Patents
Literature
141 results about "Copepod" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copepods (/ˈkoʊpɪpɒd/; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (drifting in sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.
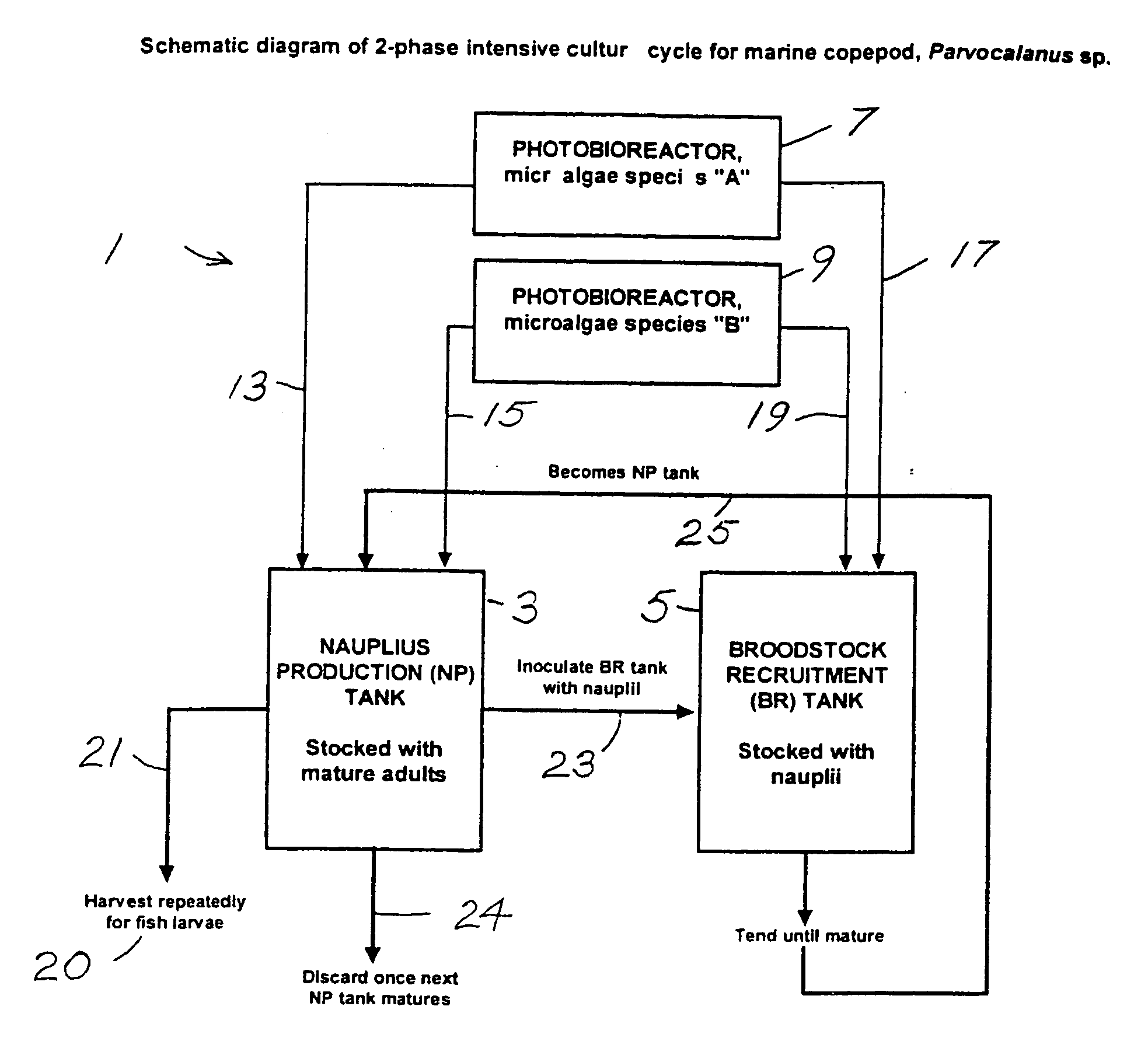
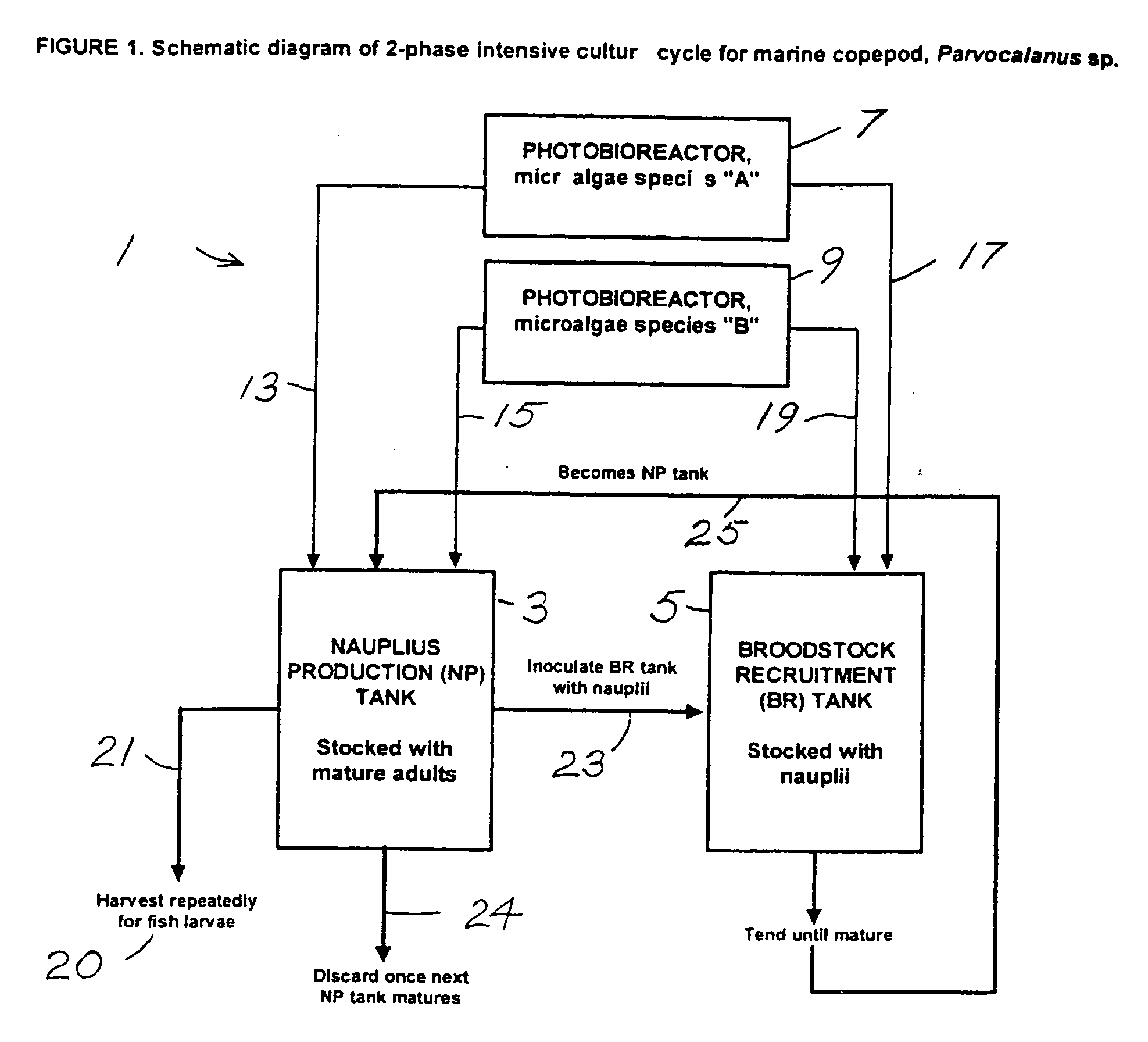
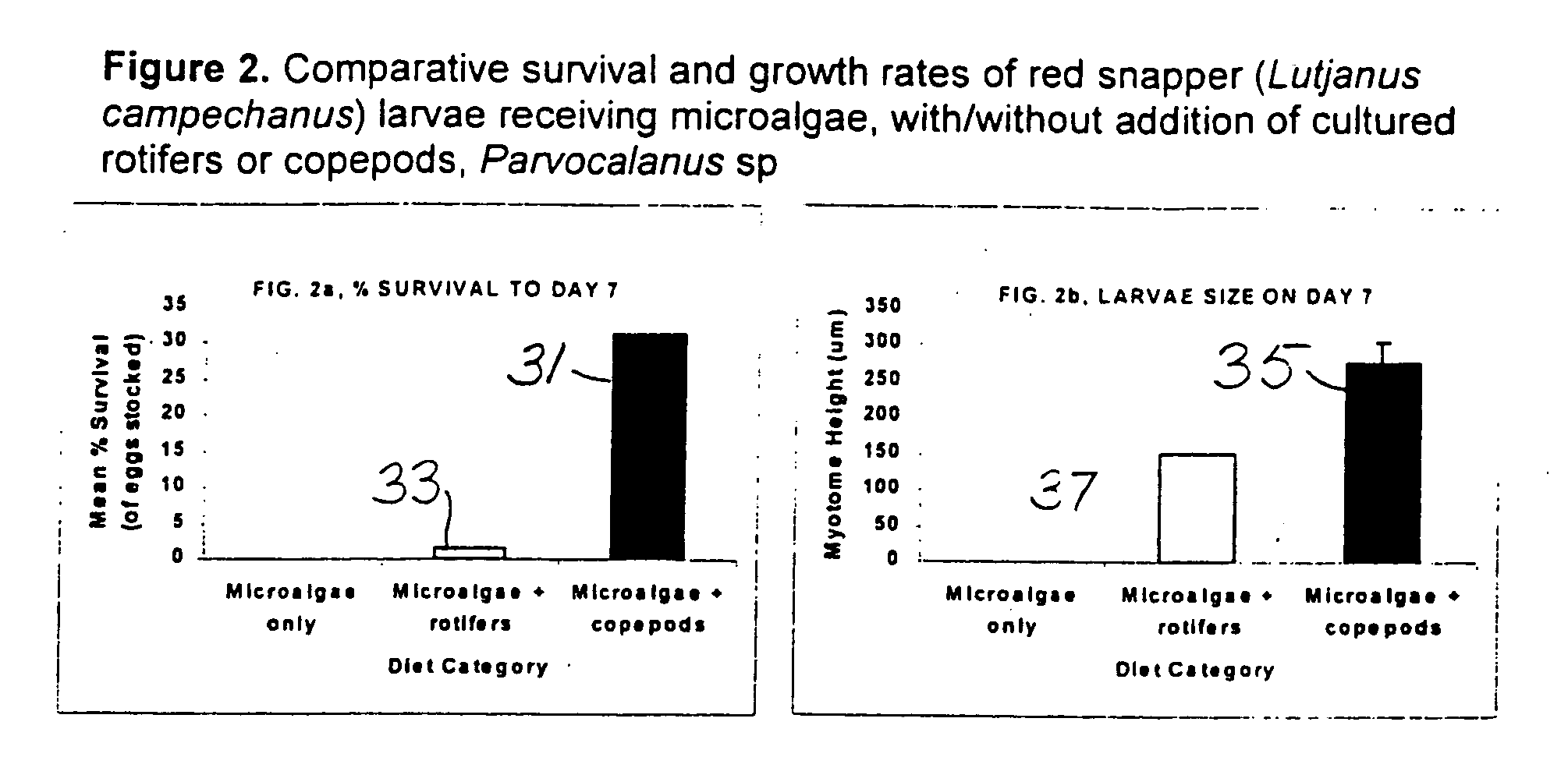
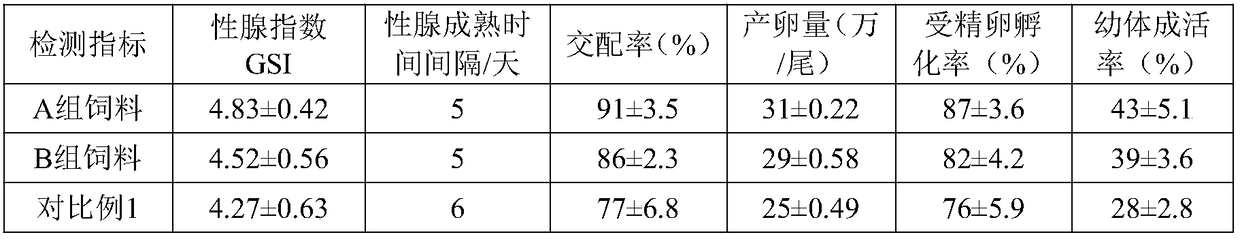
Isolation, culture, and use of marine copepods in aquaculture
InactiveUS20060169216A1Conducive to survivalPromote growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsClimate change adaptationFish larvaeJuvenile fish
Larviculture is performed using Parvocalanus sp as a feed for fish larvae. A system is described using tanks for growing Parvocalanus sp nauplii with a microalgae feed and transferring the grown Parvocalanus sp nauplii to tanks containing the fish larvae, where the functions of the tanks is interchanged. The Parvocalanus sp feed provide for higher numbers of larger juvenile fish and the rearing of larvae heretofore not reared in culture.
