Patents
Literature
87 results about "Inertial response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
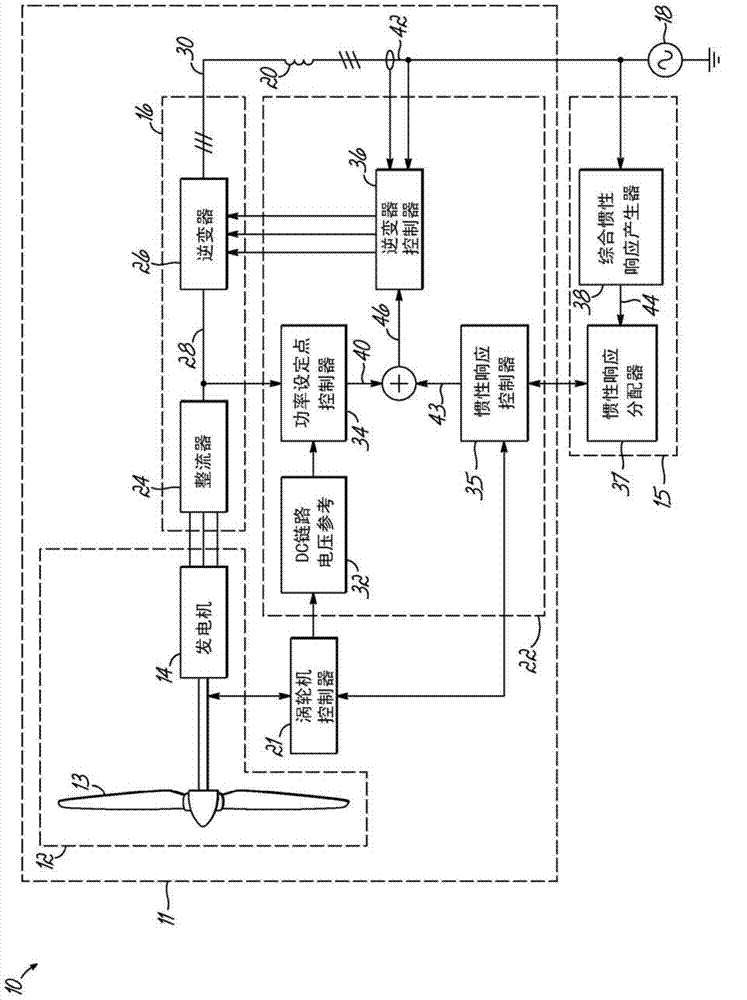
Inertial Response is a property of large synchronous generators, which contain large synchronous rotating masses, and which acts to overcome the immediate imbalance between power supply and demand for electric power systems, typically the electrical grid. Due to the ever existing power imbalance between mechanical power supply and electric power demand the rotational frequency of the rotating masses in all synchronous generators in the grid either speed up (excess power supply) or slow down (excess power demand). This enables the grid operator to rebalance the system in order to stop the speed change, resulting in a relatively small variation in AC frequency ideally within the allowable frequency range of that system. i.e. A 50 Hz system may allow a ±0.5 Hz deviation in the frequency of the AC voltage The grid frequency is the combined result of the detailed motions of all individual synchronous rotors in the grid, which are modeled by a general equation of motion called the Swing Equation.
Variable Displacement Engine Operation With NVH Management
InactiveUS20080154468A1Reduce and eliminate torque reactionNo backlashAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsClose couplingDrivetrain
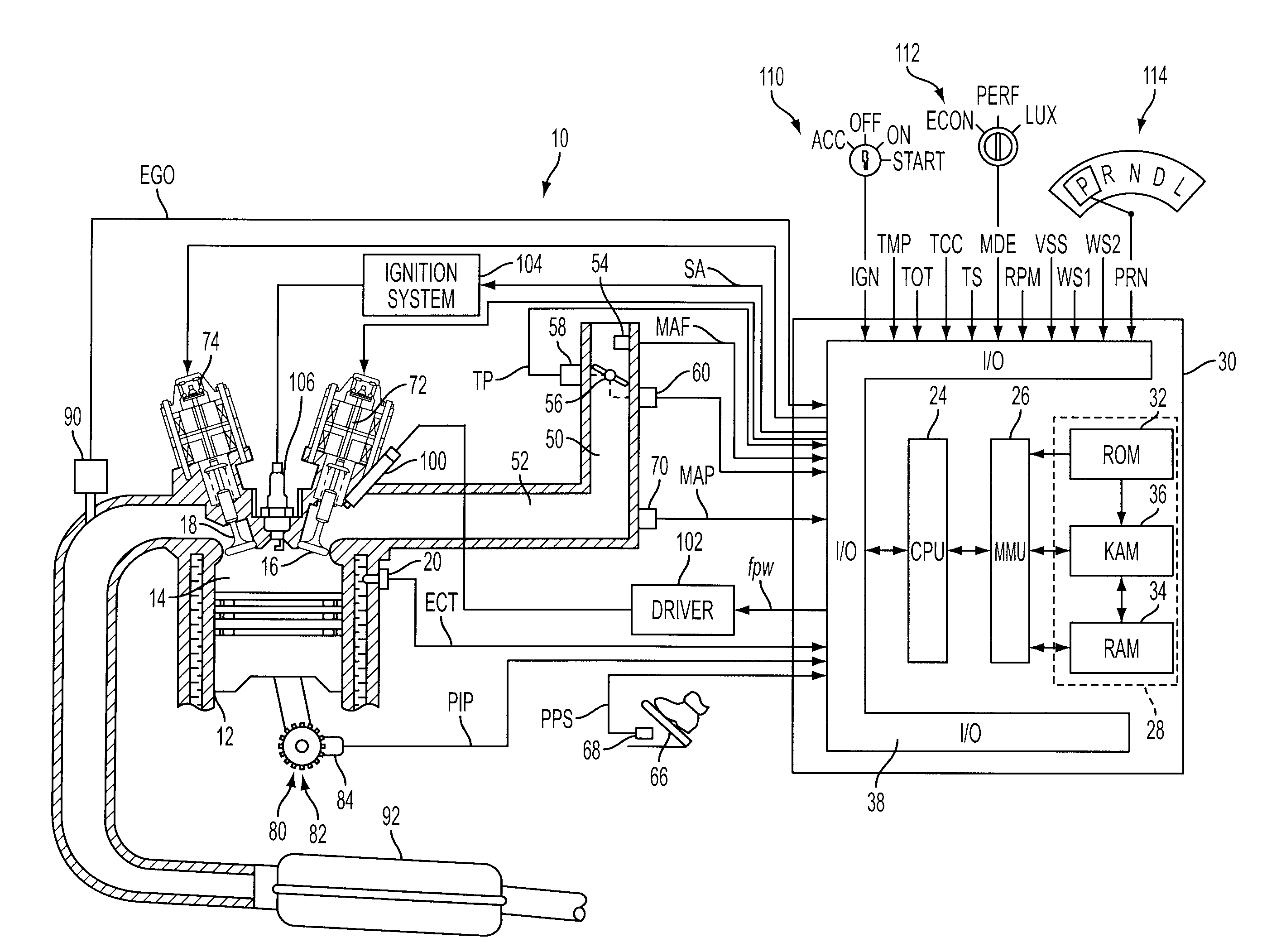
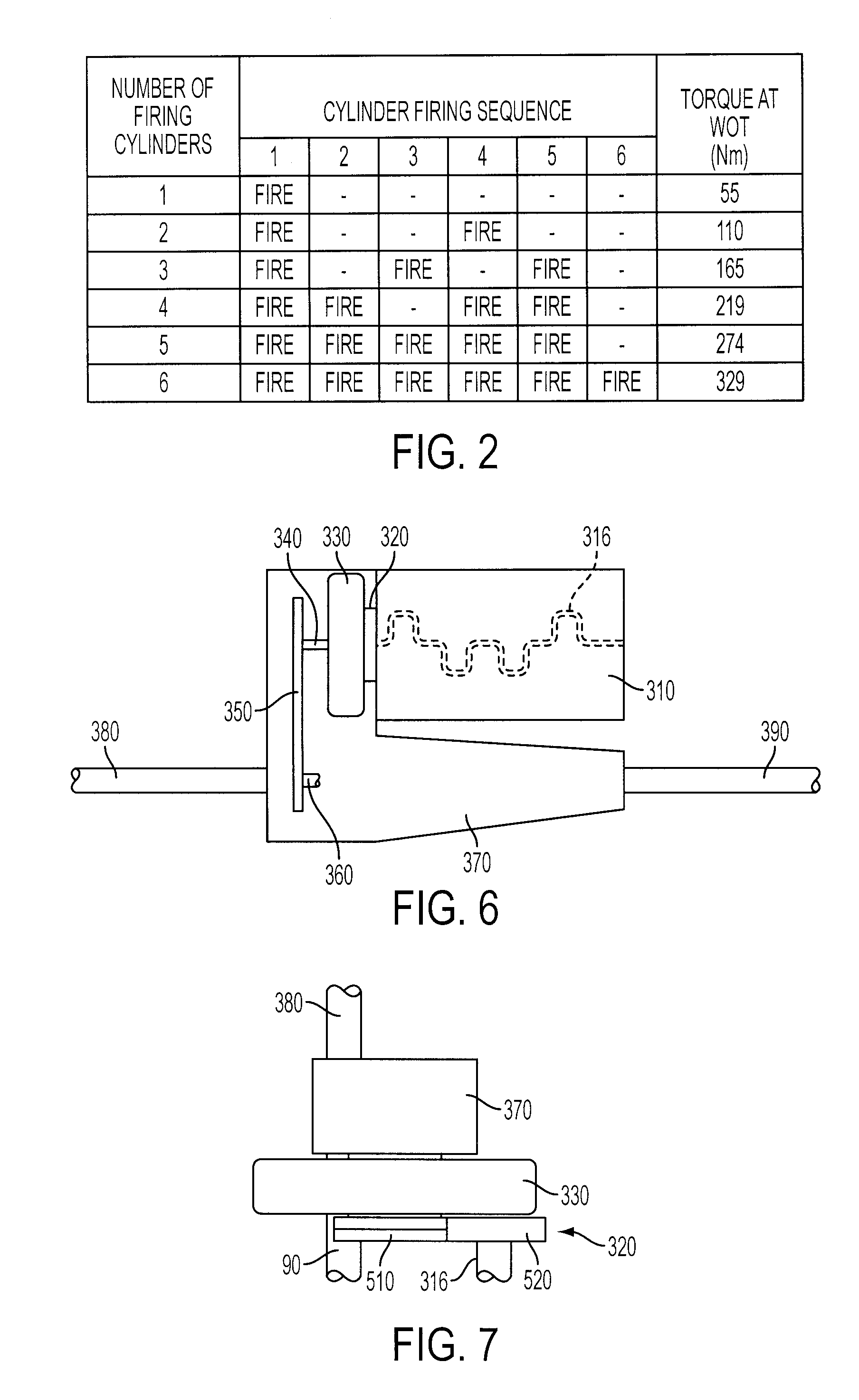
A system and method for controlling an internal combustion engine operable with a first cylinder firing frequency and a second cylinder firing frequency to reduce or eliminate transmission of torsional vibrations associated with the second cylinder firing frequency to reduce or eliminate constraints on reduced displacement mode operation using a closely coupled drive train component rotating in an opposite direction relative to rotating components of the engine. A close coupling device allows the inertia of the counter-rotating elements to reduce or eliminate the torque reaction of the drivetrain associated with acceleration and deceleration of the engine crankshaft in response to the second cylinder firing frequency in the reduced displacement mode.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
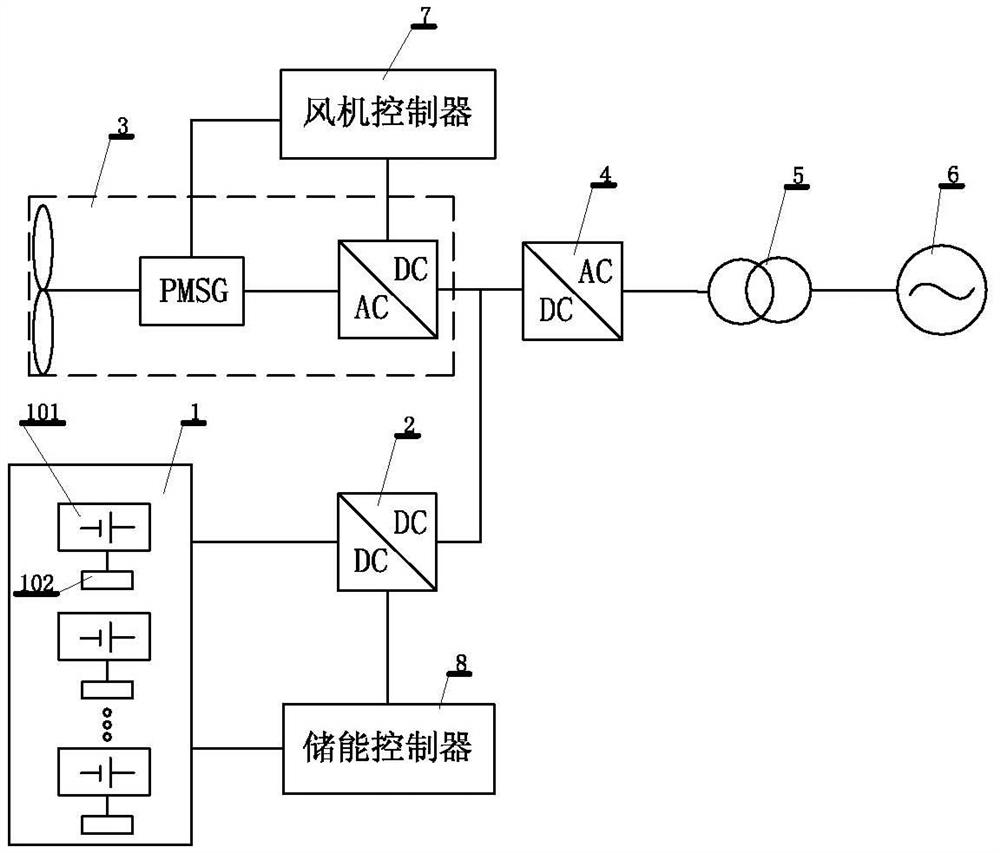
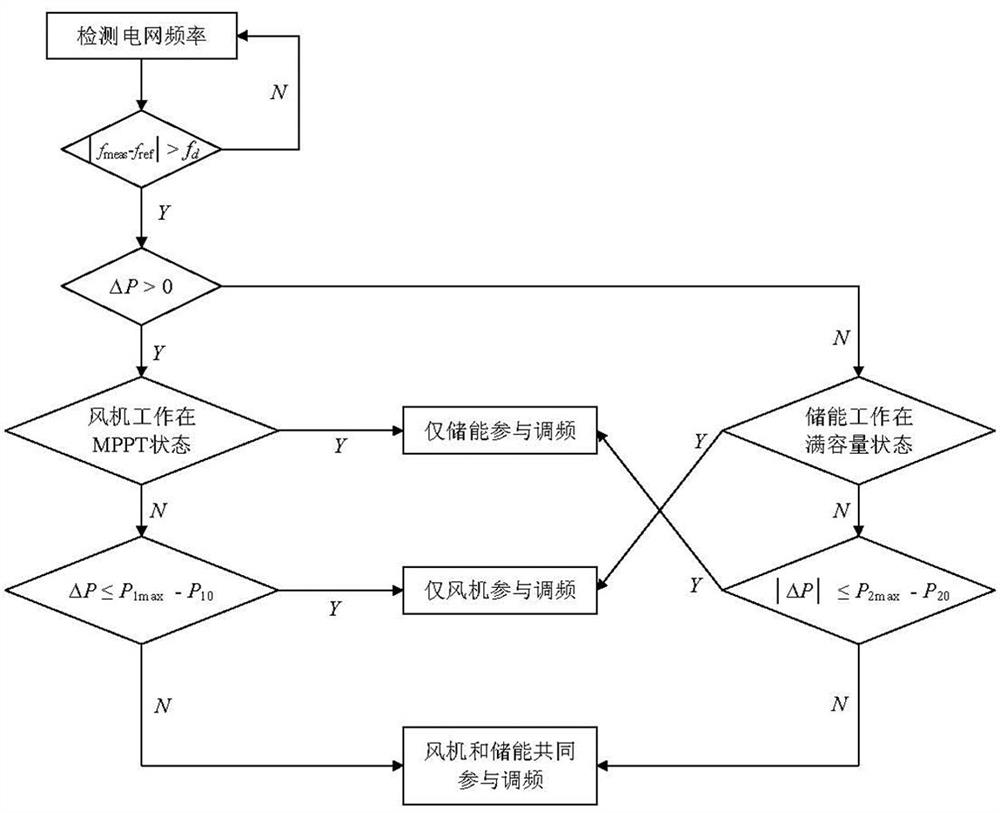
A method and apparatus for an energy storage system to participate in power grid frequency control
ActiveCN105449701AHigh speedImprove the ability to resist load disturbanceAc network load balancingPower oscillations reduction/preventionControl powerTime delays
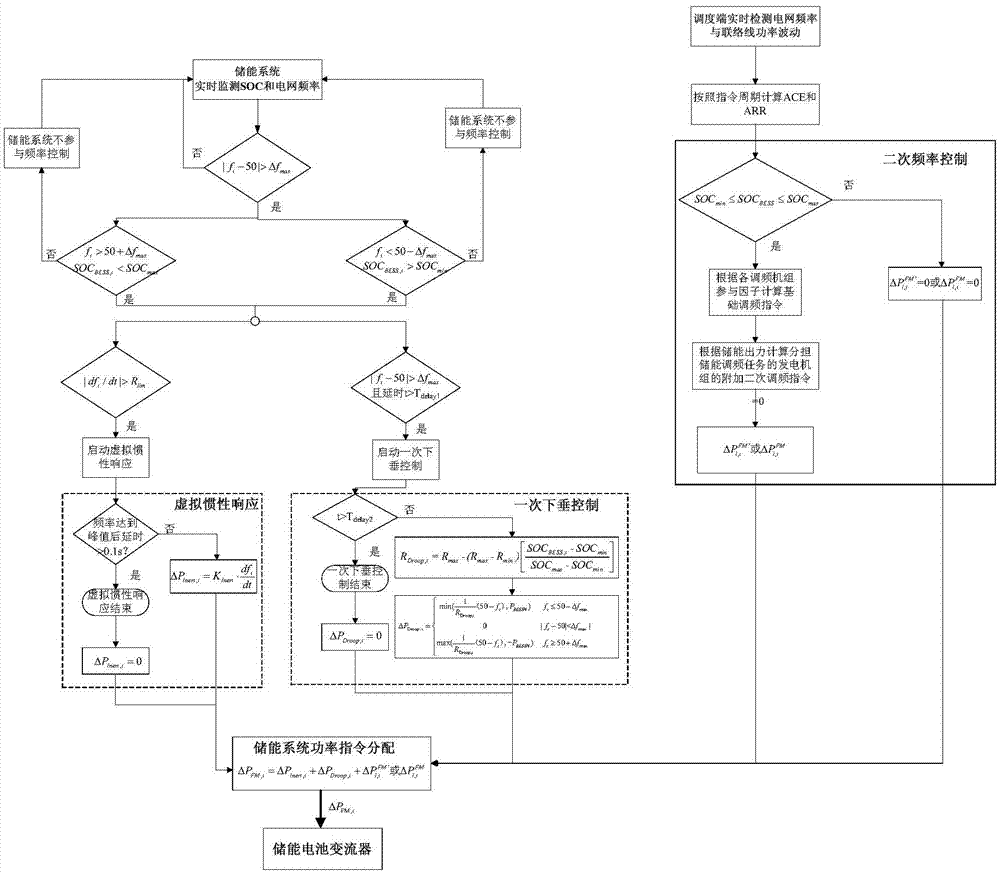
The invention provides a method and apparatus for an energy storage system to participate in power grid frequency control. The method comprises the steps of monitoring power grid frequency and charged states of an energy storage system in real time; if a power grid frequency offset exceeds a maximum frequency deviation, determining the energy storage system to participate into power grid primary frequency modulation according to deviation directions and the charged states; when a primary frequency modulation starting condition is satisfied, calculating virtual inertia response, a primary variable sagging control power adjustment value and a primary frequency modulation active control instruction; according to the primary frequency modulation active control instruction, carrying out primary adjusting of active power output of the energy storage system; starting secondary frequency modulation after time delay to determine a secondary frequency modulation instruction; according to the virtual inertia response, the primary variable