Method of utilizing filter-feeding organisms to remove algae
A biological and filter-feeding technology, applied in the field of environmental ecology, can solve problems such as reducing nutrient levels, increasing light, and reducing water turbidity, so as to improve the ability to digest algae, promote growth, and eliminate algae.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
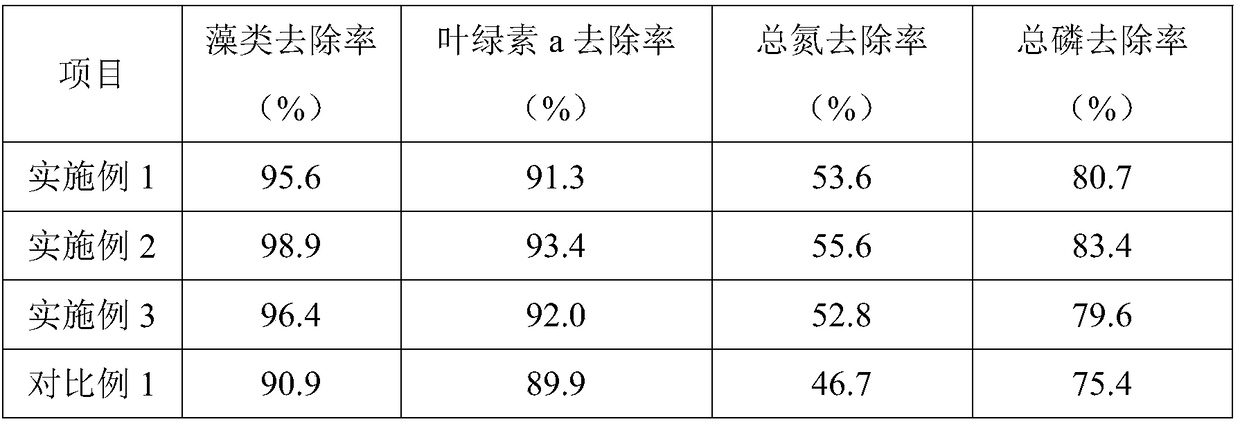
[0020] A method for algae removal using filter-feeding organisms, in which algae-containing water flows through series-connected water storage facilities in sequence, and the water storage facilities are sequentially released into copepods, filter-feeding shellfish-filter-feeding fish, copepods, filter-feeding Shellfish - filter-feeding fish. The algae removal method of the present invention alternately breeds copepods or filter-feeding shellfish-filter-feeding fish in two adjacent water storage facilities, and integrates the mechanism that different aquatic organisms have control and removal effects on planktonic algae, and utilizes copepods The connection of filter-feeding shellfish and filter-feeding fish and the difference in feeding habits achieve the purpose of algae removal, thereby overcoming the singleness of biological methods, and can remove algae in eutrophic water as a whole; in addition, the filter used in the algae removal method Food-eating organisms can filter...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method of algae removal using filter-feeding organisms. Four water storage facilities are connected in series. The four water storage facilities are successively put in the spindle water that feeds on small algae, blue mussels-sardines, and spindle water that feeds on small algae. Fleas, blue mussels-sardines, the stocking ratio of blue mussels-sardines is 1:0.65, and the stocking density is 300g / m 3 , and then the algae-containing water flows through each water storage facility in turn, stays in the copepod water storage facilities for 2 days, and stays in the blue mussel-sardine water storage facilities for 7 days.
[0031] The above-mentioned nets for the water storage facilities of the spindle daphnia that feed on small algae are titanium alloys, the nets are coated with anti-corrosion coatings, and the meshes are 1.2mm. 40mm; D-rhamnose, rhamnolipid and Tween 80 were also added to the above-mentioned copepod water storage facilities, and the amount of input was 0...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A method of algae removal using filter-feeding organisms. Four water storage facilities are connected in series. The four water storage facilities are successively put in the spindle water that feeds on small algae, the river clam-silver, and the spindle water that feeds on small algae. Fleas, river clams - silver carp, the stocking ratio of river clams - silver carp is 1:0.8, and the stocking density is 400g / m 3 , and then the algae-containing water flows through each water storage facility in turn, stays in the copepod water storage facilities for 2.5 days, and stays in the river clam-silver carp water storage facilities for 10 days.
[0035] The above-mentioned nets for the water storage facilities of the spindle water fleas that feed on small algae are made of titanium alloy, the nets are coated with anti-corrosion coating, and the mesh size is 2mm, and the mesh size of the nets for the water storage facilities for putting blue mussels and sardines is 60mm. D-rhamno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com