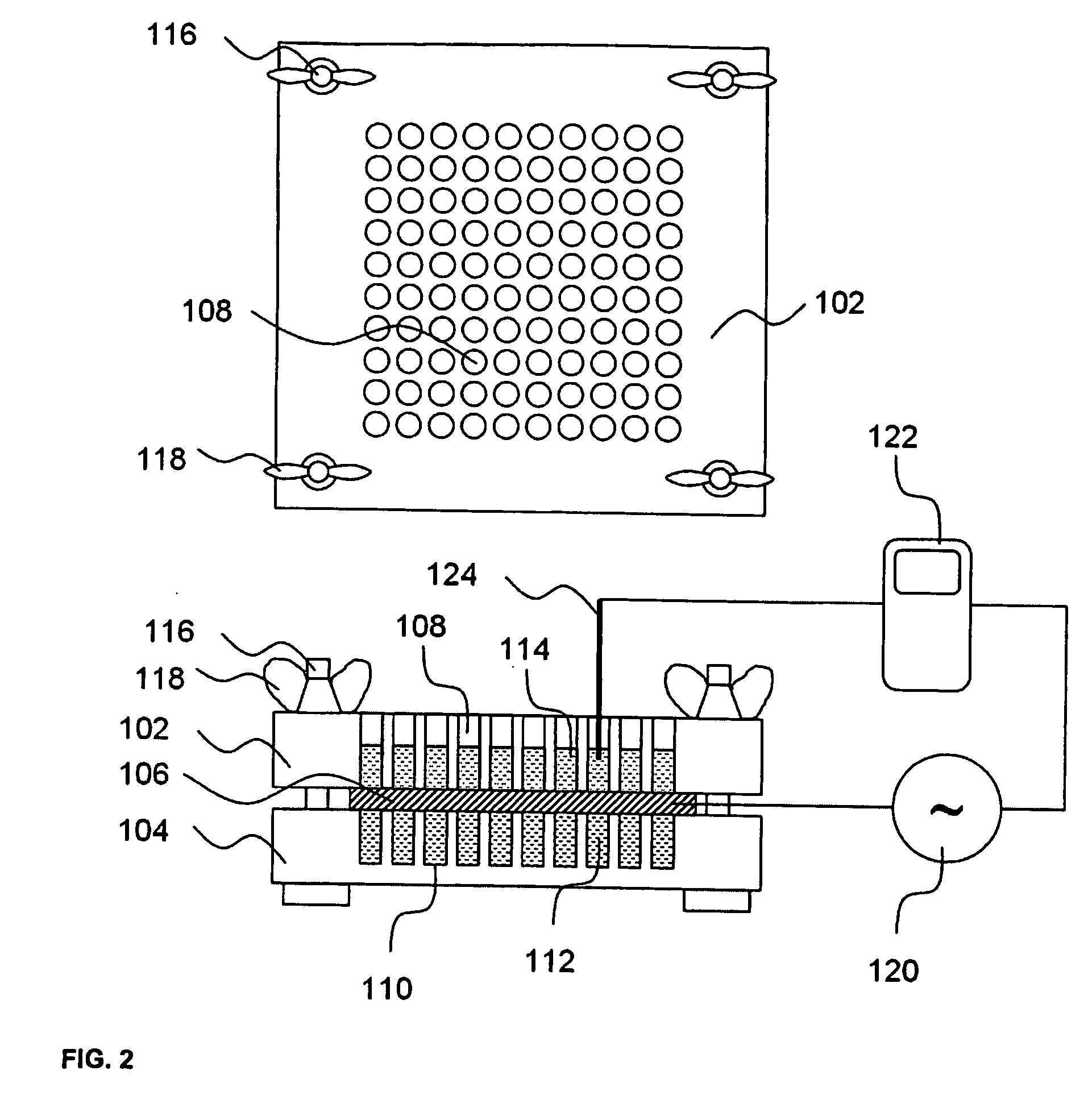
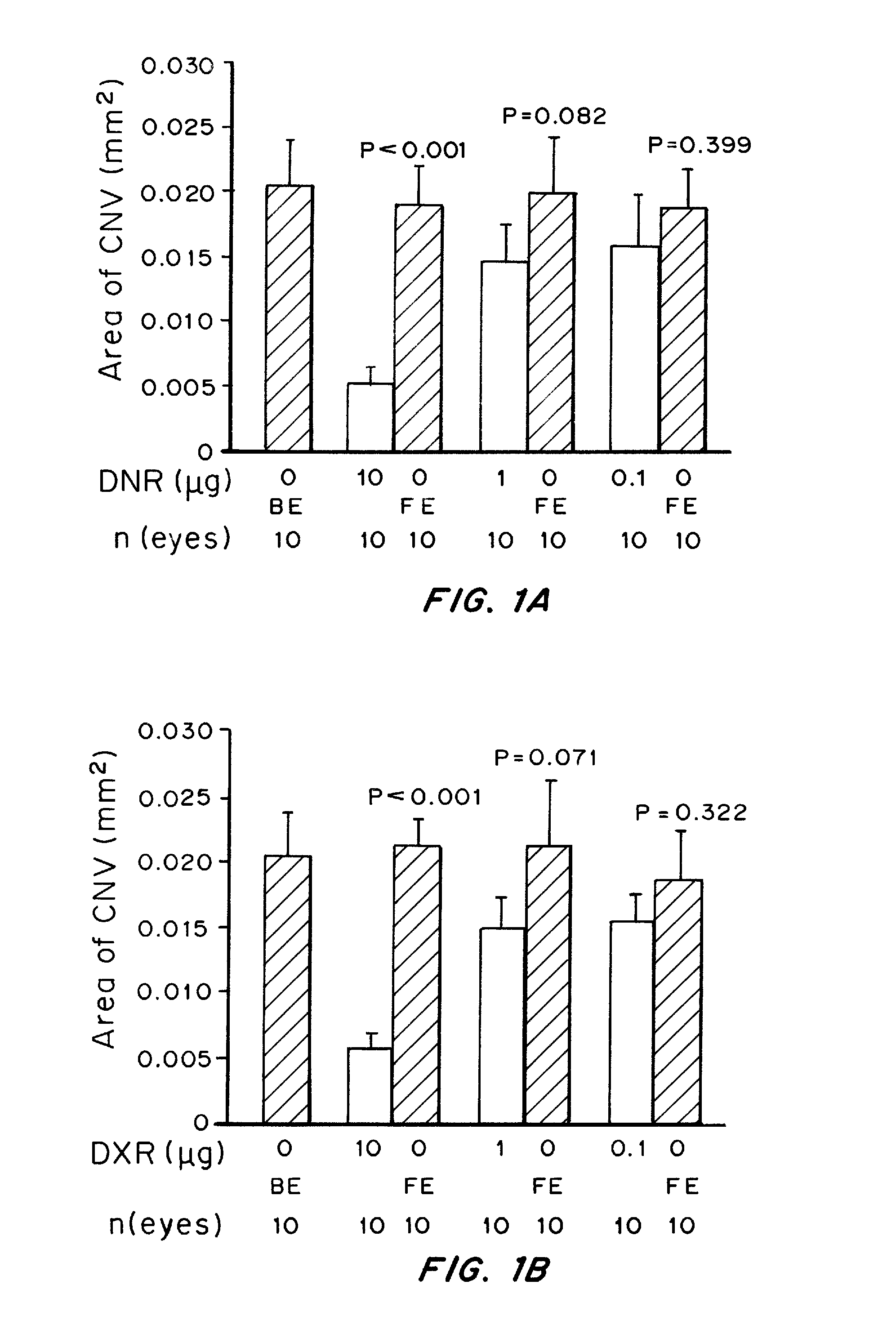
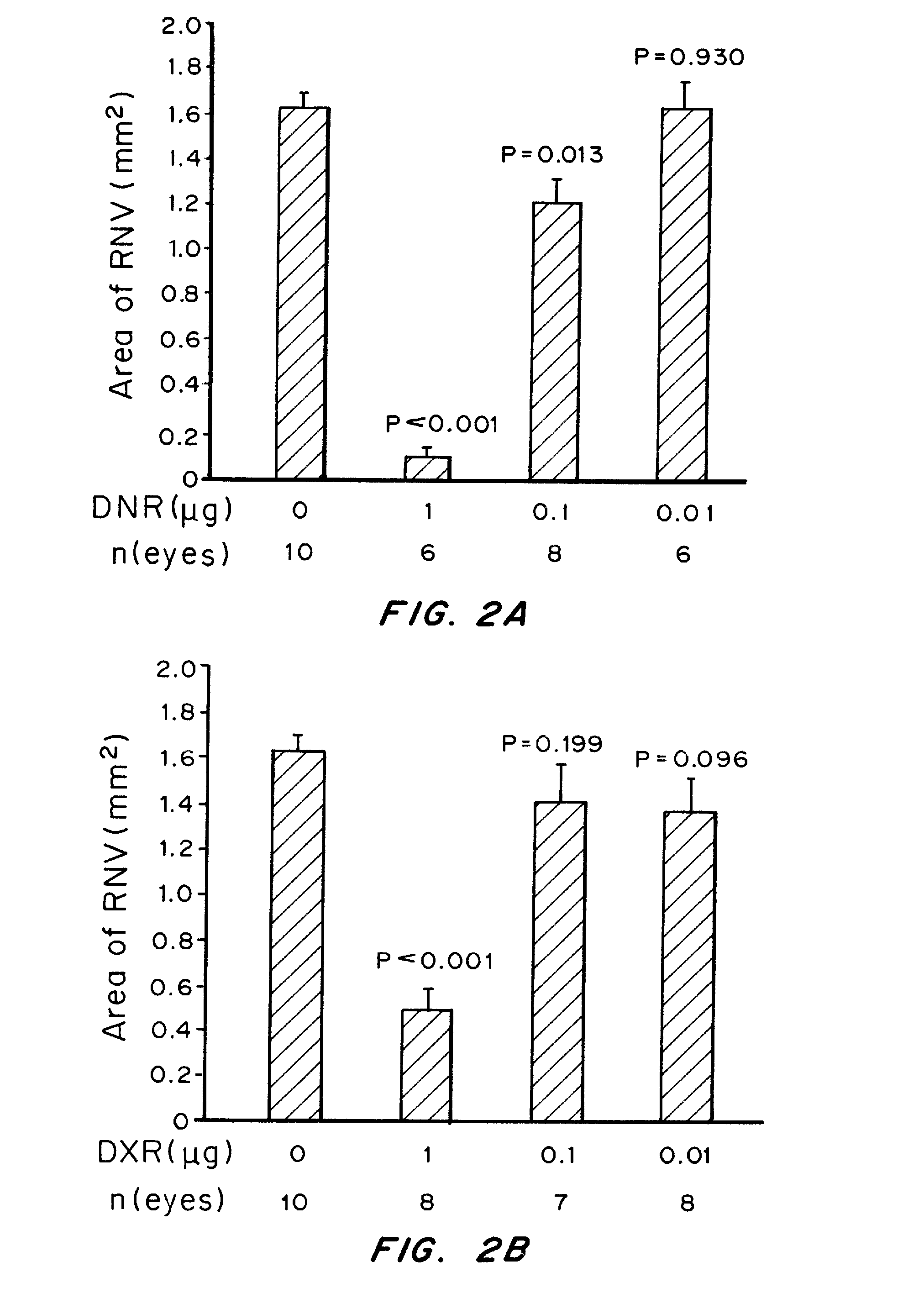
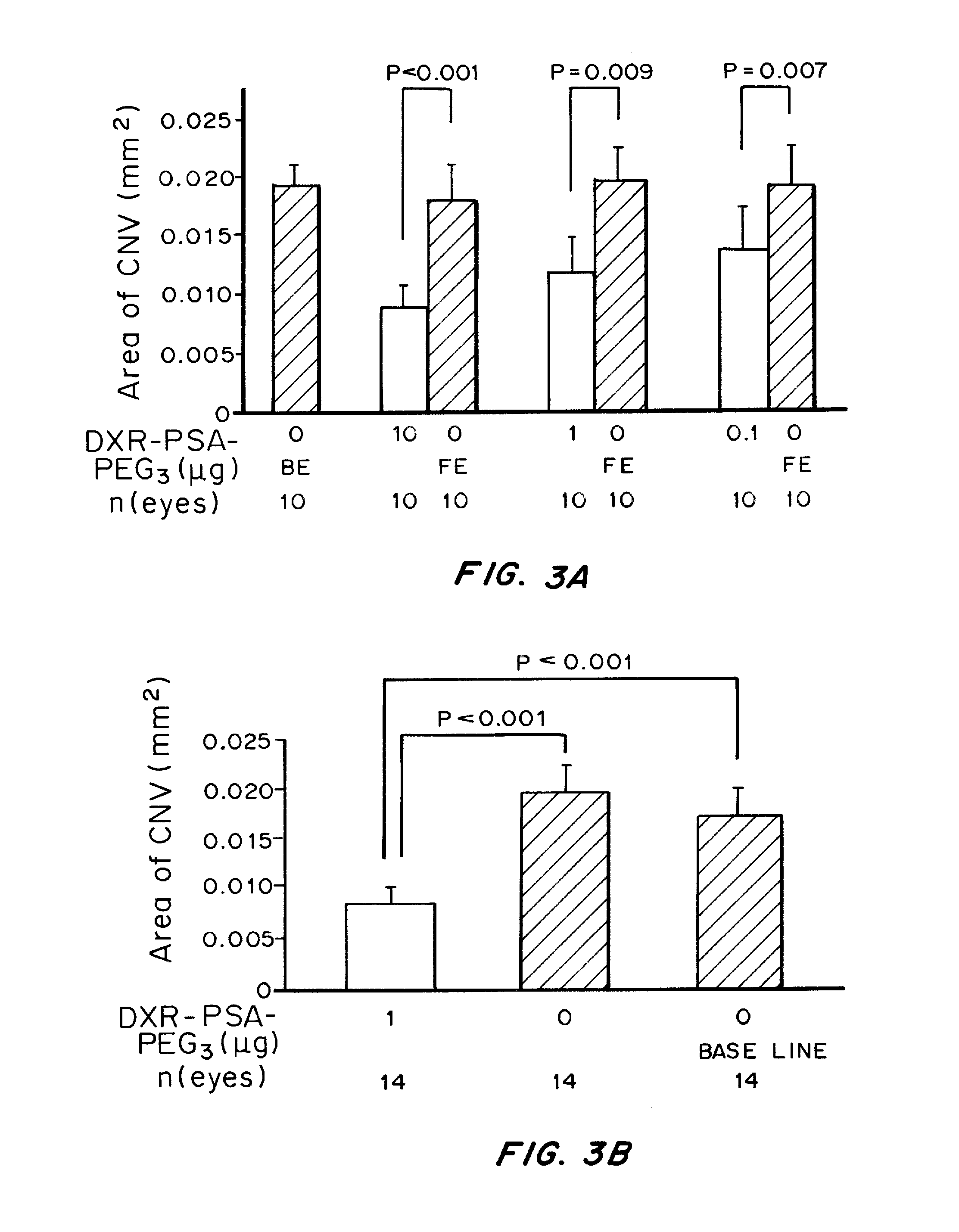
Patents
Literature
273 results about "Treatment level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
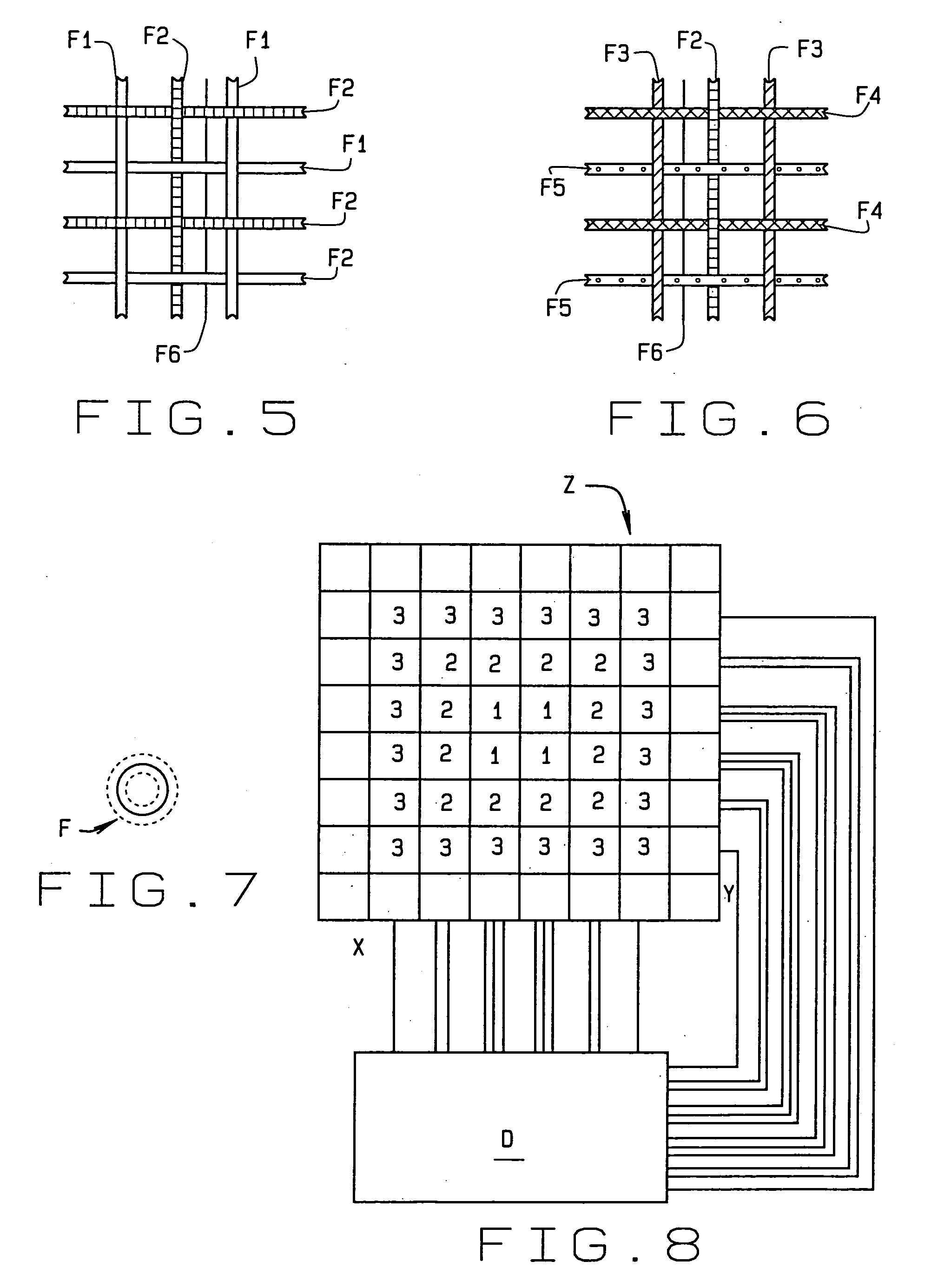
Definition of Treatment level. Treatment level means one of six levels (A, B, C, D, E, and N) used in these rules to: Sample 1. Sample 2.