sagging control power adjustment value and the secondary frequency modulation instruction, determining a secondary frequency modulation active control instruction; and according to the secondary frequency modulation active control instruction, carrying out secondary adjusting of the active output power of the energy storage system. Through adoption of the method and apparatus of the invention, coordination and cooperation between the energy storage system and other machine sets in aspects of primary frequency modulation and secondary frequency modulation can be well solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST +2
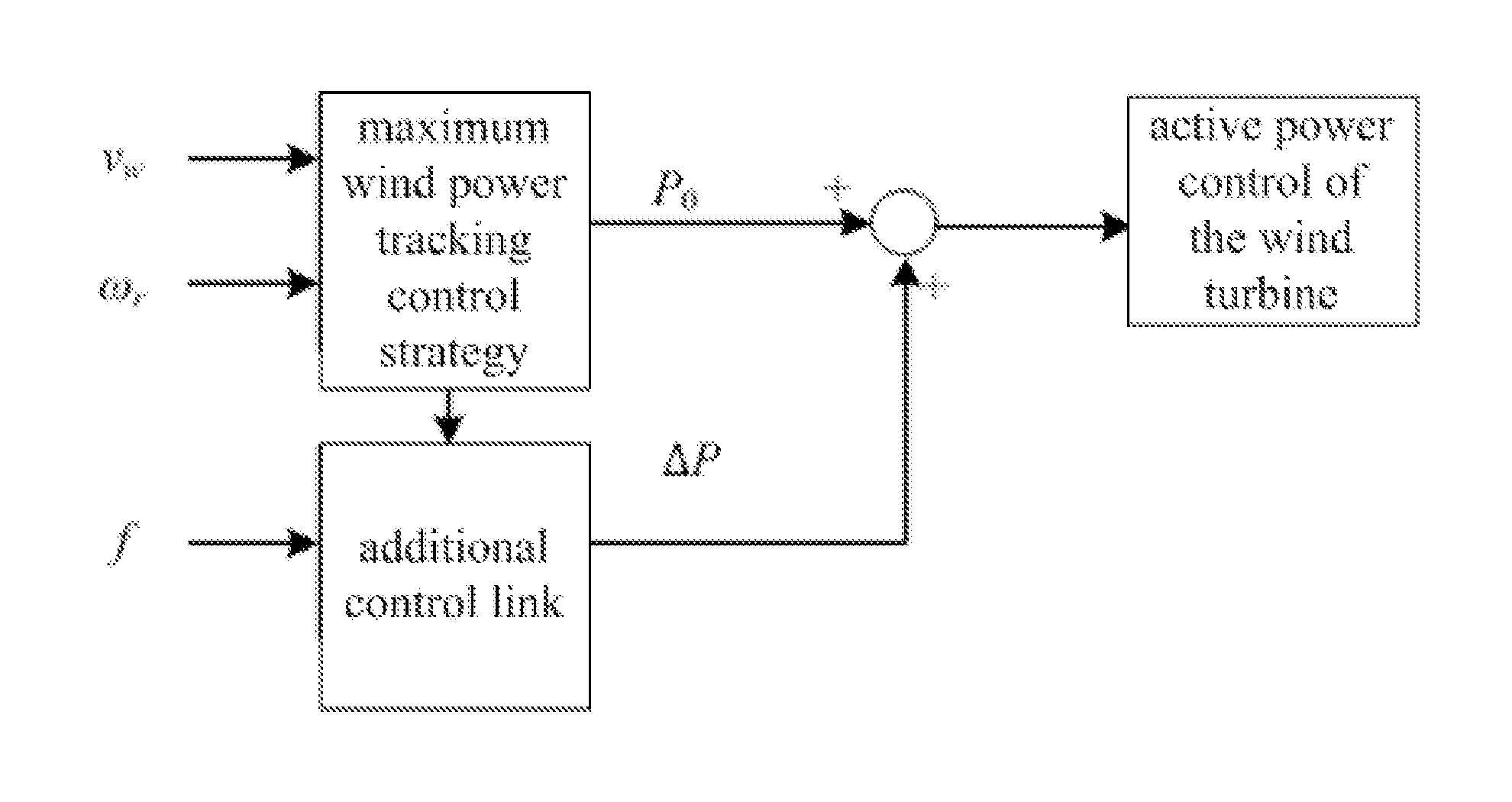
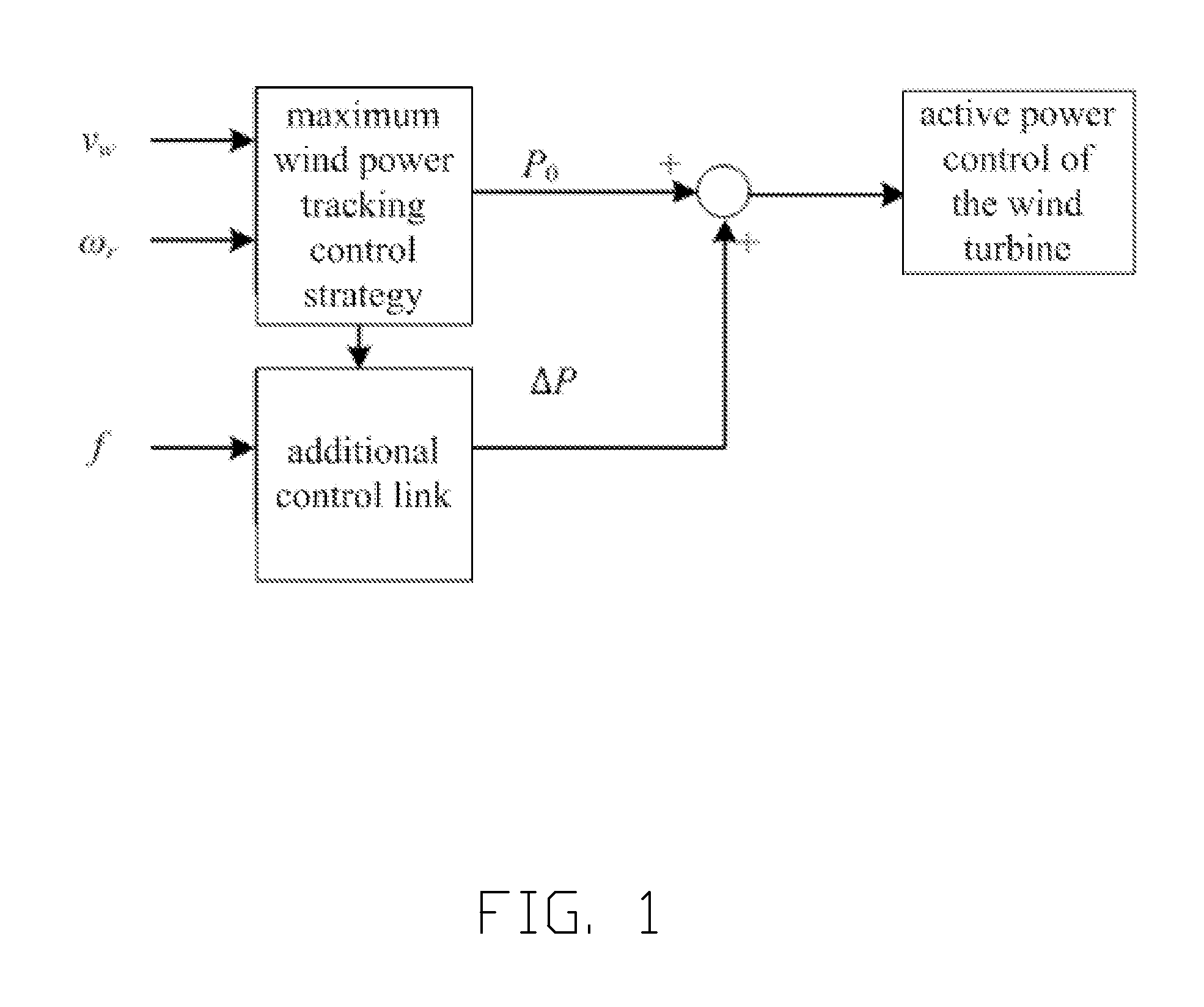
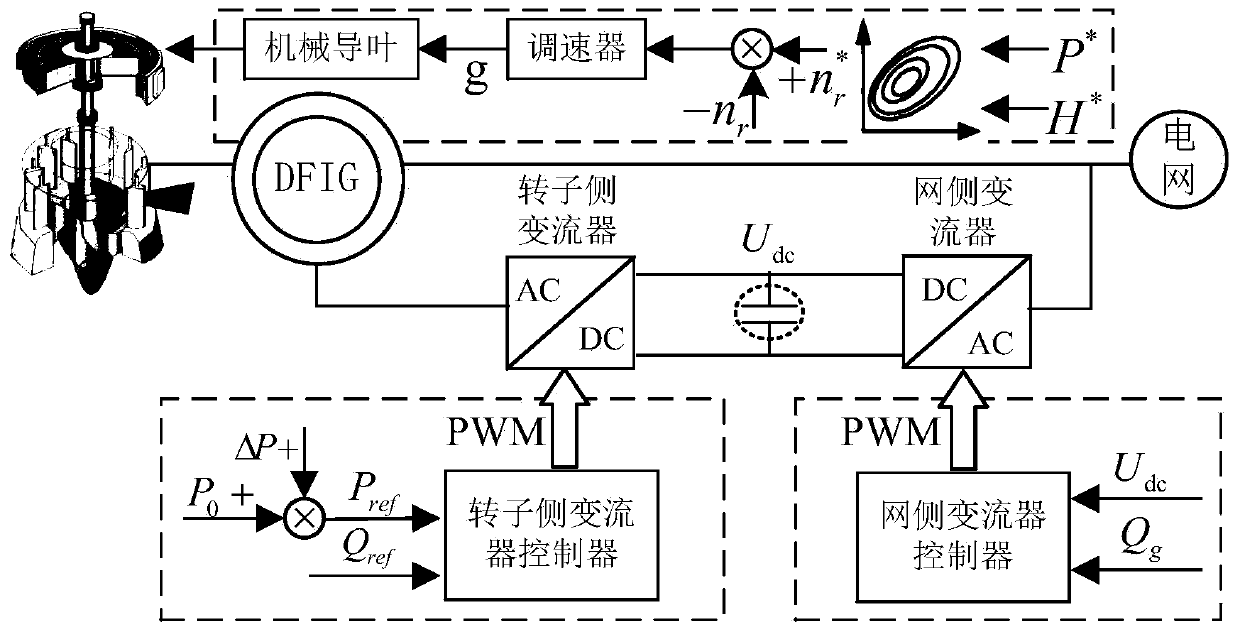
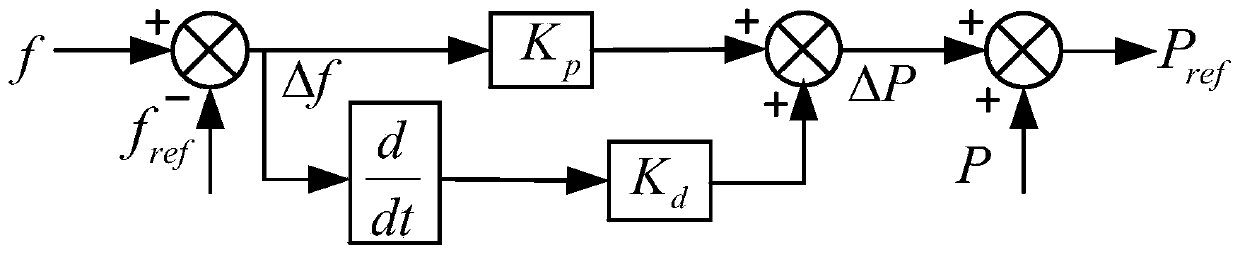
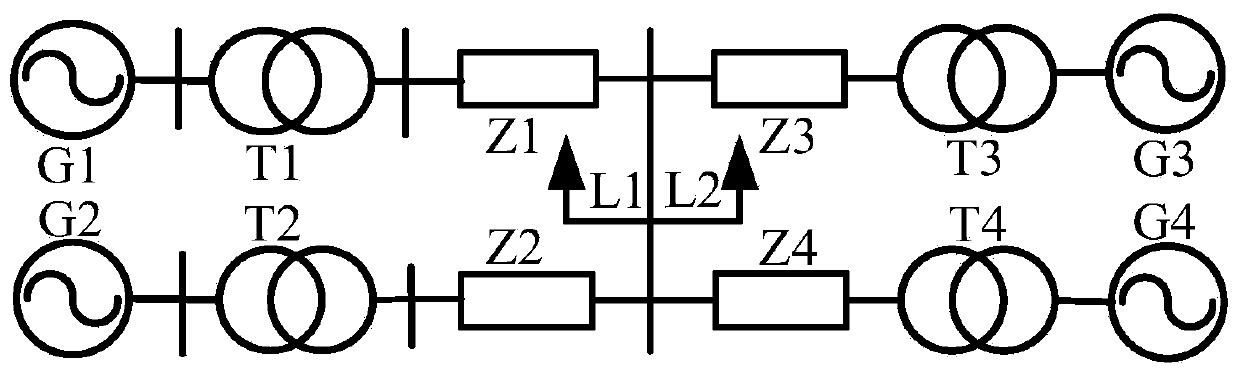
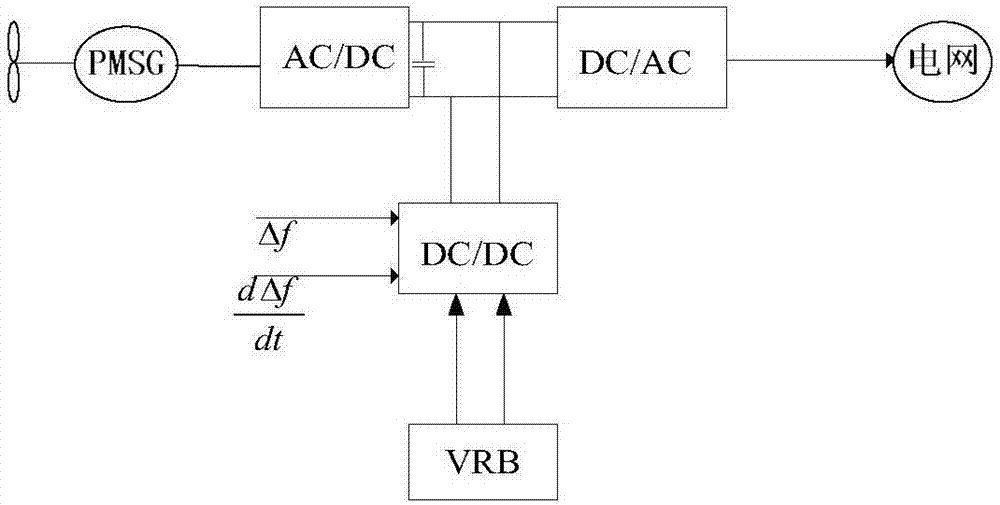
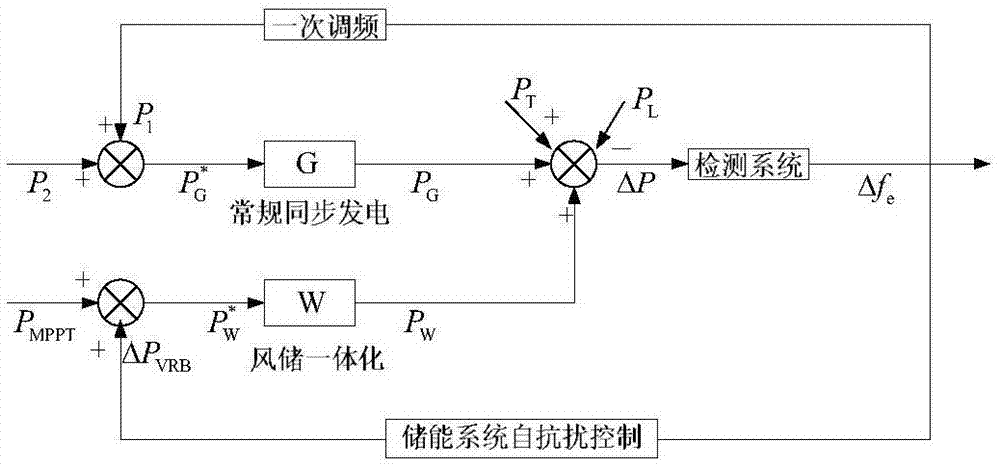
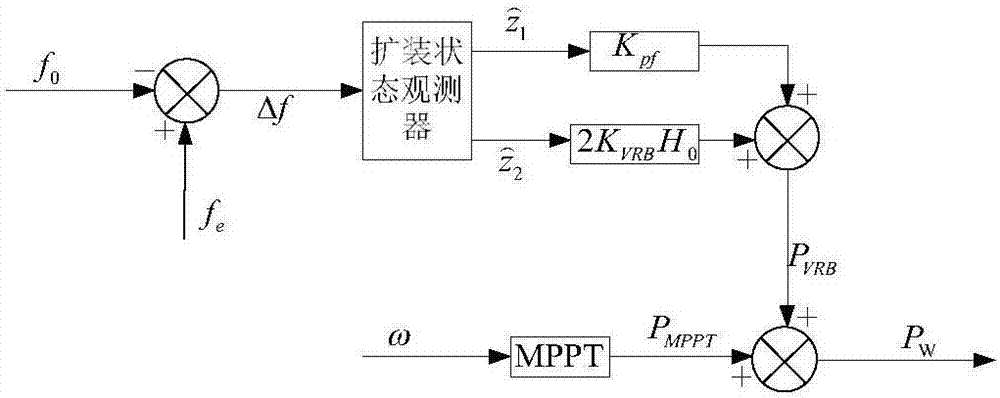
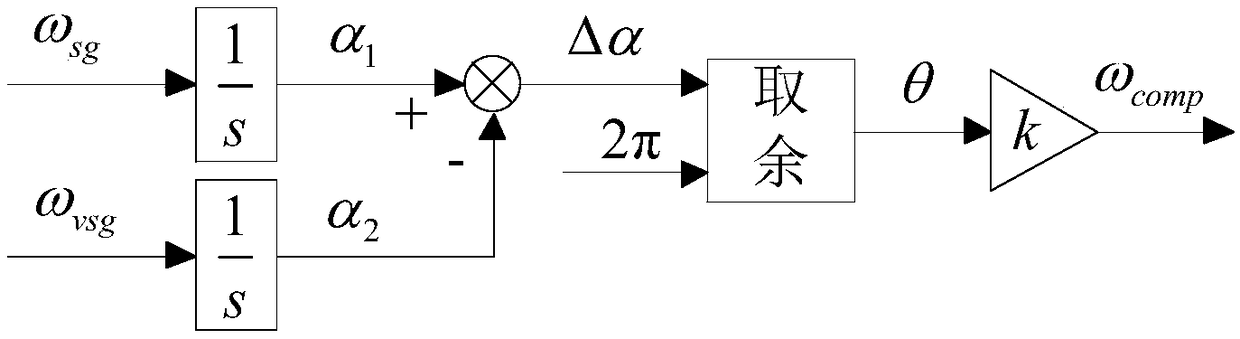
Method for controlling inertia response of variable-speed wind turbine generator
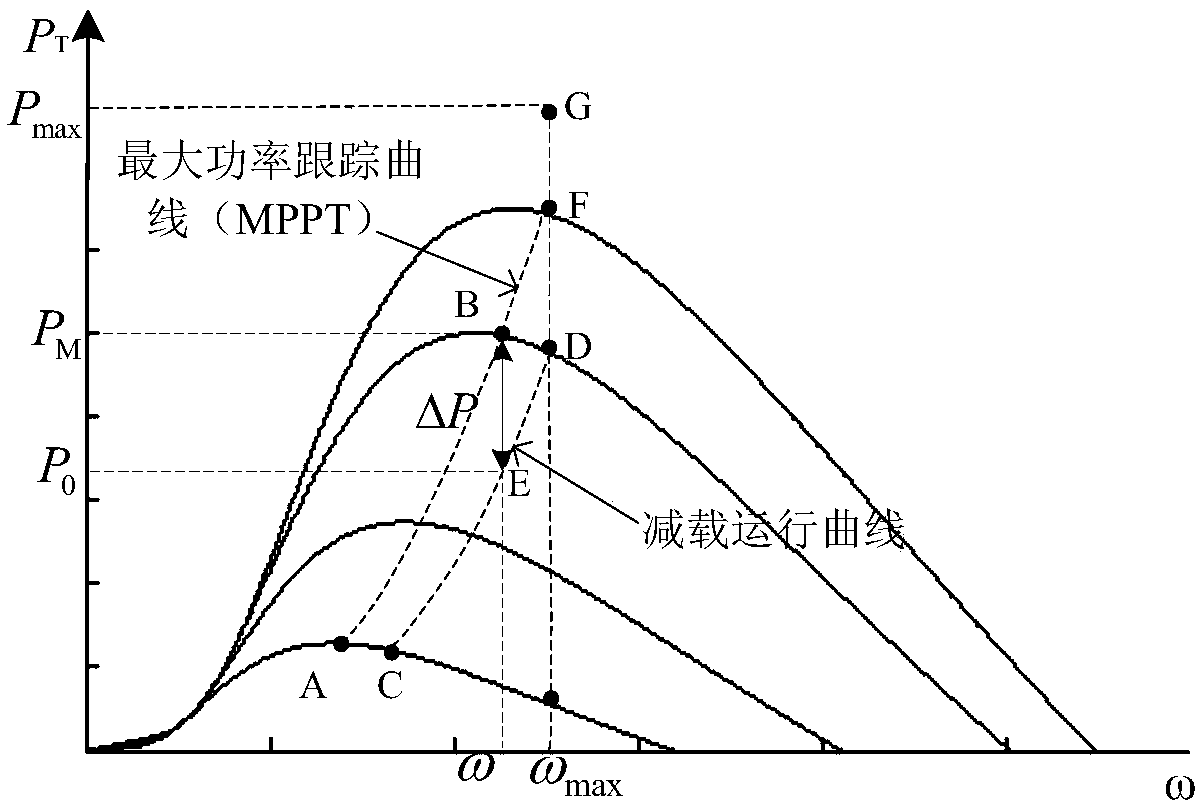
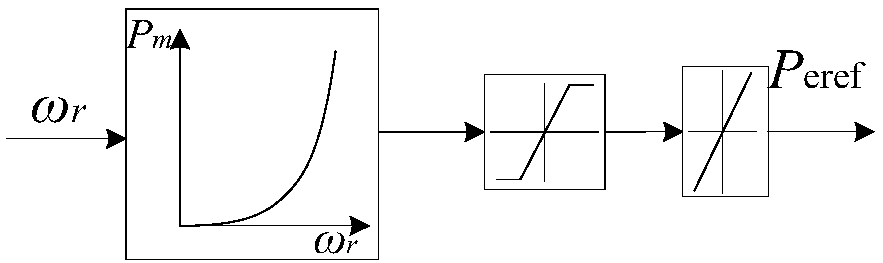
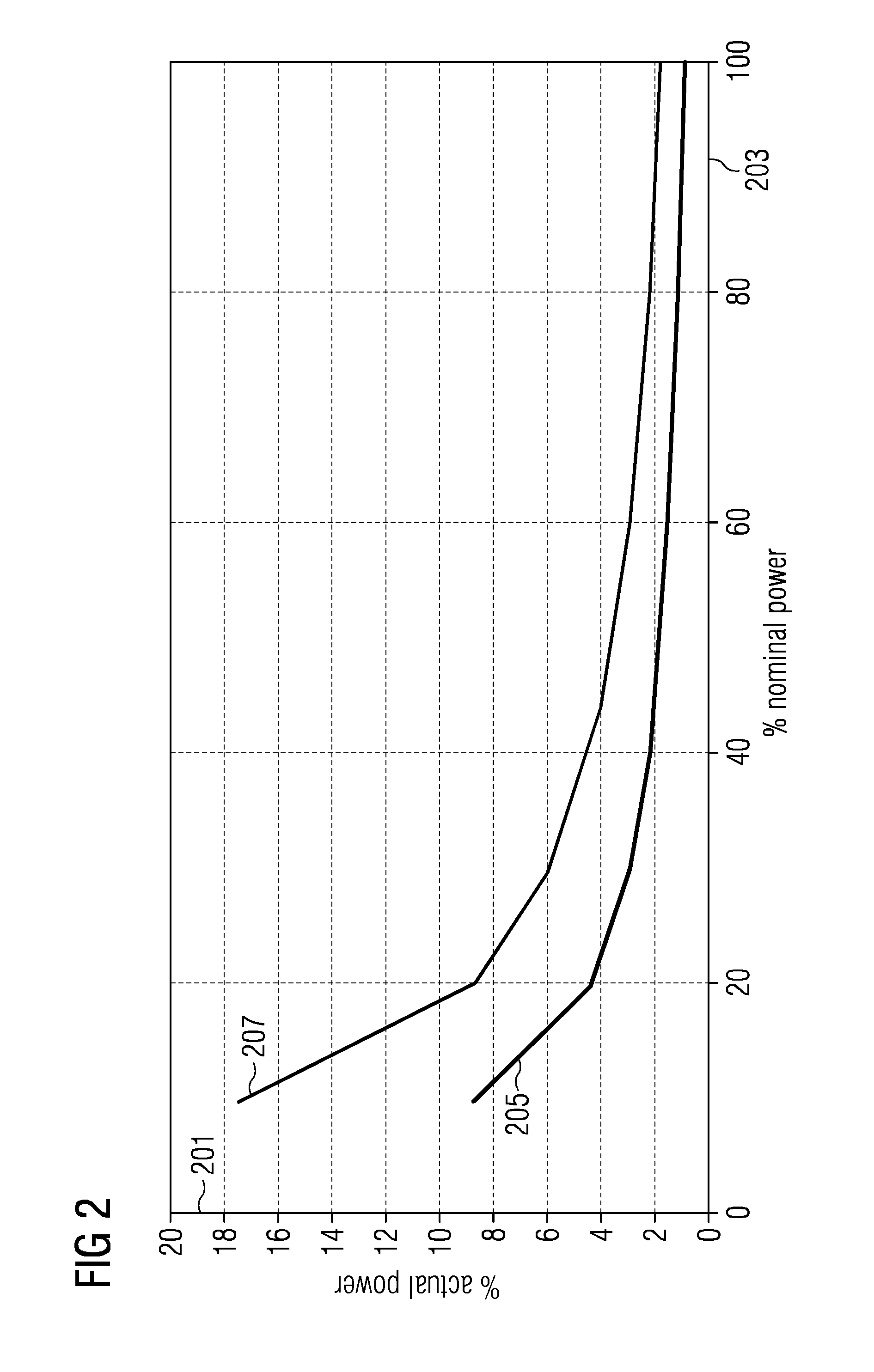
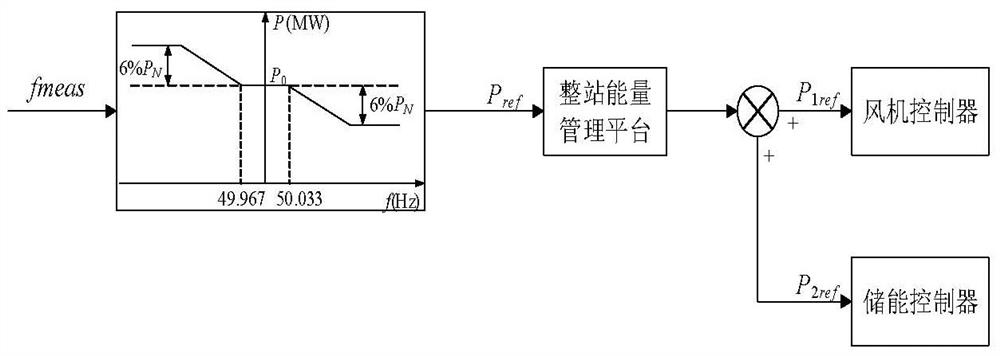
A method of controlling inertia response of variable-speed wind turbine generator includes following steps. A maximum wind power of the wind turbine is gotten through a wind speed νw and a rotation speed ωr at the hub of the wind turbine based on a maximum wind power tracking control strategy. The maximum wind power is set as an active power control reference value P0 of the wind turbine. A grid frequency f is obtained via a frequency measurement equipment. An additional active power control reference value ΔP of the wind turbine is generated based on the grid frequency f via an additional control block, and the additional active power control reference value ΔP is added on the active power control reference value P0, wherein a total of active power control reference value of the wind turbine is P0+ΔP.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Wind power penetration limit calculating method that considers frequency constraint and wind power frequency modulation
ActiveCN108832658AImprove robustnessImprove adaptabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationWind power penetrationPower limits
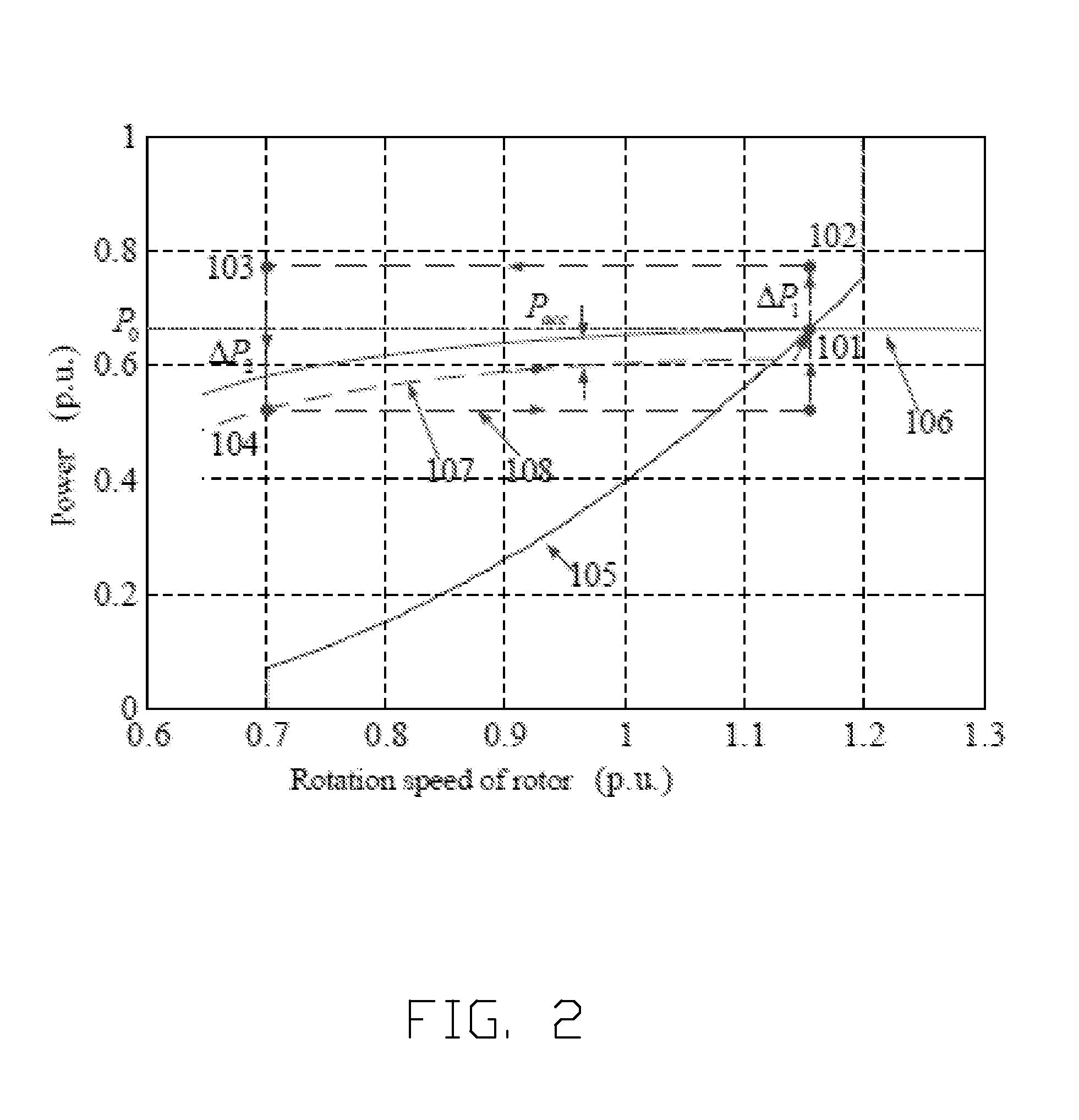
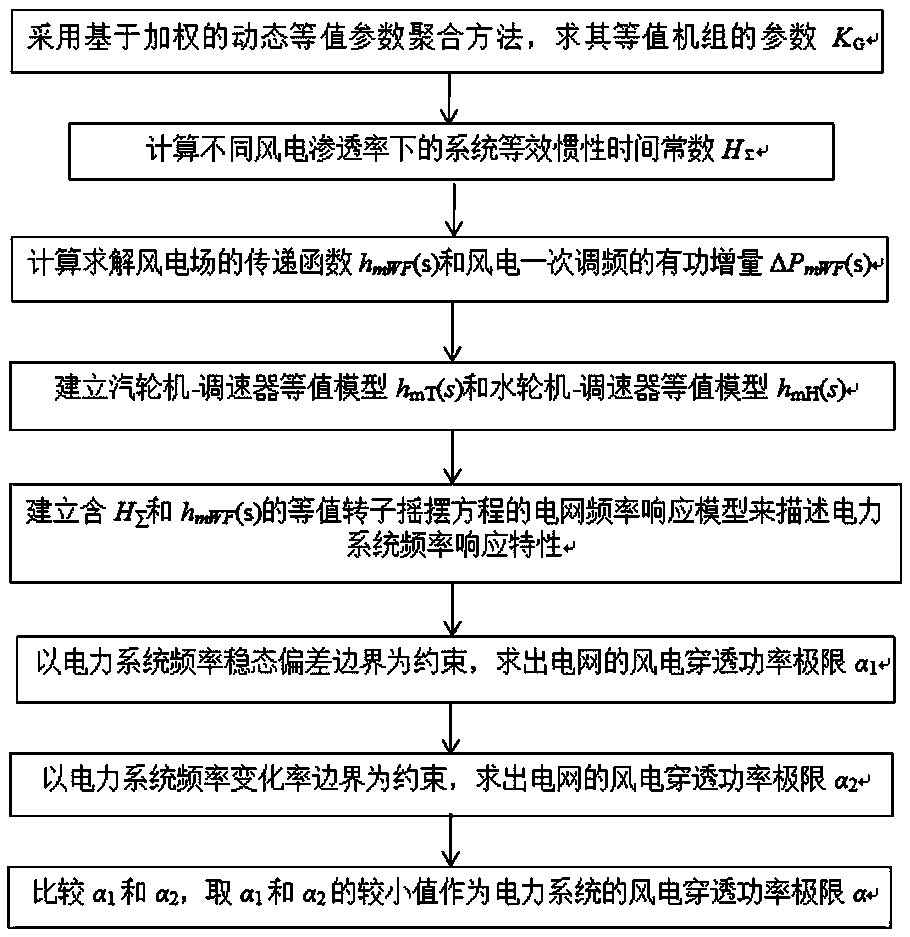
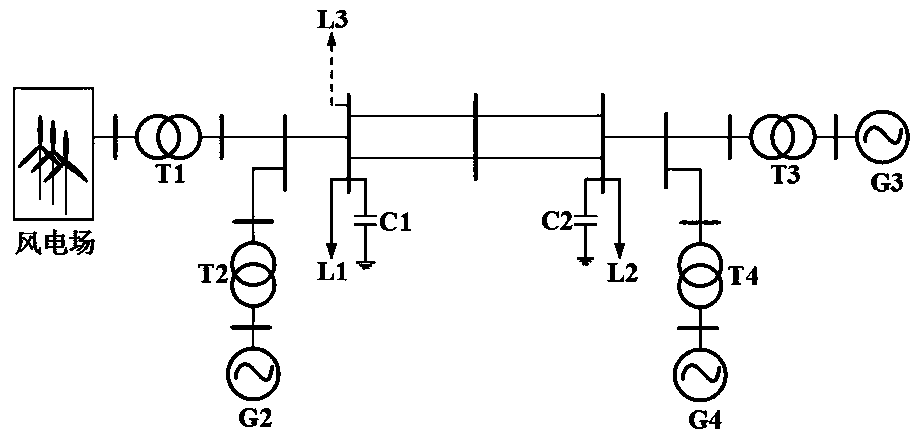
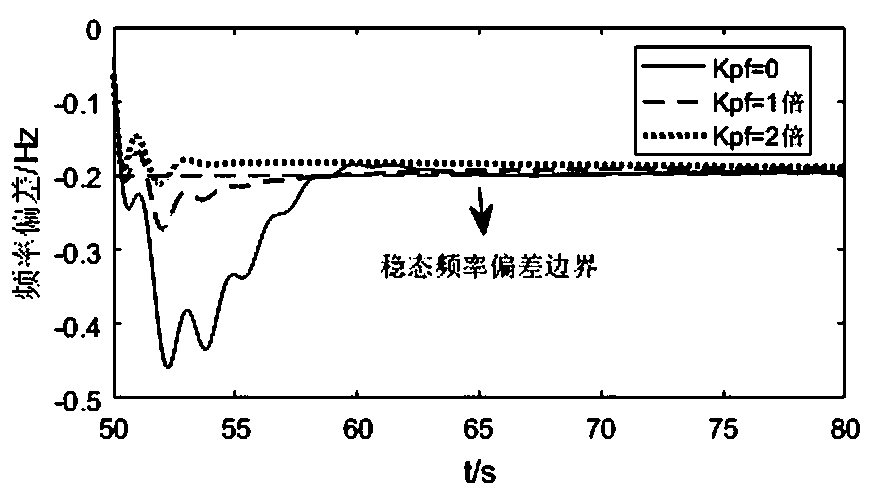
A wind power penetration limit calculating method that considers frequency constraint and wind power frequency modulation; the method comprises the following steps: using a weight equivalence polymerization method to solve a wind power plant primary frequency modulation response transfer function model and a wind power primary frequency modulation active increment; considering a wind power virtualinertia control strategy, and solving a power system equivalent inertia time constant under different wind power penetration rates; calculating a load damping effect, building a power grid frequencyresponse model that is equivalent to a rotor swing equation, and using the model to describe power system frequency response characteristics; using the power system frequency stable state deviation boundary and frequency rate of change boundary as constraints, and proposing the power grid wind power penetration limit calculating method. The method introduces the real wind power virtual inertia response, the active increment formed by the primary frequency modulation response and the power system frequency constraint into the wind power penetration limit calculation, thus improving the power grid robustness under the wind power grid connection condition, ensuring the power grid to stable and safely operate, and providing important guiding meanings for wind power grid connection planning construction.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
