Patents
Literature
52 results about "Acridine orange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
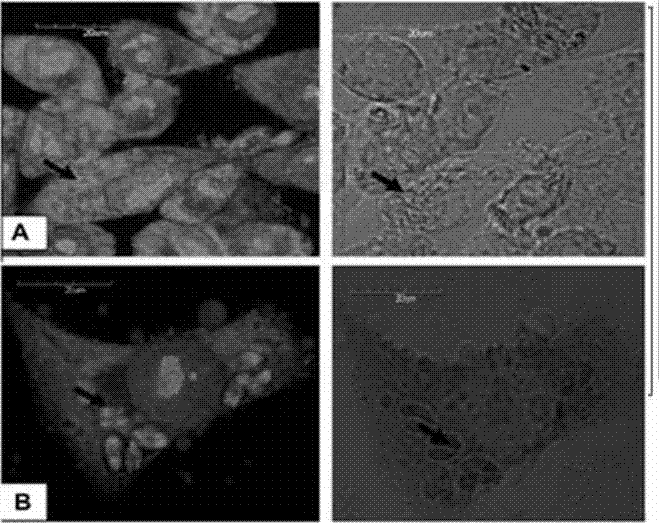
Acridine orange is an organic compound. It is used as a nucleic acid-selective fluorescent cationic dye useful for cell cycle determination. Being cell-permeable, it interacts with DNA and RNA by intercalation or electrostatic attractions respectively. When bound to DNA, it is very similar spectrally to fluorescein, with an excitation maximum at 502 nm and an emission maximum at 525 nm (green). When it associates with RNA, the excitation maximum shifts to 460 nm (blue) and the emission maximum shifts to 650 nm (red). Acridine orange will also enter acidic compartments such as lysosomes where it becomes protonated and sequestered. Within these low pH vesicles the dye emits red fluorescence when excited by blue light. Thus, acridine orange can be used to visualize primary lysosomes and phagolysosomes that may include products of phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. The dye is often used in epifluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry.
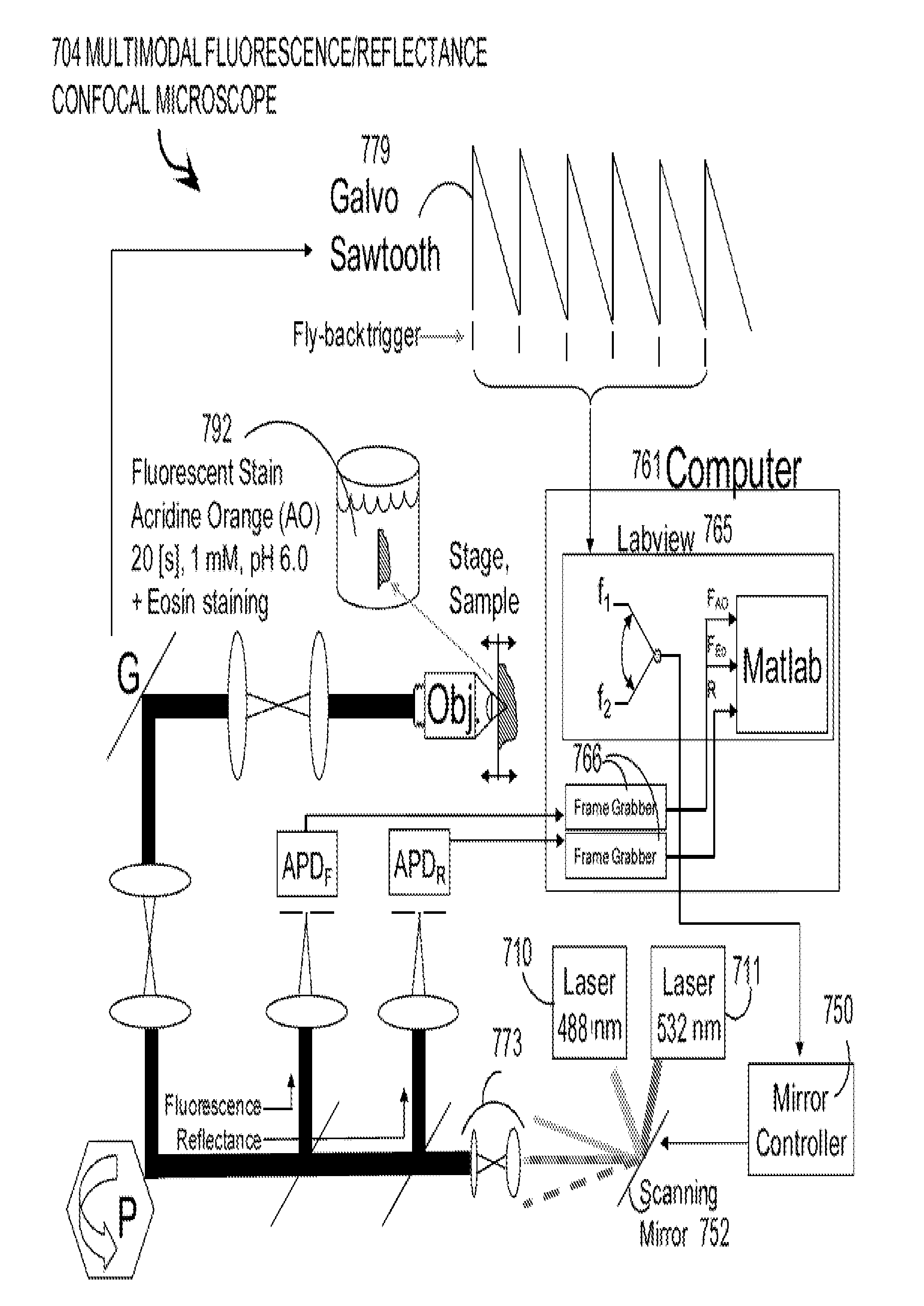
Rapid confocal microscopy to support surgical procedures
ActiveUS20110116694A1Prevent lateral movementMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationOptical propertyFluorescence
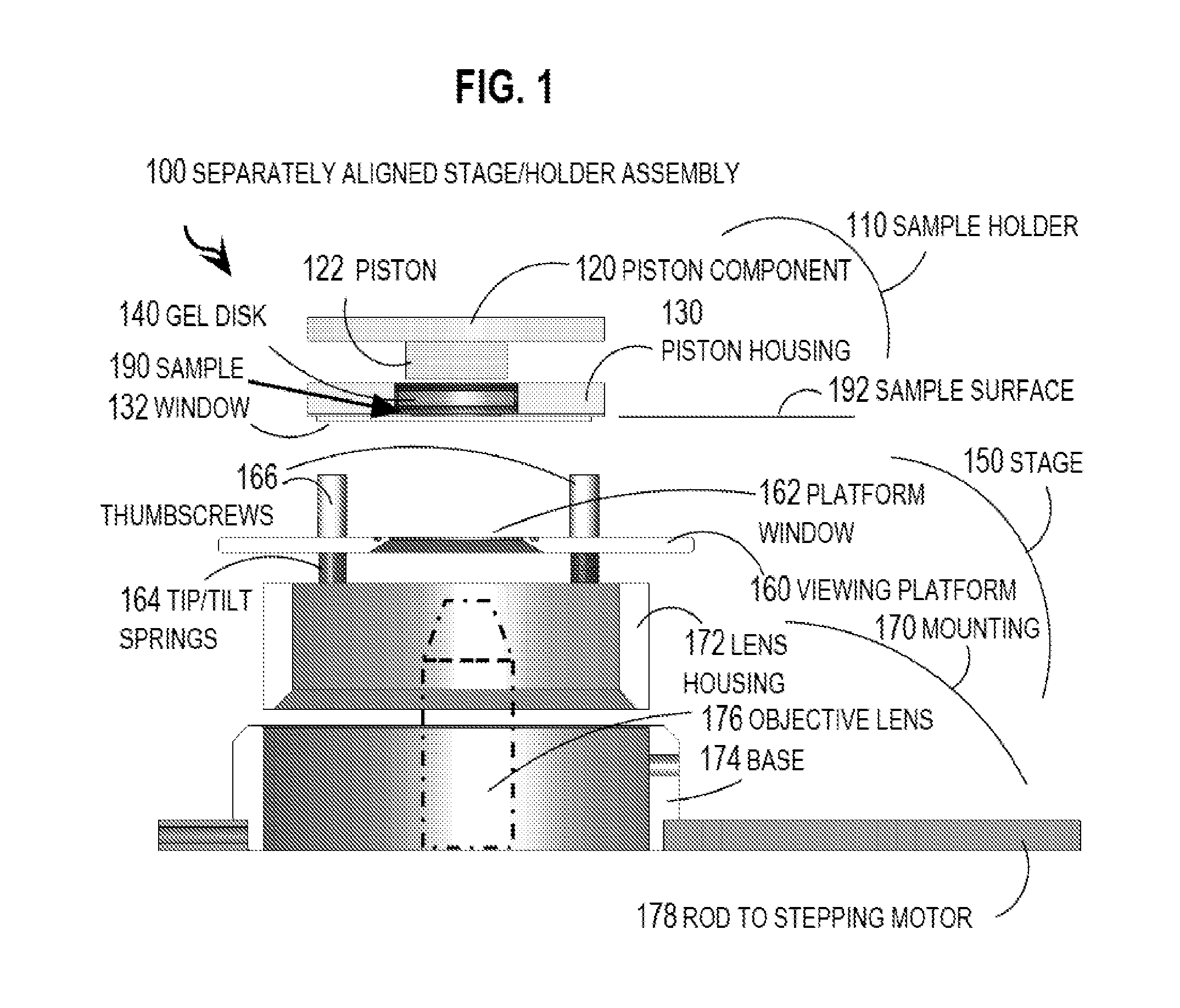
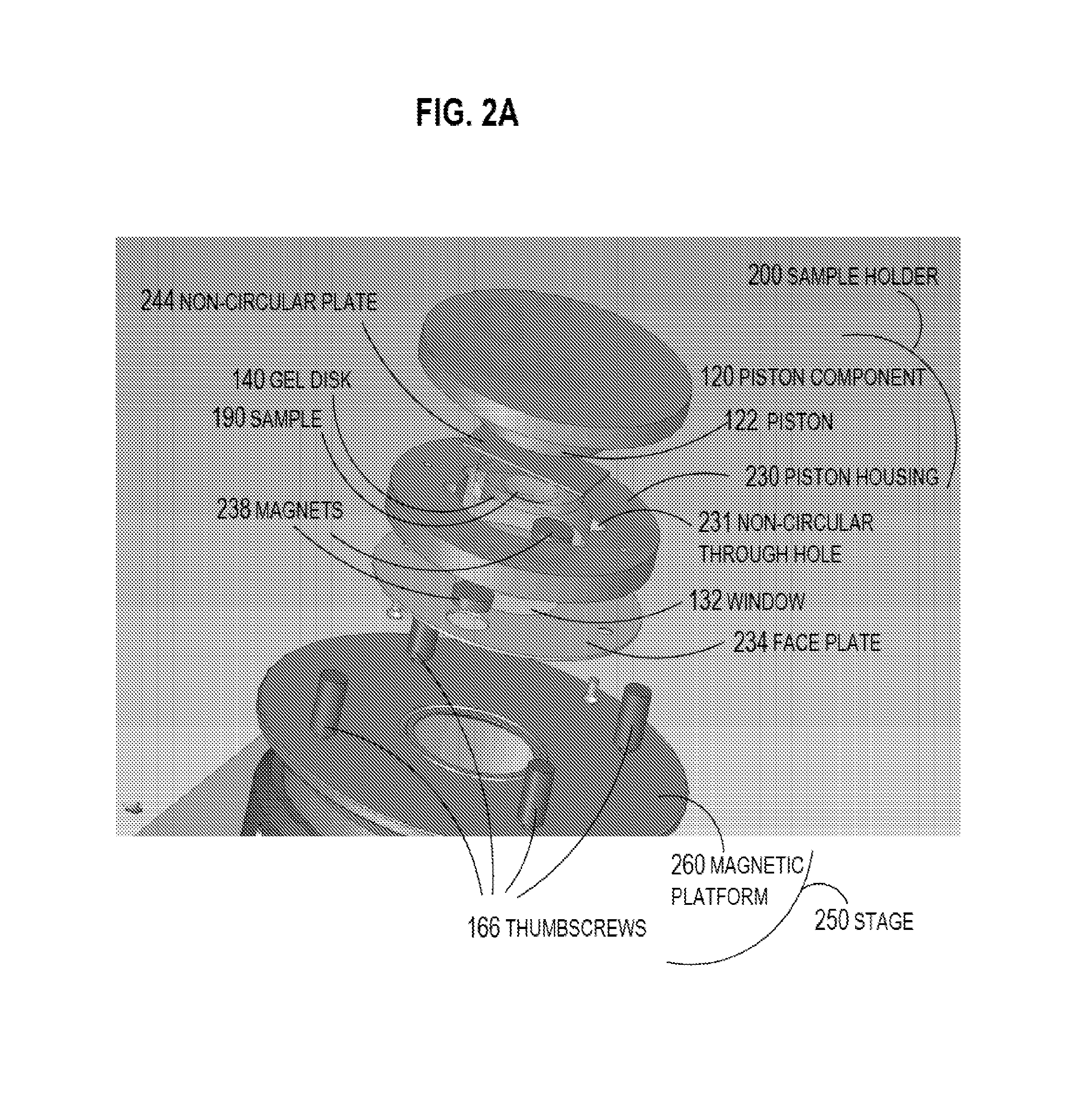
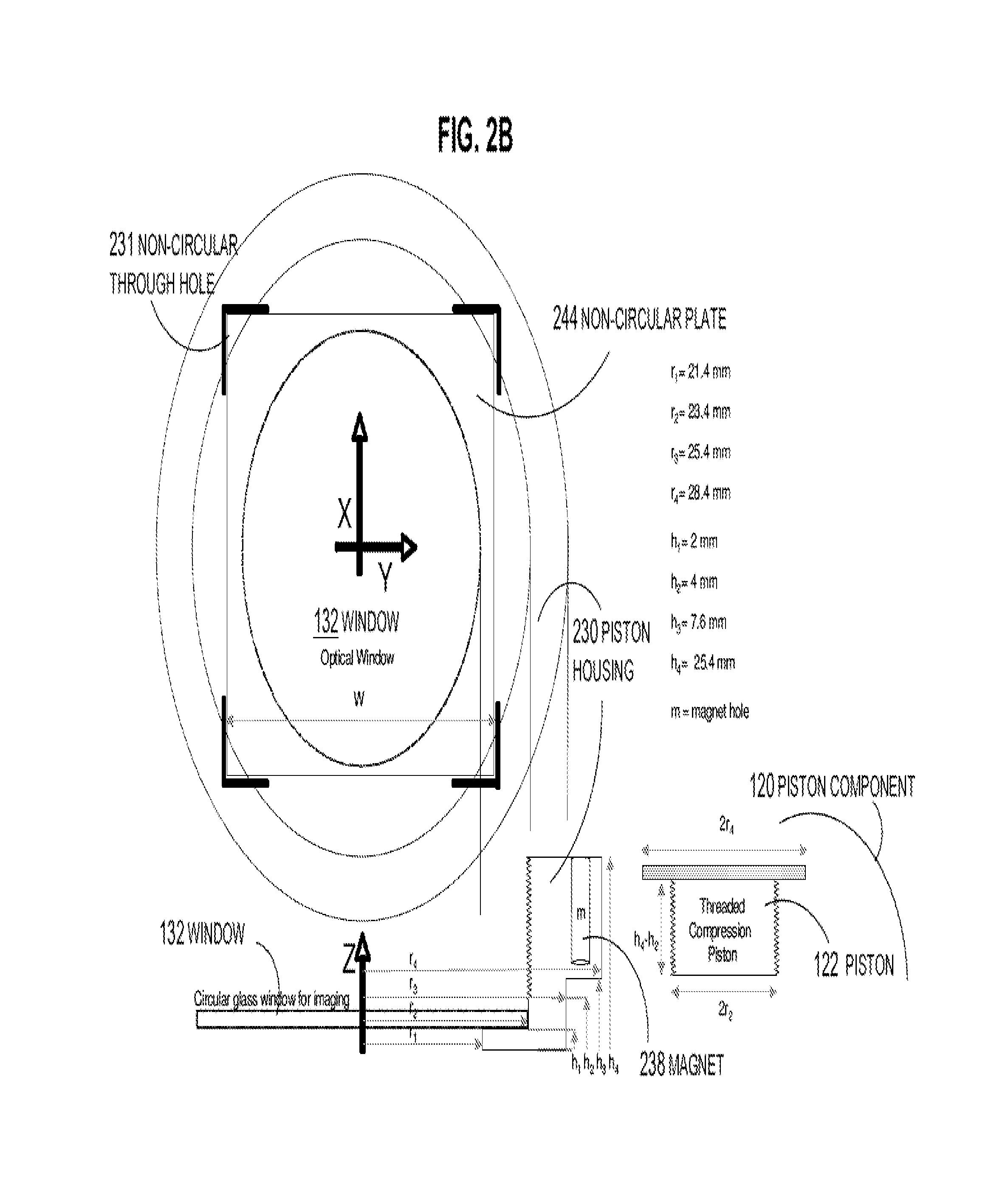
One embodiment of techniques for confocal microscopy includes illuminating a spot on a surface of a biological sample. A first emission intensity from the spot is detected in a first range of optical properties; and a second emission intensity in a second range. A pixel that corresponds to the spot is colored using a linear combination of the first and second emission intensities. Sometimes, the pixel is colored to approximate a color produced by histology. In some embodiments, a surface of a sample is contacted with a solution of acridine orange. Then, a spot is illuminated with a laser beam of wavelength about 488 nanometers (nm). Fluorescence emission intensity is detected above about 500 nm. Sometimes, a certain illumination correction is applied. In some embodiments, a sample holder that compresses a sample is removable from a stage that is fixed with respect to a focal plane of the microscope.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
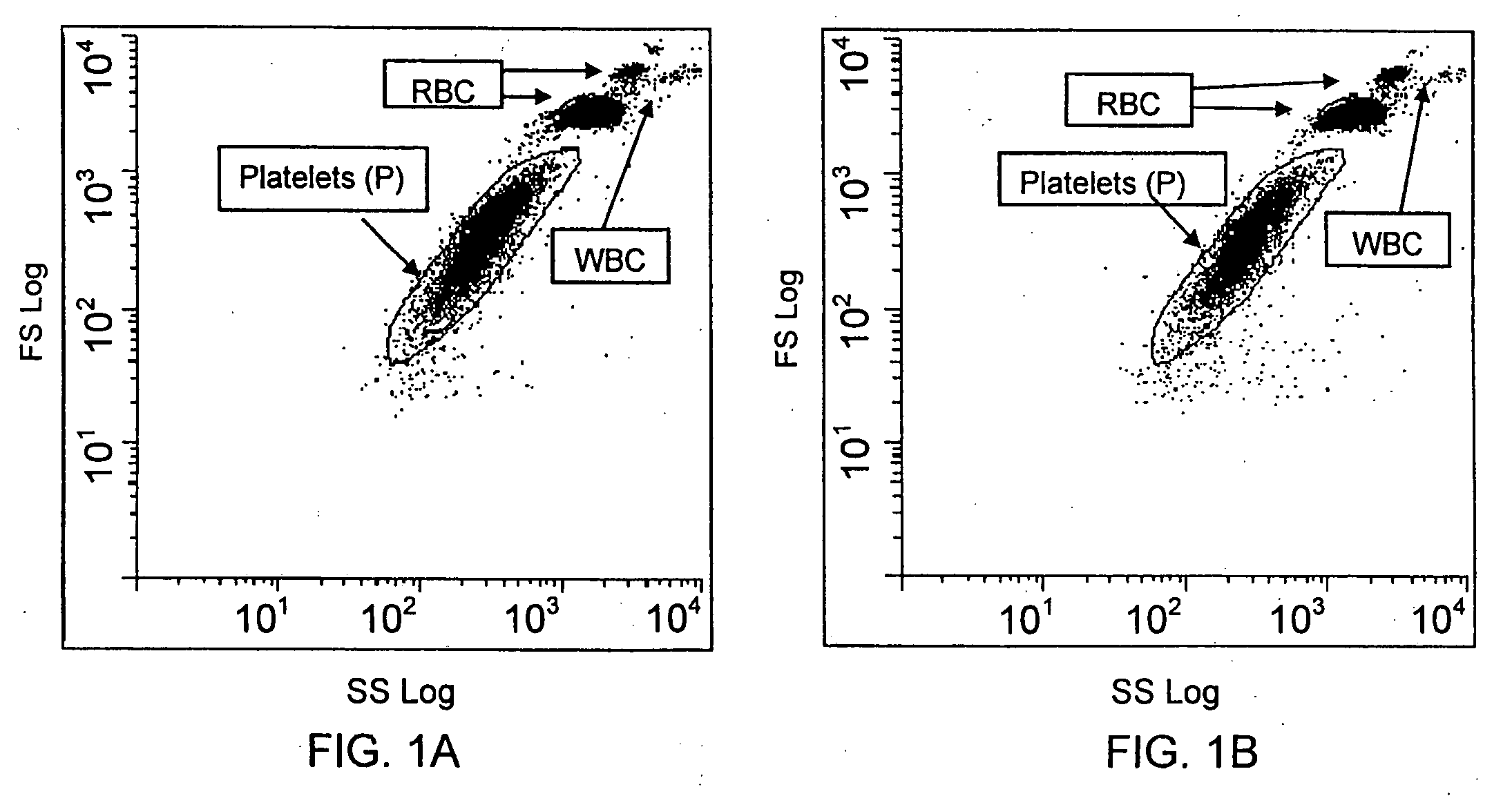
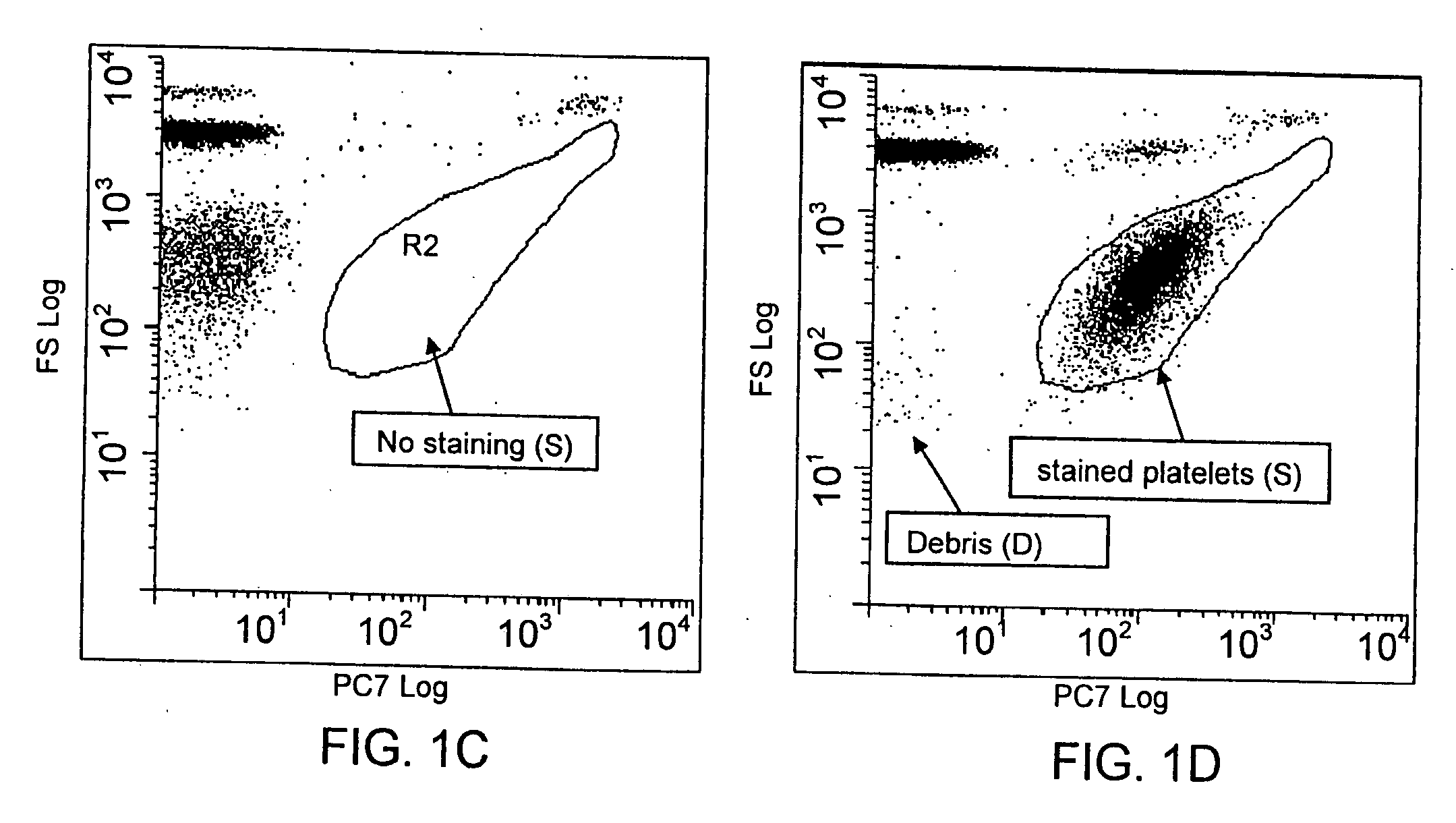
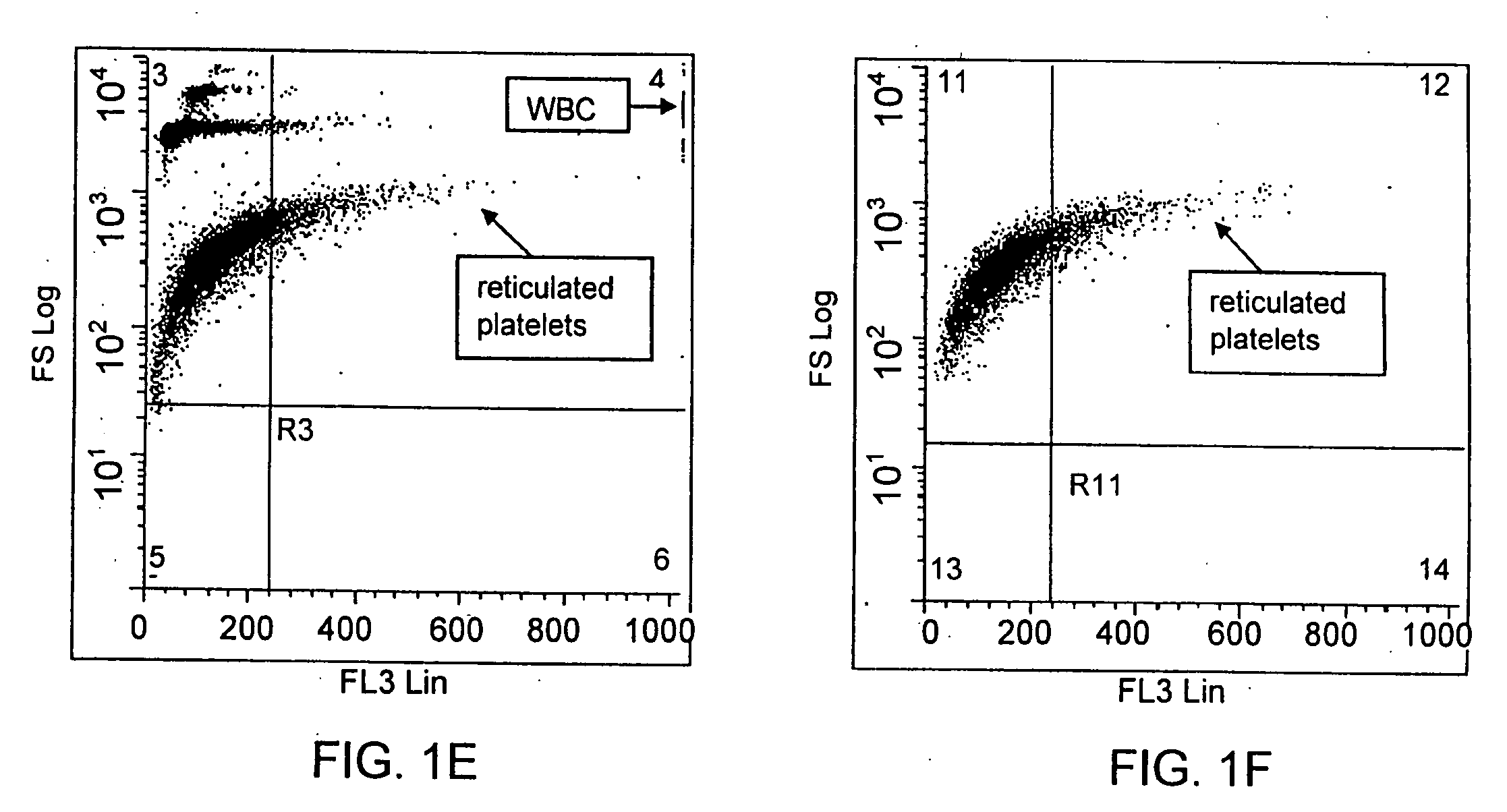
Method for a rapid antibody-based analysis of platelet populations
ActiveUS20090111118A1Quick analysisShort incubation timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceLaser light
