Patents
Literature
444results about How to "Raise the resonant frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
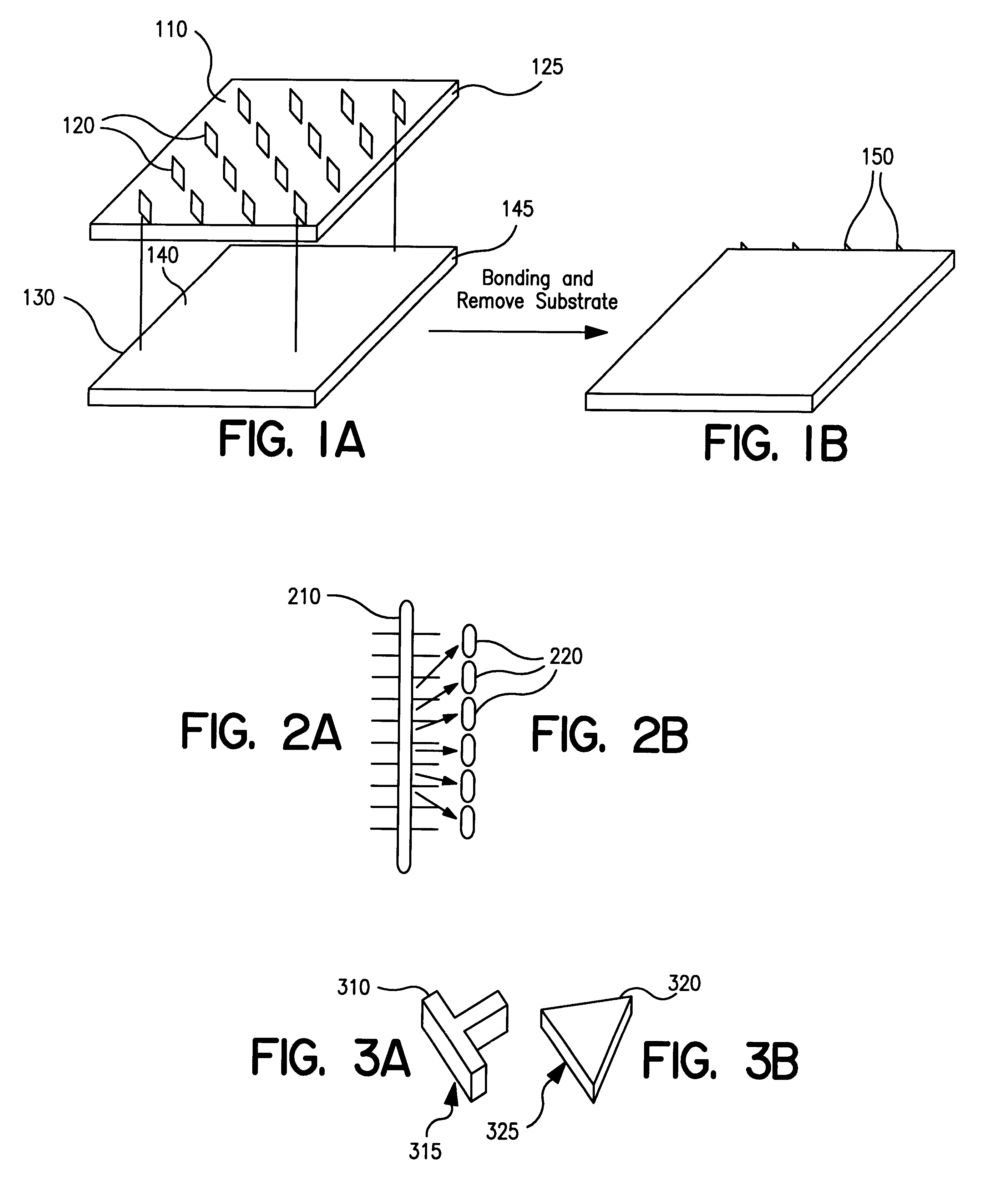
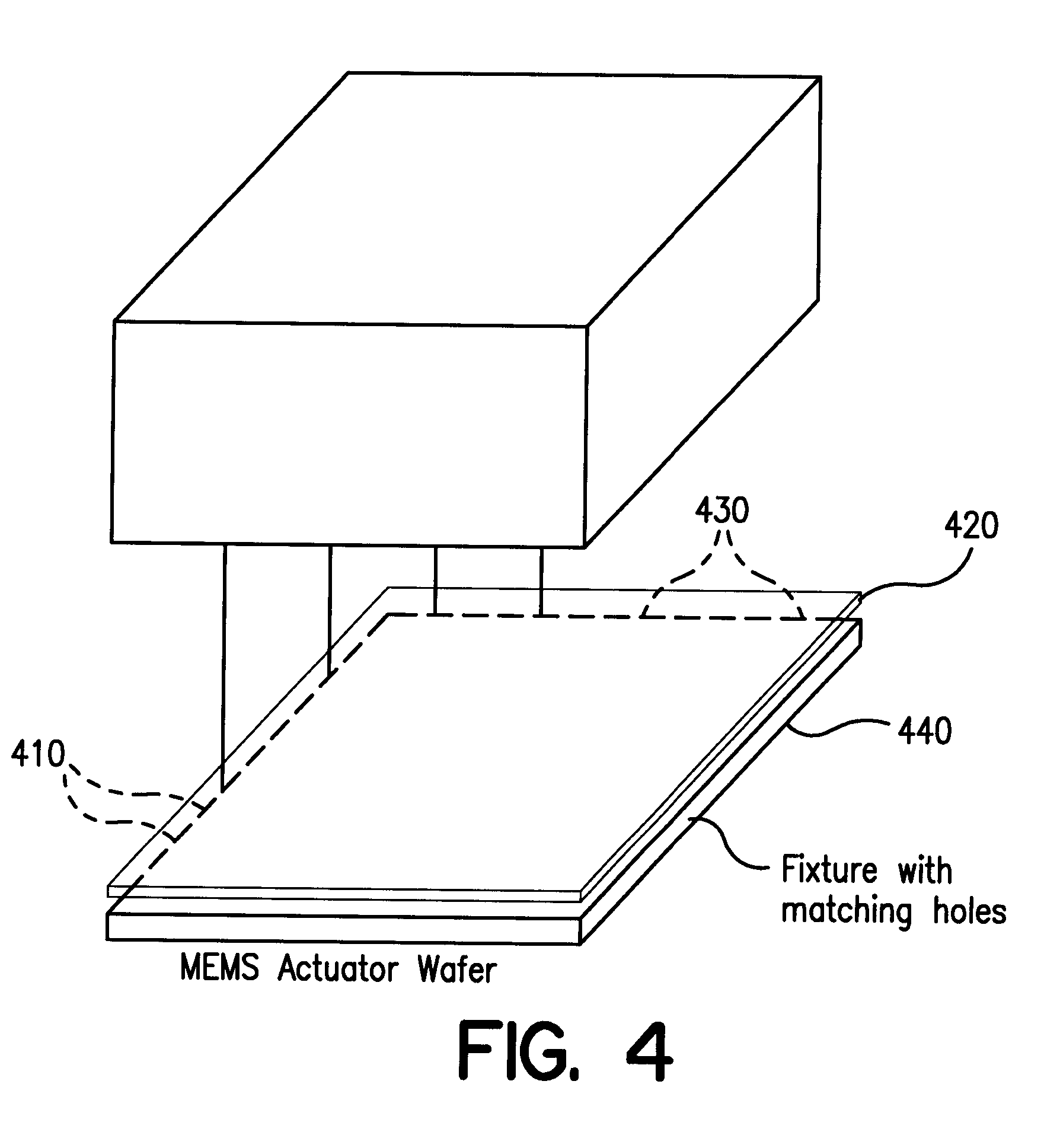
Method of using a plurality of smaller MEMS devices to replace a larger MEMS device
ActiveUS20100116632A1Resolution in capacitanceDesired capacitancePrinted electric component incorporationCapacitor with electrode distance variationOxide semiconductorSignal averaging
Embodiments disclosed herein generally include using a large number of small MEMS devices to replace the function of an individual larger MEMS device or digital variable capacitor. The large number of smaller MEMS devices perform the same function as the larger device, but because of the smaller size, they can be encapsulated in a cavity using complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) compatible processes. Signal averaging over a large number of the smaller devices allows the accuracy of the array of smaller devices to be equivalent to the larger device. The process is exemplified by considering the use of a MEMS based accelerometer switch array with an integrated analog to digital conversion of the inertial response. The process is also exemplified by considering the use of a MEMS based device structure where the MEMS devices operate in parallel as a digital variable capacitor.
Owner:QORVO US INC
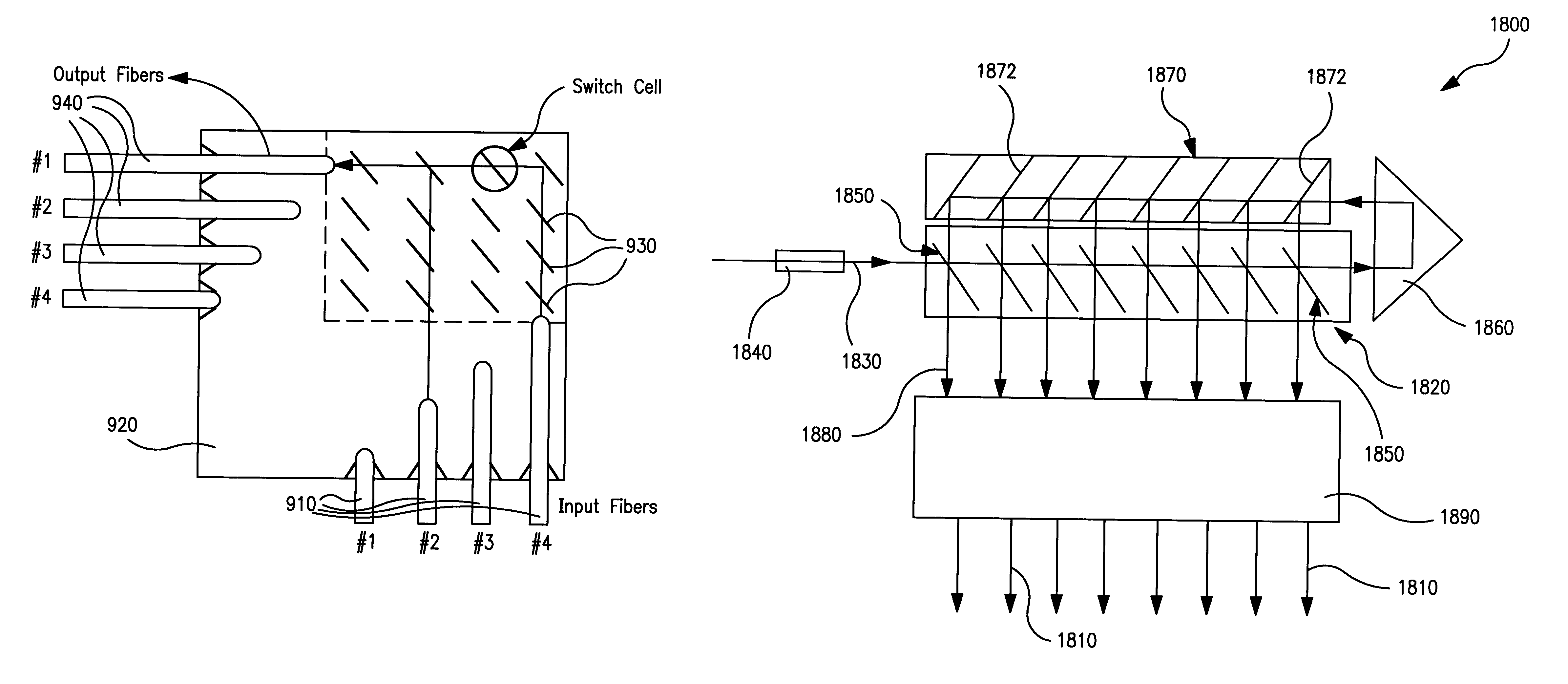
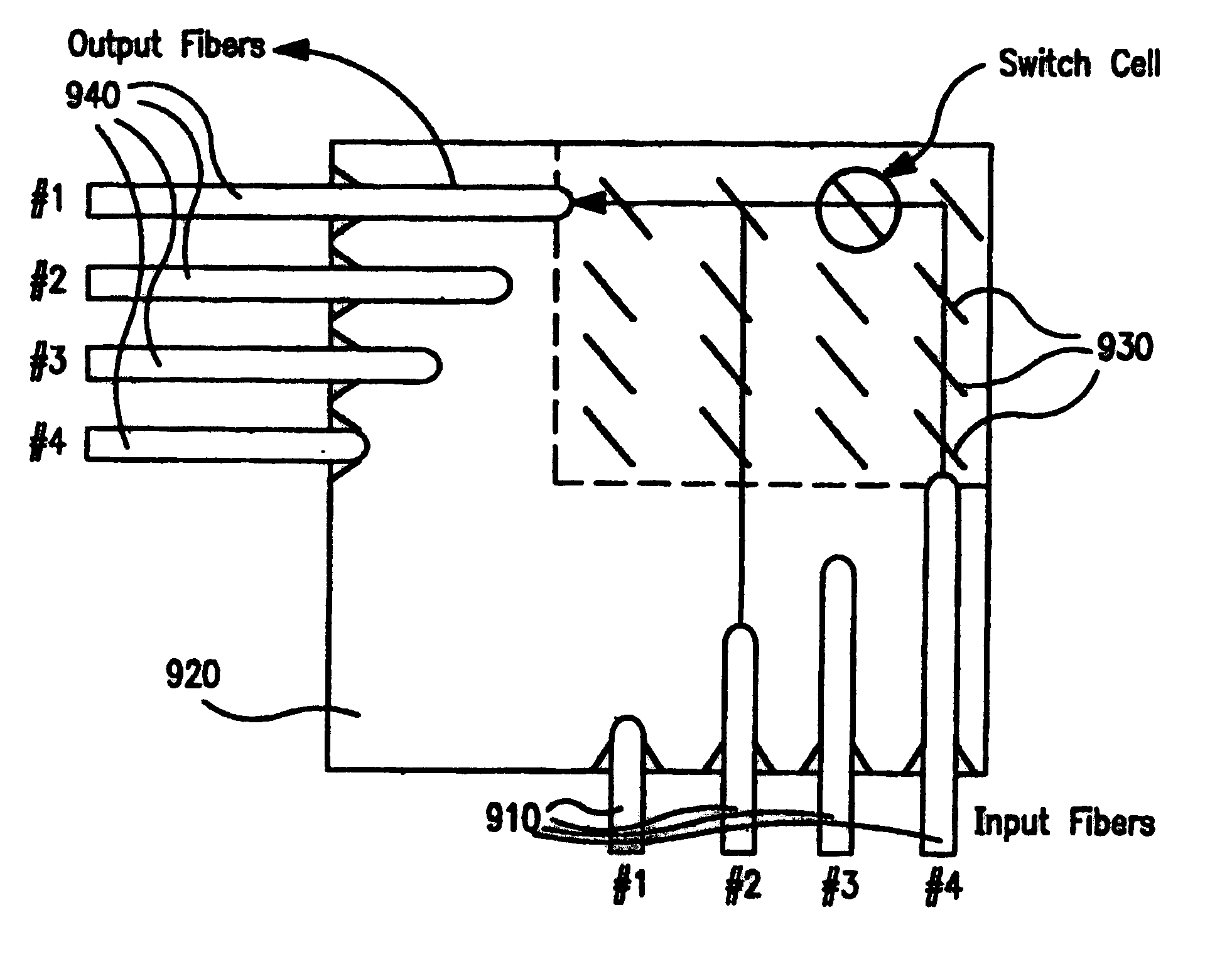
Micromachined optomechanical switching devices
InactiveUS6449406B1Reduce packaging costsSmall massMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesEngineeringActuator
Various configurations of micromachined optomechanical switching cells are disclosed herein. In accordance with the invention, an optomechanical switching cell is provided which includes an actuator positioned on a substrate and a mirror coupled to the actuator. The switching cell also includes an electrode disposed upon the substrate under the actuator. An insulator may also be interposed between the substrate and the electrode. In another aspect of the present invention the switching cell includes a latch having a first end region connected to the substrate and a second end region engaged by the mirror.