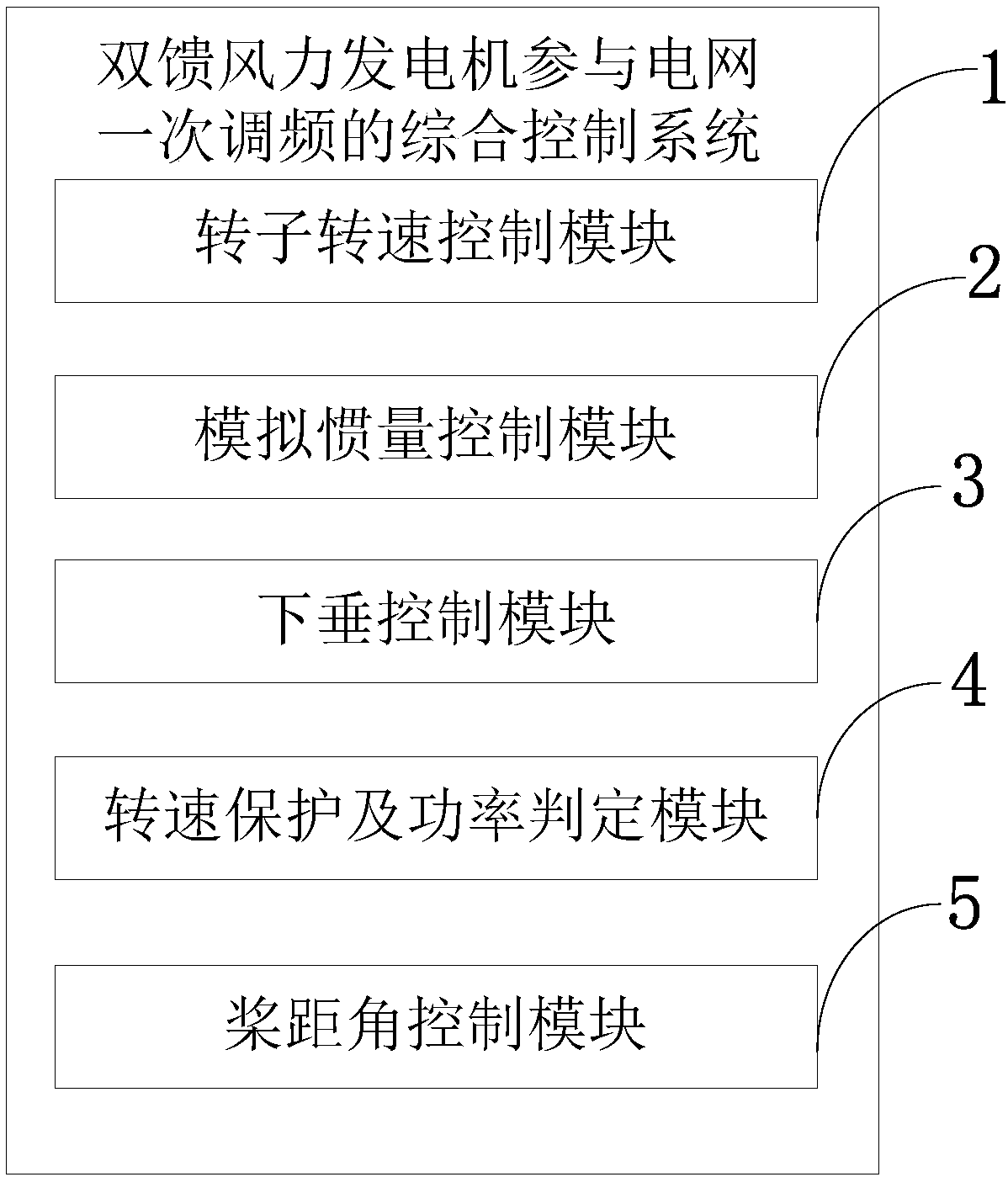
Comprehensive control system adopting doubly-fed wind generator participated in power grid primary frequency modulation
InactiveCN108448623AVerify availabilityReduce active powerSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionControl systemFrequency modulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of wind power generation, and discloses a comprehensive control system adopting a doubly-fed wind generator participated in power grid primary frequency modulation. The control system comprises a rotor rotary speed control module, a simulation inertia control module, a droop control module, a rotary speed protection and power determination module and apitch angle control module. After the wind generator is participated in frequency modulation, the power grid inertia is equivalently enlarged, so that the doubly-fed asynchronous wind generator can have inertia response on the power grid frequent as the conventional synchronous generator, thereby lowering change rate of the power grid frequency; and by controlling the rotary speed and the pitch angle, the wind generator output is lowered, so that the wind generator has certain active backup capacity to be participated in primary frequency modulation, thereby lowering steady-state error of thefrequency.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
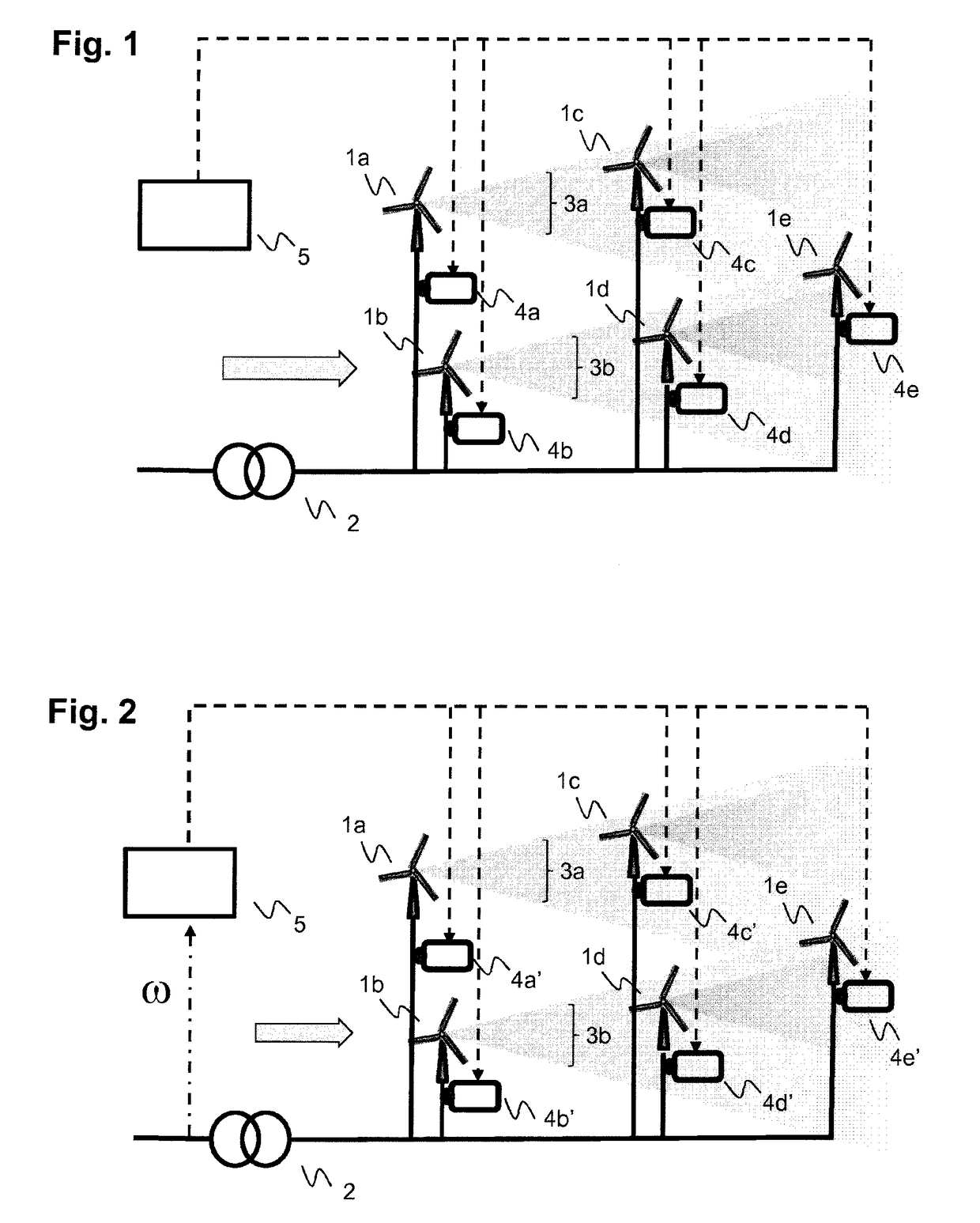
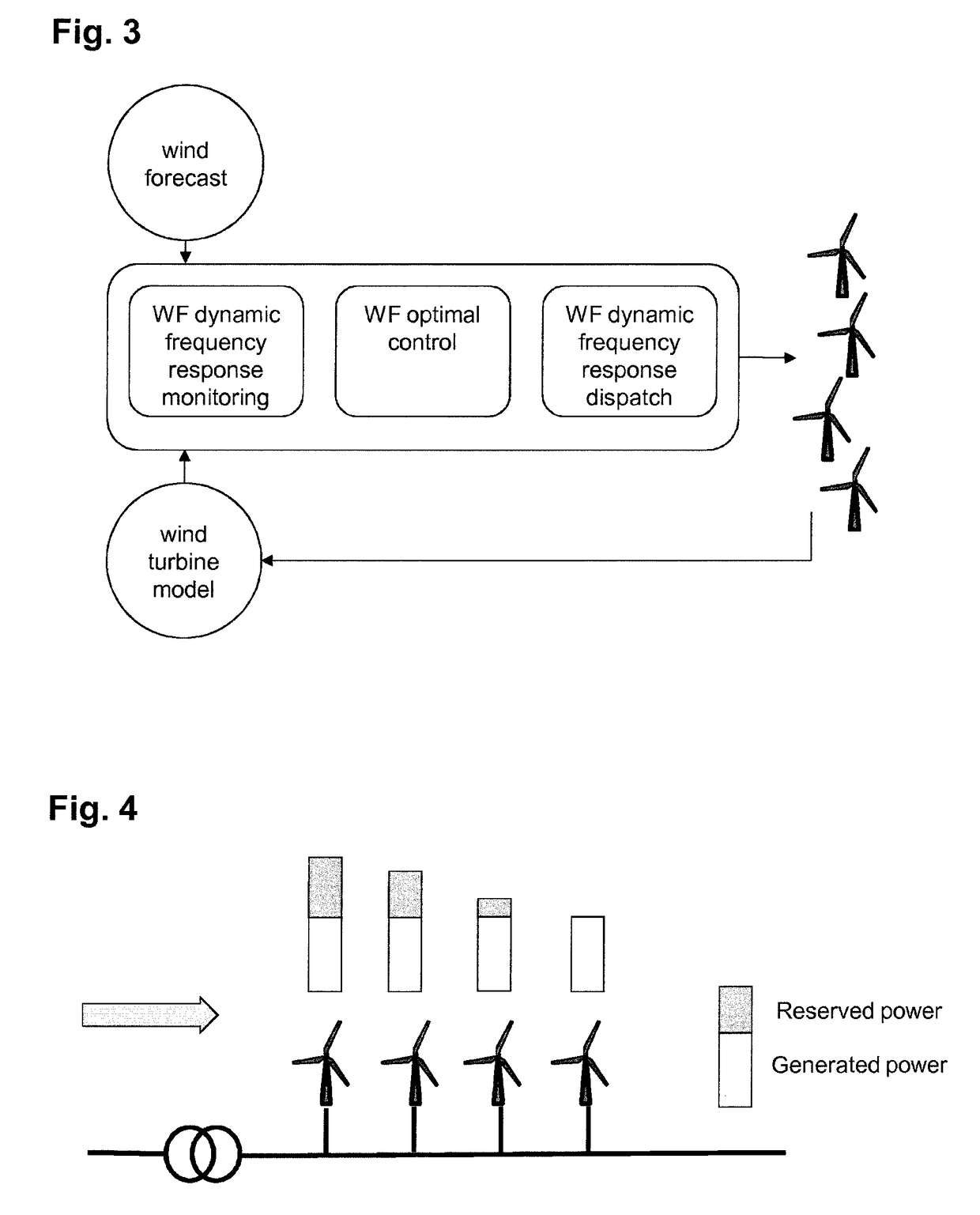
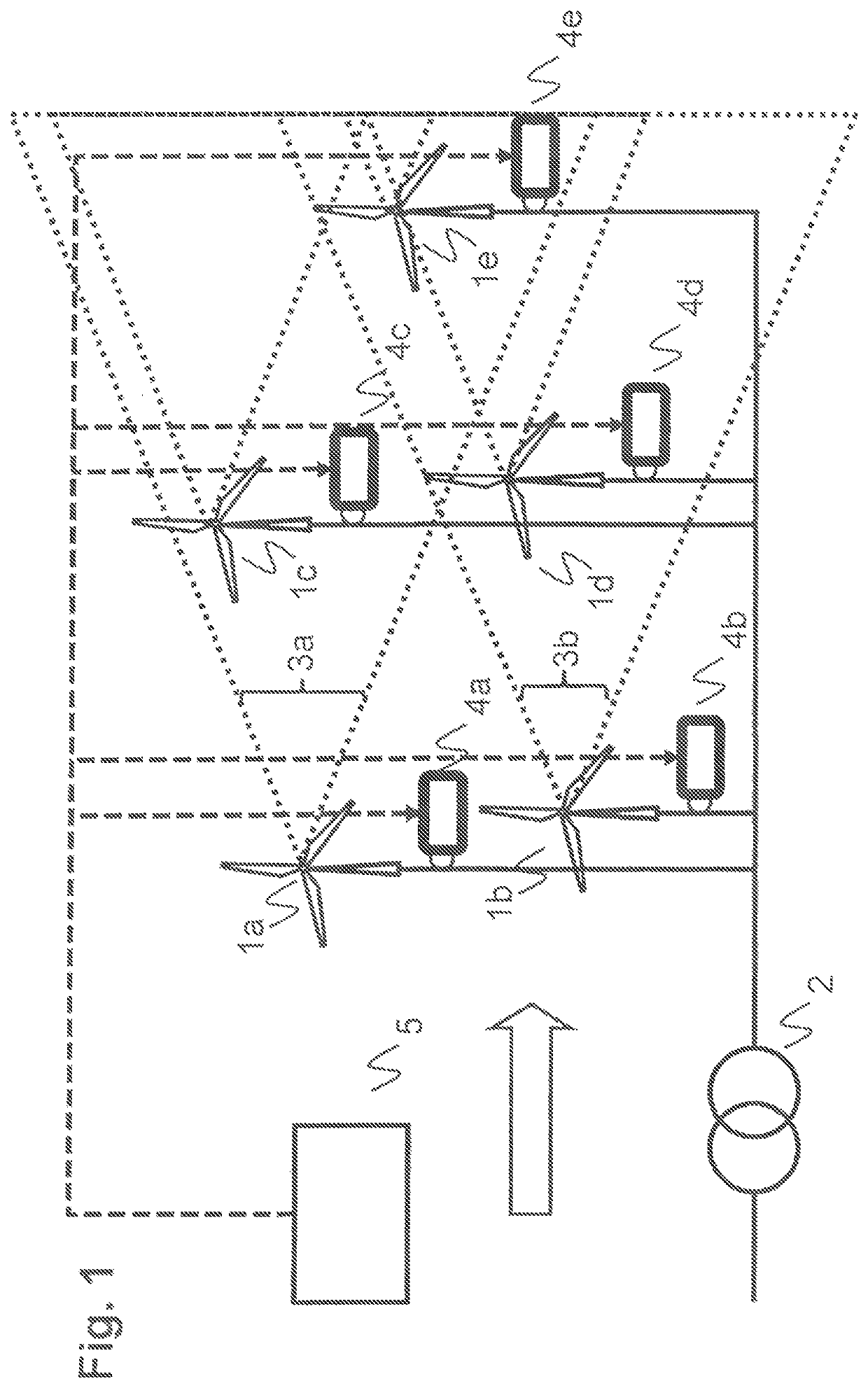
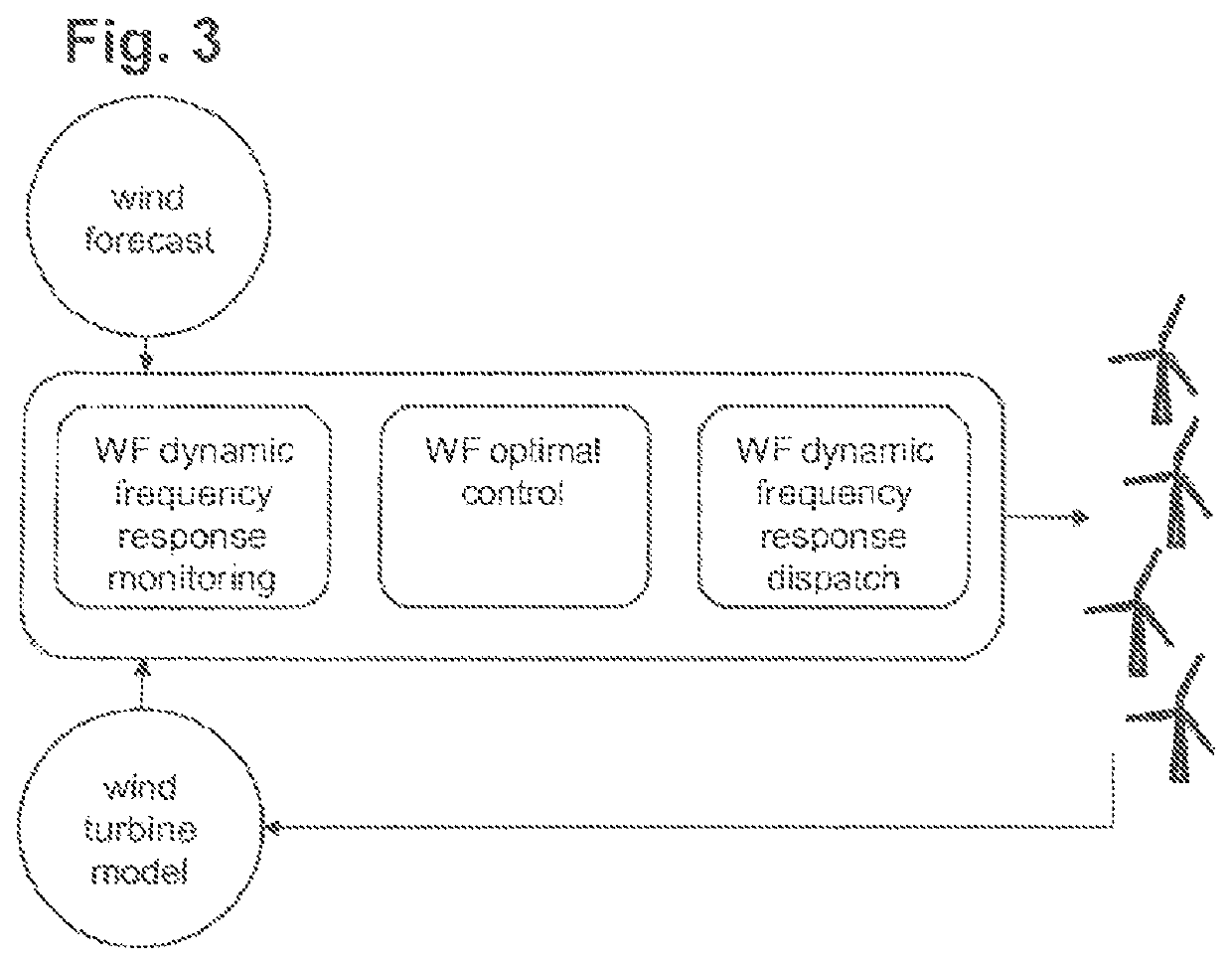
Wind farm inertial response
ActiveUS20180073486A1Prediction is accurate and reliablePromote resultsOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlWind forecastPower grid
The present invention is concerned with an operation of a wind farm with a plurality of wind turbines in view of a dynamic frequency response. According to the invention, dynamic frequency support and power production for all wind turbines in a wind farm are handled concurrently in a single optimization step and taking into account wake effects within the wind farm as well as optional wind forecast information. The dynamic frequency support capability of the entire wind farm is planned in advance according to grid requirements and power system condition changes. While existing methods de-load wind turbines with a static percentage in order to supply additional power when needed, the proposed method incorporates the dynamic frequency support into the optimal operation system of wind farm.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
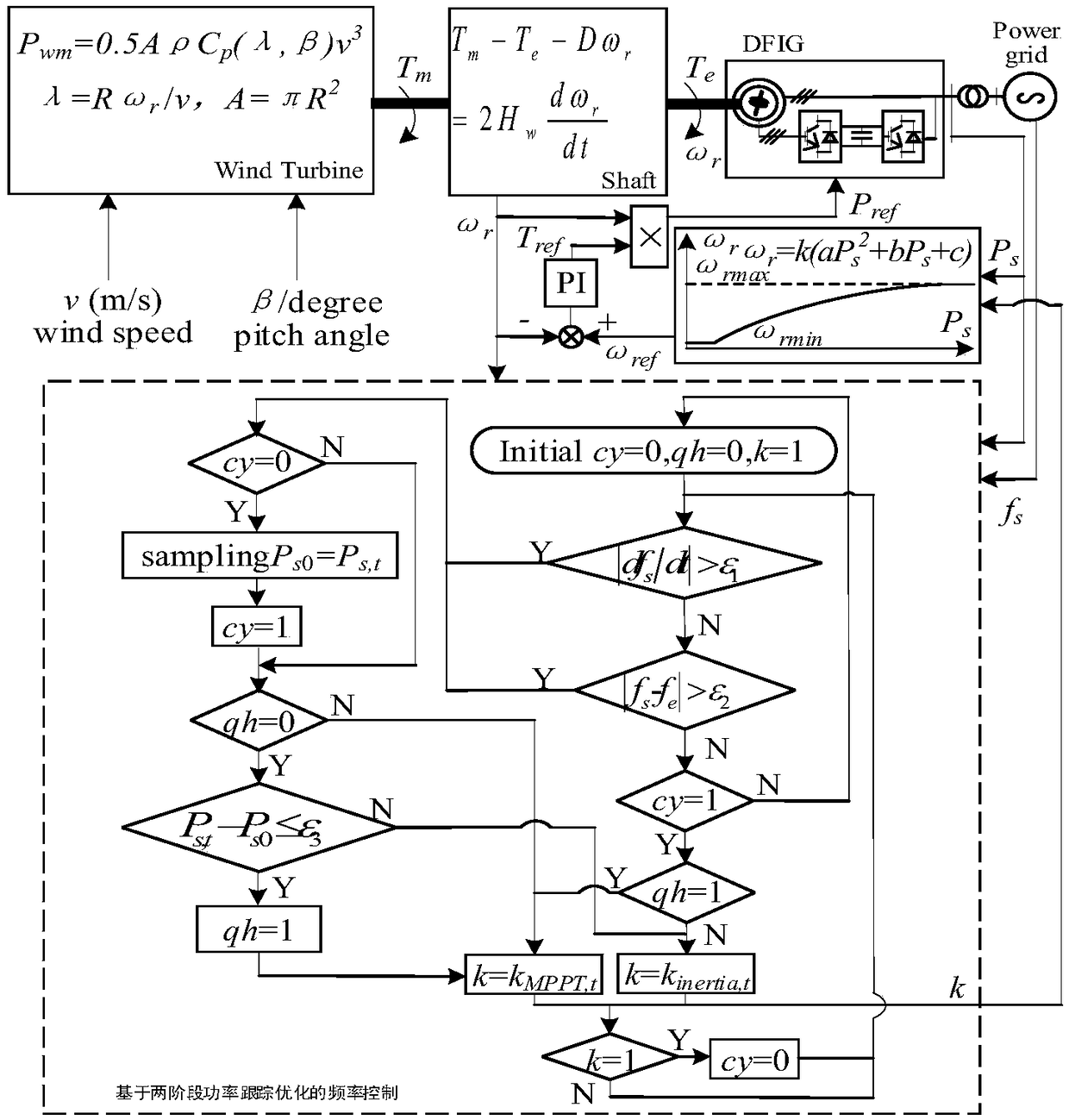
Frequency support control method used for doubly-fed wind generation set and based on two-stage power tracking optimization
ActiveCN109449954AAvoid secondary perturbationImprove FM dynamicsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectricityFuzzy control system
