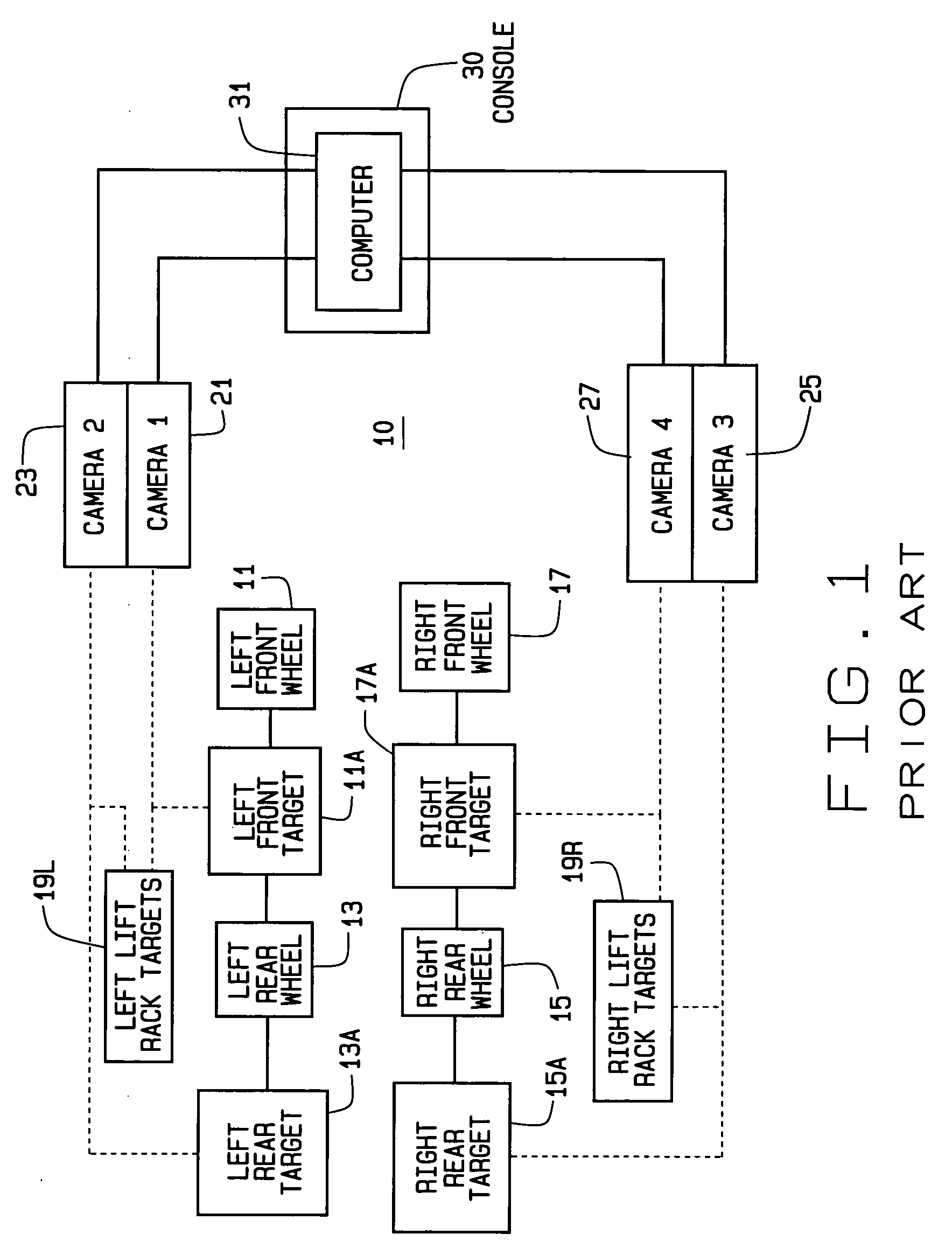
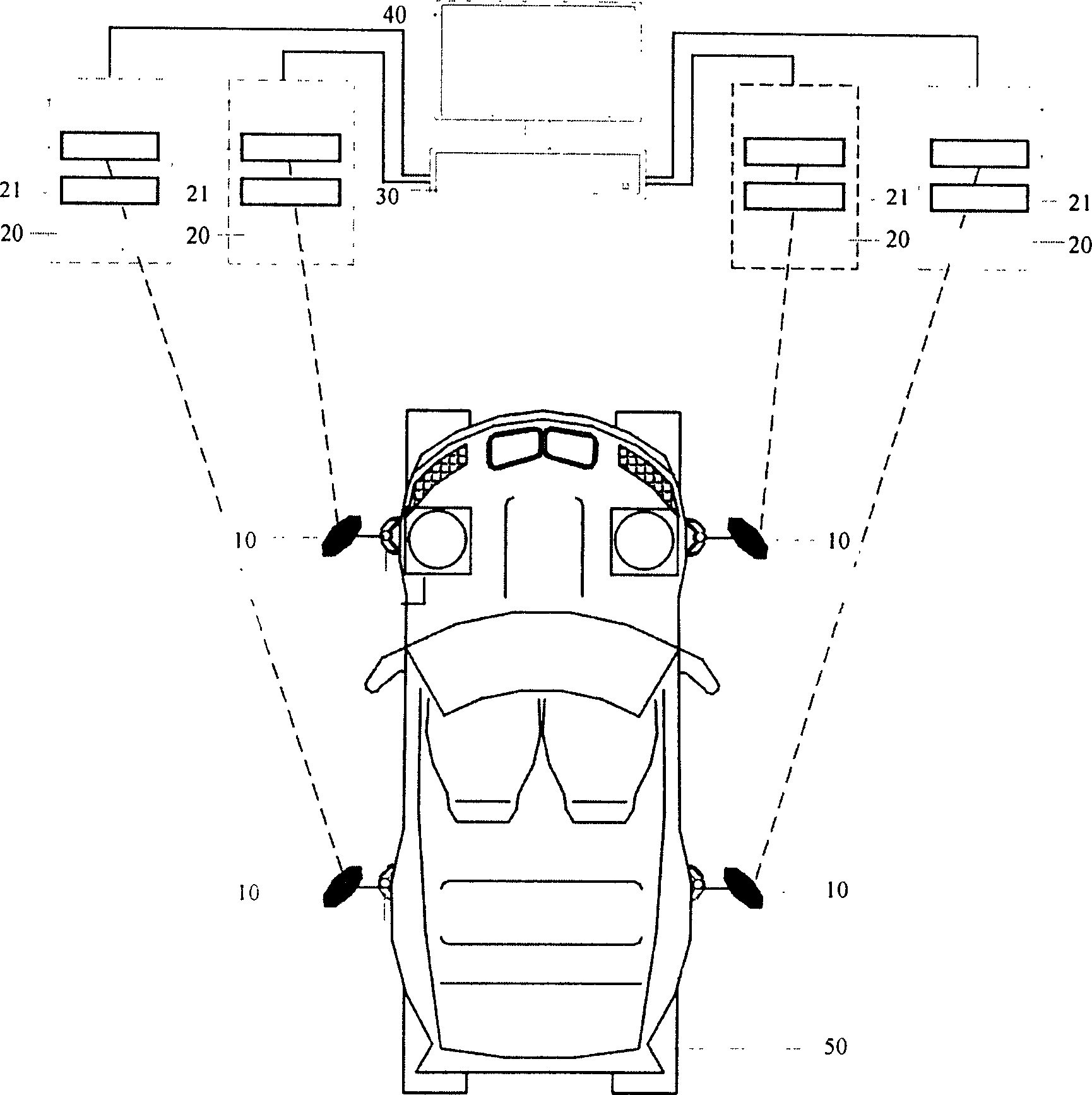
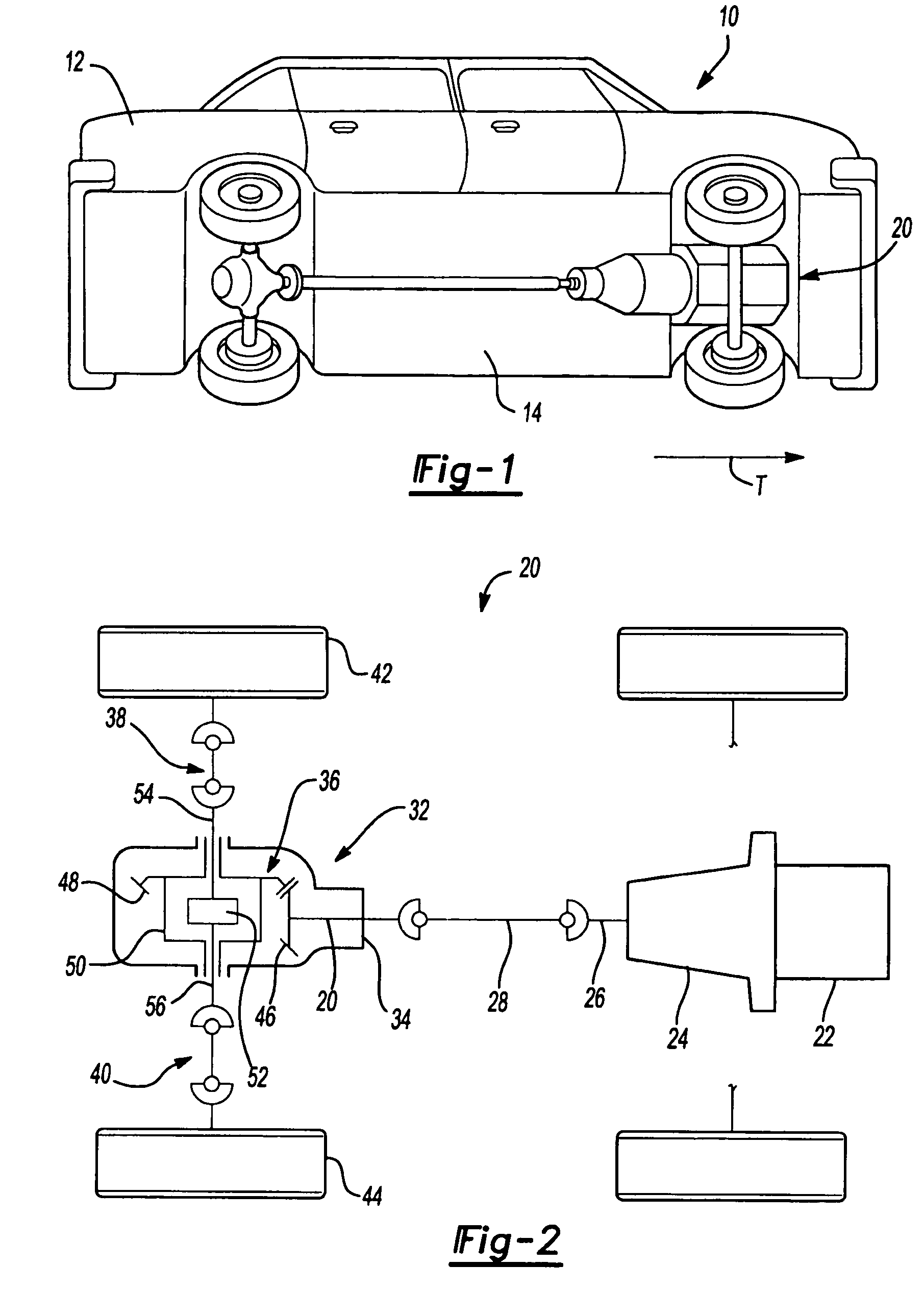
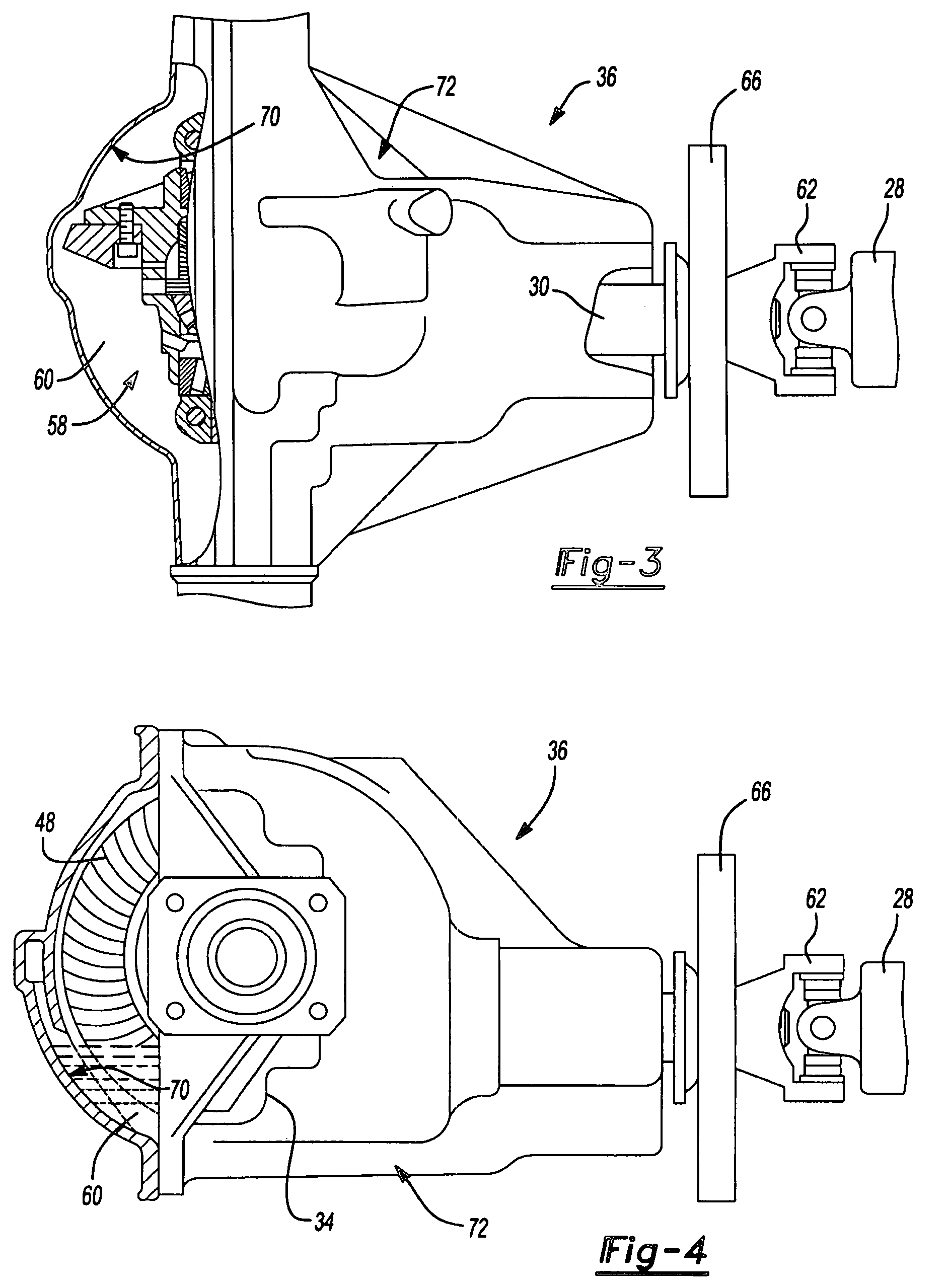
Patents
Literature
639 results about "Wheel alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
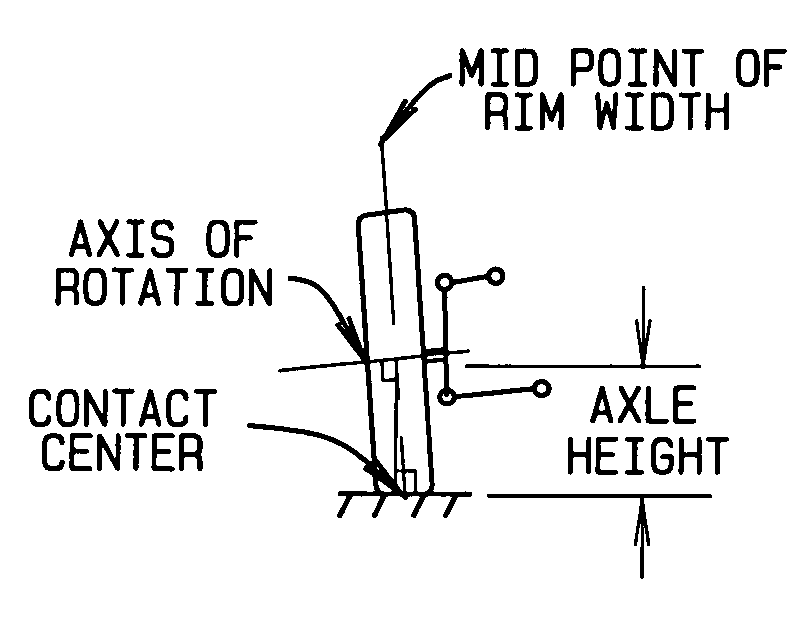
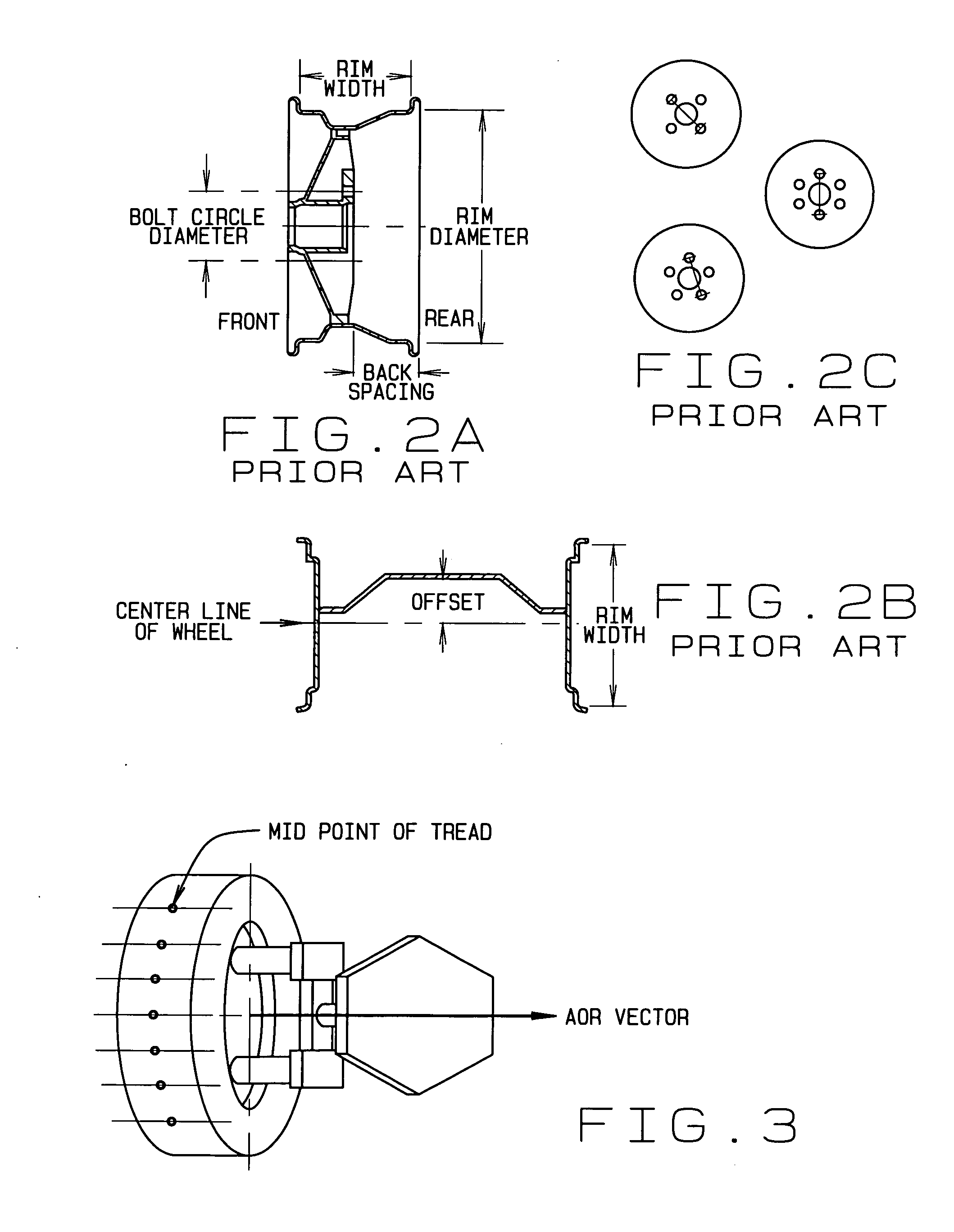
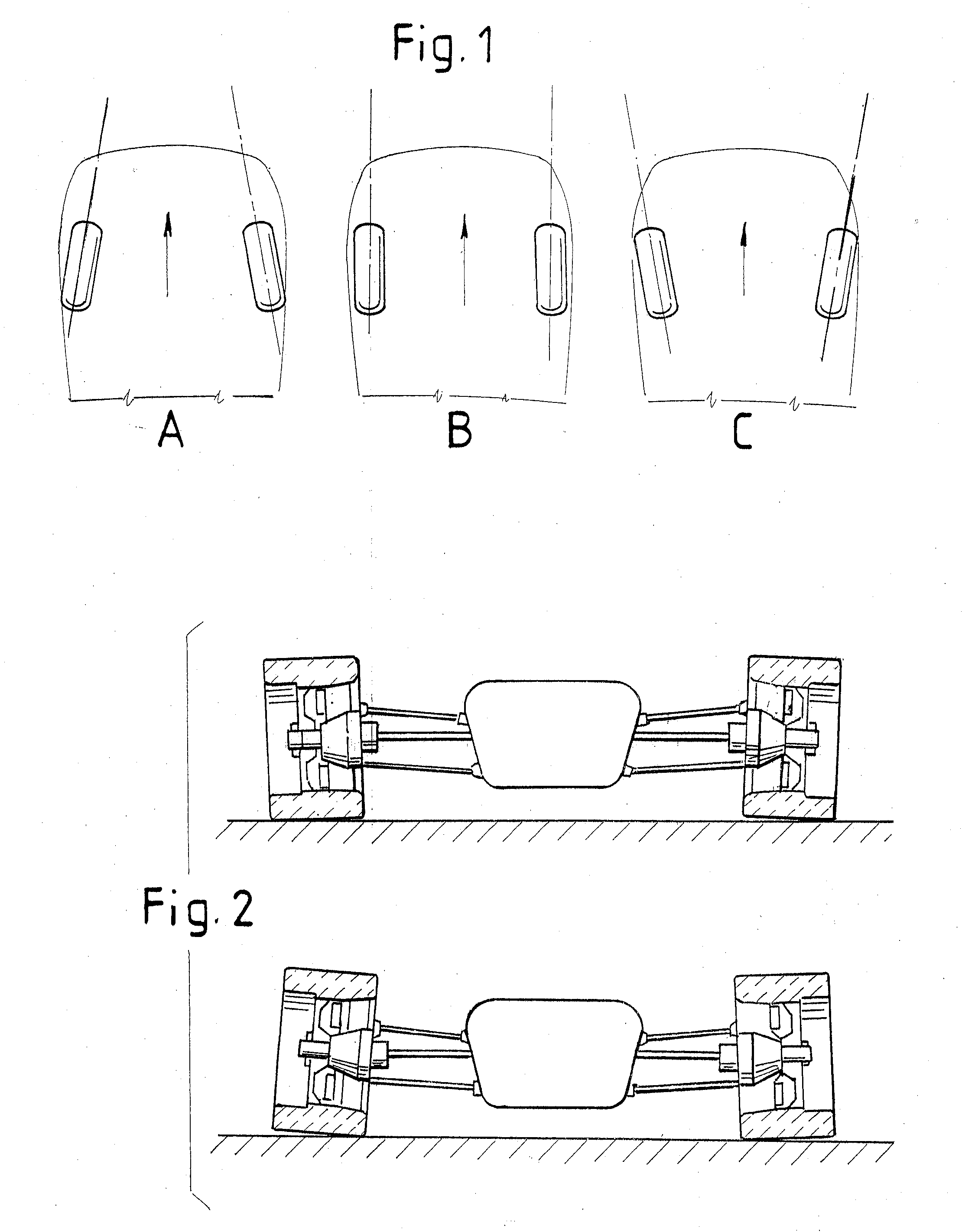
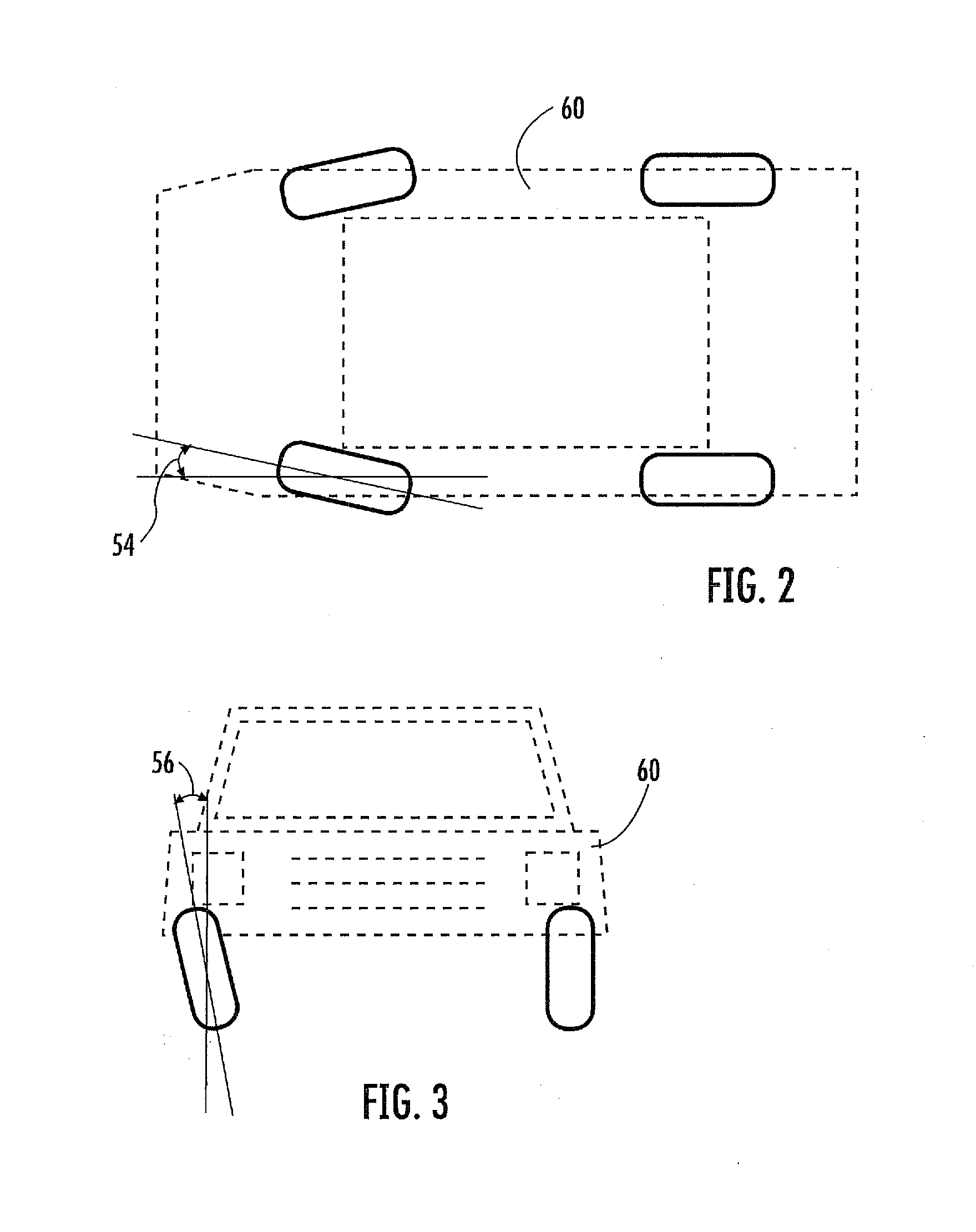
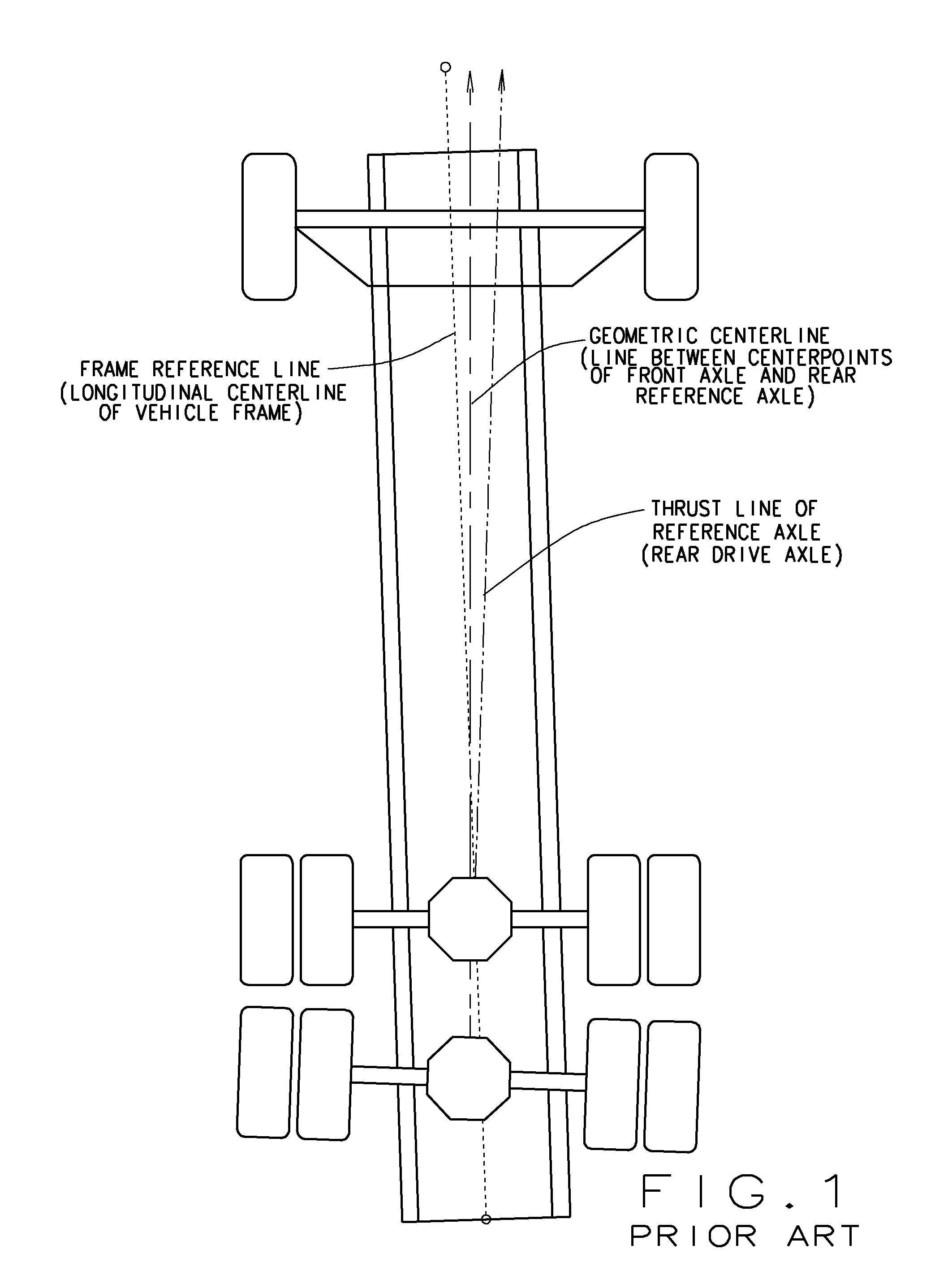
Wheel alignment, sometimes referred to as breaking or tracking, is part of standard automobile maintenance that consists of adjusting the angles of wheels to the car manufacturer specifications. The purpose of these adjustments is to reduce tire wear, and to ensure that vehicle travel is straight and true (without "pulling" to one side). Alignment angles can also be altered beyond the maker's specifications to obtain a specific handling characteristic. Motorsport and off-road applications may call for angles to be adjusted well beyond "normal", for a variety of reasons.
