Patents
Literature
159 results about "Genomic information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
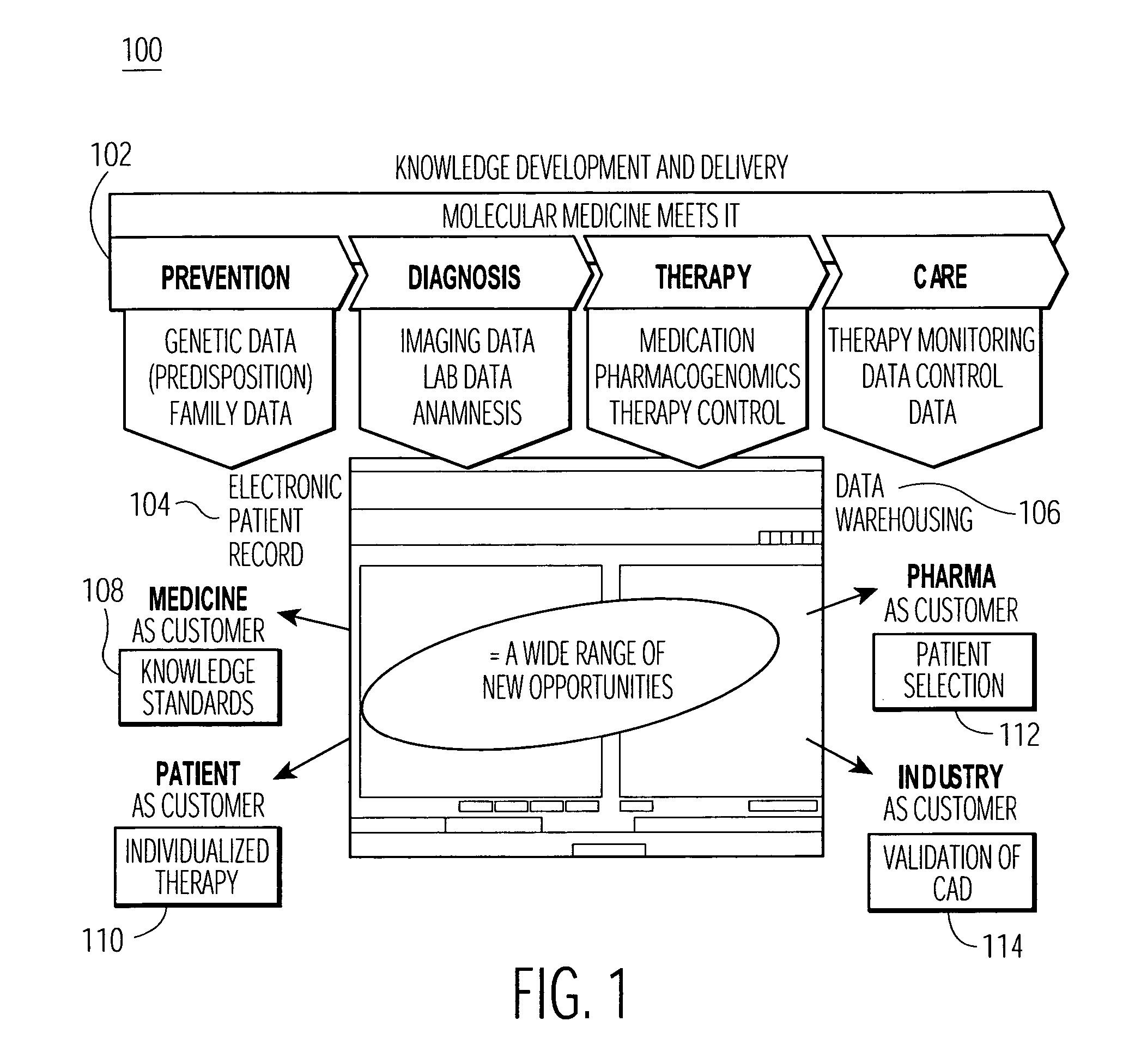
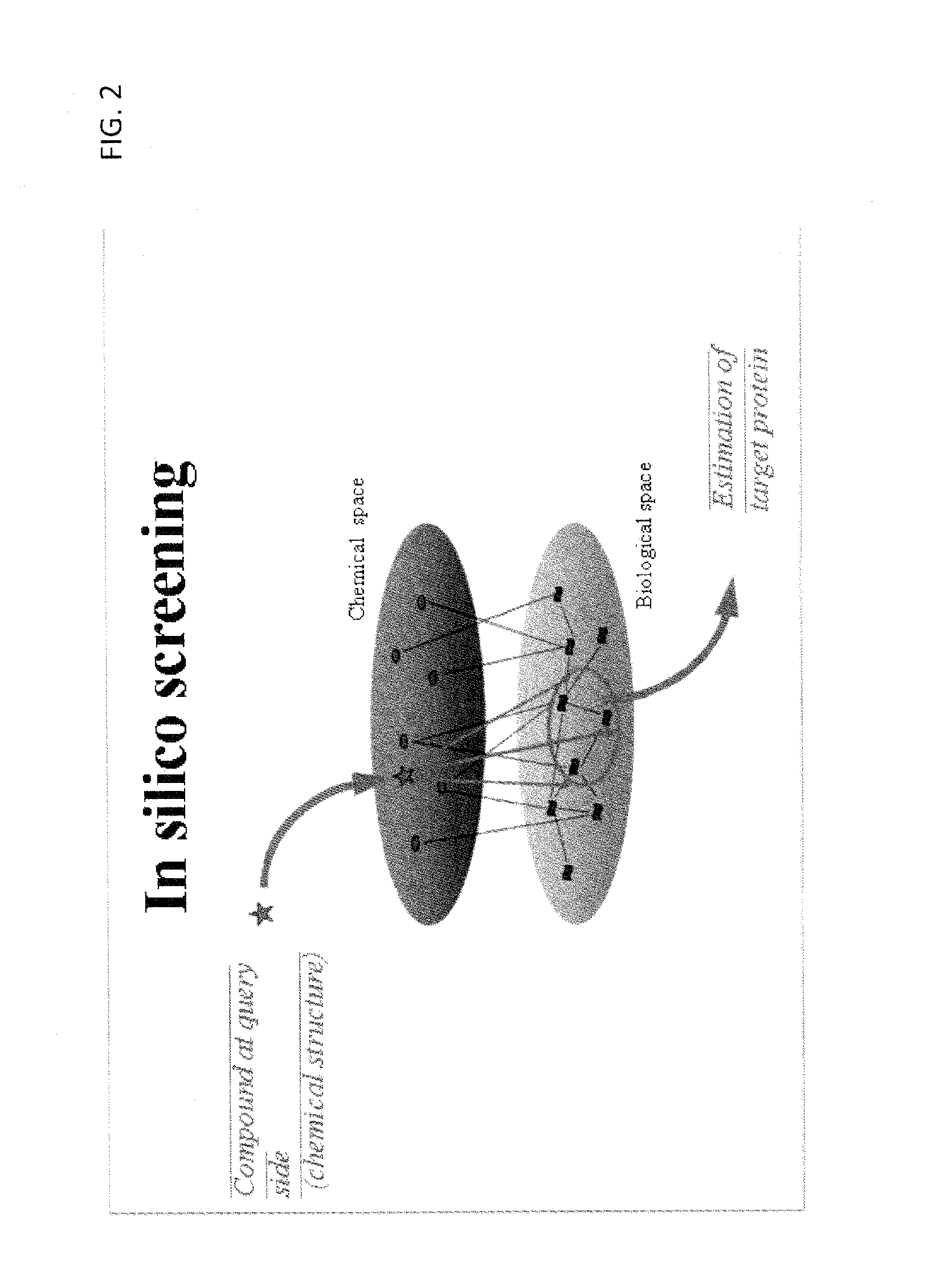
A Brief Guide to Genomics. Genomics is the study of all of a person's genes (the genome), including interactions of those genes with each other and with the person's environment. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the chemical compound that contains the instructions needed to develop and direct the activities of nearly all living organisms.
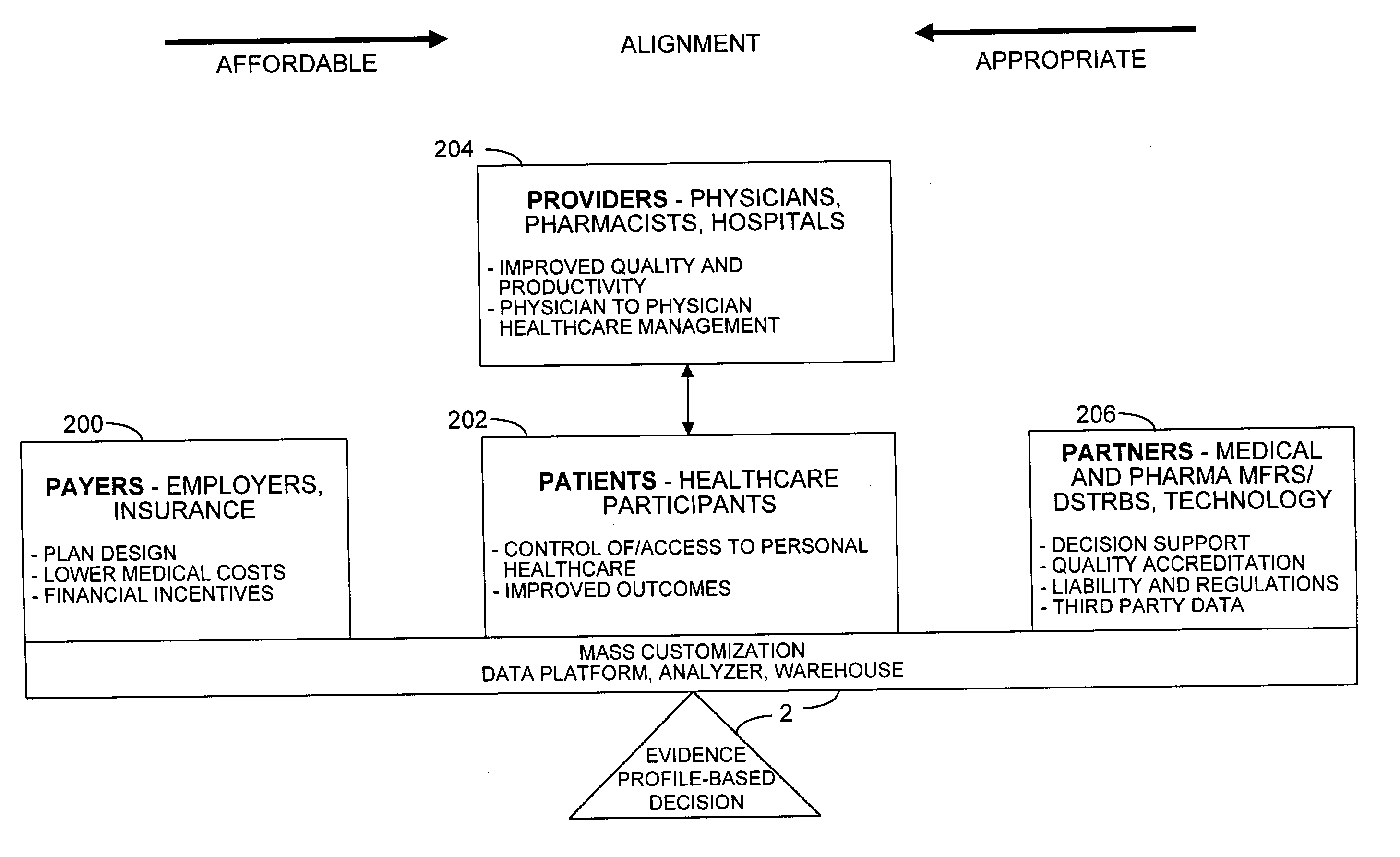
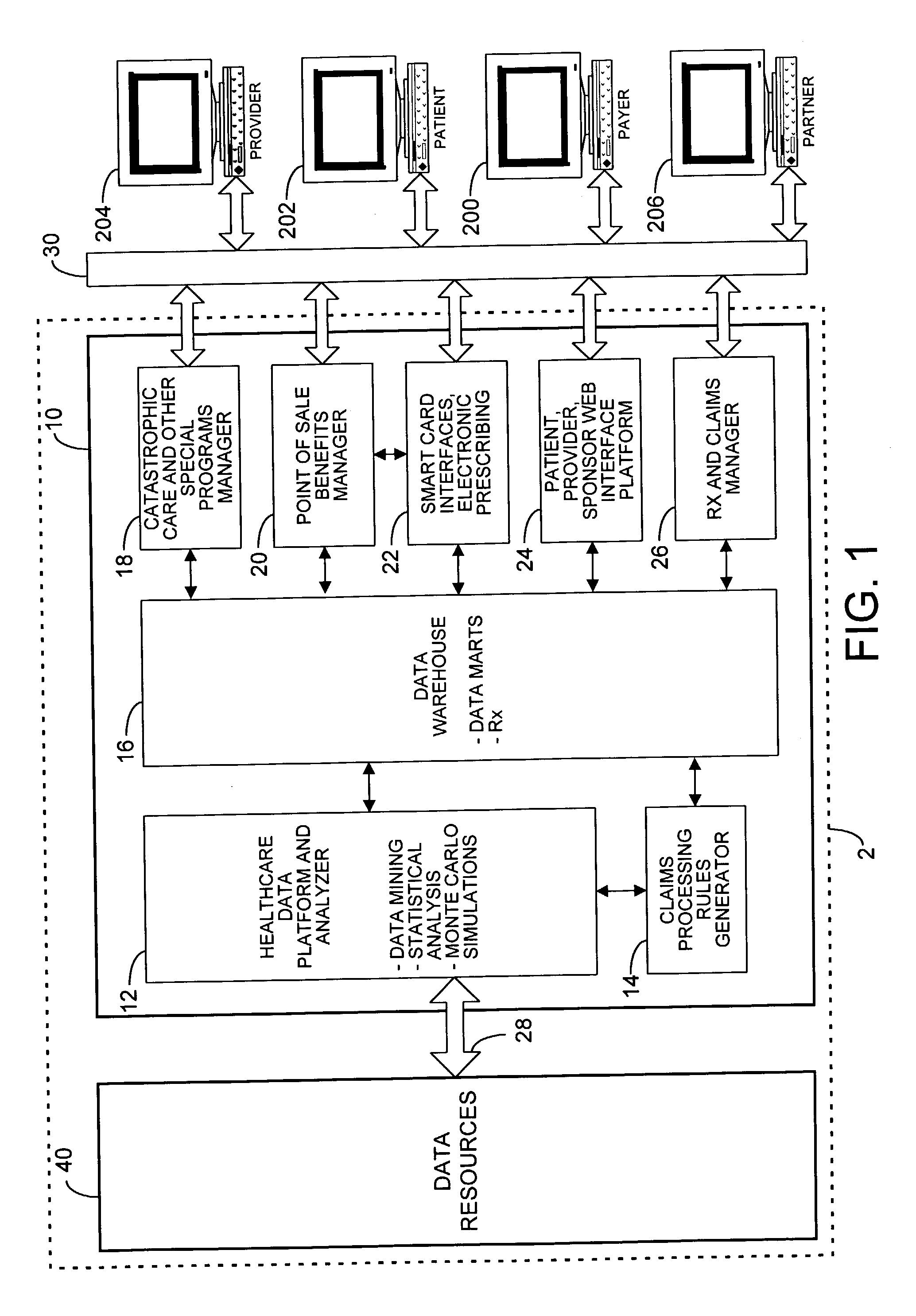
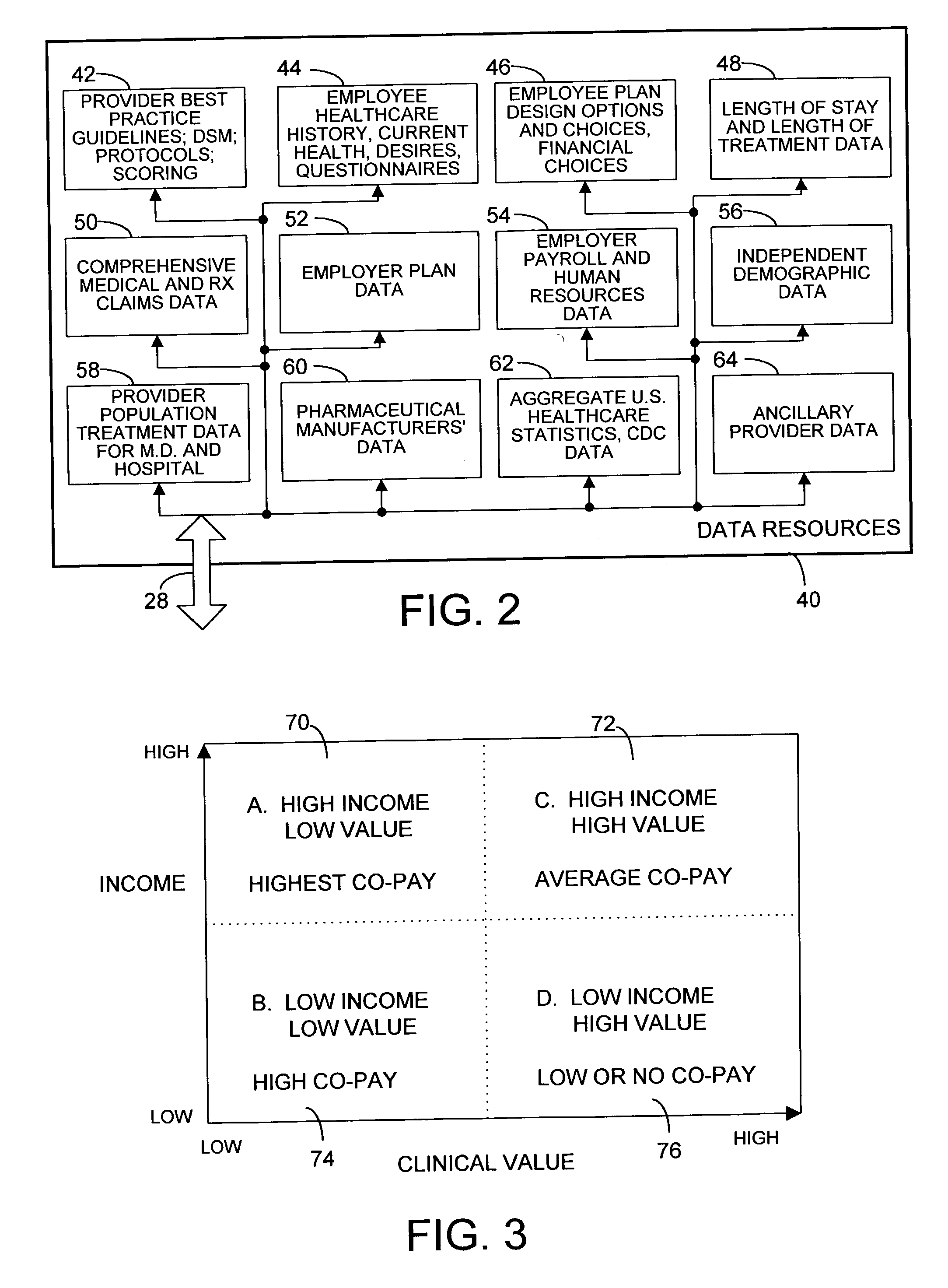
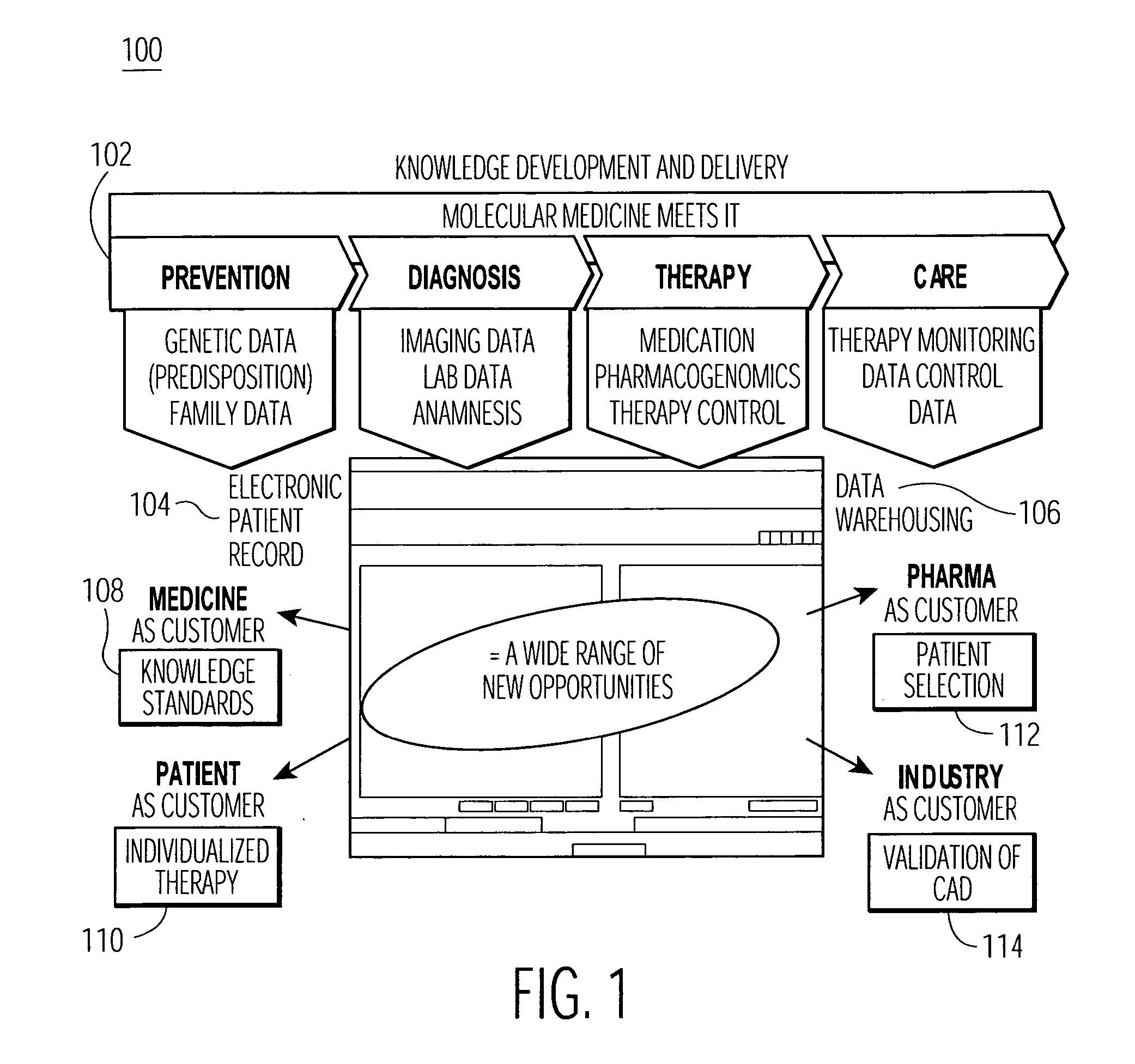
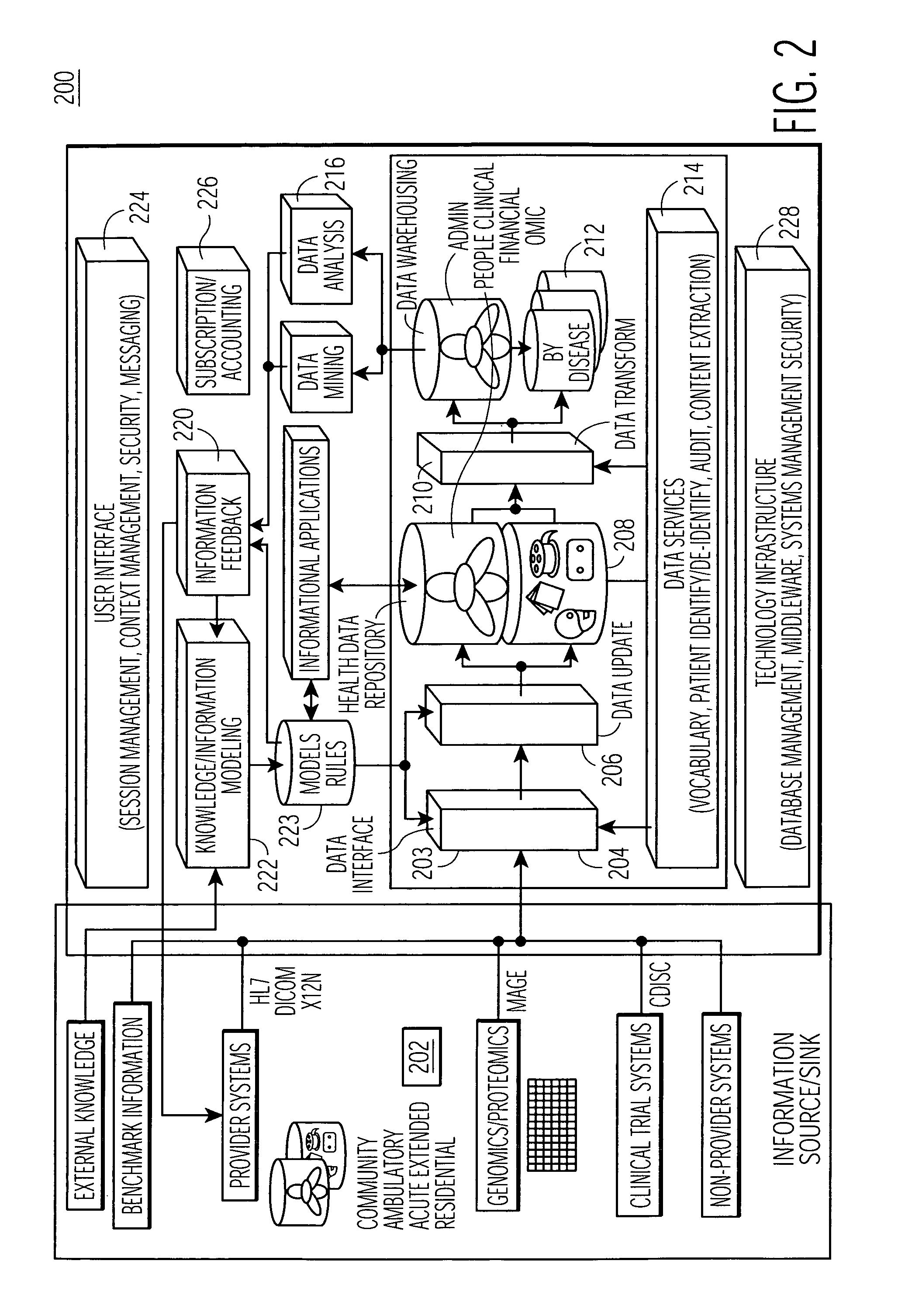
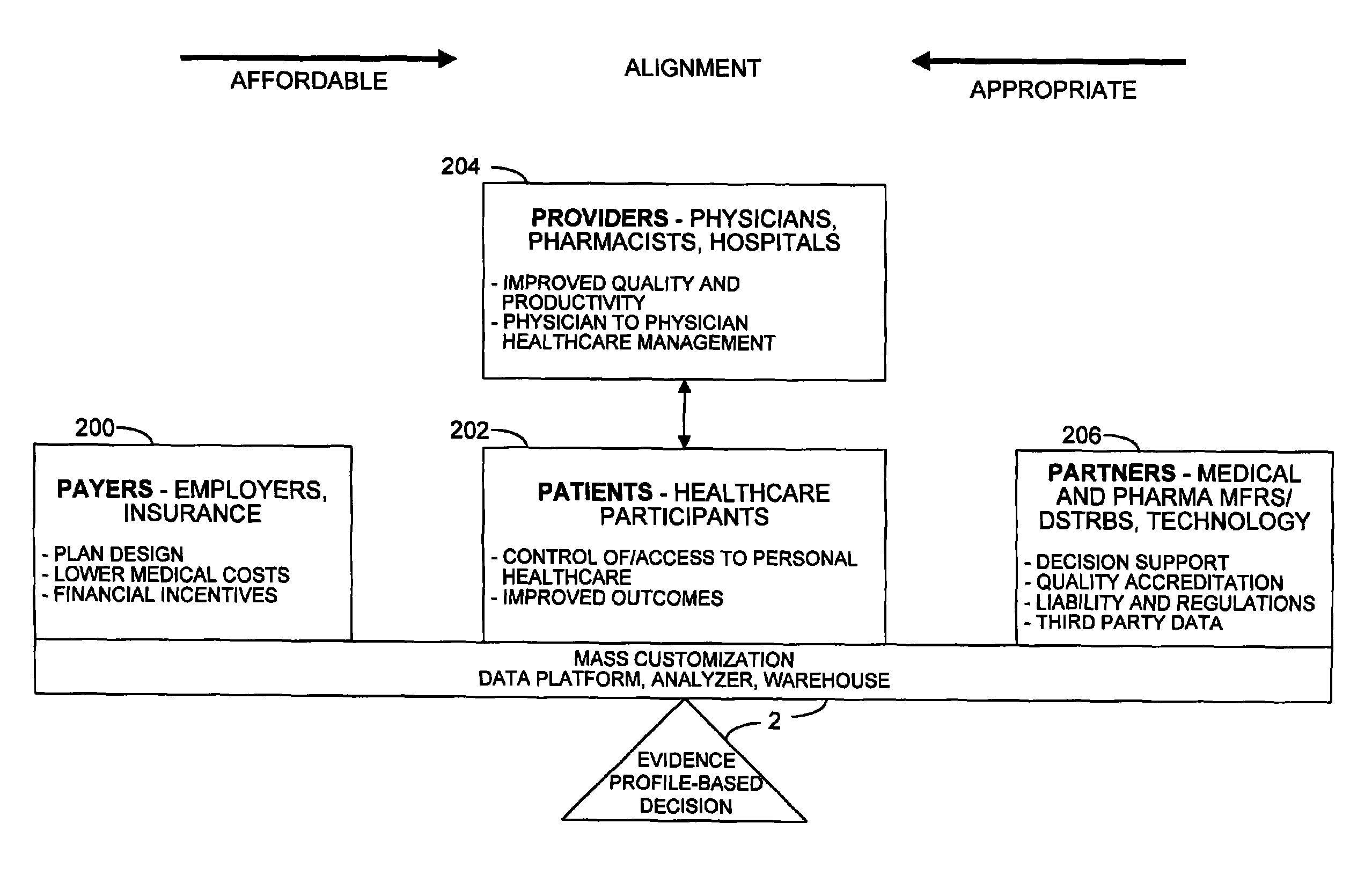
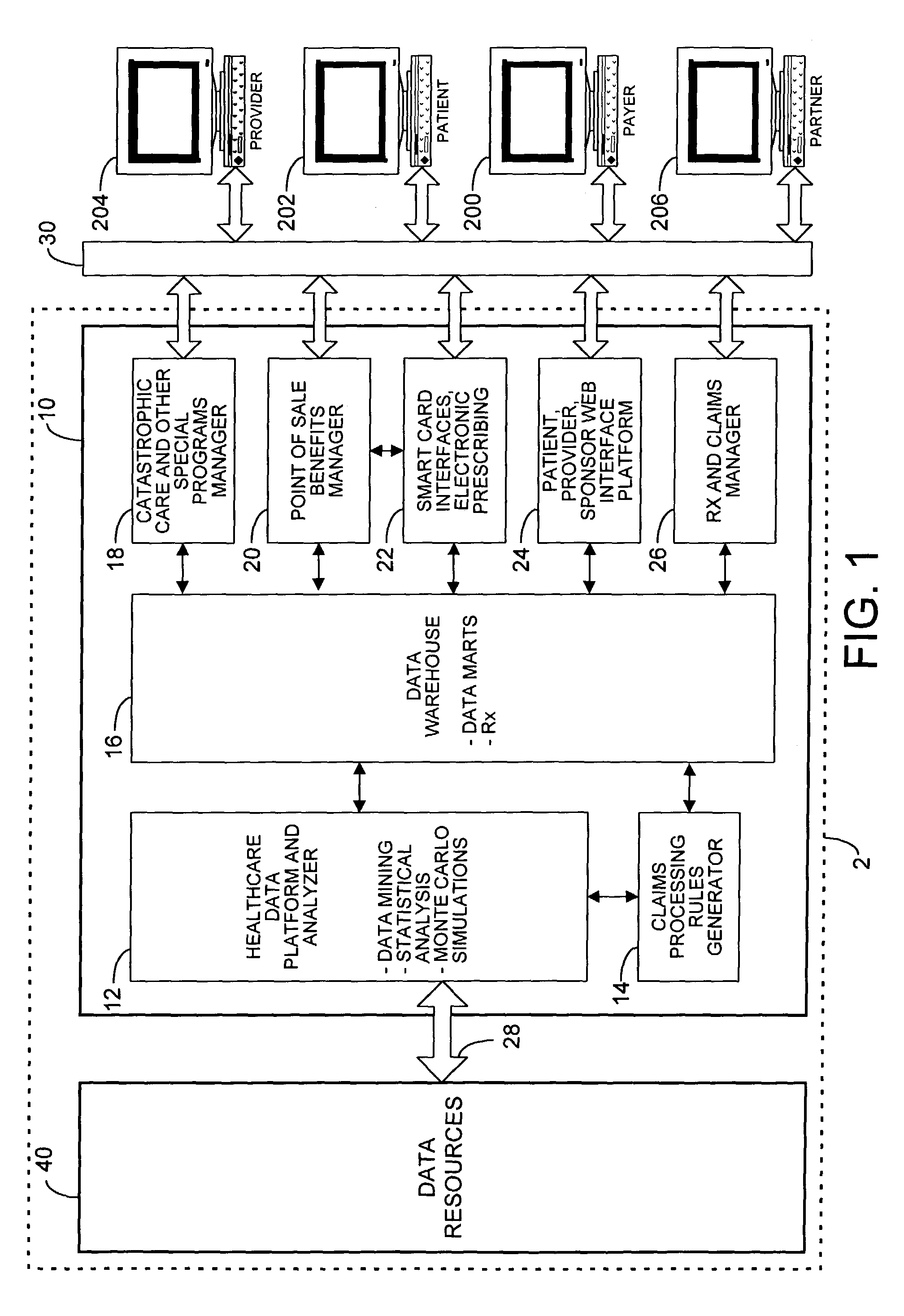
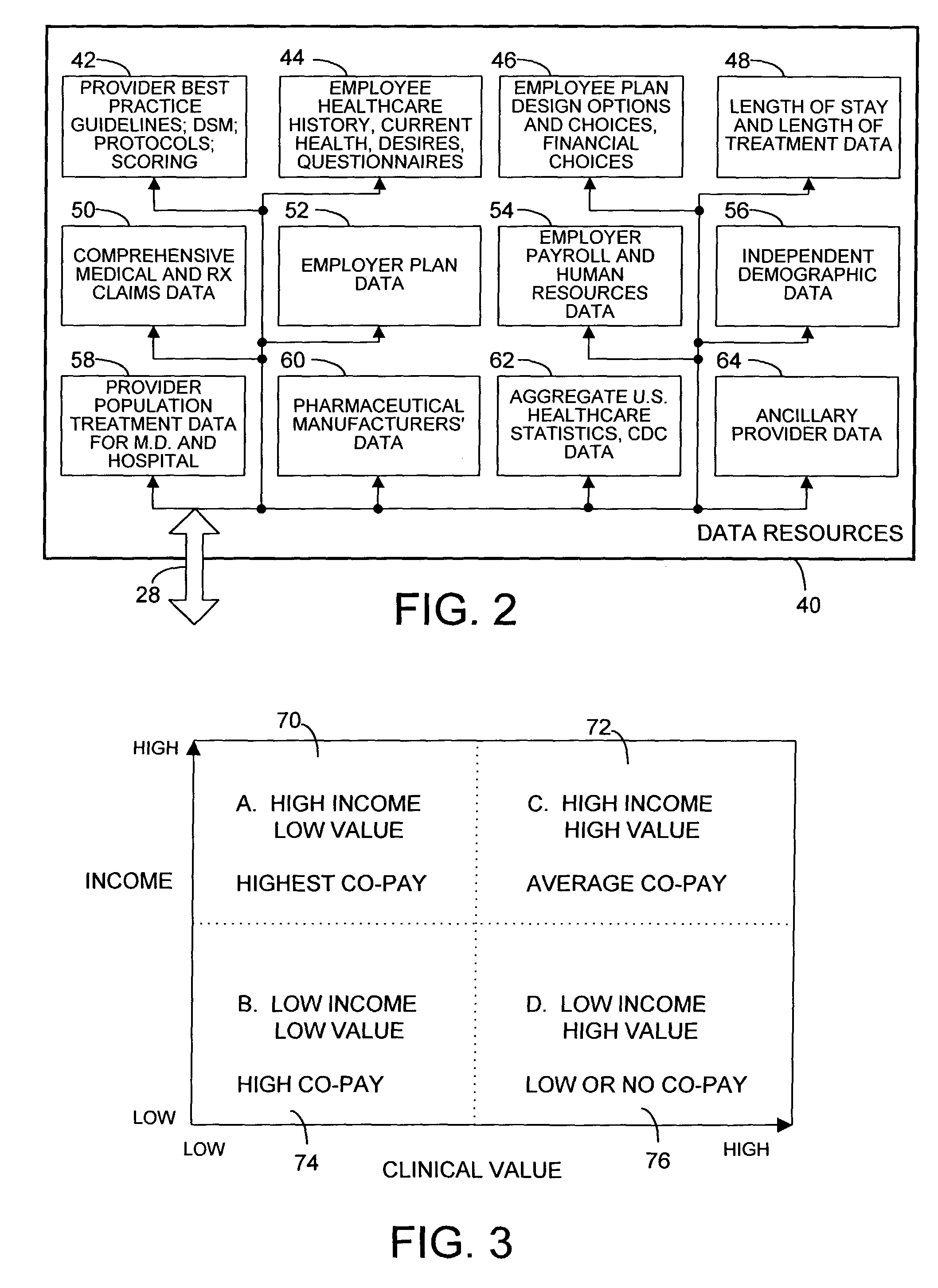
Mass customization for management of healthcare
ActiveUS20060178915A1Deter unnecessary utilizationCost optimizationDiscounts/incentivesDrug and medicationsMass customizationProgram planning
A healthcare mass customization infrastructure individualizes plan designs by incorporating demographics, income, drug history, medical history, lab values, and future genomic information for appropriate and affordable access to medications. The mass customization infrastructure results in quality outcomes for the patients, improved care and productivity for the providers, and lower medical costs for the payers.
