Patents
Literature
61results about How to "Low ability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
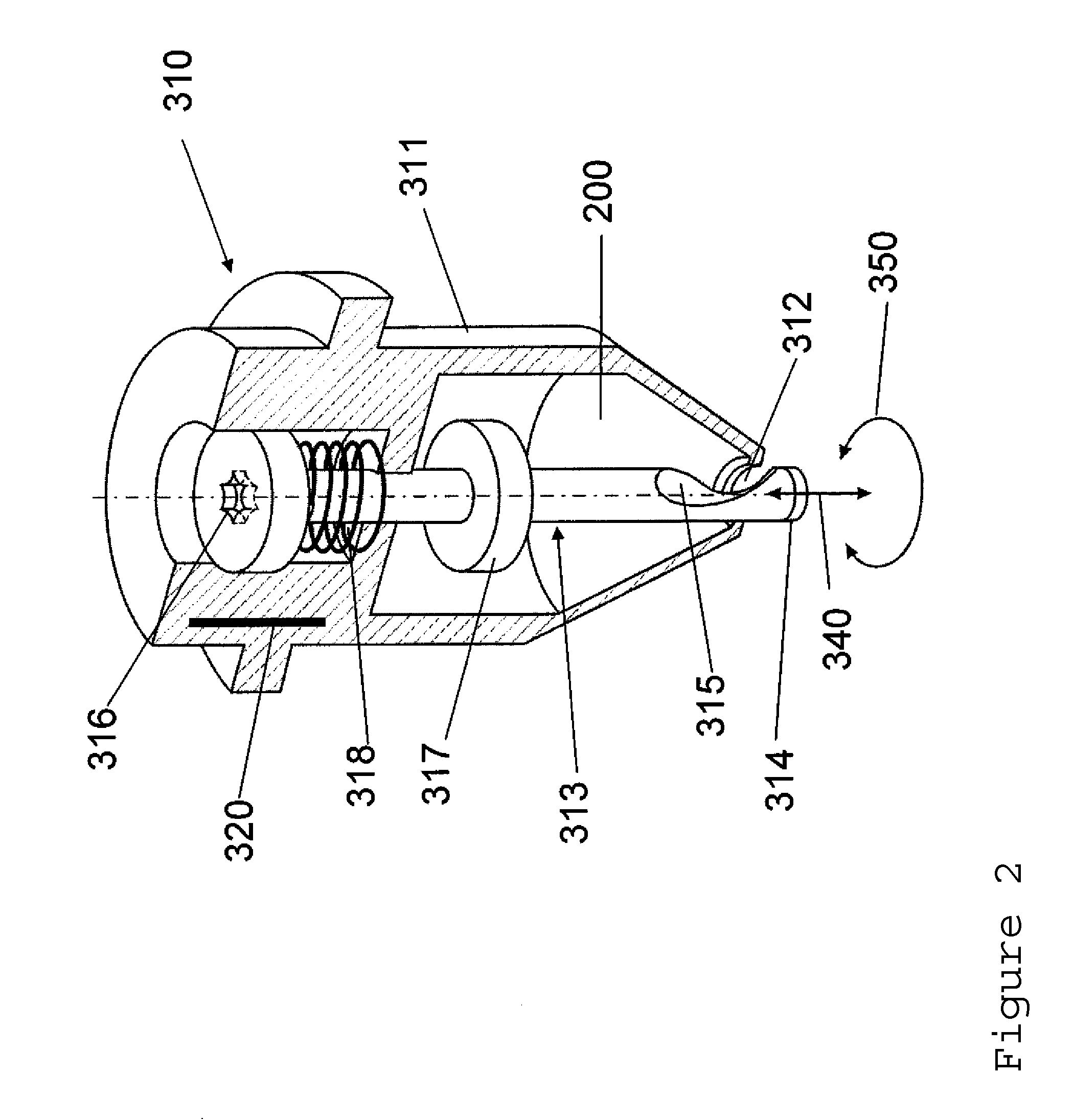
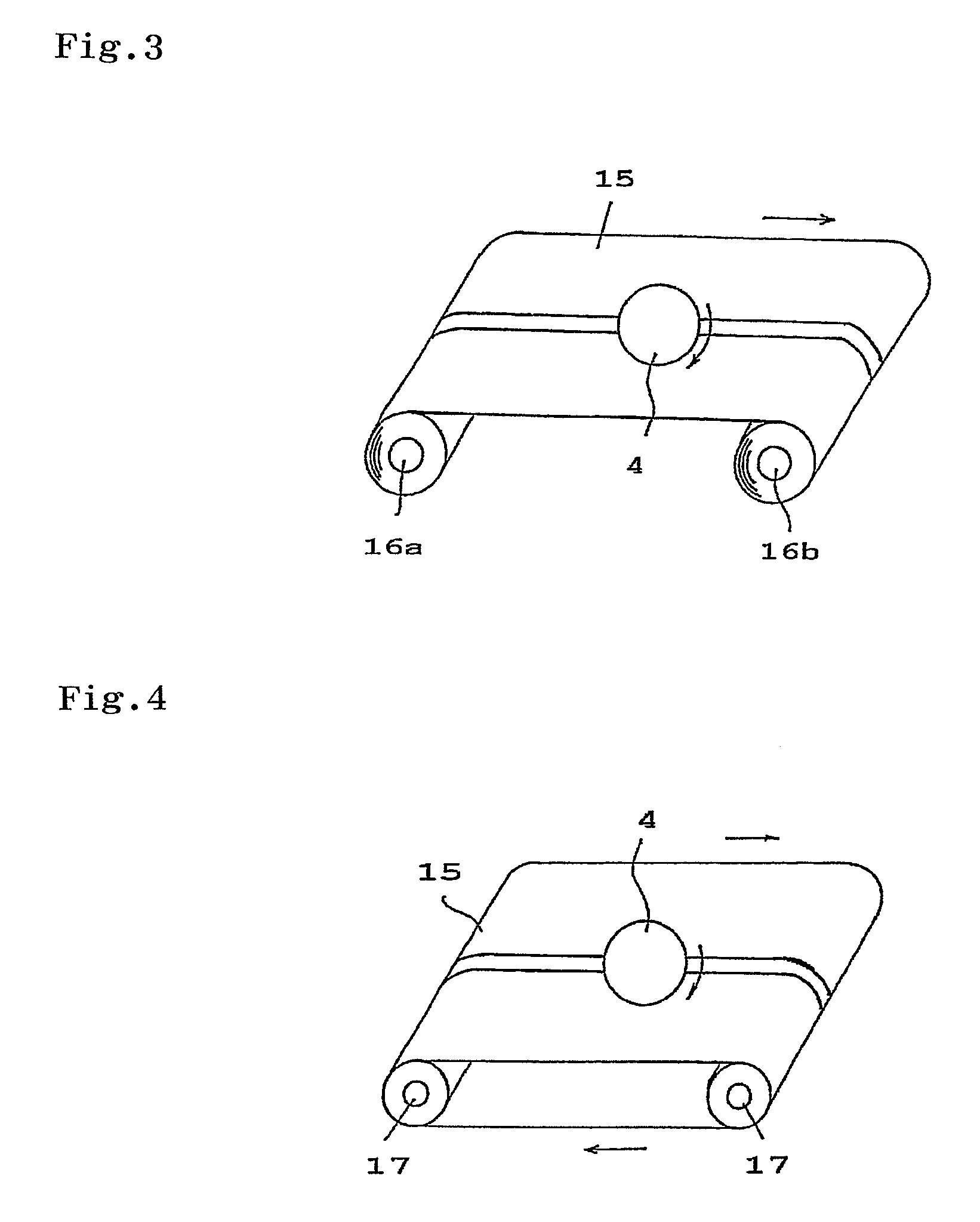
Apparatus and method for allowing user to track path of travel over extended period of time
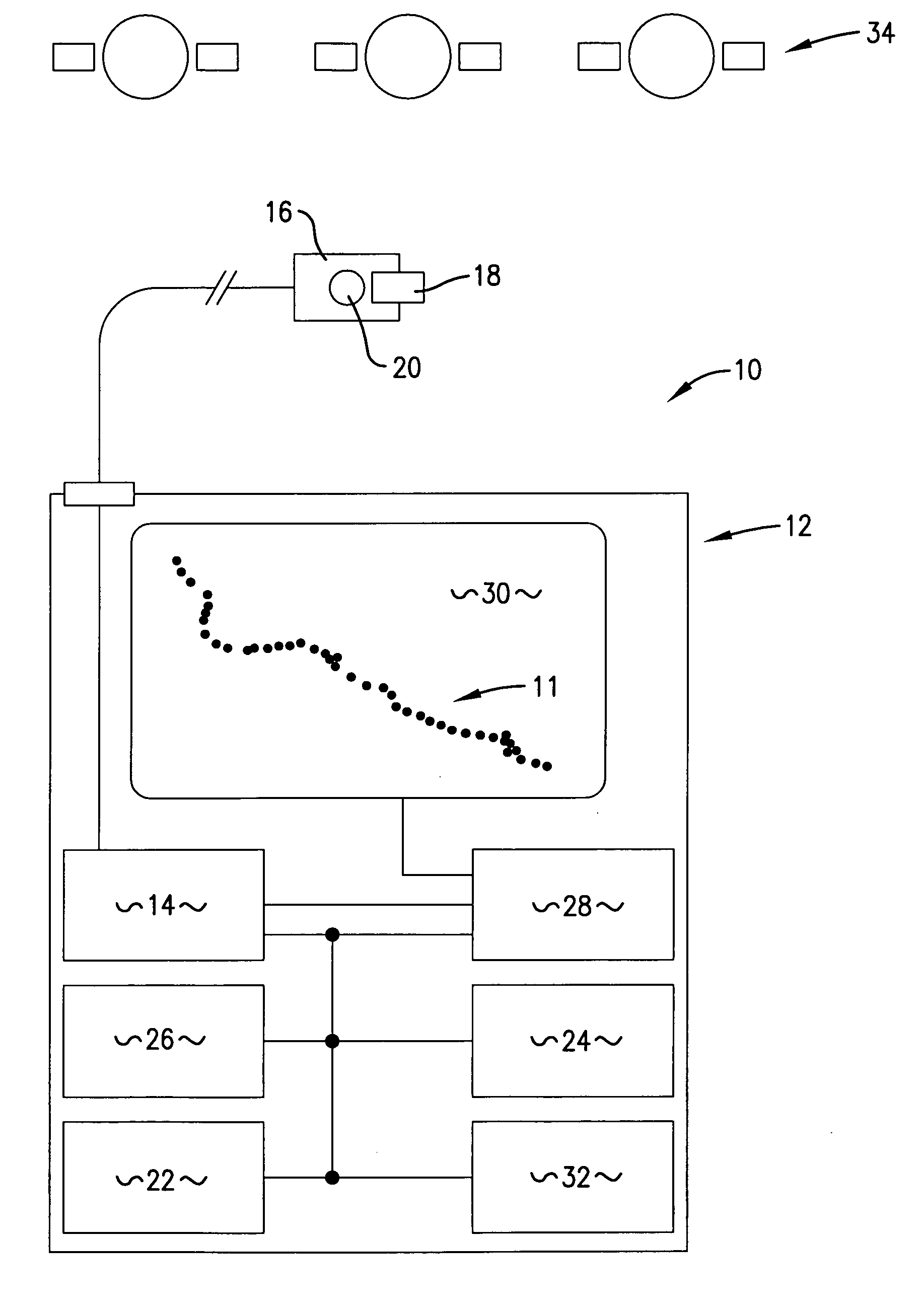
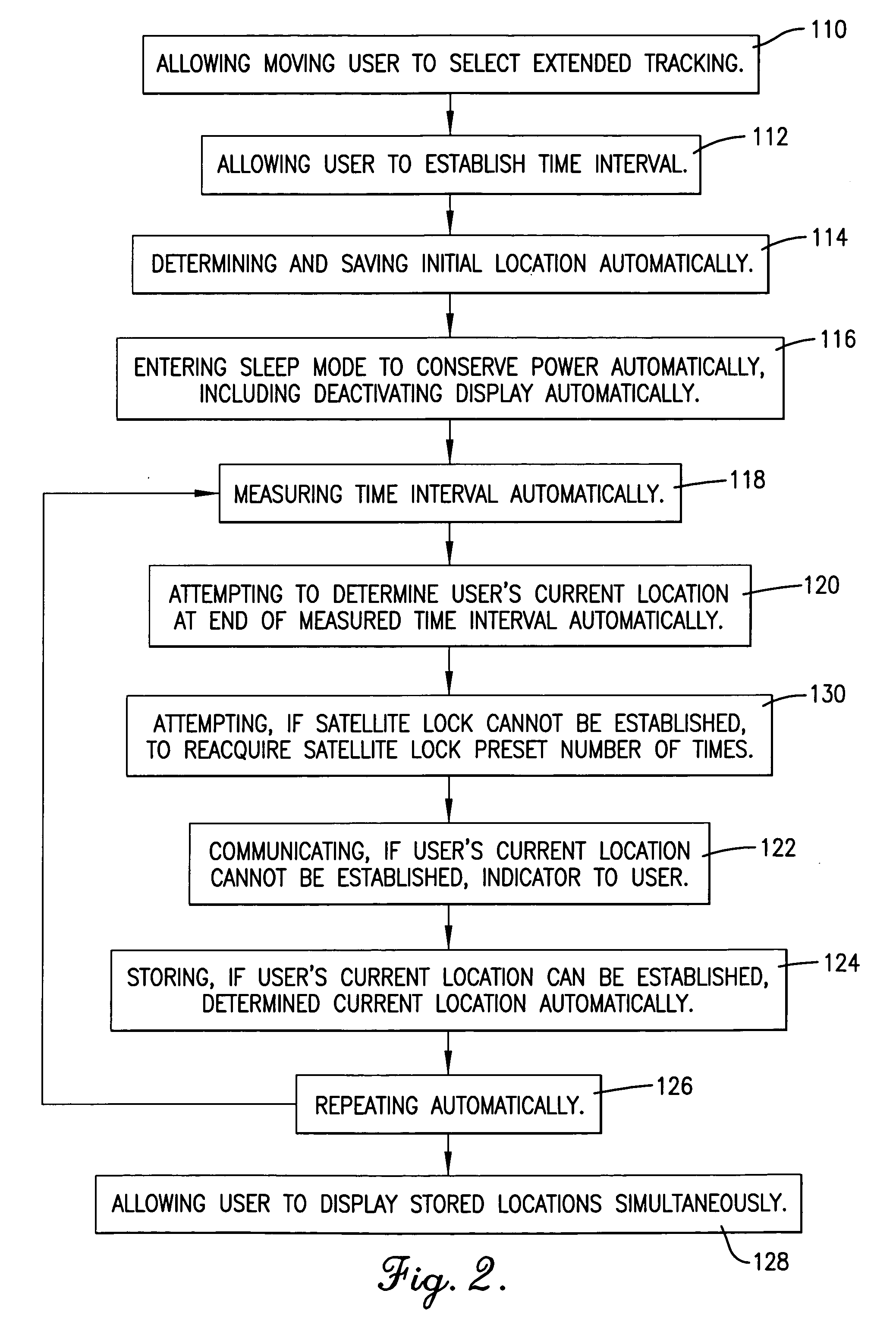
ActiveUS7123189B2Easy to receiveLow abilityEnergy efficient ICTInstruments for road network navigationEngineeringTimer
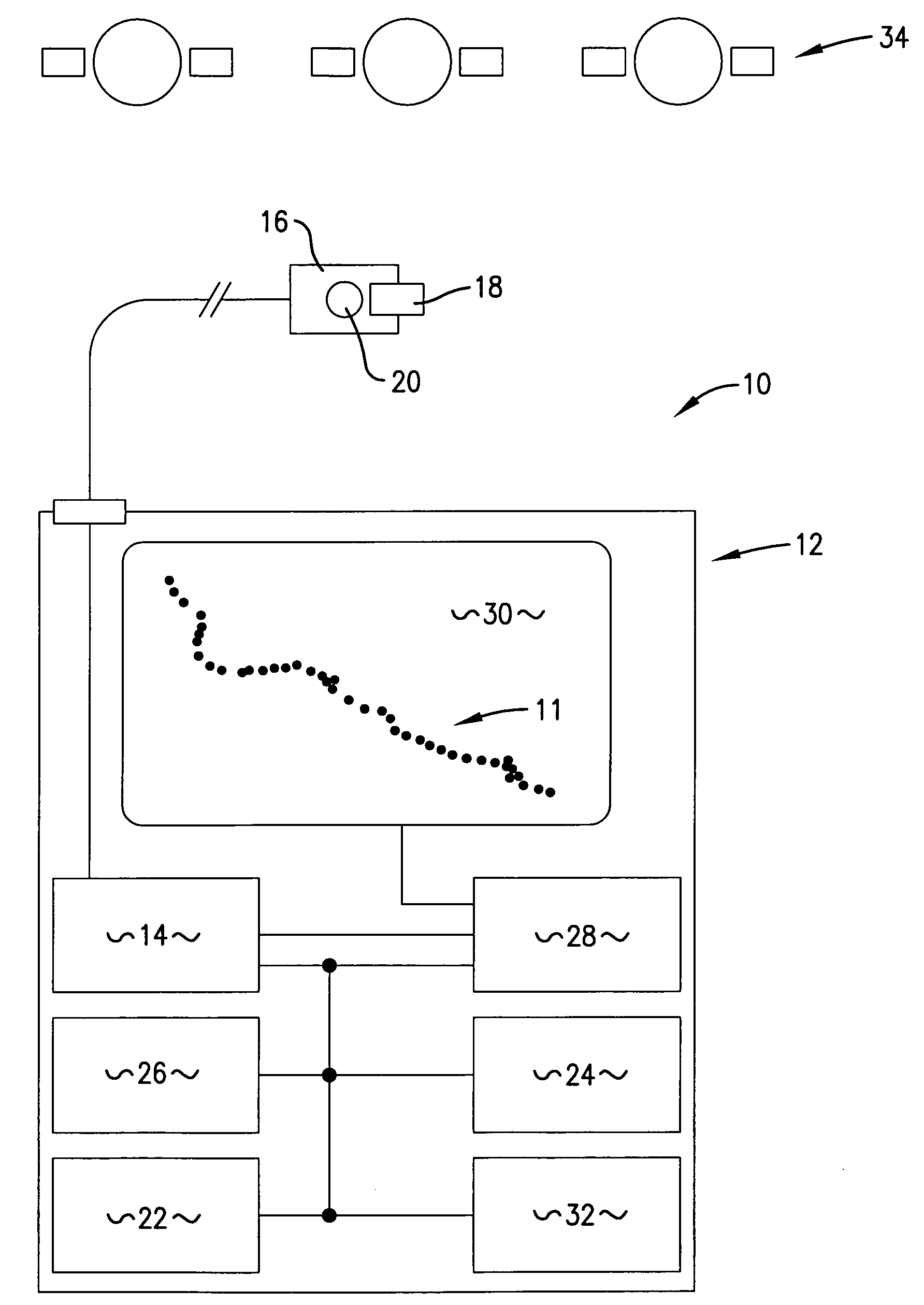
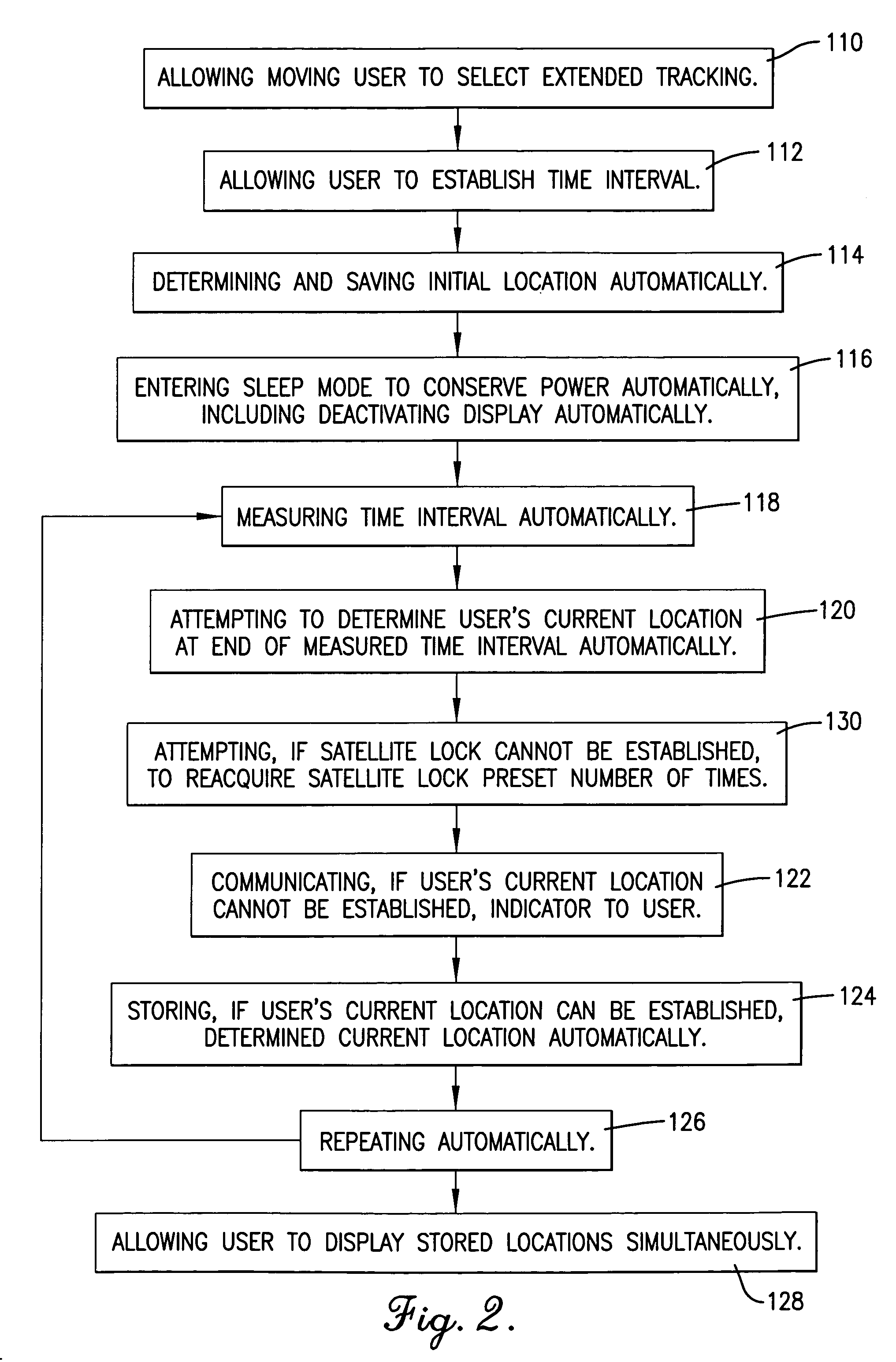
An apparatus (10) and method for allowing a moving user to automatically determine and store locations (11) over an extended period of time, to display the series of such locations (11), and to actively assist in returning to an earlier location. The apparatus (10) includes an antenna (16) for facilitating satellite lock, a fastening mechanism (18) for positioning the antenna (10) for best reception, and a satellite lock indicator (20) for communicating loss of satellite lock. The apparatus (10) also includes a timer (26) for measuring an interval during which the apparatus (10) is in a power-conserving sleep mode, and after which the user's current location is automatically determined. Active assistance in returning to an earlier location, either by traveling back along the path earlier traveled or by traveling along a more direct route, is accomplished by warning the user whenever the user's course deviates from the path or route.
