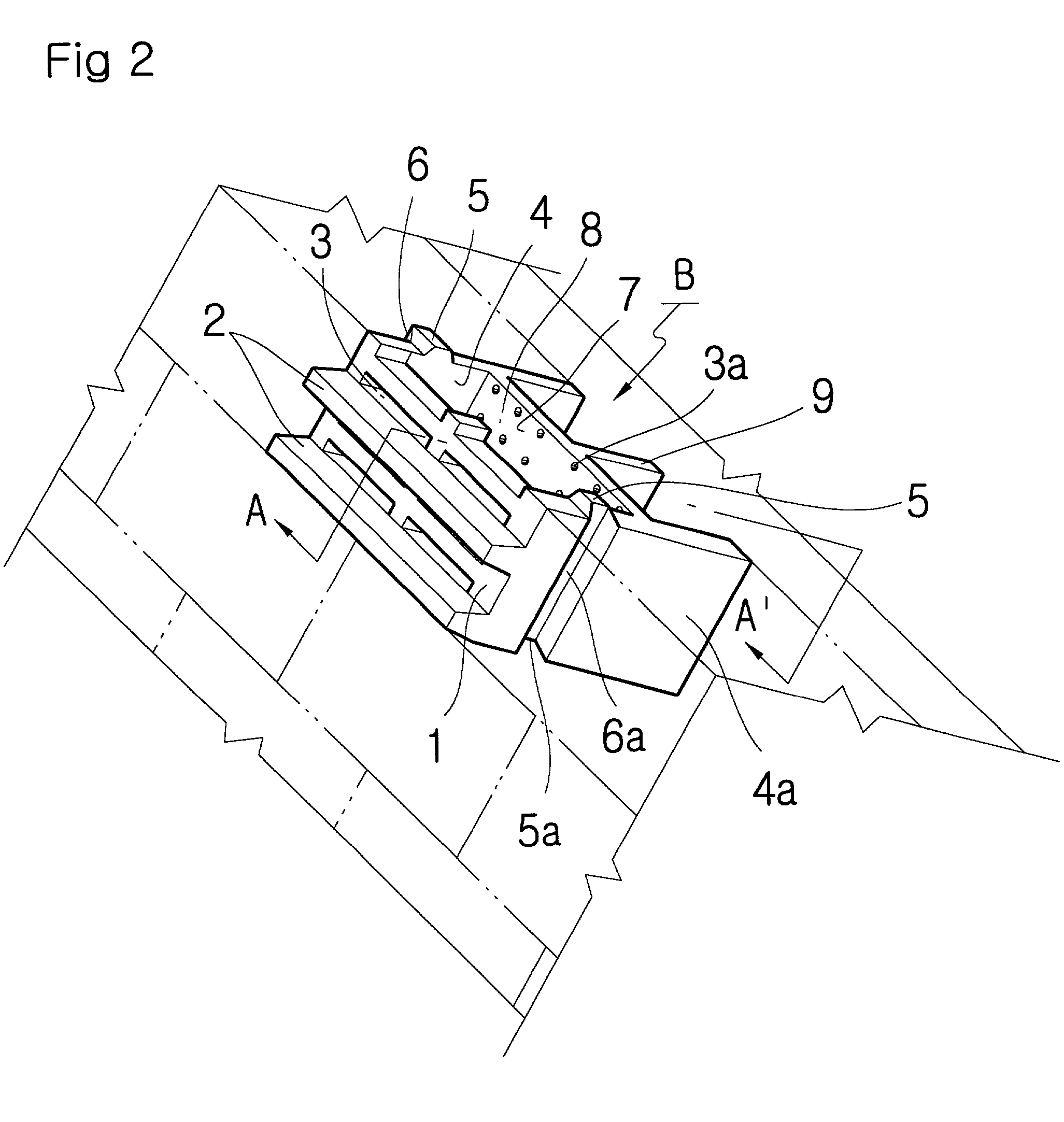
Covering block for decreasing wave forces
A block for constructing a breakwater comprises a front wall in which horizontal projections are formed with transverse rectangular-shaped holes therebetween. Side walls extend from both ends of the front wall. A partition wall in which multiple holes are formed to communicate with the transverse rectangular-shaped holes is jointed to the side walls at both ends and spaced from the front wall. A detention area is defined by the front wall, partition wall and side walls for receiving the overflow waves through the transverse rectangular-shaped holes in the front wall.
Owner:YANG WON HOI
Method for identifying longitudinal motion models of trimaran
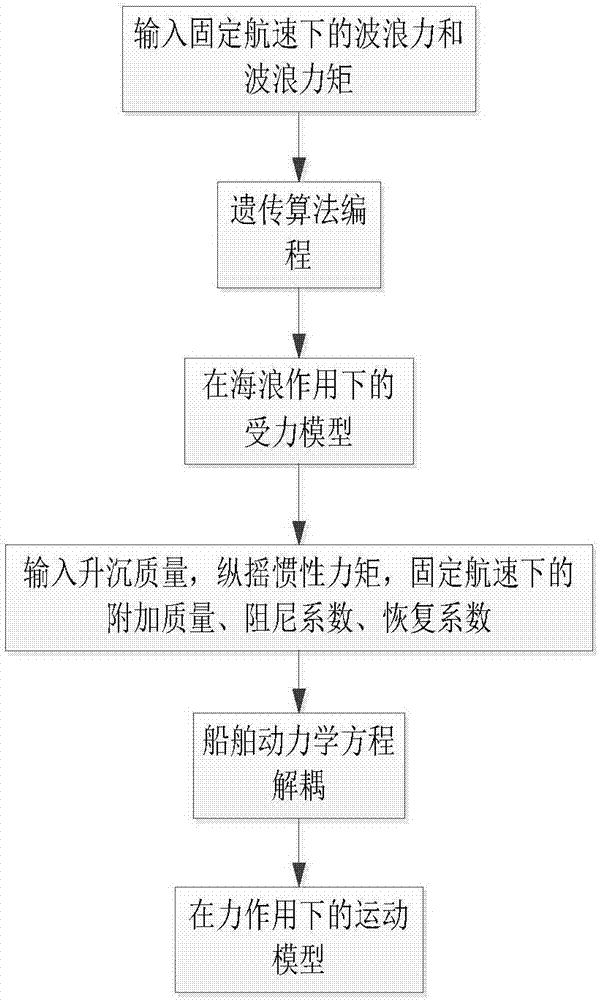
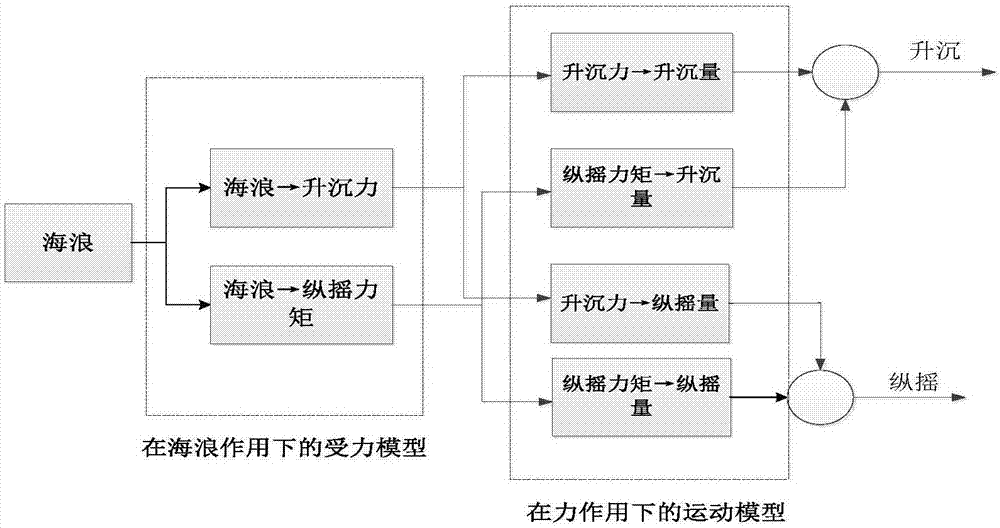
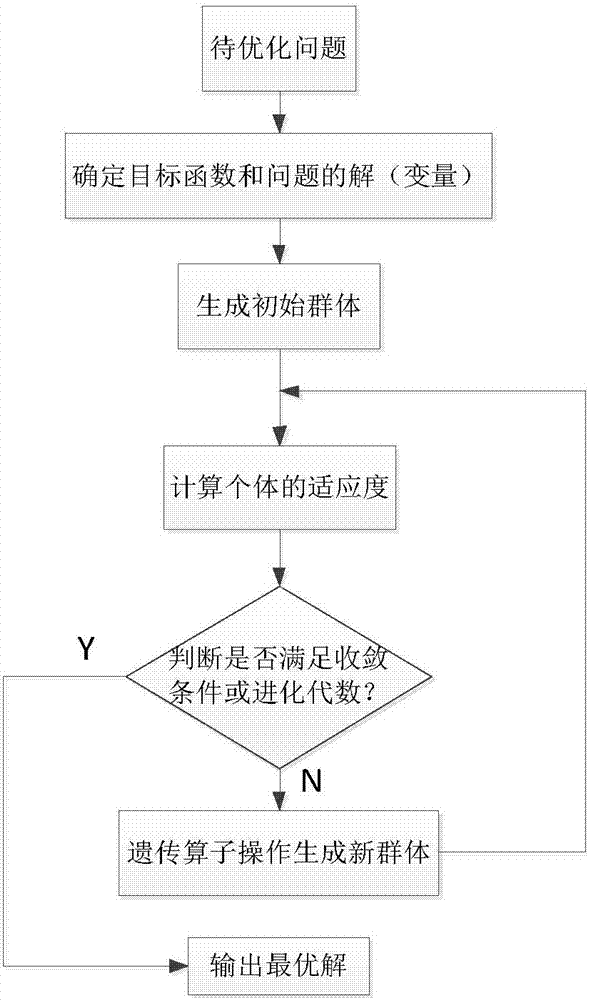
ActiveCN107330164AAccurate identificationAccurate estimateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationDamping factorGenetic algorithm
The invention designs a method for identifying longitudinal motion models of a trimaran. The longitudinal motion models are mainly a force bearing model of the trimaran under the action of waves based on a genetic algorithm and a motion model of the trimaran under the action of force based on equation decoupling. Wave force and wave torque are obtained according to towing experiments of the trimaran, and the genetic algorithm is utilized to identify the force bearing model of the trimaran under the action of the waves. Additional mass, a damping coefficient, a recovery coefficient, heaving mass and longitudinal inertia torque are obtained according to the towing experiments of the trimaran, and a kinetic equation of ships is decoupled to identify the motion model of the trimaran under the action of the force. The method for identifying the longitudinal motion models of the trimaran is applicable to the analysis of the motion of the trimaran under complex sea conditions and widely applied to the anti-pitching control of the ships; the rapidity and intellectuality of the algorithm can ensure that the actual motion can be accurately estimated under high-speed and complex sea conditions through the adoption of the obtained trimaran models.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
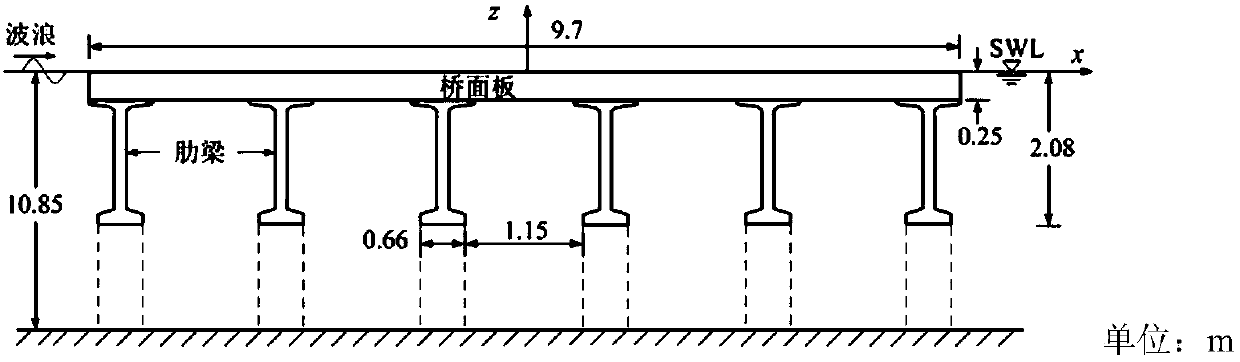
Method for calculating wave force borne by sea-crossing bridge foundation
ActiveCN106202629ARealize computingSolve the problem that the wave force cannot be calculatedGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsBridge engineeringCross bridge
The invention discloses a method for calculating wave force borne by the sea-crossing bridge foundation and relates to the field of bridges. The sea-crossing bridge foundation comprises a pile foundation, a bearing platform and a bridge pier, wherein the pile foundation comprises a plurality of single piles, one end of the pile foundation is connected with the sea bed, and the bearing platform is arranged at the other end of the pile foundation; the bearing platform adopts an integrated structure and is connected with all the single piles, and the bridge pier is arranged at the top end of the bearing platform; the bridge pier is smaller than the bearing platform. The method for calculating the wave force borne by the sea-crossing bridge foundation comprises steps as follows: calculating the wave force borne by the bridge pier; calculating the wave force borne by the bearing platform; calculating the wave force borne by the pile foundation; calculating the wave force borne by the sea-crossing bridge foundation. By means of the method for calculating the wave force borne by the sea-crossing bridge foundation, the overall wave force borne by the sea-crossing bridge foundation can be more simply and conveniently calculated, and the problem that the overall wave force borne by the sea-crossing bridge foundation comprising the bridge pier, the bearing platform and pile foundation in sea-crossing bridge engineering cannot be calculated is solved.