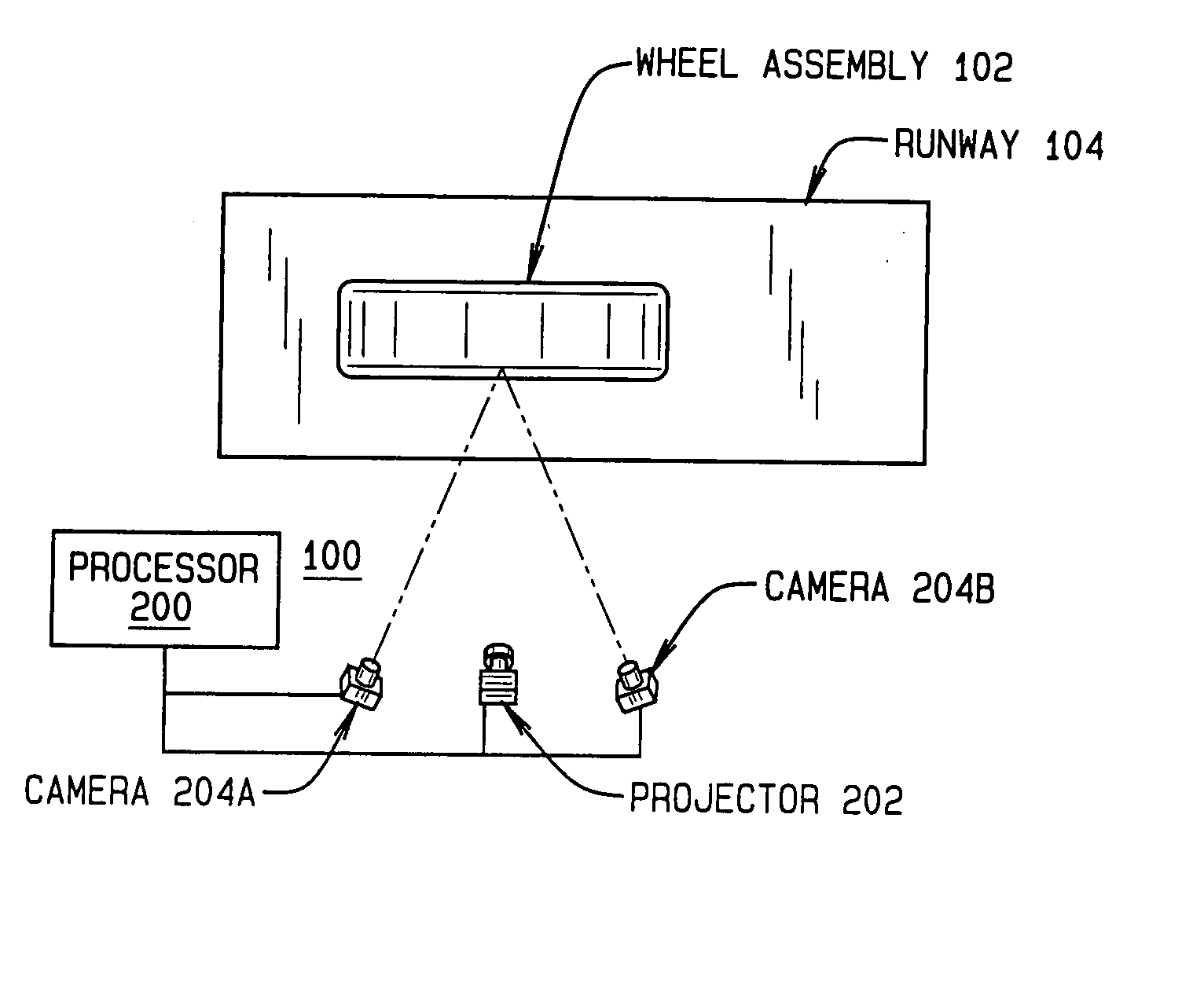
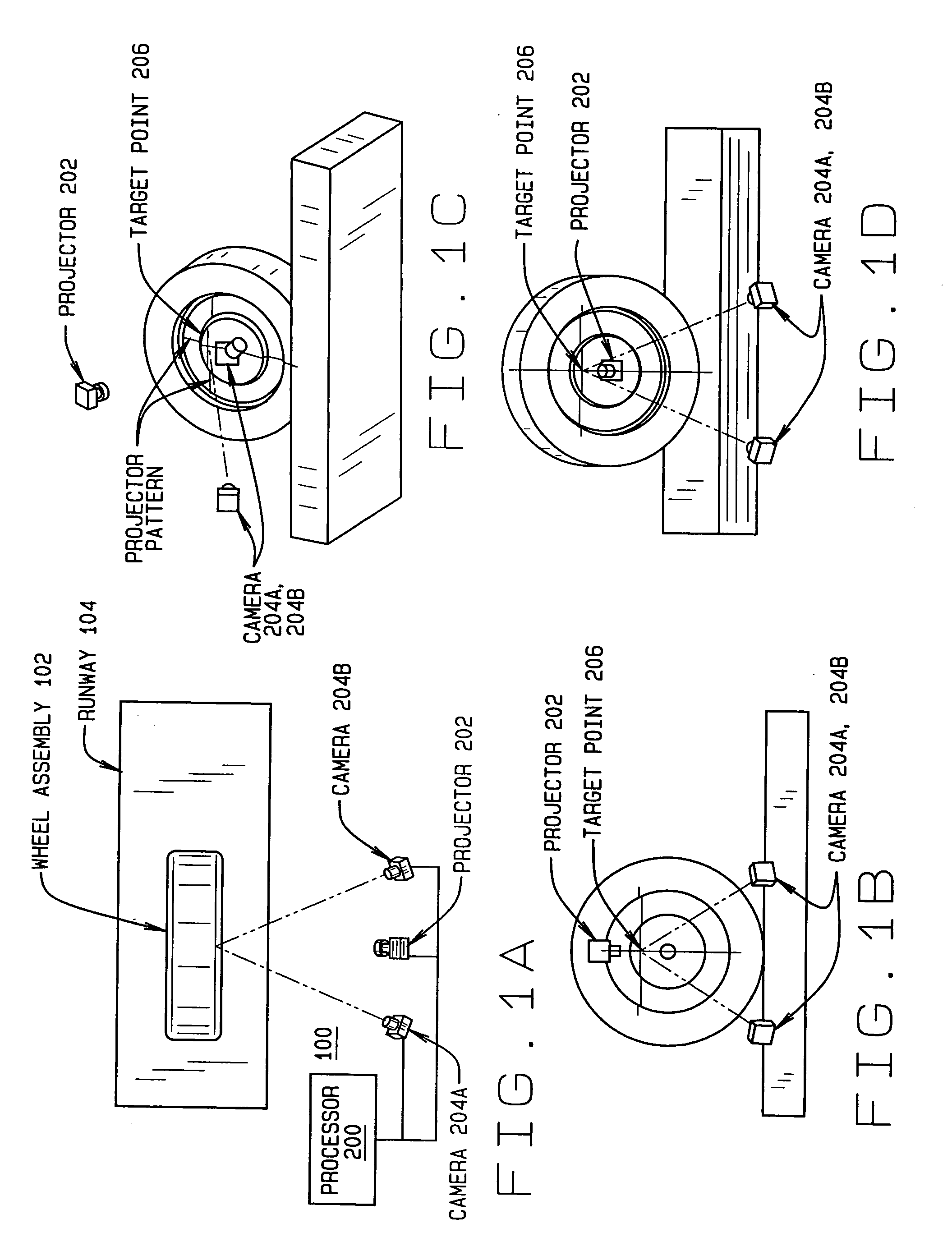
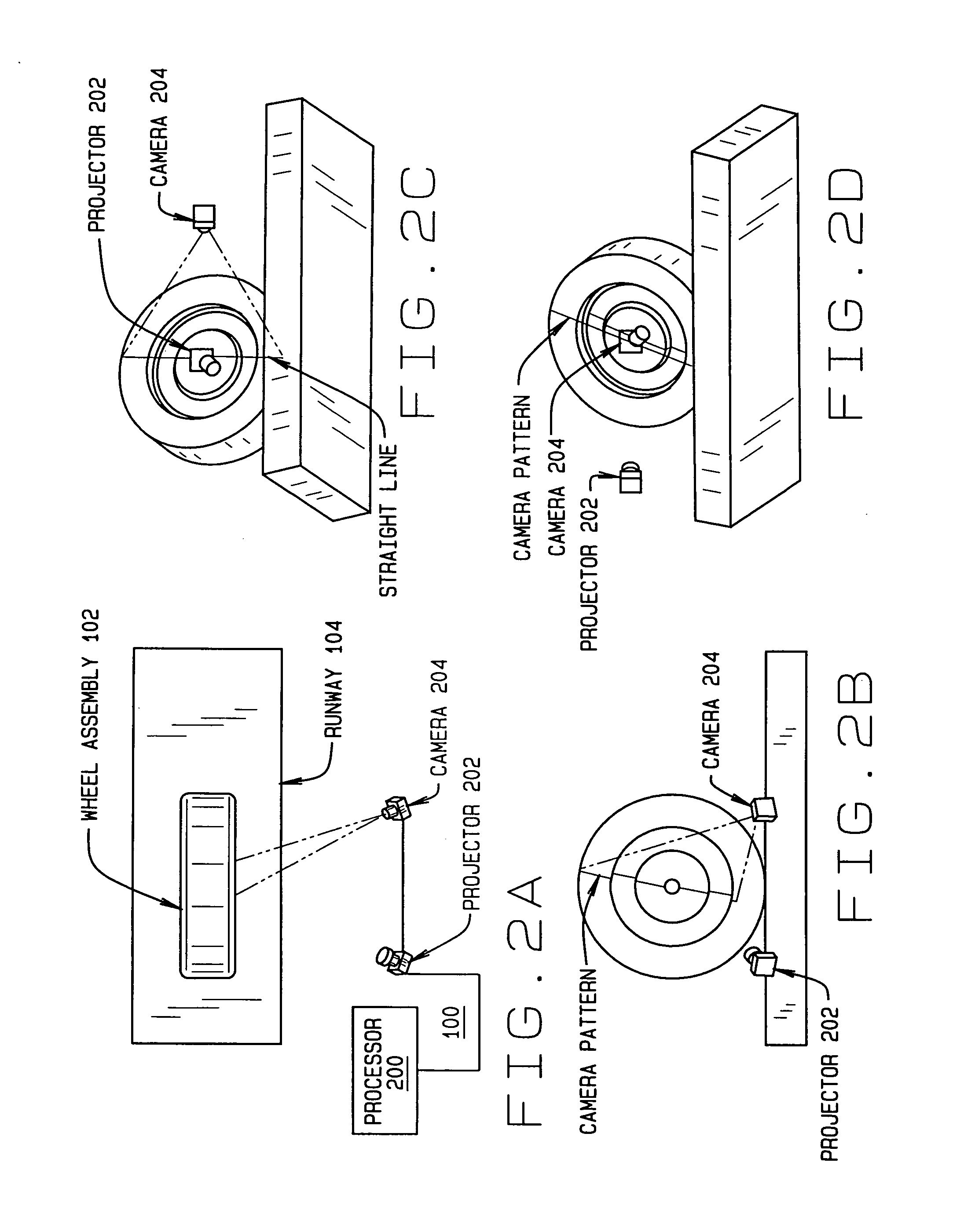
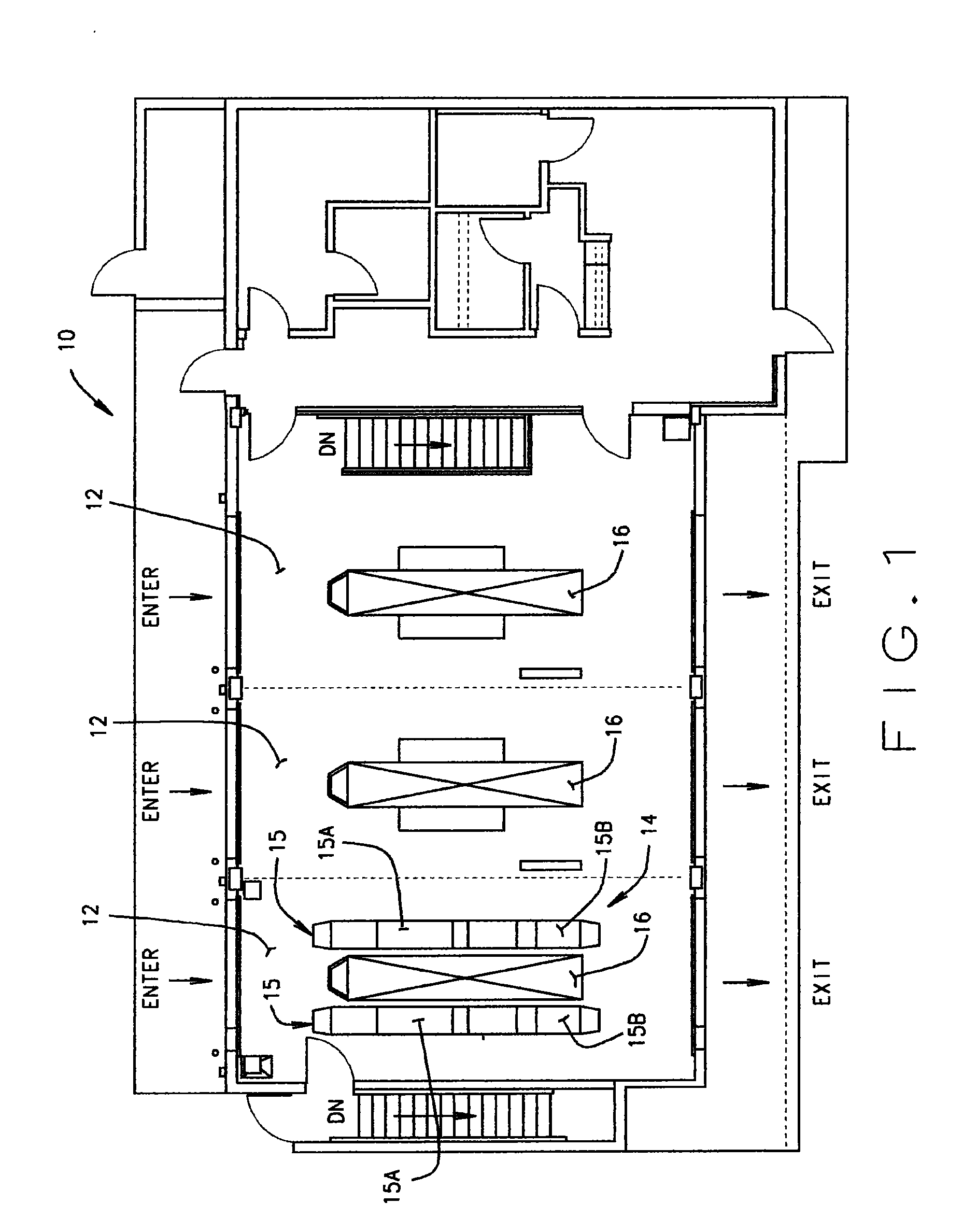
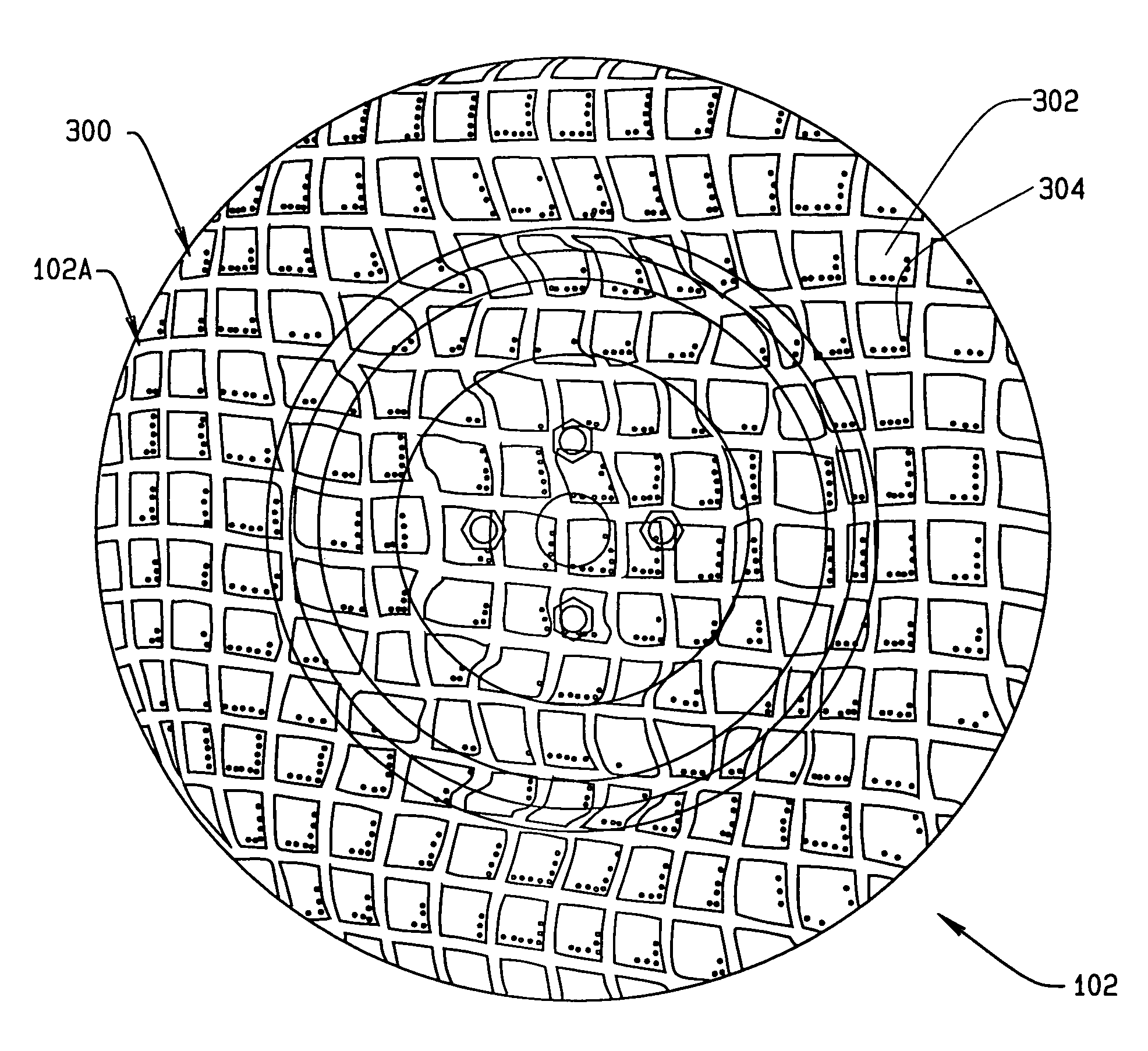
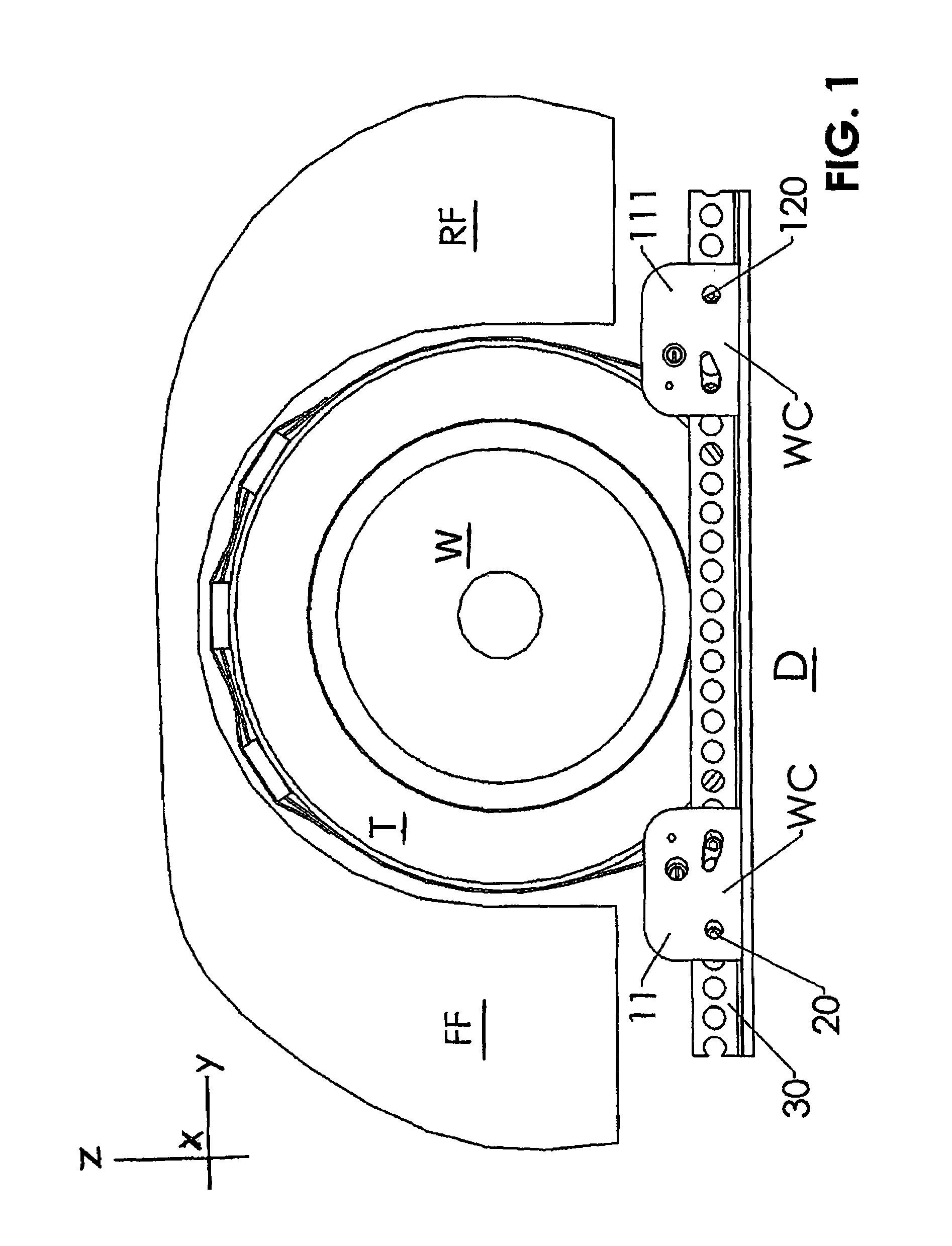
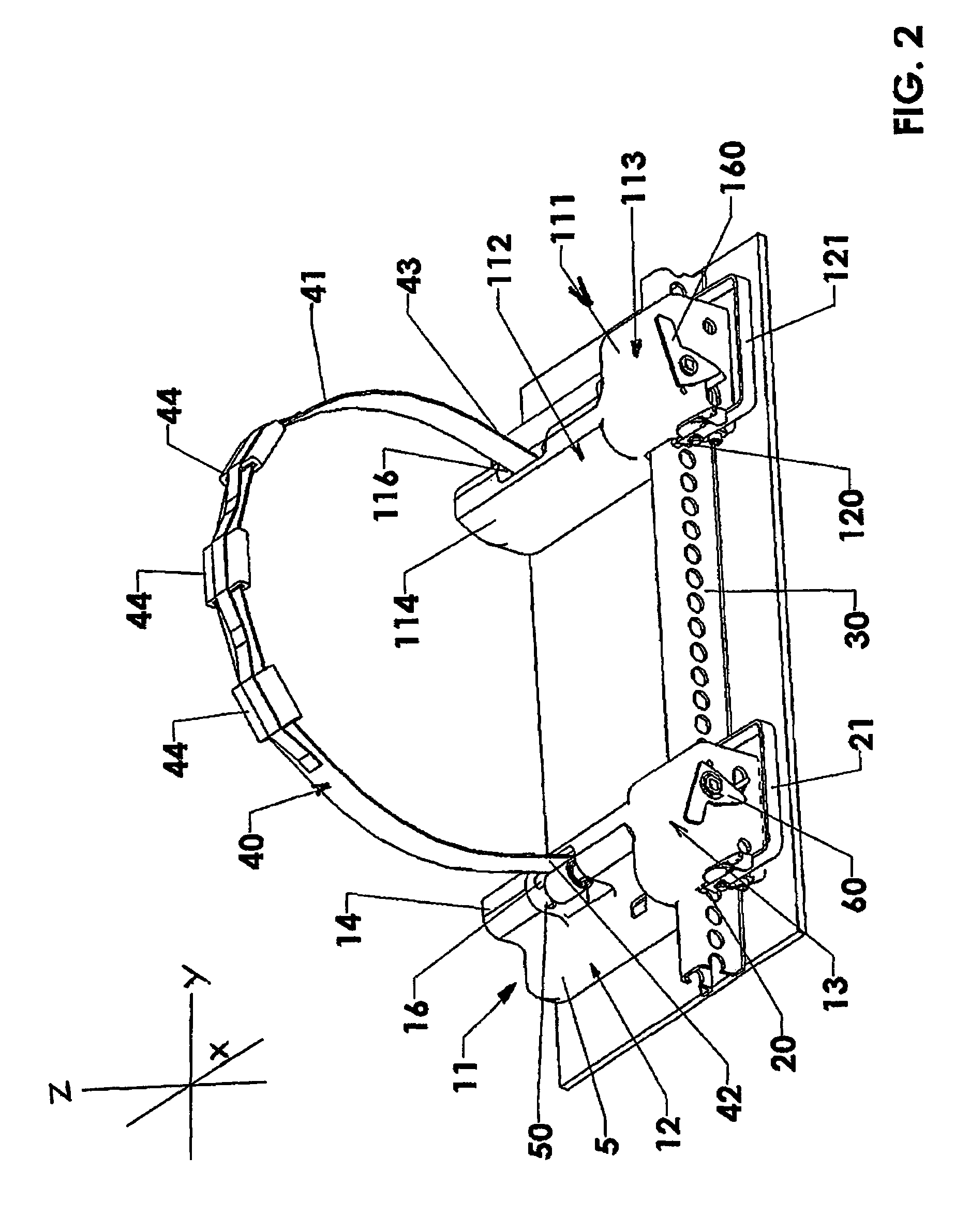
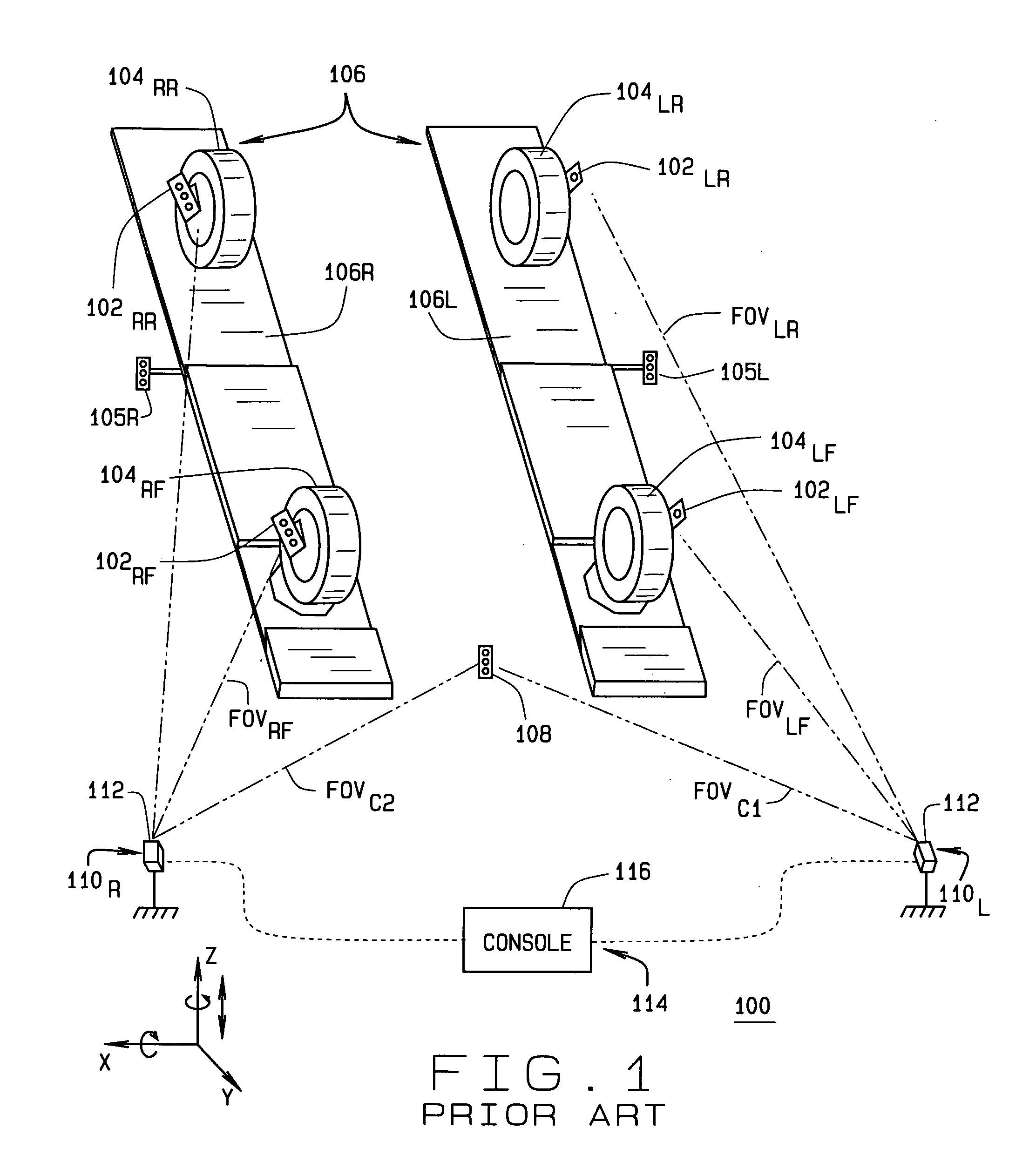
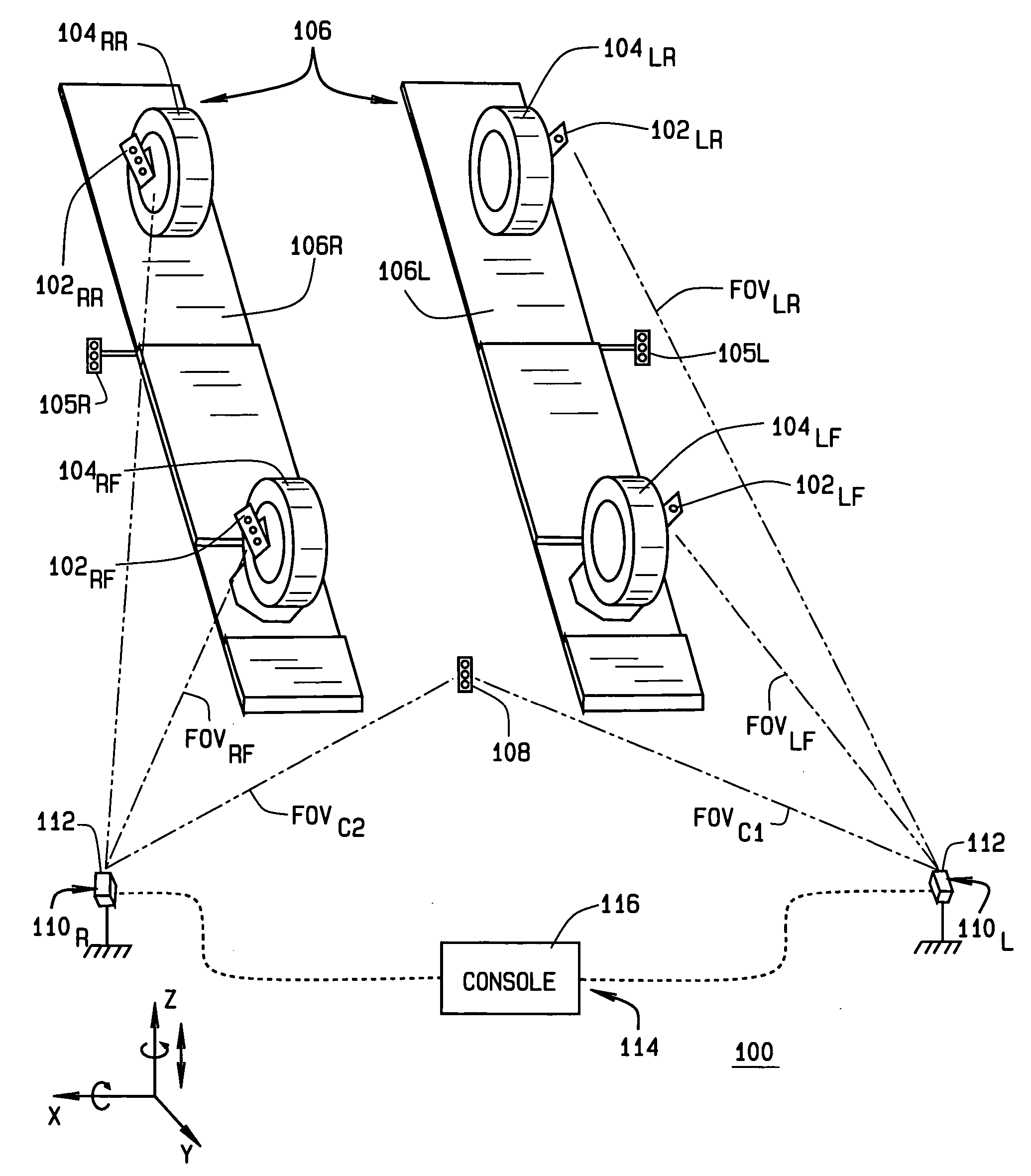
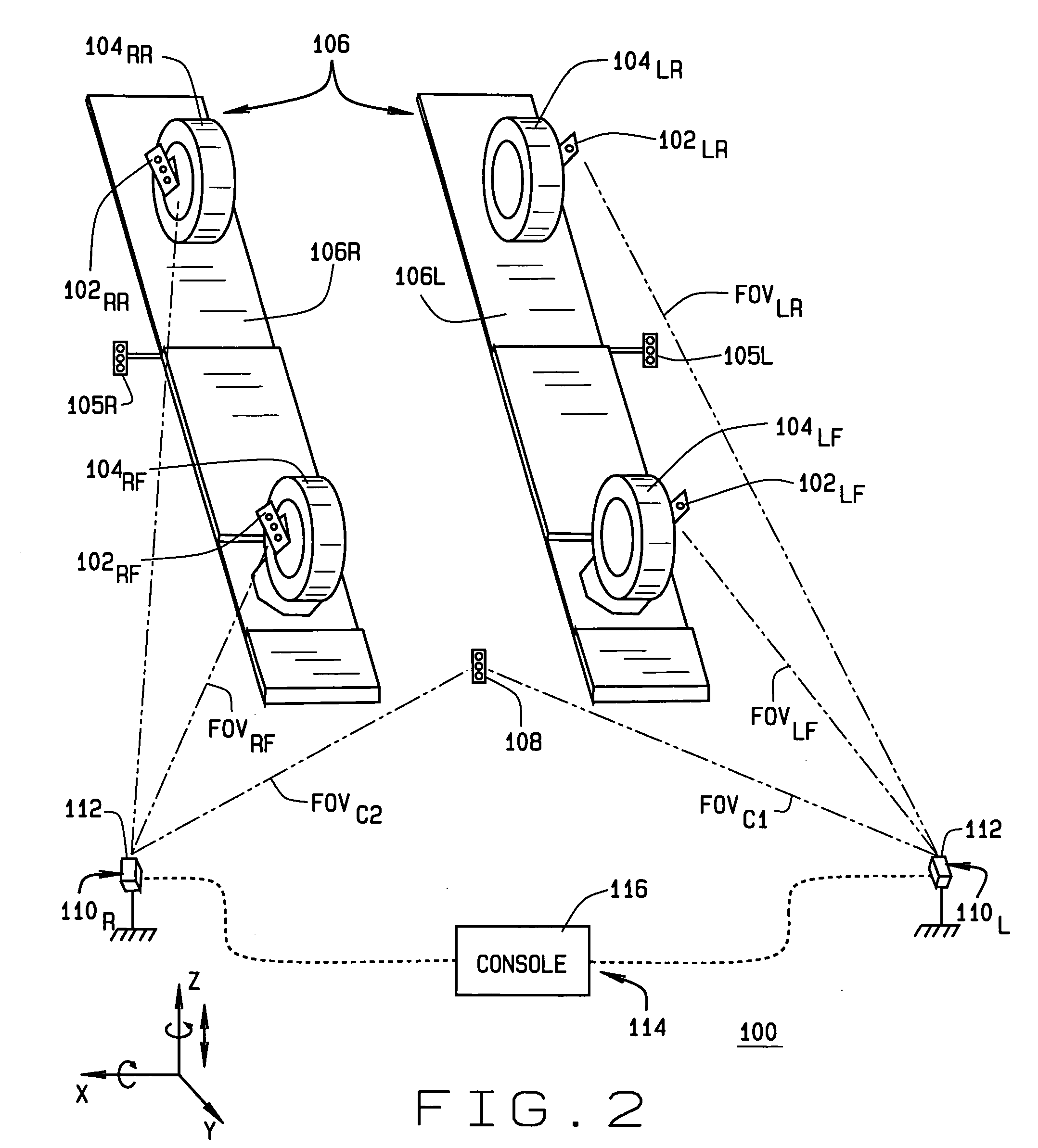
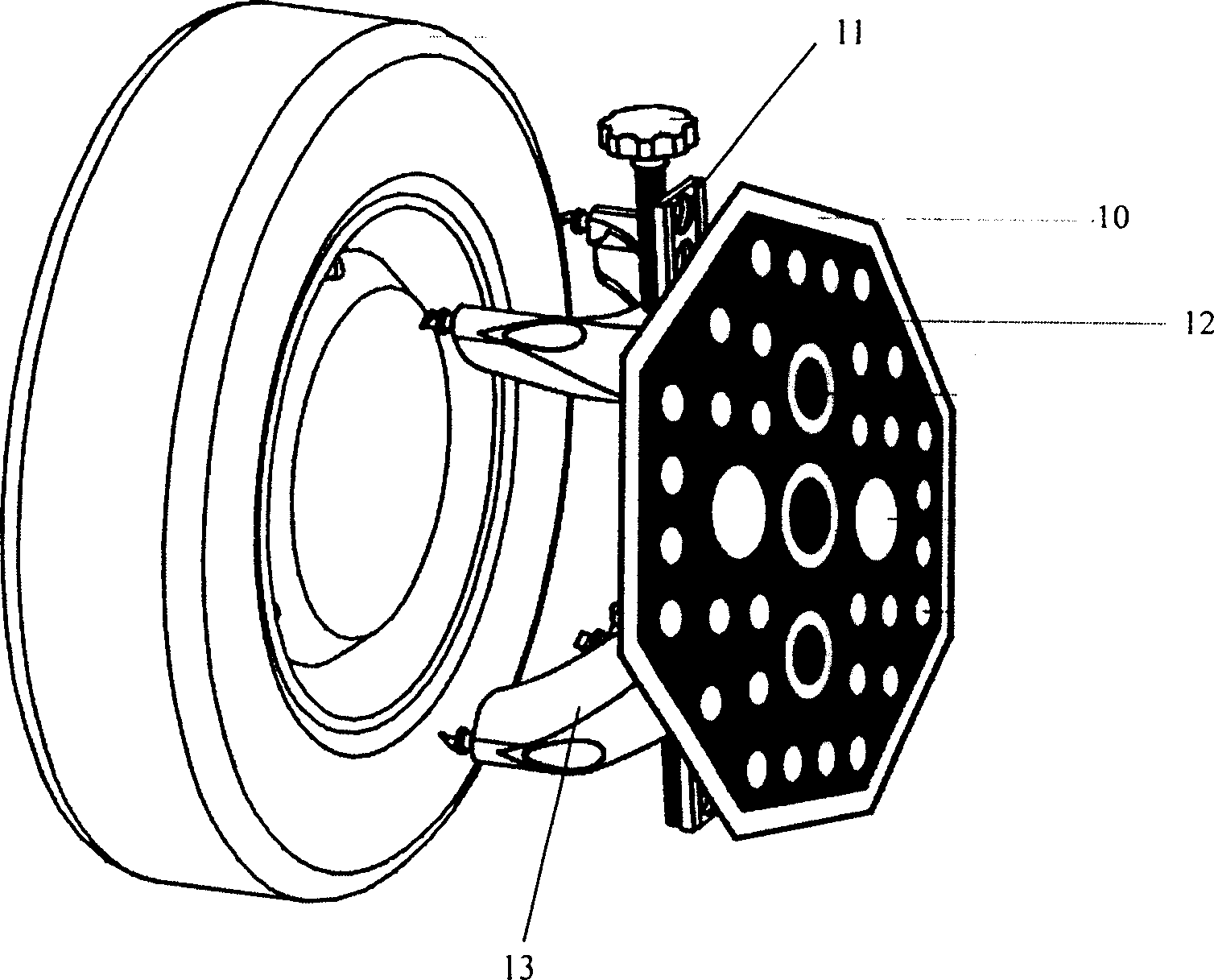
Method and Apparatus for Wheel Alignment System Target Projection and Illumination
ActiveUS20070124949A1Angles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansMachine visionThree-dimensional space
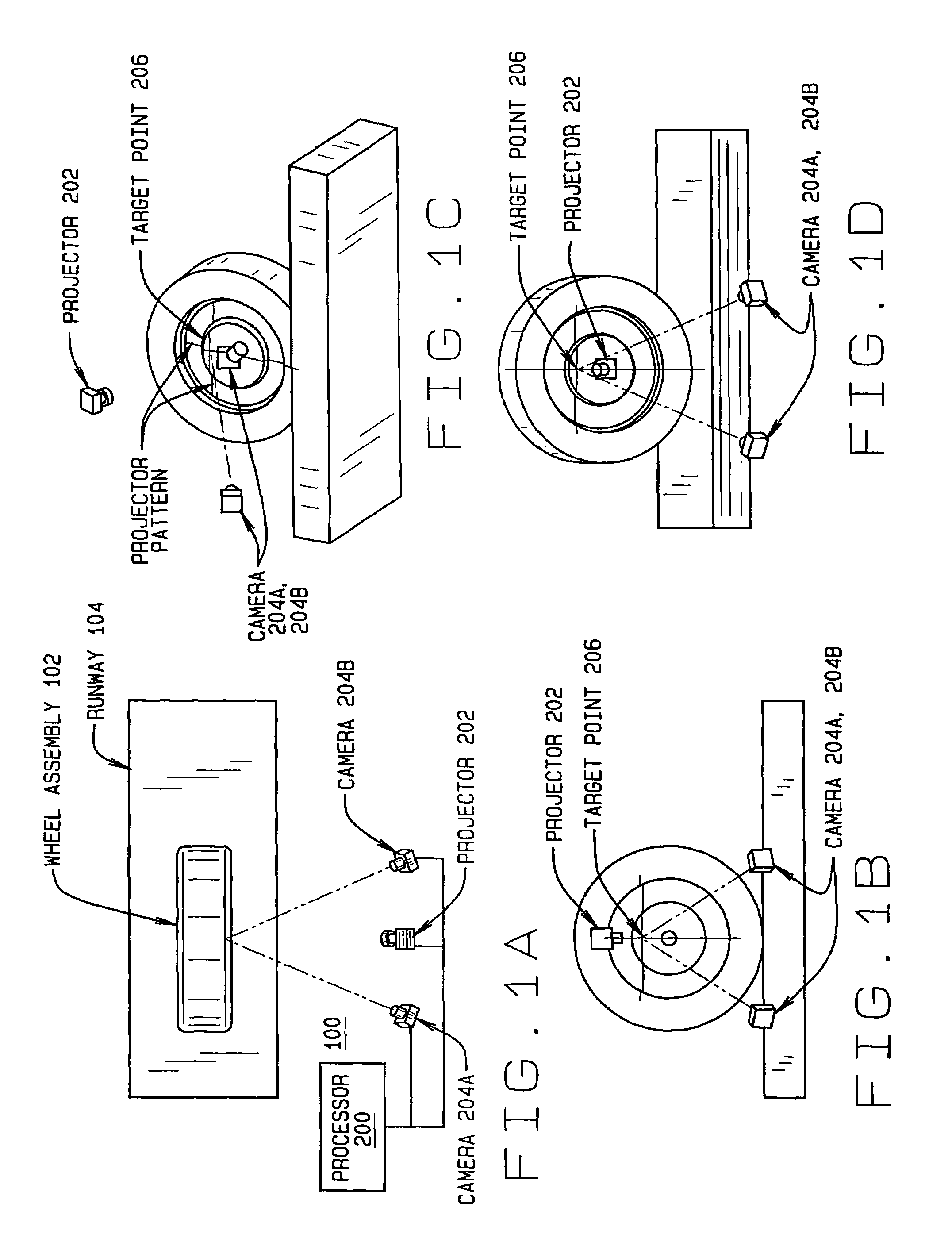
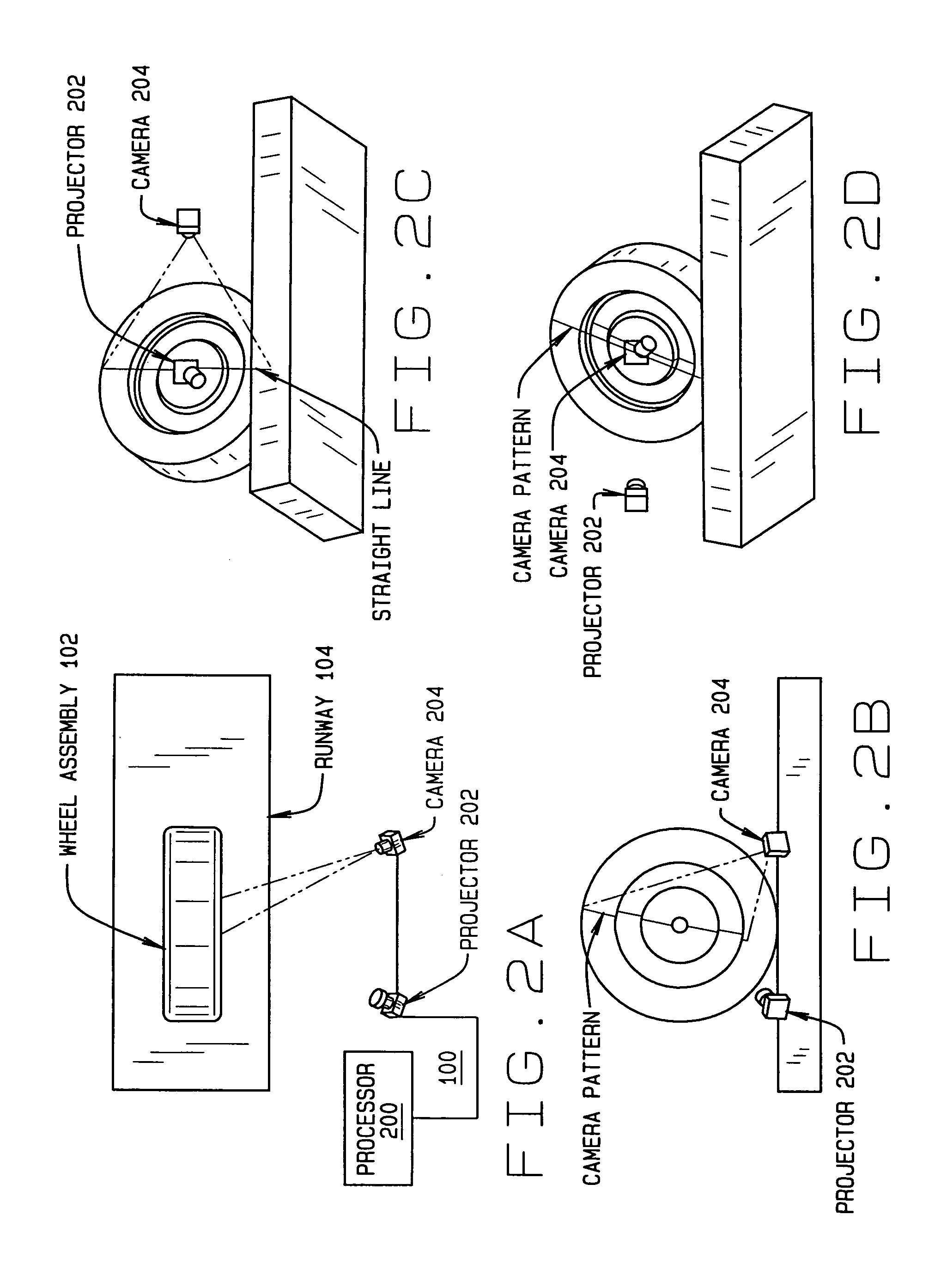
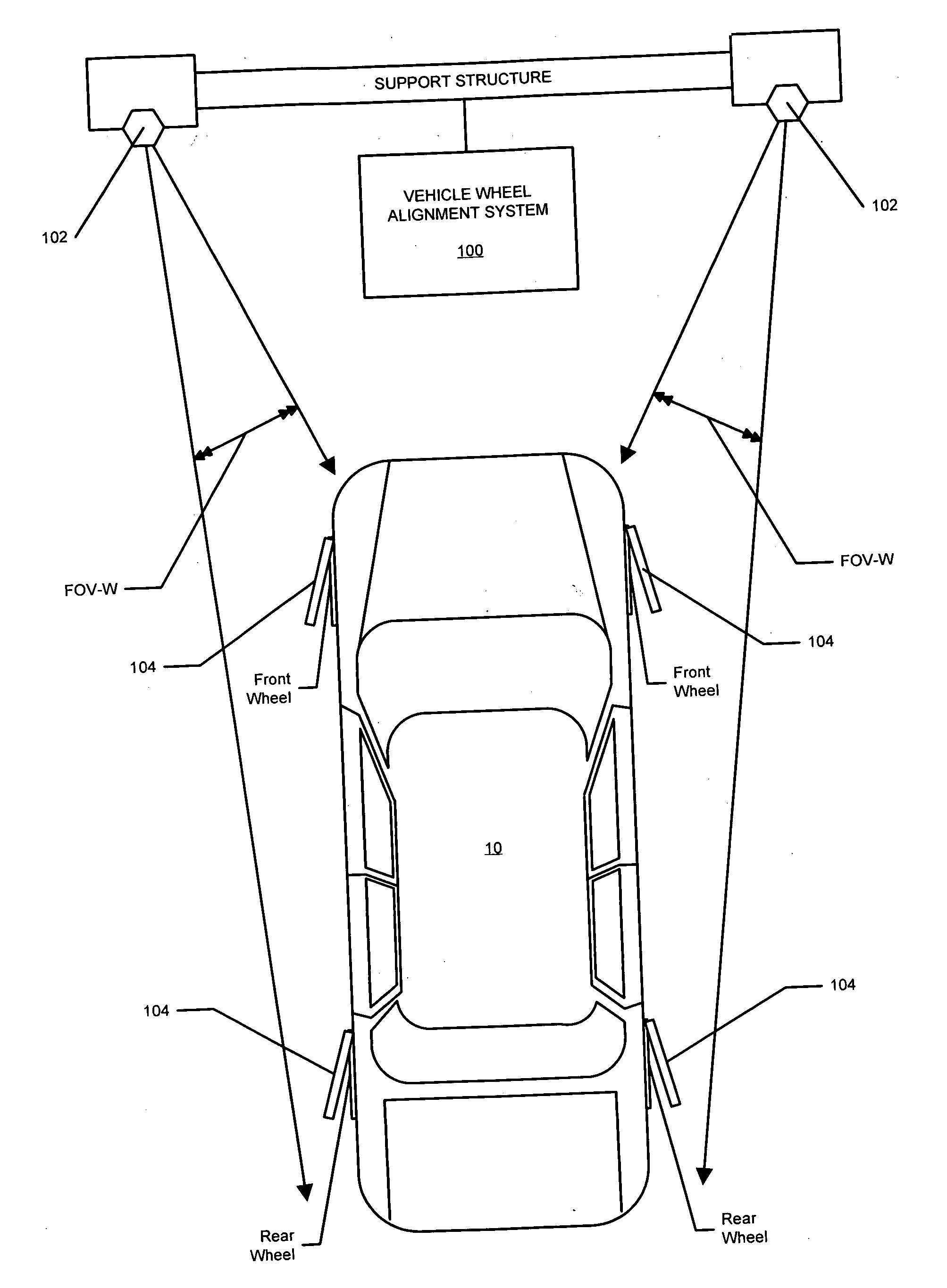
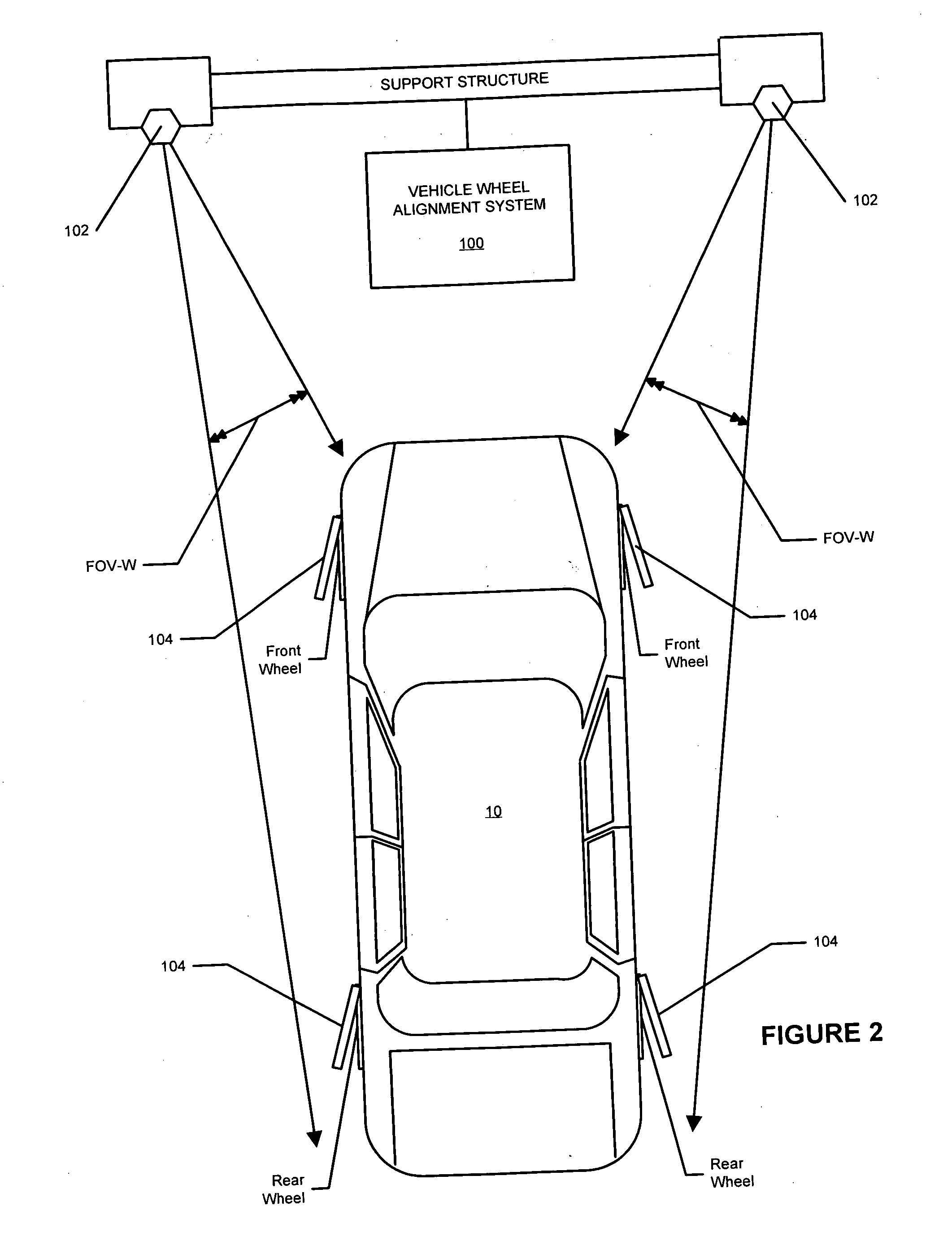
A machine vision vehicle wheel alignment system configured with at least one cameras for acquiring images of the wheels of a vehicle, and an associated light projectors configured to project a pattern image onto the surfaces of vehicle components such as vehicle wheel assemblies. Images of the projected patterns acquired by the camera, are processed by the vehicle wheel alignment system to facilitate a determination of the relative orientation and position of the surfaces such as wheel assemblies in three dimensional space, from which vehicle parameters such as wheel alignment measurements can be subsequently determined.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
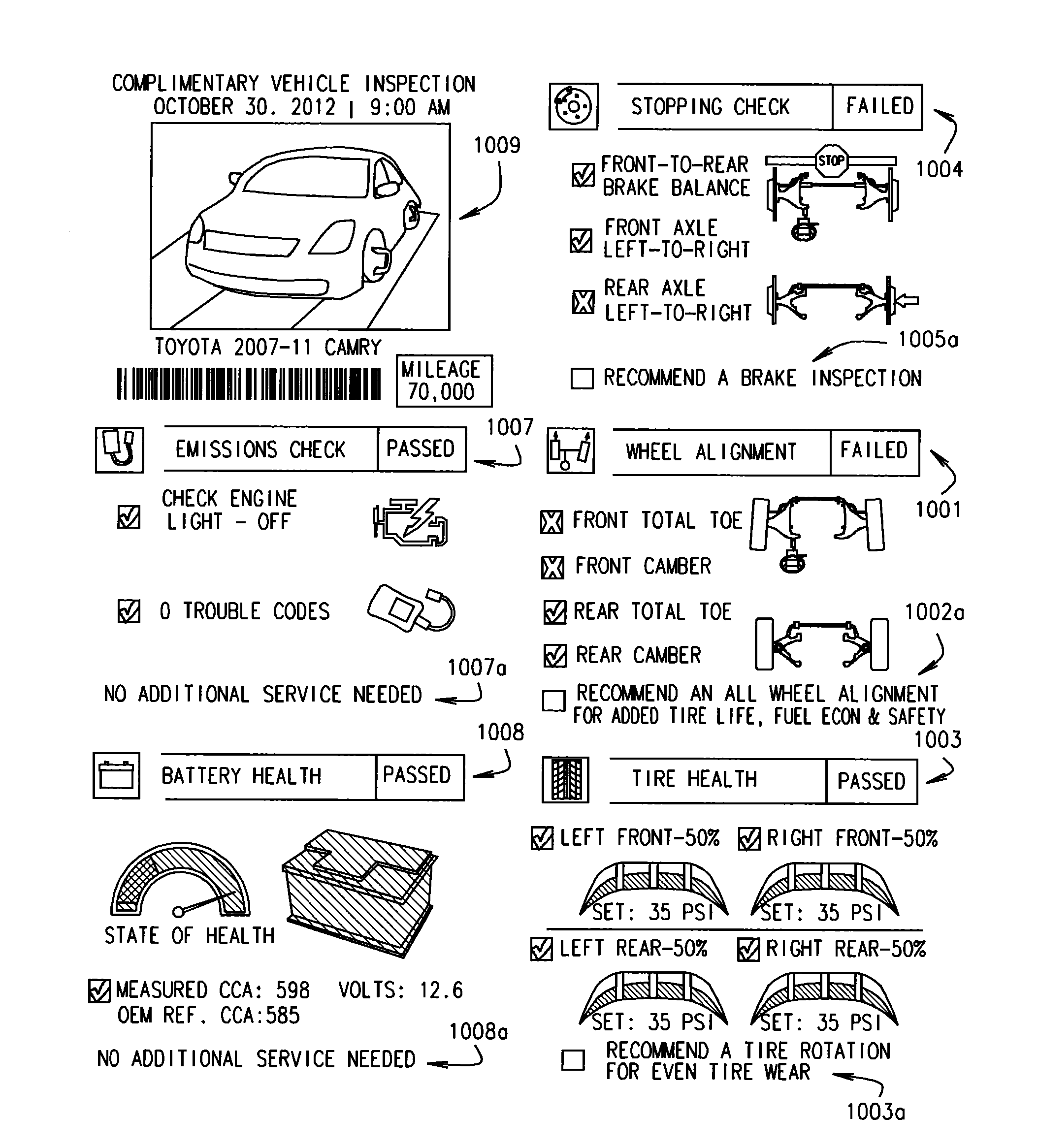
Vehicle Service Procedures
ActiveUS20130158777A1Fast resultsEasy to completeVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesVisual inspectionSingle vehicle
A method and apparatus for carrying out a set of vehicle inspections including, but not limited to, wheel alignment measurement, brake testing, tire tread depth measurement, tire pressure monitoring, vehicle battery testing, and a review of vehicle diagnostic trouble codes in an efficient manner using a multi-function vehicle service system and a single vehicle service bay or inspection lane. Results of the vehicle inspections are incorporated into customized reports generated for a customer or for a technician, and which may be utilized to obtain approval from the customer to conduct necessary repairs and / or provide beneficial vehicle services.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
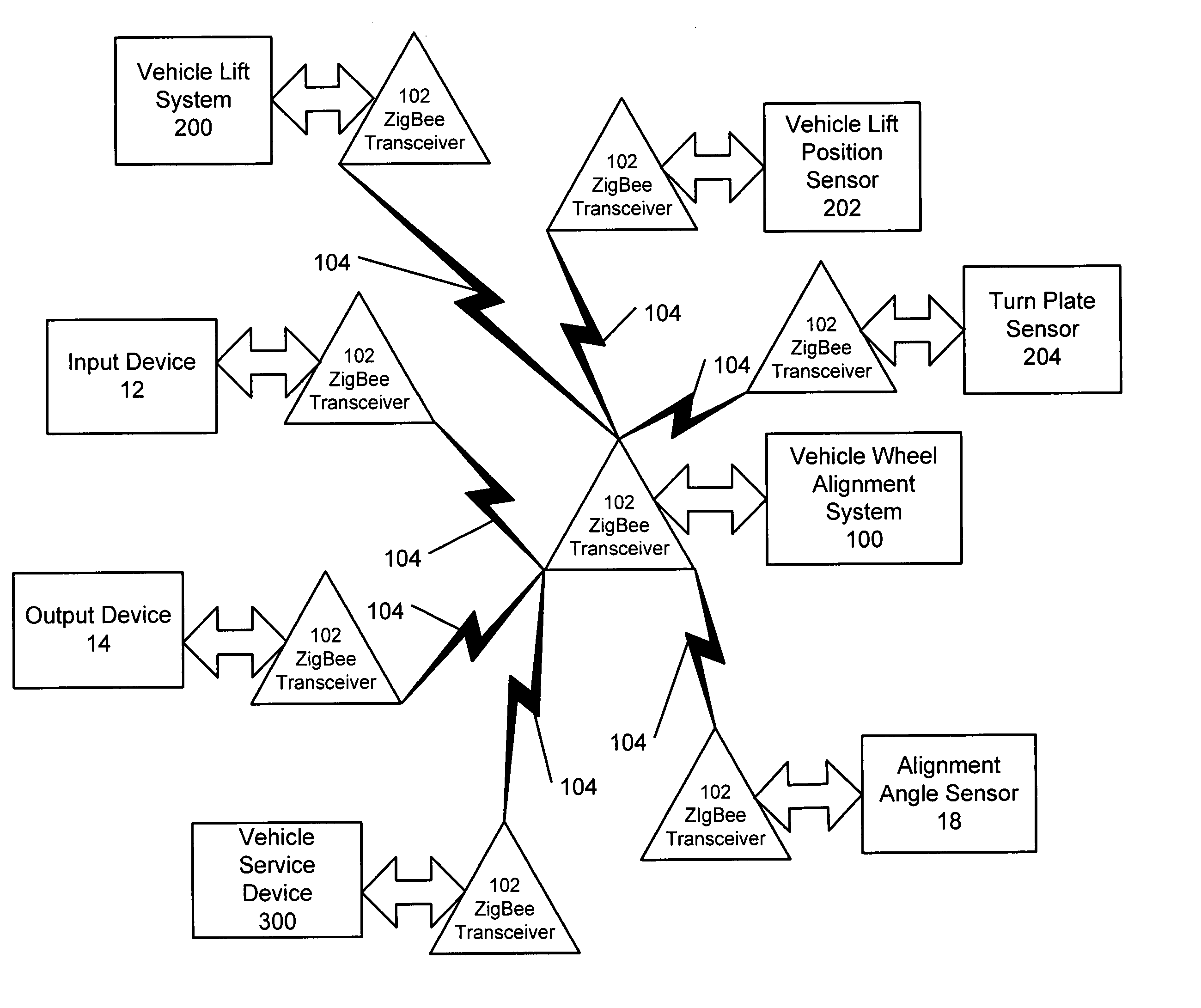
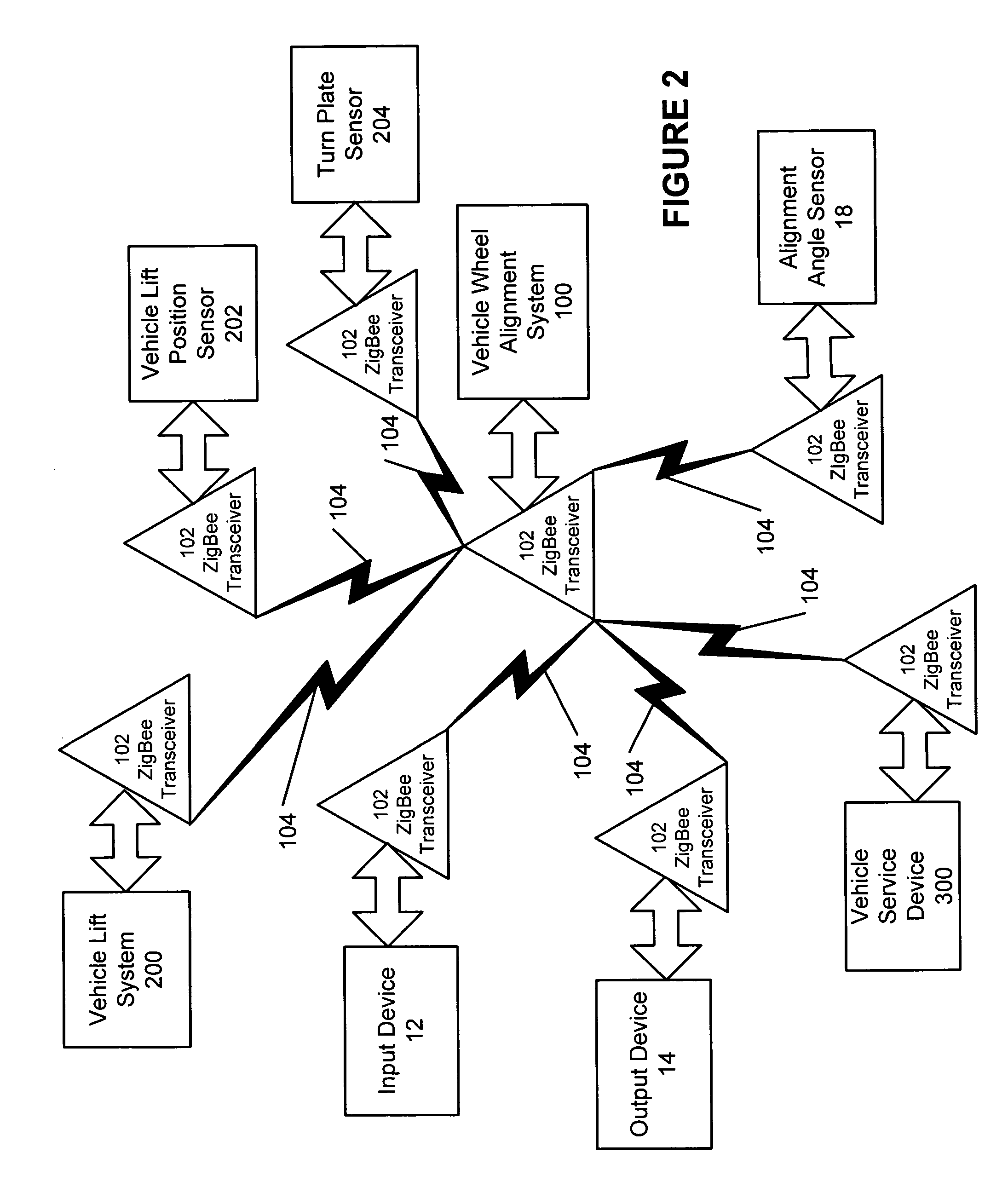
Method and apparatus for wireless networks in wheel alignment systems
InactiveUS20050171662A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTelecommunications linkTransceiver
A vehicle service system having a processing system operatively coupled to a transceiver compliant with the IEEE 802.15.4 standard physical layer. The transceiver is configured to establish a wireless communications link based on an IEEE 802.15.4 packet structure and modulation format between the processing system and at least one additional transceiver located in proximity to the vehicle service system, enabling the processing system to utilize the wireless communications link to receive data from a system or component associated with the additional transceiver.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
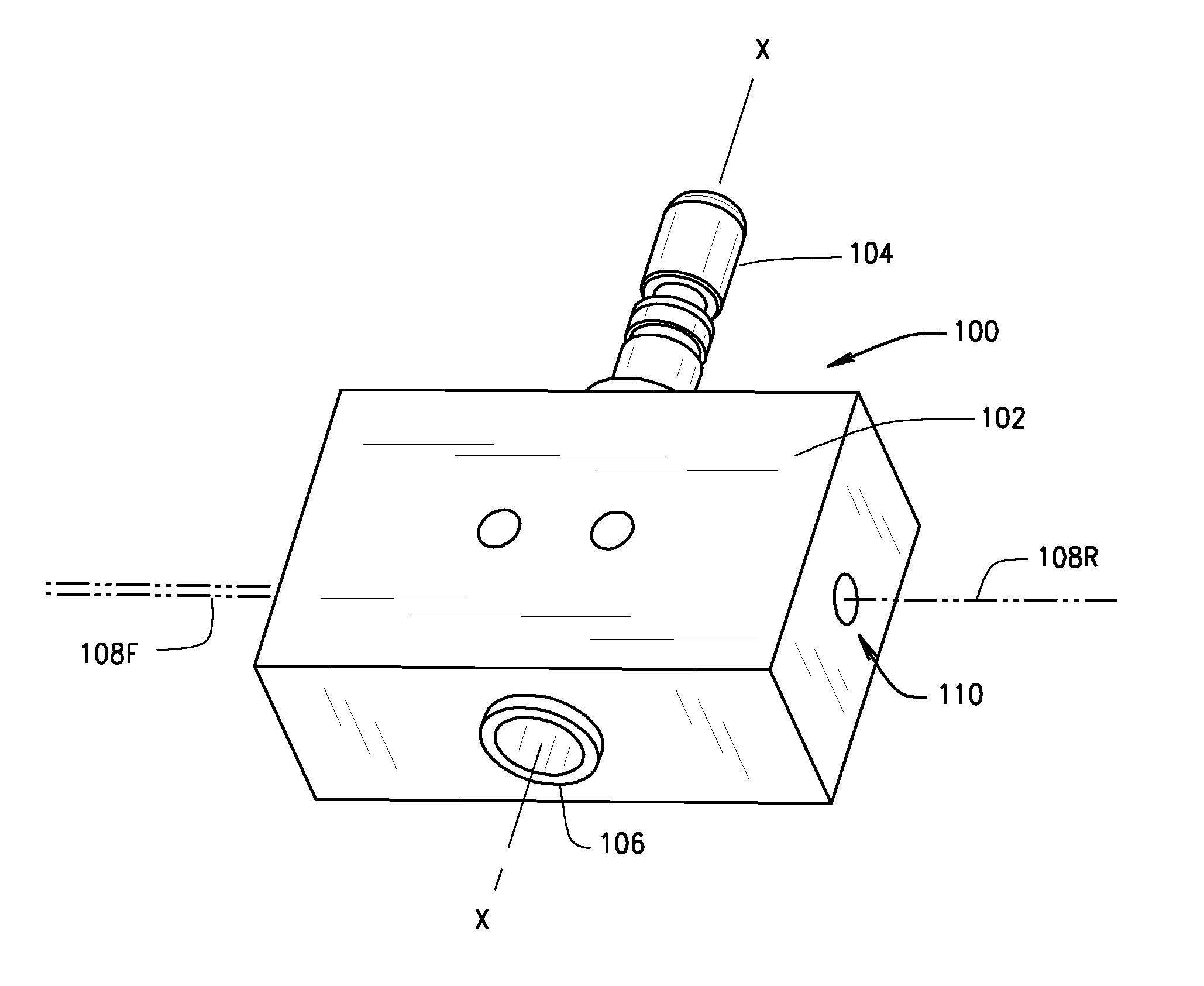
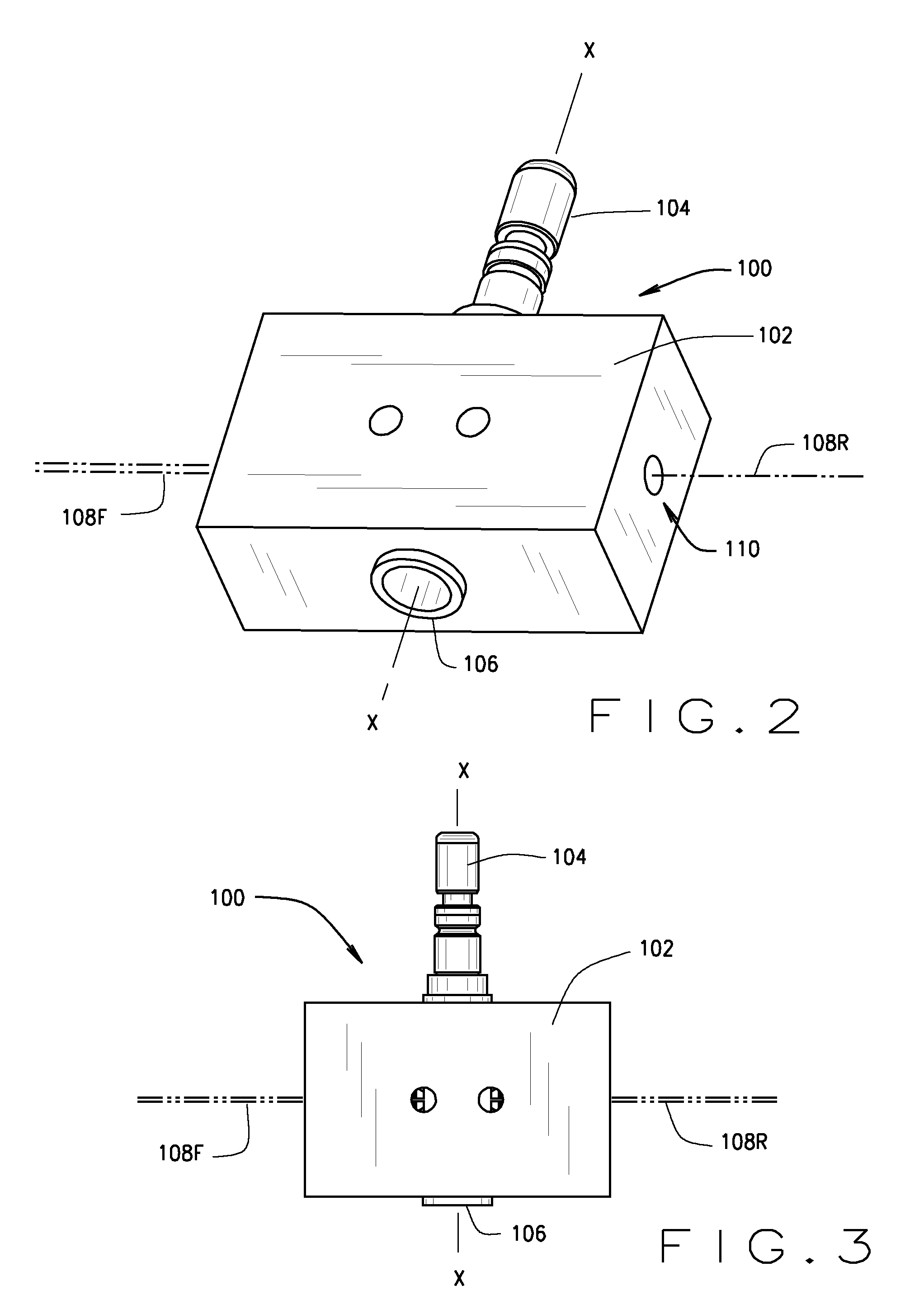
Method and Apparatus For Positioning A Vehicle Service Device Relative To A Vehicle Thrust Line
ActiveUS20130110314A1Good orientationEasy to placeDigital data processing detailsUsing optical meansLaser adaptorReference line
