Method for efficiently modifying filamentous fungi and strain of modified filamentous fungi
A filamentous fungus, high-efficiency technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and enzymology, can solve the problems that do not involve simultaneous interference, achieve the effect of reducing downstream isolation costs, fast transformation process, and reduced expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
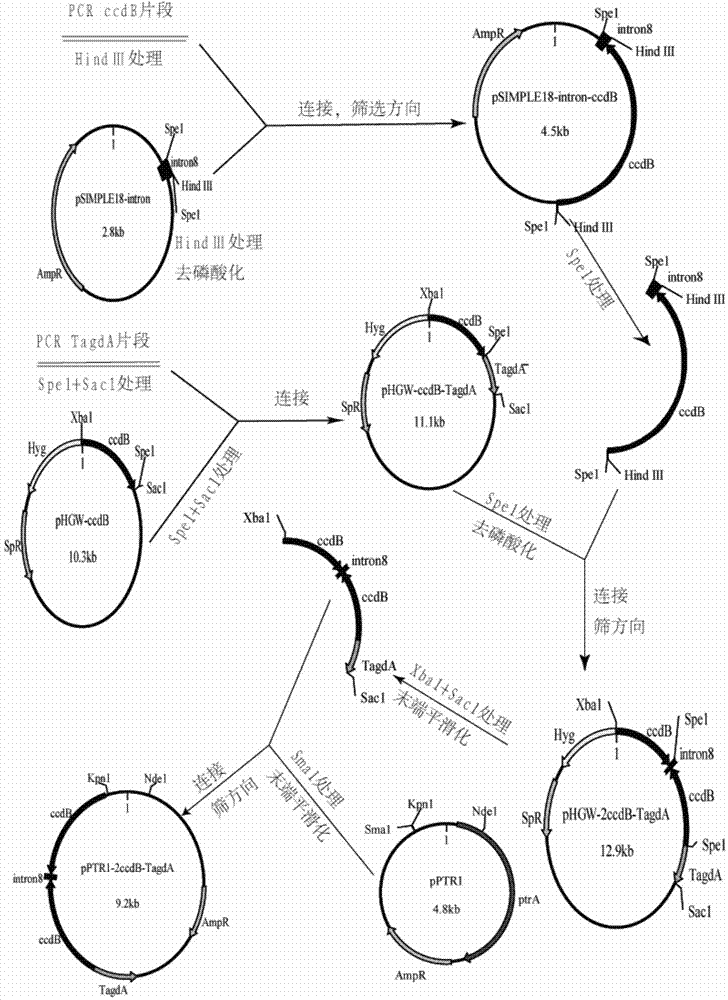
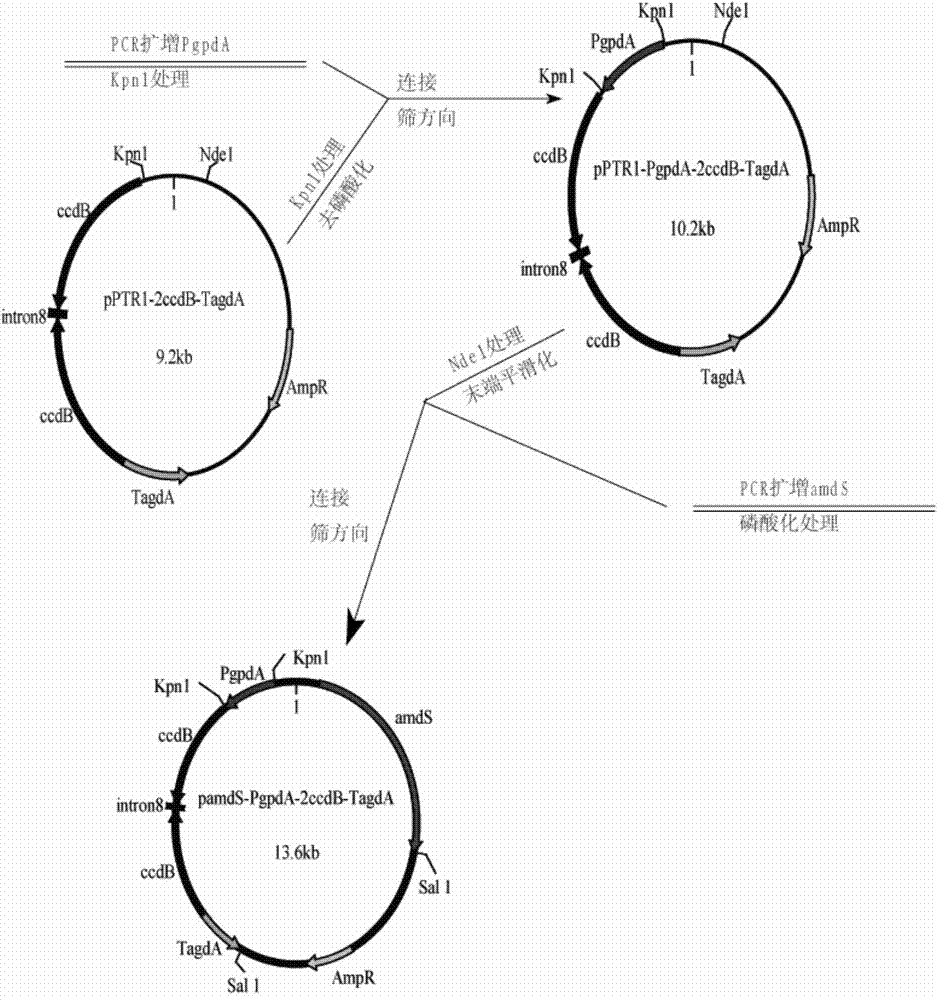
[0041] Construction of RNA interference backbone vector pamdS-PgpdA-2ccdB-TagdA
[0042] 1.1 Extract the genome of Aspergillus niger (Aspergillus niger) CBS513.88.
[0043] The washed and dried Aspergillus niger CBS513.88 cells (American Type Culture Collection ATCC) were ground with liquid nitrogen, and the genomic DNA of Aspergillus niger was extracted with phenol chloroform.
[0044] 1.2 Construction of intermediate plasmid pHGW-ccdB-TagdA
[0045] Using Aspergillus niger CBS513.88 genomic DNA as a template, the fragment amplified by PCR with primers SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 was named TagdA. The TagdA fragment treated with SpeI and SacI was inserted into SpeI and SacI of the plasmid Phgw-ccdB to obtain pHGW-ccdB-TagdA. The plasmid was sent to Huada Gene Company for sequencing, and the result showed that the DNA sequence of the amplified glycosidase A terminator was SEQ ID NO.31.
[0046] 1.3 Construction of intermediate plasmid pSIMPLE18-intron8
[0047] Aspergillu...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Construction of plasmids containing single gene interference constructs
[0060] 2.1 Construction of single gene interference intermediate vectors pDONR221-long and pDONR221-short
