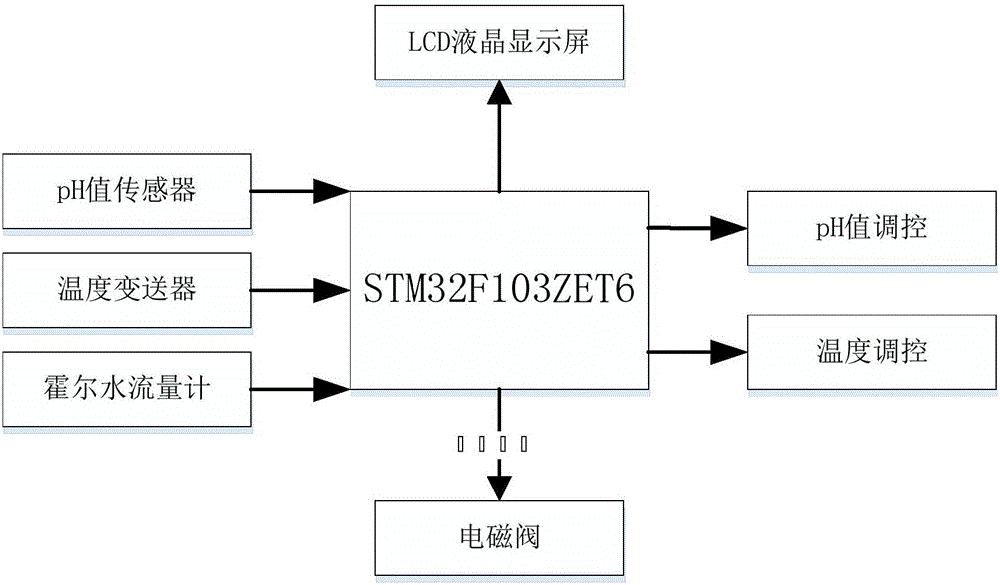
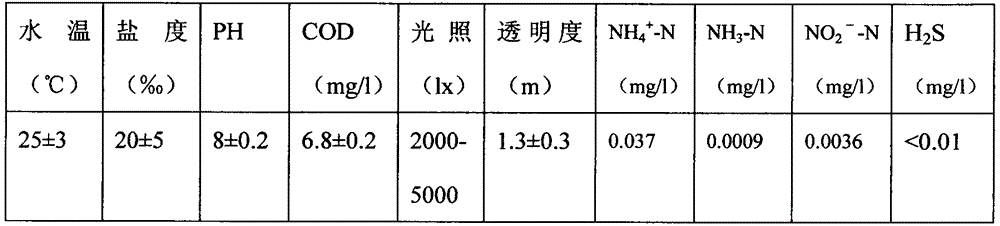
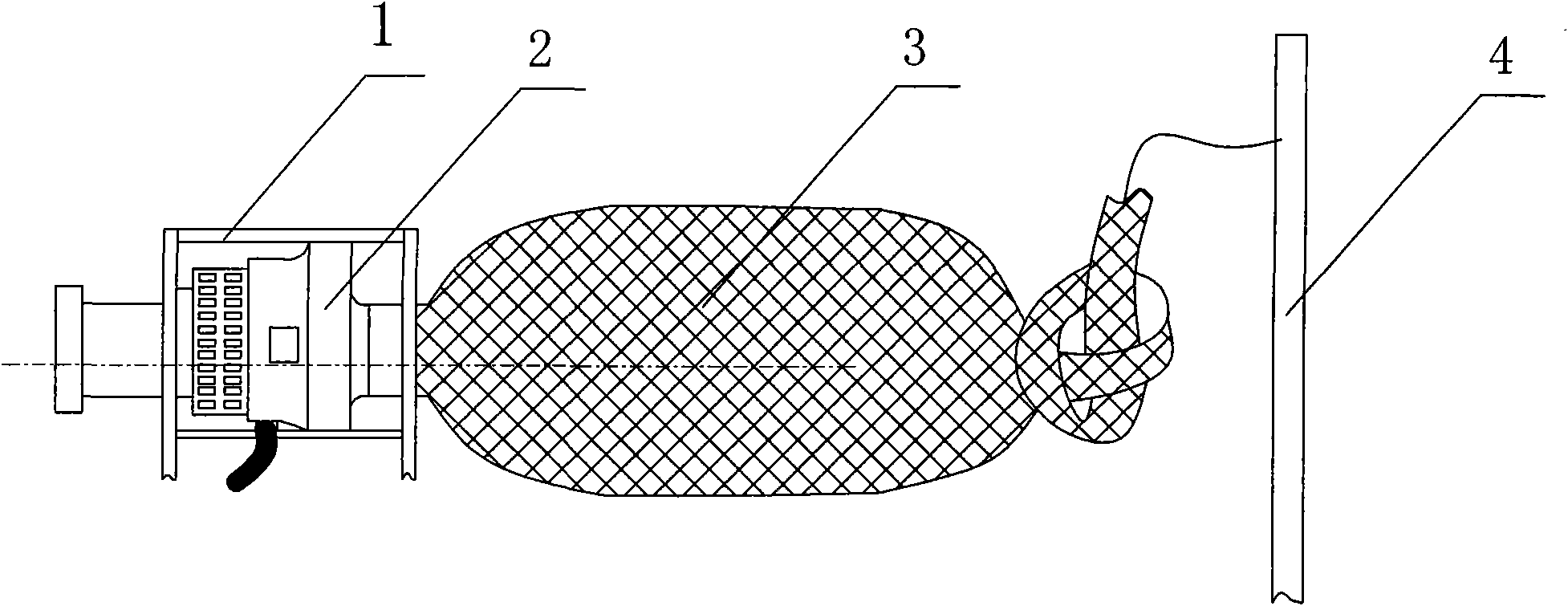
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Order copepoda" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copepods form a subclass belonging to the subphylum Crustacea (crustaceans); they are divided into 10 orders. Some 13,000 species of copepods are known, and 2,800 of them live in fresh water.
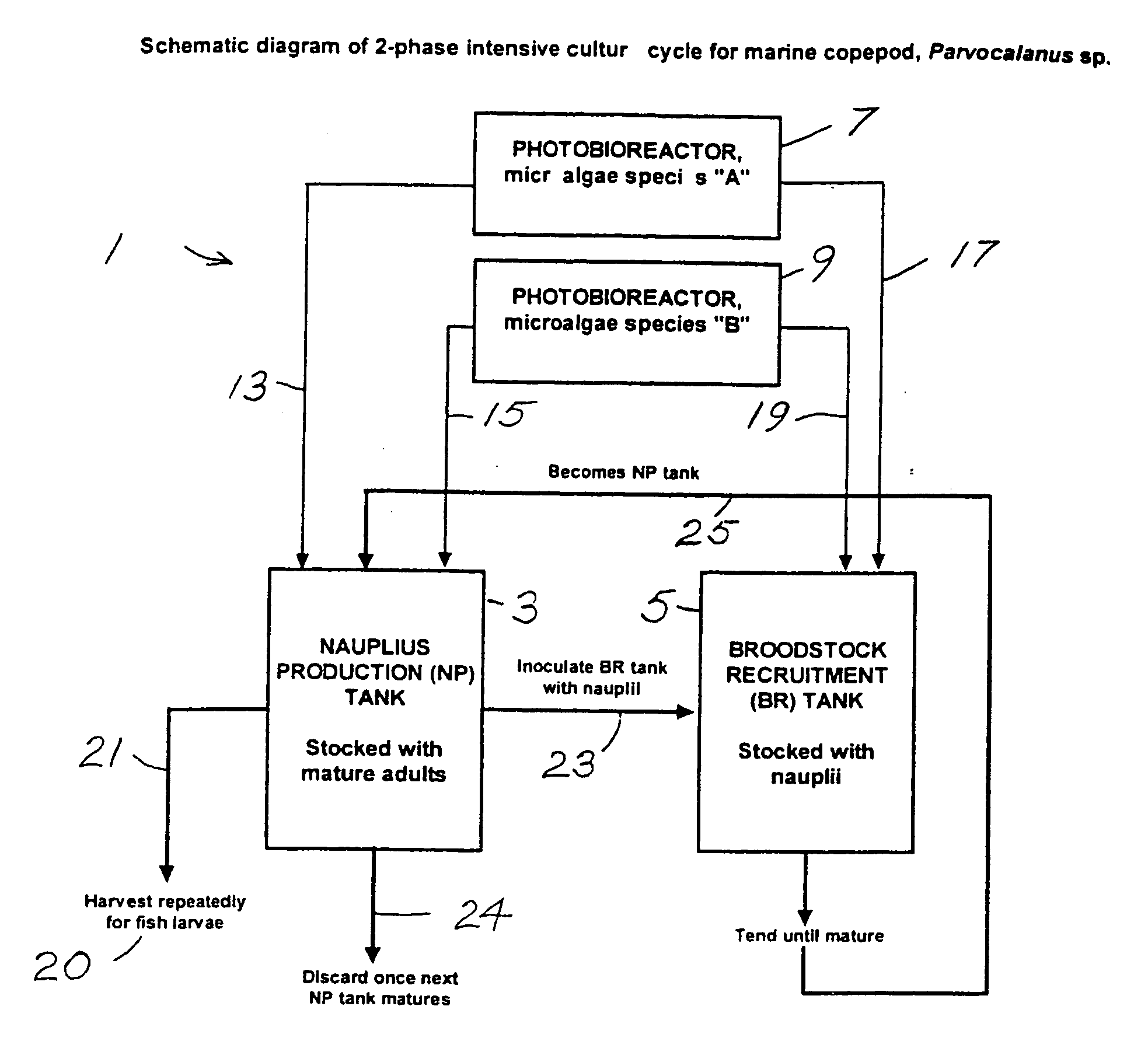
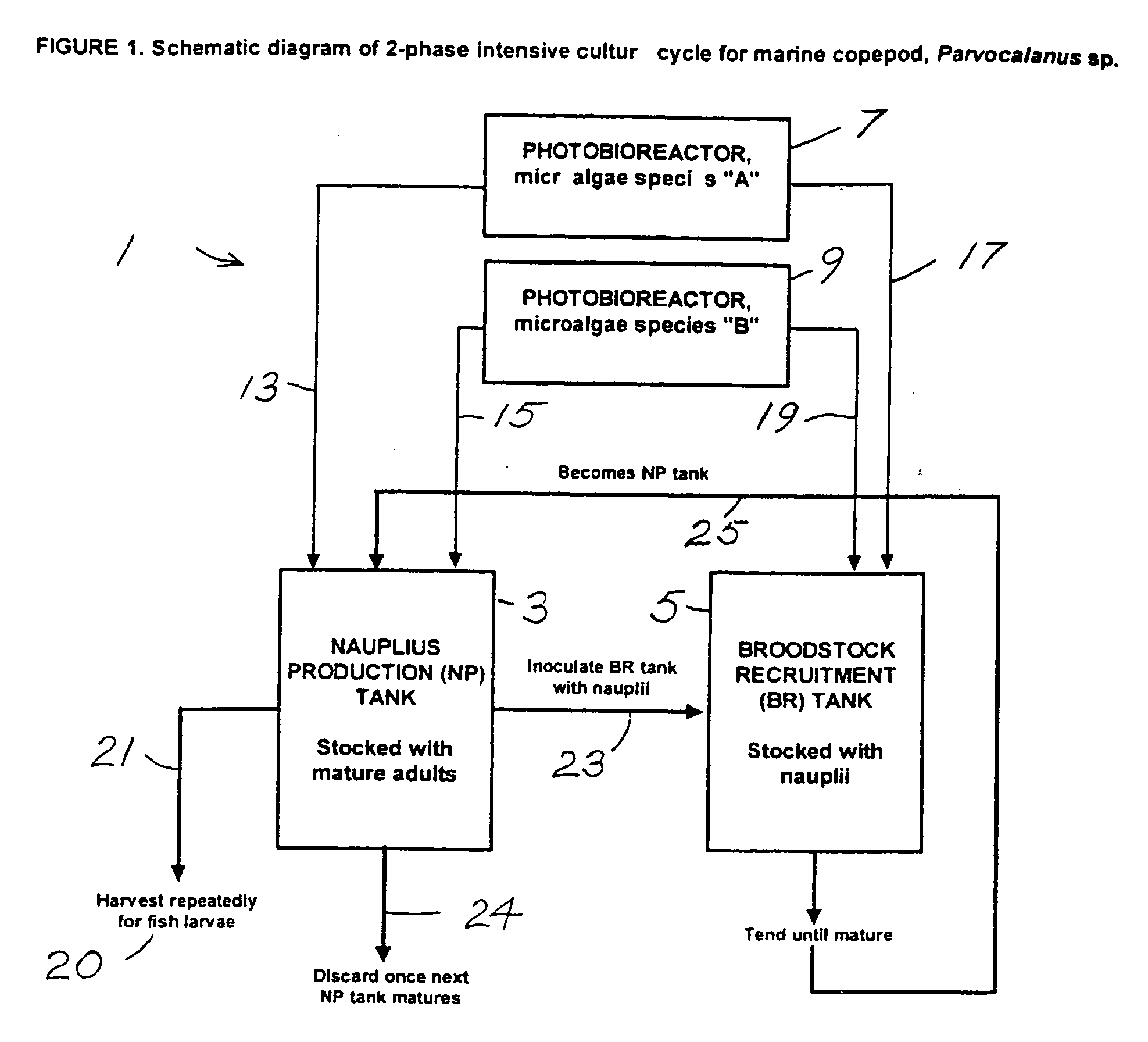
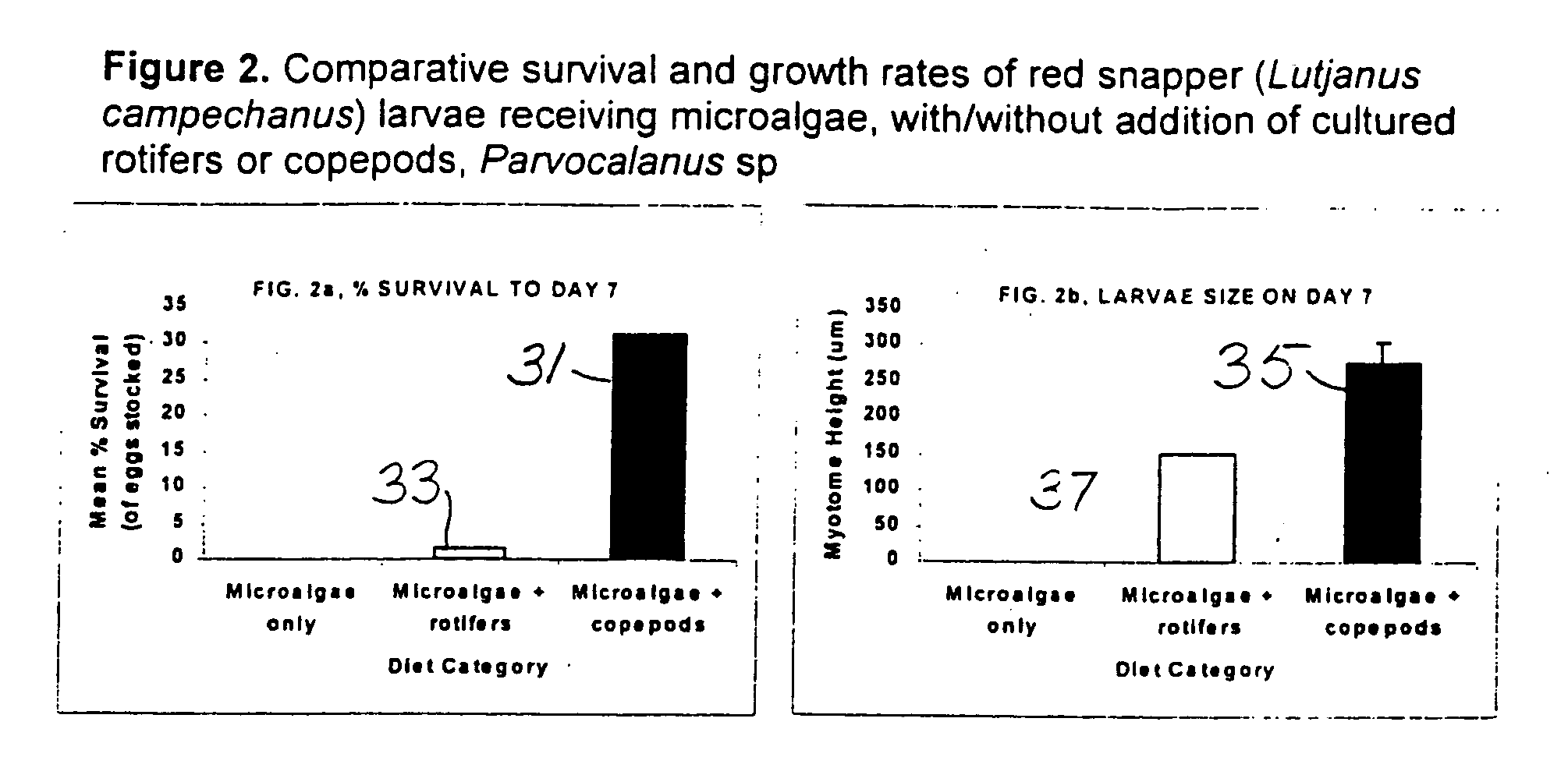
Isolation, culture, and use of marine copepods in aquaculture
InactiveUS20060169216A1Conducive to survivalPromote growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsClimate change adaptationFish larvaeJuvenile fish
Larviculture is performed using Parvocalanus sp as a feed for fish larvae. A system is described using tanks for growing Parvocalanus sp nauplii with a microalgae feed and transferring the grown Parvocalanus sp nauplii to tanks containing the fish larvae, where the functions of the tanks is interchanged. The Parvocalanus sp feed provide for higher numbers of larger juvenile fish and the rearing of larvae heretofore not reared in culture.
Owner:SHIELDS ROBERT JOHN +1
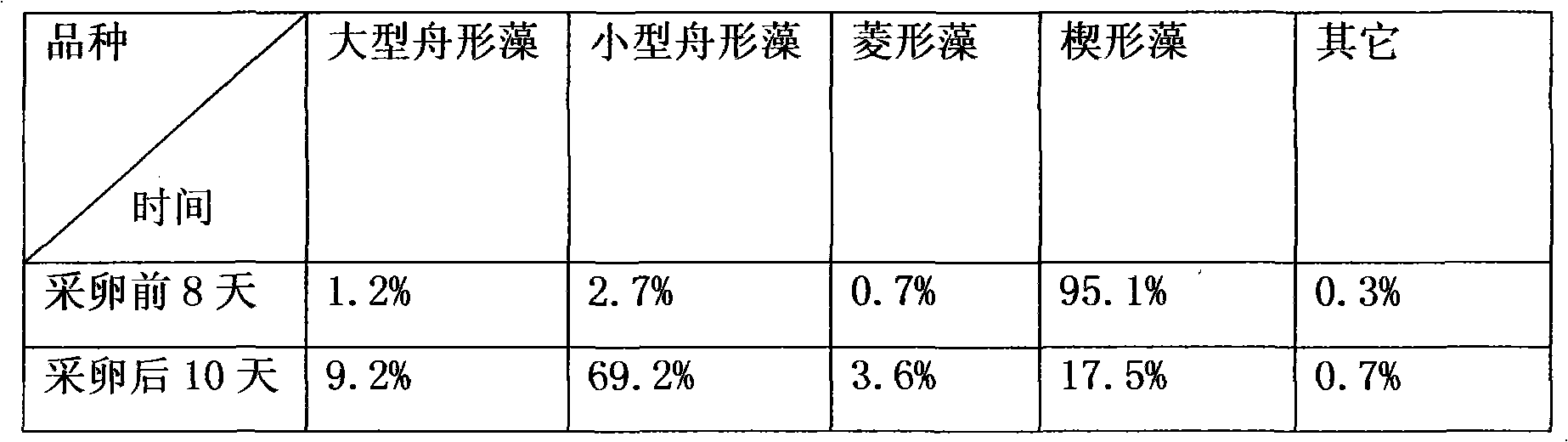
Benthic diatom culture method for growing seedlings and abalone fry culture method
InactiveCN101647406AImprove farming outputUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationDiseaseOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a benthic diatom culture method for growing seedlings and an abalone fry culture method, which relate to an abalone culture technology. The invention is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) starting culturing algaes 45 days before pulling seedlings, keeping the culture water temperature at 14 DEG C and the illuminance between 20001 and 30001x, controlling the light between 10001 and 15001x at the last culture after screening and eliminating algae culture for one and half a month, and laying ovum after 7 days; (2) adding nutrient salt at primary culture,wherein the adding ratio of N:P:Si:Fe is 5:1:1:1(ppm); (3) laying ovums about 5 millions for each pool and carrying out micro inflation; (4) changing water regularly after the ovums are laid and changing water twice a measuring range which is 24 hours; (5) carrying out running water culture after the ovums swim for 5 to 6 days and are adhered; (6) controlling the illuminance within 10001x after larvas metamorphose; and (7) dumping the pool after treating copepods at about 30 days of the culture period, adjusting the illuminance between 15001 and 20001x and peeling off baby abalones after about45 days. The methods have the advantages of improving the yield and preventing and treating a plate stripping disease.
