Aptamer-guided gene targeting
a technology of aptamer and target genes, applied in the field of molecular biology and gene editing, can solve the problem of low frequency of target genes in many organisms and cell types
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
nsformation Data
[0114]
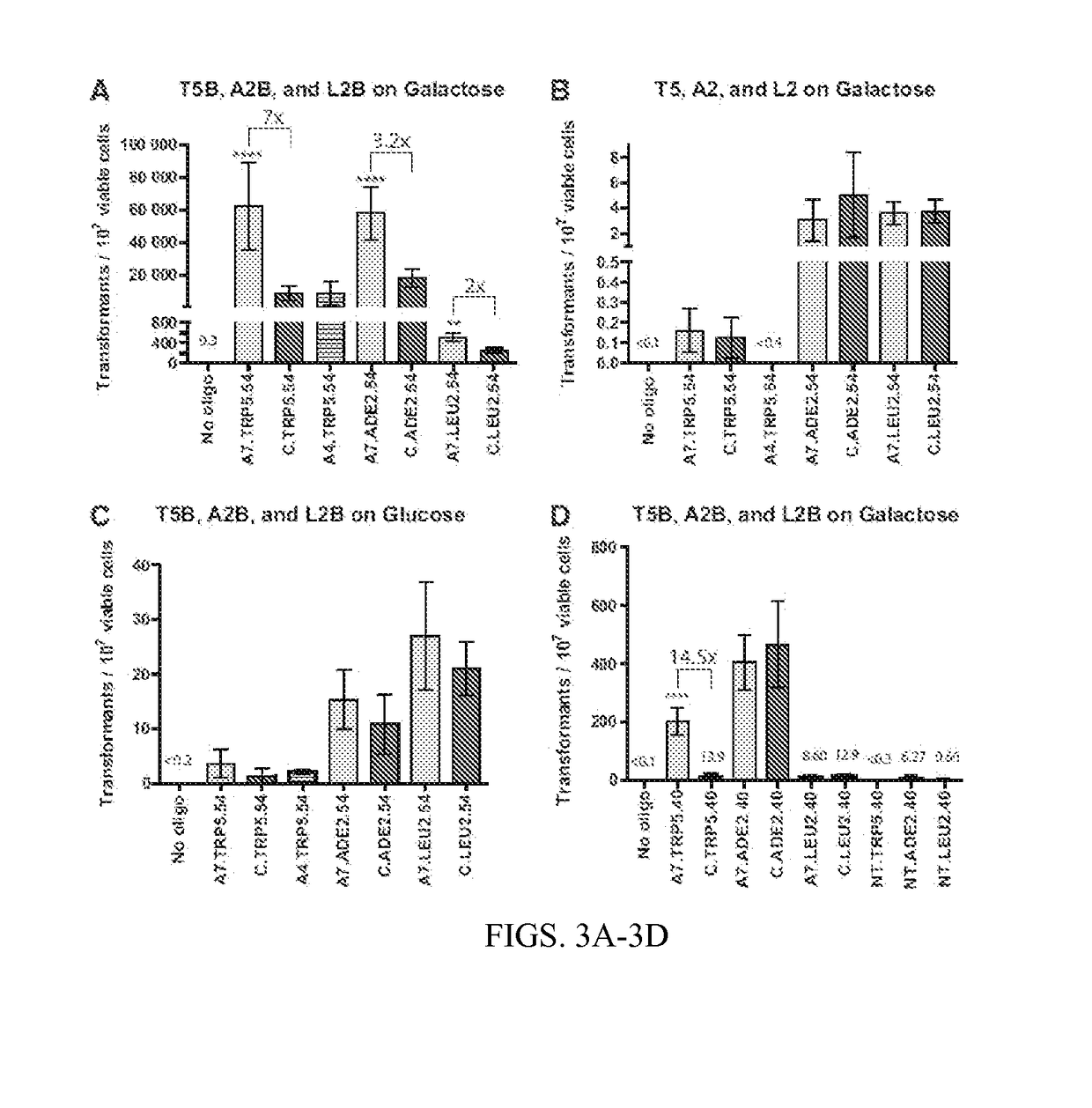
TABLE 4OligoBreak on GalBreak on GluNo Site on GalANo oligo0.54(0-1.36)(0-0)(0-0)(TRP5)A7.TRP5.5462,500(35,800-89,200)3.64(1.00-6.28)0.16(0.05-0.27)C.TRP5.548,950(4,170-13,700)1.21(0-2.69)0.13(0.03-0.23)A4.TRP5.549,030(2,120-15,900)2.09(1.71-2.47)(0-0)No oligo(0-0)(0-0)(0-0)(ADE2)A7.ADE2.5457,900(41,500-74,300)15.4(3.28-27.5)3.07(0-7.01)C.ADE2.5418,200(12,800-23,500)10.9(0-22.9)5.03(0-13.0)No oligo(0-0)(0-0)(0-0)(LEU2)A7.LEU2.54522(333-712)27.0(17.1-36.9)3.61(1.70-5.52)C.LEU2.54253(163-343)21.0(16.0-26.1)3.74(1.77-5.71)BNo oligo(0-0)(0-0)0.2(0-0)(TRP1)A7.TRP1.5425.8(18.7-32.8)10.8(7.10-14.5)2.23(−0.01-4.48)C.TRP1.5410.7(5.77-15.7)8.75(4.91-12.6)4.56(1.47-7.66)No oligo(0-0)(0-0)(0-0)(ADE2)A7.ADE2.5446.2(39.4-53.0)(0-0)(0-0)C.ADE2.5415.4(11.9-18.8)(0-0)(0-0)No oligo(0-00)0.69(0-3.64)0.4(0-0)(LEU2)A7.LEU2.5497.1(73.3-121)12.8(4.57-21.1)8.92(5.58-12.0)C.LEU2.5461.8(50.4-73.2)12.5(4.96-20.0)7.90(5.38-10.4)
[0115]In Table 4 (A) the frequency of transformant colonies p...
example 2
for an Aptamer to I-SceI
[0118]A fluorescently-labelled DNA library consisting of singlestranded 74-mer oligonucleotides containing a central 36-nt variable region (Table 1) was loaded with I-SceI protein on CE with LIF. Two rounds of selection were done to obtain DNA aptamers to I-SceI. Several potential aptamers from the selection pool of aptamers were again run with I-SceI and weak, moderate and strong binding aptamers were identified. The 17 strongest binding aptamers identified were selected for sequencing. Several of the sequences were repeated, such that there were only 11 unique strong binding aptamer sequences (Table 1), which showed no general consensus sequence. Of the 11 unique sequences, only three contained the original length of the aptamer region, 36 bases, from the random DNA library. The difference in sequence length from the starting library is not uncommon in aptamer selection (Mahlknecht, et al., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 110:8170-8175 (2013); McKeague, et al., ...