Owner:CHINA MAJOR BRIDGE ENERGINEERING
Estimation method of wave force submerging offshore bridge upper structure
InactiveCN107644144AVerify validityVerify accuracySpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomEstimation methods
The invention provides an estimation method of wave force submerging an offshore bridge upper structure. A theory accrual model of the wave action of a bridge upper structure in a submerging state isbuilt based on a potential flow wave theory, a control equation of the model is a Laplace's equation, boundary conditions such as impassable and impermeable characteristics of a free surface and a seabed and zero object plane normal velocity are met, a velocity field can be solved by solving a control equation and by the aid of continuity of velocity potential and horizontal velocity, and the waveaction force can be solved by the aid of a Bernoulli's equation. By a built wave action force computing method, maximum wave action force applied to an offshore bridge structure in the submerging state can be accurately calculated, and accuracy is obviously improved as compared with a previous method.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-body combined floating platform, floating man-made island based on platform, and construction method of man-made island
PendingCN110239684AGuaranteed stabilityEnsure safetyFloating buildingsAnchoring arrangementsElastomerEngineering
The invention provides a novel multi-body combined floating man-made island scheme to solve the problem of an overlarge shaking range existing in a rigid integral-floating man-made island. The floating man-made island comprises a floating platform with a bearing function, the floating platform is connected through at least two floating body components in a splicing mode, and the adjacent floating body components are mutually connected by using connection parts; and the connection parts are elastomers, and make the floating body components constituting the floating platform relatively deflect or displace, and deflection or displacement can be recovered. According to the scheme, the problem of the overlarge shaking range of the floating man-made island under the function of wave force, and the floating man-made island can adapt high seas and other stormy wave sea areas.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
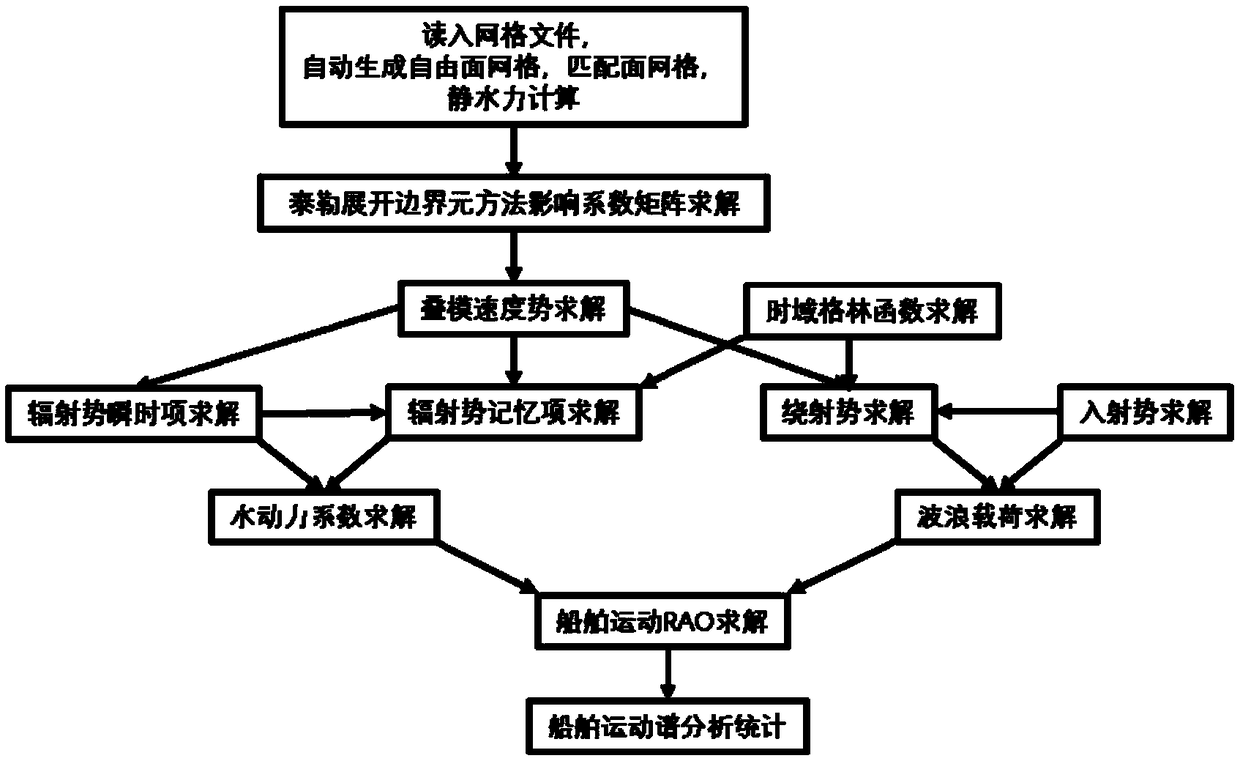
Ship motion prediction method based on Taylor expansion boundary element method
ActiveCN109446634ARapid Prediction of Hydrodynamic CoefficientsGeometric CADSustainable transportationFull waveVelocity potential
The invention provides a ship motion prediction method based on a Taylor expansion boundary element method. The method comprises the steps of reading the grid file and carrying out hydrostatic calculation; calculating the influence coefficient matrix of a boundary integral equation needed by the taylor expansion boundary element method; solving the velocity potential of laminated modes and its spatial first and second derivatives and Mj terms; solving the green's function in time domain and its spatial derivative; solving the instantaneous terms of radiation velocity potential and their spatial first and second derivatives; solving the radiation velocity potential memory term and its spatial first and second derivatives; solving the impulse response function of added mass, wave-making damping and radiation wave force; solving the impulse response function of whole wave incident velocity potential; diffraction velocity potential and its first and second derivatives in space, solving theimpulse response function of diffraction wave force; solving the ship motion in full wave direction; analyzing and calculating the ship motion spectrum under different sea conditions. The invention can predict the hydrodynamic coefficients of three main ship types, wave loads, six-degree-of-freedom motion of the ship in full wave direction, and ship motion spectrum analysis under various sea conditions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
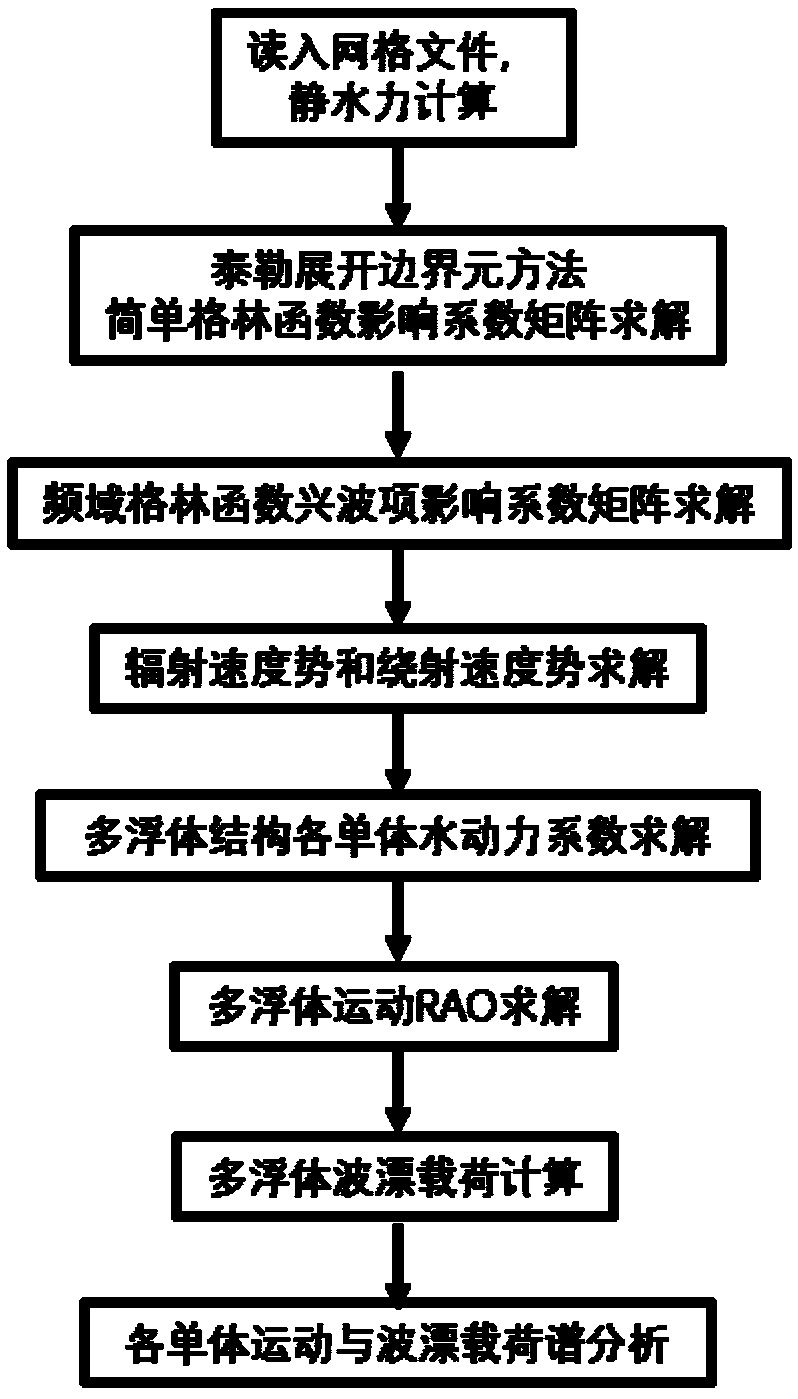
Three-dimensional frequency domain numerical method for predicting wave drift load of a multi-floating body structure
ActiveCN109344531AImprove convergence rateAccurately predict hydrodynamic coefficientsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary element methodVelocity potential
The invention provides a three-dimensional frequency domain numerical method for predicting wave drift load of a multi-floating body structure. The method comprises the following steps: Reading the mesh file, using the mesh information to carry on the ship hydrostatic calculation; calculating The influence coefficient matrix of simple Green's function Calculating The influence coefficient matrix of complex frequency domain Green's function. Taking The Taylor expansion boundary element method solve the unit radiation velocity potential, diffraction velocity potential and their spatial derivatives. solving Hydrodynamic Coefficients of Multiple Floating Body Structures; solving multi-floating body motion equation; solving The wave forces and wave drift loads of each unit for the whole multi-floating structure. According to the response RAO of floating body motion, anyalzing and calulating the floating body motion spectrum in irregular waves. The method of the invention can accurately predict hydrodynamic coefficients, motion RAO, wave forces, wave drift loads in a six-degree-of-freedom direction of each unit of a multi-floating body structure and results of floating body motion spectrum analysis.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for analyzing vibration characteristic of optical fiber composite submarine cables under ocean current scour