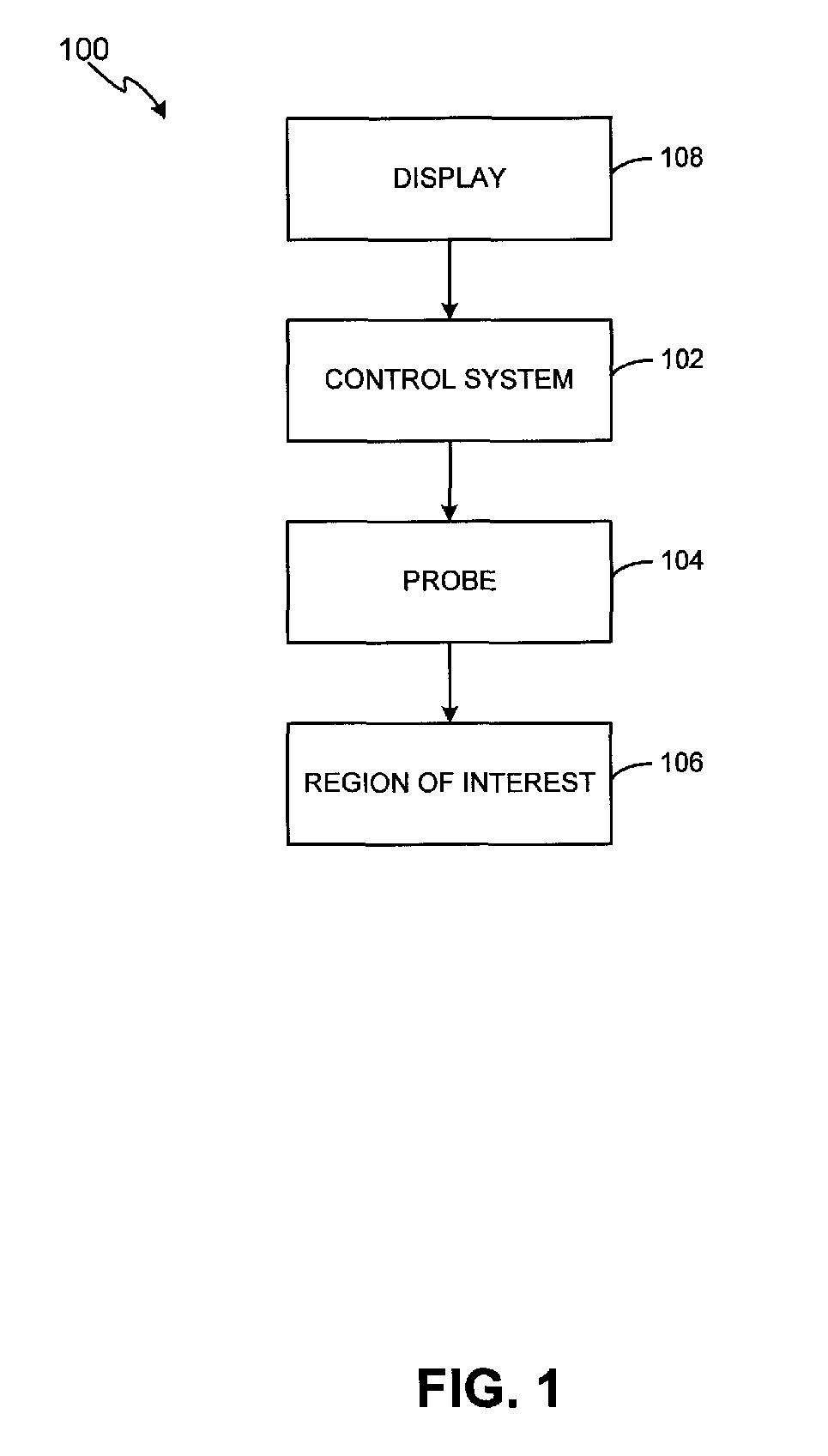
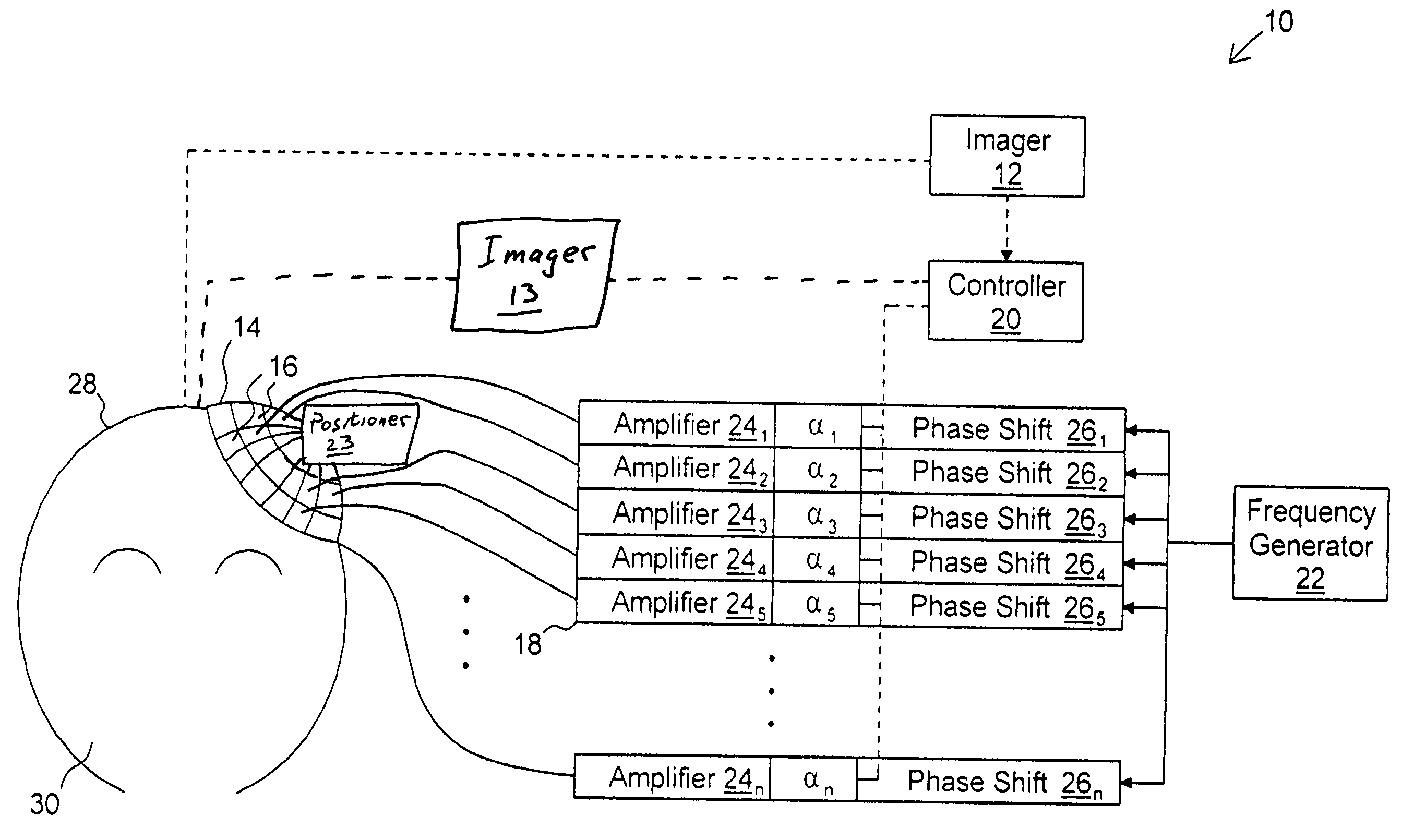
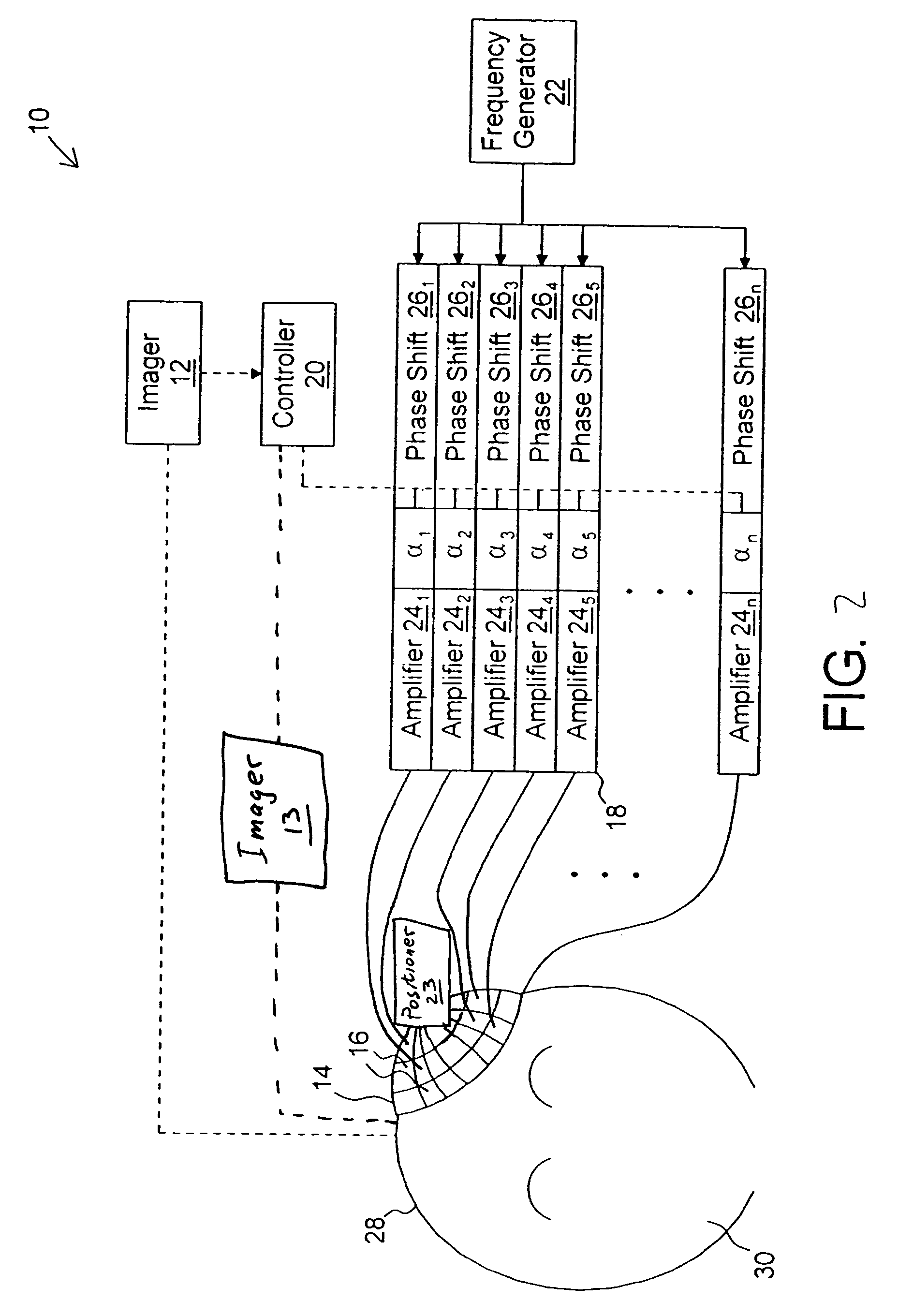
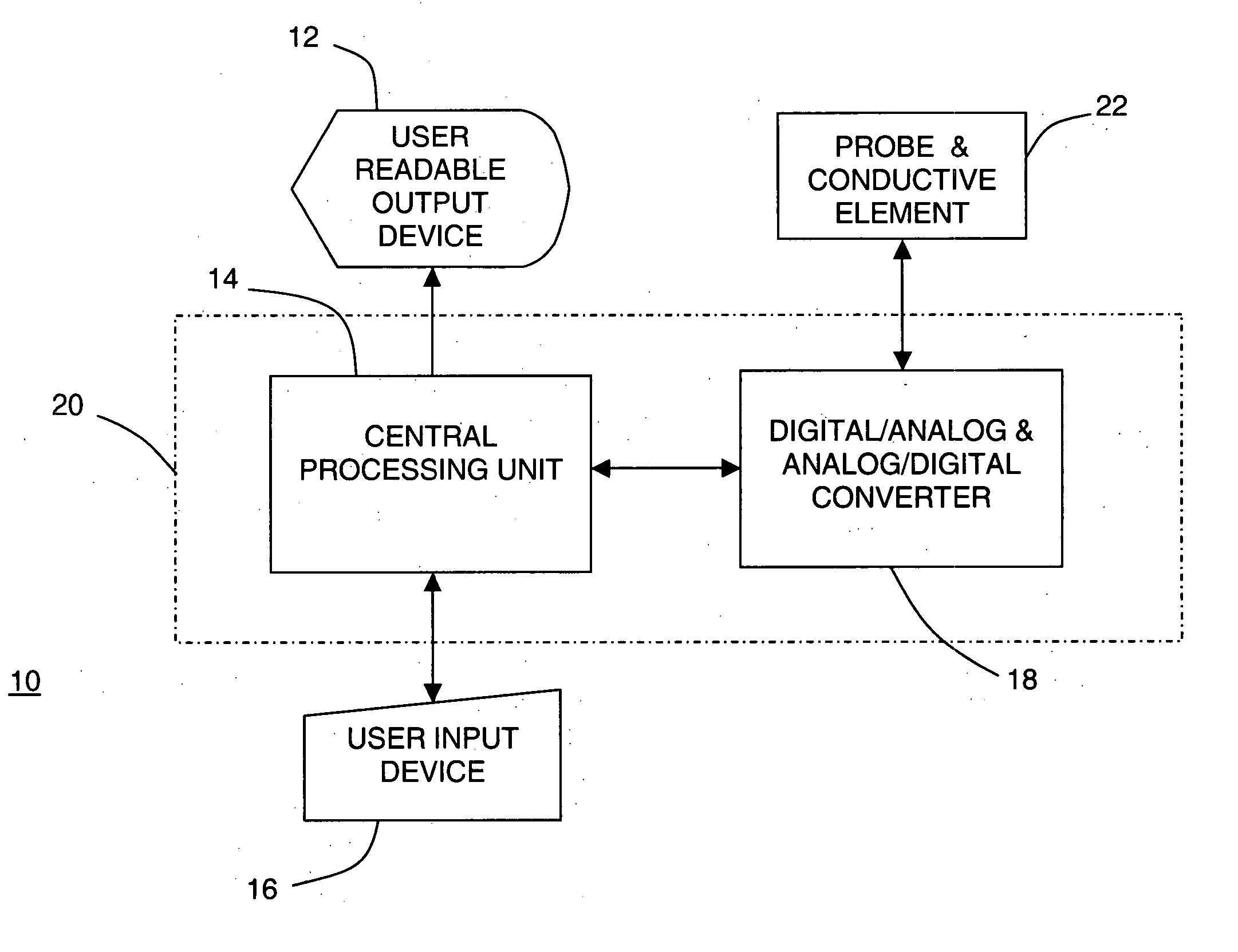
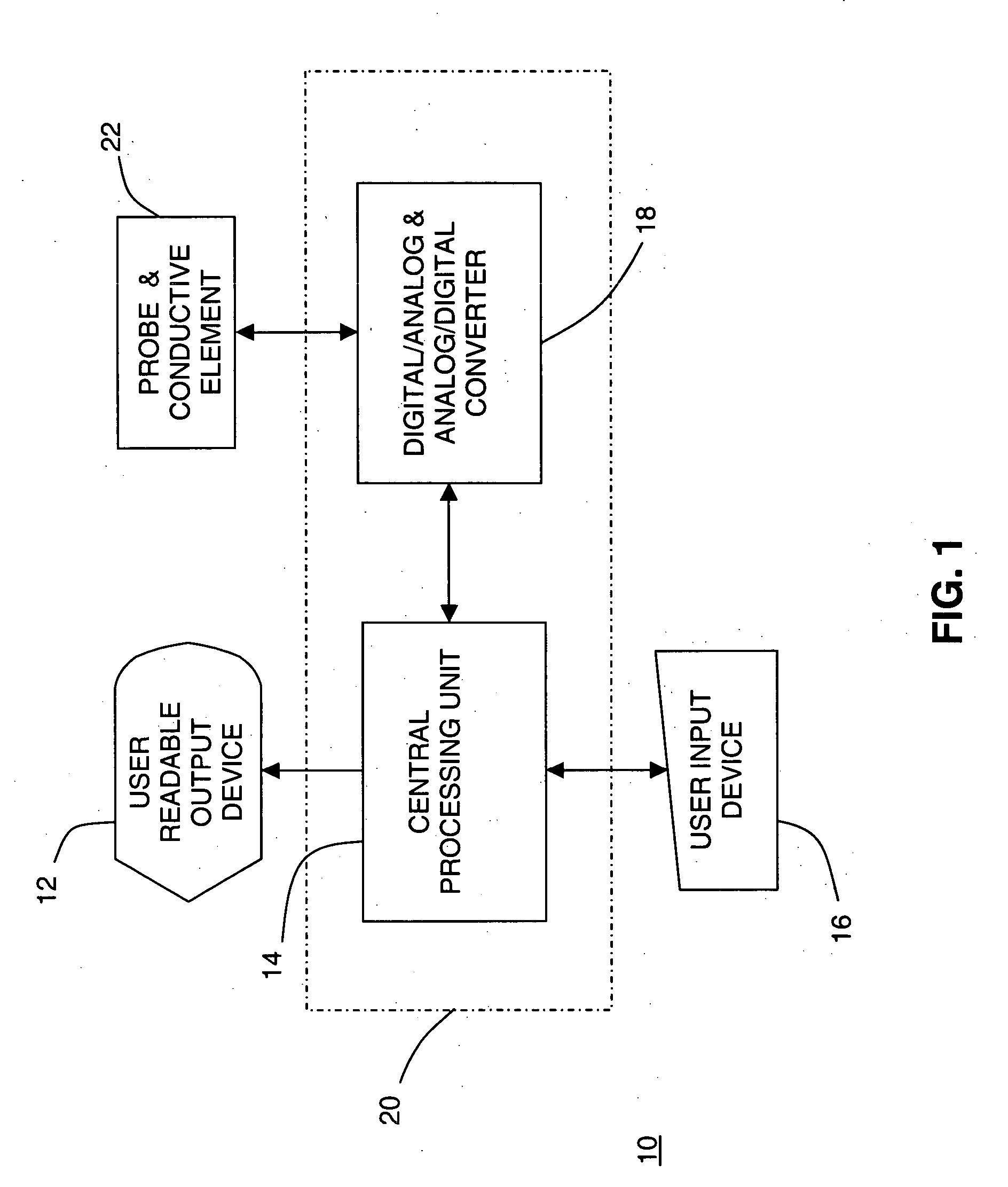
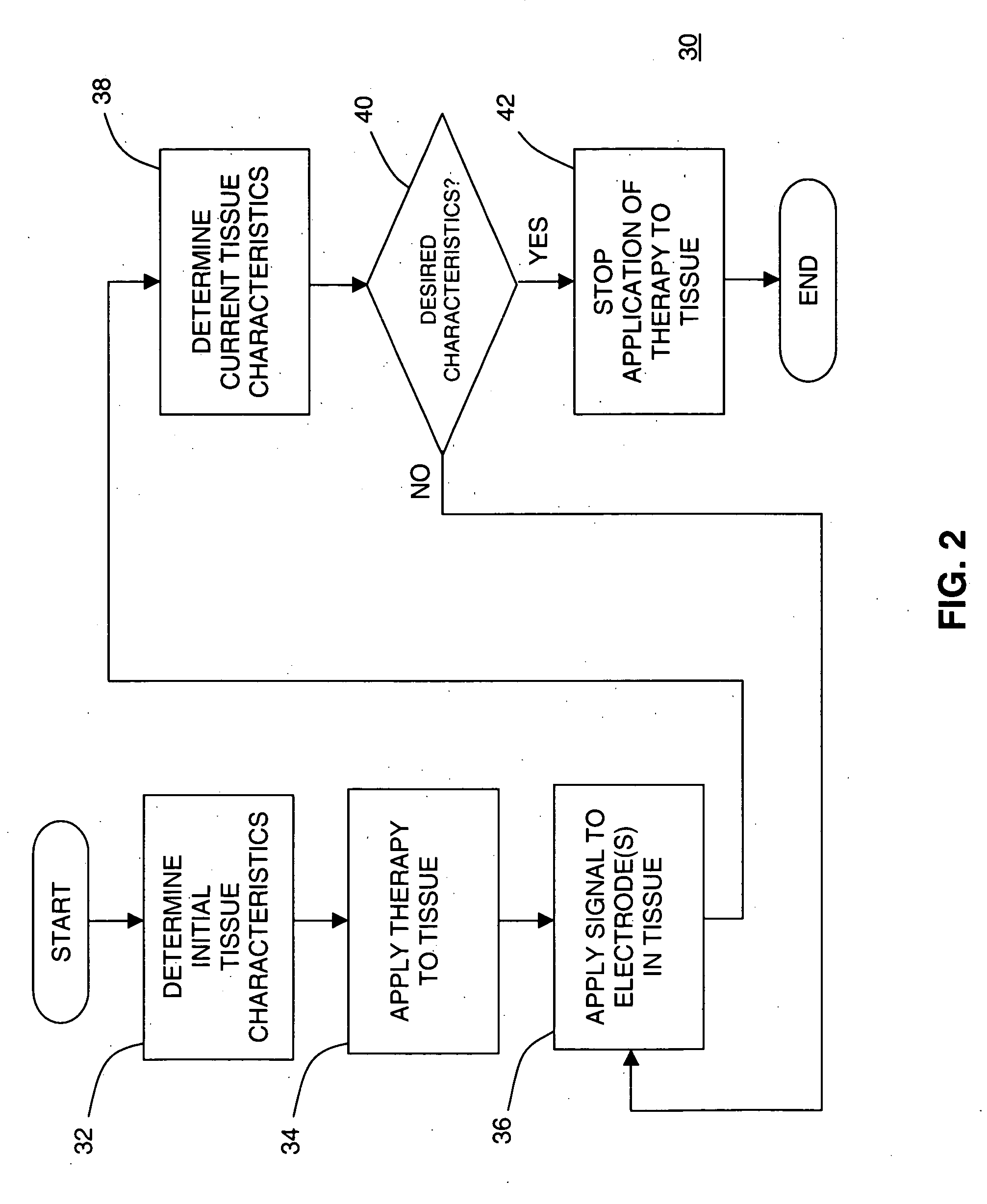
Tissue discrimination and applications in medical procedures
InactiveUS7050848B2Different transmission propertyDifferent capacitanceElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisTissues typesBone Cortex
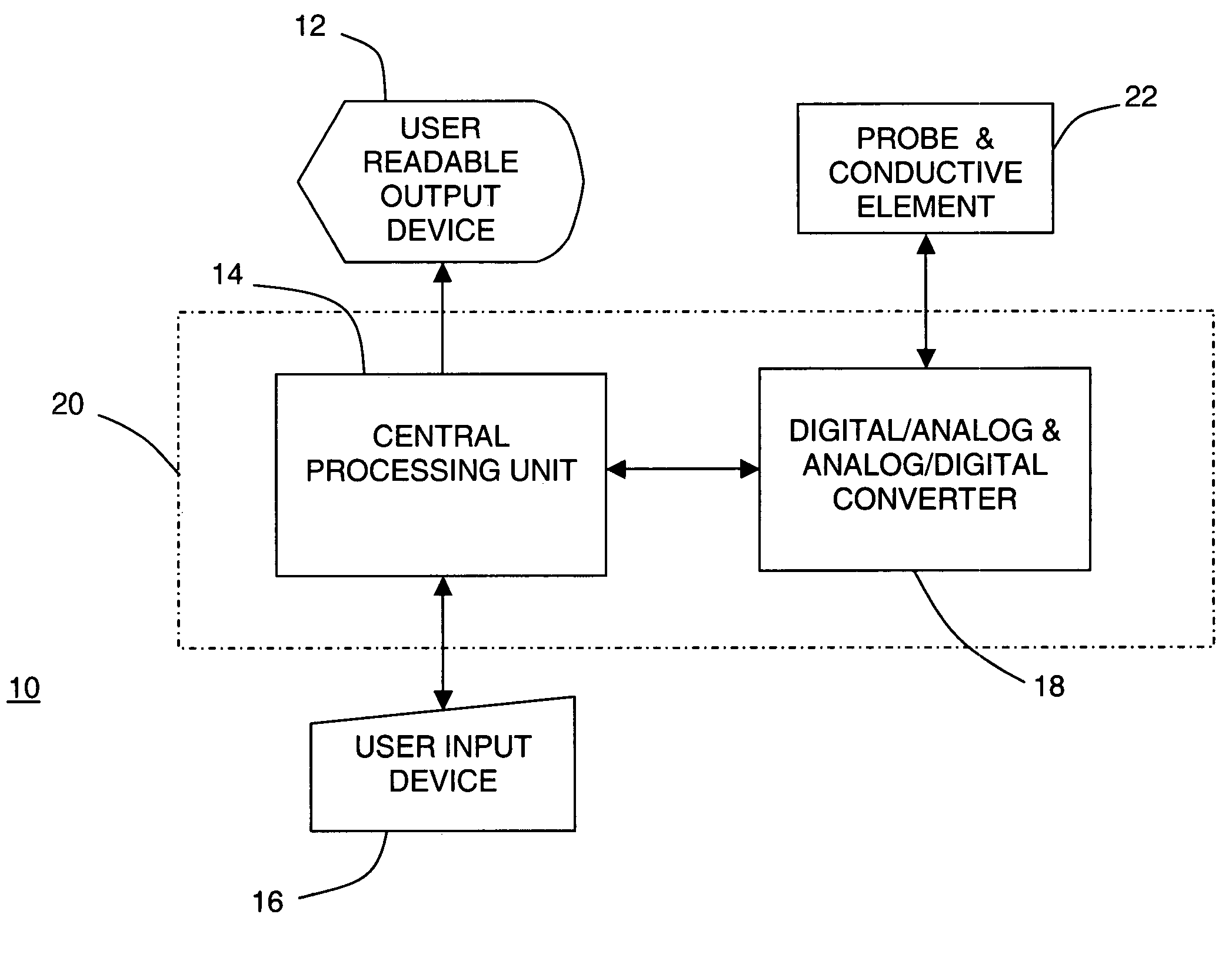
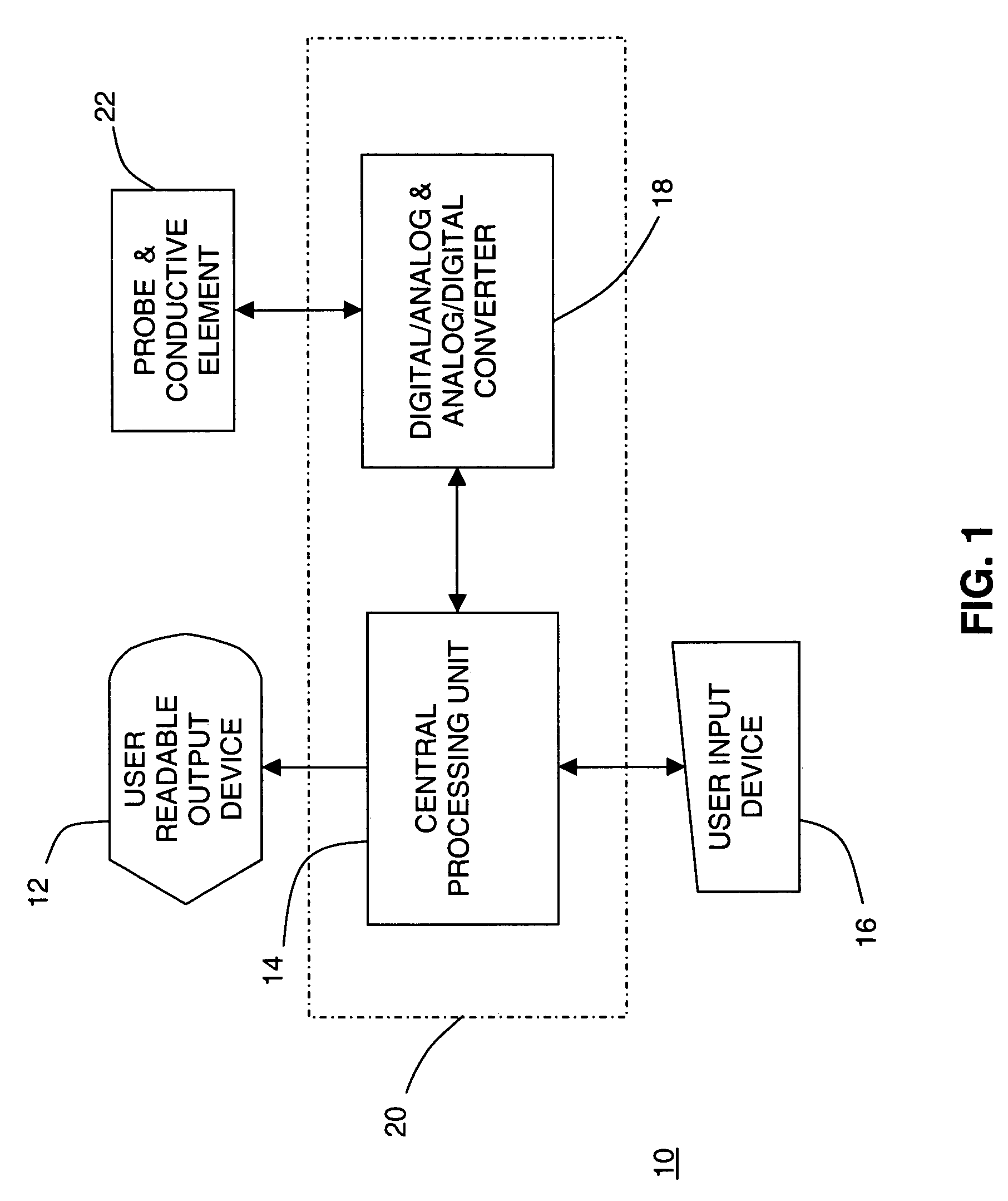
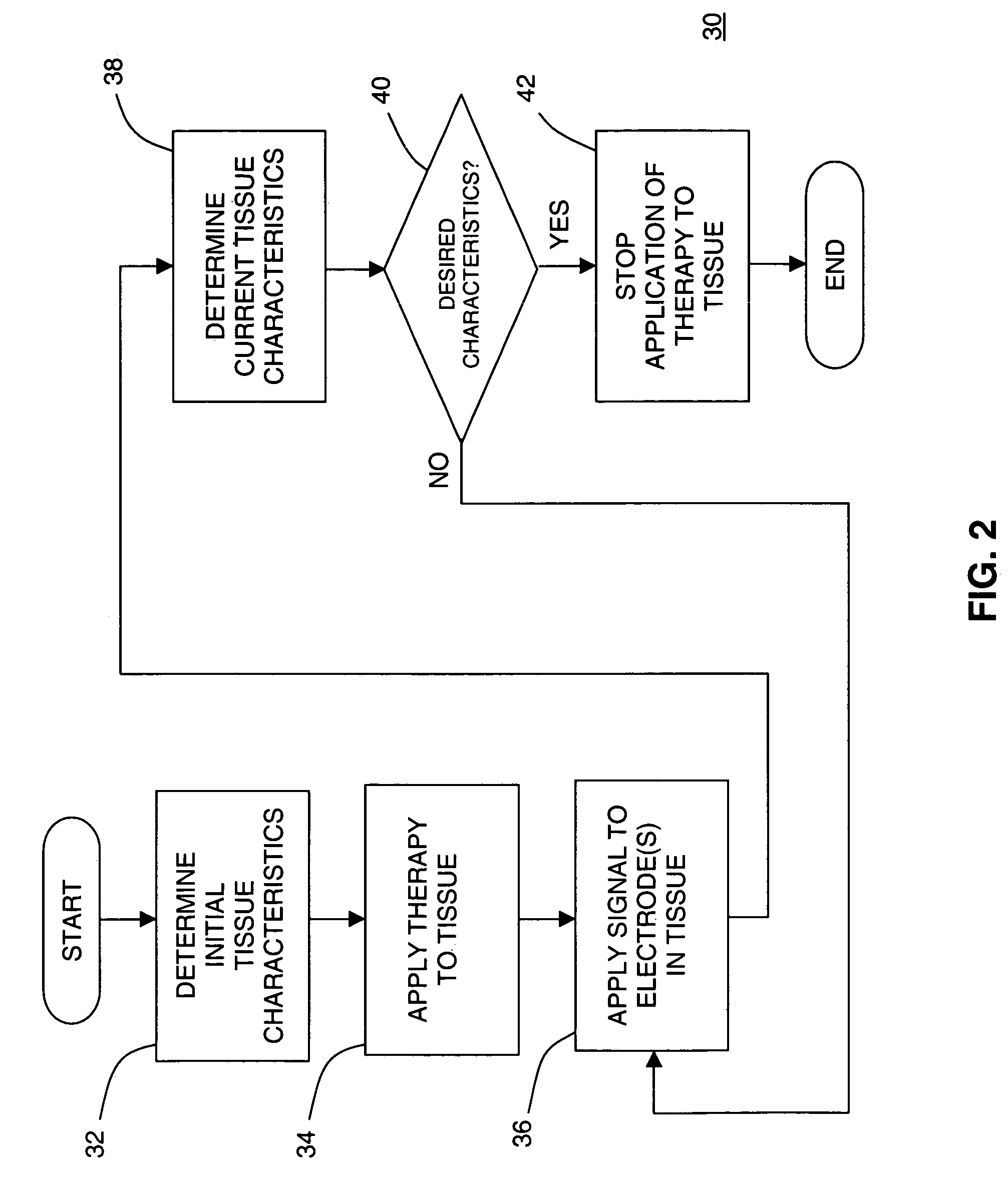
A system and method for discriminating tissue types, controlling the level of therapy to tissue, and determining the health or a known tissue by measuring the characteristics an electrical signal applied to conductive element located within or by the tissue. Additionally, the system and method may be used for determining whether the conductive tip of a pedicle probe or pedicle screw is located in one of cortical bone, cancellous bone, and cortical bone near a boundary with soft tissue, whether the conductive tip of a cannula is located adjacent to one of nerve tissue and annulus tissue, and whether the conductive tip of a cathode is located adjacent to one of nerve tissue and prostate gland tissue.