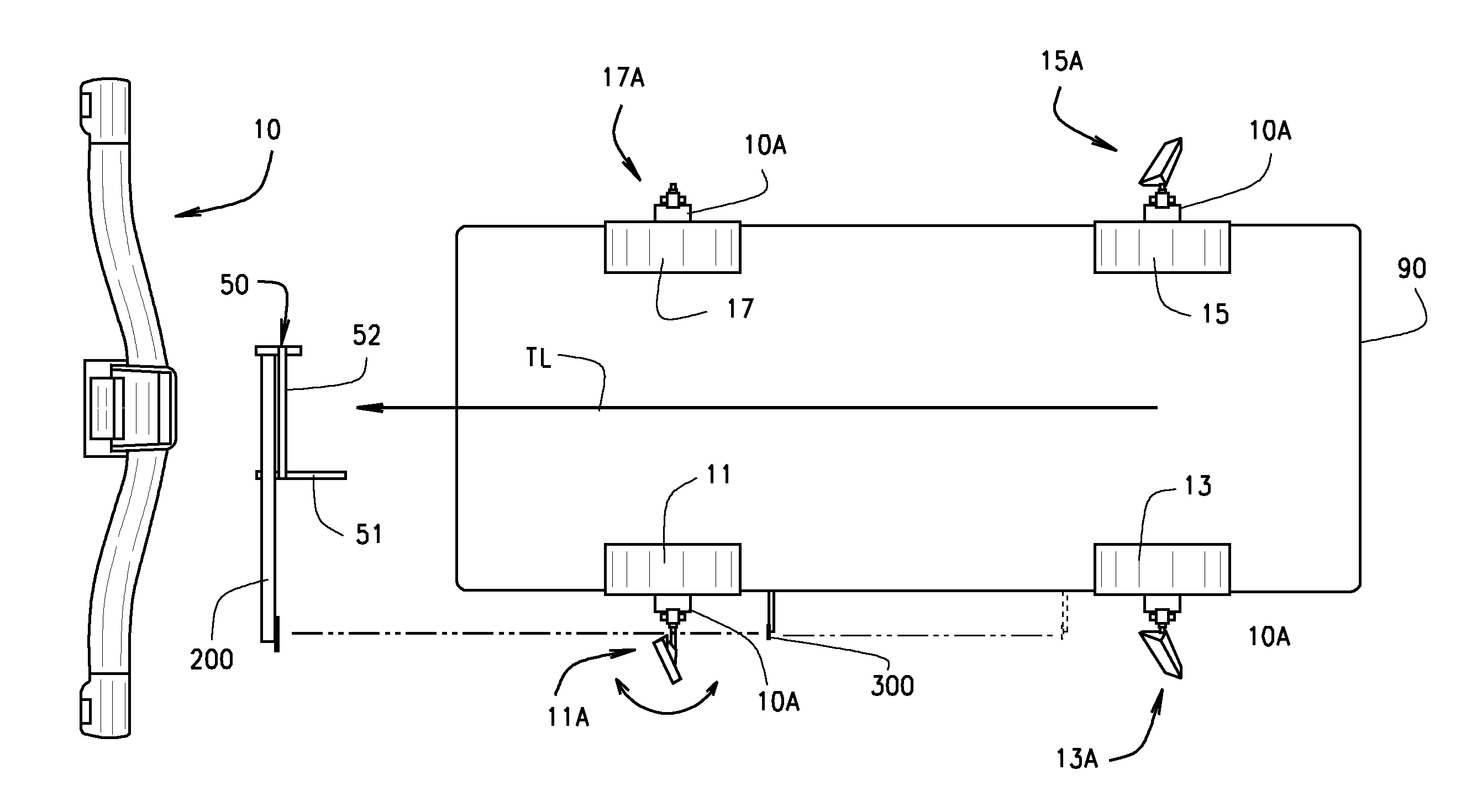
A method and apparatus for utilizing a vehicle wheel alignment system to guide the placement and orientation of a vehicle service apparatus or alignment fixture relative to the thrust line of a vehicle. A laser adapter for projecting a reference line is mounted to a steerable wheel of the vehicle, and is aligned relative to both a line of the vehicle and to the supporting surface on which the vehicle is disposed. The vehicle line is determined by the vehicle wheel alignment system, and the steerable wheel, together with the adapter, are steered relative to the determined vehicle line, such that a projected reference line defined by the position and orientation of the adapter is established parallel to both the supporting surface and the vehicle line. The placement and orientation of the vehicle service apparatus or alignment fixture is subsequently adjusted relative to the projected reference line.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Method and apparatus for wheel alignment system target projection and illumination
A machine vision vehicle wheel alignment system configured with at least one cameras for acquiring images of the wheels of a vehicle, and an associated light projectors configured to project a pattern image onto the surfaces of vehicle components such as vehicle wheel assemblies. Images of the projected patterns acquired by the camera, are processed by the vehicle wheel alignment system to facilitate a determination of the relative orientation and position of the surfaces such as wheel assemblies in three dimensional space, from which vehicle parameters such as wheel alignment measurements can be subsequently determined.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
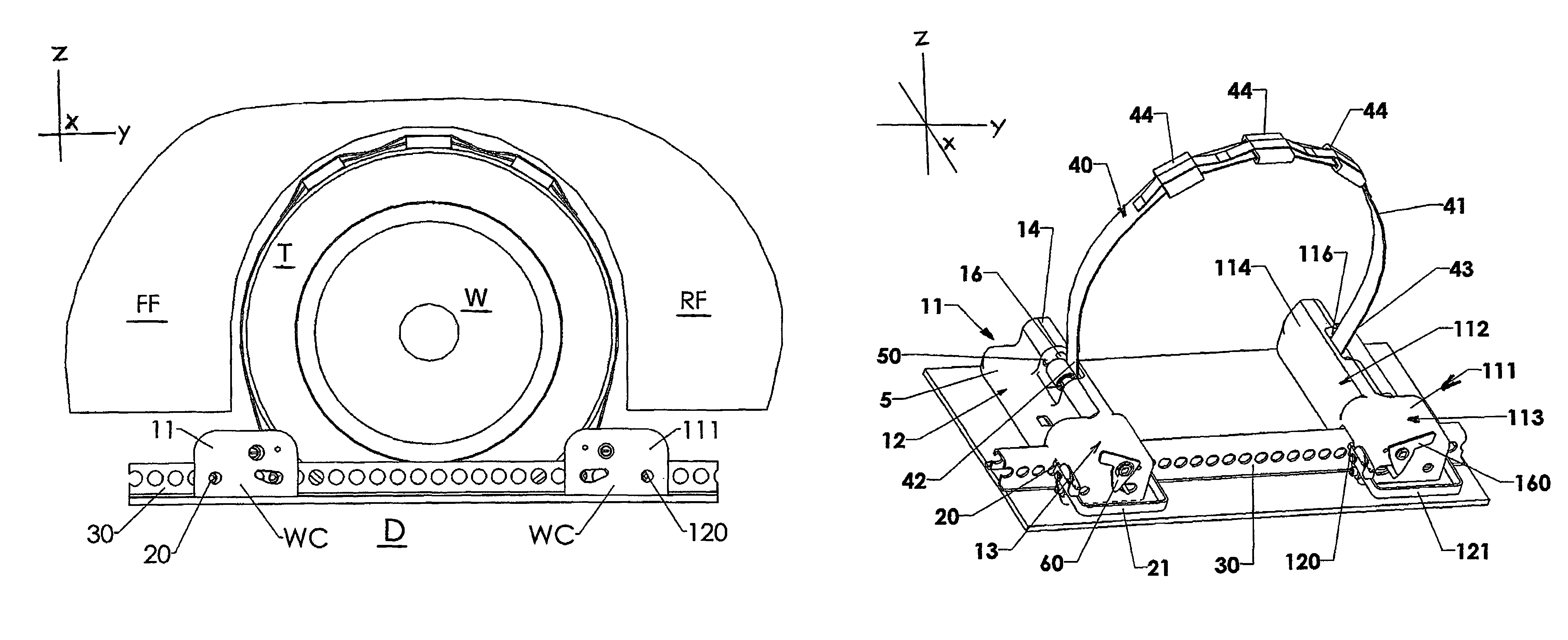
Low-profile wheel chock assembly
ActiveUS7513725B1Improve rigidityHigh strengthLoad securingItem transportation vehiclesEngineeringMirror image
A low elevational profile of each of a pair of first and second wheel chocks for restraining a current “low-drag” motor vehicle in a carrier, such as a railway car, is derived from each wheel chock having an internally webbed, elongated stepped-box body terminated with a relatively short rectangular box having its inner wall integrally formed with the stepped-box body. The body of the first chock is essentially a mirror-image of the second chock body. The low profile of a wheel chock allows each to be positioned under a vehicle the rocker panel of which has its lower edge only 148 mm (5.82 inches) above the surface upon which the vehicle's tire rests, so that the installed chock height is reduced to 47.6 mm (1.87″) under the components of the vehicle's body. The assembly may include a pair of “active” chocks; or, one active chock and one anchor chock. A single window in the upper portion of the stepped-box provides access for a strap of a wheel harness, which strap is wrapped around a torque tube in an active chock. The torque tube in one chock is rotatable in a direction opposite to that of the torque tube of the other chock. With a pair of active chocks, hooks on straps of a prior art harness are eliminated because it is difficult and time-consuming to manipulate a tire harness with its straps and hooks to secure the tire between the wheel chocks. When one chock is an anchor chock, one end of the strap is provided with a hook which is anchored to a rod or tube which is substituted for the rotatable torque tube.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