InactiveCN107633109AUnderstand the forceResearch is intuitive and effectiveSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomTerrain
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a vibration characteristic of optical fiber composite submarine cables under ocean current scour, and relates to submarine cable analysis methods. Submarine cables are laid on a seabed or seabed sludge generally, are subject to mechanical damage under influence of submarine complex terrains, ocean currents, and tide scour, and there is on a visual andeffective method currently. The method includes the following steps: performing finite element modeling of submarine cables under the action of wave force; performing finite element result data extraction and analysis; performing submarine cable vibration analysis; monitoring a submarine cable situation through optical fiber vibration according to a relation among a displacement, the accelerationand the frequency of an optical unit. The technical scheme can perform dynamics finite element analysis under the action of the wave force, can know the stress acted on each layer of the submarine cables, can provide a theoretical basis for monitoring of the working state of submarine cables by using a distributed optical fiber vibration sensing technology, can complete real-time monitoring of submarine cable vibration through the optical fiber sensing technology, is low in cost, can perform off-site determination, is high in efficiency, and is visual and effective in submarine cable research.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +2
Method for calculating ship parameter-strength excited rolling response probability under random sea conditions
InactiveCN107256280ASacrifice time and efficiencyCalculation speedVessel designingDesign optimisation/simulationSpectral analysisAnalysis method
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Multi Mode Wave Energy Converter With Elongated Wave Front Parallel Float Having Integral Lower Shoaling Extension
ActiveUS20170022964A1Minimal energy consumptionWEC cost (CAPEX)Buoyancy controlMachines/enginesEngineeringEnergy expenditure
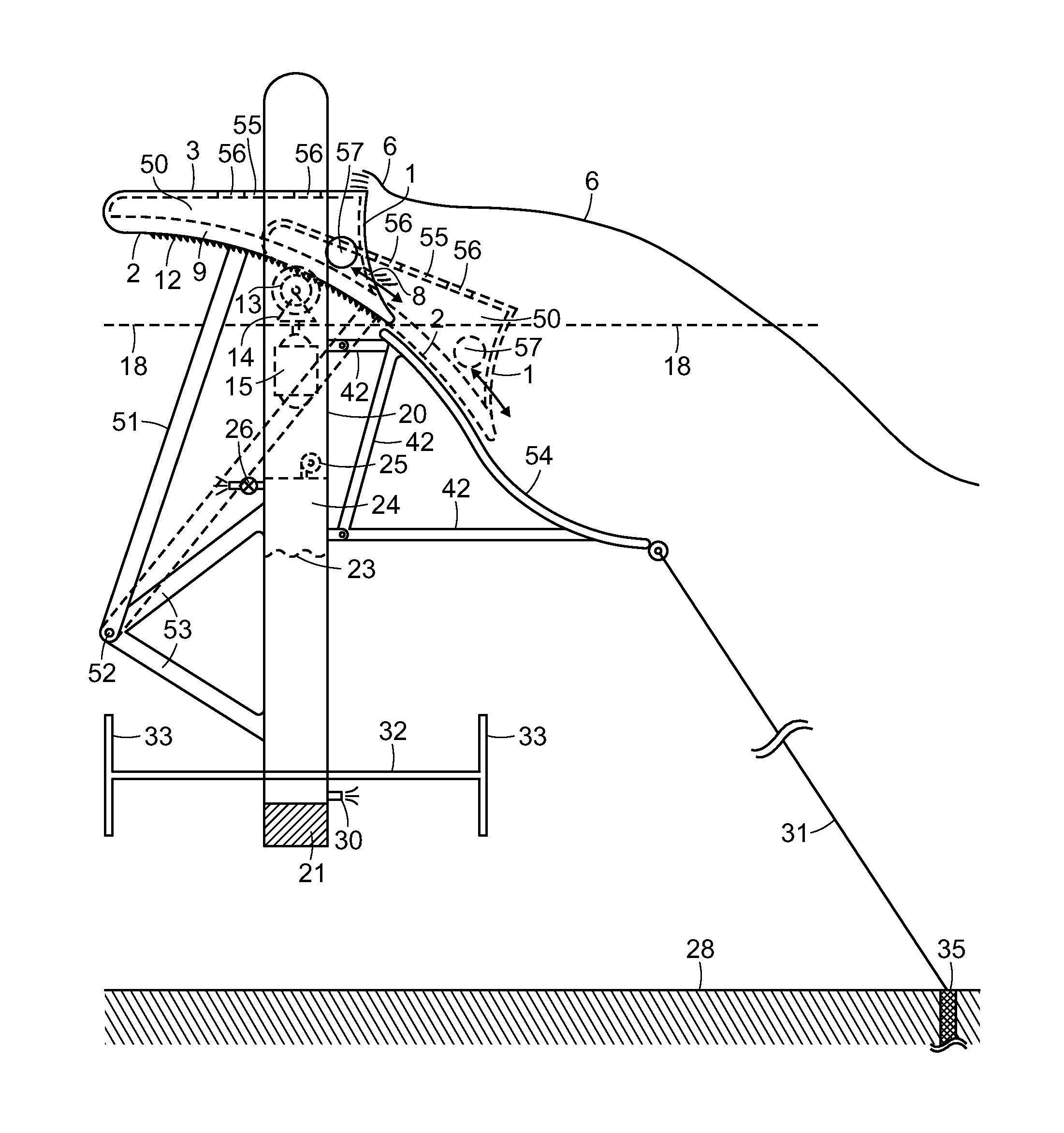
A wave barrier or wave terminator type ocean wave energy converter (WEC) utilizing one or multiple adjacent floats together forming an elongated wave front parallel (EWFP) float rotatably connected by at least one swing or drive arm to a secondary floating or shore or seabed fixed body or frame, such that the at least one swing arm is rotating about a submerged pivot point or axle on such body or frame and constraining the motion of the float(s) relative to the body or frame when wave forces are applied against the float(s). Relative to the direction of oncoming wave fronts and relative to the still water line (SWL), the at least one EWFP float is substantially forward of, and above, the pivot point such that the float concurrently moves both upward and rearward on wave crests and returns both forward and downward on ensuing wave troughs. The rear surface of the EWFP float is substantially arcuate and concave with a radius approximating its distance from the pivot point such that the float produces minimal energy consuming back waves when it is being moved by oncoming wave forces. The lower rear arcuate surface of the float can extend below the bottom of the float deeper into the water column to capture additional wave energy.
Owner:ROHRER TECH
Energy collection unit and ratchet wheel and a wave force engine
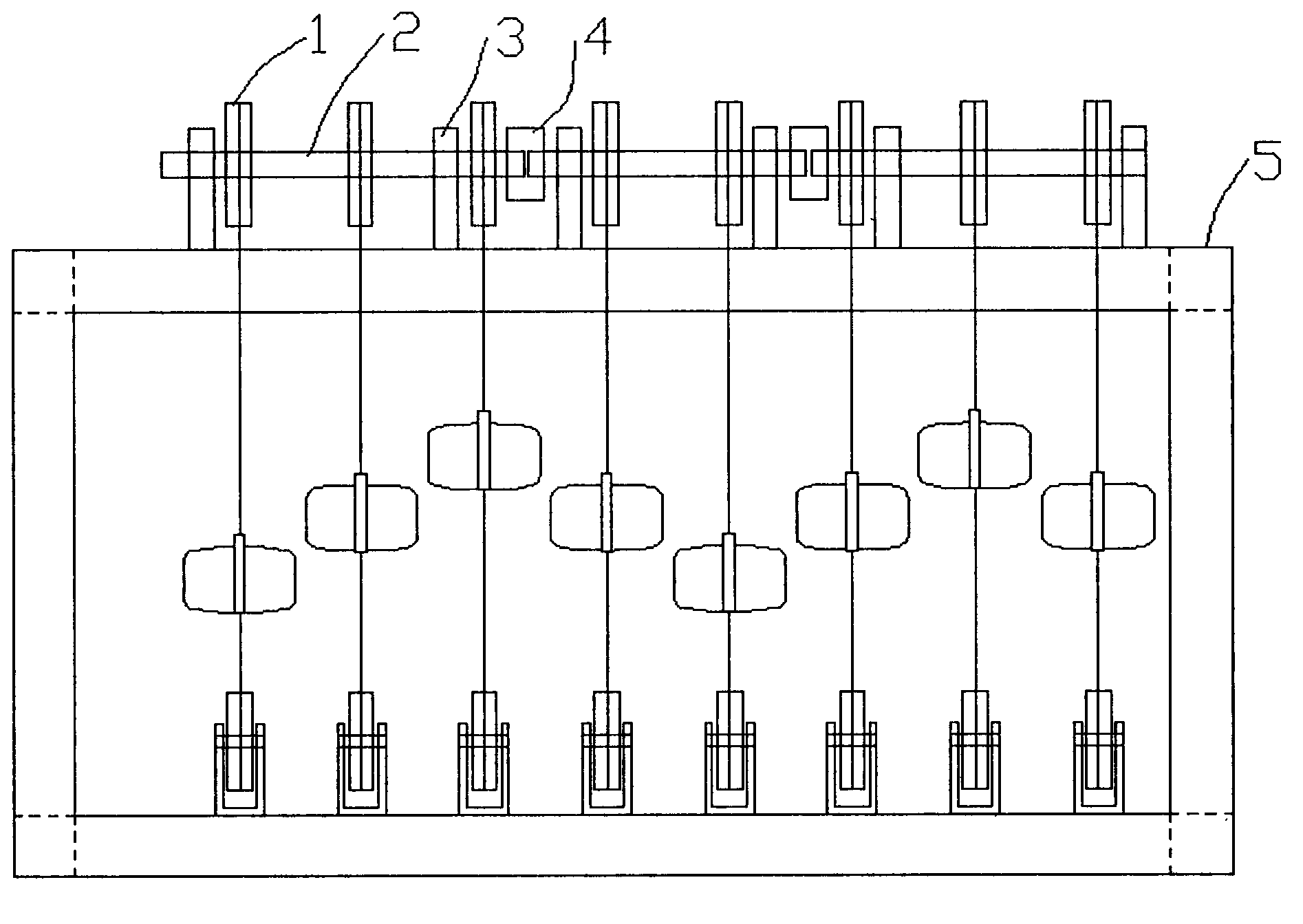
ActiveCN102979661AReduce conversion linksSimple structureGeneral water supply conservationGearingHydrogenLow speed
The invention provides an energy collection unit and a ratchet wheel and a wave force engine. The energy collection unit and the ratchet wheel and the wave force engine are used for collecting and gathering low-speed unordered and intermittent mechanical energy to form mechanical energy which is powerful, stable and continuous in output. The energy collection unit and the ratchet wheel and the wave force engine are particularly suitable for wave energy of rivers, lakes and oceans. The energy collection unit and the ratchet wheel and the wave force engine comprise a frame, a synchronous shaft, bearing seats, and an energy collection unit. The synchronous shaft is installed on the upper portion or the lower portion of the frame through the bearing seats. The synchronous shaft is namely a power output shaft. At least one set of the energy collection unit is installed on the synchronous shaft. Flexible transmission parts of the energy collection unit form a closed polygon force transmission structure through pulleys, floaters, pre-tensioners, and a ratchet wheel device, wherein the pulleys are installed on the lower portion and the upper portion of the frame, and the ratchet wheel device is installed on the synchronous shaft. The development of wave energy is renewable energy utilization which is green, clean and environmental friendly, material resources are not consumed, no emission or waste is produced, affects of wave sizes and tidal levels are overcome, and meanwhile, the collected standing wave energy, traveling wave energy and tidal energy can be used for power generating, sea water desalination, hydrogen generation, mechanical energy required for various processing methods, and the like.