Owner:OMM +1
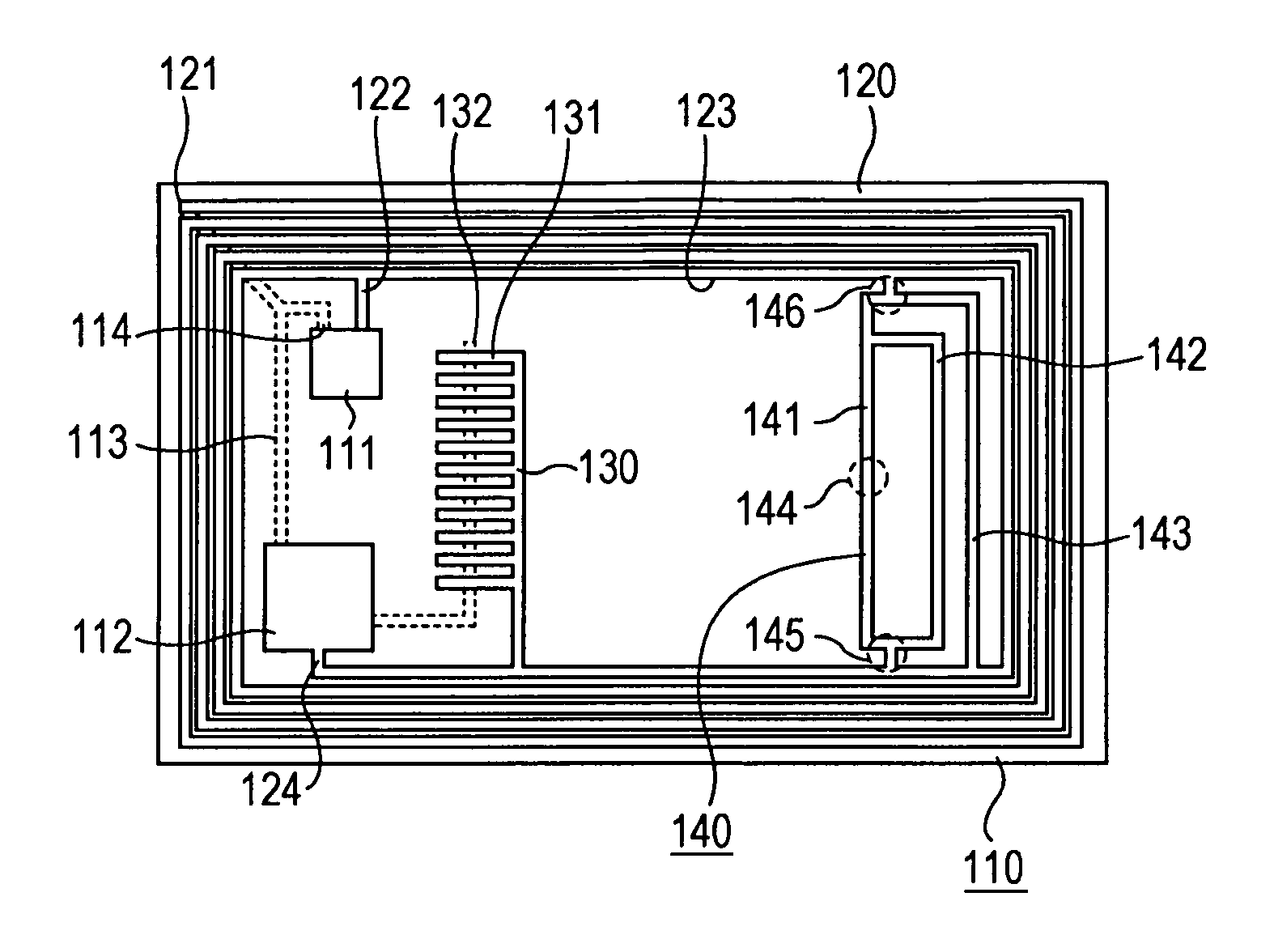
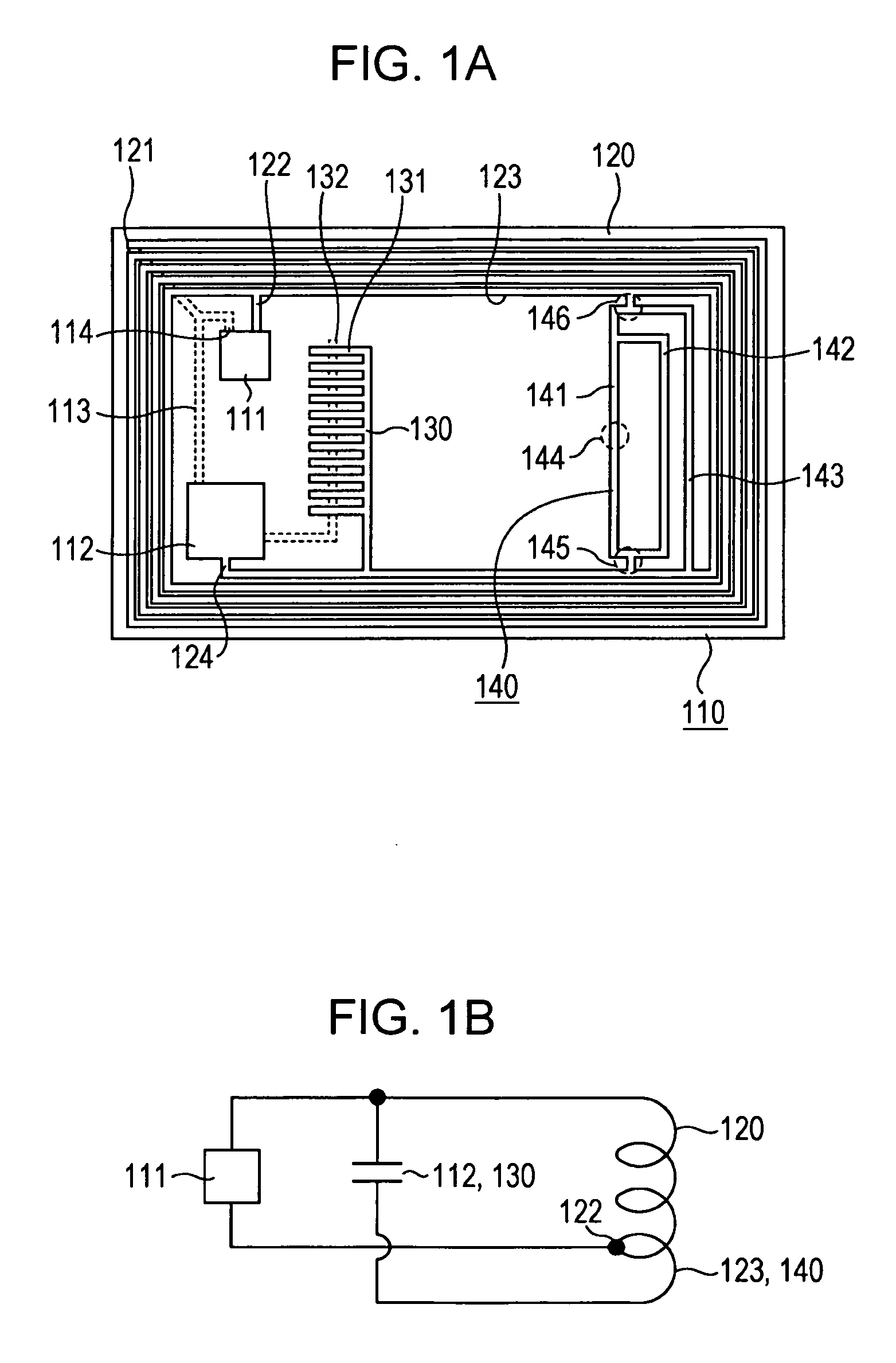
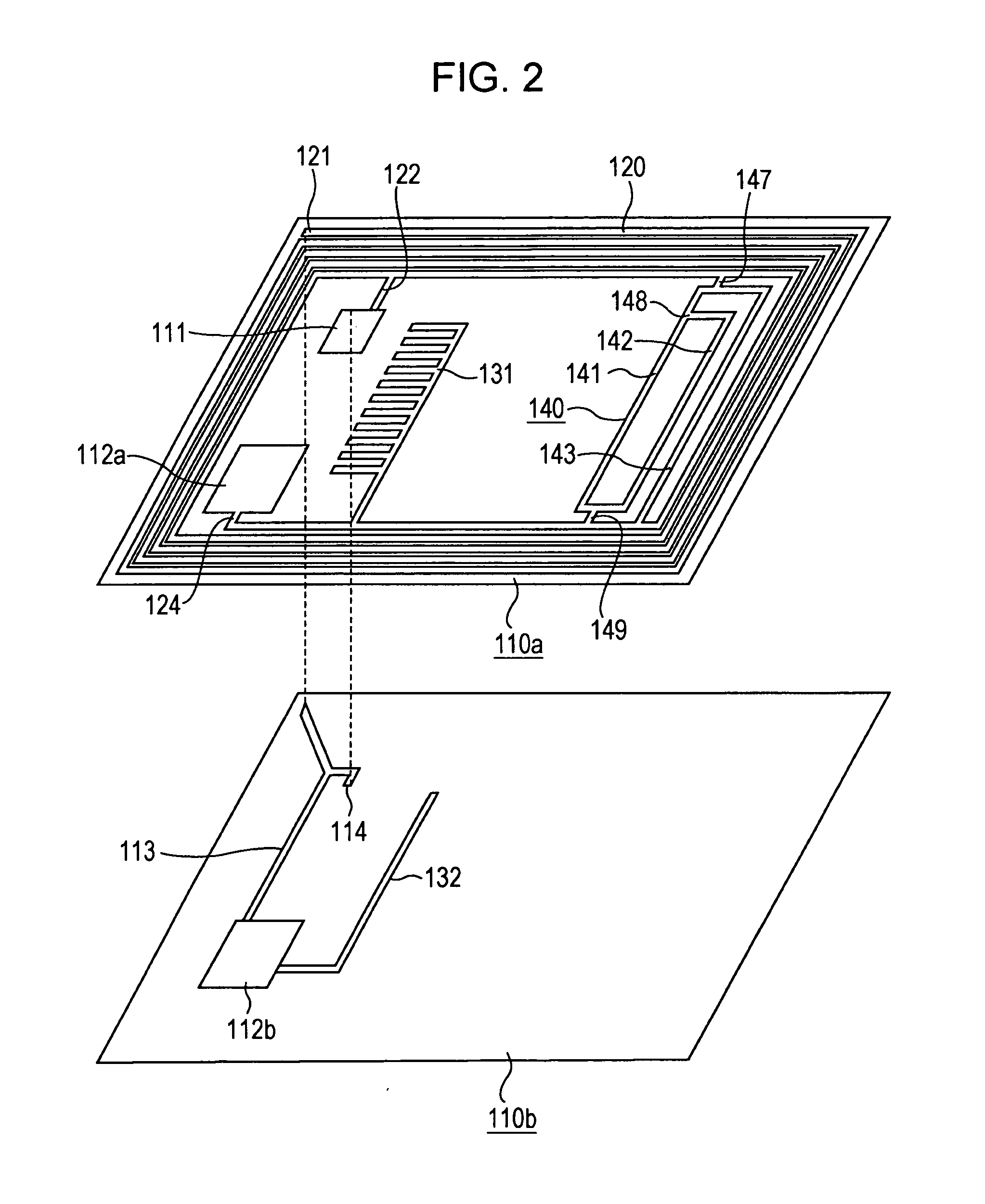
Contactless communication medium, antenna pattern-placed medium, communication apparatus, and antenna adjusting method
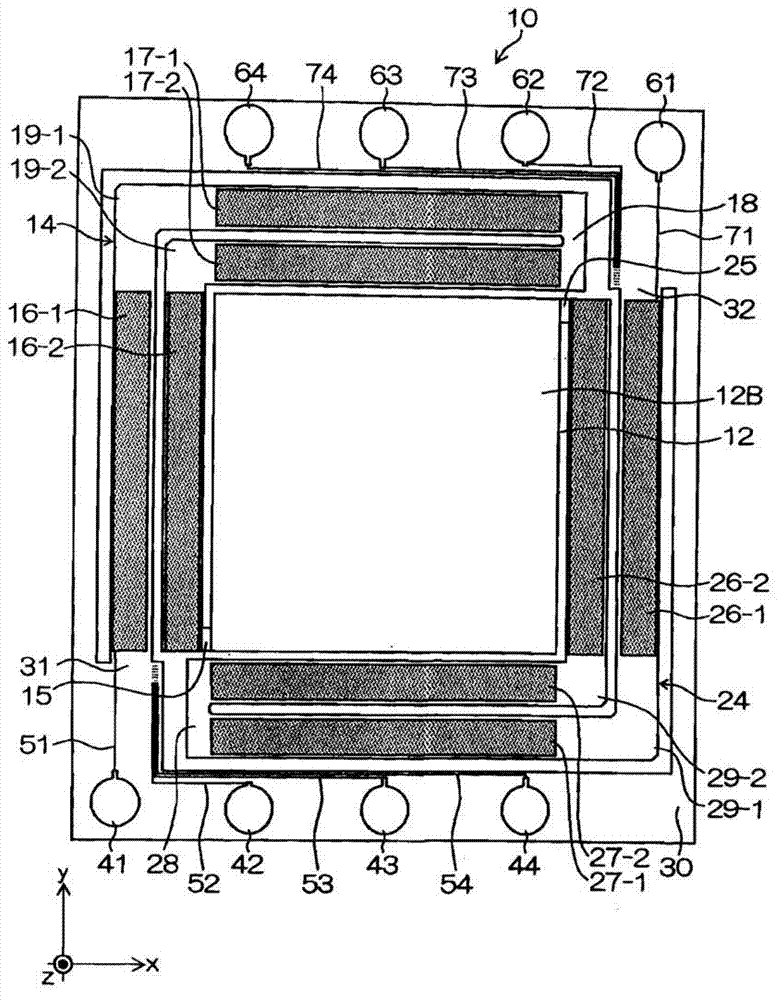
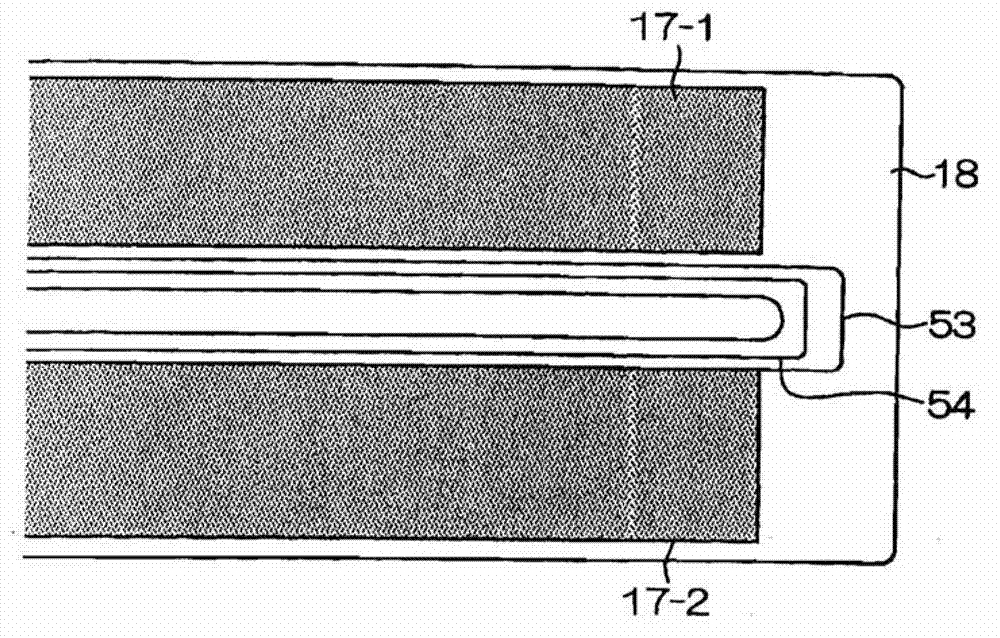
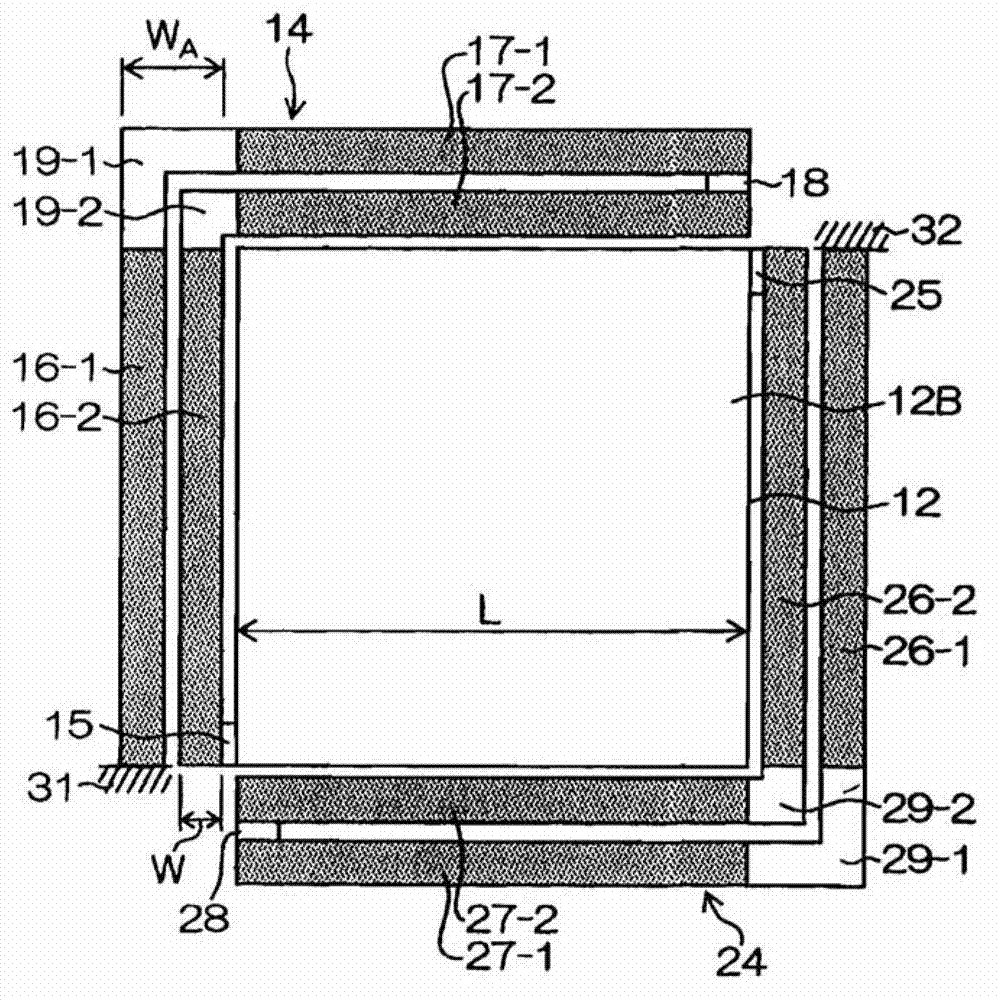
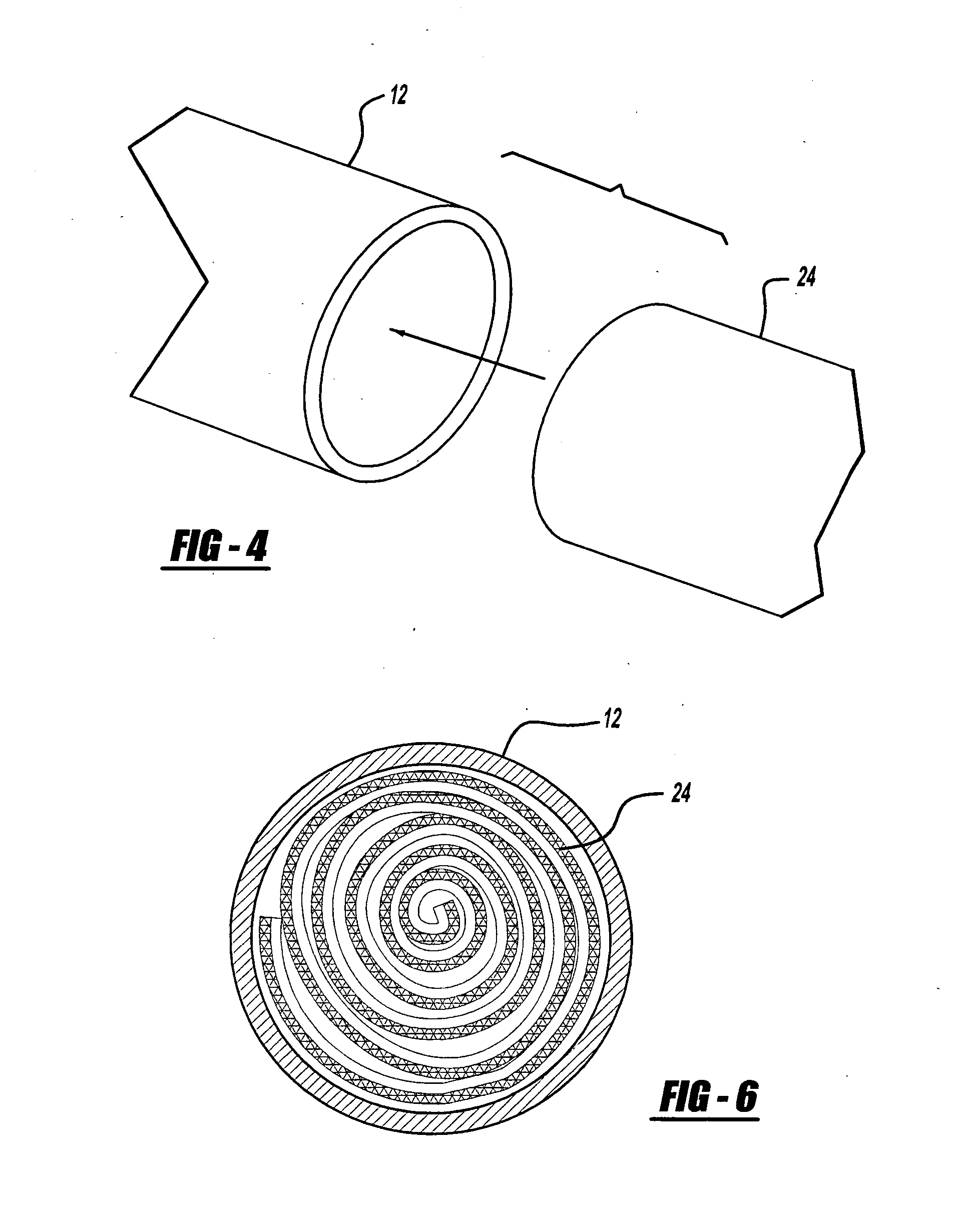
InactiveUS8774712B2Reduce capacitanceRaise the resonant frequencyResonant long antennasNear-field transmissionElectrical conductorEngineering
A contactless communication medium includes a base made of an insulating material, an antenna coil section including a conductor wound in a planar shape on the base, an inductance adjusting conductor pattern that is connected in parallel to a part of the conductor in the antenna coil section, and is placed on the base, a capacitor connected to the antenna coil section, and a communication processing section that is connected to the antenna coil section and the capacitor to perform contactless communication processing.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optomechanical matrix switches including collimator arrays
InactiveUS6445841B1Reduce packaging costsSmall massMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesActuatorOptical alignment
Various configurations of optomechanical matrix and broadcast switches are disclosed herein. One such optomechanical matrix switch includes a substrate and a plurality of optomechanical switching cells coupled thereto. Each of the optomechanical switching cells includes a mirror and an actuator. The matrix switch further includes an array of collimator elements, each of the collimator elements being in optical alignment with one of the optomechanical switching cells. Also disclosed herein is a distributed matrix switch including first and second optomechanical matrix switches. The first and second optomechanical matrix switches respectively include first and second pluralities of optomechanical switching cells mounted upon first and second substrates. A collimator array is interposed between the first and second matrix switches in optical alignment with the first and second pluralities of optomechanical switching cells.