The invention relates to a frequency support control method used for a doubly-fed wind generation set and based on two-stage power tracking optimization. The invention starts from optimization of frequency support dynamic characteristics of a wind generation set and provides a frequency support control method used for the wind generation set and based on two-stage variable proportion coefficient optimized power tracking. On the basis, a variable proportion coefficient control strategy in an inertial response stage is derived based on a virtual inertia time coefficient and a rotor movement equation, and for quick recovery of a maximum power tracking operation mode of the wind generation set after inertial support and avoiding secondary disturbance from being produced on system frequency adjustment in a recovery process, a variable proportion coefficient control strategy in a maximum power tracking operation mode recovery stage is designed by adopting fussy control. The frequency supportcontrol method provided by the invention has control robustness, a control structure is simple, engineering implementation is easy, and the quick recovery of the maximum power tracking operation modeof the doubly-fed wind generation set after inertial response and inertial support on a power grid frequency can be realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
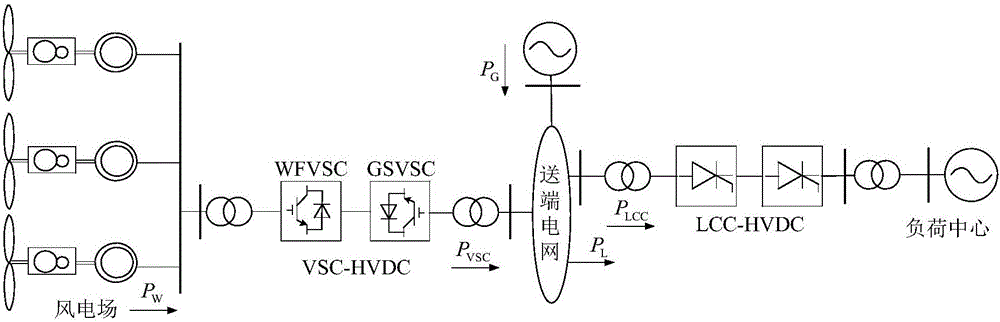
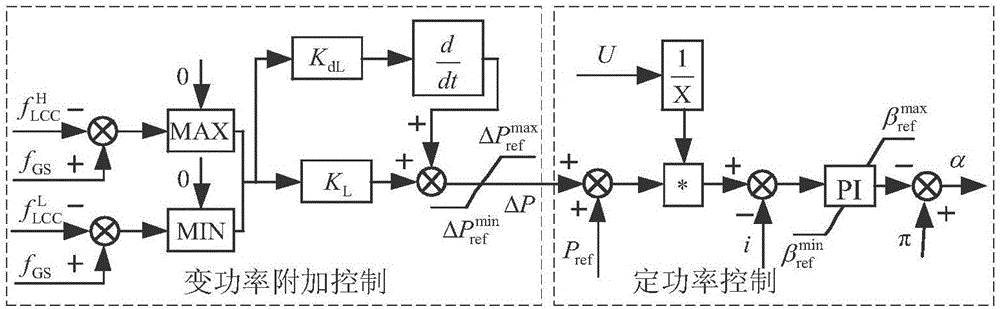
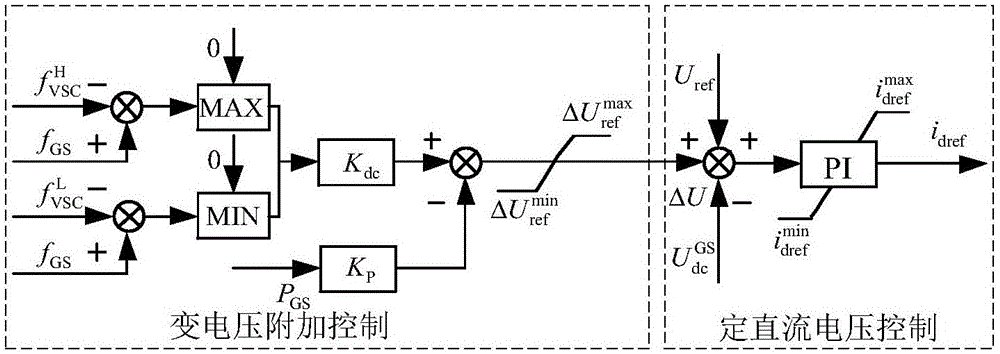
Wind farm direct current grid connection and direct current transmission source net coordination control method
ActiveCN106816887AReduce volatilityReasonable distribution of unbalanced powerElectric power transfer ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransmitted powerInertial control
The invention discloses a wind farm direct current grid connection and direct current transmission source net coordination control method. The wind farm direct current grid connection and direct current transmission source net coordination control method comprises steps that LCC-HVDC additional control is additionally provided, and power-frequency slope characteristics provided with dead zones and inertia control are introduced in LCC-HVDC rectifier station fixed power control, and then transmitted power is capable of responding to frequency of a sending-end power grid; VSC-HVDC additional control is additionally provided; draught fan additional control is additionally provided, and active-frequency slope characteristic and the inertial control are introduced in draught fans, and then active power output by the draught fans is capable of responding to changes of WFVSC side frequencies; coordination of controllers is additionally provided, proper motion dead zones are arranged, and then the various controllers are coordinated. By increasing the power-frequency statistic characteristic coefficient and the inertia response coefficient of the system of the sending-end power grid, the inertia of the sending-end power grid is increased, and the frequency stability of the system is improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
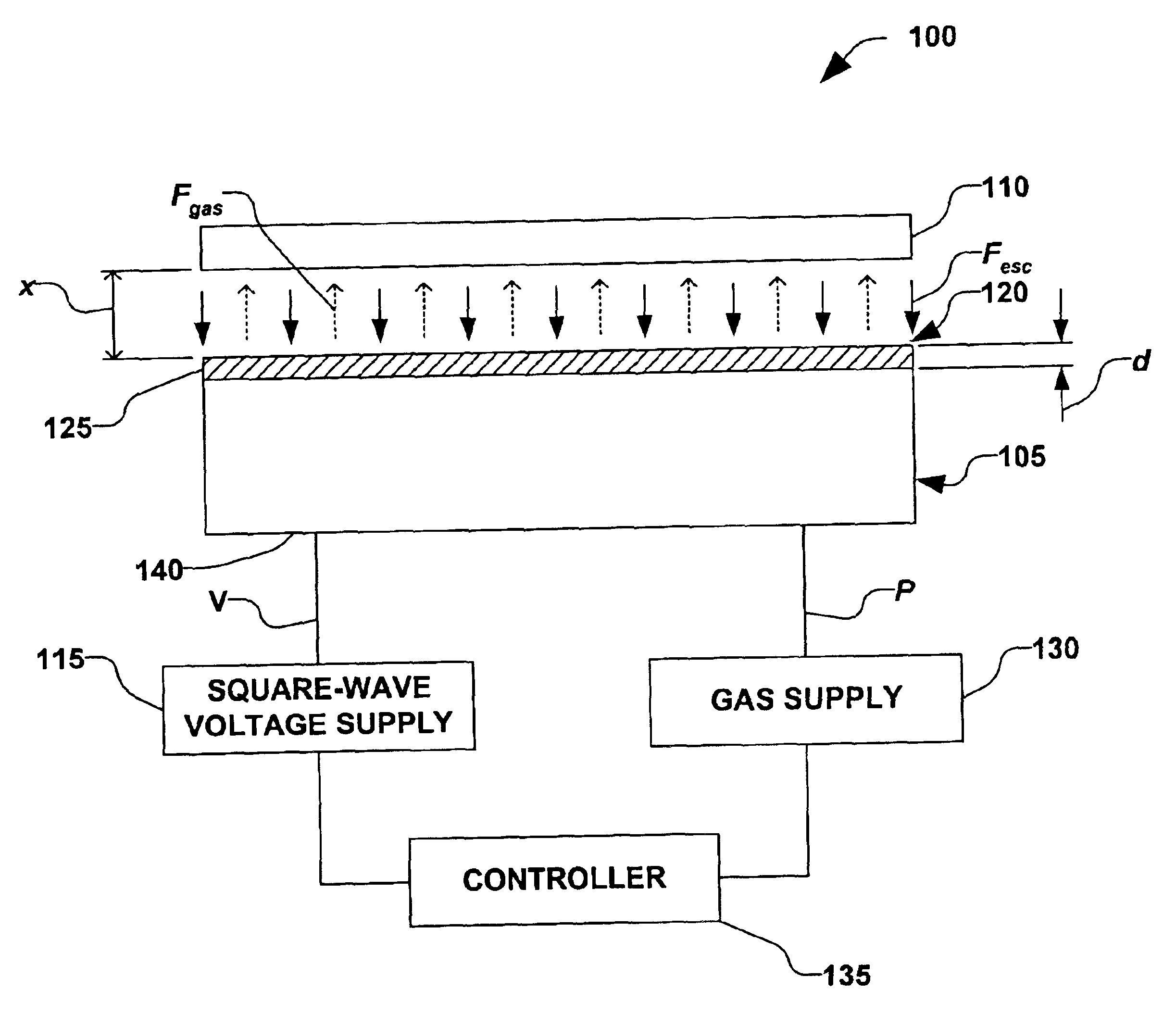
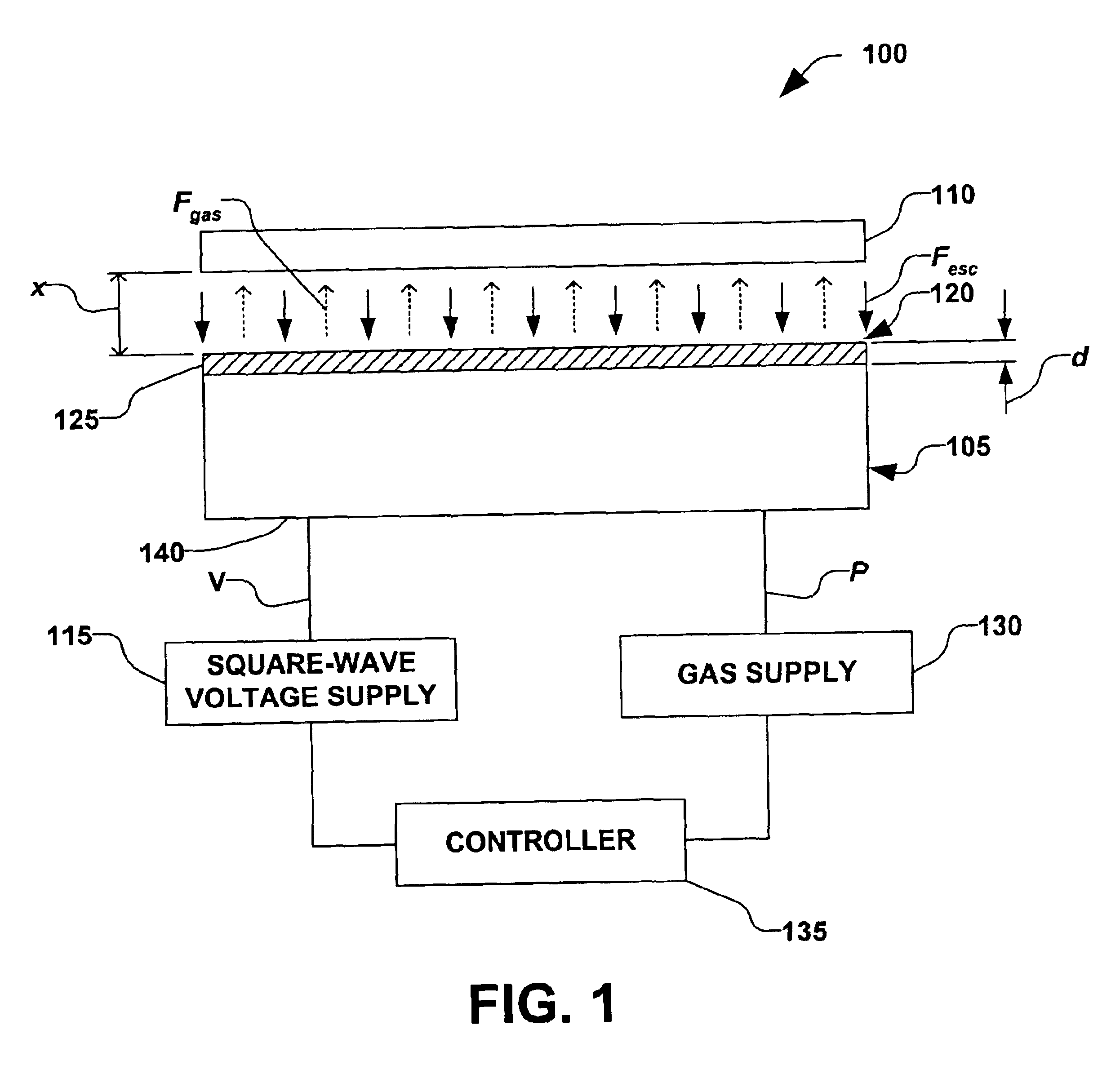
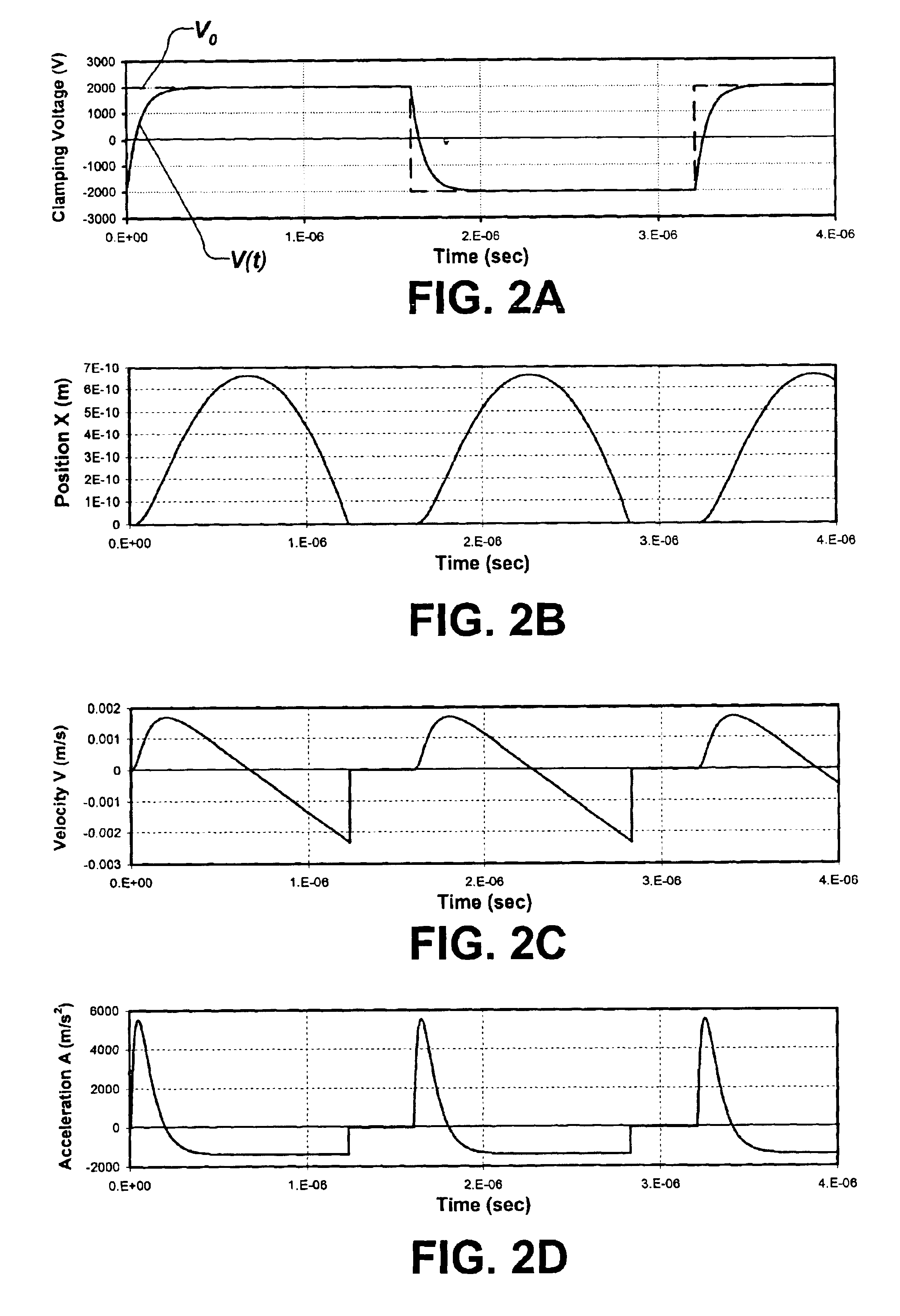
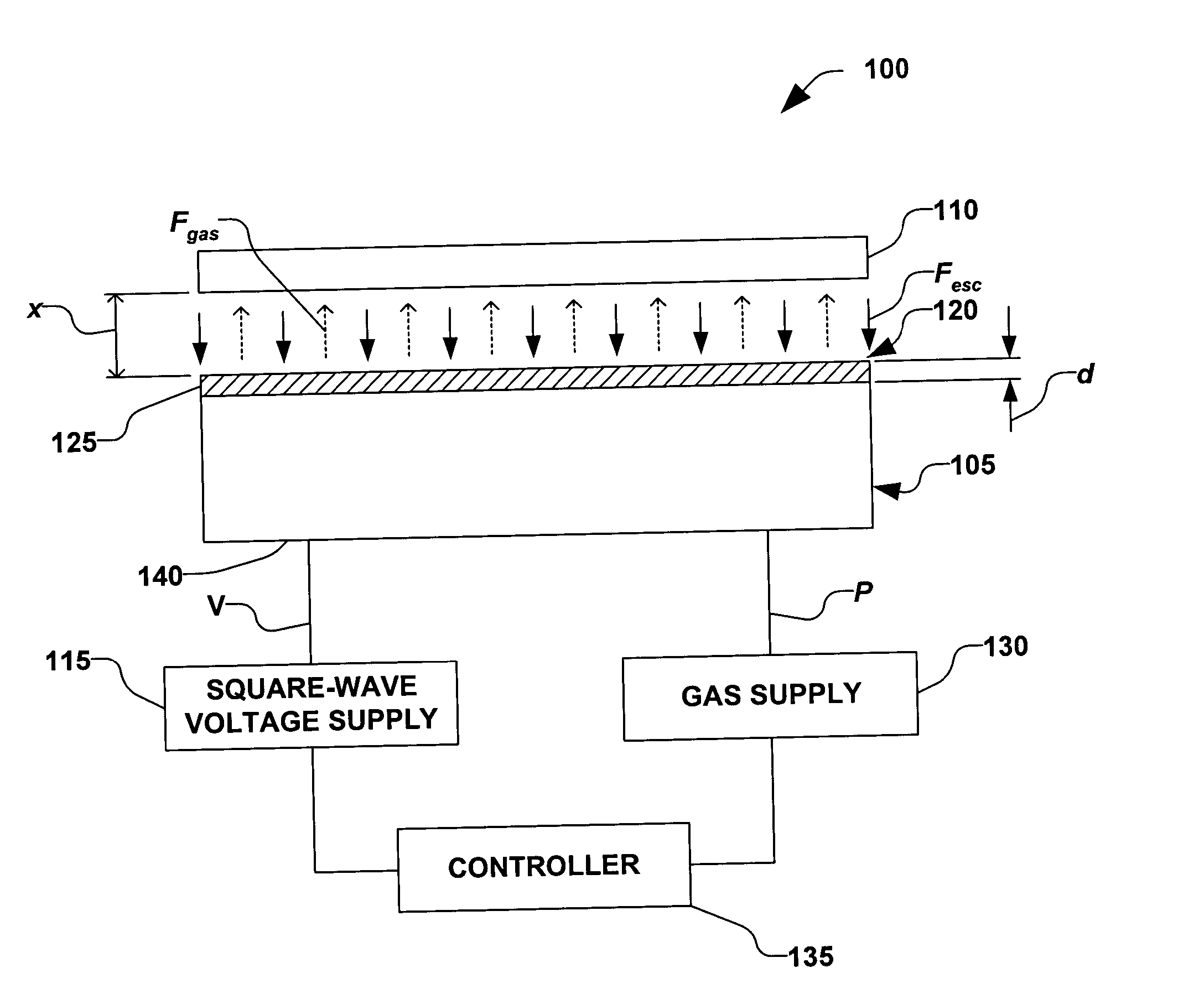
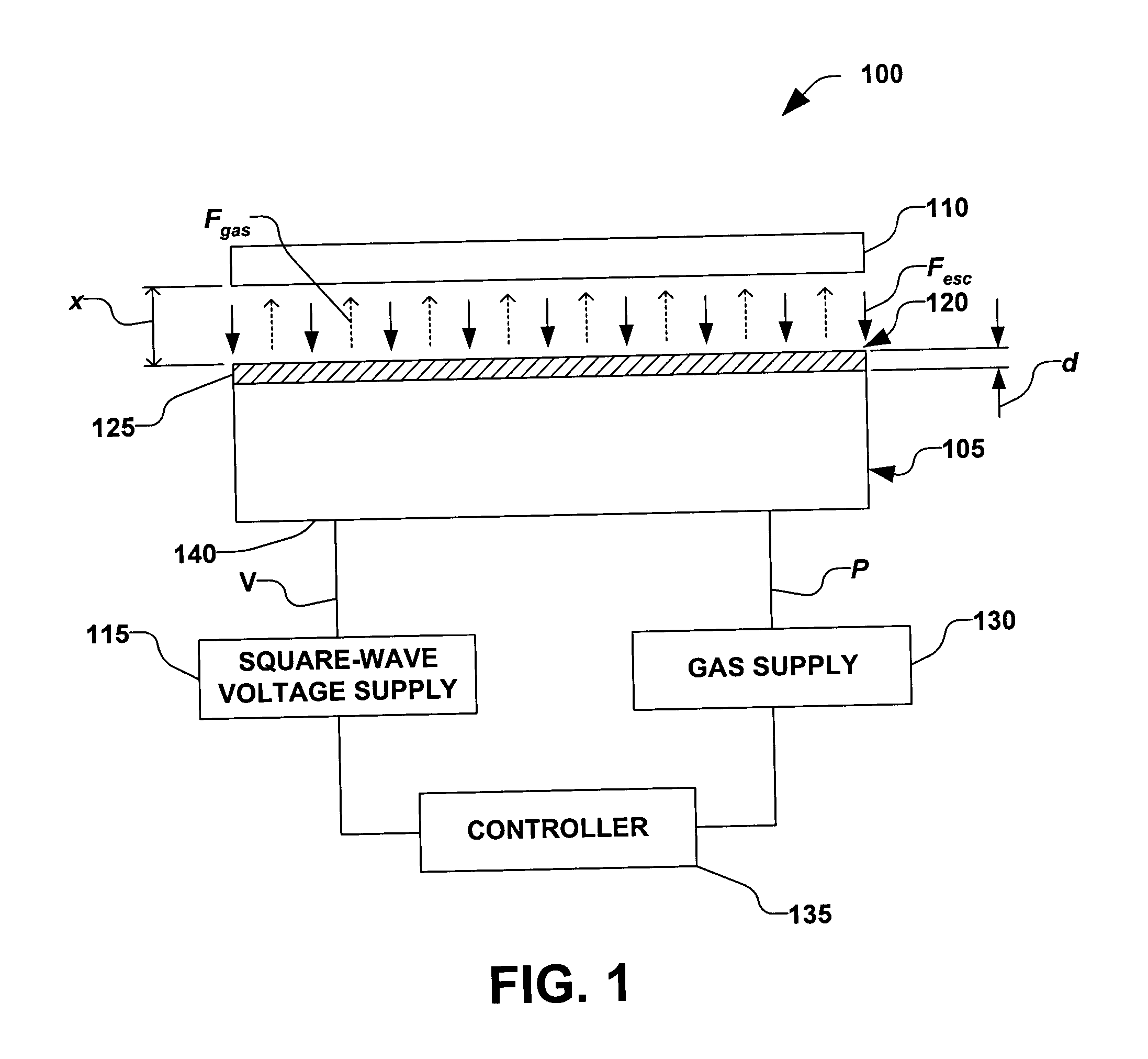
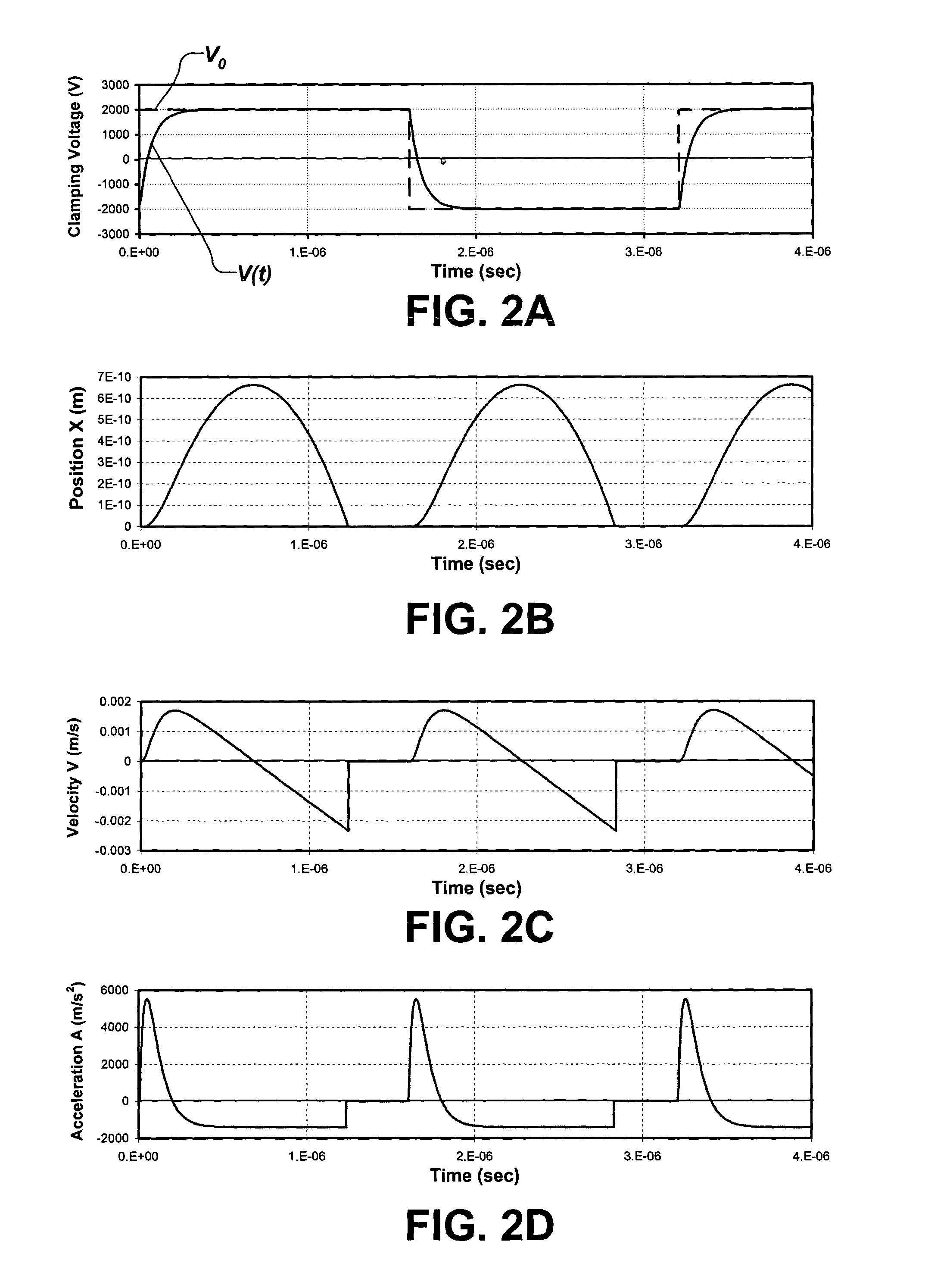
Clamping and de-clamping semiconductor wafers on an electrostatic chuck using wafer inertial confinement by applying a single-phase square wave AC clamping voltage
InactiveUS6947274B2Simple and inexpensive apparatusMinimize timeMagnetic bodiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
The present invention is directed to a method for clamping a wafer to an electrostatic chuck using a single-phase square wave AC clamping voltage. The method comprises determining a single-phase square wave clamping voltage for the electrostatic chuck, wherein the determination is based, at least in part, on an inertial response time of the wafer. The wafer is placed on the electrostatic chuck, wherein a gap between the electrostatic chuck and the wafer is defined. The determined single-phase square wave clamping voltage is then applied, wherein the wafer is generally clamped to the electrostatic chuck within a predetermined distance, while an amount of electrostatic charge is generally not allowed to accumulate, thereby enabling a fast de-clamping of the wafer.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
