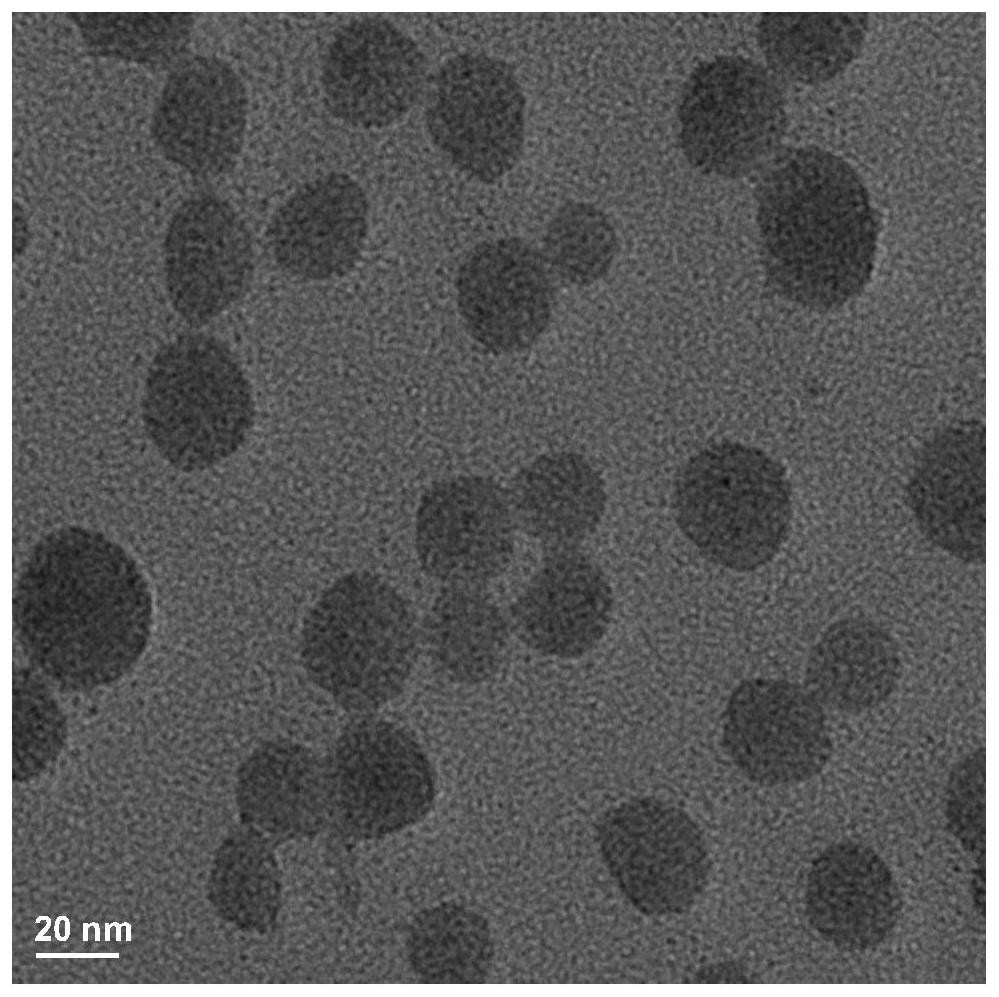
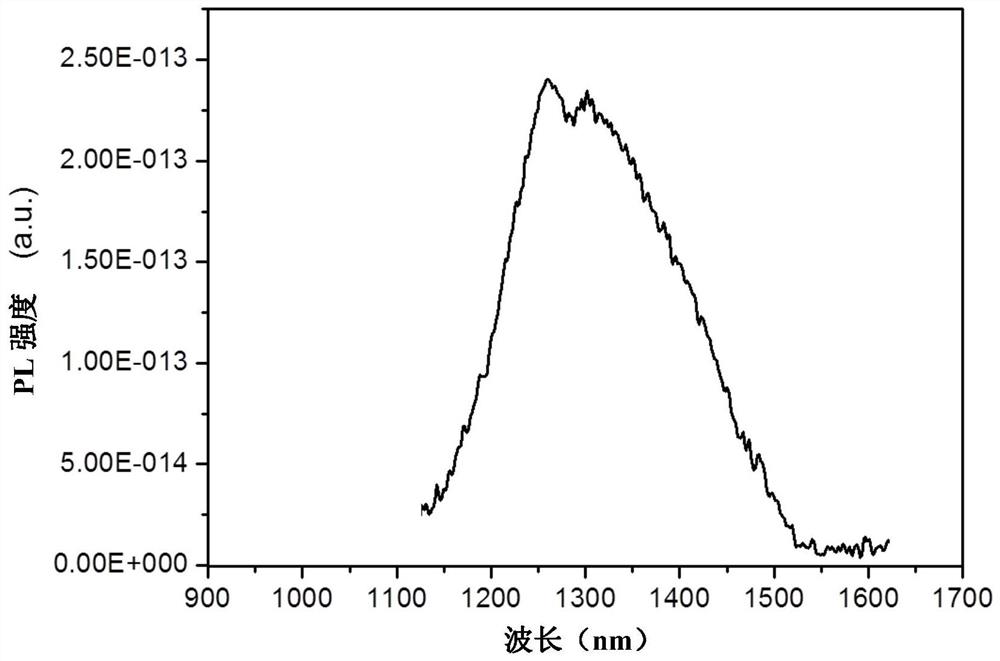
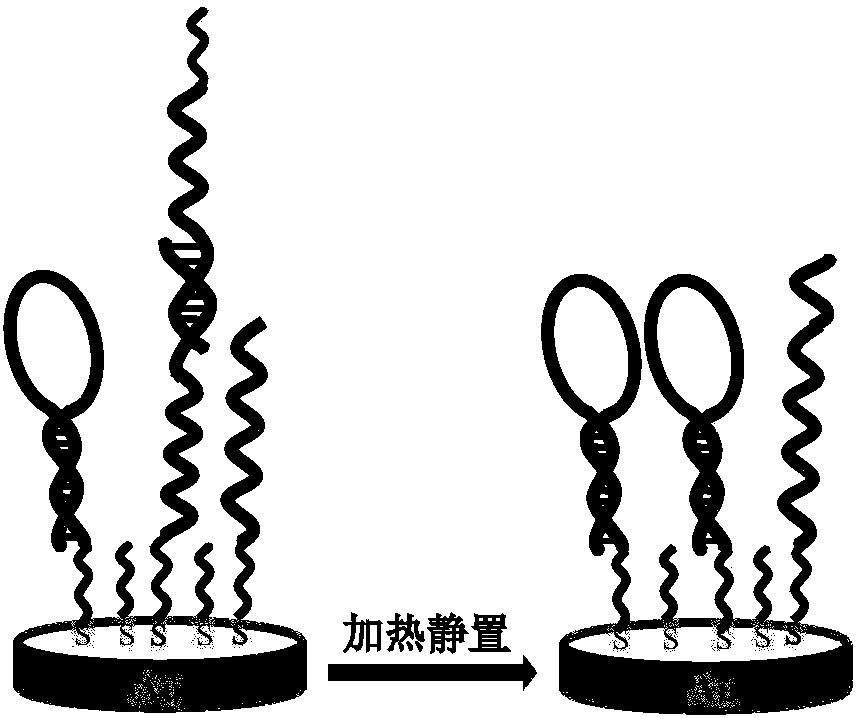
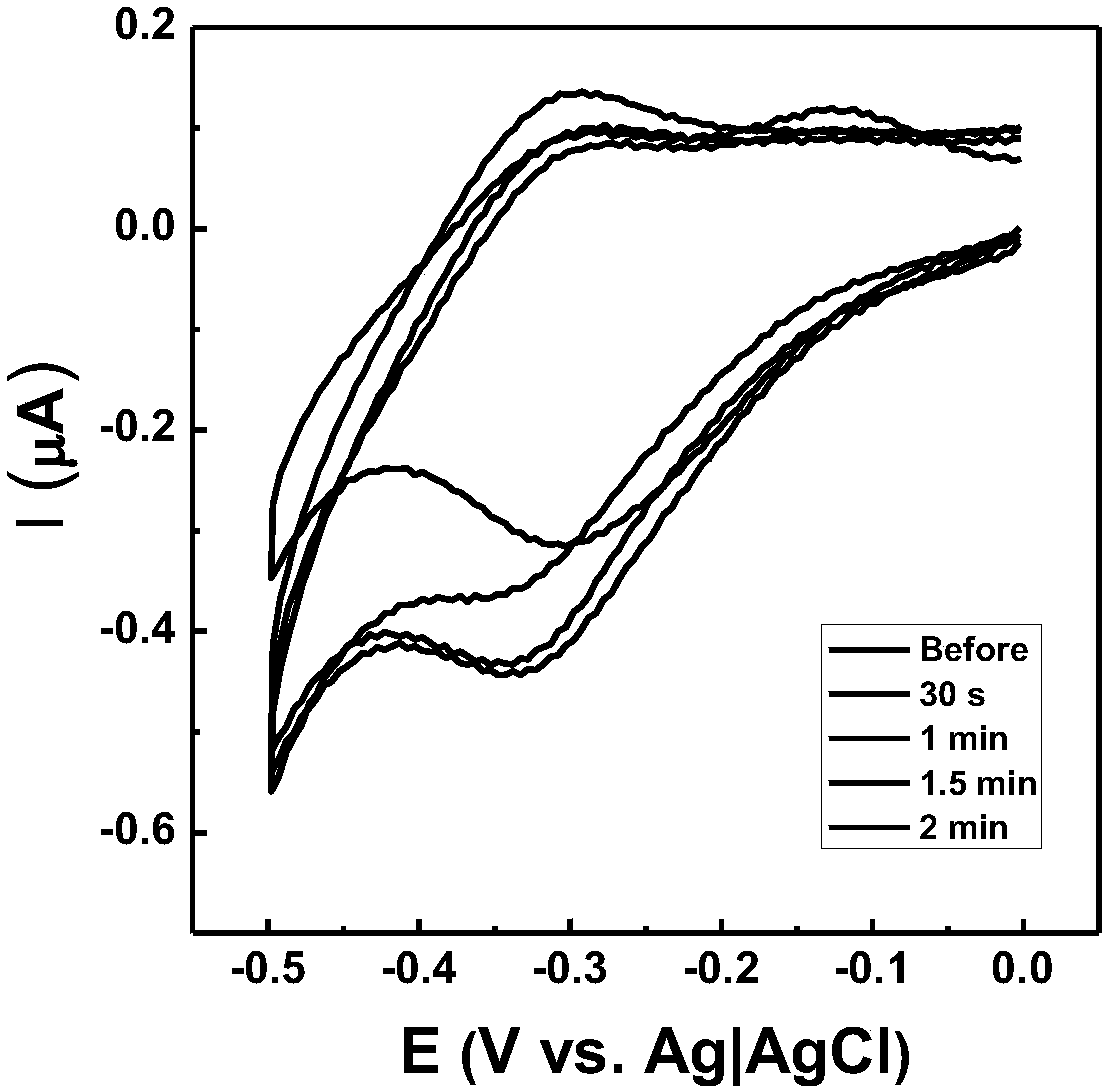
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Dna hairpin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A system of two complementary DNA hairpin loops is a candidate fuel for an autonomous DNA motor. A hairpin loop forms from a single strand of DNA that contains two complementary neck domains separated by a loop domain.
Therapeutic methods for benzodiazepine derivatives
This invention provides an antibody with high affinity for single-stranded DNA, low or no affinity for double-stranded DNA, and capable of specifically binding a DNA hairpin and the hybridoma cell lines which produces these monoclonal antibodies. A chimeric mouse comprising these hybridoma cell lines and a histocompatible mouse is further provided. A method for screening for an agent which will inhibit anti-DNA antibody.DNA binding. One such agent is a benzodiazepine derivative. This invention therefore provides a method of inhibiting the binding of an anti-DNA antibody to its DNA ligand in a sample by contacting the sample with an effective amount of a benzodiazepine derivative.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method for detecting miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) based on graphene/nucleic acid dye platform
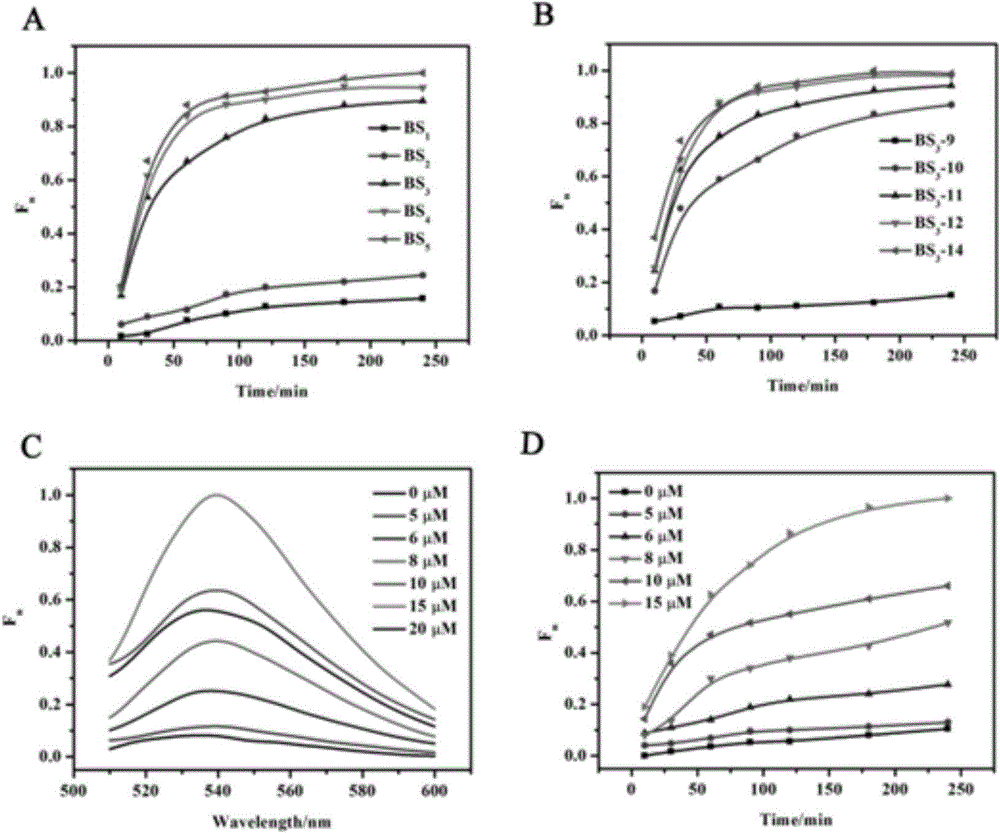
InactiveCN102703594AHigh sensitivityEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSequence designFluorescence
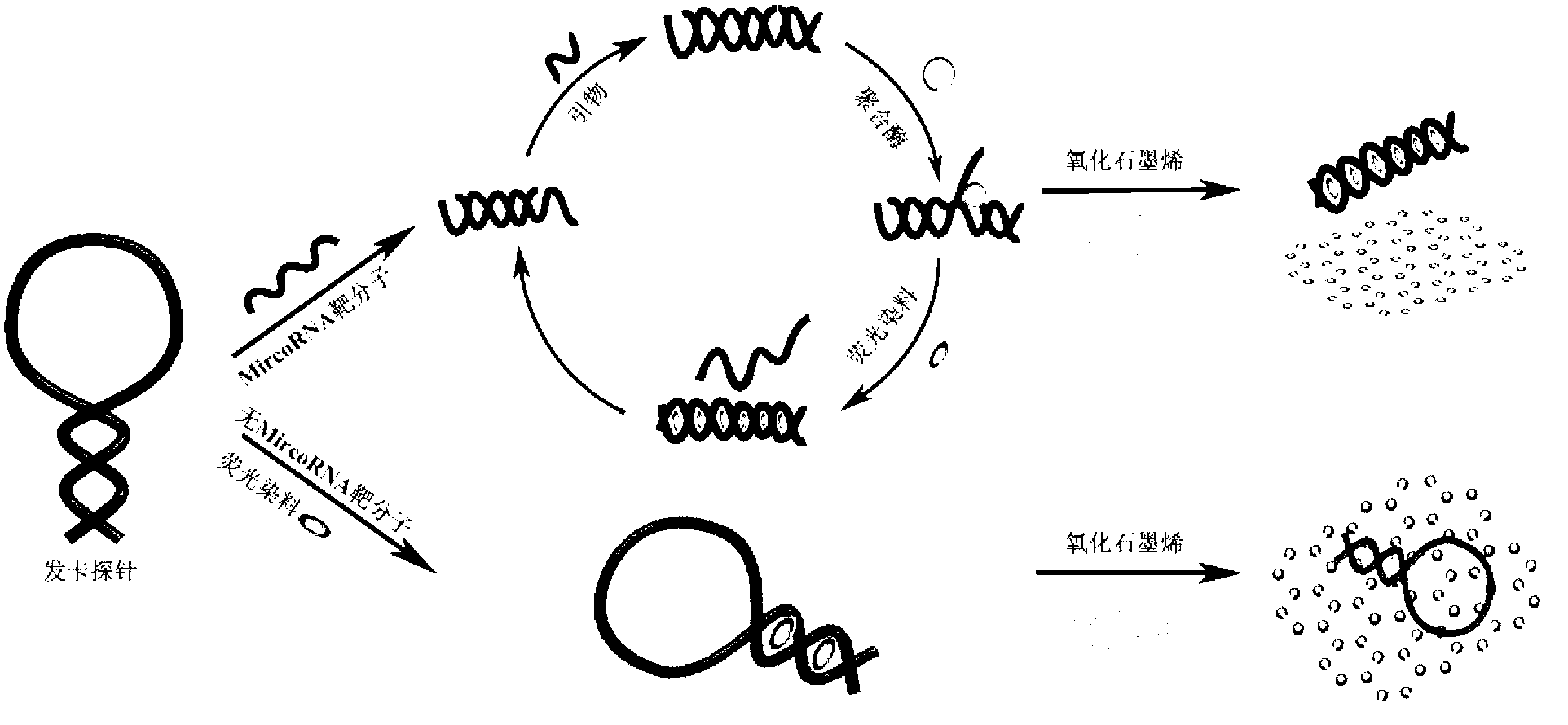
The invention discloses a method for detecting a miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) based on a graphene oxide / nucleic acid dye detection platform and a nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification technology. The method comprises the following steps of: first, designing a specific DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) hairpin probe and an amplification primer according to the sequence of a target miRNA, mixing the DNA hairpin probe, the primer, the target miRNA, DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide), an enzyme with a strand displacement amplification property and necessary reactants to carry out a constant-temperature amplification reaction, and then, adding the graphene oxide / nucleic acid dye detection platform to incubate, and carrying out fluorescence detection. When the target miRNA exists, a detection system has an obvious fluorescent signal enhancement phenomenon, and in a condition that the target miRNA does not exist, a fluorescent signal of the detection system is quite weak. By using the method, the purpose of highly sensitively, specifically, simply and quickly detecting a target molecule by using a non-modifying probe is realized, and the method is quite suitable to popularize in the application of actual detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Oligonucleotide probe, and method for detecting target molecule through using it
ActiveCN102827836ARealize quantitative detectionReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence designNucleic Acid Probes
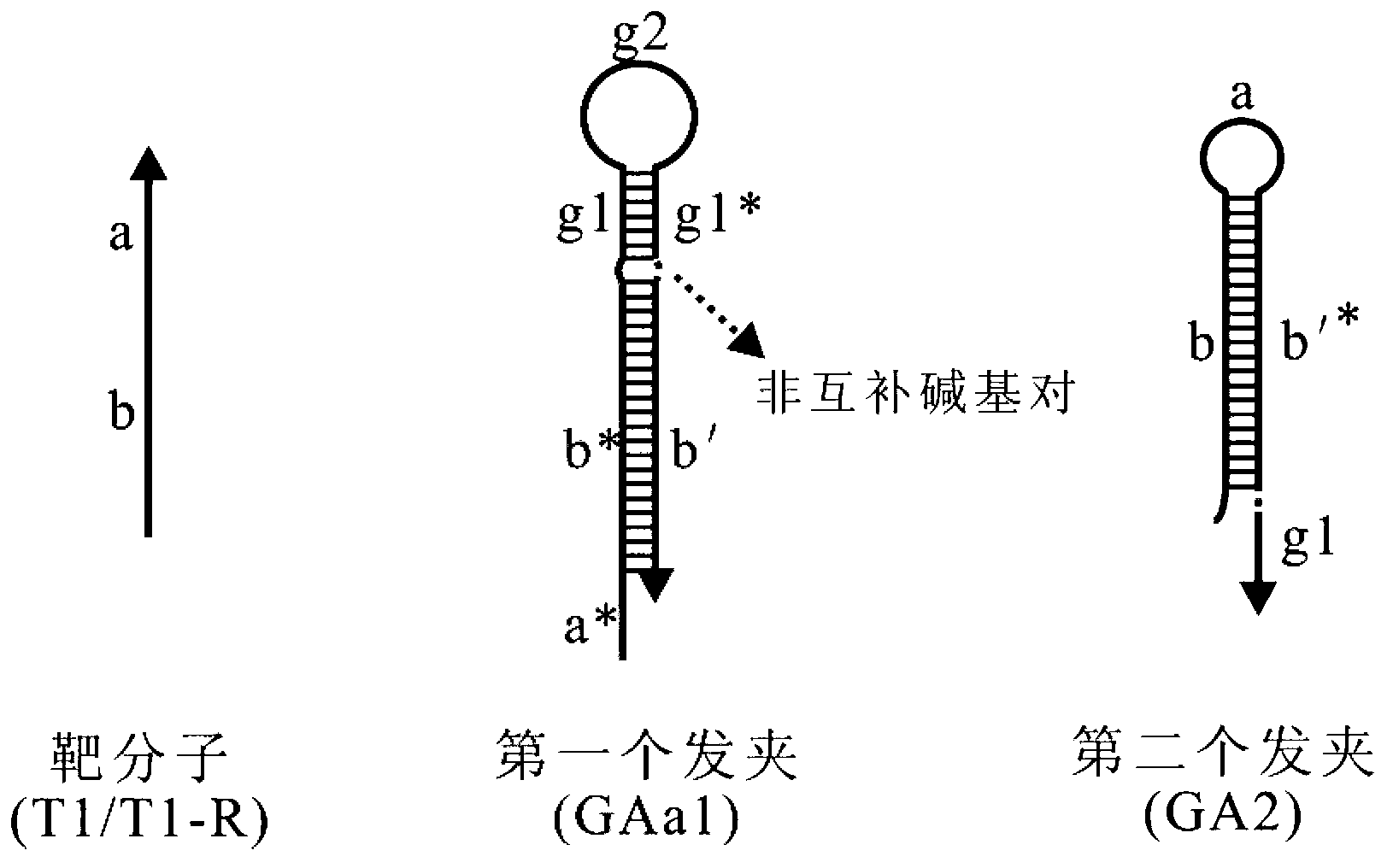
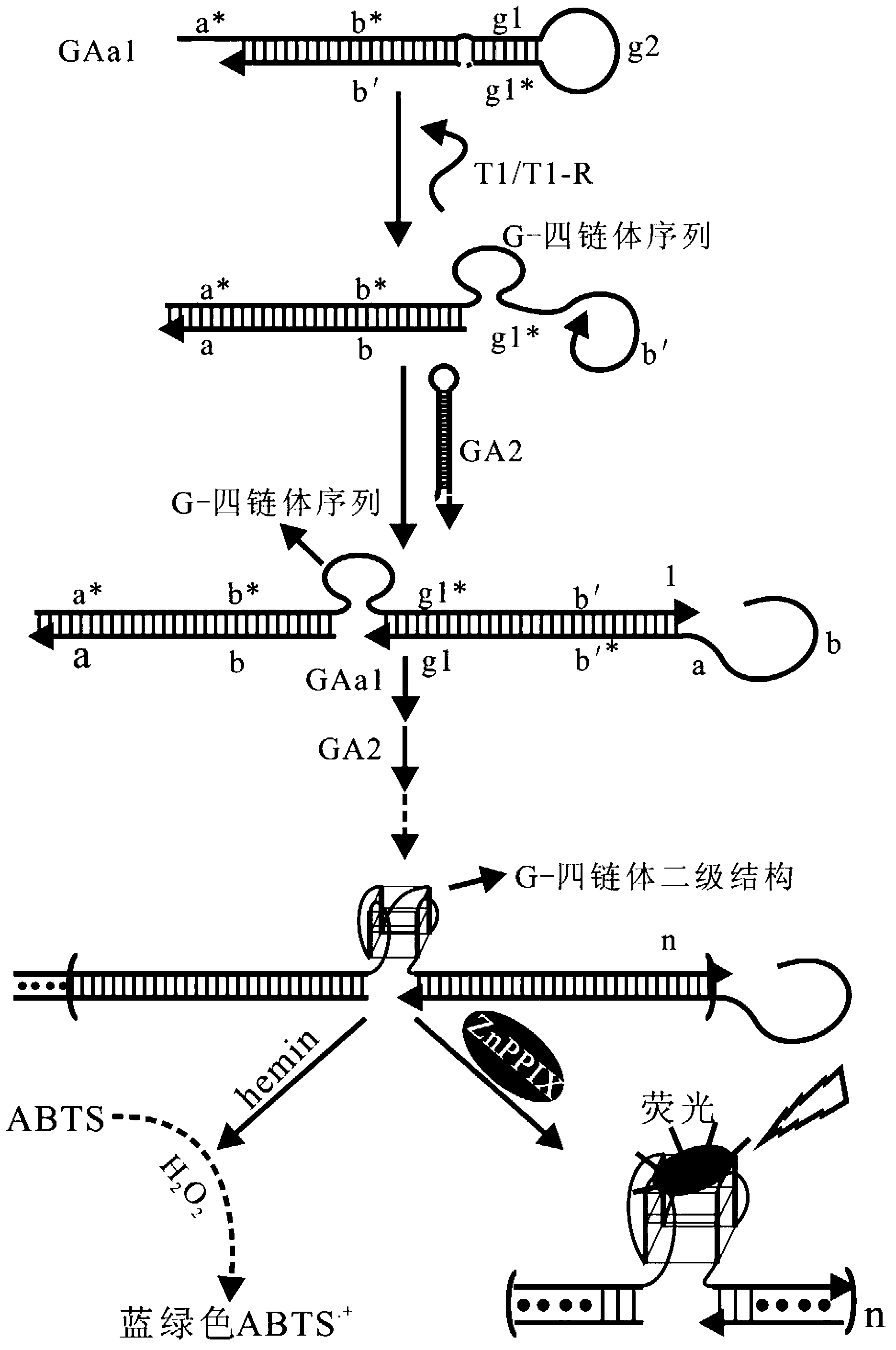
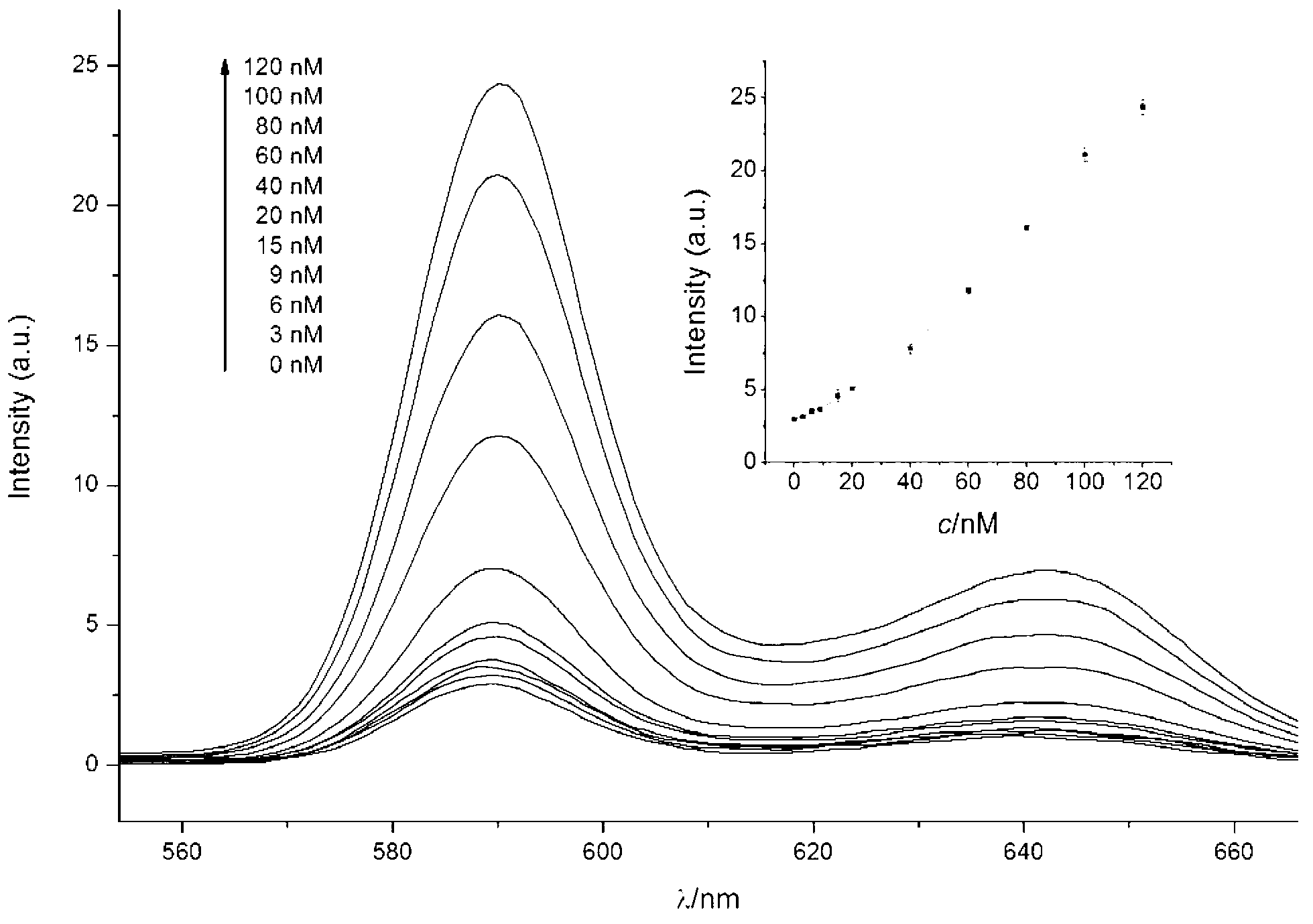
The invention provides a signal amplification and signal reporting integrated oligonucleotide probe. The probe is a pair of DNA hairpin sequences designed on the basis of a target molecule and having cohesive ends, substantially is a product combining a hybridization chain reaction fuel molecule with a G-quadruplex sequence, has the characteristic of target molecule signal cascade amplification of the hybridization chain reaction in an enzyme-free isothermal manner, and enables the amplified target molecule signal to be conveniently and simply detected through the introduction of a signal reporting element G-quadruplex sequence. The invention also provides a method of an enzyme-free isothermal nucleic acid probe mediated by the above probe. The method enables the signal of an object to be detected to be amplified and detected under a normal temperature condition without any enzymes, and has the advantages of sensitivity, accuracy, simplicity, and easy implementation.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
MicroRNA trace detection method based on exponential order non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemical luminescence principle