Owner:BUSHNELL
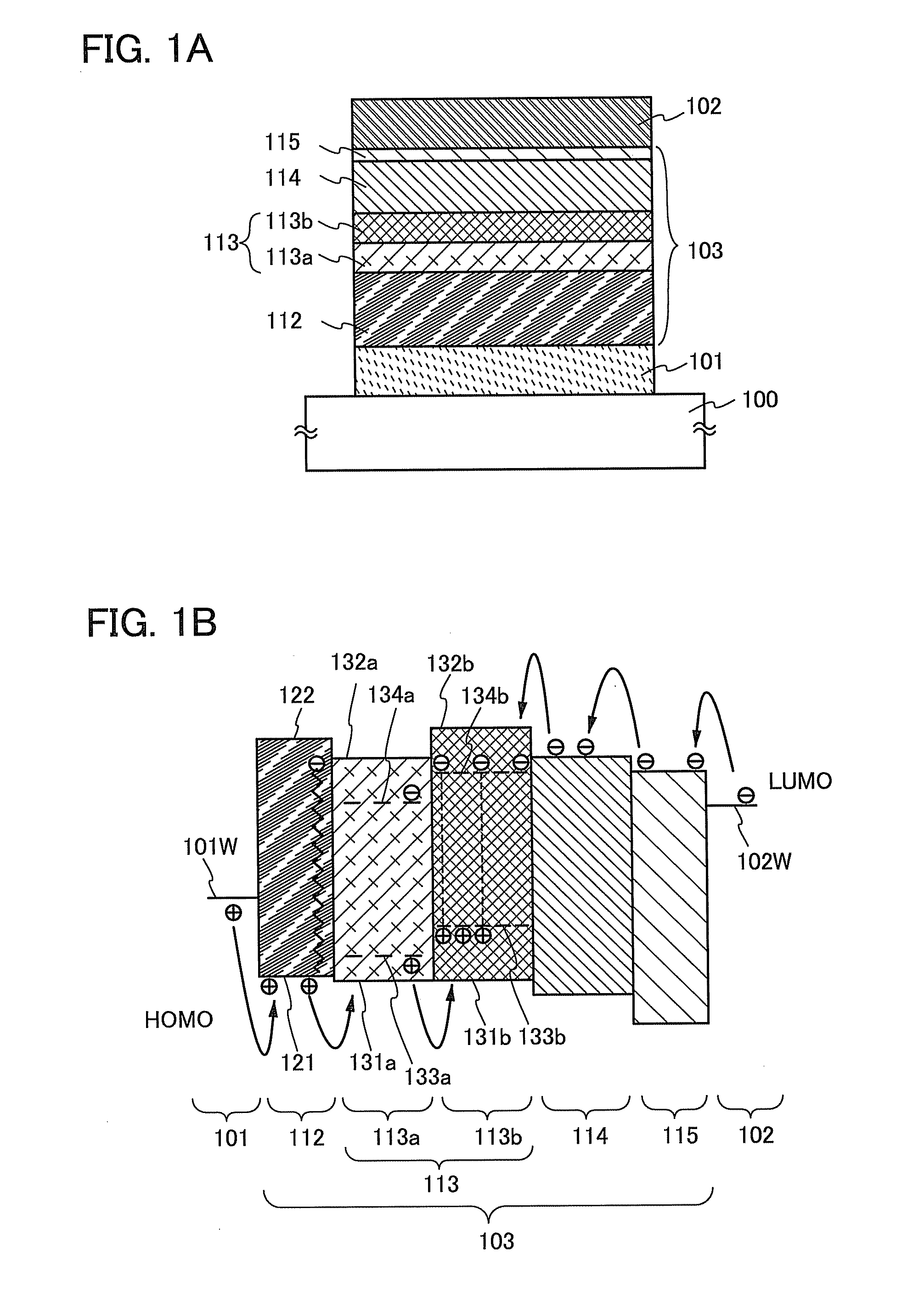
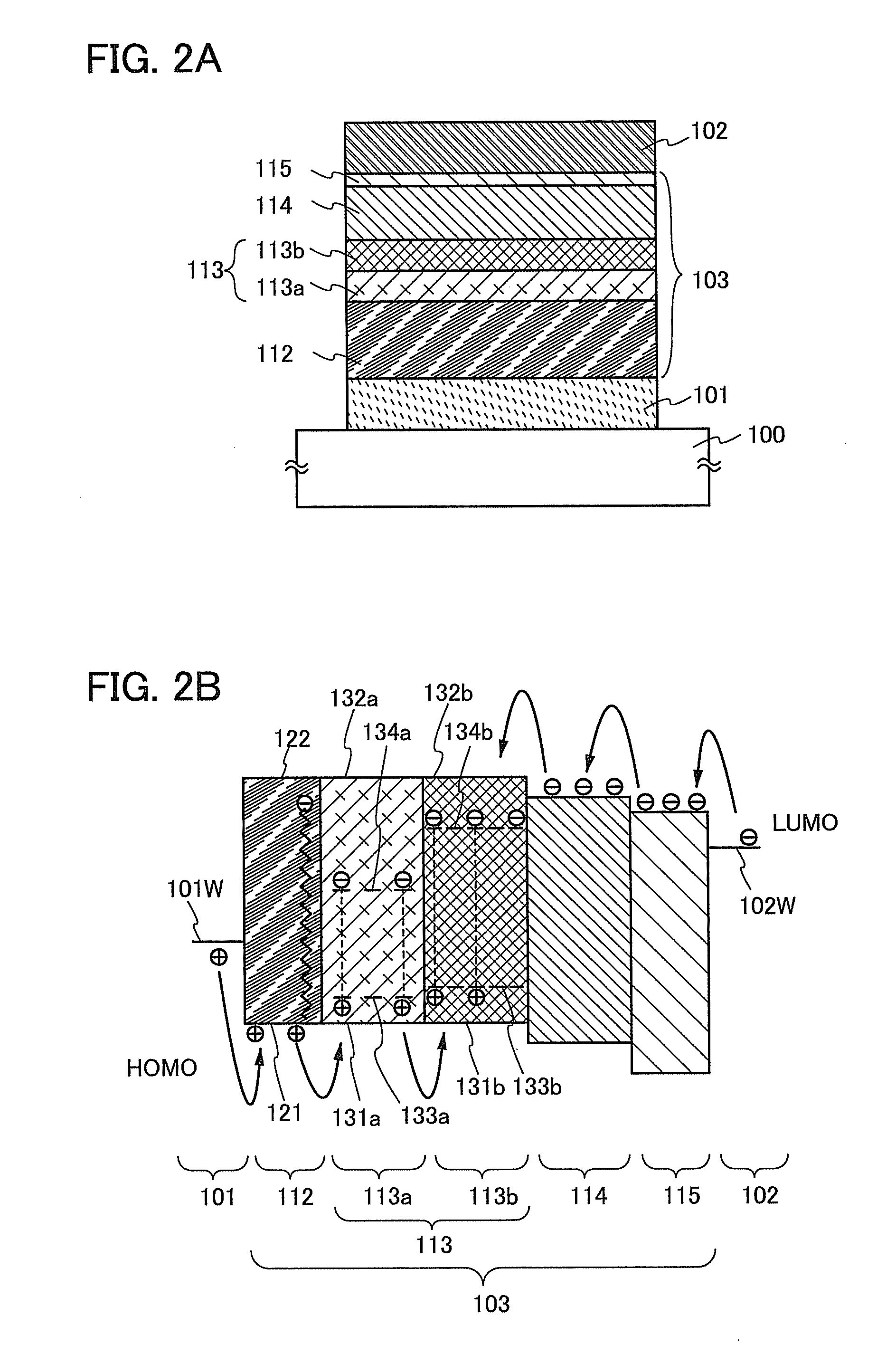
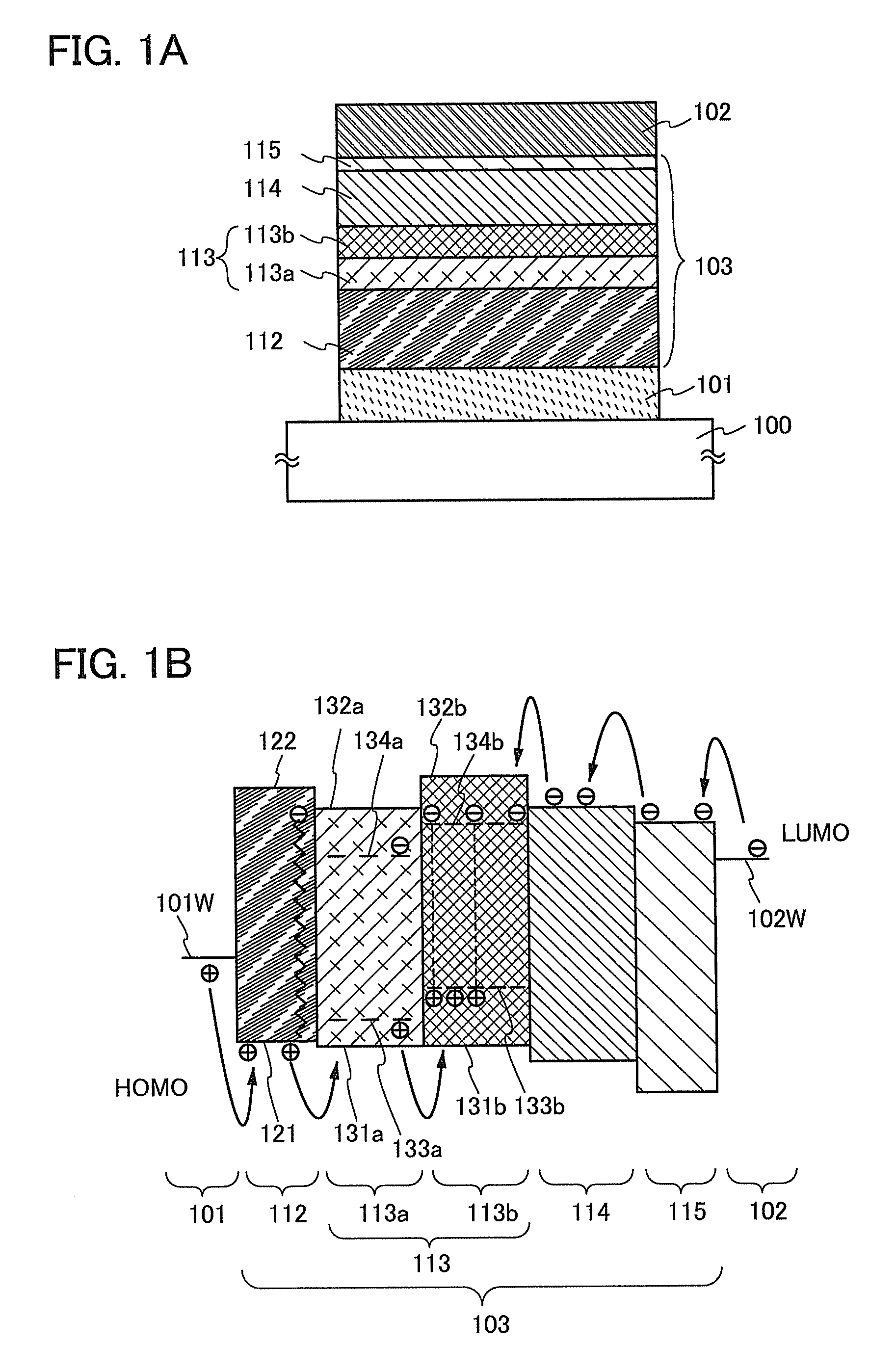
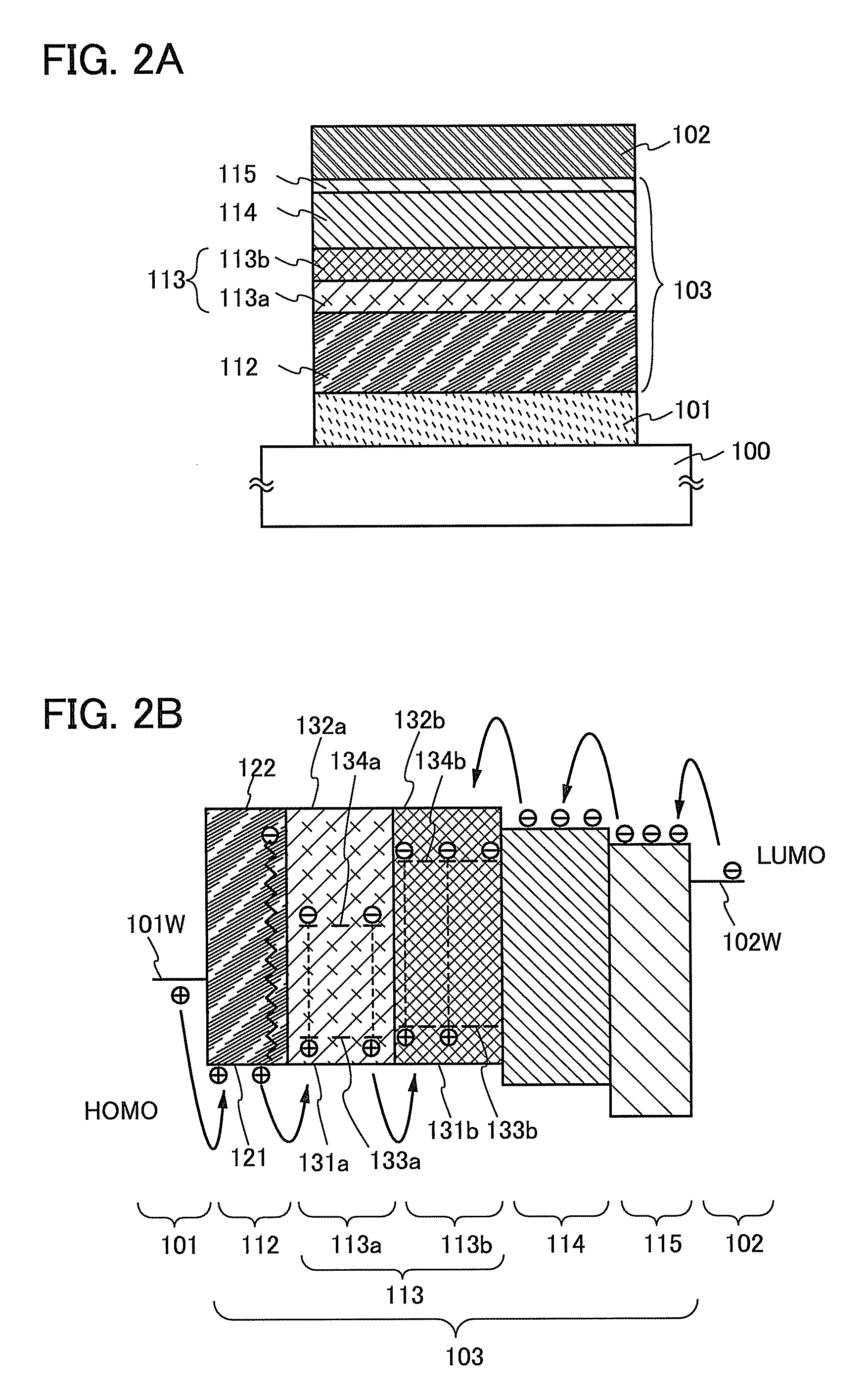
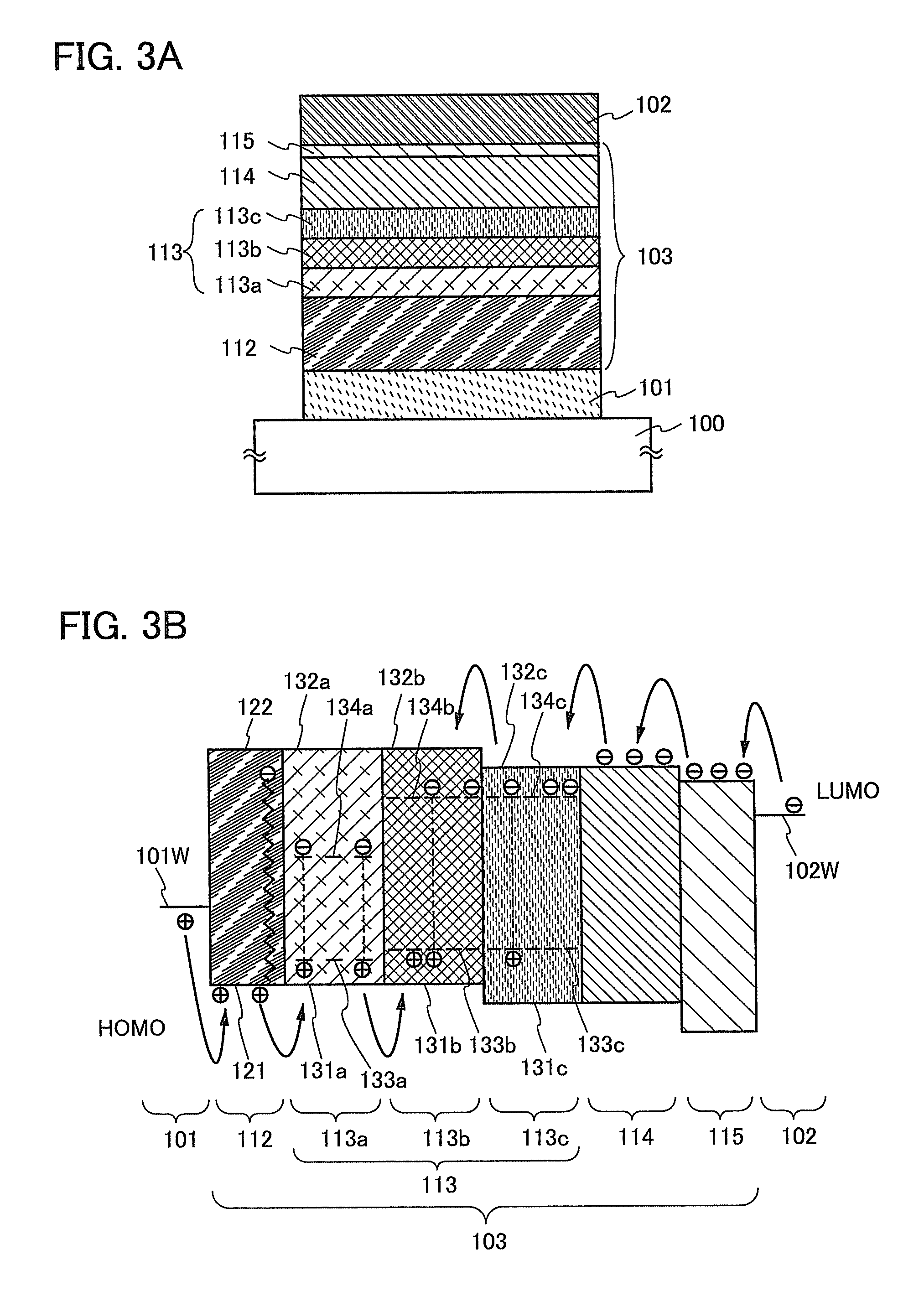
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, and Method for Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20110057178A1Improve emission efficiencyImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHost materialEngineering
Disclosed is a light-emitting element which includes a first light-emitting layer over and in contact with a hole-transport layer and a second light-emitting layer over and in contact with the first light-emitting layer. The first and the second light-emitting layers contain a bipolar host material and an emissive guest material. The guest material in the first light-emitting layer has a lower ability for capturing a hole than a guest material in the second light-emitting layer; therefore, the hole-transport property of the first light-emitting layer can be controlled to be higher than that of the second light-emitting layer. The difference in hole-transport property between the first and second light-emitting layers allows a recombination region to be widely spread in the light-emitting layers. An anti-reducing material may be provided in the hole-transport layer, which prevents the hole-transport layer from being reduced by electrons which fail to undergo recombination in the light-emitting layers.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Harm-removing agent and method for rendering halogen-containing gas harmless and uses thereof
InactiveUS6649082B2Low abilityImprove abilitiesGas treatmentDecorative surface effectsAlkaline earth metalSulfur dioxide
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Helmet
InactiveUS20130305435A1Easy to detect triggeringImprove bending resistanceHelmetsHelmet coversEngineeringMechanical engineering
A head protection helmet comprises an impact resistant shell comprising a cavity for accommodating a user's head and an array of crushable bodies having a hollow closed configuration, e.g. flutes in corrugated material. The crushable bodies each having an axis that extends outwardly from the cavity to absorb impact forces exerted along the direction of the axis.