Owner:刘运桃
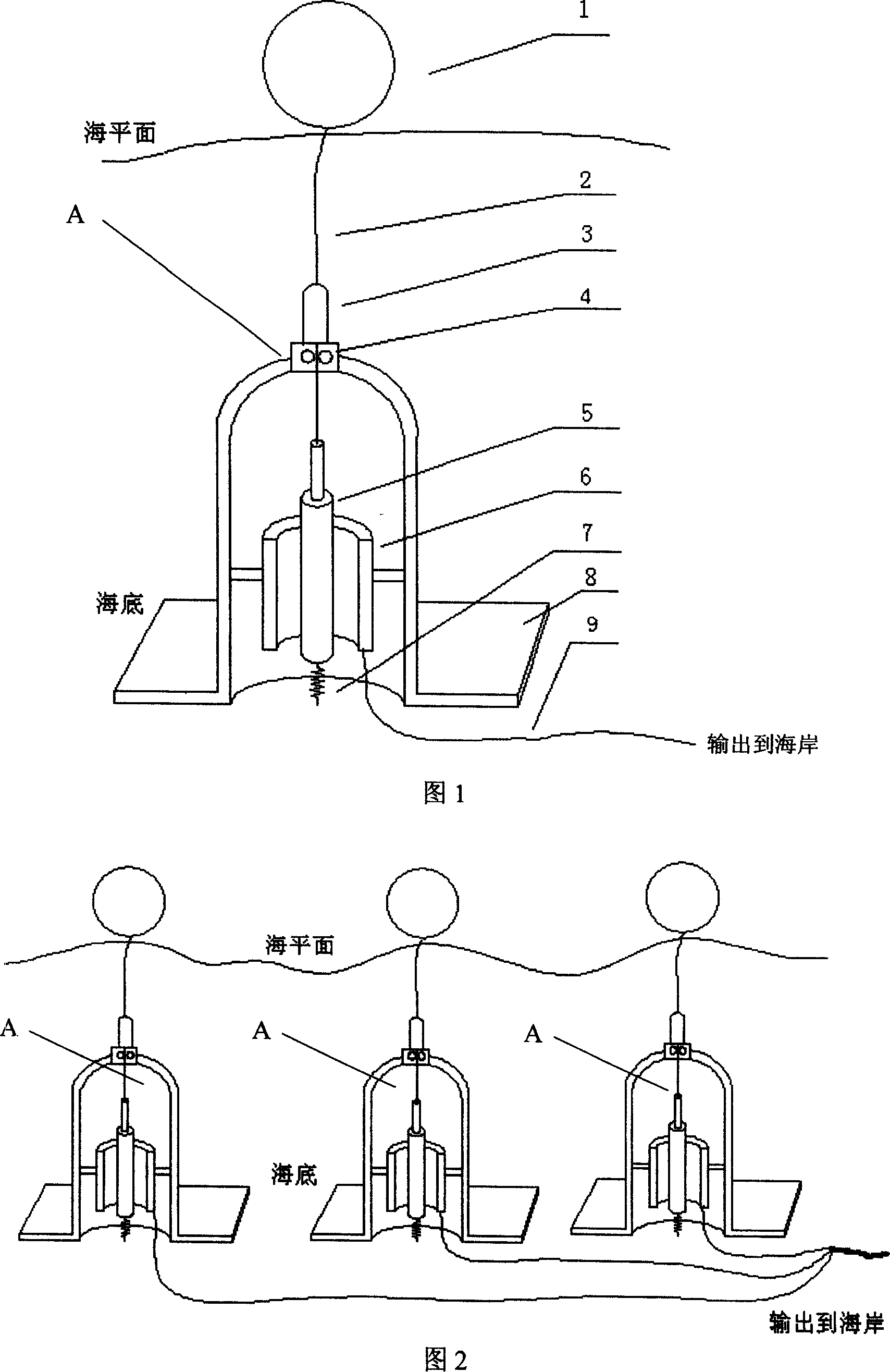
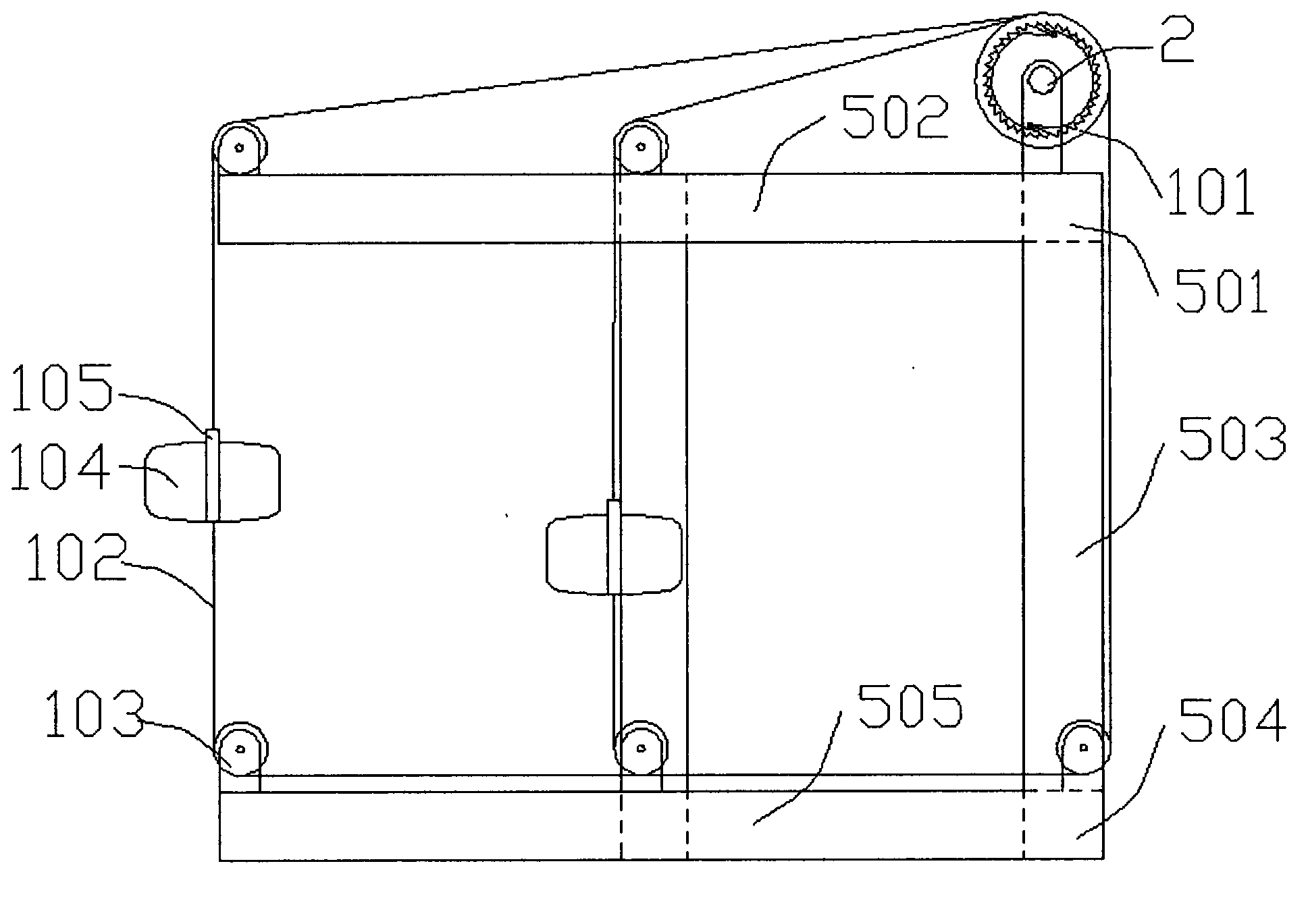
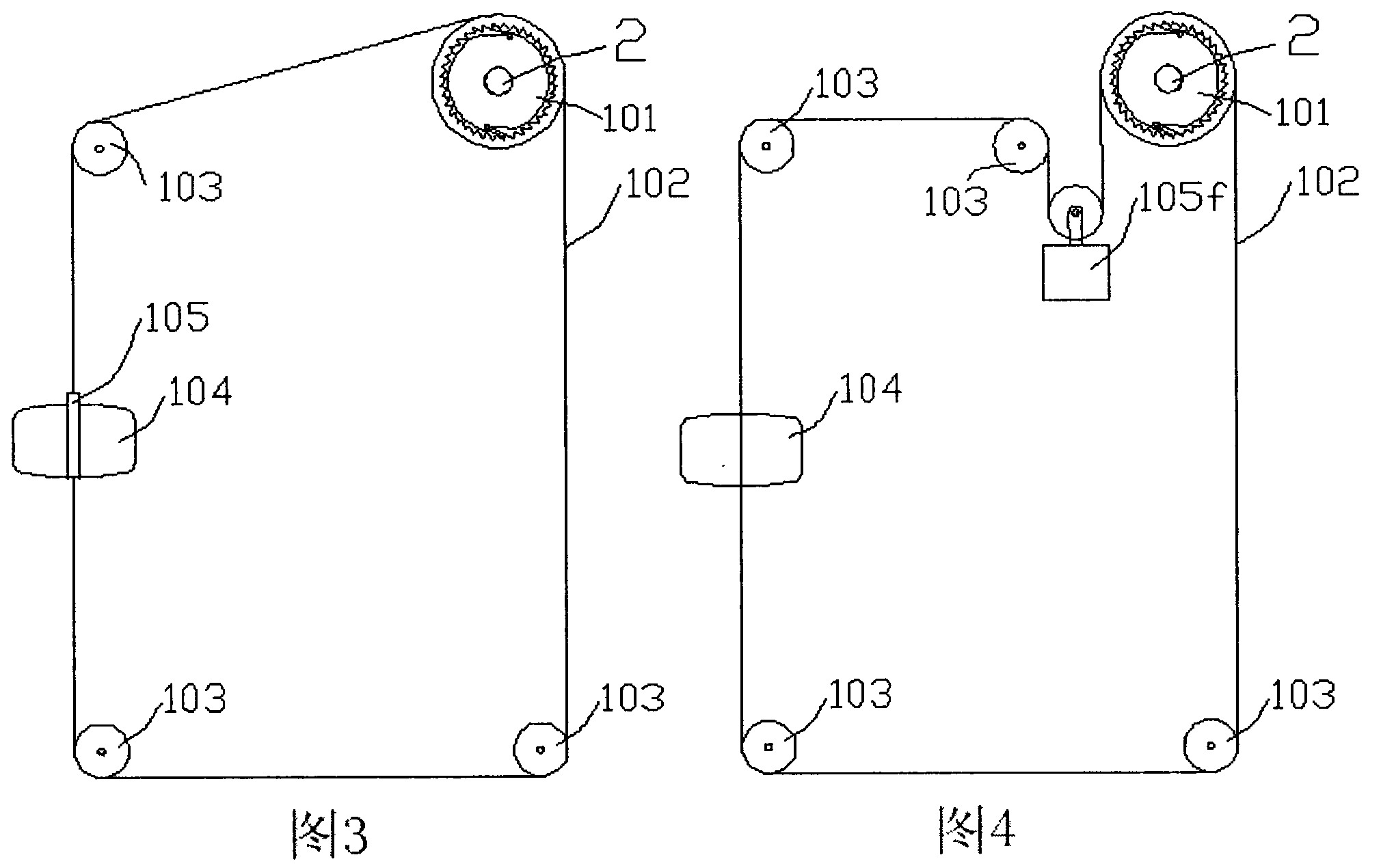
Marking buoy device using a wave-force generation to emit light by converting wave force to electric energy
A mark floating apparatus is provided to improve the efficiency, to excellently operate functions of main units in a rough sea-weather condition and to improve the durability by converting wave force to electric energy. A supporting member is combined with an upper and a lower supports and a pair of guide rodsvertically. A mark light is combined with the upper part of the upper support. A resistance plate moves the guide rods upward and downward by forming in a downward curvature. An operating device drives a generator by the vertical movement of a shaft and a floating to be combined with the resistance plate and charges a battery through a charging controller. A buoyancy member is a cylindrical shape to generate the buoyancy by combining with the middle of the supporting member. The buoyancy member stores the operating device in an additional space hermetically. A flickering controller operates the mark light in a preset flickering cycle by installing in the upper support. Thereby, a mark floating apparatus emits light by converting wave energy to electric energy.
Owner:车奉烈
Covering block for decreasing wave forces
A covering block for constructing a breakwater comprises a front wall in which horizontal projections are formed up and down transversal rectangularshaped openings therebetween, in parallel rows, side walls left and right jointed at the both ends of the front wall, a partition wall in which multiple holes are formed to communicate with the above said openings, being jointed to the side walls at both ends, and a detention pond surrounded by the above four walls for reserving the overflow waves, are designed concrete stacked, assembling devices which are very convenient for constructing and handling.
Owner:YANG WON HOI
A method and system for measuring hydrodynamic response of a floating body under wave action
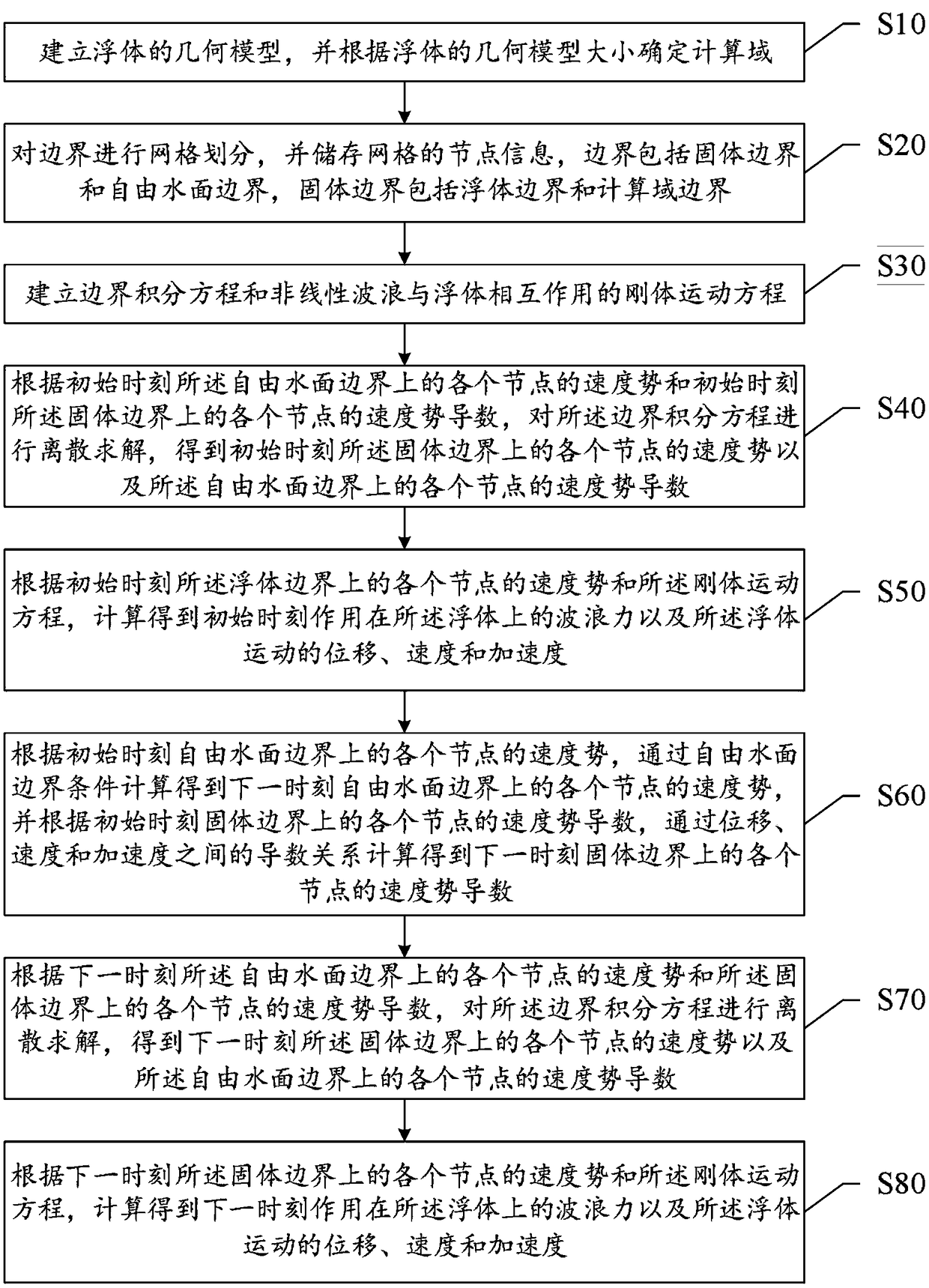