Owner:NUVASIVE
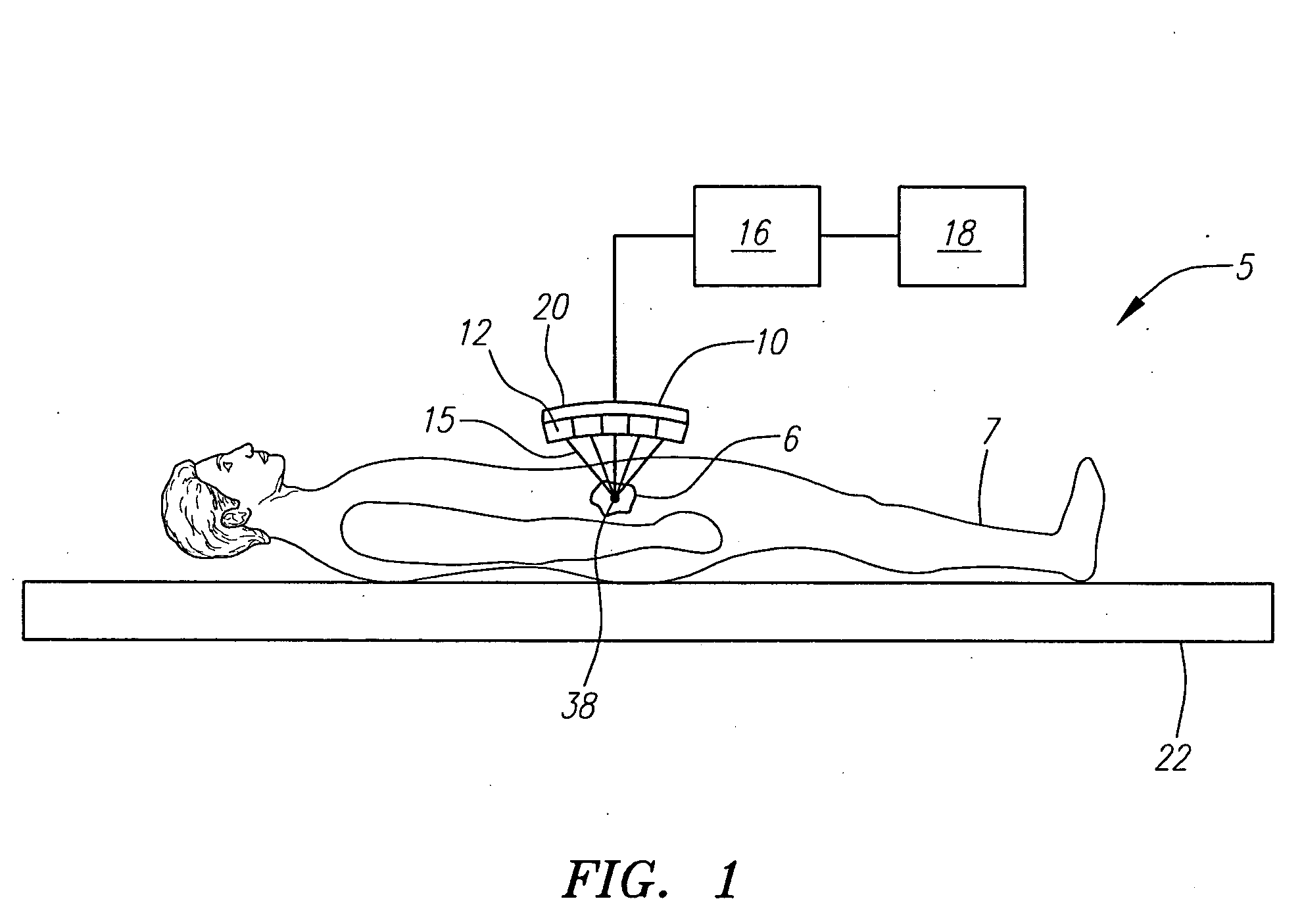
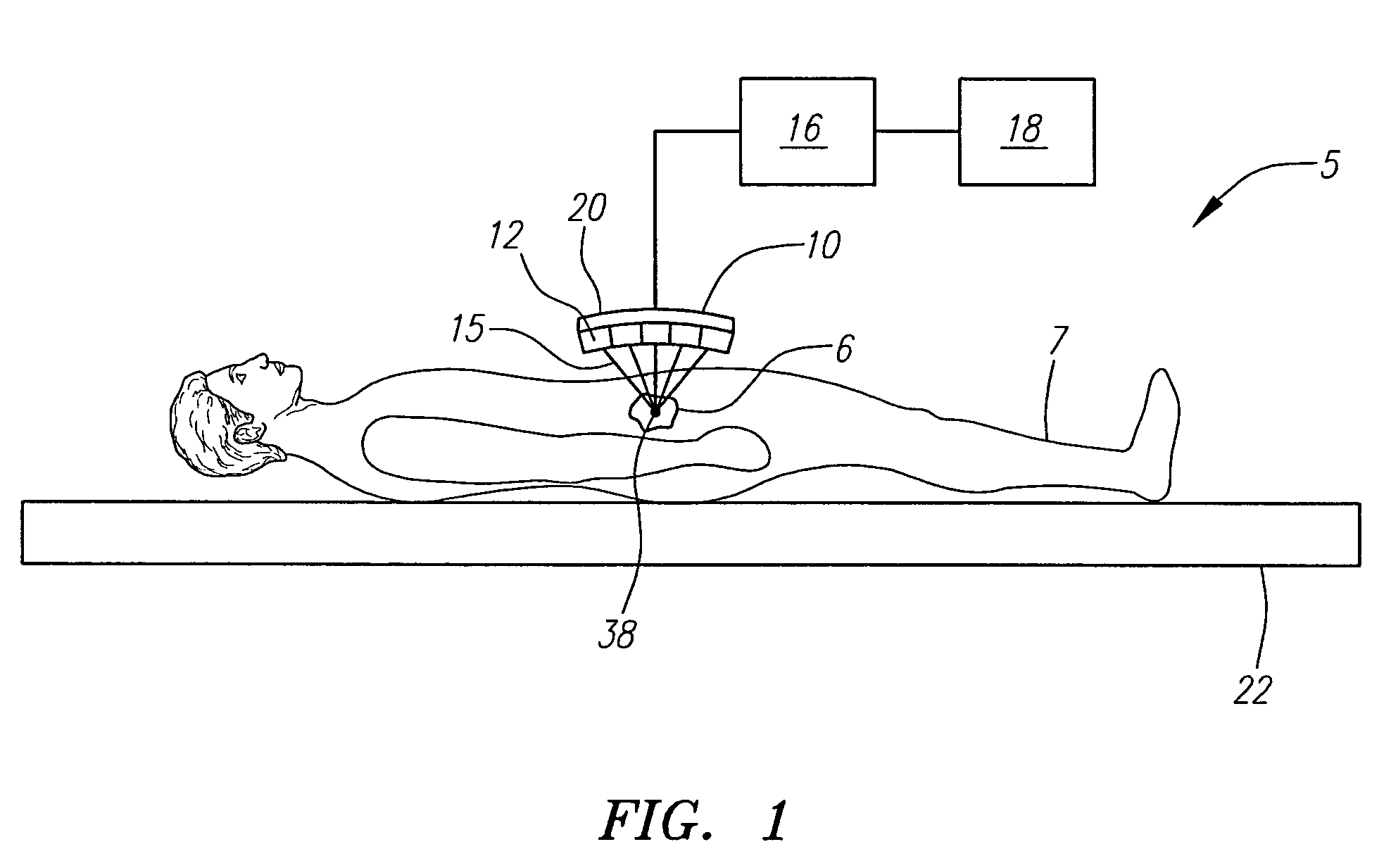
Focused ultrasound system with adaptive anatomical aperture shaping
ActiveUS20060058671A1Reducing ultrasound energyUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationTransducer
A method of treating tissue within a body includes directing an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of transducer elements towards target body tissue, and delivering ultrasound energy towards the target tissue from the transducer elements such that an energy intensity at the target tissue is at or above a prescribed treatment level, while an energy intensity at tissue to be protected in the ultrasound energy path of the transducer elements is at or below a prescribed safety level.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
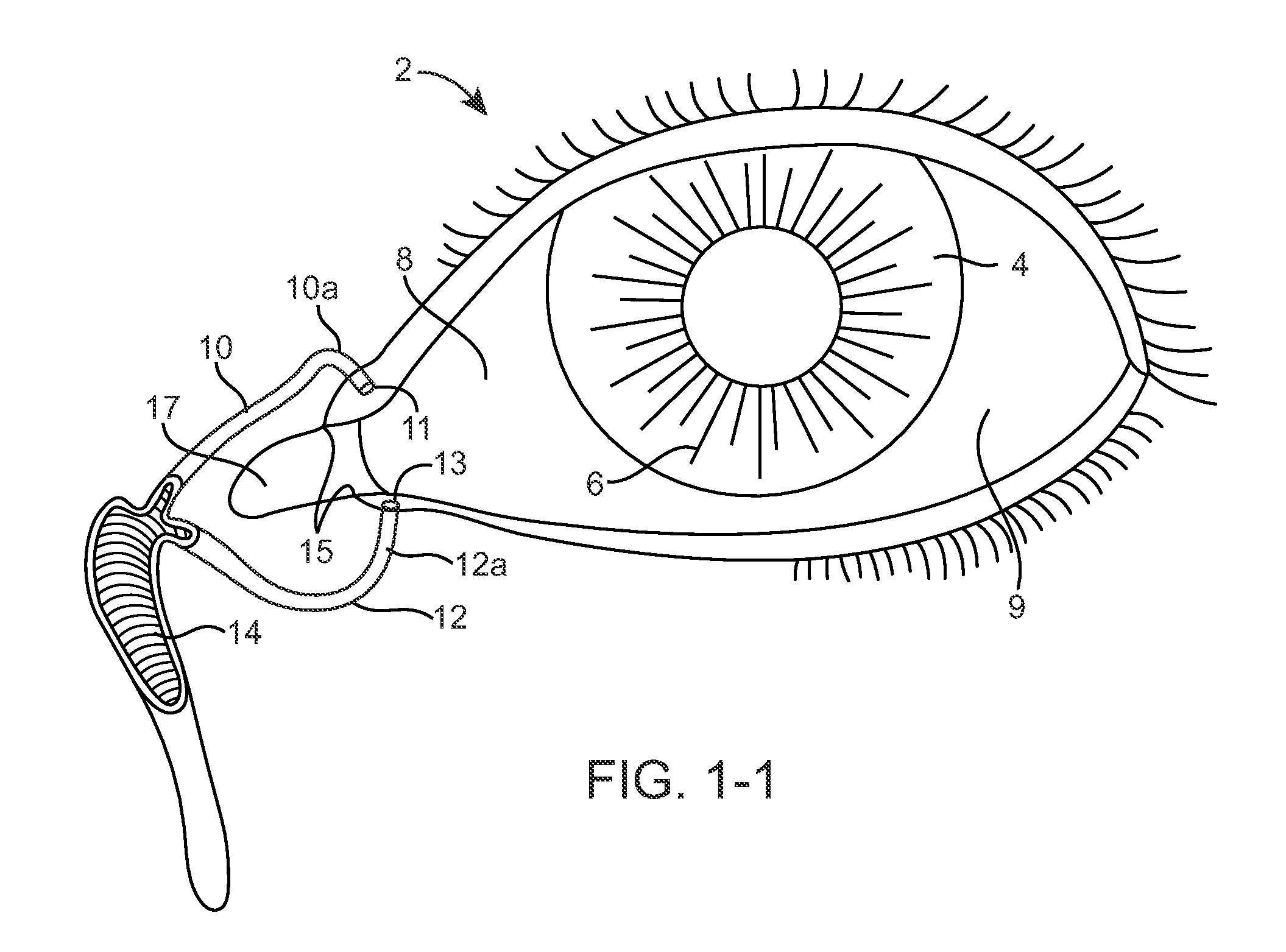
Nasolacrimal Drainage System Implants for Drug Therapy
ActiveUS20070243230A1Reduce deliveryAvoid flowAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderShape-memory alloyImplanted device
Implant devices, systems and methods for insertion into a punctum of a patient optionally comprises a drug core and a sheath body disposed over the drug core. The drug core includes a therapeutic agent deliverable into the eye, and the sheath defines at least one exposed surface of the drug core. The exposed surface(s) of the drug core may contact a tear or tear film fluid and release the therapeutic agent at therapeutic levels over a sustained period when the implant is implanted for use. The implant may include a retention element to retain the drug core and sheath body near the punctum, optionally comprising a shape memory alloy that can resiliently expand. An occlusive element may be attached to the retention element to at least partially occlude tear flow through the canalicular lumen.
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
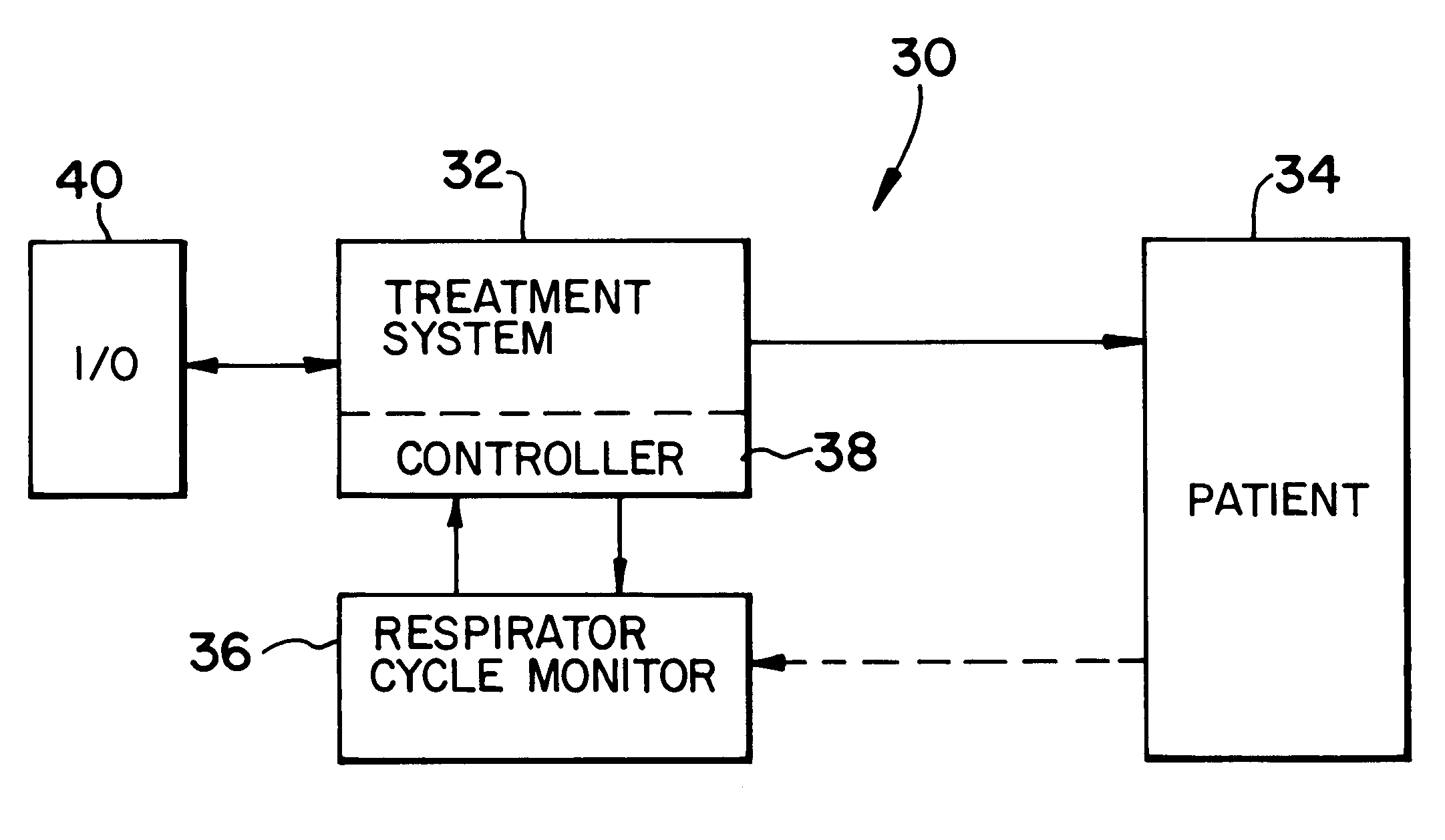
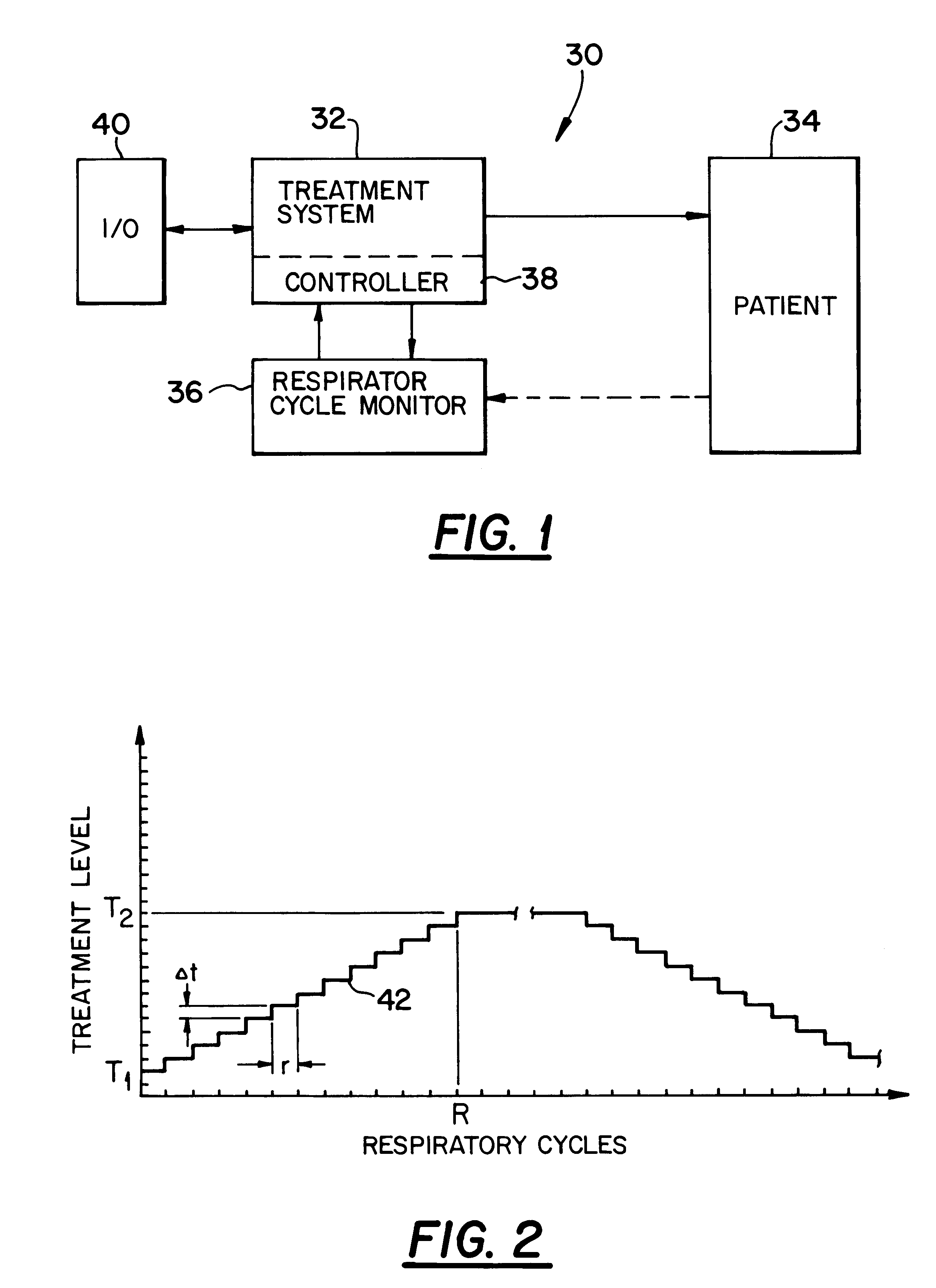
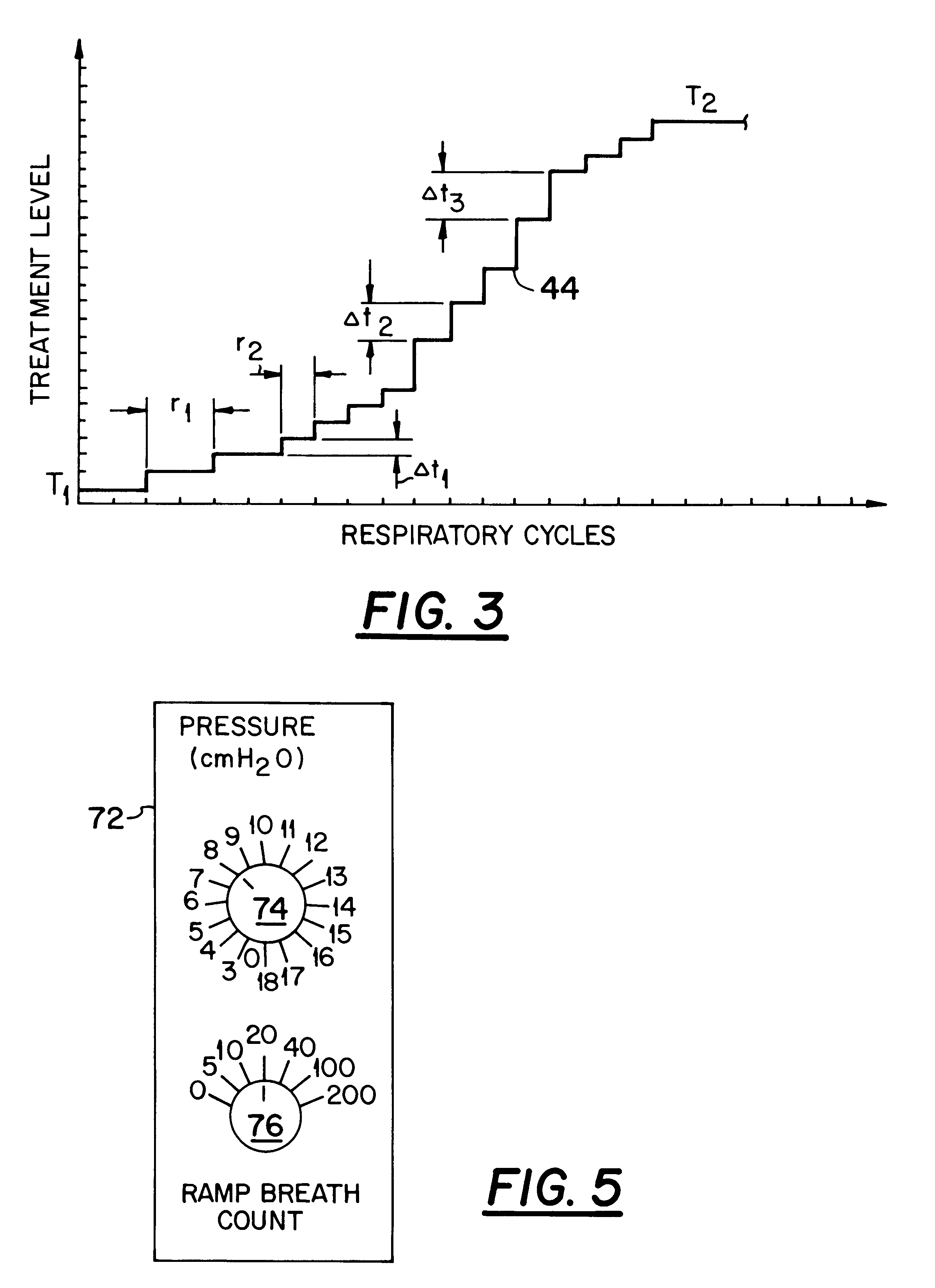
Breath-based control of a therapeutic treatment
A system and method for providing a therapeutic treatment, such as a flow of breathing gas, to a patient at variable treatment levels. A respiratory cycle monitor detects the patient's respiratory cycles and a control unit incrementally adjusts the treatment level from a first predetermined level to a second predetermined level over a first predetermined number of respiratory cycles. The amount of the incremental adjustment and the frequency of such adjustments over the course of the first predetermined number of respiratory cycles can be controlled to achieve a desired change in the therapeutic treatment over the course of the patient's respiration.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
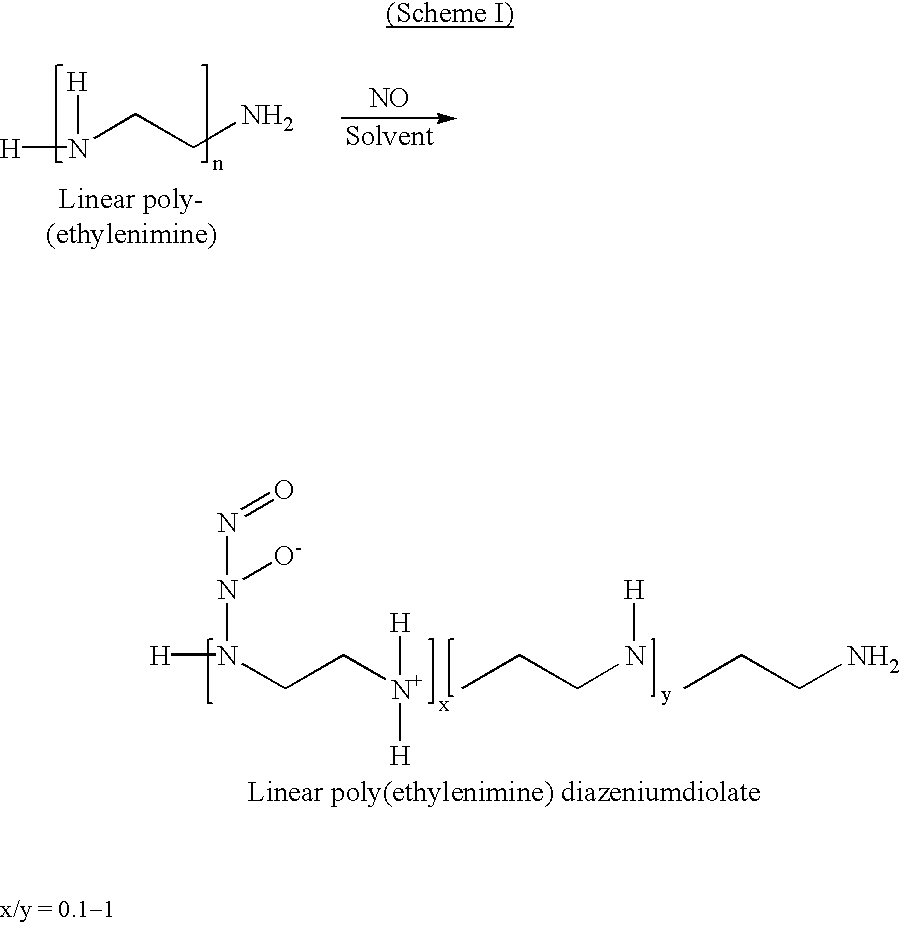
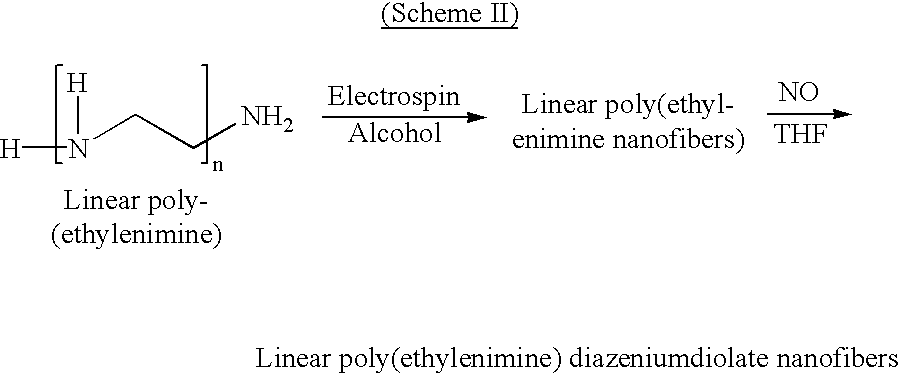
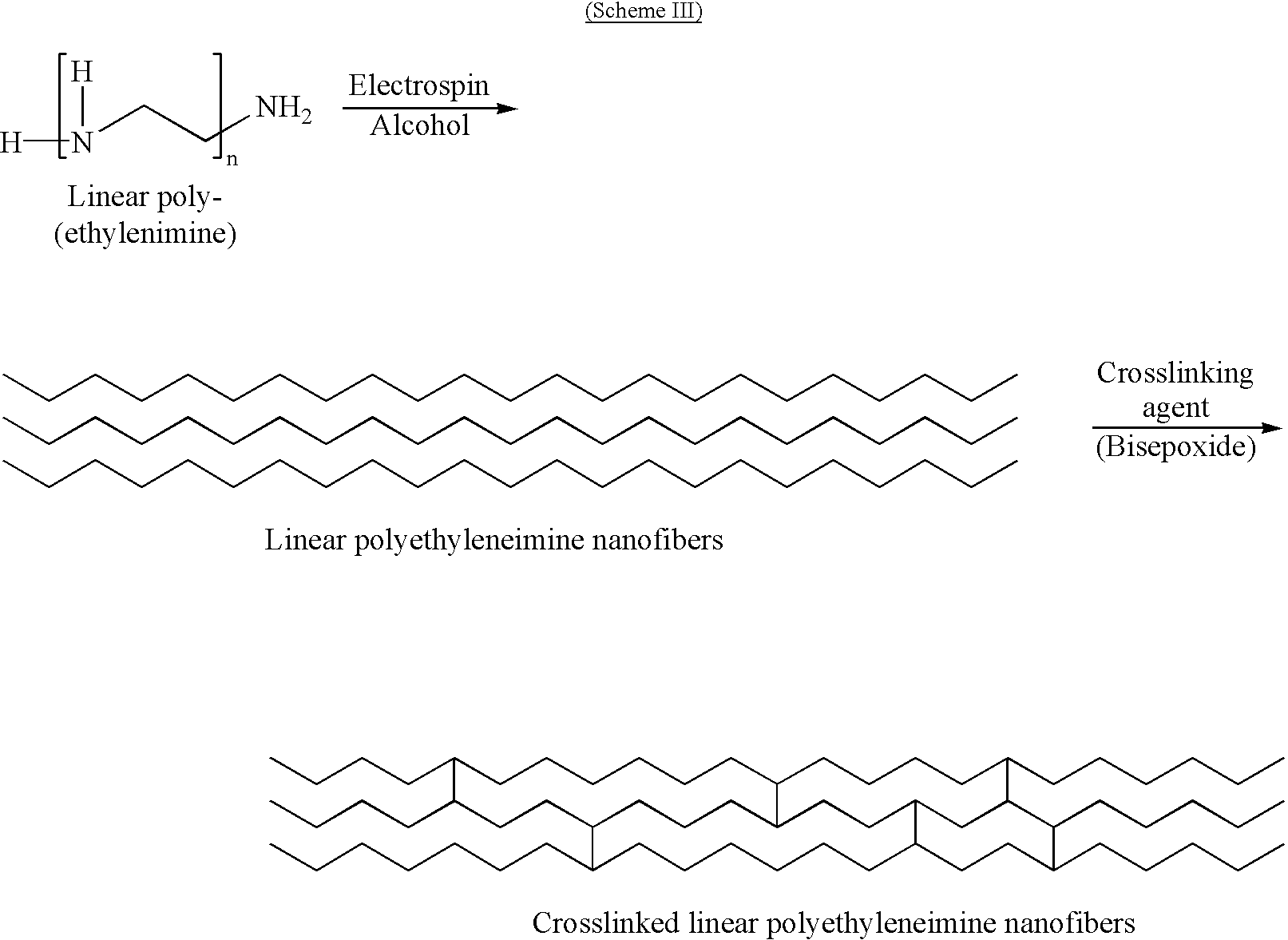
Nitric oxide-modified linear poly(ethylenimine) fibers and uses thereof
A novel coating for medical devices provides nitric oxide delivery using nanofibers of linear poly(ethylenimine)diazeniumdiolate. Linear poly(ethylenimine)diazeniumdiolate releases nitric oxide (NO) in a controlled manner to tissues and organs to aid the healing process and to prevent injury to tissues at risk of injury. Electrospun nano-fibers of linear poly(ethylenimine) diazeniumdiolate deliver therapeutic levels of NO to the tissues surrounding a medical device while minimizing the alteration of the properties of the device. A nanofiber coating, because of the small size and large surface area per unit mass of the nanofibers, provides a much larger surface area per unit mass while minimizing changes in other properties of the device.