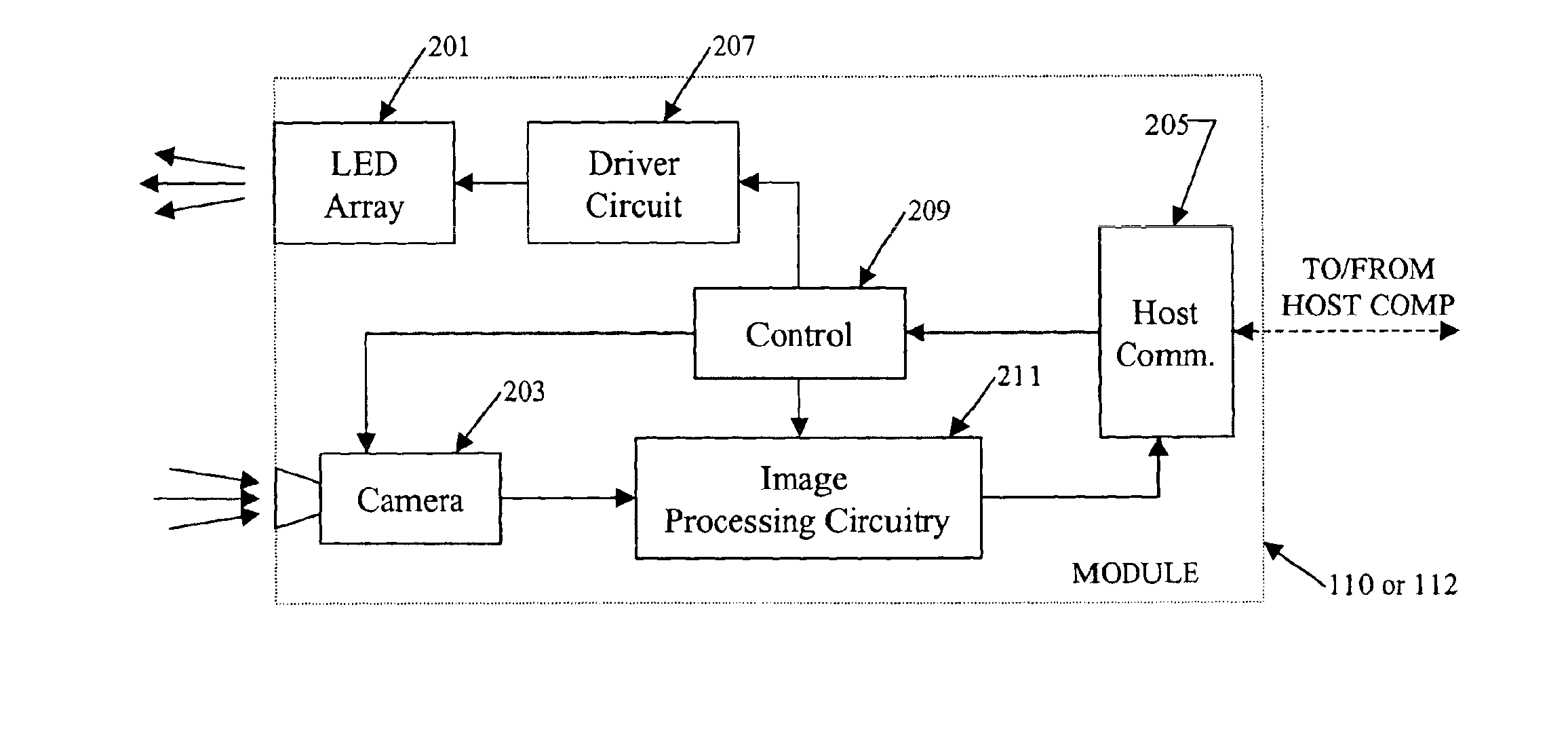
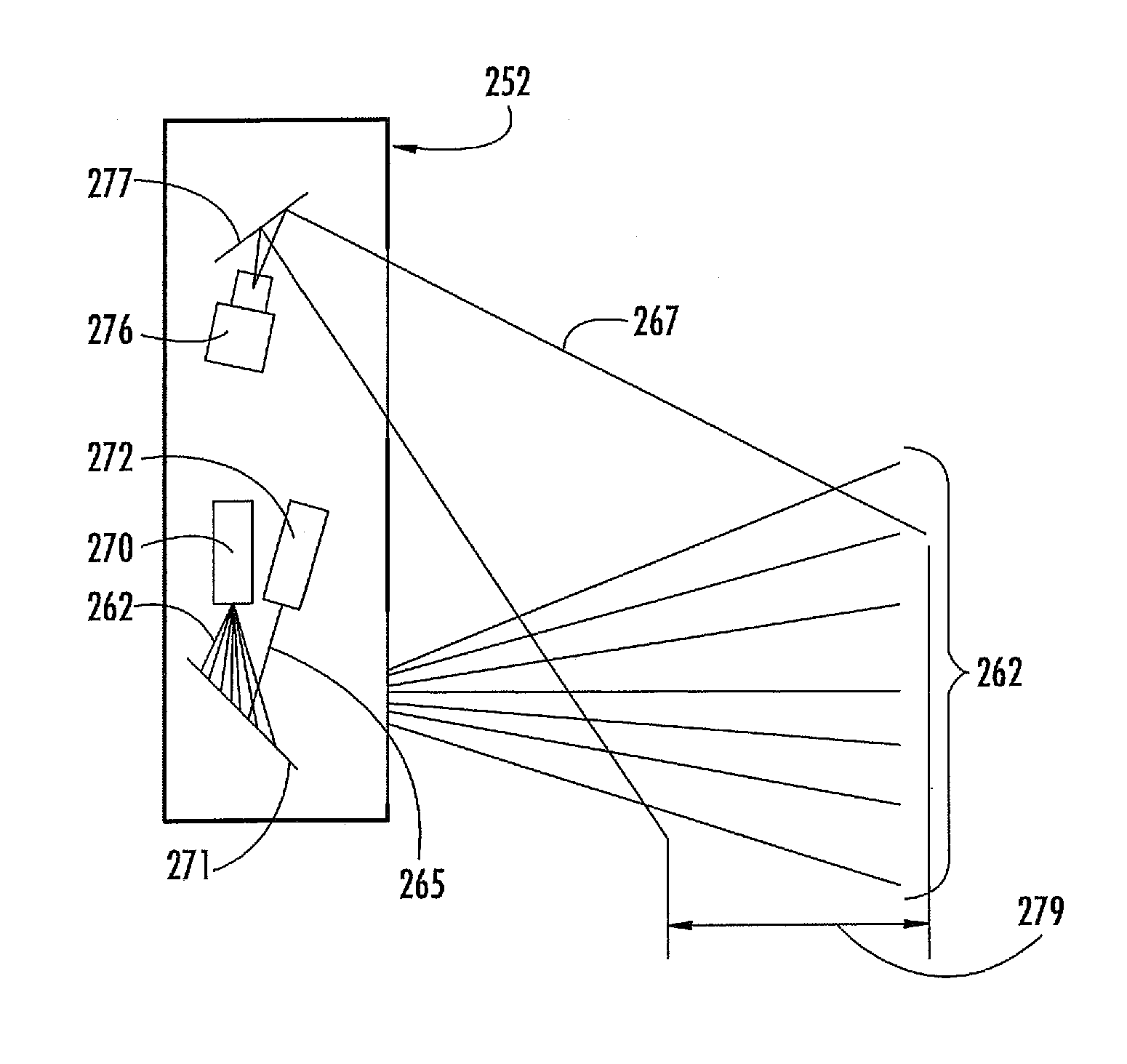
Gradient calculating camera board
InactiveUS6871409B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsNot require as complex (or expensive) hardwareAngles/taper measurementsAngle measurementCamera controlVisual perception
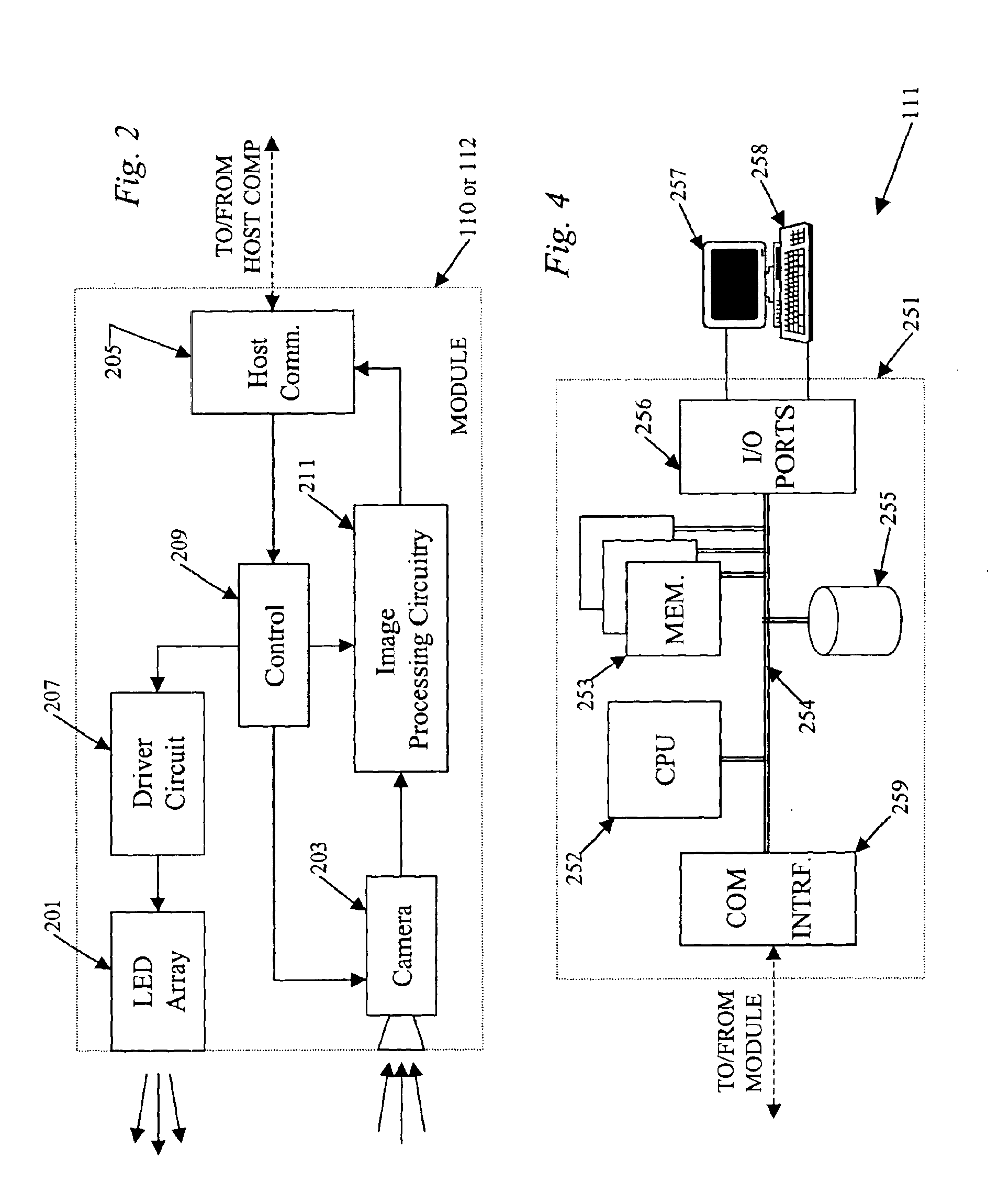
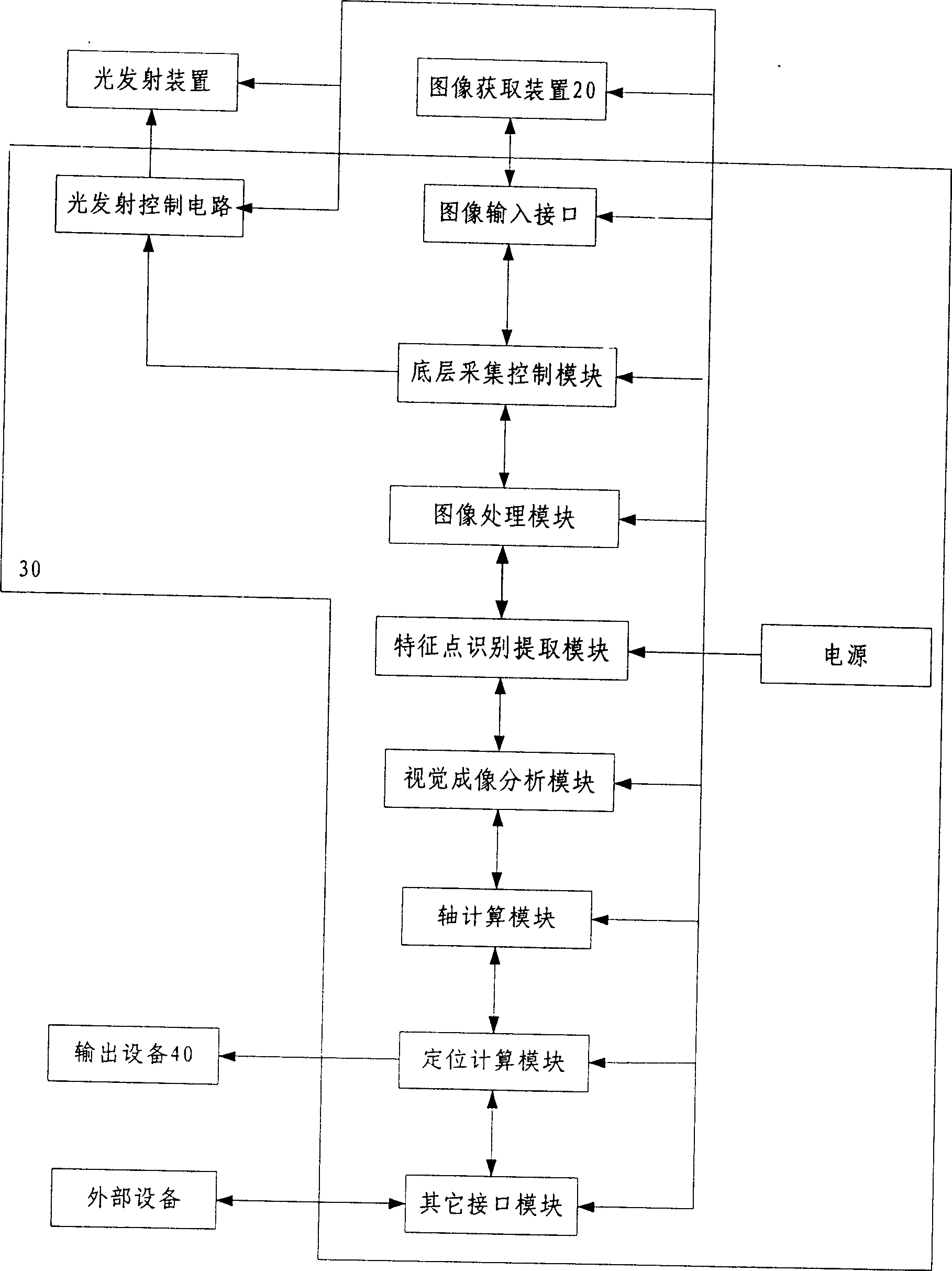
In a machine vision system utilizing computer processing of image data, an imaging module incorporates the image sensor as well as pre-processing circuitry, for example, for performing a background subtraction and / or a gradient calculation. The pre-processing circuitry may also compress the image information. The host computer receives the pre-processed image data and performs all other calculations necessary to complete the machine vision application, for example, to determine one or more wheel alignment parameters of a subject vehicle. In a disclosed example useful for wheel alignment, the module also includes illumination elements, and the module circuitry provides associated camera control. The background subtraction, gradient calculation and associated compression require simpler, less expensive circuitry than for typical image pre-processing boards. Yet, the pre-processing at the imaging module substantially reduces the processing burden on the host computer when compared to machine vision implementations using direct streaming of image data to the host computer.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
Vehicle wheel alignment system scanned beam imaging sensor
A vehicle wheel alignment sensor for a machine-vision vehicle wheel alignment system comprising a scanned beam camera incorporating an illumination source, a means for deflecting light emitted by the illumination source along a path within a field of view, and a detector array for receiving illumination reflected from objects within the field of view to generate an image which is representative of a region of interest within the field of view.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Non contact wheel alignment sensor and method
ActiveUS7864309B2Good precisionHigh sensitivityAngle measurementImage analysisEngineeringWheel alignment
Owner:VERHAERT NEW PROD & SERVICES +1
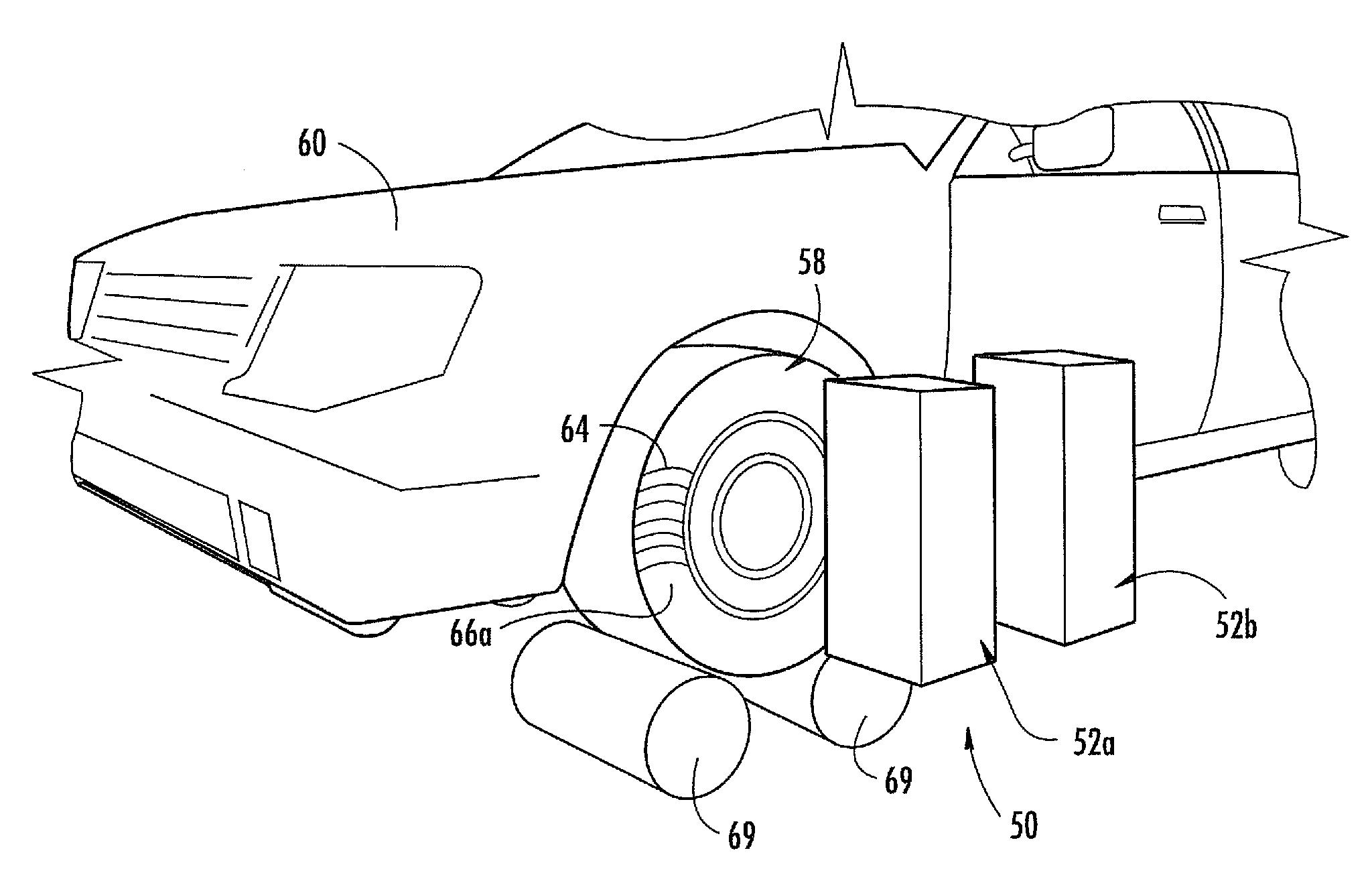
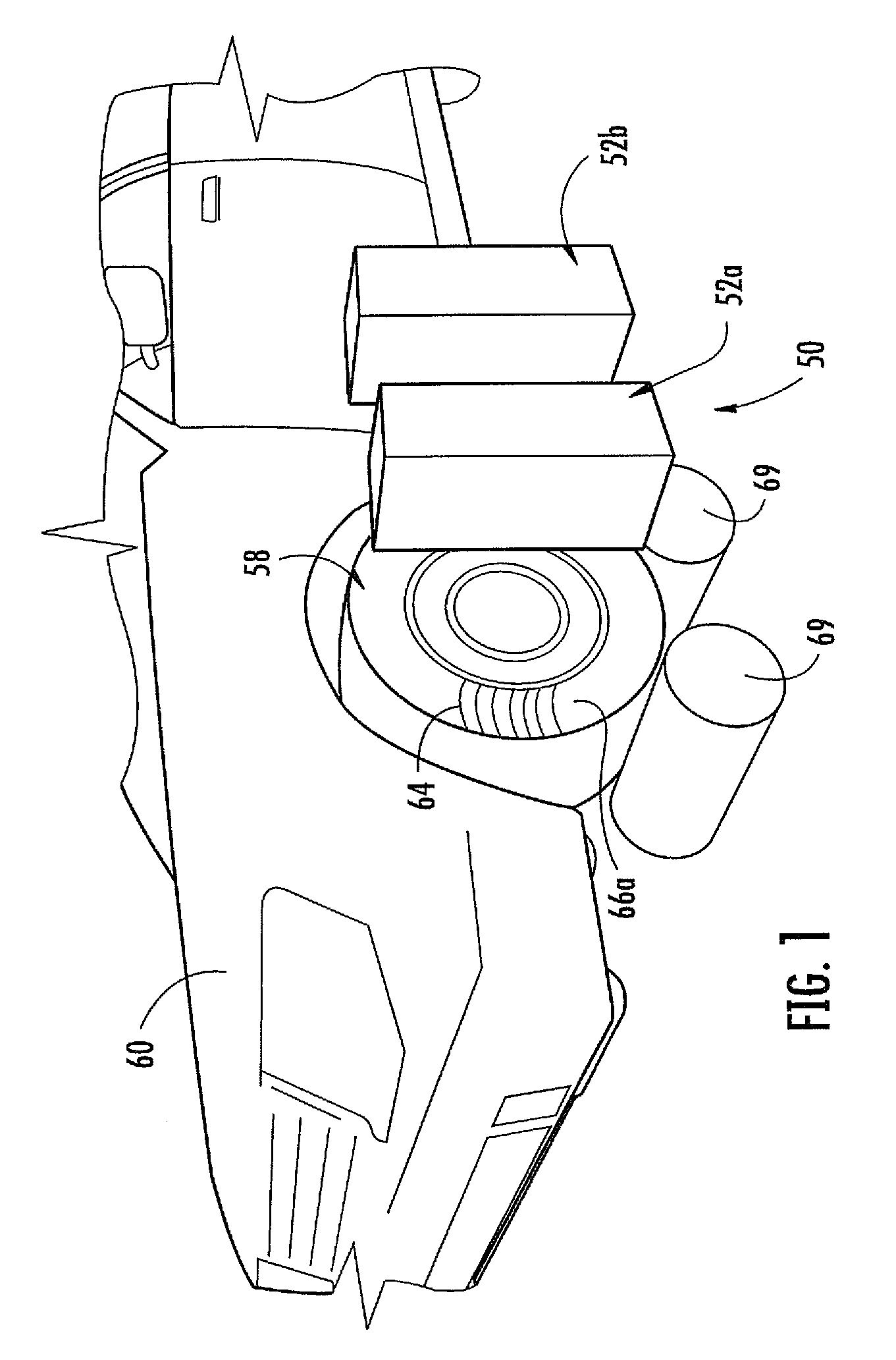
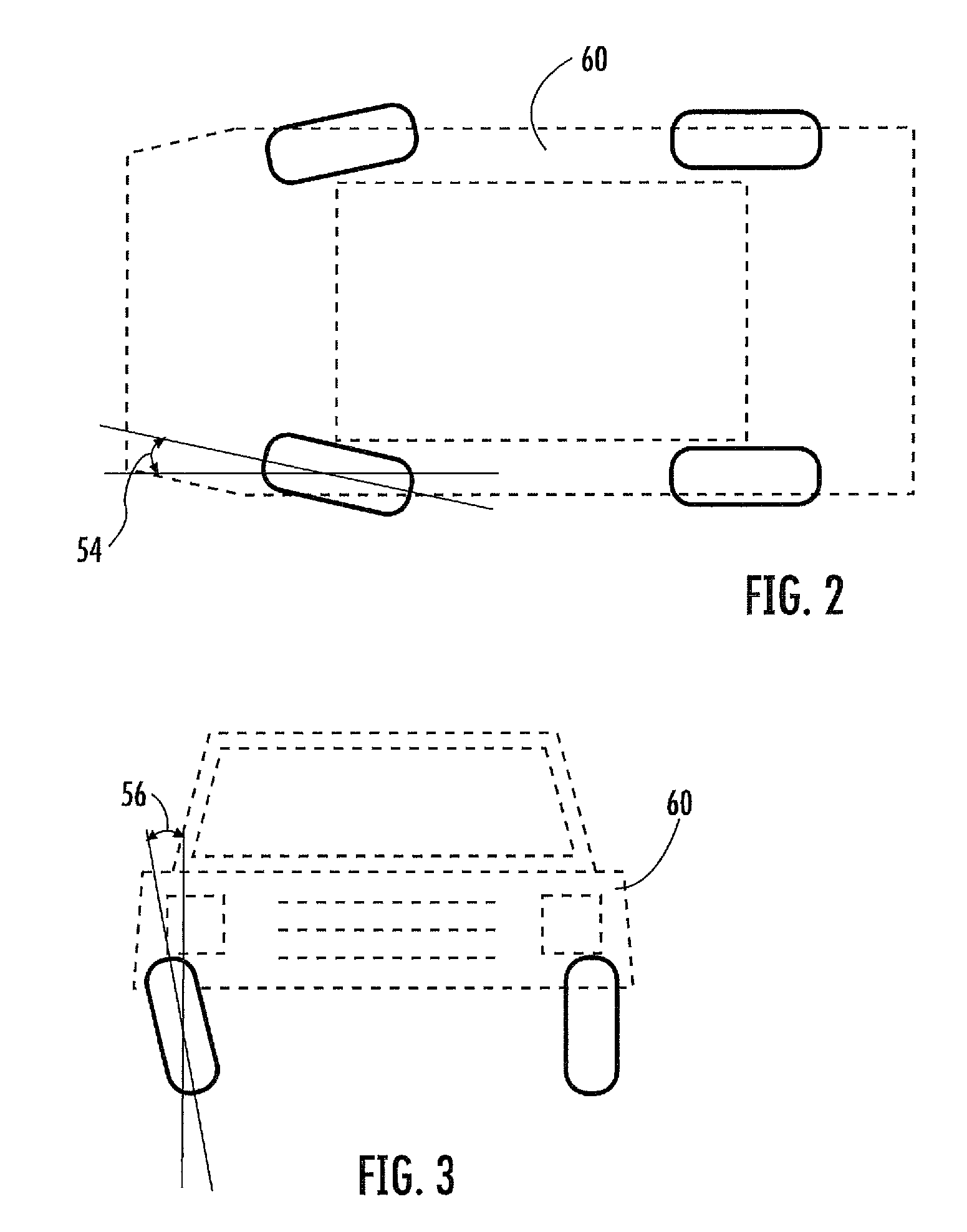
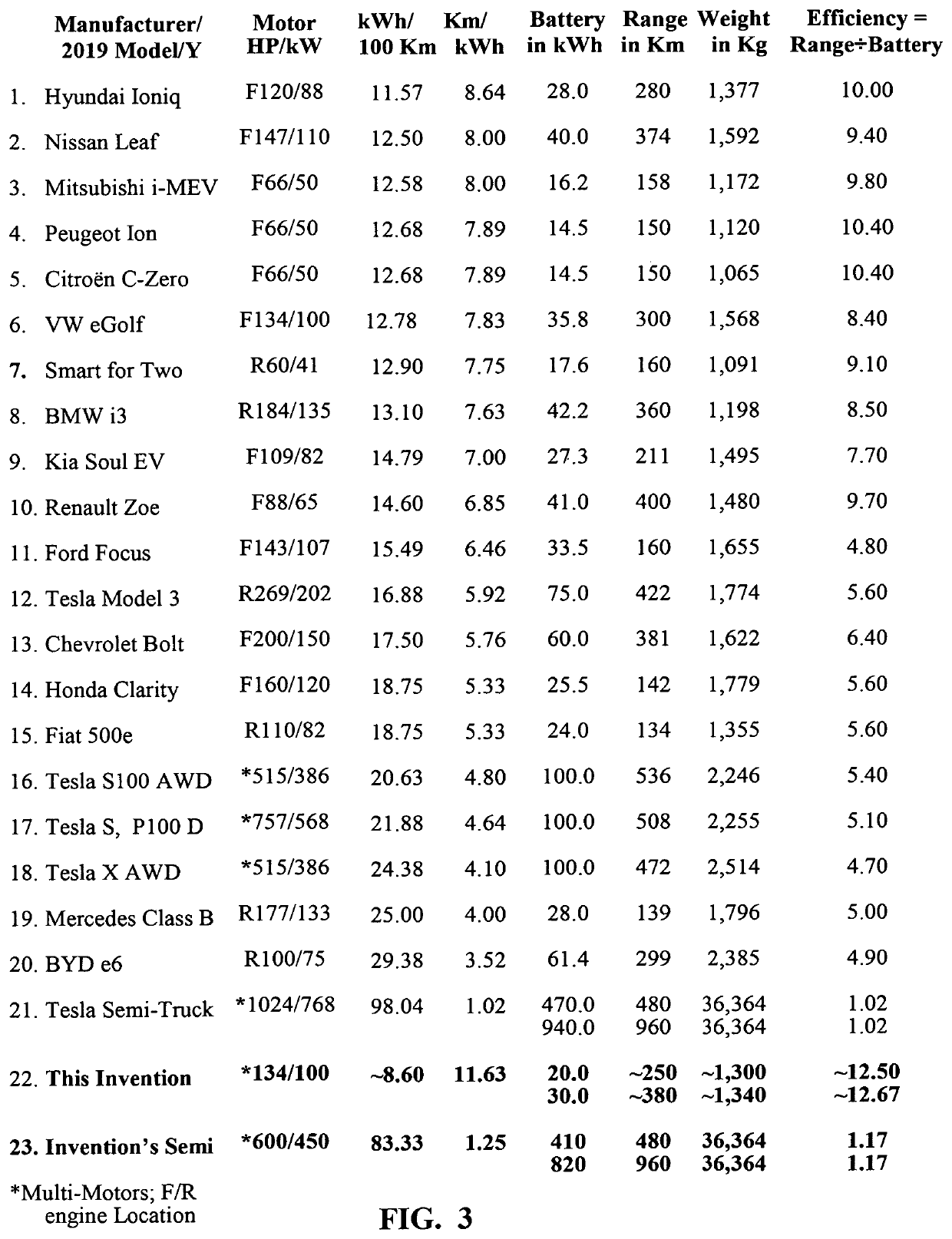
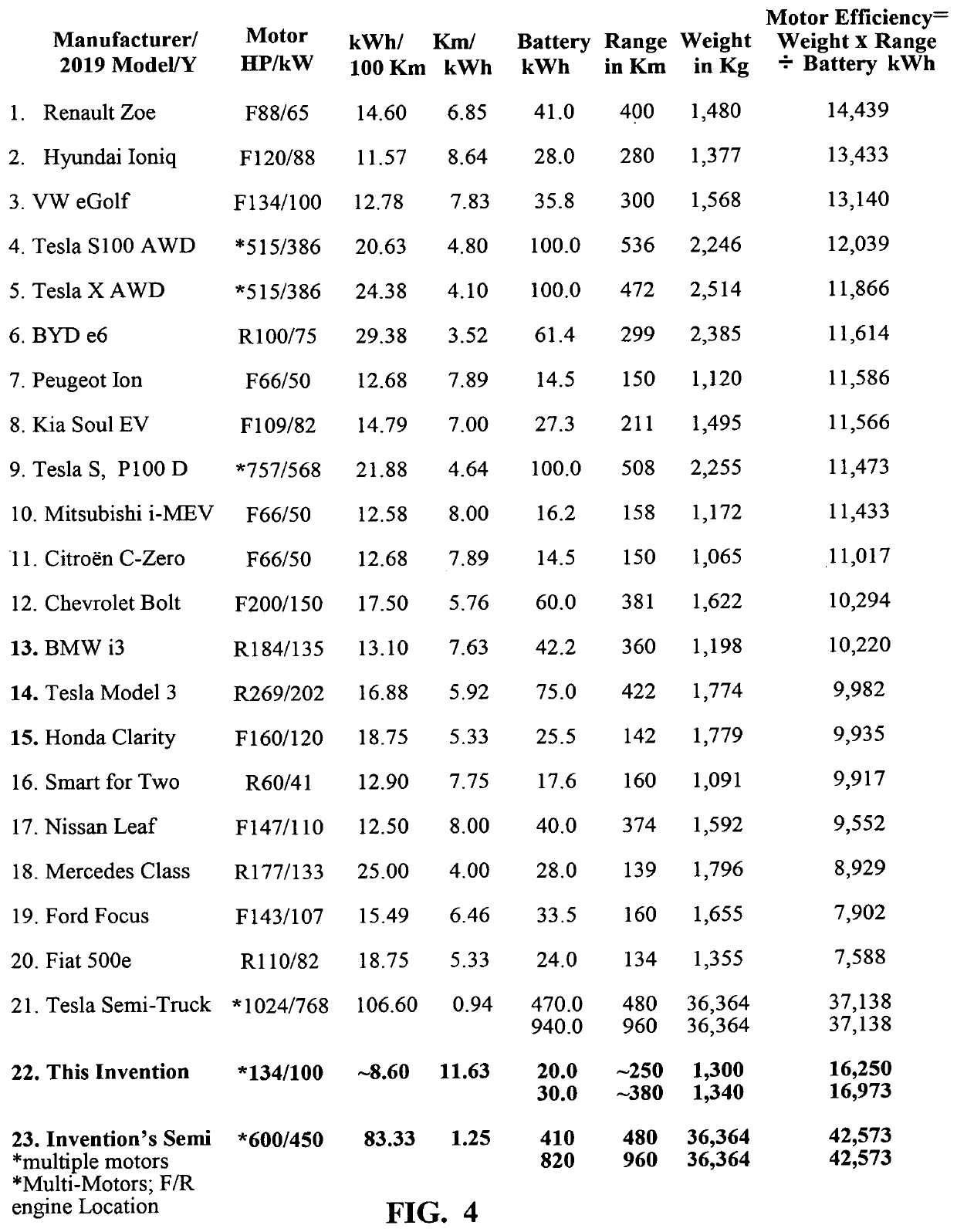
INTEGRATED PROPULSION & STEERING For Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV), AV (Autonomous Vehicles); Electric Trucks, Buses and Semi-Trailers
InactiveUS20190351895A1Stable tractionEasy to operateHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresEngineeringActuator
A vehicle, integrated all-wheel propulsion and steering system with plurality of propulsion and steering power sources, designed with enumerate specifications are coupled to, and de-coupled from a final drive of the vehicle propulsion system. A controller receives input-signals from the driver steering-wheel sensor; computes a set of reactions to the plurality of steering-actuators, wherein feedback-mechanism with each wheel-position sensor, the controller secures each wheel in its computed angle. In different speed and load conditions, the controller is programmed to compute a desired power demand then couple to the final drive[s] the propulsion power source[s] that is designed to do-the-job with the least energy consumption. When the vehicle changes speed and load, the controller couples a different power source[s], and de-couples the previous power source[s] to meet the power demand. In turning-modes, whilst positioning every wheel in its computed position, the controller computes the different distances the left and the right wheels of the vehicle have to travel, wherein the controller moves-up the propulsion power sources velocity to the wheels opposite to the turn to make a perfect turn without EPS assistance.