Owner:CROSSFIBER +1
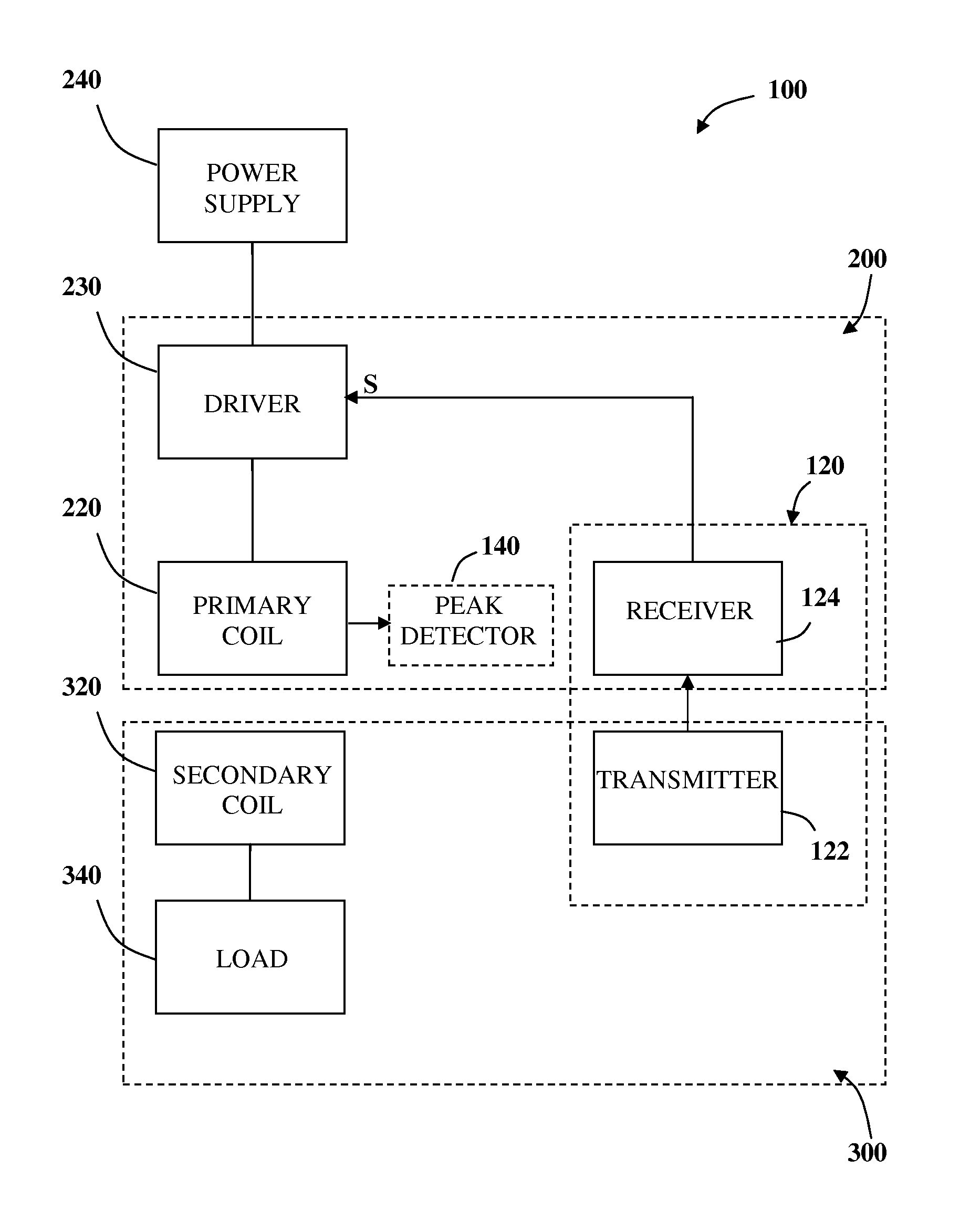
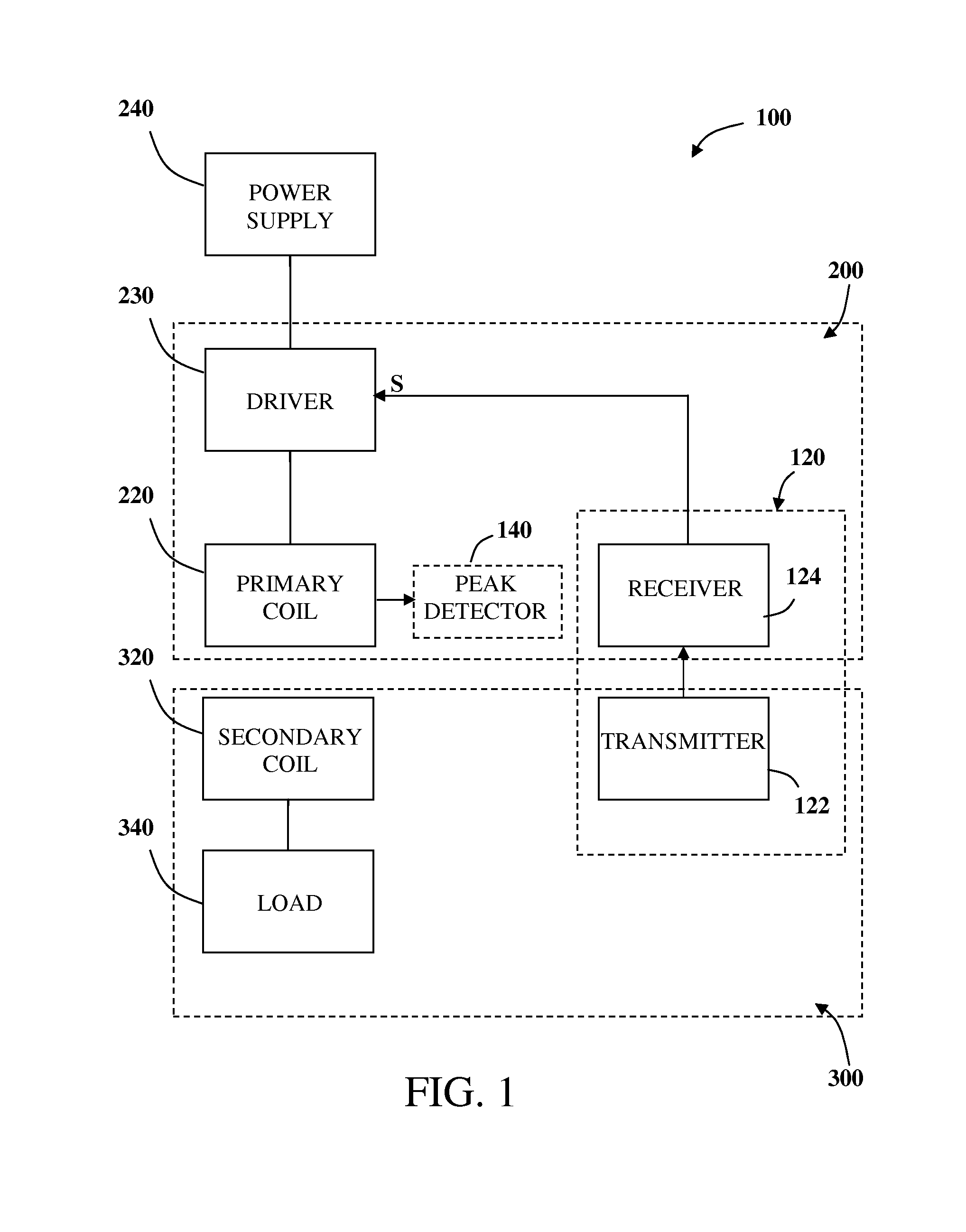
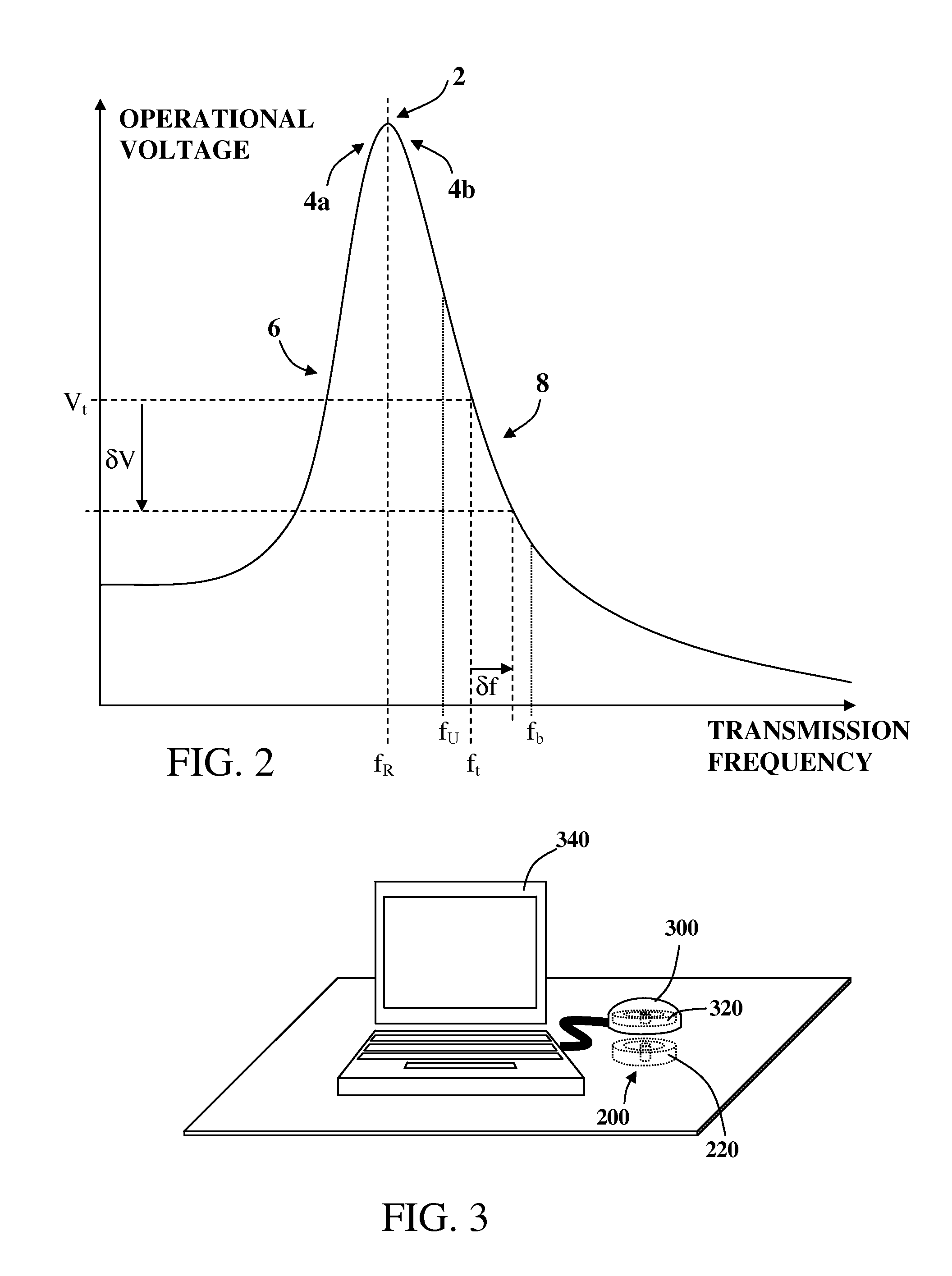
Inductive power transmission system and method for concurrently transmitting digital messages
ActiveUS20140239732A1Raise the resonant frequencyNear-field transmissionTransformersElectric power transmissionSignal generator
An inductive power receiver including a resonant circuit, a rectifier, a rectified current sense, and a communication and control unit includes a communications modulator and at least one signal generator operable to generate a set of communication signals including a series of pulses generated at characteristic frequencies. Communication signals provide instructions for an inductive power outlet to regulate power transfer to the inductive power receiver.