Owner:AKRON THE UNIV OF
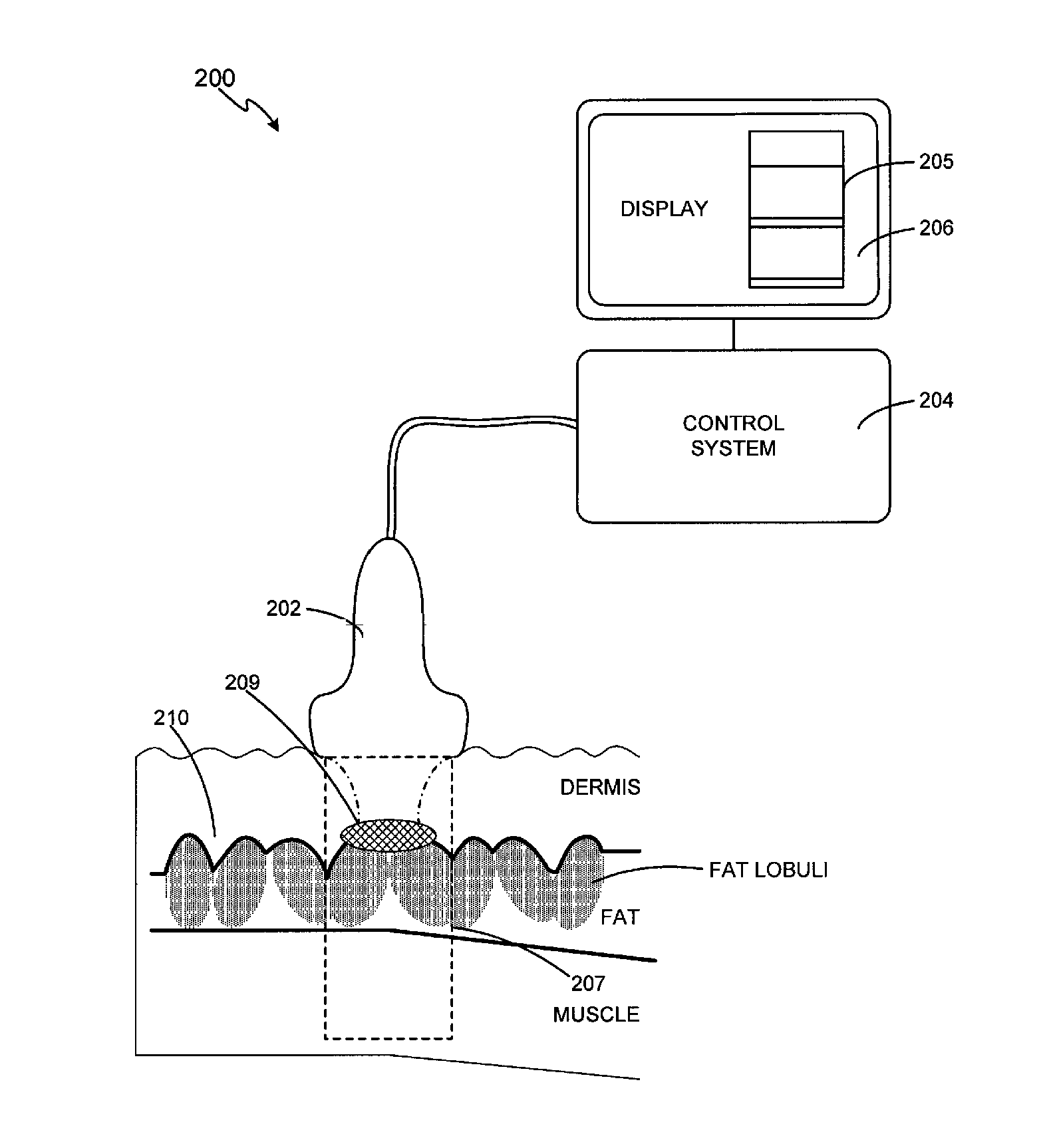
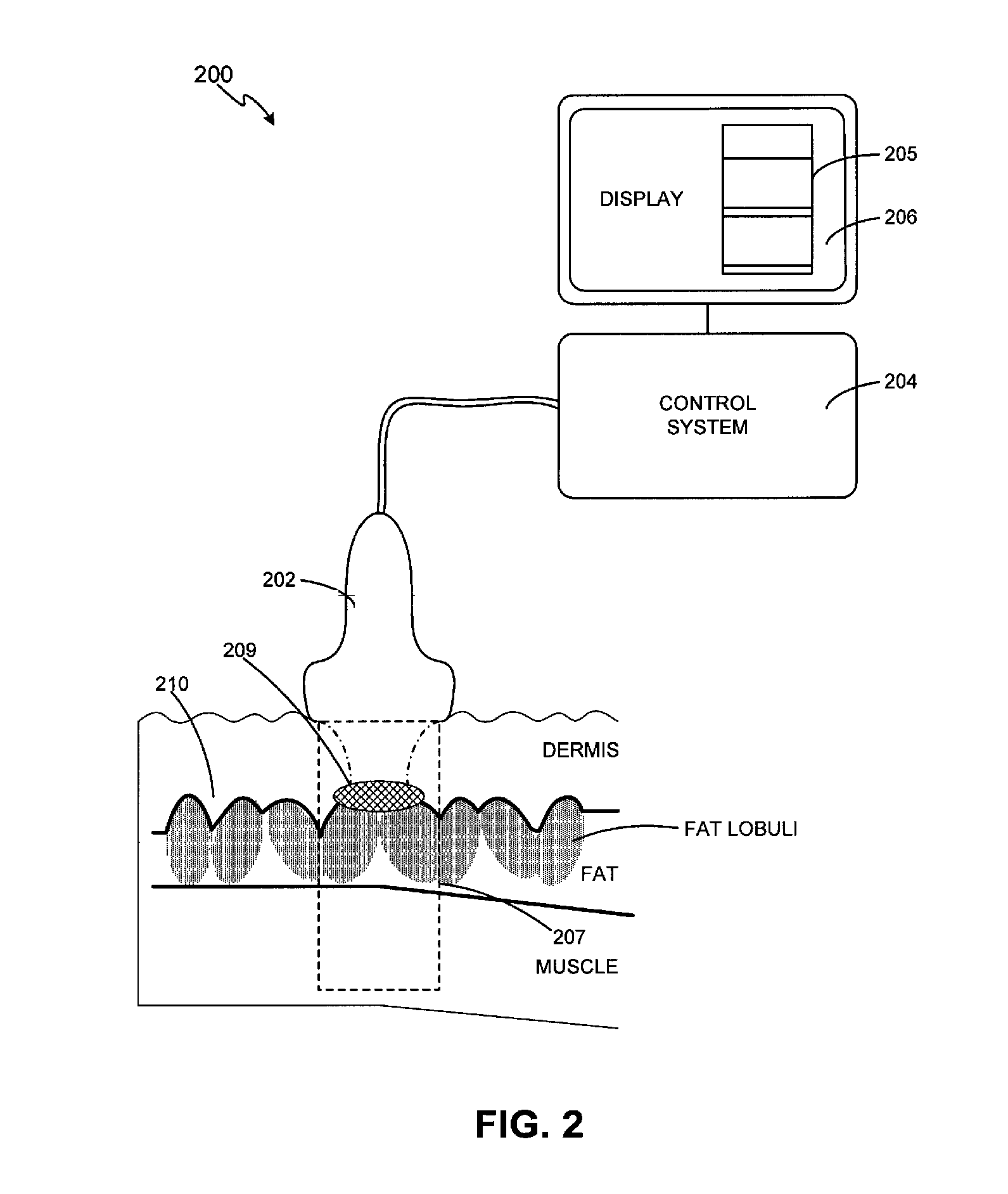
Method and system for treating cellulite
ActiveUS8133180B2Good lookingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyThermal injuryUltrasound imaging
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
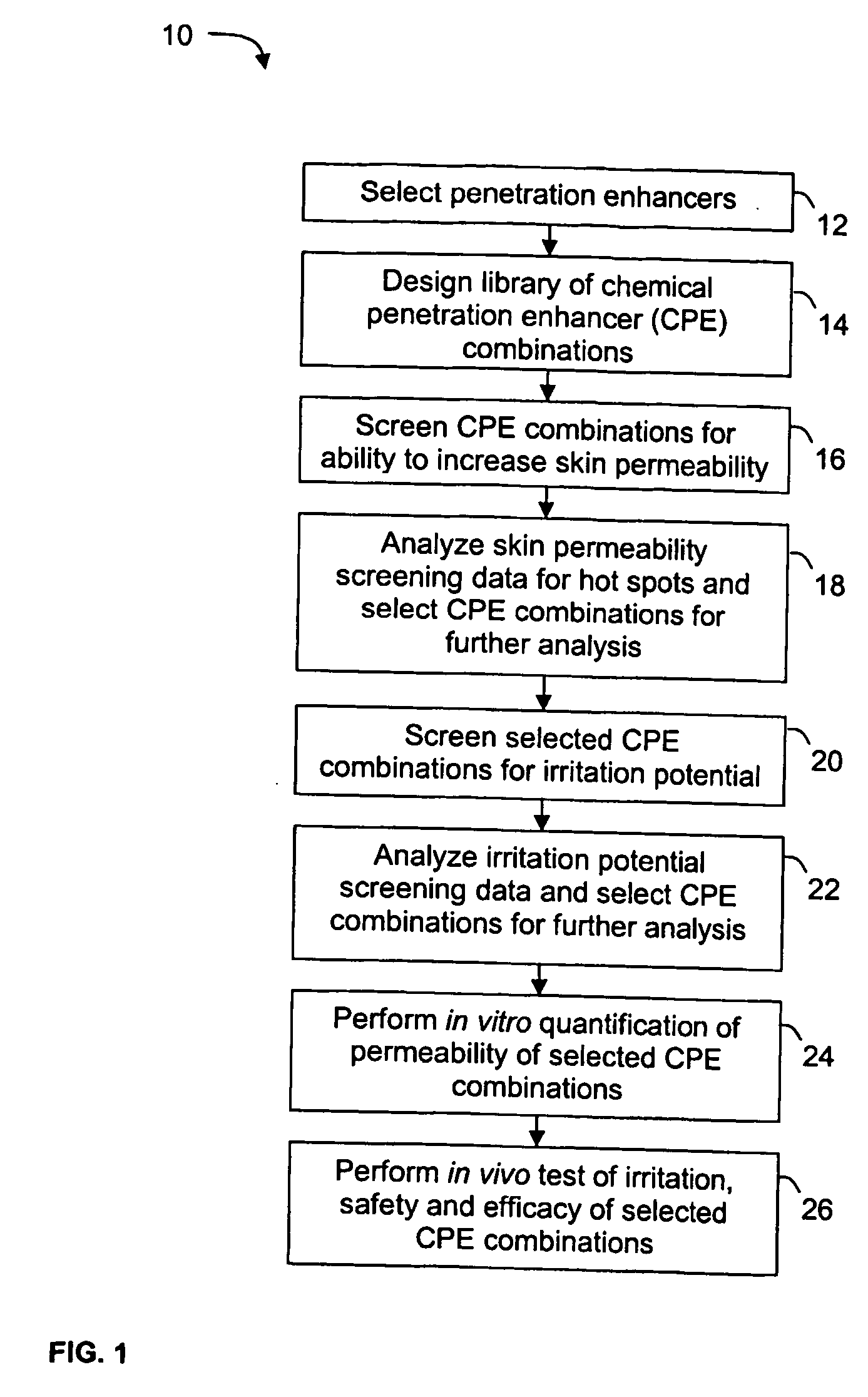
Penetration Enhancer Combinations for Transdermal Delivery
InactiveUS20070269379A1Easy to transportLess irritatingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsIrritation
A high throughput screening and isolation system identifies rare enhancer mixtures from a candidate pool of penetration enhancer combinations. The combinations are screened for high penetration but low irritation potential using a unique data mining method to find new potent and safe chemical penetration enhancer combinations. The members of a library of chemical penetration enhancer combinations are screened with a high throughput device to identify “hot spots”, particular combinations that show higher chemical penetration enhancement compared to neighboring compositions. The irritation potentials of the hot spot combinations are measured to identify combinations that also show low irritation potential. A active component, such as a drug, is then combined with the combination in a formulation which is tested for the ability of the drug to penetrate into or through skin. It is then assessed whether the formulation can deliver the quantity of drug required, and animal tests are conducted to confirm in vivo the ability of the chemical penetration enhancer combinations to facilitate transport of sufficient active molecules across the skin to achieve therapeutic levels of the active molecule in the animal's blood. The invention provides specific unique and rare mixtures of chemical penetration enhancers that enhance skin permeability to hydrophilic macromolecules by more than 50-fold without inducing skin irritation, such as combinations of sodium laurel ether sulfate and 1-phenyl piperazine, and combinations of N-lauryl sarcosine and Span 20 / sorbitan monolaurate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Non-Linear Multiblock Copolymer-Drug Conjugates for the Delivery of Active Agents
ActiveUS20130272994A1Improve propertiesControlled drug and drug release profilePowder deliverySenses disorderUveitisDisease
Non-linear multiblock copolymer-drug conjugates for the treatment and prevention of diseases and disorders of the eye are provided. The polymer-drug conjugates can form nanoparticles, microparticles, and implants that are capable of effectively delivering therapeutic levels of one or more active agents for an extended period of time. Administration to the eye of an active agent in the form of a non-linear multiblock copolymer-drug conjugate produces decreased side effects when compared to administration of the active agent alone. Also provided are methods of treating intraocular neovascular diseases, such as wet age-related macular degeneration as well as diseases and disorders of the eye associated with inflammation, such as uveitis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Sustained release cannabinoid medicaments
The present invention provides a medicament which results in delivery of a therapeutic level of one or more cannabinoids during a clinically relevant therapeutic window. The therapeutic window is a longer window than provided by an immediate release medicament such as Marinol containing an equivalent amount of the cannabinoid. Oral administration of the present compositions provides therapeutic dosing while maintaining safe, side effect sparing, levels of a cannabinoid. The present invention also provides methods of treating cannabinoid-sensitive disorders.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
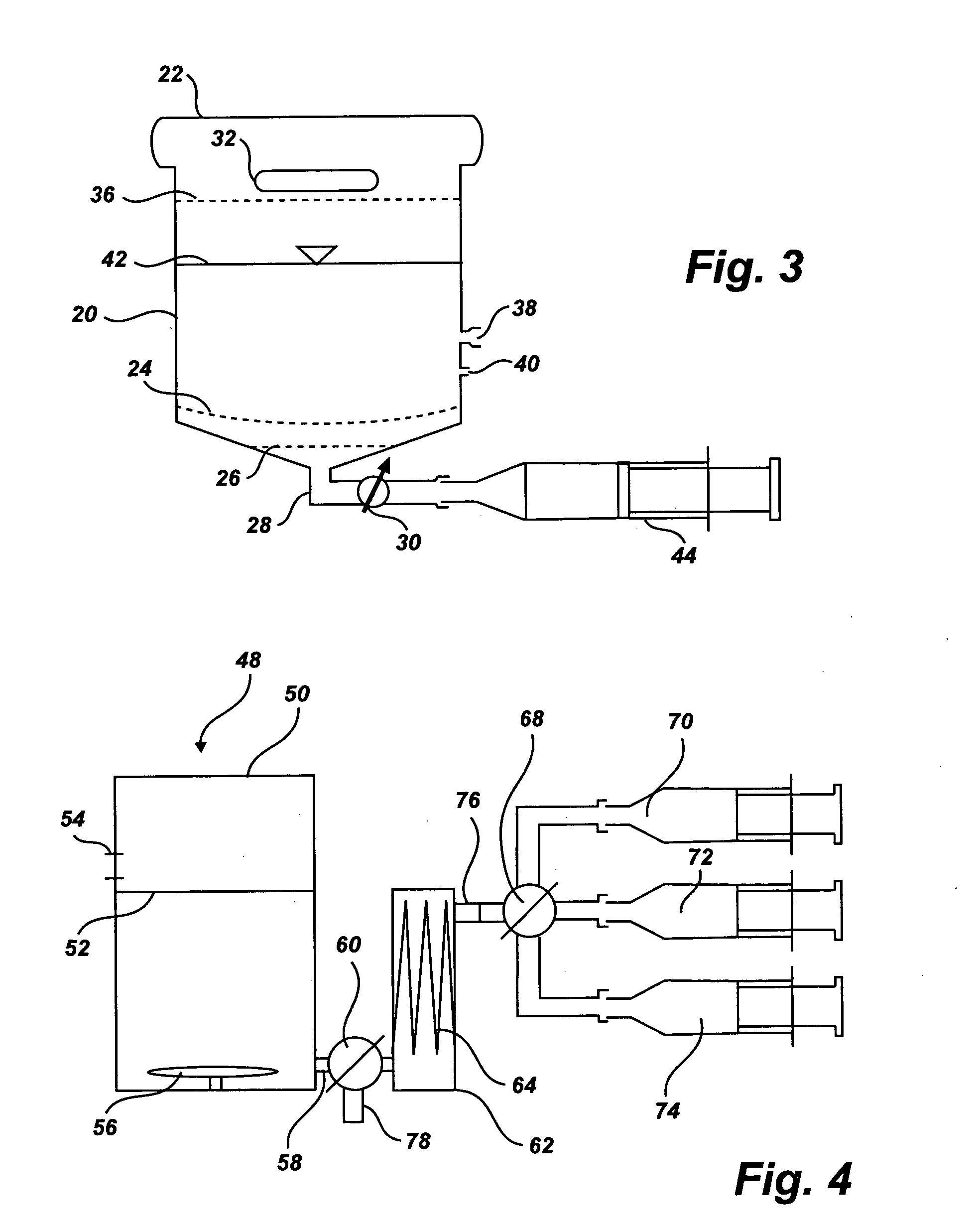
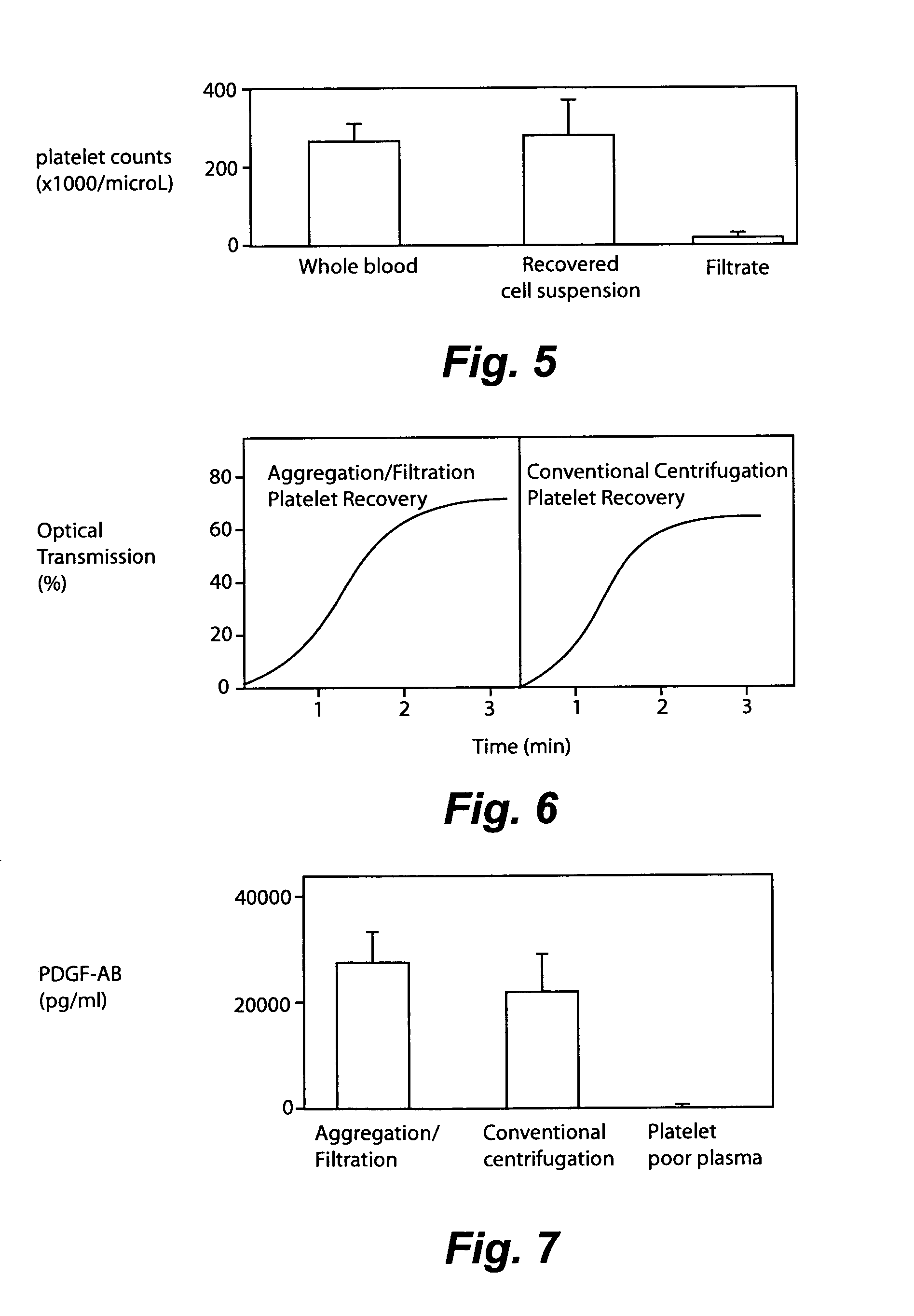
Separation of platelets from whole blood for use as a healant
InactiveUS7011852B2Rapidly and conveniently and cost-effectively harvestEliminate useSurgical adhesivesMammal material medical ingredientsFiltrationBlood plasma
Owner:MOHAMMAD S FAZAL +1
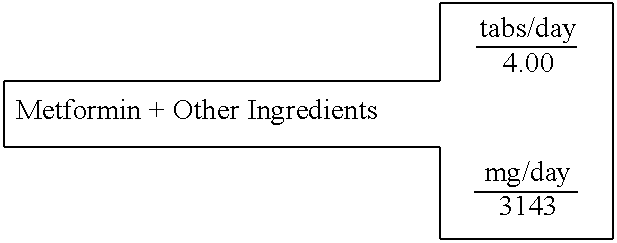
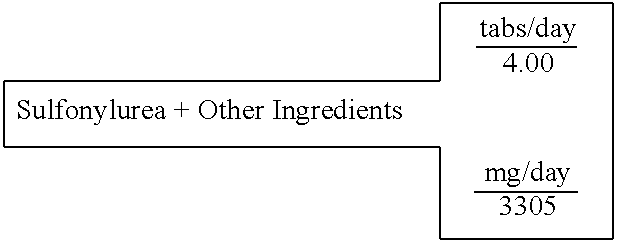
Biguanide and sulfonylurea formulations for the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
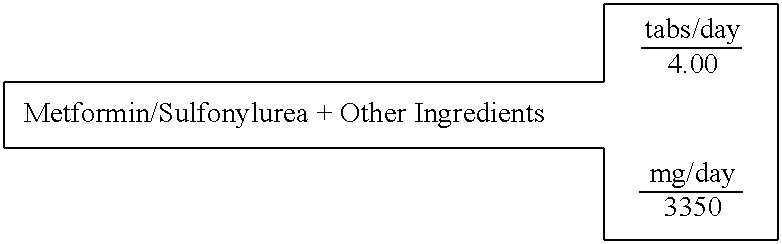
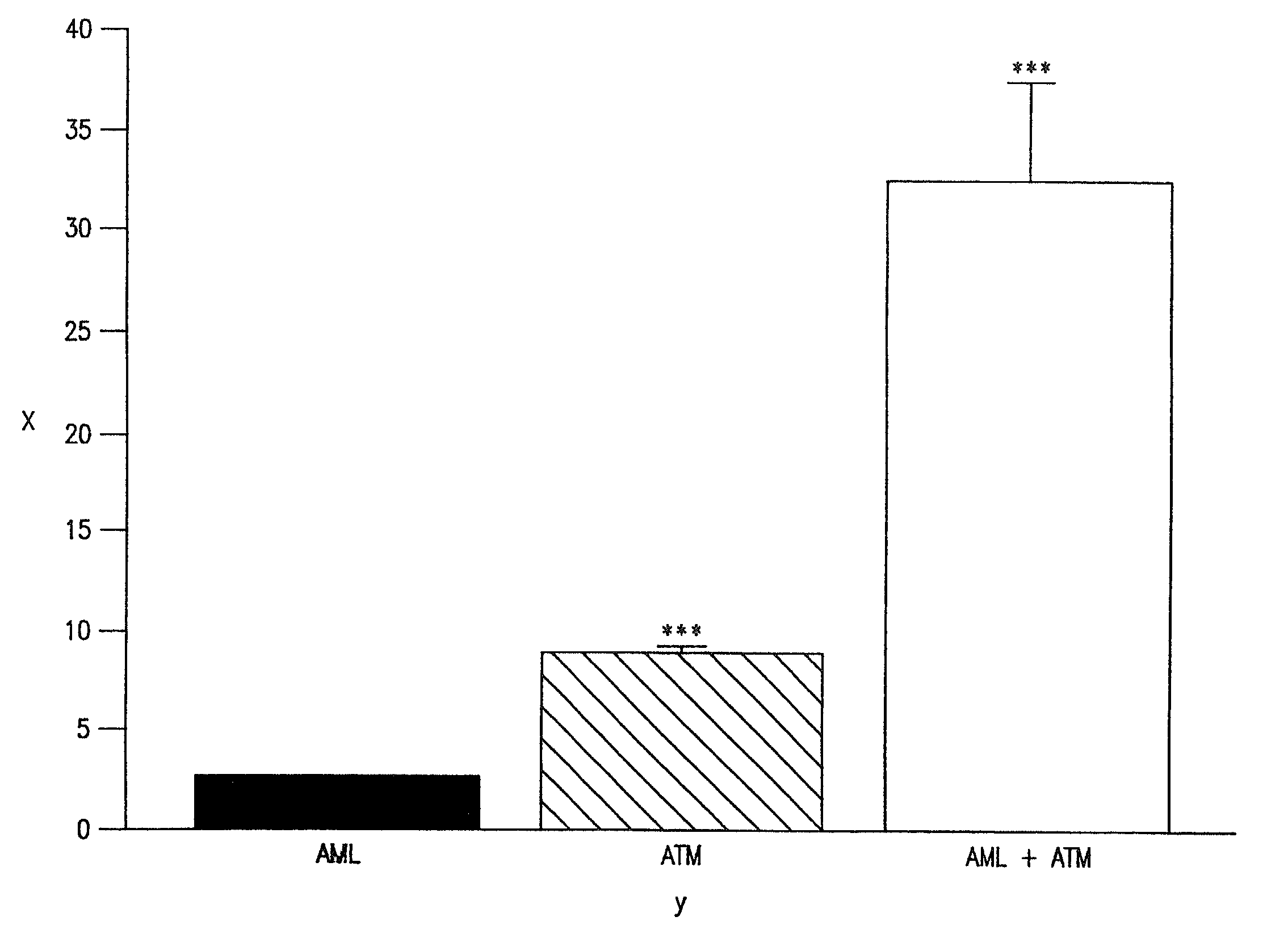
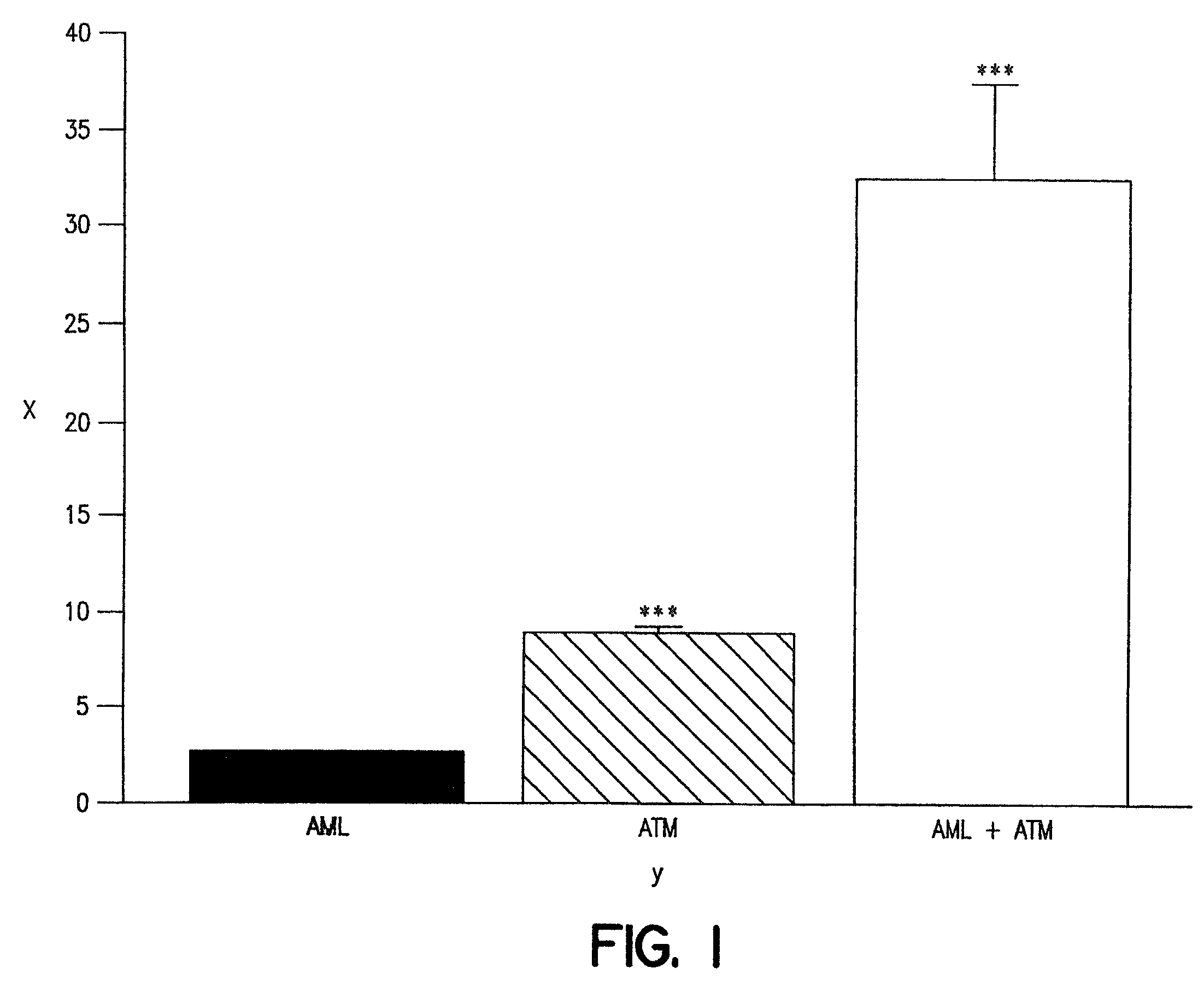
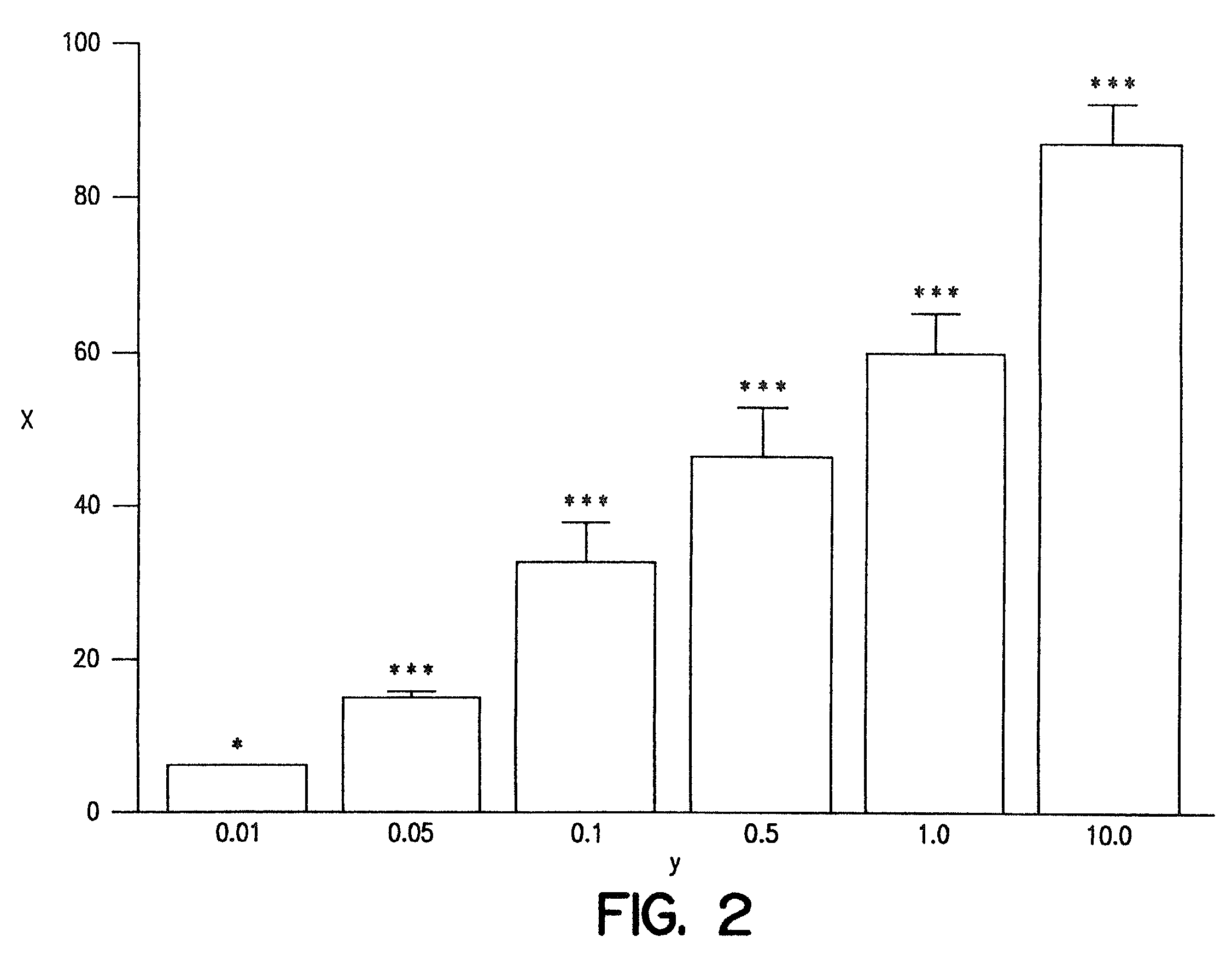