Owner:FUJIAN LANJING AQUATIC PRODS
Composite nutrition enhancer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101810246AImprove survival rateImprove disease resistanceAnimal feeding stuffOrder copepodaPhaffia rhodozyma
The invention relates to a composite nutrition enhancer and a preparation method thereof, relating to a feed additive. The invention provides the composite nutrition enhancer, which not only contains large amount of DHA, ARA and natural yeast astaxanthin, but also contains multiple Omega 3 unsaturated fatty acids, multiple amino acids and trace elements. The composite nutrition enhancer is formedby composition of fission chytrid microalgae and phaffia rhodozyma with the weight ratio of 50 percent to 80 percent and 20 percent to 50 percent. All the components are weighed and mixed according to matching ratio after being crushed, mixed evenly, powder-sieved till the particle size is 8-25mum, inspected, weighed and packaged. The invention is especially applicable to feeding of live eels fryand shrimp postlarvae, artificial seawater seedling enhanced artemia salina sinnaeus, rotifer and cladocera (micrura), copepods and the like and various egg-laying poultries.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
Method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton
The invention relates to a method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton, belonging to the technical field of fish culture. The method comprises the following steps of selecting collecting water areas of river channels, ditches or ponds and the like the zooplankton density of which is higher than 10 / ml in water bodies; fixing a collecting device and starting a submersible pump to ensure that the water inlet of the submersible pump is 30-50cm away from water surface, and collecting the zooplankton once every 1-2 hours after the pump is started; and separating the collected zooplankton according to different application with different mesh bolting silk and cleaning for 1-3 times with clean pond water. The device employed by the invention has simple structure, easy material obtainment and convenient use; the natural zooplankton resources naturally breeding and easily regenerating in various fresh water bodies can be sufficiently utilized, thereby greatly reducing the labor intensity and being suitable for use in standing water, slow flow water areas and water bodies with different sizes. The method has the characteristics of high efficiency, economy, practicality and the like.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
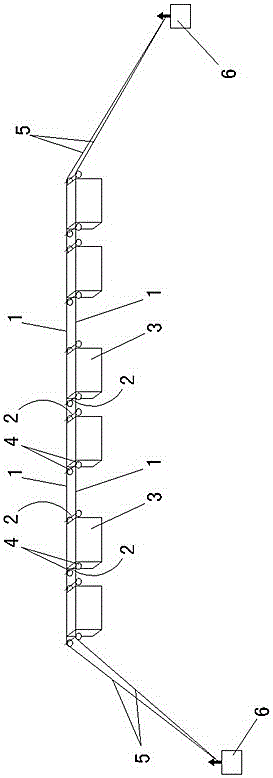
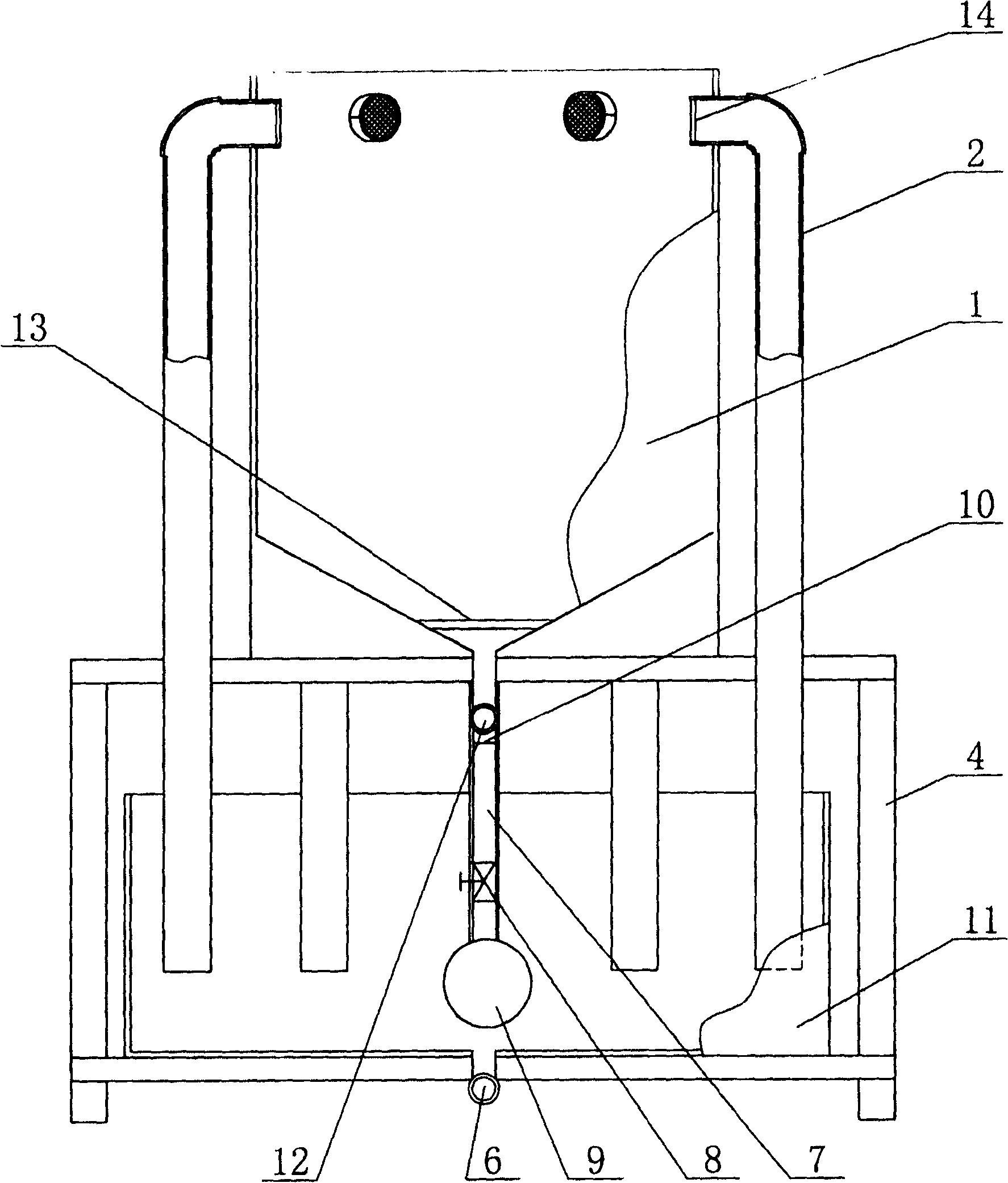
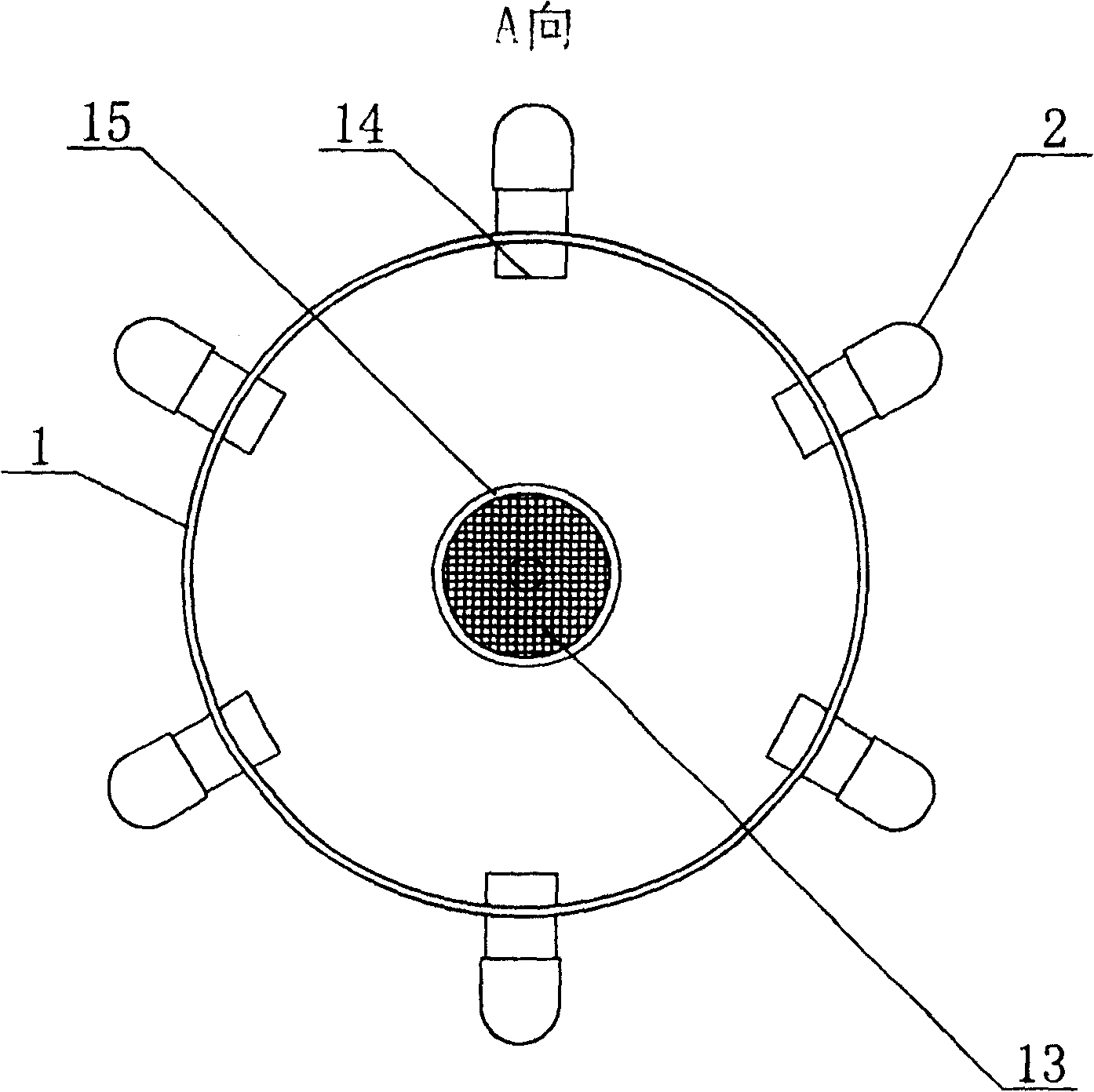
Indoor culture device of copepoda population
InactiveCN1736183AHigh reproductive survival rateAchieve separationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRefluxWater quality
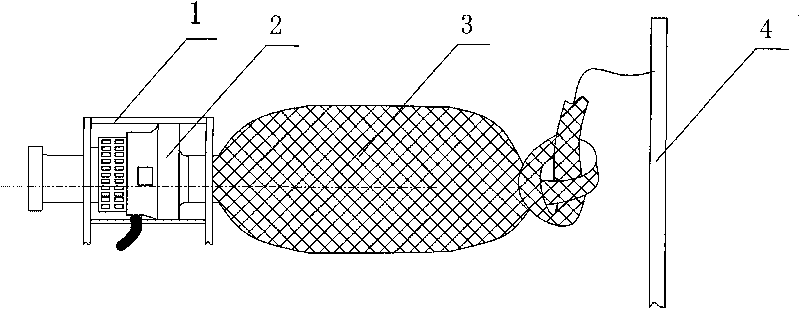
The invention discloses an apparatus for trainring copepods species in-doors, including a incubator, the lower part of which connects to a water quality regulating tank, a reflux pipe arranged on the outer wall of the incubator, and the upper part of which communicates with the upper part of the incubator, while the lower part is positioned inside the water quality regulating tank, whereof a pump is fixed inside; the pump connected to the incubator by a water pump, which linked to an end of a taking-off ovum tube, while the other end of the taking-off ovum tube arranged outside of the water quality regulating tank,; the top of the incubator as open type; the bottom of the water quality regulating tank lied an fall tube. The apparatus applied to mass propagate copepods species in-doors, so as to simplify the training method, decrease the cost, and improve the efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for killing copepods in rotaria culture
InactiveCN1989803ADoes not affect growthLess damage in a short timeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpOrder copepoda
A method to killing copepod in Rotifer culture relates to bait applicator culture aimed at solving the problem of killing copepod in Rotifer culture. The technology program of the invention includes: equipping inflatable stone in the pool, injecting seawater and seawater Chlorella, it is characterized by equipping inflatable stone in the pool by one / m2, injecting seawater and seawater Chlorella by3:1 to 4:1, the salinity of mixed seawater is 15-20%., the rotifer asylum density is 1000-1500 / ml, the water temperature is 25-30degreeC, pouring the anthon solution into the pool by the density of 1.2g / m3, collecting the rotifer using the 250 mesh sieve silk bags after 24 hours and maintaining inflatable in the rotifer process. The invention applies to the bait applicator culture of fish, shrimp, crab seed.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
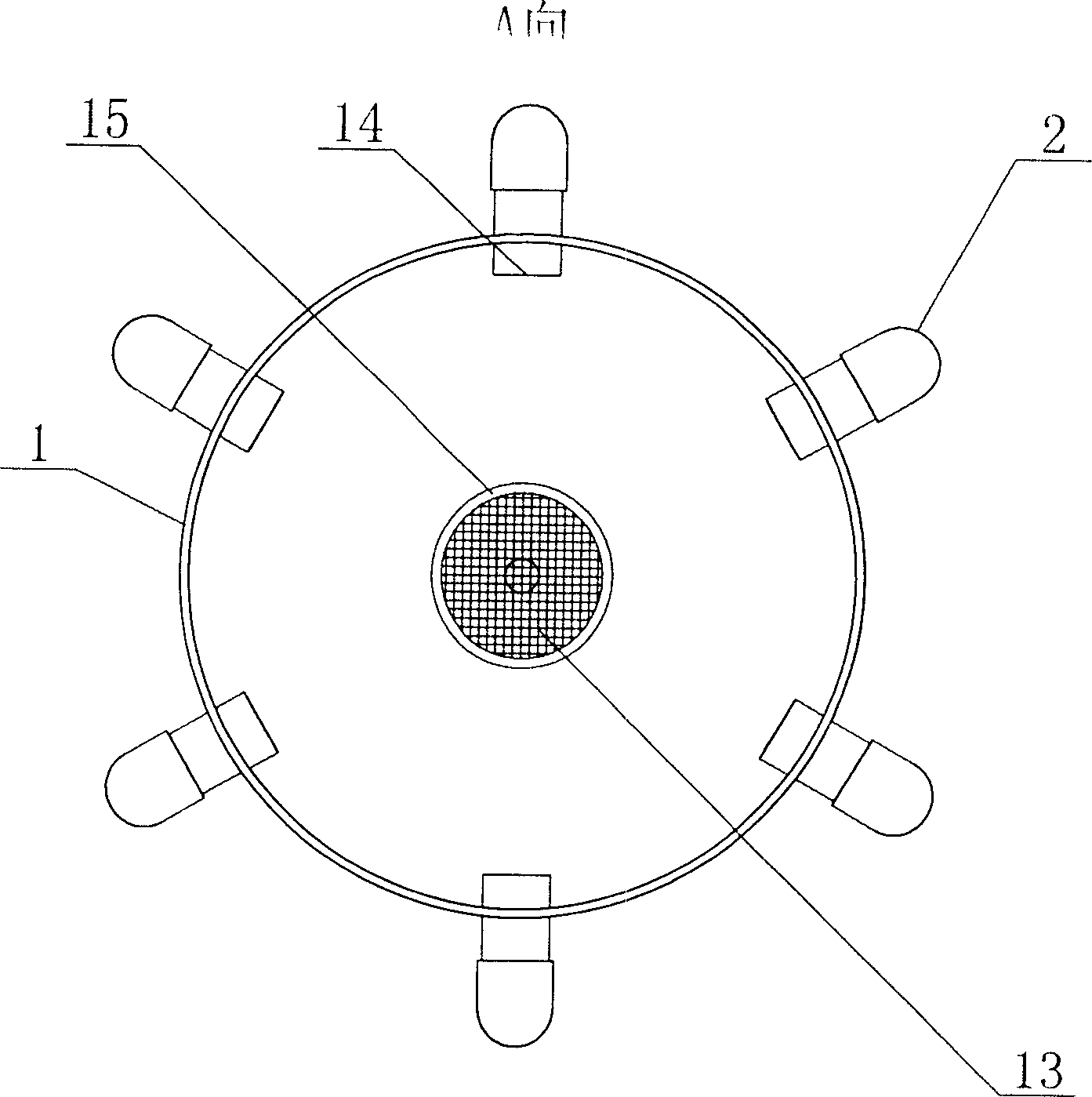
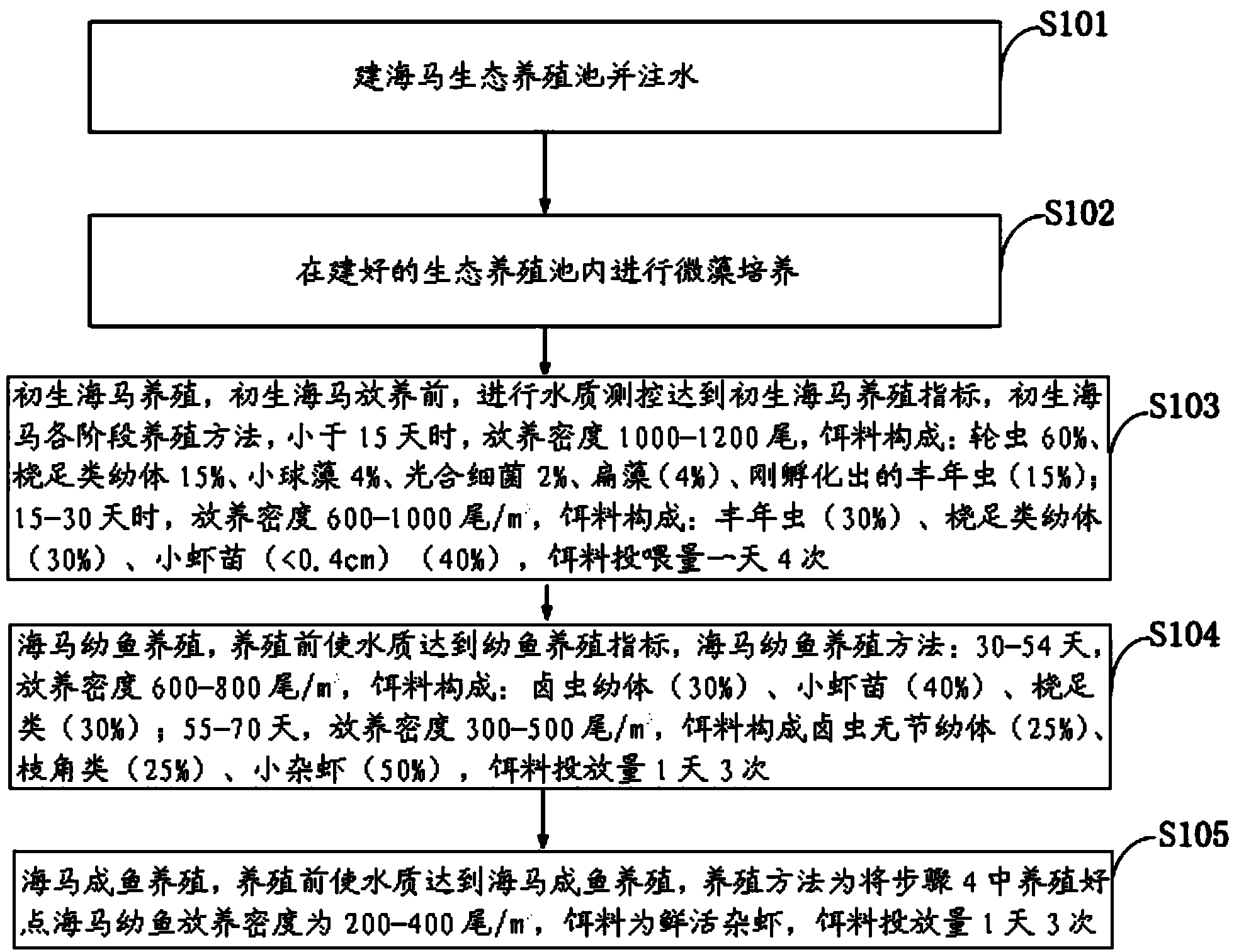
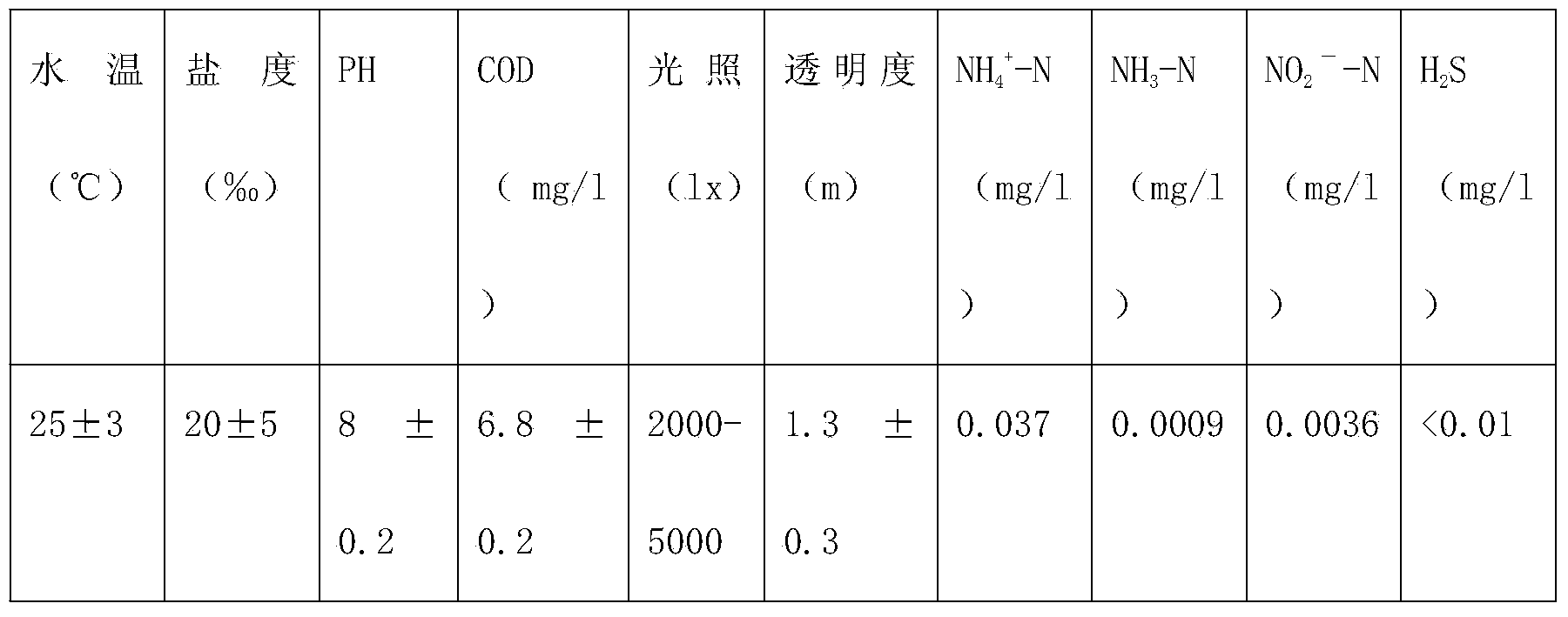
Ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method
InactiveCN103960185ASuitable for artificial breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpJuvenile fish