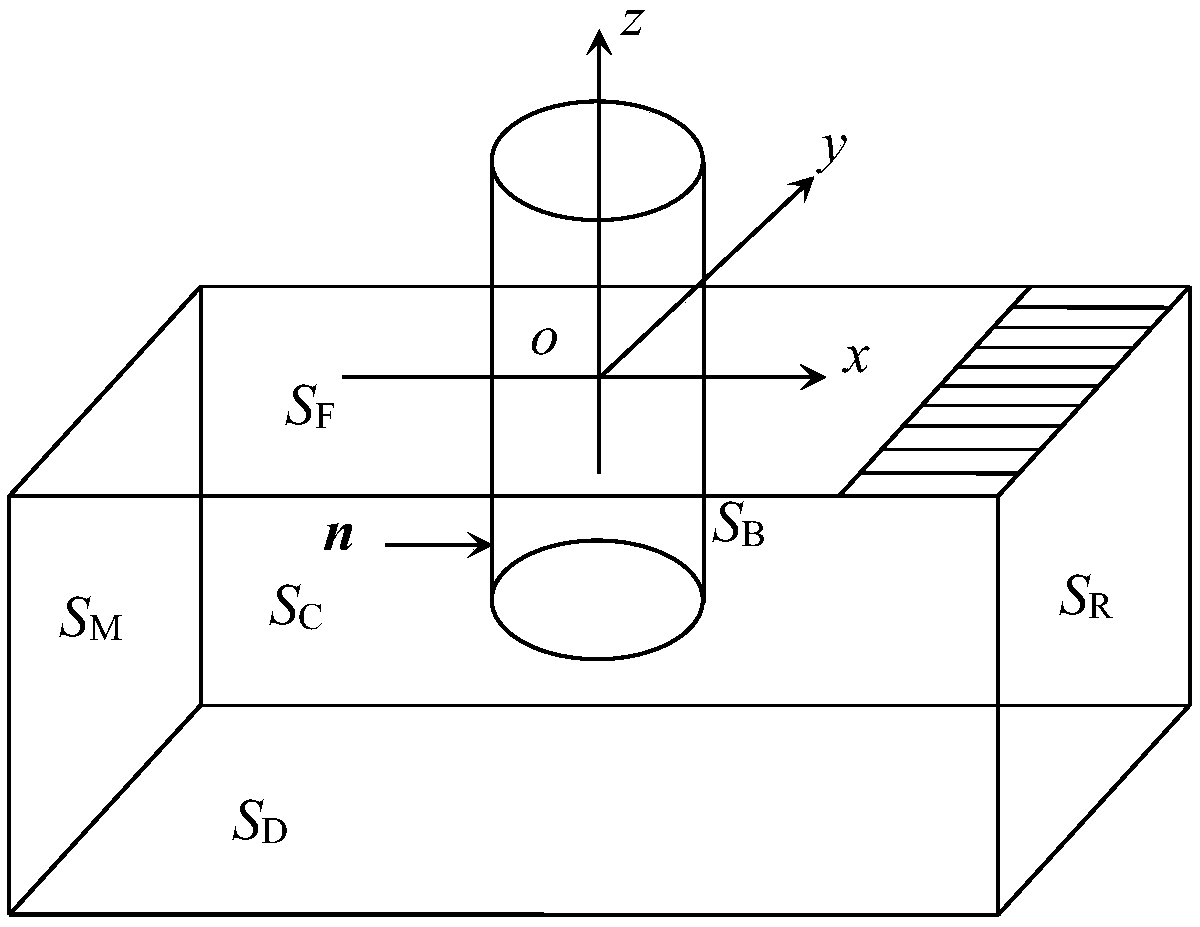
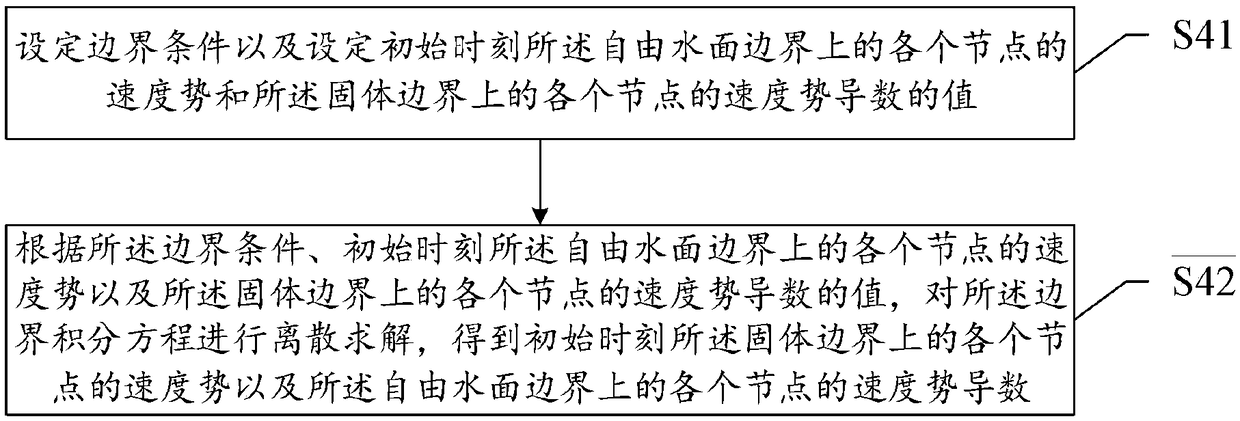
ActiveCN109446581ASolve the problem of insufficient consideration of nonlinearityImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADHydrodynamic testingComputer scienceVelocity potential
The invention discloses a method and system for measuring the hydrodynamic response of a floating body under the wave action. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a floating body geometric model and determining a calculation domain; meshing the boundary and storing the node information of the mesh; establishing boundary integral equation and rigid body motion equation; solvingthe boundary integral equation and rigid body motion equation at the initial time, and obtaining the velocity potentials of each node on the solid boundary at the initial time, the velocity potentialderivatives of each node on the free surface boundary, the wave forces on the floating body and the displacement, velocity and acceleration of the floating body motion; according to the parameters ofeach node at the initial time, calculating the velocity potential of each node on the solid boundary at the next time, the velocity potential derivative of each node on the free surface boundary, thewave force on the floating body and the displacement, velocity and acceleration of the floating body motion. The present invention solves the problem of insufficient consideration of nonlinearity in the process of interaction between wave and structure in the prior art, and improves the calculation accuracy.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
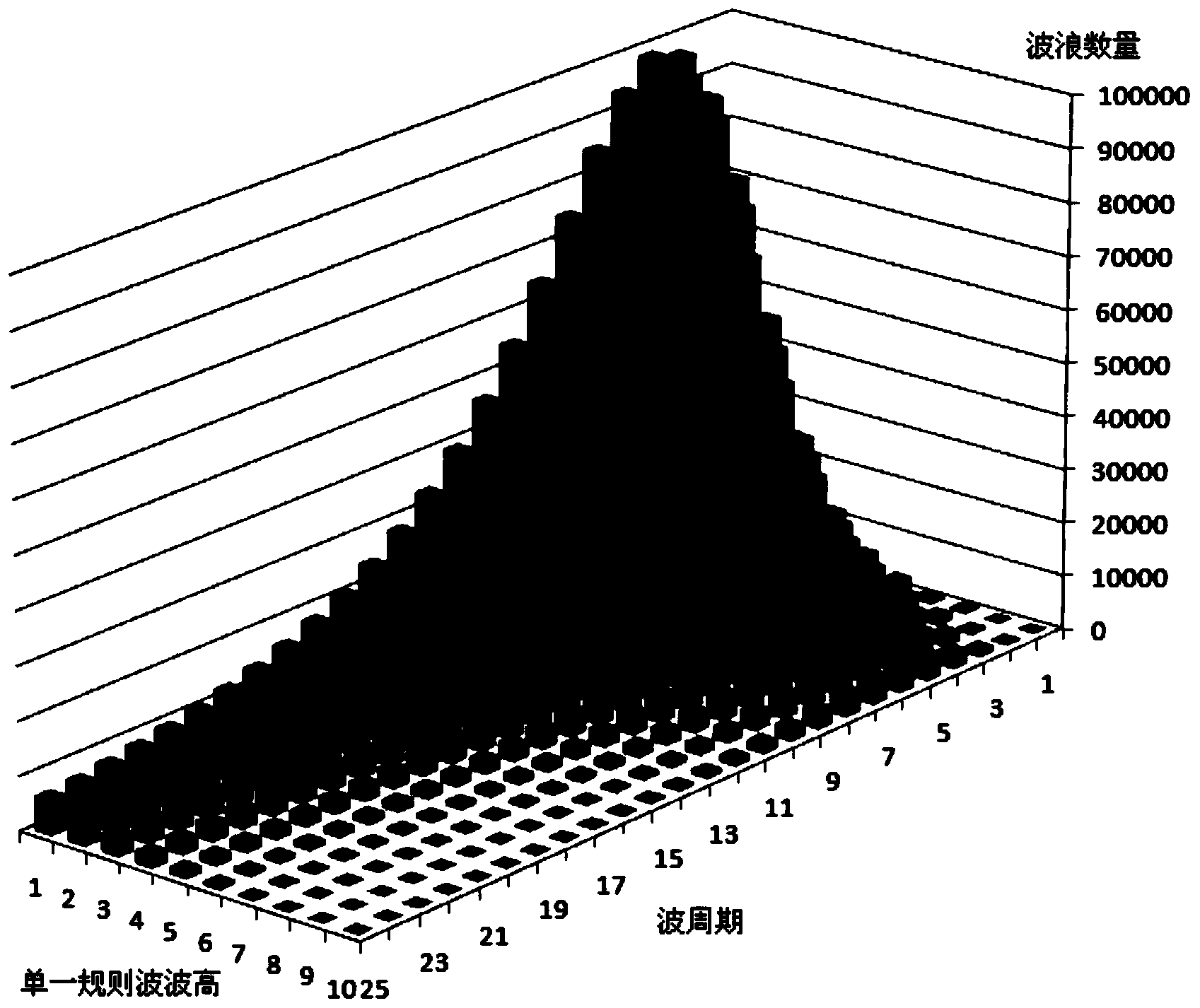
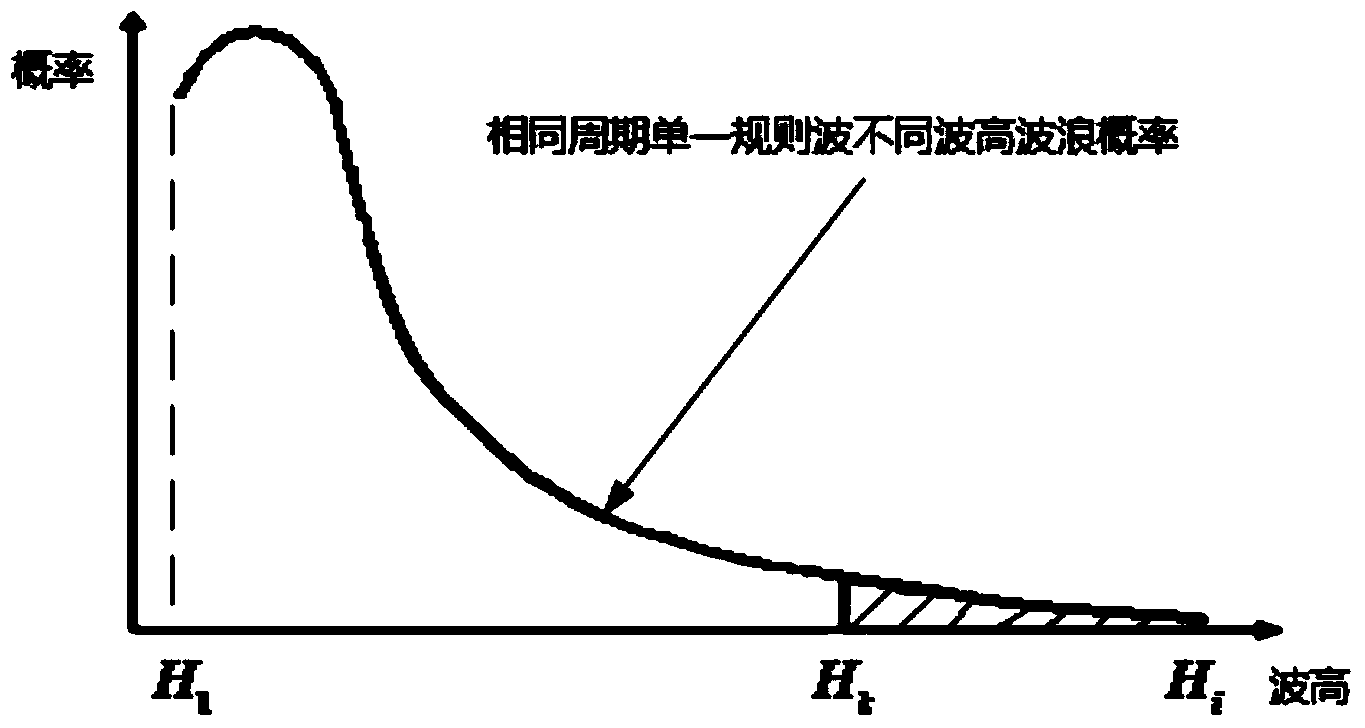
Fundamental wave determining method for jacket platform frequency spectrum fatigue analysis
ActiveCN104021288AAddressing Fatigue Prediction ErrorsGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumLinear relationship
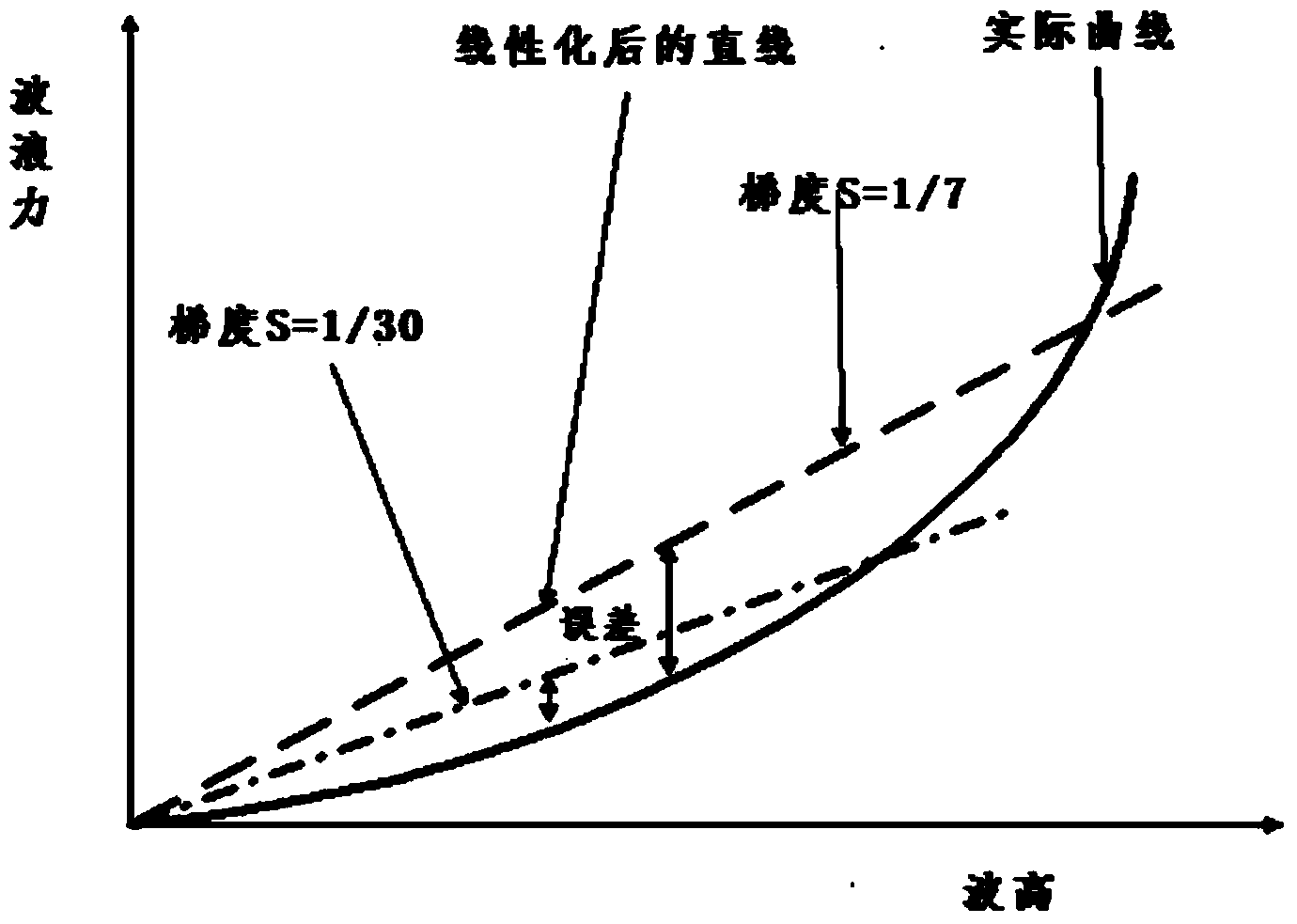