InactiveCN104450920AThe principle is simpleReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexProtein detection
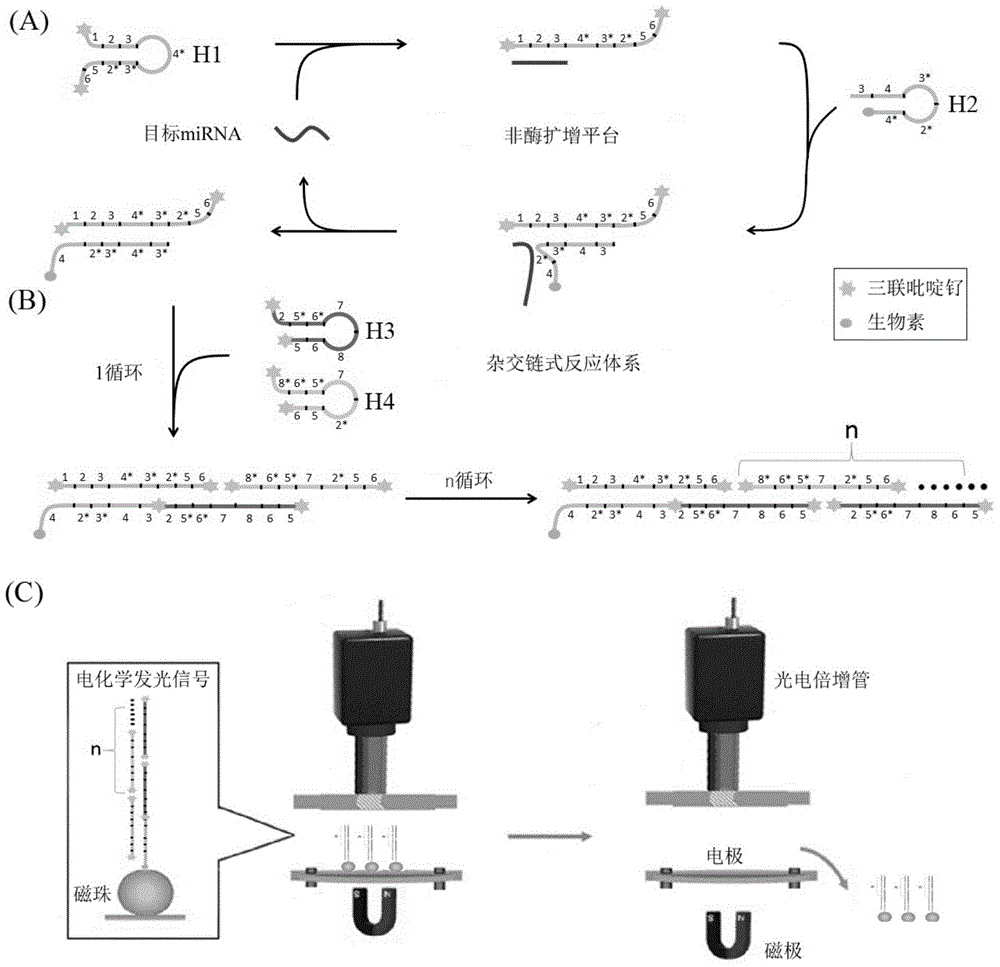
The invention discloses a microRNA trace detection method based on an exponential order non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemical luminescence principle. A non-enzymatic amplification and hybrid chain type reaction system is adopted, and the specific sequences of DNA hairpin probes H1, H2, H3 and H4 are designed based on a detection target microRNA sequence; when an amplification system contains to-be-detected microRNA, the subsequent hybrid chain type reaction process is triggered by virtue of an H1+H2 double-chain composite structure, and is finished by H3 and H4 together; and moreover, an amplification product is captured by virtue of streptavidin magnetic bead capture, and an electrochemical luminescence signal is generated and detected by virtue of an electrochemical detection system. According to the method, an enzyme is not involved in the whole process, the principle is simple, and the detection cost is low; and the method has the advantages of constant temperature amplification, high sensitivity, simple operation, simplicity in popularization and the like. The method is applied to nucleic acid detection and can be combined with a protein aptamer related technology to be used for protein detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Local DNA hairpin strand displacement reaction-based XOR gate and complementing circuit
InactiveCN105930586AHigh precisionBuild fastCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsDna strand displacementDisplacement reactions
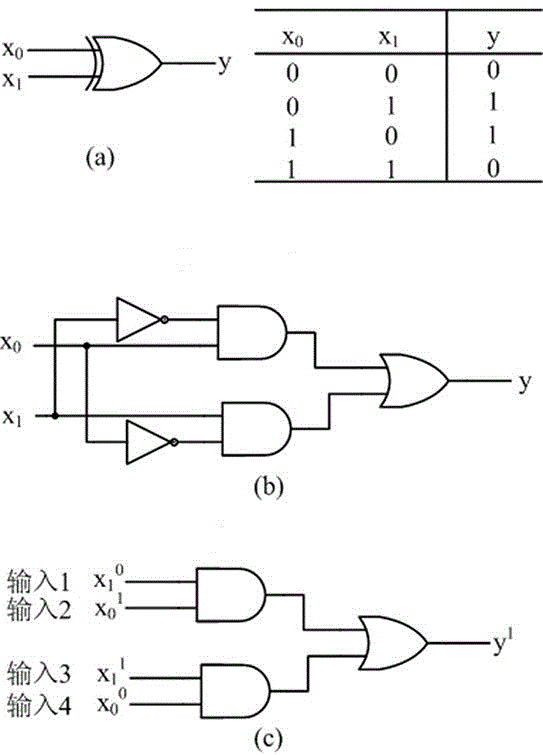
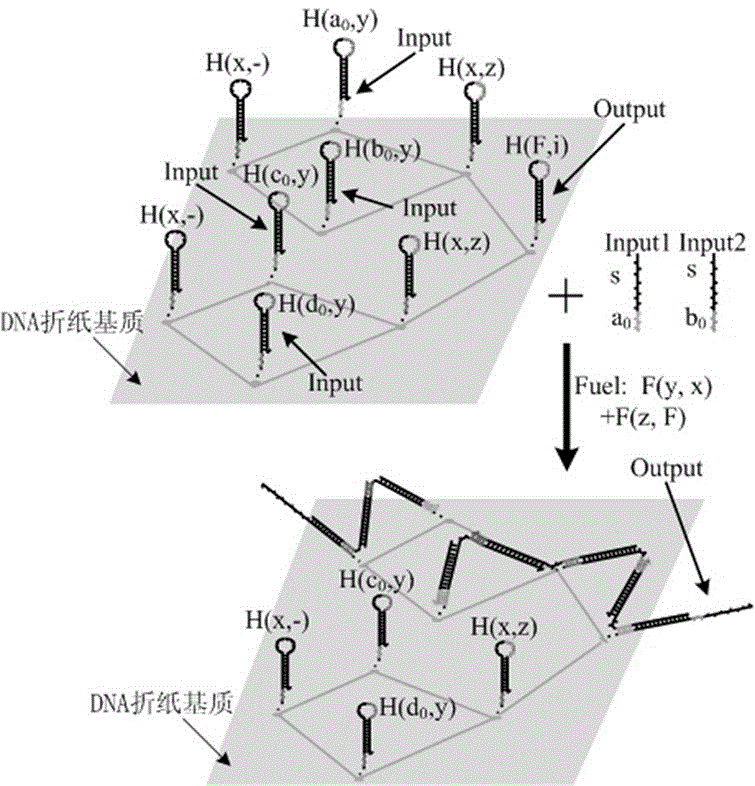
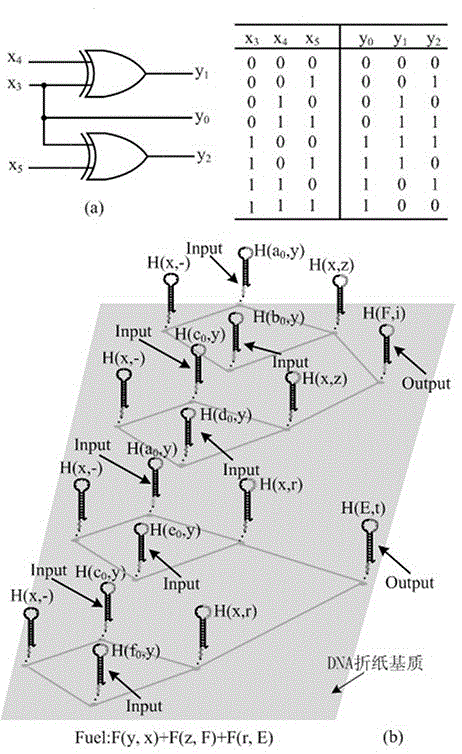
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular circuit-based design and particularly relates to a DNA strand self-assembly principle-based and local DNA hairpin strand displacement reaction-based XOR gate and a complementing circuit constructed by utilizing the same. The XOR gate is constructed by adopting double-rail logic and comprises a single-stranded DNA input, a fuel hairpin and a DNA hairpin fixed to a fold paper substrate. The complementing circuit belongs to a three binary input complementing circuit and is composed of two parallel XOR gates. According to the provided XOR gate, the occurrence probability of wrong strand displacement reactions is relatively low and the DNA strand displacement reaction efficiency is improved. According to the provided complementing circuit, parallel computing can be realized without mutual interference; and a simulation result for Visual DSD of the complementing circuit shows that the complementing circuit is reasonable to construct, has good performance and has the advantages of high construction speed, high precision, high expandability and the like in construction of a large complex molecular system.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Surface-enhanced Raman technology based on signal-off and used for detecting intracellular telomerase activity
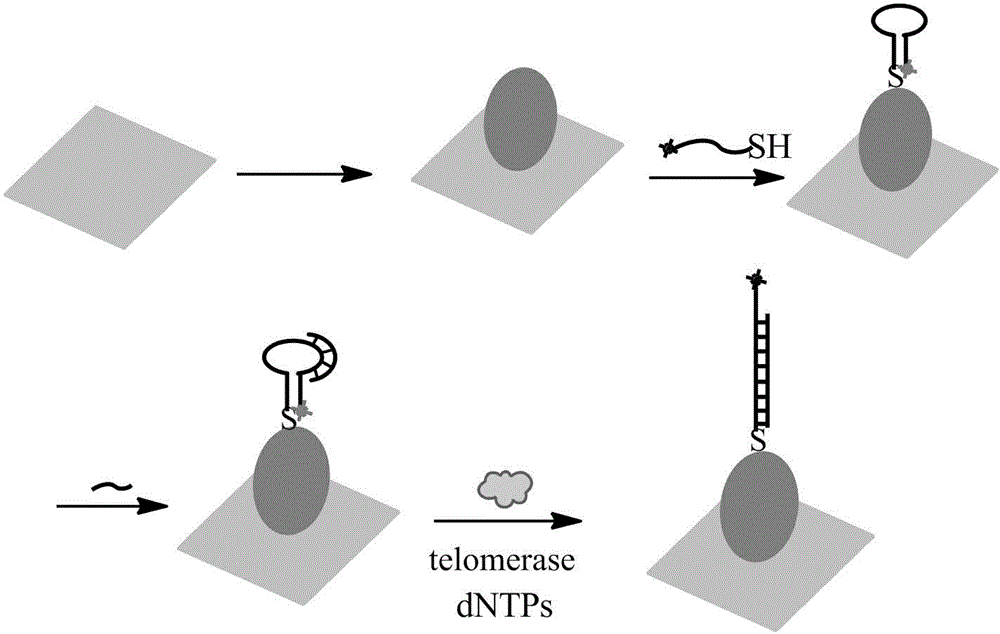
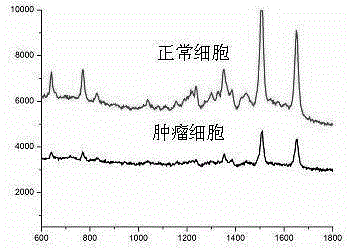
InactiveCN104611416ARealize highly sensitive detectionEnhanced Raman signalMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseSignalling molecules
The invention relates to a surface-enhanced Raman technology based on signal-off and used for detecting intracellular telomerase activity. According to the technology, graphene, carbon nitride, MoS2, SiO2 and the like are taken as carriers, nano-gole or nano-silver with controllable dimension and morphology or a composite magnetic nano-particle with a core-shell structure is supported by the carriers, and then a hairpin probe containing a telomerase primer and a Raman molecule beacon is fixedly disposed on the nano=particle surface, so that the high-sensitivity high-selectivity SERS detection method based on signal-off is established. When a target exists, the primer extends and generates a DNA chain with a repeat sequence under the effect of telomerase, and the DNA chain is hybridized with the probe molecule, then the DNA hairpin structure is opened, a Raman signal molecule with the single-chain labeled end is far away from a Raman substrate, the Raman signal is reduced, and high-sensitivity detection on telomerase is realized. The probe prepared by taking Hela cervical carcinoma cell as a model realizes intracellular telomerase activity detection and dynamic detection on intracellular telomerase activity variation under effect of a telomerase inhibiting medicament. By using multiple cells for imaging, the probe is confirmed to be capable of distinguishing tumor cells and normal cells.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