Owner:SHIELDS ROBERT JOHN +1
Method for artificially breeding sepia lycidas gray
ActiveCN102939924AImprove hatchabilityImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOpossumAnimal science
The invention discloses a method for artificially breeding sepia lycidas gray, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) parent breeding: selecting a harmless parent with complete body into a temporary culture cement tank to be temporarily cultivated, feeding the parent with chilled fishes twice a day, wherein the feeding quantity is 2 to 5 percent of the weight of the sepia lycidas gray; (2) artificial breeding: placing an egg attaching device inside the temporary culture cement tank, mating the male and the female parents to lay eggs, and then transferring the eggs into a hatching tank to be hatched; and (3) offspring breeding: transferring the hatched seedlings into a seedling tank, feeding fairy shrimp nauplius or copepoda in the early stage, feeding copepoda, opossum shrimp or larval prawn in the middle stage, and feeding fresh live fishes and small shrimps in the late stage, completing the breeding of the seedling when the length of the seedling is more than 2cm, the trunk length is more than 1.2cm, the trunk width is more than 0.9cm and the weight is more than 0.3g, and taking out the seedlings with water. The method has the advantages of high survival rate, easiness in cultivation, large cultivation specification, strong disease resistance and fast growth.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Benthic diatom culture method for growing seedlings and abalone fry culture method
InactiveCN101647406AImprove farming outputUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationDiseaseOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a benthic diatom culture method for growing seedlings and an abalone fry culture method, which relate to an abalone culture technology. The invention is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) starting culturing algaes 45 days before pulling seedlings, keeping the culture water temperature at 14 DEG C and the illuminance between 20001 and 30001x, controlling the light between 10001 and 15001x at the last culture after screening and eliminating algae culture for one and half a month, and laying ovum after 7 days; (2) adding nutrient salt at primary culture,wherein the adding ratio of N:P:Si:Fe is 5:1:1:1(ppm); (3) laying ovums about 5 millions for each pool and carrying out micro inflation; (4) changing water regularly after the ovums are laid and changing water twice a measuring range which is 24 hours; (5) carrying out running water culture after the ovums swim for 5 to 6 days and are adhered; (6) controlling the illuminance within 10001x after larvas metamorphose; and (7) dumping the pool after treating copepods at about 30 days of the culture period, adjusting the illuminance between 15001 and 20001x and peeling off baby abalones after about45 days. The methods have the advantages of improving the yield and preventing and treating a plate stripping disease.
Owner:FUJIAN LANJING AQUATIC PRODS
Indoor cement pond culture technique of Yangtze River Coilia ectenes
ActiveCN103026987AImprove controllabilityImprove management levelClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOpossumShrimp
The invention relates to an indoor cement pond culture technique of Yangtze River Coilia ectenes, belonging to the field of Coilia ectenes culture. The indoor cement pond culture technique of the Yangtze River Coilia ectenes comprises the steps of fingerling acquisition and transportation, temporary culture and domestication, indoor culture and overwintering culture. The indoor cement pond culture technique of the Yangtze River Coilia ectenes is characterized in that juvenile fish with body length being 8-12cm is acquired in September to October and is put in an indoor cement pond for temporary culture; after the juvenile fish is domesticated for 2-4 weeks, the juvenile fish is transferred into an indoor small cement pond for culture; when the juvenile fish is cultured to November to December of each year and the water temperature is below 15DEG C, the Coilia ectenes is transferred for the overwintering culture, the overwintering culture of the Coilia ectenes is conducted at room temperature and the water temperature is kept above 8DEG C to keep the juvenile fish to intake food; during overwintering, live seawater copepods are used as fish feed, and if the live fish feed is not enough, the live fish feed can be replaced by frozen opossum shrimps or slow-sinking compound feed; and after the spring of the next year begins, the juvenile fish is cultured according to the indoor culture method.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Composite nutrition enhancer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101810246AImprove survival rateImprove disease resistanceAnimal feeding stuffOrder copepodaPhaffia rhodozyma
The invention relates to a composite nutrition enhancer and a preparation method thereof, relating to a feed additive. The invention provides the composite nutrition enhancer, which not only contains large amount of DHA, ARA and natural yeast astaxanthin, but also contains multiple Omega 3 unsaturated fatty acids, multiple amino acids and trace elements. The composite nutrition enhancer is formedby composition of fission chytrid microalgae and phaffia rhodozyma with the weight ratio of 50 percent to 80 percent and 20 percent to 50 percent. All the components are weighed and mixed according to matching ratio after being crushed, mixed evenly, powder-sieved till the particle size is 8-25mum, inspected, weighed and packaged. The invention is especially applicable to feeding of live eels fryand shrimp postlarvae, artificial seawater seedling enhanced artemia salina sinnaeus, rotifer and cladocera (micrura), copepods and the like and various egg-laying poultries.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