The invention provides a fundamental wave determining method for jacket platform frequency spectrum fatigue analysis. The method includes the steps that firstly, sea condition data are obtained; secondly, the sea condition data are processed; thirdly, wave spectra corresponding to sea conditions in all single directions are calculated; fourthly, the height of single rule waves of each sea condition and probability distribution of the cycle of the corresponding wave in each single direction are obtained; fifthly, the number of the single rule waves is calculated; sixthly, the heights of the same single rule waves and the numbers of the single rule waves of the corresponding wave cycles are accumulated, and a distribution histogram of the heights of the single rule waves, the wave cycles and the wave numbers is obtained; seventhly, the numbers of the single rule waves are expressed in a percentage mode according to the corresponding relation of the heights of the single rule waves and the number of the waves in each wave cycle, and the heights of the fundamental waves which exceed the percentage with the determined cycle are determined. According to the fundamental wave determining method for the jacket platform frequency spectrum fatigue analysis, a calculation result is not affected by the non-linear relationship between the heights of the ocean waves and wave force, and the accuracy of frequency spectrum fatigue analysis calculation is ensured.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Viscous potential flow theoretical analysis method
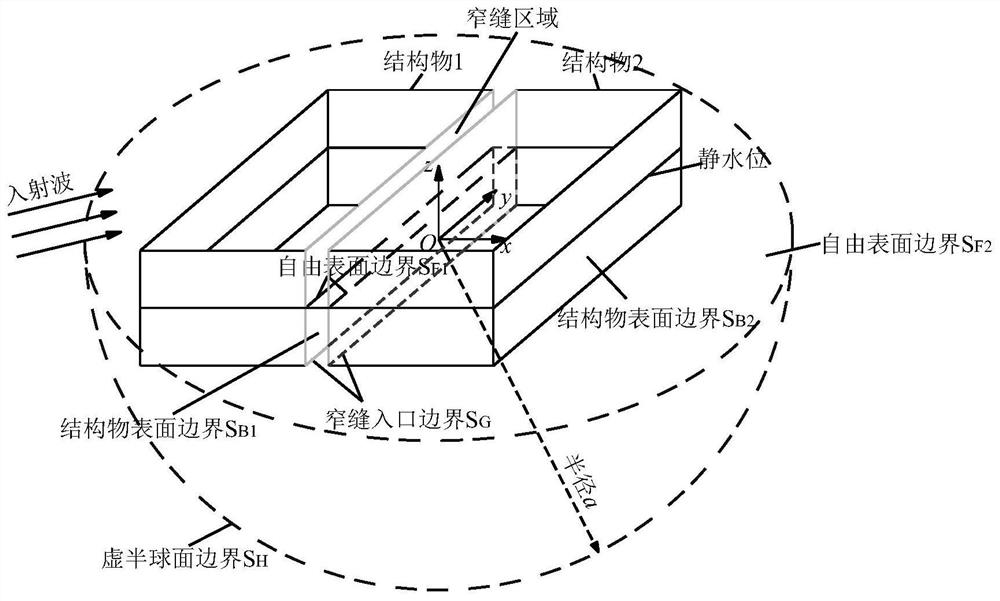
ActiveCN112182995AReduce the scope of the computational domainImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsWave heightMechanical engineering
The invention provides a viscous potential flow theoretical analysis method, which belongs to the technical field of hydrodynamic analysis. According to the theoretical analysis method, a nonlinear pressure loss condition is introduced into the narrow slit inlet boundary of the ocean structure, the whole fluid domain is divided into a plurality of areas in the analysis and solving process, and a multipole expansion method is used for obtaining a speed potential series expression of an external open fluid area; and finally, the boundary is