Owner:MEDIMPACT HEALTHCARE SYST
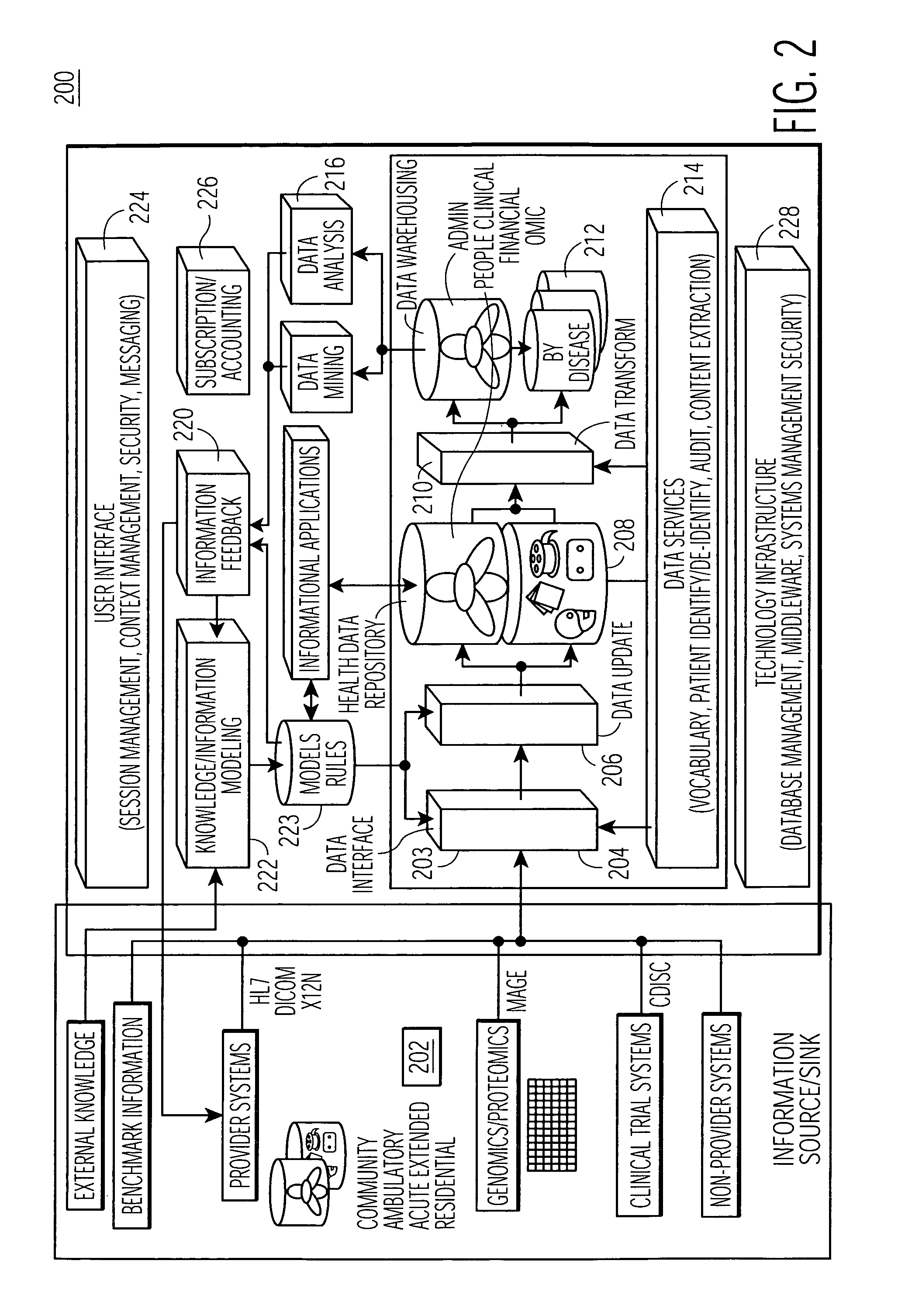
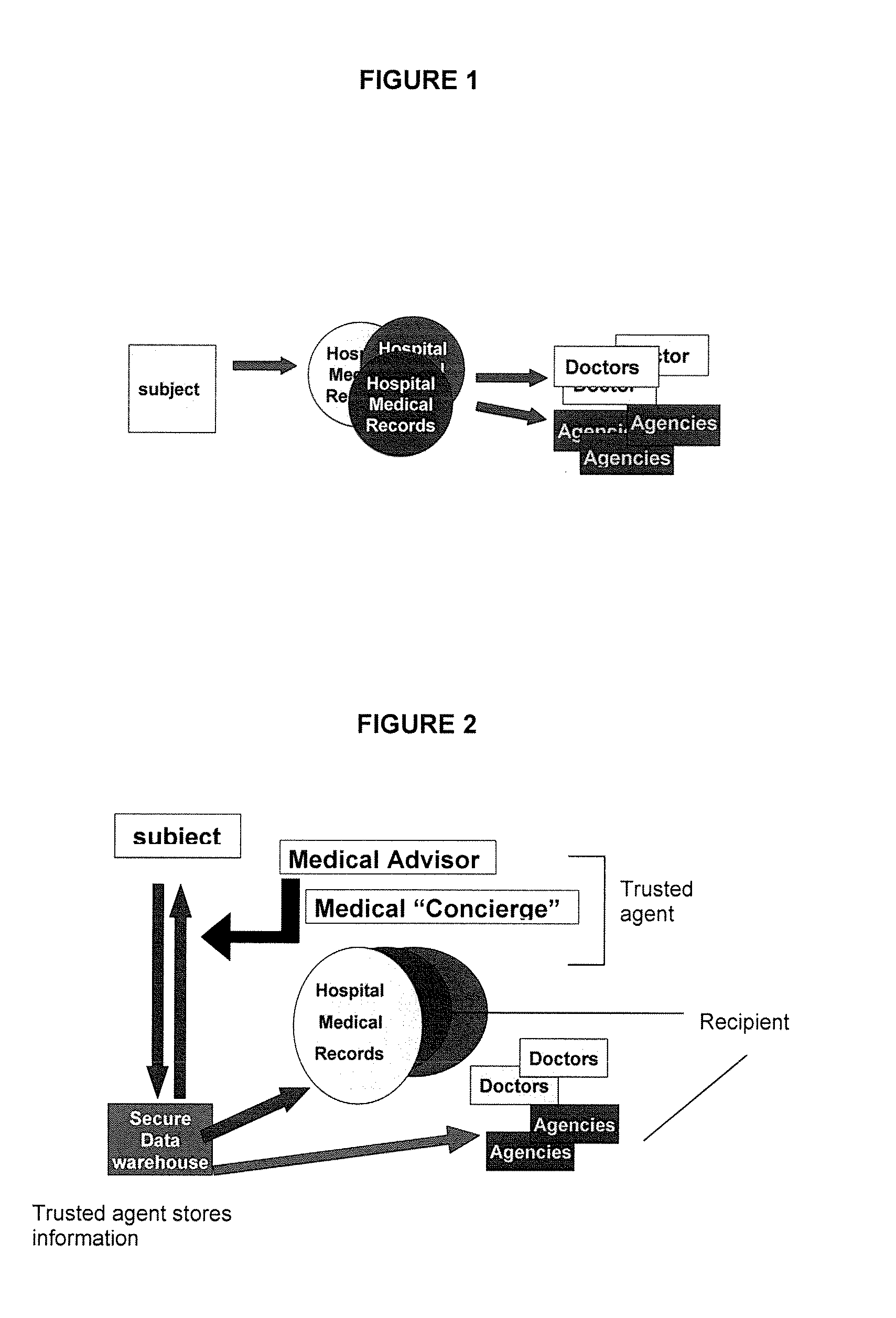
System for managing healthcare data including genomic and other patient specific information
ActiveUS7788040B2Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical recordGenomic information
A system, for processing patient medical information for storage in an electronic patient medical record repository, includes an interface, a repository, and a data processor. The interface receives data representing genomic information of a patient. The repository includes a patient record incorporating data representing genomic information specific to a particular patient. A data processor compares the genomic information specific to a particular patient with the received genomic information. The data processor identifies a genomic match in response to the comparison and predetermined matching criteria. The data processor initiates processing of patient record information specific to the particular patient in response to an identified match.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
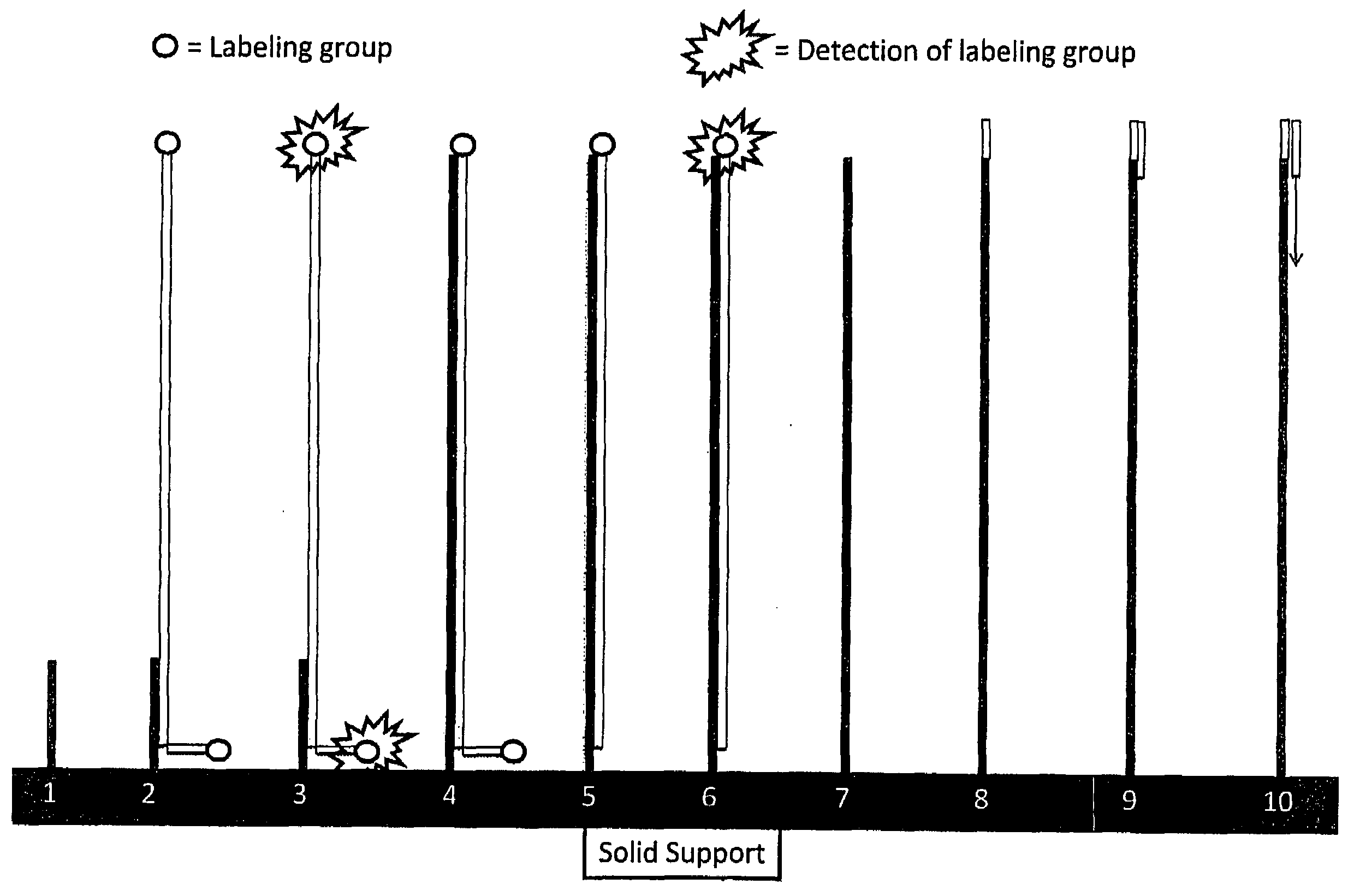
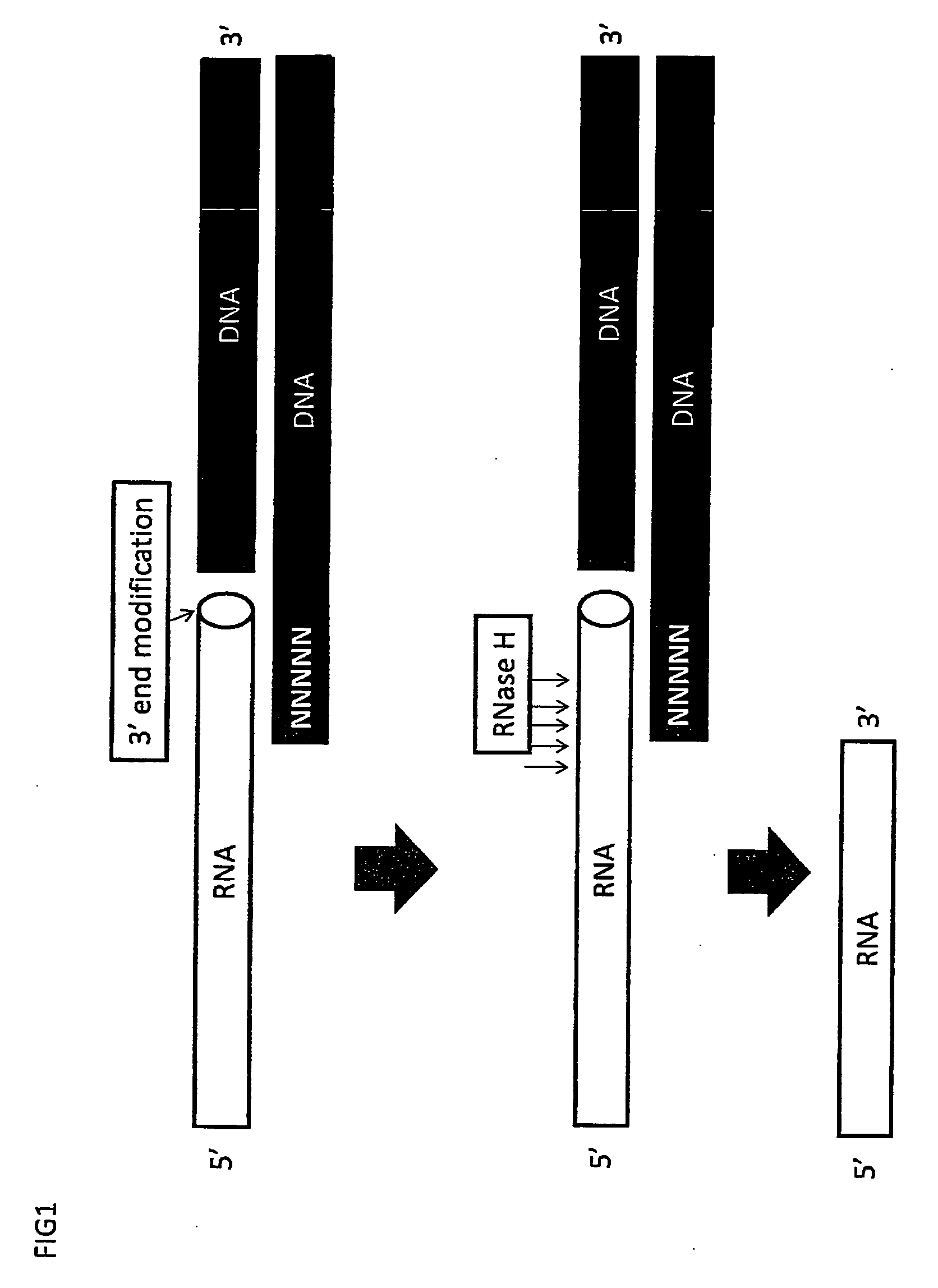
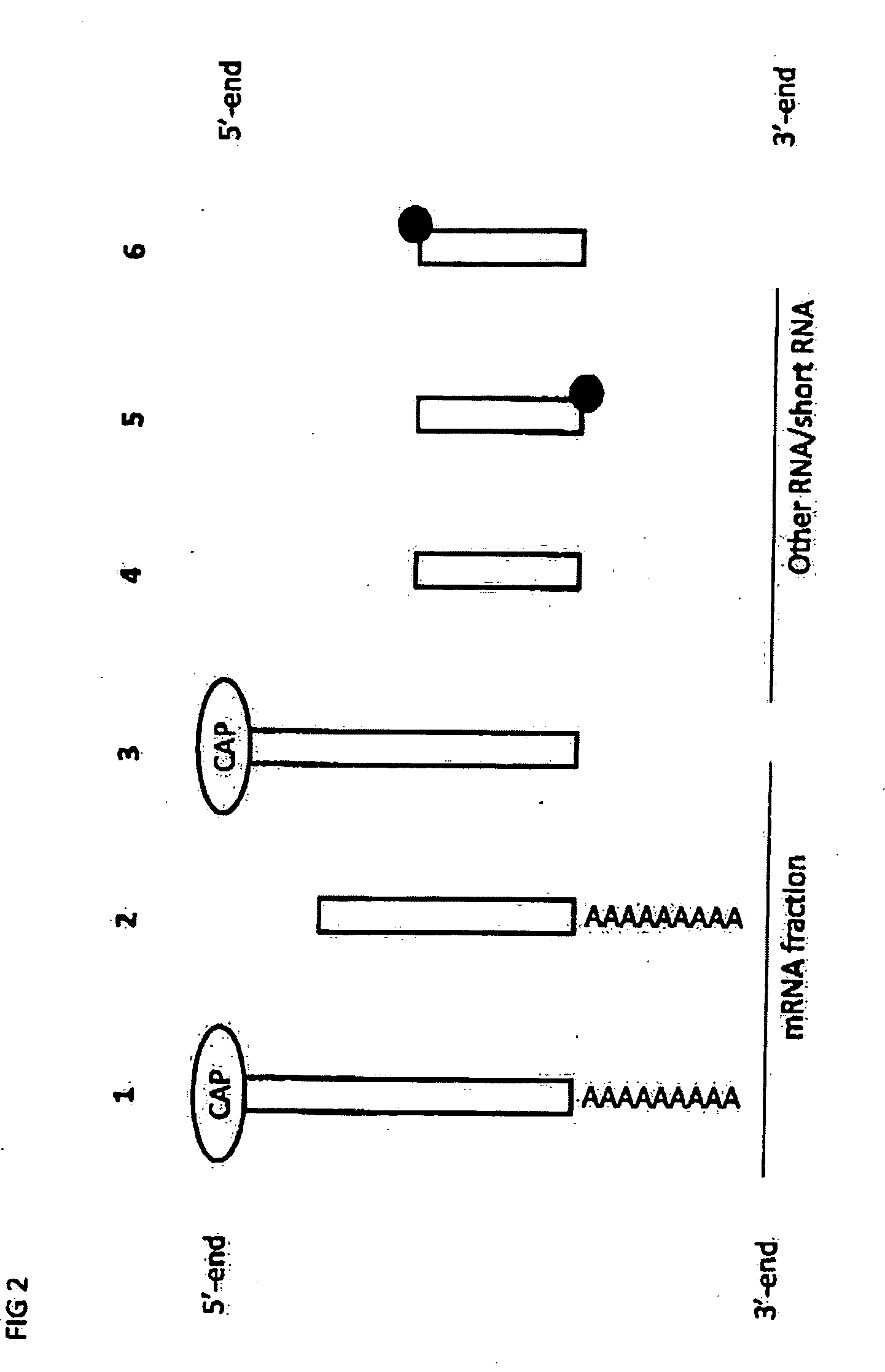
RNA sequencing and analysis using solid support
InactiveUS20100035249A1Facilitate direct bindingReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyGenomic information
The present invention provides methods for the sequencing of all RNA species within an RNA sample, such as the RNA content obtained from a cell, a tissue, a living organism, or from an artificial source. RNA molecules within the samples are labeled in a RNA-specific manner prior to immobilization on a solid support. One label is used to mark the location of the RNA molecule on the solid support, whereas the second label is used to mark selectively the S′ end of full-length mRNA molecules. RNA molecules are sequenced while being bound to the solid support in one or more sequencing reactions, and sequences of individual RNA molecules can be forwarded to computational analysis for assembling sequence information from individual sequencing reads obtained from the same location on the solid support. Not only unsupervised expression profiling on a genome-wide scale, but also the direct analysis of RNA-RNA interactions become possible as revealed by the analysis of the sequencing information obtained along with genomic information.