A method for identifying a platelet population, preferably a population of immature, reticulated platelets, in a biological sample involves incubating the biological sample for less than minutes with at least one labeled, ligand (e.g., monoclonal antibody) that binds to an epitope or antigen on platelets and with a nucleic acid dye. In one embodiment, the dye is Acridine Orange and the label on the ligand is PE-Cy7. The sample is then analyzed and one or more platelet populations is rapidly identified or quantified by passing the incubated sample through a sensing region of a flow cytometer. In one embodiment, this method occurs without a washing or physical cell separation step. The incubated sample is irradiated with a laser light source, and fluorescence of the labeled ligand and the nucleic acid dye are measured along with at least one additional parameter, e.g., light scatter, direct current, axial light loss, opacity, radio frequency, and fluorescence. These parameters are used to identify qualitatively or quantitatively the platelet populations in the sample. This rapid analytic method is particularly valuable in clinical situations where either low platelet counts or interfering conditions lead to inaccuracies of the platelet measurement. This method is suitable for performance in an automated hematology analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method for producing high-yield gamma-propalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN102174449ALow costImprove brain functionBacteriaChemical industryFood engineeringBioconversion
The invention relates to a method for producing high-yield gamma-propalanine and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biotechnology medicine and food engineering. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out strain separated screening, acridine orange-ultraviolet ray mutagenesis and N<+> injection mutagenesis to obtain a high-yield gamma-propalanine LactobacillusbrevisTCCC (CGMCC No.3414) strain; optimizing a fermentation medium and fermentation conditions; coupling fermentation of the gonotokont of the strain with resting cell biotransformation of the strain to produce the gamma-propalanine; employing the membrane filtration technology, the adsorbent resin decoloration technology, the strong acid resin cation exchange technology, the ethanol recrystallization technology, the preparative chromatography technology and the energy-saving and cost-reducing technology to separate the gamma-propalanine from the fermentation fluid and the biotransformation fluid; and then carrying out purification to obtain the crystallized gamma-propalanine with the purity of 99%. The method has the advantages of cheap raw materials, low energy consumption for production, low production cost, good product security and easy realization of industrialized production. Applied to glutamic acid fermentation waste liquor for producing the gamma-propalanine, the strain has good potential for generating social and economic benefits.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
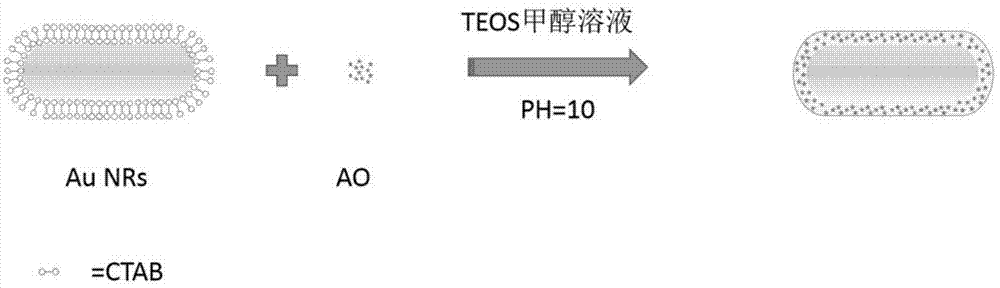
Nanometer golden rod used for detecting bovine serum albumin and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104707998AGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityFluorescence