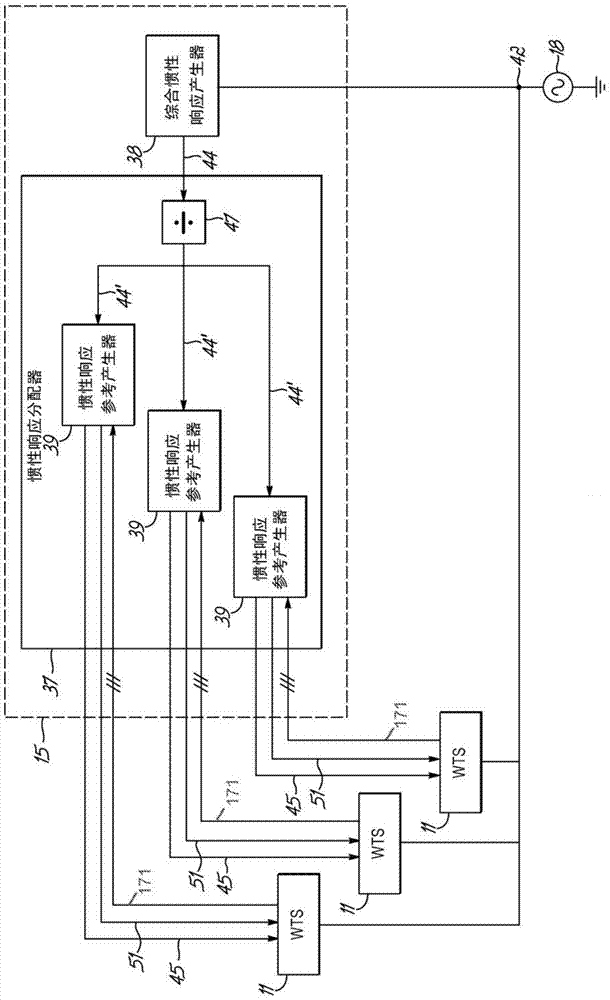
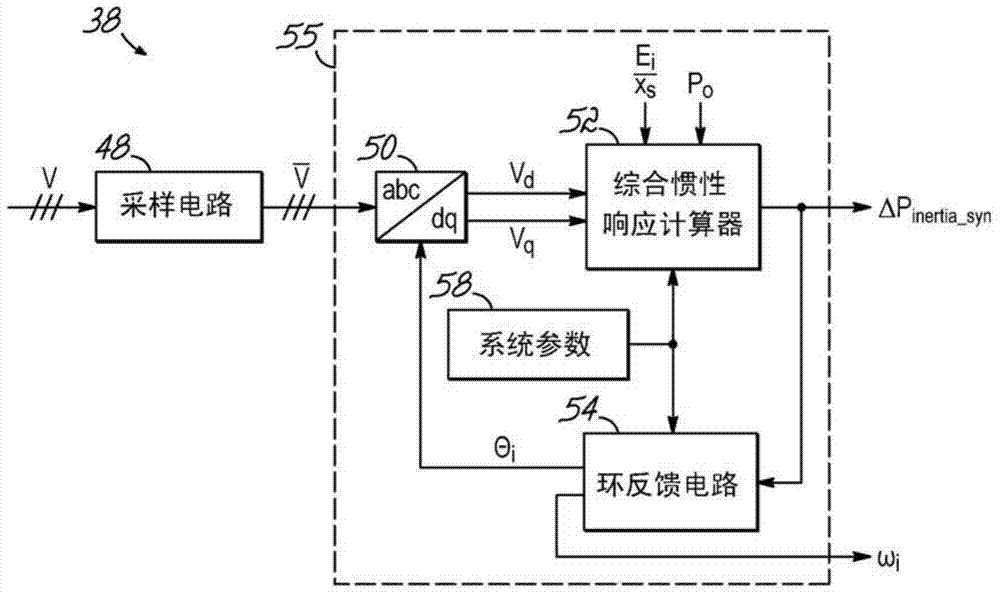
System and method for generating an inertial response to a change in the voltage of an electricial grid
ActiveCN103718410AWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVoltage referenceElectrical grid
Systems, methods, and computer program products for providing an inertial response by a wind power system to power fluctuations in an electrical grid. The system includes a synthetic inertial response generator configured to generate a power offset in response to fluctuations in grid voltage. The power offset signal is generated by determining a quadrature component the grid voltage using an internal reference voltage having an angular frequency and phase angle that is synchronized to the electrical grid by a control loop. The quadrature component is used to determine a synchronous power level. A control loop error signal is produced by the difference between the synchronous power level and the wind turbine system power output. Changes in the grid frequency produce an error signal that is added to the power set point of wind turbine system output controllers to provide a power system inertial power output response.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
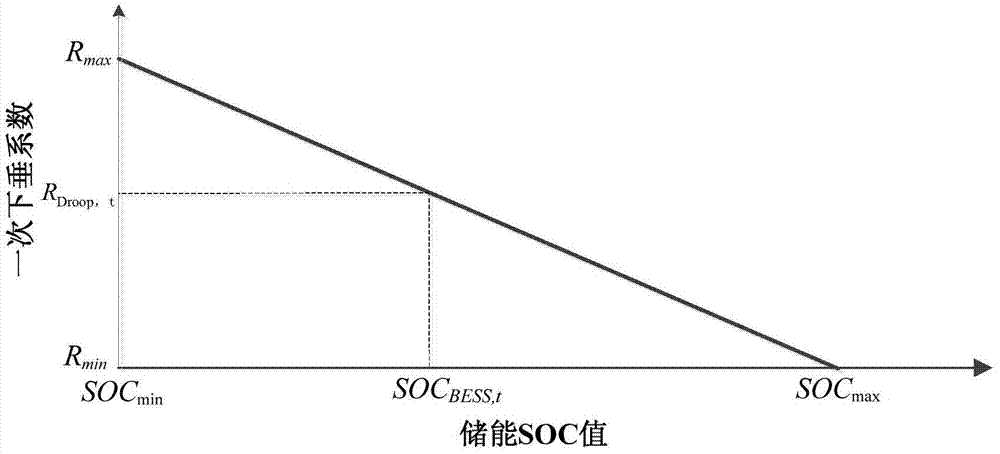
Self-adaptive dynamic virtual inertia frequency modulation method for double-fed variable-speed pumped storage unit
ActiveCN110120677AStable supportRaise the lowest point of dropSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingFrequency stabilizationAutomatic control
The invention relates to a self-adaptive dynamic virtual inertia frequency modulation method for a double-fed variable-speed pumped storage unit, and the method is suitable for a combined island system comprising the variable-speed pumped storage unit and a wind generating set. The method comprises the steps: starting the inertia response of the variable-speed pumped storage unit through an inertia control starting module; detecting the frequency deviation value change rate df / dt, introducing a correction factor to change the control coefficient, and automatically controlling the active outputof the unit, thereby achieving a purpose that the double-fed variable-speed pumped storage unit can provide dynamic frequency support for a power grid; stopping the inertia response of the variable-speed pumped storage unit through an inertia control stop module. When a system frequency accident occurs, compared with traditional droop control and fixed parameter virtual inertia control, the method can effectively improve the lowest frequency drop point of the system, reduce the frequency drop speed and reduce the frequency stabilization time by dynamically compensating the machine-side reference power of the double-fed converter, and has better inertia supporting capability and primary frequency modulation response capability for the power system.
Owner:SOUTHERN POWER GRID PEAK LOAD & FREQUENCY REGULATION GENERATING CO LTD +1
Method for responding to a grid event
InactiveUS20170298904A1Reduce electricity demandIncreased power extractionWind motor controlWind energy with electric storagePower stationSimulation