Owner:DNAFORM +1
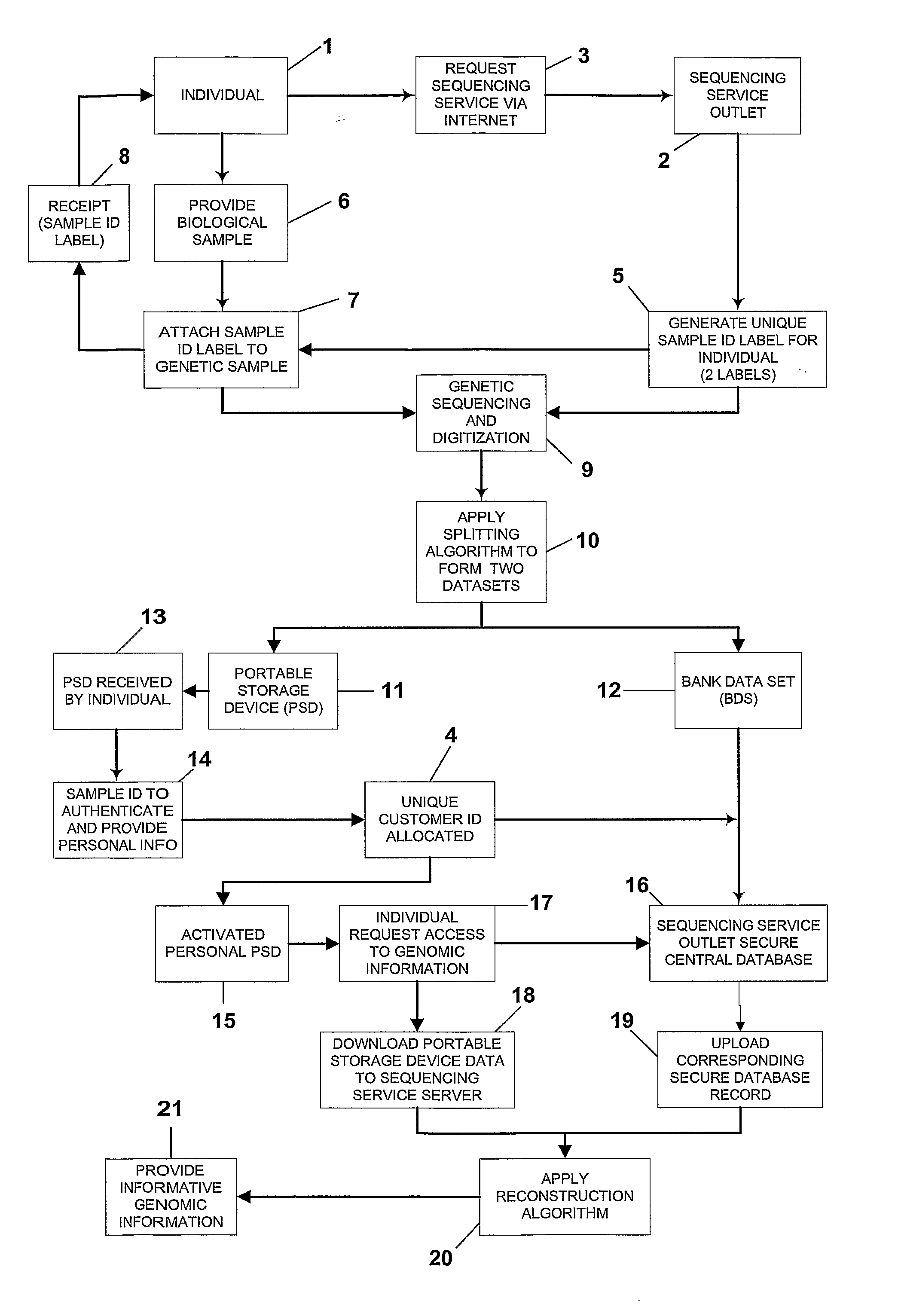
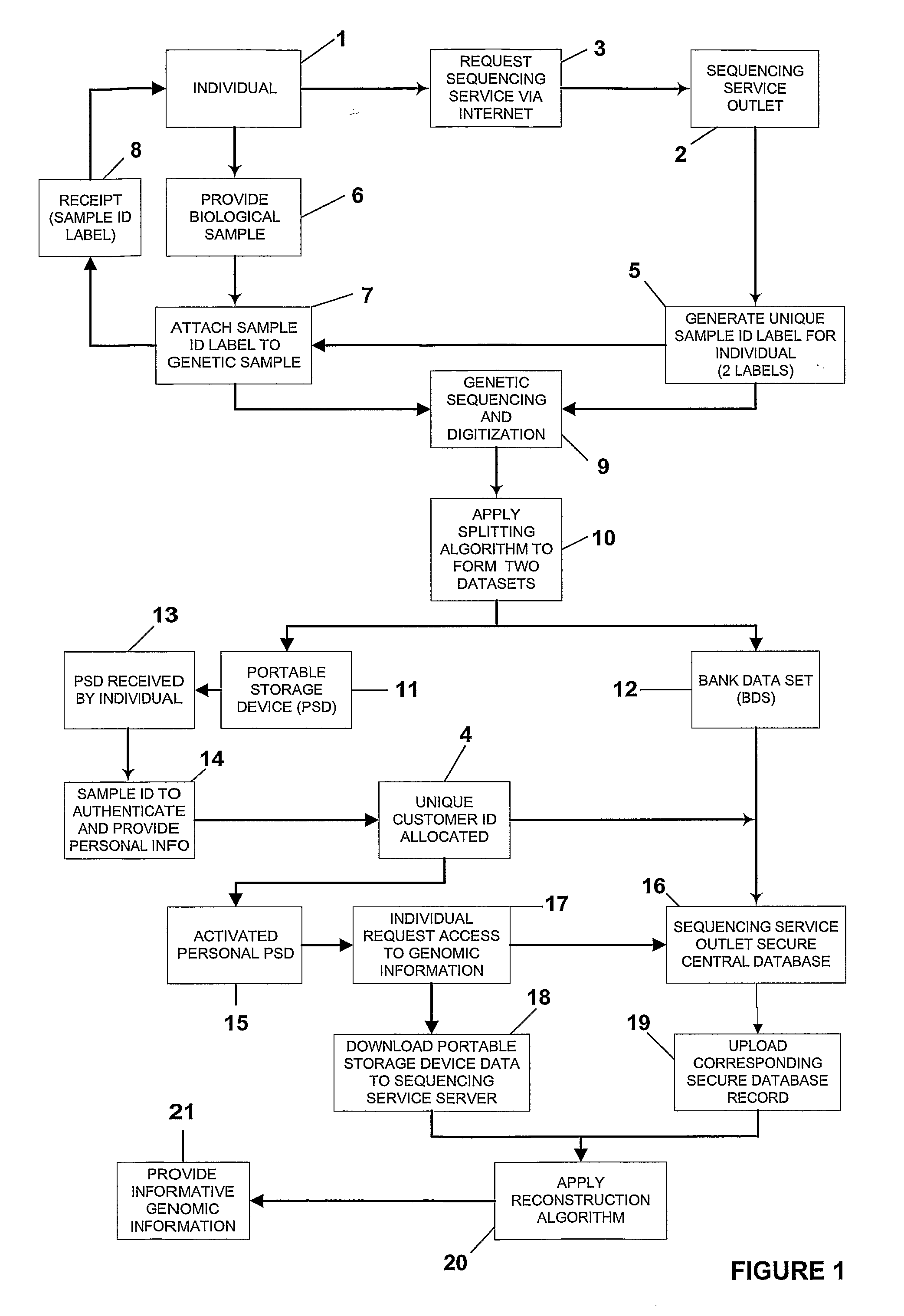
Secure Transaction of Dna Data
InactiveUS20070271604A1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionData setInternet privacy
A system and method for processing and storing personal information in a secure manner is described. In particular, a system and method for processing, splitting and storing genomic information or portions thereof in a secure electronic format is disclosed. An individual's genomic sequence is digitized and a splitting algorithm applied to fragment and randomise the digitized genomic information into at least two separate datasets. One dataset is retained by the individual and the second dataset is stored on a central server as a secure database record. Each dataset in isolation presents uninformative data and it is only when both datasets are combined, using a reconstruction algorithm to recombine the separate dataset data for an individual that the digitized data is capable of being presented into a useable and informative format.
Owner:FIDELITYGENETIC
System for managing healthcare data including genomic and other patient specific information
ActiveUS20050158767A1Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical recordGenomic information
A system, for processing patient medical information for storage in an electronic patient medical record repository, includes an interface, a repository, and a data processor. The interface receives data representing genomic information of a patient. The repository includes a patient record incorporating data representing genomic information specific to a particular patient. A data processor compares the genomic information specific to a particular patient with the received genomic information. The data processor identifies a genomic match in response to the comparison and predetermined matching criteria. The data processor initiates processing of patient record information specific to the particular patient in response to an identified match.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
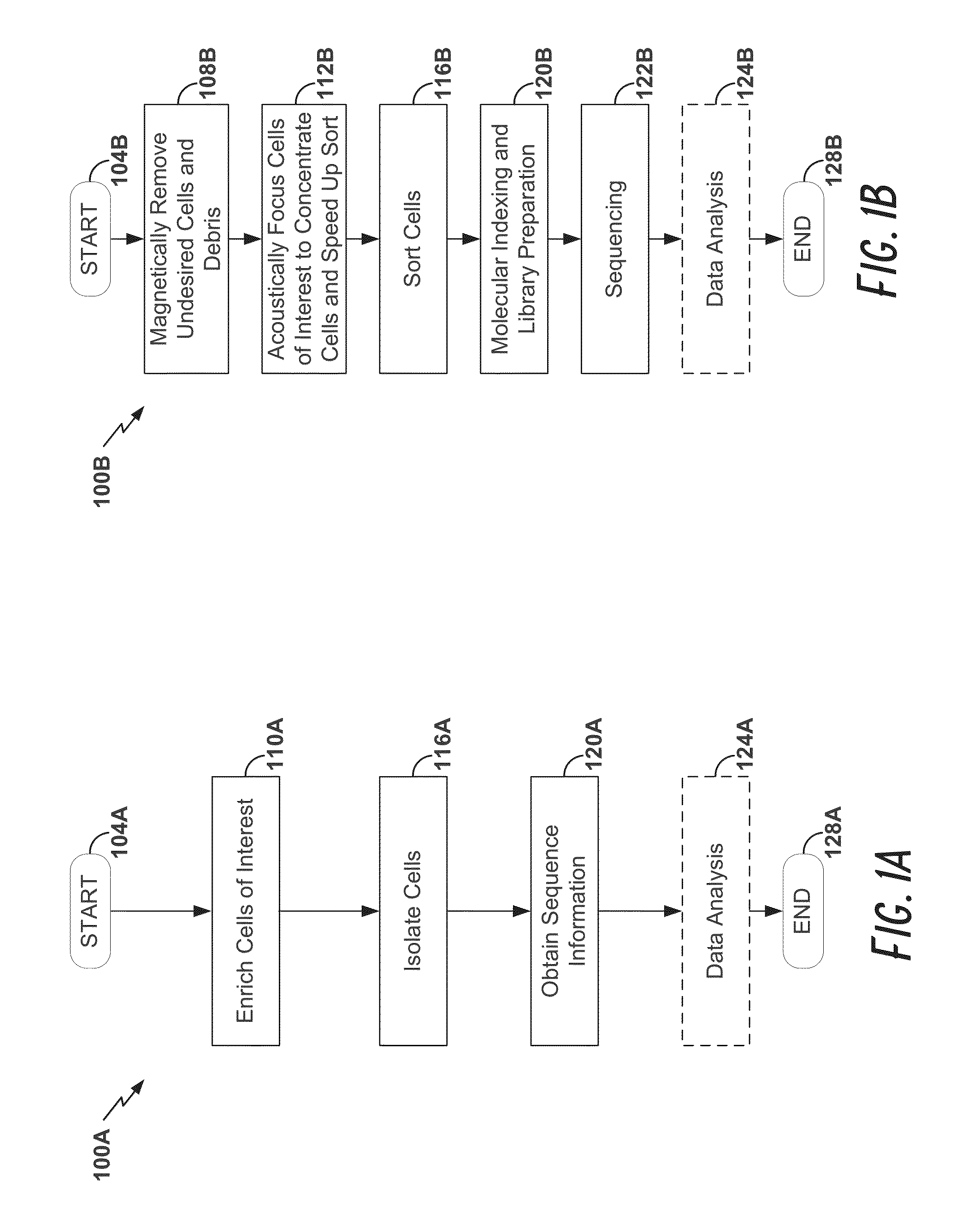
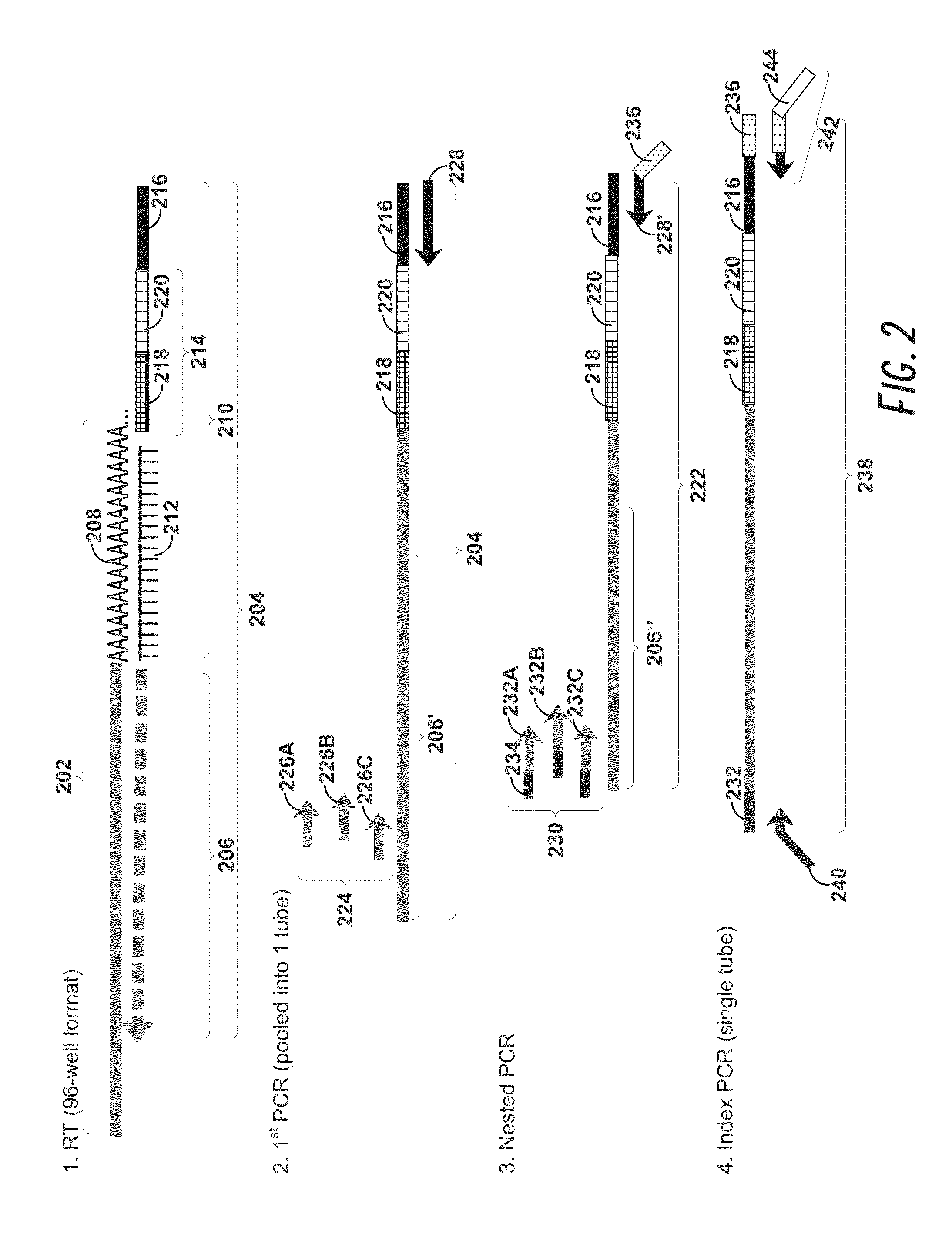
High-throughput single-cell analysis combining proteomic and genomic information
ActiveUS20160244828A1Predict susceptibilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsPolynucleotide
Disclosed herein are methods for single-cell sequencing. In some examples, the methods include enriching a sample comprising a plurality of cells for cells of interest to produce an enriched cell sample; isolating one or more cells of interest in the enriched cell sample; and obtaining sequence information of one or more polynucleotides from each of the one or more isolated cells. Obtaining sequence information may include generating a molecularly indexed polynucleotide library from the one or more isolated cells. Enriching the sample may include focusing cells of interest in the sample using acoustic focusing.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
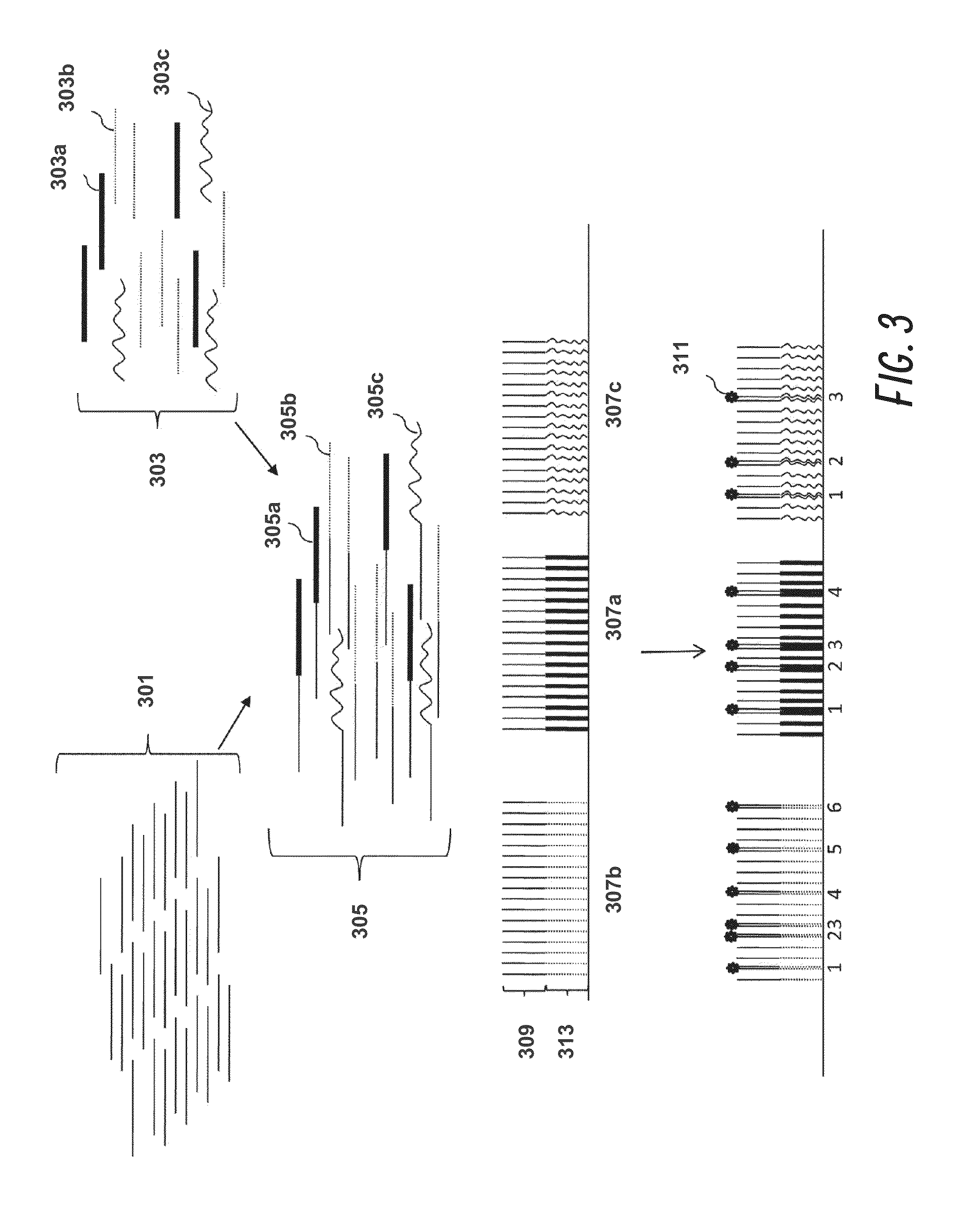
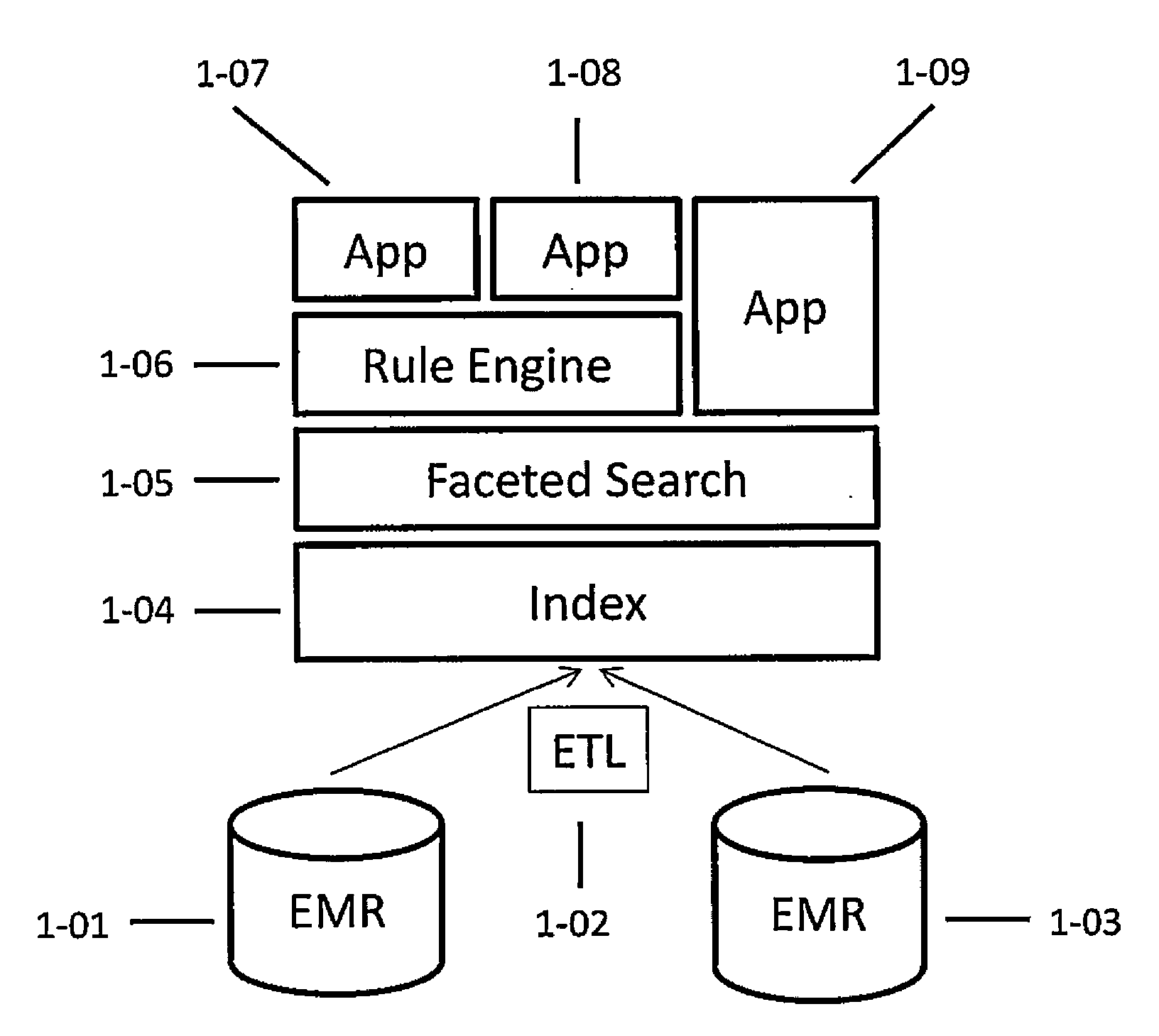
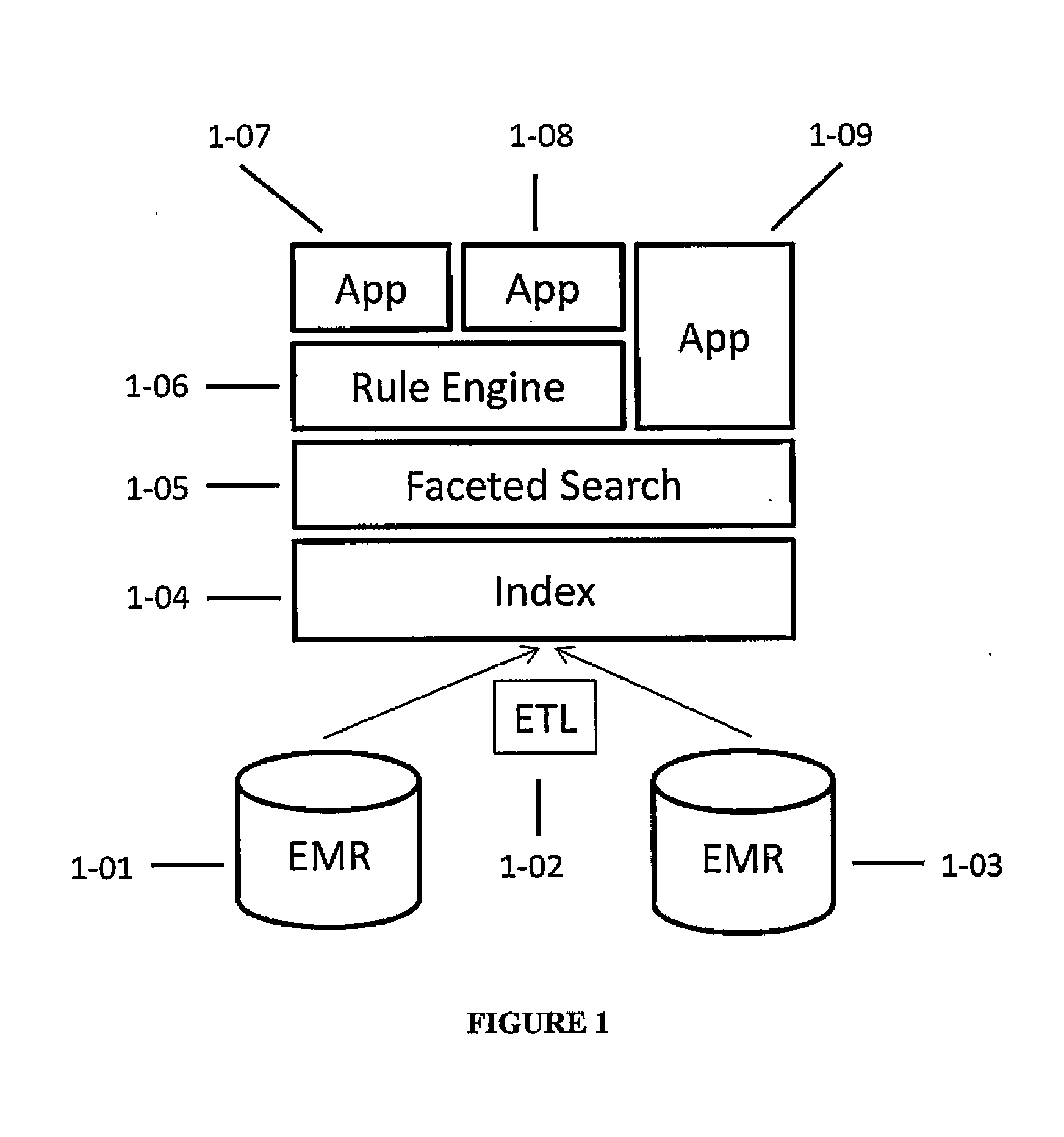
Systems and methods for searching genomic databases
InactiveUS20140046926A1Digital data processing detailsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionClinical valueData source
The invention described herein solves the challenges encountered in searching for clinical and genomic information from multiple data sources. Systems, methods, and devices of the invention allow a user to search a number of dissimilar information sources simultaneously, and view, process, and perform correlations on the information. The invention uses faceted search to process clinical values, genomic data, subject characteristics, and population characteristics, thereby providing a user with an array of information useful for monitoring or improving the state of health of a subject or a subject population. The invention allows a user to evaluate clinical and research information in a subject-centric way, and analyze information at either the individual or the population level.
Owner:MYCARE
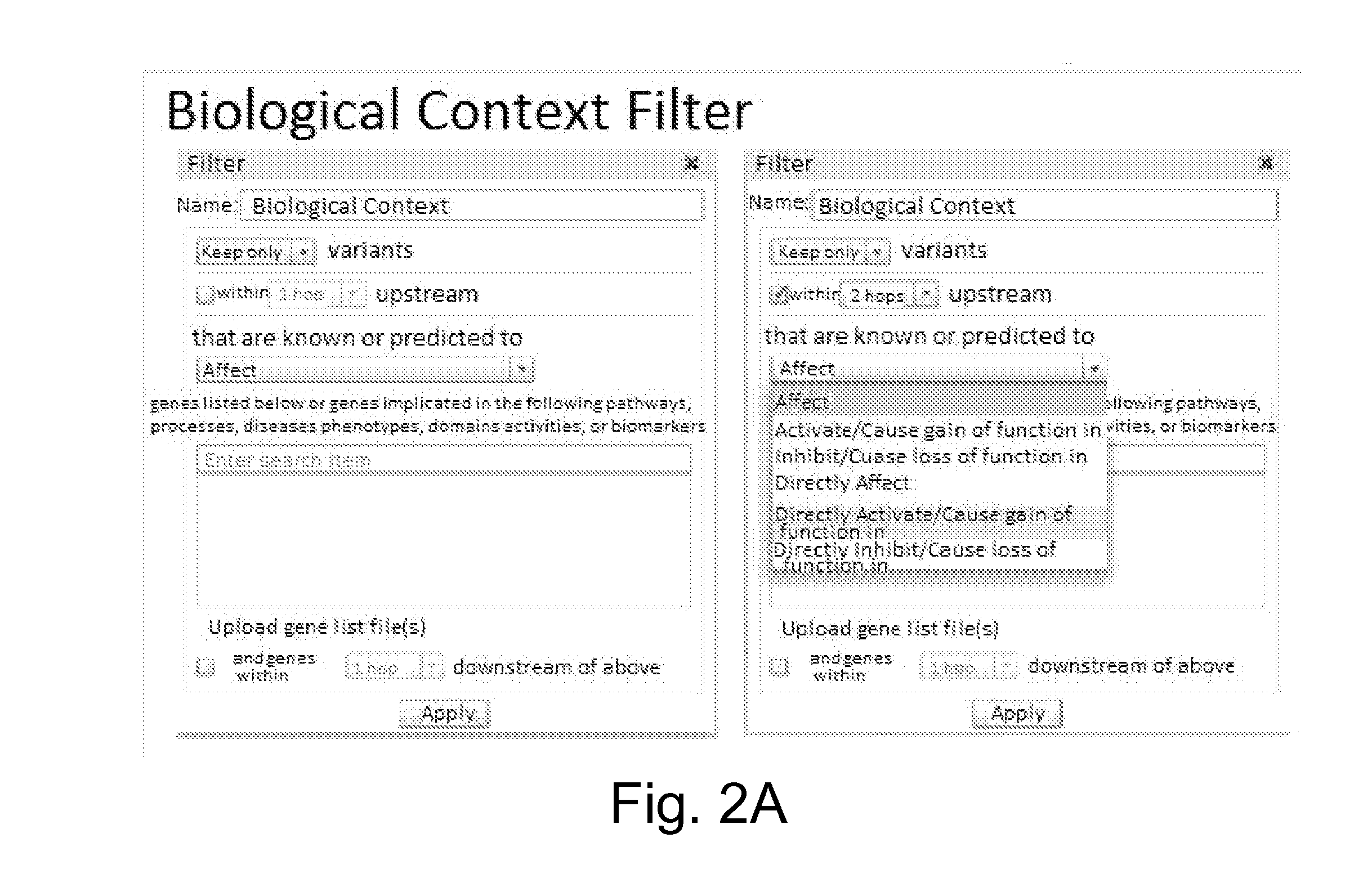
Methods and Systems for Identification of Causal Genomic Variants
PendingUS20140359422A1Chemical property predictionDigital data information retrievalData setGenomic information
Methods and systems for filtering variants in data sets comprising genomic information are provided herein.