Owner:POWERMAT TECHNOLOGIES
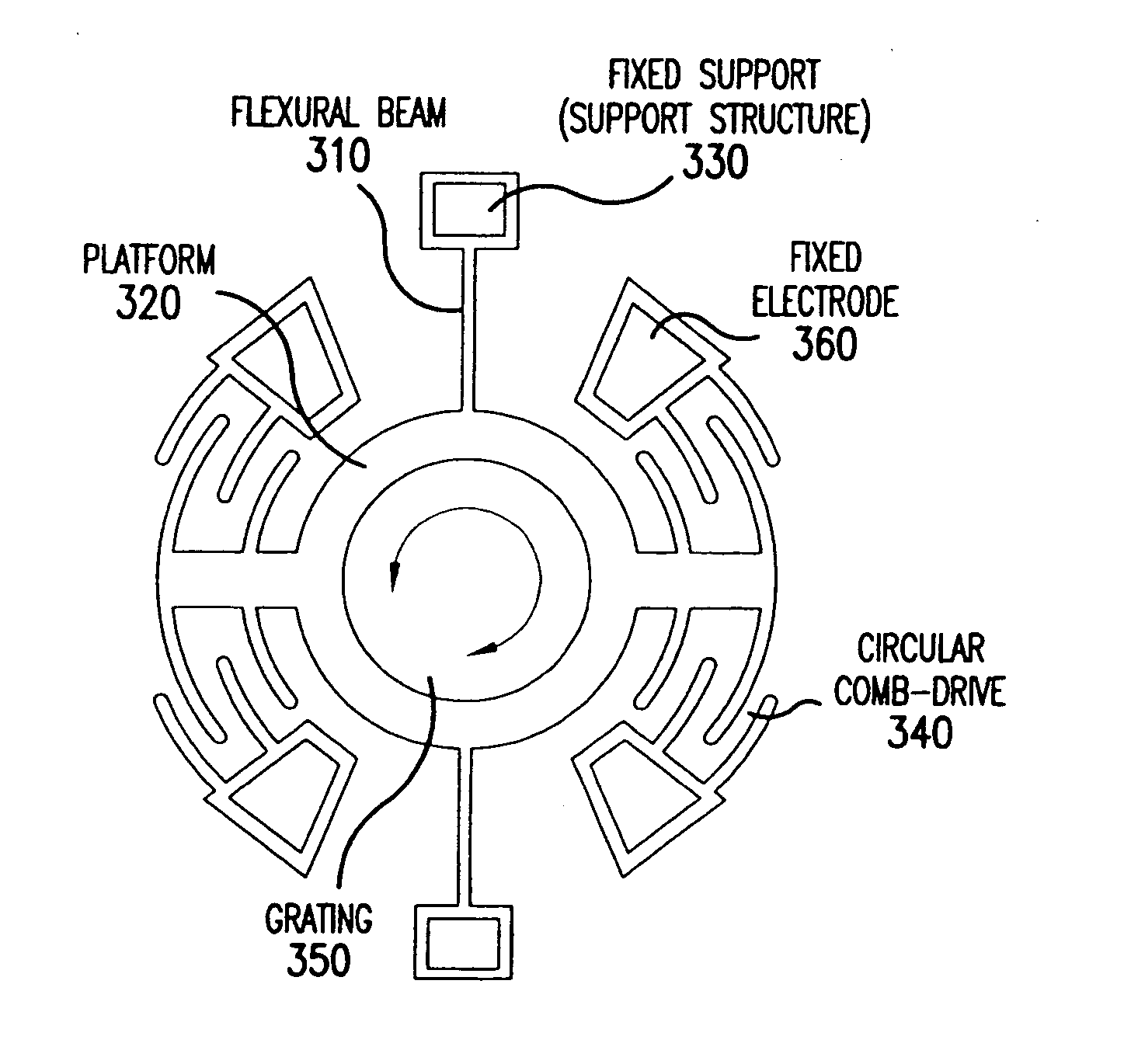
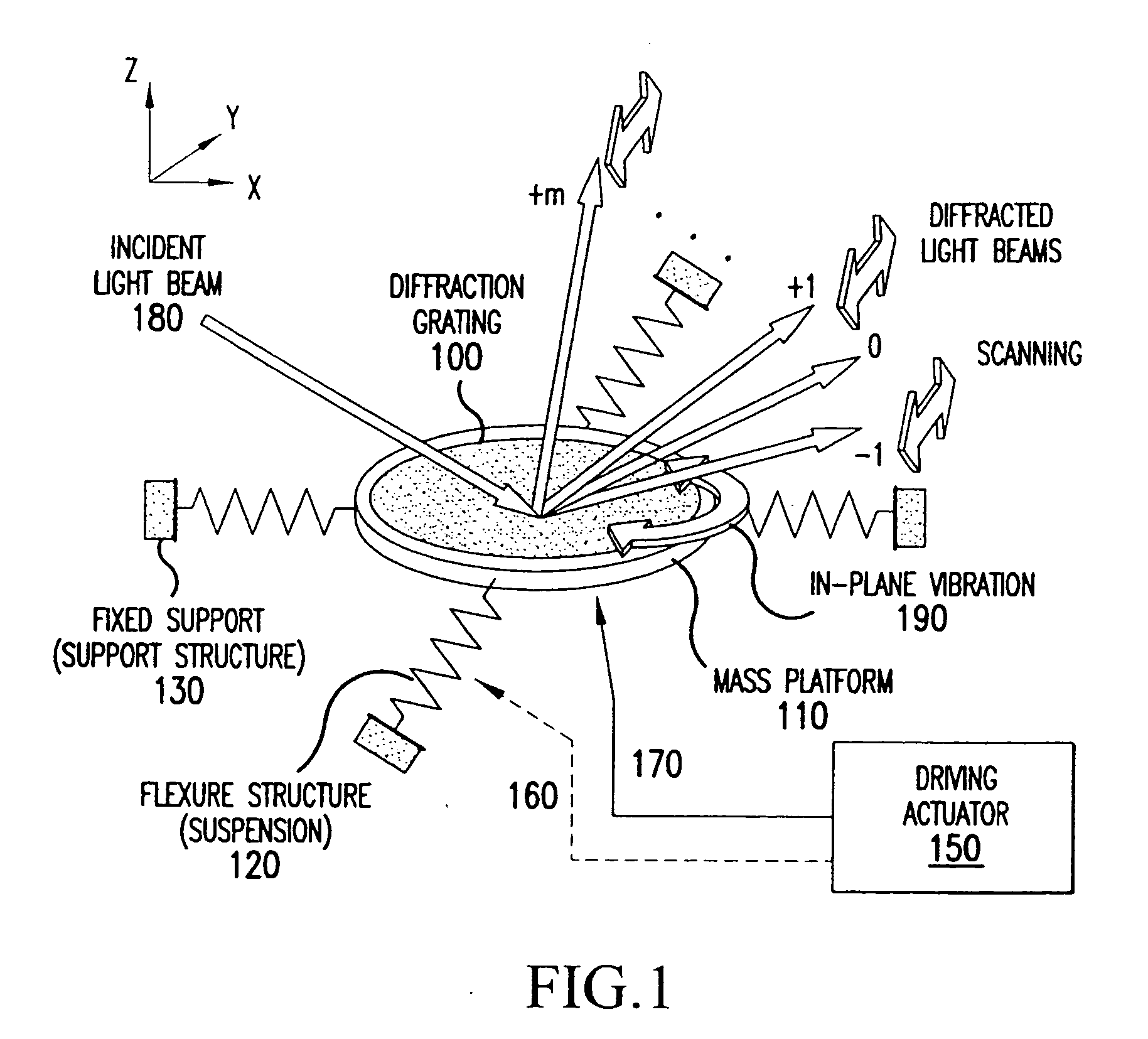
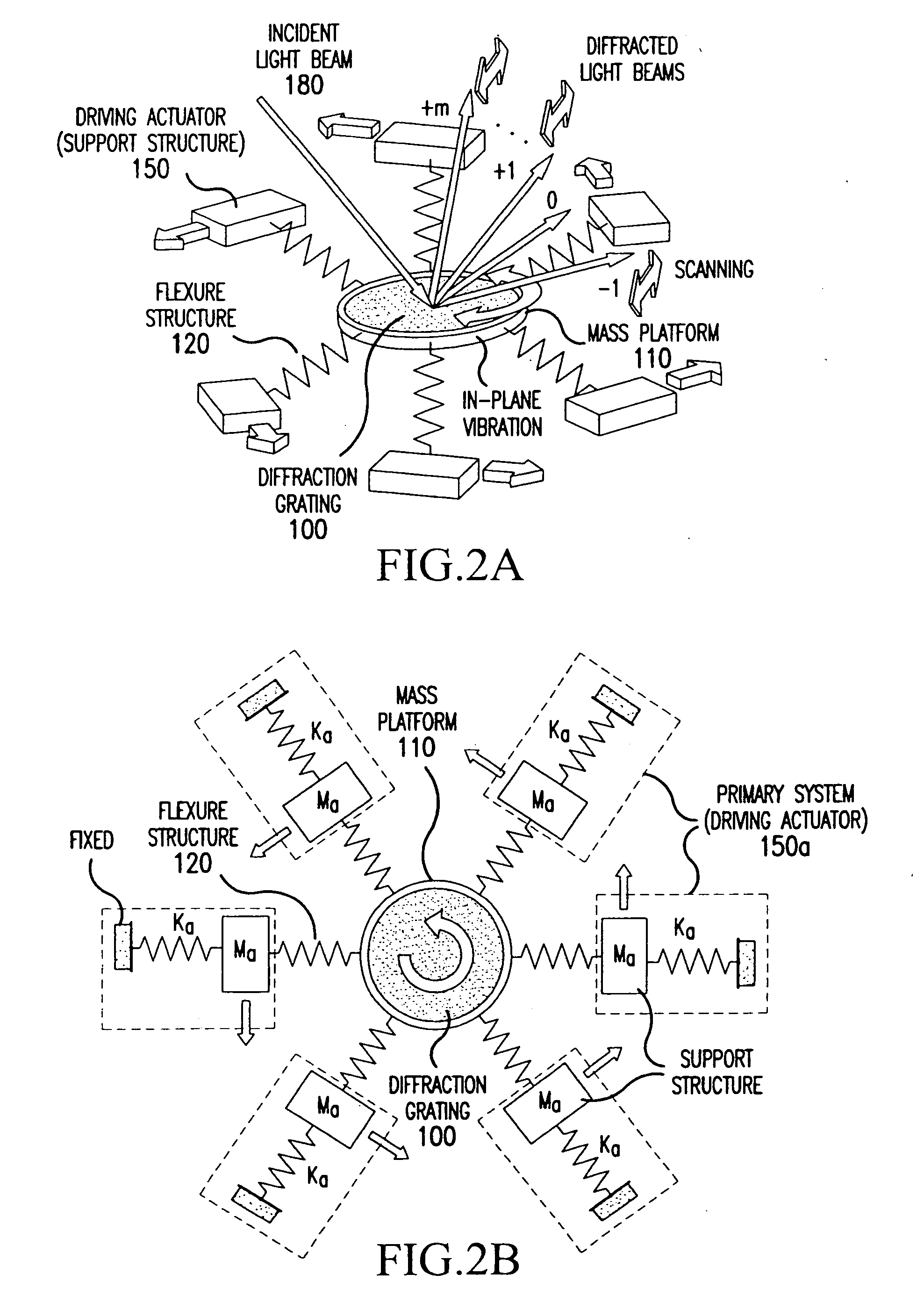
Optical scanning using vibratory diffraction gratings
InactiveUS20050156481A1Low working voltageImprove optical resolutionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTelevision system scanning detailsIn planeClassical mechanics
An optical scanning apparatus includes an in-plane vibratory mass platform having at least one diffraction grating formed thereon as the scanning element, at least one flexure structure that connects the mass platform to at least one fixed support, and at least one driving actuator that drives the mass platform into an in-plane vibratory motion which can be rotational and / or translational. The apparatus may also be formed by a mass platform having at least one diffraction grating formed thereon as the scanning element, at least one driving actuator connected to the mass platform through at least one flexure structure. The driving actuator drives the mass platform into an in-plane vibratory motion.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
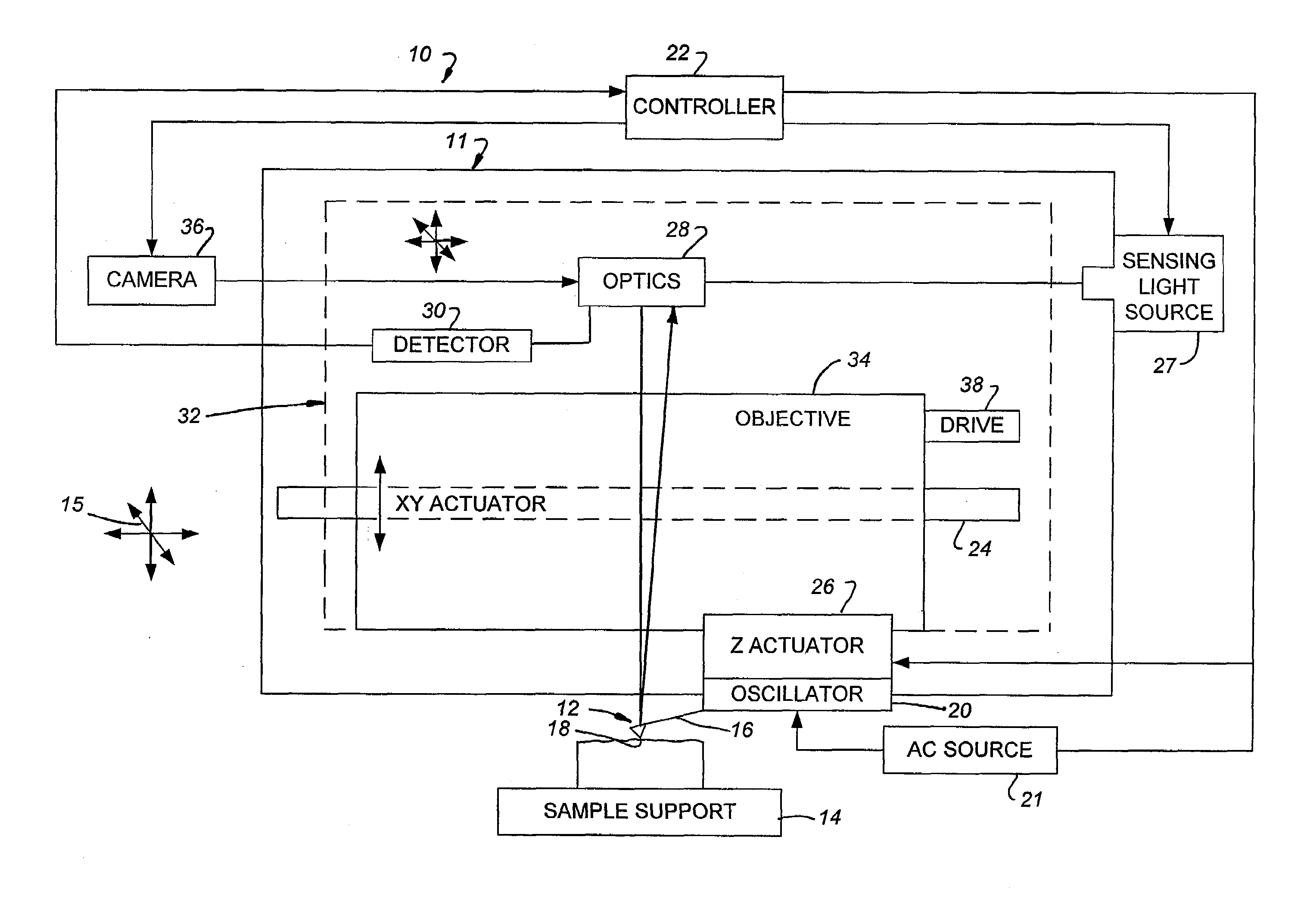
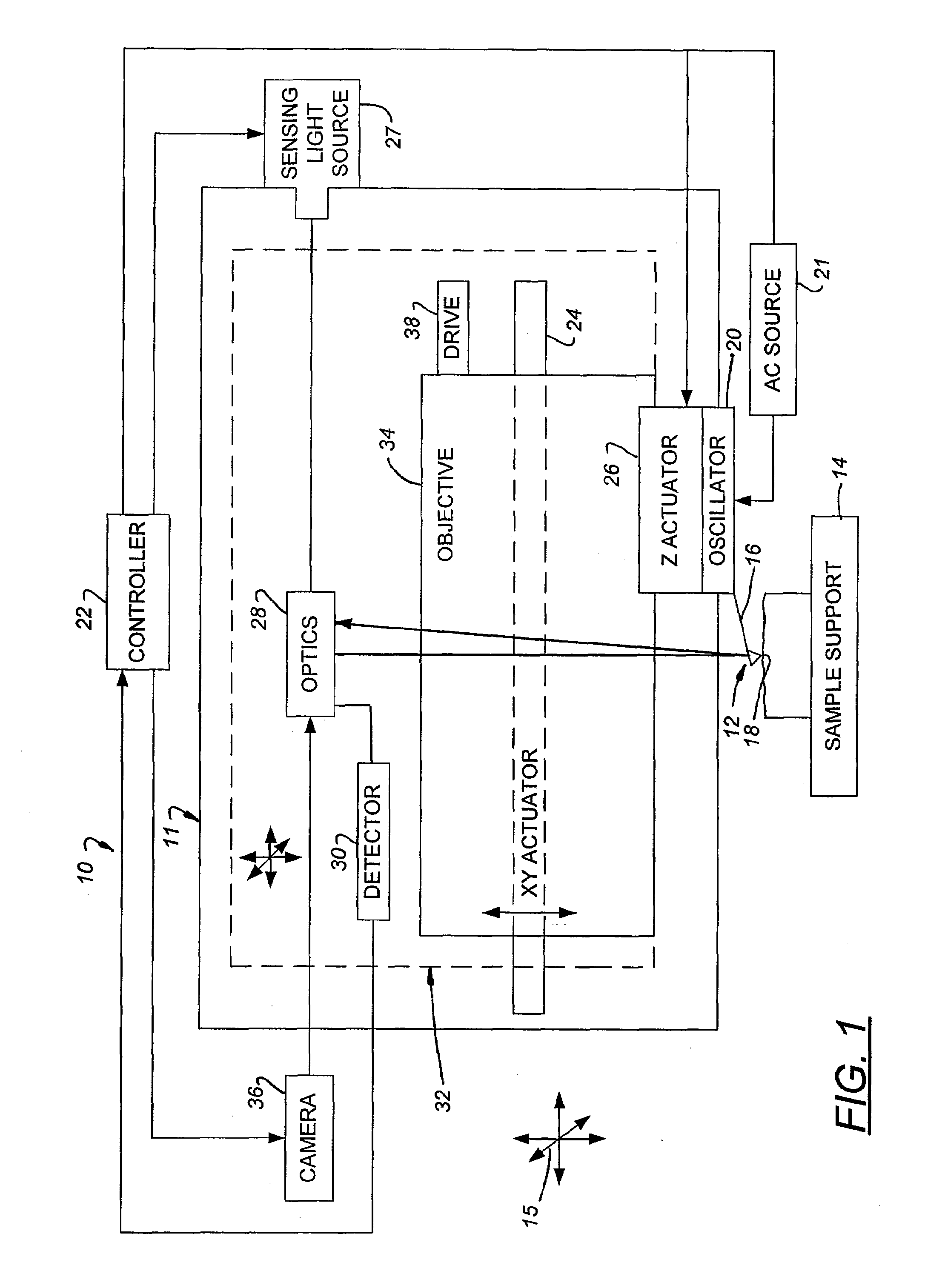
Fast-Scanning SPM Scanner and Method of Operating Same
ActiveUS20080223119A1Increased focus rangeImage data is accurateNanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsHigh bandwidthImage resolution
A high-bandwidth SPM tip scanner is provided that additionally includes an objective that is vertically movable within the scan head to increase the depth of focus for the sensing light beam. Movable optics also are preferably provided to permit targeting of the sensing light beam on the SPM's probe and to permit the sensing light beam to track the probe during scanning. The targeting and tracking permit the impingement of a small sensing light beam spot on the probe under direct visual inspection of focused illumination beam of an optical microscope integrated into the SPM and, as a result, permits the use of a relatively small cantilever with a commensurately small resonant frequency. A high-bandwidth tip scanner constructed in this fashion has a fundamental resonant frequency greater than greater than 500 Hz and a sensing light beam spot minor diameter of less than 10 μm. Images can be scanned on large samples having a largest dimension exceeding 7 mm with a resolution of less than 1 Angstrom and while scanning at rates exceeding 30 Hz.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Thin-film piezoelectric resonator and filter circuit
ActiveUS20070252485A1Increase resonant frequencySimple structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksPiezoelectric resonatorsOptoelectronics
A thin-film piezoelectric resonator has a piezoelectric film which is formed via a space on a substrate and is supported on the substrate at least one location, an upper electrode which has a plurality of electrode layers and a connection part connecting the electrode layers to each other, each of the electrode layers being formed on the piezoelectric film, having the same width and being arranged at the same interval as the width, a lower electrode formed under the piezoelectric film, a first pad which is formed on the substrate and is electrically connected to the upper electrode, and a second pad which is formed on the substrate and is electrically connected to the lower electrode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Micromachined optomechanical switching cell with parallel plate actuator and on-chip power monitoring
InactiveUS6453083B1Reduce packaging costsSmall massMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesParallel plateOptical power
A number of micromachined optomechanical switching cells and matrix switches including such switching cells are disclosed herein. One optomechanical switching cell of the present invention includes a parallel plate actuator positioned on a substrate. A mirror coupled to the actuator is disposed to selectively redirect an incident optical beam. The present invention also contemplates an optomechanical matrix switch including a substrate and a plurality of optomechanical switching cells coupled thereto. The matrix switch further includes an arrangement for monitoring the optical power incident upon, and output by, the matrix switch.