MicroRNA detection method based on non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemiluminescence principles
InactiveCN103383355AThe principle is simpleLow costChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceNucleic acid detectionMicroRNA
The invention relates to the technical field of nucleic acid detection, in particular to a microRNA detection method based on non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemiluminescence principles. The detection method comprises the steps of: 1) designing DNA hairpin probes, i.e. designing the hairpin H1 and hairpin H2 sequences required by a non-enzymatic amplification system according to a non-enzymatic amplification principle and a detected microRNA sequence; 2) conducting electrochemiluminescence group marking; 3) performing hairpin probe pretreatment; 4) constructing a non-enzymatic amplification detection system; 5) carrying out product cleaning and separation; and 6) conducting signal detection. The method has the characteristics of high sensitivity, accuracy, fastness and simple operation, and the whole amplification process does not involve enzyme, so that the detection cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Suturing Toehold activation method used for controlling DNA strand displacement reaction and toolkit
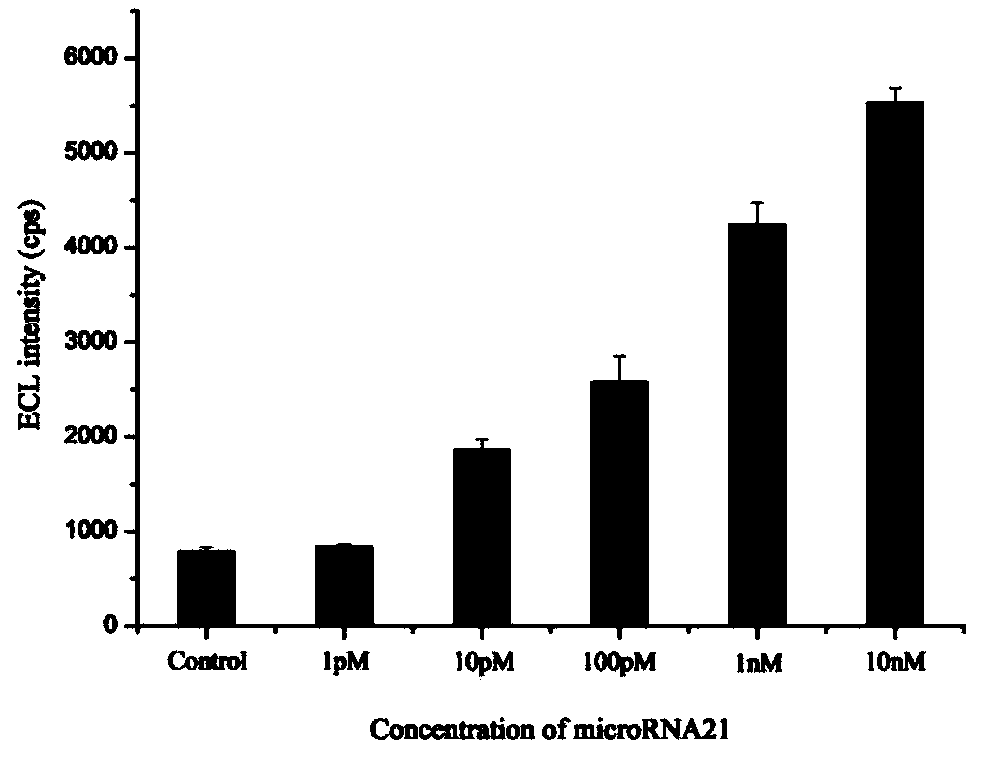
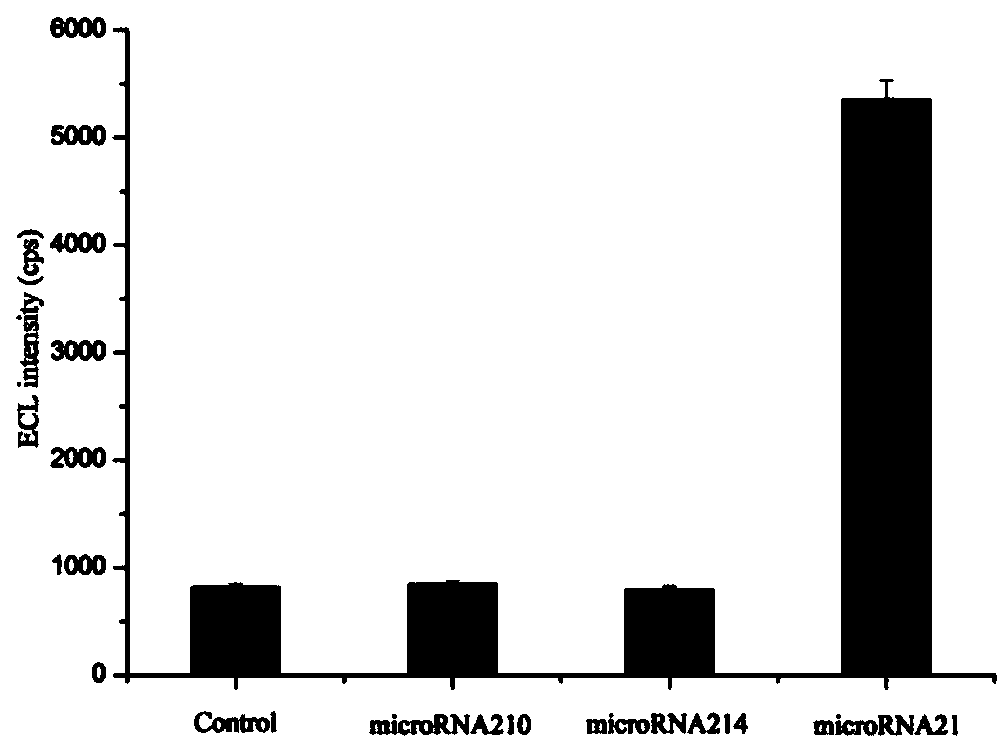
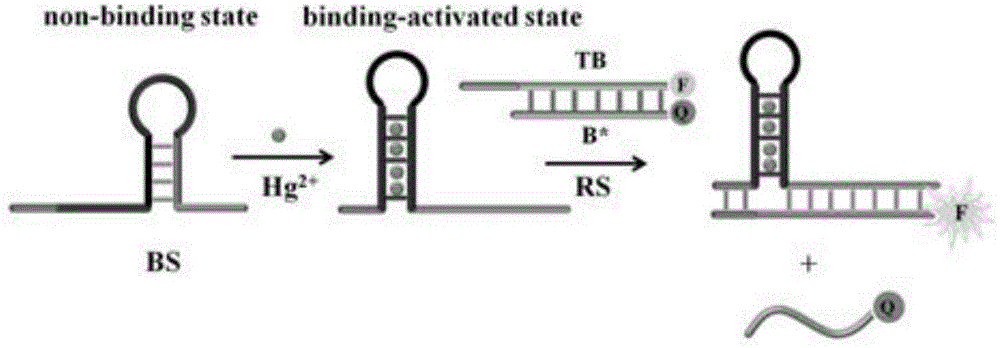
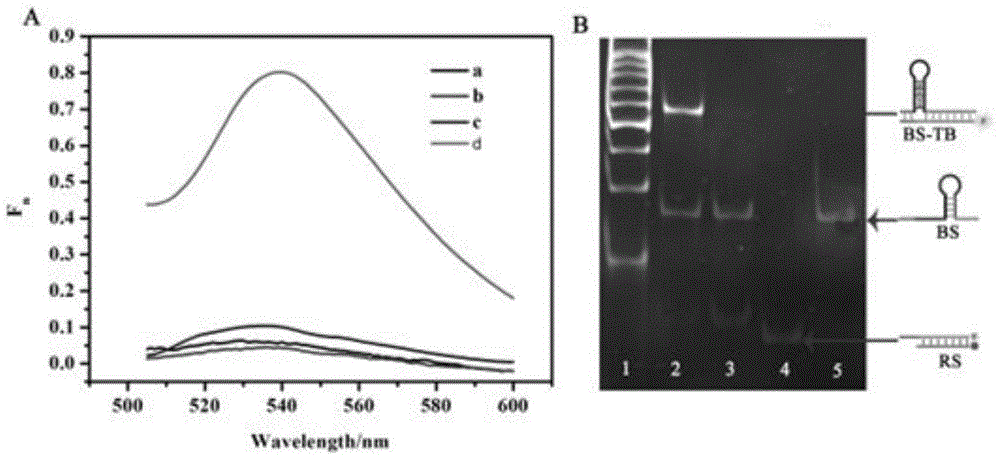
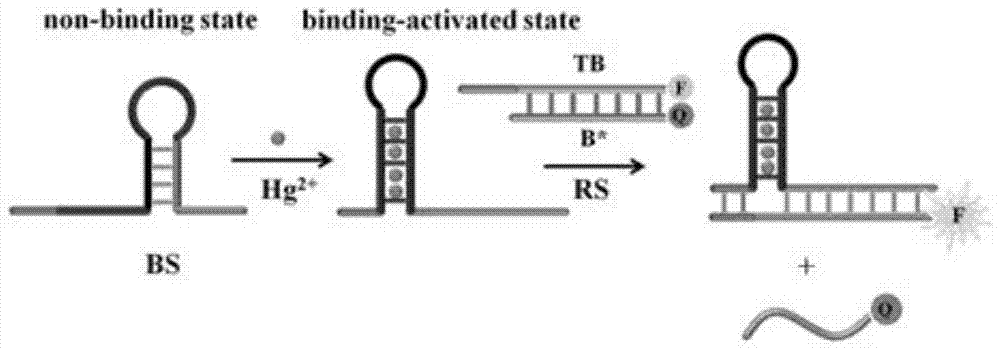
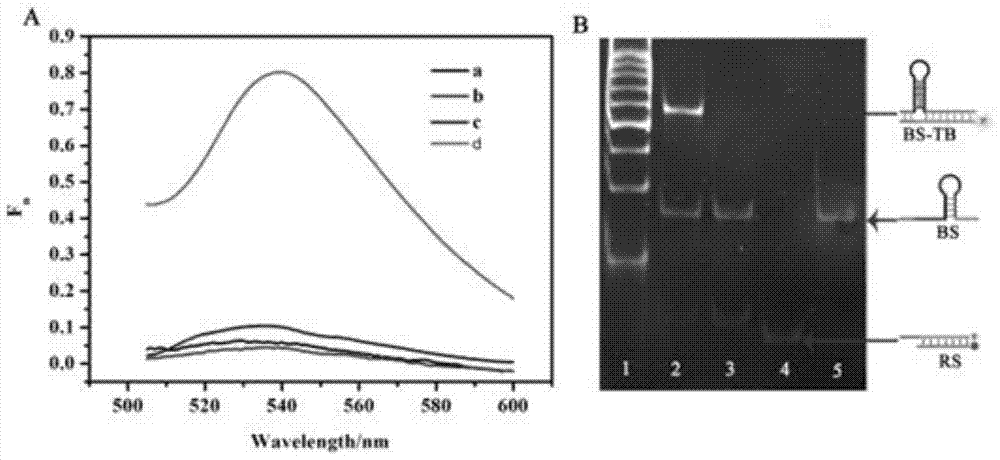
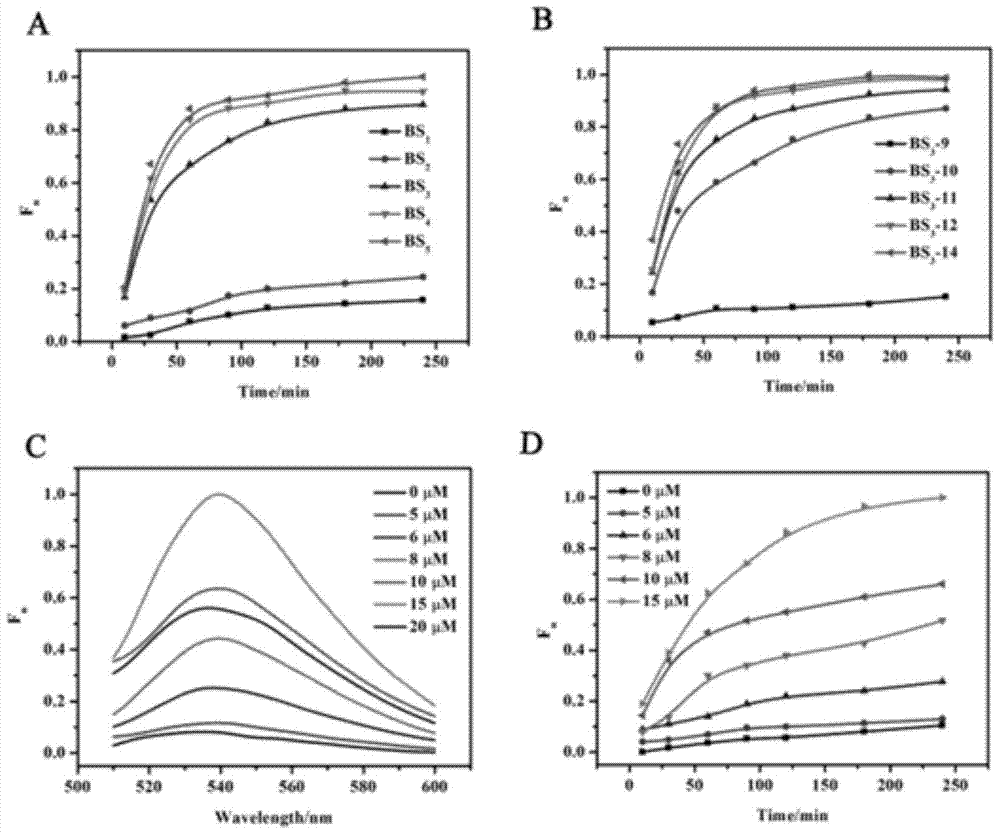
The invention provides a suturing Toehold activation method used for controlling a DNA strand displacement reaction and a toolkit. A novel Toehold activation method is developed based on hairpin reconstruction caused by mutual action of a DNA hairpin structure and different environmental irritants (Hg2+ or ATP). The invention develops a novel Toehold activation method. The extra level of the DNA strand displacement reaction can be accurately controlled by changing the concentration of the environmental irritants.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Nucleic acid detection method based on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) hairpin and RCA (Rolling Circle Amplification)
InactiveCN103014168AHigh sensitivitySimple processMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADna hairpin
The invention provides a nucleic acid detection method based on a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) hairpin and RCA (Rolling Circle Amplification). The detection method comprises the steps of: modifying the DNA hairpin to a solid carrier, wherein the circular part of the DNA hairpin is complementary with a target DNA and the stem part of the DNA hairpin is complementary with an an annular DNA; adding the annular DNA, an enzyme, an amplification raw material and the like; complementing and pairing a target nucleic acid molecule and the loop of the DNA hairpin when the target nucleic acid molecule is added into a detection system; opening a hairpin-loop structure; hybridizing a base of the hairpin and the circular DNA; performing RCA; opening different hairpin-loop structures when the target nucleic acid molecular weights are different; and quantifying the target nucleic acid molecule by using an optical or electric method. According to the nucleic acid detection method, as the DNA hairpin is used as a detection probe of RCA, the step of detecting the molecule by RCA is simplified, the detection cost is reduced, the advantage of high sensitivity of RCA for nucleic acid detection is simultaneously kept, and the nucleic acid detection method is suitable for popularization and use.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Highly sensitive and decomposable quantum dot nanosphere probe and preparation method thereof
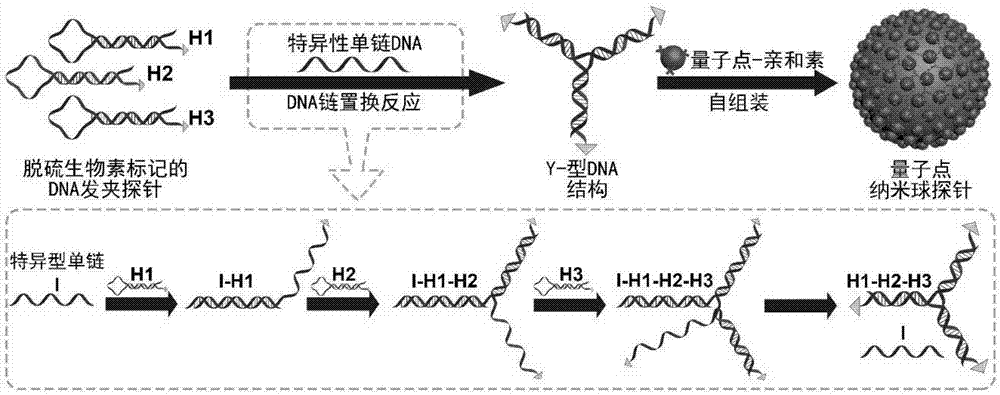
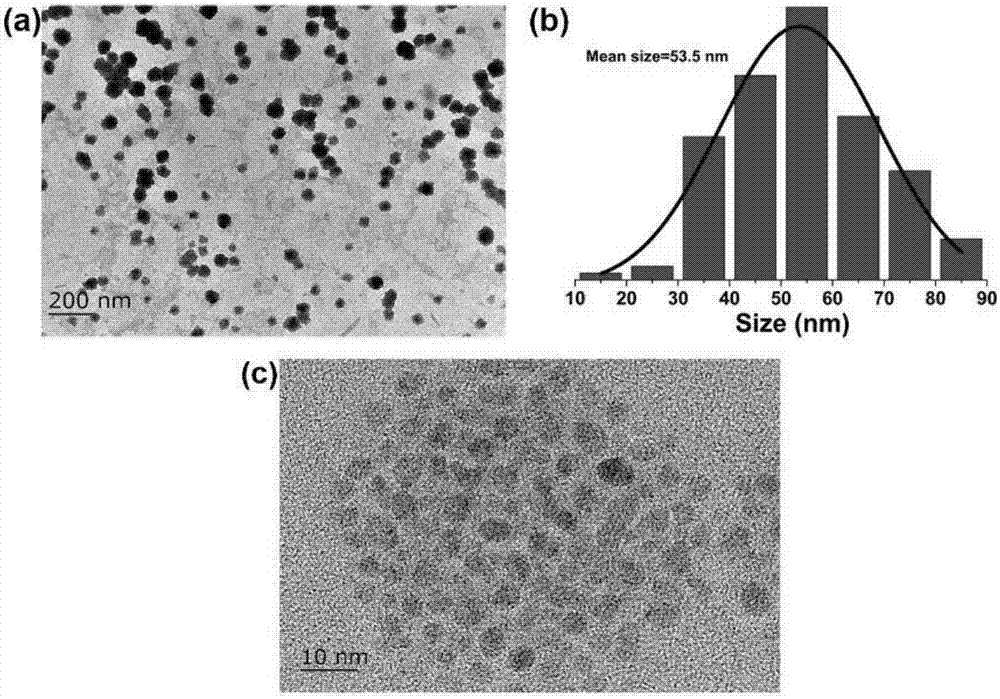
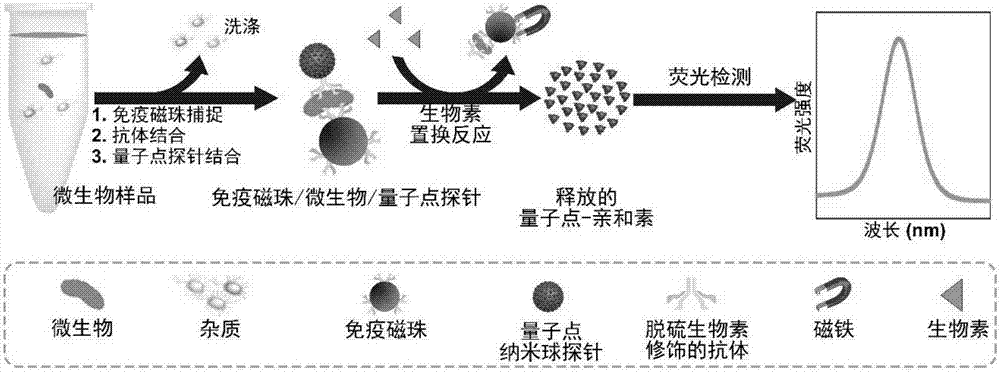
ActiveCN107462705AEnhanced detection signalGood dispersionBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexFluorescence
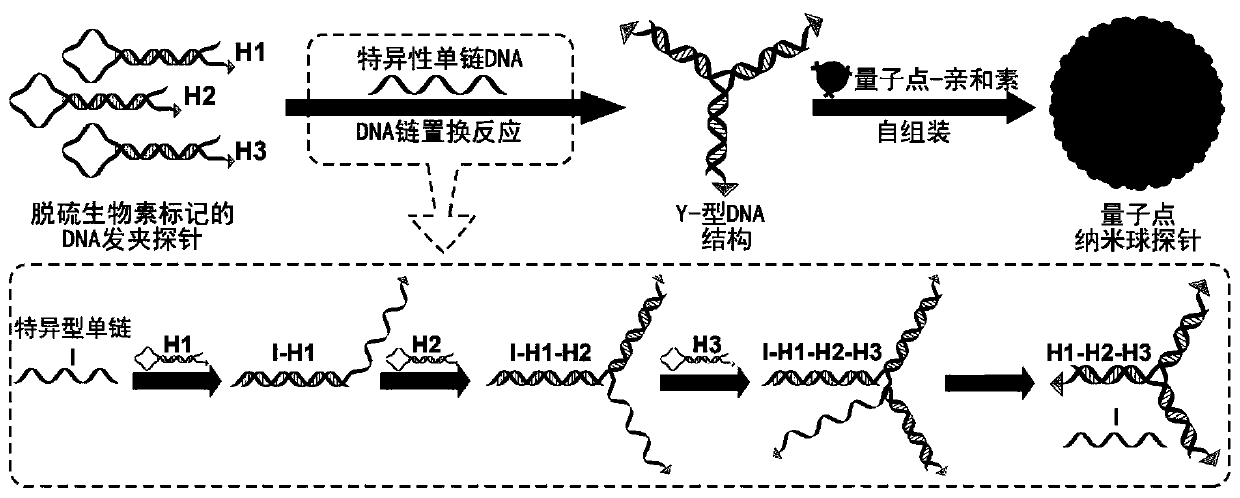
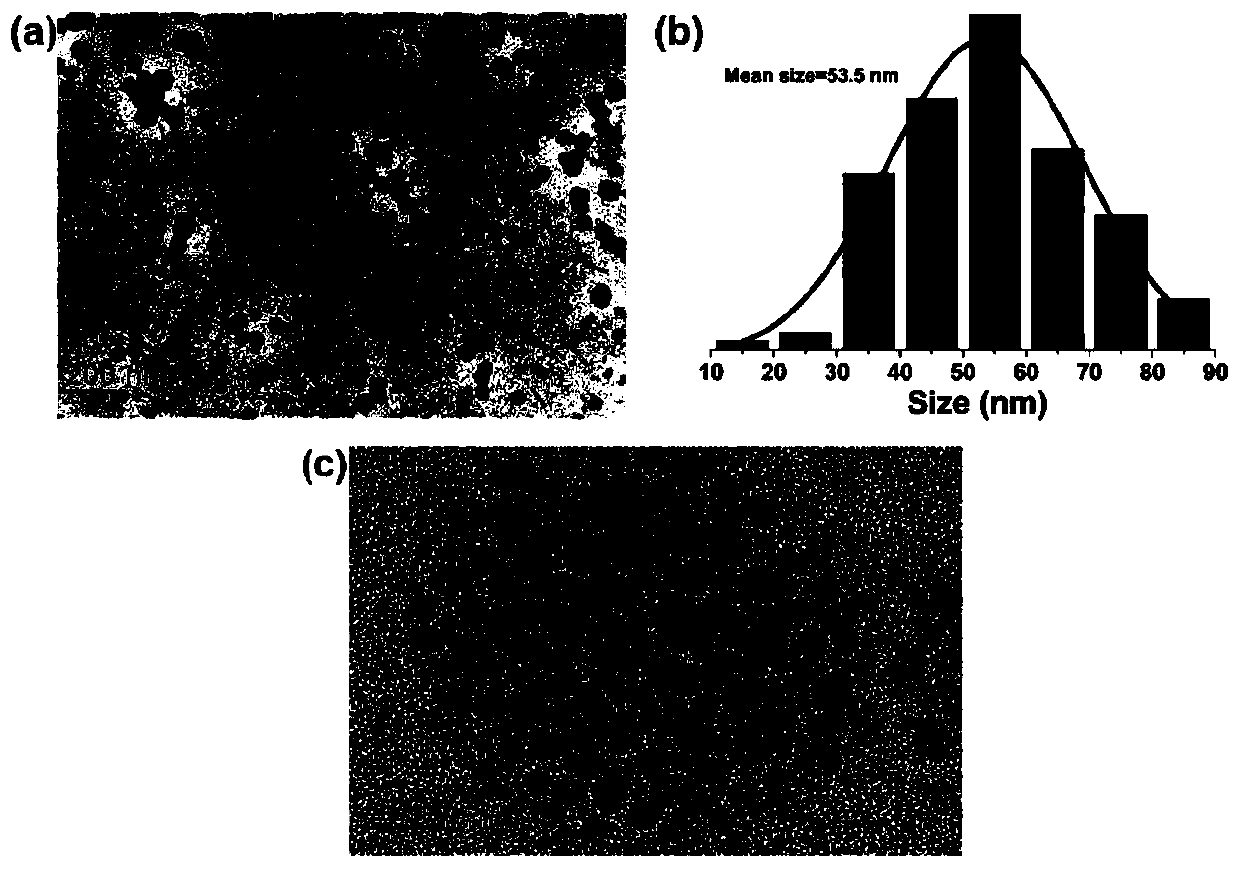
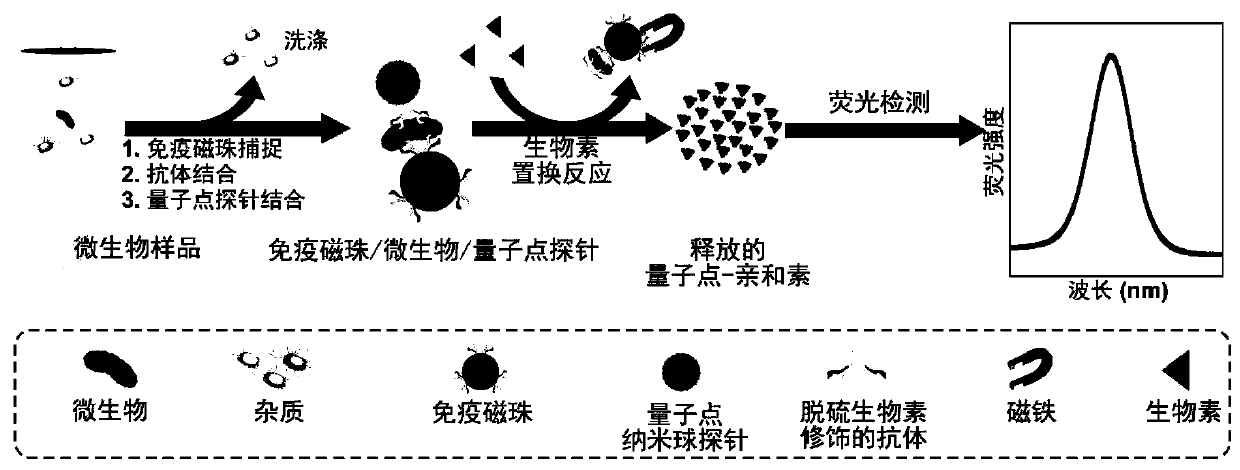