Owner:QIAGEN REDWOOD CITY
Cancer chemosensitivity prediction technique based on molecular subnet and random forest classifier
InactiveCN104573410ADefine biological functionImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmPredictive methods
The invention discloses a cancer chemosensitivity prediction technique based on a molecular subnet and a random forest classifier. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of fusing data of oncogene expression profile, information of tumor mutation genome information and information of protein-protein interaction group, and excavating carcinogenic and cancer suppressor gene molecular subnets to realize feature extraction; taking the feature extraction as an input feature, designing a training model based on a random forest algorithm, and using the training model to be used for the testing of an independent test set, so as to obtain a chemosensitivity assessment of a patient. If the method provided by the invention is used for screening patients with effective chemotherapy effects before chemotherapy, the method has a significant meaning on cancer therapy.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Mitochondria genome amplified universal primer mixture as well as design and amplification method thereof
ActiveCN105506103AEfficient and specific enrichmentAchieve deep coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic informationMitophagy
The embodiment of the invention discloses a universal primer mixture for animal mitochondria genome amplification as well as a design and amplification method thereof, and a kit comprising the universal primer mixture. By utilizing the primer mixture or the kit and the animal mitochondria genome amplified method and combining the novel high throughput sequencing technique, the animal mitochondria genome information can be efficiently obtained in low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
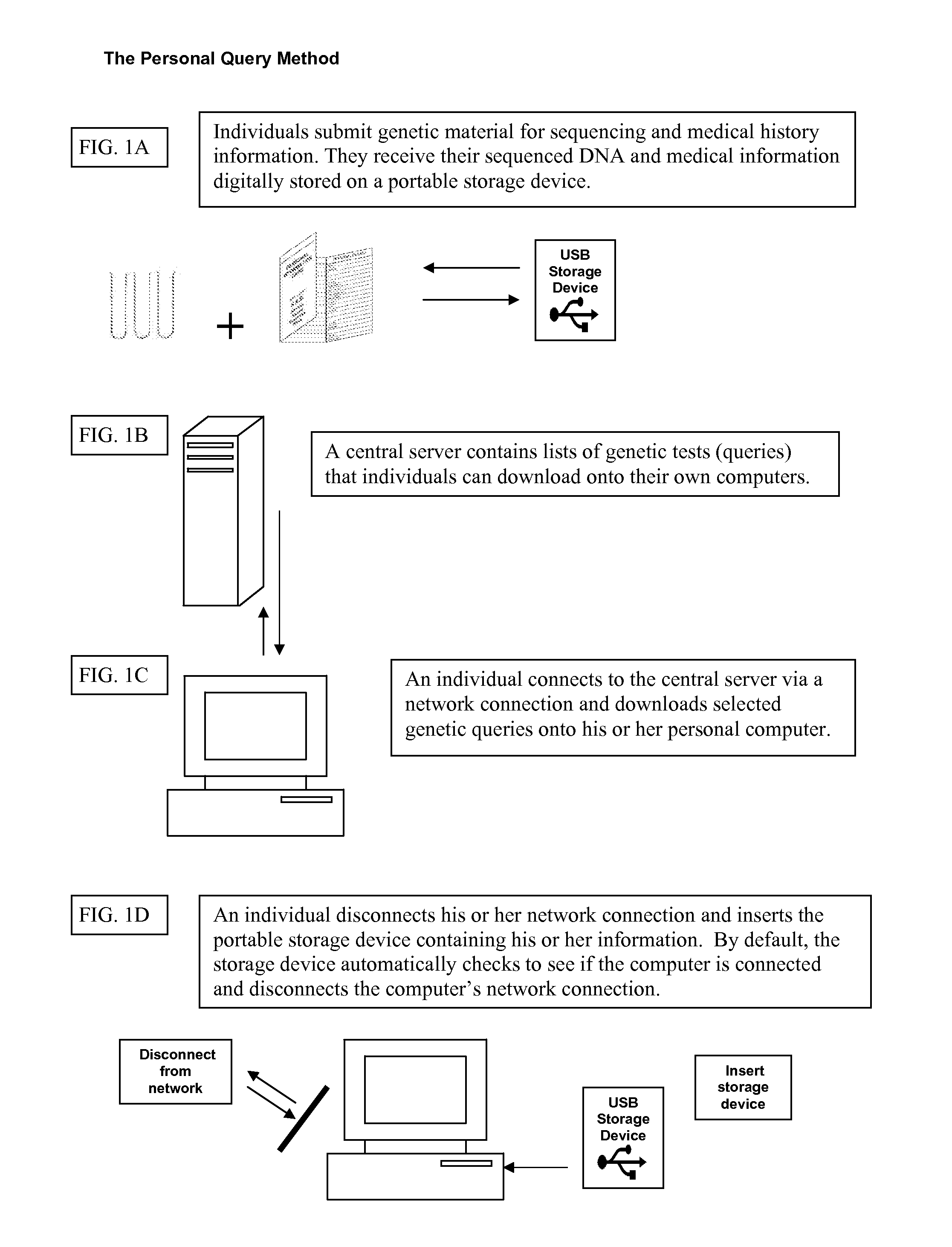
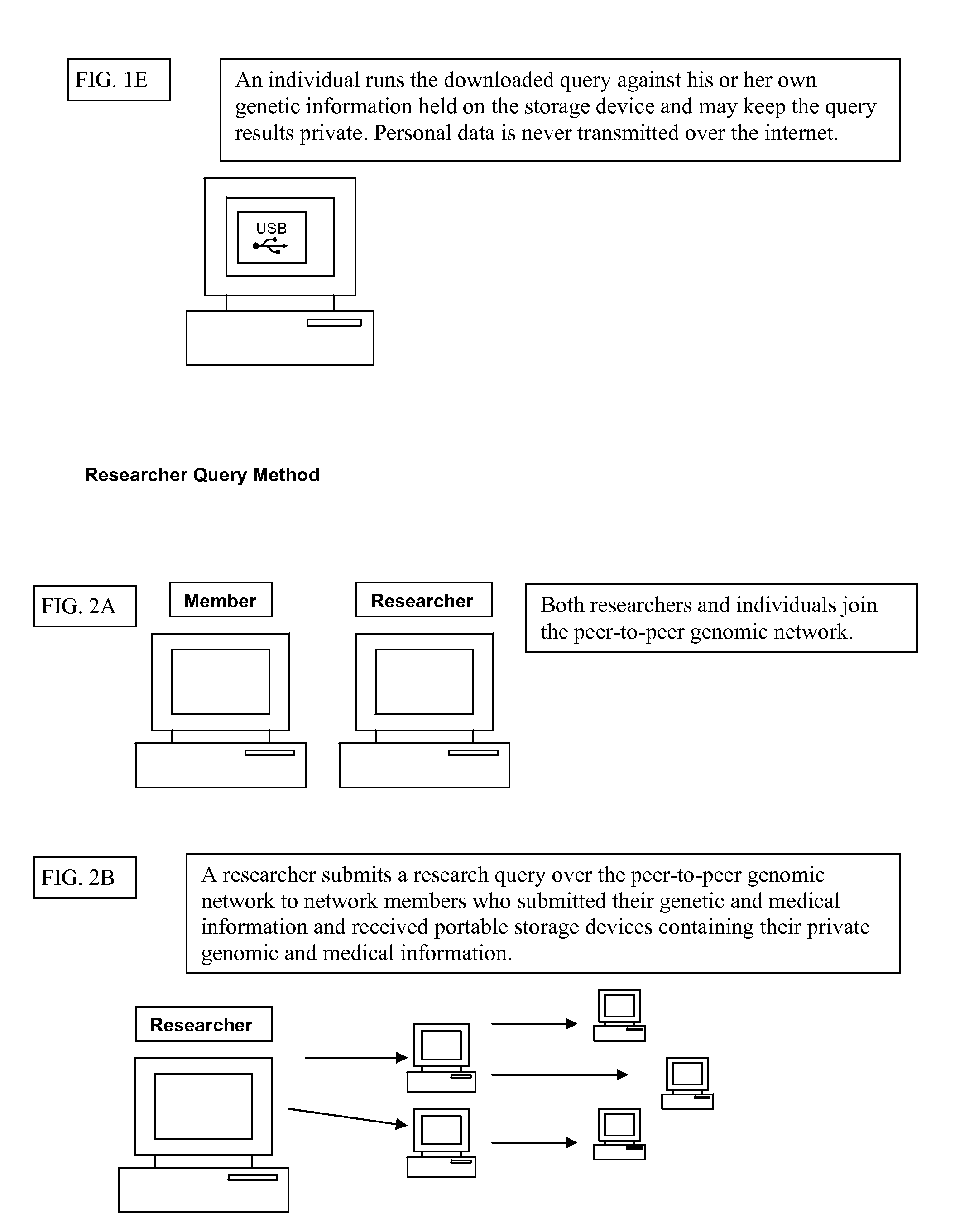
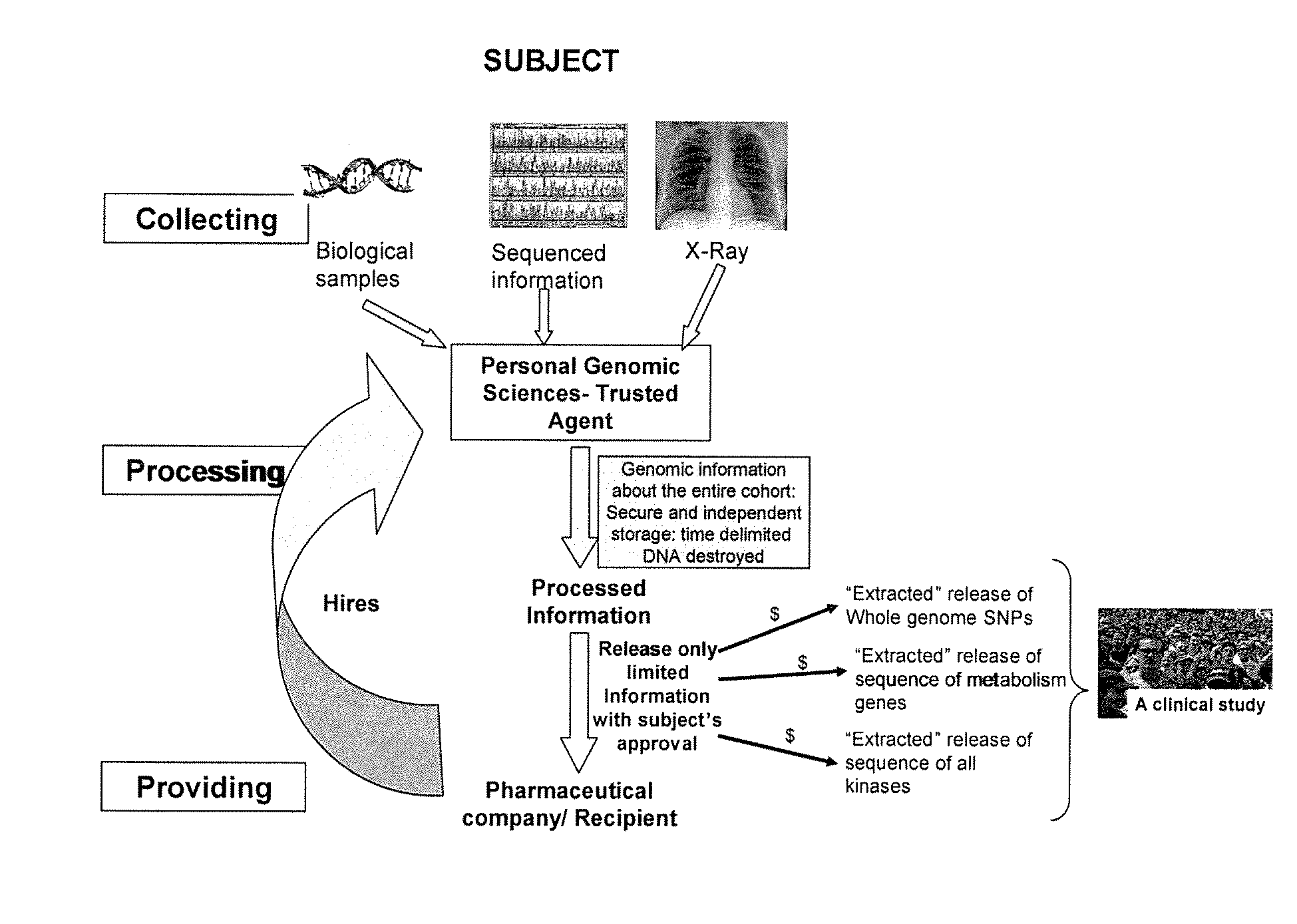
Personally controlled storage and testing of personal genomic information
InactiveUS20100121872A1Easy to shareControl over personal dataDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsDiseaseGenomic data
Owner:KNOME
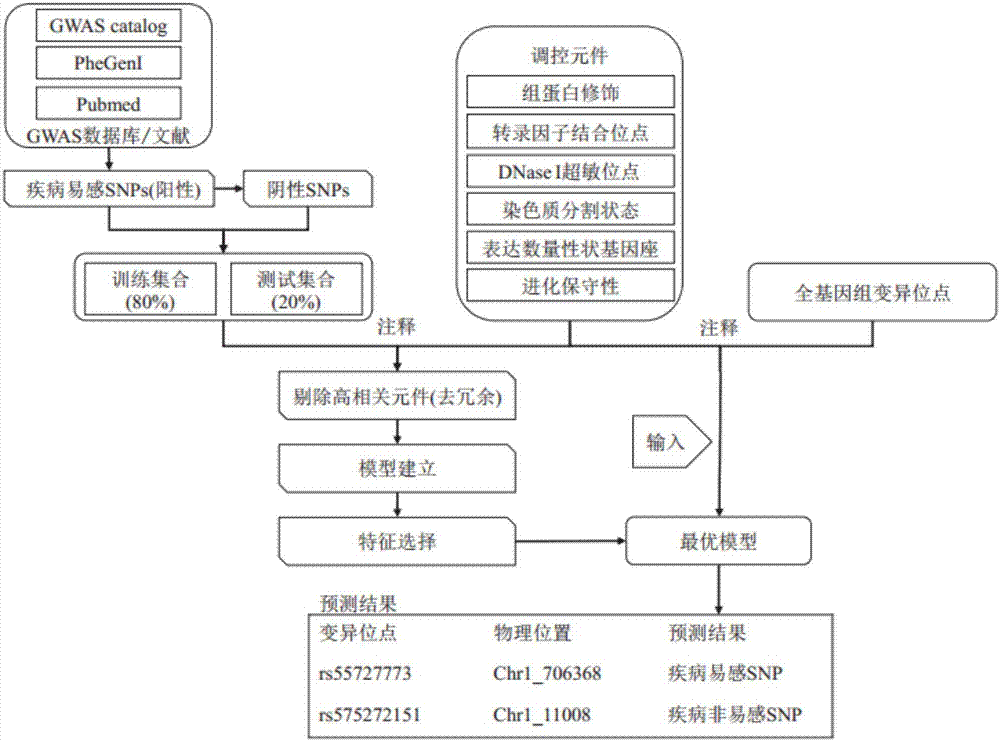
Method for utilizing machine learning to predict complex disease susceptibility locus
The invention discloses a method for utilizing machine learning to predict a complex disease susceptibility locus. The method comprises the following steps of 1, collecting a known complex disease susceptibility locus as a positive set of a machine learning model, predicting a locus irrelevant to a complex disease according to the positive set as a negative set, and annotating an epigenetic regulation element; 2, utilizing machine learning to establish a complex disease epigenetic model; 3, predicting all loci in a whole-genome range according to the established model to obtain a final prediction result as a potential susceptibility locus of the complex disease. According to the method for utilizing machine learning to predict the complex disease susceptibility locus, epigenetic information and genome DNA information are combined, epigenetic element features are extracted through machine learning, the susceptibility locus of the complex disease is further predicted in a whole-genome range, heritability explained by the found susceptibility locus can be obviously improved, and a potential target is provided for subsequent medicine design and disease detection.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
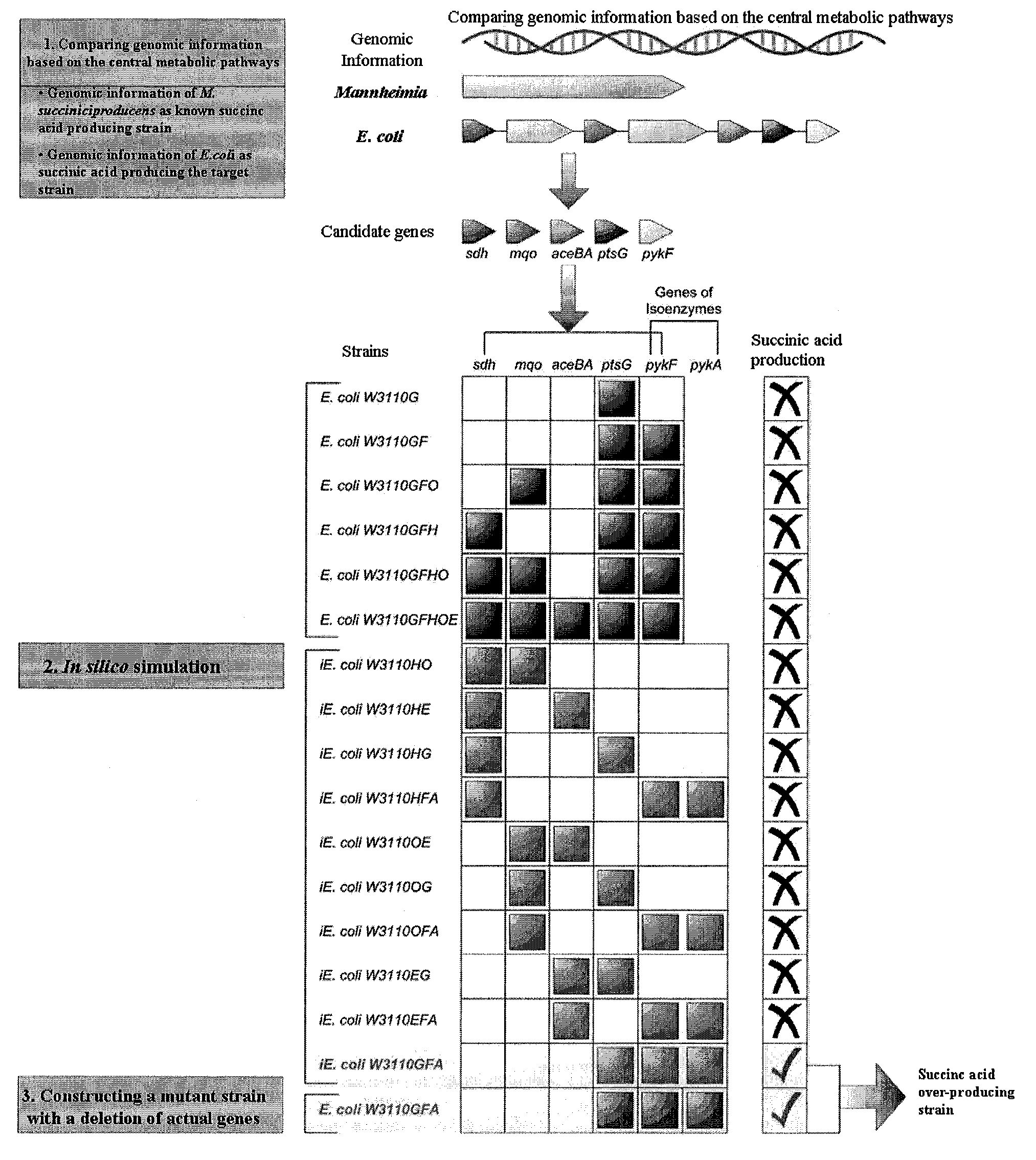
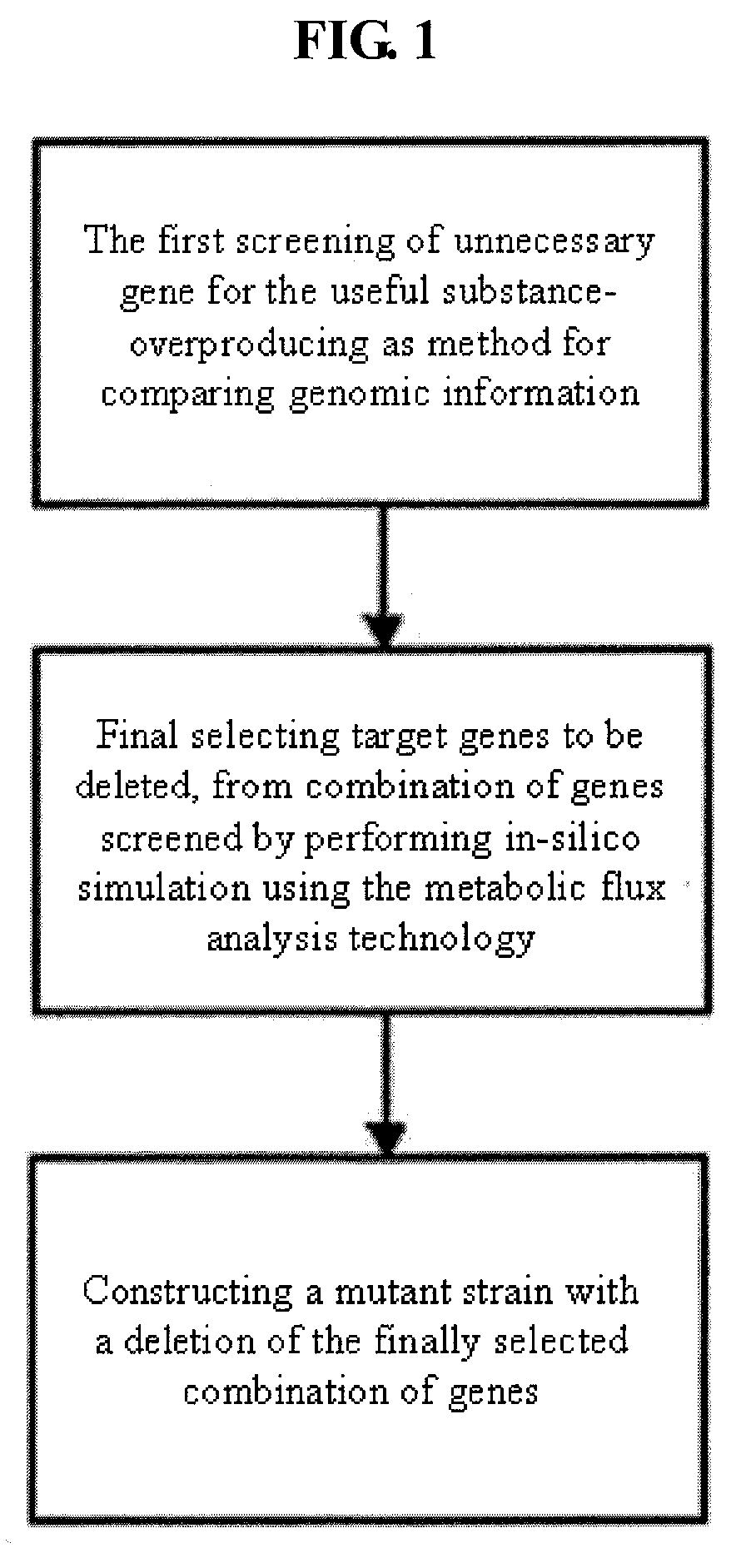
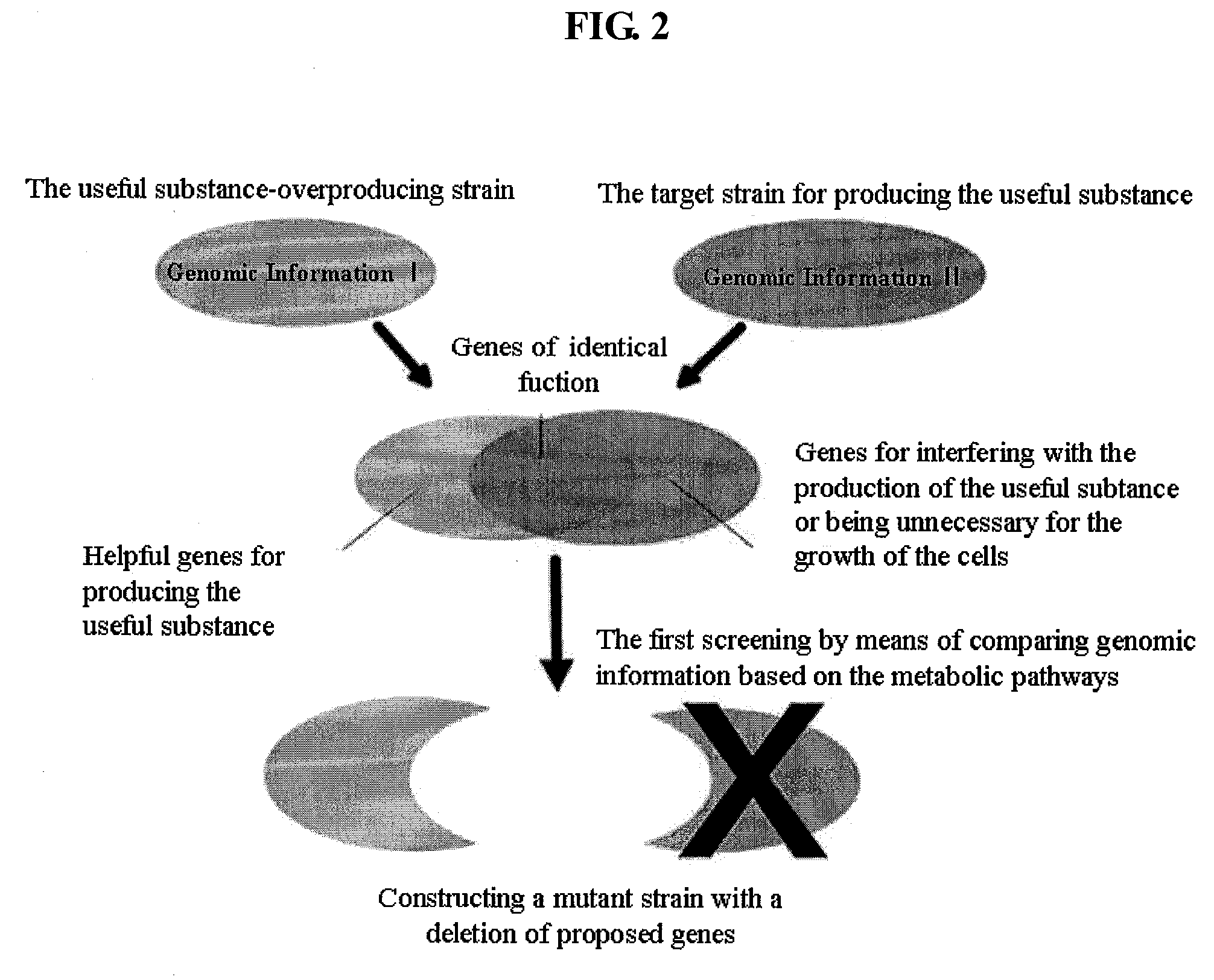
Method For Improving A Strain Based On In-Silico Analysis
InactiveUS20090075352A1Increase strainHigh yieldBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCandidate Gene Association Study
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Mass customization for management of healthcare
ActiveUS8799023B2Cost optimizationQuality improvementMedical communicationMedical data miningMass customizationProgram planning
Owner:MEDIMPACT HEALTHCARE SYST
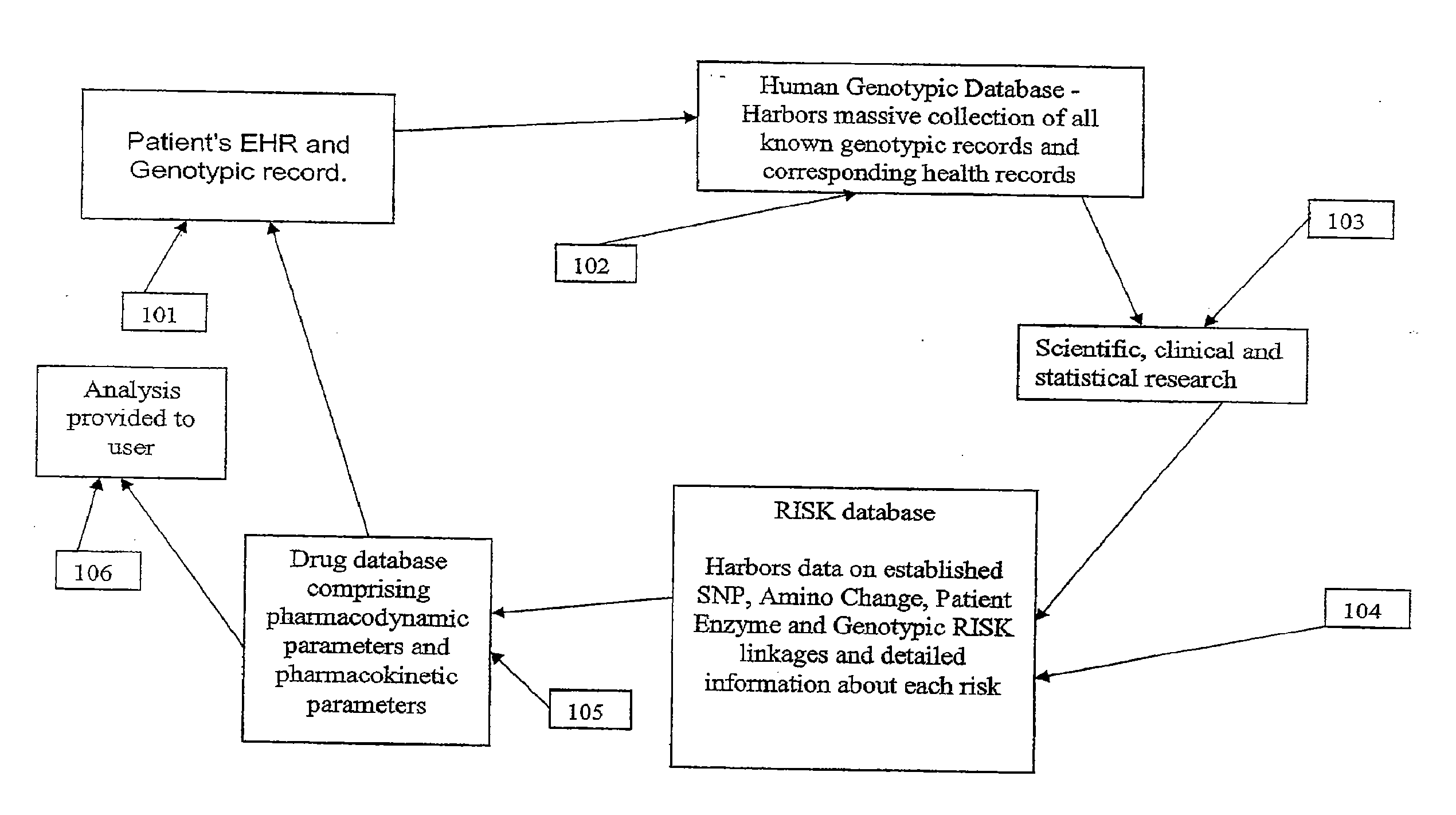
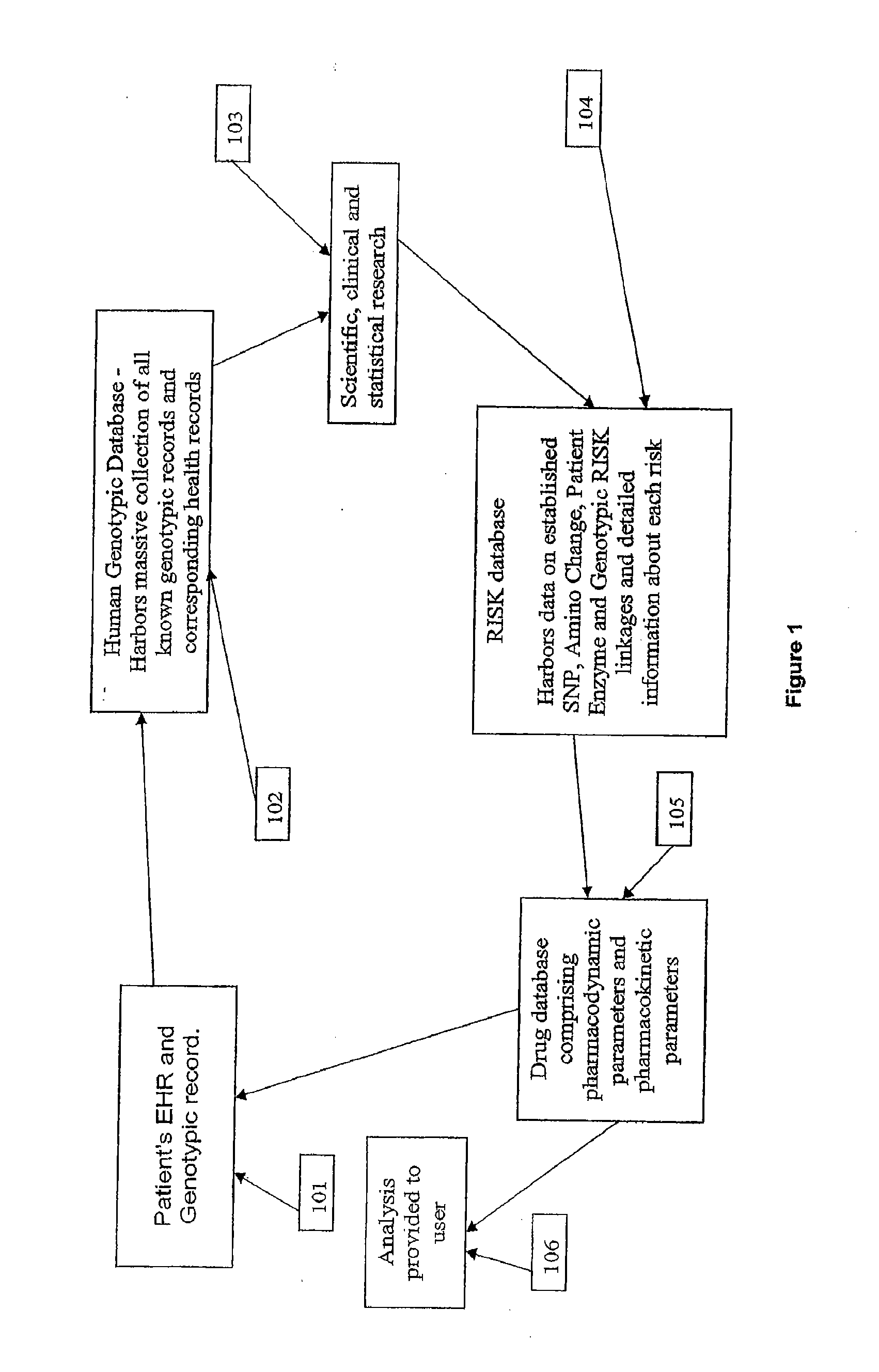
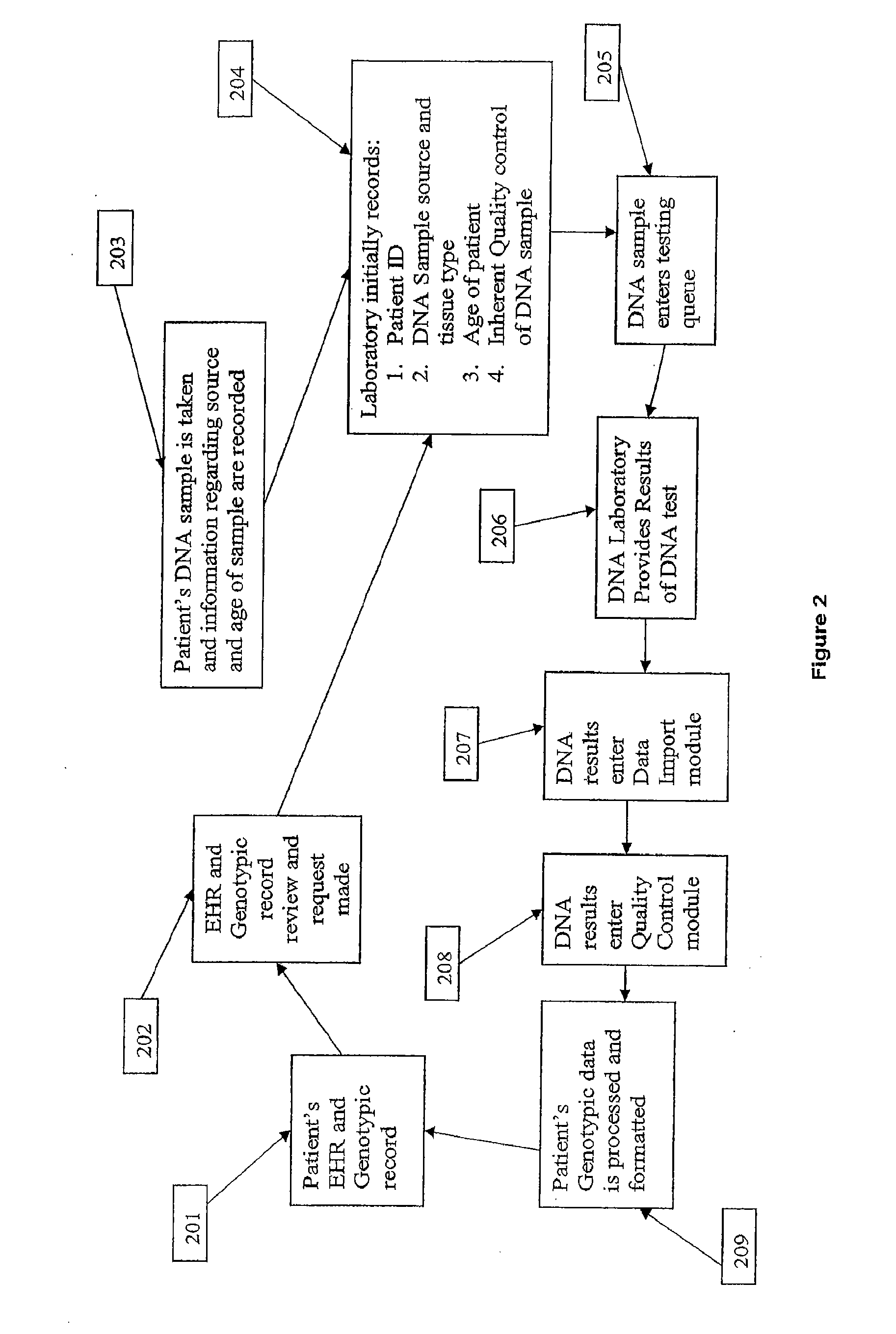
Method for patient genotyping
The present invention is a system and method for utilizing human genetic and genomic information to guide prescription dispensing and improved drug safety in a pharmacy setting. The system and method of the present invention utilizes a dedicated information management system and software to utilize patient-specific genetic information to screen for increased risk of adverse drug reactions and therapeutic responses at the time of drug dispensing.
