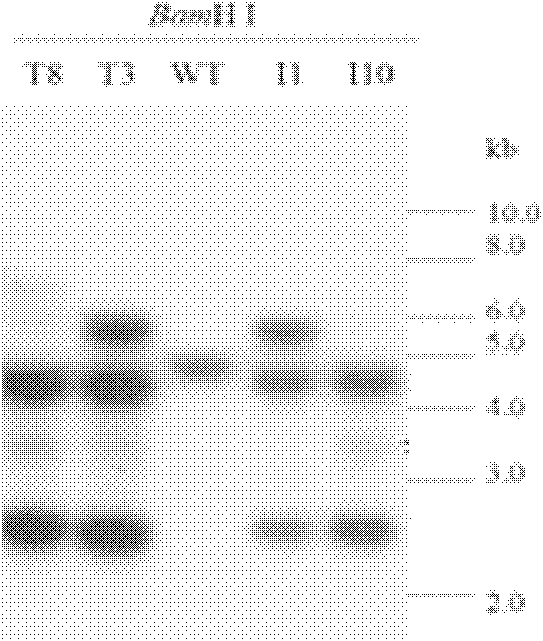Tobacco chloroplast genome recombination hotspot short-sequence NtcpRH23
A genome and tobacco leaf technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of molecular operations and the cumbersome construction process of chloroplast transformation vectors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] Example 1: Southern hybridization proves that recombination events occur in the genomic DNA of transgenic tobacco chloroplasts
[0012] In the study of tobacco chloroplast transgenesis, we found that the introduction of exogenous DNA led to the recombination of tobacco chloroplast genome, resulting in recombinant DNA. use Bam The chloroplast genomes of wild-type tobacco and transgenic tobacco were digested with H I and hybridized with exogenous genes as probes (see figure 1 ), multiple hybridization bands of the same size appeared in the chloroplast genome DNA of four independently obtained transgenic tobacco materials T3, T8, I1 and I10, in contrast, there was only one distinct hybridization band in the chloroplast genome of wild-type TW, This indicated that site-specific recombination events occurred in the transgenic tobacco chloroplast genome, and presumed that the recombination occurred at a relatively fixed position.
Embodiment 2
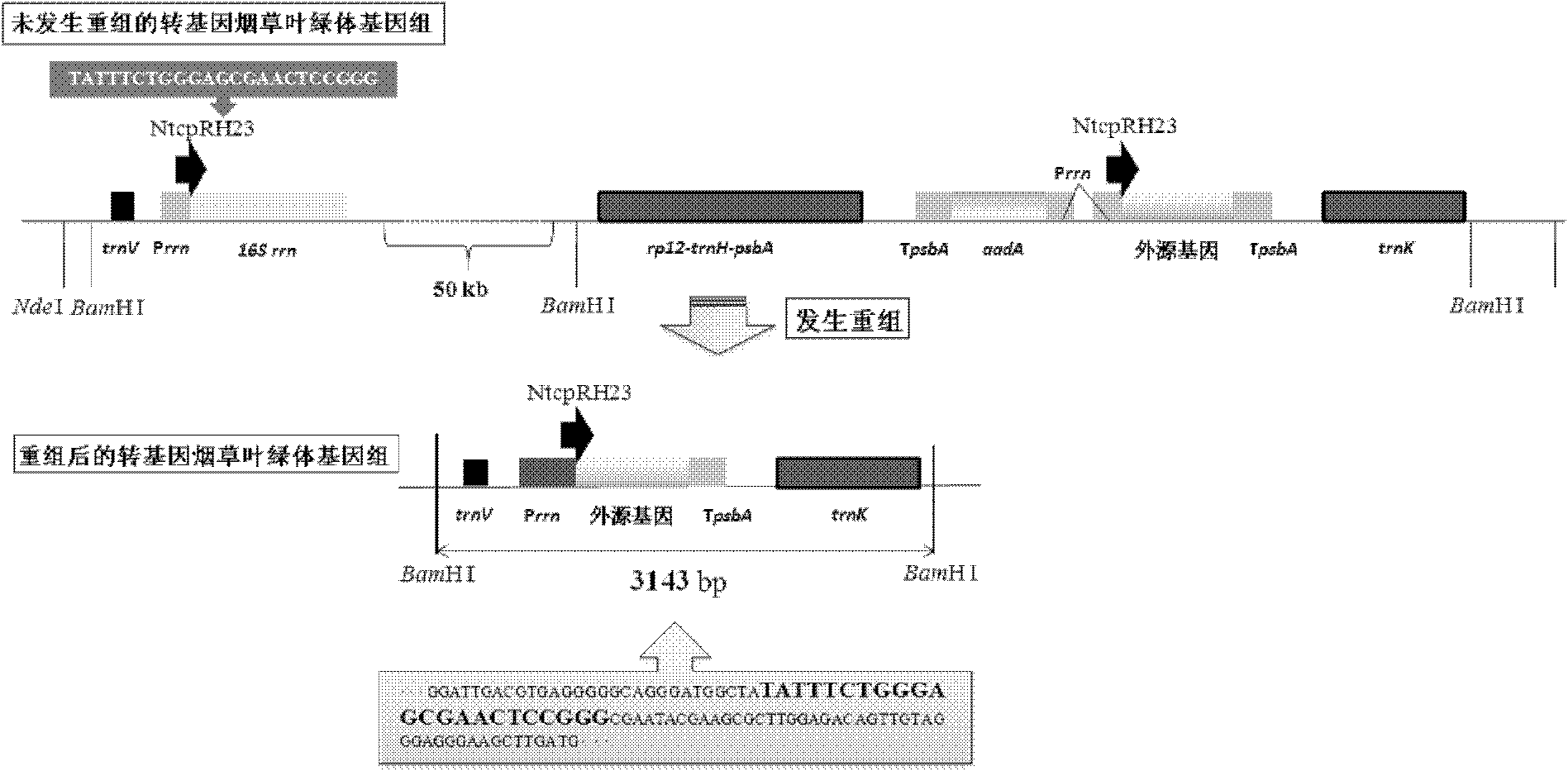
[0013] Example 2: Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Transgenic Tobacco Chloroplast Recombinant Fragments