The invention discloses a highly sensitive and decomposable quantum dot nanosphere probe and a preparation method thereof. Through a fulcrum-mediated strand displacement reaction, a DNA hairpin probe modified by three desulfated biotins is self-assembled into a Y-type DNA nanostructure; and the Y-type DNA structure and quantum dots coupled to streptavidin are self-assembled to form the quantum dot nanosphere probe. The prepared quantum dot nanosphere probe and an immunomagnetic separation technology are combined to be applied to quick detection of a target analyte. Because of a binding force between biotin and streptavidin stronger thana binding force of desulfurized biotin, the quantum dot nanosphere probe is decomposed, and thus quantum dots are released; the target analyte concentration is determined by detecting the fluorescence value of a quantum dot solution, and a shielding effect of immunomagnetic beads on the quantum dots is overcome. The method has high sensitivity and the detection limit of microorganisms is 1.37 cfu / mL. This method is good in specificity, and common other microorganisms do not affect the detection.
Owner:天泓(济南)智能装备产业研究有限公司
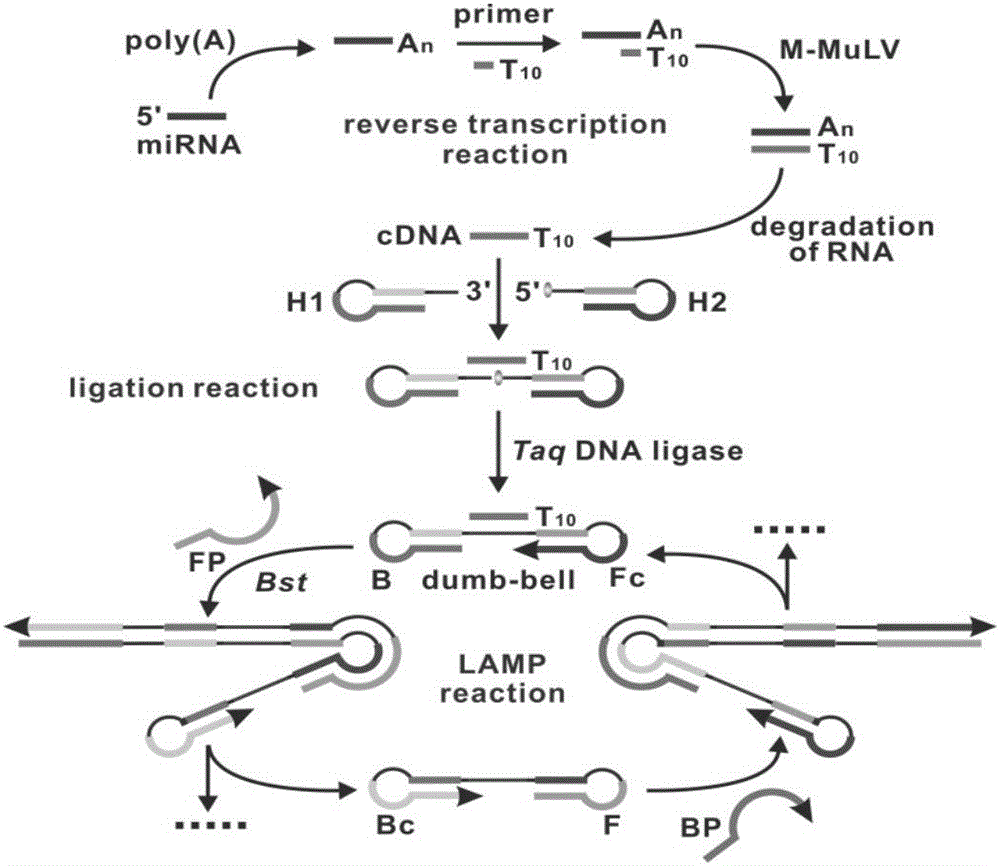
Gene mutation detection method using connection-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology
InactiveCN106148549AHigh selectivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDumbbellFluorescence
The invention provides a gene mutation detection method using a connection-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) designing two DNA hairpin probes H1 and H2 by taking target DNA as a template; (2) in the presence of target, performing annealing hybridization of the target DNA with the H1 and H2; and in the case of complete complementation of the 3' end of H1, connecting the H1 and H2 by ligase to form a double-dumbbell DNA structure; (3) performing a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by taking the double-dumbbell DNA as a template to obtain a loop-mediated isothermal amplification product; (4) adding DNA double-chain specific dye SYBR GreenI into the loop-mediated isothermal amplification product to enhance the fluorescence signal, and implementing quantitative detection of gene mutation through fluorescence signal detection. The gene mutation detection method provided by the invention has remarkably low lower detection limit and relatively high selectivity and specificity.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
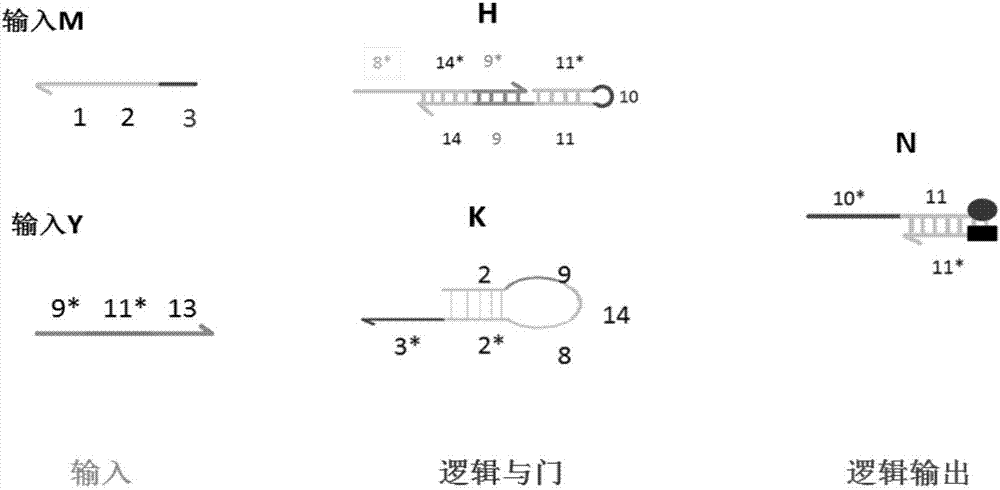
AND gate molecular circuit, NOT gate molecular circuit, XOR molecular circuit and half-subtracter molecular circuit based on DNA hairpin structure
The present invention relates to an AND gate molecular circuit, a NOT gate molecular circuit, an XOR molecular circuit and a half-subtracter molecular circuit based on a DNA hairpin structure, belonging to the biocomputer technology field. The principles of the DNA single hairpin structure, the double hairpin structure and the two-way strand displacement reaction are employed to design a strand displacement reaction structure taking a conventional small fulcrum as an identification area to realize the construction of AND gate, NOT gate and XOR gate basic logic operation structures and perform globality simulation argumentation. A basic logic circuit is employed to perform combination design of the half-subtracter molecular circuit and perform argumentation simulation of the circuit feasibility.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Preparation method of paper-based ratio photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting microRNA
InactiveCN111024788AReduce internal and external interferenceReduce false positive/negative signalsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesSilver iodideA-DNA
The invention discloses a preparation method of a paper-based ratio photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting microRNA. Gold nanoparticles grow on the surfaces of paper-based dual electrodes composed of a working electrode and an internal reference electrode, then cuprous oxide is electrodeposited, graphene quantum dots and silver iodide nanoparticles are sensitized, and a photocurrent signal is enhanced; when the target microRNA exists, DNA probes output by microRNA-induced double-stranded specific nuclease reactions with different concentrations and constant concentrations are respectively incubated on the surfaces of the working electrode and the internal reference electrode; DNA bridge chains and DNA hairpins H1 and H2 on the surface of the electrode are combined to form a DNA bridge nano structure through induction; and the silver iodide nanoparticles marked at the end parts of the H1 and the H2 are far away from the surface of the electrode, so that the photocurrent signal isreduced, and the sensitive detection of the microRNA is realized based on the ratio of the working current signal to the internal reference current signal.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