InactiveUS20030078269A1Maximum complementarityImprove effectivenessBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSulfonylureaTreatment level
The invention describes formulations that include either metformin, sulfonylurea or a biguanide-sulfonylurea combination as one active ingredient in addition to specific, other active ingredients. The compositions and dosage forms of the invention are clinically useful as methods for increasing the effectiveness, efficiency and safety of the included biguanide (metformin) and / or sulfonylurea in the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. The carefully chosen additional active ingredients of the invention are designed in a modular fashion to prevent and rectify adverse events associated with insulin resistance syndrome and diabetes mellitus, and those adverse incidences associated with the concurrent use of metformin and / or the sulfonylureas. When clinically administered, the invention will provide therapeutic levels of metformin and of a sulfonylurea, alone or in combination, and broaden their usefulness. The invention will retard the progression of insulin resistance to type 2 diabetes, and reduce the serious microvascular and macrovascular complications commonly associated with insulin resistance syndrome and diabetes mellitus.
Owner:CHRONORX
Shear mode therapeutic ultrasound
A method of delivering ultrasound signals using shear waves includes applying a portion of at least a first ultrasound beam to a subject at at least a first incident angle relative to the surface of the subject to induce shear waves in the subject, energy in the shear waves forming a substantial part of energy of first ultrasound waves at a desired region in the subject at a therapeutic level.
Owner:HYNYNEN KULLERVO +1
Tissue discrimination and applications in medical procedures
InactiveUS20040181165A1Different transmission propertyDifferent capacitanceElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisNerves tissueTreatment level
A system and method for discriminating tissue types, controlling the level of therapy to tissue, and determining the health or a known tissue by measuring the characteristics an electrical signal applied to conductive element located within or by the tissue. Additionally, the system and method may be used for determining whether the conductive tip of a pedicle probe or pedicle screw is located in one of cortical bone, cancellous bone, and cortical bone near a boundary with soft tissue, whether the conductive tip of a cannula is located adjacent to one of nerve tissue and annulus tissue, and whether the conductive tip of a cathode is located adjacent to one of nerve tissue and prostate gland tissue.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Focused ultrasound system with adaptive anatomical aperture shaping
ActiveUS7699780B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocus ultrasoundSonification
A method of treating tissue within a body includes directing an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of transducer elements towards target body tissue, and delivering ultrasound energy towards the target tissue from the transducer elements such that an energy intensity at the target tissue is at or above a prescribed treatment level, while an energy intensity at tissue to be protected in the ultrasound energy path of the transducer elements is at or below a prescribed safety level.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
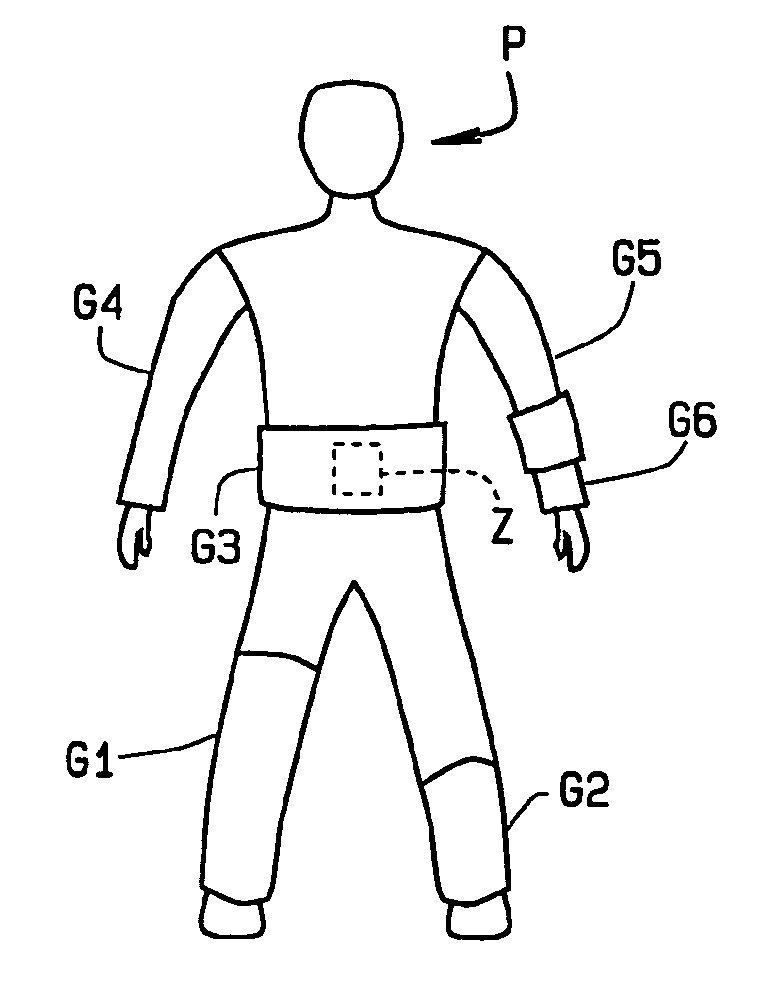
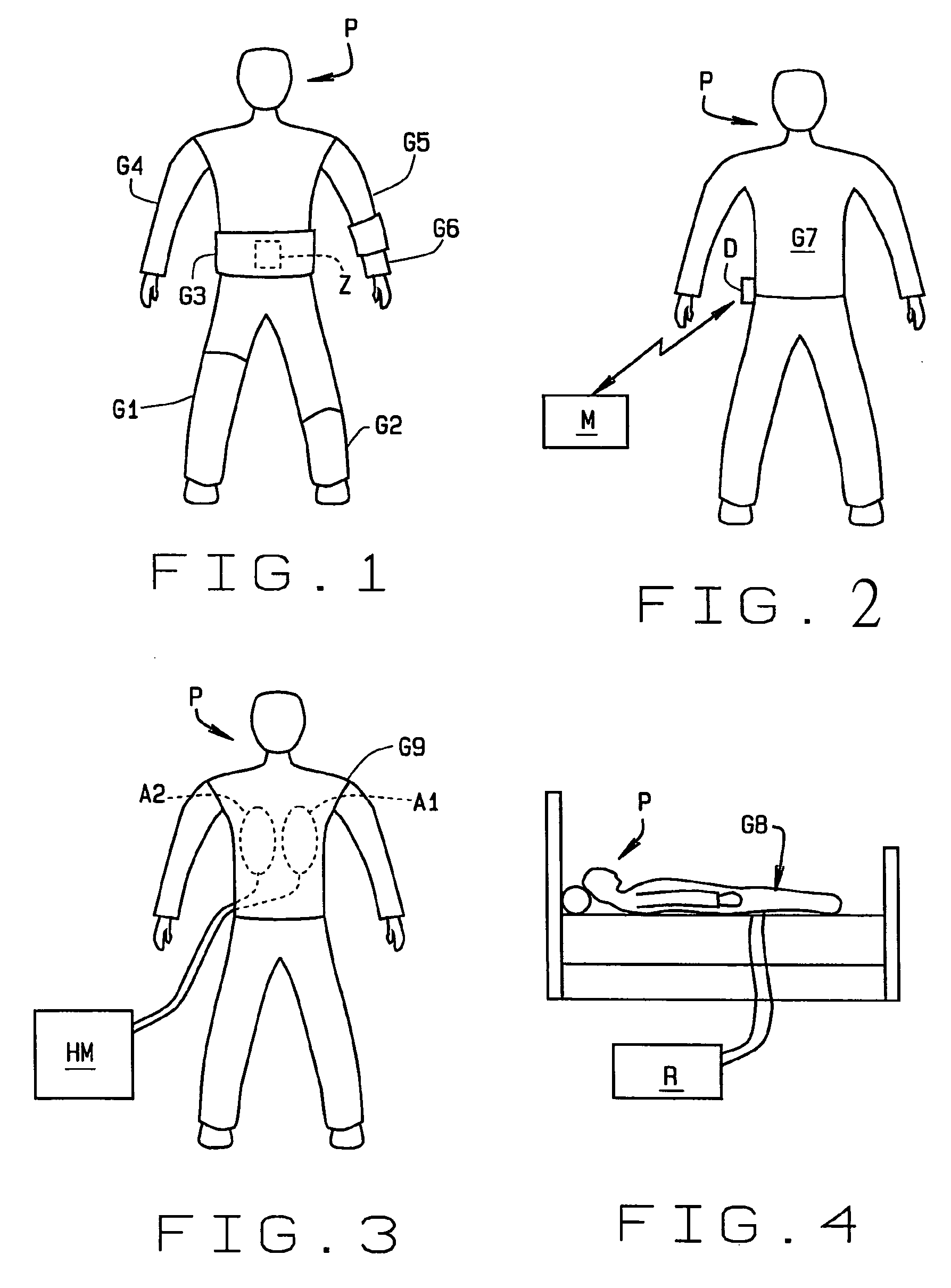
Therapeutic "smart" fabric garment including support hose, body garments, and athletic wear
InactiveUS20060122544A1Facilitate zonal treatmentConveniently beneathElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesPulse rateTreatment level
Athletic and sports wear, and medical or therapeutic garments (G1-G8), all made from a “smart” fabric. The fabric is woven from, or incorporates, one or more components that allows the fabric to change size or shape, project heat or cooling to a part of the wearer's body, to monitor body vital signs such as temperature and pulse rate, etc. The fabric can be used in a garment covering only part of a patient's body, or substantially all of the body. Besides targeting specific areas of a body for treatment, garments made from the fabric facilitate zonal treatments; that is, areas of the body that require therapy but in which certain portions of the area require different levels or intensity of treatment than others. A variety of materials and their various capabilities are disclosed.