Owner:KANE MICHAEL D +3
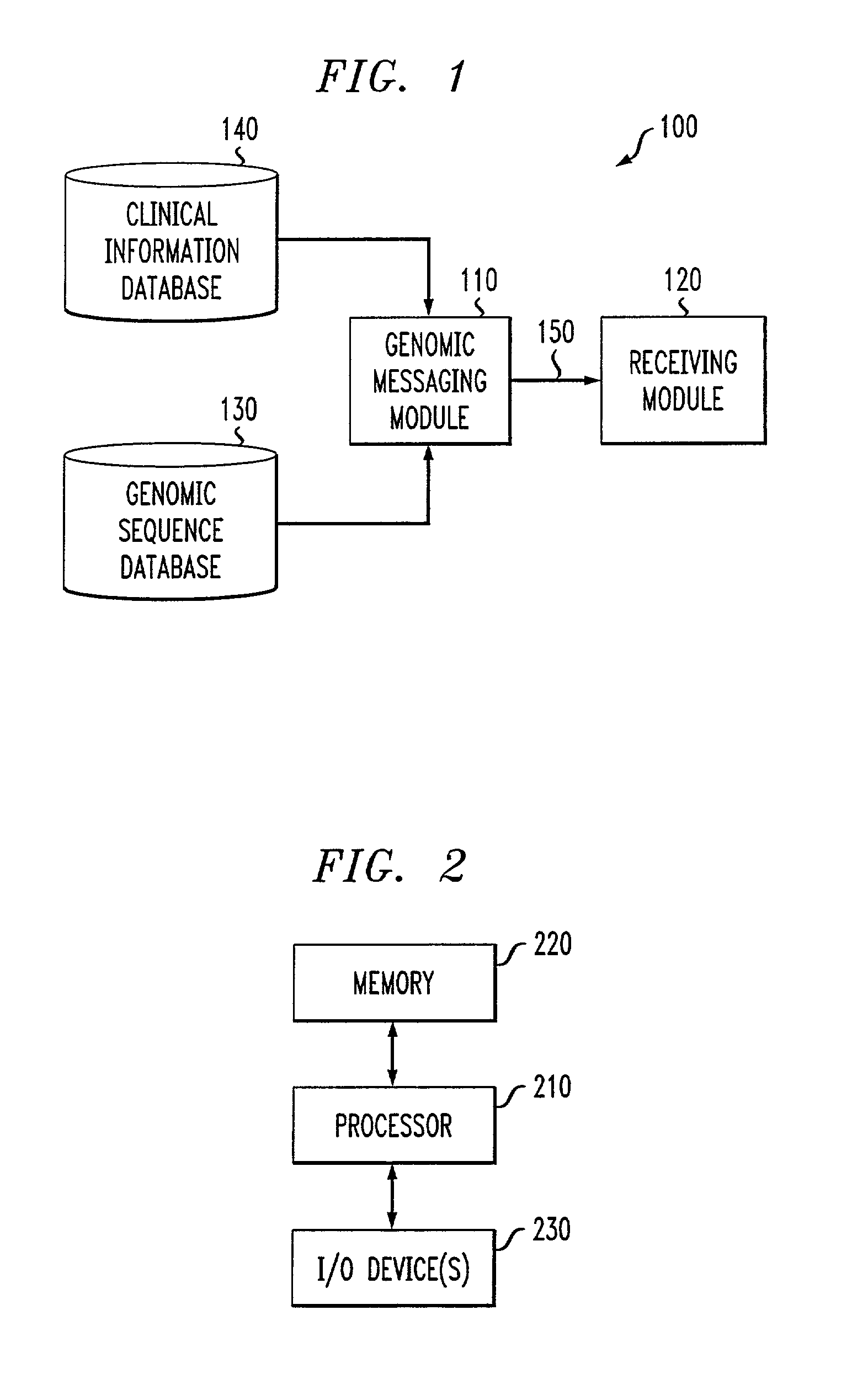
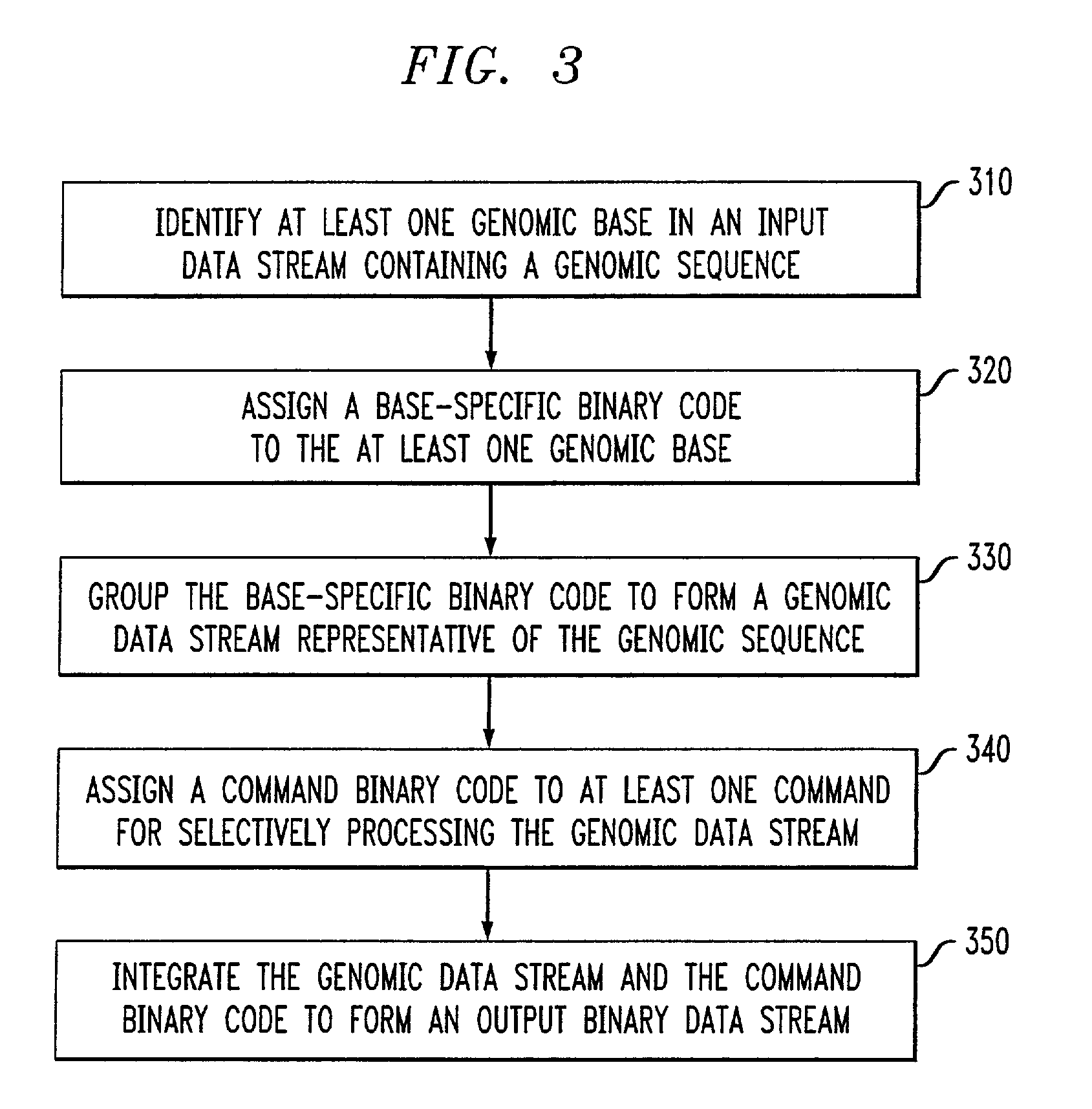
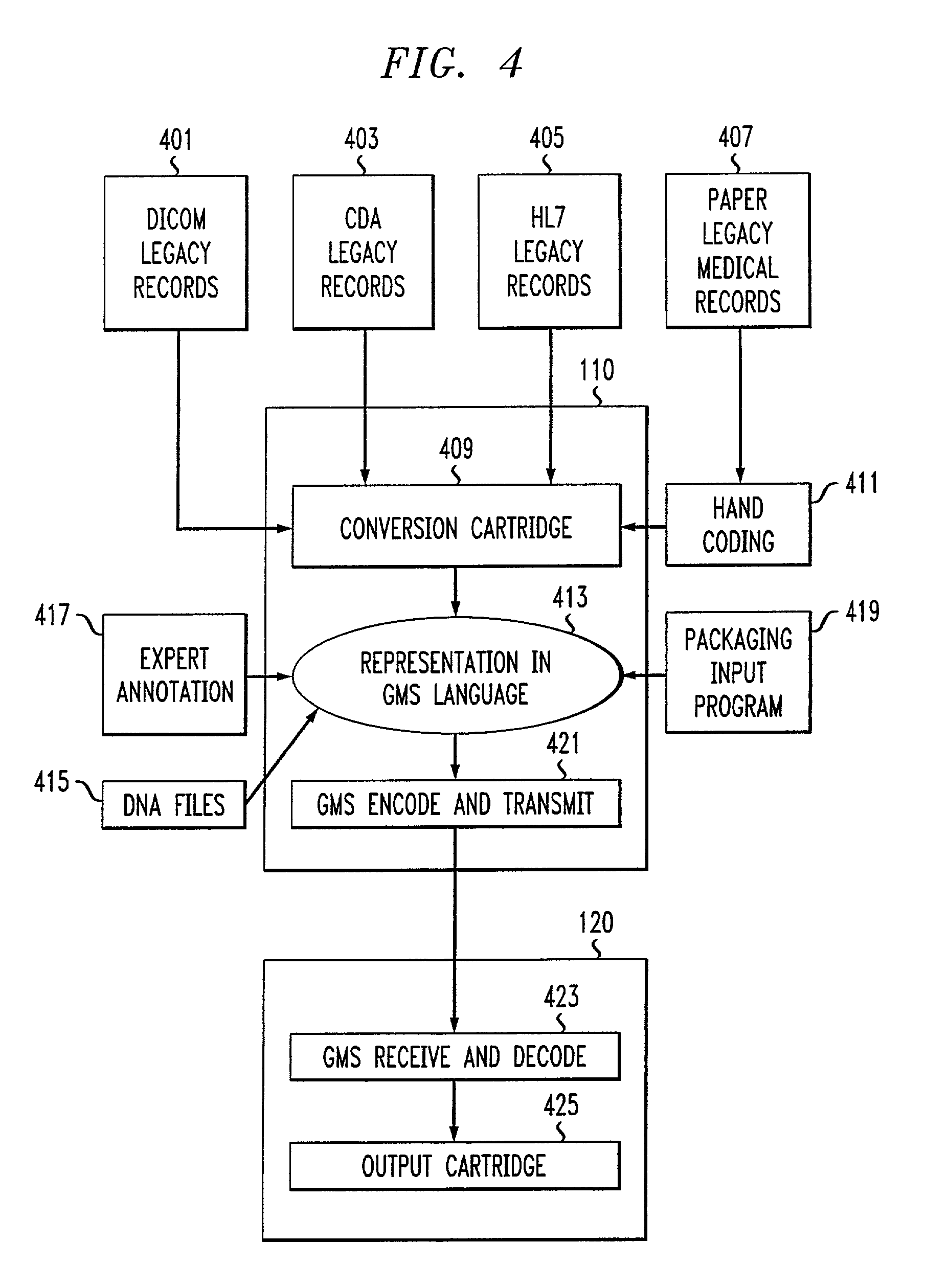
Genomic messaging system
A computer-based method is provided for transferring data that includes a genomic sequence. The method includes identifying at least one genomic base in an input data stream comprising said genomic sequence; assigning a base-specific binary code to the at least one genomic base; grouping the base-specific binary code to form a genomic data stream representative of the genomic sequence; assigning a command binary code to at least one command for selectively processing said genomic data stream; and integrating said genomic data stream and said command binary code to form an output binary data stream.
Owner:IPG HEALTHCARE 501 LTD
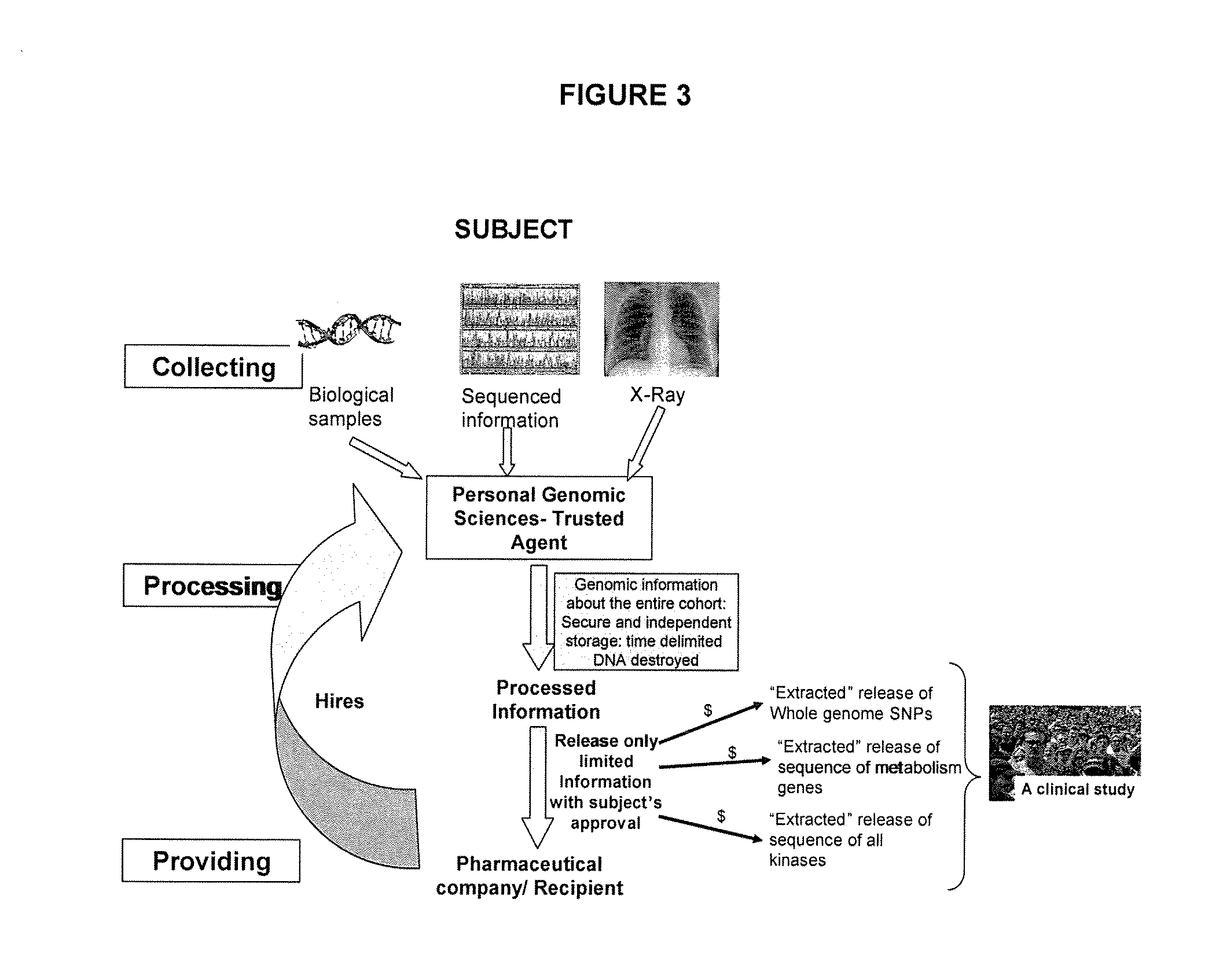
Method of processing genomic information
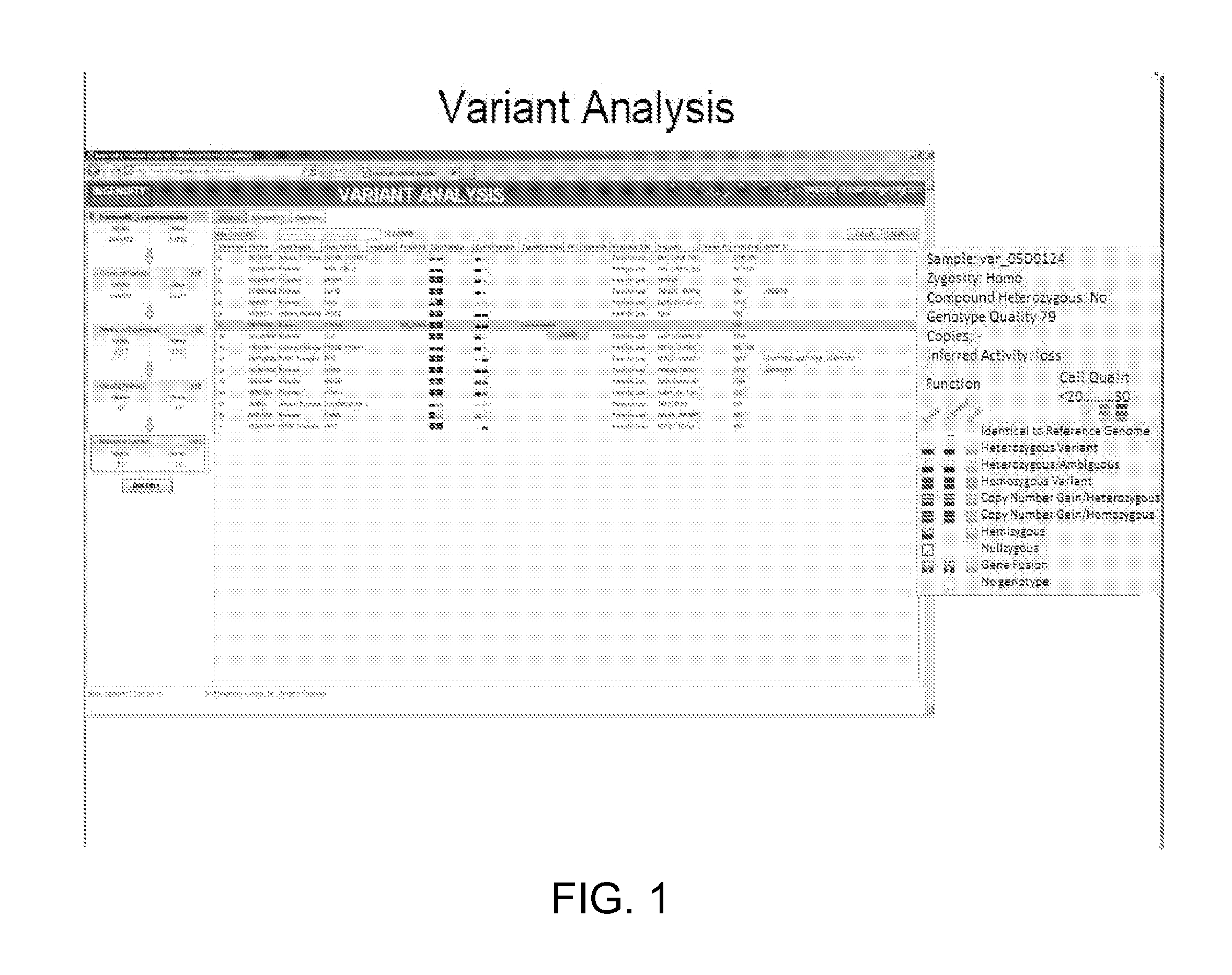
InactiveUS20090182579A1Easy accessData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisGenomic informationComputer science
The present invention relates to a method for processing and / or providing genomic, proteomic, biochemical, and / or metabolic information collected from at least one subject wherein the processing and / or providing of the information is under the control of the subject. There is also provided an apparatus and a system for processing and / or providing of genomic, proteomic, biochemical, and / or metabolic information.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
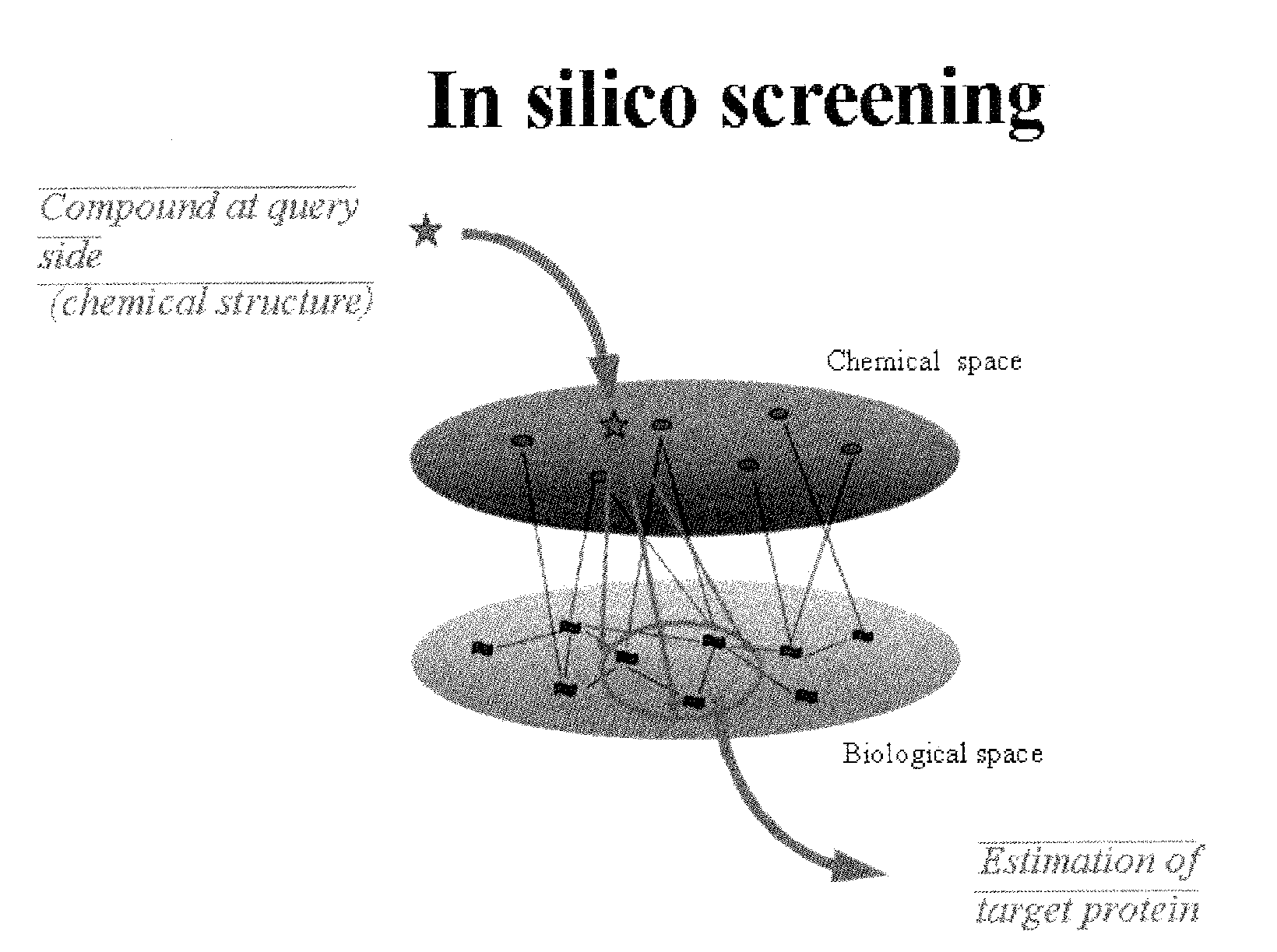
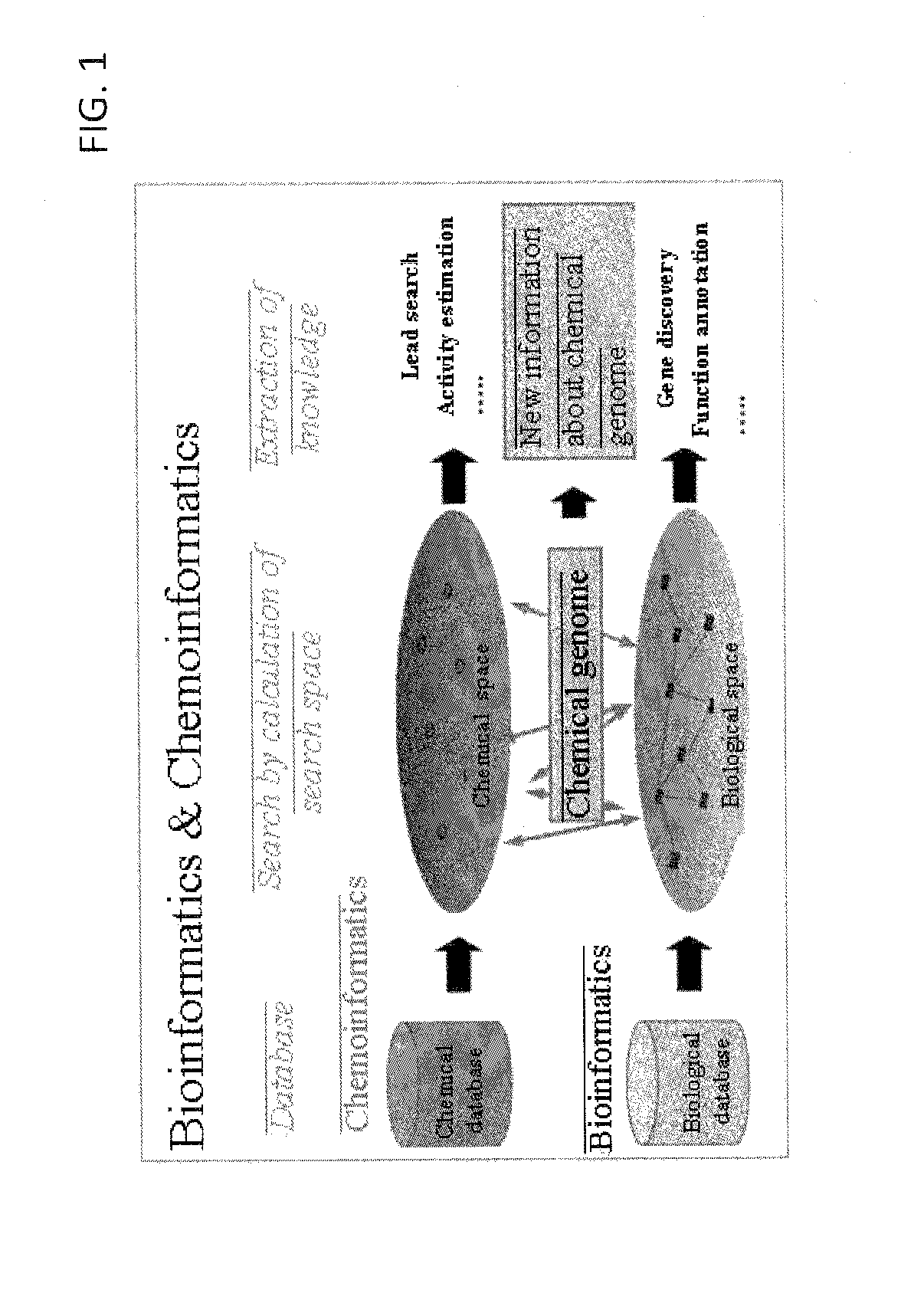
Estimation of protein-compound interaction and rational design of compound library based on chemical genomic information
InactiveUS20100099891A1Easy to understandLower performance requirementsOrganic chemistryMolecular designStudy methodsMultivariate analysis
A data processing method for an estimation of compound-protein interaction using both chemical substance information, such as a chemical property of the compound, and biological information, such as sequence information of genes to rationally and efficiently screen compounds. First space representing space coordinates of a first chemical substance group and second space representing space coordinates of a second chemical substance group are defined, and the first chemical substance group is characterized by a first characteristic amount and the second chemical substance group is characterized by a second characteristic amount, and map transformation of the coordinates of the first space and the coordinates of the second space results in the solution so as to increase the correlation between the first space and the second space using a multivariable analysis technique or a machine learning method.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
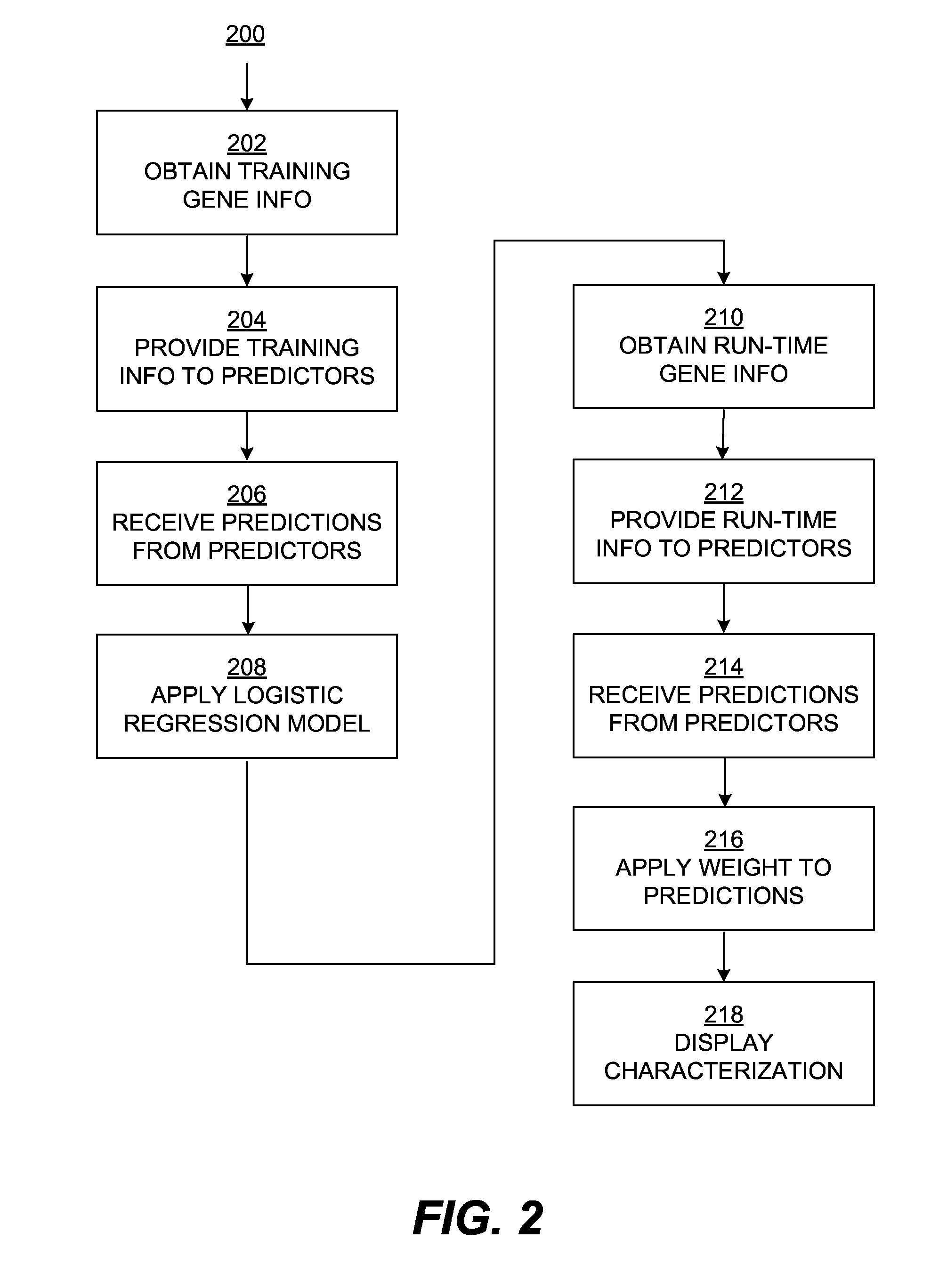
Characterizing uncharacterized genetic mutations