Owner:OMM
Structure of surface acoustic wave device on basis of flexible substrate and manufacturing method of surface acoustic wave device
InactiveCN102420582ARaise the resonant frequencyNo drop in Q valueImpedence networksEngineeringAcoustic wave
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
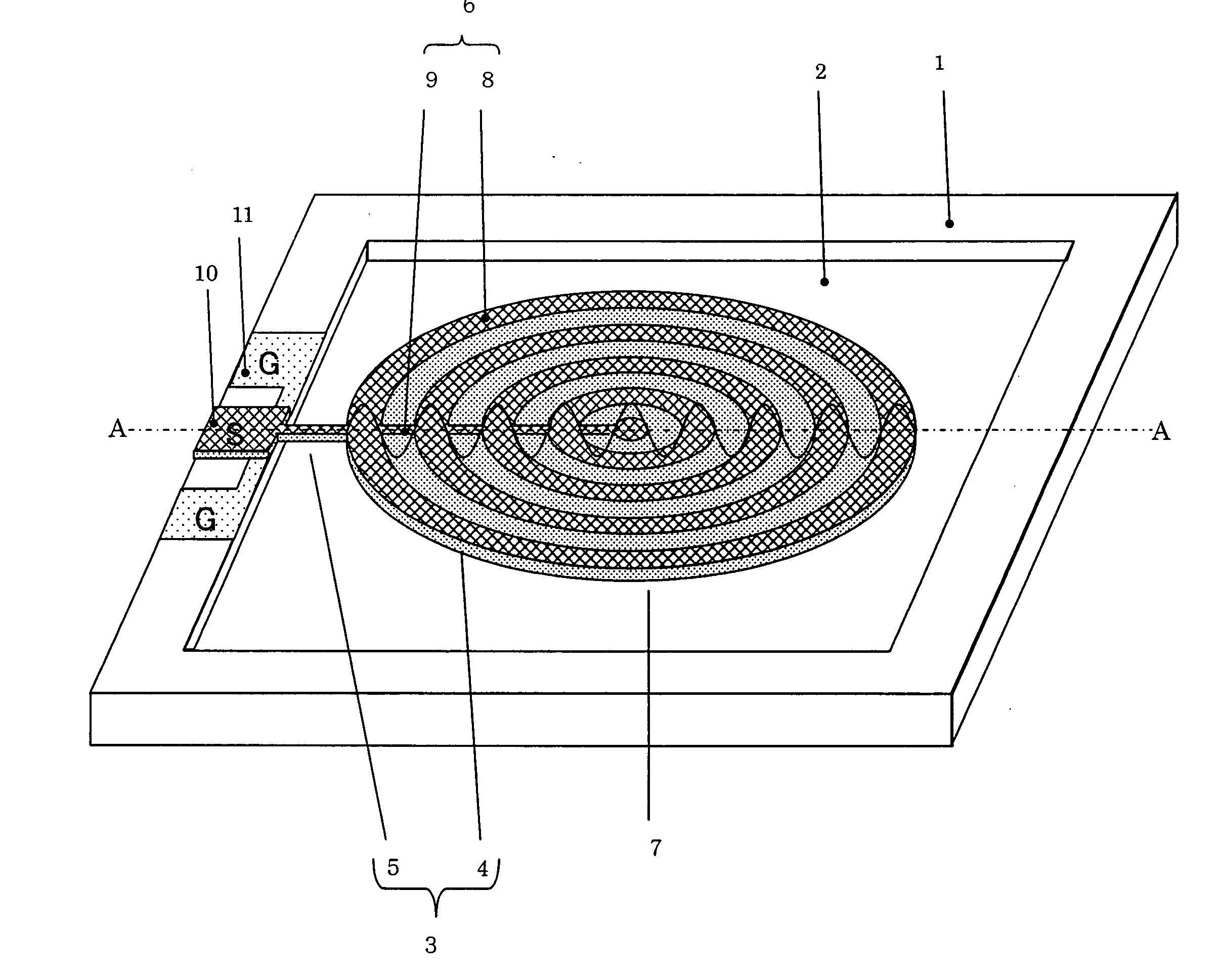
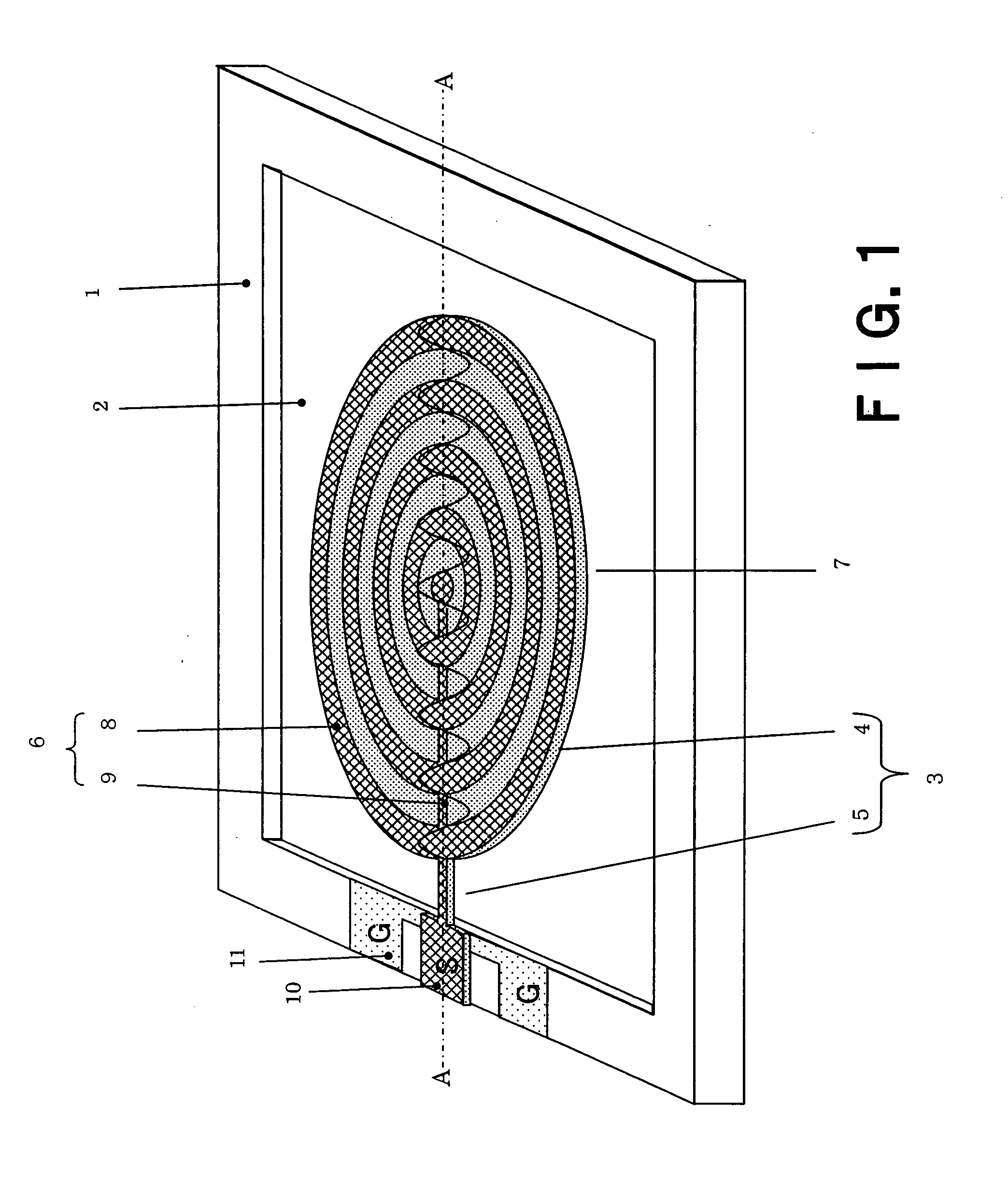
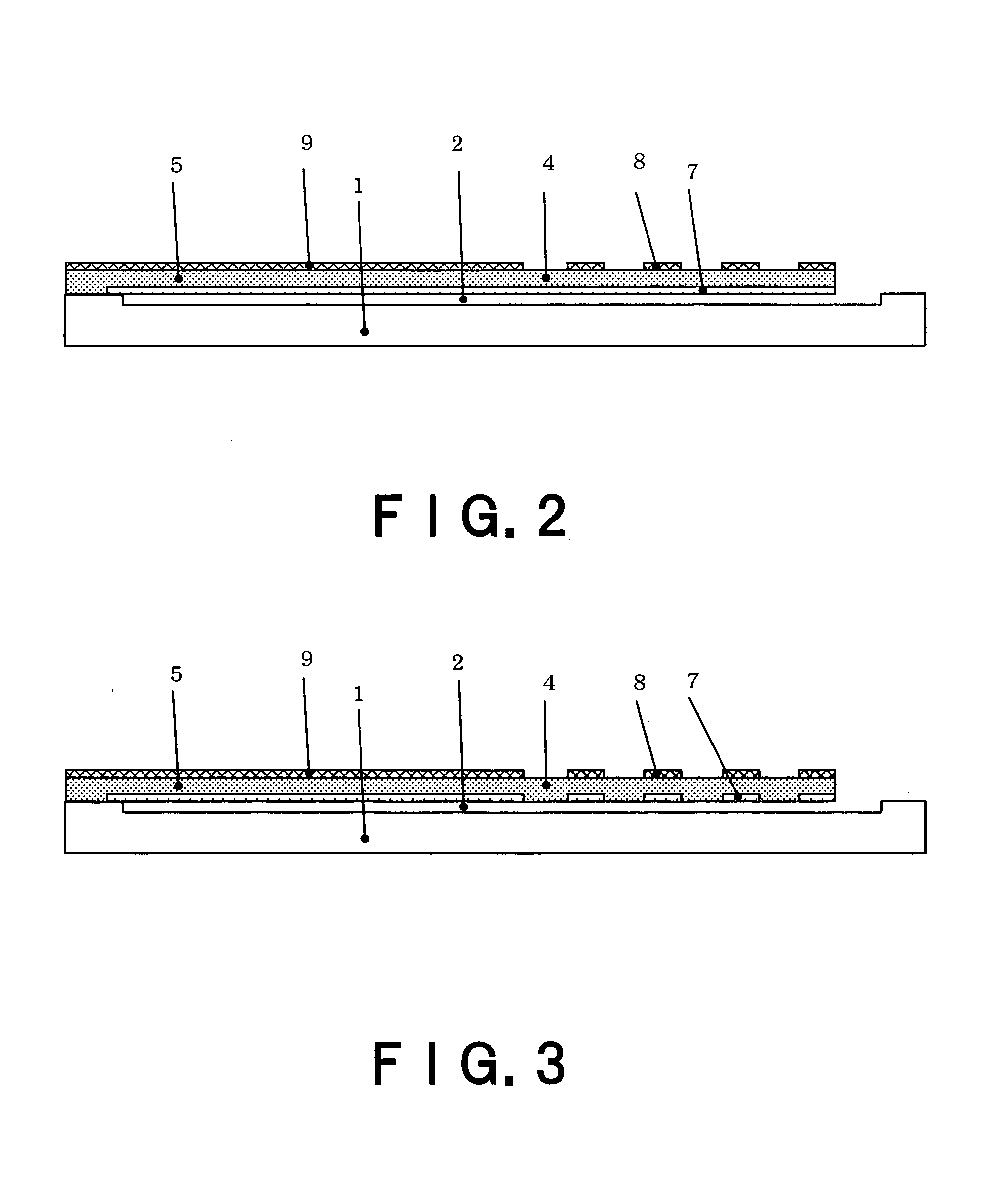
Spiral inductor semiconducting device with grounding strips and conducting vias
InactiveUS20020084509A1Useful operationGood effectTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSpiral inductor
An integrated semiconducting device comprises a semiconducting substrate, a plurality of grounding strips disposed above the substrate in a lower metal level of the semiconducting device, an inductor positioned in an upper metal level of the semiconducting device, and a plurality of conducting vias connected to and extending away from the grounding strips towards the inductor. The inductor, conducting via, ground strips structure forms a Faraday cage that acts as a shield against electromagnetic radiation. The number and placement of the conductive vias are adjustable and can be optimized based on the relative importance of maximizing the quality factor Q of the inductor or minimizing the capacitance between the inductor and ground.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Micromachined optical switching devices
InactiveUS6445840B1Reduce packaging costsSmall massMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesOptical alignmentOptical switch
Various 3-port and 4-port micromachined optomechanical matrix switches are disclosed herein. In accordance with one aspect of the invention there is provided an optomechanical matrix switch including a substrate and a first plurality of optomechanical switching cells coupled thereto. Each of the first plurality of optomechanical switching cells is arranged to be in optical alignment with a first input port. A second plurality of optomechanical switching cells is also coupled to the substrate, each of the second plurality of optomechanical switching cells being in optical alignment with a second input port. In another aspect of the present invention an optomechanical matrix switch is provided which includes a substrate and a first plurality of optomechanical switching cells coupled thereto. Each of the first plurality of optomechanical switching cells is placed in optical alignment with one of a corresponding first plurality of input ports and with one of a corresponding first plurality of output ports. The matrix switch further includes a second plurality of optomechanical switching cells coupled to the substrate. Each of the second plurality of optomechanical switching cells is placed in optical alignment with one of a corresponding second plurality input ports and with one of a corresponding second plurality of output ports.