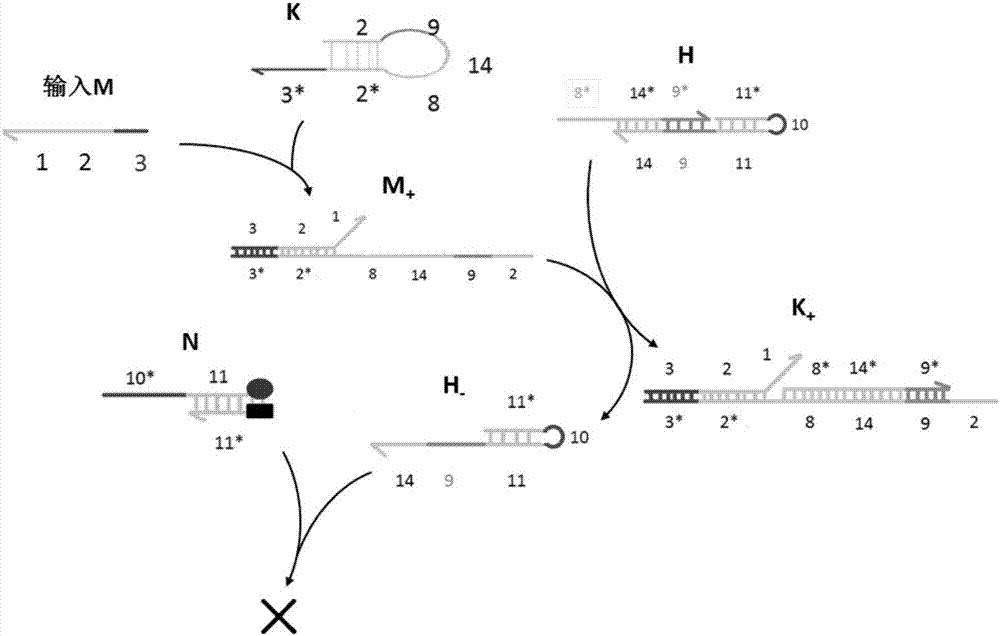
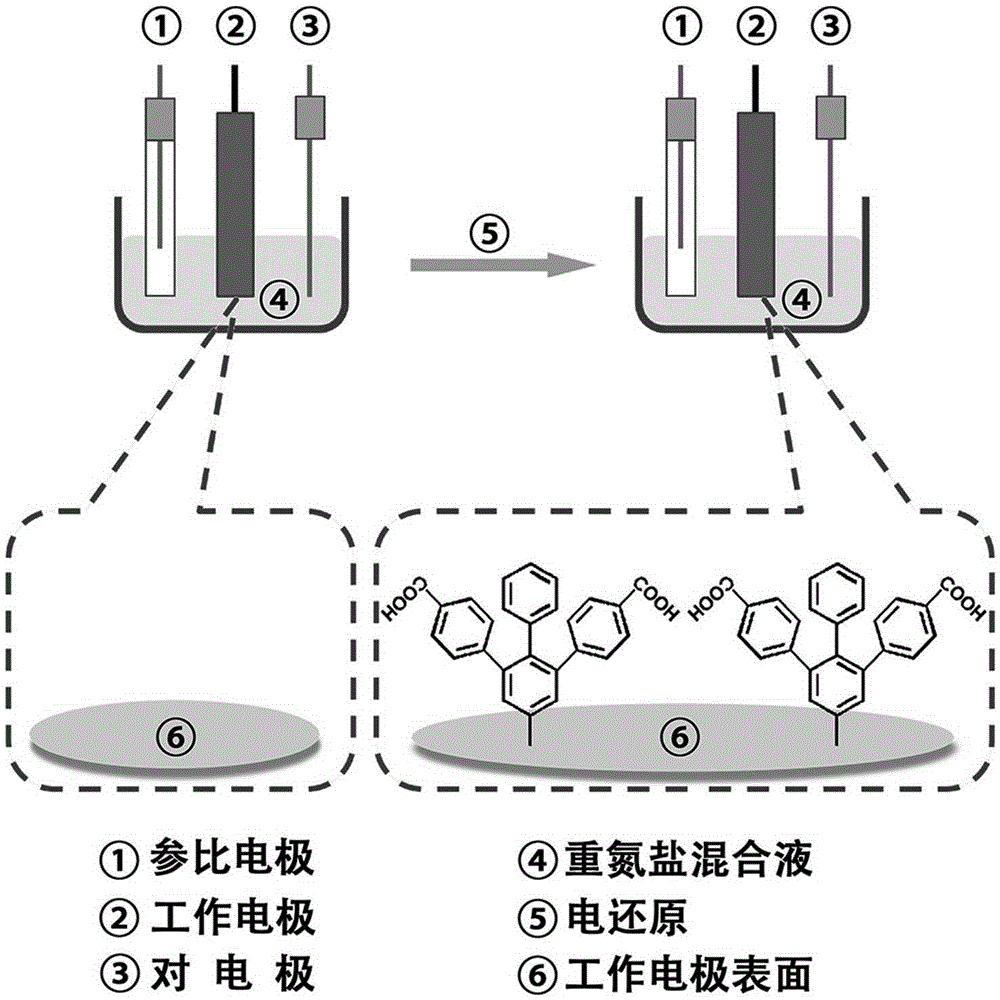
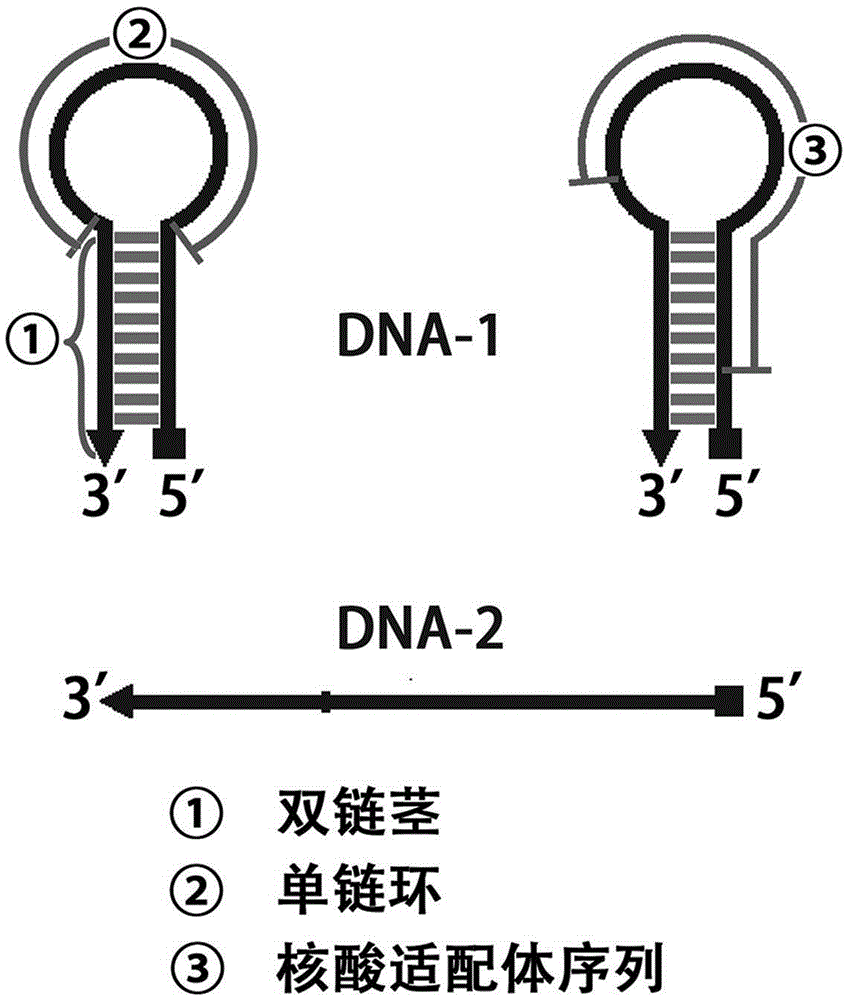
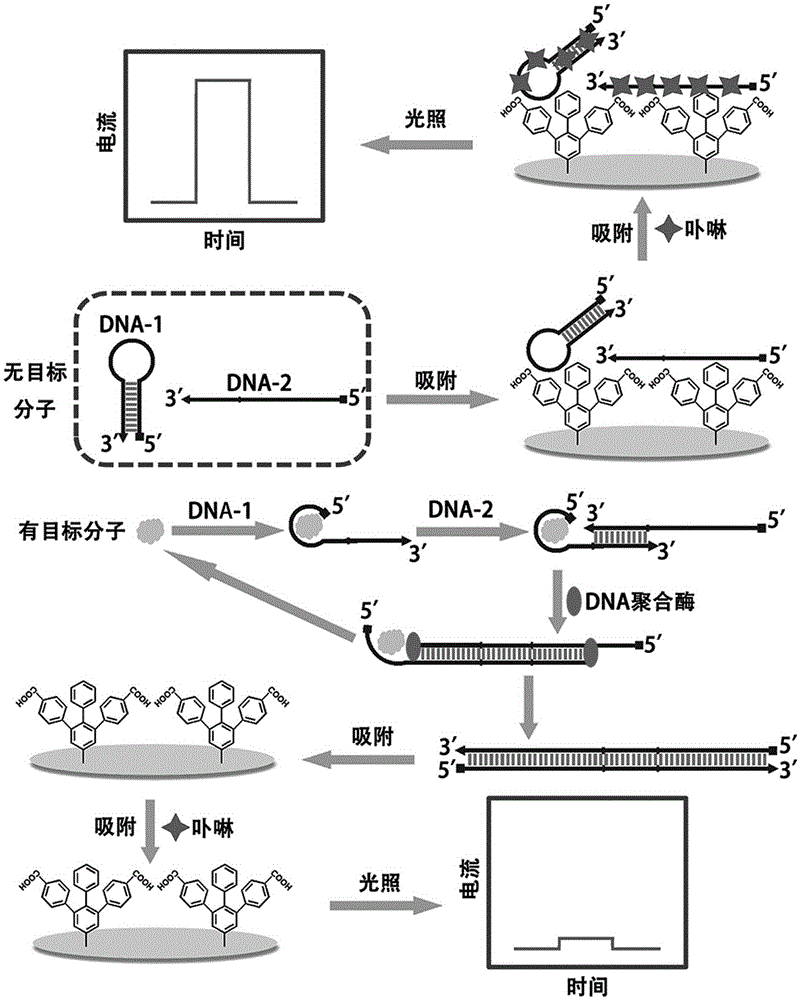
Preparation of fixation-free biological sensing electrode and application of fixation-free biological sensing electrode to label-free homogeneous photo-electrochemical pesticide residue detection and cancer diagnosis
InactiveCN105259349AHigh sensitivityHigh selectivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseCancers diagnosis
The invention discloses preparation of a fixation-free biological sensing electrode and the application of the fixation-free biological sensing electrode to label-free homogeneous photo-electrochemical pesticide residue detection and cancer diagnosis. An electroreduction way is adopted to co-modify a phenyldiazonium salt which contains a negative group and the phenyldiazonium salt which does not contain the negative group on the surface of a base electrode. The electrode only adsorbs a single-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and does not adsorb a double-stranded DNA and is high in stability and reproducibility. The electrode can be applied to a label-free homogeneous photo-electrochemical biosensing method. The method comprises a biochemical reaction loop triggered by a target molecule, wherein the biochemical reaction loop contains a label-free DNA hairpin (DNA-1) and a single strand (DNA-2). When the target molecule does not exist, the DNA-1 and the DNA-2 can be both adsorbed onto the surface of the electrode, porphyrin can be adsorbed onto the surface of the electrode by means of the DNA-1 and the DNA-2, and photo-electrochemical signal response is generated; when the target molecule exists, the DNA-1 and the DNA-2 are hybridized with each other, under the action of a polymerase, a large number of DNA-1s and DNA-2s are changed into long double-stranded DNAs, the adsorbing capacity of the DNA-1 and the DNA-2 on the surface of the electrode is reduced, and the porphyrin photo-electrochemical response is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
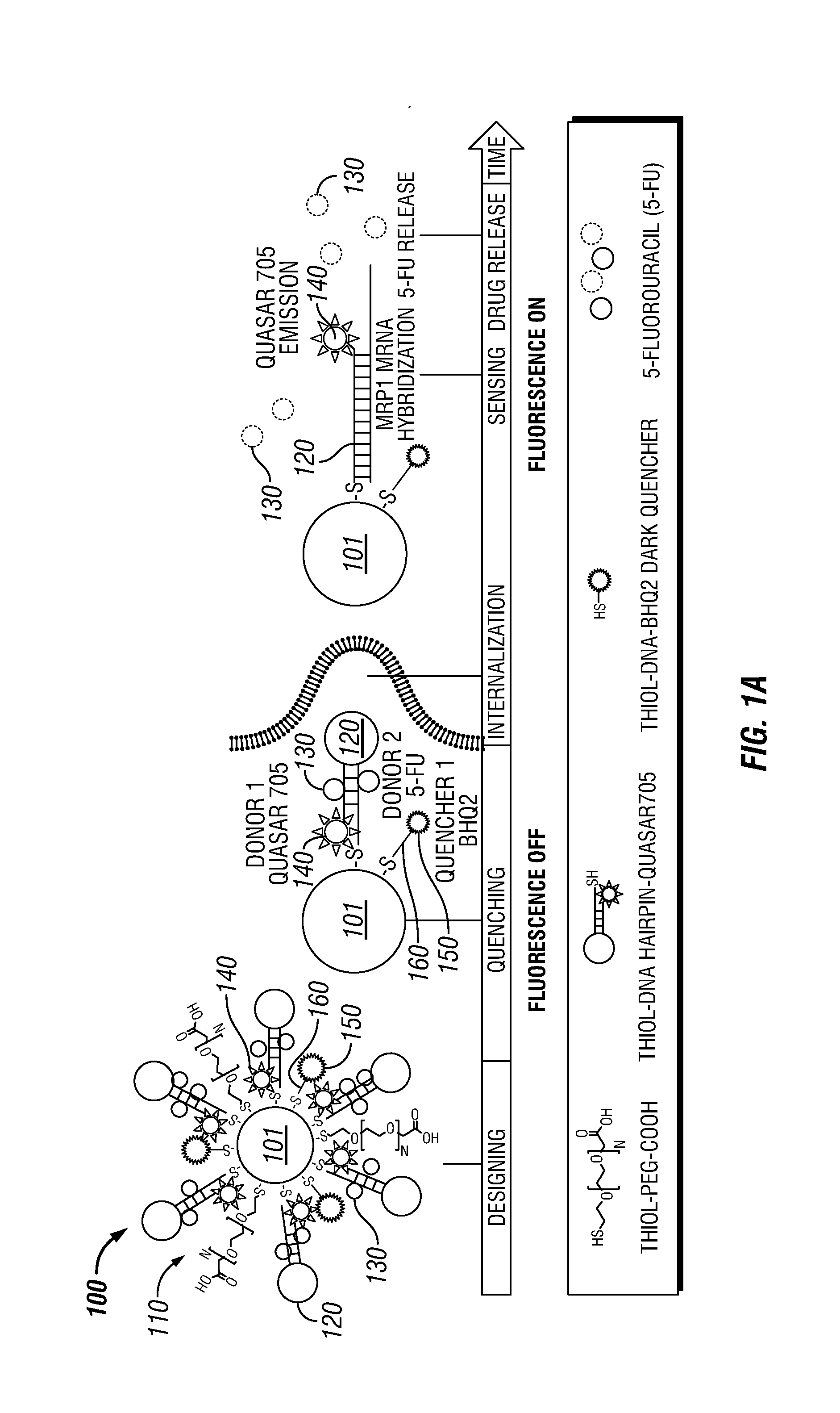
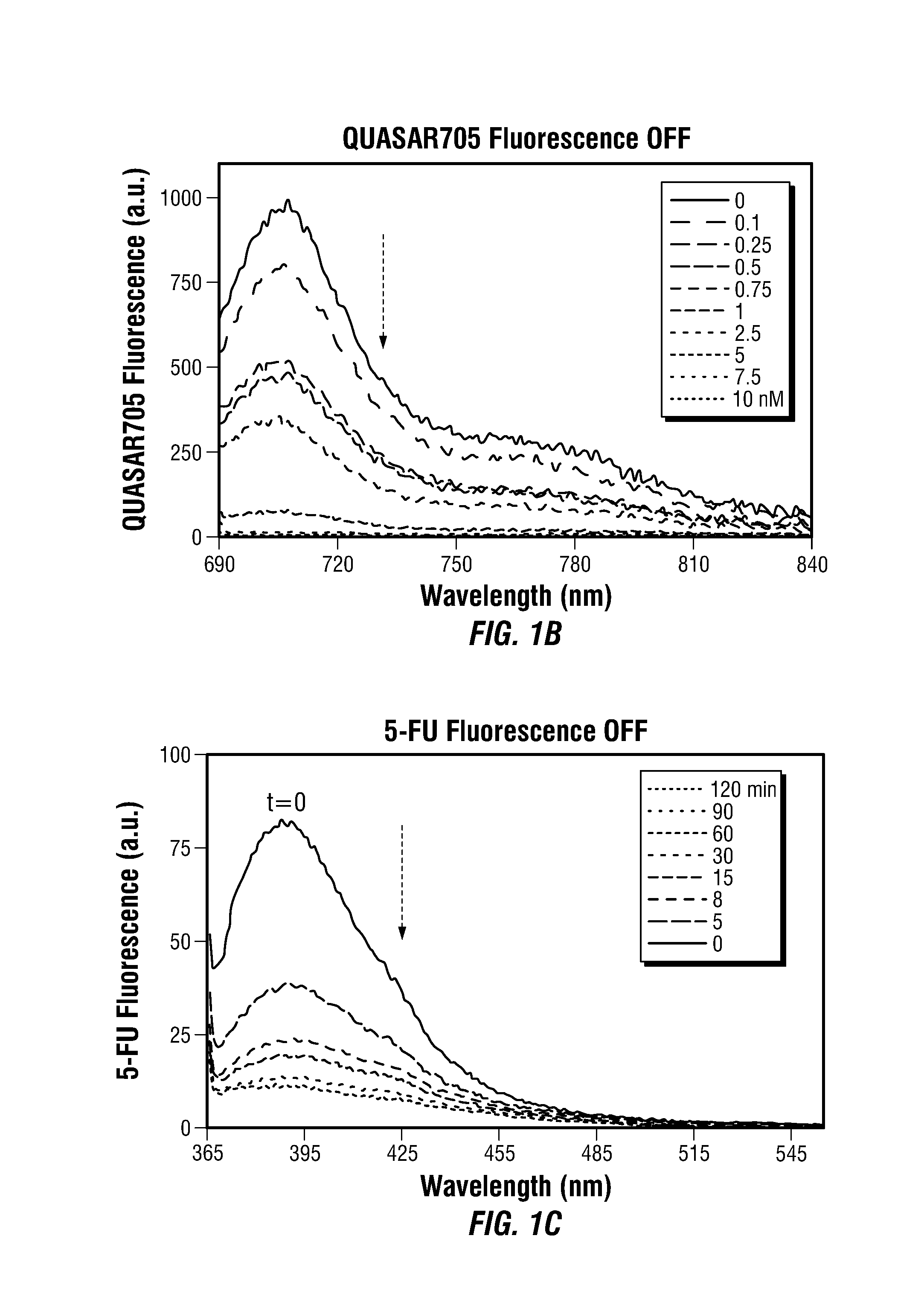
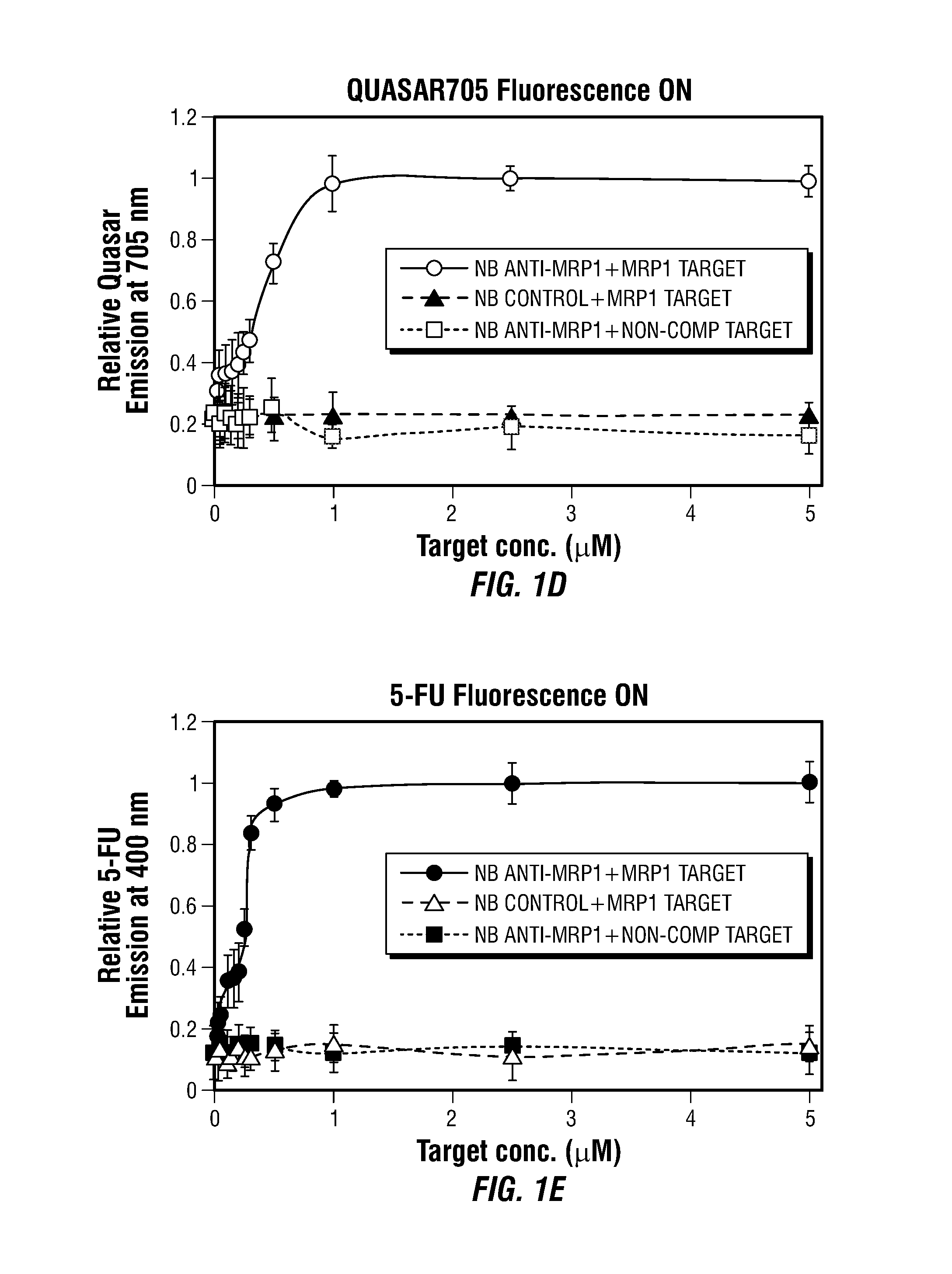
Theranostic Nanoprobes for Overcoming Cancer Multidrug Resistance and Methods
Theranostic nanoprobes are provided for overcoming cancer multidrug resistance, and methods for treating biological tissue, including cancerous tissue. The theranostic nanoprobes may include gold nanoparticles functionalized with DNA-hairpin. The DNA-hairpin may be configured to hybridize to a complementary target, which may silence or lessen the multidrug resistance of cancer cells. The theranostic nanoprobes may be configured to release a chemotherapeutic agent upon hybridization of the DNA-hairpin to a target molecule.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
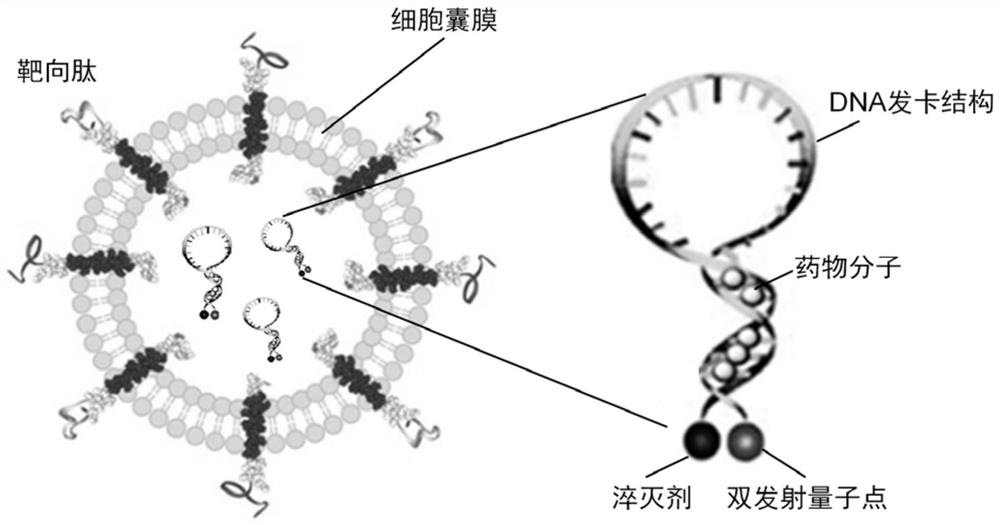
Ratio type near-infrared II-region fluorescent probe as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN111643058AReflect heterogeneityReduce mistakesDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsFluoProbesDelivery vehicle
The invention discloses a ratio type near-infrared II-region fluorescent probe as well as a construction method and application thereof. The ratio type near-infrared II region fluorescent probe comprises a DNA hairpin structure serving as a breast cancer specific miRNA recognition and signal amplification unit; a fluorescence donor and a fluorescence acceptor used as signal reporting units and modifying on the DNA hairpin structure, wherein the fluorescence donor comprises double-emission quantum dots of which the emission wavelength is in a near-infrared II region waveband; a drug molecule loaded on the DNA hairpin structure; and a cell capsule derived from a biological cell as a targeted delivery vehicle. By means of the ratio type fluorescent nanoprobe, in-situ, real-time, high-sensitivity and high-specificity breast cancer staging and typing evaluation can be achieved.