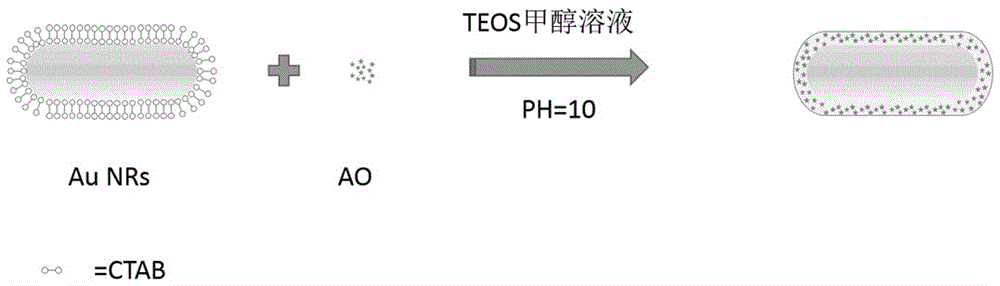
The invention discloses a nanometer golden rod which is wrapped in fluorescent dye, provided with a core-shell structure and used for detecting bovine serum albumin and a preparation method and application thereof. First, HAuCl4 in a CTAB solution at a certain concentration is reduced through NaBH4 so that gold seeds can be obtained; then silver nitrate is added in a solution containing CTAB and sodium oleate, and HAuCl4 is added after standing; ascorbic acid is added, finally, the gold seeds which are obtained before are added, mixtures grow overnight, and the gold nanorod which is uniform in shape is finally obtained; acridine orange dye is added in a gold nanorod solution at a certain concentration under the condition of violent stirring, the pH value is adjusted to 10 through a NaOH solution, then, a mixed solution is slowly stirred, a methanol solution of tetraethyl silicate is added many times in the mode that a small number of methanol solution of the tetraethyl silicate is added each time, finally the solution is stirred for 24 hours so that the gold nanorod of the core-shell structure can be obtained. The composite nanometer materials obtained through the synthesis method are good in water solubility and biocompatibility and uniform in shape, when the bovine serum albumin is detected, signals are stable, linearity is good, and detection is fast and easy.
Owner:JIANGSU DONGRUN MEDICAL SCI & TECH
Method for measuring carbendazim in water by using supramolecular complex fluorescence probe
ActiveCN104819970ARapid Field DetectionSimple methodFluorescence/phosphorescencePesticide residueAcridine orange
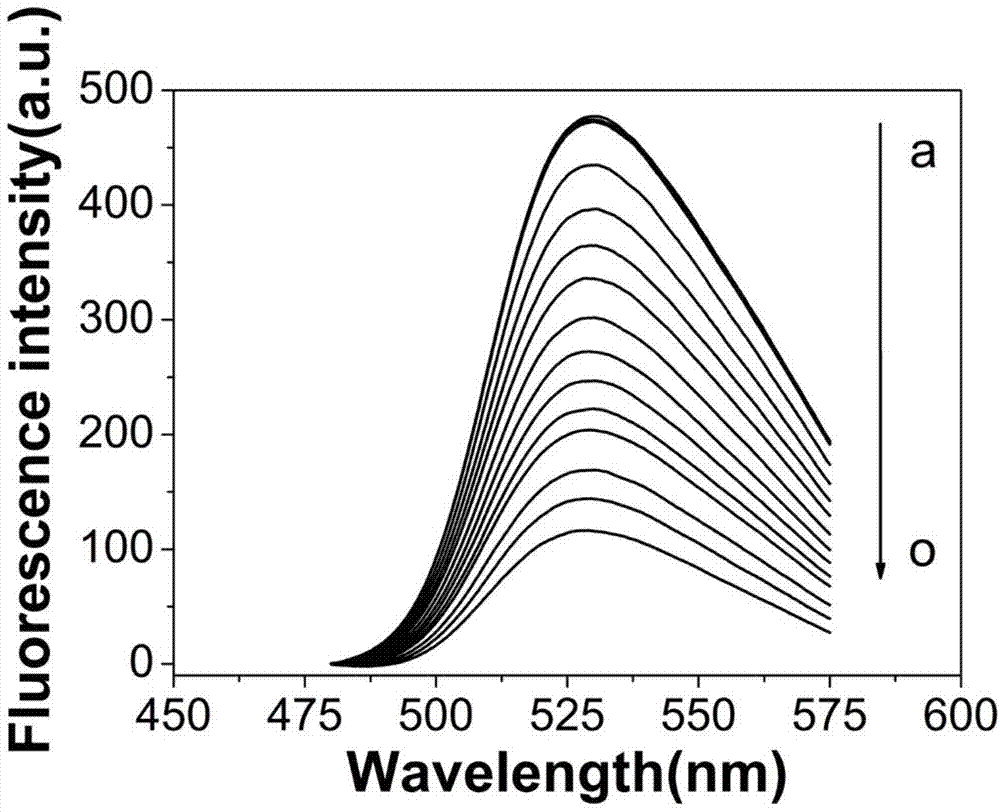
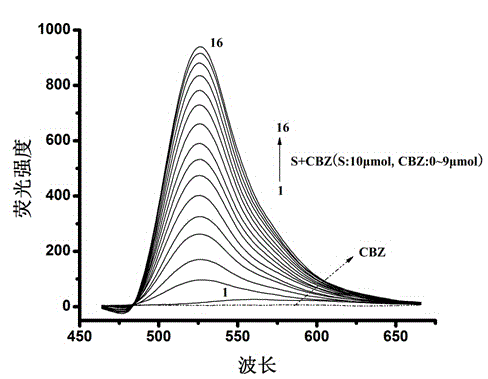
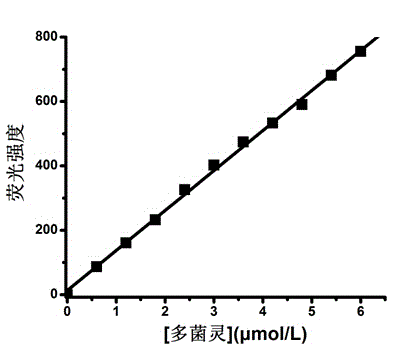
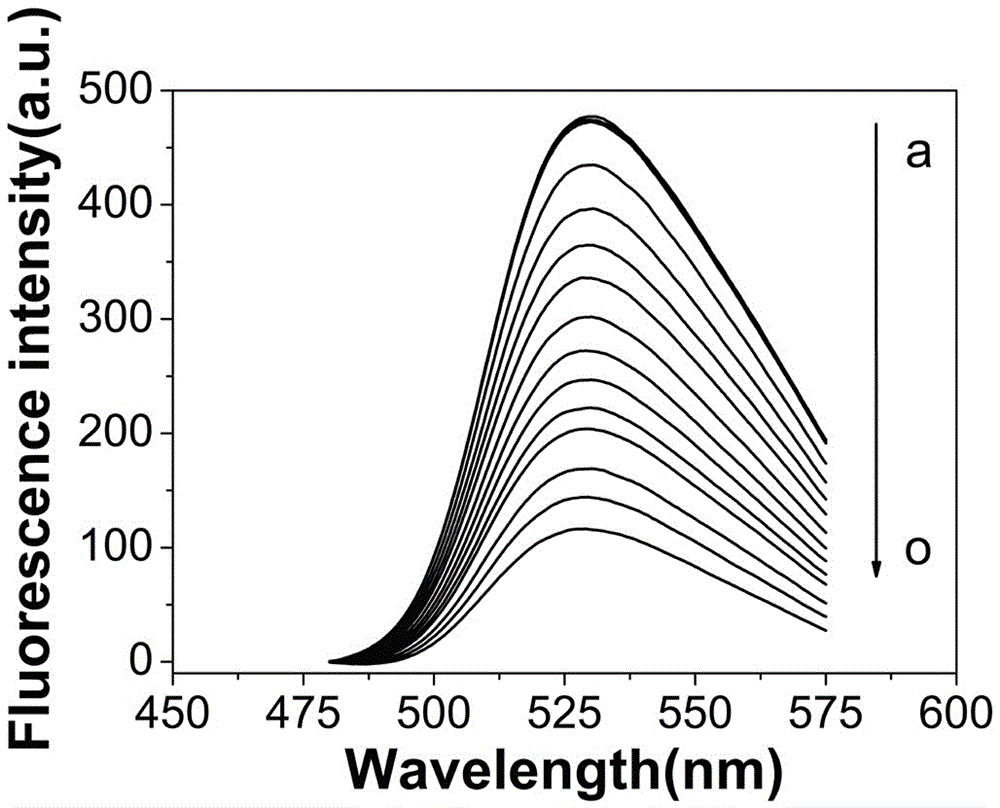
The invention relates to a method for measuring carbendazim in water by using a supramolecular complex fluorescence probe, belonging to the technical field of analytical chemistry. According to the principle that fluorescence quenching of a dye acridine orange can be caused according to a Cucurbit(8) uril supramolecular complex generated by Cucurbit(8) uril and acridine orange and the fluorescence intensity of the Cucurbit(8) uril supramolecular complex can be enhanced by virtue of carbendazim, the Cucurbit(8) uril supramolecular complex formed by the Cucurbit(8) uril and acridine orange according to the molar concentration ratio of 1:1 serves as a fluorescence probe, the fluorescence intensity at the fluorescence emission wavelength of 529nm is obviously enhanced after the carbendazim is added into the fluorescence probe solution, change of the fluorescence intensity of the probe and the concentration of the carbendazim have a good linear relation in a certain range, and the residual carbendazim in the water can be detected. According to the method, the carbendazim in the water can be simply, rapidly and sensitively detected, and a novel method is provided for detecting pesticide residues.