Method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton
The invention relates to a method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton, belonging to the technical field of fish culture. The method comprises the following steps of selecting collecting water areas of river channels, ditches or ponds and the like the zooplankton density of which is higher than 10 / ml in water bodies; fixing a collecting device and starting a submersible pump to ensure that the water inlet of the submersible pump is 30-50cm away from water surface, and collecting the zooplankton once every 1-2 hours after the pump is started; and separating the collected zooplankton according to different application with different mesh bolting silk and cleaning for 1-3 times with clean pond water. The device employed by the invention has simple structure, easy material obtainment and convenient use; the natural zooplankton resources naturally breeding and easily regenerating in various fresh water bodies can be sufficiently utilized, thereby greatly reducing the labor intensity and being suitable for use in standing water, slow flow water areas and water bodies with different sizes. The method has the characteristics of high efficiency, economy, practicality and the like.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
Hierarchical cultivation method of seahorse seedlings
InactiveCN102265799APromote growthNeat specificationClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPrawnMysis
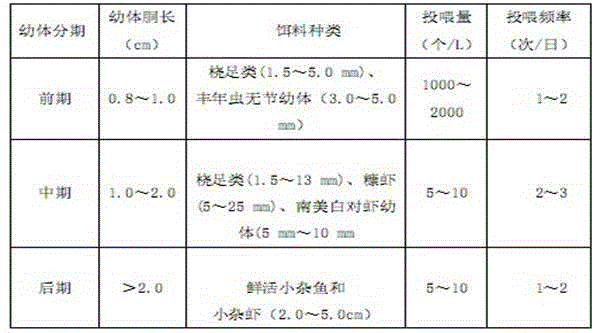
The invention discloses a hierarchical cultivation method for seahorse seedlings. The primary cultivation is carried out in a glass box filled with light green seedling-raising water. Artemia larvae are firstly fed, and then 80-mesh copepods are used for feeding. The seahorse seedlings The growth is good, and the seedlings are cultivated to a length of more than 15mm; the second, third, fourth and fifth grades are cultivated in indoor nursery ponds with light green seedling water, and the bait for the second grade cultivation is copepods over 80 mesh, which is conducive to feeding and growth , cultivated until the seedling body length is more than 25mm, the bait for the third-level cultivation is mysis or shrimp seedlings, the third-level cultivation is until the seedling body length is more than 40mm, and the fourth-level cultivation starts to domesticate and feed the bait by gradually increasing the frozen shrimp, and cultivate to the seedlings The body length is more than 55 mm, and no mysis or shrimp seedlings are added at the end of the five-level cultivation, and the frozen shrimp is completely fed, and the seedlings are cultivated to a body length of more than 70 mm; the hippocampus seedlings cultivated by the method of the present invention have neat specifications and good adaptability , a higher growth rate.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
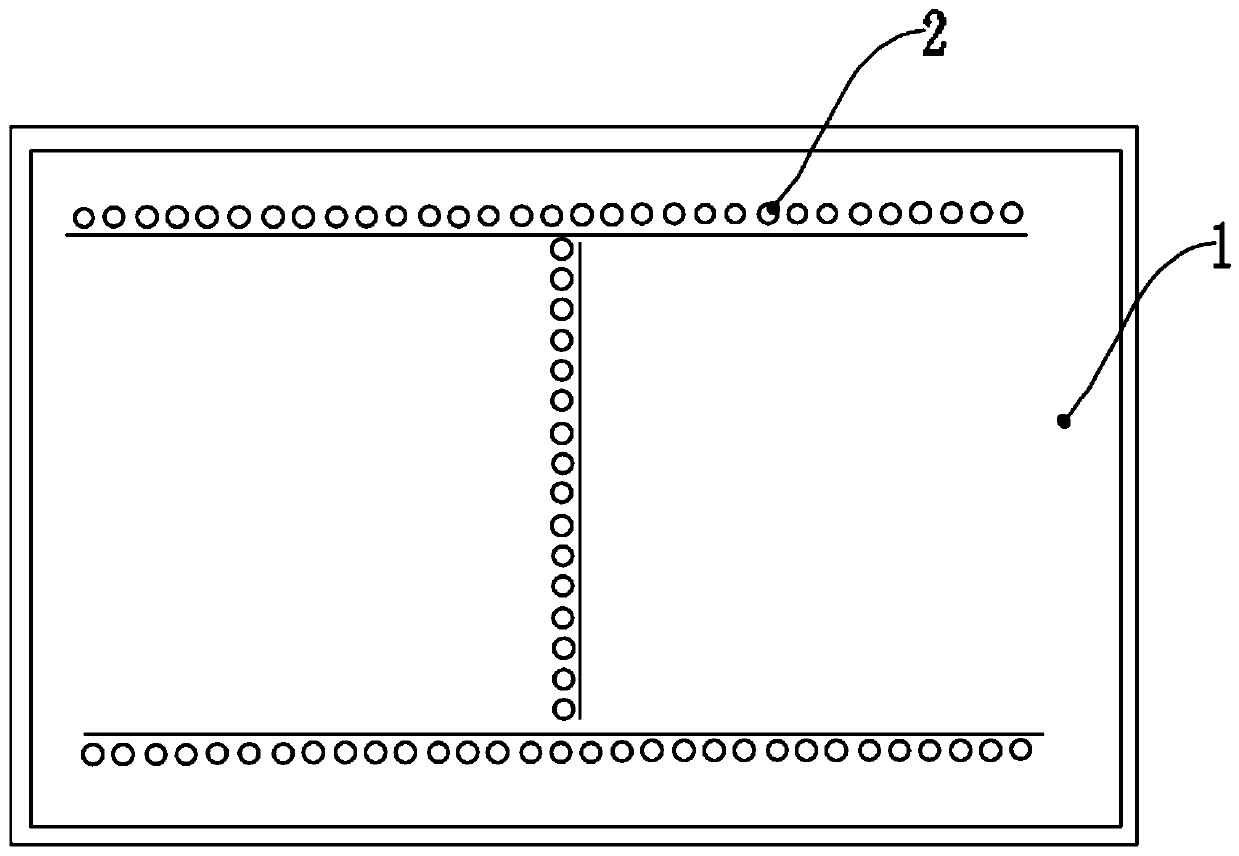
Indoor culture device of copepoda population
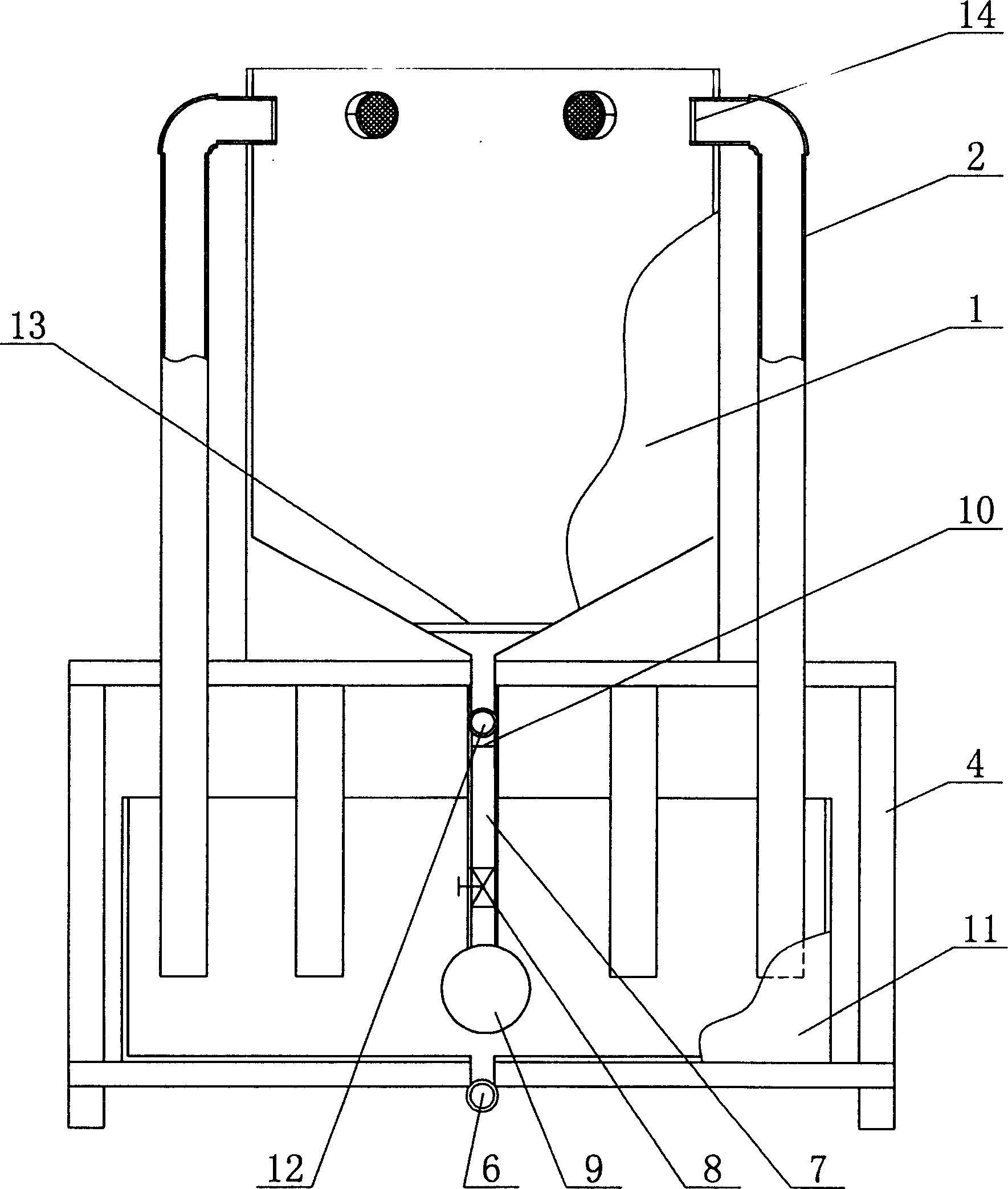
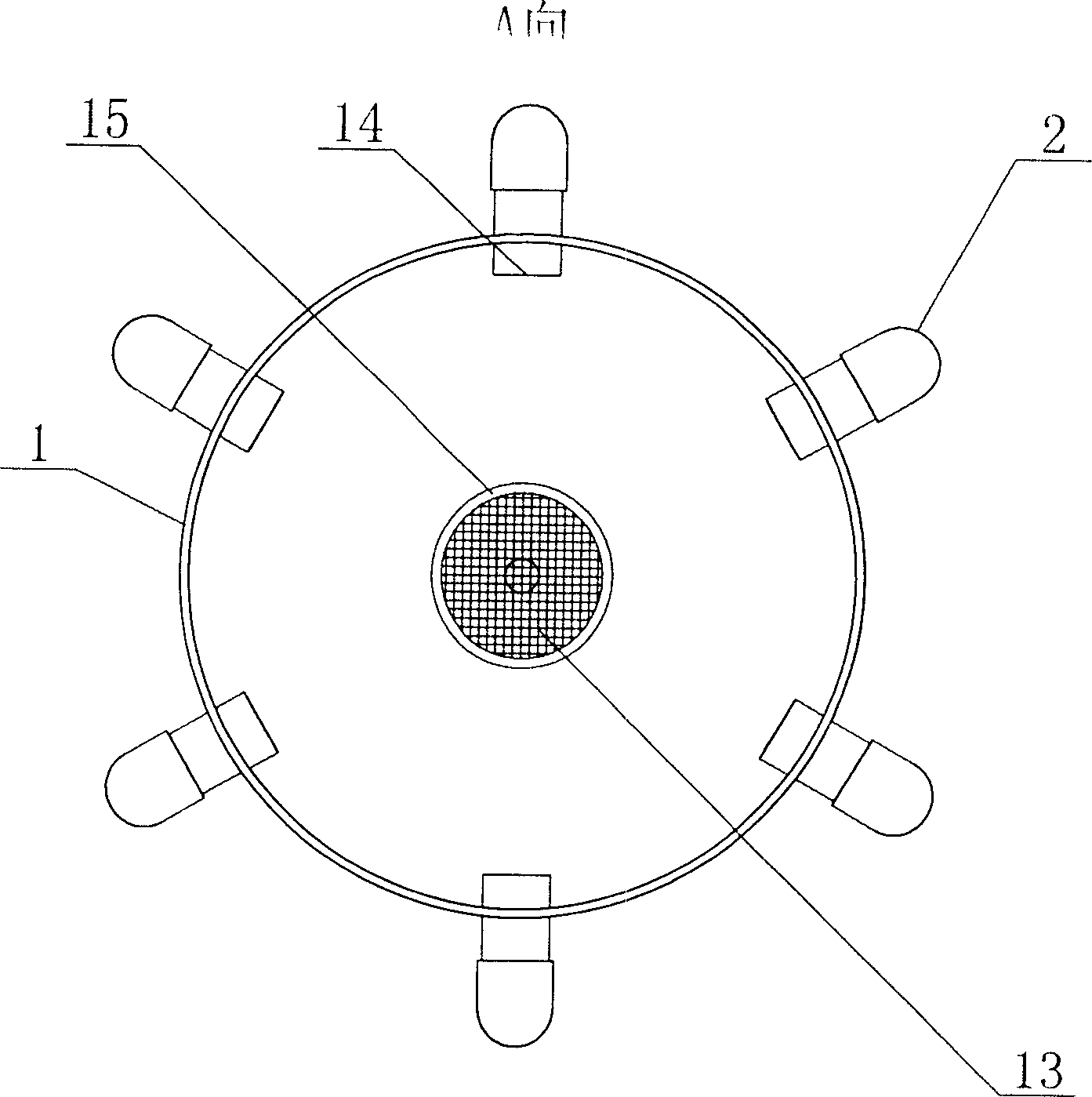
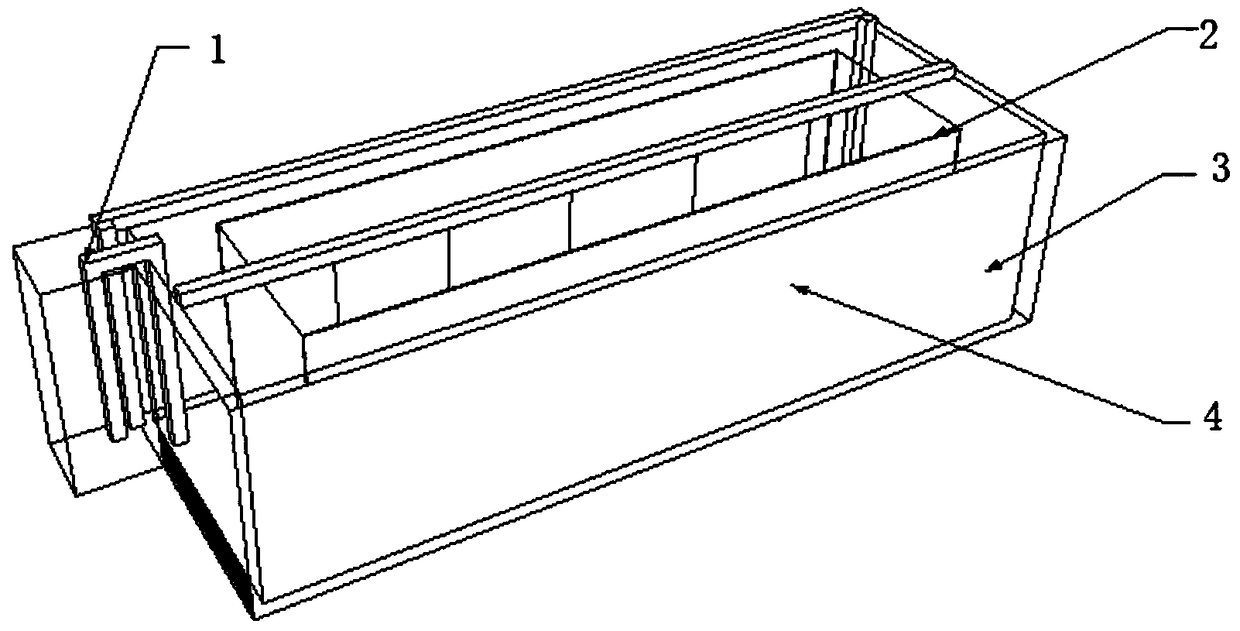
InactiveCN1736183AHigh reproductive survival rateAchieve separationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRefluxWater quality
The invention discloses an apparatus for trainring copepods species in-doors, including a incubator, the lower part of which connects to a water quality regulating tank, a reflux pipe arranged on the outer wall of the incubator, and the upper part of which communicates with the upper part of the incubator, while the lower part is positioned inside the water quality regulating tank, whereof a pump is fixed inside; the pump connected to the incubator by a water pump, which linked to an end of a taking-off ovum tube, while the other end of the taking-off ovum tube arranged outside of the water quality regulating tank,; the top of the incubator as open type; the bottom of the water quality regulating tank lied an fall tube. The apparatus applied to mass propagate copepods species in-doors, so as to simplify the training method, decrease the cost, and improve the efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for killing copepods in rotaria culture
InactiveCN1989803ADoes not affect growthLess damage in a short timeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpOrder copepoda
A method to killing copepod in Rotifer culture relates to bait applicator culture aimed at solving the problem of killing copepod in Rotifer culture. The technology program of the invention includes: equipping inflatable stone in the pool, injecting seawater and seawater Chlorella, it is characterized by equipping inflatable stone in the pool by one / m2, injecting seawater and seawater Chlorella by3:1 to 4:1, the salinity of mixed seawater is 15-20%., the rotifer asylum density is 1000-1500 / ml, the water temperature is 25-30degreeC, pouring the anthon solution into the pool by the density of 1.2g / m3, collecting the rotifer using the 250 mesh sieve silk bags after 24 hours and maintaining inflatable in the rotifer process. The invention applies to the bait applicator culture of fish, shrimp, crab seed.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method
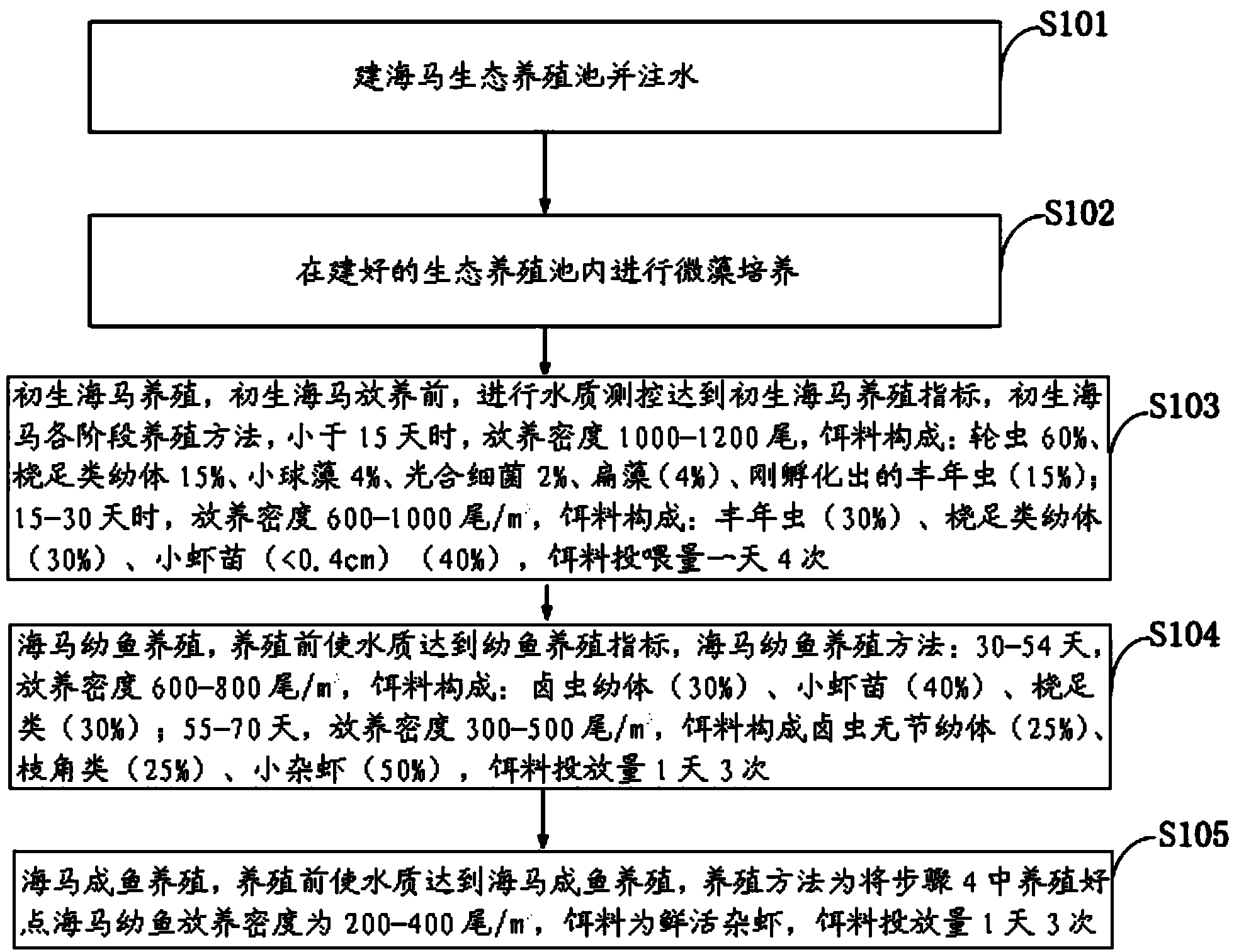
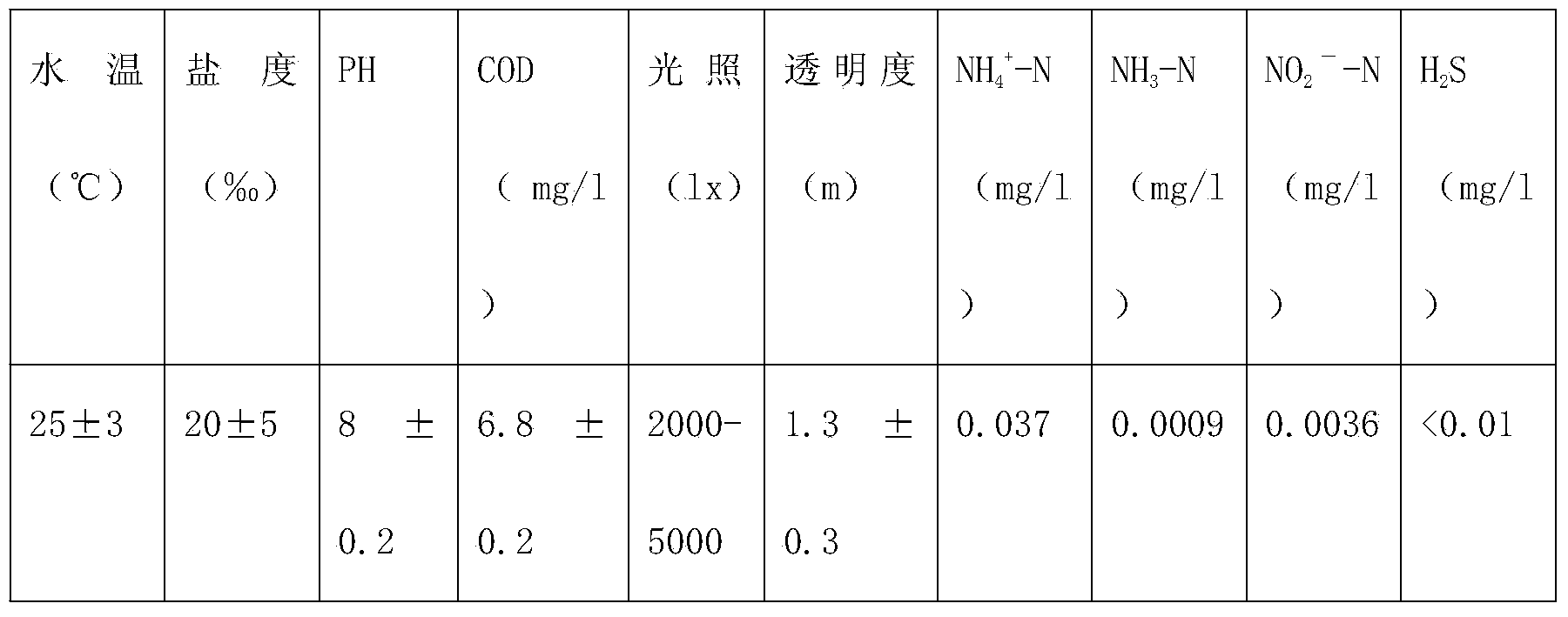
InactiveCN103960185ASuitable for artificial breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpJuvenile fish