Owner:CROSSFIBER +1
Two-dimensional high load-bearing large-caliber rapid control reflector
The invention relates to a two-dimensional high load-bearing large-caliber rapid control reflector. An outside surface of a rotating body and an inside surface of a supporting reflector frame of the reflector are both one part of a sphere surface. The two components are assembled in a mode that the spheres share the same spherical center and are in rigid connection with each other by a ball to form a rotary assembly similar to a bearing. The rotating body can universally rotate in the supporting reflector frame. Therefore, under the driving of a linear voice coil motor, the invention can realize high-frequency rapid two-dimensional rotation of the rotating body in the reflector frame and guarantees working stability and reliability of the rapid control reflector. On the other hand, the loads of rotating parts including a plane mirror is rigidly supported by the supporting reflector frame through the ball, which greatly improves bearing capacity and environmental suitability of the rapid control reflector.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Linear compressor of plate spring supporting system adopting two different types of lines
InactiveCN101892971ACompact structureRaise the resonant frequencyPiston pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesLinear compressorMagnet
The invention discloses a linear compressor of a plate spring supporting system adopting two different types of lines. The main assemblies thereof comprise four parts which are respectively a compressor assembly, a linear motor assembly, a piston assembly and a supporting system assembly. The compressor comprises a stand, a compressor shell, a compressor cylinder, an exhaust hole and a suction hole; the linear motor assembly comprises an inner yoke iron, an outer yoke iron, a permanent magnet, an anti-collision gasket, a coil framework and a coil on the upper surface thereof; a piston comprises a main piston shaft and a piston head; and a supporting system comprises two groups of plate spring groups with different types of line structures and a connecting frame. The structure has the characteristics that a spiral type plate spring supporting piston shaft assembly is adopted at one end with lighter mass of the piston head, and a spiral arm plate spring supporting piston head adopted at the end of the piston head moves in the cylinder to ensure clearance sealing; a linear arm plate spring is adopted at the rear end of the piston assembly to supply better support for the movement of the end with larger mass, the quantity of plate springs is reduced, and the volume of the compressor is saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Monolithic capacitor and mounting structure thereof
ActiveUS20070121275A1Low ESLHigh suppression characteristicsMultiple fixed capacitorsFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitanceEngineering
A monolithic capacitor includes a main capacitor unit having first capacitor portions and a second capacitor portion arranged in a direction of lamination, with the first capacitor portion located towards at least one end in the direction of lamination, so that the first capacitor portion is located closer to a mounting surface than the second capacitor portion. The number of pairs of third and fourth lead-out portions for third and fourth internal electrodes in the second capacitor portion is less than the number of pairs of first and second lead-out portions for first and second internal electrodes in the first capacitor portion, so that the first capacitor portion contributes to decreasing ESL while the second capacitor portion contributes to increasing ESR.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
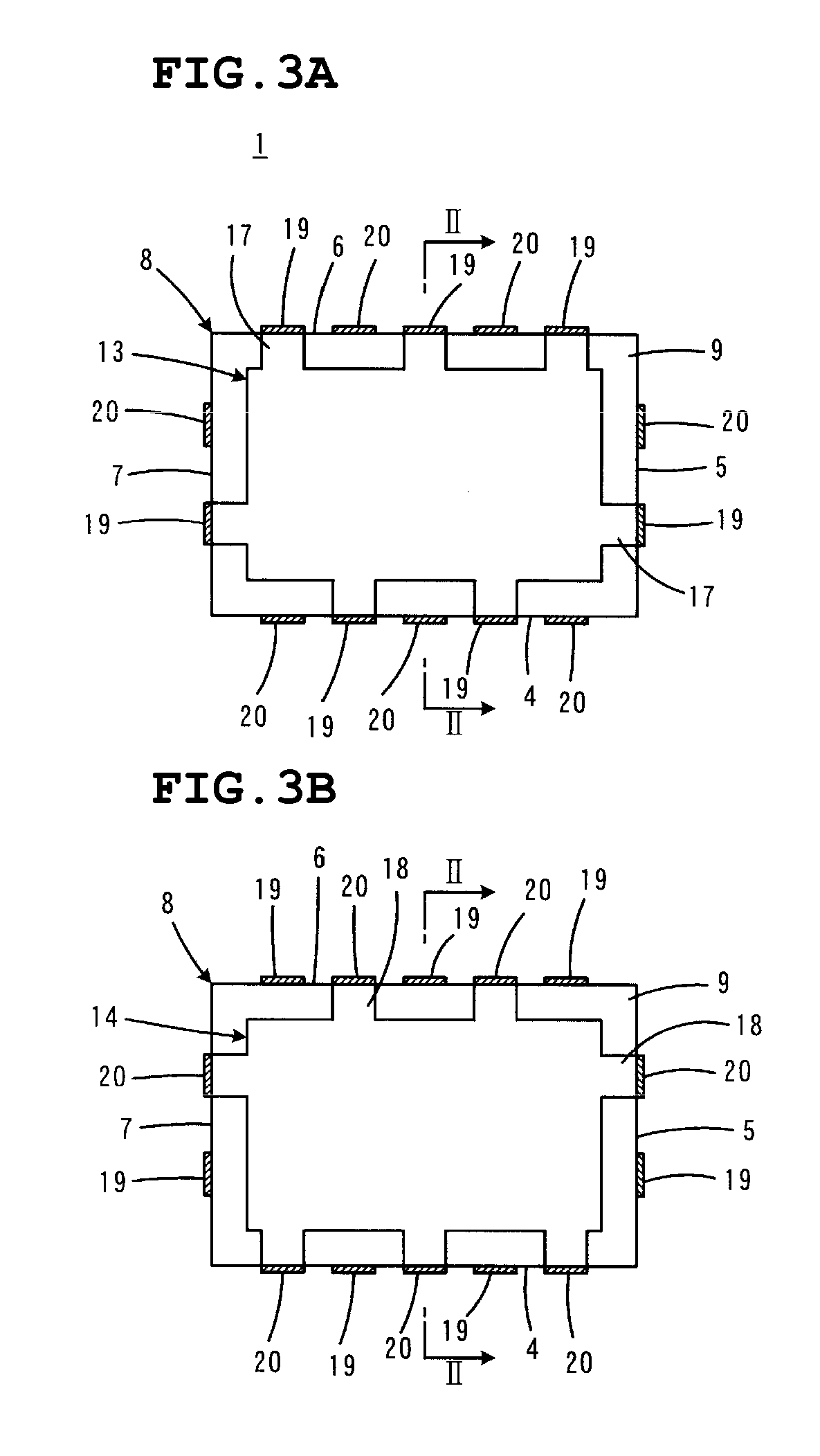
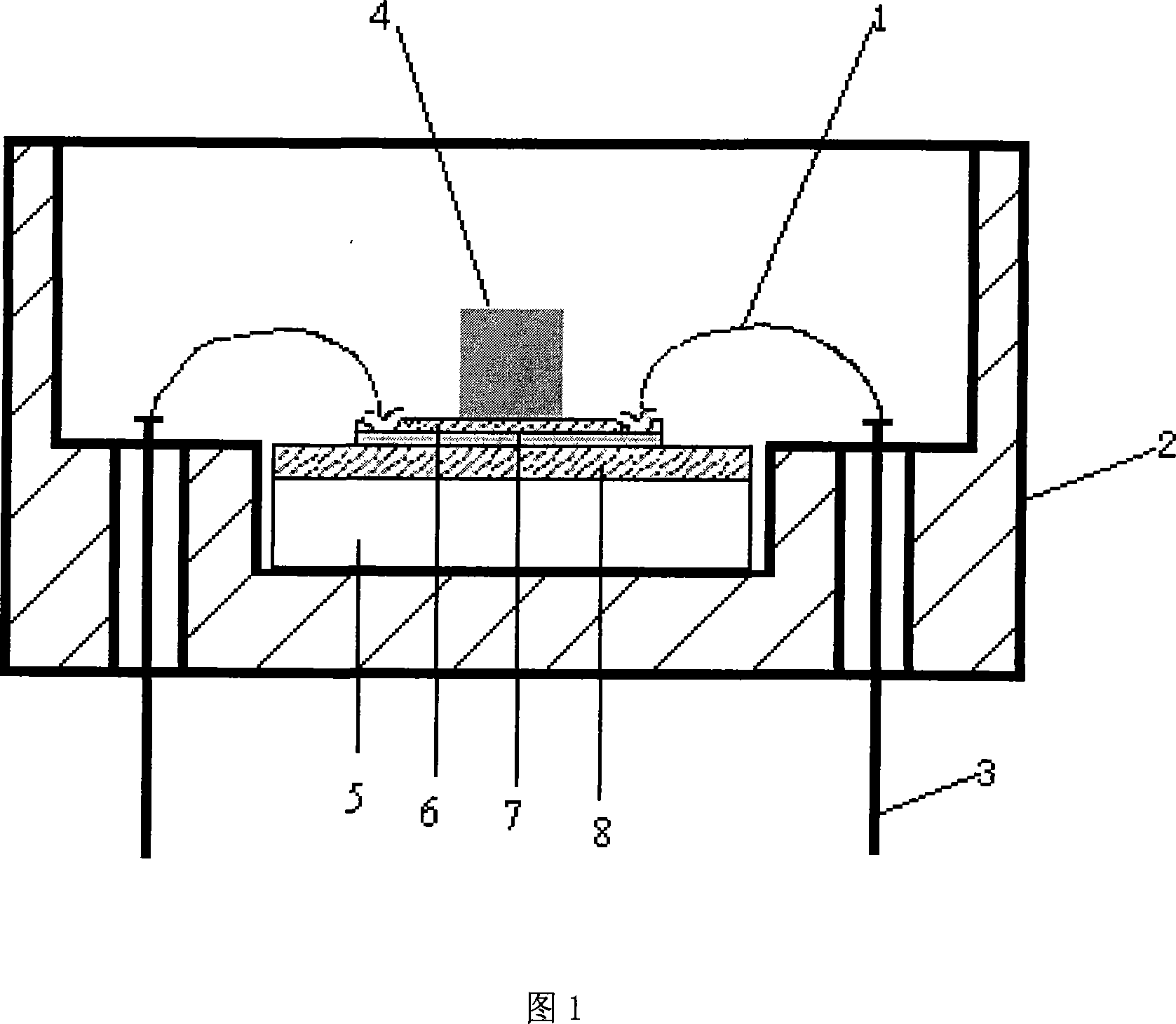
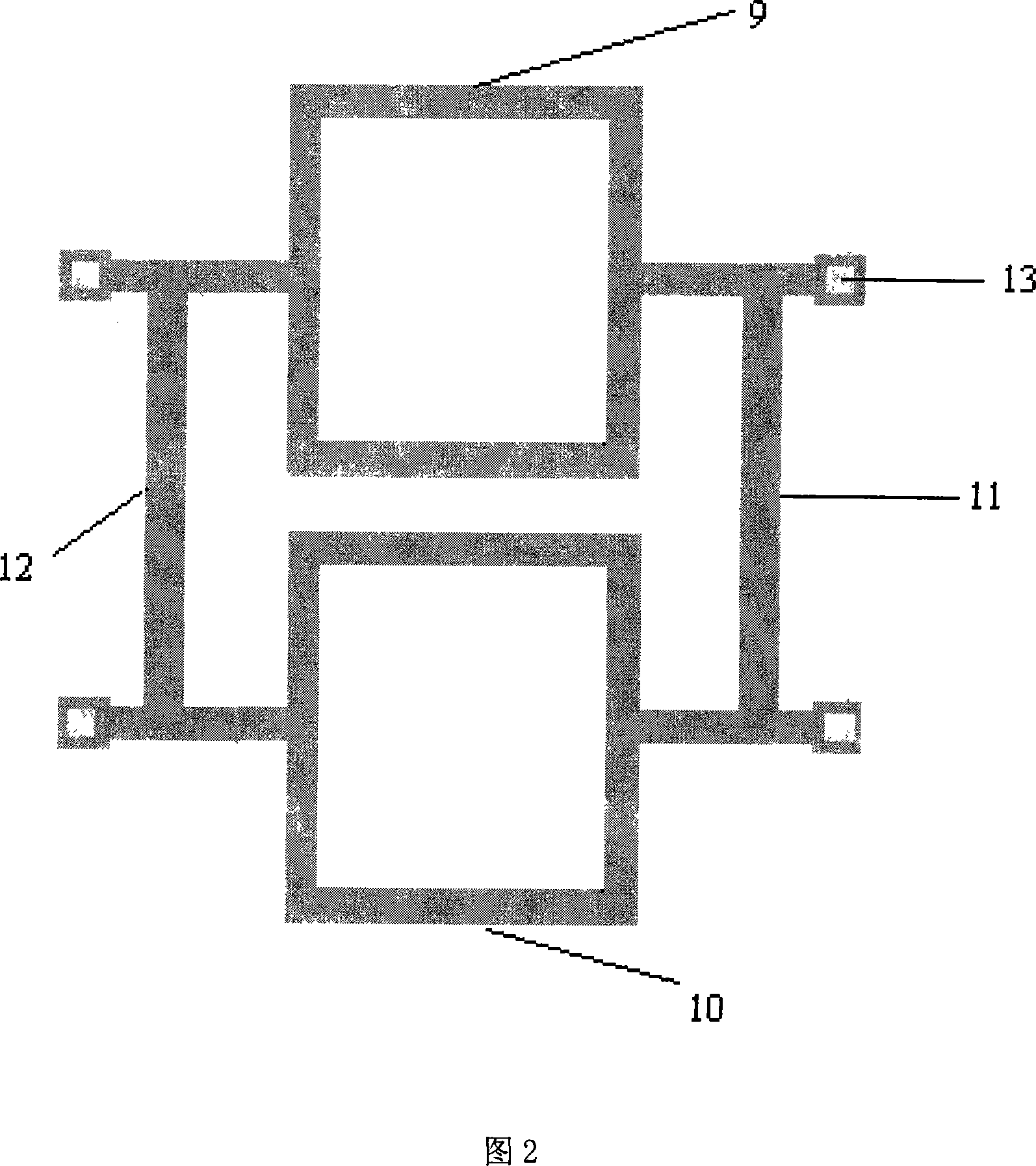
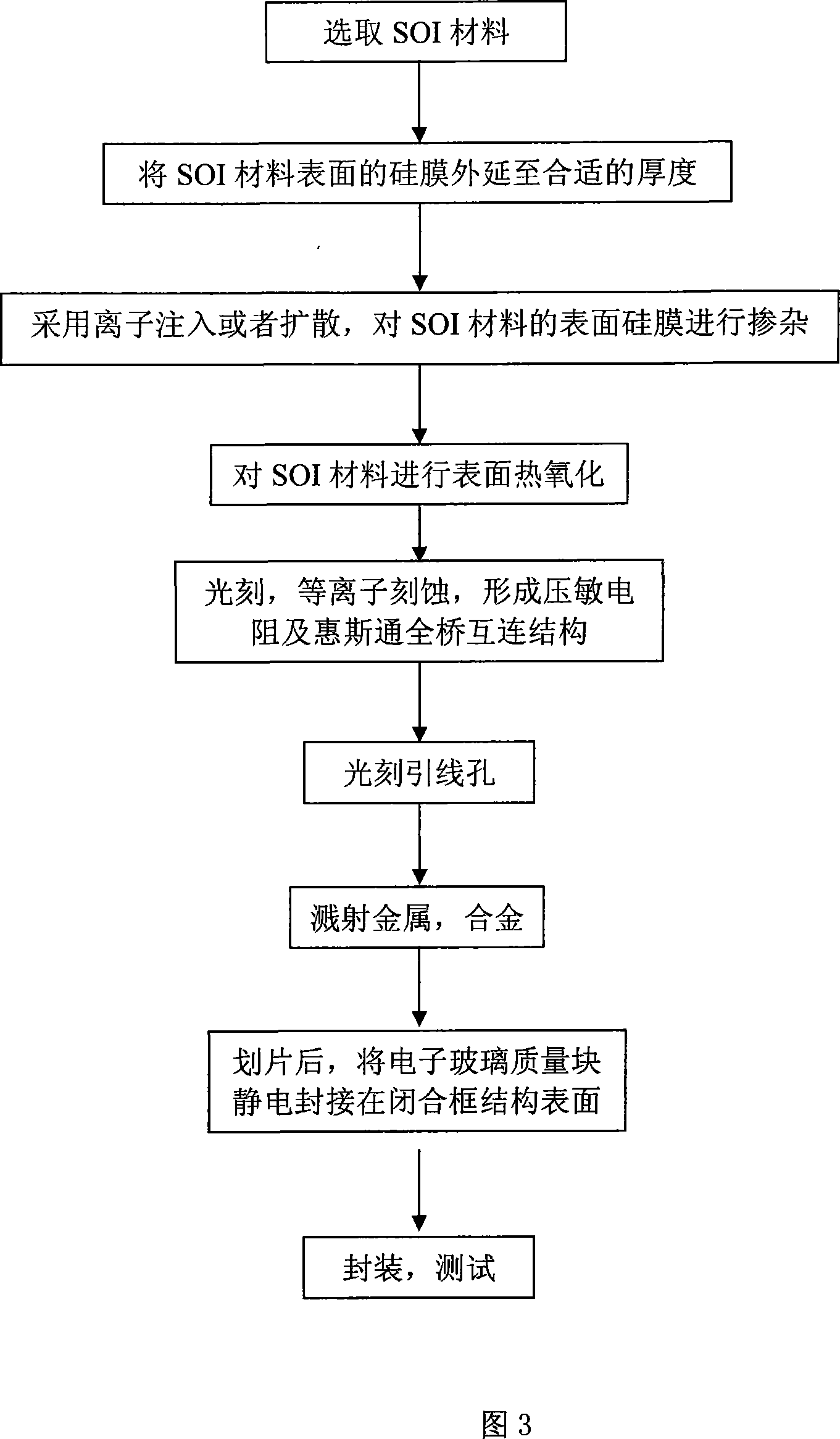
Novel piezoresistance type pressure pickup and method for making same
InactiveCN101082525AWork reliablyEffective galvanic isolationFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsPhotoengravingAlloy
This invention is neotype pressure resistance pressure sensor, including inward-leg wire, package outer, outward-leg wire, pin hole, substrate and the piezoresistor, installing the close structure piezoresistor and the banding piezoresistor,; the four piezoresistors make up of the Wheatstone bridge interconnect structure, a-alloy sputtering from the pin hole, installing the electronic glass mass on the surface of close structure outer. The production method is: (1)mixing; (2)surface thermal oxidization; (3)technic-processing of photoetch and plasma corrosion;(4)photoengraving the pin hole; (5)sputtering a-alloy; (6)static electrostatic encapsulating electronic glass; (7)testing and capsulation. The technic-scheme of this invention makes the production-craft more simple, and compatible with the craft of CMOS integrated circuit plate, and have more high harmonic frequency, and can work in the high temperature circumstance and assuring the compatibility of the production performance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Dual-band antenna with easily and finely adjustable resonant frequency, and method for adjusting resonant frequency
InactiveUS6995720B2Reduce path lengthIncrease path lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectromagnetic couplingDual band antenna
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Oversize metal wood with power shaft
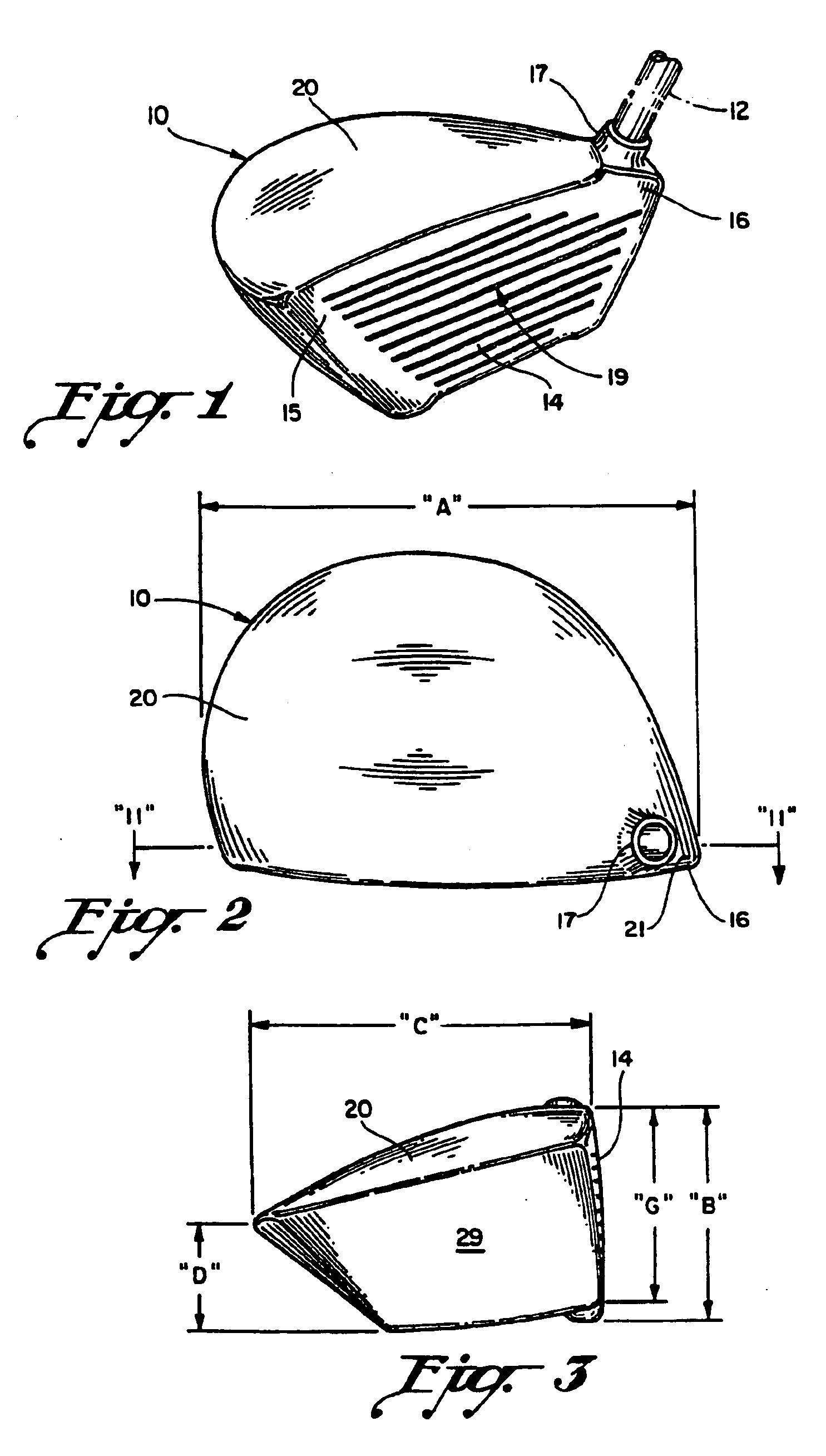
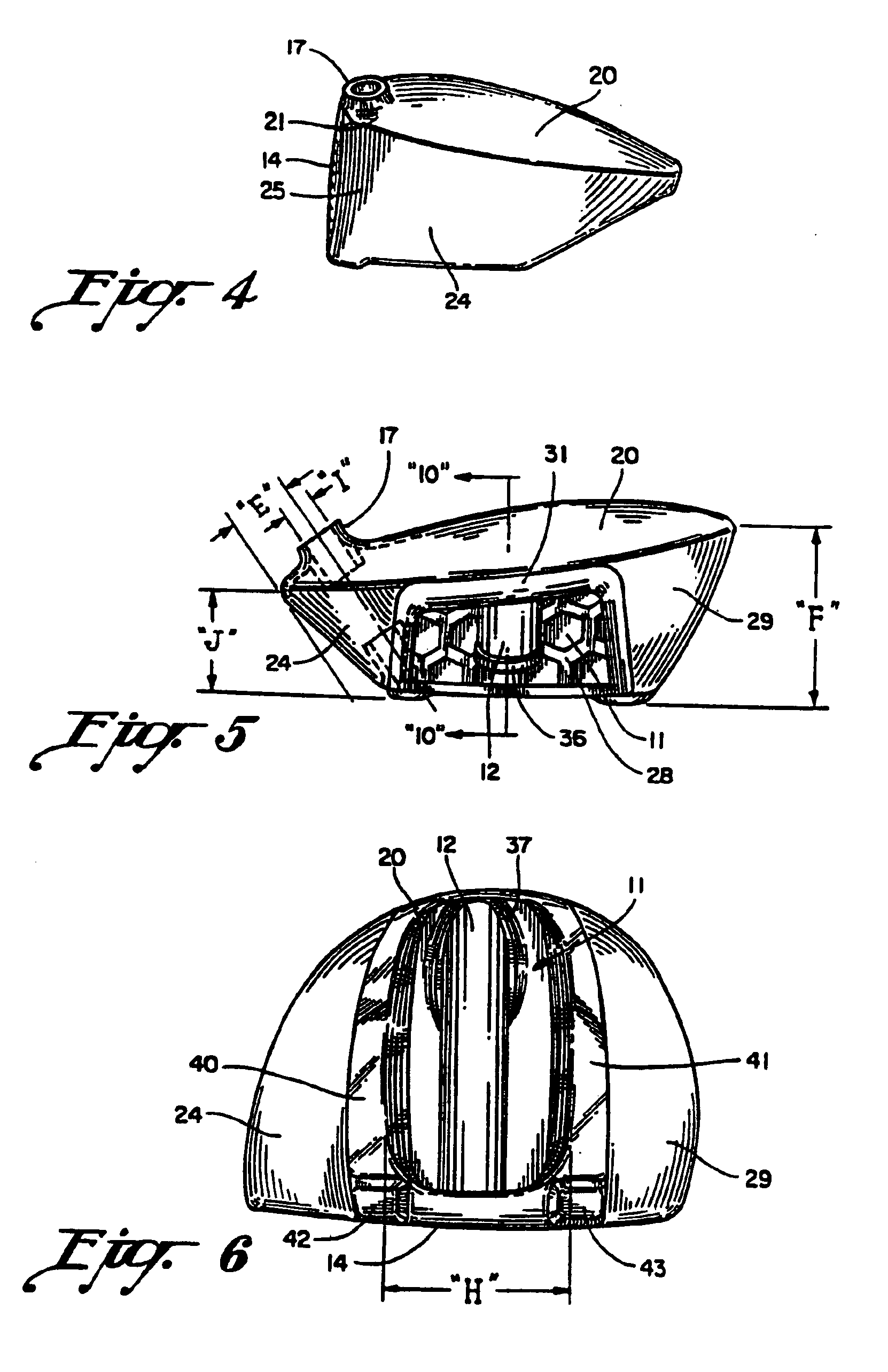
InactiveUSRE39178E1Imparting more energyIncreasing ball distance travelGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
A wood-type golf club having an enlarged club head in the range of 250 to 300 cm.3 constructed of a material lighter than steel to maintain the total club head weight within normal limits including the weight of novel power shaft according to the present invention. The club head, without the power shaft, is approximately 175 gms. and the power shaft weighs approximately 25 gms., so the total club head weight is approximately 200 gms. and within normal limits. The power shaft, integral with the rear of the ball striking face wall at its forward end and integral or cast into the rear of the club head at its rear end, while reinforcing the ball striking face wall, increases the resonant frequency of the face wall to synchronize face wall rebound to the player's swing speed. Face wall resonant frequency is varied by changing the size and weight of the power shaft.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP
MEMS device with tandem flux concentrators and method of modulating flux
InactiveUS20100039106A1Minimize noiseIncreased magnetic sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleElectrodynamic magnetometersMagnetic transducersHigh flux