Owner:KRANIUM SPORTS
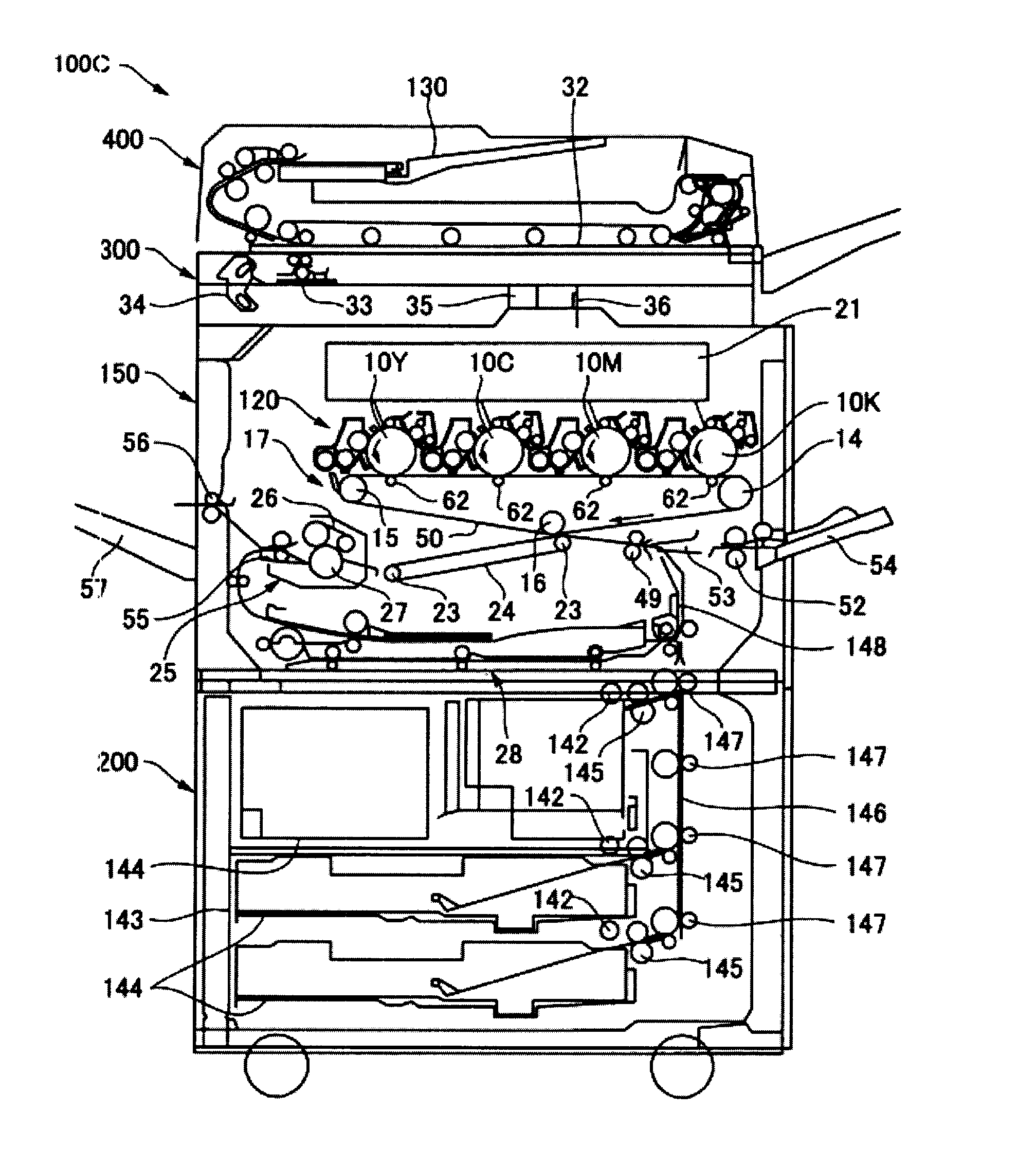
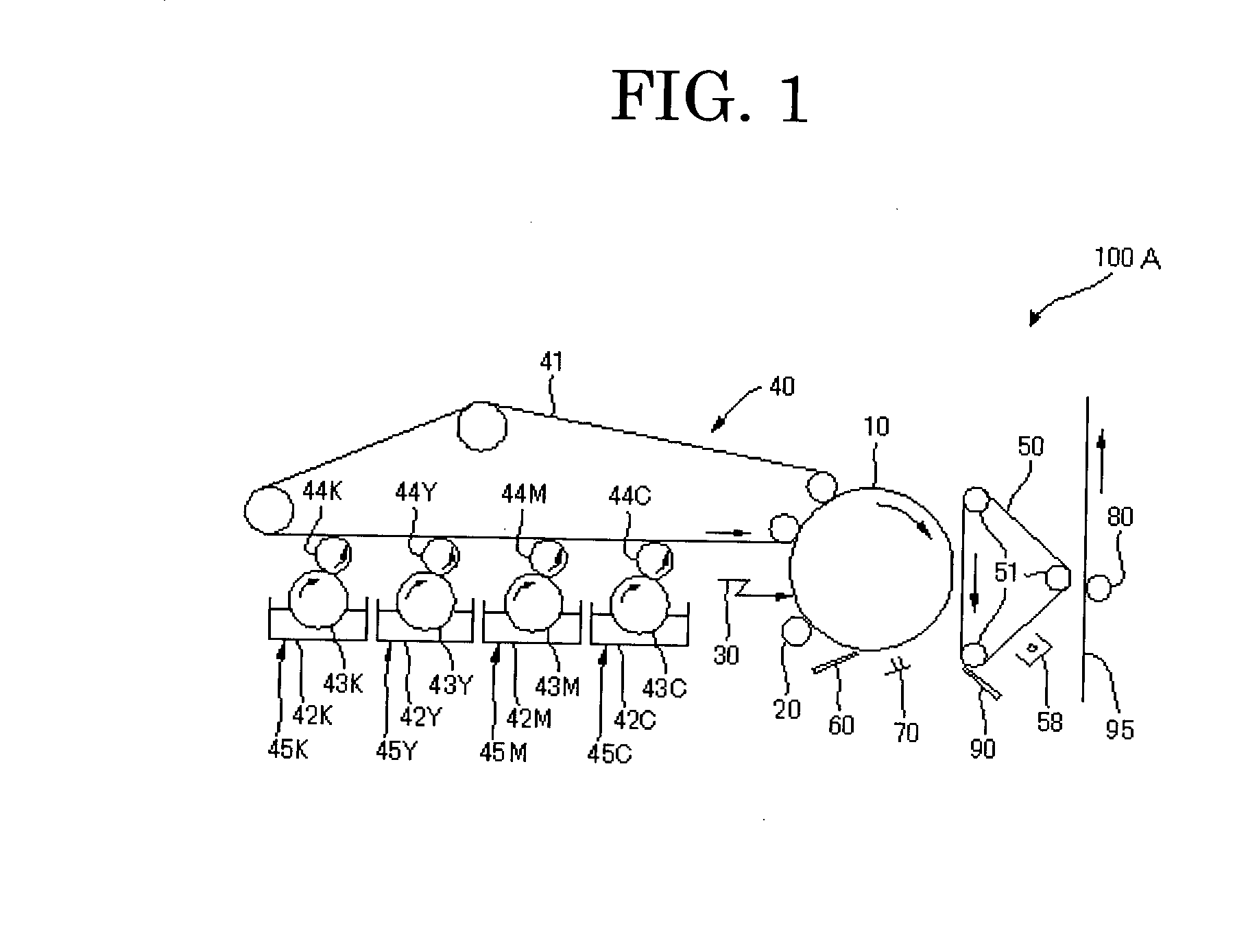
Toner, developer, and image forming method
ActiveUS20110065036A1Wide fusing temperature rangeHigh image densityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternCarboxylic acidOrganic compound
A toner including: a first binder resin; a colorant; a releasing agent; and a crystalline organic compound, wherein the first binder resin contains an amorphous polyester resin (a) having a polyhydroxycarboxylic acid skeleton derived from optically active monomers in a part of a main chain of the amorphous polyester resin, and the polyhydroxycarboxylic acid skeleton has an optical purity X, calculated on the monomer basis, of 80% or less, and the optical purity X is determined from the equation,Optical Purity X (%)=|X (L-form)−X (D-form)|wherein the crystalline organic compound is any one of a crystalline polyester resin (b) and a crystalline low molecular compound having a melting point of 60° C. to 100° C., and being selected from a group consisting of fatty acid having 16 to 24 carbon atoms, alcohol having 16 to 24 carbon atoms, a fatty acid ester compound, and aliphatic carboxylic acid amide.