The invention discloses an ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method comprises the steps of building an ecological sea horse breeding pond one week before breeding, cultivating microalgae in the built ecological breeding pond, and measuring and controlling water quality to reach newborn sea horse breeding indexes before newborn sea horses are bred. When the newborn sea horses is younger than 15 days, the released density is 1000-1200 tail / m<3>, and baits are composed of rotifer, copepods larvae, chlorella, photosynthetic bacteria, tetraselmis and fairy shrimps which are just incubated. During 15-30 days, the released density is 600-1000 tail / m<3>, baits are composed of fairy shrimps, copepods larvae and shrimp seeds, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond four times per day. A sea horse juvenile fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach juvenile fish breeding indexes before breeding. During 30-40 days, the released density is 600-800 tail / m<3>, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. A sea horse adult fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach sea horse adult fish breeding indexes. The released density of sea horse adult fish is 200-400 tail / m<3>, baits are fresh and alive shrimps, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method has the advantages of reducing production cost.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Cultivation method for green crab seedlings in pond
InactiveCN103141422AThe advantages of breeding seedlings are significantObvious advantagesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a cultivation method for green crab seedlings in a pond. The cultivation method consists of seedling cultivating facilities and a seedling cultivating process and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a mud or sediment bottom seedling cultivating pond; arranging miropores for inflating and an aerator in the seedling cultivating pond; carrying out pond cleaning and sterilization on a water reservoir and the seedling cultivating pond before the seedling is cultivated; filtering inflowing water by using a bolting-cloth mesh bag with 120 meshes; directly incubating green crab larva in the seedling cultivating pond; starting all aerating facilities from the second day after the green crab larva are incubated; feeding the green crab larva with the following baits: feeding with wheel animalcule at the earlier stages of Z1 to Z3, preventing copepods from entering into a seedling cultivating water body at the stages of Z1 to Z2, feeding with the wheel animalcule and supplementing the feeding of the copepods with small specifications at the later stage of Z3, feeding with the copepods with small specifications at the stage of Z4 and feeding with the copepods at the stage of Z5; and gradually adding new water from the stage of Z3, wherein the water level at the initial stage of seedling cultivation is 70-80cm and the water quality indexes during seedling cultivation are that dissolved oxygen is not smaller than 5mg / L, the contents of ammonia and nitrogen are not greater than 0.4mg / L, the pH value is 7.8-8.5 and the salinity is 28-34.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Color enhancing feed for leopard coral groupers, and preparation method of color enhancing feed
ActiveCN108185117AImprove body colorSolve the color is easy to fadeFood processingClimate change adaptationBetaineLeopard
The invention discloses a color enhancing feed for leopard coral groupers, and a preparation method of the color enhancing feed. The feed is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 5-30% of natural krill powder, 20-60% of white fish meal, 3-10% of yeast, 10-30% of artemia, 5-15% of turmbicula akamushi, 5-16% of hydrolyzed protein, 10-30% of high gluten flour, 5-20% of squid powder, 5-15% of spirulina, 1-5% of fish oil, 1-3% of lecithin, 1-3% of betaine, 1-2% of a vitamin mixture, 2-4% of a mineral element mixture, 1-5% of a microorganism preparation, 1-3% of a compound immunity reinforcing agent, 1-5% of copepods, 1-3% of casein, 1-3% of EPA, 1-5% of DHA, 1-5% of ARA, and 1-2% of a phagostimulant. The feed disclosed by the invention can effectively improve body color,and the problems that color is gloomy, color enhancement is difficult, and the color is liable to be light and not liable to recover under stress state are solved. Besides, according to the preparation technology, the digestibility and the absorbability of the feed are improved, nutrient elements are not destroyed, and the freshness and the food calling properties of the feed are guaranteed.
Owner:广东越群海洋生物科技股份有限公司
Method for culturing and transplanting Scylla fries stage by stage
InactiveCN101990850ATo achieve the goal of stable and high productionReduce carnageClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLive foodOrder copepoda
The invention provides a method for culturing and transplanting Scylla fries stage by stage, which relates to a Scylla culture method. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing zoeae in a culture pond for culturing for 12 to 18 days, and transferring the zoeae into a megalop culture pond with the area of 100 to 300 square meters for further culture; culturing live foods such as algae, fairy shrimps, copepods and the like in the megalop culture pond; transferring the fries at the last day of the fifth stage of the zoeae or at the first day of megalop, wherein the culture density of the megalop is controlled to be 1,000 to 2,000 fries per cubic meter; or culturing the zoeae at the fifth stage for 4 to 8 days, wherein the culture density is 2,000 to 4,000 fries per cubic meter; the water temperature of the megalop culture pond is between 24 and 32 DEG C; and the salinity is 1.5 to 2.6 percent; and transferring the megalop into a young Scylla culture pond, wherein the area ofthe young Scylla culture pond is 0.5 to 3 mu; the water temperature is between 26 and 33 DEG C; and the salinity is 1.0 to 2.0 percent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Breeding method for amphiprion ocellarises
InactiveCN104170777AUniversalPromote spawningClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSmall animalJuvenile fish