Owner:CILUFFO GARY
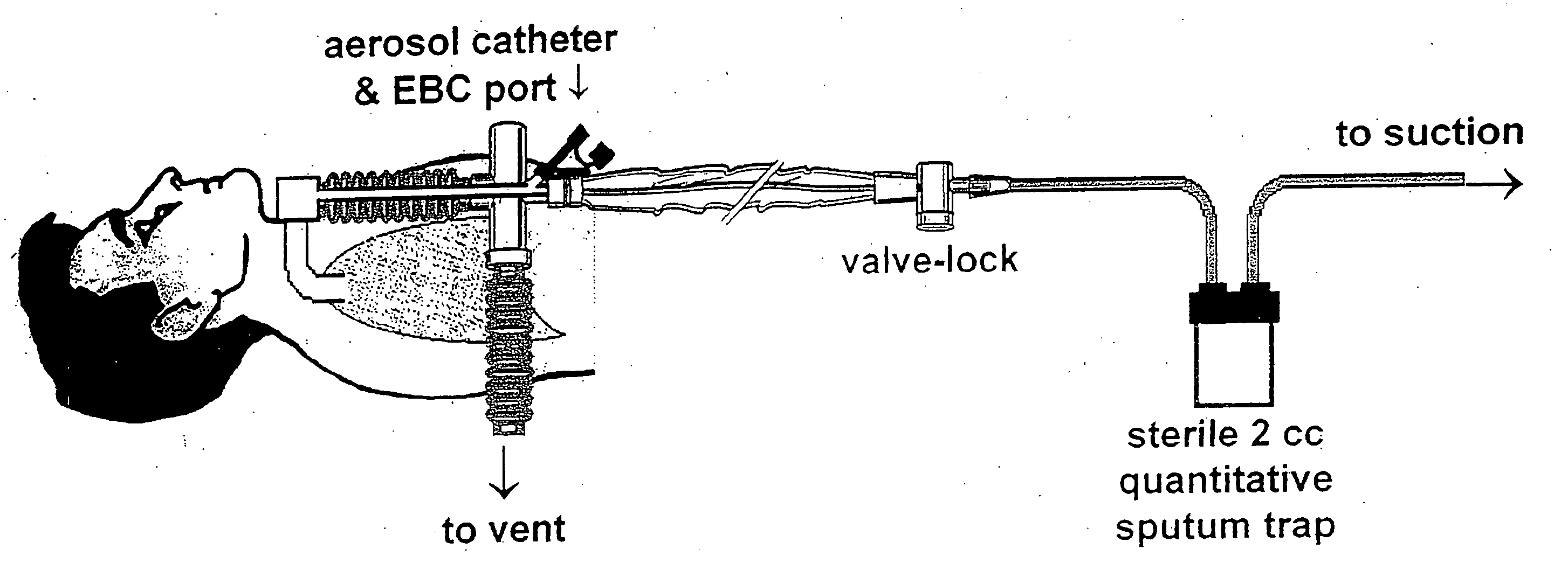
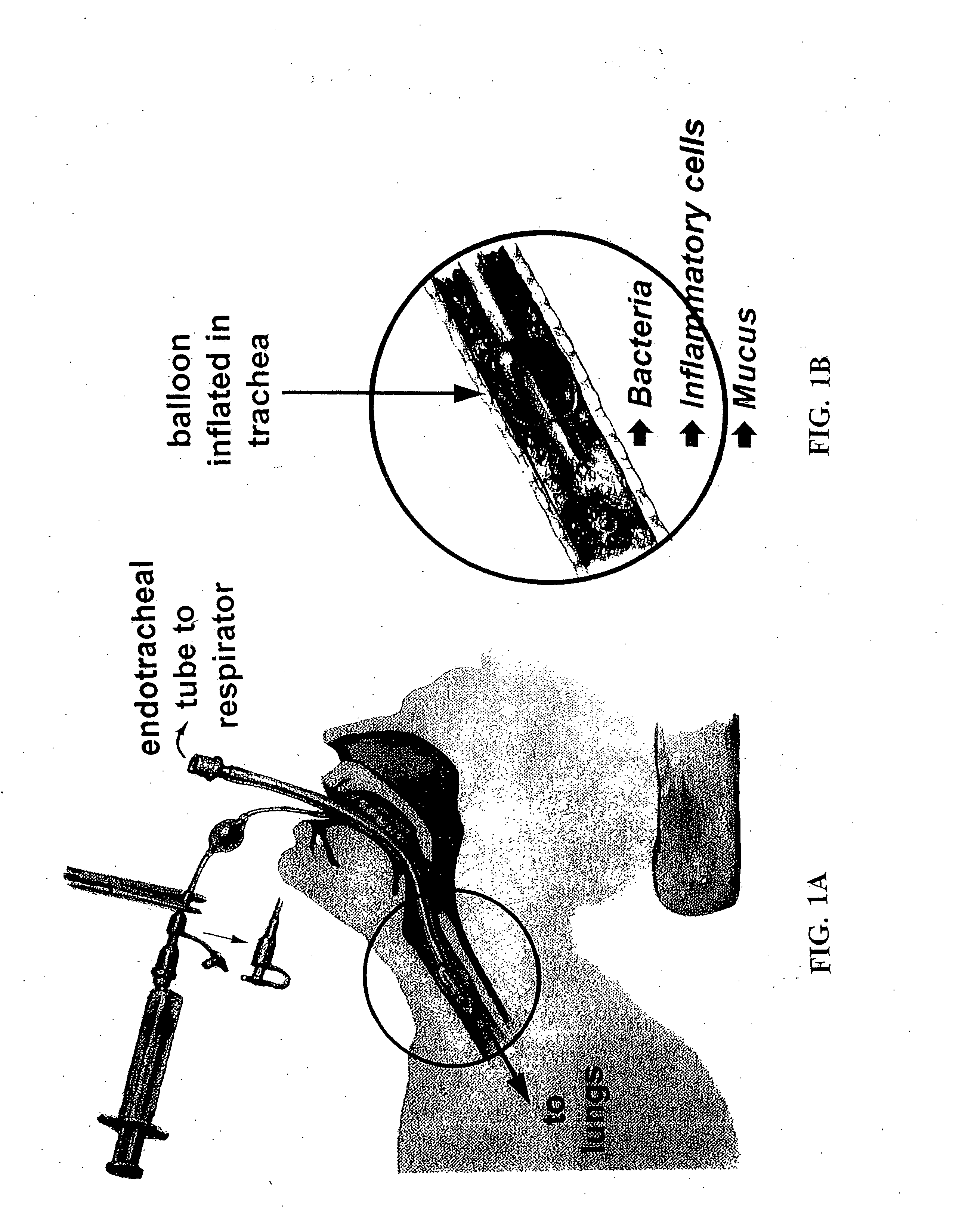
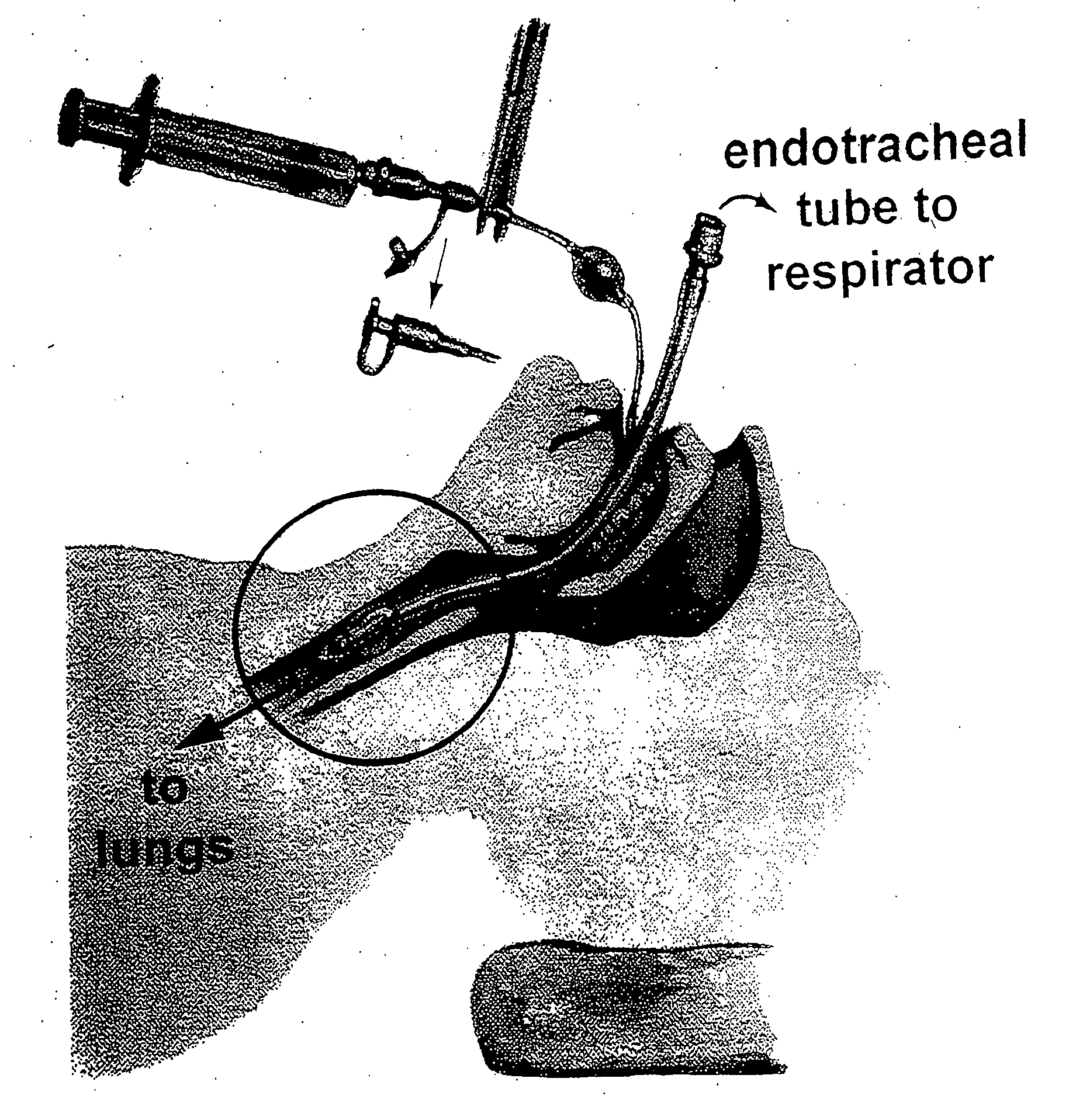
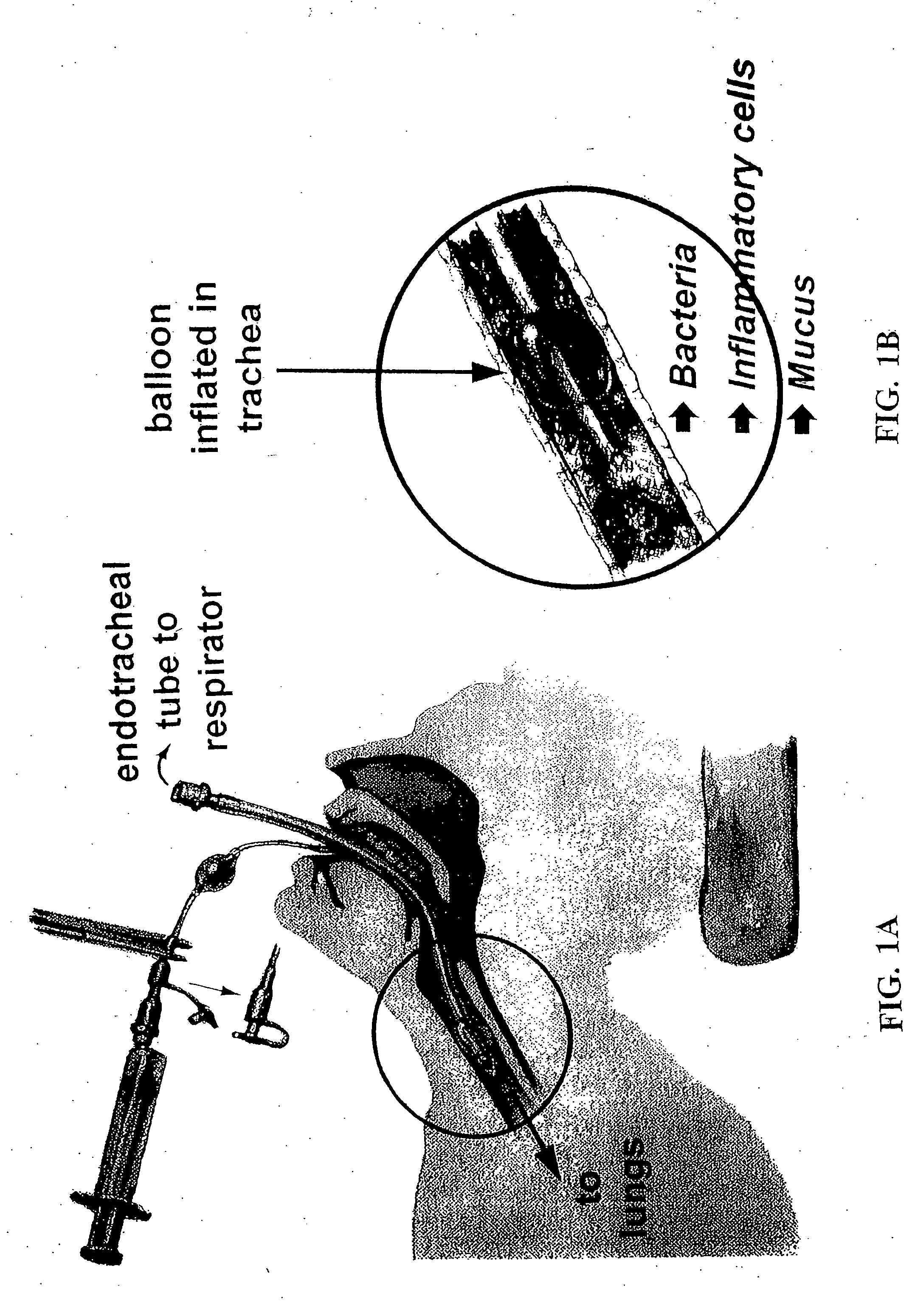
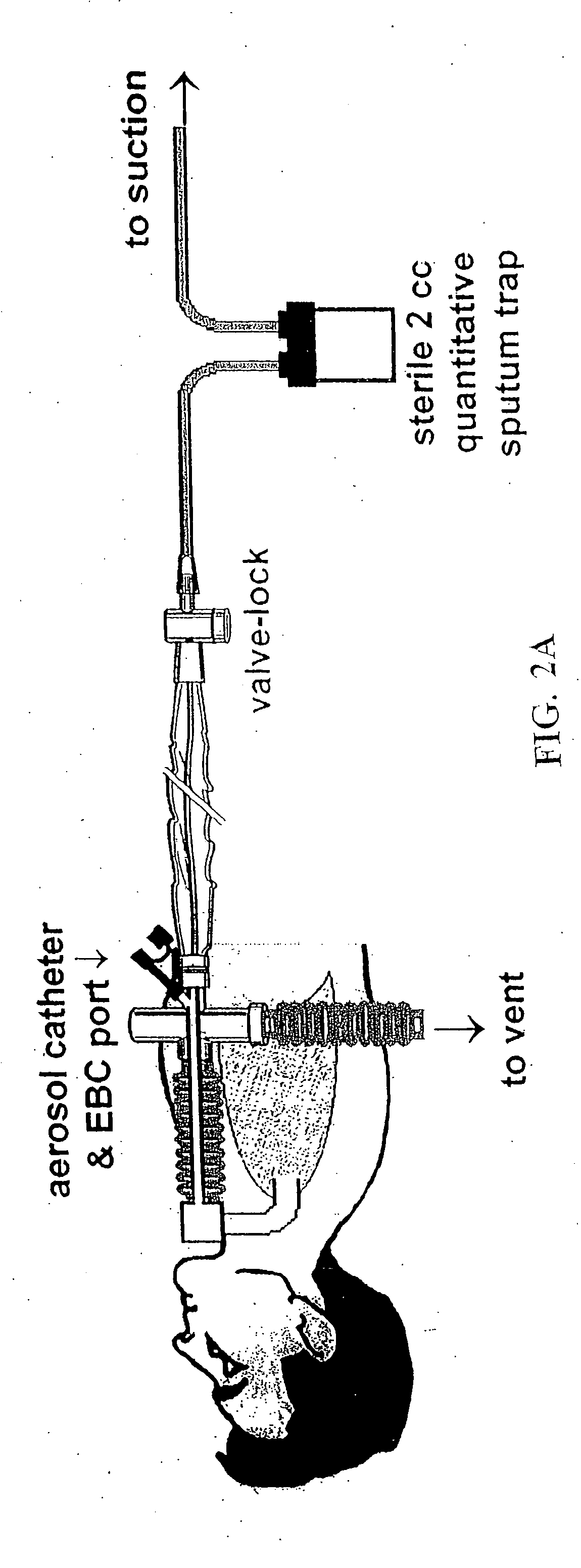
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS20050235987A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsTracheal tubesTracheobronchitisRegimen
The present invention provides an improved means of treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the nosocomial patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airways distal of the ventilator circuit. The treatment means eliminates the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment means also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Glp-1 and methods for treating diabetes
InactiveUS20060057137A1Prevent and treat diseasePrevent and treat and delay onset of and reduce symptomPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
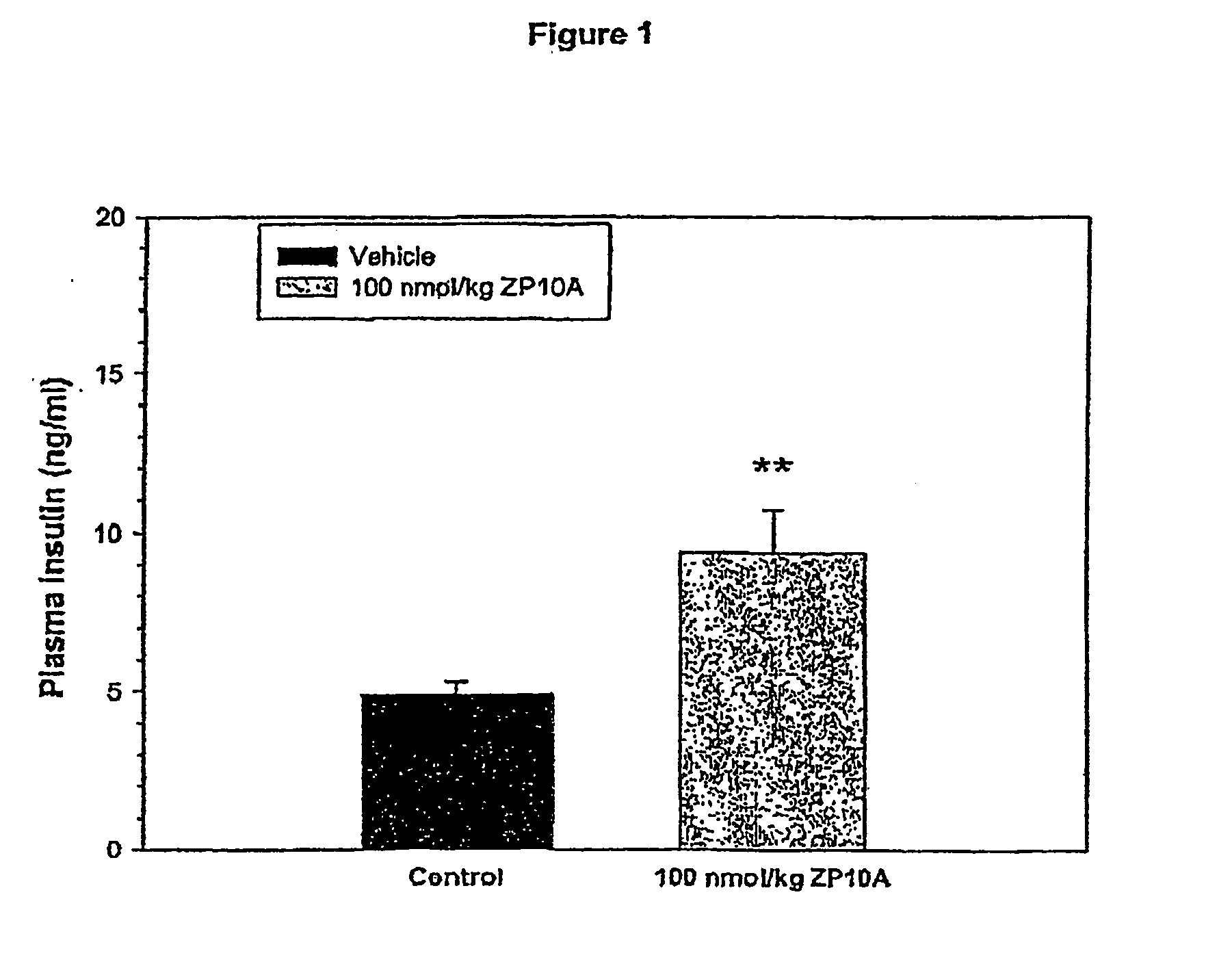
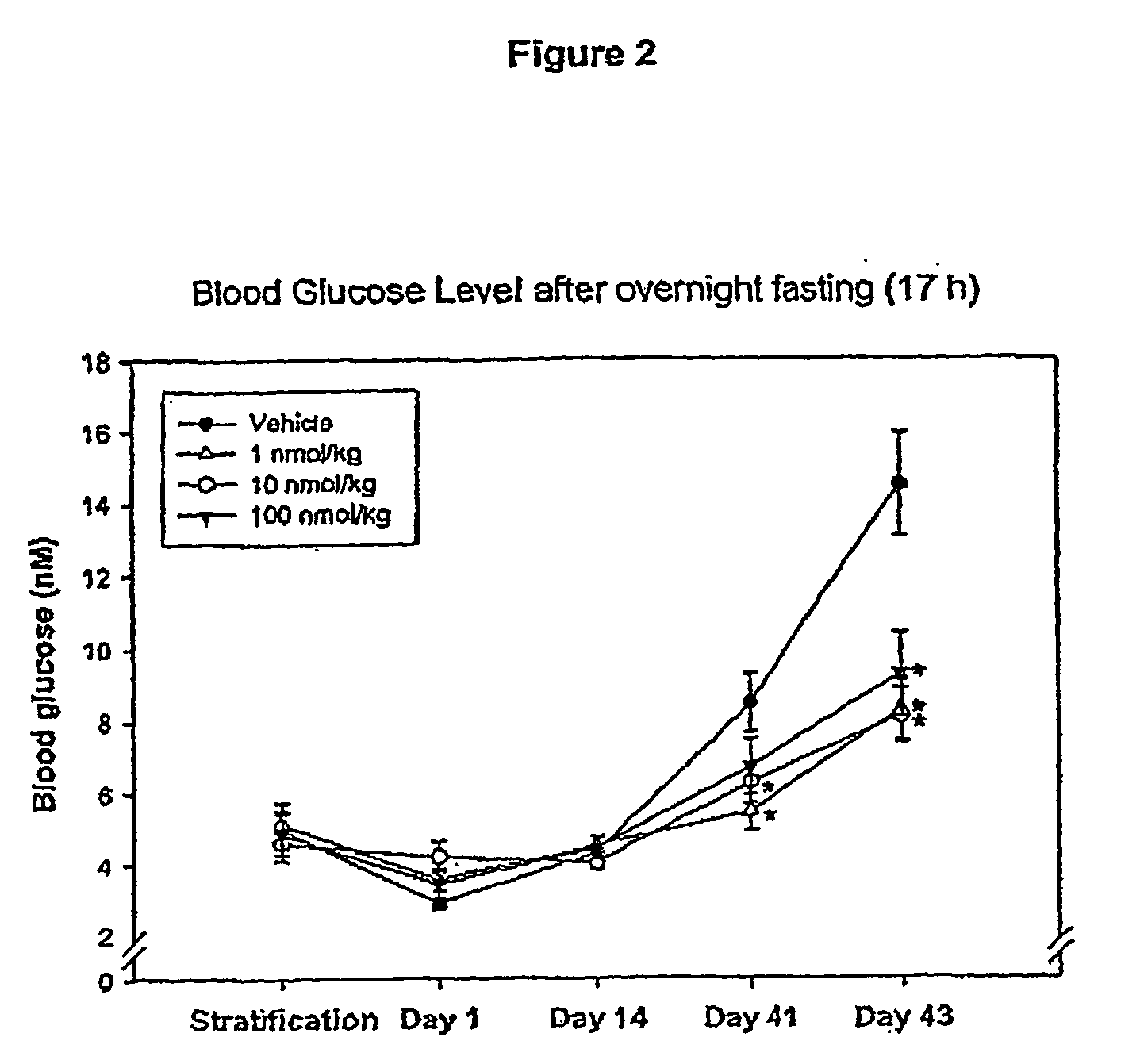
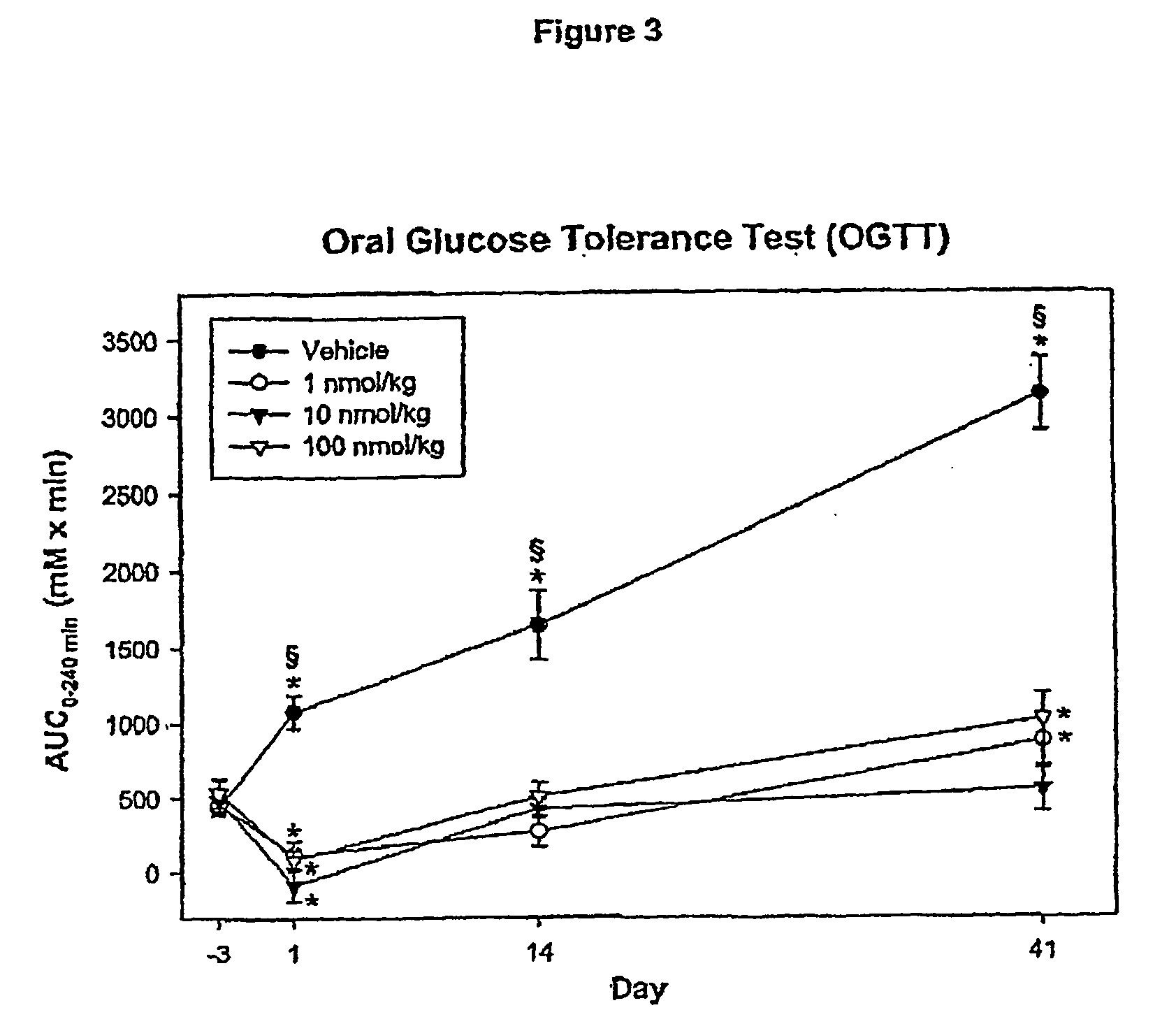
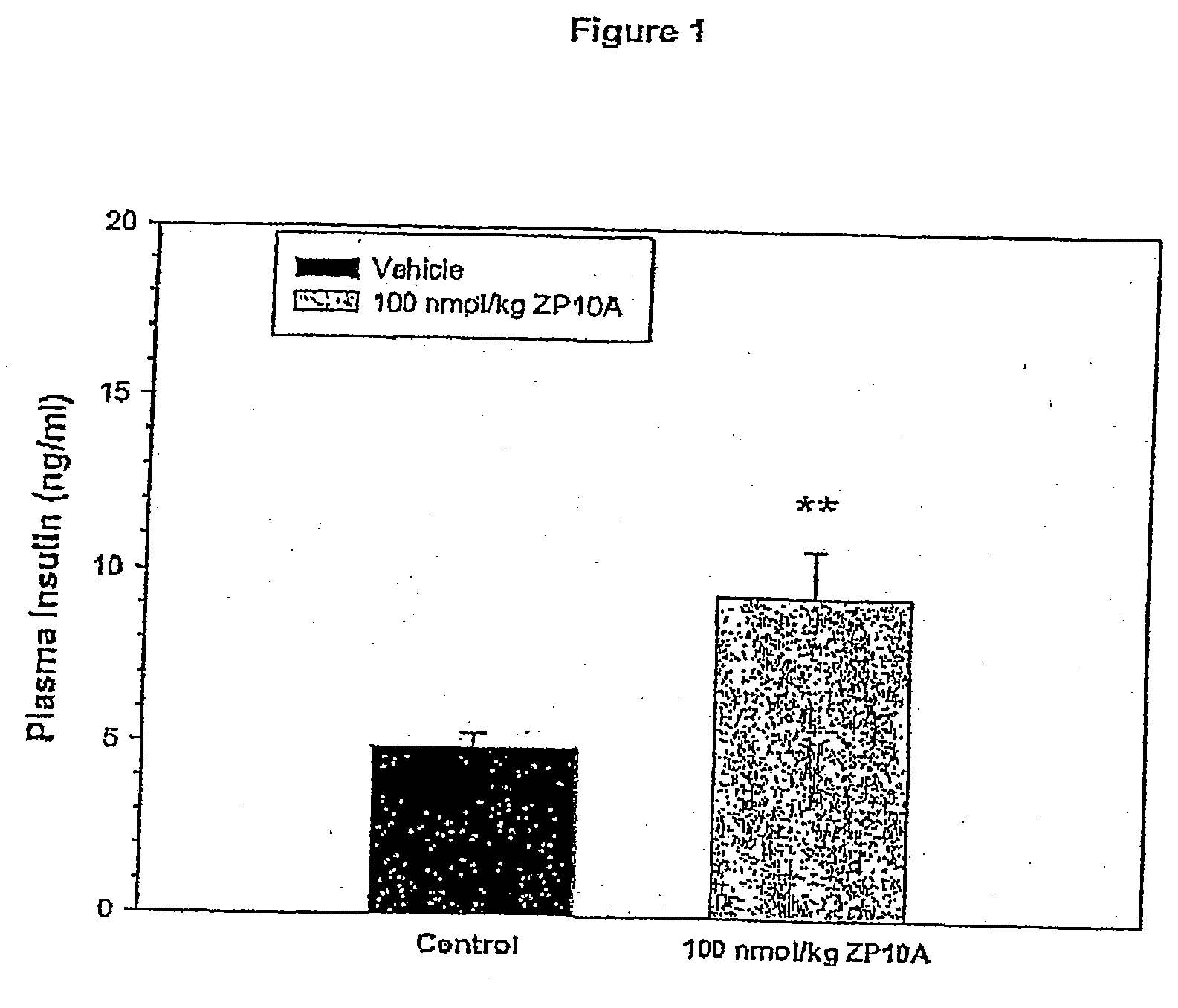
The present invention relates to use of GLP-1 or a related molecule having GLP-effect for the manufacture of a medicament for preventing or treating diabetes in a mammal. The amount and timing of administration of said medicament are subsequently reduced to produce a “drug holiday”. Practice of the invention achieves effective therapy without continuous drug exposure and without continuous presence of therapeutic levels of the drug. The invention also discloses a method of treating diabetes and related disorders in a mammal by administering glucagons like peptide (GLP-1) or a related molecule having GLP-1 like effect and thereby providing a therapeutically effective amount of endogenous insulin.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Glp-1 and methods for treating diabetes
InactiveUS20090088369A1Reduce the amount requiredPrevent and treat diseasePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusTreatment level
The present invention relates to use of GLP-1 or a related molecule having a GLP-effect for the manufacture of a medicament for preventing or treating diabetes in a mammal. The amount and timing of administration of said medicament are subsequently reduced to produce a “drug holiday.” Practice of the invention achieves effective therapy without continuous drug exposure and without continuous presence of therapeutic levels of the drug. The invention also discloses a method of treating diabetes and related disorders in a mammal by administering glucagon like peptide (GLP-1) or a related molecule having GLP-1 like effect and thereby providing a therapeutically effective amount of endogenous insulin.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Apparatus and method for injecting dry bulk amendments for water and soil treatment
InactiveUS20040042335A1Avoid dischargeReduce laborControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFlow mixersSoil treatmentChemical composition
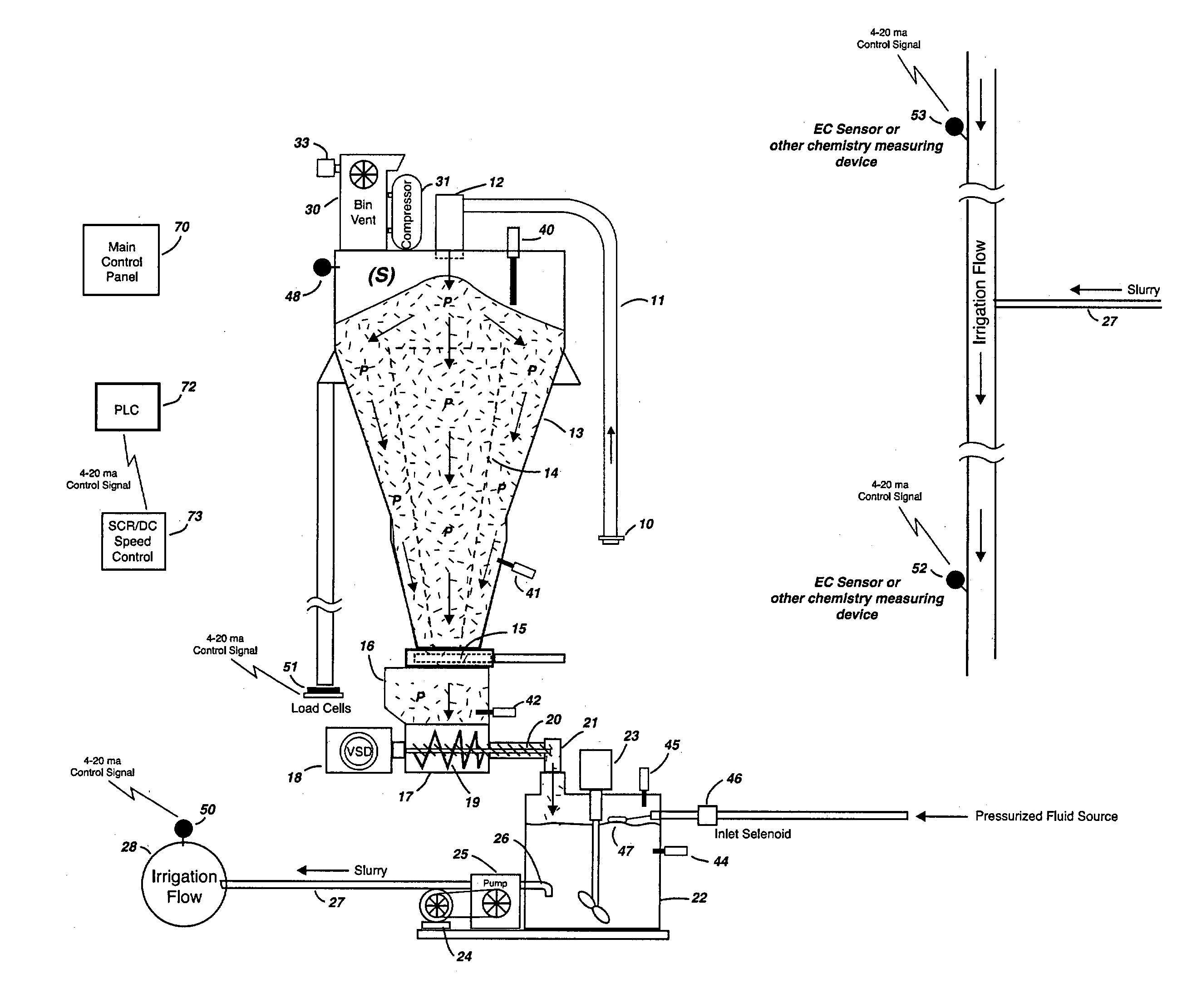
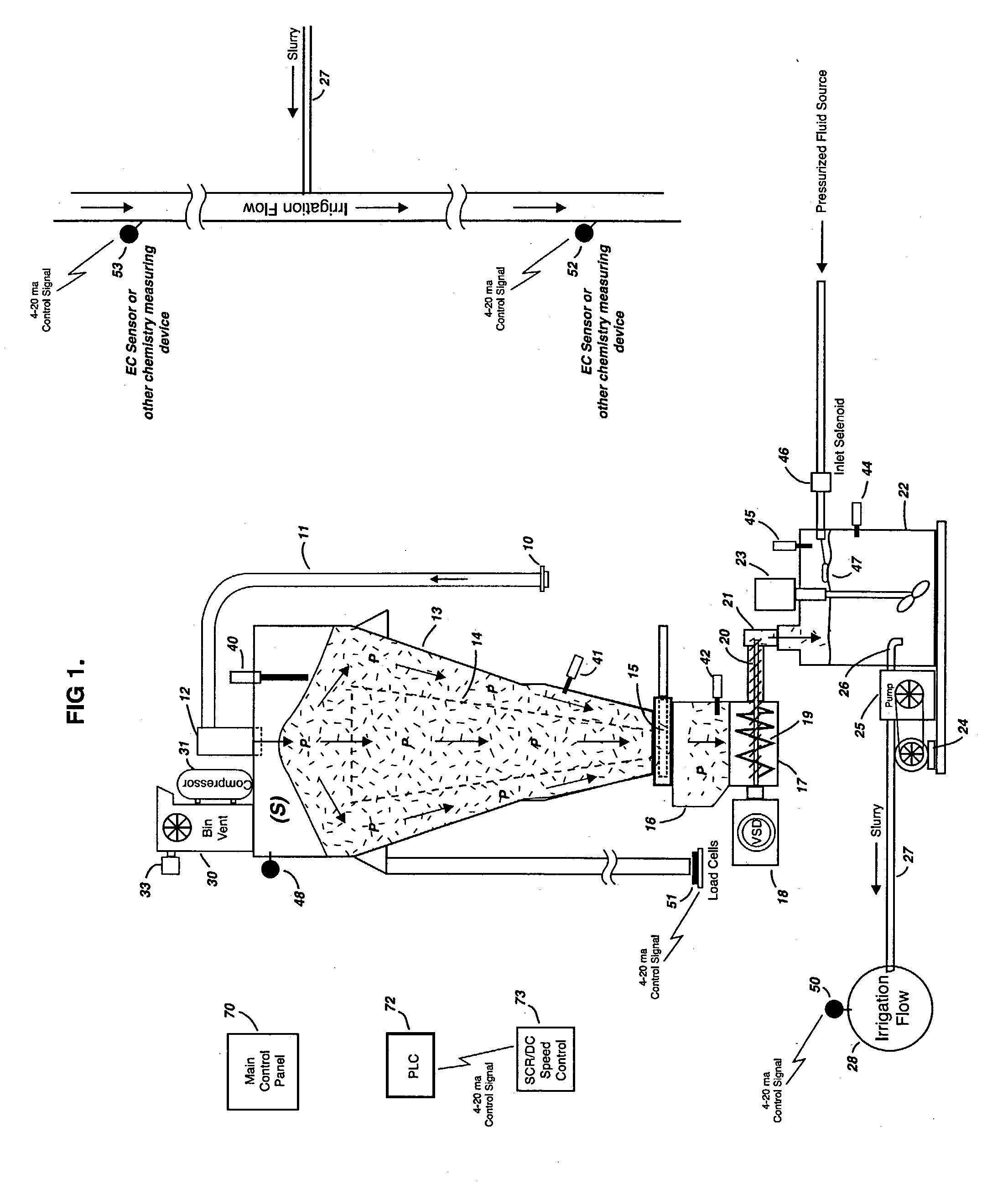
The present invention is an apparatus and method for introducing a dry material into a fluid stream in a way that ensures a predictable, highly accurate and consistent application of the material where the fluid stream may be fixed or variable, where the material is handled and metered in dry bulk form and may be highly soluble or nearly insoluble, and in a manner that continuously and automatically adjusts the application rate to compensate for varying material bulk density, as well as, and in addition to, varying fluid flow rates or chemical composition, in order to provide a precise fluid treatment level at all times. The present invention incorporates the necessary means to store large quantities of the dry process amendment as an integrated and dust-free function of the apparatus and process, and is capable of monitoring and adjusting material levels and introduction rates in real time in response to variations in density, fluid flow rate and / or chemistry composition.
Owner:WASTEWATER SOLUTIONS
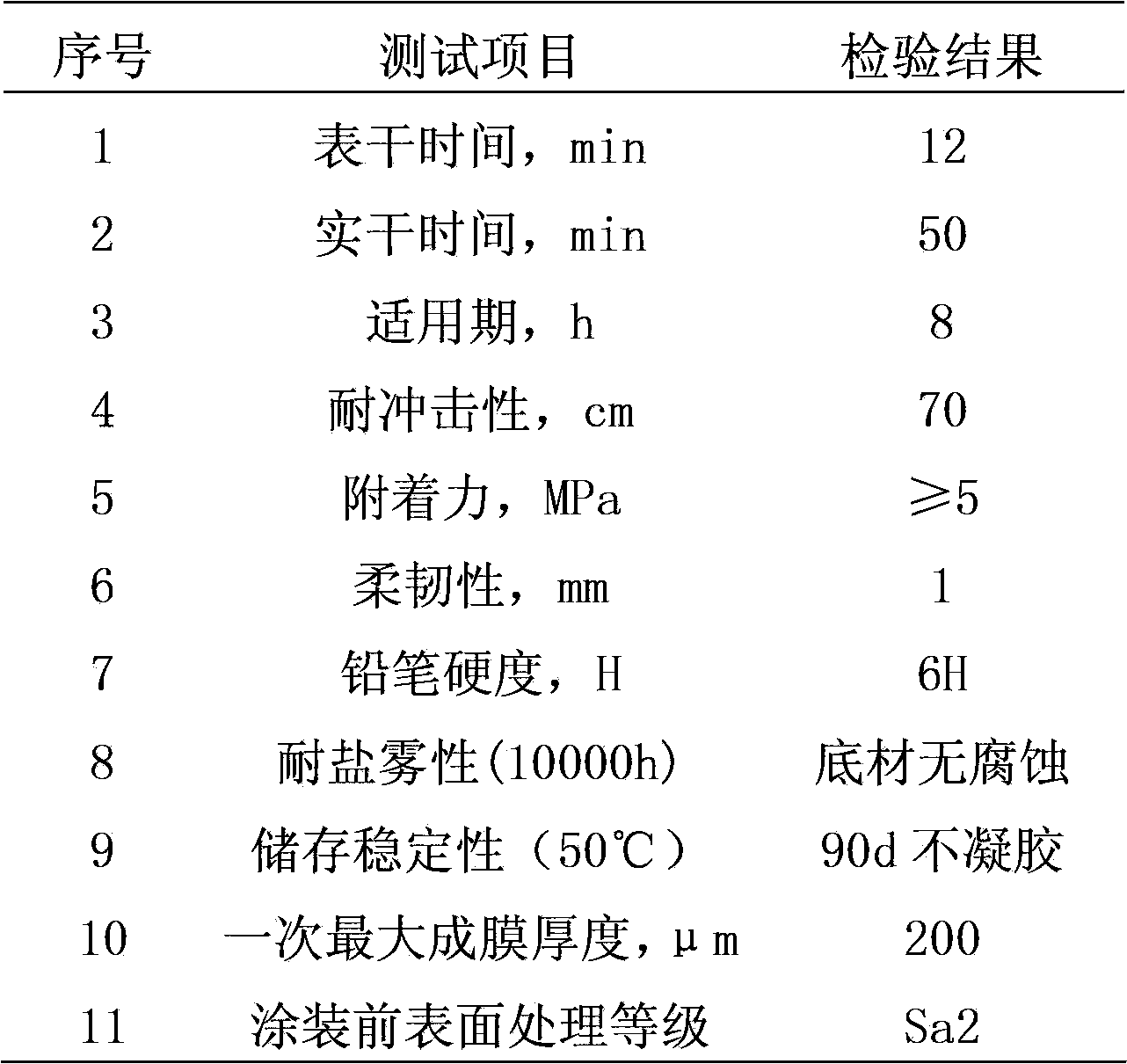
Water-soluble inorganic zinc-rich paint and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103788734AUniform particle size distributionUniform reaction rateAlkali metal silicate coatingsStress concentrationPowder mixture
The invention provides a water-soluble inorganic zinc-rich paint and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dropwise adding aluminum-modified silica sol into potassium silicate solution with low modulus, so as to obtain a high-modulus potassium silicate solution as a binder; and adding a catalyst, a siloxane oligomer and a modifier to ensure that the high-modulus potassium silicate solution are uniform in size distribution, and does not have gelatinization reaction for a long time, wherein after the high-modulus potassium silicate solution and a zinc powder mixture are stirred uniformly, the zinc-rich paint has the advantages that reaction rates of all parts of a coating are uniform, and no stress concentration phenomenon exist. Proved by experiments, the zinc-rich paint provided by the invention has no gel after being stored for 90 days at 50 DEG C, the thickness of a film formed once can reach 200 mu m, no cracking or bubbling phenomenon exists, construction can be carried out after the treatment level of the steel surface reaches Sa2, and the salt fog resistance of the coating can reach 10000 hours.