A method is provided for controlling a wind power plant, in particular in case of a frequency drop in a utility grid to which the wind turbines are connected, the method including: Combining demand response, inertial response and spinning reserve for given wind speeds in order for wind power plants to deliver fast aggregate under frequency response for a wide wind speed range with minimal recovery time and minimal production loss at each wind speed. In case of the frequency drop the utility grid is additional stabilized by active power, which is provided from a static VAR-compensator and which is fed into the grid. The static VAR-compensator is connected with the wind turbine via a transmission system. The static VAR-compensator is based on using super-capacitors thus it can provide an amount of active power for grid support in case of the frequency drop.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
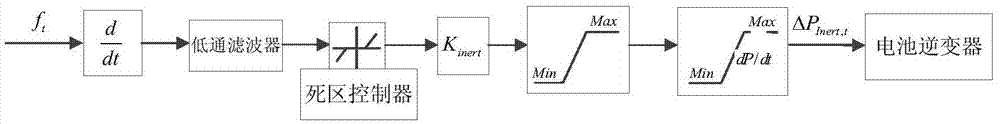
Control method for battery energy storage system participating in primary frequency modulation of power grid
ActiveCN111614106AReduce configurationPrevent overcharge and overdischargeEnergy storageAc network load balancingPower gridEngineering
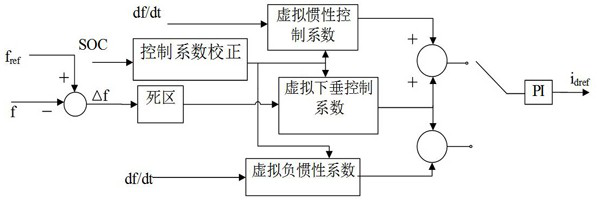
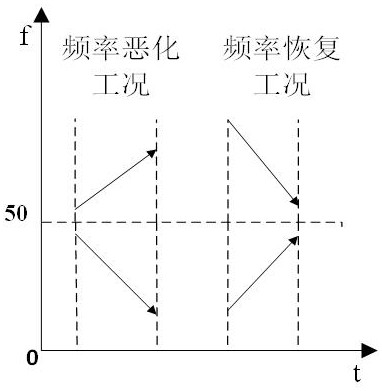
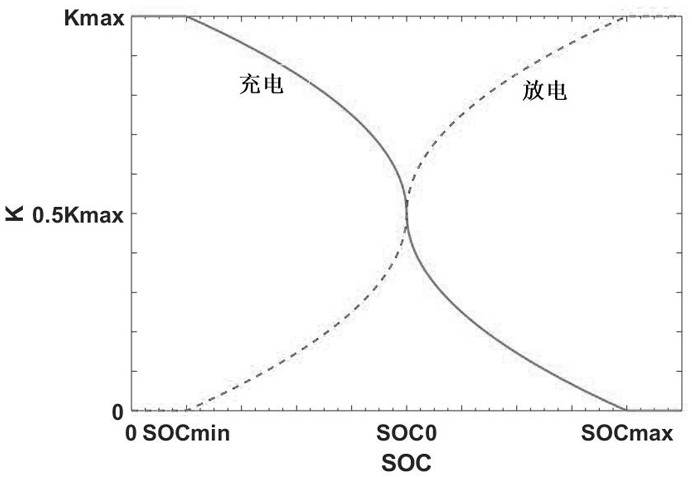
The invention provides a control method for a battery energy storage system participating in primary frequency modulation of a power grid, which adopts three frequency modulation modes, namely, virtual inertia response, virtual negative inertia response and virtual droop control, to participate in frequency modulation of the power grid according to different working conditions of the power grid. When the frequency is in a deteriorated working condition, virtual inertia response and virtual droop control are adopted to jointly participate in frequency modulation of the power grid; and when thefrequency is in the recovery working condition, virtual negative inertia response and virtual droop control are adopted to jointly participate in frequency modulation of the power grid. According to the frequency modulation control strategy, frequency deviation and frequency deviation change rate characteristics in the primary frequency modulation process are comprehensively considered, the advantages of the virtual inertia mode and the virtual droop mode are combined, comprehensive use of the three control modes at the same moment is achieved, the primary frequency modulation effect is improved, and the energy storage capacity requirement is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +1
Device containing plurality of smaller MEMS devices in place of a larger MEMS device
ActiveUS8861218B2Raise the resonant frequencyLess-prone to vibration noiseAcceleration measurement using interia forcesCapacitor with electrode distance variationCMOSAccelerometer
Embodiments disclosed herein generally include using a large number of small MEMS devices to replace the function of an individual larger MEMS device or digital variable capacitor. The large number of smaller MEMS devices perform the same function as the larger device, but because of the smaller size, they can be encapsulated in a cavity using complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) compatible processes. Signal averaging over a large number of the smaller devices allows the accuracy of the array of smaller devices to be equivalent to the larger device. The process is exemplified by considering the use of a MEMS based accelerometer switch array with an integrated analog to digital conversion of the inertial response. The process is also exemplified by considering the use of a MEMS based device structure where the MEMS devices operate in parallel as a digital variable capacitor.