An ensemble predictor for characterizing uncharacterized genetic mutations is disclosed. A first set of genomic information representing a particular (e.g., harmful) mutation is obtained. The first set of genomic information is provided to a number of underlying mutation impact predictors. Predictions are obtained from the underlying predictors. The predictions predict whether the first set of genomic information represents the particular mutation. The predictions and the particular (known) mutation are provided to a logistic regression model, which provides a coefficient for each underlying predictor. A second set of (uncharacterized) genomic information is obtained. The second set of genomic information is provided to the underlying predictors. Predictions are obtained from the underlying predictors and are then weighted using the coefficients. A characterization (e.g., as harmful or not) of the second set of genomic information is provided by the ensemble predictor based on the weighted underlying predictions and may be displayed.
Owner:DNANEXUS
Simultaneous collection of DNA and non-nucleic analytes
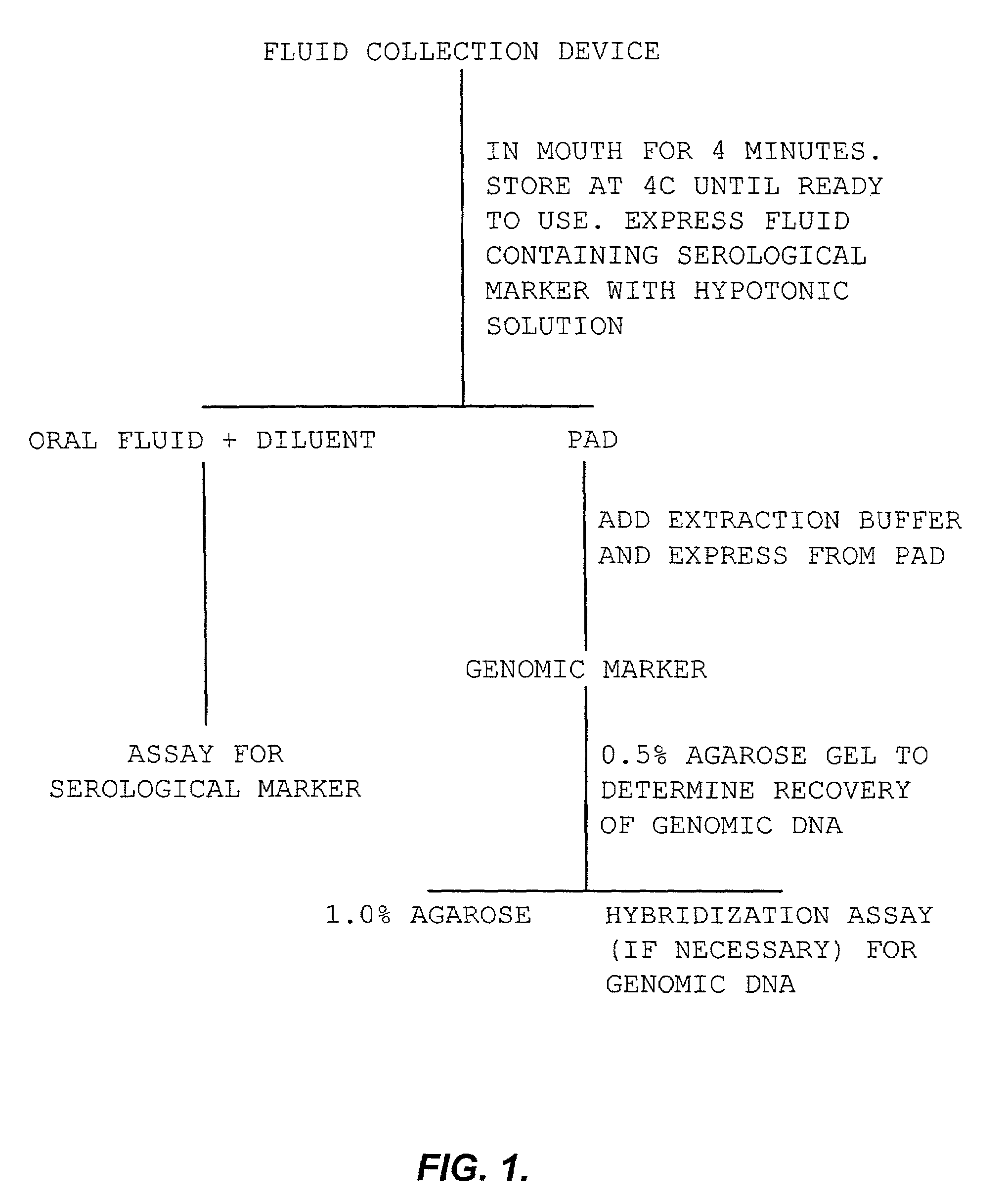
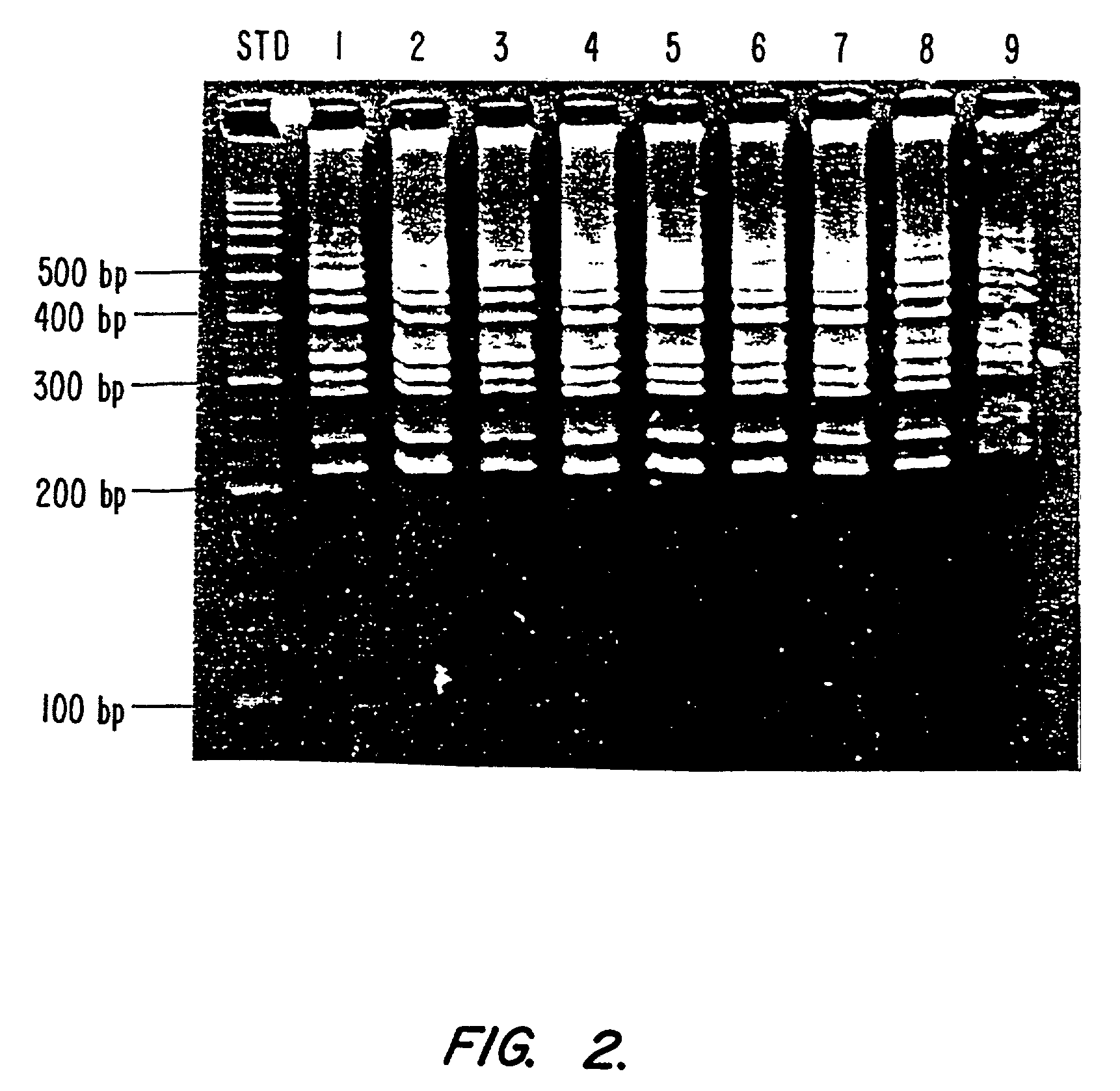
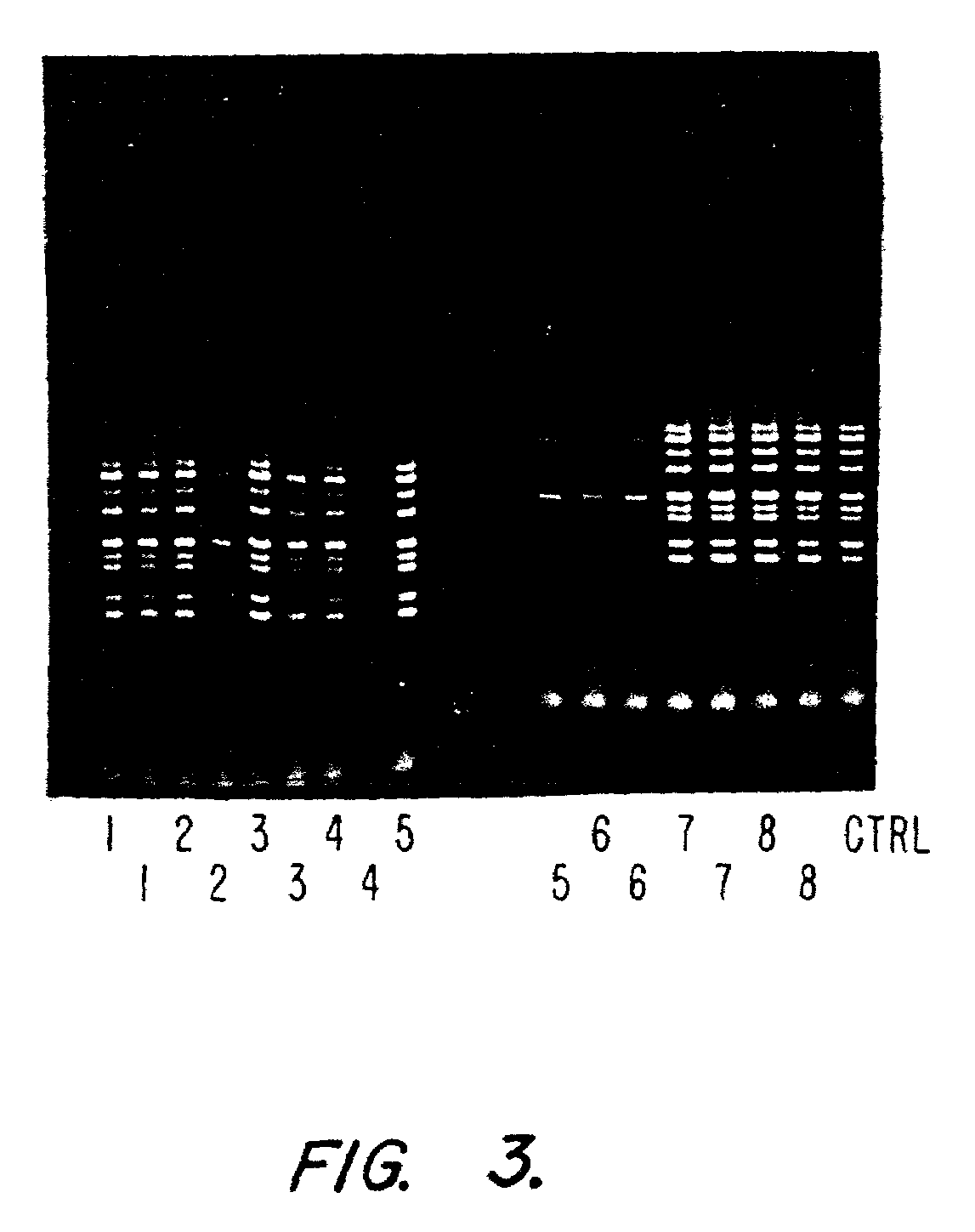
InactiveUS7544468B2Rapid and convenient methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle samplePcr assay
This invention provides for a rapid and convenient method of simultaneous collection of both genomic and diagnostic information from a single sample on a bibulous pad by differential extraction of the diagnostic information from the genomic information. It is a surprising discovery of this invention that a PCR assay on the contents of the bibulous pad provides results comparable in reliability, specificity, and sensitivity to the best available serum (blood) based assays. The assays of this invention can be used to confirm each other, either by detecting the genomic information leading to the diagnostic information, or by detecting in the genomic information, a predisposition to a disease and confirming the presence of the disease through diagnostic testing.
Owner:ORASURE TECHNOLOGIES
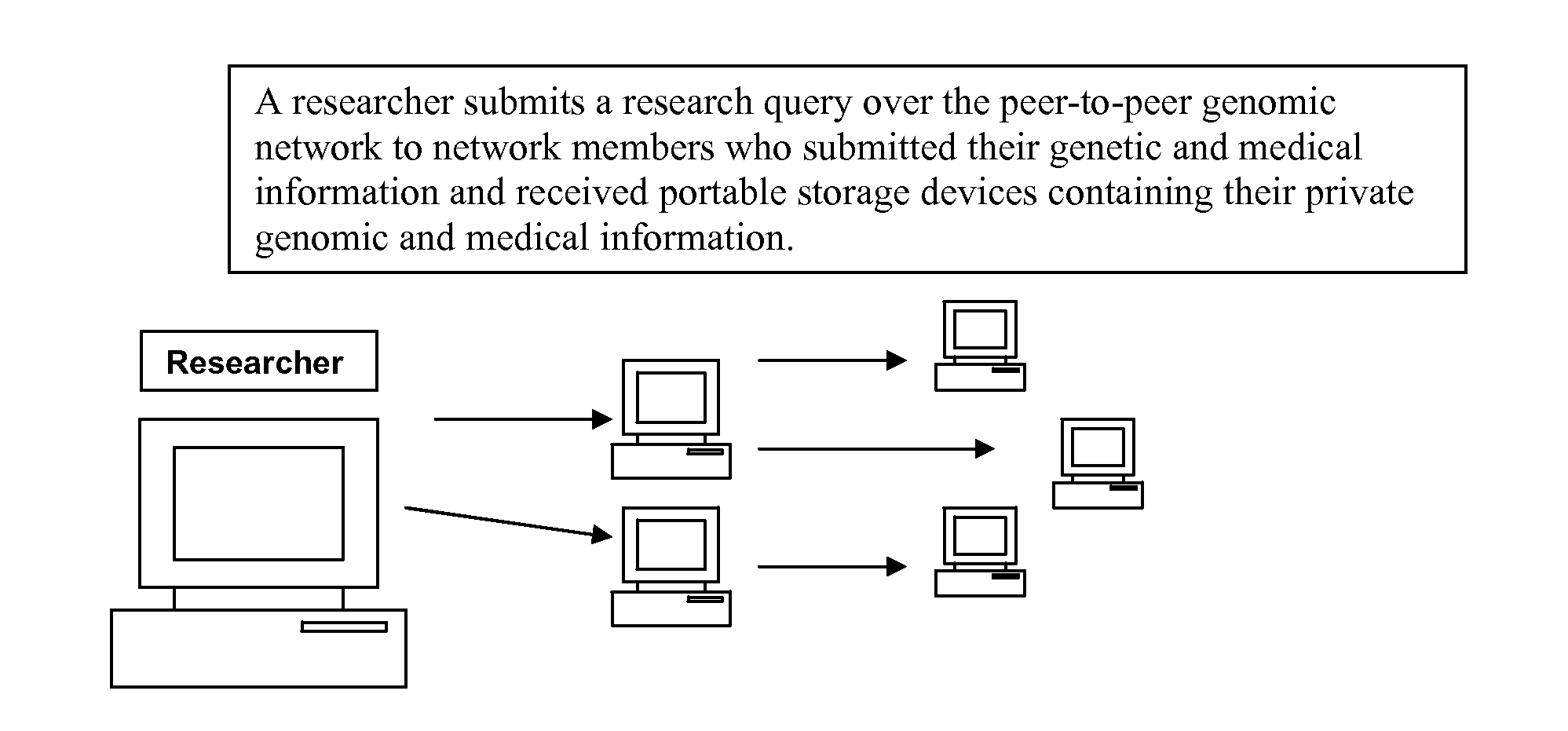
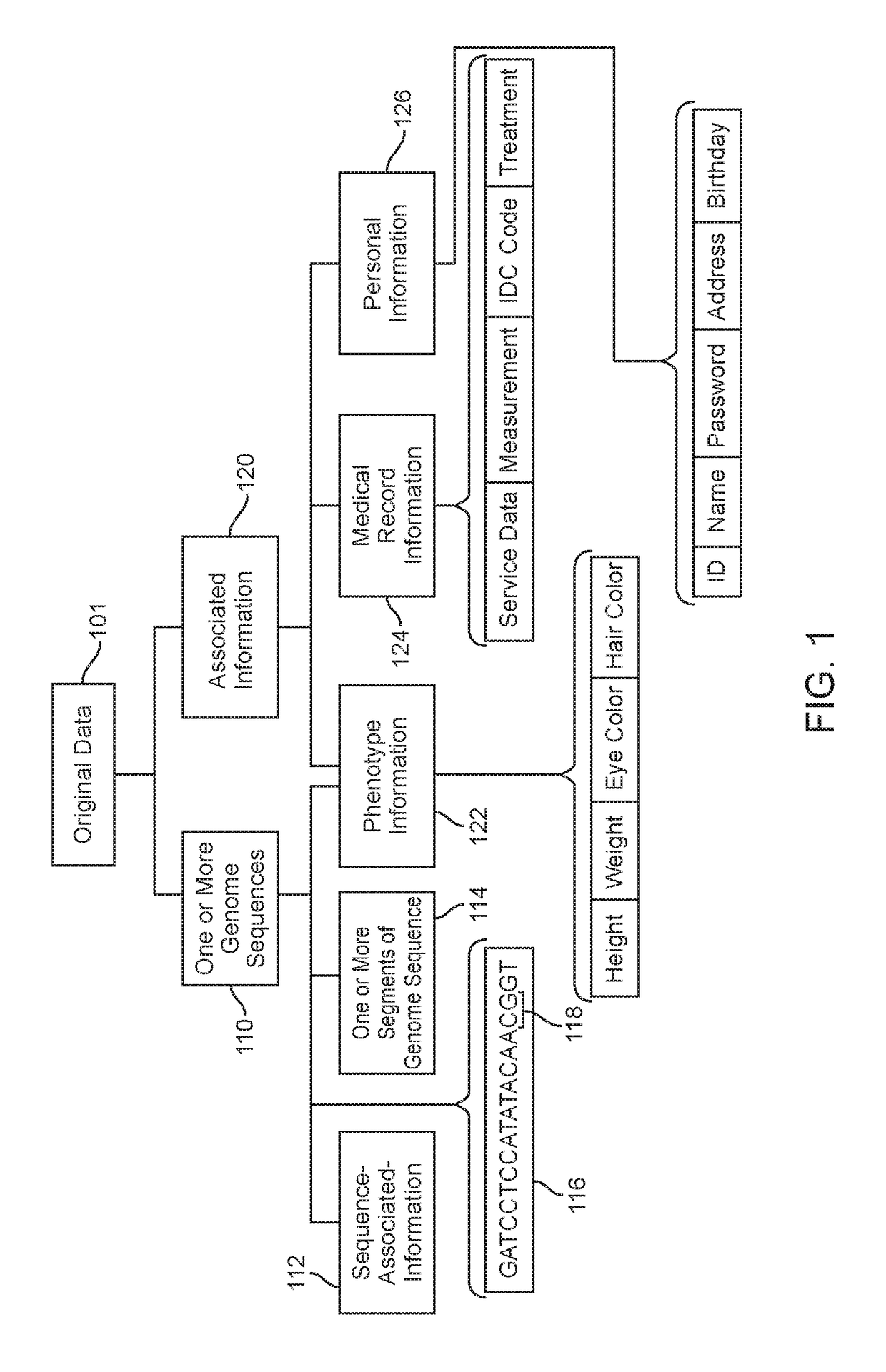
Methods and systems for anonymizing genome segments and sequences and associated information
ActiveUS20170308717A1Prevent and minimize and mitigate identificationMinimize storage spaceDigital data protectionBioinformaticsGenomic SegmentRelevant information
Various methods and systems for processing at least some of genome sequences and at least some of associated information, for an individual, may be described and disclosed herein. A purpose of such processing may be to prevent, minimize, and / or mitigate against (1) identification of the individual from such genome sequence information and / or from associated information; and / or (2) using such genome sequence information and / or associated information as a basis for discriminating against the individual. In some embodiments, such processing may comprise one or more of: segmenting genome sequences for at least a purpose of anonymizing genome information; using anchor segments for a purpose of minimizing storage space in storing of genetic sequence information; generating at least one linkage record; generating at least one anonymized linkage record; processing a request for genetic study results; processing genetic study results received; and / or generating personalized information of interest pertaining to the individual.