Owner:中知在线股份有限公司
Dyeing liquid as well as dyeing method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101225428ASignificant production and application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic examColor changes
The invention relates to a dyeing liquor used to discriminate the protozoan cell activity, a method to discriminate the protozoan cell activity and the application of the method to discriminate activity of nosema bombycis, which is characterized in that: the dyeing liquor comprises the following components: three acridine oranges with the concentration of 0.05% to 0.3% and one propidium iodide with the concentration of 0.0067% to 0.026%; the acridine oranges and the propidium iodide are prepared by NaCl solution with the concentration of 0.38%; the method to discriminate the protozoan cell activity comprises adequate material choosing, dyeing liquor preparing, dyeing, microscopic examination and protozoan cell activity discriminating based on the color change of microscopic examination results. The dyeing liquor used to discriminate the protozoan cell activity has the advantages that: the spore activity of nosema bombycis can be discriminated quickly, sensitively, accurately and visually; the deficiency of the prior art is overcome.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for producing high-yield gamma-propalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN102174449BLow costImprove brain functionBacteriaChemical industryFood engineeringBioconversion
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing pH-responsive carbon nanotube fluorescent probe
InactiveCN101592611ASimple manufacturing methodImprove controllabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for preparing pH-responsive carbon nanotube fluorescent probe in the technical field of nano materials, which comprises the following steps: mixing a carbon nanotube raw material and an oxidizing acid, sequentially subjecting the mixture to supersonic treatment, stirring treatment and suction filtration, and washing the product of the suction filtration till the product is neutral to obtain purified carbon nanotubes; mixing the purified carbon nanotubes with the oxidizing acid again, sequentially subjecting the mixture to supersonic treatment, secondary stirring treatment and suction filtration, and washing the product of the suction filtration till the product is neutral to obtain purified cut nanotubes; and subjecting aqueous solution of purified cut nanotubes to supersonic treatment, adding acridine orange into the aqueous solution, subjecting the mixture to supersonic treatment again, keeping the mixture away from light, stirring the mixture, subjecting the mixture to suction filtration, washing and dialyzing the product of the suction filtration, and drying the product at room temperature under vacuum to obtain the pH-responsive carbon nanotube fluorescent probe. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, easy to implement and high in controllability. The product of the method has a unique pH- responsive property and has wide application prospects in terms of nanoscience, materials science, biomedical science and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
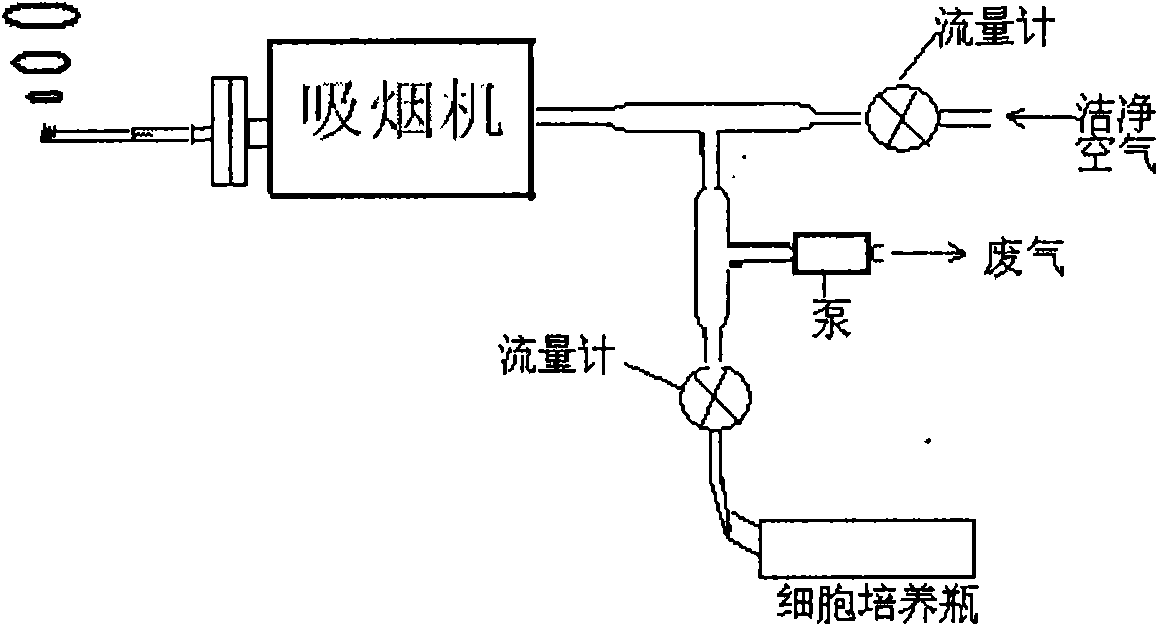
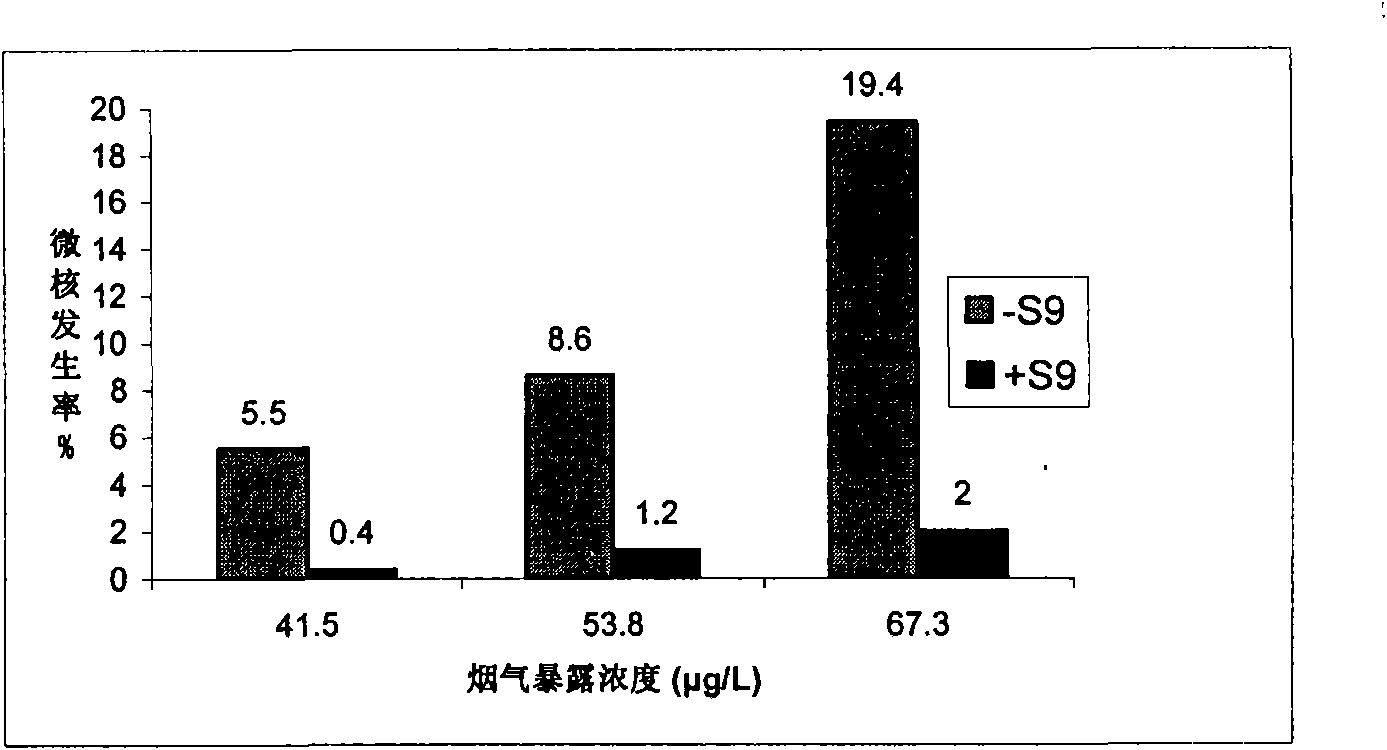
Cigarette mainstream smoke genotoxicity measurement method
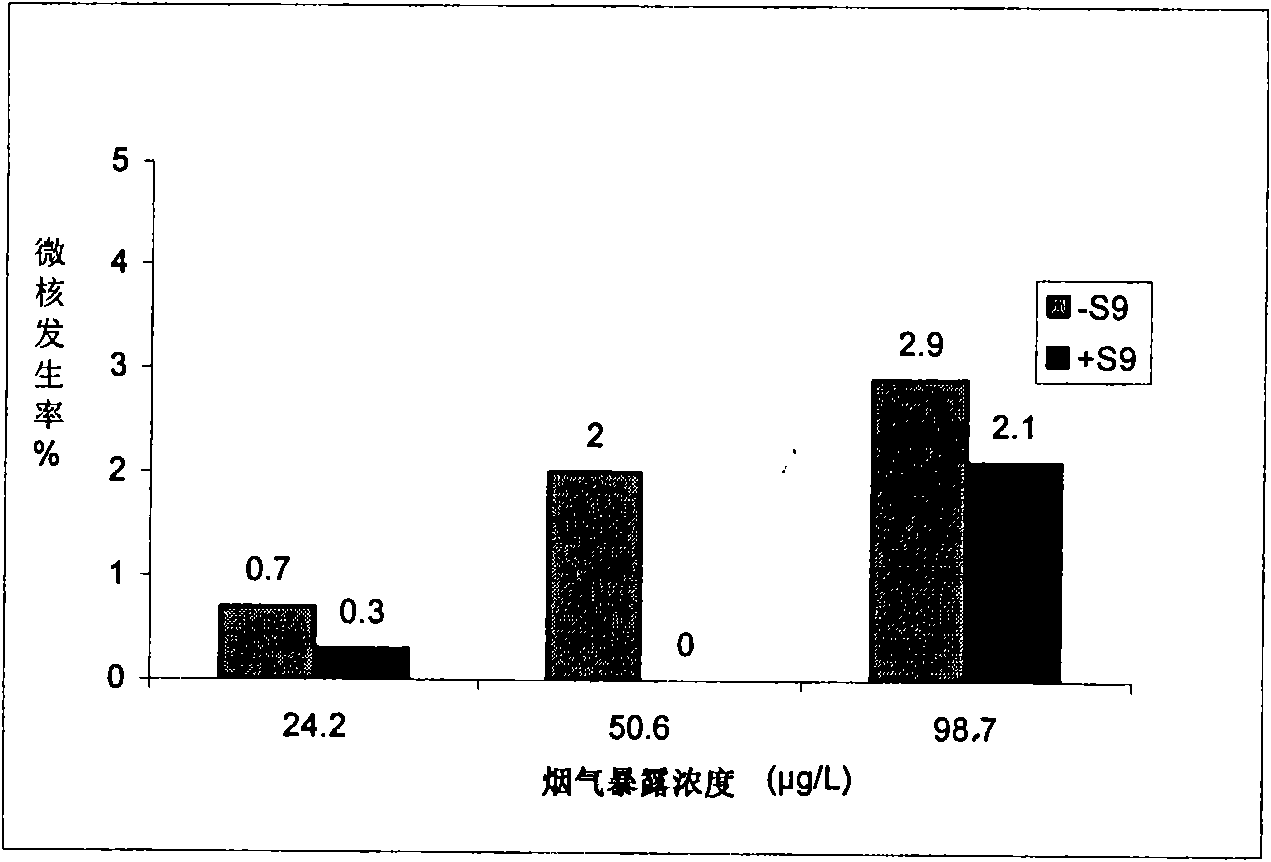
ActiveCN101580869AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMultinucleateFluorescence
A cigarette mainstream smoke genotoxicity measurement method is characterized in that: the cultured cells are directly placed in cigarette mainstream smoke diluted by pure air to expose, the exposed cells are cultured, centrifuged and fixed by cold methanol, acridine orange solution is used for the fluorescent staining for the cells, the stained cells are observed in low power lens to select the region which is distributed evenly and stained well and calculate the number of cells with microkernel(including mononuclear, binuclear and multinuclear) of 500 cells in each sample under fluorescent microscope, the samples is compared with the control sample exposed in pure air to judge whether the cigarette mainstream smoke can increase the cell micronucleus and judge the genotoxicity of the cigarette mainstream smoke. The genotoxicity of the cigarette mainstream smoke can be quantitative evaluated by the invention and the invention has simple operation, high sensitivity and reliable result, thus establishing a new method for measuring cigarette mainstream smoke genotoxicity.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
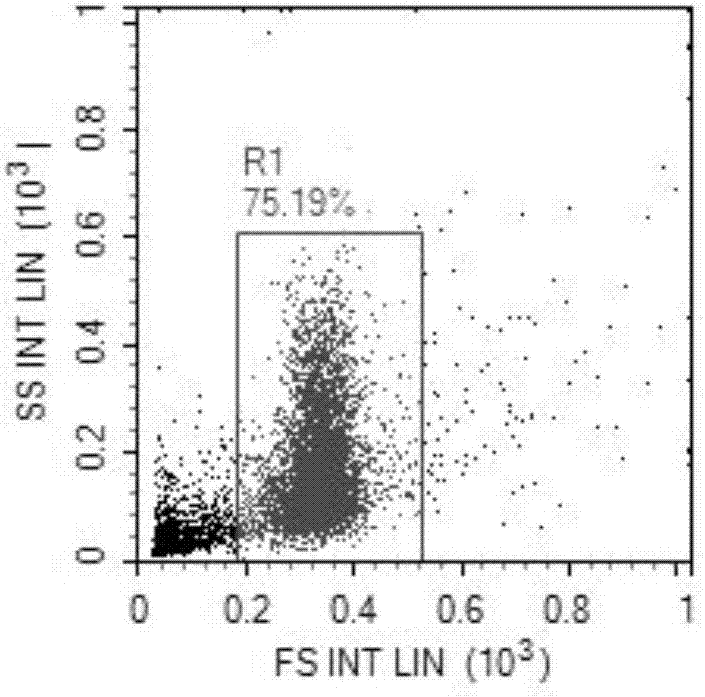
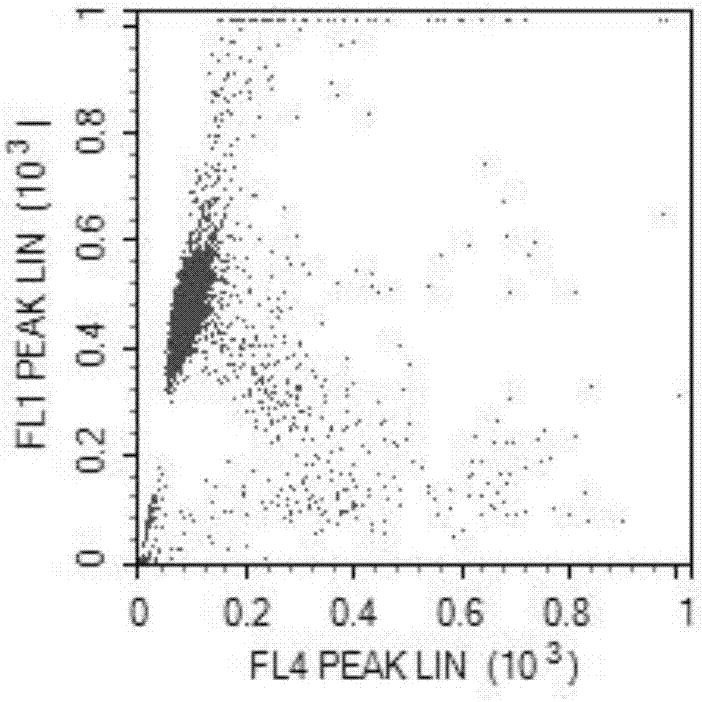
Sperm DFI (DNA Fragmentation Index) detection method based on flow cytometry
InactiveCN106932330AEasy to detectQuick checkIndividual particle analysisStatistical analysisSoftware
The invention discloses a sperm DFI (DNA Fragmentation Index) detection method based on flow cytometry. The sperm DFI detection method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) diluting liquefied seminal fluid to 1-2*10<6> / mL by a buffer solution at the temperature of 37DEG C; (2) adding 500mu L of diluted sperms into a flow cytometer sample loading tube, adding an acidizing buffer solution, and adding an AO (Acridine Orange) staining solution after 30s; (3) setting the calibration of a flow cytometer, putting a detection tube on a machine, and measuring each tube sample for at least two continuous times, wherein each tube sample at least records 5000 cells and carries out statistical analysis by DFIView software; (4) judging ways to carry out result judgment; (5) after measurement is carried out, respectively using decolorizer, sample feeding tube detergent and degerming double distilled water to thoroughly remove cell debris and fluorescent dye in a sample feeding line of the flow cytometer. The sperm DFI detection method has the advantages of simpleness in operation, accurate detection result, stability, reliability, good repeatability and easiness in clinical popularization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CELLPRO BIOTECH
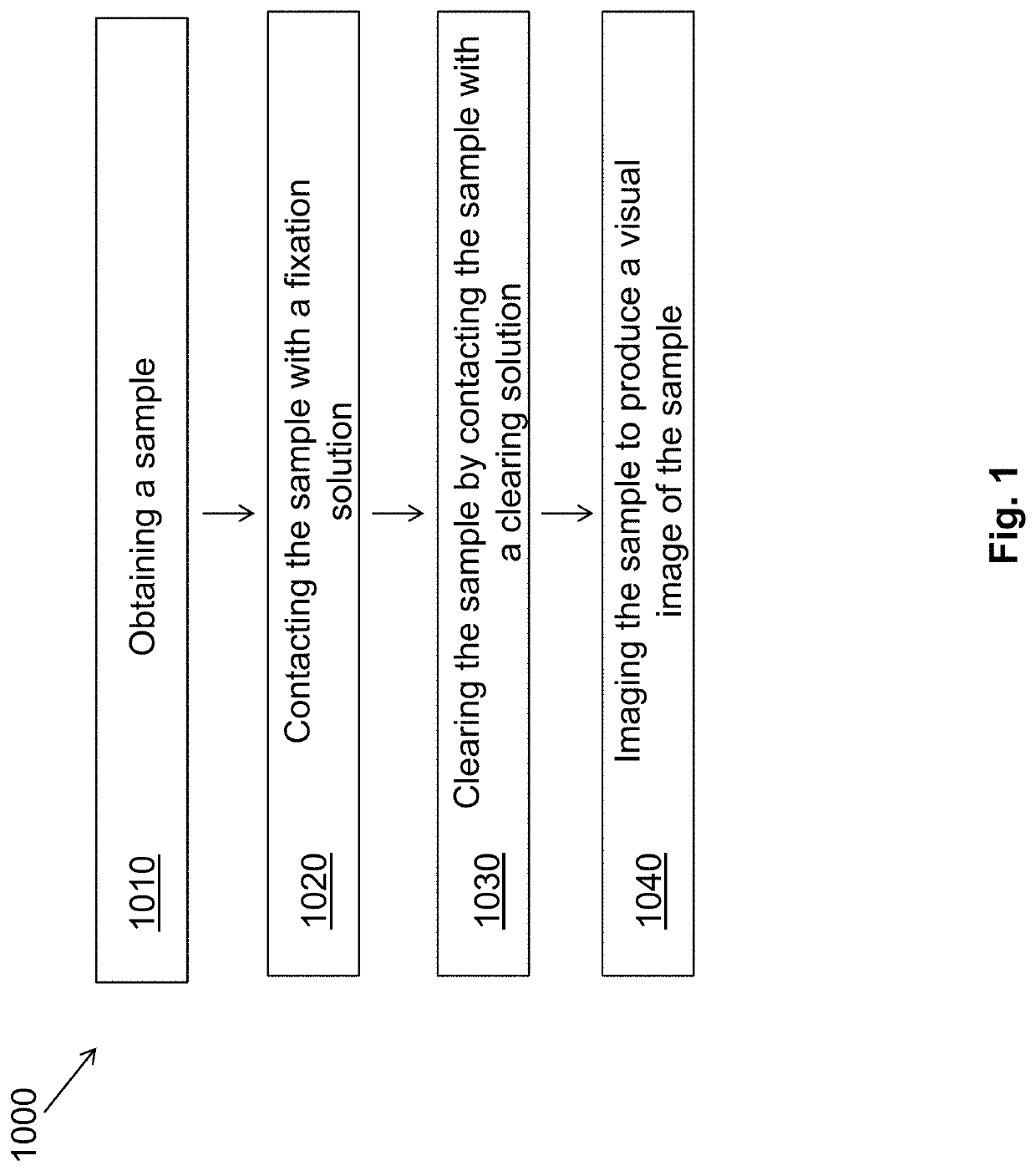
Simultaneous dehydration and staining of tissue for deep imaging