The invention provides a breeding method for amphiprion ocellarises. The breeding method comprises the following three steps: a. breeding parent fishes; b. incubating oosperms; c. breeding young juvenile fish. Fry is bred for 60 d after being incubated, the overall length of the juvenile fish is up to 2 cm to 3 cm, and the breeding process is ended up; during the breeding process, the minced-meat-shaped fresh bait made of rotifer intensified by seawater chlorella for 24 h, artemia and copepods intensified by DHA and the chlorella for 12 h, and marine small animals of which phospholipid content is more than 25% in succession and compound feed are fed as the bait in an individual manner or a superimposed manner; furthermore, water is changed and the amphiprion ocellarises are divided and put in fish tanks in proper time. The breeding method for the amphiprion ocellaris, provided by the invention, provides a way which can be operated in an industrialized and large-scale manner; compared with the prior art, as the breeding method provided by the invention is of popularity to a higher degree, a foundation is provided for large-scale breeding of the amphiprion ocellaris.
Owner:浙江华兴水产科技有限公司 +1
Bait feeding method for farmed hippocampus erectus
InactiveCN103999808AGuaranteed feeding efficiencyLow costClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaNutritive valuesBody height
The invention relates to a bait feeding method for farmed hippocampus erectus. During the farming period of the young hippocampus erectus, bait feeding is performed according to the following steps that before the body height of the young hippocampus erectus reaches 6.5 cm, copepods are fed to the young hippocampus erectus, wherein the feeding density is 15-20 pieces per milliliter; after the body height of the young hippocampus erectus reaches 6.5 cm, the copepods continue being fed to the young hippocampus erectus, wherein the feeding density is 15-20 pieces per milliliter; adult brine shrimps are fed to the young hippocampus erectus in an auxiliary mode, and the daily feeding amount accounts for 10 percent -12 percent of the weight of the young hippocampus erectus. According to the growth of the young hippocampus erectus, bait of different specifications is fed, and the two kinds of bait with different specifications and different nutritive values are mixed together for feeding; in this way, the feeding efficiency and feeding quality of the young hippocampus erectus can be guaranteed, and therefore cost of bait for the young hippocampus erectus during the stage of 6.5 cm-9.5 cm of the body length of the young hippocampus erectus is lowered by 50 percent; besides, maturing time can be shortened by about 9 days, so that energy consumption and labor cost are lowered, and the system utilization rate is increased. Accordingly, the bait feeding method has good application prospects.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Special compound feed for breeding parent shrimps of Litopenaeus vannamei
InactiveCN108771051AGood immune effectGood for healthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPenaeus marginatusRhodotorula
The invention discloses a special compound feed for breeding parent shrimps of Litopenaeus vannamei. The special compound feed contains the following components in percentage by weight: 20%-45% of whole squid meal, 5%-20% of Peru fish meal, 5%-15% of copepod dry powder, 2%-5% of enzymolysis fish soluble meal, 2%-8% of spirulina powder, 3%-10% of fly maggot meal, 5%-20% of oyster powder, 1%-4% of enzymolysis beer yeast powder, 1%-4% of sea rhodotorula, 5%-20% of alpha-starch, 1%-3% of soybean lecithin, 1%-5% of squid liver oil, 0.5%-2% of calcium dihydrogen phosphate and 1%-3% of a compound premix. The special compound feed is specially used during the breeding of the parent shrimps of Litopenaeus vannamei and is used for supplying nutrients required by the parent shrimps in the breeding stage; by adding multiple components which can mutually generate synergistic interaction effects, the digestion and utilization of the main nutrients are promoted, the immune capacity and health condition of prawns can be improved, the gonadal maturation quality is improved, and the hatching rate of fertilized eggs and the survival rate of larvae are increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG YUEHAI FEED GROUP
Indoor cement-pool artificial breeding method for oplegnathus punctatus
ActiveCN111183928AEasy to trainReduce stress responseFood processingClimate change adaptationFish larvaeCopepod
The invention provides an indoor cement-pool artificial breeding method for oplegnathus punctatus. The method comprises the following steps: (1) water-quality regulation and control: before hatched fish larvae are put, adding an EM probiotic preparation and natural alga cultivating pool water into a pool in each day; (2) pool entry: before the hatched fish larvae are put, distributing air stone ina transverse H manner, and putting the fish larvae in the pool, wherein the putting density is 13000-15000 fish larvae per cubic meter; (3) feeding management: feeding the fish larvae which are 20-40days old with baits including copepods and living mysis, and feeding the fish larvae which are over 30 days old with microencapsulated opening baits; (4) water change and illumination management: after the fish larvae are fed for 30-49 days, replacing water with 100%-150% of filtered seawater, and carrying out indoor illumination on the fish larvae which are 20-35 days old at 2500x-30001x, so asto realize light induced food intake; and (5) larvae outputting: transferring the larvae into a maritime net cage for breeding. According to the indoor cement-pool artificial breeding method, the growth quality of the fish larvae is improved, the death rate of the fish larvae is decreased, stress reaction of the fish larvae on a net cage breeding environment is reduced, and the survival rate of adult fish is increased.
