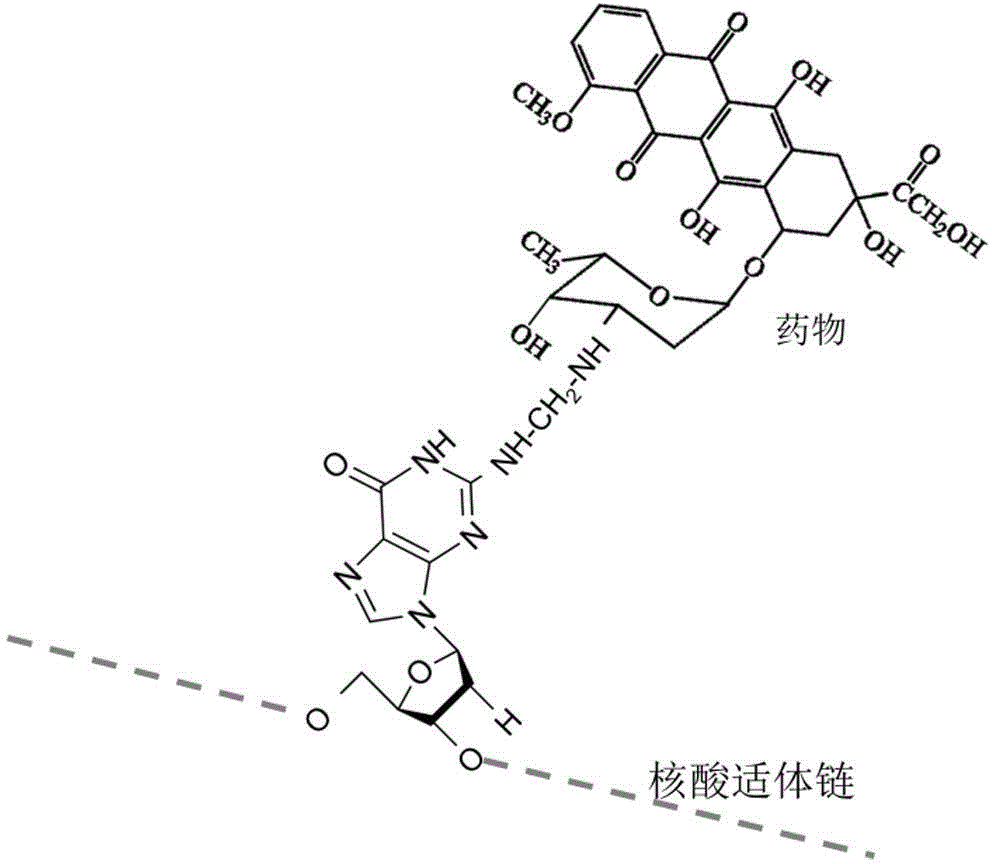
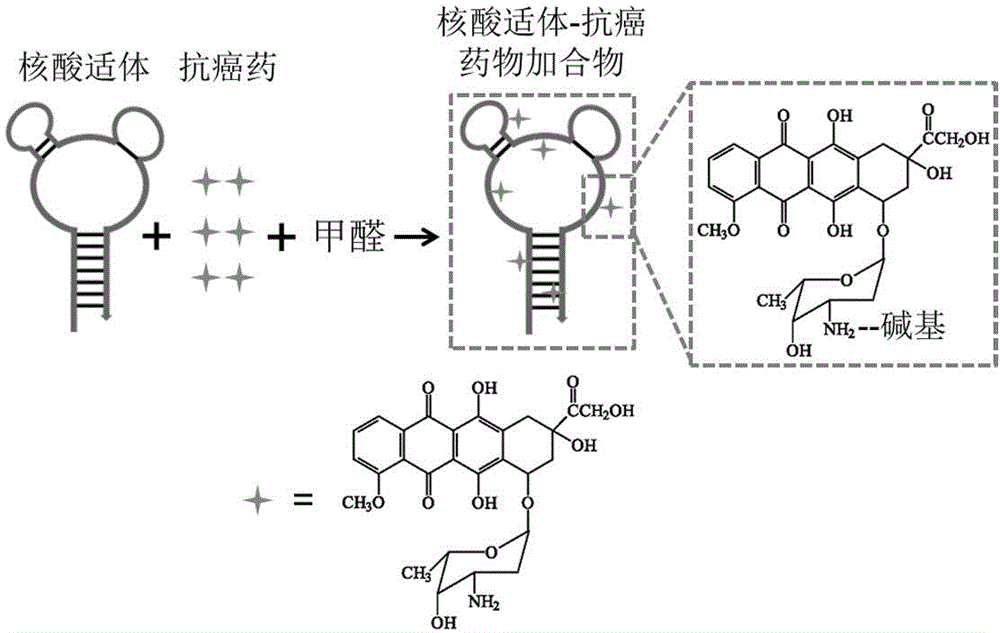
Nucleic acid medicine loading system for targeted therapy and preparation method of nucleic acid medicine loading system
A drug-carrying system and targeted therapy technology, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as lack of drugs, unstable complexes, complex organic reactions, etc. , to achieve the effect of simple and efficient preparation process, inhibition of cancer cell growth, and high drug loading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Using an automatic DNA synthesizer, synthesize 1 μmole of the required nucleic acid aptamer by solid-phase synthesis. The resulting product was deprotected, the DNA was dropped from the glass beads used in the synthesis, and the DNA was precipitated with ethanol (70%, 2.5 times the volume of the DNA solution) and NaCl (3 M, 0.1 times the volume of the DNA solution). The precipitated DNA was dissolved in TEAA (0.1 M).