Owner:BEN ARI JACOB
Method and Apparatus For Wheel Assembly Force Moment Arm Measurement
InactiveUS20080119978A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMachine visionMeasurement point
A machine vision vehicle wheel alignment system configured to measure non-traditional vehicle wheel alignment angles and to determine dynamic behavior of a vehicle suspension system by observing optical targets or visible features, attached to points of interest on the vehicle body or vehicle wheels. The vehicle wheel alignment system characterizes the suspension geometry with respect to the body of the vehicle and to a rolling surface by measuring, in three-dimensions, points and / or angles on the vehicle body as well as the vehicle wheels, enabling measurement of specific non-traditional vehicle parameters, including wheel assembly braking force and lateral force moment arms.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Method and Apparatus For Vehicle Service System Optical Target
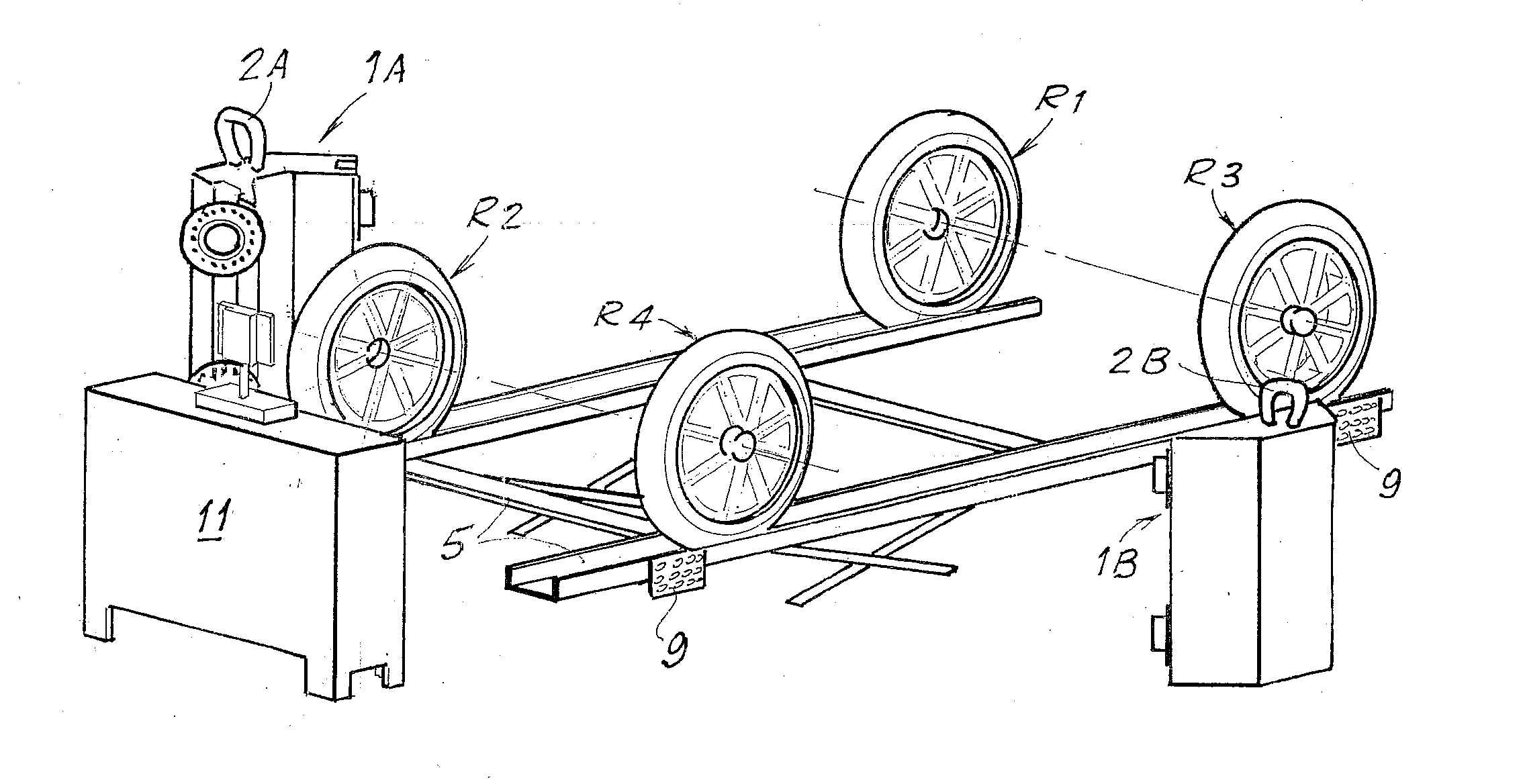
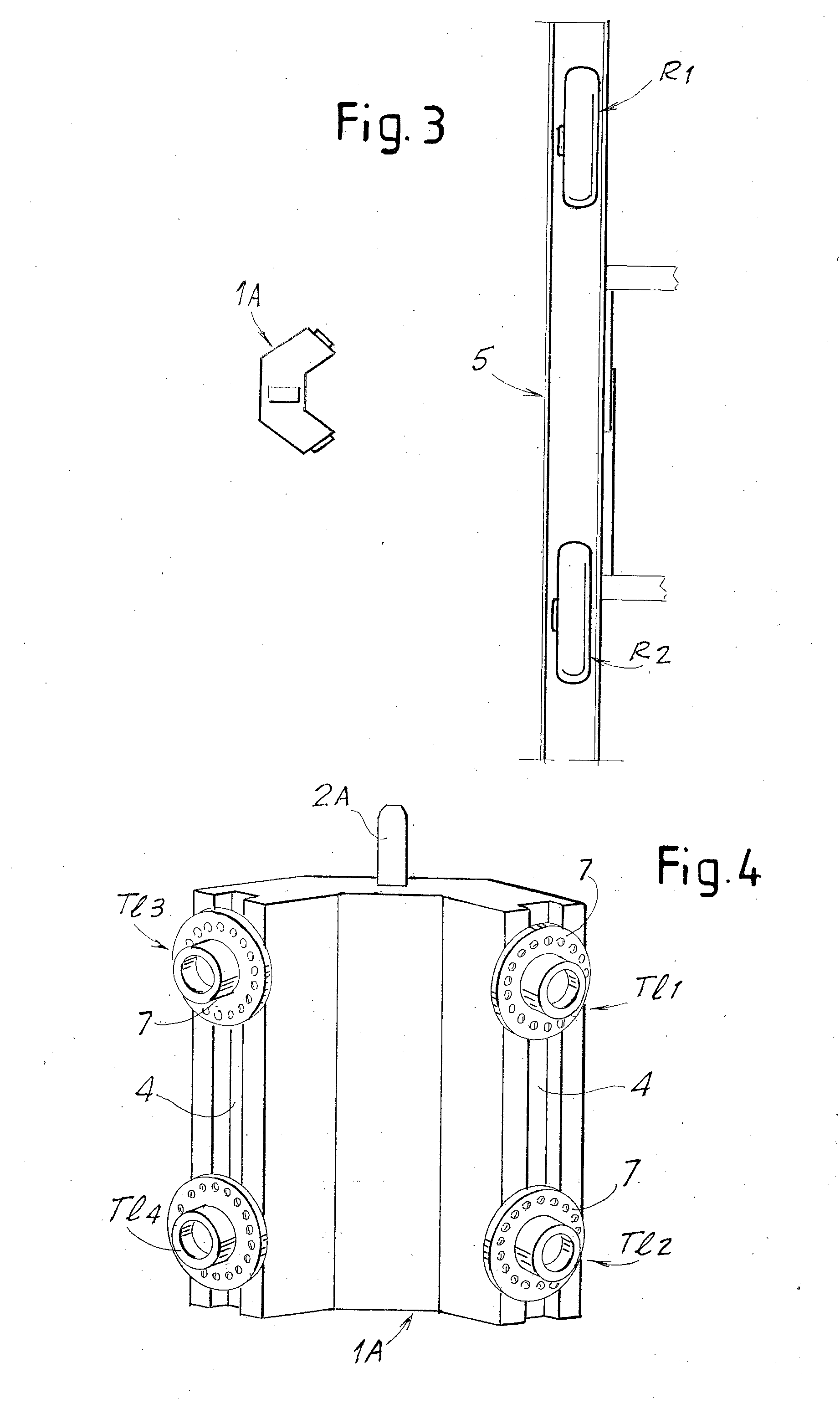
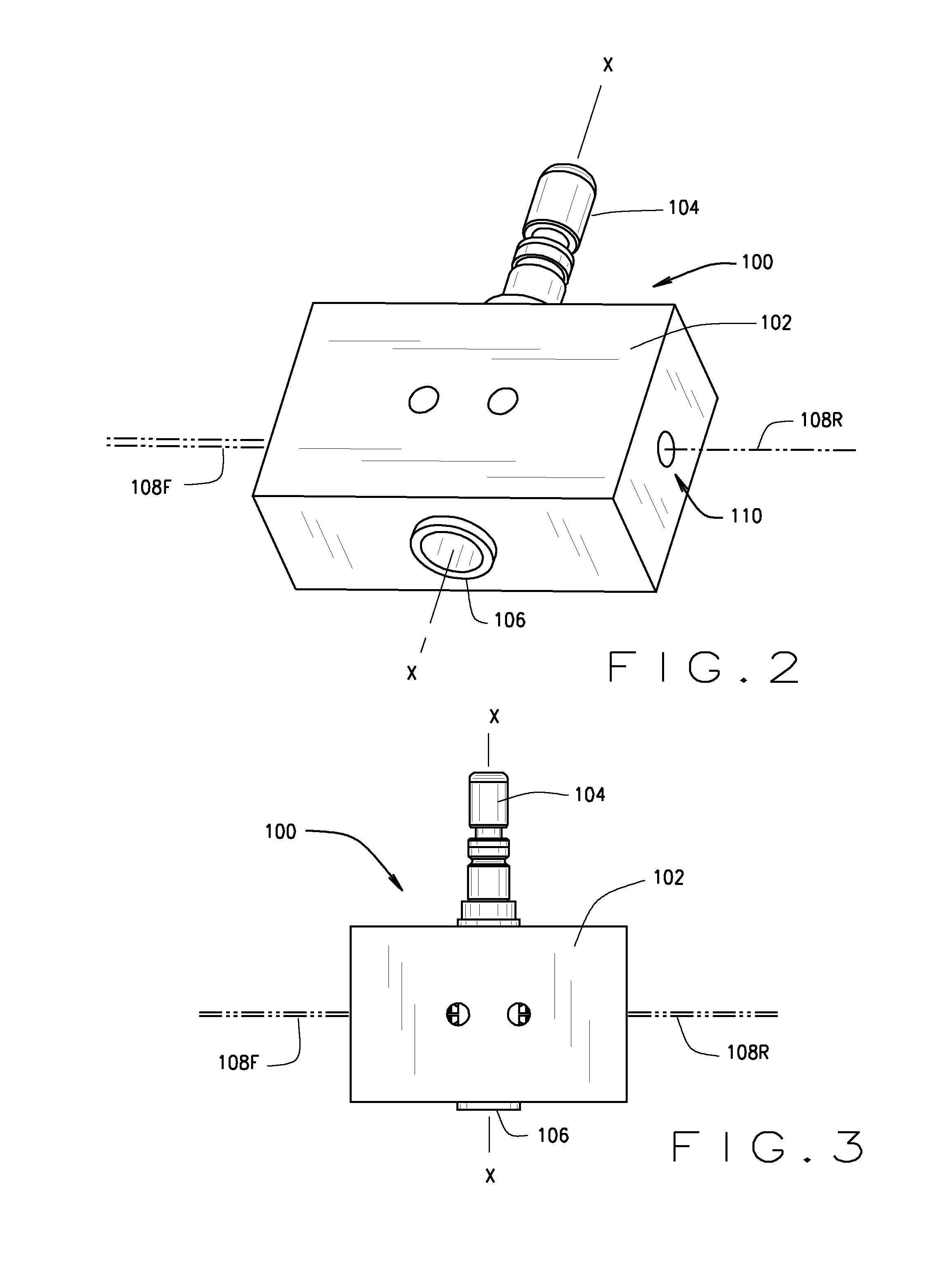
A machine vision vehicle wheel alignment system optical target assembly incorporating an adaptor for attachment of an optical target to a vehicle wheel assembly. The adaptor includes at least three contact points for abutment against surfaces of a vehicle wheel assembly, and an attachment mechanism configured to grip surfaces of a tire mounted to the wheel rim to hold the optical target assembly in contact with the wheel assembly surface. The optical target is secured to the adaptor, and maintained in a fixed relationship to the wheel assembly thereby during a vehicle wheel alignment measurement procedure.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
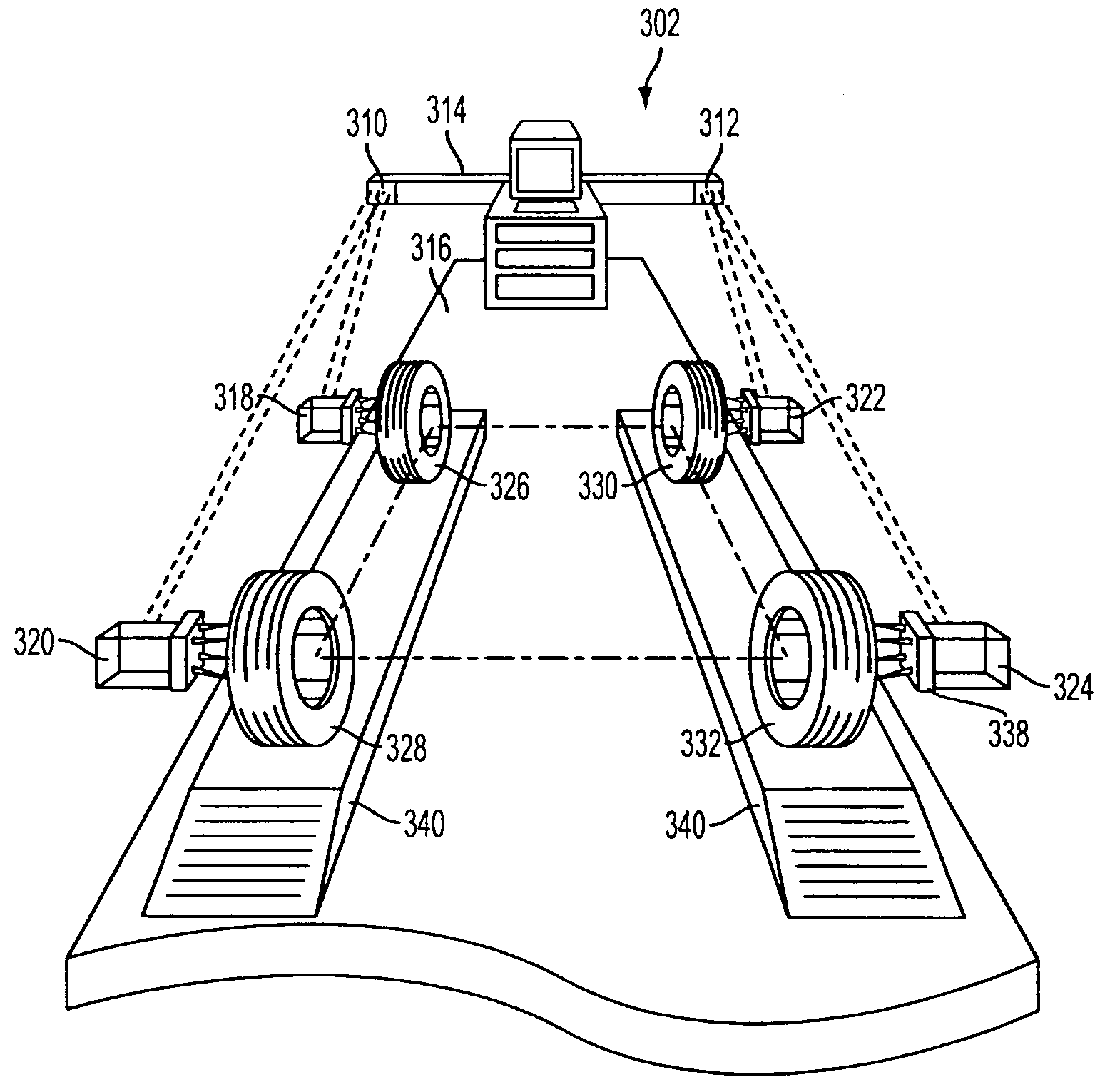
Method and device for non-contact measurement of the alignment of motor vehicle wheels
ActiveUS20080148581A1Improve accuracyEasy to useAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansMobile vehicleTriangulation
The invention relates to a method for non-contact measurement of the alignment of the wheels of a motor vehicle. In practice, the method provides for the steps of: applying a plurality of markers to the wheels of the motor vehicle along a line approximately substantially coaxial with the wheel; positioning, at each wheel for which the characteristic angles must be acquired, two image acquisition devices, with different inclinations with respect to said wheel; acquiring for each of said wheels, through each of said two image acquisition devices, at least one image of said wheel with the relative markers; determining, through epipolar and triangulation geometrical calculations, the equation of an approximate plane in which said markers lie in space, with respect to a reference system; determining the camber and toe angles of said wheel on the basis of the equation of said plane and of the equation of the reference planes with respect to which the motor vehicle takes a known position.