Owner:QORVO US INC
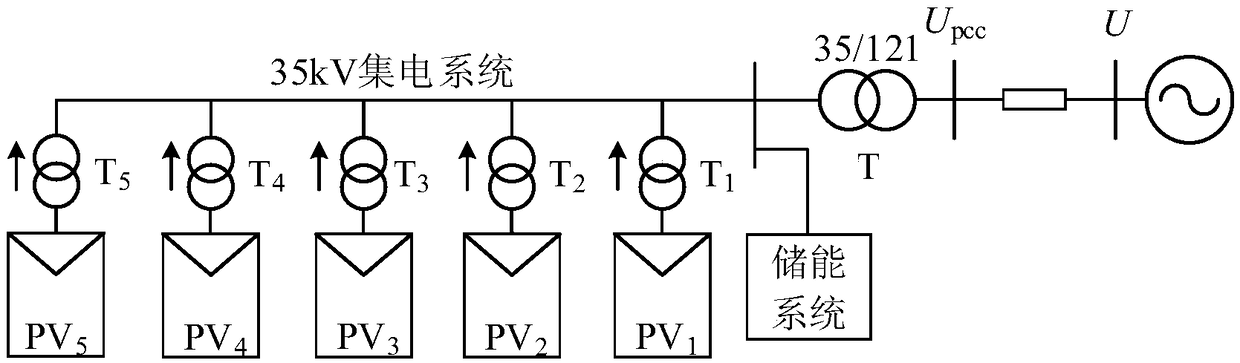
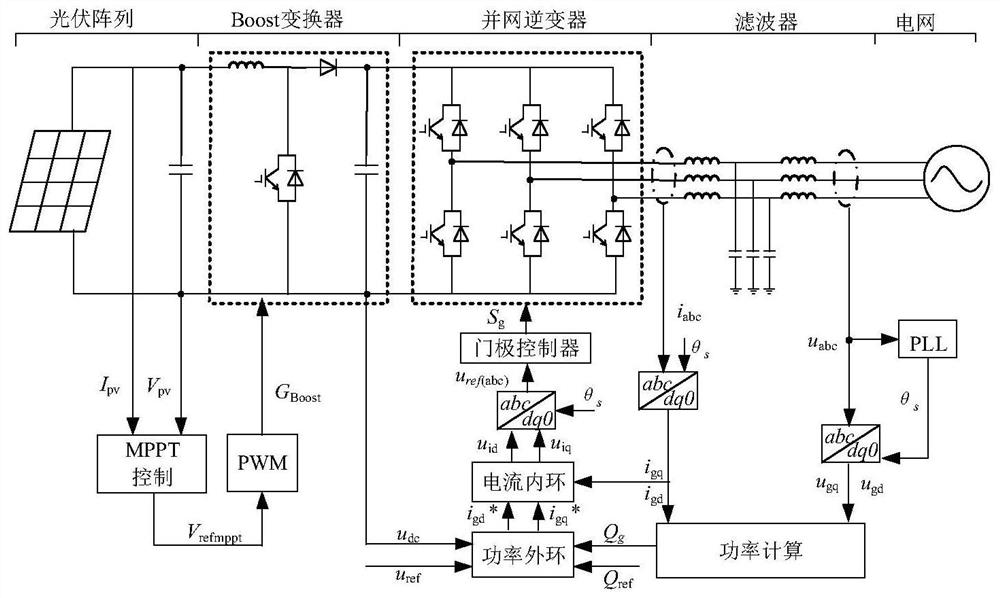
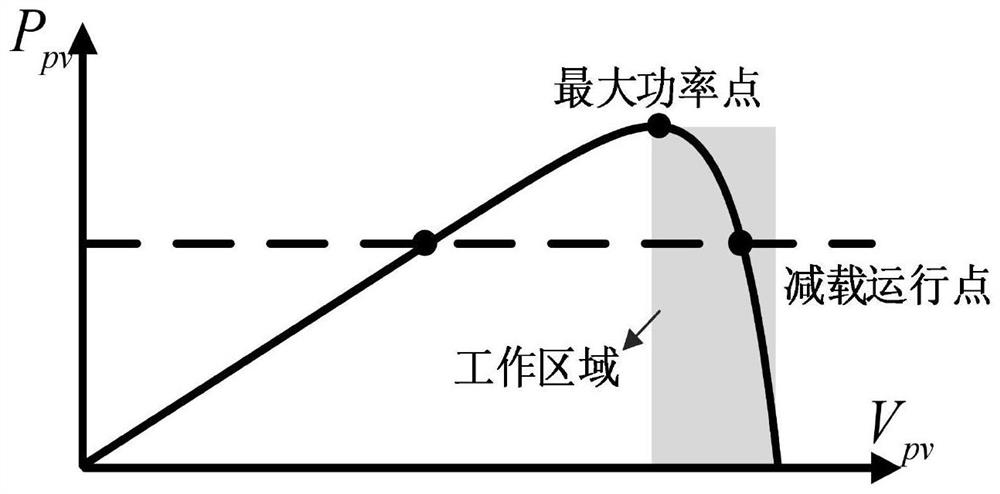
Centralized photovoltaic power station and control method and system for participating in power grid frequency modulation by employing same
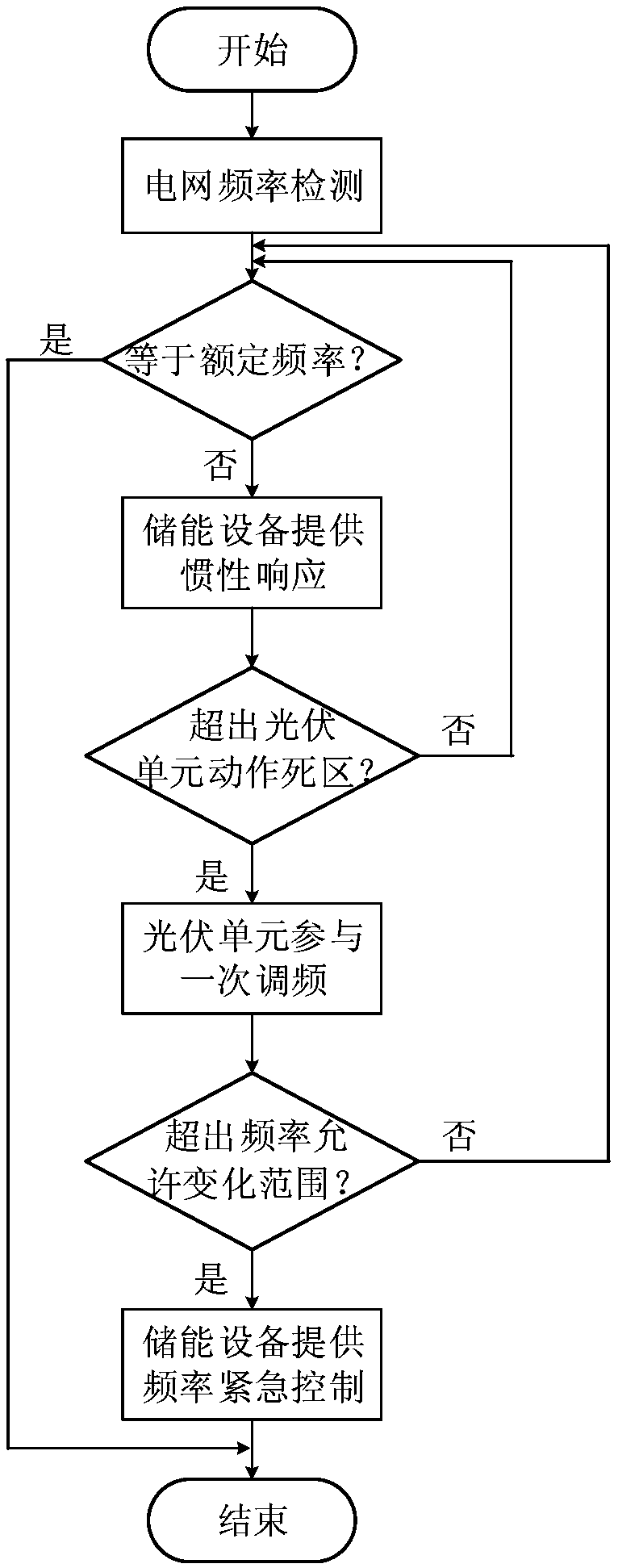
InactiveCN109494768AWith FM capabilityReduce lossSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageControl systemEngineering
The present invention discloses a centralized photovoltaic power station and a control method and system for participating in power grid frequency modulation by employing the same. The method comprises the steps of: (1) detecting grid frequency, determining whether the grid frequency is equal to a rated frequency or not, if yes, finishing the steps, or else, supplying inertia response by a first energy storage system; (2) determining whether the grid frequency exceeds a frequency dead zone of the motion of photovoltaic power generation units or not, if yes, allowing the photovoltaic power generation units to participate in the primary frequency regulation of the power grid one by one according to a frequency change condition, or else, returning the steps; and (3) determining whether the grid frequency exceeds an allowed normal operation change range or not, if yes, outputting active power by a second energy storage system, and providing the emergency control of the frequency, or else,returning the step (1). The centralized photovoltaic power station and the control method and system for participating in power grid frequency modulation by employing the same can coordinate with theactive control of a plurality of photovoltaic power generation units in a photovoltaic power station to allow the centralized photovoltaic power station to participate in the frequency regulation of the electric system so as to facilitate safety and stability of the power grid in a large-scale photovoltaic grid connected condition.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID QINGHAI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +3
Power system emergency reserve capacity configuration method
InactiveCN105790287ARaise the level of transient safetyEnsure safetyFlicker reduction in ac networkPower network operation systems integrationTransient stateElectricity
The present invention provides a power system emergency reserve capacity configuration method. The method comprises: a system secondary frequency modulation reserve R2 is determined according to a cost effectiveness method; the system secondary frequency modulation reserve R2 is taken as a basis, and the maximum steady state frequency fluctuation [Delta]fw,0 of a system after the occurrence of an extra high-voltage direct current bipolar locking fault is simulated and determined; if the [Delta]fw,0 is larger than an allowable limit, a generation side and a load side are taken as reserved sources, a lowest cost is the standard, and an added primary frequency modulation reserve [Delta]R1,w is determined, or else, the [Delta]R1,w is equal to zero; the R2 and the [Delta]R1,w are taken as a basis, the maximum frequency fluctuation [Delta]fh,0 of the system after the occurrence of an extra high-voltage direct current bipolar locking fault is simulated and determined; if the [Delta]fh,0 is larger than an allowable limit, the generation side and the load side are taken as reserved sources, the lowest cost is the standard, and an added inertia response reserve [Delta]R1,h is determined, or else, the [Delta]R1,h is equal to zero; and finally, an optimum emergency reserve capacity R in an electrical area in the whole process of frequency fluctuation after a large-scale direct current locking fault is determined. The power system emergency reserve capacity configuration method is able to improve the transient state safety level of a system after the occurrence of faults so as to comprehensively guarantee the safety of the system after the occurrence of faults.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
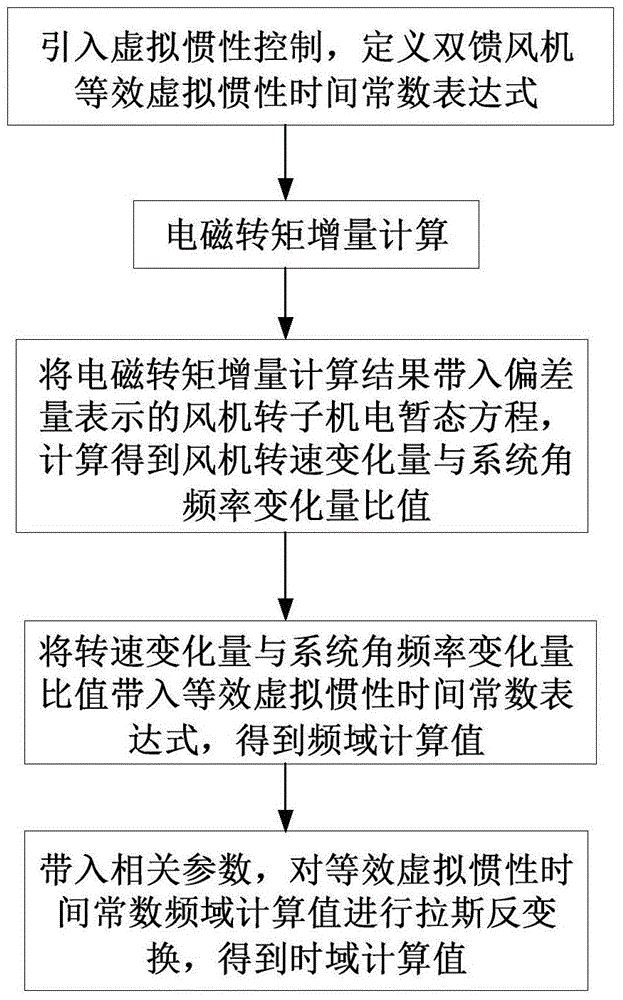
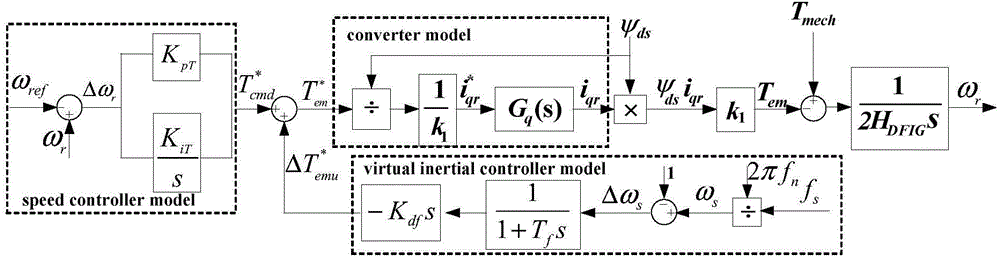
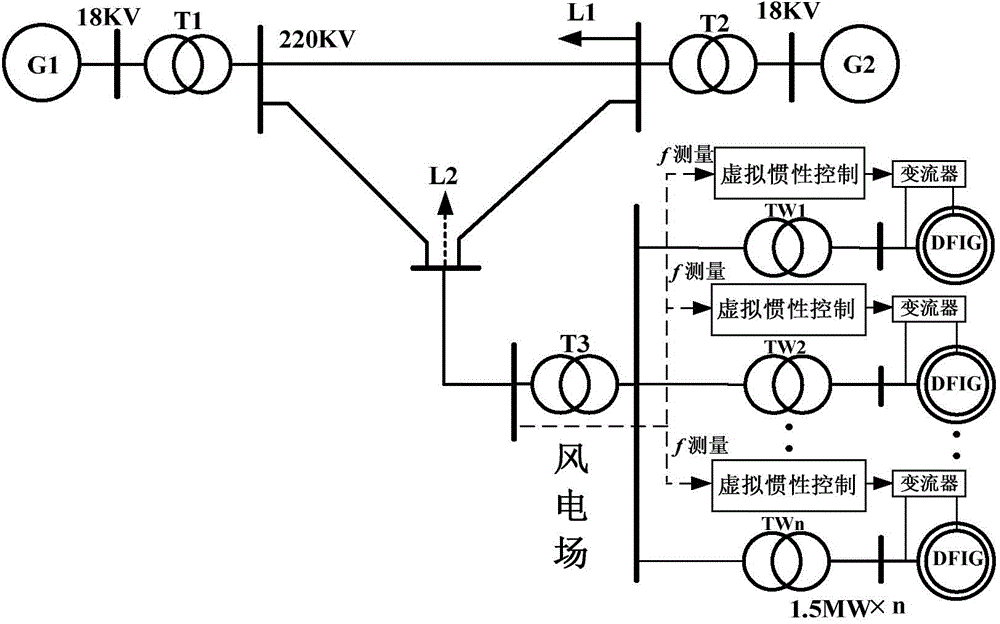
Calculation method for equivalent virtual inertia time constant of double-fed wind driven generator
ActiveCN104795837AHigh precisionLoad forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsResponse processWind driven
The invention discloses a calculation method for an equivalent virtual inertia time constant of a double-fed wind driven generator. According to the calculation method, a virtual inertia control technique is introduced, the virtual inertia time constant of the double-fed wind driven generator is defined, and the value of the virtual inertia time constant is calculated quantitatively; to be more specific, electromagnetic torque increments in speed control and inertia control steps related to an inertia response process are calculated and are substituted into a rotor electromechanical transient equation represented by deviation values to acquire the ratio of an system synchronization angular frequency increment to a wind driven generator rotor angular frequency increment; the ratio is substituted into a definition expression to acquire a frequency domain expression of the virtual inertia time constant, a time domain value is acquired through Laplace inverse transform, and accuracy of the expression is verified through comparison between a calculation result and a simulation result. The calculation method has the advantages that the equivalent virtual inertia time constant of the double-fed wind driven generator is different from a fixed inertia time constant of a wind generating set, the value of the equivalent virtual inertia time constant changes along with time during inertial response, and accuracy of the calculation result is high; the calculation method is the important foundation of further research on electric system dynamic frequency characteristics with wind power inertial responses.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Clamping and de-clamping semiconductor wafers on an electrostatic chuck using wafer inertial confinement by applying a single-phase square wave ac clamping voltage
InactiveUS20050052817A1Simple and inexpensive apparatusMinimize timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrographic process apparatusSemiconductorSquare wave
The present invention is directed to a method for clamping a wafer to an electrostatic chuck using a single-phase square wave AC clamping voltage. The method comprises determining a single-phase square wave clamping voltage for the electrostatic chuck, wherein the determination is based, at least in part, on an inertial response time of the wafer. The wafer is placed on the electrostatic chuck, wherein a gap between the electrostatic chuck and the wafer is defined. The determined single-phase square wave clamping voltage is then applied, wherein the wafer is generally clamped to the electrostatic chuck within a predetermined distance, while an amount of electrostatic charge is generally not allowed to accumulate, thereby enabling a fast de-clamping of the wafer.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
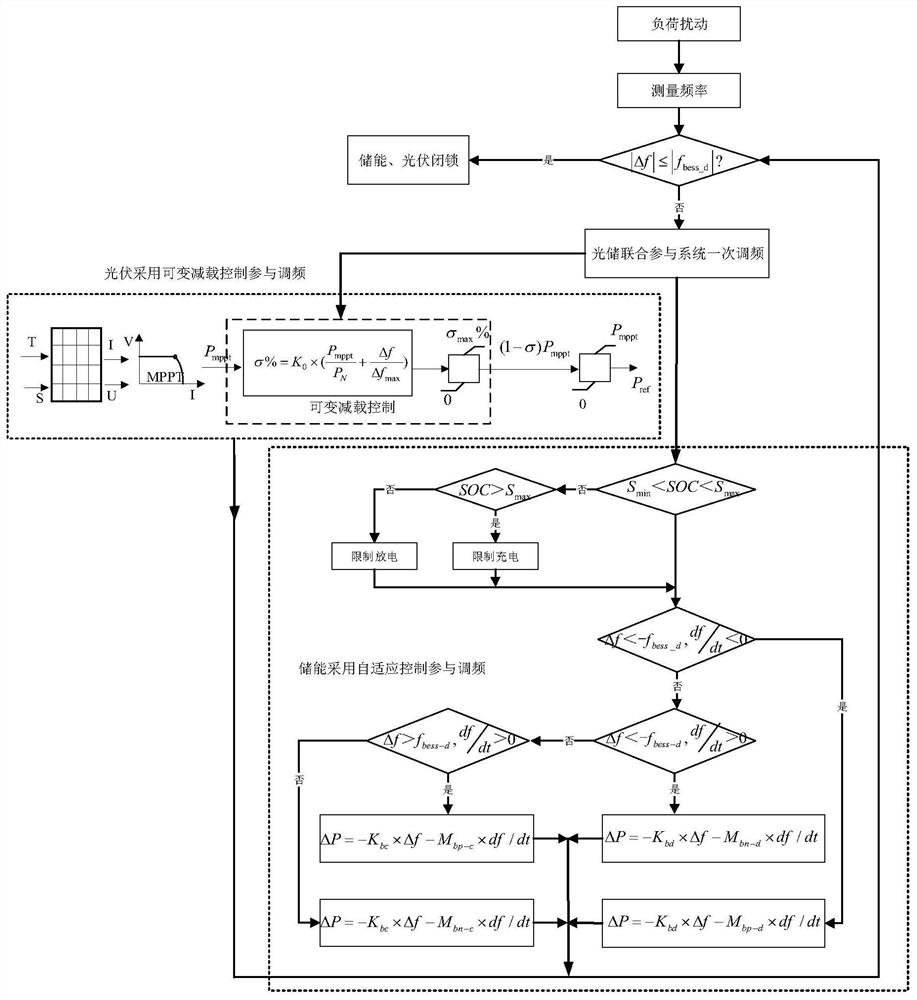
Coordination control method for light-storage combined participation in primary frequency modulation of power grid
ActiveCN113013896AAchieve normal operationFlexibleSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageNew energyControl engineering
The invention discloses a coordination control method for light-storage combined participation in the primary frequency modulation of a power grid, and the method comprises the steps of modeling a photovoltaic power generation system and an energy storage system, and obtaining a photovoltaic power generation system model and an energy storage system model; enabling the photovoltaic power to participate in power grid frequency modulation through a dynamic variable load shedding method changing along with system output and frequency; on the basis of coordinated droop control and positive and negative virtual inertia control, adopting the energy storage combined frequency modulation based on an energy storage variable coefficient adaptive control strategy to set the energy storage capacity, so that the inertia response matched with a synchronous generator set can be provided, and the coordination control over the primary frequency modulation of a light storage supporting power grid is achieved. According to the present invention, the inertia and frequency response capability of the light storage system can be improved, the frequency modulation and energy storage capacity maintaining effect can be considered, comprehensive benefits can be brought into play, and the utilization rate of new energy is improved while the stability level of the system is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Virtual synchronous control method for double-fed fan with low-voltage ride through function
ActiveCN110048457AMeet the requirements of low voltage ride through abilityRealize inertial supportSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationDamping factorVoltage amplitude
The invention discloses a virtual synchronous control method for a double-fed fan with a low voltage ride through function. The method is characterized in that the original power and current double closed-loop vector control structure of the fan converter is not changed, and inertia support of grid-connected point frequency and voltage can be realized only by constructing a virtual synchronous control loop. The process is as follows: when the power grid frequency fluctuates or the voltage amplitude drops slightly, the virtual synchronous control loop calculates according to a set droop coefficient to obtain a power compensation instruction, and sets inertia response time through the damping controller and then compensates the power compensation instruction to an original power instructionof the converter. Meanwhile, when the voltage of the grid-connected point drops deeply, the response rate of reactive compensation under the working condition of the fault power grid is improved by automatically adjusting the damping coefficient of the damping controller, and the requirement of the grid-connected standard for the low-voltage ride-through capability of the fan is met.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Frequency modulation control method for integral wind storage system
InactiveCN108011381AWith inertial response characteristicsSuppression of noise amplification effectsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionWhole bodyResponse characteristics
The invention discloses a frequency modulation control method for an integral wind storage system. According to the method, an energy storage device is connected onto the direct current bus of a converter of a wind turbine generator in parallel, the wind turbine generator and the energy storage device are taken as a whole body for supplying power for the system, an energy storage system is actively and reasonably controlled, namely the generator has the inertia response characteristic of a traditional synchronous generator while the power of the energy storage device is controlled to realize the maximum power of the wind turbine generator, the integral wind storage system has the inertia response characteristic similar to that of the traditional synchronous generator, and the primary frequency modulation of a power grid is actively participated. According to the method, the wind turbine generator has the inertia response characteristic which is the same as that of the traditional generator while the tracking control of the maximum power for the wind turbine generator is not influenced, and the primary frequency modulation of the power grid can be participated. Moreover, according to the control method, the differential signal of frequency does not need to be obtained directly in the implementation process, the noise amplification effect in the frequency signal can be inhibitedmore effectively, and finally quick recovery of system frequency is realized.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Inertial response function for grids with high turbine penetration