Owner:苏州影睿光学科技有限公司
Method for quantitative evaluating HP DNA hairpin configuration on substrate surface based on enzymic hydrolysis ability and background signal eliminating method based on enzymic hydrolysis ability
InactiveCN108195919AEfficient removalWon't hurtMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityElectrochemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of DNA self-assembled membranes, particularly to a method for quantitative evaluating the HP DNA hairpin configuration on a substrate surface based on enzymic hydrolysis ability and a background signal eliminating method based on enzymic hydrolysis ability. The specific steps comprise: removing dimers through high temperature denaturation; immersing a substrate in an exonuclease I buffer solution having an enzyme amount of 100-300 U, and carrying out hydrolysis; and determining the proportion of the HP DNA hairpin configuration on the surface of anelectrode by using an electricity integration technology. According to the present invention, exonuclease has difference between in hydrolysis of ssDNA and in hydrolysis of HP DNA hairpin configuration, and the electrochemical method is combined to quantitatively evaluate the proportion of the HP DNA hairpin configuration on the surface of the substrate; and with the exonuclease I, the backgroundsignal caused by non-hairpin configuration can be effectively eliminated so as to substantially improve the detection sensitivity of the Hairpin DNA-based biosensor.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Amphiphilic DNA nano-micelle and preparation method and application thereof
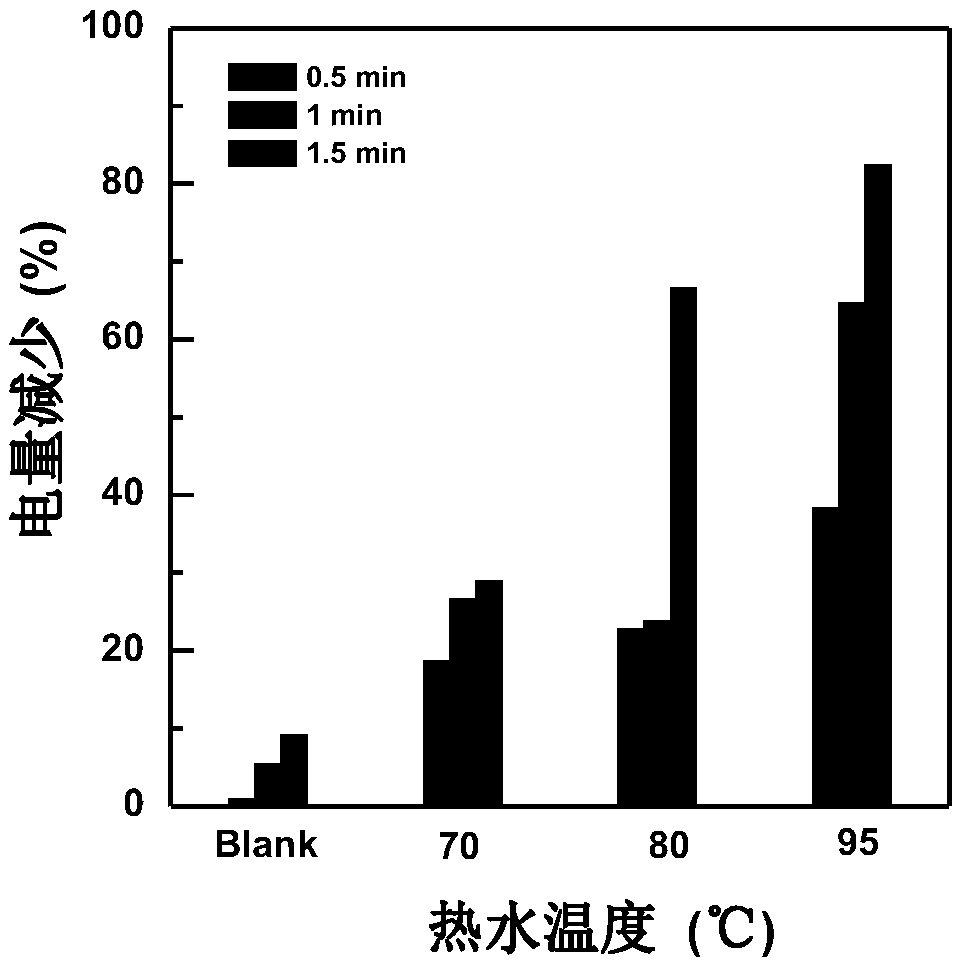
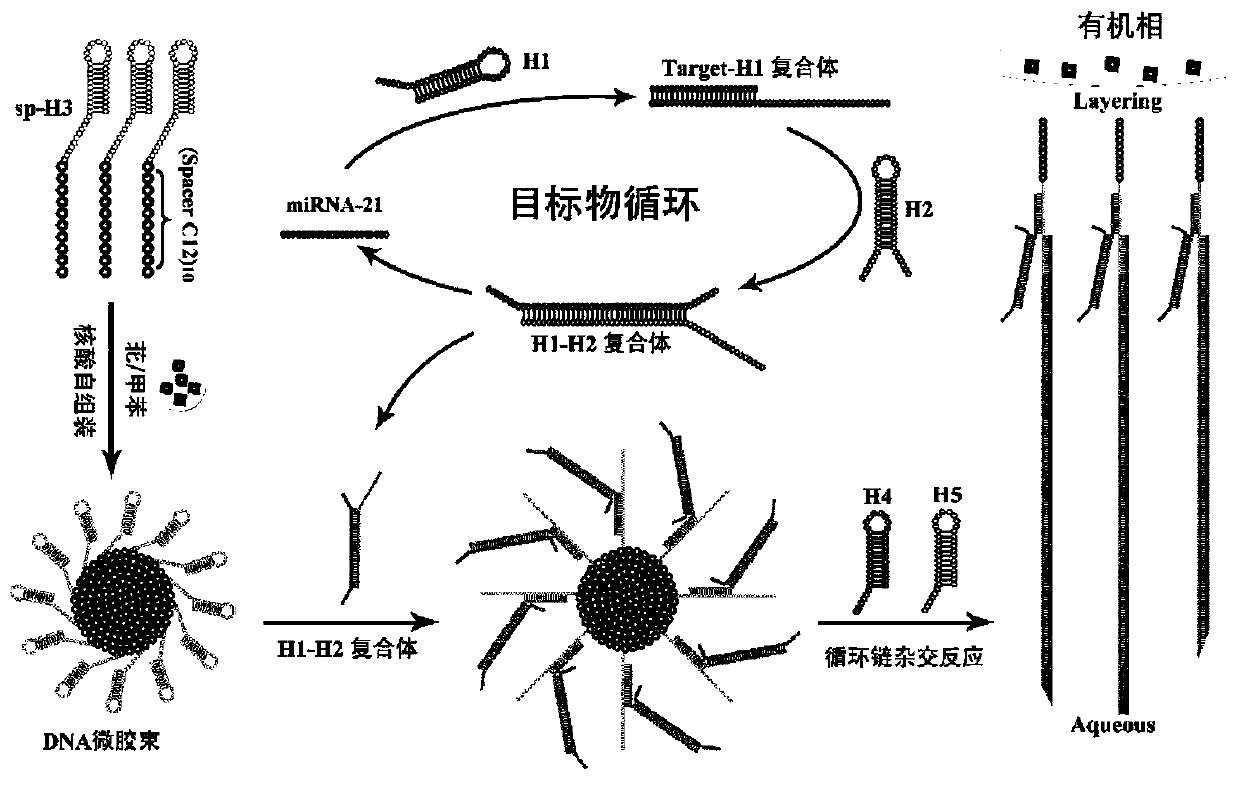
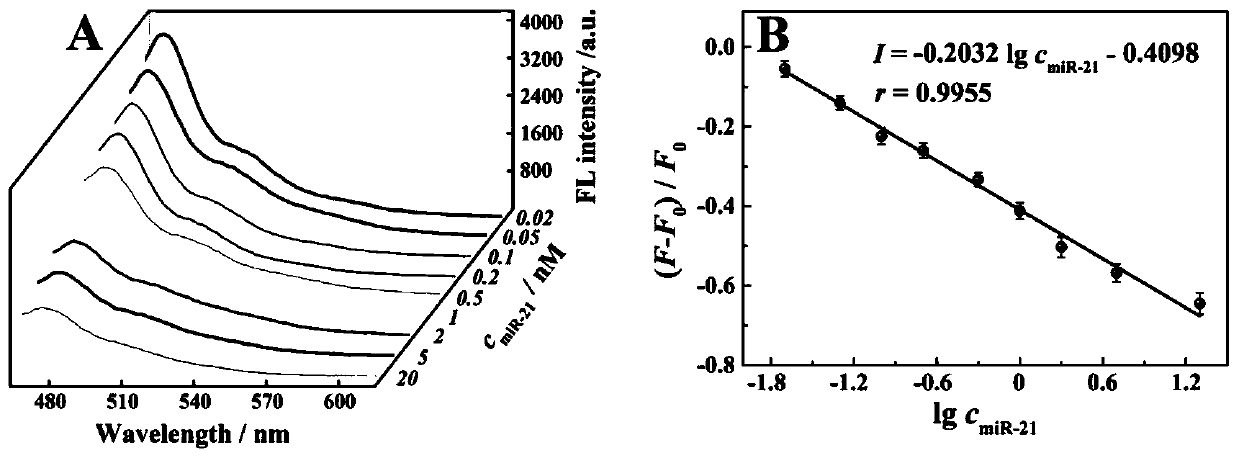
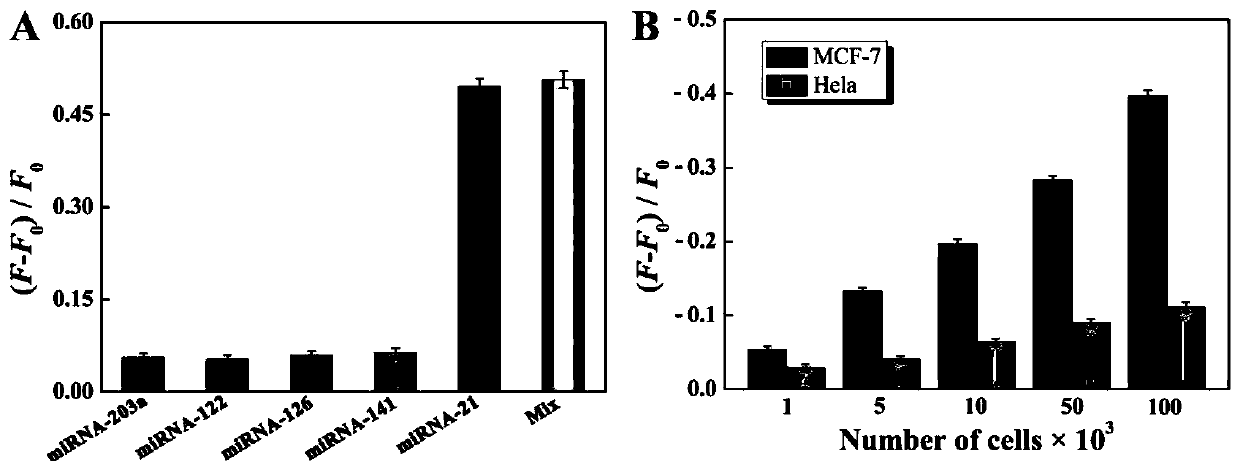
ActiveCN111549102AQuick assemblySave assembly timeMicrobiological testing/measurementNanomedicineAlkaneDna hairpin
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioluminescence analysis, and particularly relates to an amphiphilic DNA nano-micelle and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparationmethod comprises the following steps: 1, designing a specific DNA hairpin sequence H1-5 of a target miRNA, modifying a hydrophobic C12 alkane chain at the tail end of H3 to prepare sp-H3 freeze-driedpowder, preparing a sp-H3 dispersion liquid with a hairpin structure from the obtained sp-H3 freeze-dried powder, finally adding a fluorescent dye into the dispersion liquid, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain the DNA nano-micelle. The invention also provides an application of the DNA micelle nanometer in label-free detection of target miRNA. The DNA micelle constructed by the invention not only can be quickly assembled into a spherical nano structure, but also has relatively large immobilization capacity, meanwhile, the amphiphilic DNA nano-micelle has the characteristics of goodselectivity, convenience in operation and the like, and has important significance for measuring small biological molecules.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Ratio-type electrochemical biosensor for eliminating LAMP background interference, construction method and application
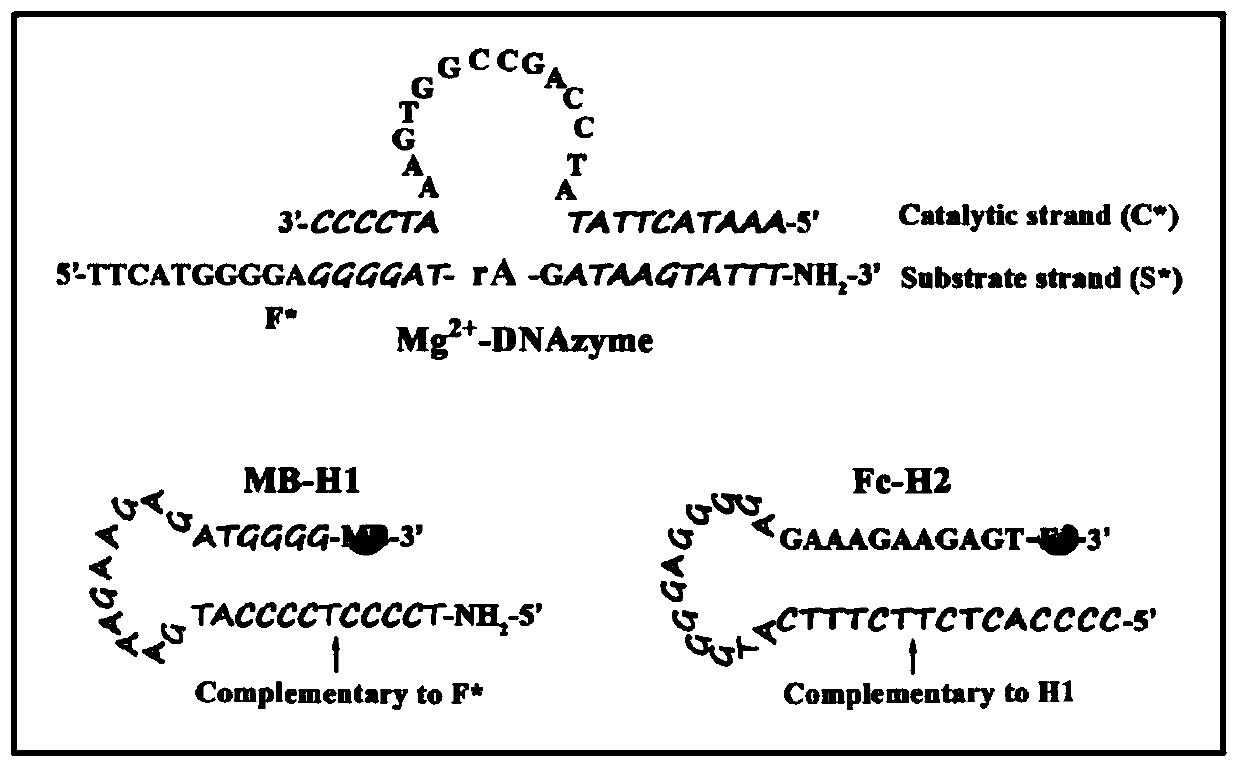
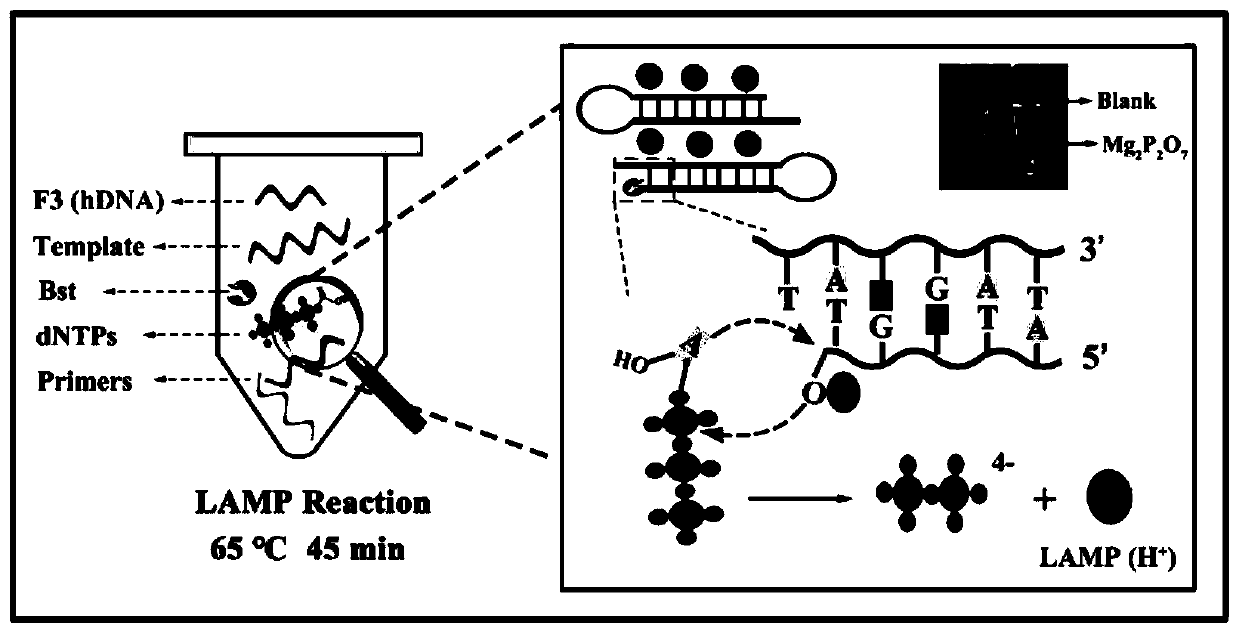
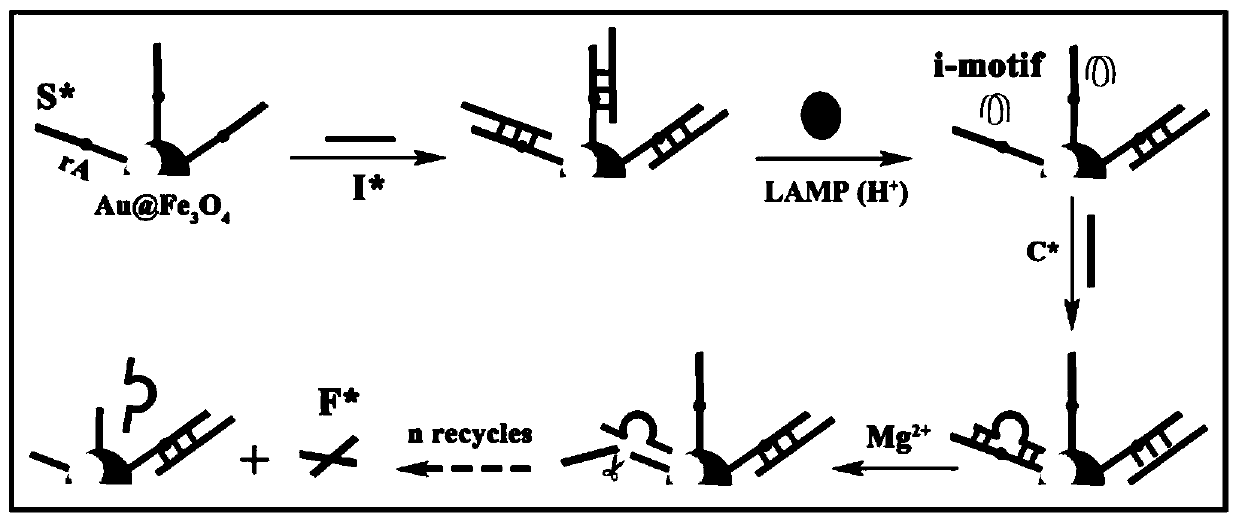
ActiveCN111060577AReduce false positive signalsHigh detection sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorDna hairpin
The invention relates to a ratio-type electrochemical biosensor for eliminating LAMP background interference, a construction method and application. According to the method, a target object short-chain DNA is used as an LAMP amplification outer primer, the byproduct hydrogen ions induce i-motif conformation transformation, metal ions DNAzyme are assembled, cyclic shearing is carried out, and separation and purification of an LAMP complex system and products are achieved; two DNA hairpins marked with electroactive probes methylene blue and ferrocene respectively are triggered on the surface ofthe electrode for directional hybridization without any enzyme intervention, and when the two DNA hairpins are far away from and close to the surface of the electrode respectively, the current signalratio has high-sensitivity and high-specificity target concentration linear correlation. The electrode reaction of the established ratio-type sensor is more simplified, background interference and false positive signals are effectively reduced, the sensitivity is remarkably improved, and a new thought and a technical means are provided for electrochemical detection of DNA of various disease markers.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Single-molecule mechanical method for measuring inhibition of small-molecule drug on protein and nucleic acid interaction
PendingCN112255396AImprove versatilityGain reliabilityMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic beadPharmacometrics
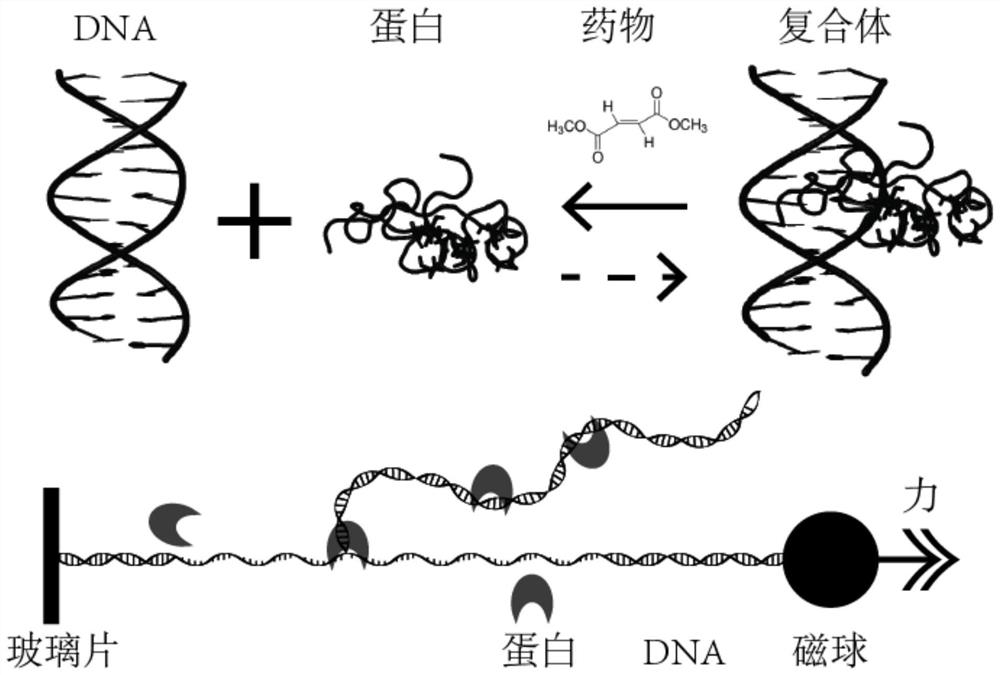
The invention relates to a single-molecule mechanical method for measuring inhibition of a small-molecule drug on protein and nucleic acid interaction. The method includes: first, designing and constructing a monomolecular reactor based on a DNA hairpin structure, the stem portion of which comprises a motif interacting with protein, and the handle portion of which is labeled with digoxin and biotin by polymerase chain reaction; secondly, preparing protein interacting with the DNA; thirdly, fixing the DNA hairpin structure between a magnetic bead and a glass sheet, and carrying out a DNA melting experiment in a microfluidic reaction tank through a monomolecular mechanics method; and finally, systematically testing the influence of the concentration of the small-molecule drug on the meltingreaction of the DNA combined with the protein, drawing a drug dose-response curve, calculating a half inhibition concentration, and evaluating the drug effect of the small-molecule drug on the proteinand nucleic acid interaction. The invention belongs to the field of biomacromolecule interaction and monomolecular pharmacology, and develops a new method for directly measuring small-molecule drug inhibition on protein nucleic acid interaction for molecular biology research, drug development and pharmacological evaluation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