dispersed, and the speed potential of each unit on allthe boundaries and the normal guide number of the speed potential are solved in combination with the nonlinear pressure loss condition of the narrow slit inlet boundary and the normal speed continuouscondition and the pressure continuous condition on the common boundary of other adjacent regions. And the resonance wave height in the narrow slits between the ocean structures and the wave force borne by the structures are obtained. According to the method, the wave energy dissipation in the narrow slit is effectively considered, the resonance wave height in the narrow slit and the wave force borne by the structure are reasonably calculated, and the calculation efficiency is high.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Multi mode wave energy converter with elongated wave front parallel float having integral lower shoaling extension
ActiveUS10094356B2Minimal energy consumptionWEC cost (CAPEX)Buoyancy controlMachines/enginesEngineeringEnergy expenditure
Owner:ROHRER TECH
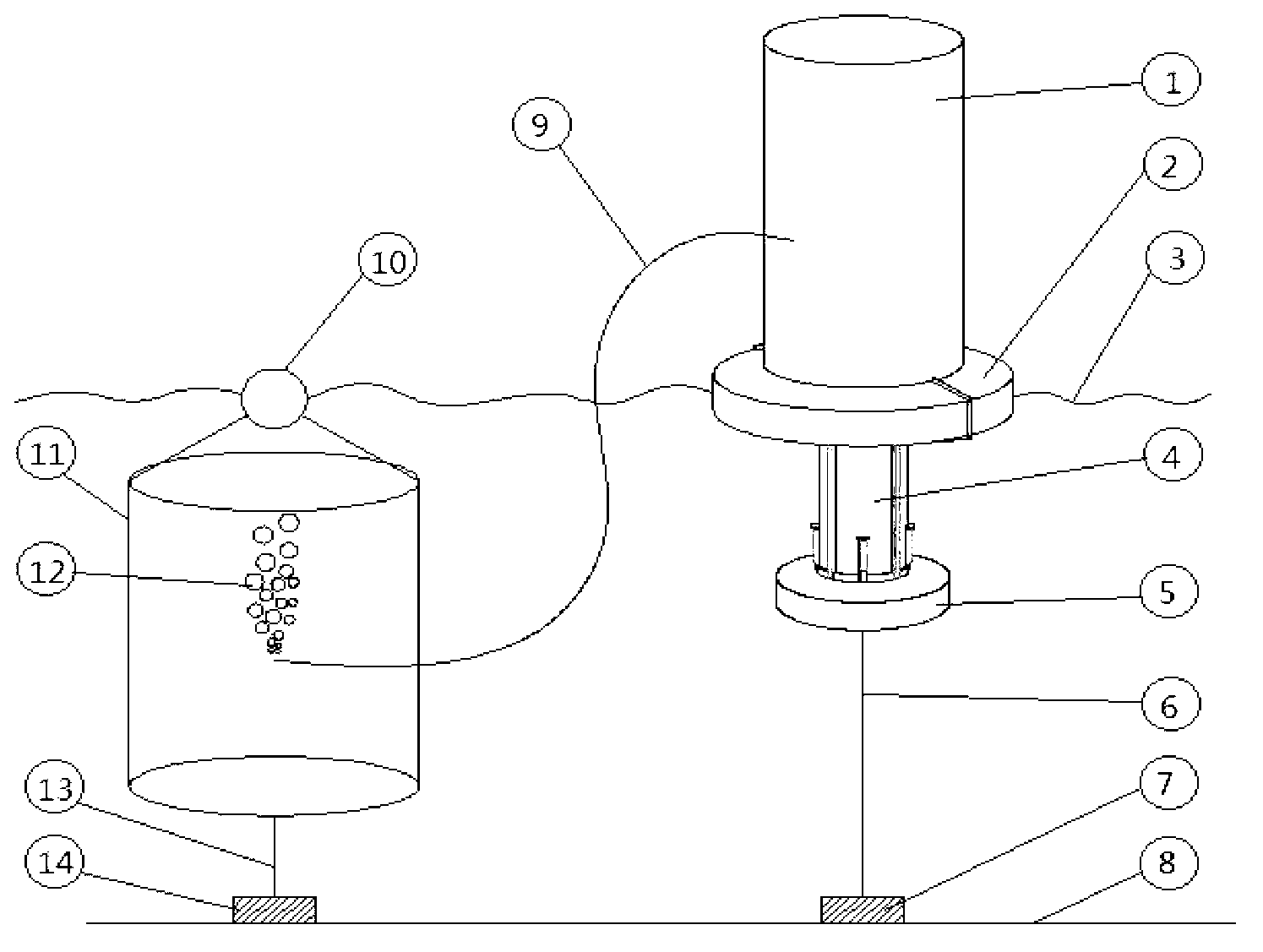
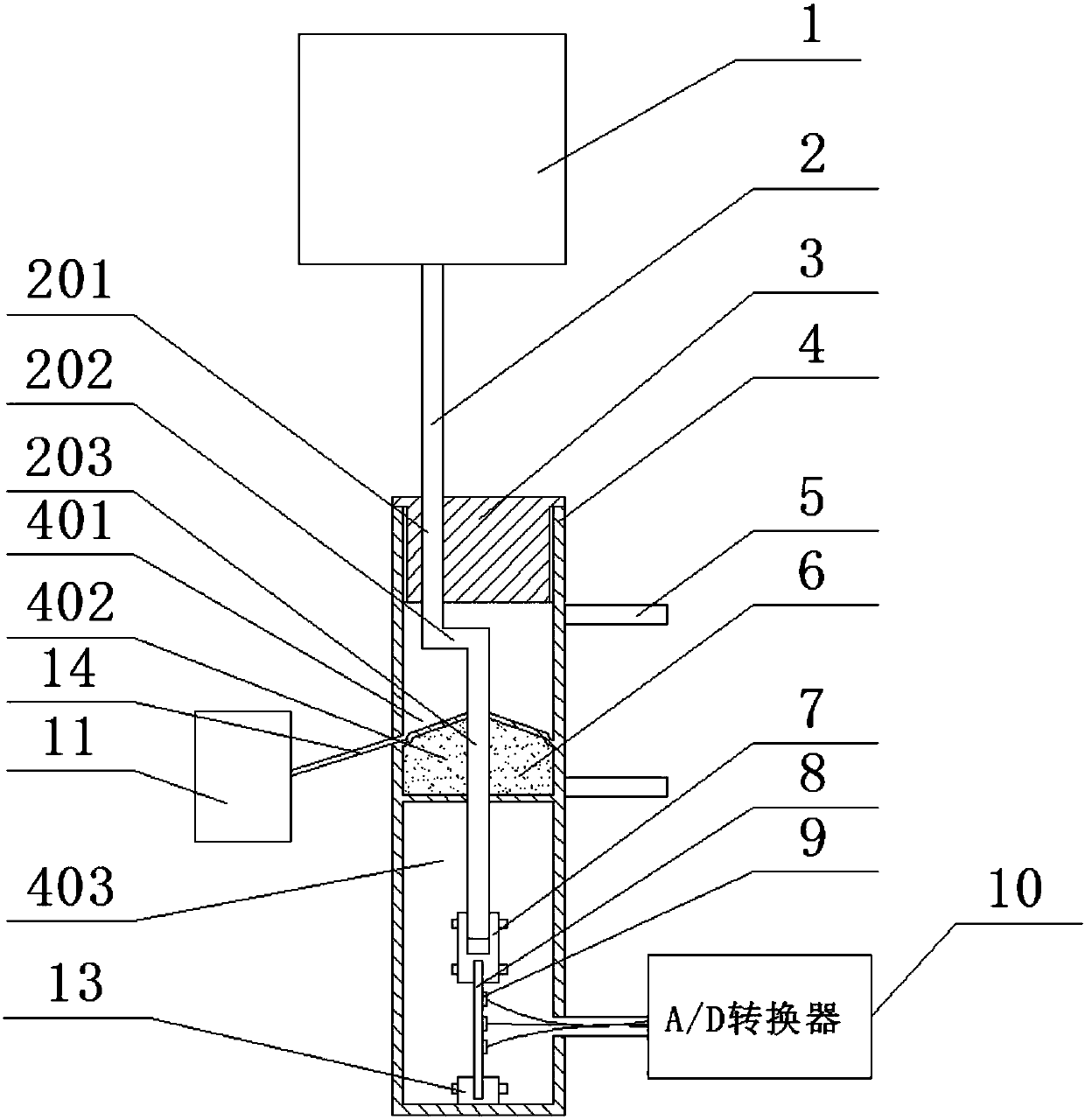
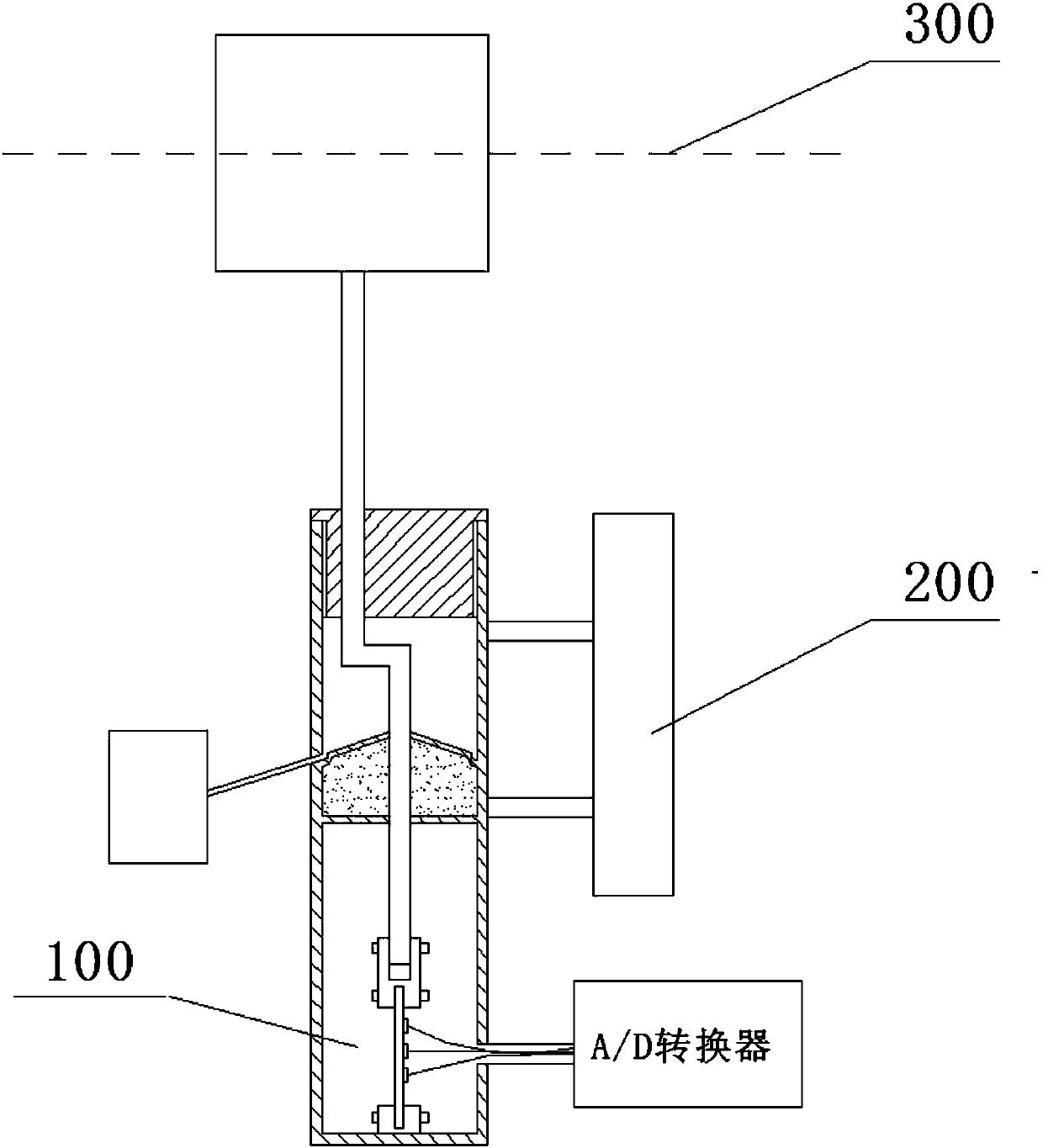
Ocean wave force monitoring device
ActiveCN107631826AEasy to installStrong structural reliabilityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsStructural reliabilitySurface ocean
An ocean wave force monitoring device disclosed by the present invention belongs to the signal monitoring technology field, and comprises a buoyancy column, a guiding rod, a sealing head, a sleeve, adrying agent, a fixing support, a connecting clamp, an elastic film, a strain gauge, a signal line, an A / D converter and a water storage tank. When the ocean waves pass the buoyancy column, and underthe action of the buoyancy, the buoyancy column drives the guiding rod to move up and down in a sliding cavity and further drives the elastic film connected at the bottom to telescope. According to the ocean wave force monitoring device provided by the present invention, the strain gauge on the elastic film real-timely outputs the strain signals of the elastic film, and the A / D