[0014] In order to further determine and analyze the chloroplast genomic DNA recombination site and formation mechanism of recombined transgenic tobacco, the chloroplast DNA of transgenic tobacco was extracted and used Bam HI digestion, followed by agarose gel electrophoresis, the electrophoresis band of the recombinant DNA fragment was recovered, and then ligated with the plasmid vector. Nucleotide sequence analysis and alignment of 3.2kb chloroplast recombined DNA fragments (sequence 1 in the sequence listing) revealed that the recombination was triggered by a short sequence of 23bp, named NtcpRH23. NtcpRH23 is a short recombination hotspot sequence that has not been reported in the world so far. The significance and value of the discovery of the recombination function of this sequence is that it can be used to construct a new chloroplast expression vector, breaking thr...
Embodiment 3
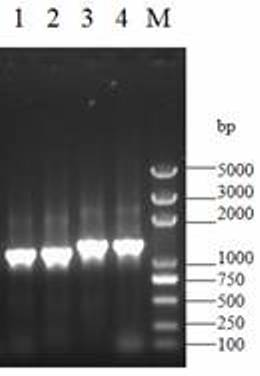
[0015] Embodiment 3: PCR verification triggers transgenic tobacco chloroplast genomic DNA recombination by NtcpRH23
[0016] In order to further prove the function of the recombination hotspot short sequence NtcpRH23 analyzed by the hybridization and sequencing results, the schematic diagram of DNA recombination in the transgenic tobacco chloroplast genome is triggered by the NtcpRH23 sequence. Downstream design of a pair of amplification primers, if transgenic tobacco does occur figure 2 Indicating chloroplast genomic DNA recombination, transgenic tobacco T3 and T8 can amplify the expected product of 1.2kb length, and transgenic tobacco I1 and I10 can amplify the expected product of 1.3kb length; if the chloroplast genome of transgenic tobacco does not recombine, the amplified Amplified products were not available beyond 50kb. image 3 The experimental results are based on figure 1 and figure 2 The analysis conclusion obtained is completely consistent with the expected l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com