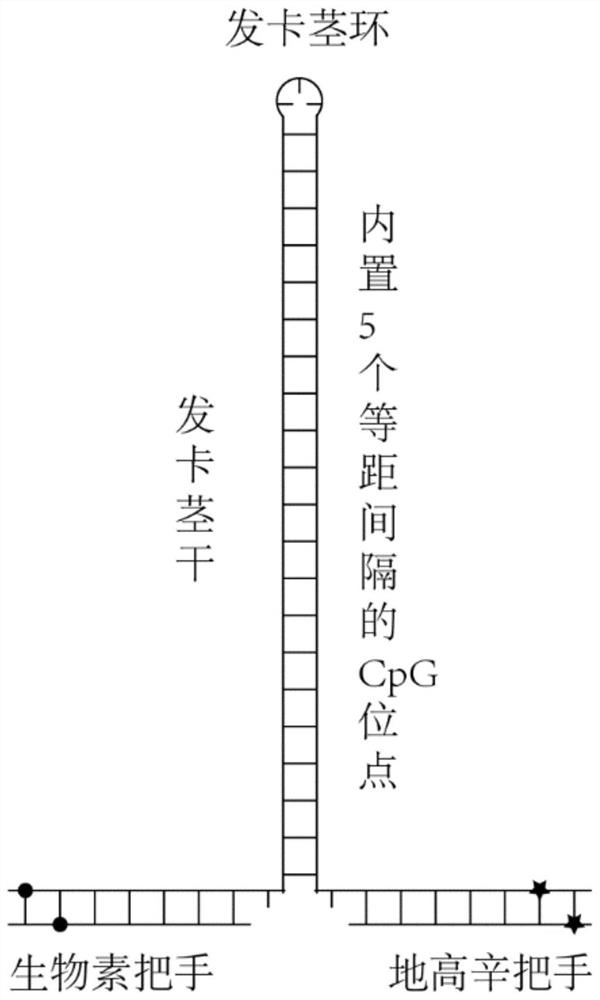
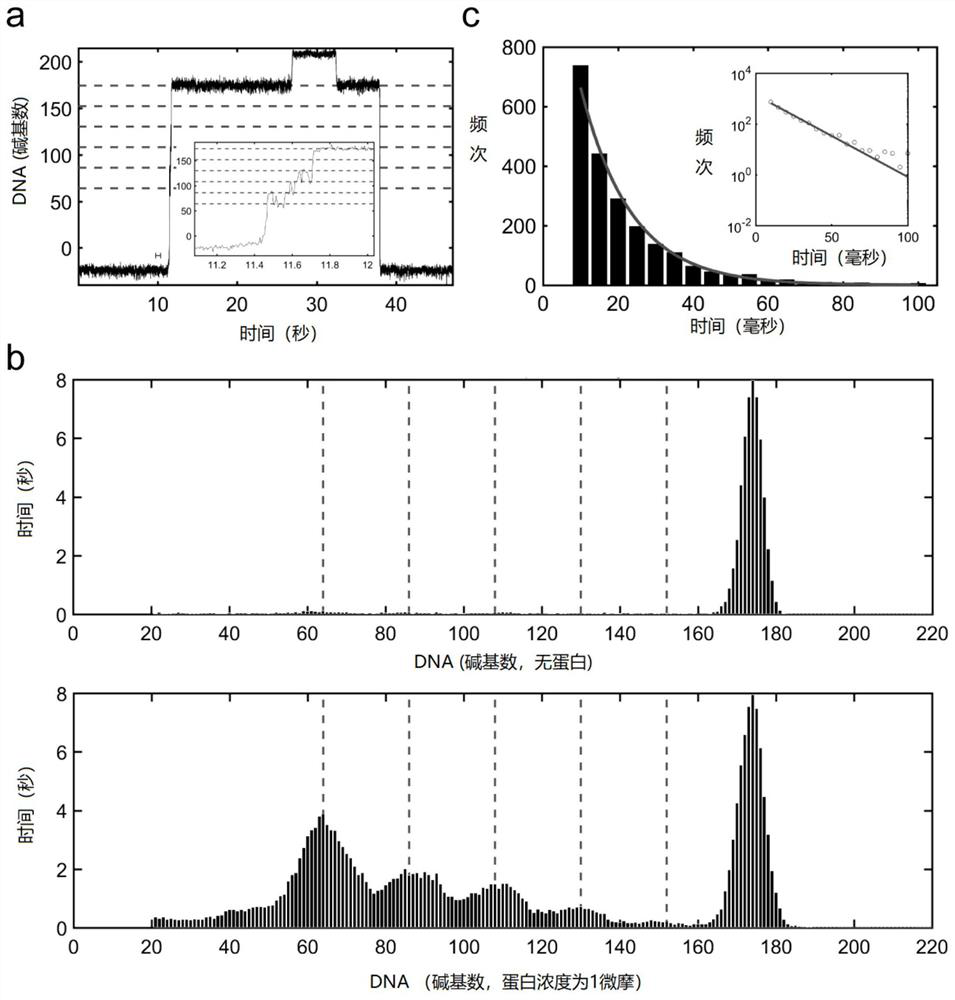
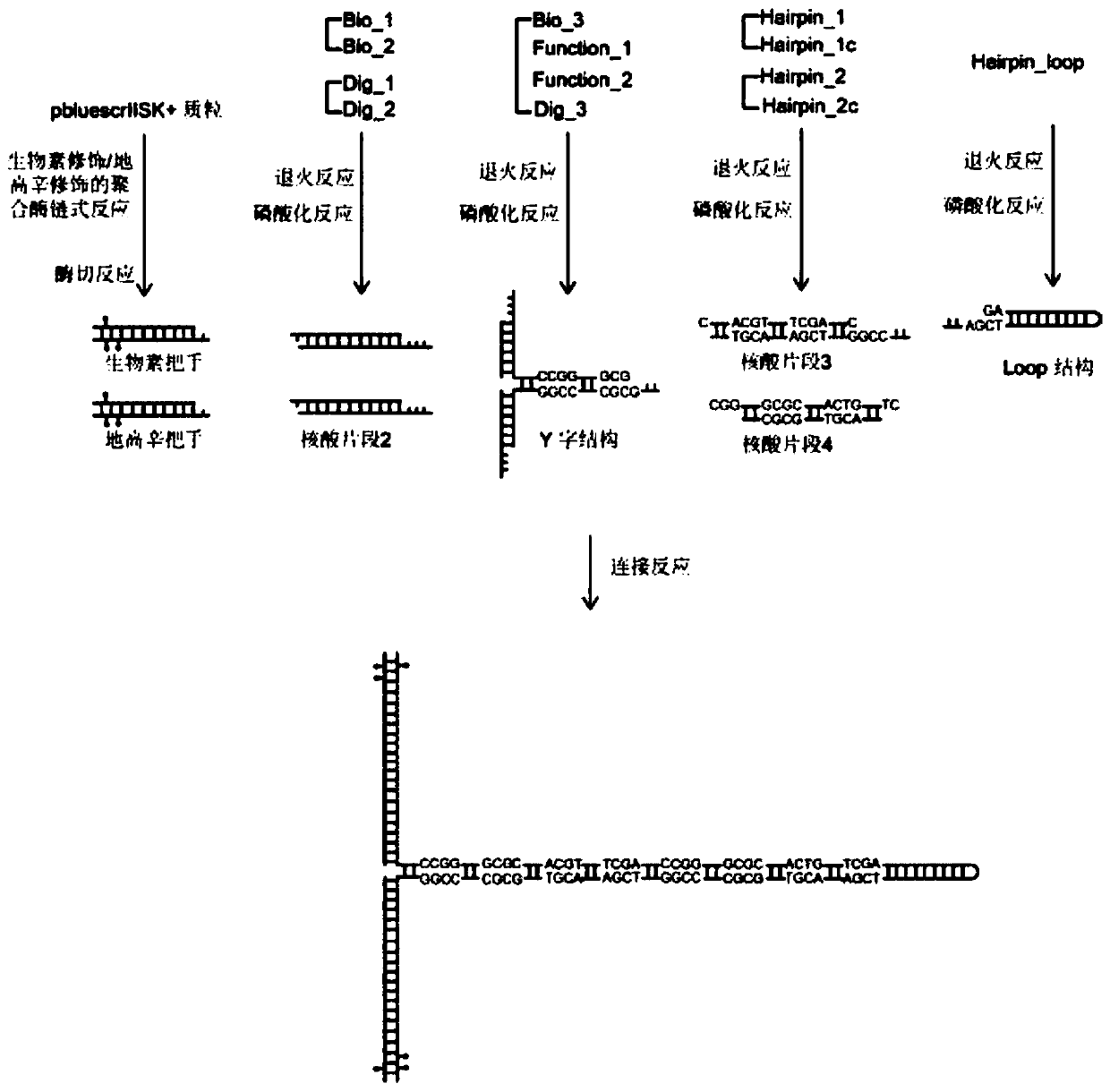
Hairpin structure containing CpG site and monomolecular mechanical method for measuring influence of CpG adjacent sequences on protein dissociation time constant
ActiveCN111269911AQuick collectionImprove accuracyBiological testingDNA/RNA fragmentationCpG siteDna hairpin
The invention relates to a monomolecular mechanical method for measuring the influence of CpG adjacent sequences on a protein dissociation time constant. Based on a single-molecule mechanical method,dissociation events of the protein from multiple CpG sites on a same DNA molecule are detected in a high-throughput manner, and the influence of different adjacent sequences on the interaction betweenthe protein and the CpG sites is compared and analyzed. According to the invention, a hairpin structure containing the CpG sites is constructed; a stem part of the structure contains a plurality of CpG sites which are distributed at equal intervals; the CpG adjacent sequences, such as CG, GC, AT and TA, can be set as required, the corresponding CpG sites of the control DNA hairpin structure onlycontain one adjacent sequence, the dissociation time of the protein at each CpG site is compared and analyzed, and how the CpG adjacent sequences influence the protein dissociation time constant can be accurately measured. The method can be used for repeatedly detecting time and probability of the interaction between the protein and different CpG sites in real time in a high-throughput manner to obtain an accurate dissociation time constant, can be widely used for precisely analyzing the interaction between protein and nucleic acid, and is beneficial to life science and medicine research and development.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Site-Specific DNA-Doxorubicin Conjugates Display Enhanced Cytotoxicity to Breast Cancer Cells
InactiveUS20180133331A1Facilitated releaseImprove retentionOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryStability studySide effect
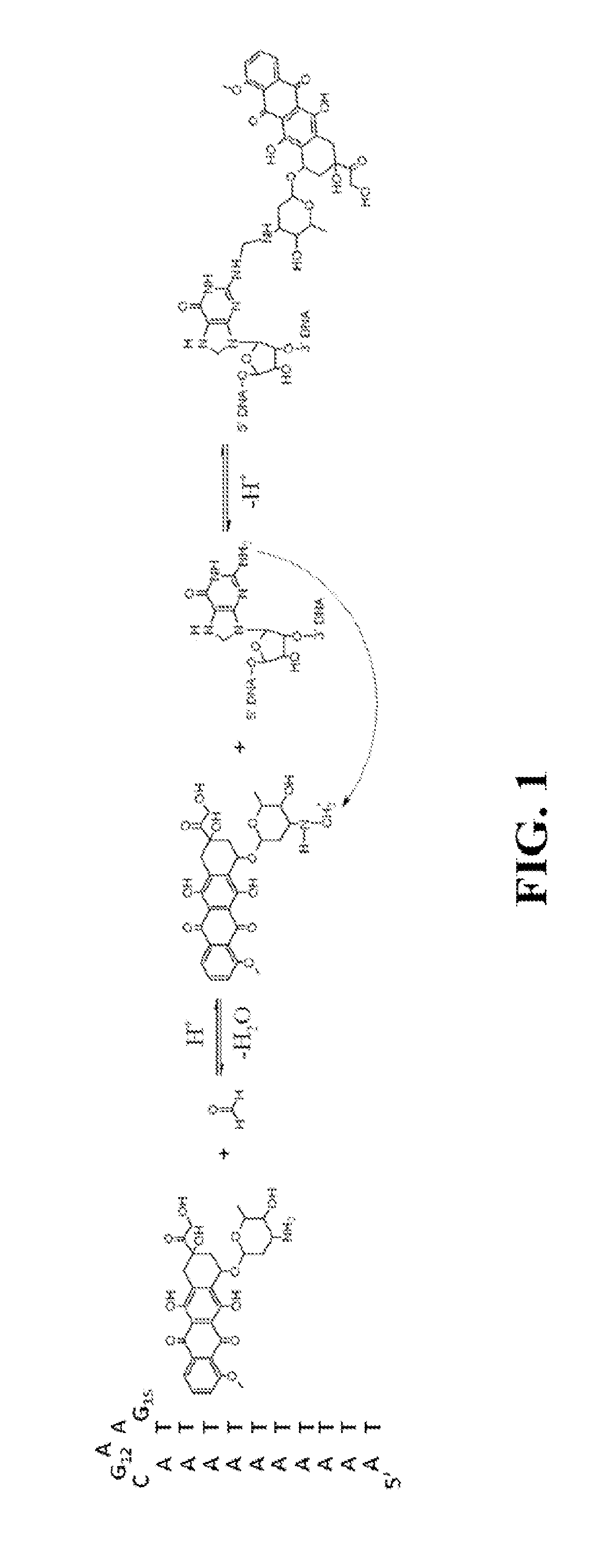
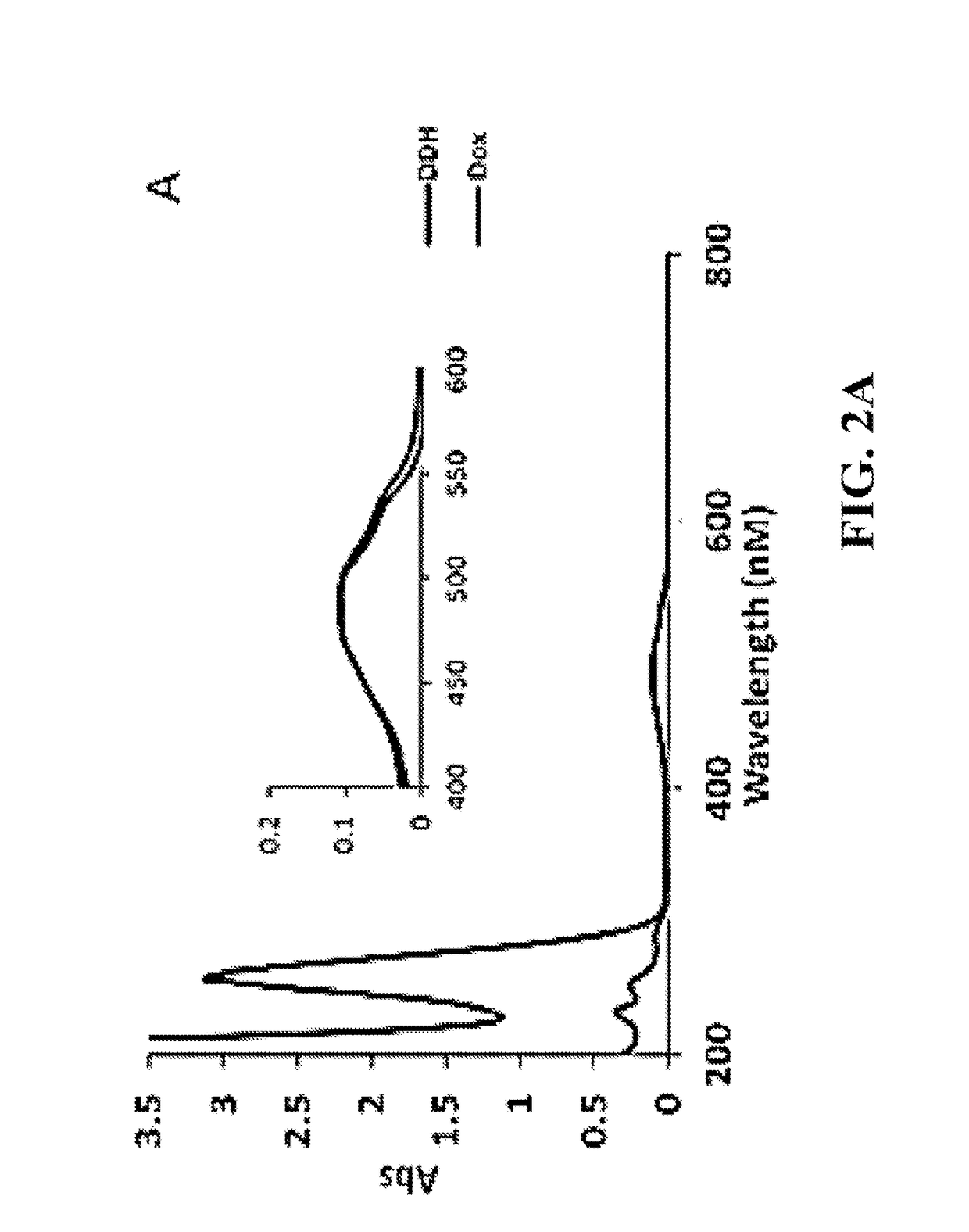
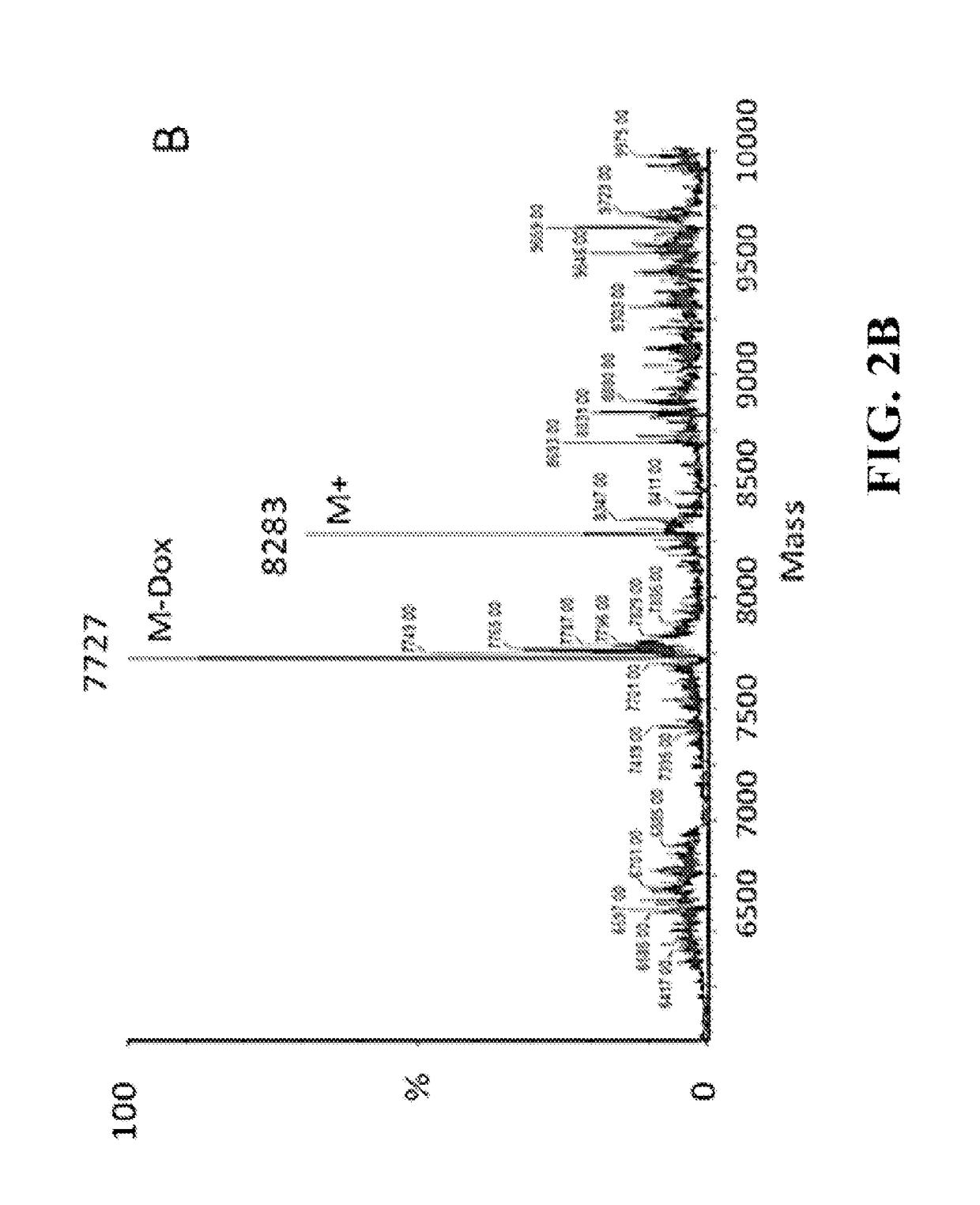
Doxorubicin (Dox) is widely used for breast cancer treatment but causes serious side-effects including cardiotoxicity that may adversely impact patient lifespan even if treatment is successful. The present invention relates to selective conjugation of Dox to a single site in a DNA hairpin resulting in a highly stable complex that enables Dox to be used more effectively. Selective conjugation of Dox to G15 in the hairpin loop was verified using site-specific labeling with [2-15N]-2′-deoxyguanosine in conjunction with [1H-15N] 2D NMR while 1:1 stoichiometry for the conjugate was validated by ESI-QTOF mass spectrometry and UV spectroscopy. Molecular modeling indicated covalently bound Dox also intercalated into the stem of the hairpin and stability studies demonstrated the resulting Dox-conjugated hairpin (DCH) complex had a half-life >30 h, considerably longer than alternative covalent and non-covalent complexes. Secondary conjugation of DCH with folic acid (FA) resulted in increased internalization into breast cancer cells. The dual conjugate, DCH-FA, can be used for safer and more effective chemotherapy with Dox and this conjugation strategy can be expanded to include additional anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
Electrochemical biosensing composition, working solution, electrochemical biosensor and application thereof
PendingCN114414636AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerElectrochemical biosensor
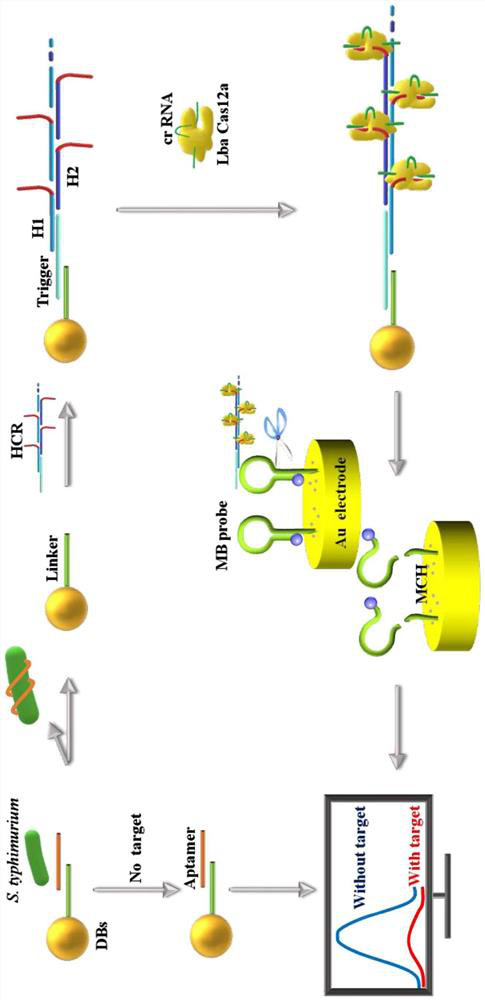
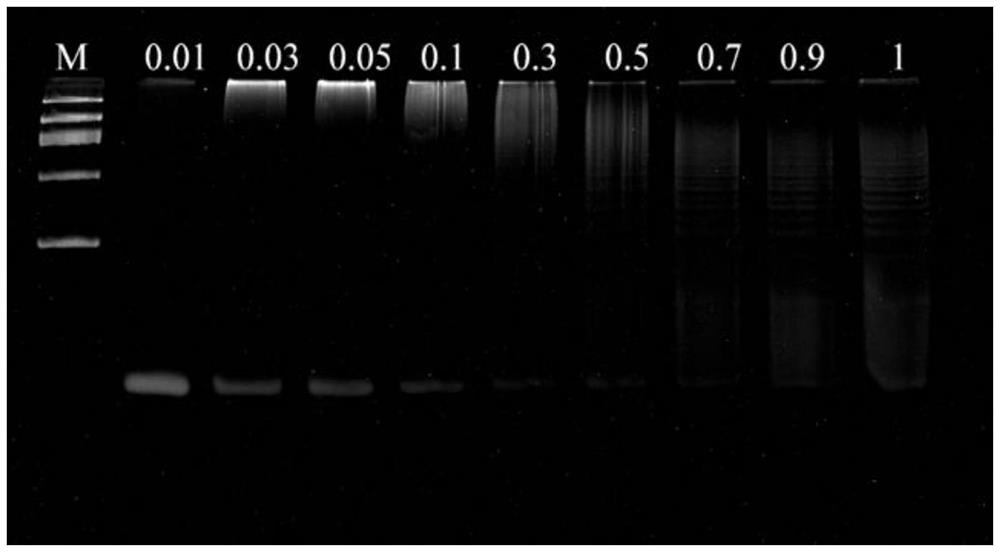
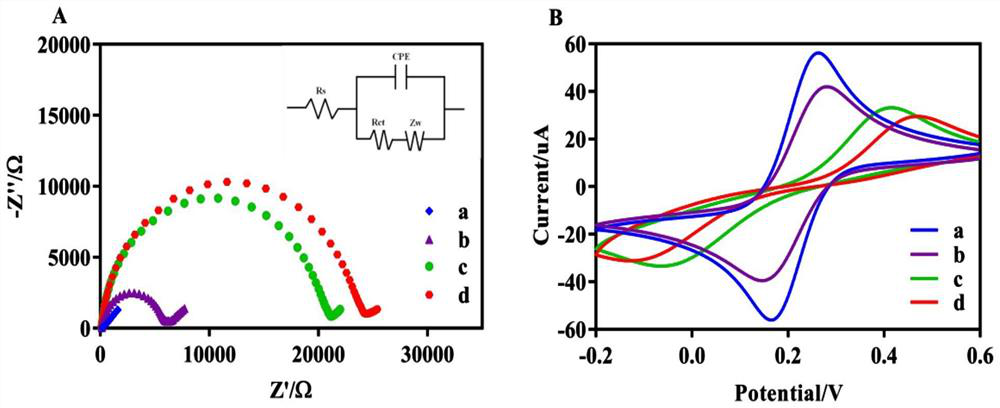
The invention relates to the field of electrochemical biosensors, in particular to a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) system of Cpf1 (Cpf1) from bacteria of the hispiraceae, and the electrochemical biosensor for detecting pathogenic bacteria salmonella typhimurium is developed by combining the CRISPR system with a hybrid chain reaction. The autonomous cross opening of the functional DNA hairpin structure of the HCR produces a double-stranded DNA line of a polymer consisting of a plurality of single-stranded DNA, and the plurality of functional single-stranded DNA initiate the trans-cleavage activity of CRISPR-Cas12a, so that the DNA hairpin ring of the MB modified on the surface of the gold electrode is selectively cleaved. The process will cause a change in electron transfer of the electrochemical tag. And the polymer double-stranded DNA of the HCR is fixed on the DBs through a salmonella typhimurium aptamer. The established method can selectively and sensitively quantify salmonella typhimurium in a sample, and the detection limit is 20 CFU / mL.
Owner:ACAD OF MILITARY SCI PLA CHINA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI INST OF MILITARY VETERINARY MEDICINE
Hybrid nucleic acid drug carrier of dna and polymer and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110403915BImproved tumor targetingIncrease intakeOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor targetBiopolymer
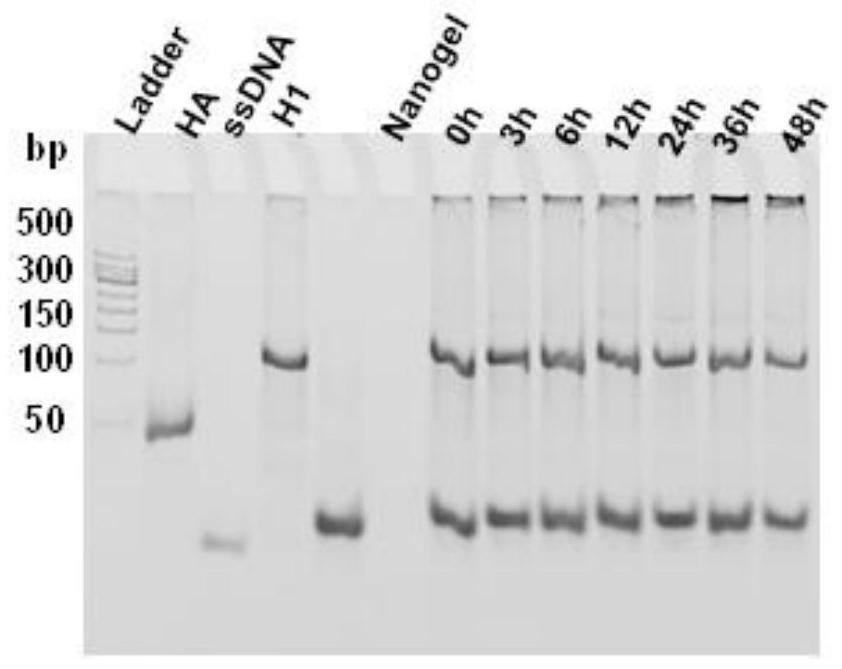
The invention discloses a DNA and polymer hybrid nucleic acid drug carrier and its preparation method and application. Firstly, acrylamide-modified DNA with initiator chain I and acrylamide are used to construct an acrylamide polymer by free radical polymerization / DNA hybrid nanogel, design DNA hairpin structure H1 and H2, the ends of H1 and H2 can be complementary base pairing or covalently linked nucleic acid drug sequence. The prepared polymer / DNA hybrid nanogel is dispersed in the solution containing the corresponding hairpin structures H1 and H2, and the efficient assembly of nucleic acid drugs in the nanogel can be realized through in situ DNA hybridization chain reaction, thereby preparing stable Targeted nucleic acid nanomedicine with high specificity and high loading efficiency. As a unique biopolymer, DNA has precise and adjustable structure, efficient and controllable assembly, and can endow nanogel with stimuli responsiveness and controllable drug release performance; acrylamide polymers have high stability and are easy to functionalize, which can improve nanogel The in vivo stability and tumor targeting ability of the gel enable efficient transfection and expression of nucleic acid drugs at tumor sites.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A suture toehold activation method and toolkit for regulated DNA strand displacement reactions