Owner:HAINAN CHENHAI AQUATIC CO LTD
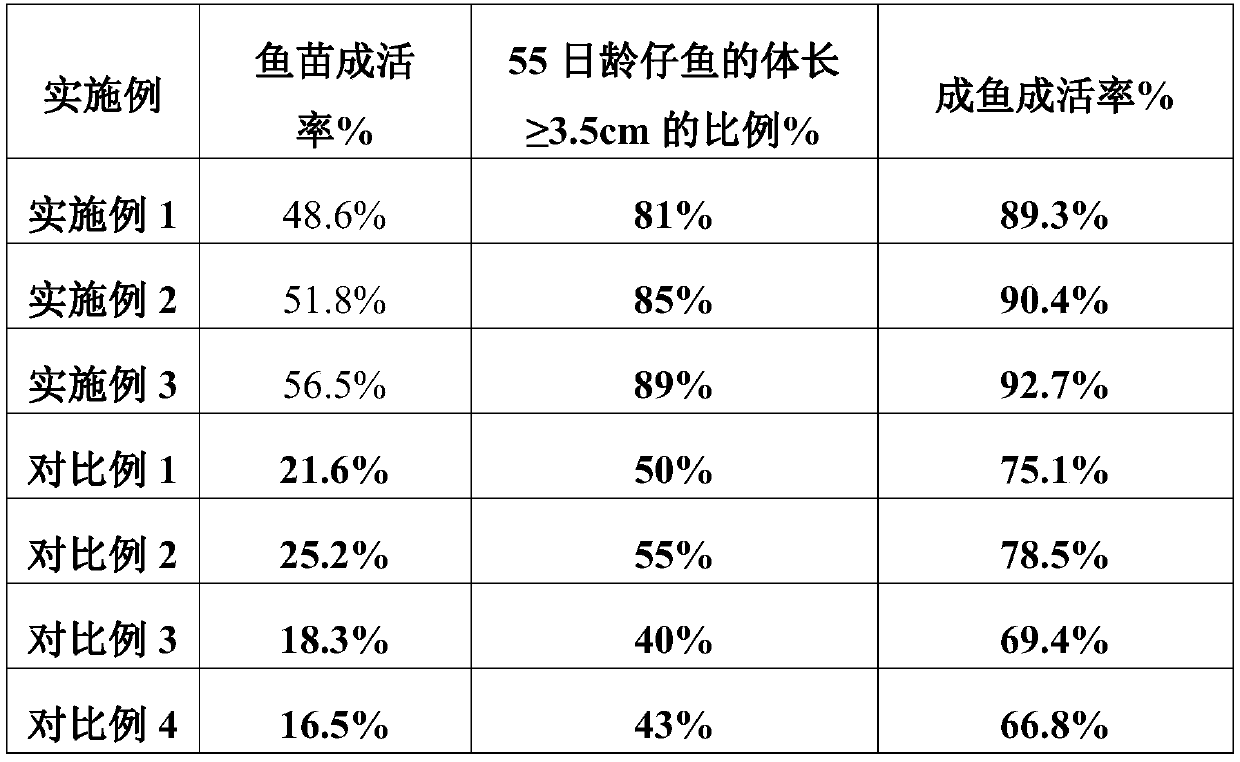
Breeding method for increasing survival rate of fish larvae
ActiveCN105830962AImprove survival rateSolve the bottleneck problem of cultivationClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceFish larvae
Owner:海南永贺生物科技有限公司
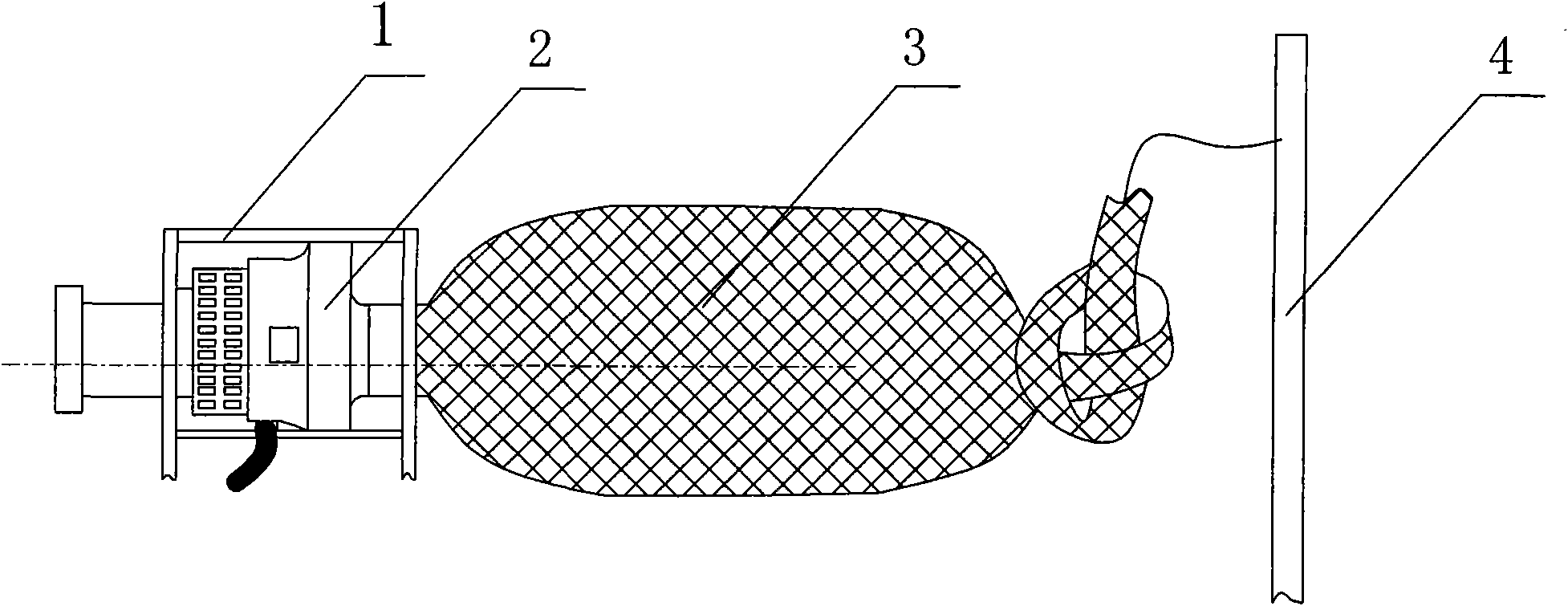
Method for fishing artificially cultured copepods in seawater pond
The invention provides a method for fishing artificially cultured copepods in a seawater pond, which includes: making a wingless trap net, which is 3.0m in opening width, 0.6m in height, 8.0m in body length and 80 in mesh number, and a cod-end 4.0m in length and 150 in mesh number; tying the whole opening of the net to a square frame which is made of plastic pipes 3cm in diameter and in 3.0m (upper edge and lower edge)X0.6m (left edge and right edge); driving two stakes 3m away from each other in the center of the pond; tying the square frame for the opening of the trap net to the two stakes; installing a 1.5kw double-wheeled waterwheel type aerator 4.0m away from the front of the opening; starting the aerator to generate water flow in the pond, which flows to the trap net, so that the copepods in the water are filtered in the cod-end of the trap net; operating the aerator for 2-4 hours every day so as to fish pure live copepods weighing about 5-15kg. The method is simple in process, can be operated by one person, and is laborsaving, timesaving and low-cost. Residual copepods, residual fertilizer, residual water and residual foundation feed in the pond can be fully used, and continuous cultivation and fishing of the copepods are guaranteed.