The invention discloses an ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method comprises the steps of building an ecological sea horse breeding pond one week before breeding, cultivating microalgae in the built ecological breeding pond, and measuring and controlling water quality to reach newborn sea horse breeding indexes before newborn sea horses are bred. When the newborn sea horses is younger than 15 days, the released density is 1000-1200 tail / m<3>, and baits are composed of rotifer, copepods larvae, chlorella, photosynthetic bacteria, tetraselmis and fairy shrimps which are just incubated. During 15-30 days, the released density is 600-1000 tail / m<3>, baits are composed of fairy shrimps, copepods larvae and shrimp seeds, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond four times per day. A sea horse juvenile fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach juvenile fish breeding indexes before breeding. During 30-40 days, the released density is 600-800 tail / m<3>, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. A sea horse adult fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach sea horse adult fish breeding indexes. The released density of sea horse adult fish is 200-400 tail / m<3>, baits are fresh and alive shrimps, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method has the advantages of reducing production cost.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Cultivation method for green crab seedlings in pond
InactiveCN103141422AThe advantages of breeding seedlings are significantObvious advantagesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a cultivation method for green crab seedlings in a pond. The cultivation method consists of seedling cultivating facilities and a seedling cultivating process and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a mud or sediment bottom seedling cultivating pond; arranging miropores for inflating and an aerator in the seedling cultivating pond; carrying out pond cleaning and sterilization on a water reservoir and the seedling cultivating pond before the seedling is cultivated; filtering inflowing water by using a bolting-cloth mesh bag with 120 meshes; directly incubating green crab larva in the seedling cultivating pond; starting all aerating facilities from the second day after the green crab larva are incubated; feeding the green crab larva with the following baits: feeding with wheel animalcule at the earlier stages of Z1 to Z3, preventing copepods from entering into a seedling cultivating water body at the stages of Z1 to Z2, feeding with the wheel animalcule and supplementing the feeding of the copepods with small specifications at the later stage of Z3, feeding with the copepods with small specifications at the stage of Z4 and feeding with the copepods at the stage of Z5; and gradually adding new water from the stage of Z3, wherein the water level at the initial stage of seedling cultivation is 70-80cm and the water quality indexes during seedling cultivation are that dissolved oxygen is not smaller than 5mg / L, the contents of ammonia and nitrogen are not greater than 0.4mg / L, the pH value is 7.8-8.5 and the salinity is 28-34.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for culturing and transplanting Scylla fries stage by stage
InactiveCN101990850ATo achieve the goal of stable and high productionReduce carnageClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLive foodOrder copepoda
The invention provides a method for culturing and transplanting Scylla fries stage by stage, which relates to a Scylla culture method. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing zoeae in a culture pond for culturing for 12 to 18 days, and transferring the zoeae into a megalop culture pond with the area of 100 to 300 square meters for further culture; culturing live foods such as algae, fairy shrimps, copepods and the like in the megalop culture pond; transferring the fries at the last day of the fifth stage of the zoeae or at the first day of megalop, wherein the culture density of the megalop is controlled to be 1,000 to 2,000 fries per cubic meter; or culturing the zoeae at the fifth stage for 4 to 8 days, wherein the culture density is 2,000 to 4,000 fries per cubic meter; the water temperature of the megalop culture pond is between 24 and 32 DEG C; and the salinity is 1.5 to 2.6 percent; and transferring the megalop into a young Scylla culture pond, wherein the area ofthe young Scylla culture pond is 0.5 to 3 mu; the water temperature is between 26 and 33 DEG C; and the salinity is 1.0 to 2.0 percent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Breeding method for amphiprion ocellarises
InactiveCN104170777AUniversalPromote spawningClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSmall animalJuvenile fish
The invention provides a breeding method for amphiprion ocellarises. The breeding method comprises the following three steps: a. breeding parent fishes; b. incubating oosperms; c. breeding young juvenile fish. Fry is bred for 60 d after being incubated, the overall length of the juvenile fish is up to 2 cm to 3 cm, and the breeding process is ended up; during the breeding process, the minced-meat-shaped fresh bait made of rotifer intensified by seawater chlorella for 24 h, artemia and copepods intensified by DHA and the chlorella for 12 h, and marine small animals of which phospholipid content is more than 25% in succession and compound feed are fed as the bait in an individual manner or a superimposed manner; furthermore, water is changed and the amphiprion ocellarises are divided and put in fish tanks in proper time. The breeding method for the amphiprion ocellaris, provided by the invention, provides a way which can be operated in an industrialized and large-scale manner; compared with the prior art, as the breeding method provided by the invention is of popularity to a higher degree, a foundation is provided for large-scale breeding of the amphiprion ocellaris.