The invention provides a suturing Toehold activation method used for controlling a DNA strand displacement reaction and a toolkit. A novel Toehold activation method is developed based on hairpin reconstruction caused by mutual action of a DNA hairpin structure and different environmental irritants (Hg2+ or ATP). The invention develops a novel Toehold activation method. The extra level of the DNA strand displacement reaction can be accurately controlled by changing the concentration of the environmental irritants.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A highly sensitive and decomposable quantum dot nanosphere probe and its preparation method
ActiveCN107462705BEnhanced detection signalGood dispersionBiological testingFluorescenceMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a highly sensitive and decomposable quantum dot nanosphere probe and a preparation method thereof. Through a fulcrum-mediated strand displacement reaction, a DNA hairpin probe modified by three desulfated biotins is self-assembled into a Y-type DNA nanostructure; and the Y-type DNA structure and quantum dots coupled to streptavidin are self-assembled to form the quantum dot nanosphere probe. The prepared quantum dot nanosphere probe and an immunomagnetic separation technology are combined to be applied to quick detection of a target analyte. Because of a binding force between biotin and streptavidin stronger thana binding force of desulfurized biotin, the quantum dot nanosphere probe is decomposed, and thus quantum dots are released; the target analyte concentration is determined by detecting the fluorescence value of a quantum dot solution, and a shielding effect of immunomagnetic beads on the quantum dots is overcome. The method has high sensitivity and the detection limit of microorganisms is 1.37 cfu / mL. This method is good in specificity, and common other microorganisms do not affect the detection.
Owner:天泓(济南)智能装备产业研究有限公司
Power load prediction method of GWO optimized Elman based on DNA hairpin variation
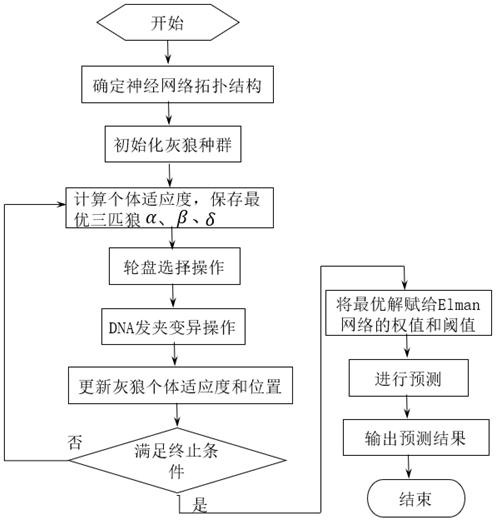
ActiveCN114841472AFast convergenceImprove convergence accuracyForecastingArtificial lifeLocal optimumAlgorithm
The invention discloses a power load prediction method for optimizing Elman through GWO based on DNA hairpin variation, an Elman power load prediction model is constructed, parameters of the Elman power load prediction model are optimized by using an improved grey wolf algorithm, and the improved grey wolf algorithm is that DNA hairpin variation is adopted to act on the grey wolf algorithm. The original grey wolf algorithm is improved, molecular biology and a GWO optimization algorithm are combined, a designed mutation operator enables the algorithm to have the capability of jumping out of local optimum, and the convergence speed and the convergence precision are improved; and compared with a static network, the Elman neural network has a relatively strong dynamic mapping characteristic through an internal feedback mechanism, so that the Elman neural network has a relatively strong capability of adapting to a time-varying characteristic, and the power load prediction speed is improved while the prediction precision is met.
Owner:四川锦城瑞知互联网科技有限公司
Method for measuring content of chloramphenicol based on biosensor of glucometer
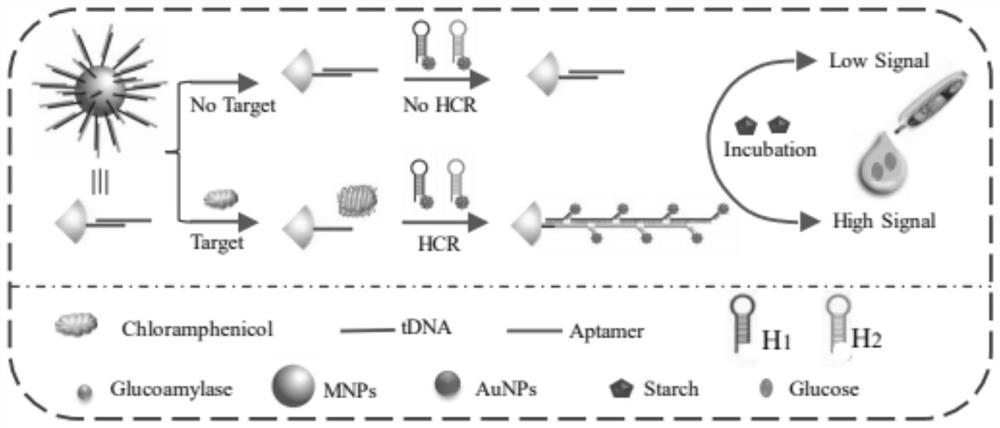
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of chloramphenicol based on a biosensor of a glucometer, which comprises the following steps: connecting a specific complementary chain DNA sequence to the surface of a magnetic particle through biotin-avidin interaction, and releasing the specific DNA sequence through the specific action of chloramphenicol and an aptamer, and initiating a cyclic self-assembly process of a hairpin structure modified with gold nanoparticles / amylase, and measuring the content of chloramphenicol by utilizing magnetic separation and collection and combining with a glucometer. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: S1, synthesizing AuNPs; S2, synthesizing aminated magnetic particles (MNPs); S3, modifying the MNPs (MNPs / tDNA / Aptamer); S4, carrying out DNA hairpin pretreatment (H1 and H2); S5, marking the NDA and glucoamylase (AuNPs / H1 / E, AuNPs / H2 / E) by using the AuNPs; S6, measuring chloramphenicol based on a glucometer; and S7, selectively investigating the content of chloramphenicol based on a glucometer. According to the method, the problem of measuring the content of chloramphenicol by using a glucometer is solved, and the detection requirement of the public on chloramphenicol is met.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Molecular circuits of AND gate, NOT gate, XOR and half-subtractor based on DNA hairpin structure
The present invention relates to an AND gate molecular circuit, a NOT gate molecular circuit, an XOR molecular circuit and a half-subtracter molecular circuit based on a DNA hairpin structure, belonging to the biocomputer technology field. The principles of the DNA single hairpin structure, the double hairpin structure and the two-way strand displacement reaction are employed to design a strand displacement reaction structure taking a conventional small fulcrum as an identification area to realize the construction of AND gate, NOT gate and XOR gate basic logic operation structures and perform globality simulation argumentation. A basic logic circuit is employed to perform combination design of the half-subtracter molecular circuit and perform argumentation simulation of the circuit feasibility.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
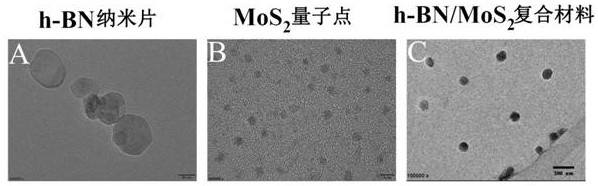
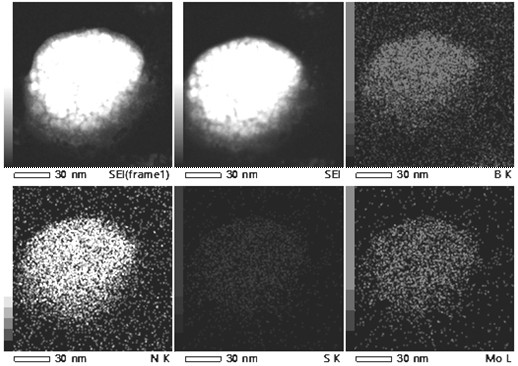
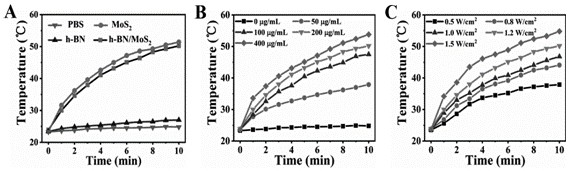
A h-bn/mos for targeted photothermal and chemical synergistic therapy 2 Nanoprobe and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN113368238BFunctionalSuitable for light-to-heat conversionMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic active ingredientsMedicineNanoprobe
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com