Owner:宁德市富发水产有限公司
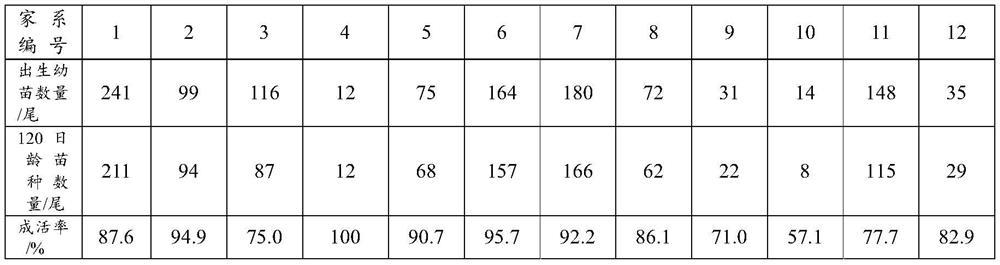
Breeding method of hippocampus abdominalis family
ActiveCN113598092AIncrease mating rateIncrease exposureClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOpossumAnimal science
The invention provides a breeding method of hippocampus abdominalis family, which comprises the following steps: S1, arranging a breeding pool with the daily water change amount of 100-300%; placing an inflatable stone and a breeding nest in the breeding pool; arranging an early-stage juvenile fish culture barrel and a later-stage juvenile fish culture barrel; placing the inflatable stone in the early-stage juvenile fish culture barrel, and placing the inflatable stone and an attachment frame in the later-stage juvenile fish culture barrel; S2, selecting healthy and mature parent male and female hippocampus abdominalis and putting the selected parent male and female hippocampus abdominalis into the breeding nest; S3, after the female and male hippocampus abdominalis lays fry, fishing out newborn hippocampus abdominalis fry and putting the fry into the early-stage juvenile fish culture barrel; S4, feeding the juvenile fishes with different birth day ages with fairy shrimp larvae and copepod with different densities, wherein the copepod is fed or opossum shrimps are fed. The breeding method of the hippocampus abdominalis family is easy to operate, and the survival rate of hippocampus abdominalis fry is high.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN +1
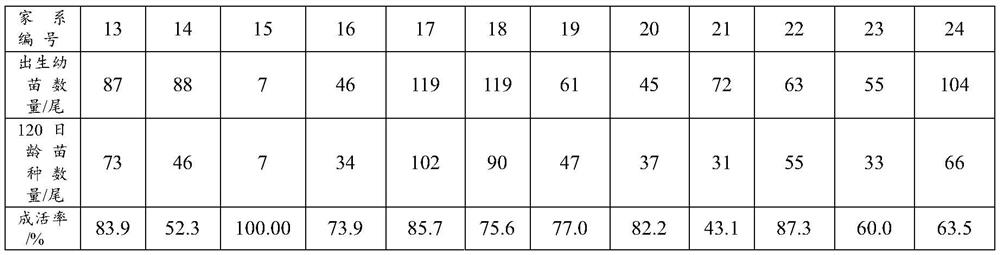
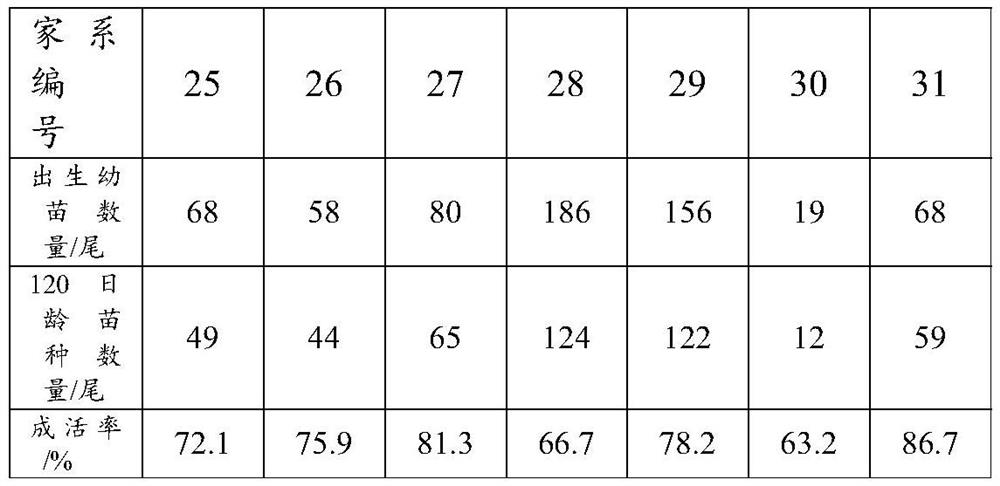
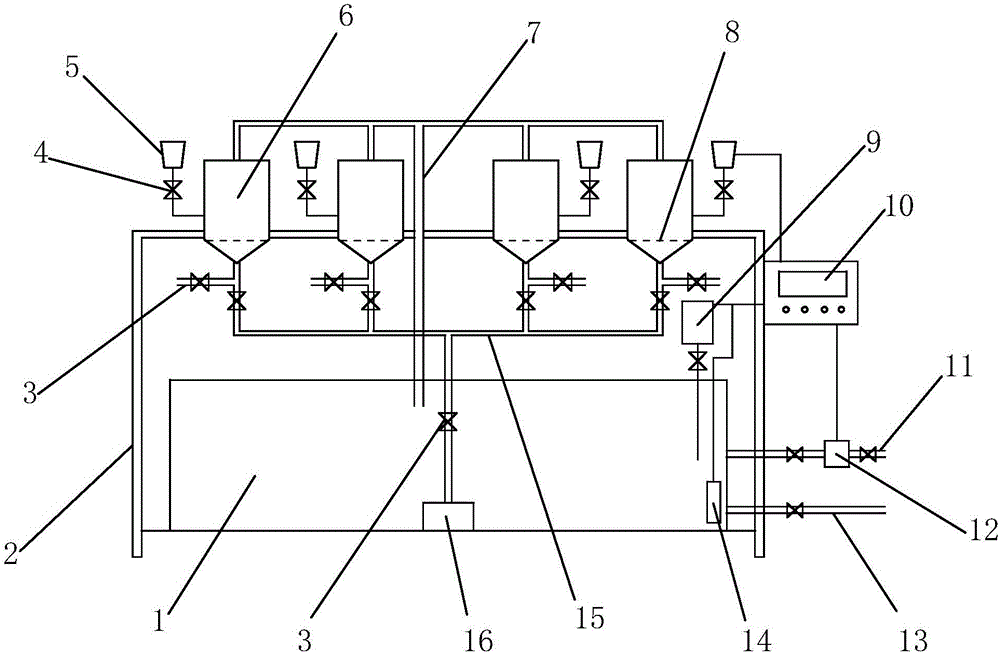
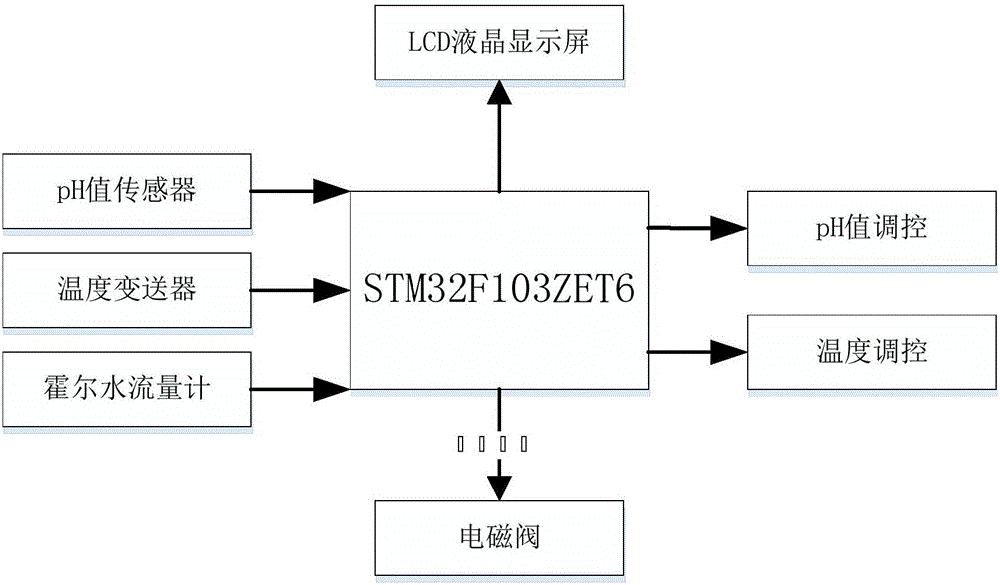
Multi-station copepod culture device and culture method thereof
ActiveCN106386637ALow costEnsure water quality consistencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater dischargeWater storage tank
The invention relates to a multi-station copepod culture device. The multi-station copepod culture device comprises a water storage tank and a water feeding pipeline connected with the water storage tank, wherein the water feeding pipeline is connected with at least one incubator; the incubator is provided with a bait box and a collection pipeline; the incubator is connected with the water storage tank through a water returning pipeline; the water storage tank is provided with a water inlet pipeline, a water discharging pipeline, an acidifying machine and a temperature sensor; each pipeline is provided with a valve; and the culture device further comprises a control box. A structural design that the same water storage tank is combined with the plurality of incubators is adopted so that an experiment method of a multi-station incubator in the same water region is realized; and a contrast experiment can be carried out on different bait feeding manners of different copepods or same copepods in the same water region, so that the consistency of water quality of the contrast experiment is guaranteed. Meanwhile, the culture efficiency is improved and the cost of culture equipment is reduced. The water storage tank realizes internal circulation and external circulation manners of a culture environment and a water body of the whole water region is updated; and the culture water quality is guaranteed, and the culture effect and survival rate of the copepods are guaranteed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in cement pond of simple plastic greenhouse
ActiveCN103026990AShorten the timeTime stretchedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in a cement pond of a simple plastic greenhouse. The cement pond is adopted, and an arch-shaped ring top is formed above the cement pond. The technology is characterized in that: a dimmable shading film covers on the arch-shaped ring top; the air density in the cement pond is 1-1.5 pieces per square meter; the stocking sizes are 10-12 millimeters in full lengths per fingerling; the stocking density is 1,000-1,500 fingerlings per square meter; the water level is 70 centimeters during stocking; 20 centimeters of fresh water is injected every day from the second day, the cement pond is full of water four days later, and 50 percent of water is changed every other day from the fifth day; after 10-15 days of cultivation, bait scraps and fish excrement are cleared; the water quality indexes are that: the salinity of sea water is 0.8-1.2 percent, the water temperature is 25-28 DEG C, the dissolved oxygen is over 5 mg / L, and the pH is 7.5-8.5; medium-sized cladocerans and copepods are fed at an earlier stage, and large frozen fairy shrimps are fed at a middle stage; and after the full lengths of fingerlings are up to 30 millimeters, a compound feed is fed instead of the frozen fairy shrimps, and an eel feed is fed completely after 3-4 days of transition.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
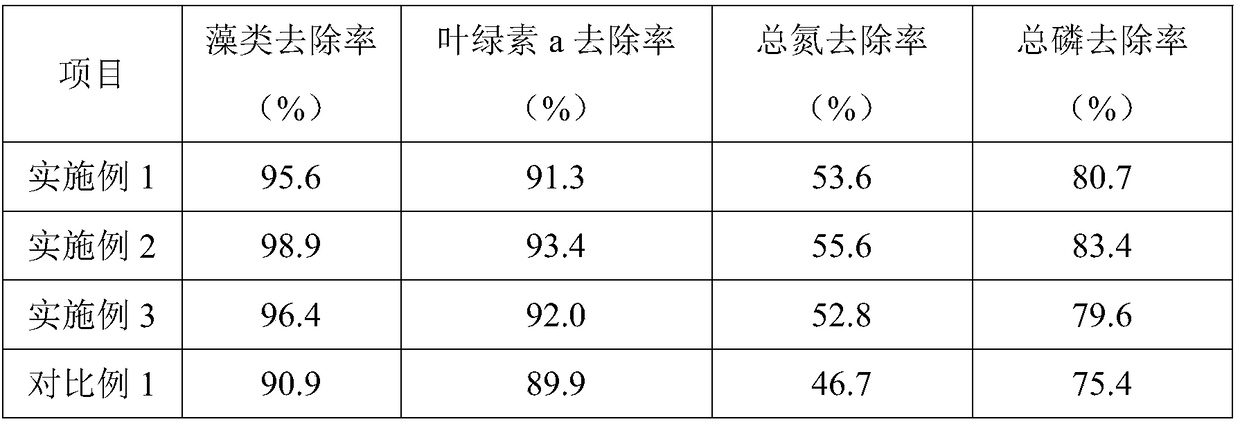
Resource utilization method of intensive litopenaeus vannamei breeding wastewater
ActiveCN107509673AAchieve recyclingProtect environmentClimate change adaptationEnergy based wastewater treatmentZooplanktonEutrophication
The invention relates to a resource utilization method of intensive litopenaeus vannamei breeding wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: step one, performing filtering on wastewater discharged from an intensive litopenaeus vannamei breeding pond by using a slant filtering screen; step two, collecting wastewater after the filtering by the slant filtering screen into a wastewater storage pond; step tree, conveying the wastewater in the wastewater storage pond to a sunlight-shed microalgae proliferation pond for culturing microalgae; and step four, conveying the cultured microalgae water into a cladoceran or a copepod cultivation pond, and harvesting cladocerans or copepods for supplementing the baits of the litopenaeus vannamei breeding. The method has the advantages that with the help of a food chain of microalgae-zooplankton-prawn, cyclic utilization of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient substances in the wastewater is realized, while the eutrophic breeding wastewater is purified, the breeding water environment is protected, and the natural baits for the intensified prawn breeding are supplemented, so that the feed cost of the prawn breeding is reduced, and the breeding benefits are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method of utilizing filter-feeding organisms to remove algae
ActiveCN109133356AReduce the concentration of nitrogen and phosphorusPromote growthWater treatment compoundsSpecific water treatment objectivesMicroorganismWater storage
The invention discloses a method of utilizing filter-feeding organisms to remove algae. The method includes: allowing algae-containing water to sequentially flow through water storage facilities in serial connection, sequentially putting copepods, filter-feeding shell-filter-feeding fishes, copepods and filter-feeding shell-filter-feeding fishes into the water storage facilities, and adding a microbial restoration agent into the water storage facilities when a lot of algae appears, wherein the microbial restoration agent comprises nitromonas, nitrosomas, bacillus subtilis, poly-phosphorus microorganism and photosynthetic bacteria. Meshes of a net for each water storage facility in which the copepods are put in are 0.5-2mm while meshes of a net for each water storage facility in which the filter-feeding shell-filter-feeding fishes are put in are 15-60mm. By the method, floating algae in a water body and nitrogen-phosphorus concentration of the water body can be reduced, growth of algaeattached on a water bottom layer is promoted, serial connection of the copepods, filter-feeding shells and filter-feeding fishes and feeding habit difference are utilized to achieve the objective of algae removal, the algae can be eliminated to greatest extent, and algae digestion capacity is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Indoor fry breeding method of hapalogenys nitens