example 3
I Aptamer Stimulates Gene Correction in Yeast
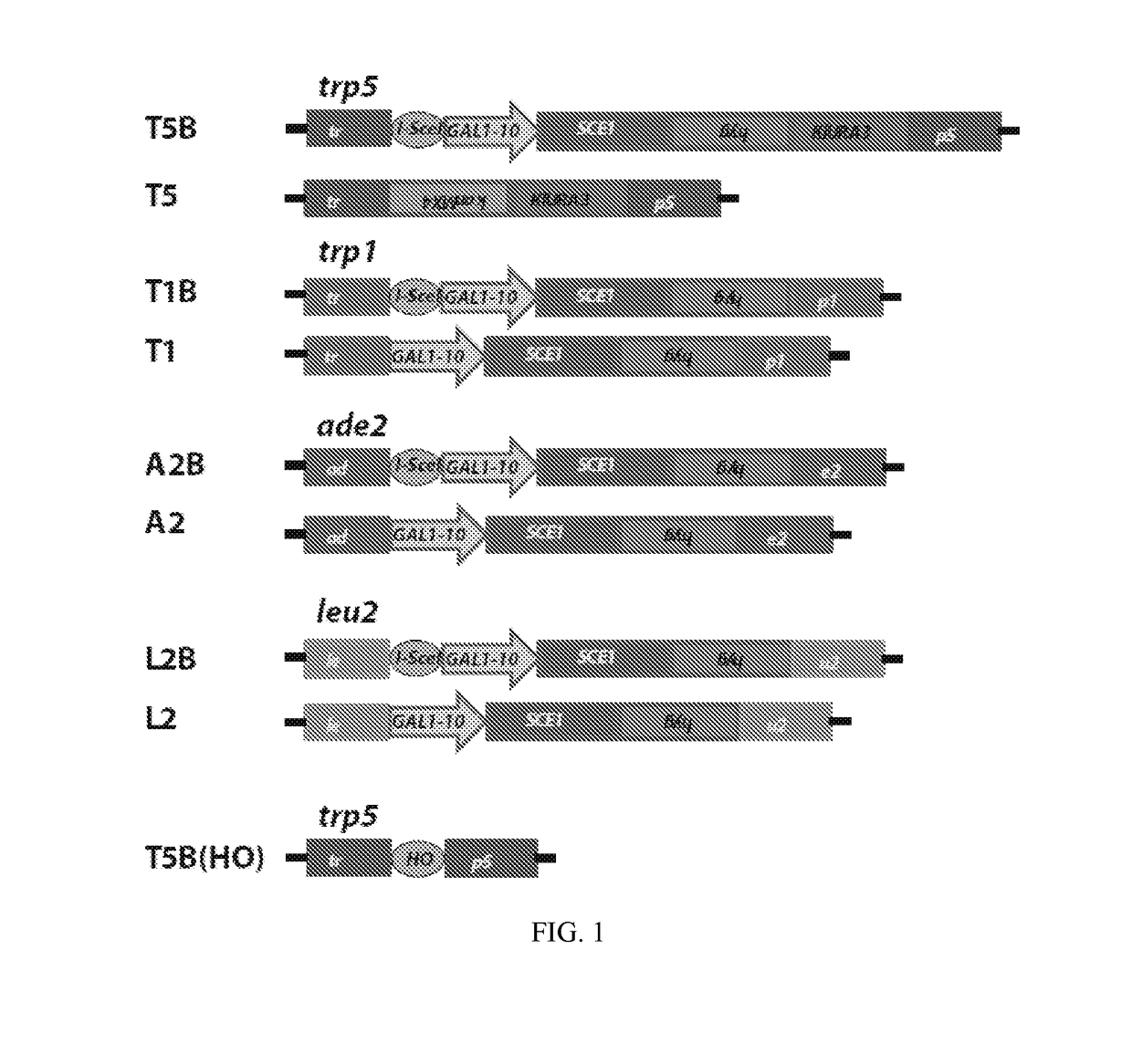
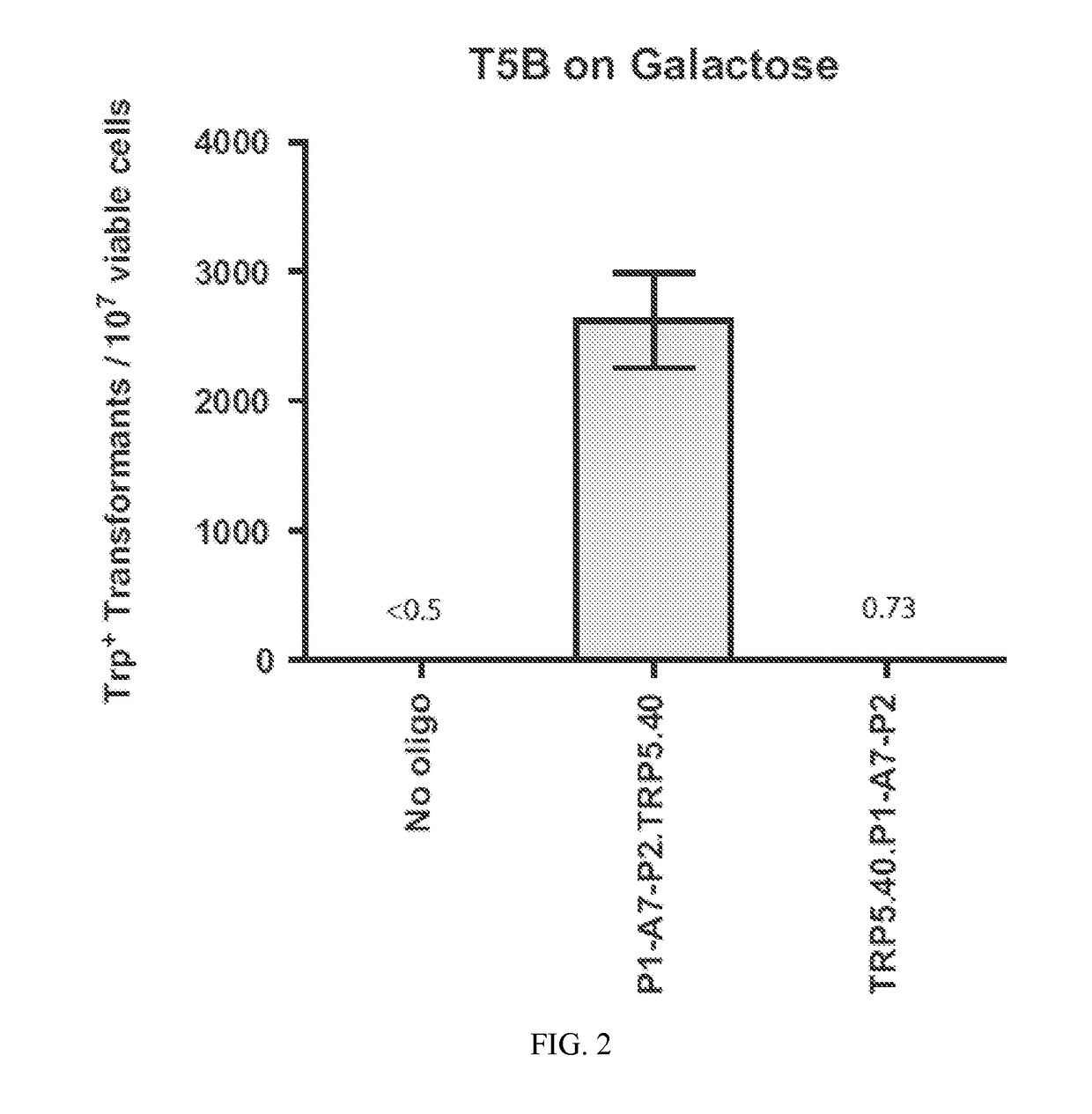
[0120]Experiments of gene correction were done in yeast S. cerevisiae cells using bifunctional single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides containing the aptamer region of the A4 or A7 I-SceI aptamer at one end, and the donor repairing sequence at the other end. First, we determined on which end (5′ or 3′) the I-SceI aptamer should be positioned in the bifunctional molecule to obtain more effective stimulation of gene targeting. For this experiment, the A7 aptamer with primers P1 and P2 from the random DNA library was synthesized as part of the 5′ end or the 3′ end of the repairing bifunctional oligonucleotides (P1-A7-P2.TRP5.40 for the aptamer with primers at the 50 end of the bifunctional oligonucleotide and TRP5.40.P1-A7-P2 for the aptamer at the 3′ end) (Table 1), which contained 40 bases of homology to correct a disrupted TRP5 gene in yeast strain FRO-155 / 156 (T5B in FIG. 1) and restore function of the TRP5 gene. Results showed that having ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com