Owner:RICOH KK
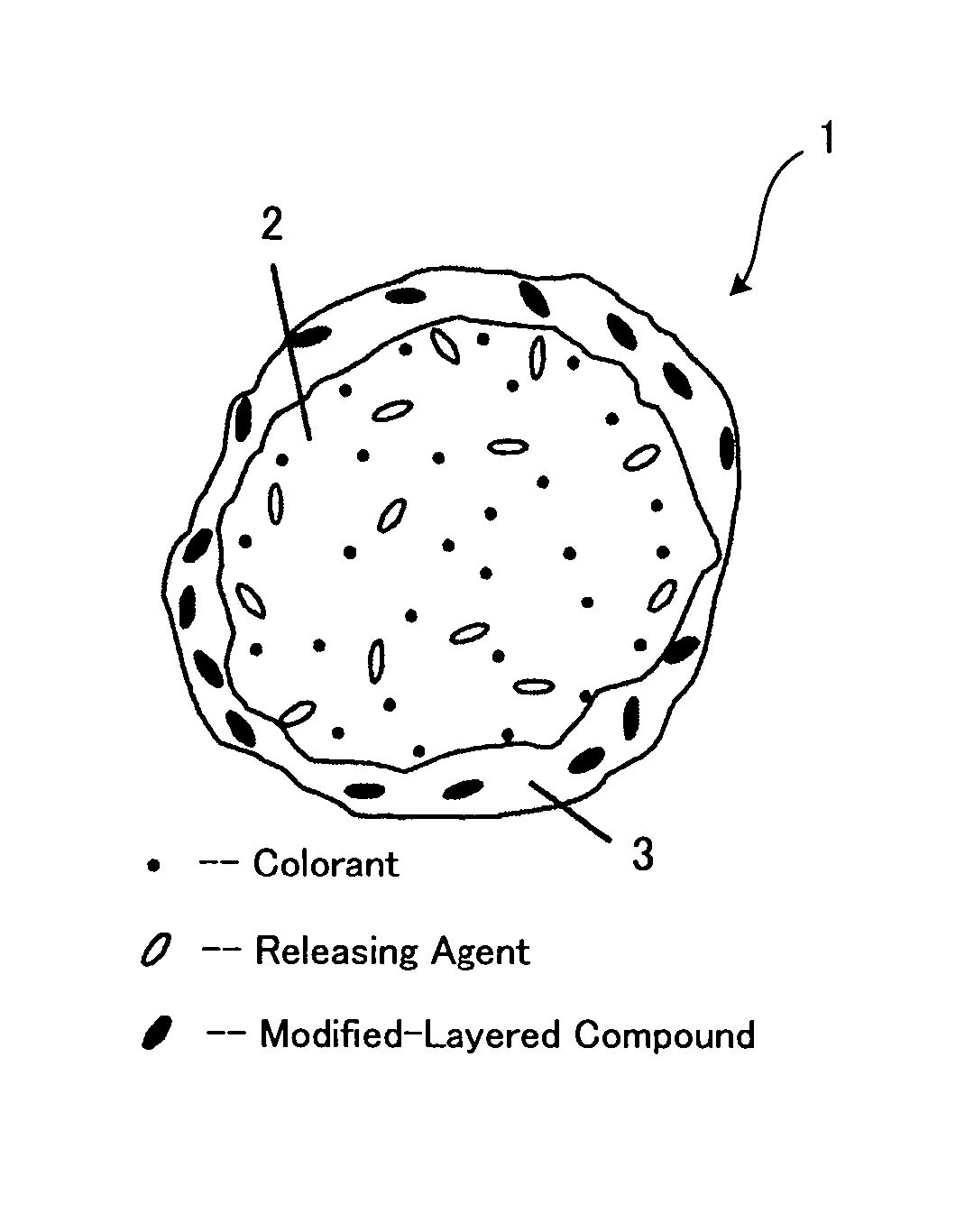
Toner, production method thereof, toner container, developer, image forming apparatus and process cartridge using the same
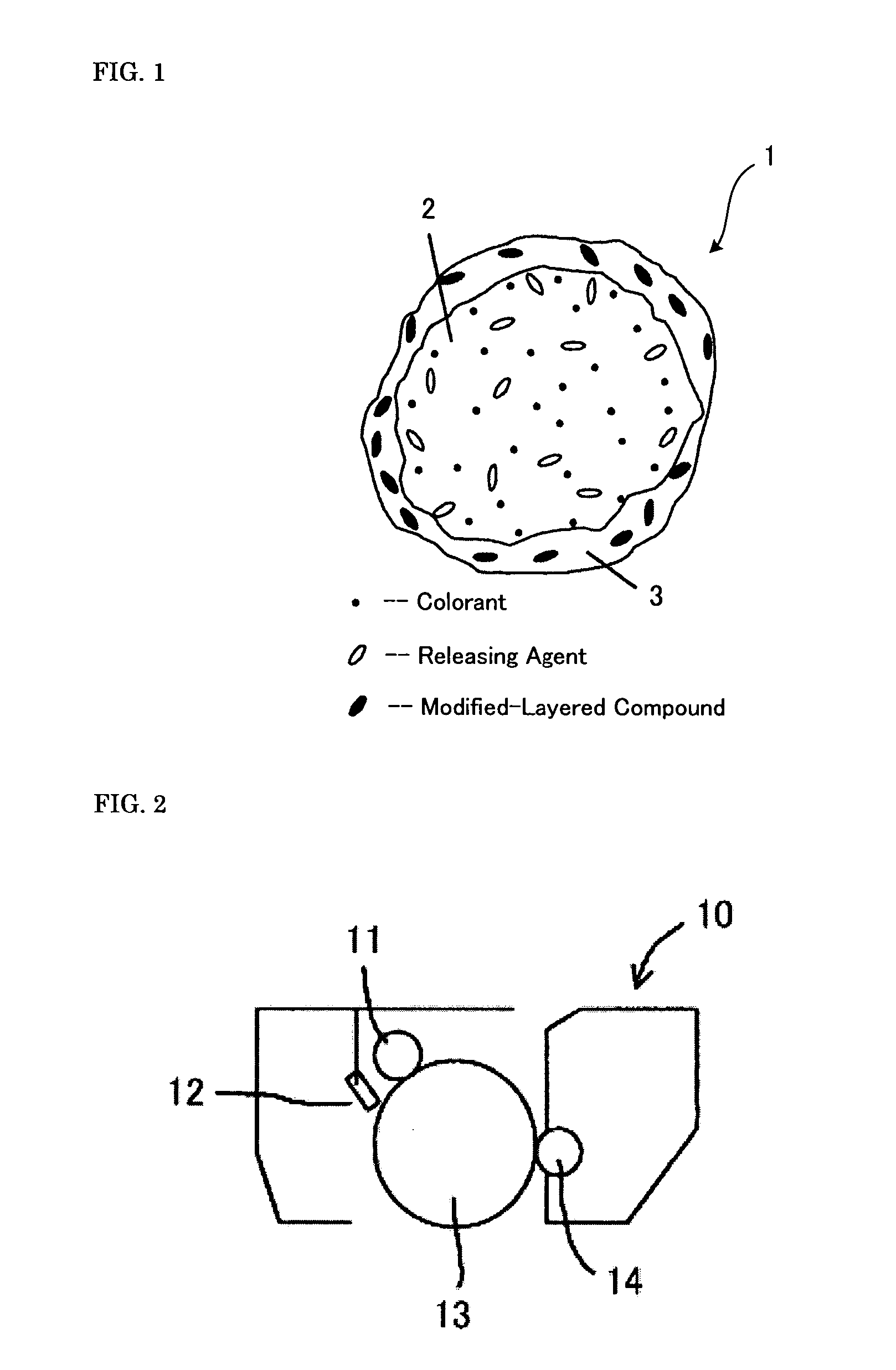
To provide a toner, having: a core and a shell which covers the core, wherein the core at least contains a colorant and a binder resin (A), the shell at least contains a binder resin (B) and a modified-layered inorganic mineral obtained by modifying at least a part of interlayer ions of a layered inorganic mineral with organic ions, the binder resin (A) at least contains a polyester resin, and the binder resin (B) at least contains a vinyl copolymer resin.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method of generation and expansion of tissue-progenitor cells and mature tissue cells from intact bone marrow or intact umbilical cord tissue
InactiveUS20080152630A1Support growthBenefit is often compromisedBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorTissue repair
Disclosed are compositions and methods of generating and expanding tissue-progenitor cells or mature tissue cells in culture, comprising culturing intact bone marrow or intact umbilical cord tissue in a cell differentiation medium whereby tissue-progenitor cells or mature tissue cells are generated from mesenchymal stem cells and various progenitor cells present in the intact bone marrow or intact umbilical cord tissue and expanded, and methods of using the tissue-progenitor cells or mature tissue cells in processes of tissue repair or regeneration.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
Apparatus and method for allowing user to track path of travel over extended period of time
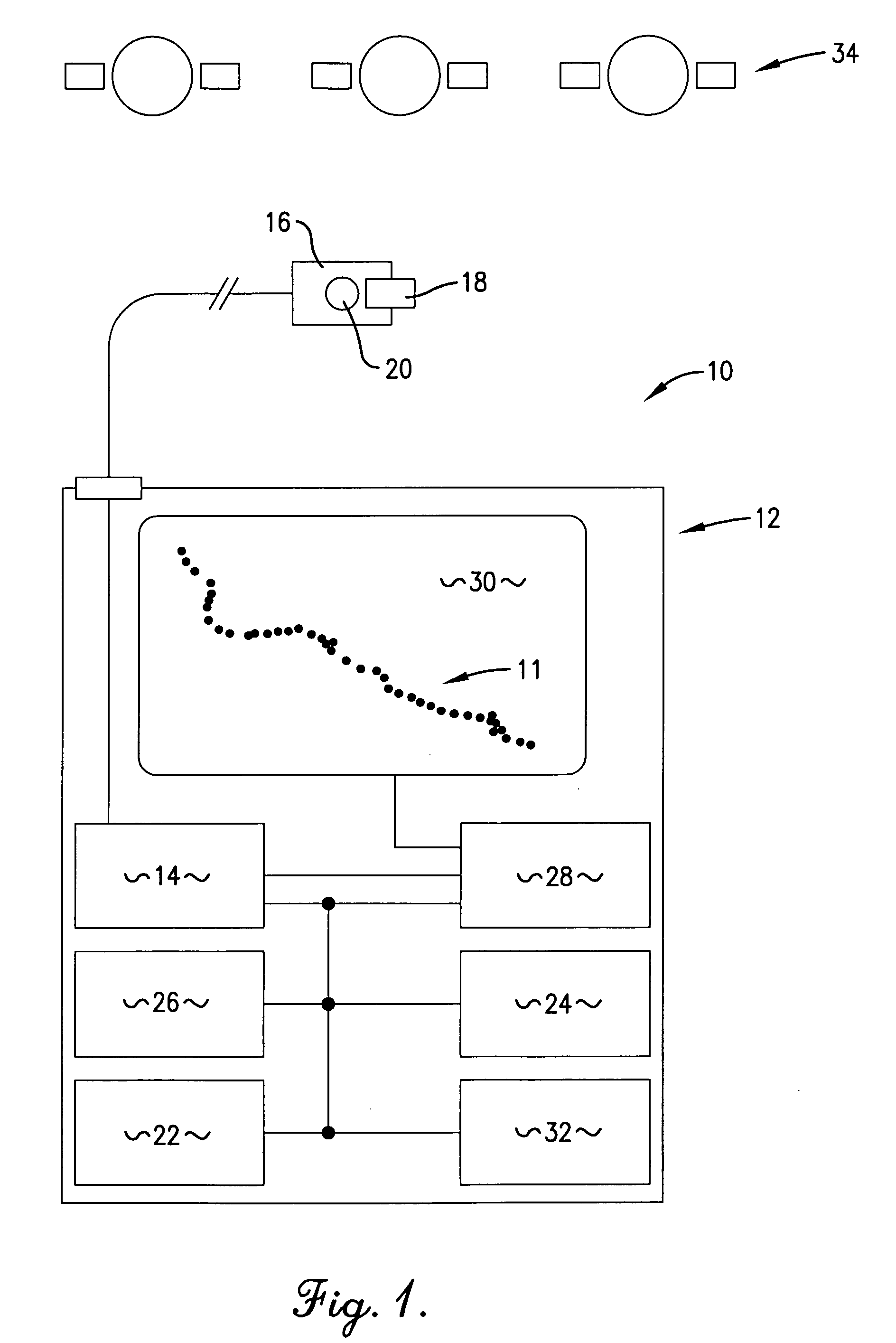
ActiveUS20050253753A1Easy to receiveLow abilityEnergy efficient ICTInstruments for road network navigationMeasuring instrumentEngineering
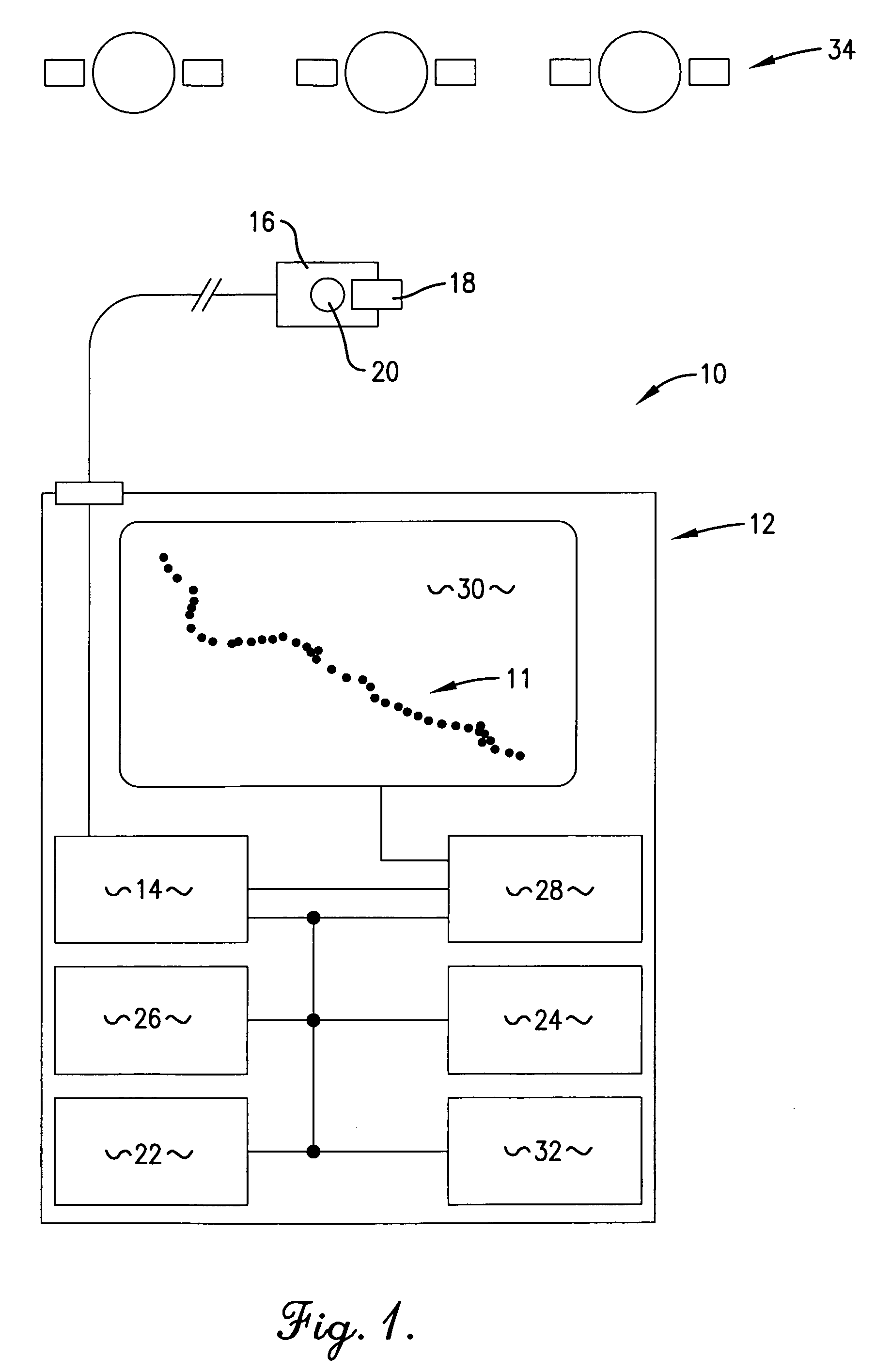
An apparatus (10) and method for allowing a moving user to automatically determine and store locations (11) over an extended period of time, to display the series of such locations (11), and to actively assist in returning to an earlier location. The apparatus (10) includes an antenna (16) for facilitating satellite lock, a fastening mechanism (18) for positioning the antenna (10) for best reception, and a satellite lock indicator (20) for communicating loss of satellite lock. The apparatus (10) also includes a timer (26) for measuring an interval during which the apparatus (10) is in a power-conserving sleep mode, and after which the user's current location is automatically determined. Active assistance in returning to an earlier location, either by traveling back along the path earlier traveled or by traveling along a more direct route, is accomplished by warning the user whenever the user's course deviates from the path or route.
Owner:BUSHNELL
Toner and developer
InactiveUS20120295193A1Excellent low temperature fixabilityResistant storage stabilityDevelopersUltimate tensile strengthPeak intensity
To provide a toner, which contains a binder resin containing a crystalline resin and a non-crystalline resin, a colorant, and a releasing agent, wherein the toner has ½ flow onset temperature T½ of 120° C. to 135° C., and wherein a peak intensity ratio of an intensity of a peak derived from the crystalline resin and the releasing agent to an intensity of a peak derived from the binder resin as measured in FTIR-ATR is 0.10 to 0.20.
Owner:RICOH KK
Compositions and methods for high-efficiency cleaning/polishing of semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS20040266635A1Low abilitySolve high residueSurface-active detergent compositionsDetergent mixture composition preparationAshingCo solvent
A composition including supercritical fluid and at least one additive selected from fluoro species, and primary and / or secondary amines, optionally with co-solvent, low k material attack-inhibitor(s) and / or surfactant(s). The composition has particular utility for cleaning of semiconductor wafers to remove post-ashing residues therefrom.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
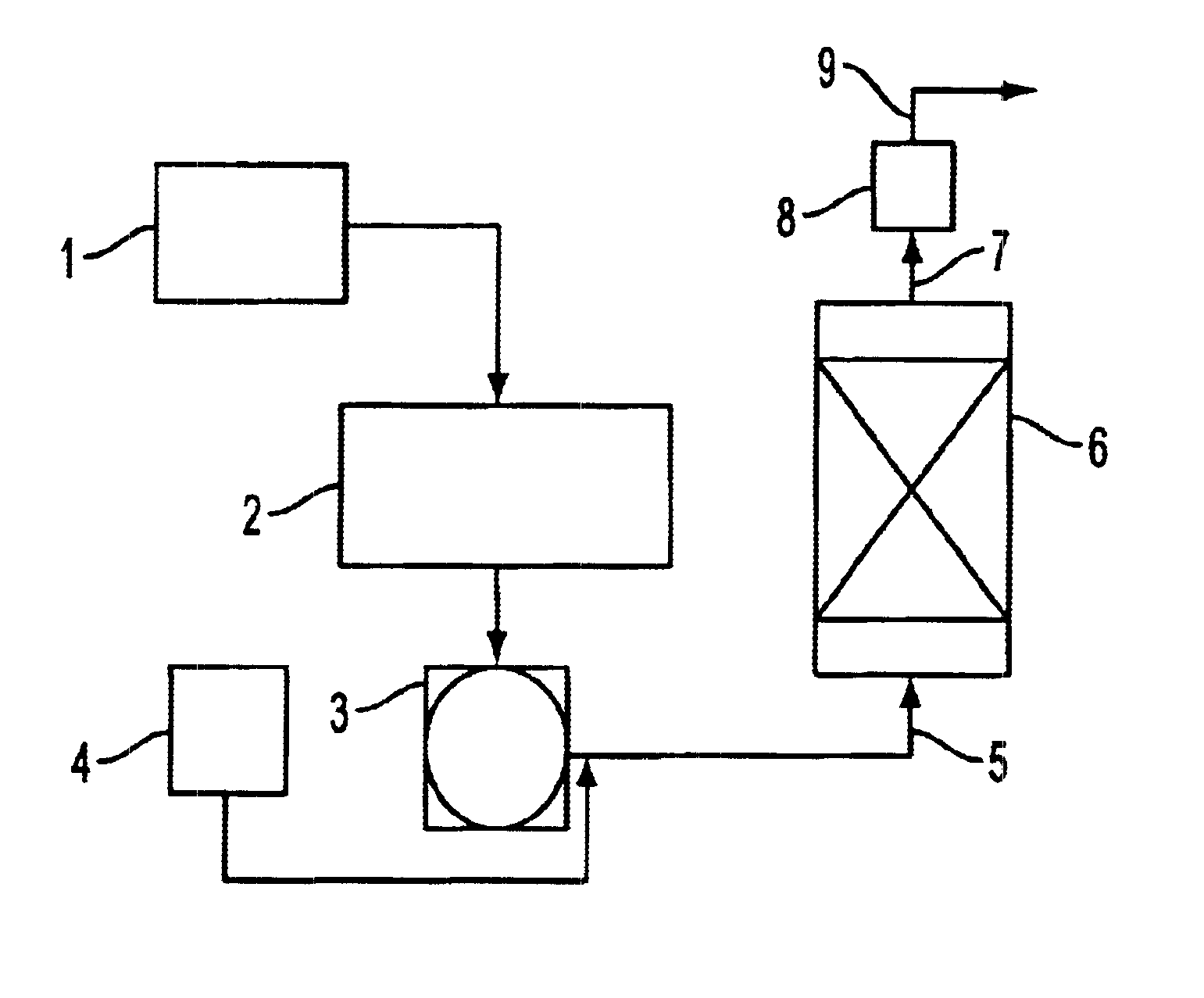
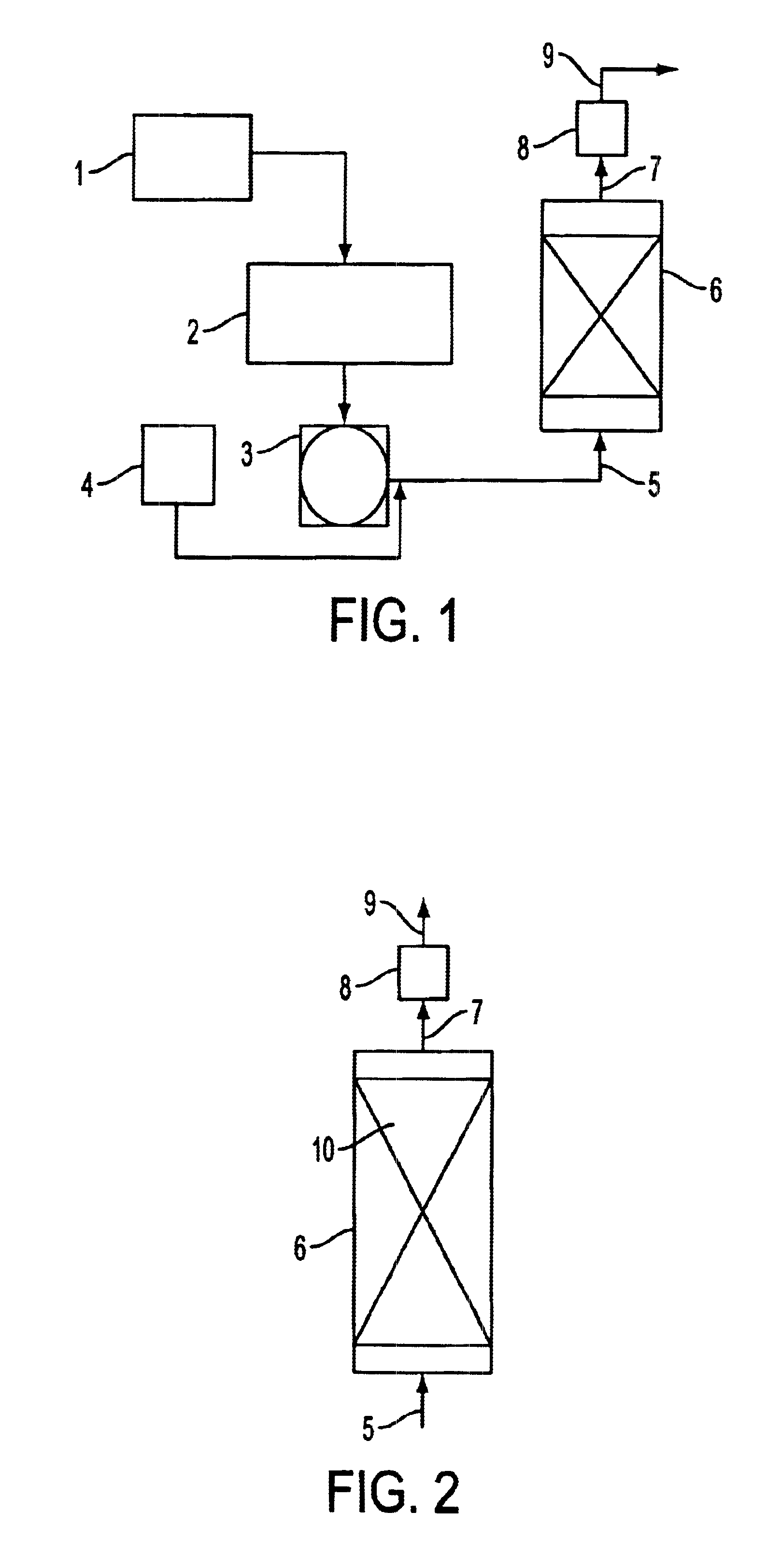
Method for removing water from an aqueous fluid mixture
InactiveUS6120651ALow abilityEnergy efficiencyOrganic compound preparationGeneral water supply conservationPlate heat exchangerOrganic fluid
A method permits concentration of a water-miscible organic liquid in a mixture of such liquid and water, with recovery of a desired concentrate of the water-miscible organic liquid and water, and a relatively clean water containing only a very low contest of the water-miscible organic liquid which enables disposal of the water in sewage systems, the method thus enhancing the ability to satisfy environmental concerns; the method has particular application to the recovery of a reusable glycol / water mixture from diluted spent aircraft deicer fluid (ADF). The diluted spent ADF is heated in a plate heat exchanger with steam to form a hot frothing mass of liquid and steam which is delivered to a cyclone concentrator, the hot frothing mass in the plate heat exchanger and the cyclone concentrator are maintained at a first pressure and a steam phase including steam bubbles in the hot frothing mass is efficiently separated from and withdrawn from a hot liquid phase which represents a more concentrated glycol / water mixture. The steam withdrawn from the hot frothing mass is compressed to a second pressure higher than the first pressure and cycled back to provide the steam input of the plate heat exchanger. After start-up the operation proceeds, with maintenance of the pressure differential, exploiting the heat of the compressed steam with no requirement for external heating. The method may be applied to other aqueous fluid mixtures.