A biopsy-sized tissue sample is stained for quick imaging. A significant amount of permeation enhancer is included in a mixed solution of permeant enhancer, fixative or dehydrant, and one or two fluorescent dyes to simultaneously dehydrate and dye the tissue sample. The permeation enhancer, e.g., 10% to 50% in the mixed solution, achieves an image of dyed tissue in the contacted tissue sample at a depth of at least 200 um within no more than 1.5 hours. One of the fluorescent dyes is a fluorescent nuclear dye such as DAPI, SYTOX green, acridine orange, propidium iodide, or a Hoechst dye. The other fluorescent dye is a fluorescent protein dye such as eosin or rhodamine B. The tissue sample is cleared with a clearing agent having a refractive index of at least 1.4[R2], e.g., using BABB. The mixed solution may further include Chloroform or other morphology preservative.
Owner:APPLIKATE TECH INC
Descaling and corrosion inhibiting composition
ActiveUS20060142170A1Efficient descalingHighly effectiveSpecific water treatment objectivesHollow article cleaningProcess equipmentAcridine orange
The present invention is directed to a composition, and a process employing same, for descaling, cleaning and inhibiting the corrosion of process equipment made of steel by including an inhibitory effective amount of acridine orange in the composition.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Novel method for in vitro culturing and staining Neospora caninum tachyzoites
InactiveCN102533556AThe cultivation method is simpleQuick observationProtozoaMicrobiological testing/measurementNeospora speciesMicroscopic observation
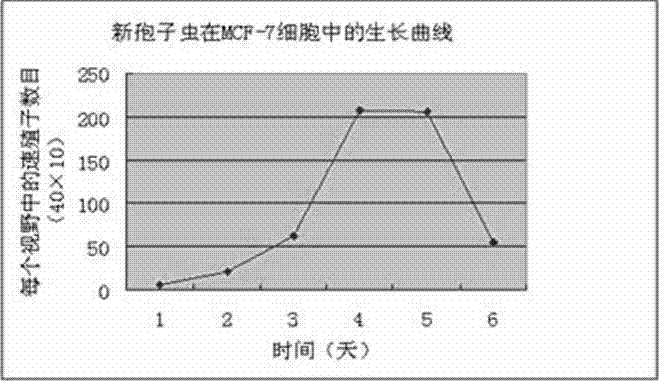
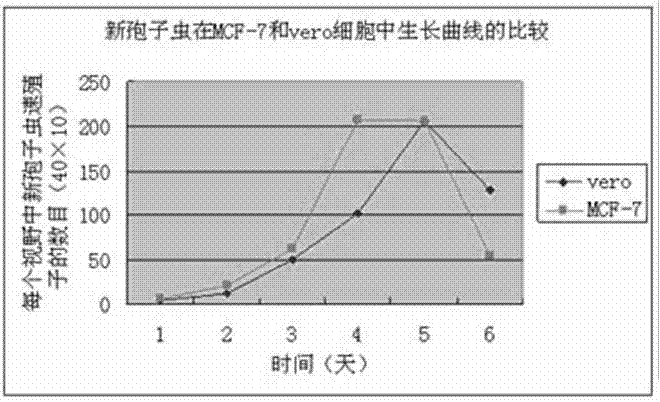
The invention relates to a novel method for in vitro culturing and staining Neospora caninum tachyzoites, which is characterized in that the concrete culturing steps are as follows: culturing MCF-7 breast cancer cells using a conventional method, inoculating in 1ml Neospora caninum at an inoculum size of 10<4> / ml after the cells grow to form a monolayer of cells, culturing with RPIM-1640 medium containing 2% fetal bovine serum, and observing the number of extracellular Neospora caninum tachyzoites with an inverted microscope everyday; and the concrete staining steps are as follows: fixing Neospora caninum tachyzoites with paraformaldehyde, staining with acridine orange, and observing and taking photos with a common fluorescence microscopy. The culturing method of the invention is simple and practical, and Neospora caninum tachyzoites can be rapidly cultured. In addition, after acridine orange staining, intracellular parasites can be rapidly, visually and clearly observed with the common fluorescence microscopy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
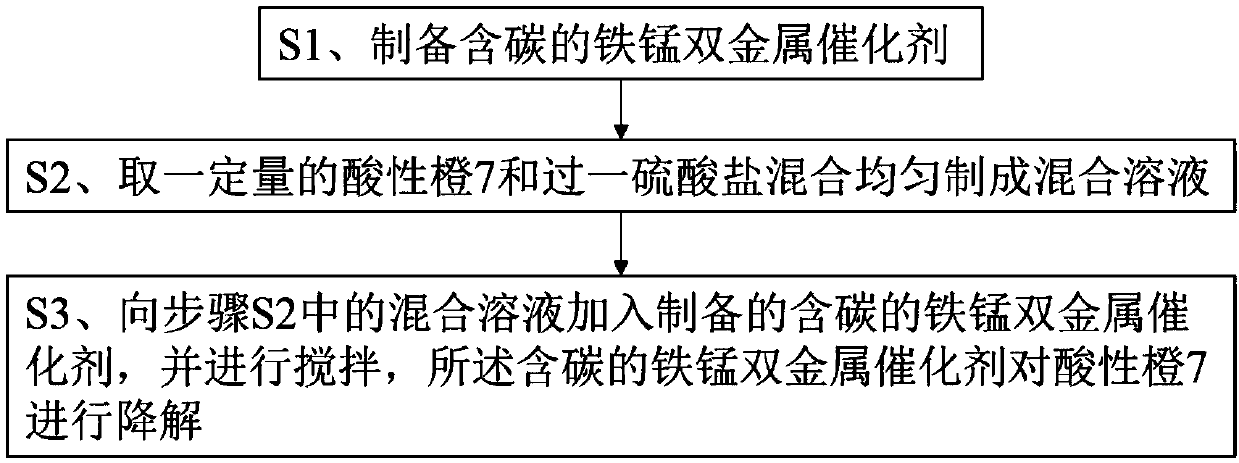
Method for degrading acid orange 7 through ferro-manganese bimetallic catalyst containing carbon
ActiveCN109626545AMagneticImprove utilization efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWater contaminantsSulfateManganese
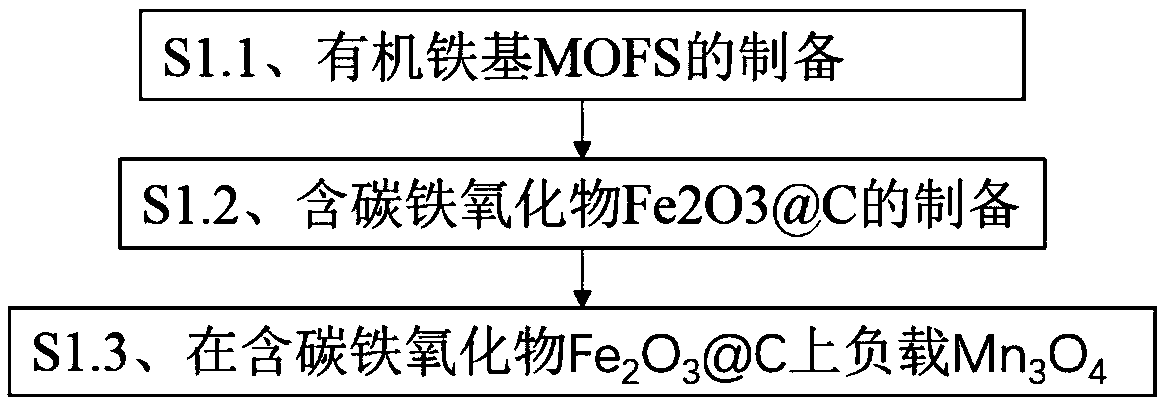
The invention relates to a method for degrading the acid orange 7 through a ferro-manganese bimetallic catalyst containing carbon and belongs to the technical field of water pollution treatment. The method for degrading the acid orange 7 comprises the specific steps that S1, the ferro-manganese bimetallic catalyst containing carbon is prepared; S2, a certain amount of acid orange 7 and peroxymonosulfate are evenly mixed to prepare a mixed solution; S3, the prepared ferro-manganese bimetallic catalyst containing carbon is added to the mixed solution in the second step, stirring is conducted, and the acid orange 7 is degraded through the ferro-manganese bimetallic catalyst containing carbon. According to the method, through the cooperation effect of iron and manganese in the ferro-manganesebimetallic catalyst containing carbon, respective reactions for circulation and catalysis of peroxymonosulfate are manually promoted, the efficiency of using the catalyst and an oxidant is high, and the effect of degrading the acid orange 7 is good. Meanwhile, the pH application range of the catalyst in the method is wide, the catalyst material has the magnetism, convenience is provided for circulation recycling of a magnetic separation method, and secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Rapid confocal microscopy to support surgical procedures
ActiveUS9176310B2Prevent lateral movementMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationOptical propertyFluorescence
One embodiment of techniques for confocal microscopy includes illuminating a spot on a surface of a biological sample. A first emission intensity from the spot is detected in a first range of optical properties; and a second emission intensity in a second range. A pixel that corresponds to the spot is colored using a linear combination of the first and second emission intensities. Sometimes, the pixel is colored to approximate a color produced by histology. In some embodiments, a surface of a sample is contacted with a solution of acridine orange. Then, a spot is illuminated with a laser beam of wavelength about 488 nanometers (nm). Fluorescence emission intensity is detected above about 500 nm. Sometimes, a certain illumination correction is applied. In some embodiments, a sample holder that compresses a sample is removable from a stage that is fixed with respect to a focal plane of the microscope.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting acid orange and application of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit
The invention provides an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting acid orange. The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit comprises an elisa plate coated with coating antigen, an acid orange monoclonal antibody, an enzyme-labeled marker, an acid orange standard product solution, a substrate coloring solution, a stopping solution, a cleaning solution and a redissolved solution, wherein the coating antigen is an acid orange coupled antigen, and the enzyme-labeled marker is the enzyme-labeled antiantibody. The invention further discloses a method for detecting acid orange by applying the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit. The method comprises the following steps: firstly conducting sample pretreatment, then detecting with the assay kit, and finally analyzing the detection results. The provided enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit can be used for quickly detecting the content of acid orange in pickled stewed meat, bean paste and chilli sauce, is simple and convenient in operation, low in cost and high in sensitivity, can realize on-site supervision and is suitable for mass sample screening.