Owner:浙江华兴水产科技有限公司 +1
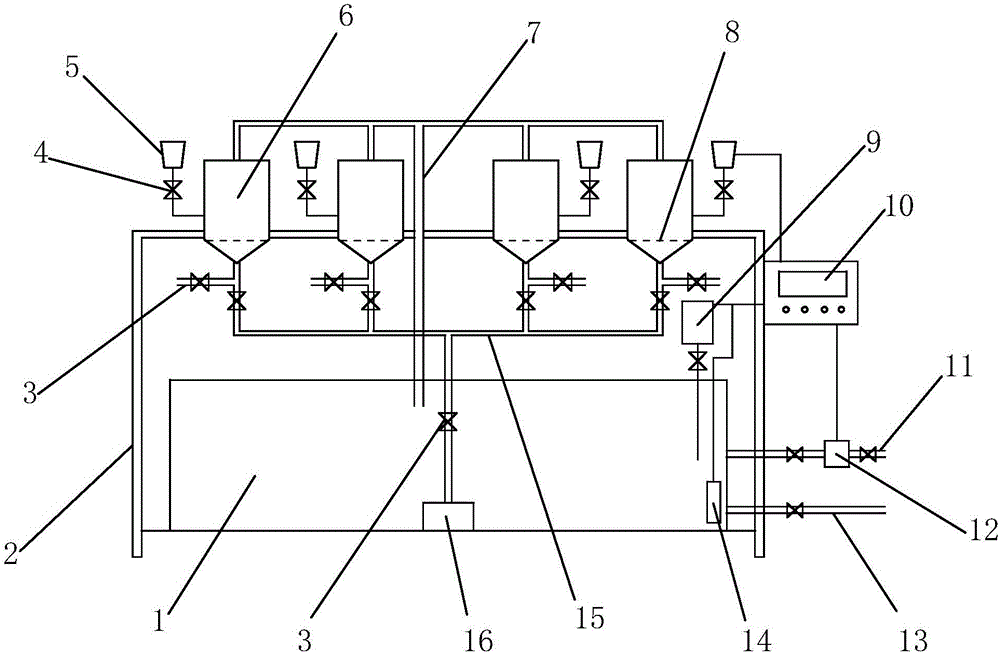
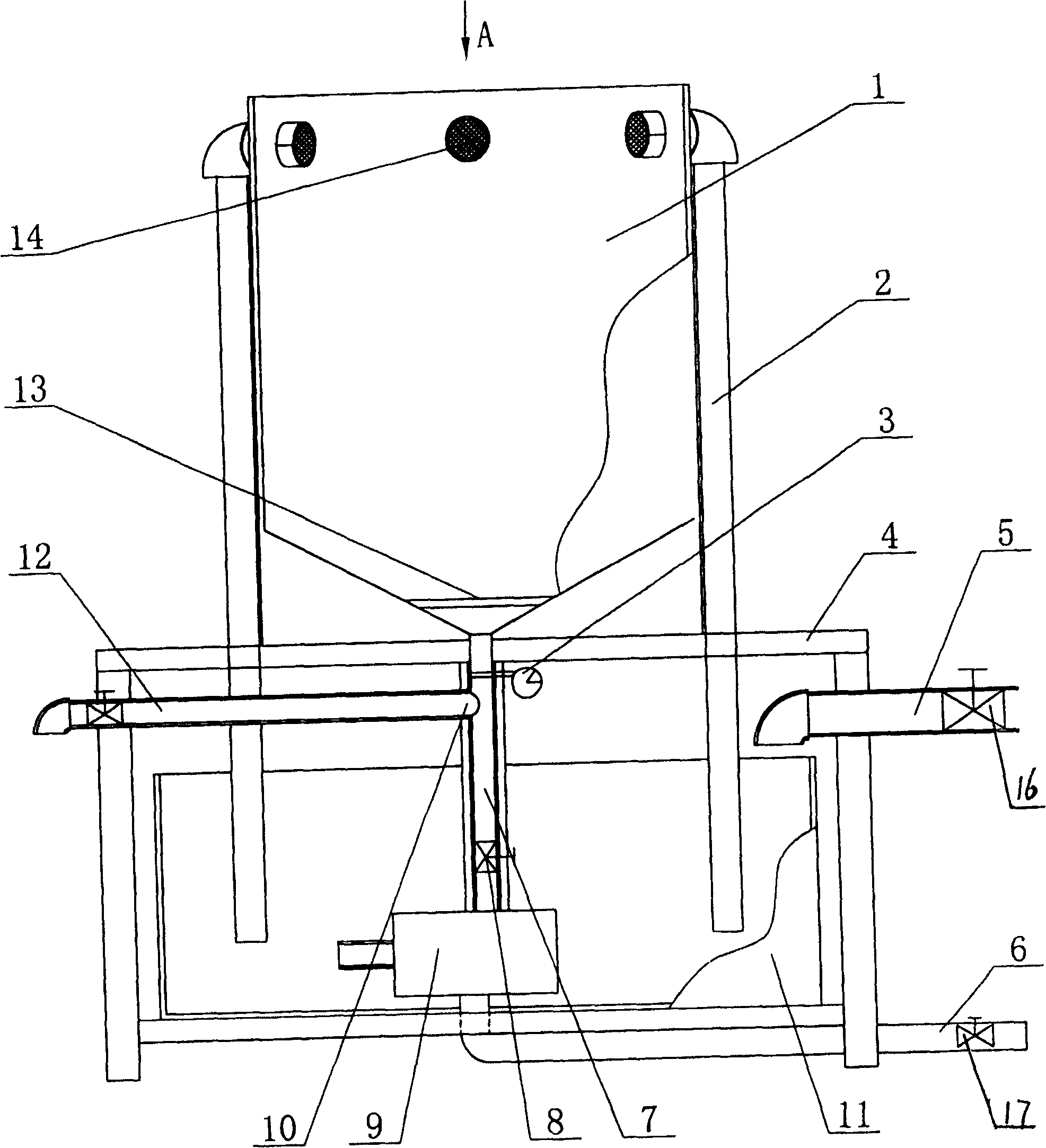
Multi-station copepod culture device and culture method thereof
ActiveCN106386637ALow costEnsure water quality consistencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater dischargeWater storage tank
The invention relates to a multi-station copepod culture device. The multi-station copepod culture device comprises a water storage tank and a water feeding pipeline connected with the water storage tank, wherein the water feeding pipeline is connected with at least one incubator; the incubator is provided with a bait box and a collection pipeline; the incubator is connected with the water storage tank through a water returning pipeline; the water storage tank is provided with a water inlet pipeline, a water discharging pipeline, an acidifying machine and a temperature sensor; each pipeline is provided with a valve; and the culture device further comprises a control box. A structural design that the same water storage tank is combined with the plurality of incubators is adopted so that an experiment method of a multi-station incubator in the same water region is realized; and a contrast experiment can be carried out on different bait feeding manners of different copepods or same copepods in the same water region, so that the consistency of water quality of the contrast experiment is guaranteed. Meanwhile, the culture efficiency is improved and the cost of culture equipment is reduced. The water storage tank realizes internal circulation and external circulation manners of a culture environment and a water body of the whole water region is updated; and the culture water quality is guaranteed, and the culture effect and survival rate of the copepods are guaranteed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in cement pond of simple plastic greenhouse
ActiveCN103026990AShorten the timeTime stretchedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in a cement pond of a simple plastic greenhouse. The cement pond is adopted, and an arch-shaped ring top is formed above the cement pond. The technology is characterized in that: a dimmable shading film covers on the arch-shaped ring top; the air density in the cement pond is 1-1.5 pieces per square meter; the stocking sizes are 10-12 millimeters in full lengths per fingerling; the stocking density is 1,000-1,500 fingerlings per square meter; the water level is 70 centimeters during stocking; 20 centimeters of fresh water is injected every day from the second day, the cement pond is full of water four days later, and 50 percent of water is changed every other day from the fifth day; after 10-15 days of cultivation, bait scraps and fish excrement are cleared; the water quality indexes are that: the salinity of sea water is 0.8-1.2 percent, the water temperature is 25-28 DEG C, the dissolved oxygen is over 5 mg / L, and the pH is 7.5-8.5; medium-sized cladocerans and copepods are fed at an earlier stage, and large frozen fairy shrimps are fed at a middle stage; and after the full lengths of fingerlings are up to 30 millimeters, a compound feed is fed instead of the frozen fairy shrimps, and an eel feed is fed completely after 3-4 days of transition.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Feeding method of controllable bait for fries of Takifugu flavidus
ActiveCN102893927ASolve the problem of difficult time matchingImprove the survival rate of breedingClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkTakifugu flavidus
The invention relates to a feeding method of controllable bait for fries of Takifugu flavidus. The feeding method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: taking egg yolk as the bait during the initial stage when the fries are aged 2-10 days, and uniformly splashing and feeding in a full pool six times per day; taking Artemia larvae which are justly hatched as the bait when the fries are aged 7-10 days, and supplementing twice per day, wherein the feeding density is 2-3 larvae / ml; taking the Artemia larvae as the bait when the fries are aged 11-19 days, and supplementing twice per day, wherein the feeding density is 3-5 larvae / ml; taking frozen copepods as the bait when the fries are aged 14-19 days, uniformly splashing and feeding in the full pool, and supplementing six times per day, wherein the feeding density is 4-6 copepods / ml; taking the frozen copepods as the bait when the fries are aged 20-25 days, uniformly splashing and feeding in the full pool, and supplementing six times per day, wherein the feeding density is 4-6 copepods / ml; taking frozen large Artemia as the bait when the fries are aged 25-35 days, melting the bait at normal temperature, feeding to a bait table, and supplementing three times per day; and feeding compound feed when the fries are aged 30-35 days, placing 4-6 blocks of the compound feed on each bait table, and feeding twice per day, wherein the compound feed is kneaded into pastes.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Method for mixed cultivation of sea horses and hemifusus ternatanus
InactiveCN105724282AAvoid wastingAvoid pollutionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseWater quality
The invention discloses a method for mixed cultivation of sea horses and hemifusus ternatanus.Hemifusus ternatanus and sea horses are cultivated inside a culture pond to construct a fish and shellfish circulation ecological cultivation system, suitable culture objects can adapt to all ecological niches and trophic levels in the culture pond, and bait waste and water pollution caused by residual bait are avoided.The sea horses and the hemifusus ternatanus occupy different ecological niches in the cultivation environment respectively, various kinds of natural bait in water and artificial feed put into the water can be sufficiently utilized, the total conversion rate of objects and energy in the culture pond is increased, the water quality is effectively stabilized, and entrance of etiology is controlled.The sea horse bait mainly includes copepods, artemia and small shrimps; the hemifusus ternatanus is demersal sarcophagy, and no additional feeding is needed in the cultivation process, so that the hemifusus ternatanus eat residual bait generated in the cultivation process of the sea horses, and the role of a scavenger is brought into play.Accordingly, the purposes that the bait utilization rate is improved, water pollution caused by residual bait is avoided, diseases are prevented and treated, and the production cost is saved are achieved.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
Method for sea anemone culture in pond
InactiveCN106386579ATake advantage ofEasy to get materialsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringOrder copepoda
A method for sea anemone culture in a pond is characterized in that a net cage suspended under the water surface of the pond is used for artificial culture. The net cage is shaped like a cuboid with dimensions of 2*1*1m, the upper face of the net cage is opened, the bottom face of the net cage and the surrounding side faces are fenced by net plates, and the net size is eight meshes; the multiple net cages are disposed and arranged in a line along the length direction of the net cages, the upper edge of each net cage is connected by two parallel main ropes, multiple supporting rods are fixed at an interval between the two main ropes, and a floating ball is connected at the joint between each supporting rod and the main rope; auxiliary ropes are connected to two end heads of the main rope, and the end head of each auxiliary rope is connected to a rope anchor located at the bottom of the pond; and an attaching baseplate is disposed in the net cage, the attaching baseplate comprises a bottom plate, a corrugated plate is fixed on the bottom plate, and through holes are arranged in the corrugated plate. Materials could be obtained easily; the method is simple; operations are easy; management is easy; sea anemones could be bred separately or bred together with trepang to eat trepang enemies such as copepod and gammarid; space in a pond water area is fully used; the survival rate is high; and the growth speed is high.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENTAL OCEAN SCI TECH
Chinese herbal medicine essence for culturing algae
InactiveCN101423439APromote growthImprove water qualityClimate change adaptationAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserDiseaseWater quality
The invention relates to a Chinese herbal medicine alga culturing essence which consists of the following raw material in weight percentage: 65 to 85 percent of poultry fermenting material, 3 to 10 percent of zeolite powder, 5 to 10 percent of diammonium phosphate, 1 to 3 percent of potassium sulfate, 0.05 to 0.08 percent of magnesium sulfate, 1 to 4 percent of gypsum and 2 to 9 percent of mung bean. The Chinese herbal medicine alga culturing essence can culture phytoplanktons and zooplanktons in a water body, wherein the phytoplanktons comprise unicellular alga such as diatom, cryptozoon and xanthophyta while the zooplanktons comprise zooplanktons such as rotifer, cladocera and copepods, and provides sufficient natural bait for fishes; simultaneously, the Chinese herbal medicine alga culturing essence remarkably promotes the growth of fishes, comprehensively improves water quality and compositions of Chinese herbal medicine and greatly improves the capability for resisting disease of the fishes; and the product has the characteristics of rapid effect, lasting fertilizer effect, high utilization rate, no pollution, low cost and the like.