Owner:INLAND TECH HLDG INC
Laundry bars comprising non-staining water soluble polymeric colorants
InactiveUS6417155B1Low costEasy to useOrganic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsStainingHazardous substance
Colored detergent bars are provided comprising water soluble polymeric colorants that exhibit excellent non-staining performance on fabrics and other contacted surfaces, including manufacturing and / or washing equipment, are easy to process into the desired detergent bar compositions, and do not exhibit any appreciable harmful effects to the environment. The particular polymeric colorants utilized in this respect are of very high molecular weight (in order to assure staining will not occur on target cleaning surfaces), are extremely water soluble, provide excellent vivid and aesthetically pleasing color shades within the target bar compositions, and are present as liquid or waxy pastes at room and at processing temperatures. The ultimate laundry bar product thus exhibits highly pleasing colors for product distinction as well as for aesthetic purposes.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Developing roller and developing device using the same
InactiveUS6393243B1Satisfactory dispersion and stabilityGood dispersionElectrographic process apparatusAdditive ingredientNitrogen
A developing roller having a superior setting ability and having a uniform and high conductivity is provided by improving dispersion and stability of carbon black mixed in a solution of a coating resin, and then forming a resin layer that has a low modulus of elasticity and a high conductivity when coated. The developing roller includes a core shaft, an elastic body layer formed around the core shaft and made of rubber as a main ingredient, and a resin layer coated at least on an outer surface of the elastic body layer. The resin layer contains carbon black having a DBP absorption amount of 80 to 110 ml / 100 g, a ratio of a DBP absorption amount to a nitrogen specific surface area being not more than 0.012 ml / m2, and a ratio of a volatile component to a nitrogen specific surface area being not more than 2.0x10-4 g / m2.
Owner:CANON KK
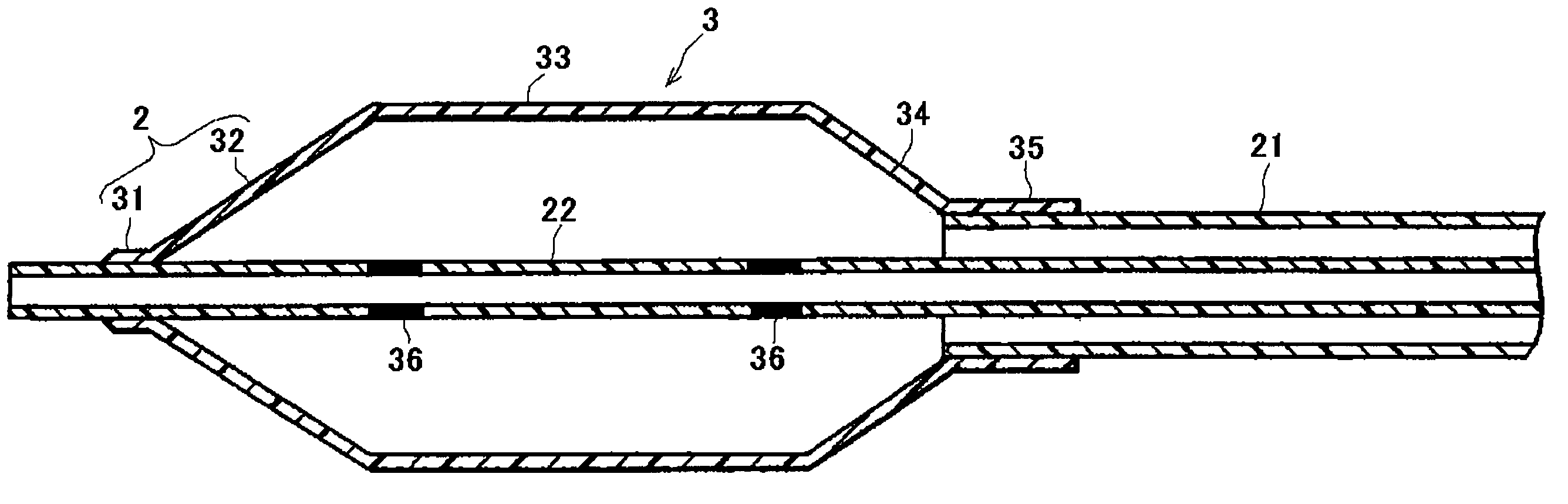
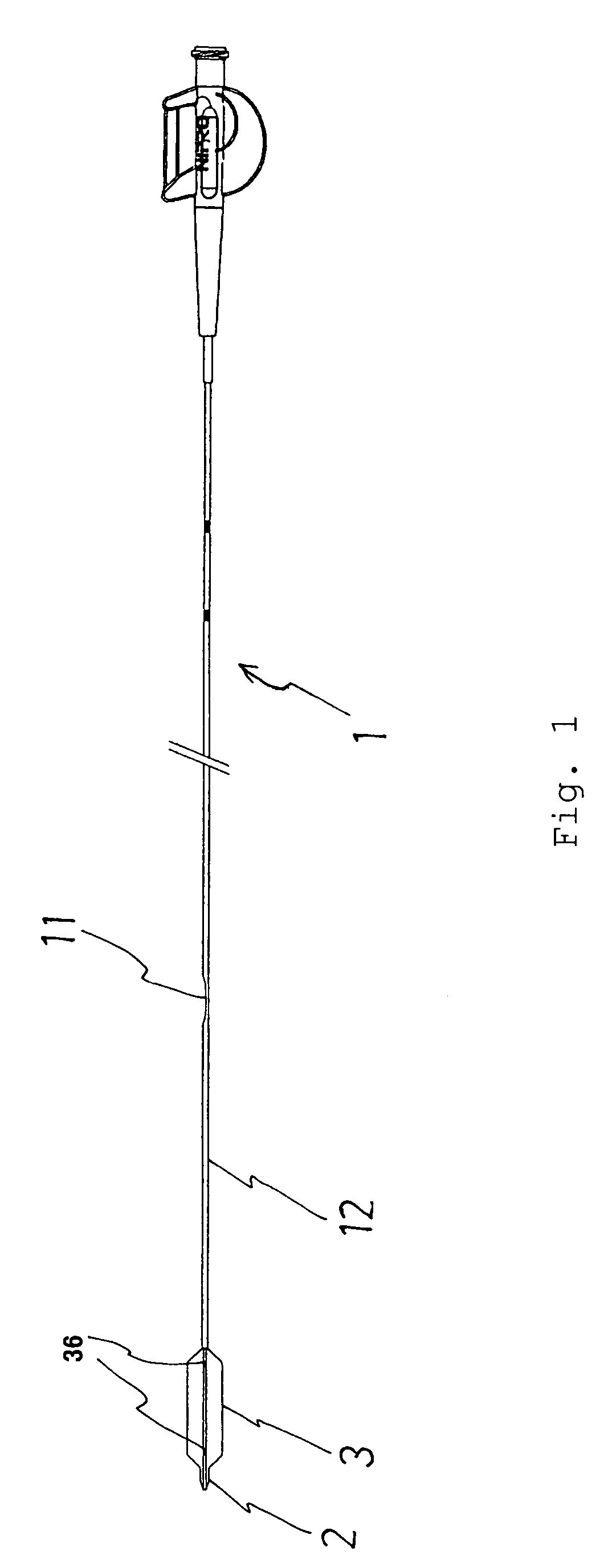
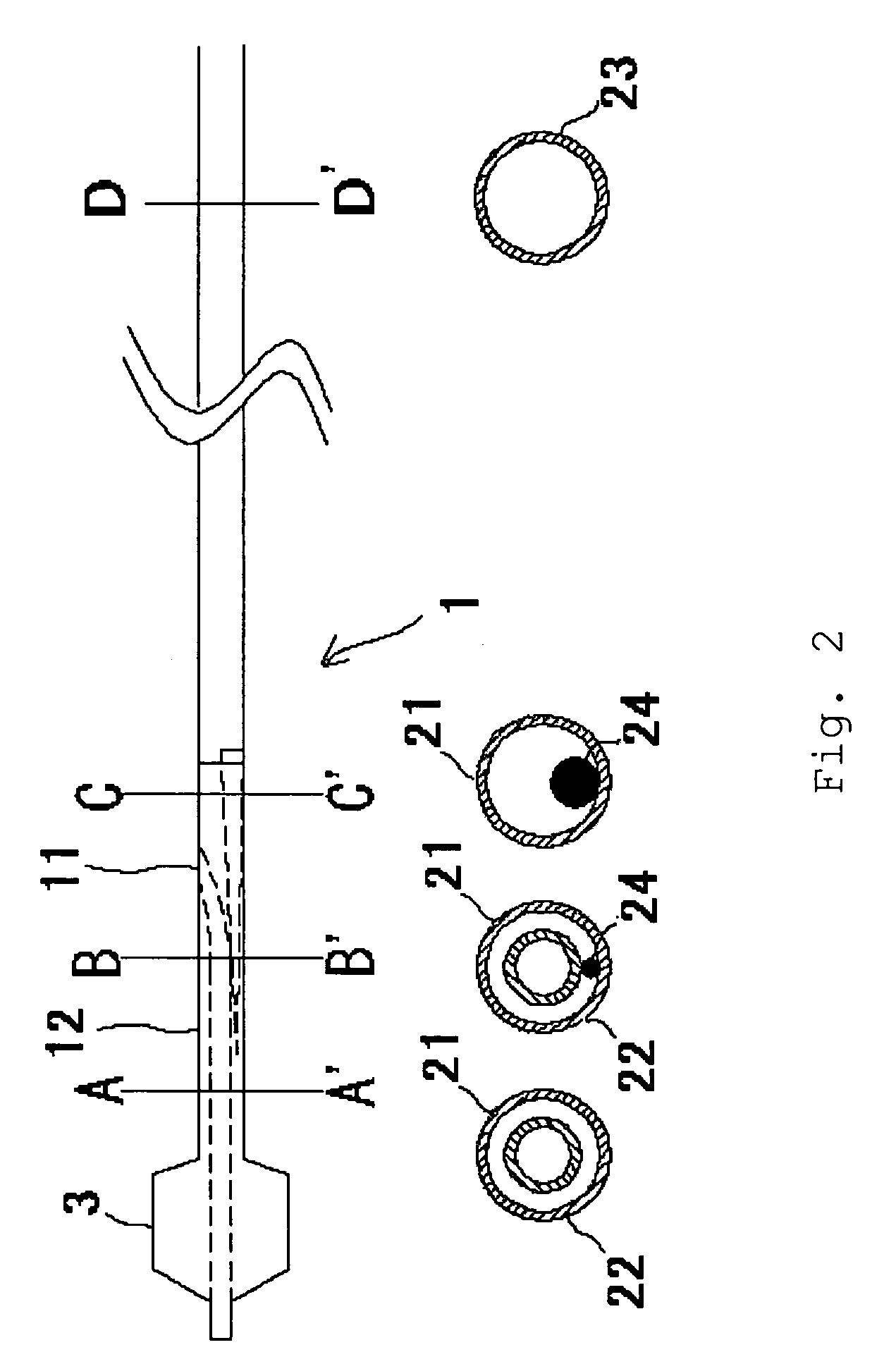
Balloon catheter suited to kissing techniques
InactiveUS7407507B2Cross abilityImprove balanceStentsBalloon catheterBalloon catheterCatheter device
A balloon catheter which is good in cross ability and is also good in gripping property so as not to cause slipping during kissing technique includes a tubular body having a balloon 3provided in a distal section 12 of a shaft 1, the shaft 1 being flexible in the distal section 12 and stiff on its proximal side, whereby gripping property and cross ability are adjusted with good balance. Specifically, the gripping property is adjusted to 3.2 N to 6.0 N, and the cross ability is adjusted so that its initial value is not higher than 0.65 N and its middle value is 0.40 N.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Harm-removing agent and method for rendering halogen-containing gas harmless and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030082918A1Efficient removalLow abilityHydrogenGas treatmentAlkaline earth metalSulfur dioxide
The present invention intends to provide an agent and a method for removing harmful gas, which exhibits high harm-removing ability per unit volume for harmful halogen-containing gas contained in the exhaust gas from the etching or cleaning step in the manufacturing process of a semiconductor device, and which is inexpensive. The invention is characterized by that halogen-containing gas is removed using a harm-removing agent comprising a specific iron oxide, an alkaline earth metal compound and activated carbon in the specific amount. In the case where the exhaust gas contains halogen gas such as chlorine or a gas such as sulfur dioxide, the gas is rendered harmless by using in combination a harm-removing agent comprising activated carbon or zeolite.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Electrophotographic toner, two-component developer containing toner, and image forming apparatus
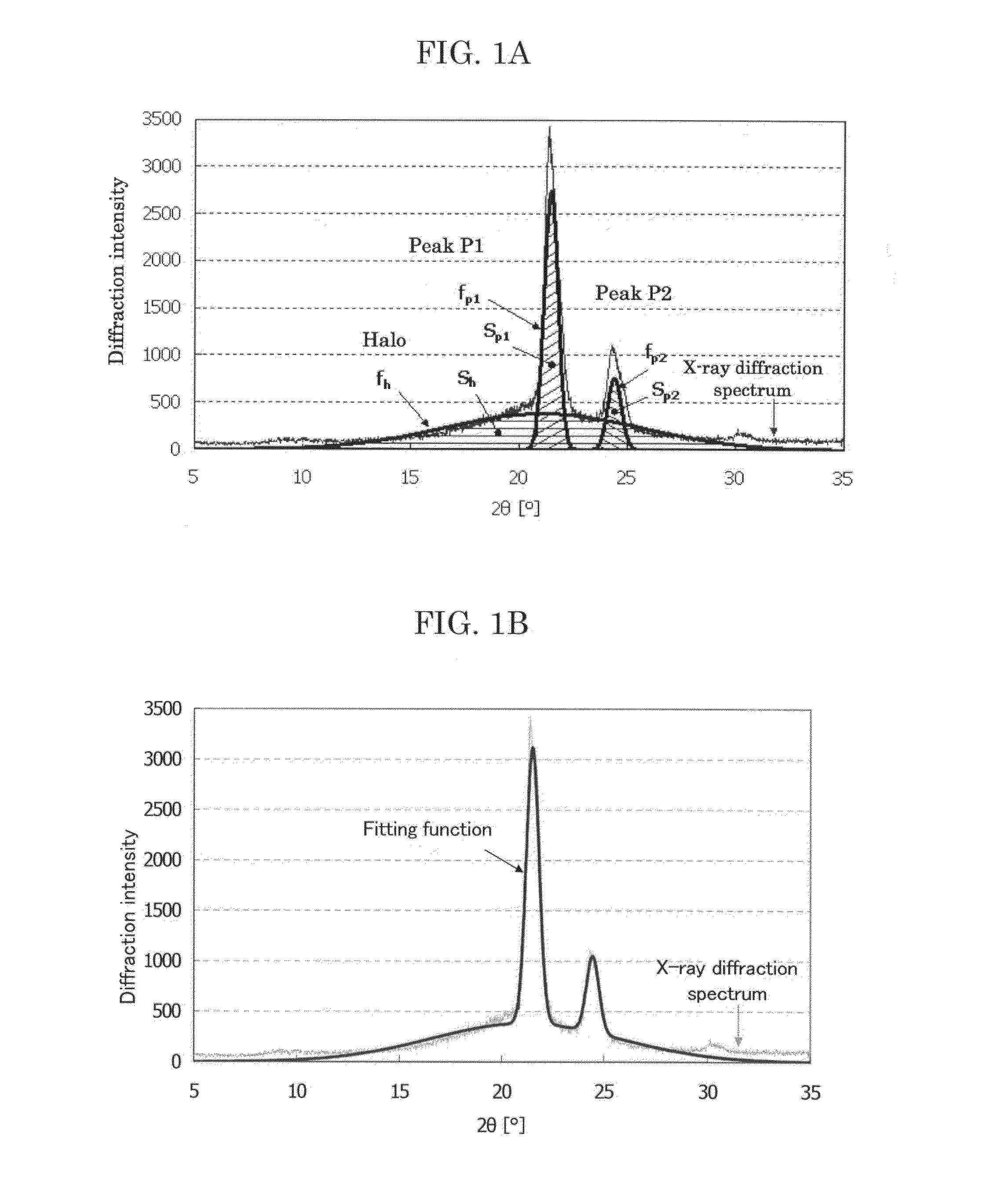
ActiveUS20140080047A1Improve the level ofLow abilityDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusX-rayCrystal structure
To provide an electrophotographic toner, which contains a crystalline resin, a non-crystalline resin, a colorant, and a releasing agent, wherein the toner has a storage elastic modulus of 5.0×104 Pa to 5.0×106 Pa at 80° C., and a storage elastic modulus of 2.0×102 Pa to 2.0×103 Pa at 140° C., and wherein the toner has a ratio (C) / ((C)+(A)) of 0.10 or greater, where (C) is an integrated intensity of a diffraction spectrum derived from a crystalline structure, (A) is an integrated intensity of a diffraction spectrum derived from a non-crystalline structure, and the diffraction spectrum is a diffraction spectrum of the toner as measured by an X-ray diffraction spectrometer.