Owner:BEIJING KWINBON BIOTECH
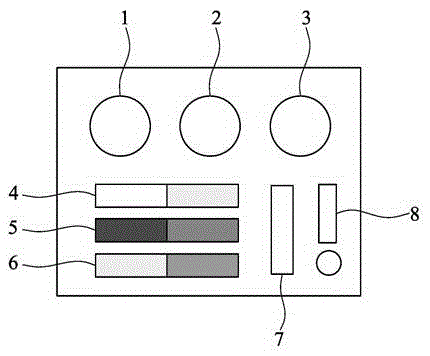
Device and method for rapidly detecting basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow
InactiveCN105588832AQuick screeningAvoid colors close toMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPipetteColorimetric analysis
The invention discloses a device for rapidly detecting basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow. The device comprises a reagent bottle filled with extraction reagent, a reagent bottle filled with a color developing agent, a reagent bottle filled with diluent, colorimetric identification cards, a filter and a transfer pipette, and the colorimetric identification cards comprise three sets of double color cards which are used for indicating existence of basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow respectively. The invention further discloses a corresponding method for rapidly detecting basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow. According to the device and method for rapidly detecting basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow, the color developing agent and the diluent are sequentially added, comparison with color of the color cards at the left side and the right side of a colorimetric card set is made, and according to the matching condition of solution color, under the action of the color developing agent and the diluent, of a sample to be detected with the color at the left side of the colorimetric card set and the color at the right side of the colorimetric card set, whether certain pigment in basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow is contained or not is judged; rapid screening can be achieved, operation is simple and efficient, and the limitation that coloring agents such as basic orange, acid orange and basic tender yellow in traditional colorimetric analysis are similar in color, so that the coloring agents are difficult to differentiate effectively and complex equipment is needed to be introduced is avoided.
Owner:XIAMEN HUAXIA UNIV
Gynecological fluorescent staining solution as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114563253ADyeing achievedClear ingredientsPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent stainingDisodium phosphate
The invention discloses a gynecological fluorescent staining solution and a preparation method and application thereof.The gynecological fluorescent staining solution comprises acridine orange, sodium chloride, EDTA-Na, disodium hydrogen phosphate and citric acid, the components can be combined with different cell substances for staining, so that fluorescence of different colors is displayed under the action of exciting light, the components are clear after staining, and the staining effect is good. Different components present different colors and are easy to identify and distinguish. The preparation method of the gynecological fluorescent staining solution is simple, and the gynecological fluorescent staining solution can be prepared and used at any time and can also be stored and used after being prepared. According to the use method of the gynecological fluorescent staining solution, two nucleic acids, namely DNA and RNA, are mainly displayed, so that the fluorescent staining solution is obvious in luminescence. The use method is simple, observation and detection can be carried out through a fluorescence microscope after the gynecological fluorescent staining solution is dropwise added, the defects of a traditional saline smear method are overcome, and the detection rate is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU XINLONG MEDICAL TREATMENT TECH CO LTD
A nano-gold rod for detecting bovine serum albumin and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN104707998BGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilitySynthesis methods
The invention discloses a nanometer golden rod which is wrapped in fluorescent dye, provided with a core-shell structure and used for detecting bovine serum albumin and a preparation method and application thereof. First, HAuCl4 in a CTAB solution at a certain concentration is reduced through NaBH4 so that gold seeds can be obtained; then silver nitrate is added in a solution containing CTAB and sodium oleate, and HAuCl4 is added after standing; ascorbic acid is added, finally, the gold seeds which are obtained before are added, mixtures grow overnight, and the gold nanorod which is uniform in shape is finally obtained; acridine orange dye is added in a gold nanorod solution at a certain concentration under the condition of violent stirring, the pH value is adjusted to 10 through a NaOH solution, then, a mixed solution is slowly stirred, a methanol solution of tetraethyl silicate is added many times in the mode that a small number of methanol solution of the tetraethyl silicate is added each time, finally the solution is stirred for 24 hours so that the gold nanorod of the core-shell structure can be obtained. The composite nanometer materials obtained through the synthesis method are good in water solubility and biocompatibility and uniform in shape, when the bovine serum albumin is detected, signals are stable, linearity is good, and detection is fast and easy.
Owner:JIANGSU DONGRUN MEDICAL SCI & TECH
Preparation method of porous graphene oxide/CaO/glucose composite adsorbent
InactiveCN109569549ASmall adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPorous grapheneExperimental methods
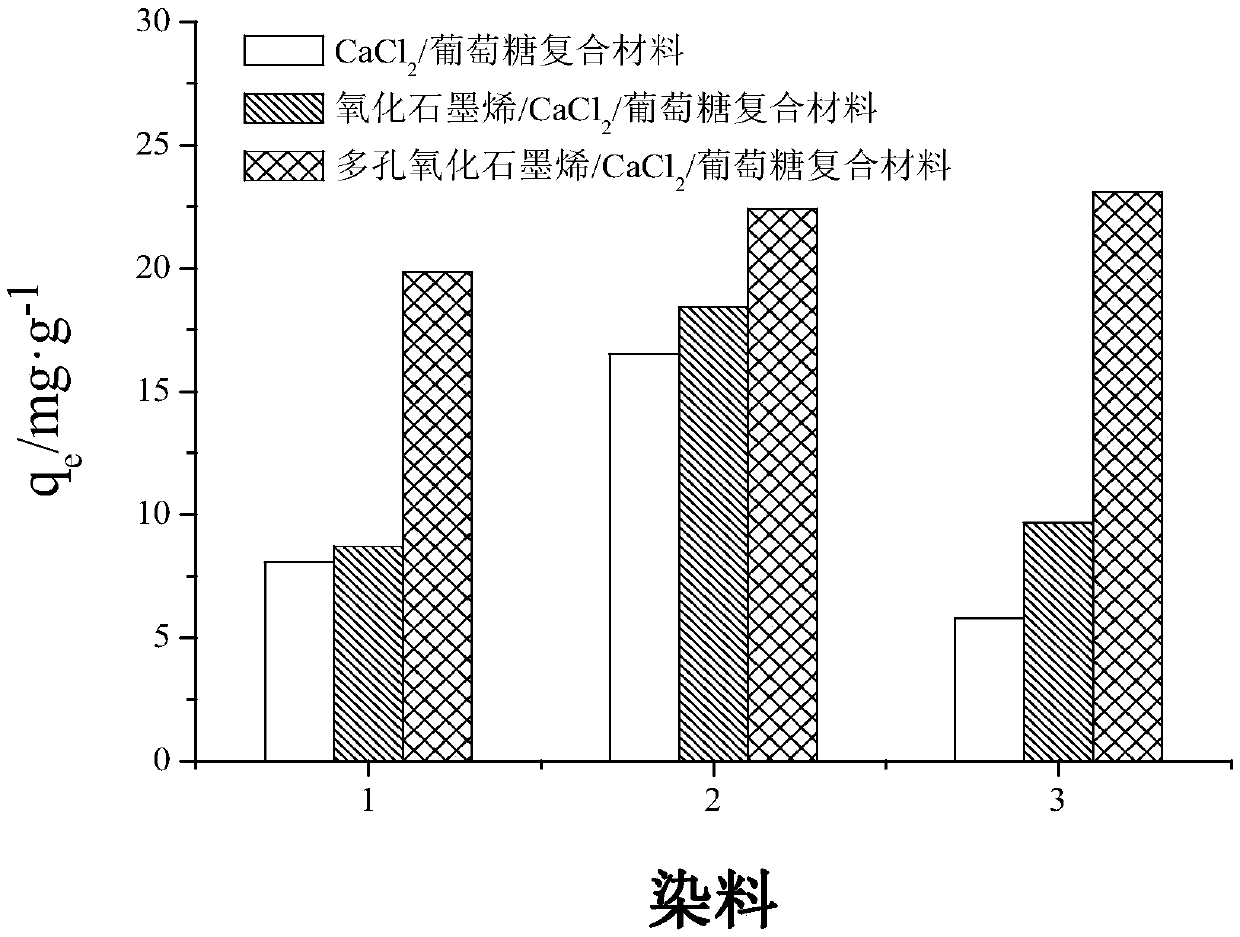
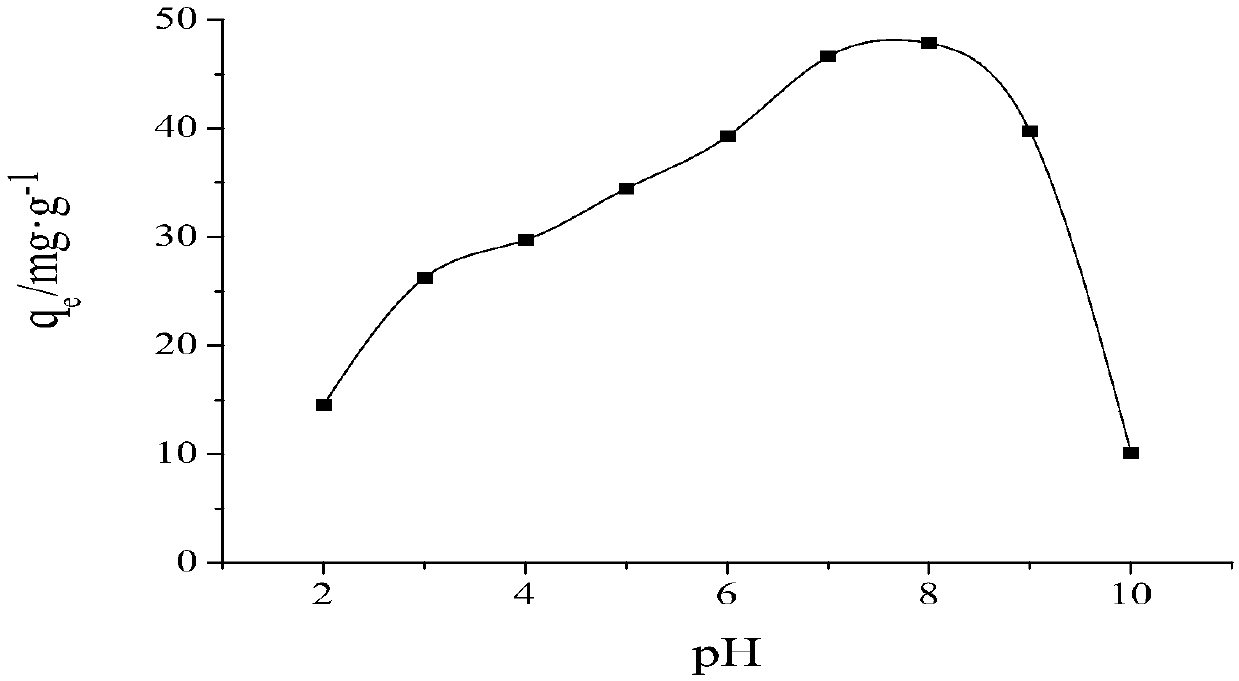
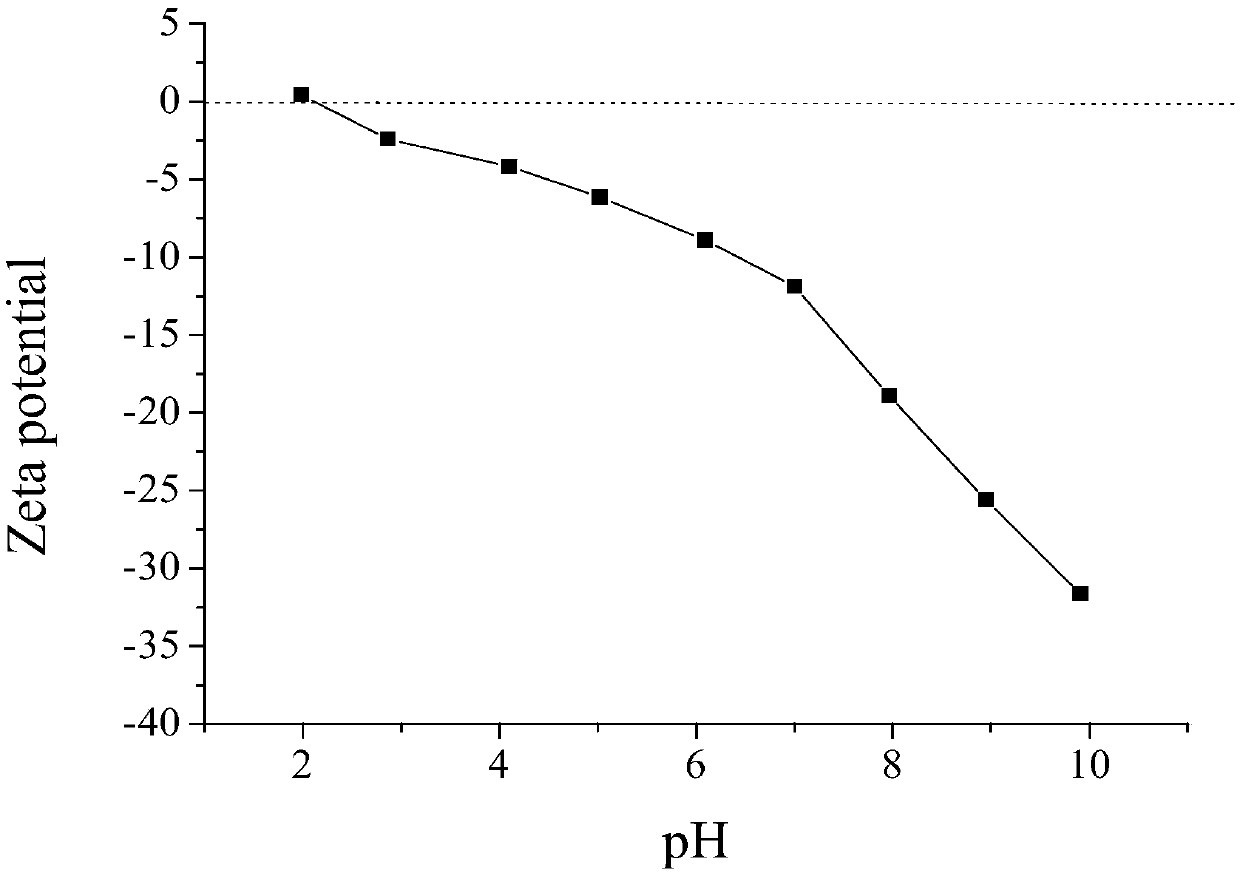
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous graphene oxide / CaO / glucose composite adsorbent, including the steps of firstly, preparation of graphene oxide, to be specific, preparing graphene oxide by a modified Hummer's experimental method; secondly, preparation of a porous graphene oxide / CaO / glucose composite. The porous graphene oxide / CaO / glucose composite has good adsorption effectto dyes of acridine orange, the optimal adsorptive pH value of the adsorbent is equal to 8, and adsorption balance is achieved at the time of 200 minutes. NaCl solution added has great influence on the adsorbability of the adsorbent and isopropanol has low influence on the adsorbability of the adsorbent, that is to say, the porous graphene oxide / CaO / glucose composite has adsorption effect to acridine orange under electrostatic interaction. The adsorbent can be reused for three times.