[0049] The above product was purified by HPLC and dried. The DMT protecting group on the DNA was removed with acetic acid, and the DNA was precipitated again by the ethanol precipitation method mentioned above, and dried. The resulting DNA was dissolved in DNA water and stored at low temperature (20 o C) Spare.
Embodiment 2
[0051] In the buffer used (20 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.0), 150 mM sodium chloride, 0.5 mM EDTA), the following reaction system was prepared: aptamer 20 μM, drug 400 μM, formaldehyde 0.37%. Put the above reaction system at 10 o C, reacted for 12 hours.
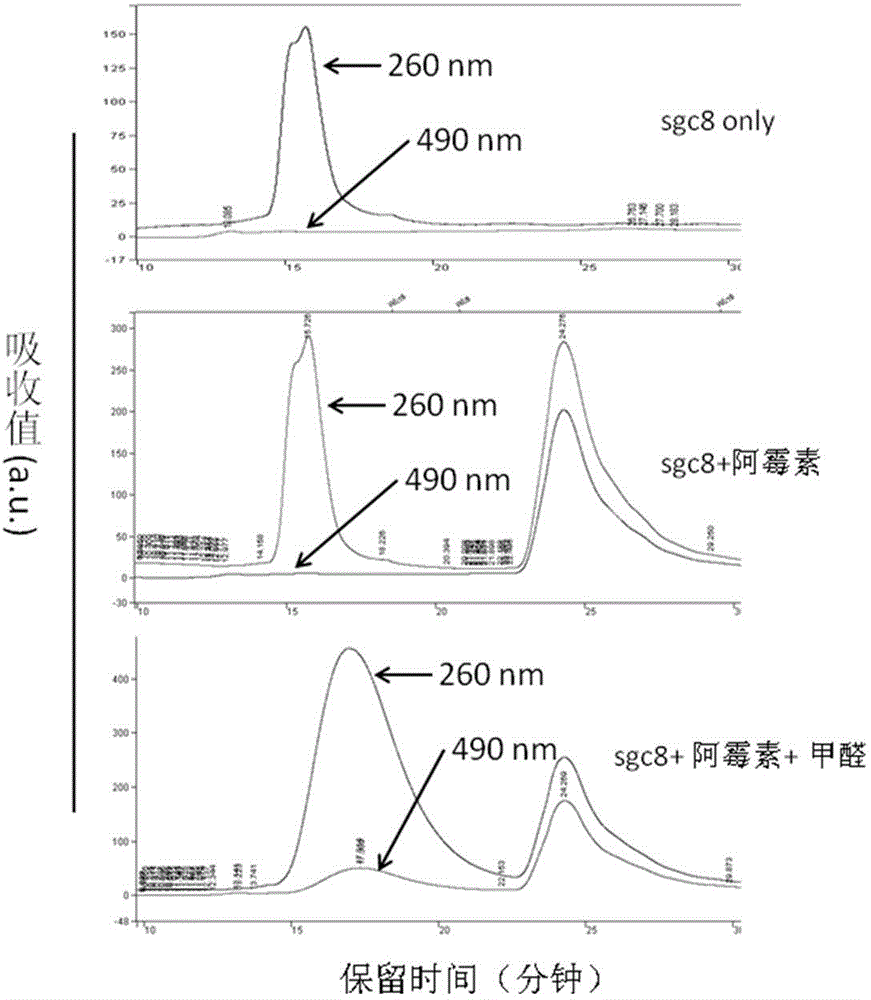
[0052] The obtained product was purified by HPLC or molecular sieve, ethanol precipitation and other methods. Such as image 3 As shown, the sample containing only nucleic acid aptamer only absorbs at 260 nm when analyzed by HPLC; in the obtained nucleic acid aptamer-drug adduct, there is both a strong light absorption at 260 nm (mainly from DNA) , also comes from the characteristic absorption of drugs (such as the absorption of doxorubicin at 490nm); in addition, the inventors have found through a large number of experiments that these methods can not only remove unreacted free drugs in the system, but also remove some Drugs that can form complexes with DNA by intercalation (formaldehyde is not added to the reaction system...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The prepared adducts were characterized by mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), the molecular weights of the adducts and an identical nucleic acid aptamer that did not form adducts were compared, and the number of drug molecules on an aptamer DNA chain was calculated. Such as Figure 4 As shown, compared with the sample containing only the nucleic acid aptamer sgc8, the adduct formed by sgc8 and Dox was analyzed by ESI-MS and showed that the adduct contained multiple products with a molecular weight larger than that of sgc8. By comparing the adducts of these products The molecular weight is higher than that of simple sgc8, and the inventors found that they are just integer multiples of the total molecular weight of one Dox and one methylene. Further calculations show that the number of Dox molecules contained in the corresponding adducts is 1-6, respectively.
[0056] The prepared adducts were characterized by fluorescence photometric analysis, and the fluorescence intensity of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com