Owner:HUANG ETHAN
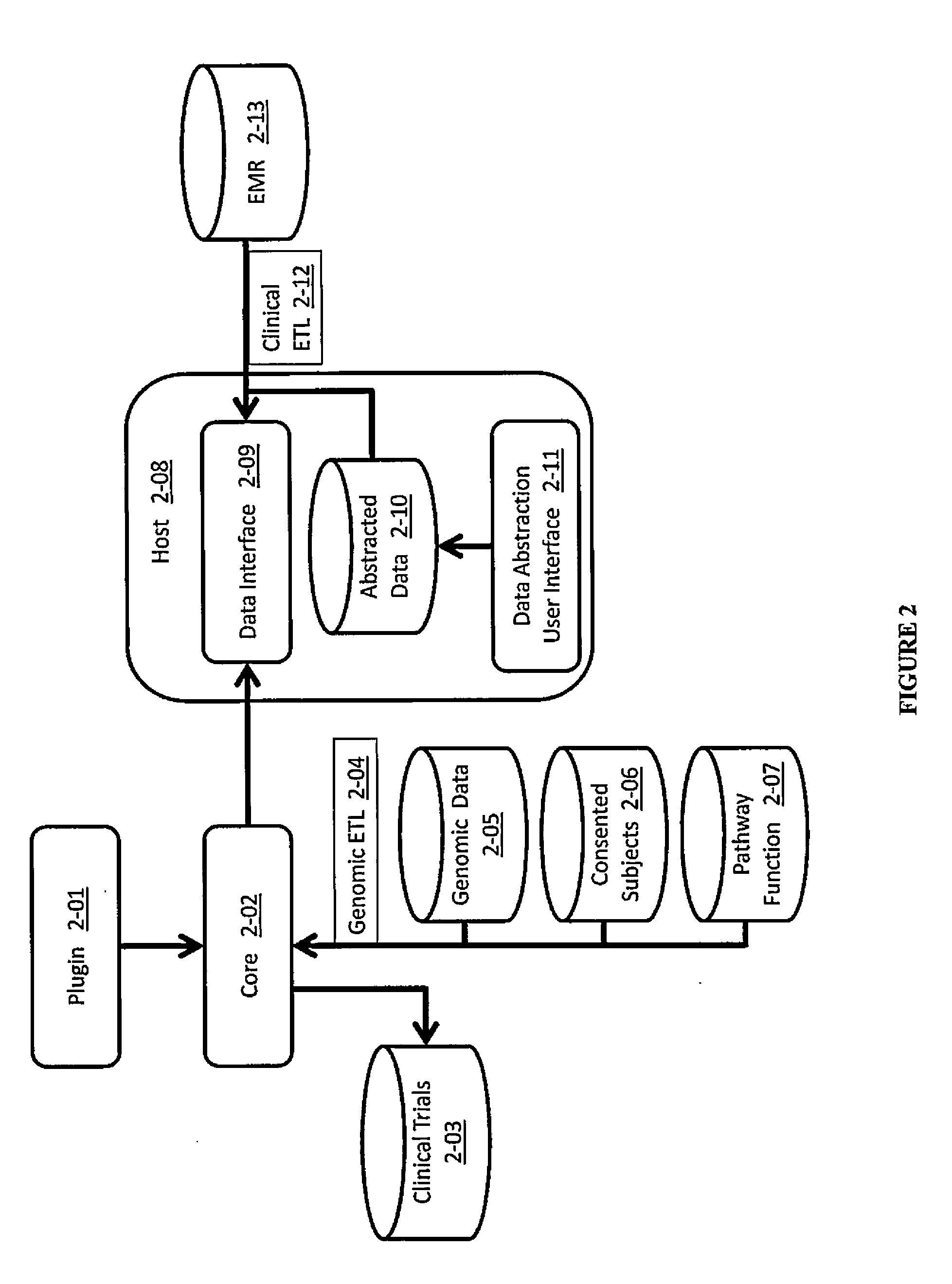
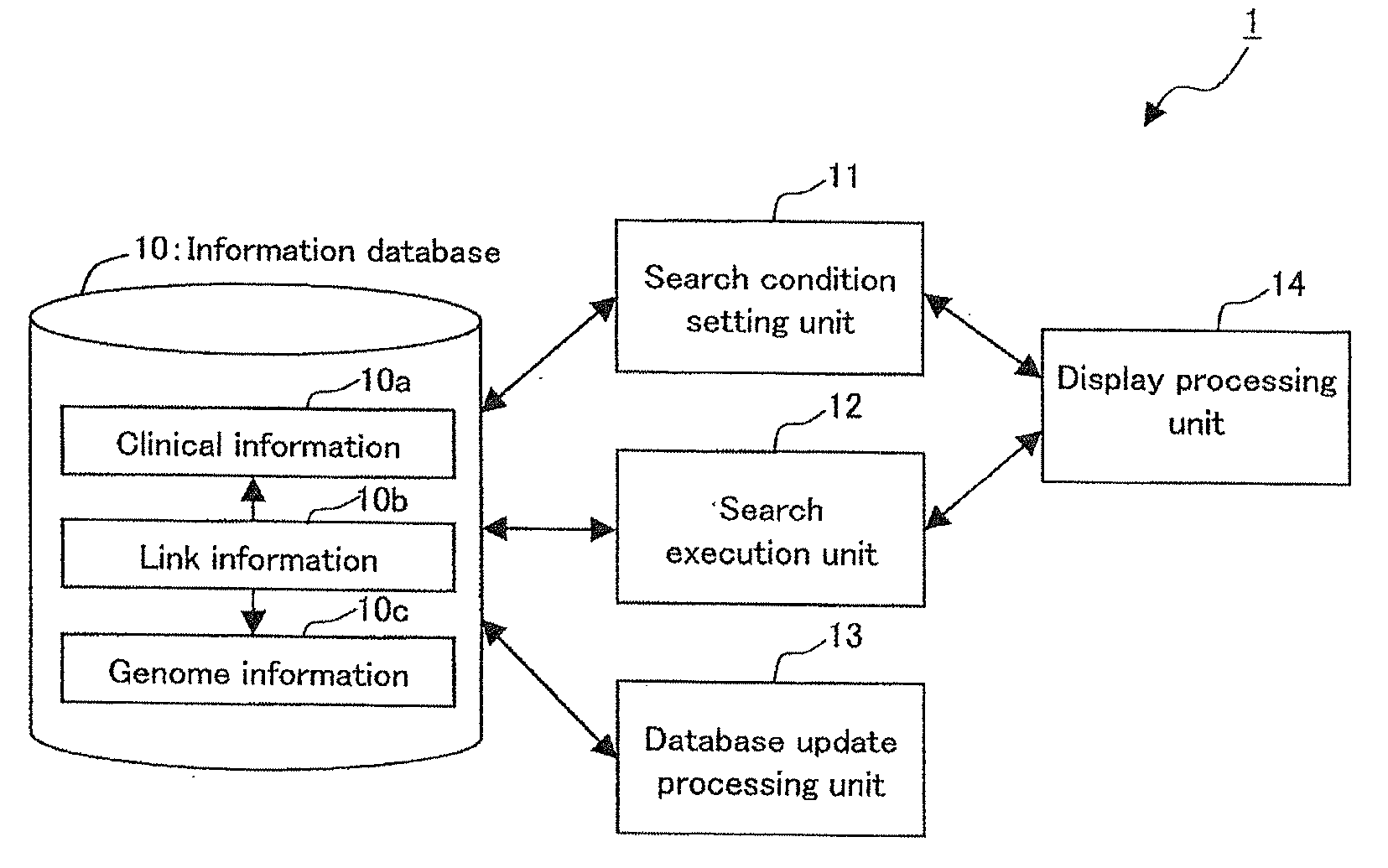
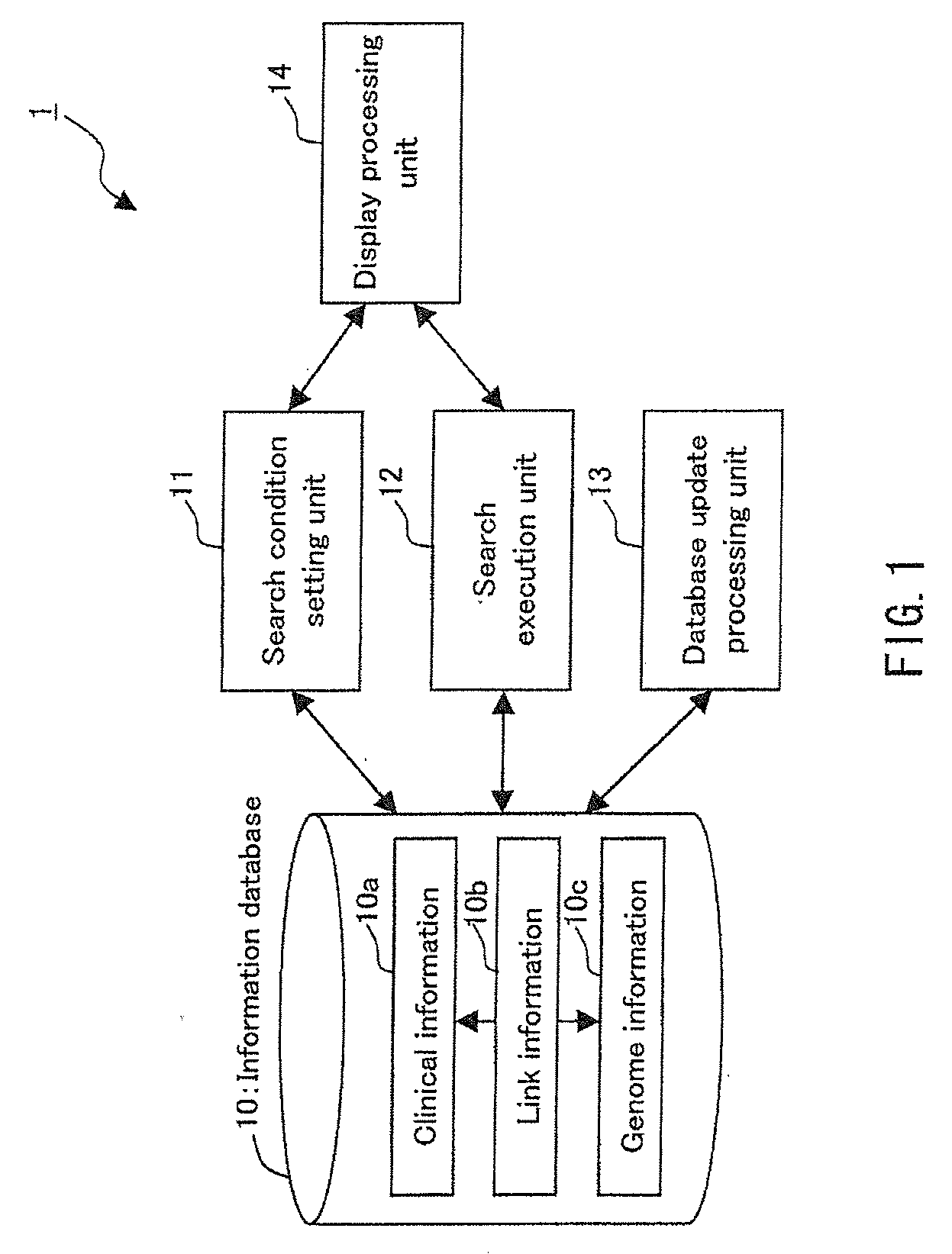
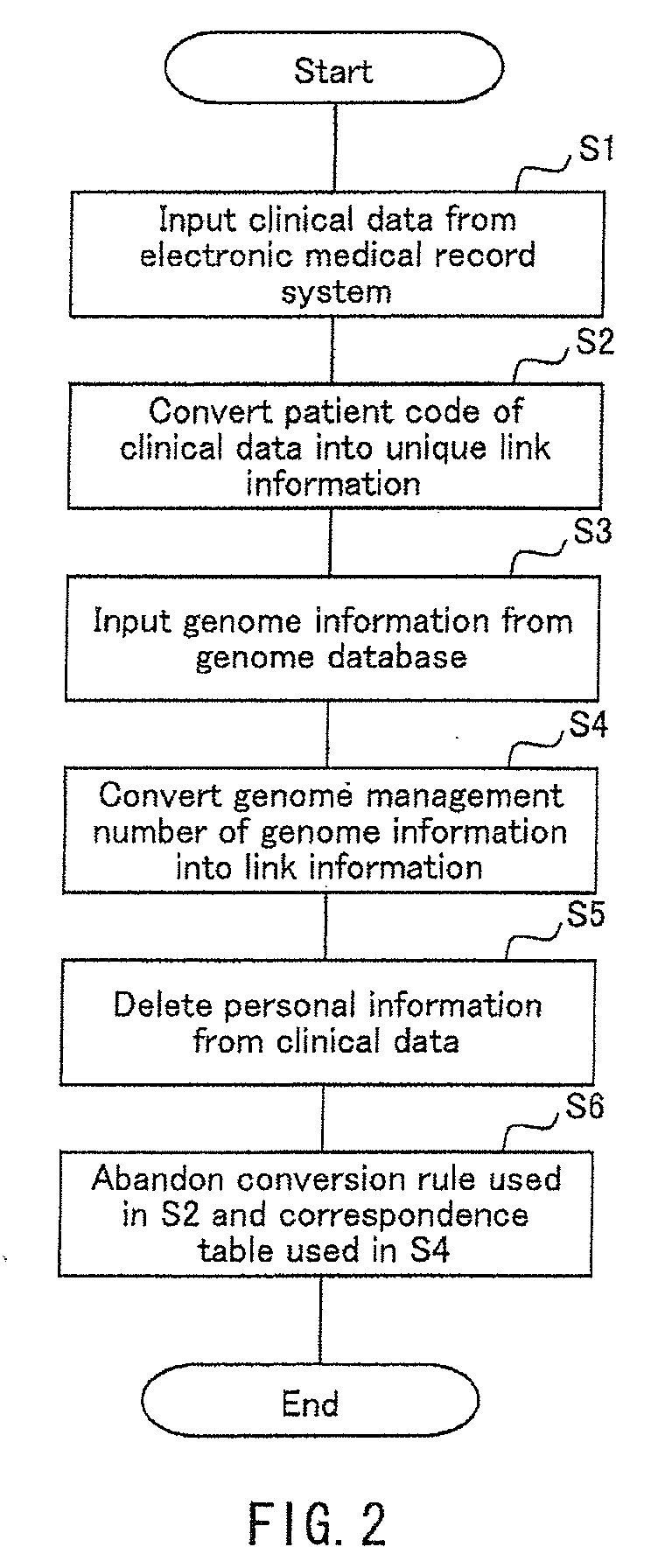
Integrated database system of genome information and clinical information and a method for creating database included therein
InactiveUS20090259489A1Save operatorNot possible to identifyData processing applicationsBioinformaticsGuidelineClinical information
There is provided an integrated database system that incorporates genome information into a clinical information database contrary to conventional databases, while complying with guidelines preventing identification of a provider of the genome information, thereby enabling an easy search for a correlation between the genome information and clinical information and the like. The integrated database system includes an information database including a data storage unit for storing clinical information of a plurality of patients and genome information of at least a part of the plurality of patients. In the data storage unit, the clinical information does not include personal information that identifies the individual patients, and the genome information and the clinical information of the same patient are stored in association with each other by link information that does not identify the individual patients.
Owner:NTT DATA TOKAI CORP +1
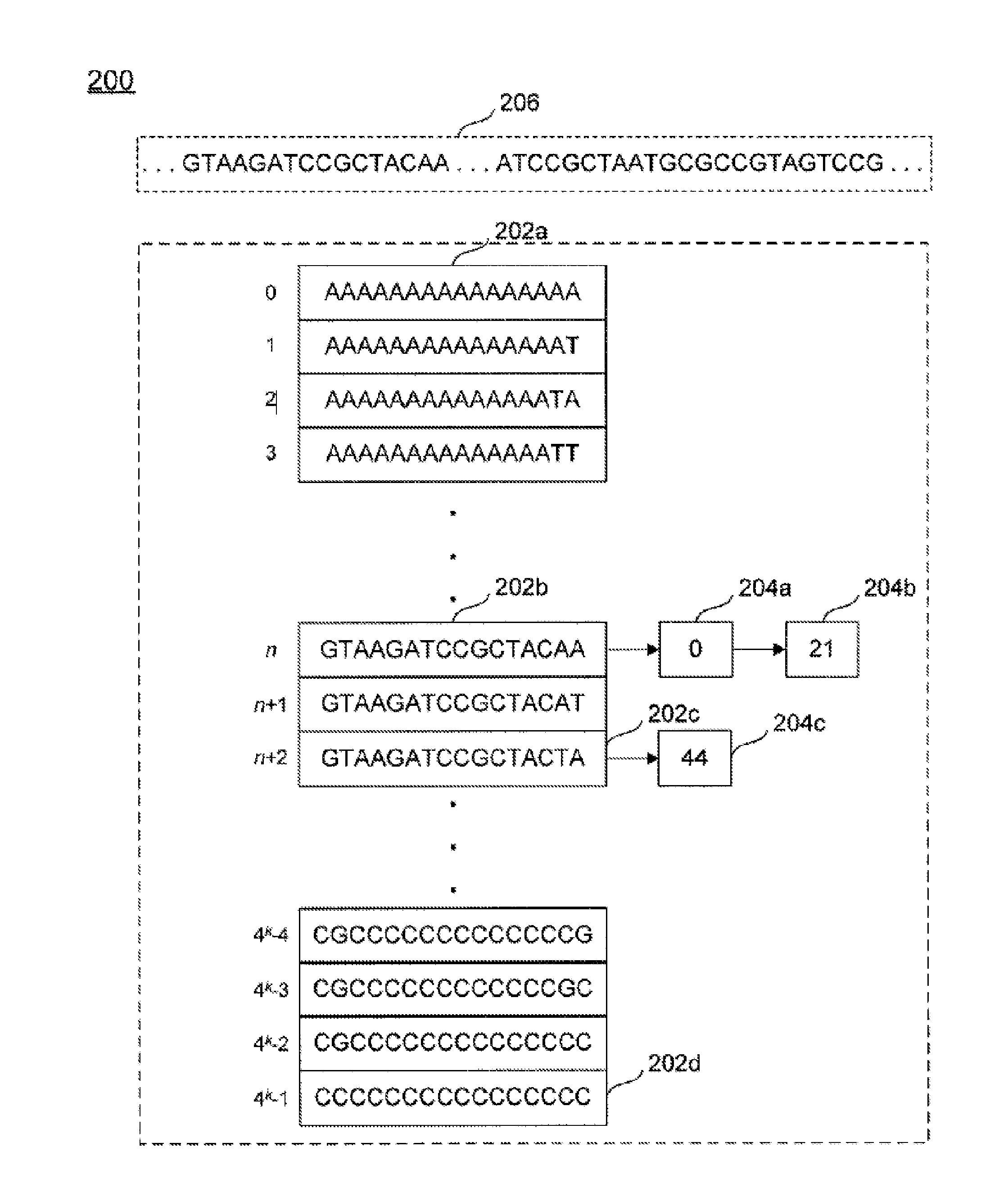
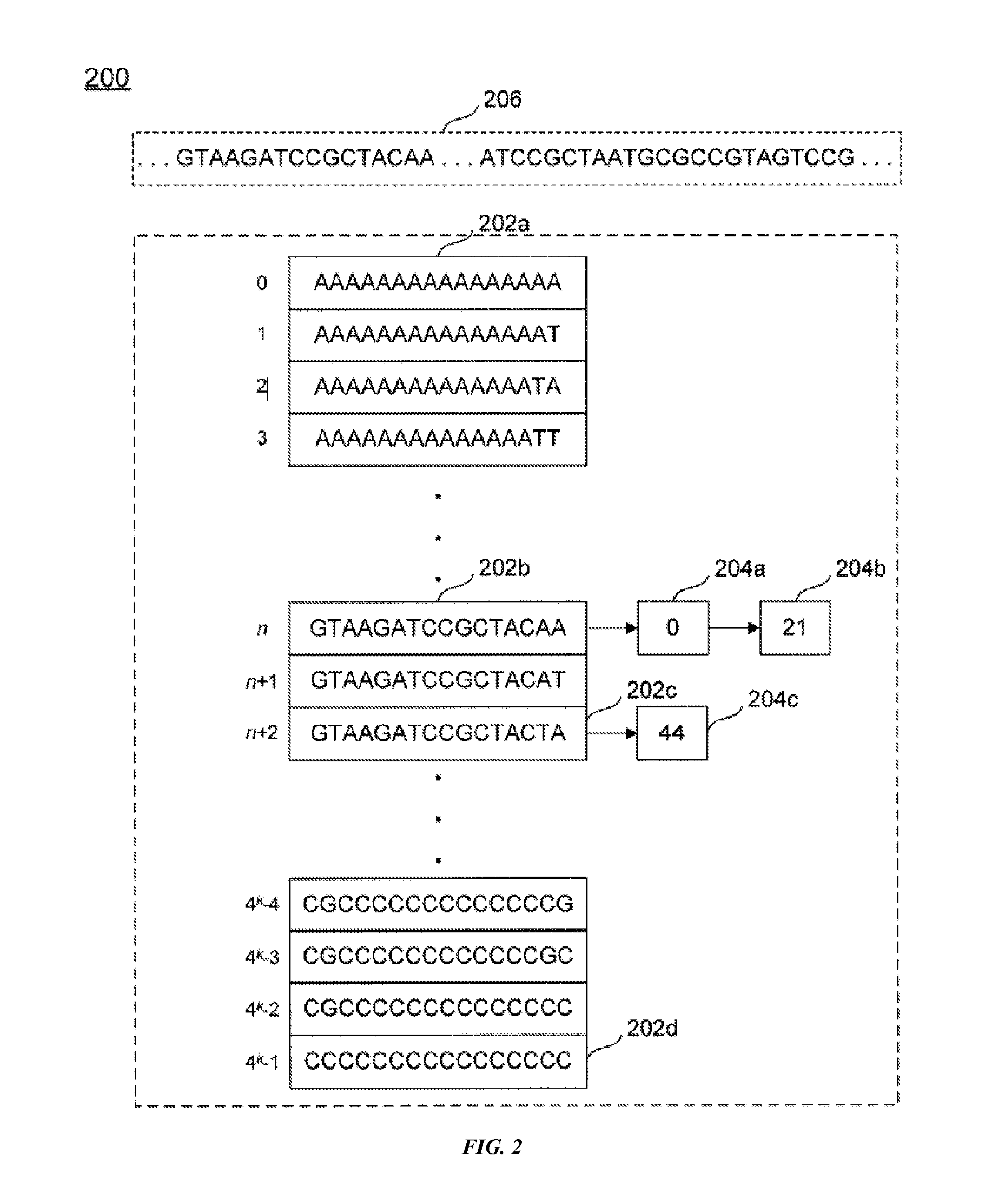
Compression and transmission of genomic information
ActiveUS20160344849A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient compression and transmission and decompressionCode conversionSequence analysisGenomic informationComputer science
Systems and methods for performing genomic information compression, transmission, and decompression are provided. A system for compression, transmission, and decompression of genomic information includes a first computer associated with a first index and a second computer associated with a second index, each index containing reference permutations of nucleic acid sequence portions, each permutation associated with a reference number. The first computer uses input genomic information and the first index to produce a compressed representation of the genomic information, and transmits the compressed representation to the second computer. The second computer uses the compressed representation and the second index to assemble a data representation of the genomic information. The compressed representation comprises references to permutations, indications of locations of each permutation in the input information, indications of variations to permutations, and / or indications of sequence length.
Owner:NOBLIS
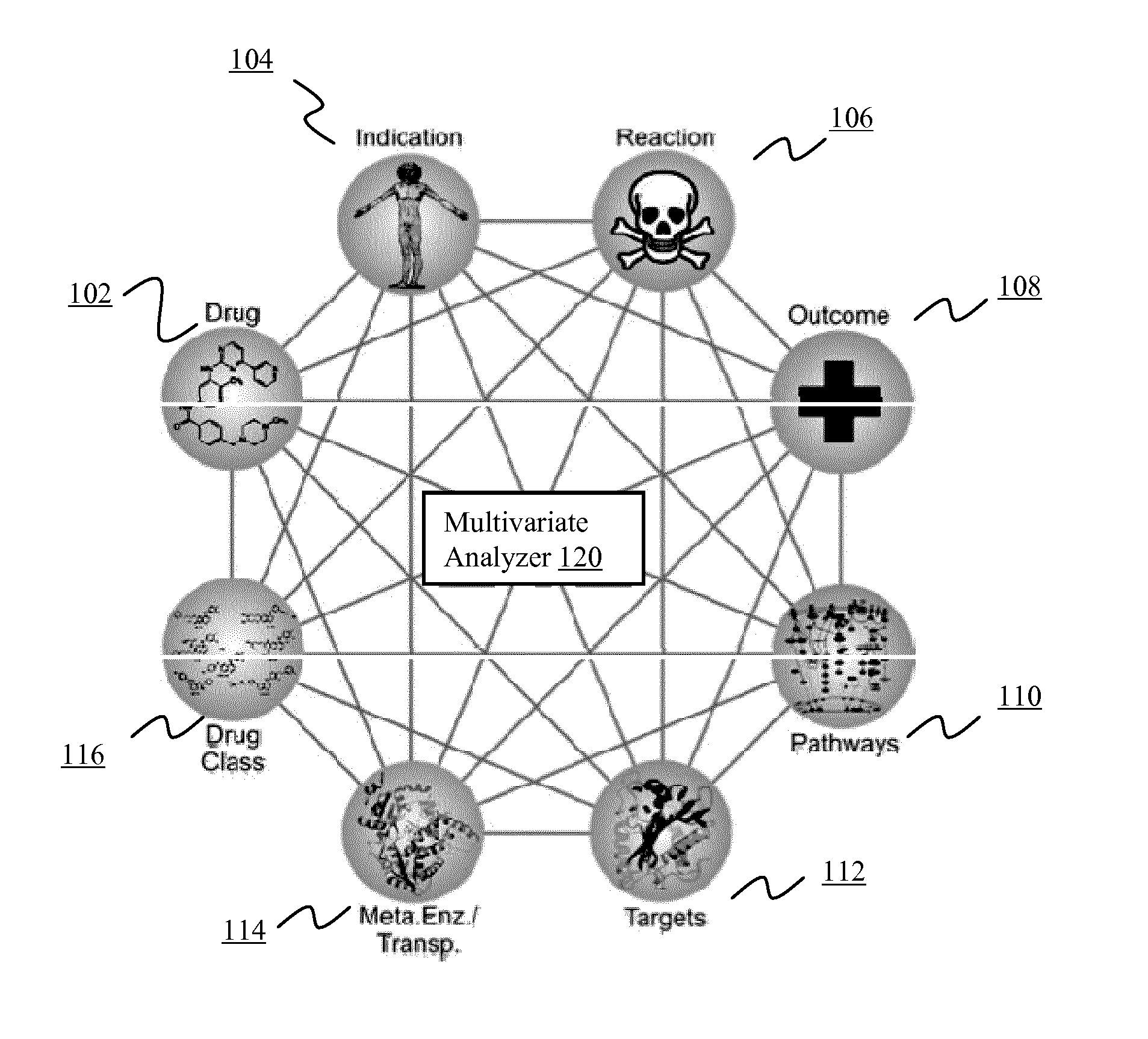
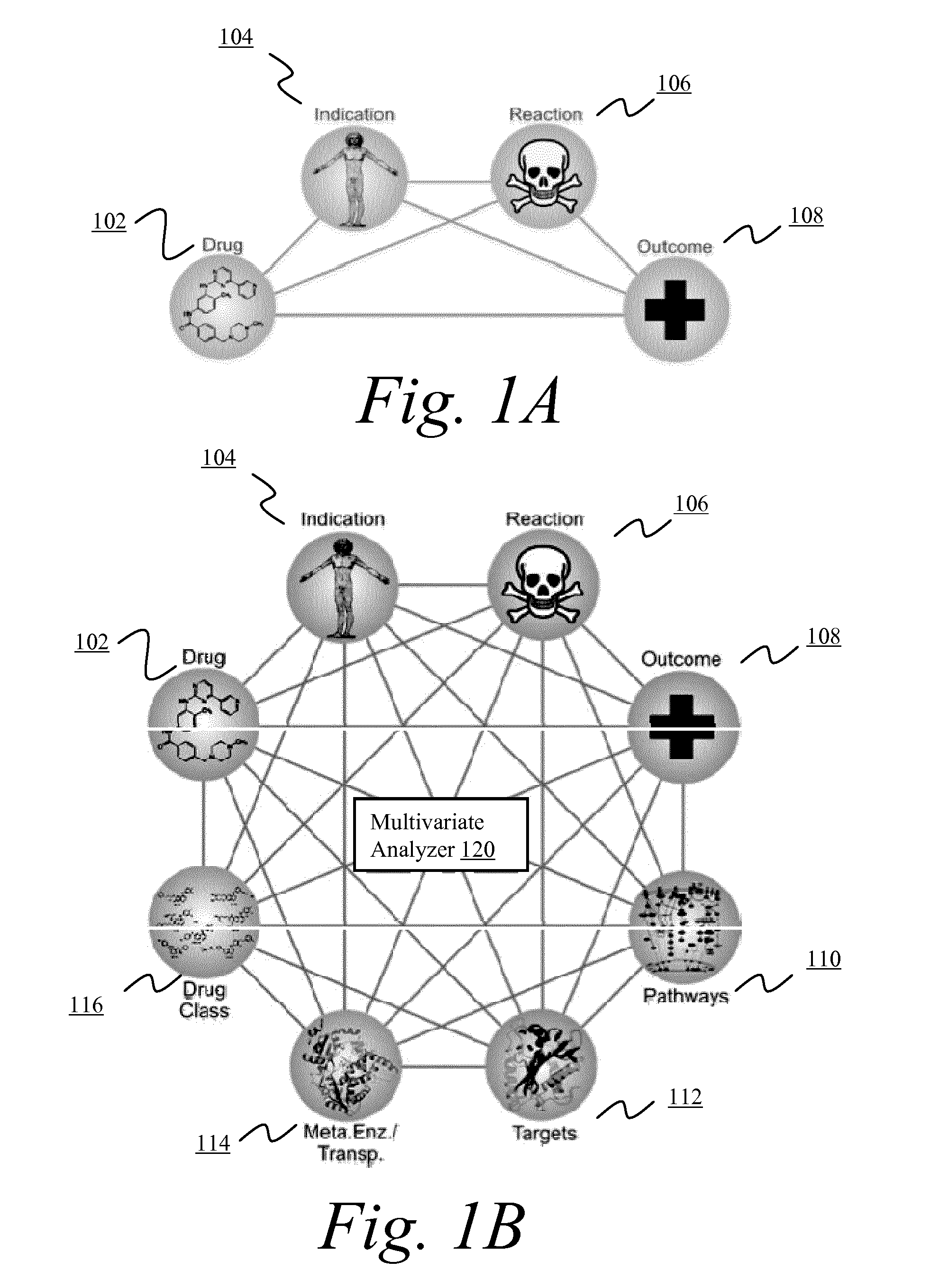
Systems and methods for multivariate analysis of adverse event data
InactiveUS20150106112A1Reduce morbidityMedical simulationData processing applicationsMedicineClinical trial
The present disclosure describes systems and methods for multivarlate analysis of adverse event data. According to a first aspect, patient-specific genomic Information is used to optimize or de-risk therapy for the patient. According to other aspects of the invention, unknown drug targets are identified via adverse event data. According to still other espects, a medication is identified to exclude from use for an indication or from a clinical trial of another medication. According to another aspect, a predicted side effect profile is generated for a medication targeting a novel target. According to still another aspect, combination therapies are identified via adverse event data. According to another aspect, molecular interactions between a plurality of molecular entities are displayed in an intuitive format. According to still another aspect, molecular entities responsible for adverse event differences between similar indications are identified. According to still another aspect, genetic variants associated with adverse events in a clinical trial are identified.