convert converts anelectric signal into a digital signal to transmit to the monitoring device. Moreover, the ocean wave force monitoring device provided by the present invention is convenient to install, is strong in structure reliability and high in sensitivity, can adapt to the complex ocean environments, can monitor the ocean wave environments, and provides the good monitoring means for the ocean engineering construction.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
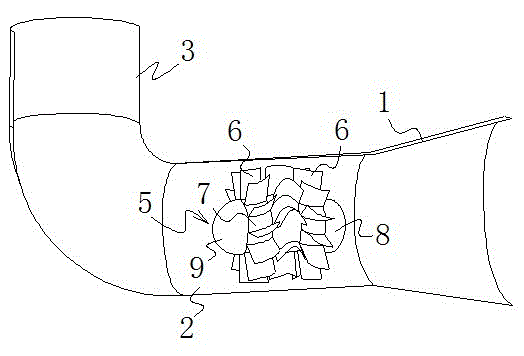
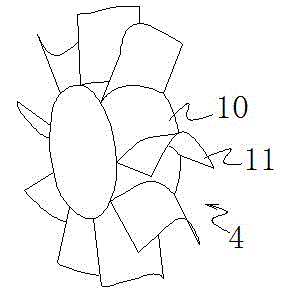
Wave force direct-driving hydraulic turbine
InactiveCN102943730ASimple structureEasy to install and maintainHydro energy generationReaction enginesWater storage tankWater flow
The invention relates to a wave force direct-driving hydraulic turbine which comprises an L-shaped body composed of a flow-guiding pipe, a flow-guiding wheel pipe and a water storage tank. Fixed type flow-guiding blades, a rotating wheel for enabling wave energy to be converted into electric energy and a flow-guiding body for placing an engine block are arranged in the flow-guiding wheel pipe. A plurality of rotating wheel blades are evenly arranged on the outer side of the rotating wheel in a circumferential direction, and an outer wall of the flow-guiding body is provided with two groups of fixed type flow-guiding blades used for guiding waves to the rotating wheel blades so as to drive the rotating wheel to rotate. The flow-guiding pipe enables the waves to be collected into the hydraulic turbine, and the water storage tank has the effect of storing flow flowing through a hydraulic turbine passageway. Within a wave period, water flow flows in and out in the hydraulic turbine to form reciprocated water flow and always drives the rotating wheel to rotate towards the same direction. The wave force direct-driving hydraulic turbine integrates wave energy capture and conversion, is simple in structure and convenient to install and maintain, has a wide high-efficiency area, and is high in adaptability to wave height changes.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com