Owner:绵阳掌元生物科技有限公司
Method for preventing and controlling copepods in stichopus japonicus seedling culture
InactiveCN102232368AQuality improvementReduce usageAnimal huntingClimate change adaptationStichopusFishery
The invention discloses a method for preventing and controlling copepods in stichopus japonicus seedling culture. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: selecting jelly fish seedlings with the umbrella diameter of 3-4 cm; putting 4-5 jelly fish seedlings into each cubic meter of water in a pond with copepods in a stichopus japonicus seedling culture workshop; determining the total number of jelly fish seedlings put into each pond, wherein the jelly fish seedlings eat the copepods in the stichopus japonicus seedling culture pond, and can eat over 95% of the copepods in the stichopus japonicus seedling culture pond after 1-2 days without hurting the young stichopus japonicus; and finally fishing out the jelly fishes in the stichopus japonicus seedling culture pond and putting into other ponds with copepods to eat the copepods continuously, wherein feeding and water exchange management during the stichopus japonicus seedling culture are the same as normal management. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the jelly fish seedlings can be uniformly distributed in water to continuously eat copepods in water so that the copepods in the stichopus japonicus seedling culture pond are eaten without using medicine; and moreover, the method prevents the death of stichopus japonicus seedlings caused by the copepods in the stichopus japonicus production, improves the survival rate of stichopus japonicus and provides guarantee to the stable high yield of stichopus japonicus seedlings on one hand, and on the other hand, reduces the application of trichlorfon and miezaoling, improves the quality of stichopus japonicus seedlings and is environment-friendly while culturing the jelly fishes and reducing the production cost.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for extracting DNA from single eggs of copepods
InactiveCN101696408AIncrease concentrationReduce lossesSugar derivativesDNA preparationTE bufferA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for extracting DNA from single eggs of copepods, relating to a DNA extraction technology. The single eggs have different egg diameters and are generated by different egg producing ways. The method can ensure the extraction efficiency of DNA, and the extracted DNA can be directly applied to downstream PCR experiments. The method comprises the following steps of placing the single eggs of copepods in a 1*TE buffer solution, adding protease K until the final concentration of the protease K reaches 2.5-5.5mg / mLto obtain a mixed extraction solution; carrying out a thermal incubation program on the mixed extraction solution obtained to obtain a crude extract of DNA of the single eggs; and depositing the crude extract of DNA of the single eggs with a nucleic acid coprecipitator to obtain DNA precipitate. The precipitate can be dissolved in sterilized water and stored in a refrigerator for later use.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Indoor culture device of copepoda population
InactiveCN100446665CHigh reproductive survival rateAchieve separationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRefluxWater quality
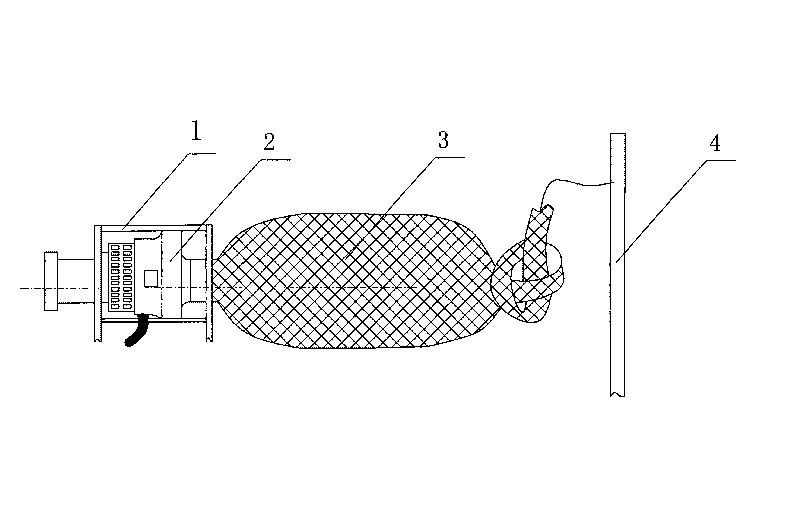
The invention discloses an apparatus for trainring copepods species in-doors, including a incubator, the lower part of which connects to a water quality regulating tank, a reflux pipe arranged on the outer wall of the incubator, and the upper part of which communicates with the upper part of the incubator, while the lower part is positioned inside the water quality regulating tank, whereof a pump is fixed inside; the pump connected to the incubator by a water pump, which linked to an end of a taking-off ovum tube, while the other end of the taking-off ovum tube arranged outside of the water quality regulating tank,; the top of the incubator as open type; the bottom of the water quality regulating tank lied an fall tube. The apparatus applied to mass propagate copepods species in-doors, so as to simplify the training method, decrease the cost, and improve the efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preventing and controlling copepods in young sea cucumber breeding pond of tropical sea cucumbers
ActiveCN103907552AImprove survival rateImprove qualityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTropicsOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a method for preventing and controlling copepods in a young sea cucumber breeding pond of tropical sea cucumbers. The method comprises the steps of after the young sea cucumbers are subjected to metamorphosis and attachment for two weeks and the length of the young sea cucumber is 0.5cm the young sea cucumber is 0.5cm long, putting amphiprioninae or chrysiptera cyaned or both into the breeding pond when copepods appear in the breeding pond, and culturing and managing the young sea cucumbers according to a conventional method. A large number of experiments show that the amphiprioninae and chrysiptera cyaned can coexist with the young tropical sea cucumbers without damaging the same and can control the copepods, so that the survival rate of the young sea cucumbers is high. Compared with the prior art, the method can reduce the use of medicines, is beneficial to protecting environments and improving the quality of sea cucumbers, and meanwhile, reduces workload in a young sea cucumber culturing period, and avoids mechanical losses of the young sea cucumbers in an operating process, thus being beneficial to the rapid and healthy growth of the young sea cucumbers.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for artificial culture of food for kanglang whitefish