[0061] During the construction of the single-gene interference plasmid, two pairs of primers were designed, and the Aspergillus niger CBS513.88 genomic DNA can be used as a template to amplify the glycoamylase coding region long through primers SEQ ID NO:9 and SEQ ID NO:10. The coding region sequence of the glucoamylase amplified by primers SEQ ID NO:11 and SEQ ID NO:12 is short.
[0062] The 5' primers of the two fragments all added the combination site for BP reaction, the forward primer added the attB1 site, and the reverse primer added the attB2 site. The amplified fragment and plasmid pDONR221 (purchased from Shanghai Yingwei Jieji) were acted on by BP Clonase II enzyme mix enzyme to perform BP reaction to generate two Entry vectors pDONR221-long and pDONR221-short. The long and short...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Construction of plasmids containing polygene interference constructs
[0067] 3.1 Amplify DNA fragments containing multiple gene coding region sequences
[0068] Using the Aspergillus niger genome as a template, the amylase amyA coding region fragment is amplified by primers SEQ ID NO:13 and SEQ ID NO:14. A fragment of the coding region of glucoamylase glaAB was amplified by primers SEQ ID NO:15 and SEQ ID NO:16. A fragment of the coding region of the prtT gene was amplified by SEQ ID NO:17 and SEQ ID NO:18. These three fragments contain overlapping regions. After purifying these fragments, the three fragments are fused together in a certain order by overlapping extension PCR technology. The sequence after the fusion of the three fragments is the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:33.
[0069] 3.2 Construction of plasmid pamdS-PgpdA-Fragments-TagdA containing polygenic interference
[0070] The 5' end and 3' end of the three fused fragments are all added sites capable of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com