Owner:RICOH KK
Motor and control circuit thereof
ActiveUS20080258584A1Current withstand ability of be reduceLow abilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringConductor Coil
A control circuit of a motor includes at least two sensor chips and at least two winding sets. The sensor chips are electrically connected to each other, and each of the winding sets has a first winding and a second winding. The first end of the first windings and the first end of the second windings are electrically connected to each other, and the second end of the first windings and the second end of the second windings are electrically connected to the sensor chips correspondingly. In addition, a motor having the control circuit is also disclosed.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Light-emitting element with multiple light-emitting layers having controlled carrier mobility and lighting device and electronic device using the same
ActiveUS9209415B2Emission reductionLow efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHost materialCharge carrier mobility
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Normally white, supertwist nematic liquid crystal display of reflective type
InactiveUS7084939B2Significant light lossComplex designLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A normally white supertwist nematic liquid crystal display of reflective type is provided. This display comprises a reflector, a layer of chiral nematic liquid crystal having a front aligning surface facing a light source and a rear aligning surface facing the reflector, and a front polarizer. The nematic liquid crystal has an optical retardation (Δnd) of the layer and a distribution of directors, wherein the chiral nematic liquid crystal has a twist angle (Φ) between an alignment direction of the director at the front aligning surface and an alignment direction of the director at the rear aligning surface. The front polarizer is disposed between the layer of chiral nematic liquid crystal and the light source. The front polarizer has a transmission axis forming an angle (α) with the alignment direction of the director at the front aligning surface of the chiral nematic liquid crystal layer. The optical retardation (Δnd) and the angle (α) are defined by the following formulas:α((Φ)=sign(Φ)·(47.0−0.4936|Φ|+2.6786×10−3·Φ2)±5, deg, andΔnd(Φ)=−11.674+0.1915·|Φ|−9.8393×10−4·Φ21.6667×10−6·|Φ|3±0.05, μm.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method and device to fill receiving containers
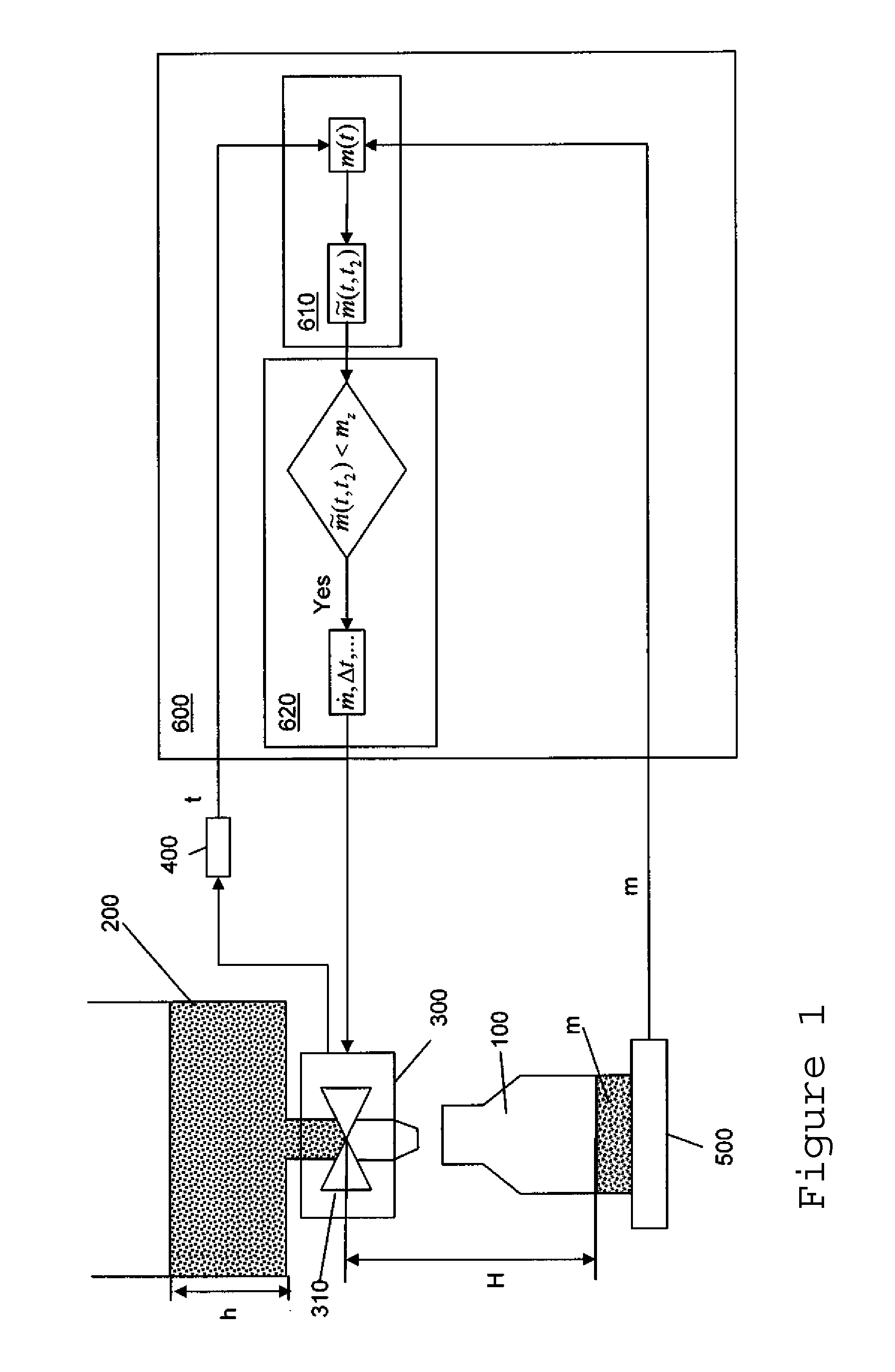
InactiveUS20090293986A1Reduce riskLow abilityBarrels/casks fillingSolid materialTime segmentEngineering
A receiving container is filled with a predetermined target mass mz of a free-flowing substance from a reservoir with the help of a dosage-dispensing device that dispenses measured doses of the substance. The device has a valve for variably setting the mass flow {dot over (m)} from the reservoir into the receiving container. The device is also able to determine the time t that has elapsed since the beginning of the fill cycle, the mass m of the substance present in the receiving container, and a unit for controlling the valve. The controller unit includes estimating and correction modules. At least once during the fill cycle, the estimating module performs an estimate of the mass {tilde over (m)}(t, t2) that is expected to be present in the receiving container at the end of the fill cycle at the time t2. This estimate is based on the assumptions that from the time t onward the valve is being closed according to a predefined closing-down profile and the fill cycle is completed at the time t2. The correction module compares the mass {tilde over (m)}(t, t2) estimated at the time t to the target mass mz. If the estimated mass {tilde over (m)}(t, t2) is smaller than the target mass mz, the valve is controlled so that the aperture associated with the mass flow {dot over (m)} that exists at the time t will be maintained longer by a differential time segment Δt, and / or the mass flow {dot over (m)} at the time t is increased.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO GMBH
Toner for developing latent electrostatic image and method for producing toner for developing a latent electrostatic image
InactiveUS20140093820A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityDevelopersInorganic saltsOrganic solvent
To provide a toner containing toner base particles, in each of which a colorant and a releasing agent are encapsulated with a binder resin, where the toner base particles are obtained by the method containing: mixing and emulsifying a mixture containing the binder resin, the colorant, the releasing agent, and an organic solvent in an aqueous medium in the presence of resin particles, wherein the aqueous medium contains a surfactant and an inorganic salt.
Owner:RICOH KK
Strains of zymomonas mobilis for fermentation of biomass
InactiveUS20090269797A1High ethanol yieldProduction cost be reduceBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMannoseChemistry
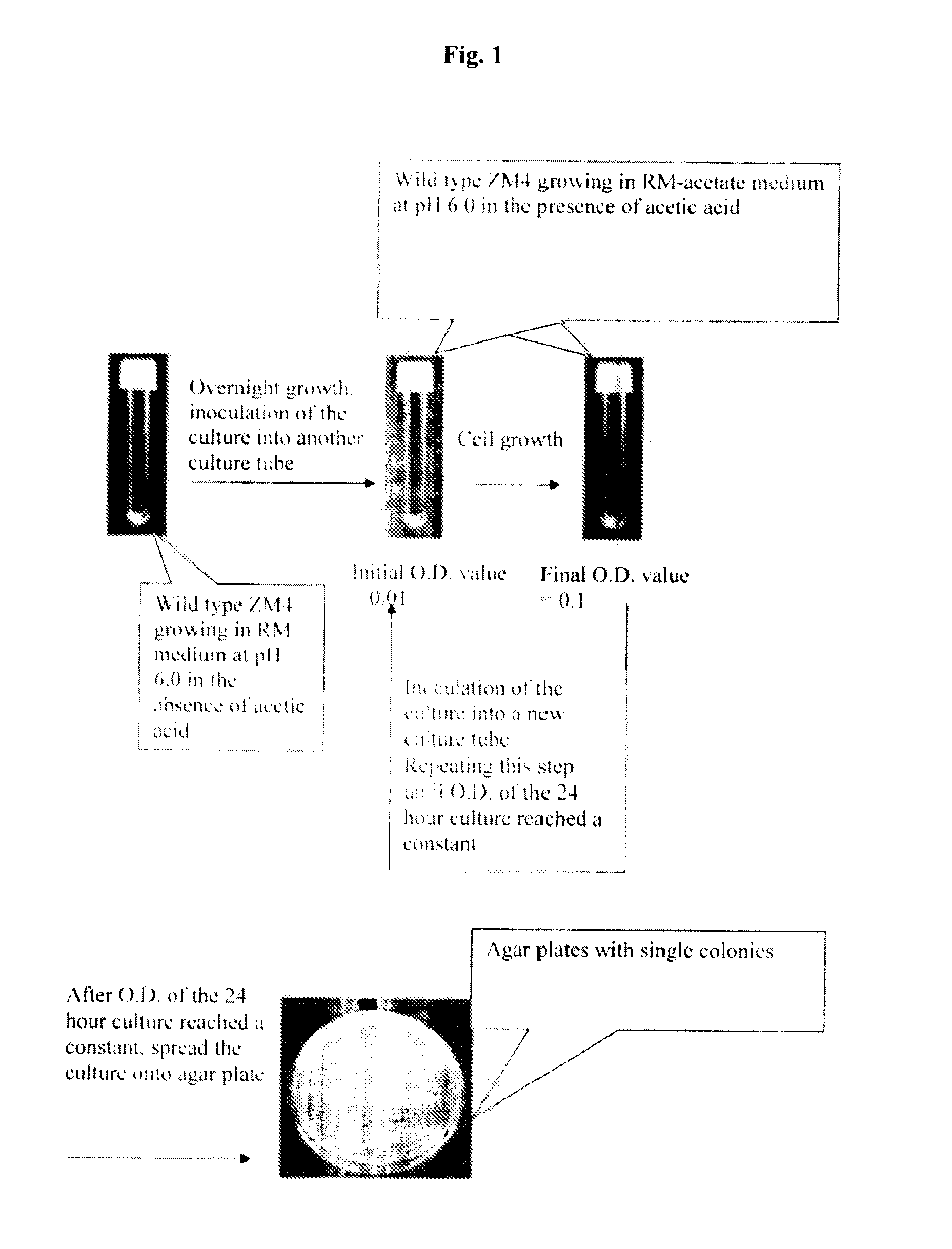
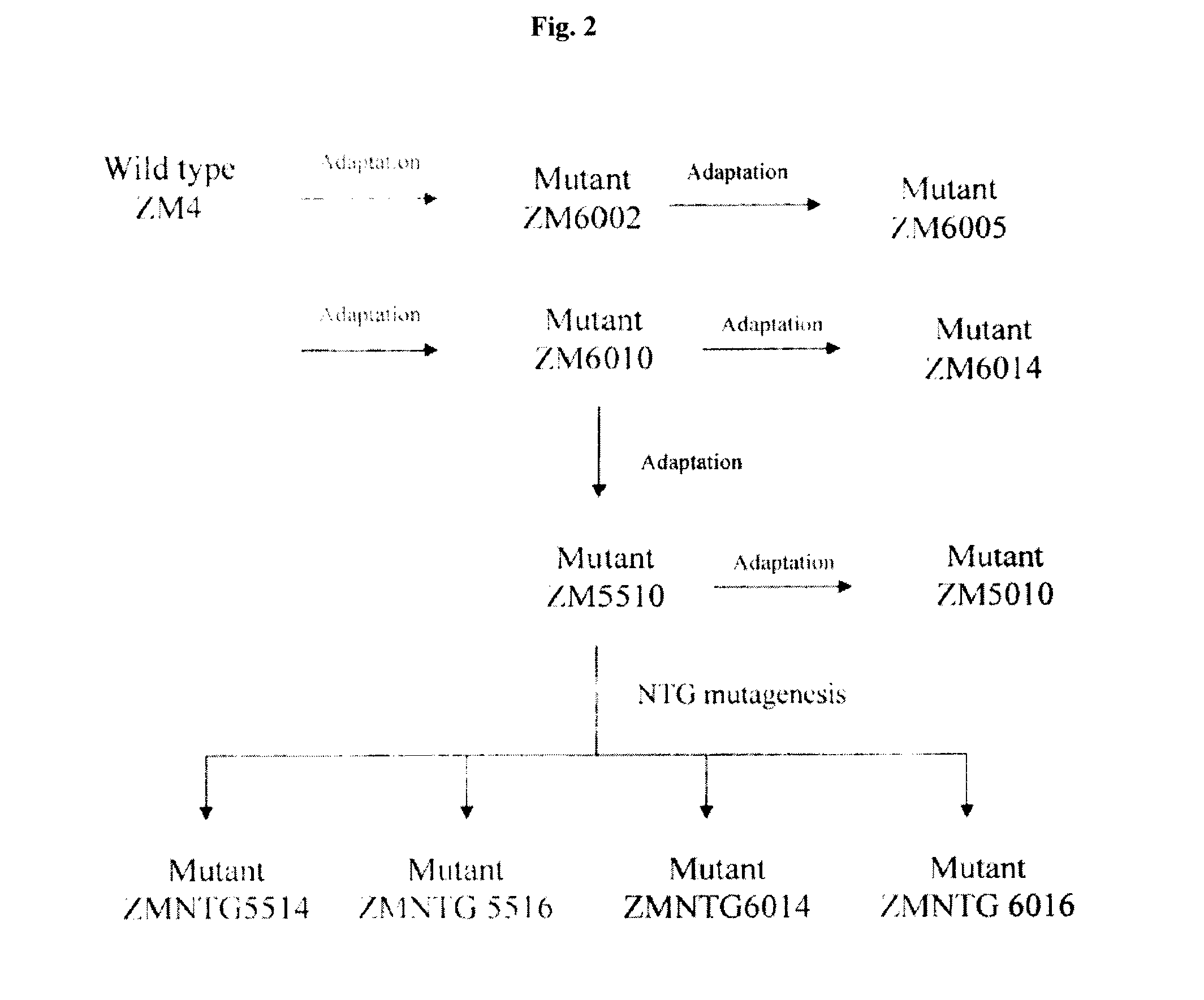
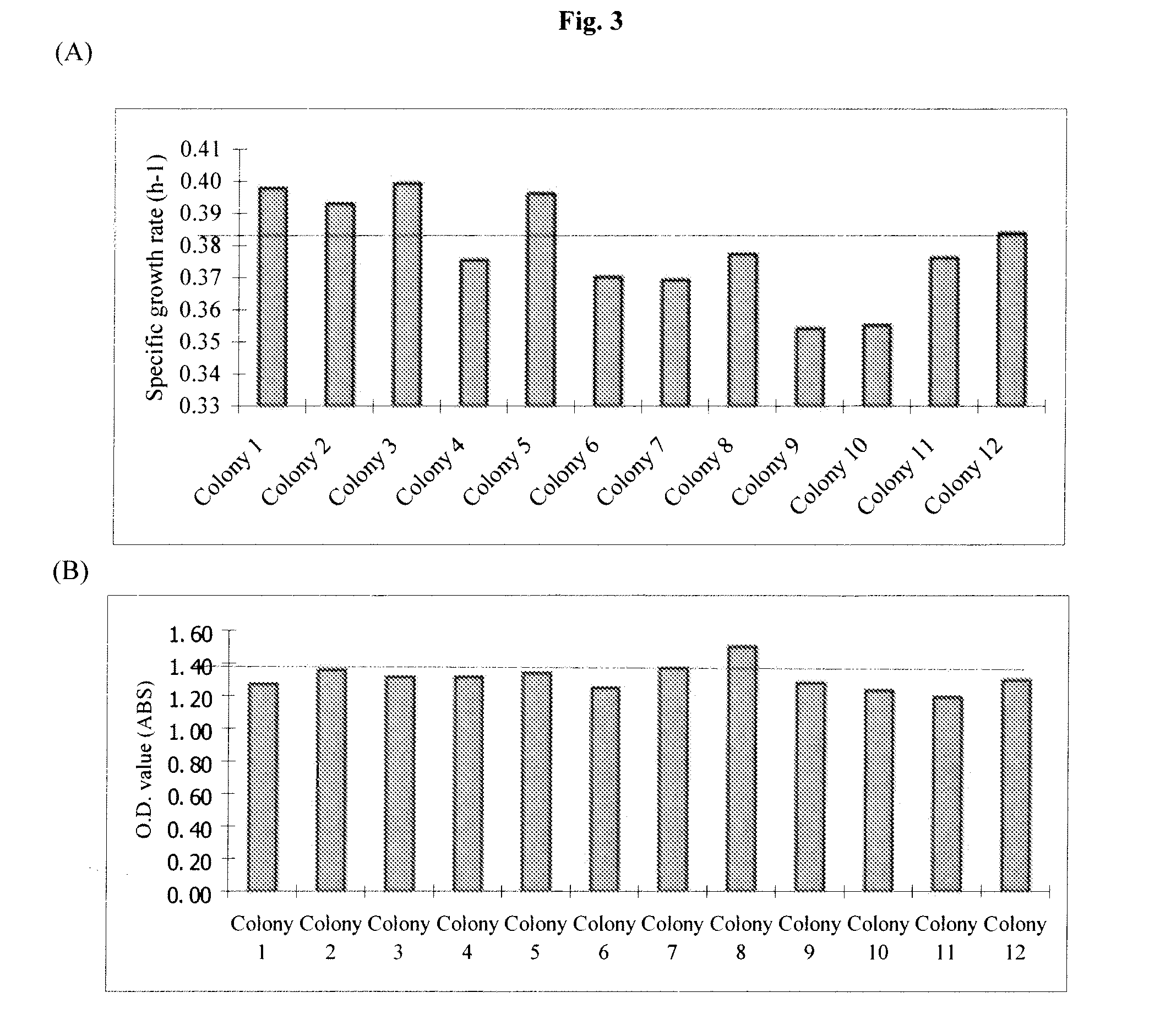
The present invention relates to methods of obtaining Z. mobilis mutant strains that are more tolerant to one or more inhibitors or more capable of efficiently fermenting one or more carbohydrates. Such inhibitors include ethanol, aliphatic acids, such as acetic acid, formic acid; furan derivatives, such as 2-furaldehyde, 2-furoic acid; and phenolic compounds, such as vanillin and hydroxybenzoic acid. Such carbohydrates may include xylose, arabinose, mannose and mixtures thereof. These mutant strains may be employed to, for example, effectively and efficiently prepare ethanol from biomass.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
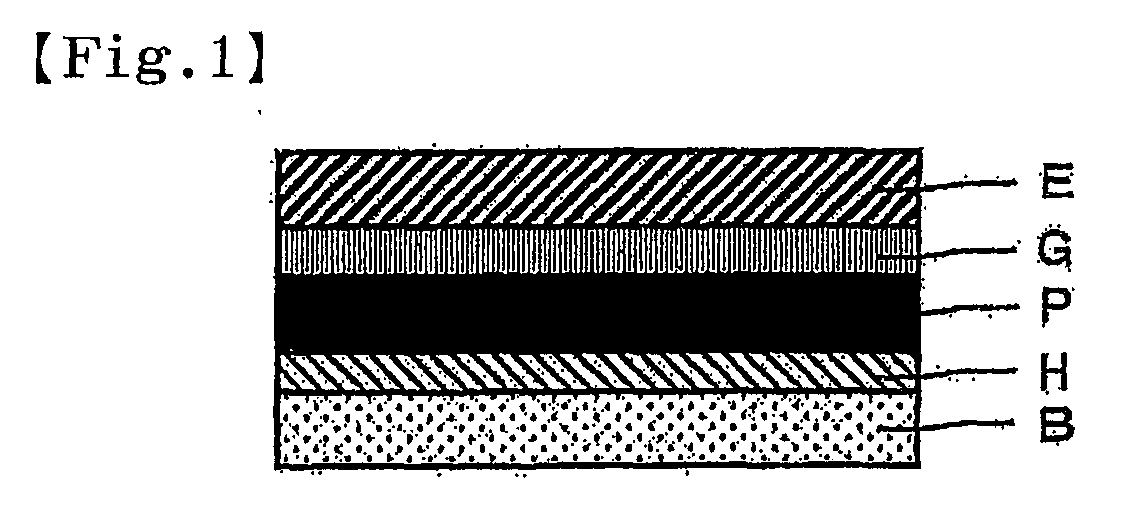
Adhesive polarization plate, image display and methods for manufacturing adhesive polarization plate and image display
InactiveUS20130098524A1Abrupt absorption and release can be preventedLow densityNitrile polymer adhesivesLaminationDisplay deviceEngineering
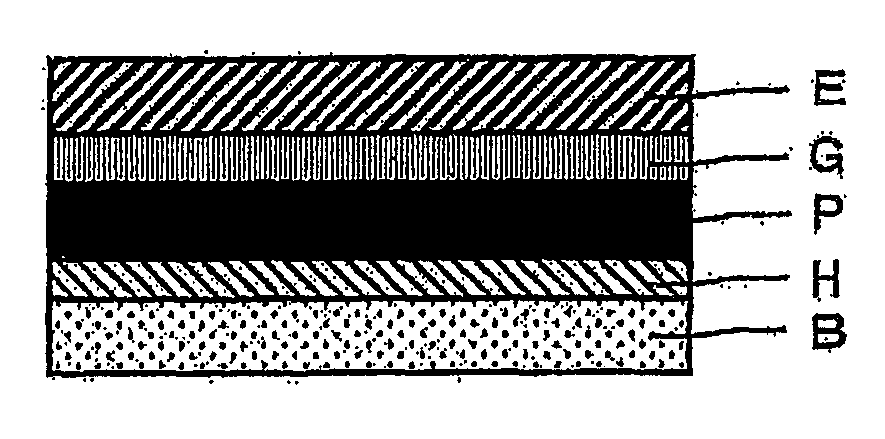
A method for manufacturing a pressure-sensitive adhesive polarizing plate comprising a polarizer (P), a transparent protective film (E) provided on only one side of the polarizer (P) with an adhesive layer (G) interposed therebetween, and a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer (B) provided on another side of the polarizer (P) with a protective layer (H) interposed therebetween, the method including forming the protective layer (H) on one side of the polarizer (P) and then placing the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer (B) on the protective layer (H), so that a laminate of the polarizer (P) and the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer (B) is formed, wherein the protective layer (H) has a tensile modulus of 100 MPa or more.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Process for manufacturing polishing pad
InactiveUS8409308B2Increase flexibilityImprove transmittanceLayered productsSpecial ornamental structuresEngineeringSlurry
A method for manufacturing a polishing pad that has a high level of optical detection accuracy and is prevented from causing slurry leak from between the polishing region and the light-transmitting region includes preparing a cell-dispersed urethane composition by a mechanical foaming method; placing a light-transmitting region at a predetermined position on a face material or a belt conveyor, continuously discharging the cell-dispersed urethane composition onto a part of the face material or the belt conveyor where the light-transmitting region is not placed; placing another face material or belt conveyor on the discharged cell-dispersed urethane composition; curing the cell-dispersed urethane composition to form a polishing region including a polyurethane foam, so that a polishing sheet is prepared; applying a coating composition containing an aliphatic and / or alicyclic polyisocyanate to one side of the polishing sheet and curing the coating composition to form a water-impermeable film; and cutting the polishing sheet.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Helmet
InactiveUS20170280810A1Improve bending resistanceBig impactHelmetsHelmet coversEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides a head protection helmet comprising an impact resistant shell comprising:a cavity for accommodating a user's head andan array of crushable bodies having a hollow closed configuration, e.g. flutes in corrugated material 14,16, the crushable bodies each having an axis that extends outwardly from the cavity to absorb impact forces exerted along the direction of the axis.