InactiveCN1435089ASolve the sourceLow costClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAnabarilius grahamiCarp
A artificial culture method for the food of Anabarilius grahami includes immersing the wormwood in the water at 20-24 deg.C in food pool for 5 days in order to reproduce algae, taking up the bottom mud from the carp pond, mixing with calcium lime, putting in said food pool, inoculating rotifer, adding soybean milk and thallus for promoting reproduction of rotifer, reproducing rotifer at 20-24 deg.C for 6 day, and reproducing cladocera and copepod food at 20-24 deg.C for 7 days. Its advantages are low cost and high feasibility.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ecological cultivating method for initial feed of sebastiscus marmoratus larva
ActiveCN106259220ASolve the problem that the low temperature season cannot be obtainedSolve the problem of not being able to getClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPenaeus marginatusPrawn
The invention relates to an ecological cultivating method for initial feed of sebastiscus marmoratus larva. The method is characterized in that a cement or film side slope is arranged in a feed cultivating pool; the non-leaking muddy or sandy sediment is arranged as the bottom sediment; the water depth is 1-2m; independent water feeding / draining facility and aerator are arranged. The method comprises the following steps: sterilizing the feed cultivating pool with water containing 20ppm bleaching powder in the period from each December to the January in next year; after 2 days, dryly disinfecting the pool with 150kg / mu quick lime; exposing for one week and then feeding water; covering a 60-mesh silk gauze at a water inlet, wherein the water resource is natural river water and the salinity is 1.2-2.0; collecting copepods from the other pond and inoculating into the feed cultivating pool, after water is fed into the feed cultivating pool for one week and water in the pool becomes yellow green; after inoculating the copepods, stocking palaemon carinicauda and 2-year old coilia ectenes and feeding prawn mixed feed for one time per day; collecting the small zooplankters including copepods nauplius, small anhistozoa, rotifer, and the like, as the initial feed of sebastiscus marmoratus larva, when the water temperature is 15 DEG C or above.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST
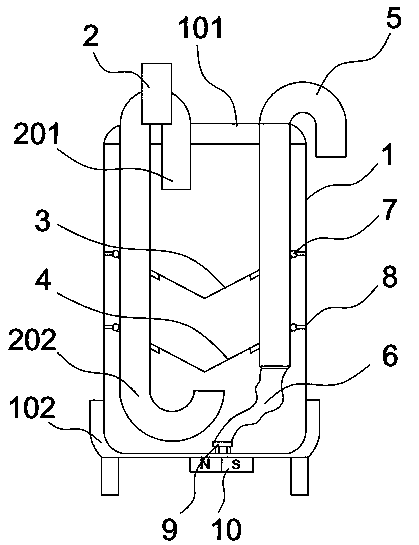
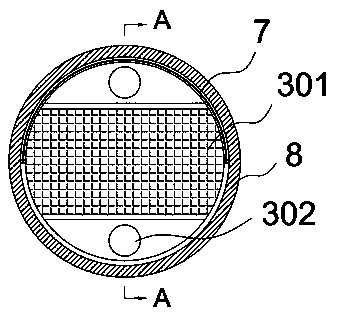
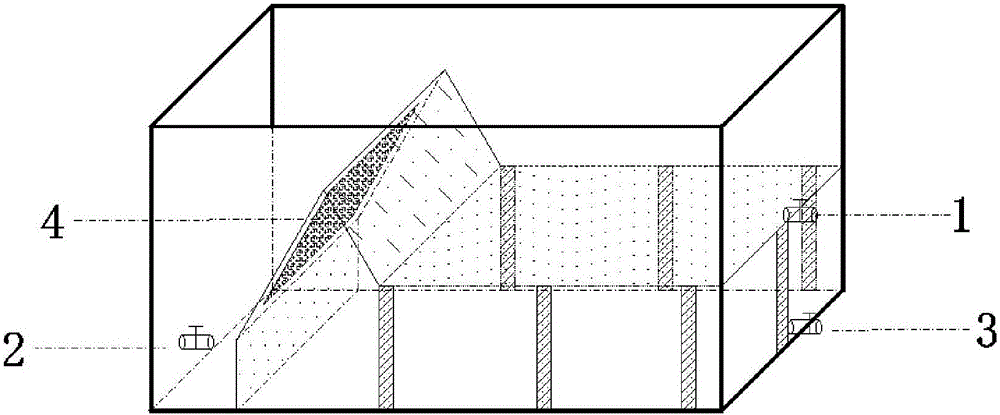
Multifunctional integrated farming system for separate-egg copepods
ActiveCN109089980AAvoid gatheringQuick collectionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringWater circulation
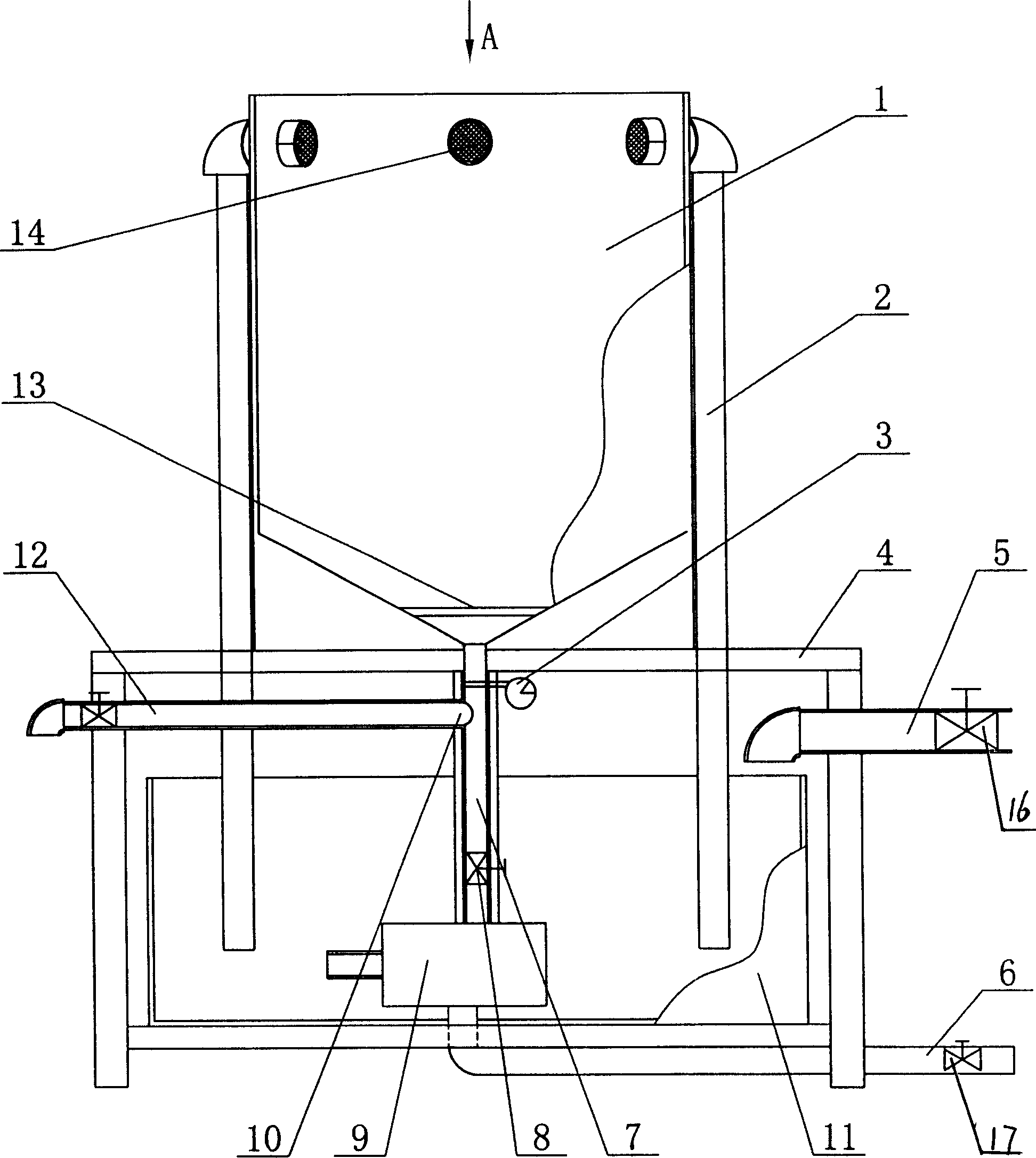
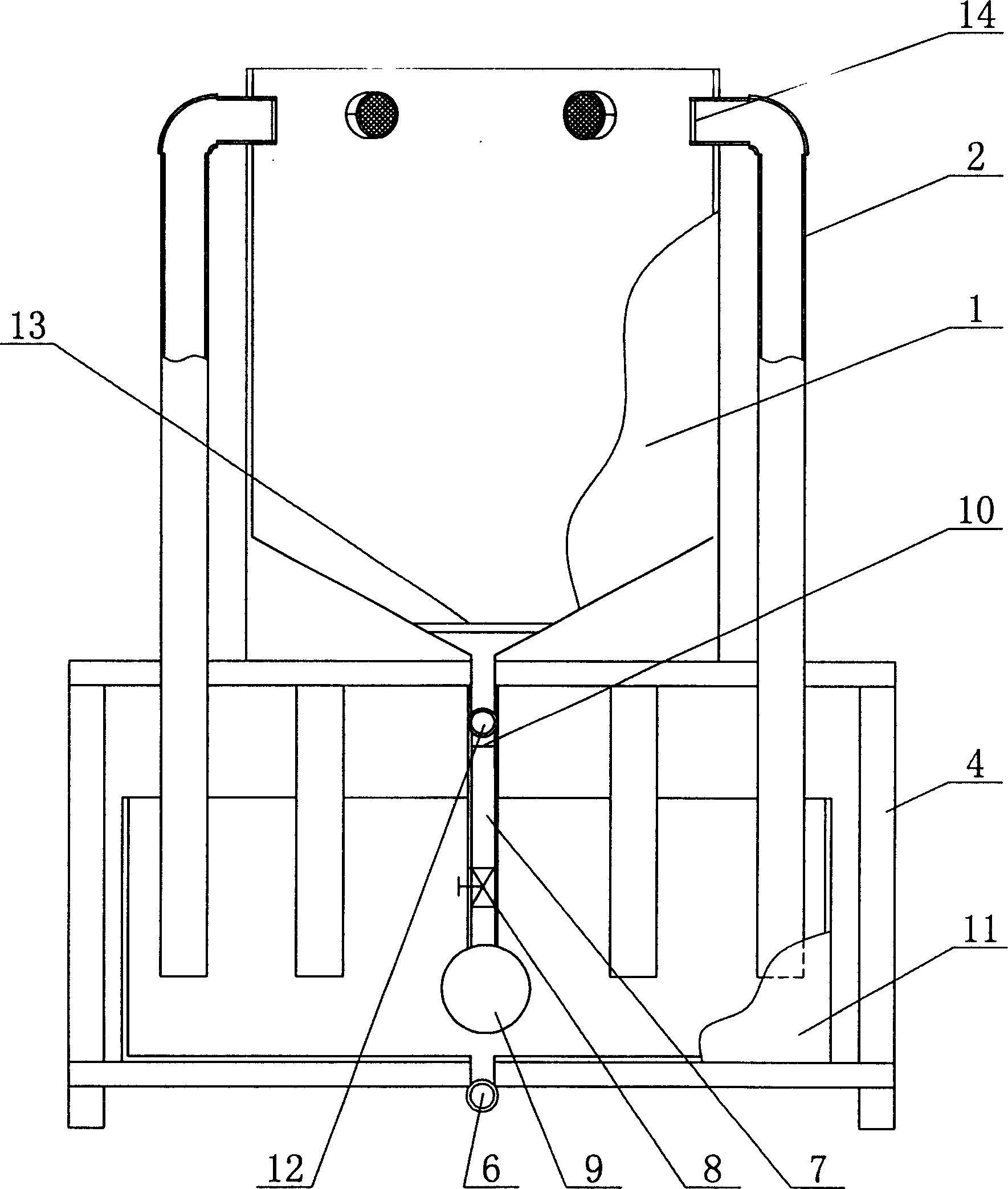
The invention provides a multifunctional integrated farming system for separate-egg copepods, comprising a farming container body; a vertical water circulation module and a cleaning and / or water changing module are arranged in the farming container body; a parent separation screen layer and an egg separation screen layer are arranged between the vertical water circulation module and the cleaning and / or water changing module from top to bottom; the parent separation screen layer has larger mesh than the egg separation screen layer. The system herein has the integrated functions of copepod farming water cleaning and changing, egg collecting and the like, provides effectively increased growth speed for copepods at the premise of reduced physical damage to parents and eggs, and has stable quality and yield of copepods.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Automatic cleaning device for copepod biological bait
InactiveCN108580377AReasonable distribution spaceEfficient removalCleaning using toolsCleaning using liquidsBiological integrityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses an automatic cleaning device for copepod biological bait and belongs to the technical field of bait cleaning devices. The automatic cleaning device comprises a bolting silk baghanging inside a box body; a jolting board is arranged under the bolting silk bag; a flipper is connected to the lower part of the jolting board through a spring; the flipper is connected to the boxbody through a support; a motor is installed at a lower side of one end of the flipper; a flushing plate is installed over the bolting silk bag. The cleaning device of the invention can automaticallyand efficiently clean the copepods, and the biological integrity after cleaning is high, saving manpower and material resources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for measuring activity of maltase in copepods
InactiveCN102634567ASimple and fast operationShort sample sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsHexokinase
The invention discloses a method for measuring activity of maltase in copepods. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding and centrifuging 5 to 15 copepods in a buffer solution, reacting with a maltose substrate in a water bath to obtain a water bath product, mixing the water bath product, Tris-HCl, MgCl2, dithiothreitol, hexokinase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP)<+>, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, performing enzymatic reaction, and calculating the activity of the maltase in each copepod according to a formula by using absorbance of reductive coenzyme II in the enzymatic reaction product and the number of the copepods as parameters. According to the method, the activity of digestive enzyme can be measured only by a few to more than ten copepods, and the absorbance of the reductive coenzyme II can be obtained by the water bath reaction and the enzymatic reaction of the maltase in the copepods; and the method is easy and convenient to operate, short in reaction time and less in errors, so the method has the advantages of easiness and convenience in operation, low sample consumption, short test time and high test efficiency.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for manually breeding Charybdis feriatus seedlings in earth pond