Owner:XIANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Helicobacter pylori fluorescent staining reagent
PendingCN110411807ACumbersome operationImprove bindingPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingSodium acetateGlycerol
The invention discloses a helicobacter pylori fluorescent staining reagent and belongs to the technical field of medical detection reagents. The helicobacter pylori fluorescent staining reagent comprises, by weight, 0.5-2 parts of acridine orange, 0.5-1.5 parts of acetic acid, 1-5 parts of sodium acetate, 1-5 parts of calcium chloride, 1-3 parts of glycerol, and 1-5 parts of a counterstain. The helicobacter pylori fluorescent staining reagent can stain helicobacter pylori orange red by acridine orange fluorescent staining, so that the helicobacter pylori can be clearly seen under a fluorescence microscope with high contrast between the bacteria and the background, and significantly higher sensitivity than that of conventional straining, the staining can be completed with one step, and a result can be obtained within about 1 minute, thus the helicobacter pylori fluorescent staining reagent is fast and efficient. In addition, acetic acid and sodium acetate are added so that acridine orange has strong binding ability with cell DNA and RNA, so as to achieve good staining effect, and the counterstain has a function of suppressing the background and reducing background stray light. The staining reagent of the invention is more stable, bright in color contrast, and convenient for observation.
Owner:江苏诺鬲生物科技有限公司
Descaling and corrosion inhibiting method
ActiveUS7731803B2Highly effectiveEfficient descalingSpecific water treatment objectivesHollow article cleaningProcess equipmentAcridine orange
The present invention is directed to a composition, and a process employing same, for descaling, cleaning and inhibiting the corrosion of process equipment made of steel by including an inhibitory effective amount of acridine orange in the composition.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
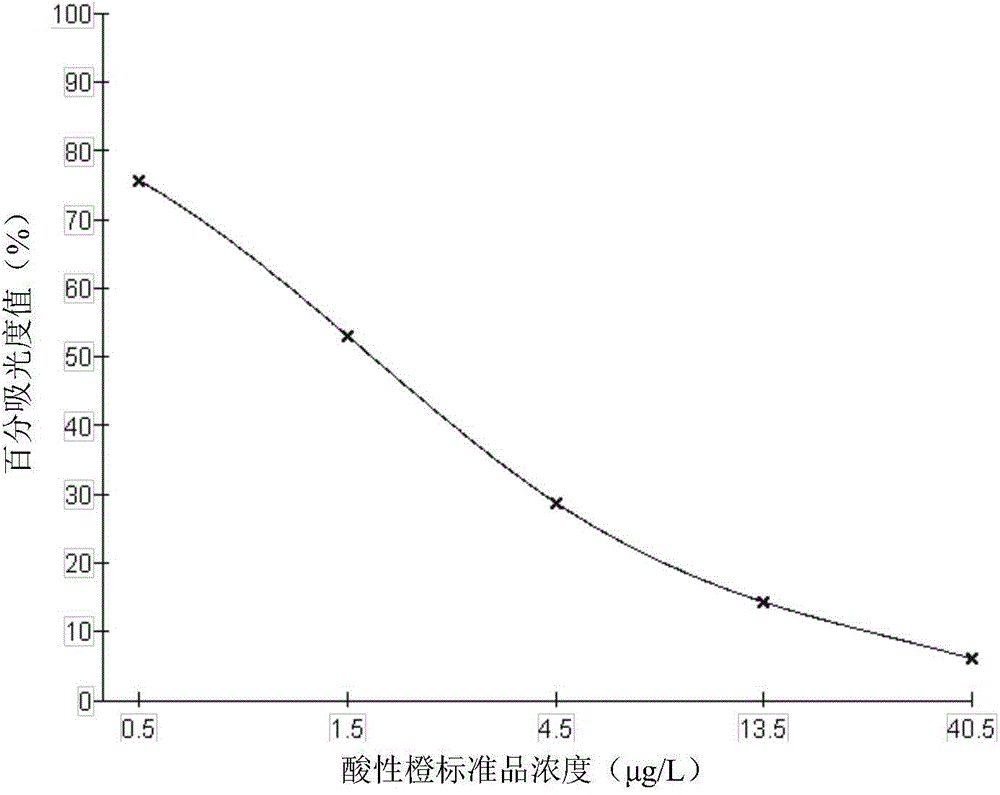
Method for detecting content of acid orange added in chilli powder
InactiveCN105486656AThe detection method has few stepsFew stepsMaterial analysis by optical meansTest sampleTransmittance
The invention discloses a method for detecting content of acid orange added in chilli powder. The method comprises the following steps: (1) chilli powder with different contents of acid orange are used as test samples, and infrared absorption spectrum of each test sample in a set wave range is obtained; (2) according to the infrared absorption spectrum of the test sample, transmissivity of characteristic absorption peak of acid orange is extracted, and absorbance of each characteristic absorption peak is obtained; (3) a linear regression model between the acid orange content and each absorbance is established; (4) absorbance of a sample to be measured at the characteristic absorption peak of acid orange is obtained, and according to the linear regression model, the content of acid orange in the sample to be measured is obtained by calculation. The method has the advantages of simplicity, rapid and high accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preprocessing raw milk
InactiveCN102071245AImprove clarityReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementSubtilisinAcridine orange
The invention relates to a method for preprocessing raw milk, in particular to the method for preprocessing the raw milk which is used for computer identification and counting of somatic cells in the raw milk. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) diluting the raw milk with water according to the weight ratio of a diluted sample to undiluted raw milk of (1-3):1; 2) hydrolyzing the diluted sample by using subtilisin solution at the concentration of between 8 to 9.5 weight percent at the temperature of between 20 and 30 DEG C for 4 to 6 minutes, wherein the subtilisin solution is added according to the volume ratio of the diluted sample to the subtilisin solution of (2.9-3.1):(0.9-1.1); and 3) dyeing the hydrolyzed sample by using acridine orange solution at the concentration of between 5 and 6 weight percent for 7 to 8 minutes, wherein the acridine orange solution is added according to the volume ratio of the hydrolyzed sample to the acridine orange solution of (98-102):1.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI MECHANIZATION SCI
A sperm chromatin structure detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN109115735ANot corrosiveNo oxidationPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisDNA fragmentationAcridine orange
A sperm chromatin structure detection kit and application thereof are provided. The kit includes an A reagent and a B reagent, with the A reagent including HCl, Tween-20 and a phosphate buffer solution, and the B reagent including acridine orange and water. The kit is used in human sperm chromatin DNA staining to determine the chromatin DNA fragmentation level and to calculate the ratio of spermswith DNA fragmentation, and can analyze the ratio of immature sperms through the degree of combination between chromatin and protein.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BOZHEN BIOTECH CO LTD
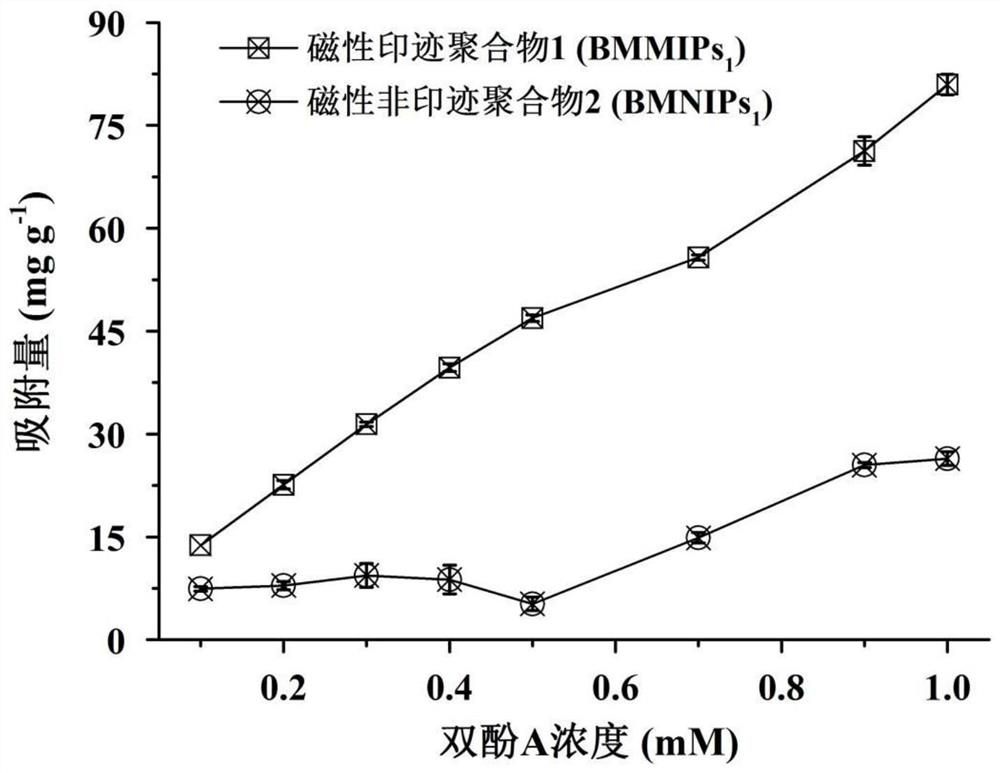
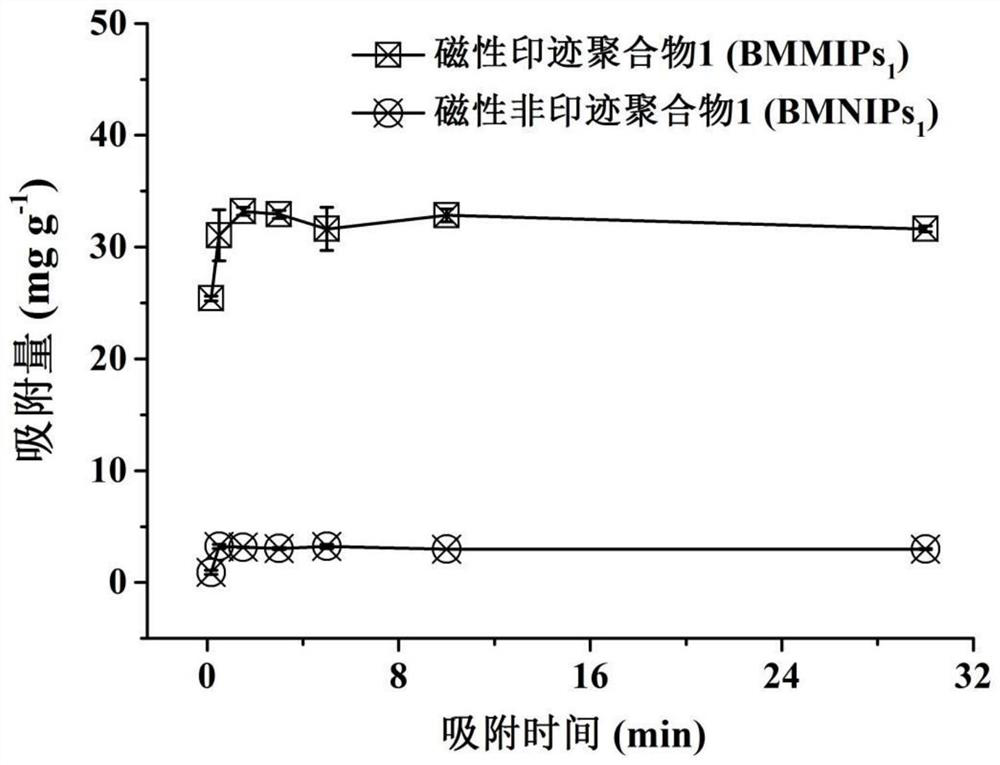
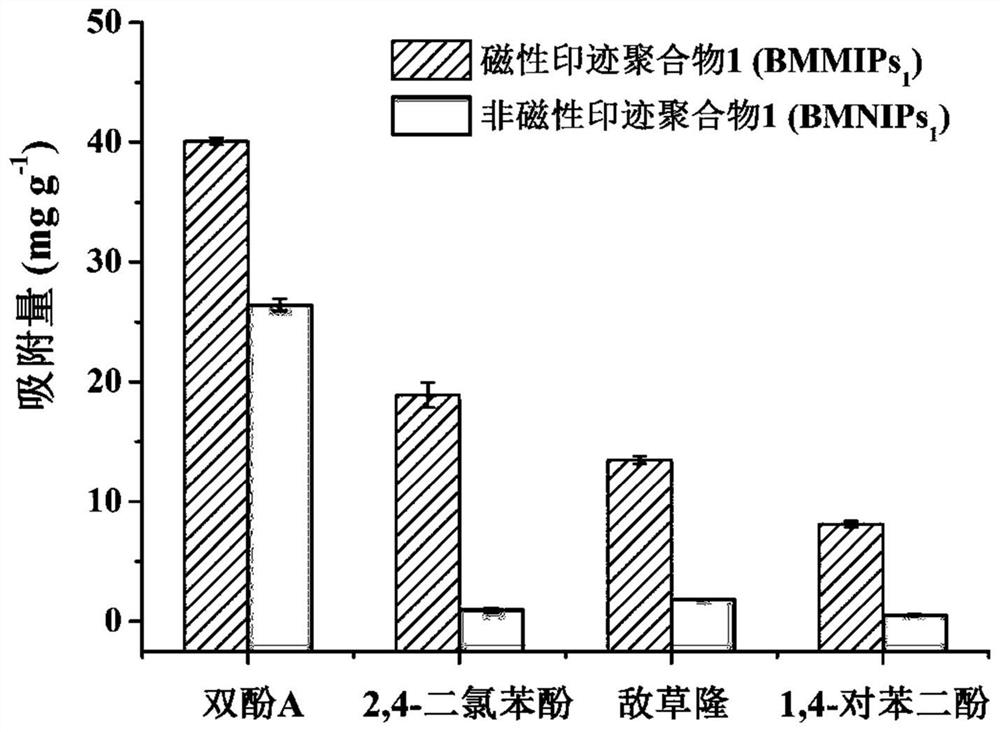
Preparation method of bisphenol A magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and application of bisphenol A magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer in bisphenol A fluorescence detection
ActiveCN112552469AImprove binding efficiencyImprove separation efficiencyComponent separationOther chemical processesSio2 nanoparticleDouble bond
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bisphenol A magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and application of the bisphenol A magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer in bisphenol A fluorescence detection, and belongs to the field of analytical chemistry. The preparation method comprises the steps of modifying the surfaces of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, synthesizing Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles through a sol-gel method on the basis, and carrying out double bond modification by using MPS to obtain the ideal magnetic core vinyl-Fe3O4@SiO2; further polymerizing with template molecules bisphenol A, 4-VP, TRIM and AIBN in an acetonitrile solution to form the BMMIPs with a novel core-shell structure; and applying the obtained BMMIPs to sample pretreatment, and establishing a rapid enrichment, separation and detection method of bisphenol A in a liquid food sample in combination of fluorescence reaction of acridine orange and bisphenol A. The method has the advantages of simple operation, stronganti-interference capability, high sensitivity, short time consumption and the like. According to the method, standard recovery is carried out on actual samples (ultrapure water, mineral water, orangejuice and the like), the recovery rate is 85.4%-88.7%, the relative standard deviation is less than 7.2%, and the sample detection limit is 16.5[mu]g L<-1>.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Improved counting method of living bacteria
PendingCN111088314AImprove counting efficiencyReduce randomnessMicrobiological testing/measurementPlate assayFiltration
The invention discloses an improved counting method of living bacteria. The improved counting method of the living bacteria comprises the following steps: (1) sterilizing a sand-core filter and a microporous filter membrane used for performing filtration, assembling the sterilized sand-core filter and microporous filter membrane, and putting the assembled sand-core filter and microporous filter membrane into a super clean bench for standby application; (2) uniformly oscillating a diluted sample solution by using a vortex mixer so as to obtain a uniformly mixed diluted sample solution; (3) performing suction filtration on the uniformly mixed diluted sample solution by using the assembled sand-core filter and microporous filter membrane, slowly attaching the microporous filter membrane to amedium, carrying out light-shielded cultivation, and carrying out immobilization by using formaldehyde so as to obtain an immobilized filter membrane; (4) dyeing the immobilized filter membrane by using acridine orange, placing the dyed filter membrane on a slide, counting fluorescent bacteria by using a microscope, and identifying growing or thickening bacteria in the field of vision as live bacteria. The improved counting method of the living bacteria disclosed by the invention is capable of reducing randomness caused by small sample size, and avoids relatively long standing time; and moreover, the method is also capable of avoiding waste of a large amount of plates in a plate assay. In addition, direct counting by the microscope is adopted, so that living bacterium counting efficiency is greatly improved; and thus, the improved counting method of the living bacteria has the advantages of being economical of materials, plenty in parallel repeats, high in efficiency and the like.