Owner:KRANIUM SPORTS
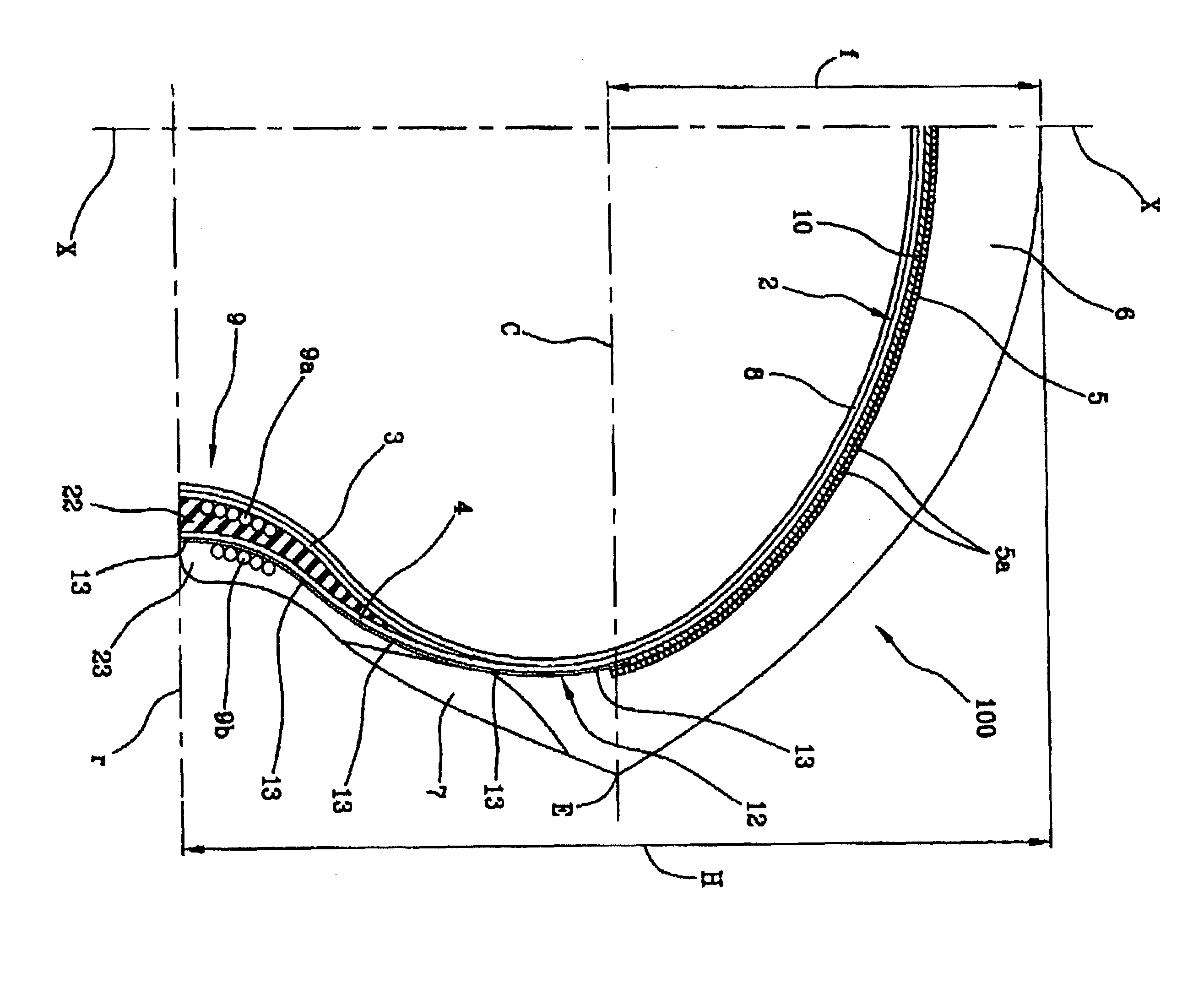
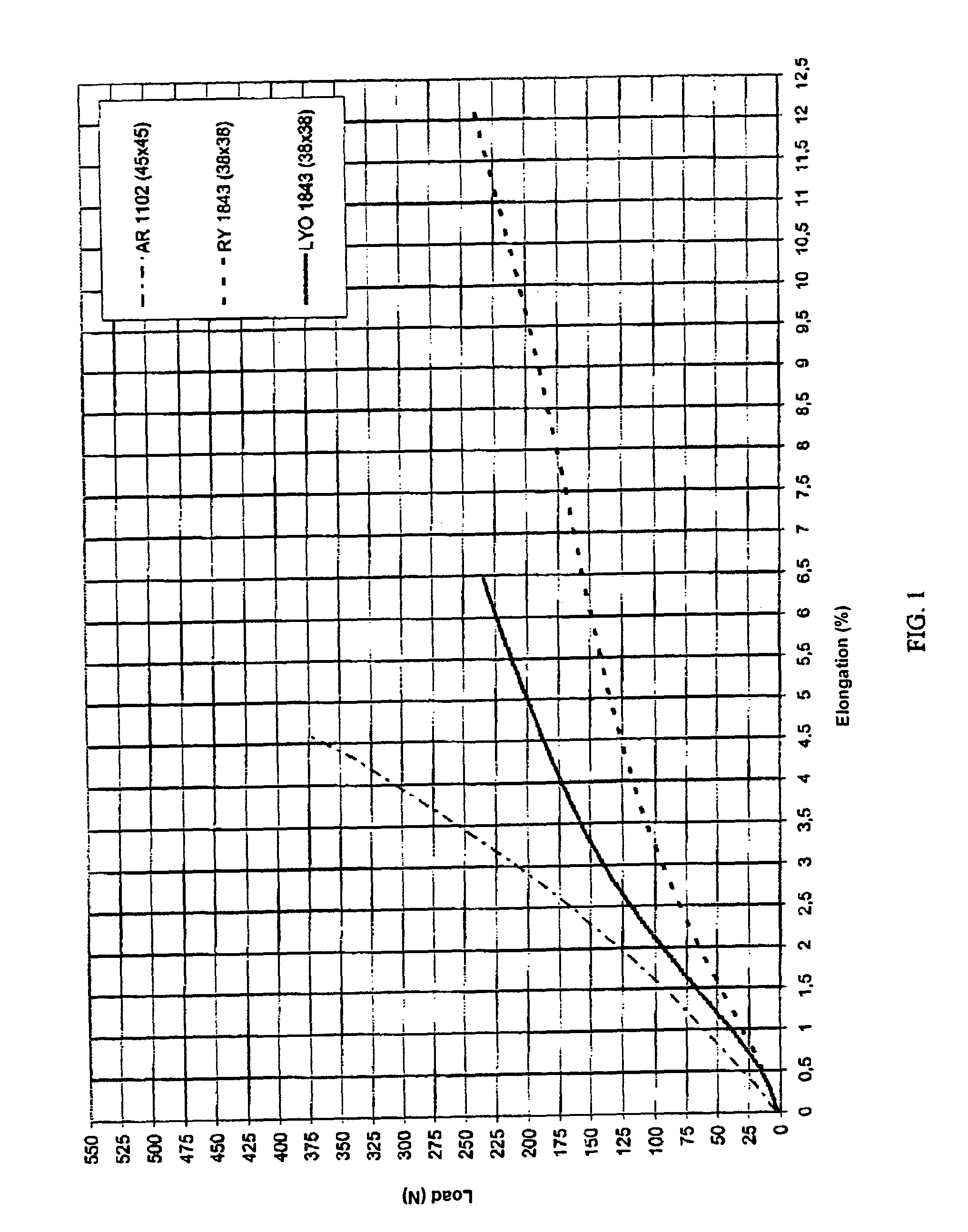
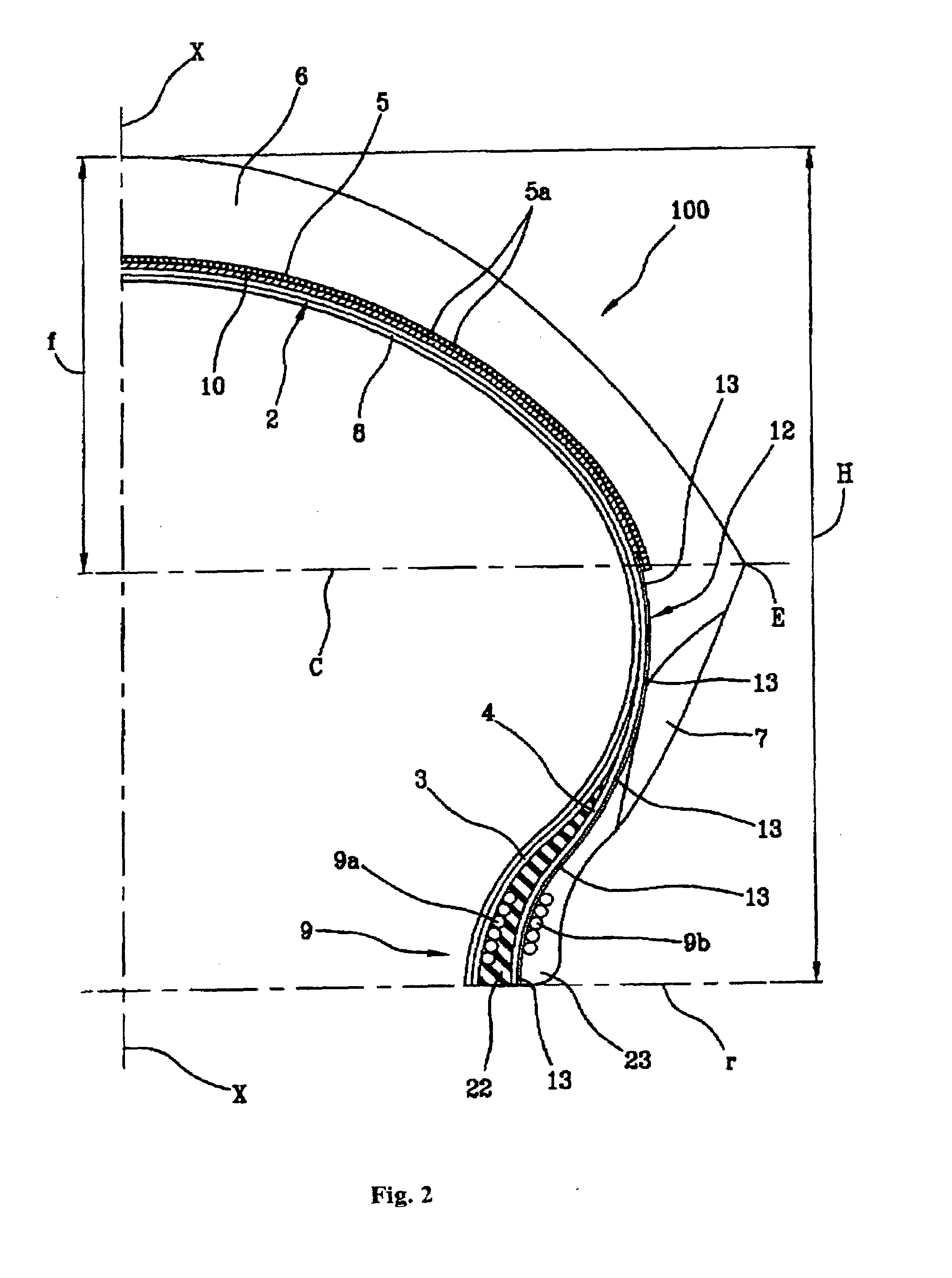
Tyre for a motor vehicle and method for controlling a motor vehicle during a manoeuvre to change direction and/or speed
InactiveUS20120118467A1Vary controlled elastic responseLarge deformationMotorcycle tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsCelluloseMotor vehicle part
A tire for a motorcycle having a transverse curvature ratio of at least 0.20 and a total height / width ratio of at least 0.5, includes a radial carcass including textile cords made from lyocell cellulose fibre.
Owner:PIRELLI TYRE SPA
Toner, developer, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20160231661A1Toner becomes greatLow temperature fixing abilityElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersChemistryTetrahydrofuran
A toner, wherein the toner has glass transition temperature [Tg1st (toner)] of 20° C. to 50° C., where the glass transition temperature [Tg1st (toner)] is measured in a first heating in differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of the toner, wherein tetrahydrofuran (THF) insoluble matter of the toner has glass transition temperature [Tg2nd (THF insoluble matter)] of −40° C. to 30° C., where the glass transition temperature [Tg2nd (THF insoluble matter)] is measured in a second heating in differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of the tetrahydrofuran (THF) insoluble matter, wherein the THF insoluble matter has a storage modulus at 100° C. [G′(100) (THF insoluble matter)] of 1.0×105 Pa to 1.0×107 Pa, and wherein a ratio of a storage modulus of the THF insoluble matter at 40° C. [G′(40) (THF insoluble matter)] to the storage modulus of the THF insoluble matter at 100° C. [G′(100) (THF insoluble matter)] is 3.5×10 or less.