ActiveCN109275600AEnsuring micronutrient supplementationGuaranteed supplementClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPhacusHermetia illucens
The invention discloses an indoor fry breeding method of hapalogenys nitens. The method comprises the following steps: screening copepods baits, screening hermetia illucens larva baits, making artificial micro fish reefs and performing placement, and feeding copepods and hermetia illucens larvae. According to the method, the trace element supplement of fries are ensured, the immunity of the friesis improved, a relatively great role is played in the fry breeding survival rate at this stage, and the highly efficient temporary-culture is realized in fry breeding rooms.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI +1
Feeding method of controllable bait for fries of Takifugu flavidus
ActiveCN102893927ASolve the problem of difficult time matchingImprove the survival rate of breedingClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkTakifugu flavidus
The invention relates to a feeding method of controllable bait for fries of Takifugu flavidus. The feeding method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: taking egg yolk as the bait during the initial stage when the fries are aged 2-10 days, and uniformly splashing and feeding in a full pool six times per day; taking Artemia larvae which are justly hatched as the bait when the fries are aged 7-10 days, and supplementing twice per day, wherein the feeding density is 2-3 larvae / ml; taking the Artemia larvae as the bait when the fries are aged 11-19 days, and supplementing twice per day, wherein the feeding density is 3-5 larvae / ml; taking frozen copepods as the bait when the fries are aged 14-19 days, uniformly splashing and feeding in the full pool, and supplementing six times per day, wherein the feeding density is 4-6 copepods / ml; taking the frozen copepods as the bait when the fries are aged 20-25 days, uniformly splashing and feeding in the full pool, and supplementing six times per day, wherein the feeding density is 4-6 copepods / ml; taking frozen large Artemia as the bait when the fries are aged 25-35 days, melting the bait at normal temperature, feeding to a bait table, and supplementing three times per day; and feeding compound feed when the fries are aged 30-35 days, placing 4-6 blocks of the compound feed on each bait table, and feeding twice per day, wherein the compound feed is kneaded into pastes.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Method for mixed cultivation of sea horses and hemifusus ternatanus
InactiveCN105724282AAvoid wastingAvoid pollutionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseWater quality
The invention discloses a method for mixed cultivation of sea horses and hemifusus ternatanus.Hemifusus ternatanus and sea horses are cultivated inside a culture pond to construct a fish and shellfish circulation ecological cultivation system, suitable culture objects can adapt to all ecological niches and trophic levels in the culture pond, and bait waste and water pollution caused by residual bait are avoided.The sea horses and the hemifusus ternatanus occupy different ecological niches in the cultivation environment respectively, various kinds of natural bait in water and artificial feed put into the water can be sufficiently utilized, the total conversion rate of objects and energy in the culture pond is increased, the water quality is effectively stabilized, and entrance of etiology is controlled.The sea horse bait mainly includes copepods, artemia and small shrimps; the hemifusus ternatanus is demersal sarcophagy, and no additional feeding is needed in the cultivation process, so that the hemifusus ternatanus eat residual bait generated in the cultivation process of the sea horses, and the role of a scavenger is brought into play.Accordingly, the purposes that the bait utilization rate is improved, water pollution caused by residual bait is avoided, diseases are prevented and treated, and the production cost is saved are achieved.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Odontobutis obscurus large-size fry artificial classification separate culture method
PendingCN109496926AAchieve indoor cultivationImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater filterOxygen
The invention relates to an odontobutis obscurus large-size fry artificial classification separate culture method. The method comprises the steps that 1, a net cage is arranged in an indoor culture groove, oxygen increasing heads are arranged on the periphery of the indoor culture groove, a water pushing device is arrange on one side, and a water filtering device is arranged on the other side; 2,newly hatched larvae of odontobutis obscurus are put in the net cage of the culture groove; 3, the culture water depth is controlled to be 0.3+ / -0.6 m, the water temperature is controlled to be 22-28DEG C, and sewage suction and water replenishing are conducted every afternoon; 4, after hatching is conducted for 3 d, cladocerans and copepods obtained after filtering through a 60-mesh sieve serveas initial feed, after 7 d, bait mainly adopts limnodrilus and secondarily adopts the cladocerans and the copepods, and after 14 d, while the limnodrilus is used for feeding, loach and newly hatched larvae of pseudorasbora parva are additionally put; 5, after hatching is conducted for about 10 d, by taking the head width as the standard, odontobutis obscurus artificial classification separate culture is conducted, and hereafter, specification screening and classification are conducted every 10 d. Accordingly, indoor odontobutis obscurus large-size fry culture is achieved, after culture is conducted for about 50 d, for the odontobutis obscurus, the average overall length reaches about 20 cm, the head width is about 3.3 mm, and the pond survival rate reaches 90%.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
Method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
Method for sea anemone culture in pond
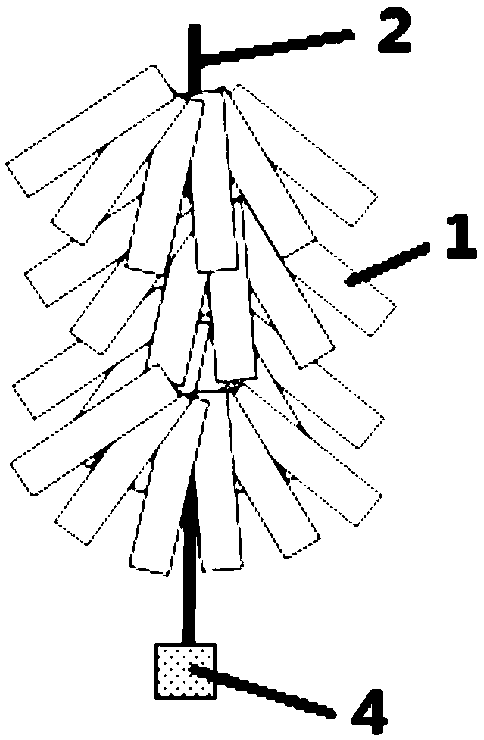
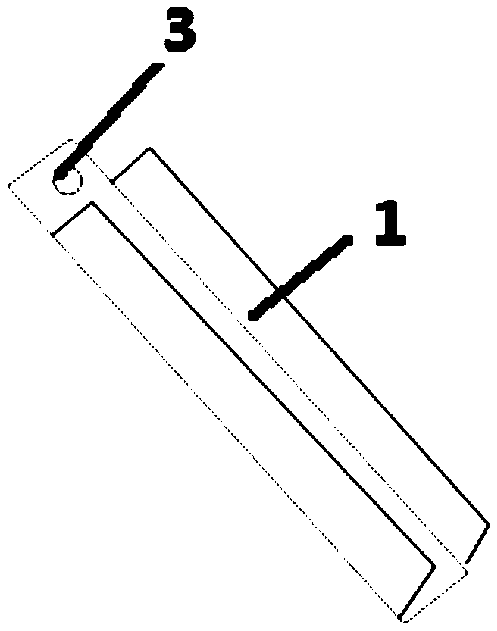
InactiveCN106386579ATake advantage ofEasy to get materialsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringOrder copepoda
A method for sea anemone culture in a pond is characterized in that a net cage suspended under the water surface of the pond is used for artificial culture. The net cage is shaped like a cuboid with dimensions of 2*1*1m, the upper face of the net cage is opened, the bottom face of the net cage and the surrounding side faces are fenced by net plates, and the net size is eight meshes; the multiple net cages are disposed and arranged in a line along the length direction of the net cages, the upper edge of each net cage is connected by two parallel main ropes, multiple supporting rods are fixed at an interval between the two main ropes, and a floating ball is connected at the joint between each supporting rod and the main rope; auxiliary ropes are connected to two end heads of the main rope, and the end head of each auxiliary rope is connected to a rope anchor located at the bottom of the pond; and an attaching baseplate is disposed in the net cage, the attaching baseplate comprises a bottom plate, a corrugated plate is fixed on the bottom plate, and through holes are arranged in the corrugated plate. Materials could be obtained easily; the method is simple; operations are easy; management is easy; sea anemones could be bred separately or bred together with trepang to eat trepang enemies such as copepod and gammarid; space in a pond water area is fully used; the survival rate is high; and the growth speed is high.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENTAL OCEAN SCI TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com