Owner:湖南景翌湘台环保高新技术开发有限公司 +1
Fluorescent staining solution for gynecology department
PendingCN113567217AReduce storage conditionsLow costPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent stainingMissed diagnosis
The invention discloses a fluorescent staining solution for gynecology department, which is characterized in that a fluorescent staining solution A liquid reagent component is prepared from the following components: 4 ', 6-diamidin-2-phenylindole, proclin300 and purified water; a fluorescent staining solution B liquid reagent component is prepared from the following components: acridine orange, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, purified water and proclin300. According to the fluorescent staining solution for gynecology department, the storage condition of a reagent is reduced, and the technological process of the reagent is optimized; the validity period of the reagent is prolonged, the reagent cost is reduced, the accuracy of gynecological leucorrhea detection is improved, and the missed diagnosis rate and the misdiagnosis rate of gynecological leucorrhea specimens are reduced.
Owner:肖波
Enhancement solution for enhancing chemiluminescence and method for preparing chemiluminescent solution
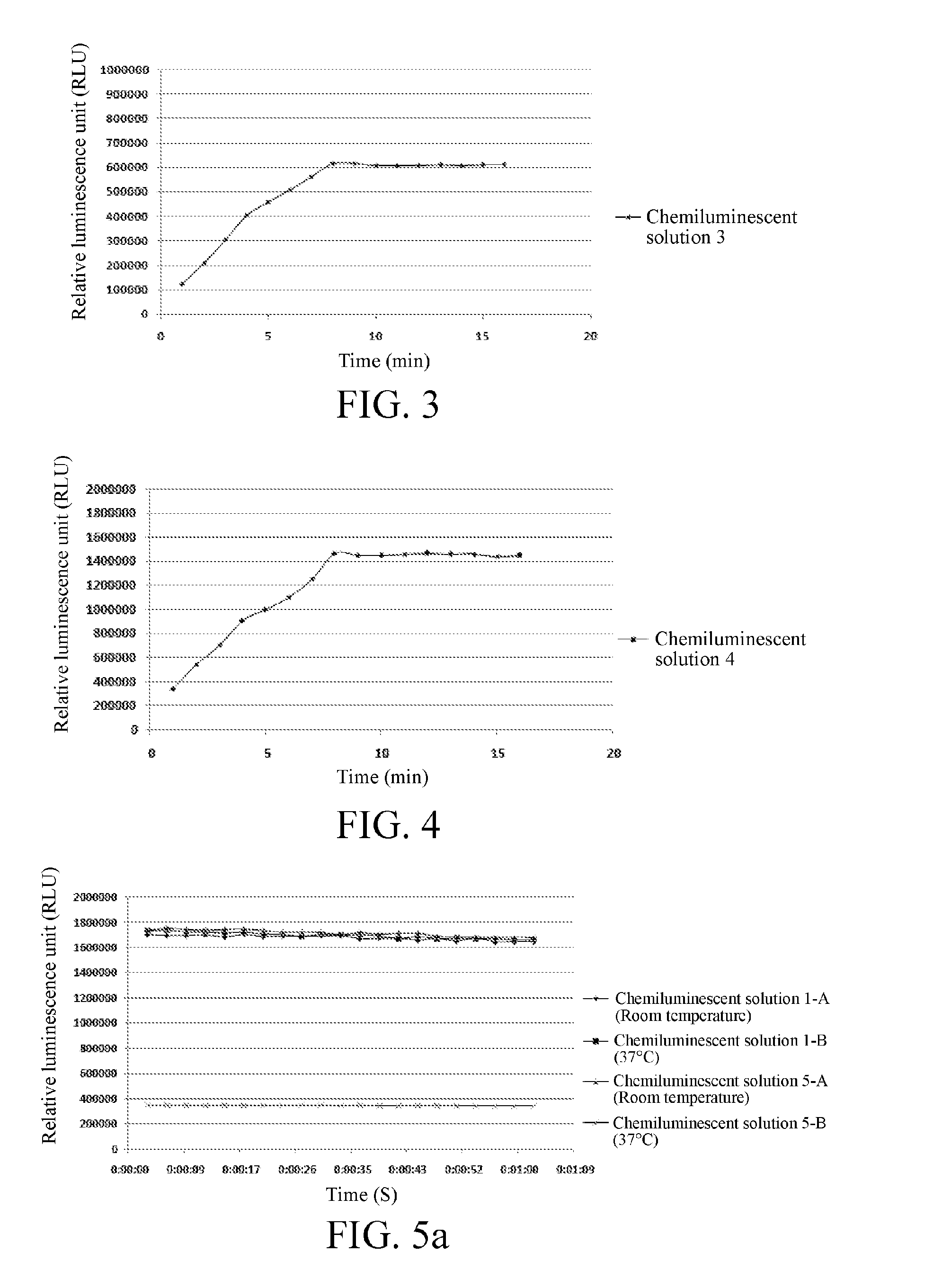
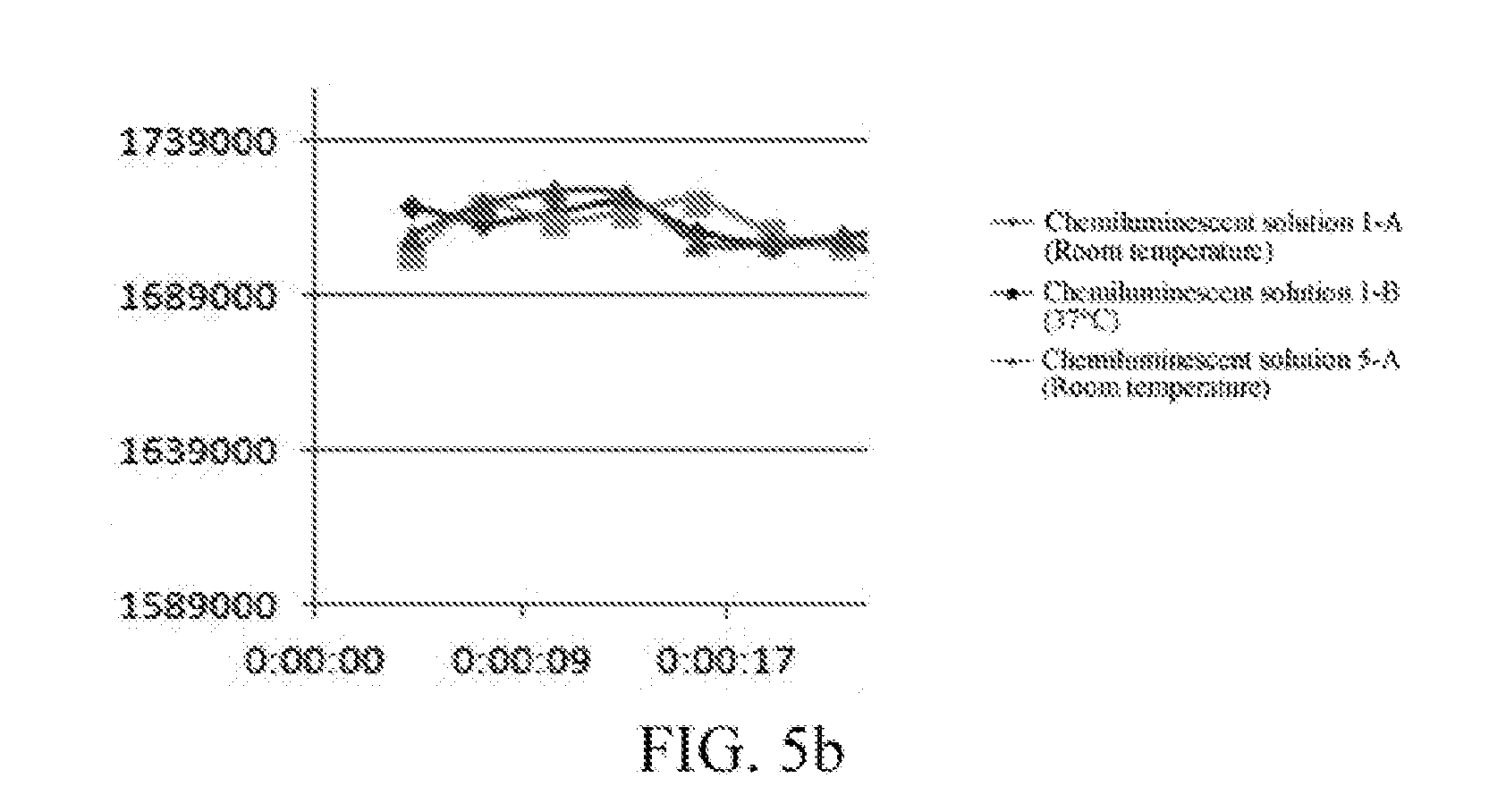
ActiveUS20170016887A1Luminescent signal of solution is increasedExtend detection timeTenebresent compositionsLuminescent compositionsGlycineAcridine orange
Disclosed are an enhancement solution for enhancing chemiluminescence, and a method for preparing a chemiluminescent solution. The method comprises Step A: dissolving methylglucamine in water, adjusting the pH to 8-9, then adding an N-alkyldimethylmannosamine quaternary ammonium salt, acridine orange, BSA, glycine, MgCl2, and ZnCl2 respectively to a diethanolamine solution, stirring to dissolve them, and diluting to a constant volume, to obtain an enhancement solution; and Step B: diluting a chemiluminescent substrate with the enhancement solution, to obtain a chemiluminescent solution. When used in the field of immunoassays, the enhancement solution of the present invention increases the sensitivity and linear range of detection, reduces the cost, and is free of contamination.
Owner:SHENZHEN MAXCHEMTECH
Ionic liquid functionalized acid orange for organic solvent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110003273AImprove solubilityThe synthesis method is simpleGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSulfonic acids salts preparationSolubilitySilver carbonate
The invention relates to ionic liquid functionalized acid orange for an organic solvent and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method for the ionic liquid functionalized acid orange for theorganic solvent provided by the invention comprises the following steps: first, first, reacting triphenylphosphine and slightly excessive bromoalkane, and washing and purifying by using ethyl acetateto prepare alkyl triphenyl bromide; performing neutral reaction on acidified acid orange and silver carbonate, and washing and drying to prepare acid orange silver salt; then, respectively performingion exchange on the prepared acid orange silver salt and different alkyl triphenyl bromide to prepare a series of novel ionic liquid functionalized acid orange which can be dissolved in a plurality of organic solvents. The synthesis reaction conditions are mild and the post-treatment is simple. The type of ionic liquid functionalized acid orange has good solubility in the plurality of the organicsolvents, and is an azo dye and an acid base indicator which can be used for the organic solvent.
Owner:ZAOZHUANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com