InactiveUS20150102679A1Frequency stabilityDc network circuit arrangementsWind motor controlPower stationPower grid
A method for compensating at least partially a frequency deviation in a grid is provided in which a grid frequency is determined and the grid frequency is applied to a grid frequency criterion. If the grid frequency meets the grid frequency criterion, a determination is made as to a set of wind turbines from a wind turbine power plant fleet based on the grid frequency criterion, and a command for a transient frequency response is transmitted to the set of wind turbines.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
An inertial matching method and a control system based on a synchronous generator and virtual synchronous generator parallel micro-network
ActiveCN109193797AGuaranteed uptimeSatisfy the cut-in conditionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionVirtual synchronous generatorSystem capacity
The invention discloses an inertia matching method and a control system based on a synchronous generator and virtual synchronous generator parallel micro-network. The method comprises the following steps: the VSG virtual inertia coefficient is designed according to the SG moment of inertia and the system capacity to ensure the matching of the transient response time between different micro-sources; according to the principle of primary frequency modulation and droop control, the proportional coefficient of prime mover governor and the droop coefficient of VSG are designed, and the load power is distributed according to the system capacity. When the micro-source and load are cut in, the given active power of VSG is adjusted dynamically according to the change of the power angle of the parallel system, and the given active power coefficient is designed according to the system damping ratio, which compensates the inertial difference caused by the inertial response delay of SG governor andrealizes the smooth cut in of VSG. The invention can eliminate power oscillation caused by micro-source and load cutting, meet power distribution requirements of micro-grid, and realize synchronous and stable operation of SG and VSG parallel micro-network.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and arrangement for responding to a grid event, such as fast under frequency combining demand response, inertial response and spinning reserve
ActiveUS8866323B2Reduce electricity demandEasy extractionLevel controlWind motor controlPower stationSimulation
A method for controlling a wind power plant in case of a frequency drop in a utility grid to which the wind turbines are connected is provided. The method includes combining demand response, inertial response and spinning reserve for given wind speeds in order for wind power plants to deliver fast aggregate under frequency response for a wide wind speed range with minimal recovery time and minimal production loss at each wind speed.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
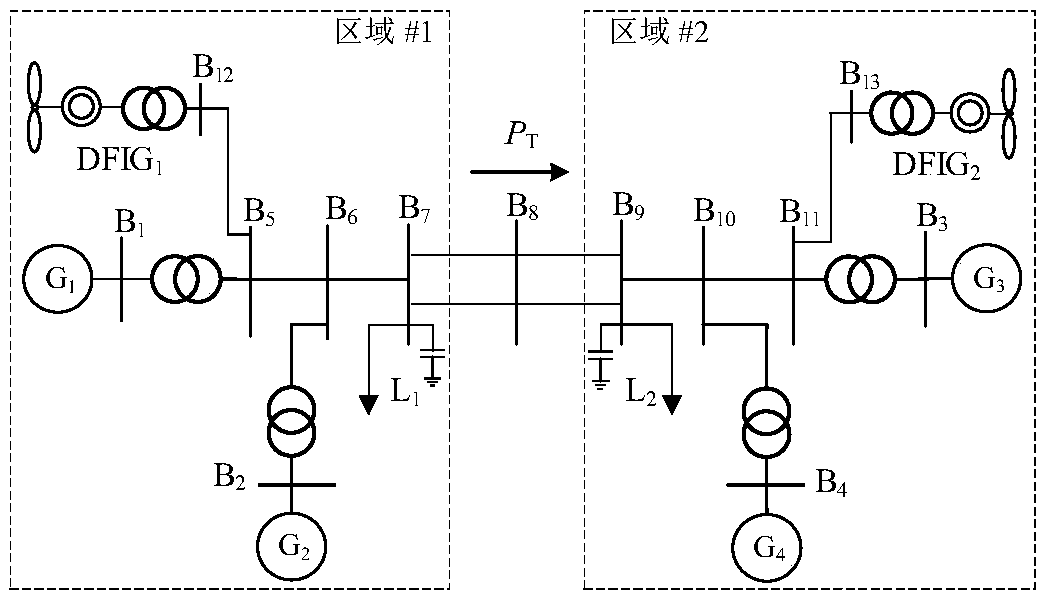
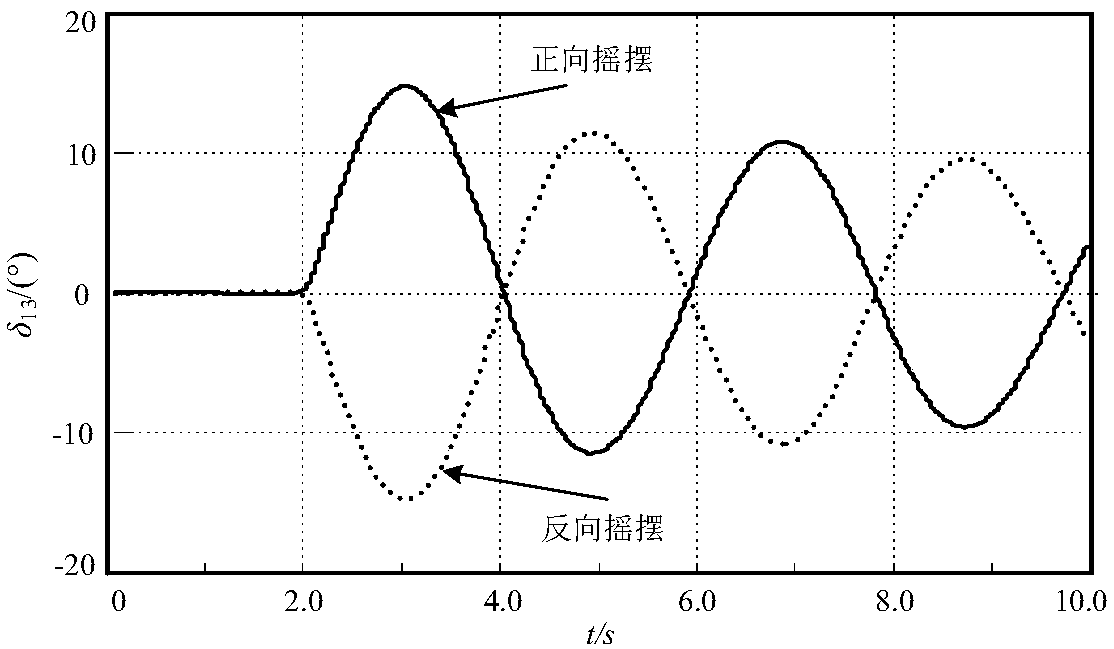
Control method for improving power angle first swing stability of power system with high-permeability wind power
ActiveCN108964130AReduce relative power angle swingChanging Transient Energy ConversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectricityTransient state
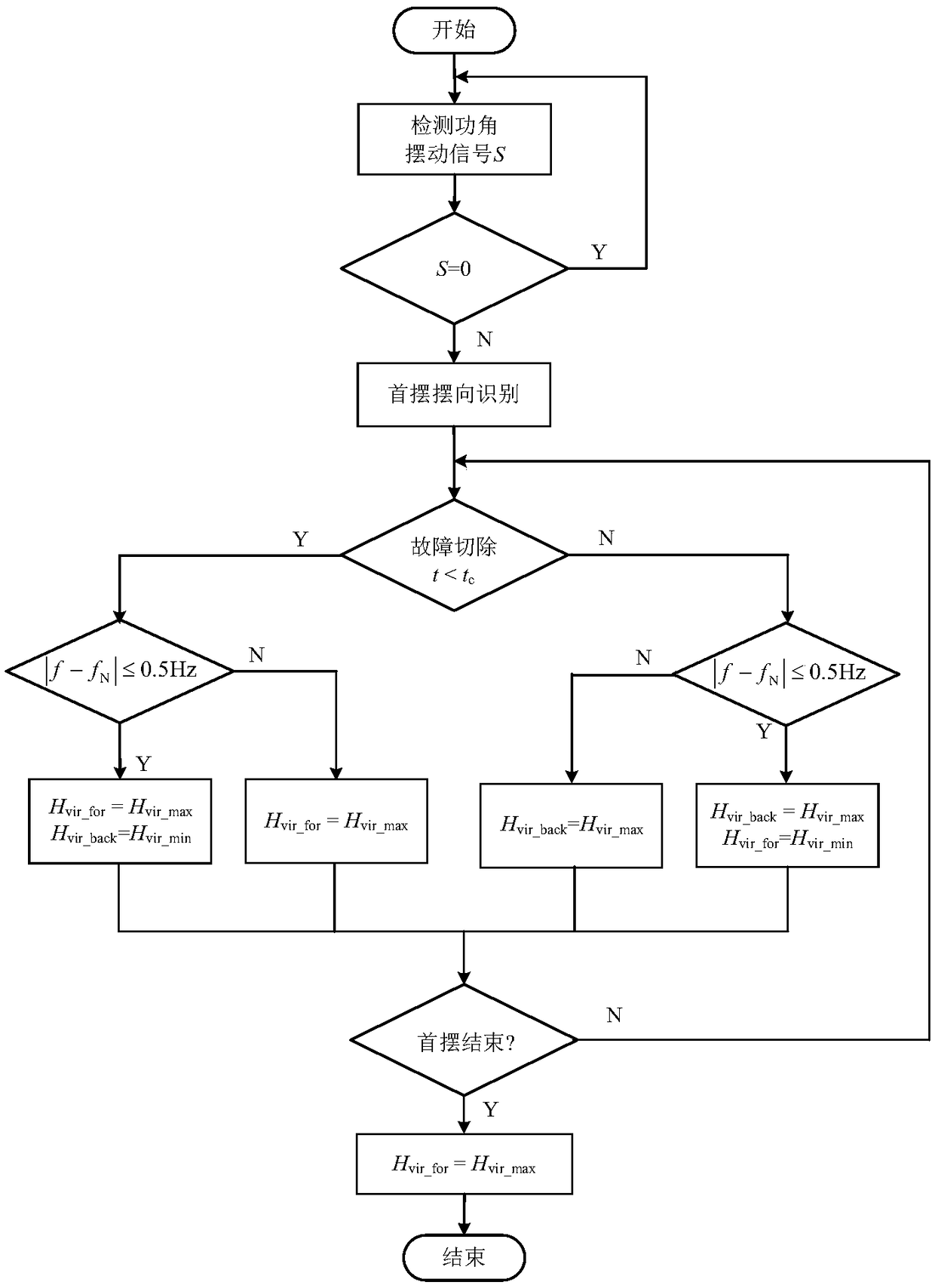
The invention discloses a control method for improving the power angle first swing stability of a power system with high-permeability wind power. The method comprises during a period from fault occurrence to fault removal, starting the virtual inertia controller of a forward unit, setting an inertia adjustment coefficient to the maximum positive value, and starting the inertia controller of a backward unit to virtualize a negative inertia response when the system frequency fluctuates within a safe range; after a fault is removed, setting the inertia adjustment coefficient of the backward unitto the maximum positive value, and setting the inertia adjustment coefficient of the forward unit to the minimum negative value after the system frequency is in a safe fluctuation range; at the end ofthe power angle first swing, setting the inertia adjustment coefficient of the forward unit to the maximum positive value, and blocking the inertia controller of the backward unit . The method reduces the transient energy accumulated by the system after transient instability, improves the transient power angle first swing stability of the system, and improves the feasibility and safety of the virtual inertia control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Novel anti-back-suction device for high-speed turbine handpiece
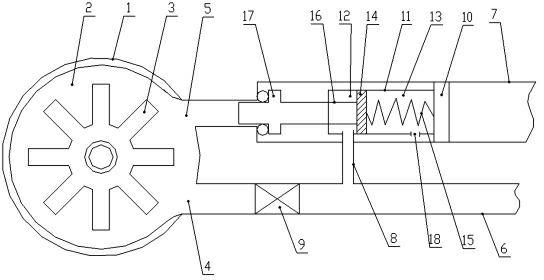
InactiveCN102198017AStop the flowPrevent inertial responseDental toolsBoring toolsCycloneEngineering
The invention discloses a novel anti-back-suction device for a high-speed turbine handpiece. The novel anti-back-suction device comprises a machine head, wherein, the inner cavity of the machine head is equipped with a rotating wind wheel component; the side part of the machine head is equipped with an air inlet and an air return vent; the air inlet and the air return vent are respectively connected with an air inlet pipe and an air return pipe; the air return pipe is internally equipped with a control valve for plugging or opening the air return vent, and an air control pipe is arranged between the control valve and the air inlet pipe; and the air inlet pipe is internally equipped with an air inlet check valve, and the air inlet check valve is positioned between the air inlet and the air control pipe. The novel anti-back-suction device has the advantages of reasonable design, simple structure, high safety and high service efficiency. In the invention, when the handpiece stops operation, the air inlet pipe and the air return pipe prevent airflow at the same time so that cyclone in the machine head stops immediately so as to prevent the inertial response of the wind wheel component and timely cause the wind wheel component to stop rotating, thus avoiding a centrifugal fan-type air suction phenomenon and a back suction effect and achieving an ideal effect of preventing back suction.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
Method and arrangement for responding to a grid event, such as fast under frequency combining demand response, inertial response and spinning reserve
ActiveUS20140001758A1Reduce electricity demandIncreased power extractionWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower stationPower grid
A method for controlling a wind power plant in case of a frequency drop in a utility grid to which the wind turbines are connected is provided. The method includes combining demand response, inertial response and spinning reserve for given wind speeds in order for wind power plants to deliver fast aggregate under frequency response for a wide wind speed range with minimal recovery time and minimal production loss at each wind speed.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Energy storage and wind power combined primary frequency modulation optimization control method
PendingCN114039386AAvoid economyAvoid the problem that the FM performance is not up to standard when FM is tuned aloneSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageNew energyFrequency modulation
The invention discloses an energy storage and wind power combined primary frequency modulation optimization control method, which comprises a wind turbine generator and an energy storage unit. The wind turbine generator is controlled by a controller to transmit electric power to a power grid and charge the energy storage unit to supplement electric energy, and the power output of the wind turbine generator has the capability of participating in the primary frequency modulation of the power grid; the energy storage unit is used for participating in primary frequency modulation of the power grid, and when the power grid has a primary frequency modulation demand, the method establishes a frequency modulation power amount [delta]P for a frequency deviation [delta]f occurring in the primary frequency modulation demand. According to the method, the fan and the energy storage are regarded as a whole to calculate the primary frequency modulation quantity, the problem of how to economically and reasonably distribute energy between the fan and the energy storage is comprehensively considered, and the primary frequency modulation performance of the whole station is improved by utilizing the rapidity of the energy storage battery; therefore, the fan has the same inertia response characteristic as a conventional thermal power generating unit while controlling the maximum power, and the admitting ability of new energy is improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER
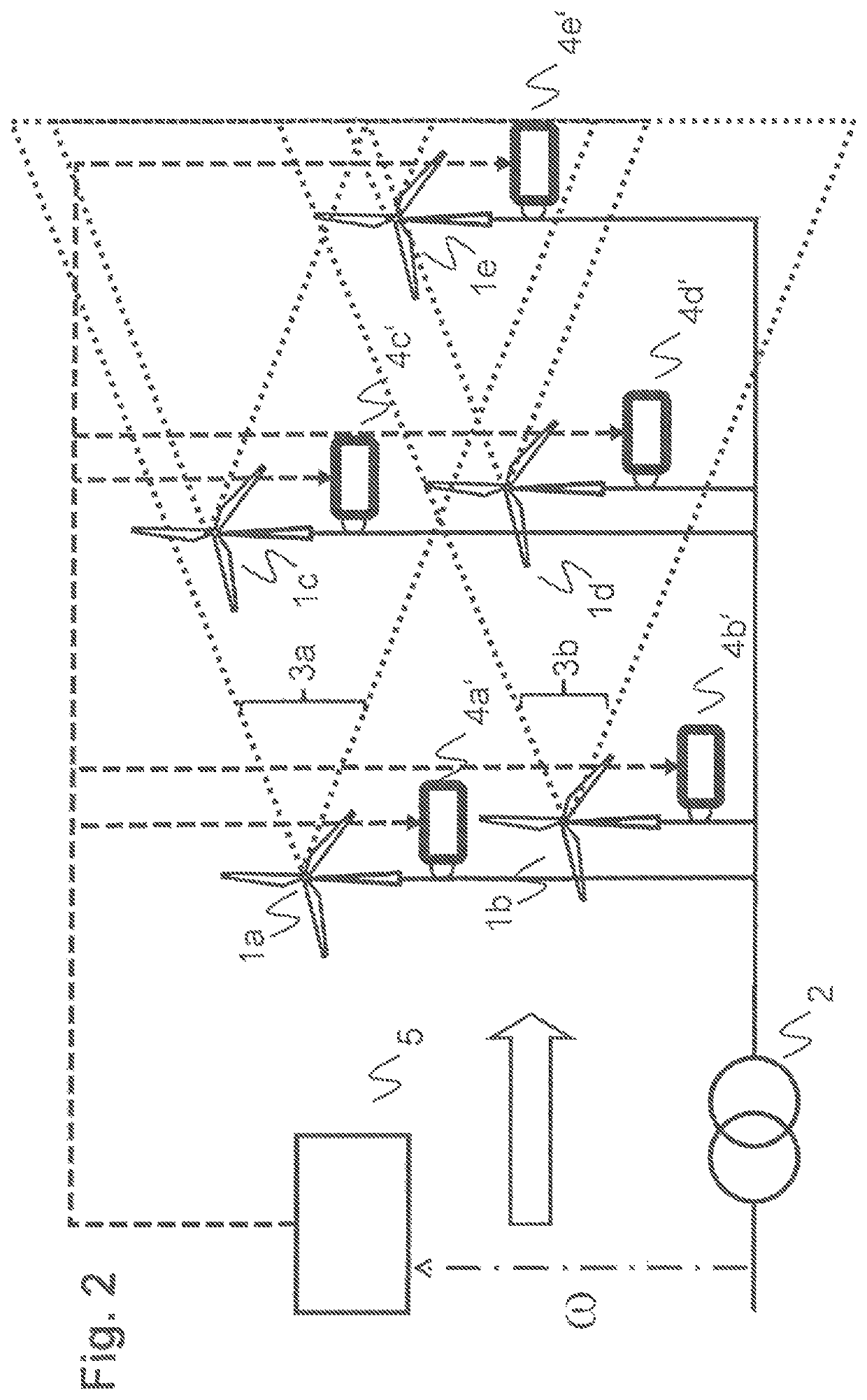
Wind farm inertial response
ActiveUS10605229B2Prediction is accurate and reliableOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlWind forecastPower grid
The present invention is concerned with an operation of a wind farm with a plurality of wind turbines in view of a dynamic frequency response. According to the invention, dynamic frequency support and power production for all wind turbines in a wind farm are handled concurrently in a single optimization step and taking into account wake effects within the wind farm as well as optional wind forecast information. The dynamic frequency support capability of the entire wind farm is planned in advance according to grid requirements and power system condition changes. While existing methods de-load wind turbines with a static percentage in order to supply additional power when needed, the proposed method incorporates the dynamic frequency support into the optimal operation system of wind farm.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY LTD
Communication-free distributed frequency supporting method and system for photovoltaic power station
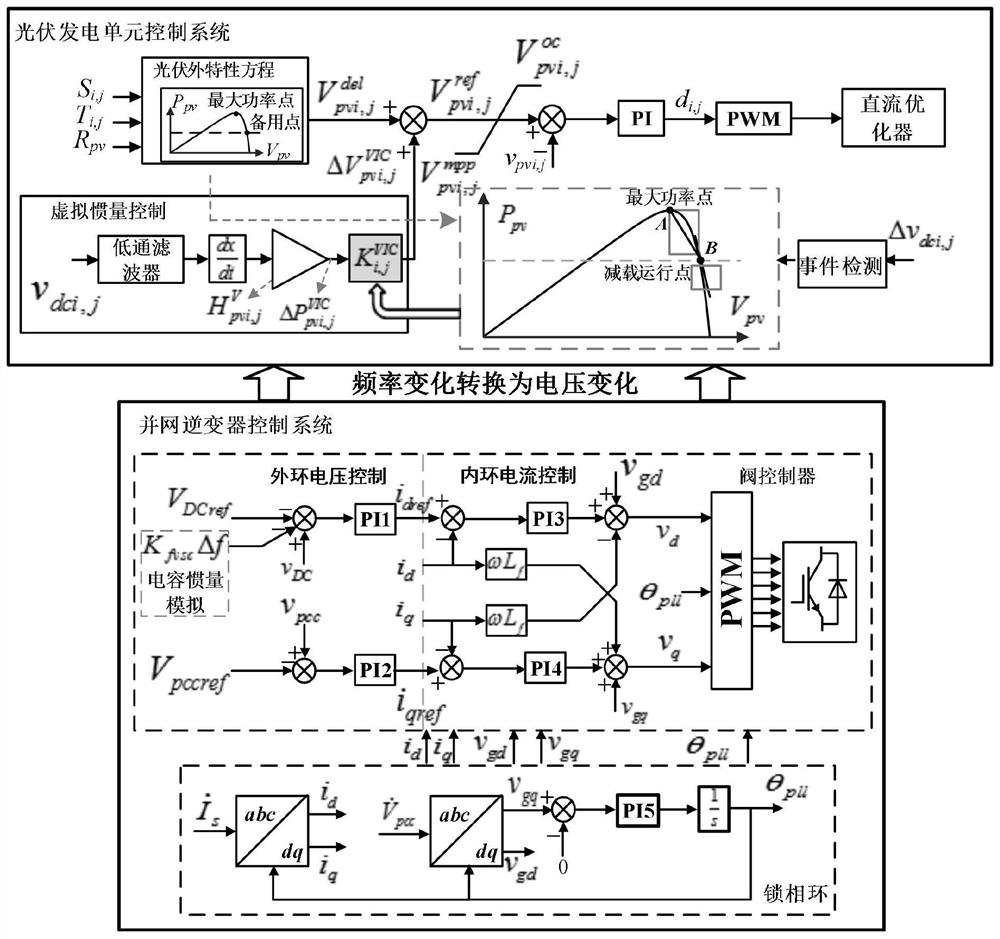
PendingCN113890085AImprove power generation efficiencyIncrease system inertiaElectric power transfer ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceLoop control
The invention discloses a photovoltaic power station communication-free distributed frequency support method and system, which are used for providing active frequency support for an alternating current system. The method is realized based on a virtual inertia strategy, and specifically comprises the following steps: deploying frequency deviation-based direct current bus voltage outer loop control in a control system of a grid-connected inverter, generating additional inertia response by using electric energy stored by a direct current bus capacitor, increasing system inertia, converting power grid frequency deviation information into change of direct current bus voltage, and realizing the communication-free frequency control; besides, deploying distributed virtual inertia control based on a direct-current optimizer, so the standby power of the photovoltaic module is fully and adaptively utilized, the active power output of each photovoltaic power generation unit is dynamically adjusted according to the voltage change caused by the frequency deviation, the inertia response similar to that of a synchronous generator is simulated, and the system inertia is further improved. The utilization efficiency of frequency modulation standby power of a large-scale photovoltaic power station can be improved, and the frequency index of an alternating current system is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com