Owner:MOLECULAR HEALTH GMBH
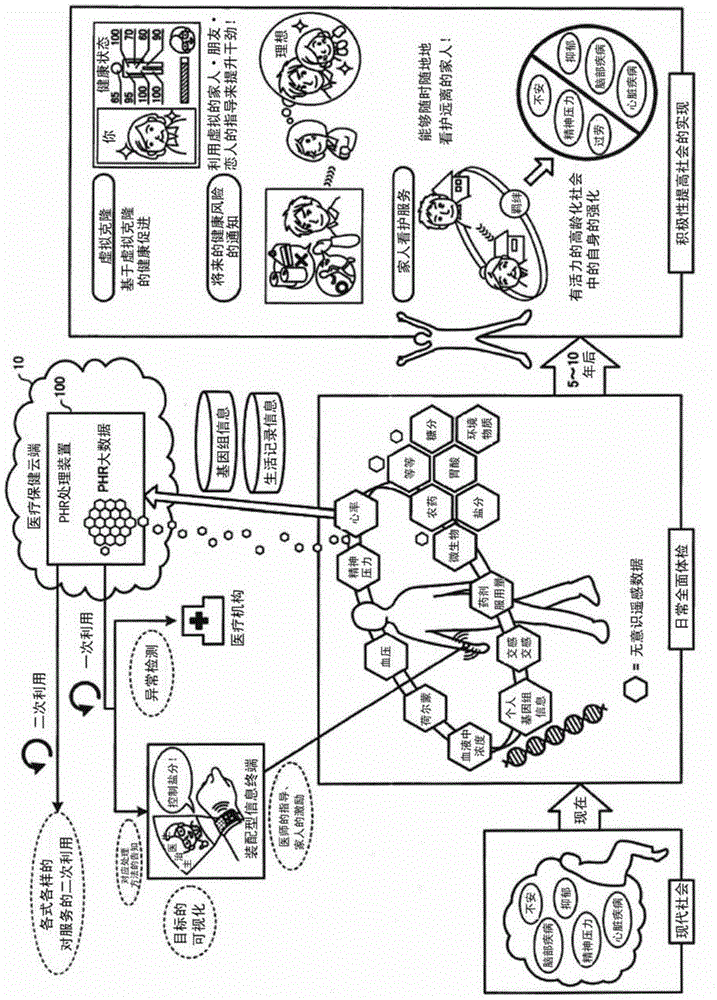
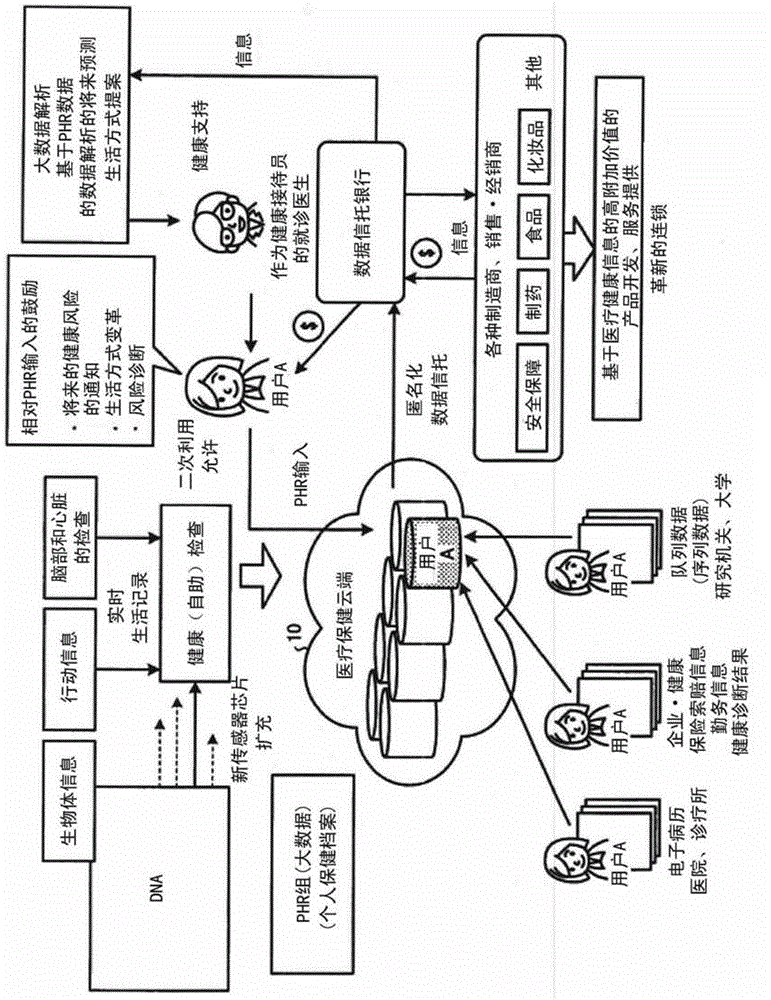
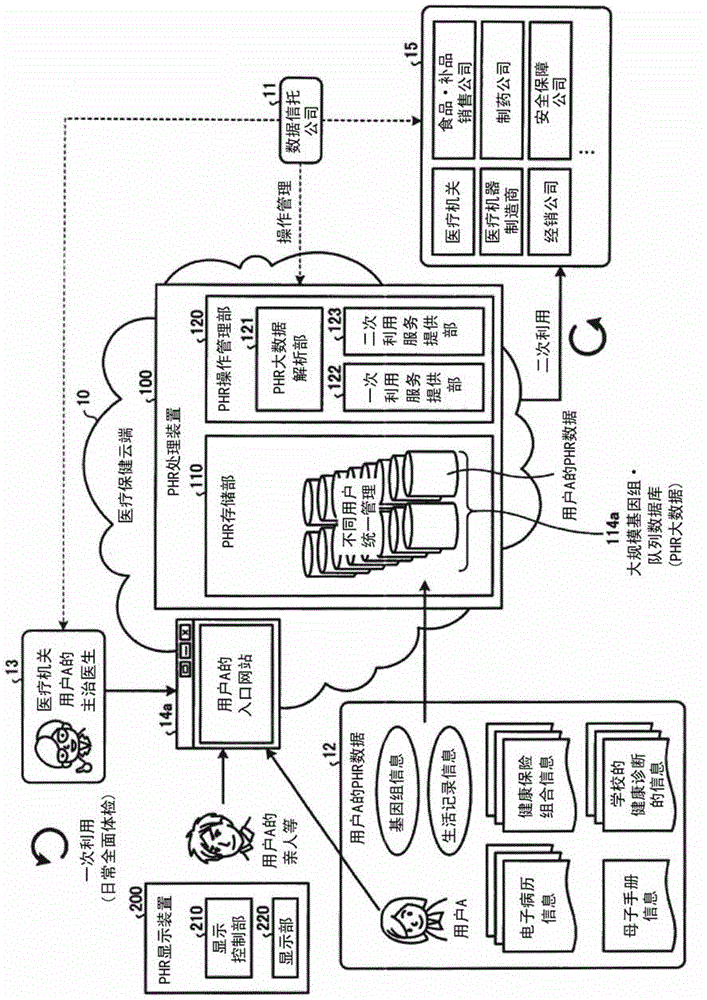
Health information procssing device, health information display device, and method
A health information processing device (100) according to an embodiment comprises an accumulation unit (110), an analysis unit (121), and an estimation unit (122). The accumulation unit (110) accumulates a plurality of users' worth of health information for each user which is genomic information, and continuously collected vital sign information and activity information. The analysis unit (121) analyzes the accumulated plurality of users' worth of health information. The estimation unit (122) estimates a prescribed user's future health risk, using the result of the analysis and the prescribed user's health information.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV +1
Aquatic product animal SNP mark screening method
InactiveCN101343667AEfficient separationImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementAquatic animalGenetic diversity
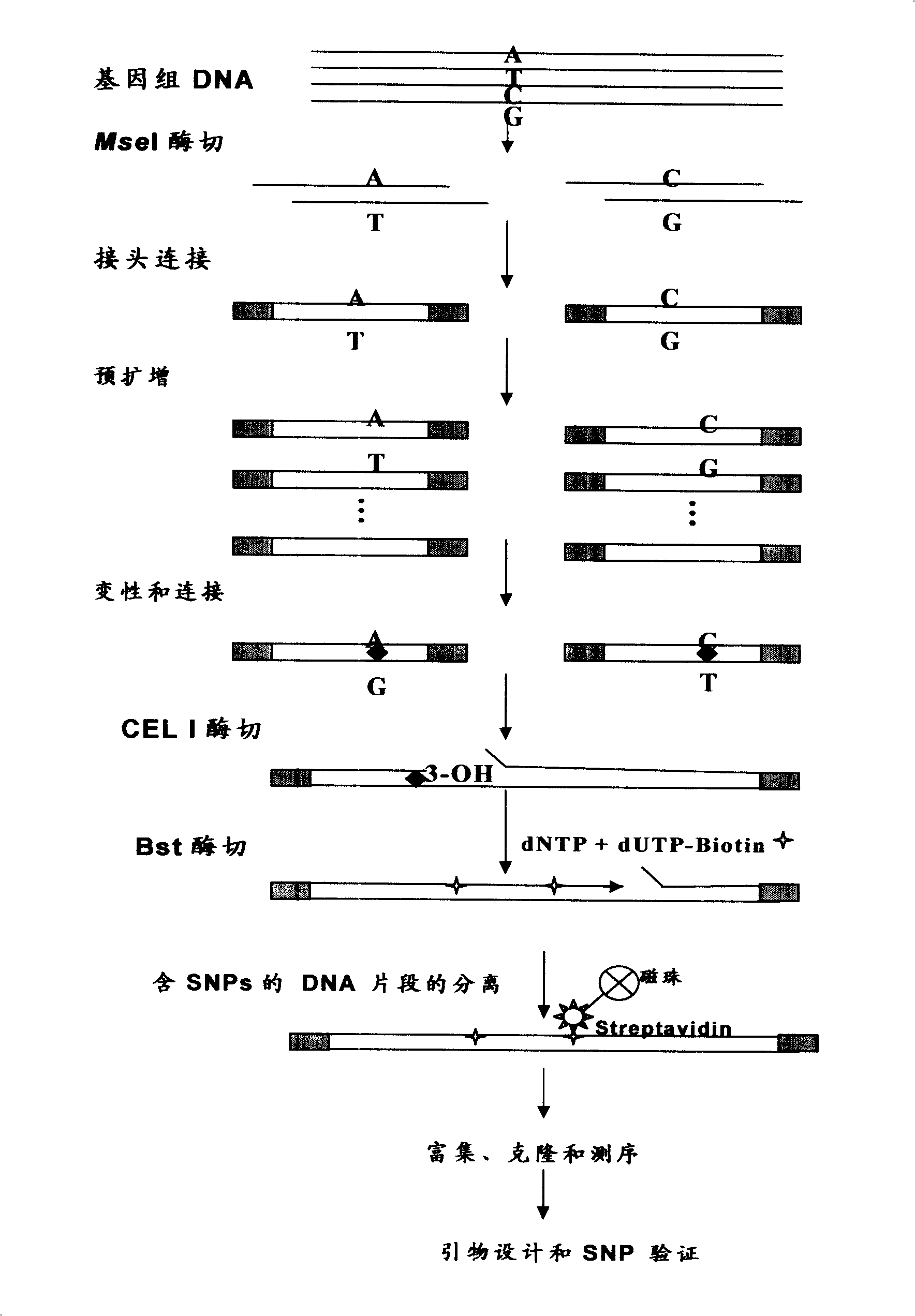
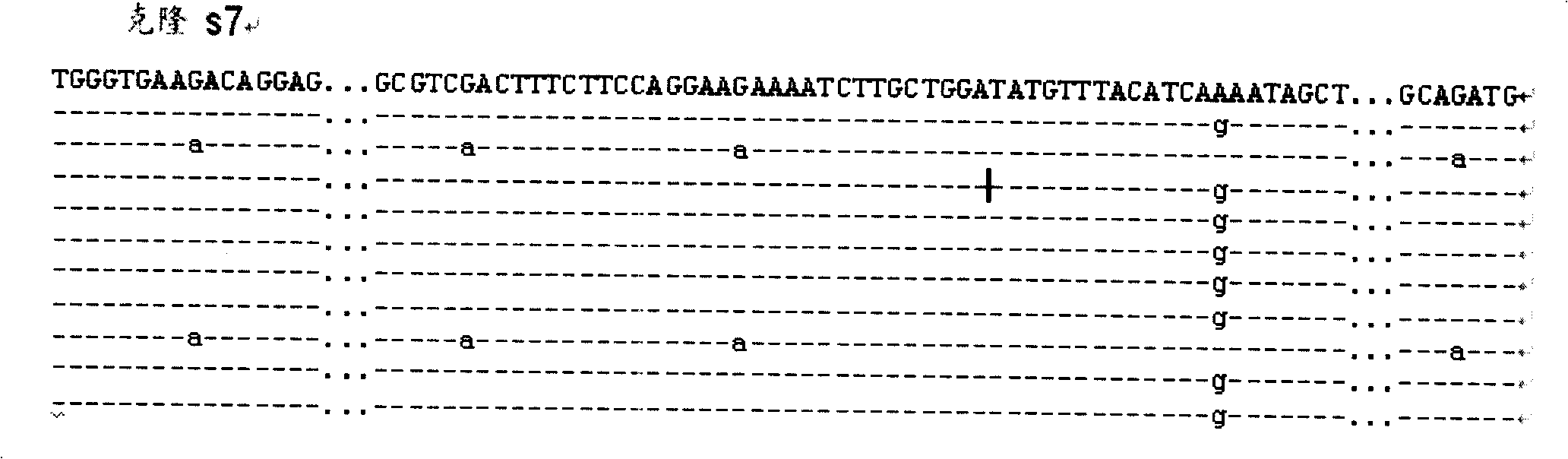
The invention provides an aquatic animal SNP marking and selection method, which can solve the problems of low efficiency and high cost existing in the current SNP marking and selection technique. The method adopts the technical proposal comprising the following steps: firstly, genome DNA abstraction; secondly, MseI restrictive enzymes cutting, connection of connecting ends and pre-amplification; thirdly, heterozygous double chain forming, CEL I enzyme cutting and Bst DNA polymerase extending; fourthly, separation of beads containing SNP locus DNA molecule; fifthly, object DNA amplification, concentration and clone sequencing; and sixthly, SNP locus identification. The new SNP marking and selection method can efficiently, plentifully and randomly separate SNP under the condition of unknown genome information, thereby being favorable for the development and the subsequent utilization of the abundant SNP, and having significant application value and popularization prospect in aquatic animal SNP marking and selection, germplasm identification, genetic diversity evaluation, molecular breeding and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Genome information assisted breeding method-breeding parent selection based on SNP clustering information and PAV variation information
InactiveCN106169034AAccurately and effectively obtainReduce workloadBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a genome information assisted breeding method for parent selection by means of SNP clustering and PAV variation. The essence of the genome information assisted breeding method is to obtain genome sequencing information of candidate parents with the help of genomic and bioinformatics methods; on one hand, a high-quality SNP data set is obtained through sequence alignment, a genetic distance matrix of the candidate parents is calculated, and the affinity between the candidate parents is judged with the help of a clustering tree; on the other hand, a Denovo assembled candidate parent contig is positioned to a reference genome, and the PAV variation of candidate parent target trait related genes is obtained according to the physical location. By combining the PAV variation and affinity information based on SNP, a parent subset is screened out from a large number of candidate parents for phenotype identification; finally, a selected breeding parent is determined by combining the phenotype identification result of the parent subset. The genome information assisted breeding method belongs to the field of rice molecular breeding, the range of the materials for phenotype identification can be effectively narrowed from the large number of the candidate parents, the workload of phenotype identification is reduced, and the breeding work efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
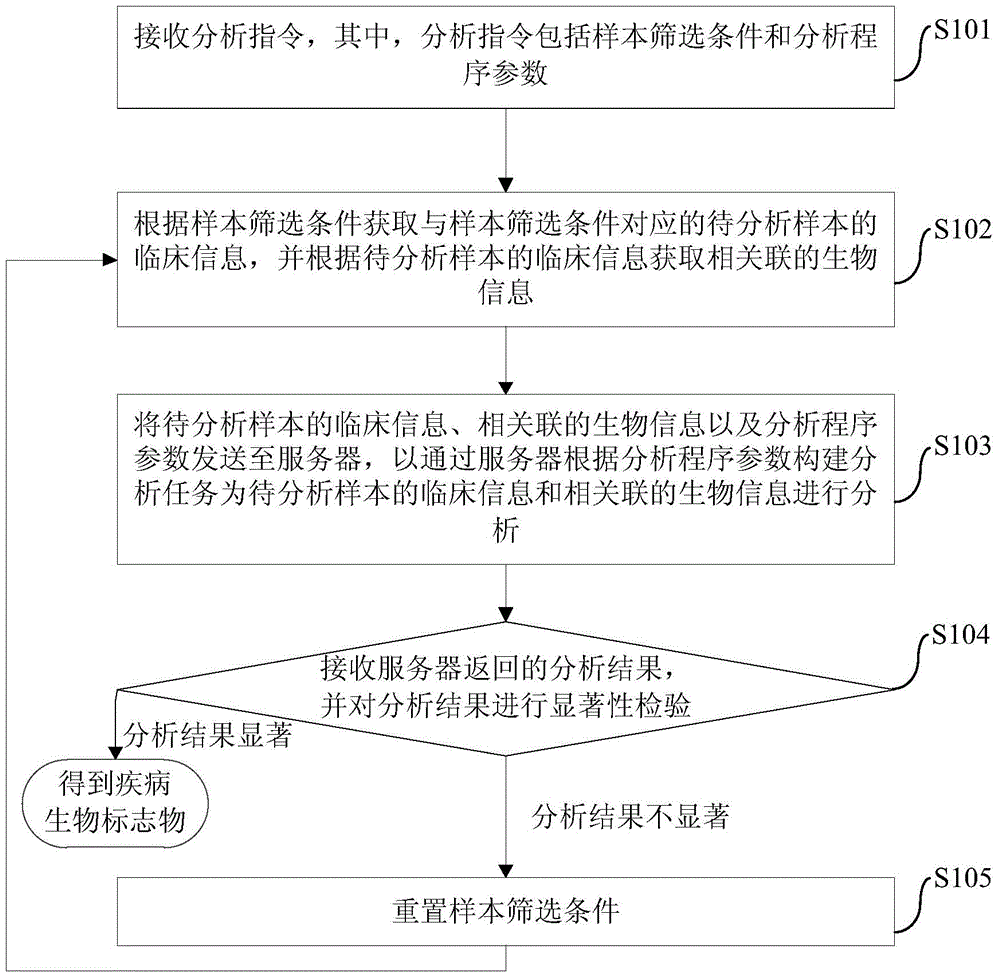
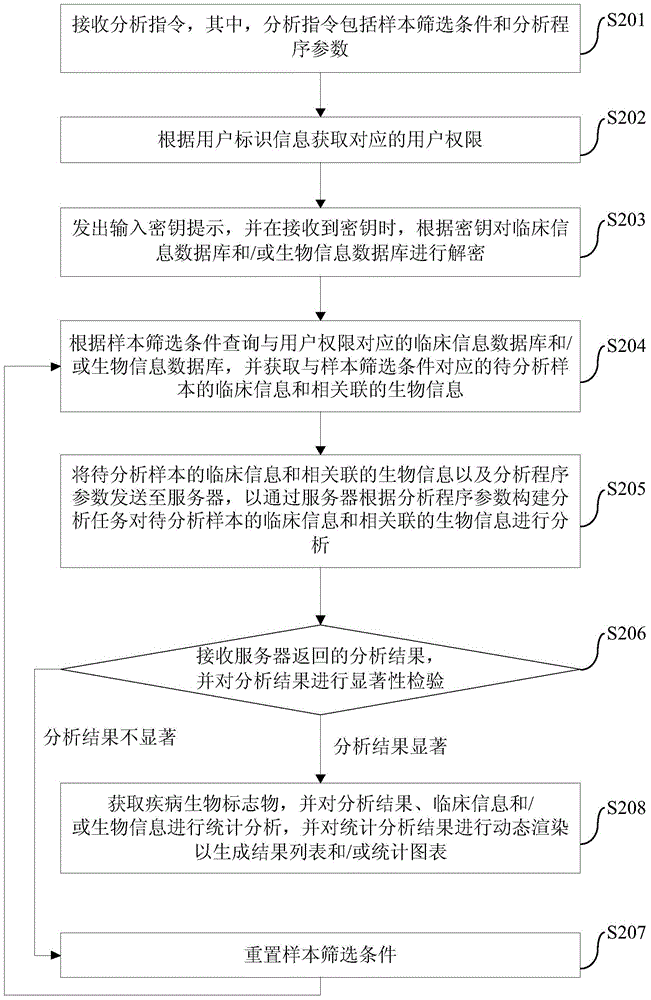
Disease biomarker screening analysis method, disease biomarker screening analysis platform, server and disease biomarker screening analysis system
The invention provides a disease biomarker screening analysis method, a disease biomarker screening analysis platform, a server and a disease biomarker screening analysis system, wherein the disease biomarker screening analysis method comprises the following steps of: receiving an analysis instruction, wherein the analysis instruction includes sample screening conditions and analysis program parameters; obtaining clinical information of samples to be analyzed corresponding to the sample screening conditions according to the sample screening conditions, and obtaining relevant biological information according to the clinical information of the samples to be analyzed; sending the clinical information of the samples to be analyzed, the relevant biological information and the analysis program parameters to the server so as to analyze the clinical information of the samples to be analyzed and the relevant biological information; receiving an analysis result returned by the server, and performing significance inspection on the analysis result; and if the analysis result is non-significant, resetting screening conditions, and performing analysis again until the analysis result is significant. The method provides a platform associating the clinical information with genome information for the genome research aspect, and the great-sample-size gene verification experiment is facilitated.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
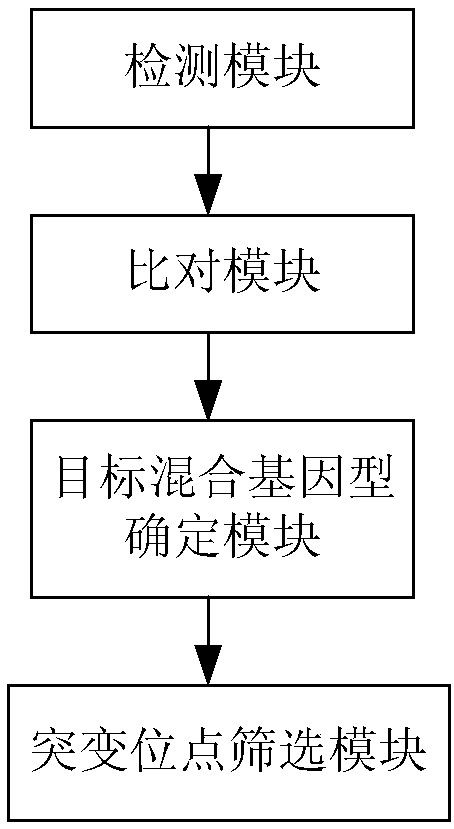
Apparatus for detecting gene mutation, and kit for typing genotype of pregnant women and fetuses
ActiveCN108277267AConvenience and diverse servicesMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisGenotype determinationTyping
The present invention discloses an apparatus for detecting gene mutation, and a kit for typing the genotype of pregnant women and fetuses. The apparatus comprises a detection module, a comparison module, a target mixing genotype determination module and a mutation site screening module, wherein the different SNP loci between maternal and fetal genomic information and a reference genome can be obtained through the detection module and the comparison module, and the mixing genotype of the pseudotetraploid comprising the pregnant woman and the fetus is typed by using the target mixing genotype determination module to obtain the maternal and fetal genotypes at each SNP locus, such that all possible genetic mutations of the fetus can be detected by using only the peripheral blood sample of thepregnant woman; and with the apparatus, the separate sequencing of the sample from the father source or the mother source is not required, and all possible genetic mutations of the fetus can be detected by only using the peripheral blood sample sequencing data of the pregnant woman, such that the convenient and diversified services are provided for the fetal gene detection.
Owner:ANNOROAD GENE TECH BEIJING +2
Screening method for anti-tumor medicine biomarker and application of anti-tumor medicine biomarker
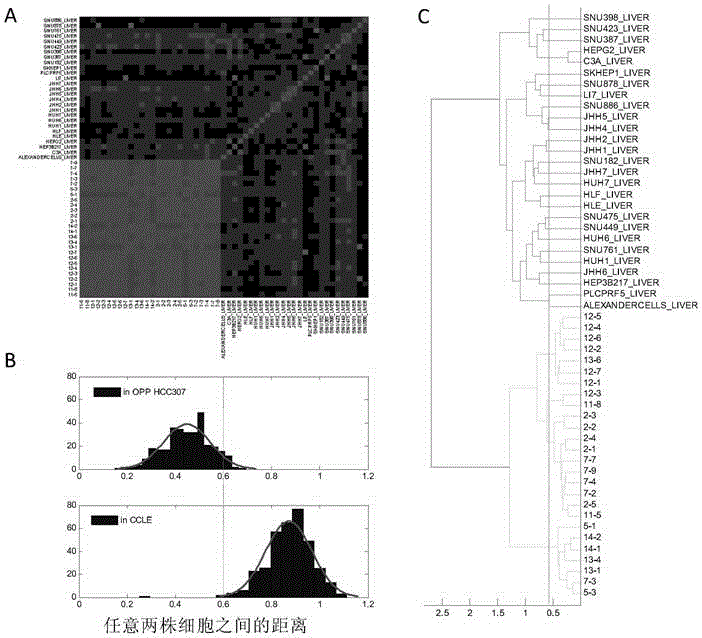
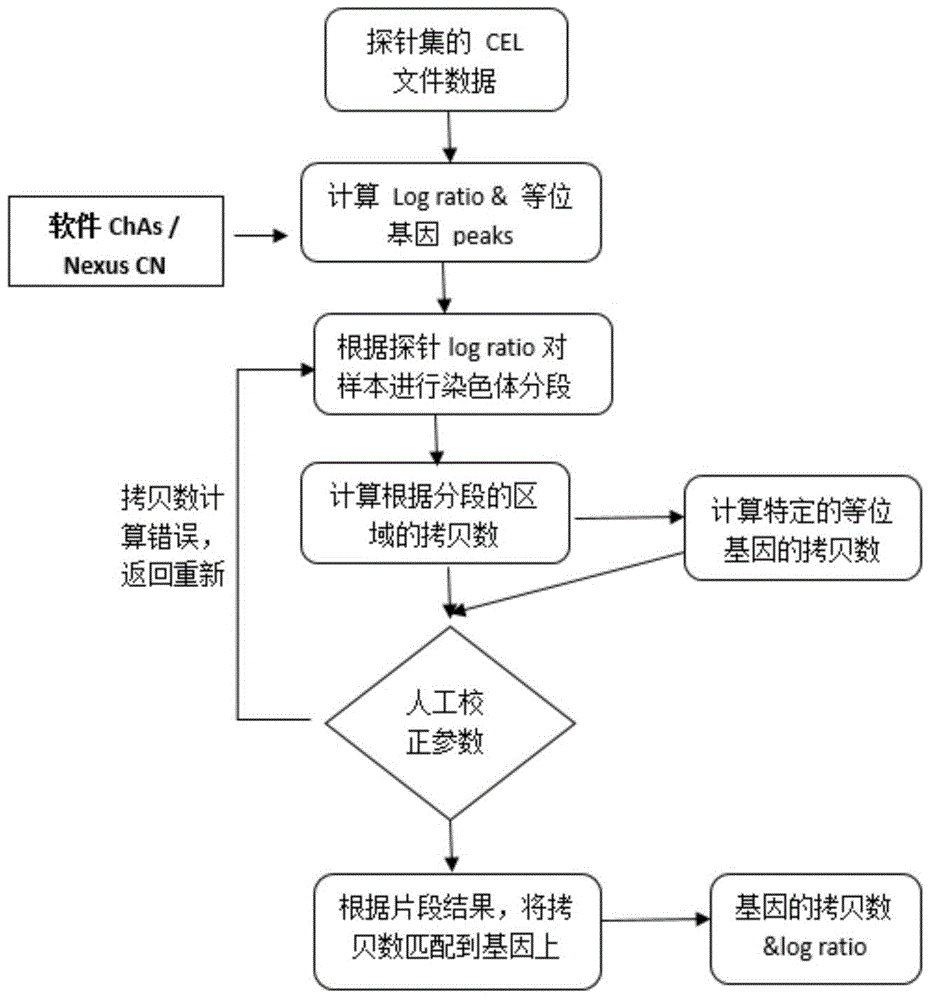
ActiveCN104975063AReduce the differenceReduce background noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsBiomarker (medicine)Biologic marker
The invention discloses a screening method for an anti-tumor medicine biomarker and an application of the anti-tumor medicine biomarker. Particularly, the method comprises the following steps: (a) providing tumor cells as initial cells, wherein the tumor cells are from the same tumor tissues of the same object; (b) carrying out passage and establishment on the initial cells, and carrying out genome information detection on the obtained cell line, so as to obtain at least five tumor cell lines which are different in genome and highly homologous; (c) carrying out anti-tumor medicine sensitivity test on the tumor cell lines obtained from the step (b), and parting the tumor cell lines based on the sensitivity of the anti-tumor medicine; and (d) analyzing the genome information of the tumor cell lines based on the parting result, so as to determine the anti-tumor medicine biomarker. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the background noise between different tumor cell lines can be reduced to the maximal extent to contribute to efficient and accurate screening of the anti-tumor medicine biomarker.
Owner:思路迪科技(上海)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com