Method for calibrating a multileaf collimator
A blade, detector technology used in the use of apertures/collimators, radiation therapy, character and pattern recognition, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
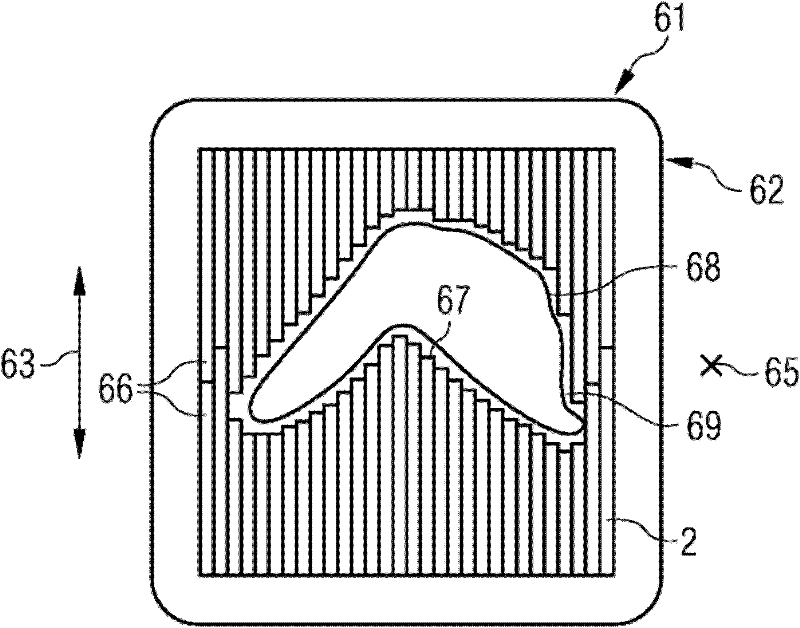
[0035] figure 1 with figure 2 The principle of a multi-leaf collimator is shown, in which the beam is shaped according to the region to be irradiated by means of the leaves. Current multi-leaf collimators have, for example, 80 leaves or lobes each with a thickness of 0.5 cm on both sides.
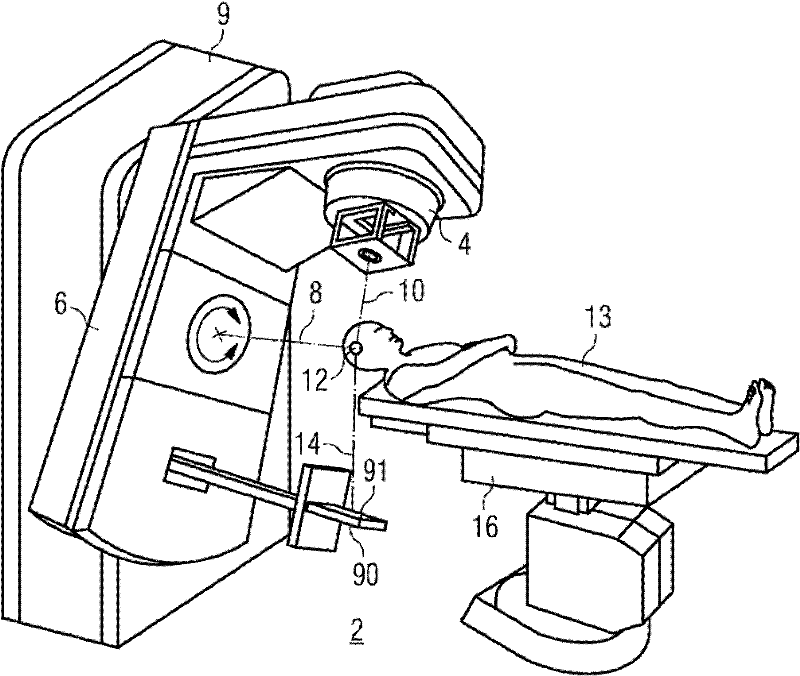
[0036] image 3 An illumination system with an electronic portal imaging device is shown.
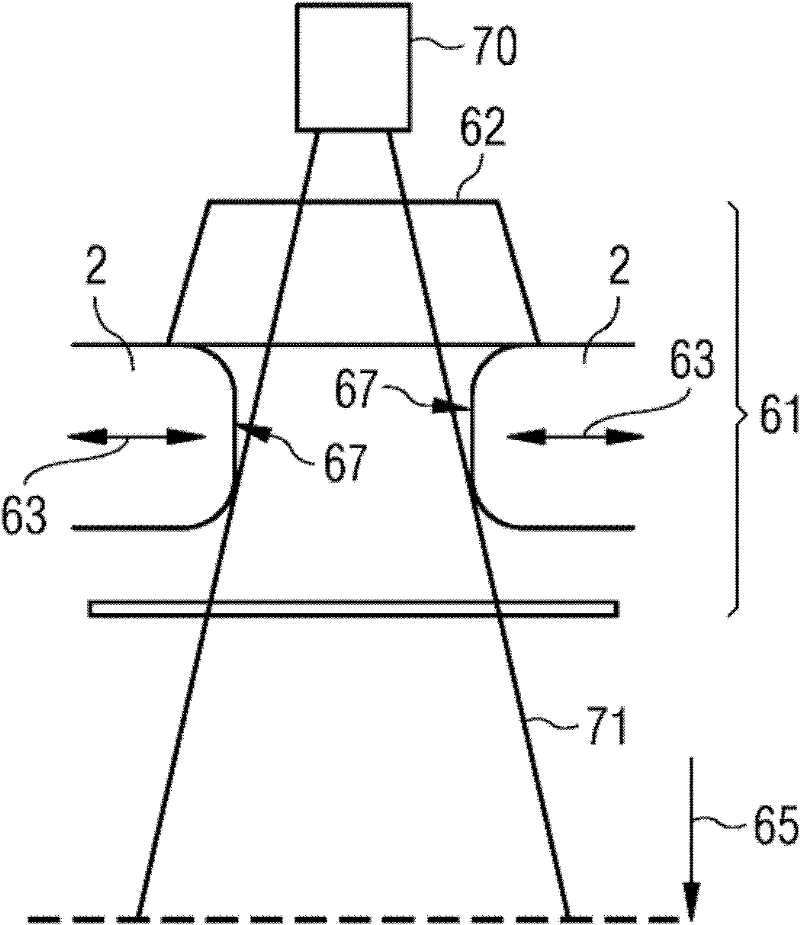
[0037] Figure 4 A first step in the calibration according to the invention is shown. What is involved in this first step is that the multi-leaf collimator and the plate of the EPID do not have to be aligned with each other in direction, ie both the multi-leaf collimator and the plate may be twisted relative to each other or may form an angle. In order to compensate for or take into account the lack of coordination in this direction, the processing takes place as shown in the figure. The first acquisition is made in the direction of the multi-leaf collimator (here marked 90°). In this recordi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com