Owner:FASEP 2000
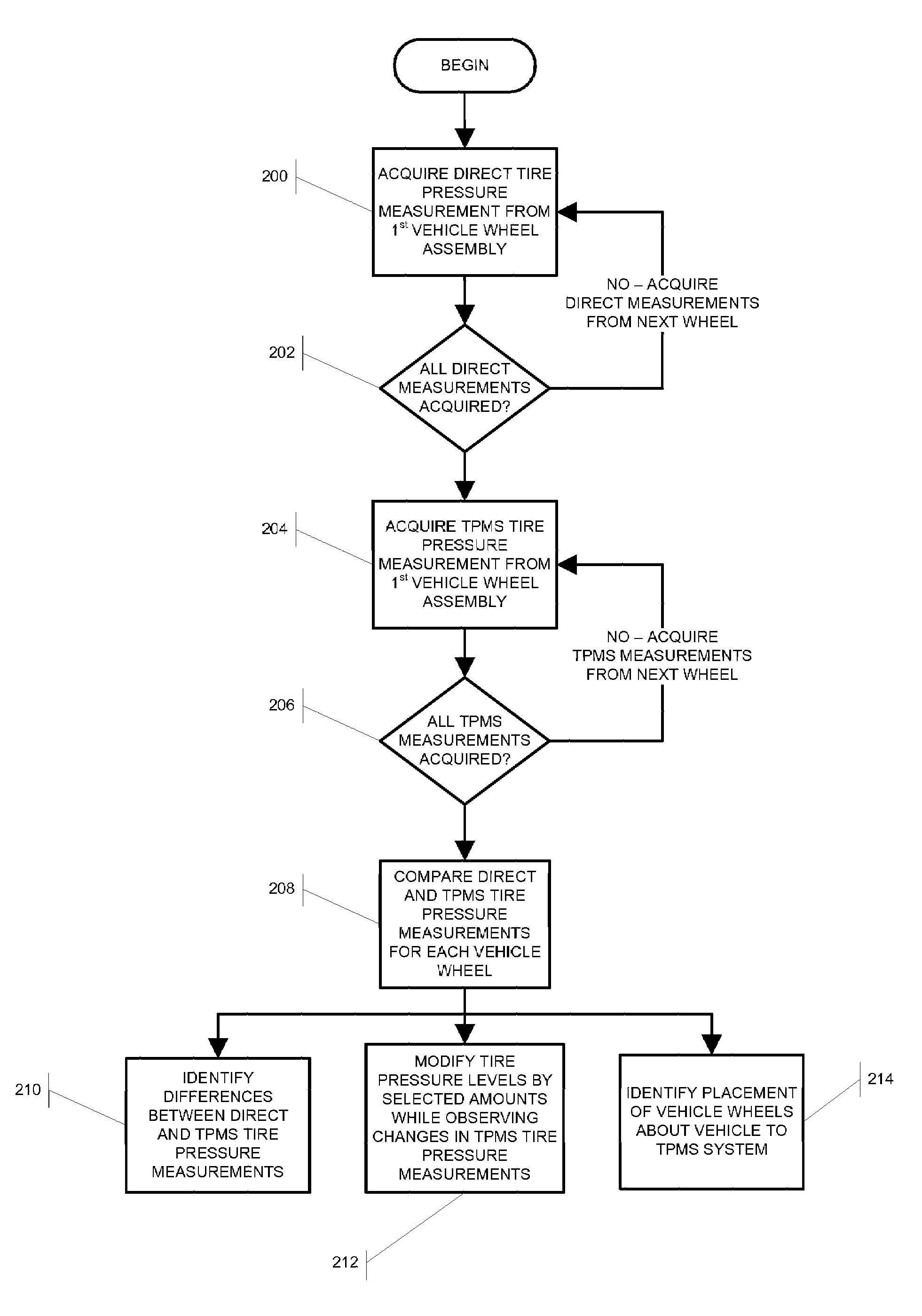
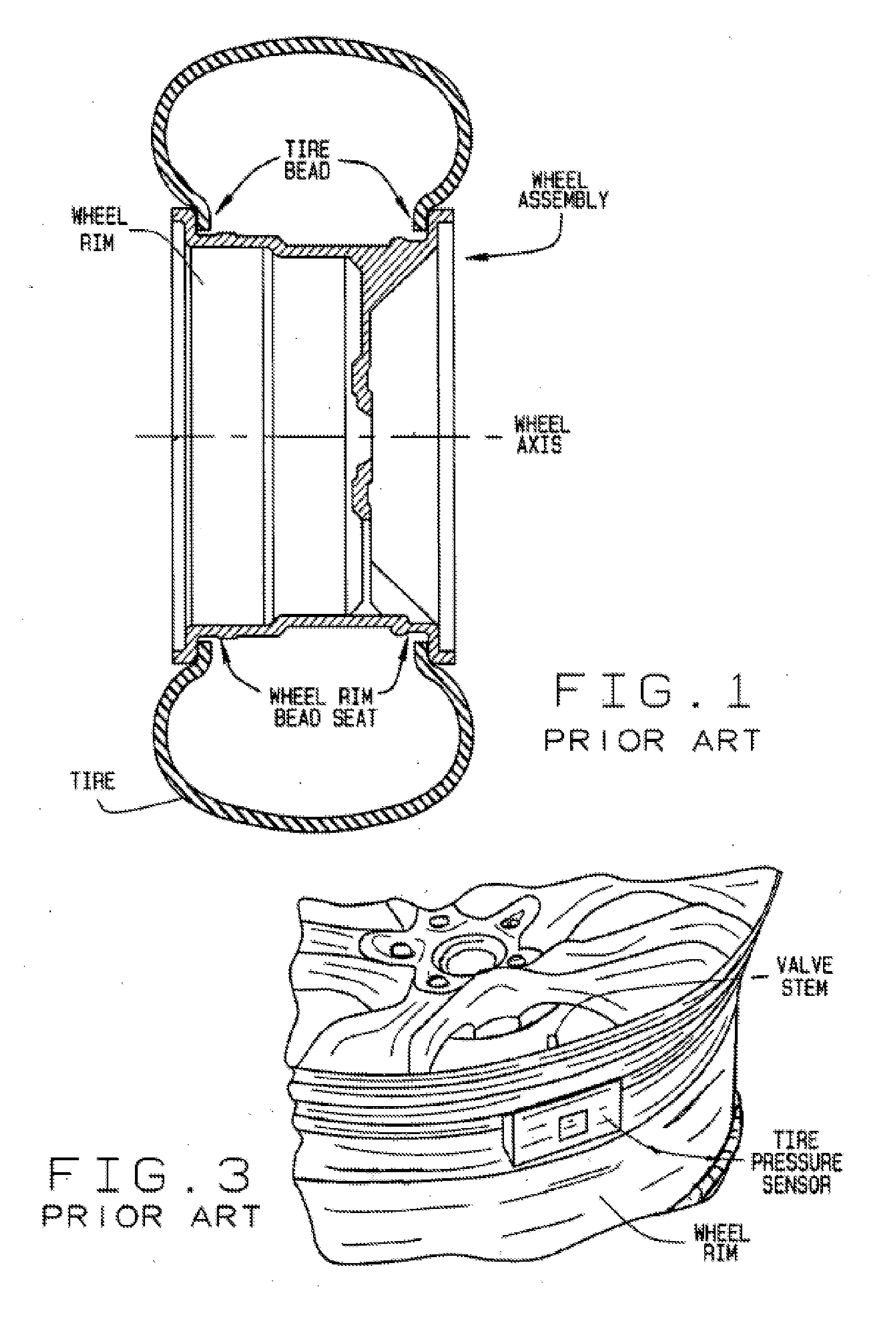
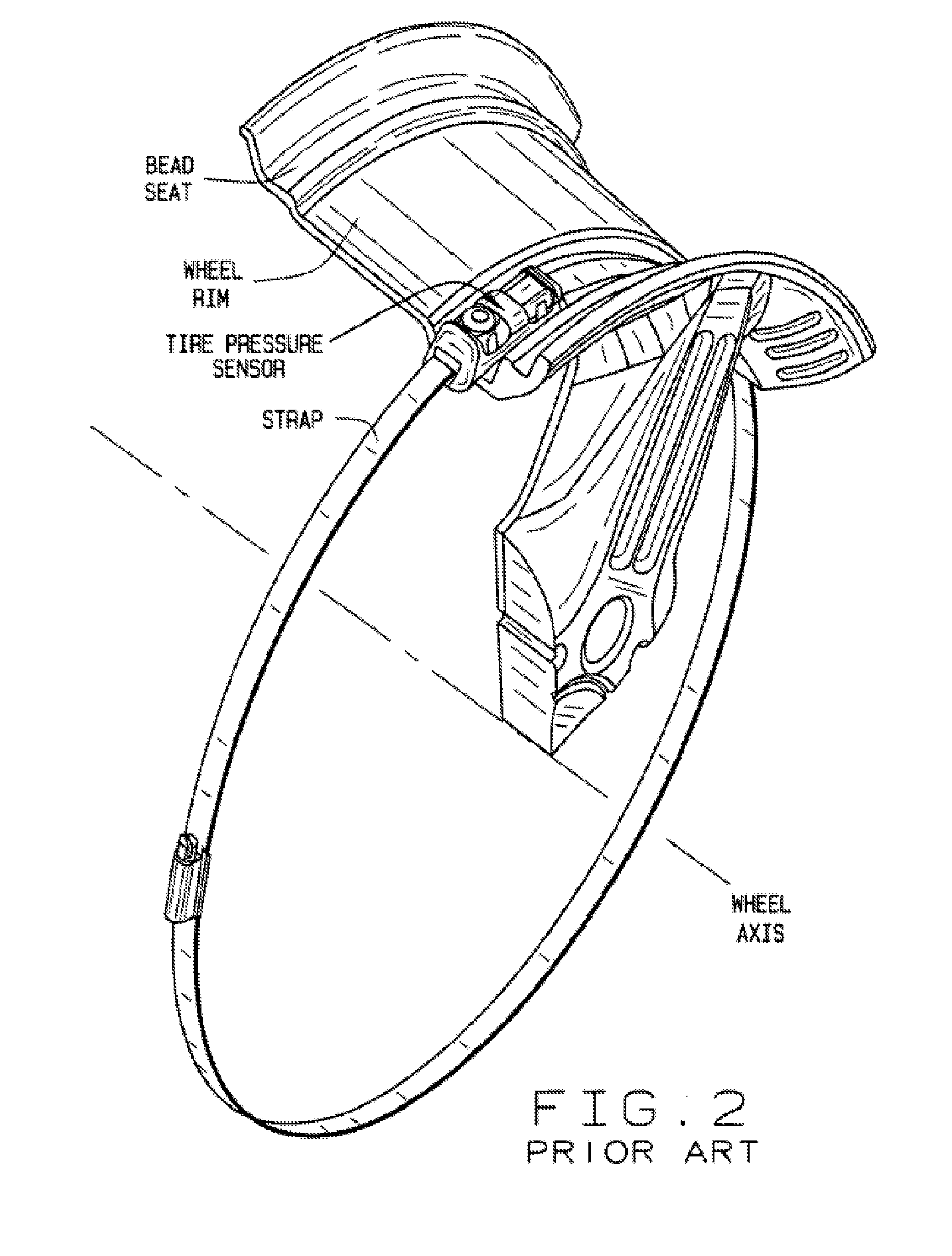
Integrated Tire Pressure Diagnostic System and Method
InactiveUS20080133081A1Accurate identificationSampled-variable control systemsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic systemRepair processes
A computer-based vehicle service system, such as a wheel alignment system, is configured to acquire and utilize measurements of the air pressure in the tires of a vehicle undergoing a service procedure.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Non contact wheel alignment sensor and method
ActiveUS20080273194A1Good precisionHigh sensitivityAngle measurementImage analysisEngineeringWheel alignment
A sensor and method of determining the orientation of an object, such as the alignment characteristics of a tire and wheel assembly mounted on a vehicle, includes projecting a plurality of light planes from a first light projector onto a tire and wheel assembly to form a plurality of generally parallel illumination lines on a tire of the tire and wheel assembly, receiving a reflected image of at least some of the illumination lines with a photo electric device reflected from the tire at an angle relative to a projecting angle of the first light projector, and determining a plane defined by spatial coordinates from a selected point located on each illumination line imaged by the photo electric device, with the plane representing the orientation of the tire and wheel assembly.
Owner:VERHAERT NEW PROD & SERVICES +1
Vehicle Wheel Optical Target Mounting Assembly
A machine vision vehicle wheel alignment system optical target assembly which incorporates an adaptor for attachment of an optical target to a vehicle wheel assembly. The adaptor includes a circular sinusoidal edge for seating in a non-determined position against surfaces of a vehicle wheel assembly, and a pair of pivoting arm assemblies capable of independent movement which are configured to position tire hooks for gripping the tread surfaces of a tire mounted to the wheel rim. Forces exerted between the pivoting arms are transferred to the tire hooks to hold the optical target assembly in contact with the wheel assembly surface. The optical target is integrated into the adaptor, and maintained in a stationary relationship to the wheel assembly thereby during a vehicle wheel alignment procedure.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
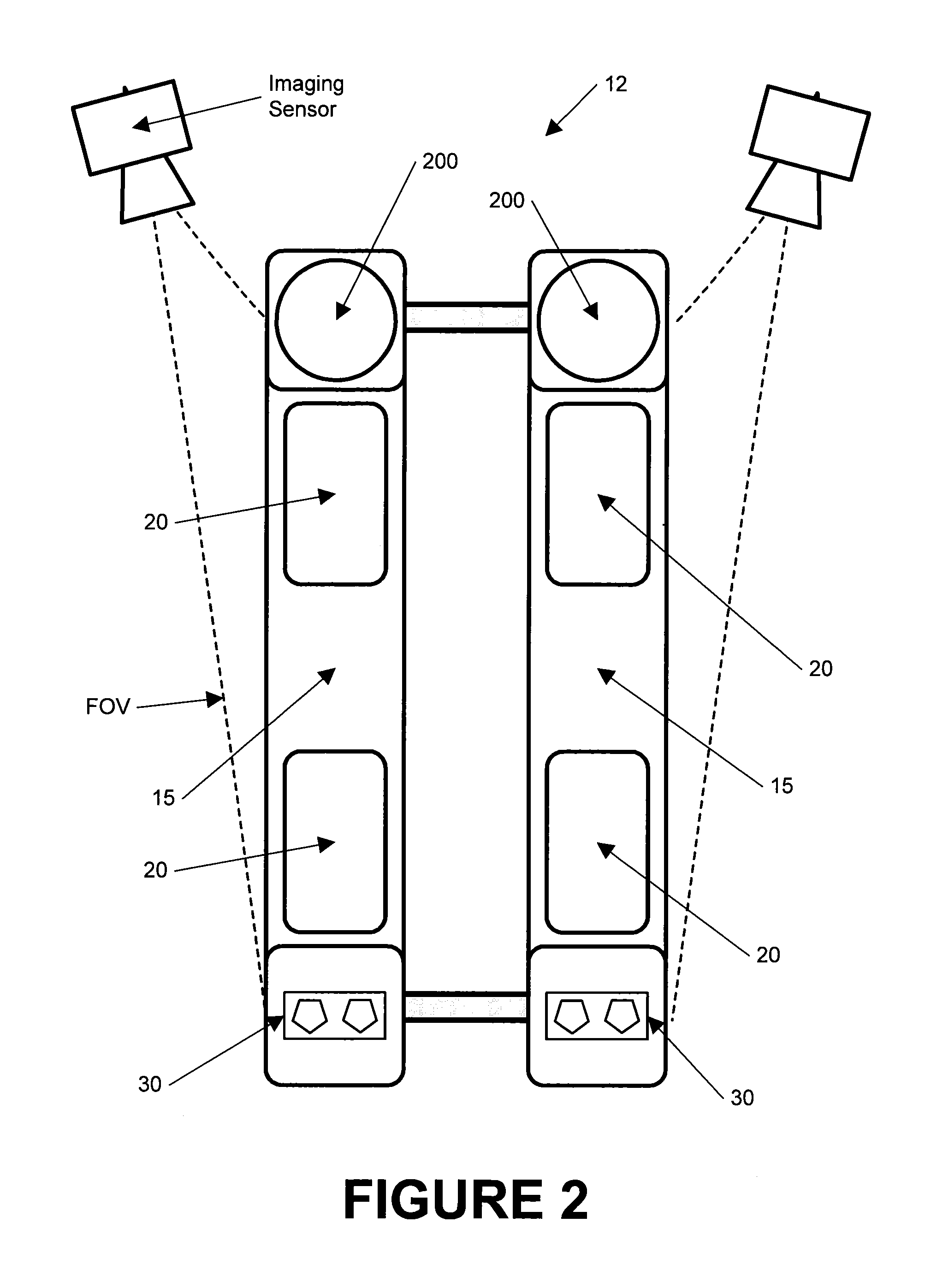
Common reference target machine vision wheel alignment system
A camera configuration for a machine vision vehicle wheel alignment system which does not dispose all of the cameras on a single rigid structure, such that cameras disposed to view the left side of a vehicle are movable independently of the cameras disposed to view the right side of the vehicle, while maintaining a common reference coordinate system for determining vehicle wheel alignment angles.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Vehicle wheel alignment check method and system
Owner:SHENZHEN SMARTSAFE TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for wheel alignment
ActiveUS20080289202A1Accurate measurementAngles/taper measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringWheel alignment
A vehicle wheel alignment method and system is provided. A three-dimensional target is attached to a vehicle wheel known to be in alignment. The three-dimensional target has multiple target elements thereon, each of which has known geometric characteristics and 3D spatial relationship with one another.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
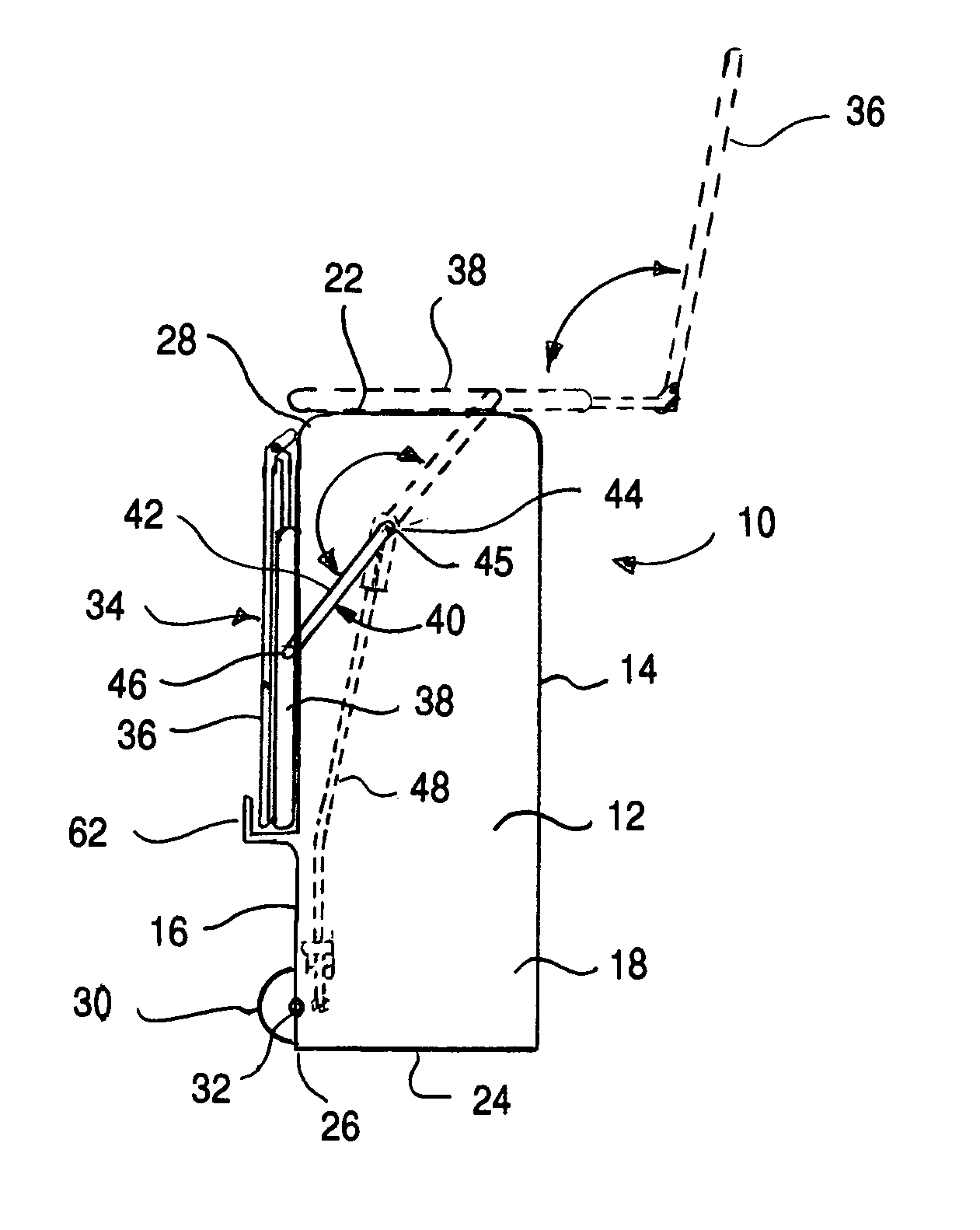
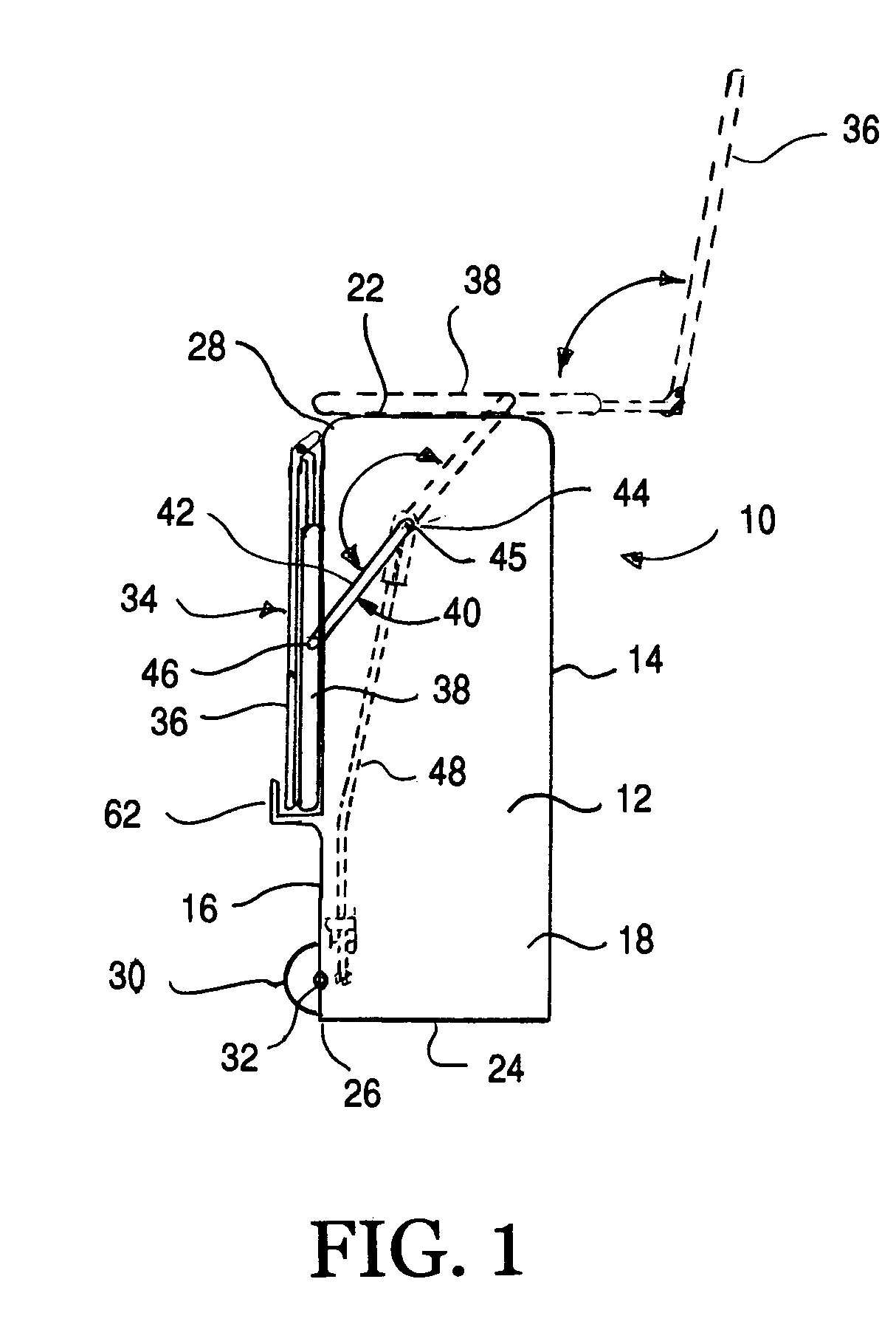
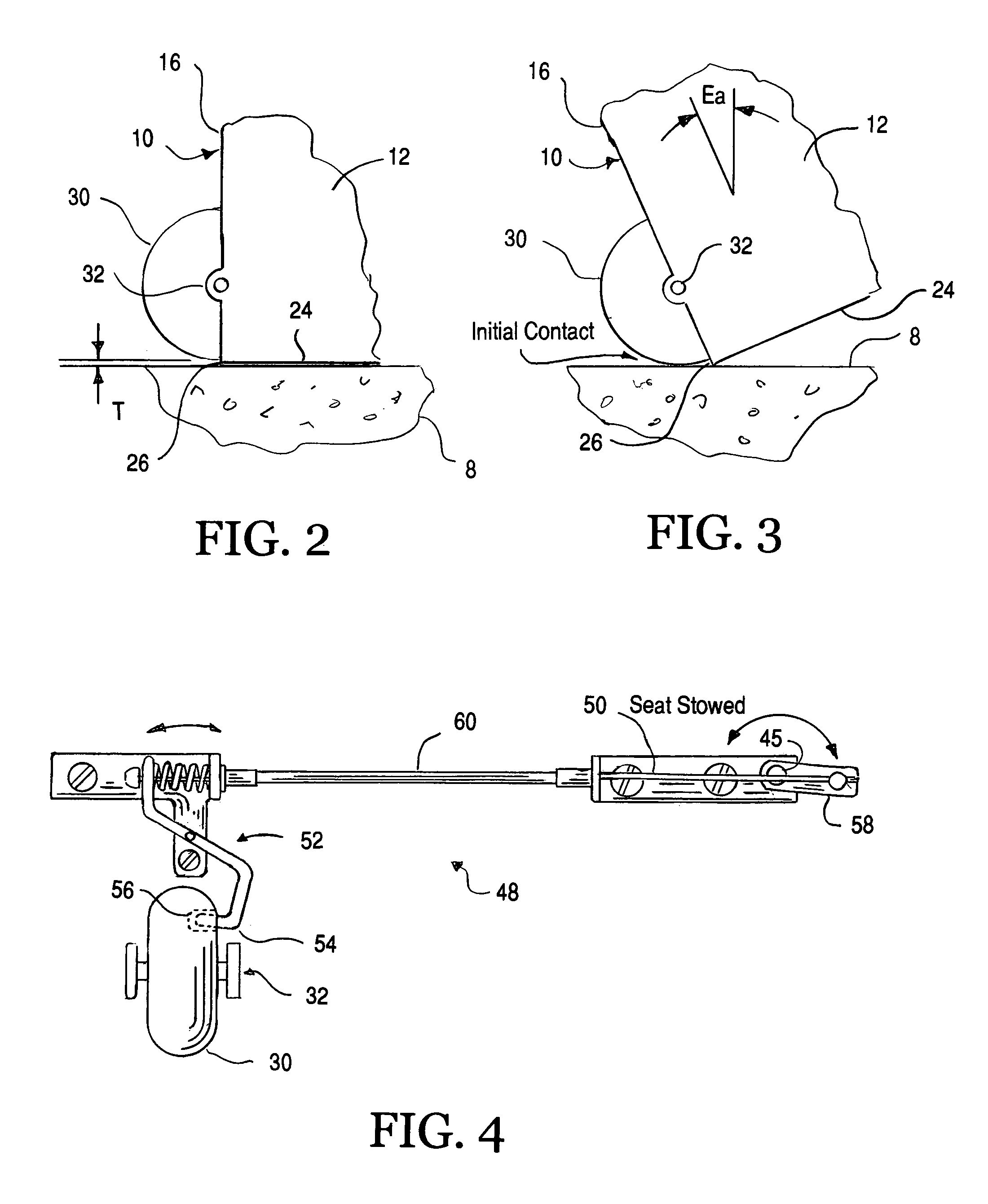
Travel suitcase with seat
A suitcase including a main body having a front surface, rear surface, first and second side surfaces, a top surface and a bottom surface, a bottom rear edge at the meeting point of the bottom surface and the rear surface as well as a top rear edge adjacent to the meeting point of the top surface and the rear surface. The suitcase also includes a seat pivotally secured to rotate about the top rear edge of the main body for pivotal motion from a storage position along the rear surface to a use position along the top surface. The seat includes a seat bottom. Wheels are coupled along the bottom rear edge, wherein the wheels are positioned such that they only engage the support surface when the suitcase is tipped from a vertical orientation exceeding a predetermined angle. A seat support structure supports the seat for rotation between its use position and its storage position. The seat support structure includes first and second seat swing arms secured to opposite sides of the suitcase. A braking device ensures the suitcase does not inadvertently roll when an individual is sitting thereon by securely locking the wheels from turning when the seat is being used.