A microelectromechanical modulating magnetic sensor comprising a base; a magnetic transducer associated with the base that provides an output in response to a magnetic field; a pair of movable flux concentrators positioned to move relative to the magnetic transducer; the pair of movable flux concentrators having a region of high flux concentration between the pair of movable flux concentrators; the pair of flux concentrators moving together in tandem with the distance between the pair remaining substantially constant during movement; support structure for supporting the pair of movable flux concentrators; a power source for causing the movable flux concentrators to move at a frequency within a predetermined frequency range; whereby when the pair of movable flux concentrators is in a first position the region of high flux concentration is in a first location, and when the pair of movable flux concentrators is in a second position, the region of high flux concentration is in a second position; such that as the flux concentrators move from the first position to the second position the intensity of the flux sensed by the transducer is modulated as the region of high flux concentration approaches and recedes from the location of the transducer.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
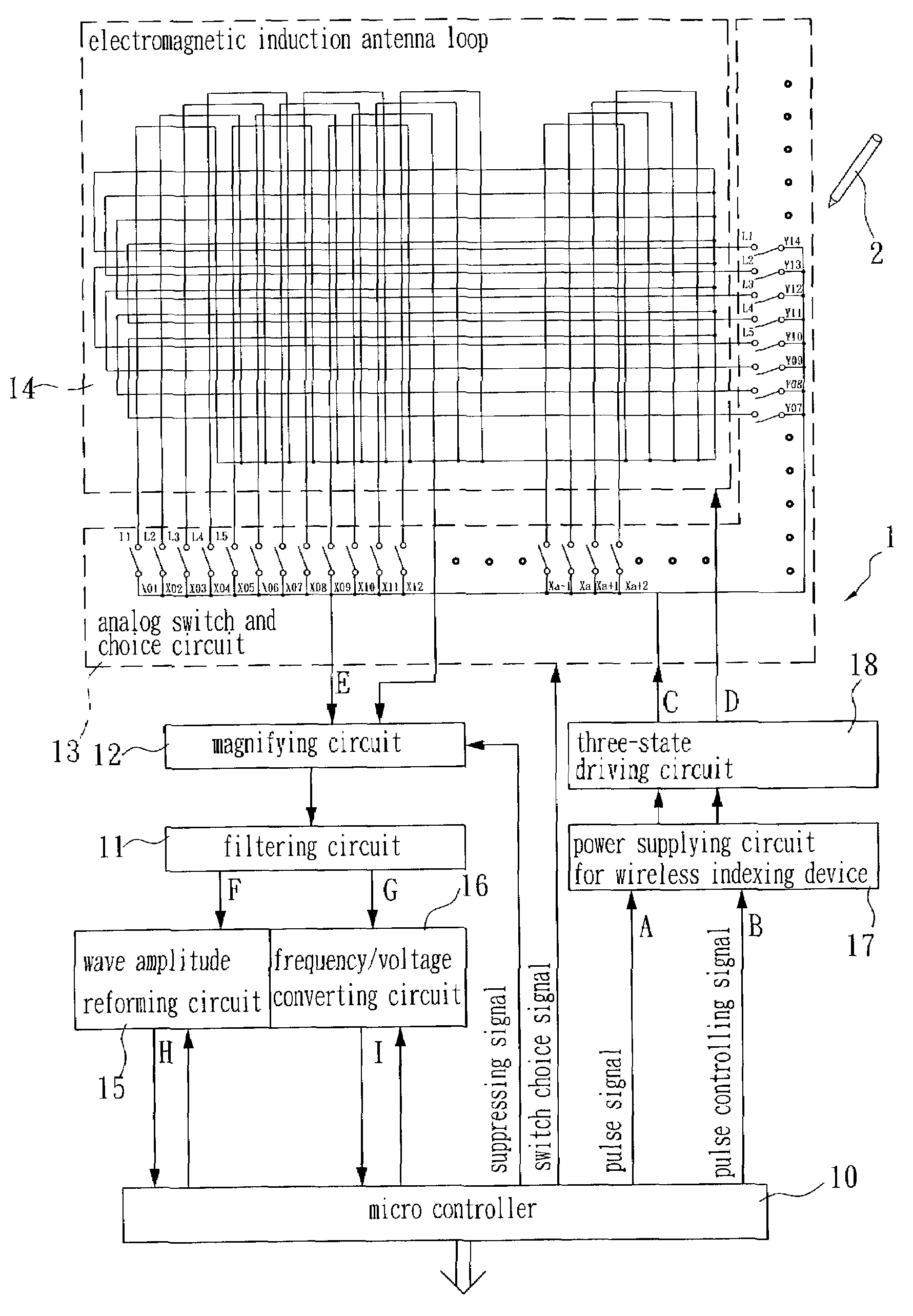
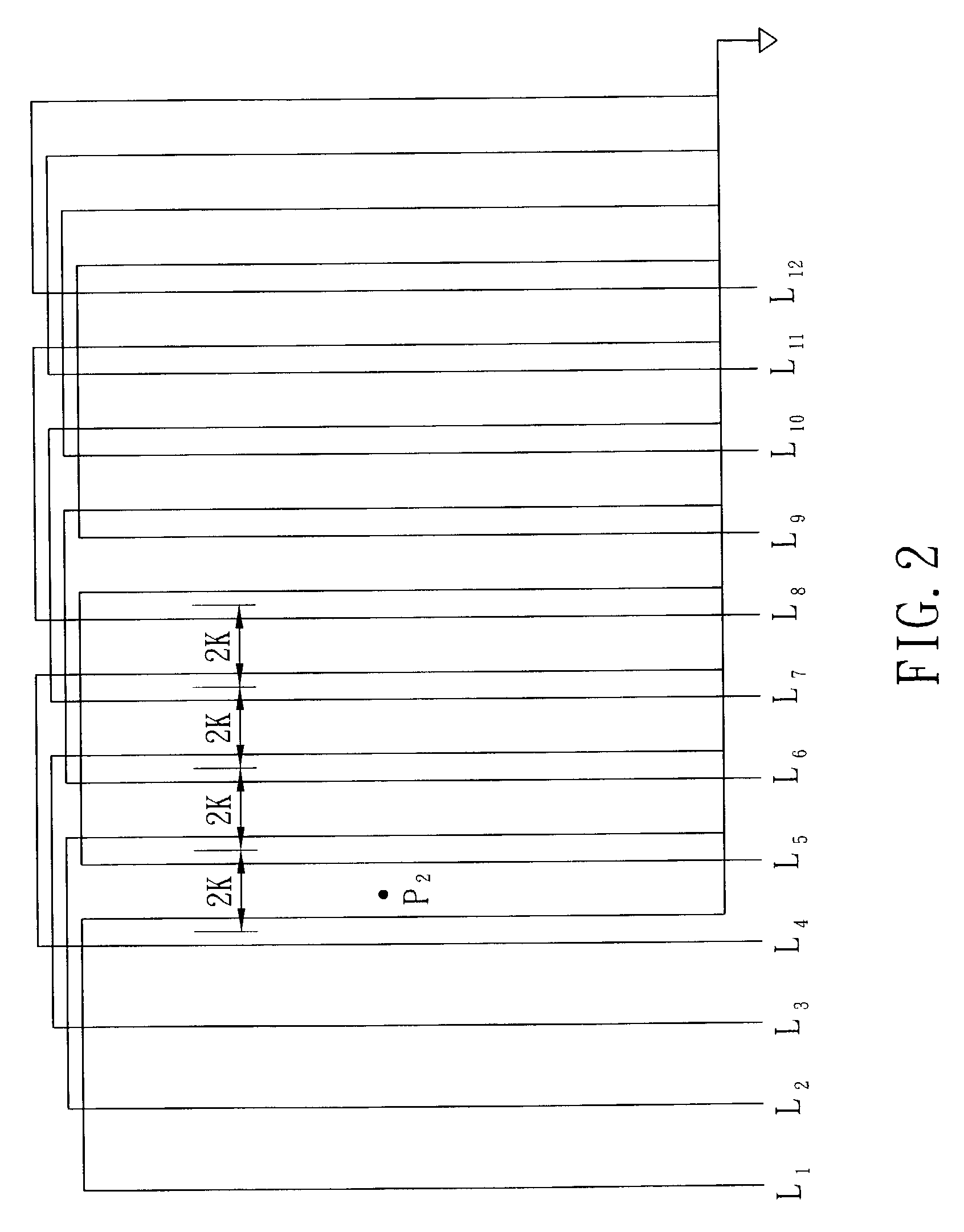
Device and method for pointer system of digitizer tablet
ActiveUS7176907B2Simplify calculation formulaReduce consumptionTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital converterInductance
The invention, an improved device and method for the pointer system of a digitizer tablet, is to repetitiously emit signals sequentially from a specific set of inductive loop when the position pointed by the wireless pointer device is located within a range formed by this specific set of inductive loop induced most intensively during a locally scanning process. After a transient energy storage of the wireless pointer device, corresponding resonant signals are emitted out and are received sequentially by several sets of inductive loop located on the digitizer tablet in the neighborhood of this specific set of inductive loop and, by these signals, the wireless pointer device's coordinate position on the digitizer tablet is calculated out relatively. Thereby, the intensities of the resonant signals received by these several sets of inductive loop will be displayed as a linear distribution, such that the calculation formula for coordinate position and the design for relative circuit elements may be simplified greatly, and the production cost and the power consumption may further be lowered down effectively.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
Loudspeaker diaphragm
The invention discloses a loudspeaker diaphragm which comprises a ball top part (20) in the center and a folding part (10) at the rim. The folding part (10) is a single layer structure made from a TPEE (thermoplastic polyester elastomer) material layer (2) or is a composite structure provided with at least one TPEE material layer (2). Compared with diaphragms made from TPU materials, the diaphragm of the invention has good toughness and strength, can effectively reduce the vibration frequency, and expand the bandwidth of a product. Further, the diaphragm is also stable in structure and reliable in withstanding power and provides good stability of vibration frequency.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
A differential type graphene resonant beam acceleration sensor
InactiveCN107015025AEliminate the effects of movementIncrease sensitivityAcceleration measurementMicroelectromechanical systemsAxial displacementGraphene
The invention discloses a differential type graphene resonant beam acceleration sensor comprising a substrate (1), a sensitive mass plate (2), a first insulating layer (3), a second insulating layer (4), a first excitation electrode pair (1), a first graphene resonant beam (6), a second graphene resonant beam (7), a third insulating layer (8), a second excitation electrode pair (1) and a vacuum cap (10). The differential type graphene resonant beam acceleration sensor of the invention adopts a direct sensitive acceleration mode: a sensitive mass block directly senses the measured accelerated speed, transforms the measured accelerated speed into a concentrated force to cause the axial displacement of the sensitive mass block and cause the change of the axial stress of the graphene resonator beams, thereby causing the changes of the resonant frequency of the beams. Through detection of the resonant frequency of the beams, measurement of the accelerated speed can be realized. The two graphene resonant beams positioned in the axial direction of the sensitive mass block work in a differential mode in the detected acceleration direction so as to enhance detection signals, raise the sensitivity and the measurement accuracy and suppress conjugate interferences.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Spiral inductor semiconducting device with grounding strips and conducting vias
InactiveUS6489663B2Good effectIncrease capacitanceTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSpiral inductor
An integrated semiconducting device comprises a semiconducting substrate, a plurality of grounding strips disposed above the substrate in a lower metal level of the semiconducting device, an inductor positioned in an upper metal level of the semiconducting device, and a plurality of conducting vias connected to and extending away from the grounding strips towards the inductor. The inductor, conducting via, ground strips structure forms a Faraday cage that acts as a shield against electromagnetic radiation. The number and placement of the conductive vias are adjustable and can be optimized based on the relative importance of maximizing the quality factor Q of the inductor or minimizing the capacitance between the inductor and ground.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Vibration motor for portable terminal
InactiveUS20100127581A1Good vibration feelingHigh frequencyMechanical vibrations separationMechanical energy handlingReciprocating motionElectric machine
Disclosed is a vibration motor for a portable terminal, including a flat spring; a cylindrical magnetic substance mounted on the flat spring; an annular magnetic substance disposed around the cylindrical magnetic substance mounted on the flat spring; and a coil disposed between the cylindrical magnetic substance and the annular magnetic substance, wherein the magnetic substances perform a linear reciprocal movement by the electromagnetic force generated between the magnetic substances and the coil and by the elastic force of the flat spring as an electric current is applied to the coil. The vibration motor operates at higher resonant frequencies than those of conventional vibration motors, thereby improving the sense of an after-vibration and realizing a delicate haptic feedback function.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Graphene high-frequency nanomechanical resonator based on flexible substrate and preparing technology of graphene high-frequency nanomechanical resonator