Owner:CENT RES INST OF BUILDING & CONSTR CO LTD MCC GRP +2
Methods related to the treatment of mucosal associated conditions
InactiveUS20060216333A1Reduce stimulationReduce riskAntibacterial agentsBiocideIrritationTreatment level
Using interrupted delivery of IRMs by intermittently applying an IRM to a mucosal surface it is possible to achieve therapeutic levels and durations of cytokine induction, while substantially reducing irritation side effects.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS20050211253A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsTracheal tubesTracheobronchitisTreatment effect
The present invention provides an improved means of treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the nosocomial patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airnvays distal of the ventilator circuit. The treatment means eliminates the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment means also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Tumor-targeted drug delivery systems and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040258747A1Improved treatment of cancerImprove localizationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTumor targetDelivery vehicle
The present invention relates to targeted delivery systems for delivering therapeutic agents to tumor. The invention further relates to methods of delivering a therapeutic agent to a tumor for the prevention and treatment of cancer by killing tumor cells and tumor-associated endothelial cells. In particular, the present invention provides a tumor-targeted drug delivery system comprising a NGR-containing molecule linked to a delivery vehicle encapsulating a therapeutic agent, preferably a drug, such as a cytotoxic agent or a chemotherapeutic agent. Specifically, the delivery systems of the present invention are capable of delivering an increased amount of therapeutic agent to a tumor as compared to other delivery systems. In particular, the delivery systems of the present invention are capable of accumulating a higher amount of therapeutic agent in a tumor, or in the vicinity of a tumor cell or tumor-supporting cell, resulting in exposure of the tumor cell and tumor-associated endothelial cell to therapeutic levels of the agent for a longer period of time as compared to other delivery systems. The present invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions comprising the delivery systems of the present invention. The present invention further relates to a tumor treatment comprising an increased amount of therapeutic agent delivered by the system of the present invention as compared to other delivery systems. The delivery systems and pharmaceutical compositions can be administered to a subject, preferably a human, alone or in combination, sequentially or simultaneously, with other prophylactic or therapeutic agents and / or anti-cancer treatments.
Owner:OSPEDALE SAN RAFFAELE SRL +2
Composition for transdermal and/or transmucosal administration of active compounds that ensures adequate therapeutic levels
InactiveUS7214381B2Easy to usePromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsGogglesActive agentTreatment level
The present invention refers to a pharmaceutical composition suitable for the transdermal or transmucosal administration of one or more active agents, in form of a gel or a solution, comprising as a permeation enhancers a combination of: a) saturated fatty alcohol of formula CH3—(CH2)n—CH2OH or saturated fatty acid CH3—(CH2)n—CH2COOH wherein n is an integer number 8÷22, preferably 8÷12, most preferably 10, or unsaturated fatty alcohol or fatty acid of formula: CH3(CnH2(n-1))—OH or CH3(CnH2(n-1))—COOH wherein n is an integer number 8÷22, b) a ternary vehicle or carrier consisting of a C1÷C4 alkanol, a polyalcohol in particular propylenglycol and water, c) optionally also a monoalkylether of diethylenglycol.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA IPL
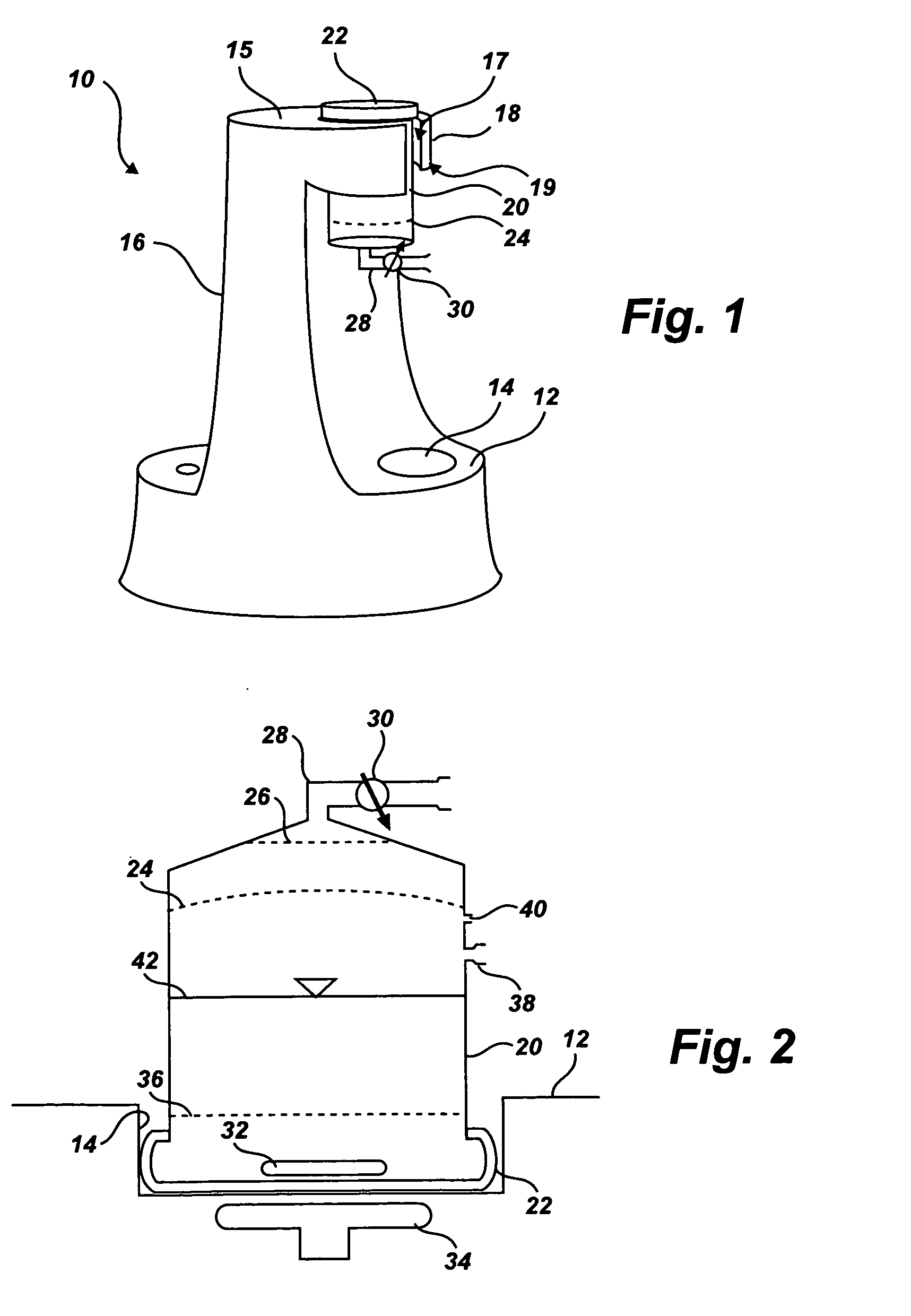
Devices and methods for non-invasive ventilation therapy
PendingUS20160367186A1Physical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTreatment levelNon invasive
Non-invasive ventilation therapy systems and methods are disclosed. The system comprises a ventilation device, a computing device coupled to the ventilation device, and a plurality of sensors for acquiring a physiological bioelectrical impedance signal from a patient, wherein the sensors are functionally connected to the computing device. The computing device receives the physiological bioelectrical impedance signal from the sensors, analyzes the physiological bioelectrical impedance signal, and, based on the analyzed physiological bioelectrical impedance signal, transmits a signal to the ventilation device to adjust therapy levels.