Owner:LACROSSE WILLS +1
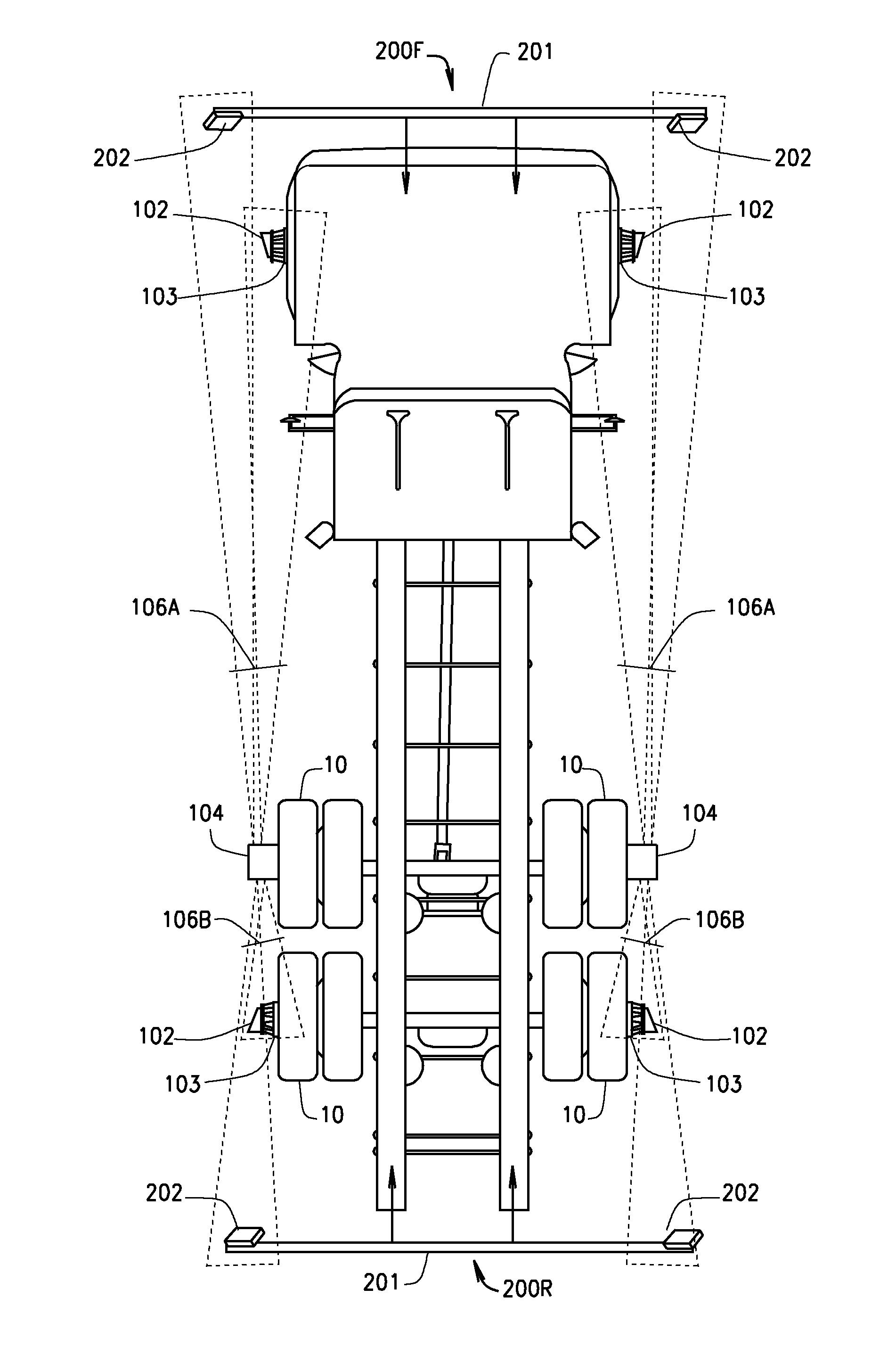
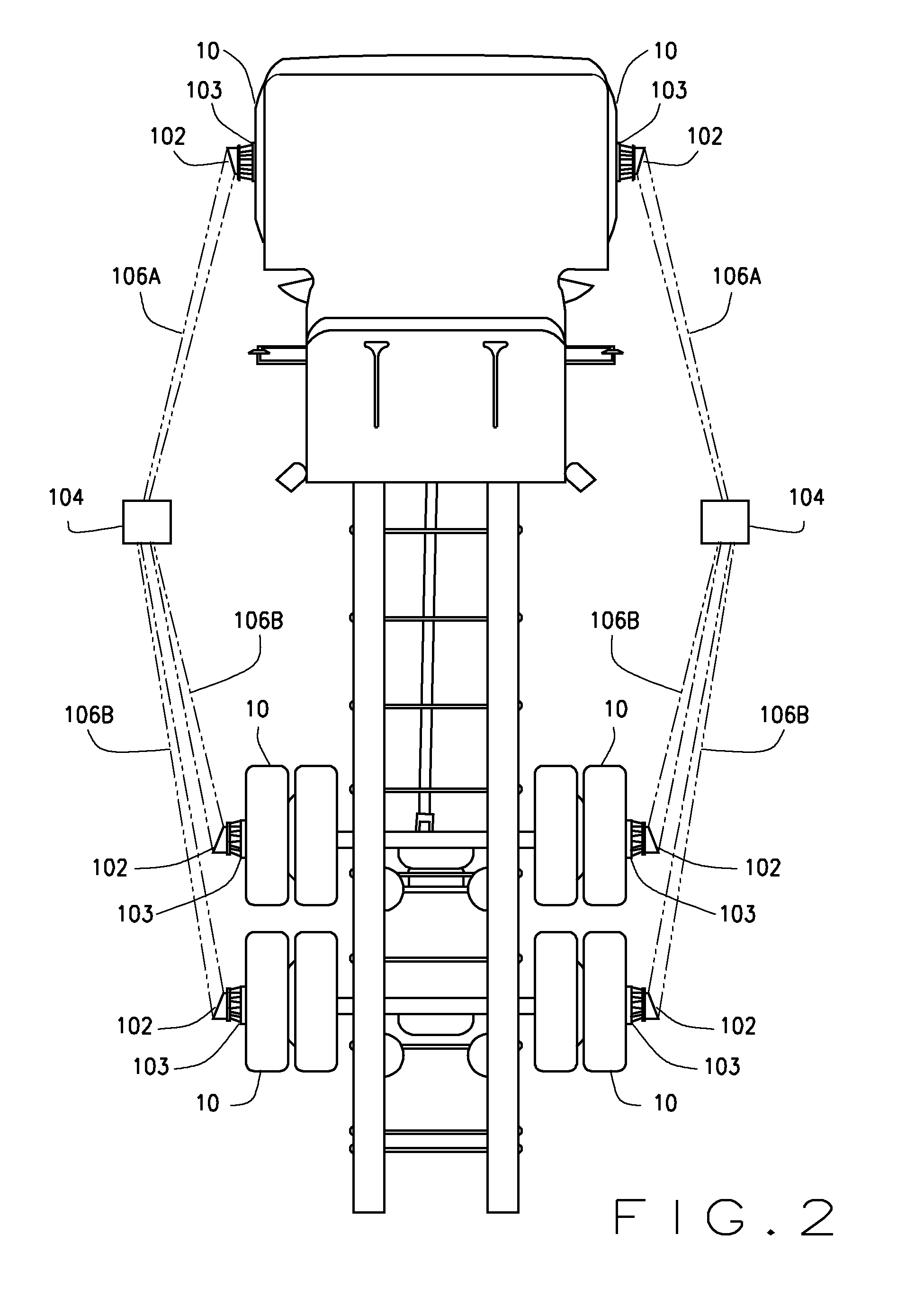
Method and Apparatus for Multi-Axle Vehicle Alignment with Vehicle Frame Reference
A vehicle wheel service system including a plurality of sensors positioned in proximity to a heavy-duty multi-axle vehicle, to measure angles associated with three or more axles of the vehicle without repositioning the mounting of the sensors after initiating a measurement procedure. Additional sensors, associated with a vehicle reference, such as the vehicle frame axis, are disposed to provide vehicle reference measurement data which is communicated to a processing system. The processing system is configured with software instructions to evaluate the measurement data and to determine various vehicle wheel alignment angle measurements and / or necessary vehicle adjustments for each axle relative to the vehicle reference or to a fixed axle having a determined relationship to the vehicle reference.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
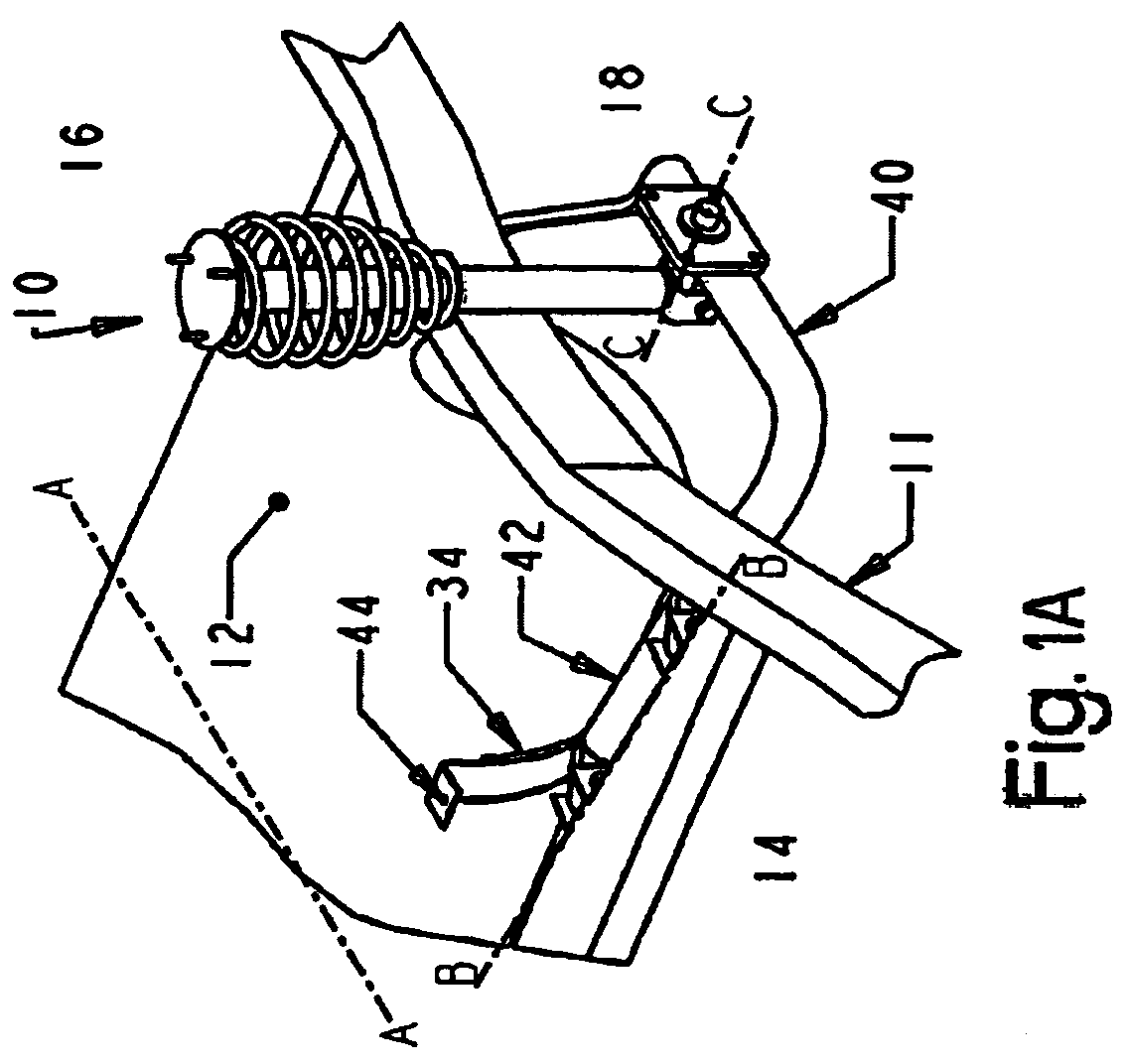
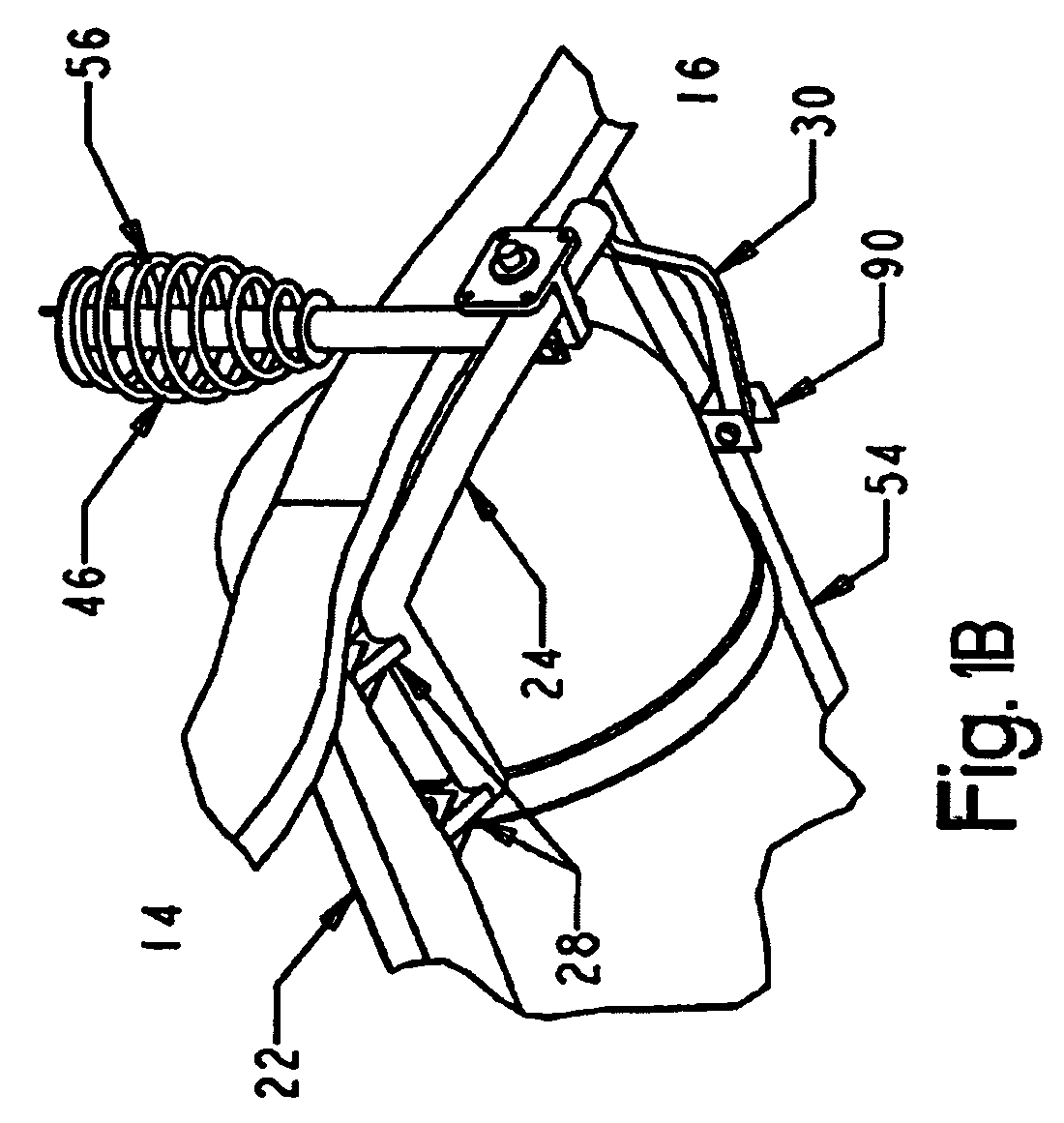
Suspension system for a vehicle with a tank for liquified gas
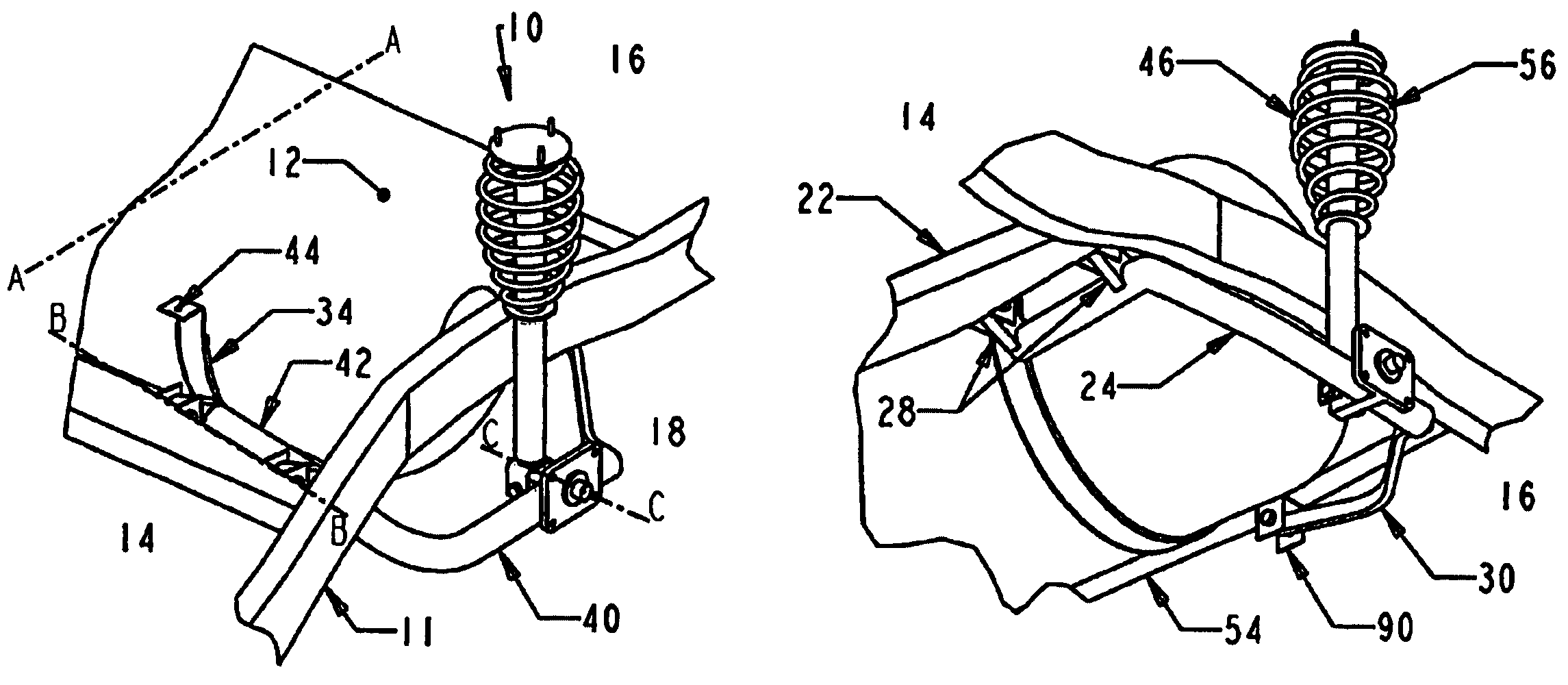
A suspension system for carrying a compressed gas fuels in vehicle. The suspensions arms and springs are configured to maximize the space between the wheels while providing a high degree of suspension stiffness to maintain proper wheel alignment during cornering, braking and in rough terrain. The suspension arms have two broadly-spaced attachment points to the chassis that provides structural rigidity to the rear suspension subassembly.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
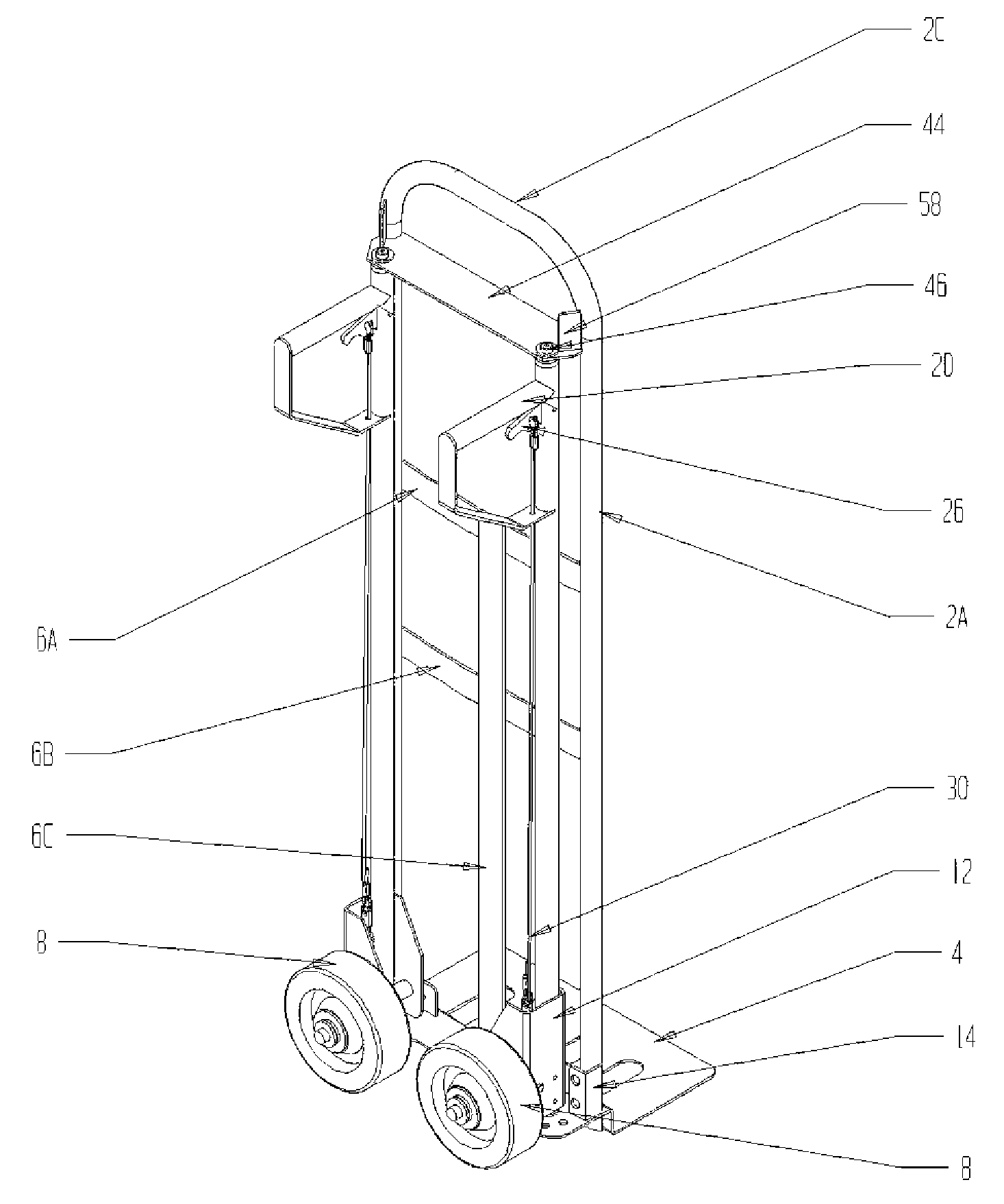
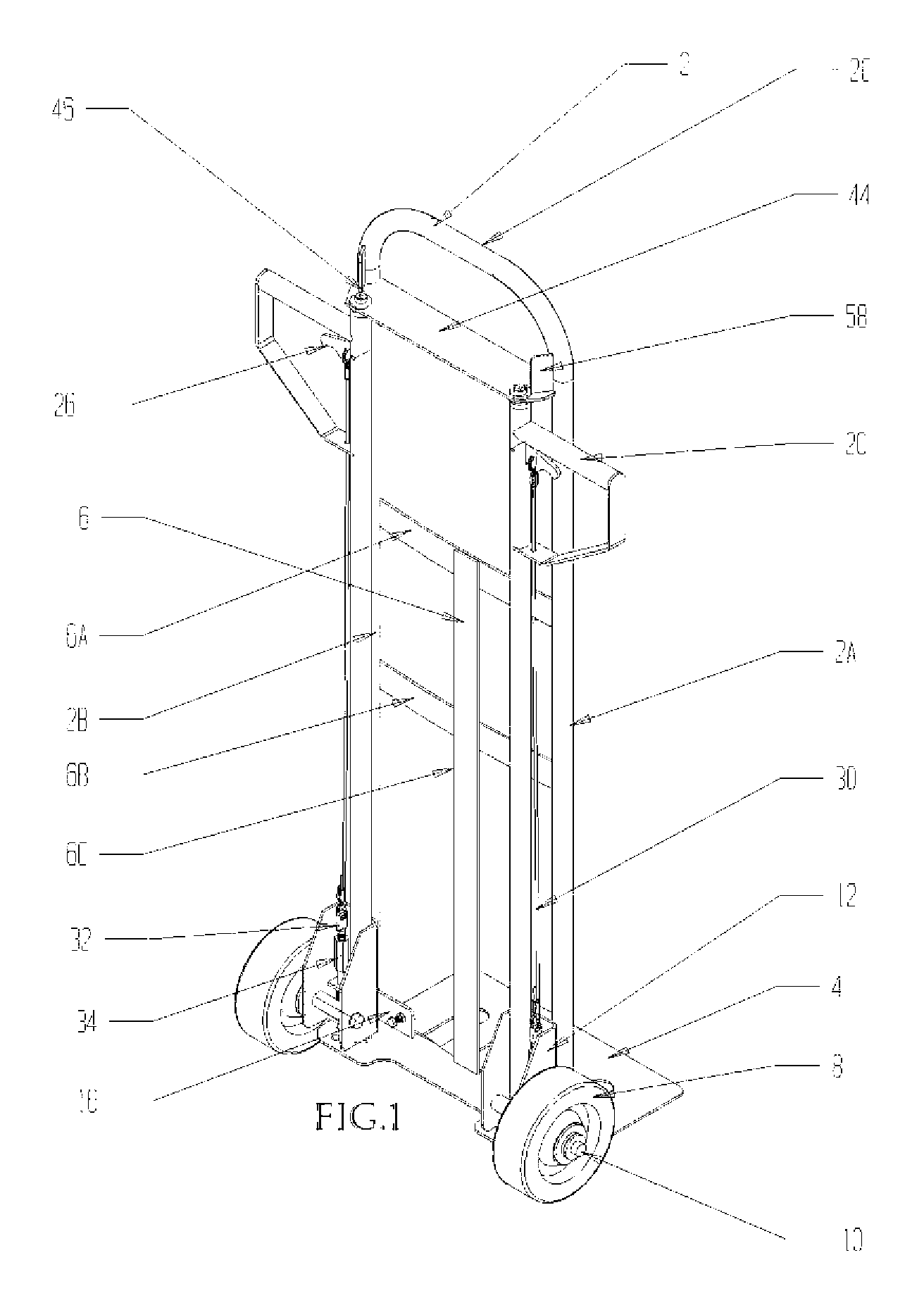
Hand truck capable of multi-directional movement
ActiveUS7464947B2Carriage/perambulator accessoriesCarriage/perambulator with single axisRange of motionEngineering
The hand truck or dolly of the present invention is capable of multi-directional movement and provides an operator with complete control of movement and directional choice for the hand truck without having to remove his hands from a handgrip location to achieve mechanical adjustments of the wheels. Rather, an operator may adjust a wheel index position on-the-fly by means of a trigger assembly to rotate a wheel assembly about a vertical axis of rotation within a range of motion of approximately 100 degrees. The two, independent wheel assemblies of the hand truck of the present invention achieve multi-directional movement through positioning of the wheels in a standard index position allowing for forward and backward movement, a lateral index position allowing for lateral, or side to side, movement, or a rotational index position allowing for rotational movement, such as for cornering and circular movement.
Owner:HAND TRUCK CO THE LLC
Wheel aligner with advanced diagnostics and no-stop positioning
InactiveUS20170097229A1Reduce weightLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementEngineeringImaging data
A vehicle wheel alignment system has a plurality of cameras, each camera for viewing a respective target disposed at a respective wheel of the vehicle and capturing image data of the target as the wheel and target are continuously rotated a number of degrees of rotation without a pause. The image data is used to calculate a minimum number of poses of the target of at least one pose for every five degrees of rotation as the wheel and target are continuously rotated the number of degrees of rotation without a pause. At least one of the cameras comprises a data processor for performing the steps of preprocessing the image data, and calculating an alignment parameter for the vehicle based on the preprocessed image data.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
Apparatus and method for testing the performance of a vehicle
InactiveUS20060130567A1Improves inventionIncrease profitEngine testingWork measurementImage resolutionEngineering
An apparatus for testing the brakes, wheel alignment, suspension, transmission, and engine of motorized wheeled vehicles, includes means such as a dynamometer for self-calibration. A platform supports a road vehicle to be tested. Two or four pairs of short high-inertia rollers are revolvably supported adjacent to said platform, and positioned to individually support either the front wheels or the back wheels of the vehicle. The rollers are drivable by a stationary vehicle resting thereon, each pair of high-inertia rollers supporting one vehicle wheel. A floating roller contacts the wheel to detect side forces. Sensor means are connected to the rollers and data processing, display and recording means are connected to the sensors. Speed of the rollers is monitored by an encoder having a resolution of at least 1000 pulses / sec. A preferred embodiment of the apparatus includes electric motors which can be connected to drive the rollers.