InactiveCN103296991ARaise the resonant frequencyReduce tensionImpedence networksCvd graphenePhotoresist
The invention relates to a graphene high-frequency nanomechanical resonator based on a flexible substrate and a preparing technology of the graphene high-frequency nanomechanical resonator and belongs to the technical field of communication electronic elements. According to the technology, the shape of a required gate electrode is etched on the flexible substrate. A metal layer is evaporated on the surface of the flexible substrate. Silicon dioxide sedimentation is conducted on the flexible substrate. Graphene is transferred to the portion right above the gate electrode and photoresist is painted on the gate electrode in a spiral mode. Titanium, platinum and gold are evaporated on a channel of the graphene so as to serve as a source electrode and a drain electrode. Finally, a whole element is coated with photoresist and the graphene high-frequency Q nanomechanical resonator of the flexible substrate can be obtained after processing. The structure of the graphene high-frequency Q nanomechanical resonator comprises the flexible substrate, a medium layer, the gate electrode and a graphene girder in a sequentially laminated mode. The source electrode and the drain electrode are located at the two sides of the graphene girder. The graphene high-frequency nanomechanical resonator is a microwave element which has the advantages of being high in frequency, high in quality factors, light, thin, soft, good in shock resistant performance and low in cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
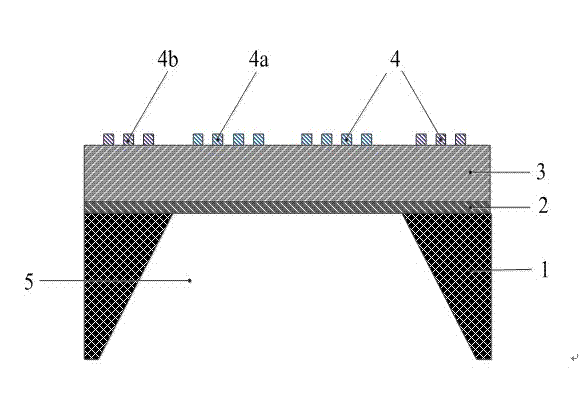
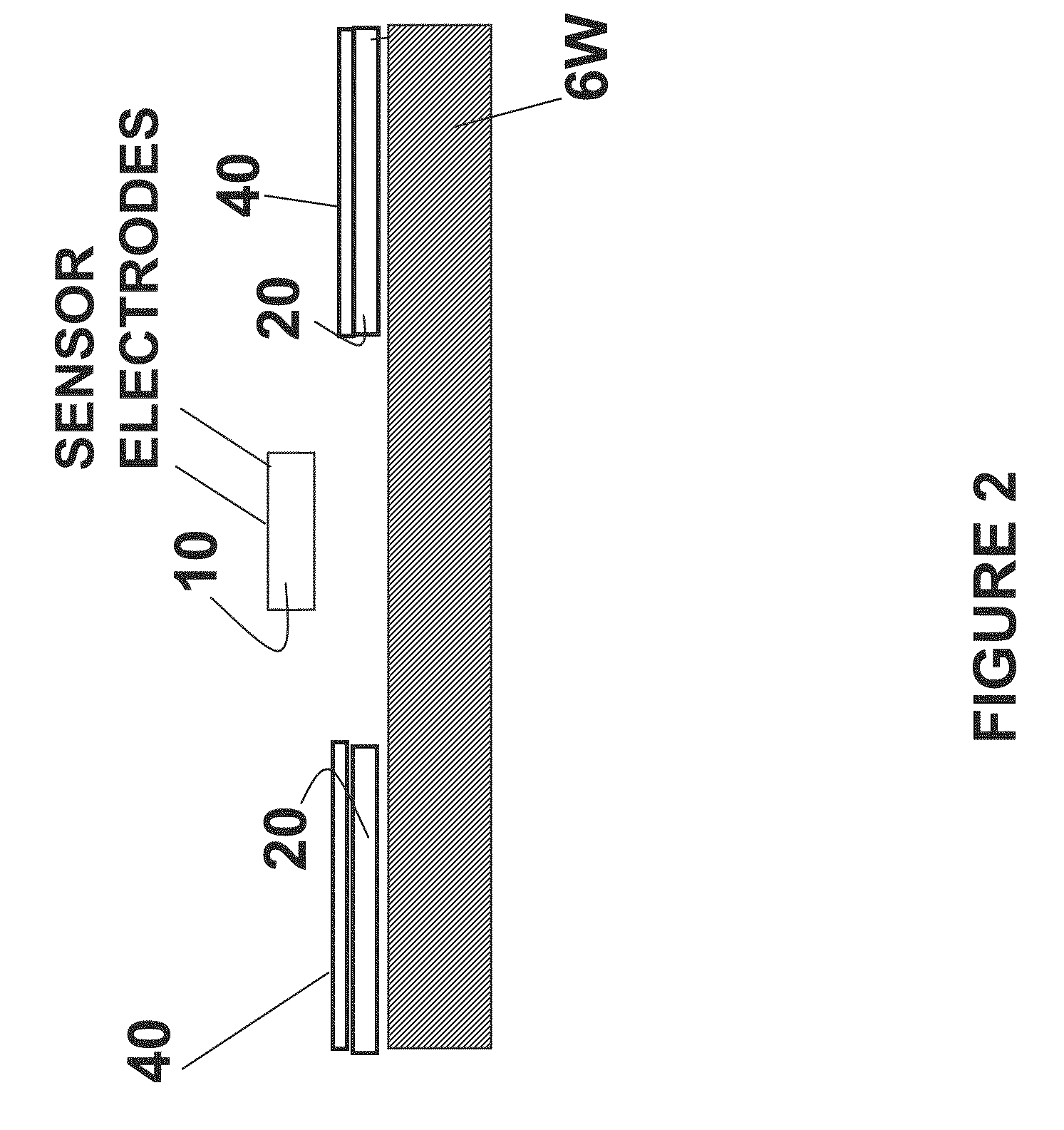
A plane capacitance resonator and its making method
InactiveCN101127514AReduce parasitic effectsReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsImpedence networksCapacitanceMetal electrodes
The utility model discloses a planar capacitance resonator and the related preparation method, comprising a resonance body, a sensor electrode, a driving electrode and a related supporting substrate. The resonator is a suspended structure, and is fixed on the substrate through an anchor point; each of the sensor electrode and the driving electrode comprises an electrode plate and a solder pad, the electrode plates of the sensor electrode and the driving electrode are arranged on the two side of the resonance body separately and keep a clearance from the resonance body, the clearance between the plates performs as the media to form the capacitor structure; the solder pads of the sensor electrode and the driving electrode are fixed on the insulating medium layer, and the solder pads are provided with metal electrodes; the insulating medium layer are fixed on the substrate. The clearance between the any two electrodes of the capacitors is narrower than 100nm. The utility model has the advantages of extremely high dynamic performance, the harmonic resonance frequency exceeding 100 MHz, and the Q factor up to 105.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Monolithic capacitor and mounting structure thereof
InactiveUS20070279836A1High suppression characteristicsESL of the main capacitor unit is decreasedMultiple fixed capacitorsFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitanceEngineering
A monolithic capacitor includes a main capacitor unit having first capacitor portions and a second capacitor portion arranged in a direction of lamination, with the first capacitor portion located towards at least one end in the direction of lamination, so that the first capacitor portion is located closer to a mounting surface than the second capacitor portion. The number of pairs of third and fourth lead-out portions for third and fourth internal electrodes in the second capacitor portion is less than the number of pairs of first and second lead-out portions for first and second internal electrodes in the first capacitor portion, so that the first capacitor portion contributes to decreasing ESL while the second capacitor portion contributes to increasing ESR.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Mirror driving device and method of controlling the device
ActiveCN103246059ASmall sizeRaise the resonant frequencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesOptical elementsPiezoelectric cantileverActuator
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
A micromass sensor based on a trough-shaped cantilever beam structure
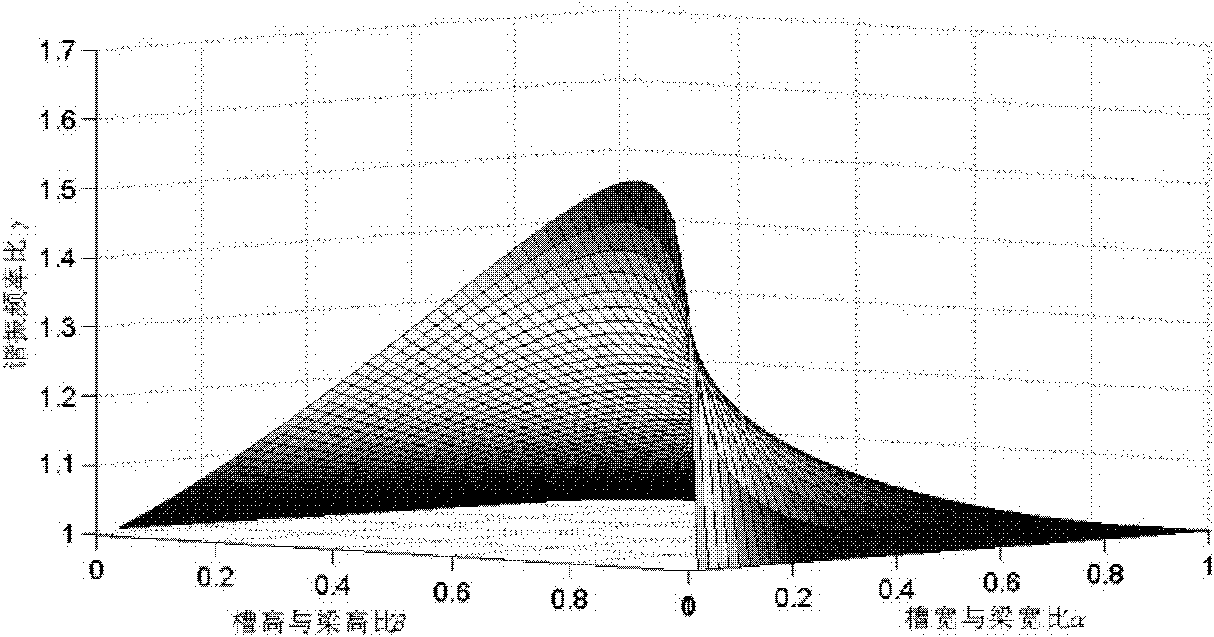
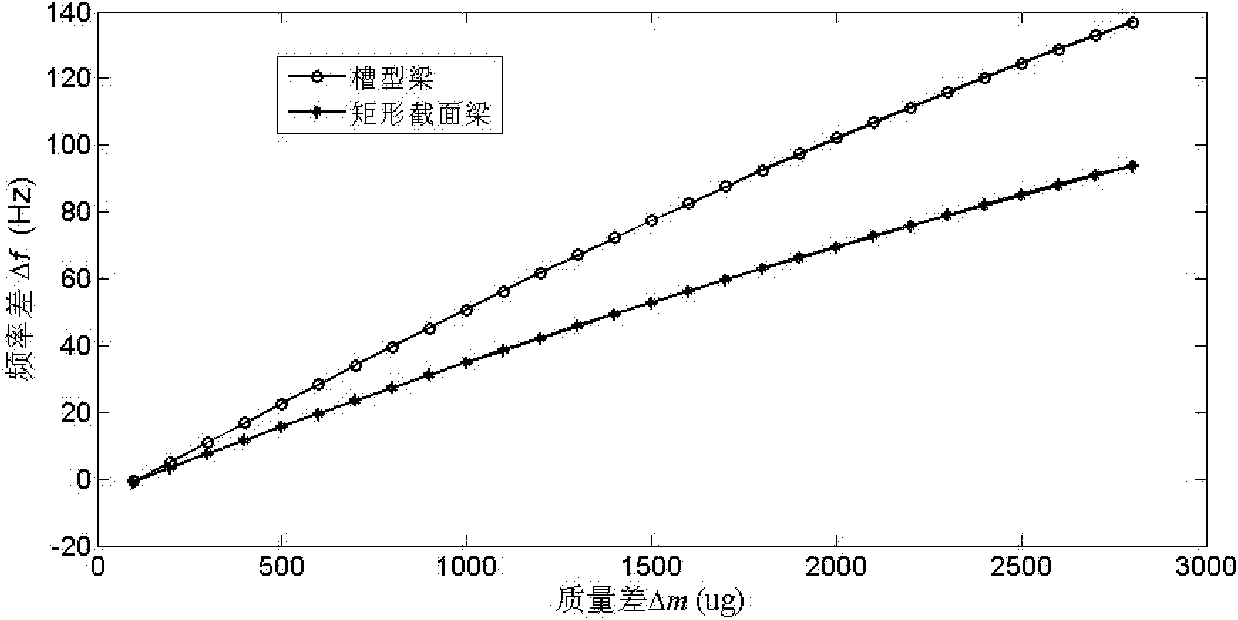
InactiveCN102269615AIncrease the adsorption areaRaise the resonant frequencyWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersElectricityCantilevered beam
The invention discloses a micro mass sensor based on a groove-shaped cantilever beam structure, and belongs to the technical field of sensors. In the groove-shaped cantilever beam of the sensor, one end of a fixed bock is provided with 1-2 same piezoelectric films, and a test substance adsorption film covers a cantilever end; and a resonant frequency difference delta f before and after the cantilever structure adsorbs a test substance is measured, and the mass m of the test substance is calculated further. By the introduction of the groove-shaped cantilever beam, the natural frequency of vibration and the adsorption area are increased, the sensitivity of the sensor is improved, and the measuring stability of the sensor is improved. The frequency change of the sensor caused by the mass of the adsorption film can be accurately measured through the piezoelectric films, and the mass of the test substance is calculated. The sensor has the characteristics of simple structure, large adsorption area, wide mass measuring range, high stability and sensitivity and the like, and the sensitivity can be improved by 20 percent to the maximum compared with that of a rectangular-section mass sensor with the same size particularly, so the sensor can be widely applied to measuring concentrations of gases / liquids, microparticles, dust, microbes such as bacteria or viruses and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Self dampening rotary shaft
InactiveUS20050215331A1Inhibit rotational energy and related noiseAvoid energyRotating vibration suppressionShaftsClutchRotational axis
A rotary shaft includes internal self-dampening means for absorbing rotational energy generated by the rear axle and / or clutch of a motor vehicle.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE NORTH AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com