ActiveCN104663543ALarge body of waterPromote growth and reproductionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityAquatic product
The invention relates to a method for manually breeding Charybdis feriatus seedlings in an earth pond and belongs to the technical field of seedling culture for aquaculture. The method comprises the following steps that incubated parent crabs subjected to intensive culture in a concrete pond are placed in an incubation basket which is prepared in the earth pond in advance, rotifers are fed at the same day of incubation, the water color of the earth pond is observed every day and the transparency of the earth pond is kept about 35 cm; after being developed to the third stage of zoea, copepods are fed to the earth pond, and the density of the copepods is kept at 5 per milliliter; during megalops period, fish and meat are fed to the earth pond according to 200% of the estimated larva weight until the larvae are developed to young cabs. During the seedling breeding period, the requirements on the water quality are that the salinity is reliably stable and is kept at 2-3%, the temperature is 26-29 DEG C, the pH is 7.8-8.6, the dissolved oxygen is more than 4 mg / L and the transparency is kept at 30-50 cm. According to the method, a technology for manually breeding the Charybdis feriatus seedlings in the earth pond is implemented, and the method is simple, quick and low in production cost, and provides a feasible way for scale production of the Charybdis feriatus.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
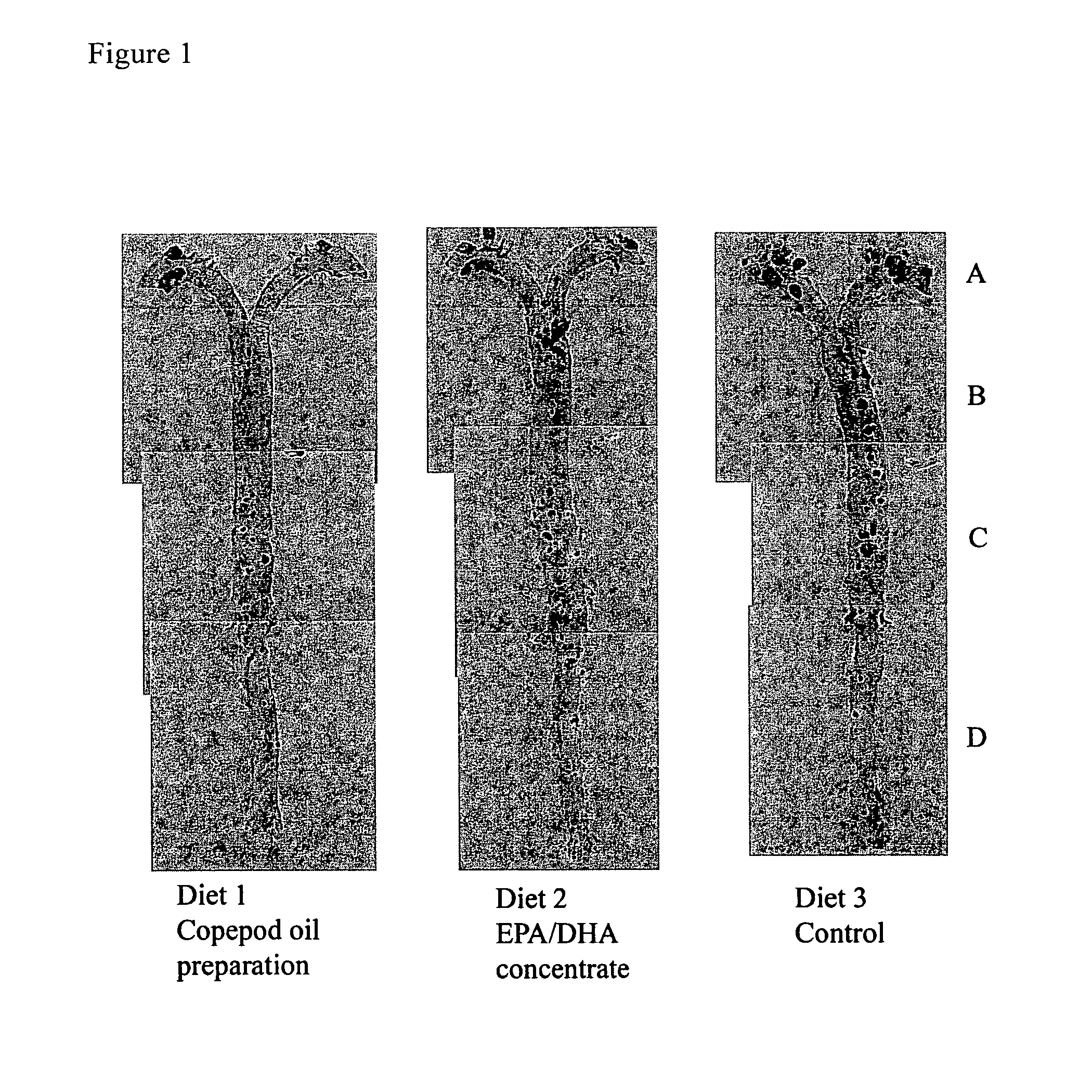
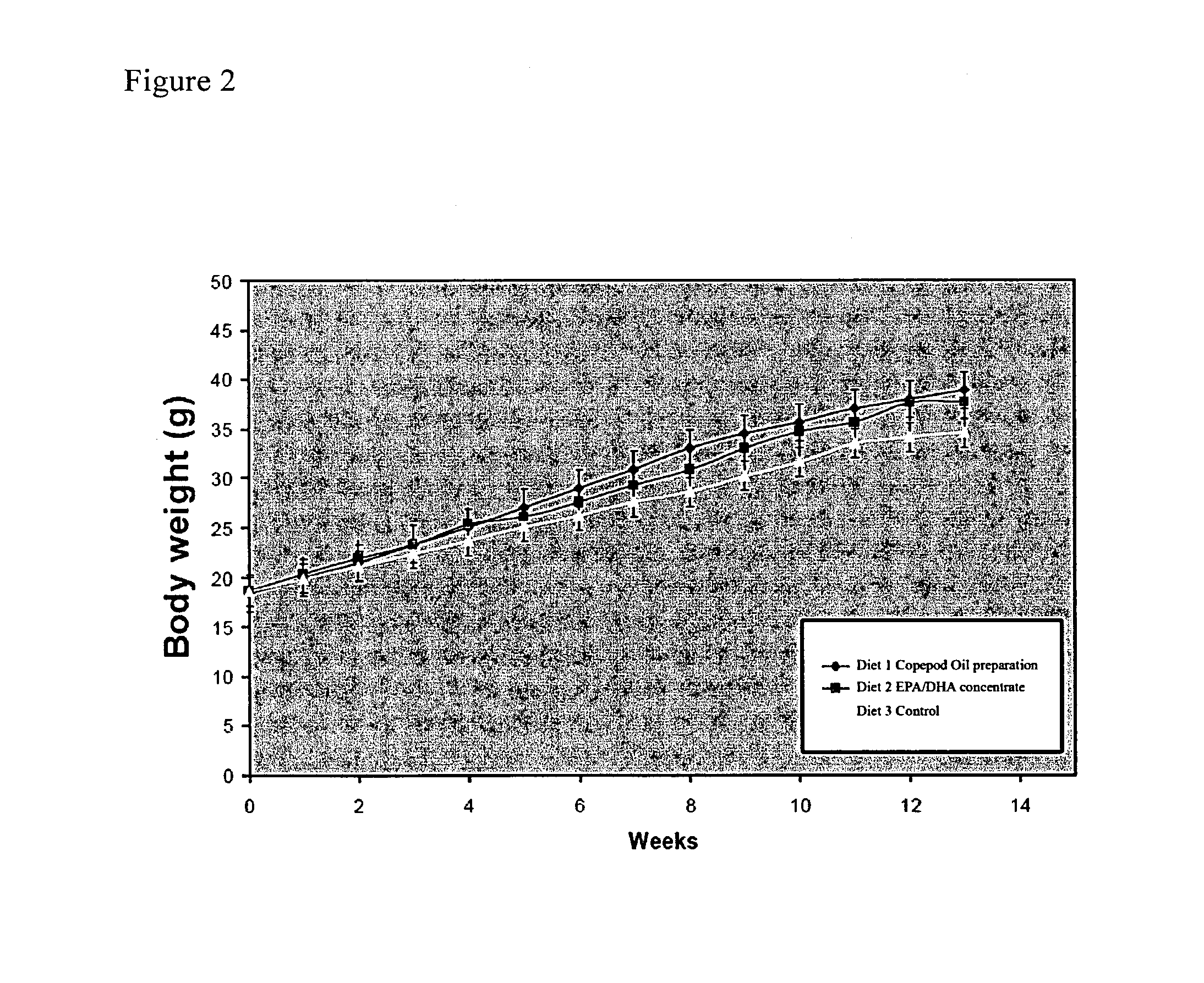
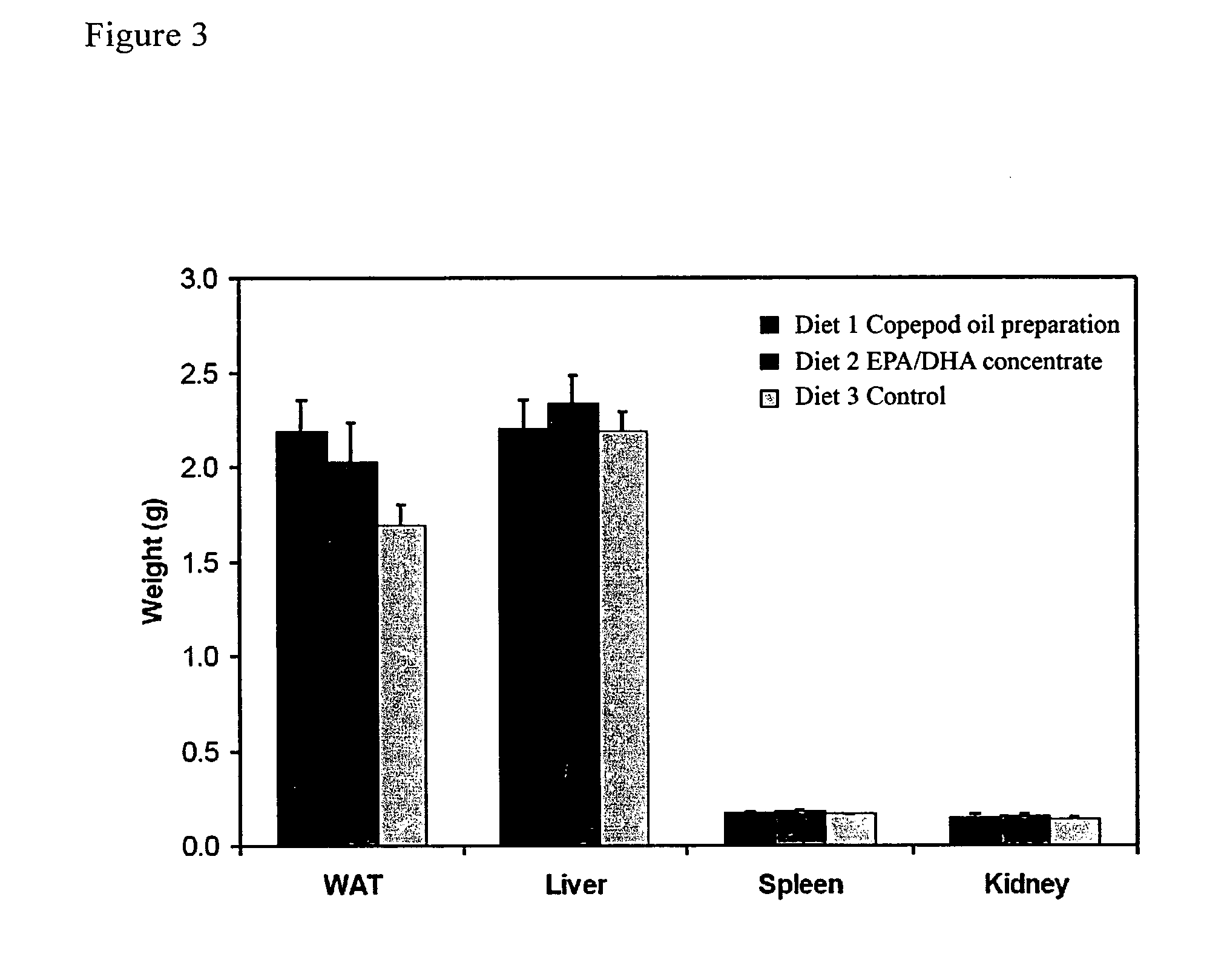
Biological oil composition, formulations comprising the oil composition, and use thereof to prevent or treat cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS20110251276A1BiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDocosahexaenoic acidCoronary heart disease
This invention relates to a biological oil composition, preferably obtained from a copepod, most preferably the copepod Calanus finmarchicus and the use thereof to prevent or treat formation of atherosclerotic plaques and hence development of coronary heart disease. The composition comprises the same marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) generally regarded as being responsible for the anti-atherosclerotic effect of marine oils, namely EPA (C20:5n-3 eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (C22:6n-3 docosahexaenoic acid). However, quite unexpectedly, it has been found that the oil composition of the present invention has a remarkably higher ability to prevent formation of atherosclerotic plaques than what can be attributed to EPA and DHA alone, and moreover, unlike EPA and DHA alone it has a notable blood cholesterol lowering effect.
Owner:CALANUS
Method for ecologically breeding coilia nasus schlegel fries in takifugu obscures culture pond
ActiveCN110074018AImprove water utilizationReduce outputClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh water organismWater quality
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, in particular to a method for ecologically breeding coilia nasus schlegel fries in a takifugu obscures culture pond, which comprises eightsteps of pond preparation, stocking of coilia nasus schlegel parents, inoculation of cladocerans and copepods, stocking of takifugu obscures, bait feeding, stocking of brooding freshwater shrimps, daily management, and net pulling for catching. The invention fully utilizes the water space of a takifugu obscurus parent culture pond, increases yield of the adult coilia nasus schlegel and large-sizedfries under the conditions of not increasing the input and not reducing the takifugu obscures parent culture density, improves the water utilization rate of the pond, improves the economic benefit, makes the water quality of the pond more stable, improves the feed utilization rate, and reduces the takifugu obscures culture cost; the method of the invention is easy to operate and can be easily accepted and promoted.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Method for automatically collecting and culturing zooplankton
The invention relates to a method for automatically collecting and culturing zooplankton, i.e., the zooplankton in a culture pool continuously enters an upper layer box body of a zooplankton automatic collecting device through a syphon pipe; under the overflow effect, the zooplankton is intercepted by a stainless steel sieve screen arranged on an overflow inclined surface under the overflow effect and is enriched in a zooplankton temporarily storage box arranged at one side of the stainless steel sieve screen of the automatic collecting device; a water body enters a lower layer water return box arranged at the other side of the stainless steel sieve screen of the automatic collecting device through meshes of the stainless steel sieve screen arranged on the overflow inclined surface, and is then pumped back into the zooplankton culture pool through a water return water outlet of the lower layer box body or is discharged. The method for automatically collecting and culturing zooplankton provided by the invention can be applicable to the zooplankton such as rotifers, cladoceran, copepods and artemia, and has the advantages that the automatic and continuous collection is realized; the labor is saved; the energy is saved; convenience is realized; the injury to the zooplankton is small.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com