Owner:BEN DAVID YONA
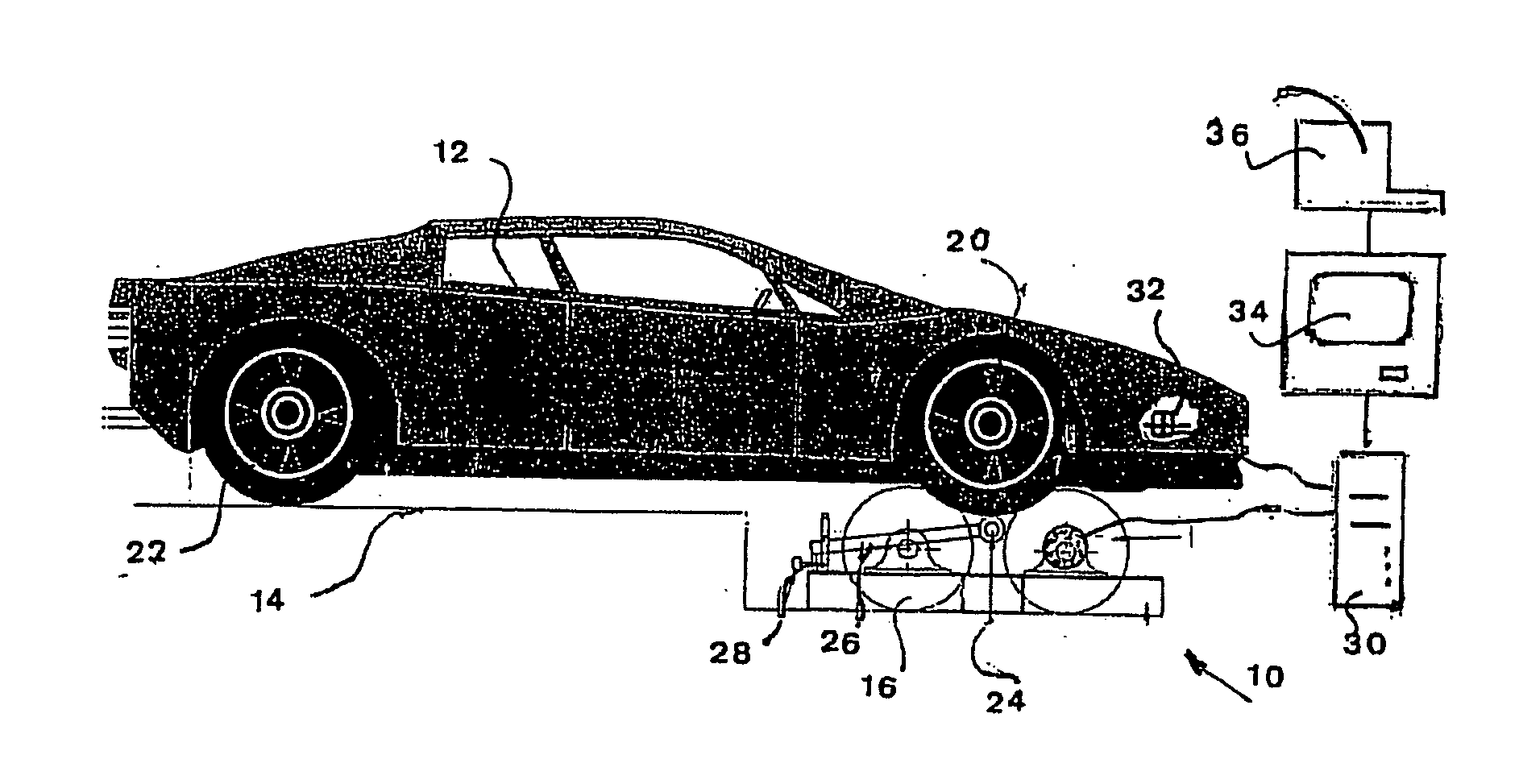
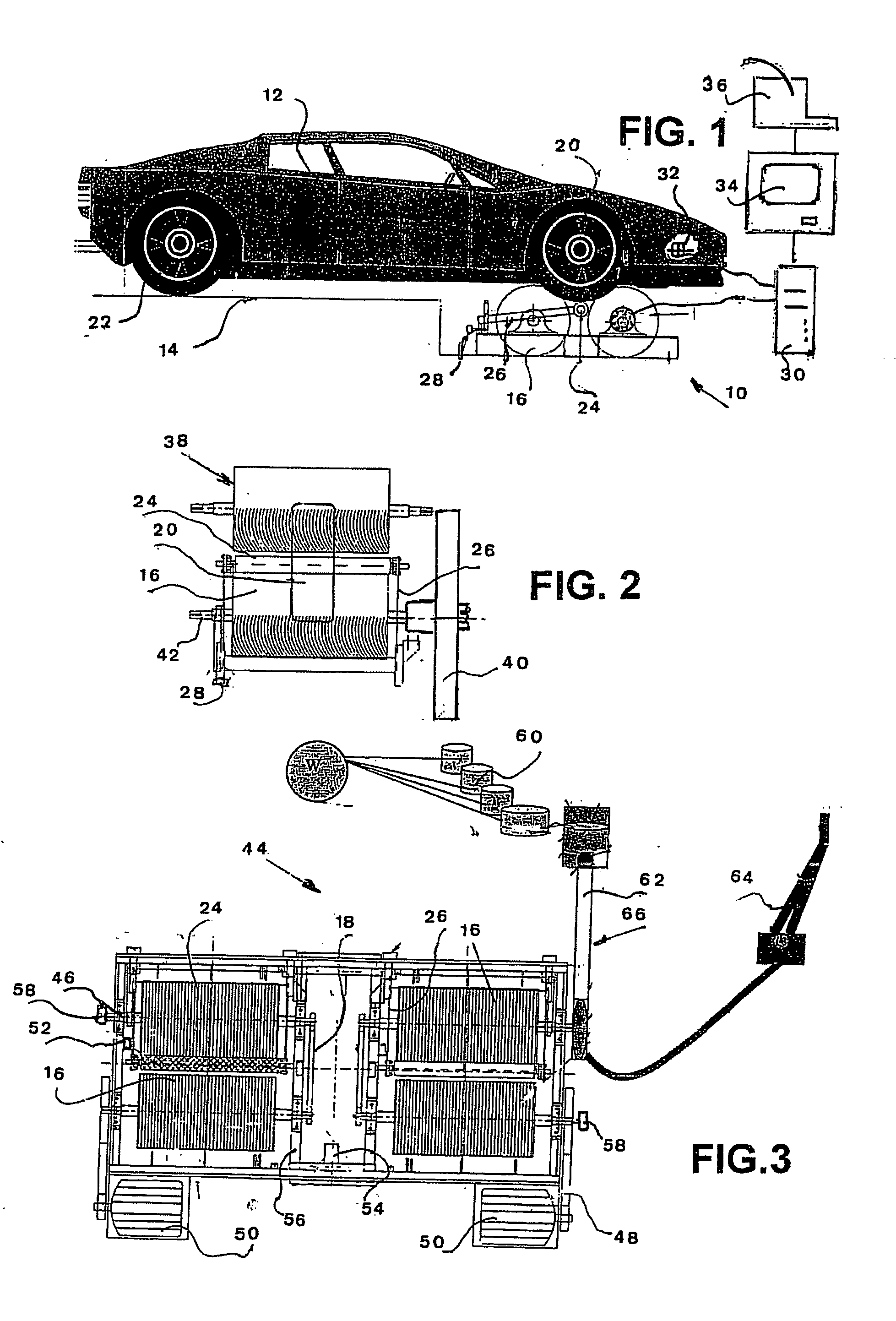
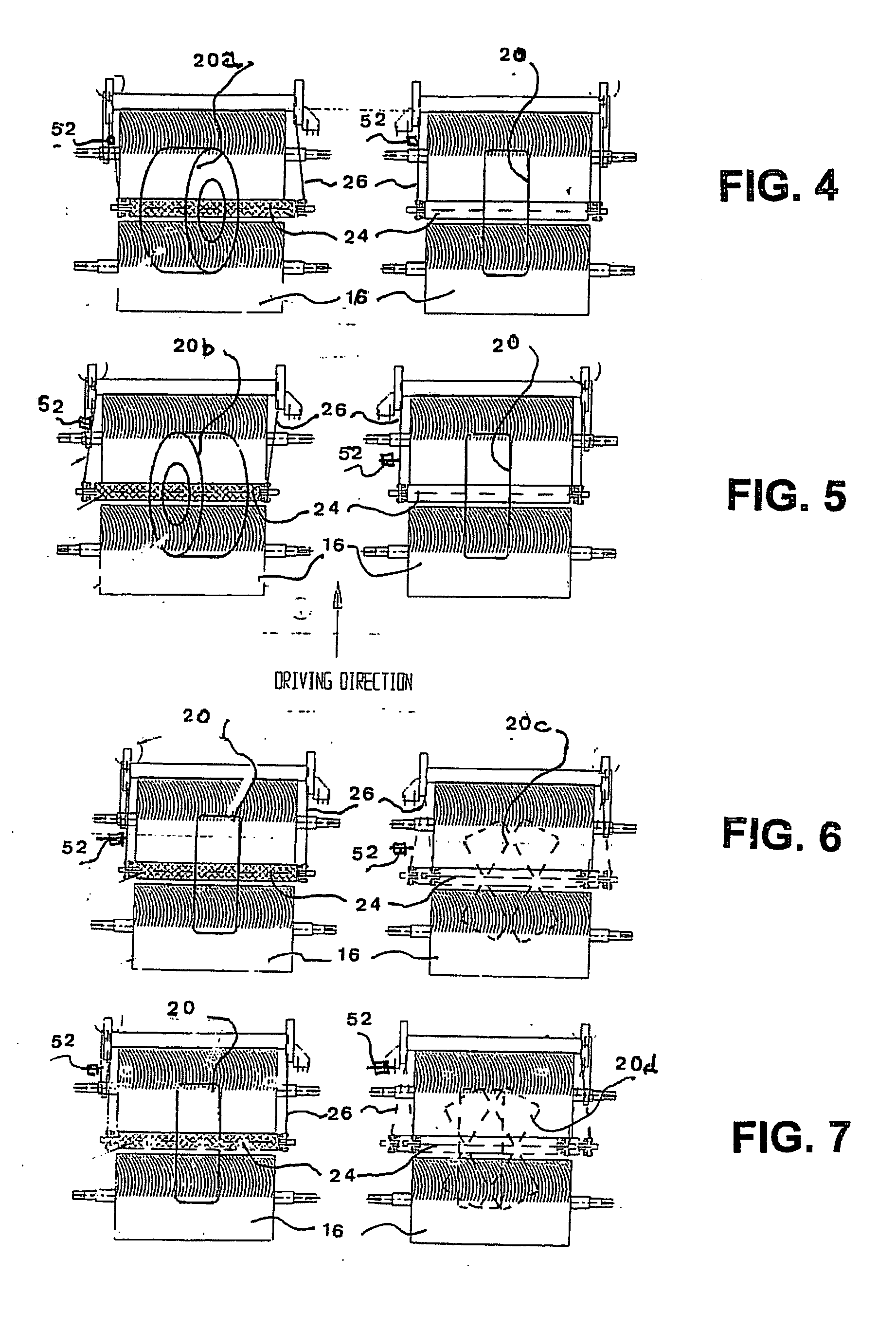
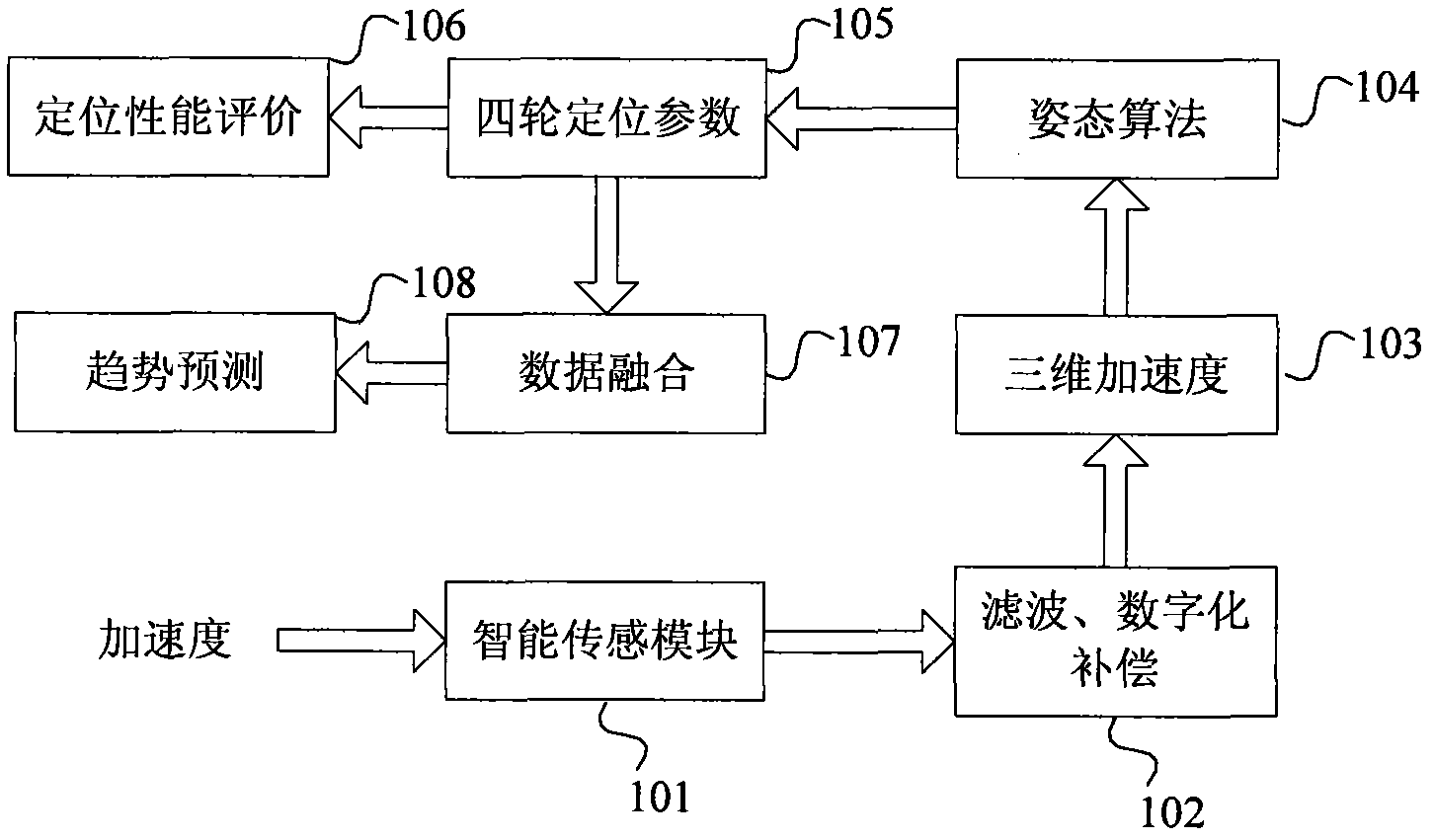
Wheel load-based type intelligent sensing four-wheel positioning measurement method
The invention discloses a wheel load-based type intelligent sensing four-wheel positioning measurement method. The method comprises the following steps of: sensing the three-dimensional accelerations of specific points of wheels by using an intelligent sensing module; acquiring initial attitude angles of the wheels by using the three-dimensional acceleration parameters of the specific points of the wheels and an attitude algorithm and solving positioning parameters of the camber and the front wheel toe-in among the four wheels; establishing a kingpin caster angle and kingpin inclination computation model and solving positioning parameters of the kingpin caster and the kingpin inclination among the four wheels; and merging and analyzing four-wheel positioning parameters of the wheels, namely the camber, the front wheel toe-in, the kingpin caster and the kingpin inclination, to acquire a variation trend of the four-wheel positioning parameters of the wheels. By performing multi-sensor data merging and analysis on the parameters, the wheel load-based type intelligent sensing four-wheel positioning measurement method has the advantages of fully monitoring and predicating a wheel positioning state, ensuring the stability and the safety of automobile driving, reducing the abrasion and the oil consumption of automobiles, improving the steering performance of vehicles and ensuring automatic aligning of steering systems, and is a novel method for wheel positioning measurement.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
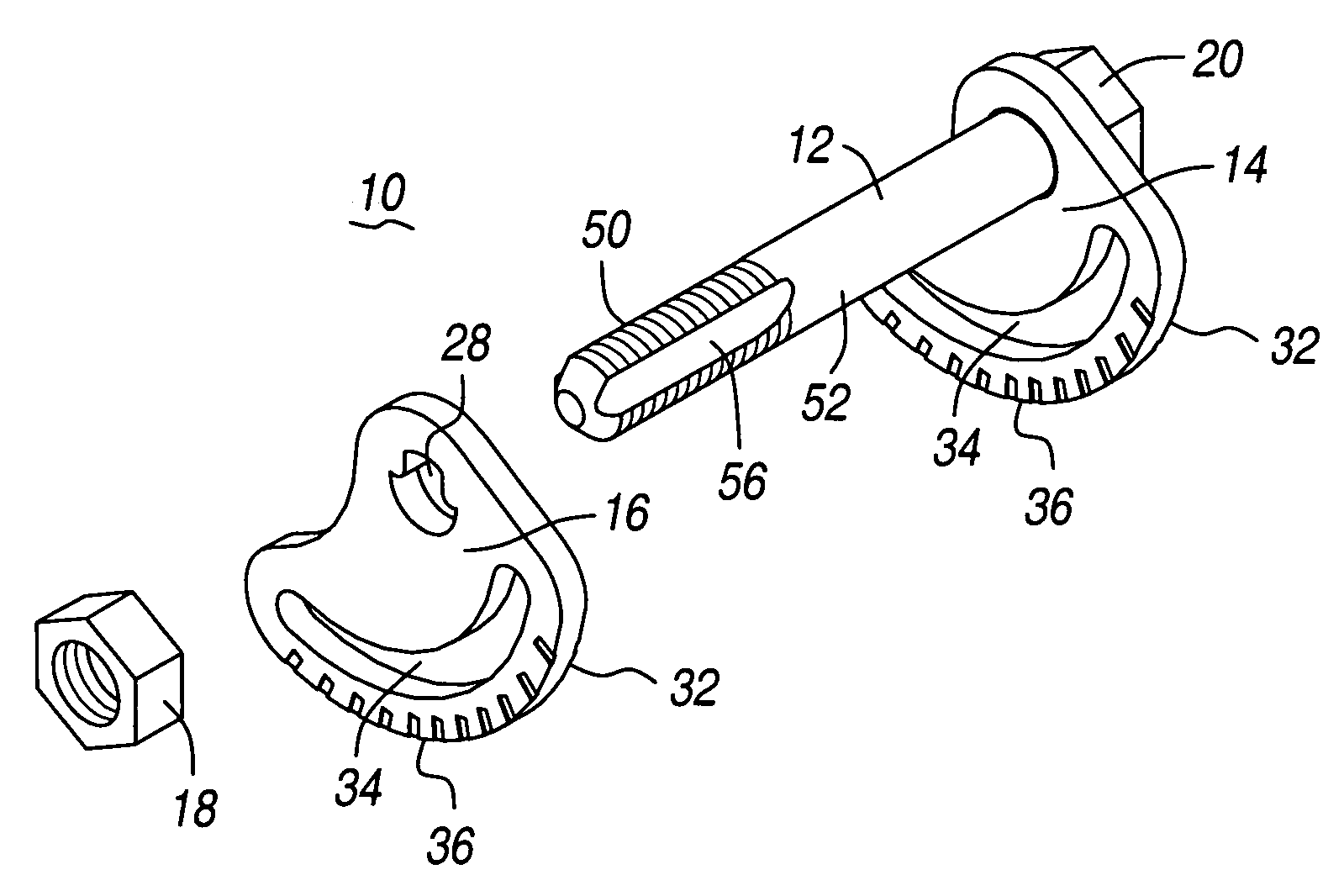
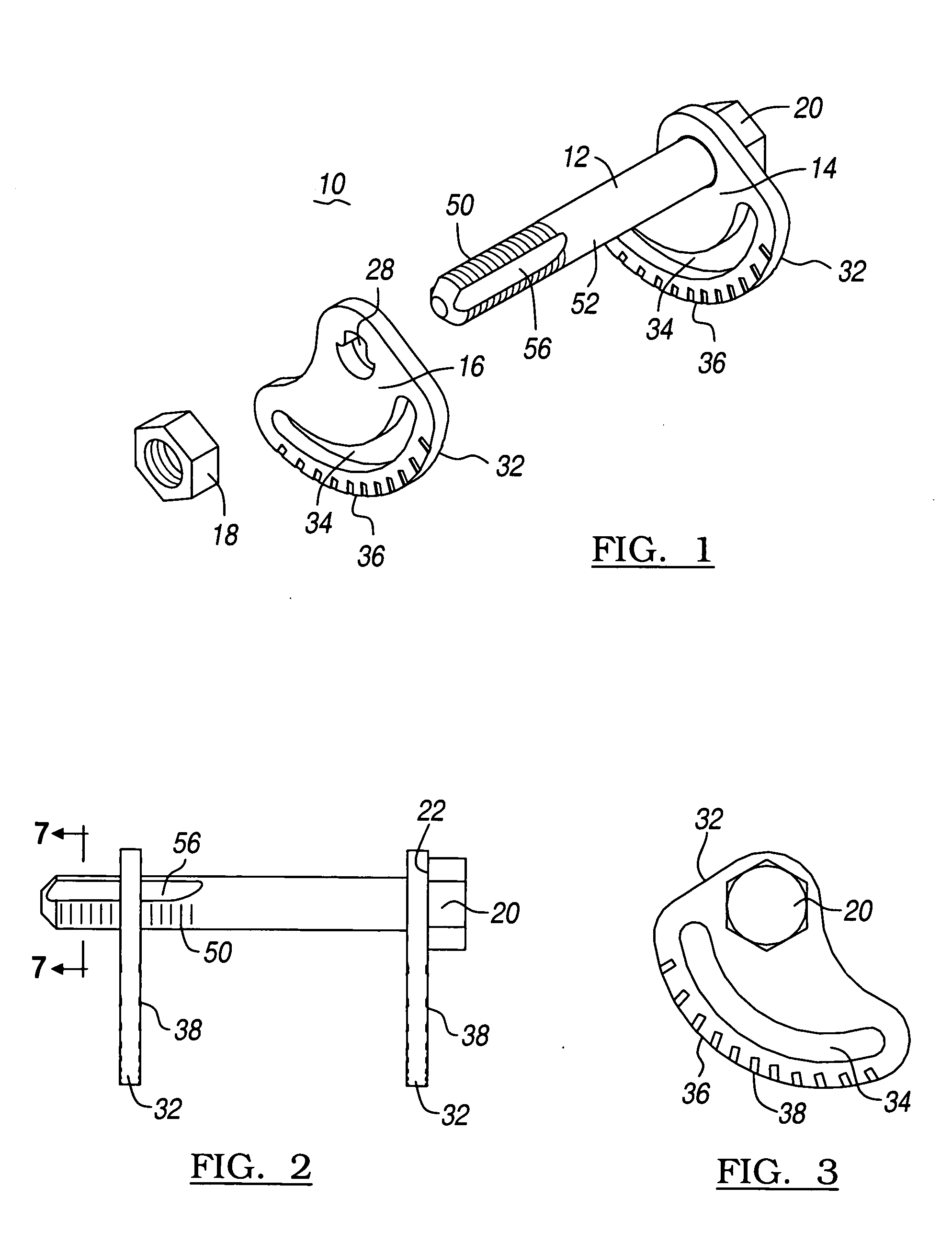
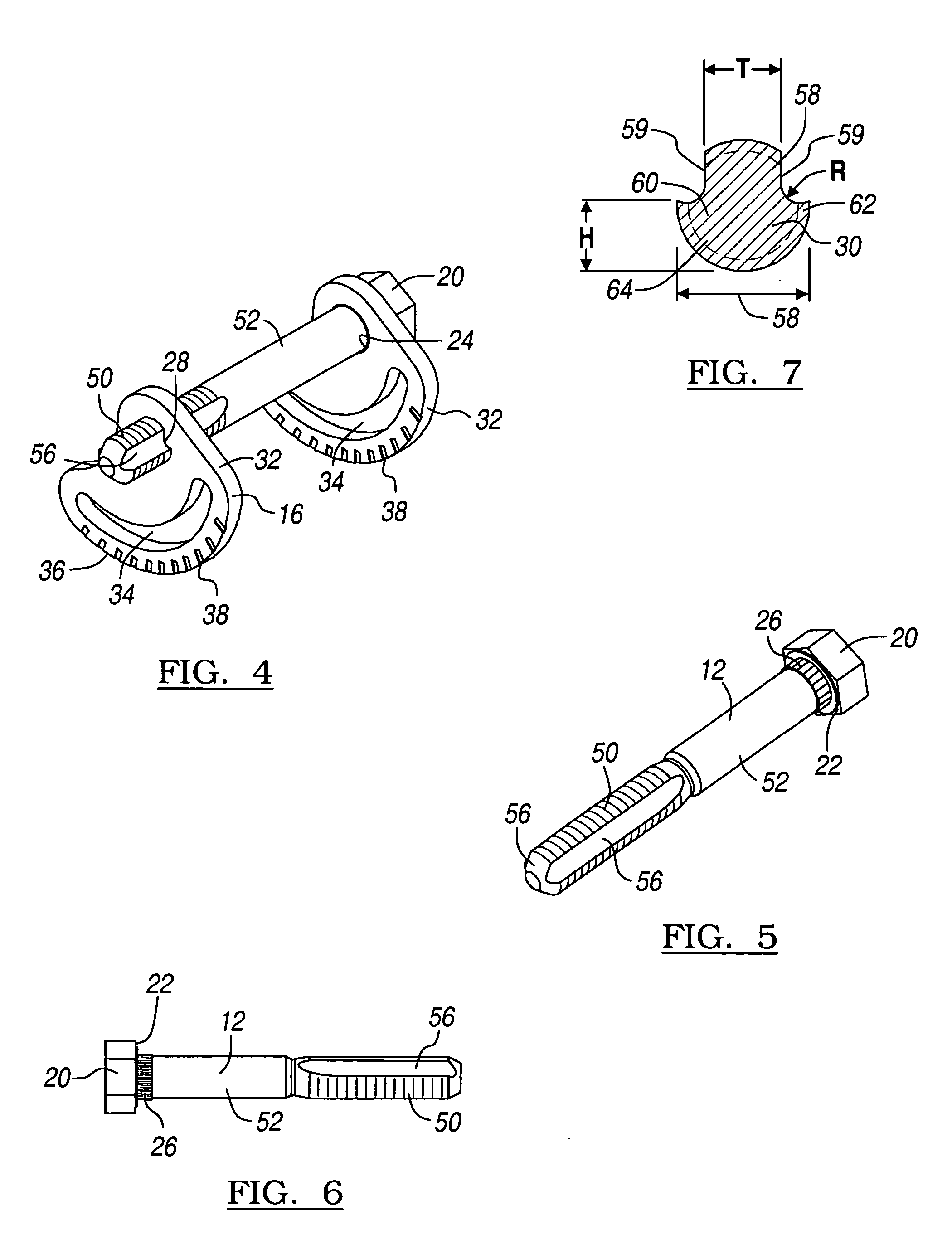
Cam-bolt assembly
A cam bolt assembly for using in a vehicle's suspension system to adjust the vehicle's wheel alignment is disclosed having a threaded fastener defining a pair of longitudinal channels, a first cam plate is coupled to the threaded bolt, a second cam plate defining an aperture is mated to the pair of longitudinal channels. At least one of the cam plates has an arcuate slot configured to mate with a component of the suspension system.
Owner:NEWFREY
Wheel alignment gauge
InactiveUS20060185180A1Accurately indicatedAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringSpoke
The present invention is a wheel alignment gauge for checking the ‘toe’ and ‘camber’ of the wheels. The gauge can be used with the vehicle on the ground. The gauge uses three identical magnet-ended extension rods which are inserted through the vent holes or spokes of the wheels. The rod's inboard ends magnetically attach to the disc brake rotor surface leaving the outboard ends clear of the vehicle's wheel and bodywork. Flat plates rest on the ground and magnetically attach to the outboard ends to create a plane parallel to the rotor and wheel. Laser-ended alignment arms magnetically attach to the plates, are level, and have forward ends that extend beyond the front of the vehicle allowing the lasers to project ate target sheets centered on the lasers. Each arm also has a perpendicular location arm that contacts the front of the wheel (or rotor when the wheels are removed). The laser's dots provide a off-center measurement, which, along with the arm's spacing, one can calculate the trigonometric SINE of the wheel's angle. The gauge can be quickly changed from vertical to horizontal for camber or toe measurements respectively. If adjustment is required, the vehicle is raised on its suspension, the wheels are removed and the gauge re-attached to locate on the rotors to direct alignment adjustments.
Owner:MACKELVIE WINSTON
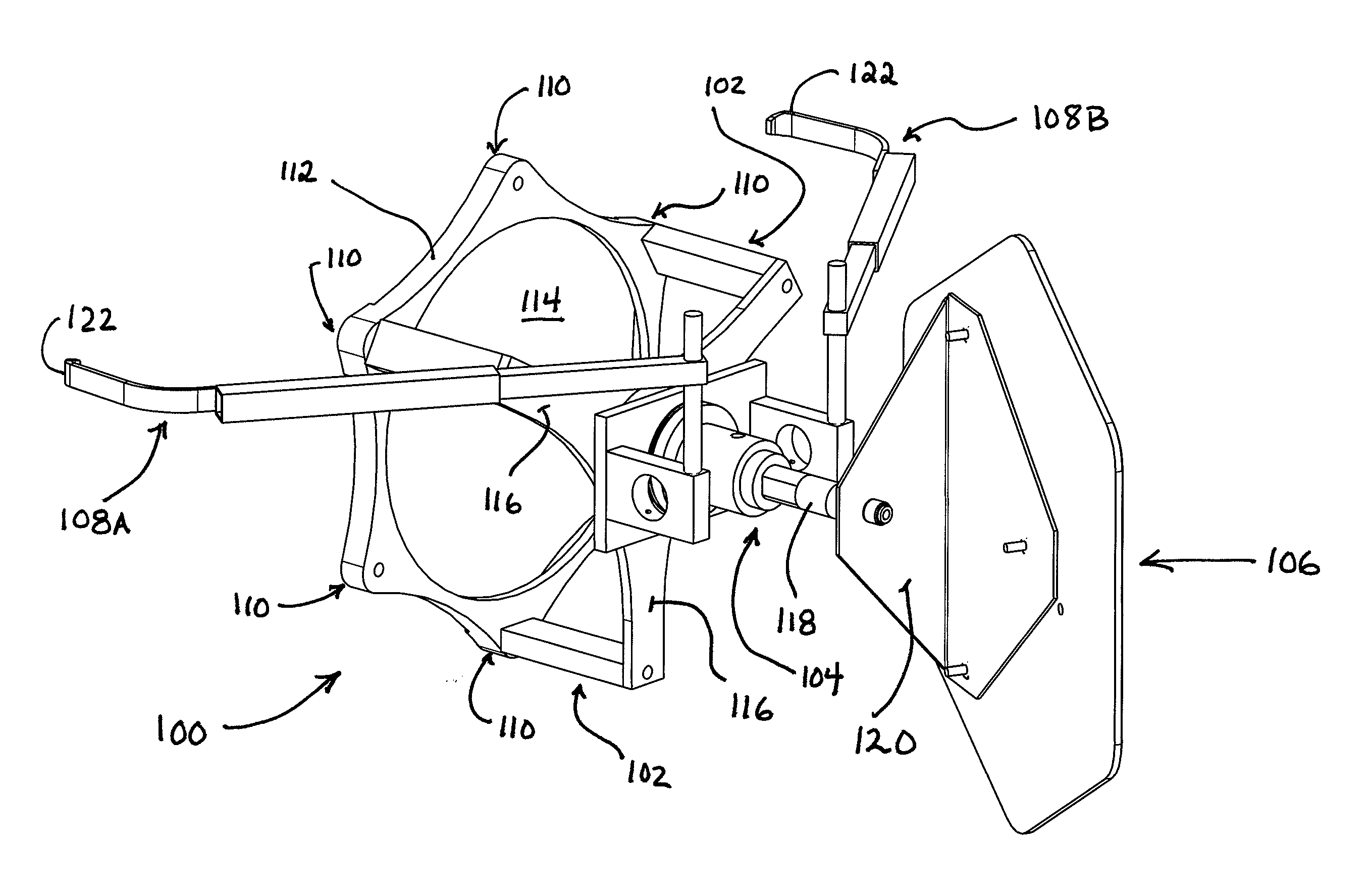
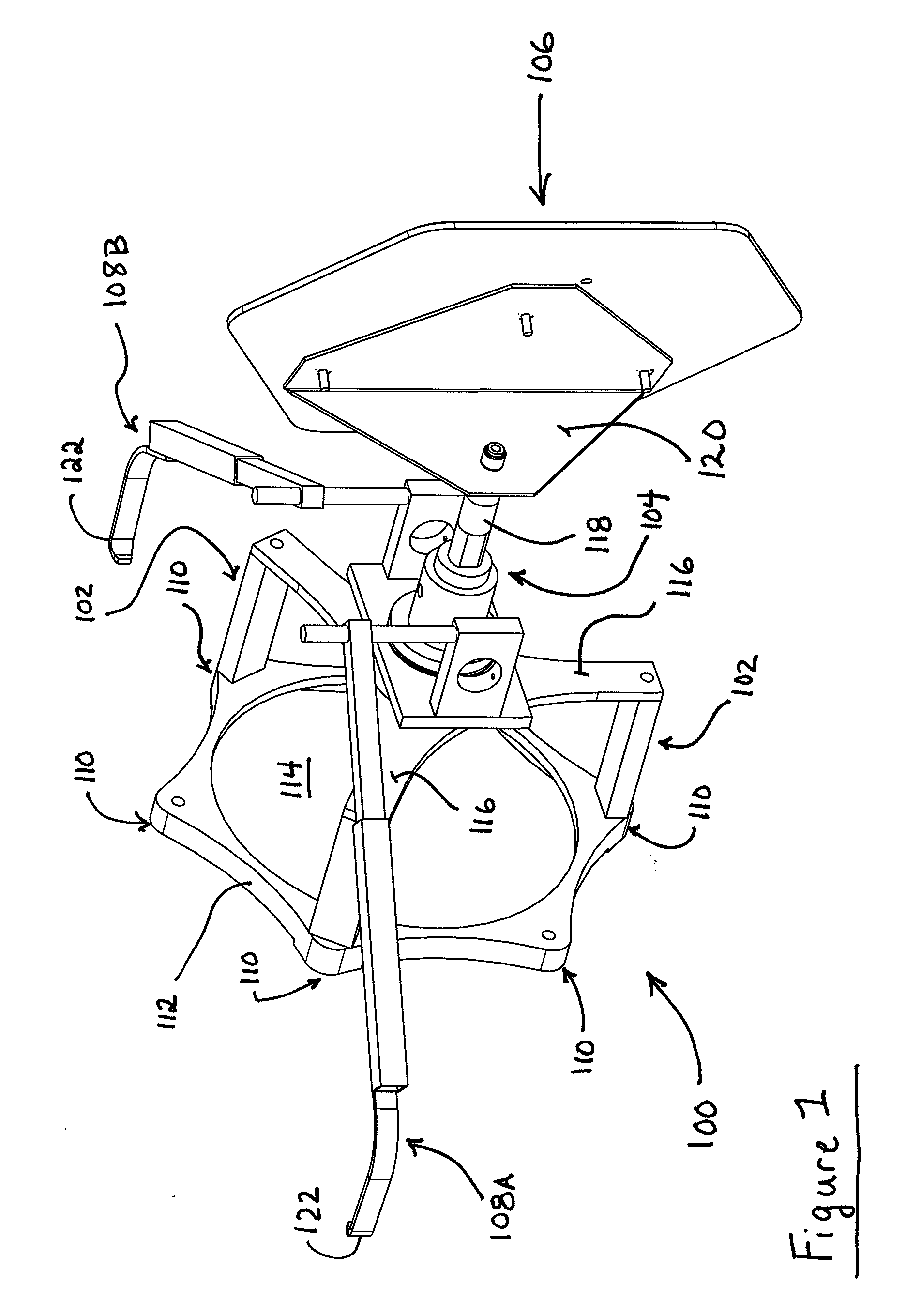
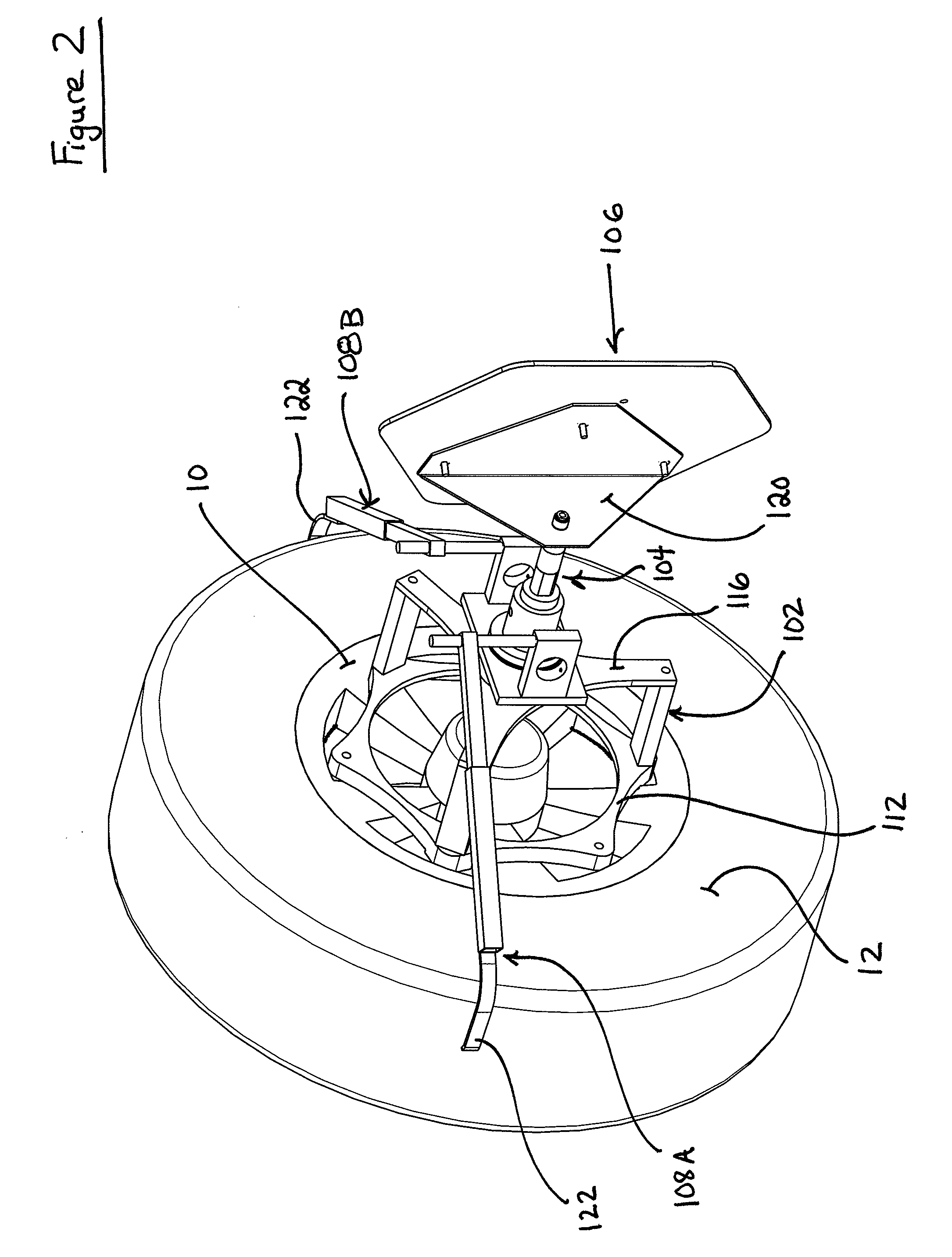
Method and apparatus for positioning a vehicle service device relative to a vehicle thrust line
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com