Owner:RICOH KK
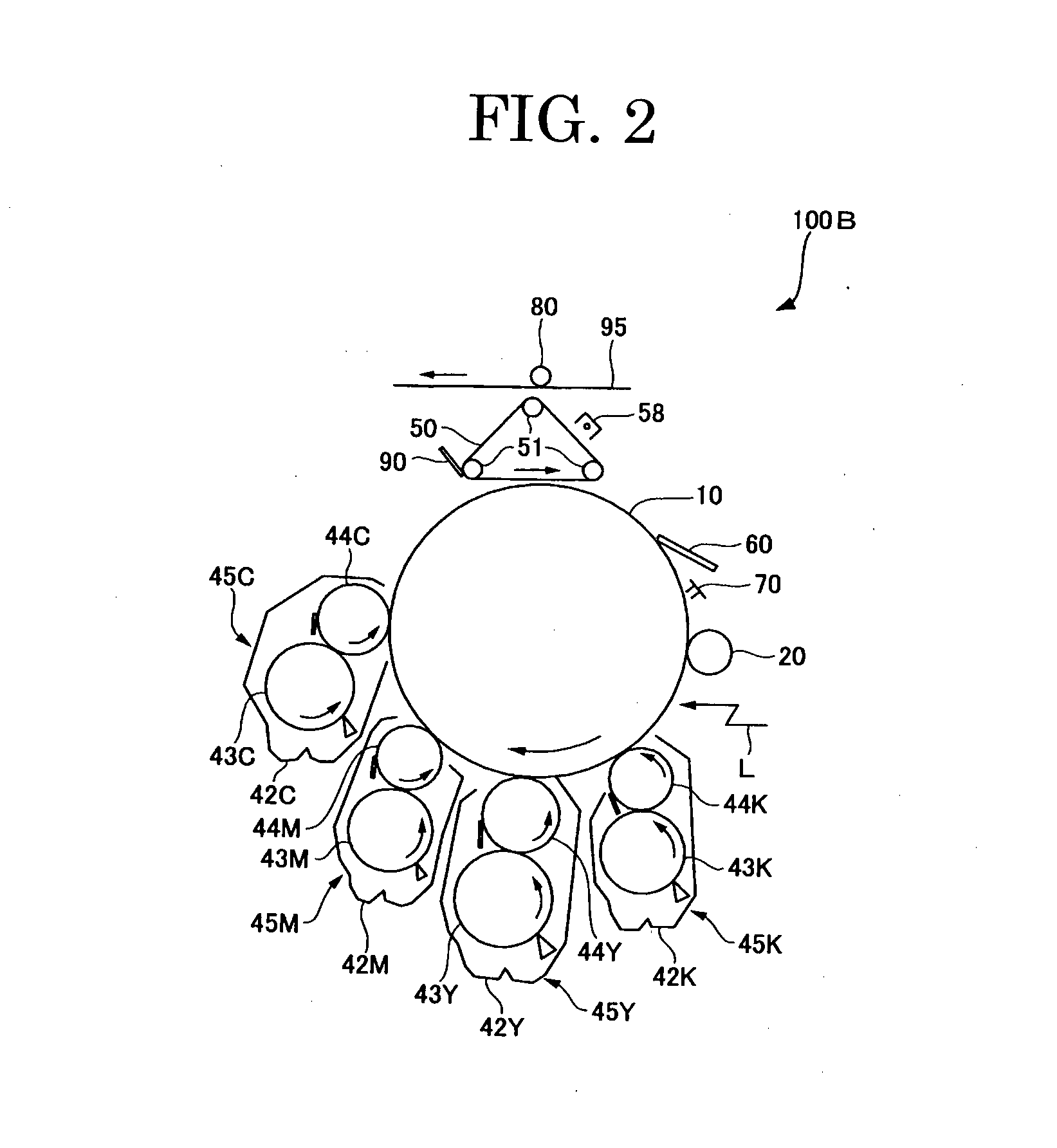
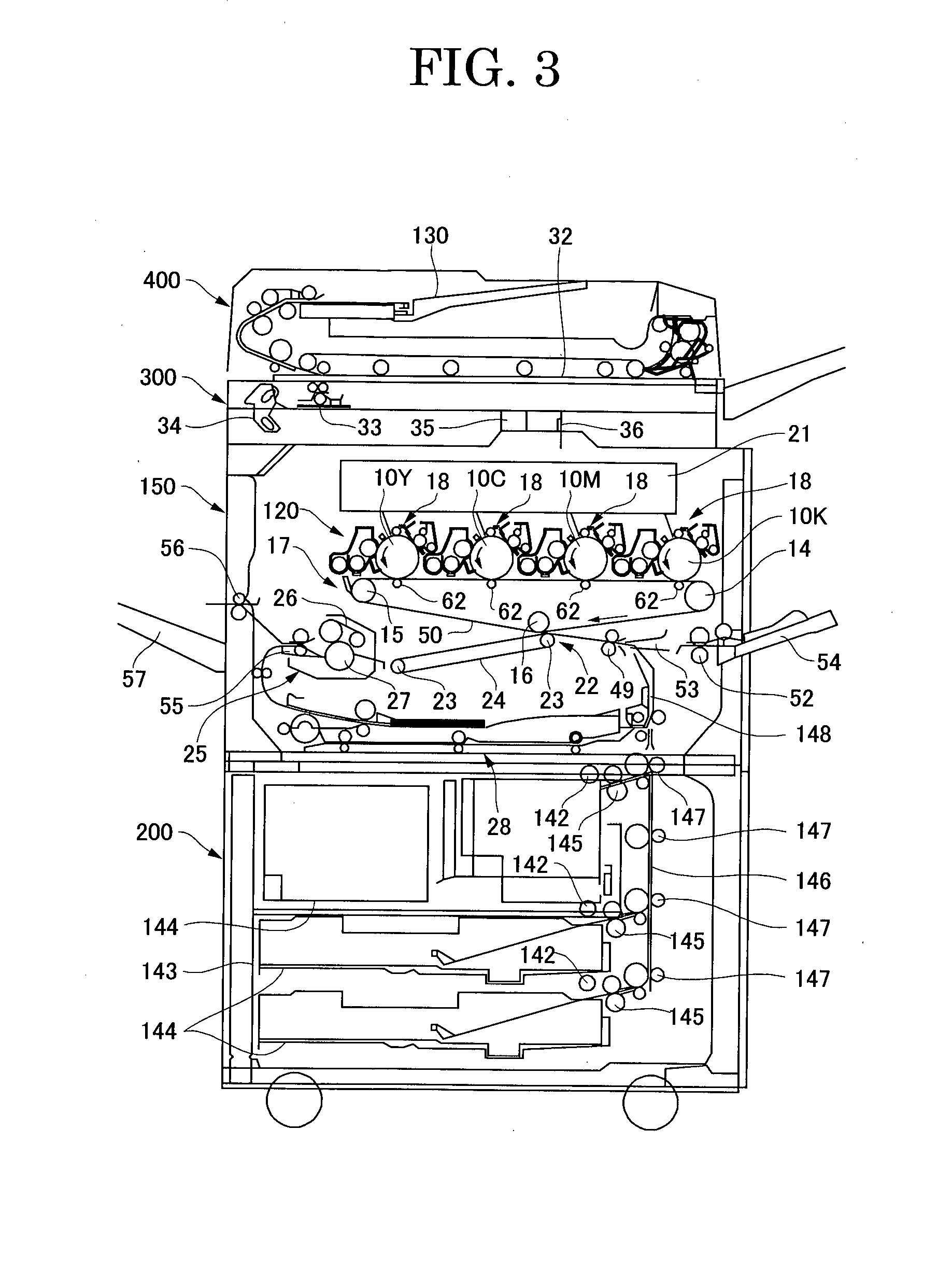
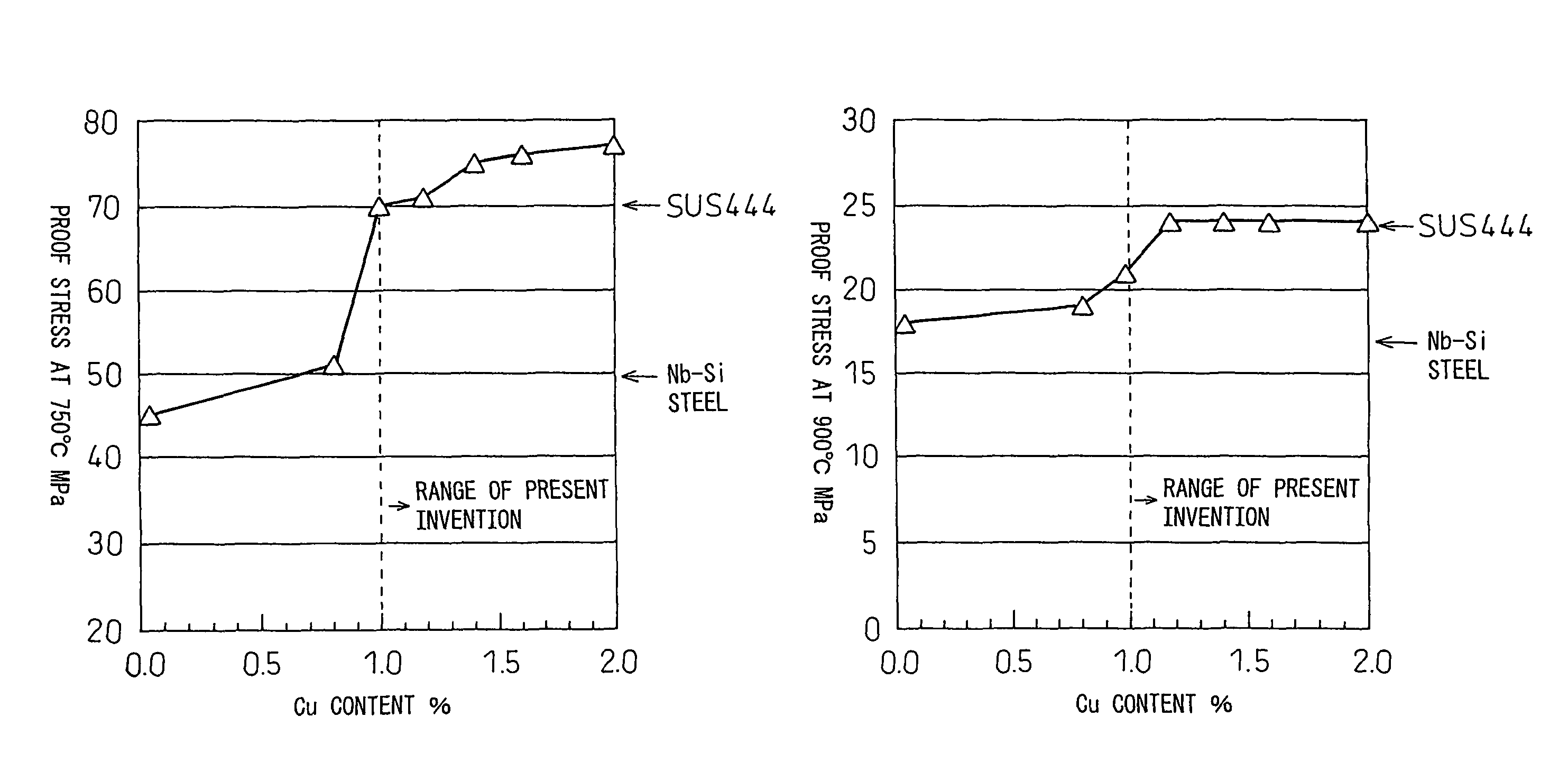
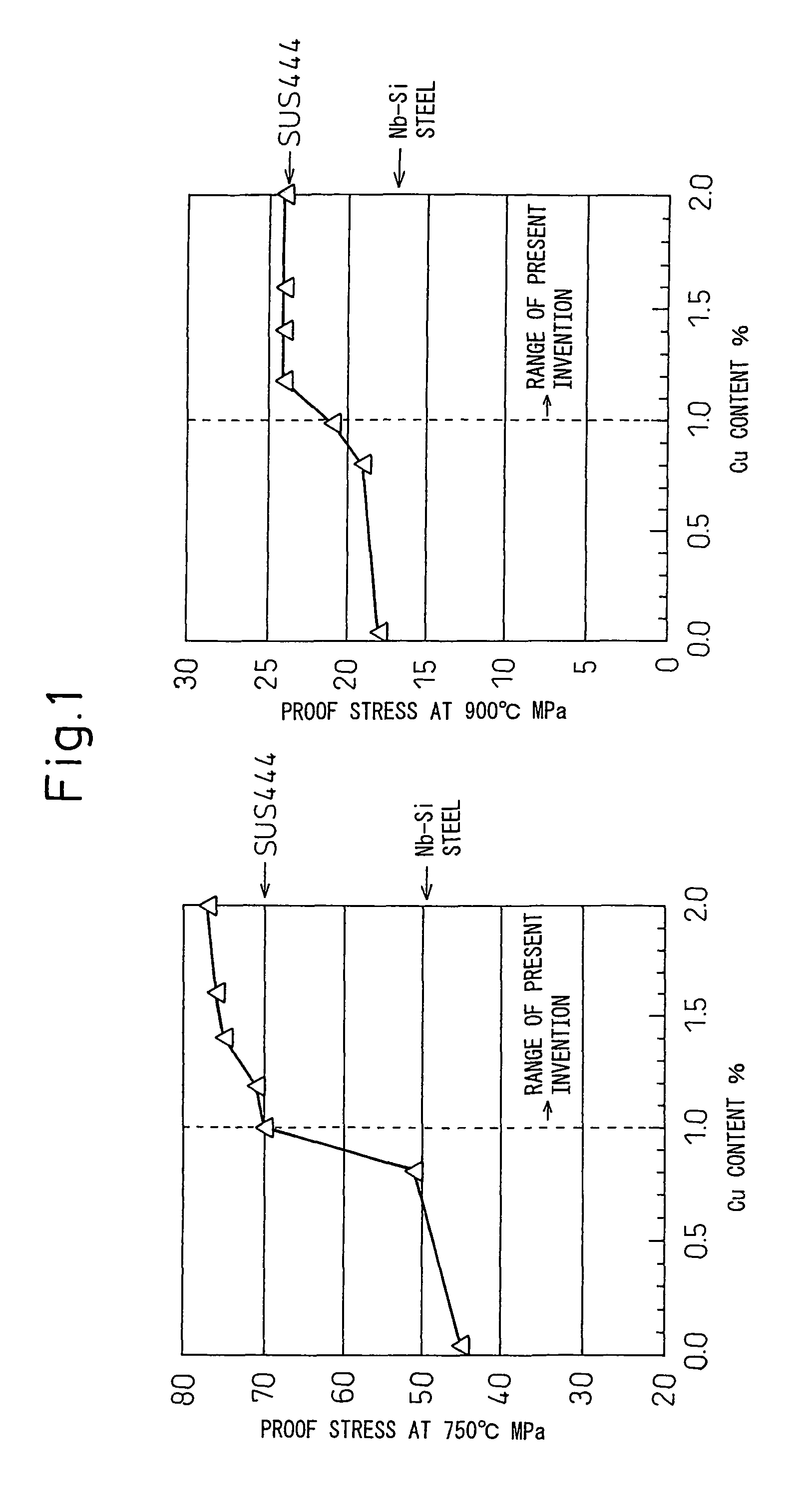
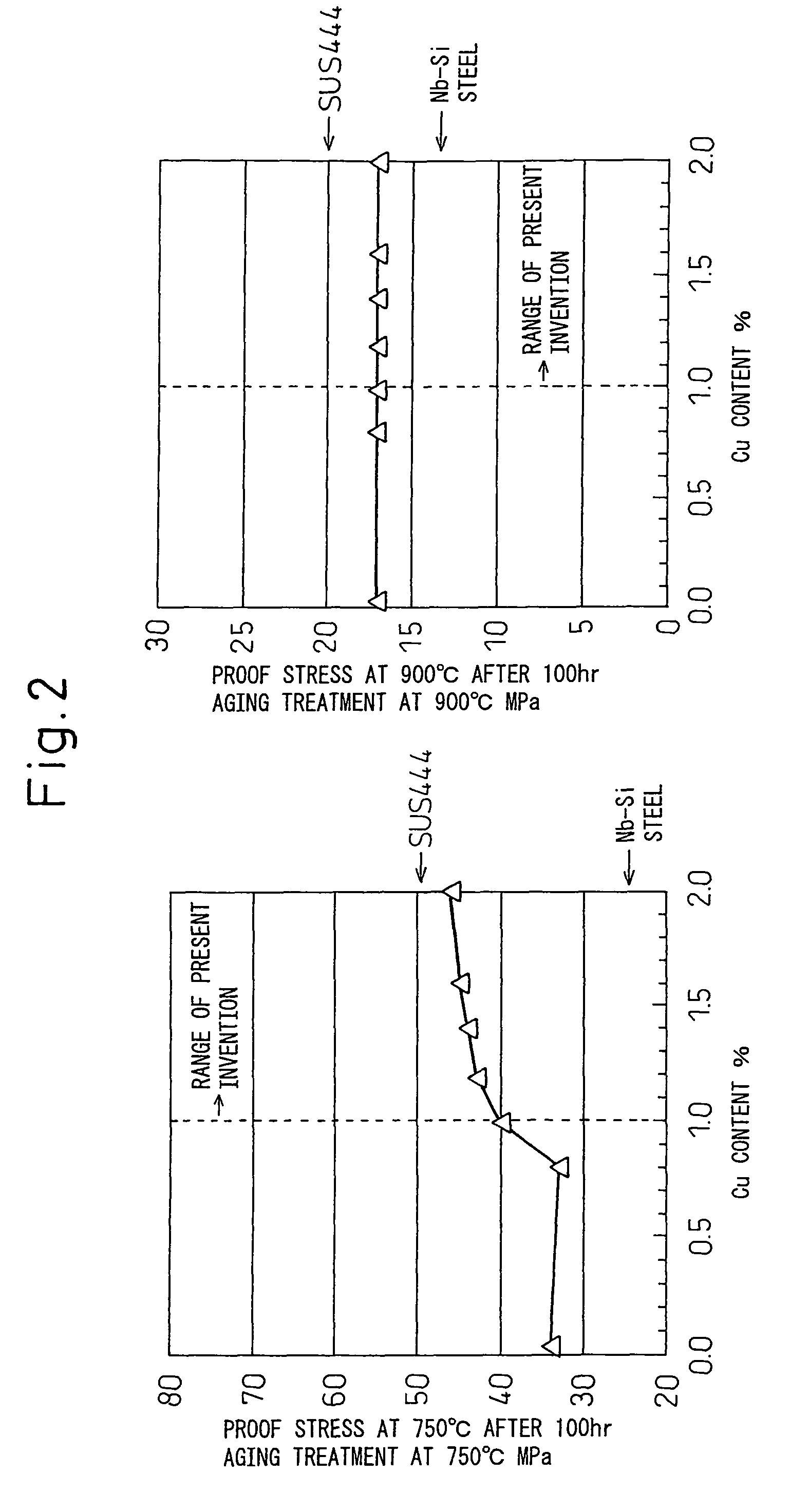
Ferritic stainless steel sheet superior in heat resistance
ActiveUS8062584B2Inhibition strength declineSuppression problemExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusMetallurgyHeat resistance
The present invention provides, as a material superior in heat resistance in a hot environment where the maximum temperature of the exhaust gas becomes 750 to 900° C., ferritic stainless steel sheet superior in heat resistance in a broad temperature region of 750 to 900° C. with long term stability by a smaller amount of addition of Mo than SUS444 containing about 2% of expensive Mo, that is, ferritic stainless steel sheet superior in heat resistance characterized by containing, by mass %, C: 0.01% or less, N: 0.02% or less, Si: 0.05 to 1%, Mn: 0.1 to 2%, Cr: 10 to 30%, Mo: 0.1 to 1%, Cu: 1 to 2%, Nb: 0.2 to 0.7%, Ti: 0.01 to 0.3%, and B: 0.0002 to 0.0050%, having a balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities, and having a 0.2% yield strength at 750° C. of 70 MPa or more.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMIKIN STAINLESS STEEL CORP
Method for producing clone seedlings
InactiveUS20120240462A1Improve productivityRapid mass productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsOxidized GlutathioneShoot
A shoot of a plant is cultivated under the presence of glutathione, so that the shoot is rooted. It is possible to cultivate the shoot under the presence of glutathione by use of a rooting medium including glutathione or by contacting a solution including glutathione with the shoot. Oxidized glutathione is preferably used as glutathione. By promoting rooting of the shoot of the plant, a rooting rate of the shoot of the plant is improved. This improves productivity of a clone seedling.
Owner:OKAYAMA PREFECTURE
Photo-bioreactor with Particle Separation and Water Recovery System
InactiveUS20110053257A1Low costEasy maintenanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWater useSystems design
The Photo-bioreactor with Particle Concentration and Water Recovery System is a bioreactor system designed to propagate algae under fully closed, controlled conditions. The system is highly efficient and has a reduced turnaround time compared to similar photo-bioreactors. The system has an integrated, gravity-flow biomass harvest and water recovery system that allows the operator to simultaneously harvest the cell concentrate and recycle the water used in the growth media. The bioreactor's scale can range from a single bench-top unit to multiple, large-scale commercial units in a manifold type array, and can utilize sunlight or artificial light.
Owner:RAGSDALE IAN LANE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com