Owner:RESPIRATORY MOTION
Synergistic effects of amlodipine and atorvastatin metabolite as a basis for combination therapy
The combination of amlodipine with atorvastatin metabolite shows a synergistic antioxidant effect on lipid peroxidation in human low-density lipoproteins and membrane vesicles enriched with polyunsaturated fatty acids. Inhibition of oxy-radical damage by this drug combination was observed at therapeutic levels in a manner that could not be reproduced by the combination of amlodipine with other statins or the natural antioxidant, vitamin E. The basis for this potent activity is attributed to the chemical structures of these compounds and their molecular interactions with phospholipid molecules, as determined by x-ray diffraction analyses. This combination therapy can be used to treat cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary artery disease, by increasing the resistance of low-density lipoproteins and vascular cell membranes against oxidative modification.
Owner:MASON R PRESTON
Topical gels compositions
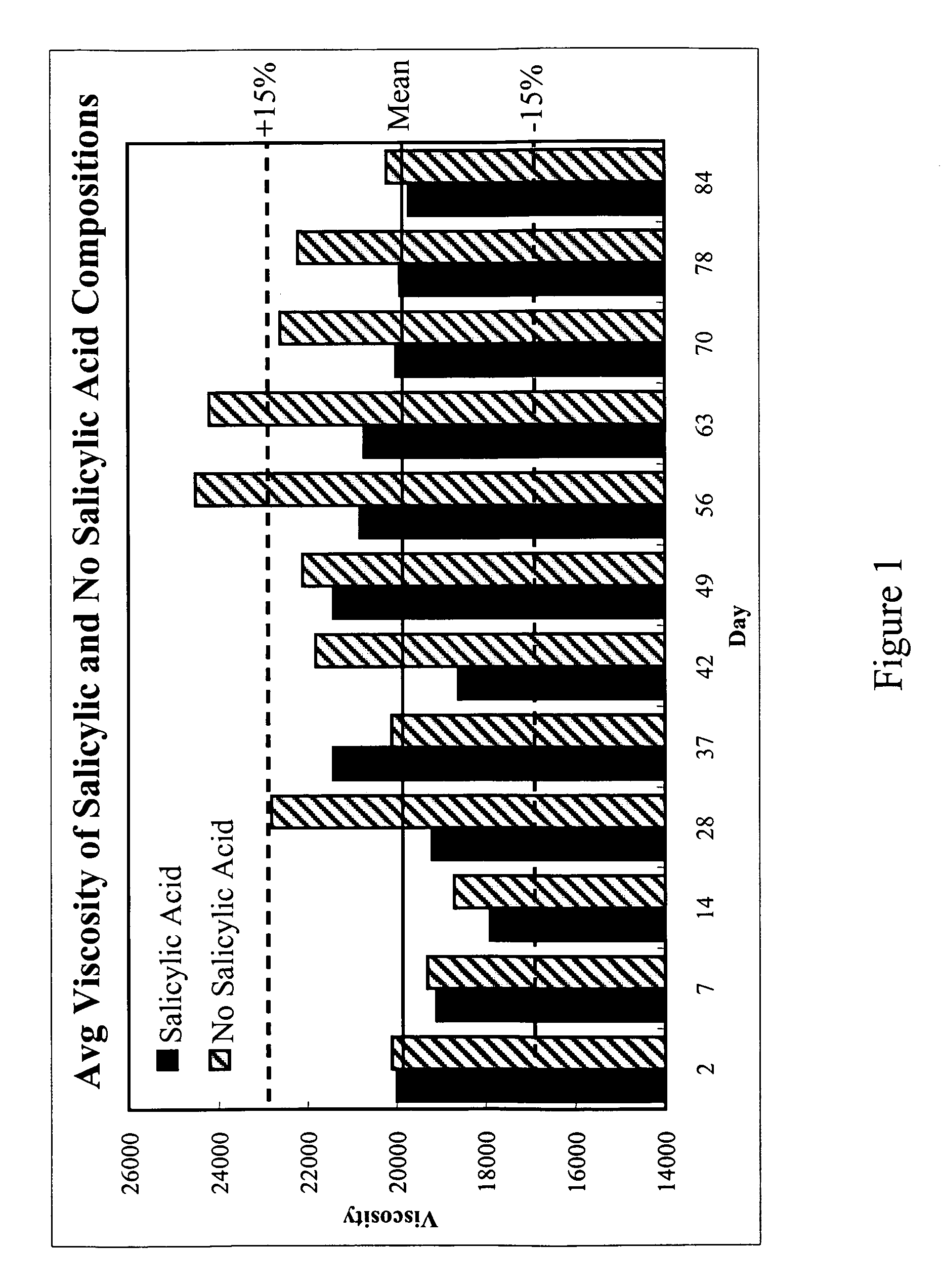
Topical alcoholic gel compositions are disclosed that are useful for delivering therapeutic levels of an NSAID to target in and below the skin. The compositions comprise a topically active drug, an alcoholic solvent, a polymeric thickener, and optionally a keratolytic agent. In one embodiment, excellent viscosity for dermal application is attained without the need of a step for neutralizing the pH of the composition. Alcoholic and alcohol-free topical compositions comprising an NSAID prodrug are also disclosed. The compositions are particularly useful for the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae.
Owner:SPANN WADE MONIQUE +1
Stimulation of a hypoglossal nerve for controlling the position of a patient's tongue
ActiveUS9308370B2Reduce signalingElectrical signal appliedSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineTreatment level
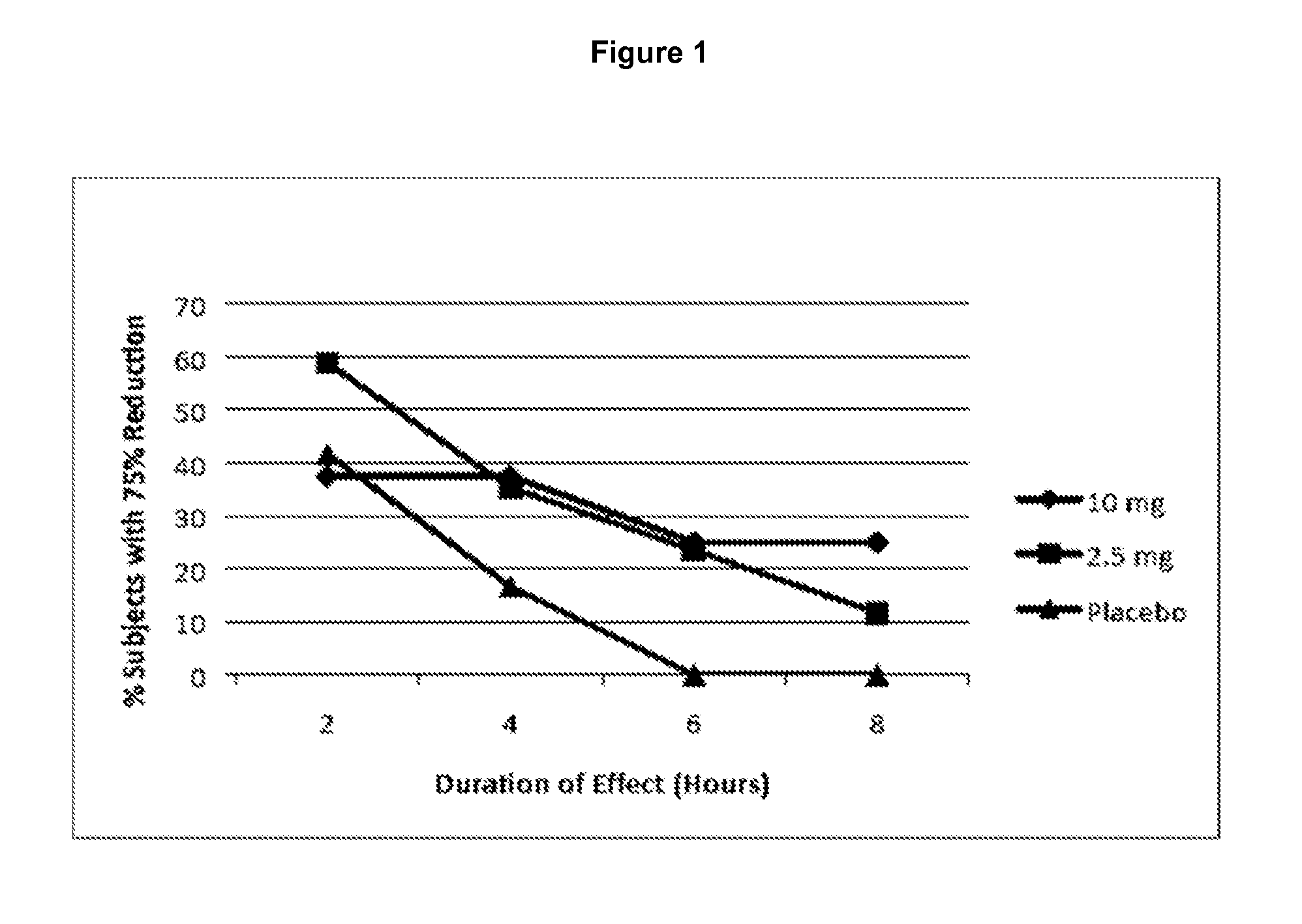
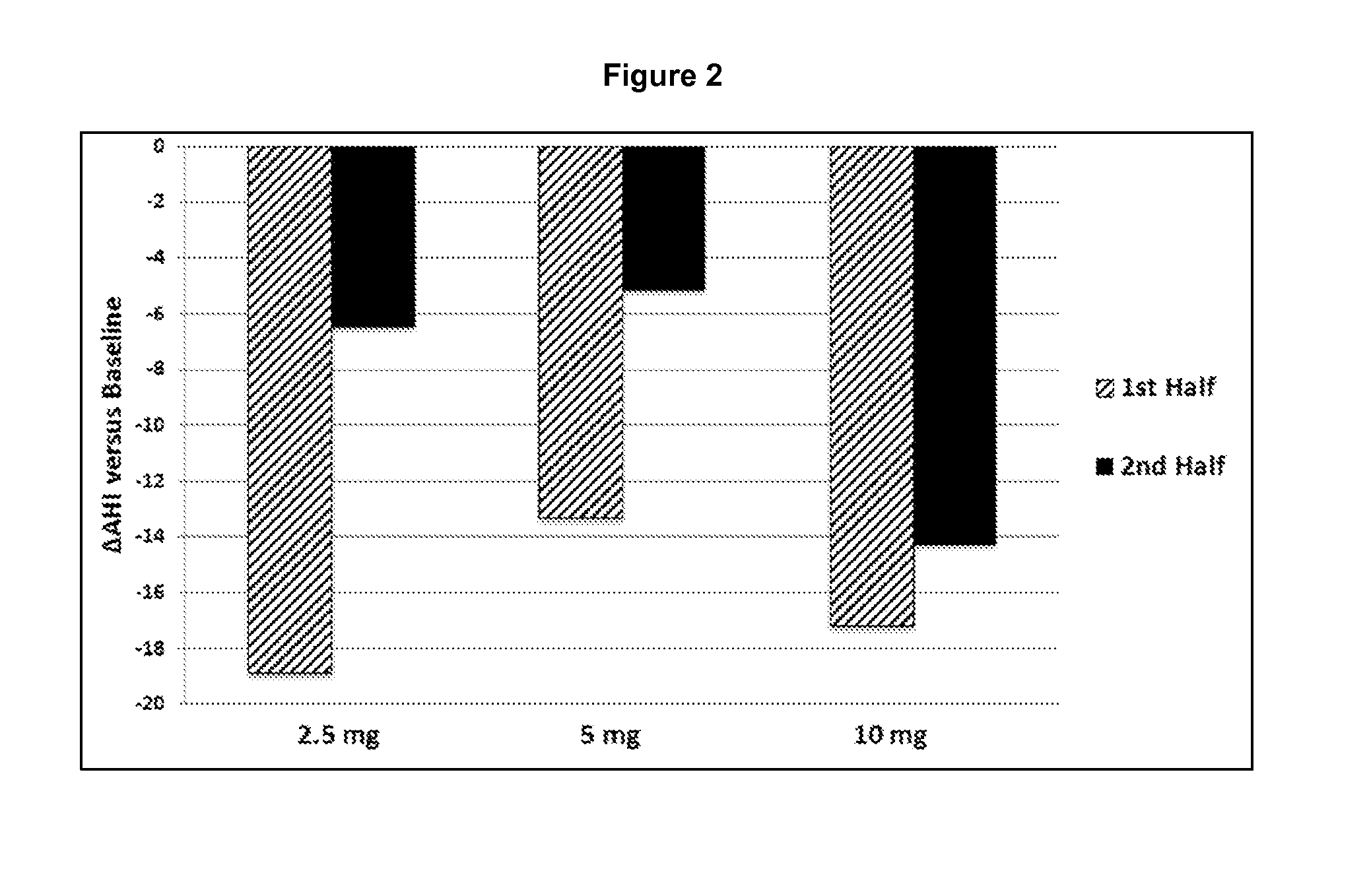
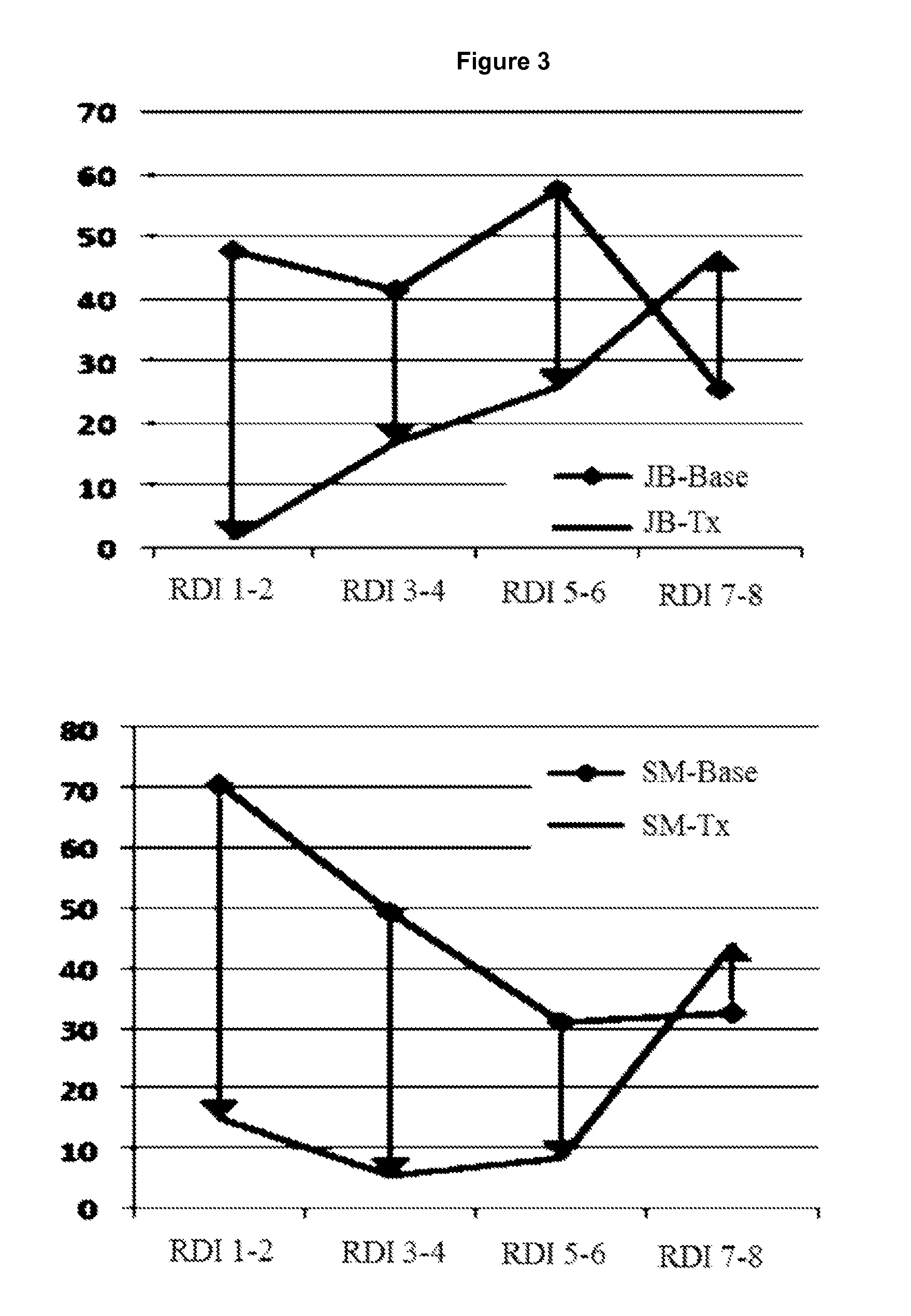
A method for controlling a position of a patient's tongue includes attaching at least one electrode to the patient's hypoglossal nerve, applying an electric signal through the electrode to the hypoglossal nerve to stimulate at least one muscle of the tongue at least until the number of obstructive sleep apnea occurrences are reduced from an initial level to a treatment level, and reducing the application of the electric signal while the number of obstructive sleep apnea occurrences remain generally at or below the treatment level.
Owner:IMTHERA MEDICAL
Topical Compositions
InactiveUS20080317684A1Maintain good propertiesAntibacterial agentsBiocidePolyethylene glycolEthanol
Topical compositions are disclosed that are useful for delivering a therapeutic level of an NSAID to a target within a subject having a local inflammatory disorder. A composition of the present invention comprises a Drug and a solvent system, wherein the solvent system comprises at least two solvent alcohols and wherein the solvent system is present in an amount sufficient to solubilize the Drug, the solvent system is a low alkanol system, and the composition is a single phase composition. Exemplary solvent systems are those for which one of the at least two solvent alcohols is polyethylene glycol, glycerin, butylene glycol, dipropylene glycol, propylene glycol, ethanol, isopropanol, or a derivative thereof. Optionally the local inflammatory disorder is pseudofolliculitis barbae, dermatitis, psoriasis, wounds, or sunburn.
Owner:ISW GRP INC
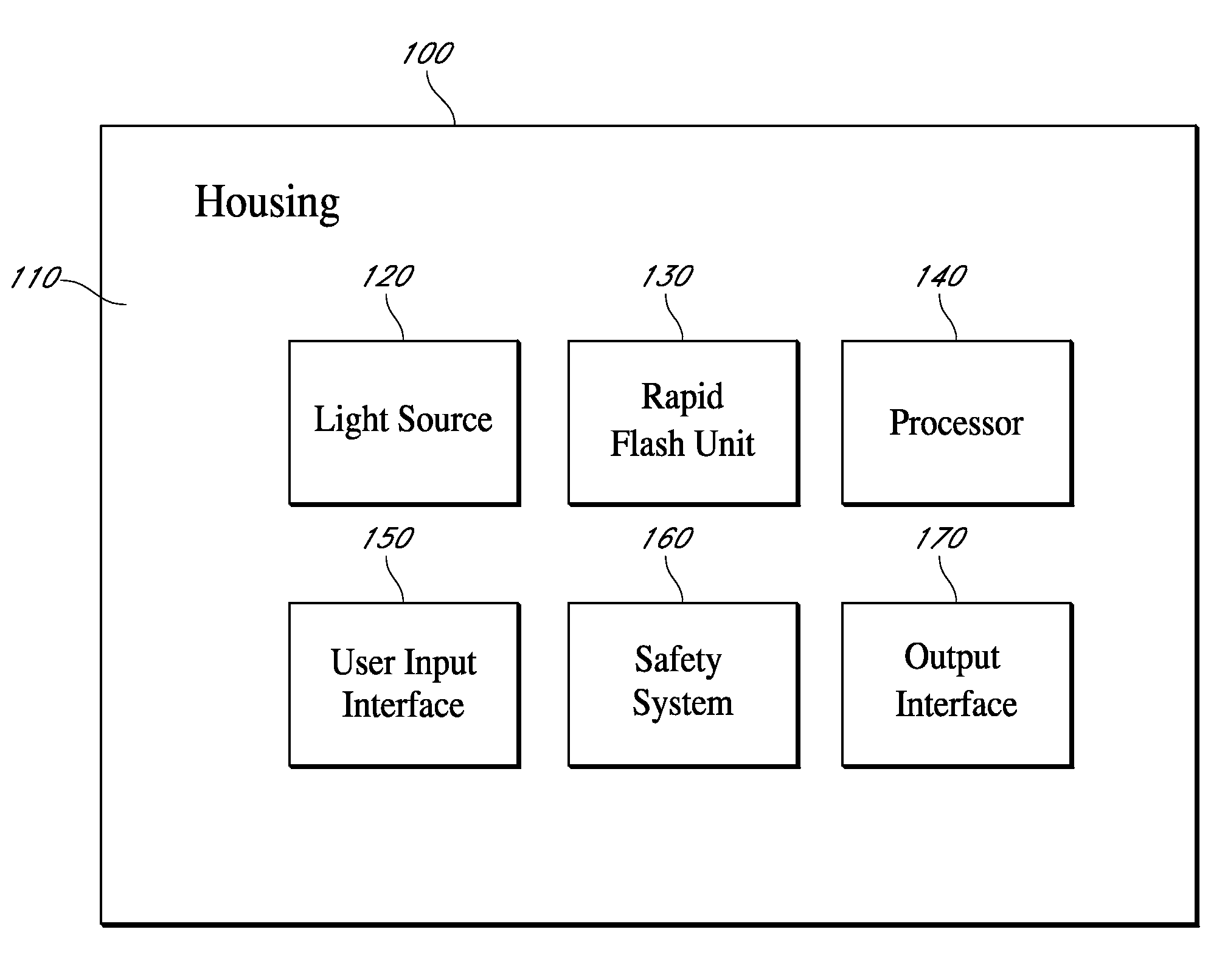
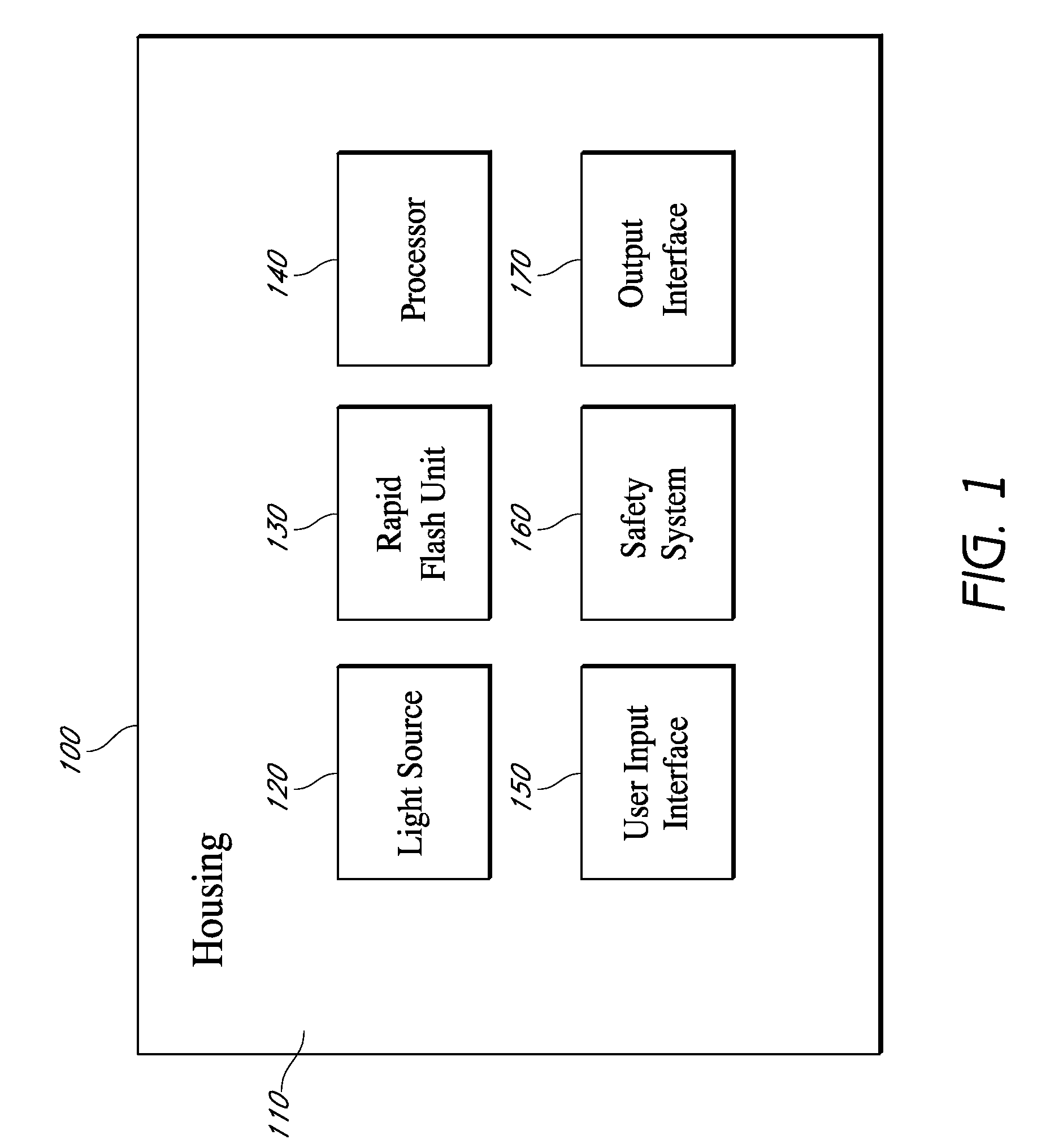
Rapid flash optical therapy
Systems and methods are disclosed for maintaining a therapeutically significant level of energy at a treatment area that can include rapid charging of a storage element and triggering of a flashlamp by discharging the storage element and repeating the charging and triggering a predetermined number of times during a treatment period to raise and maintain a temperature at the treatment area to a predetermined therapeutic level.
Owner:CLRS TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com