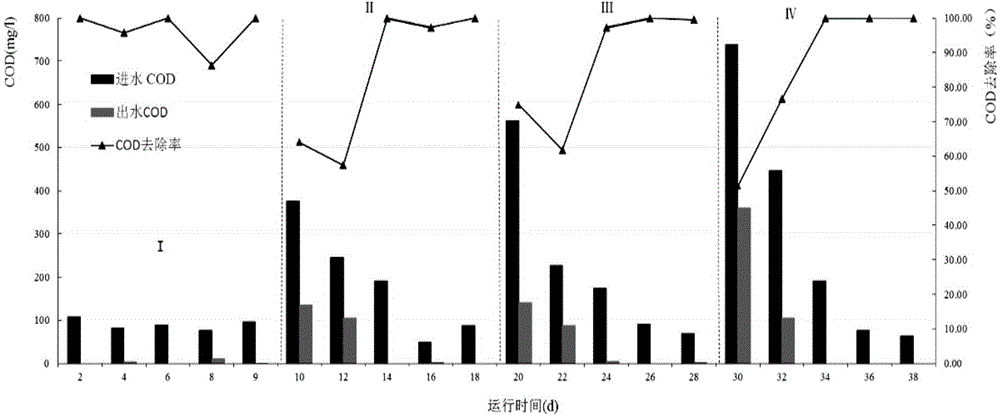
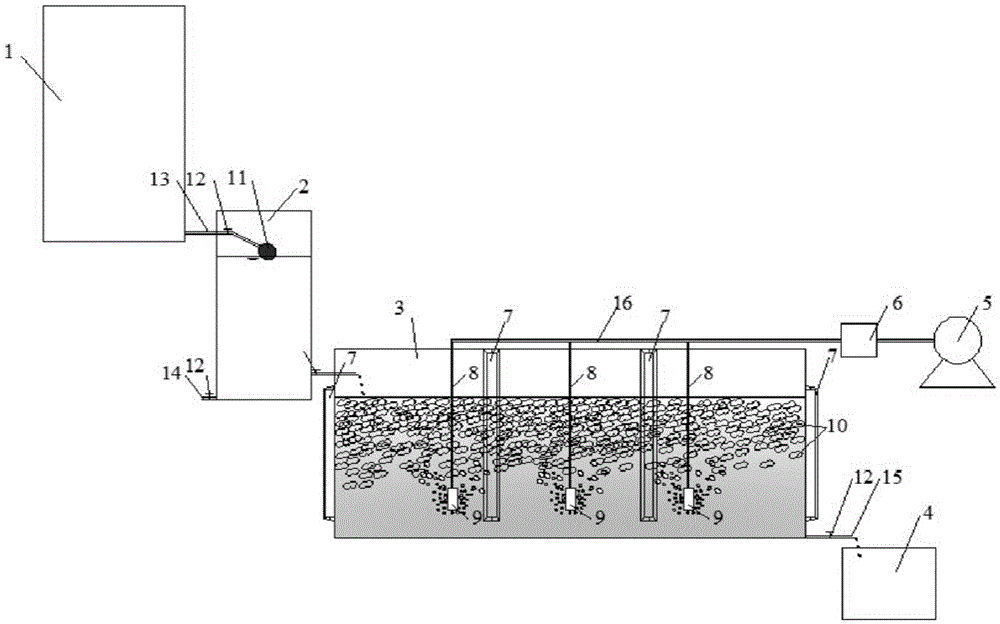
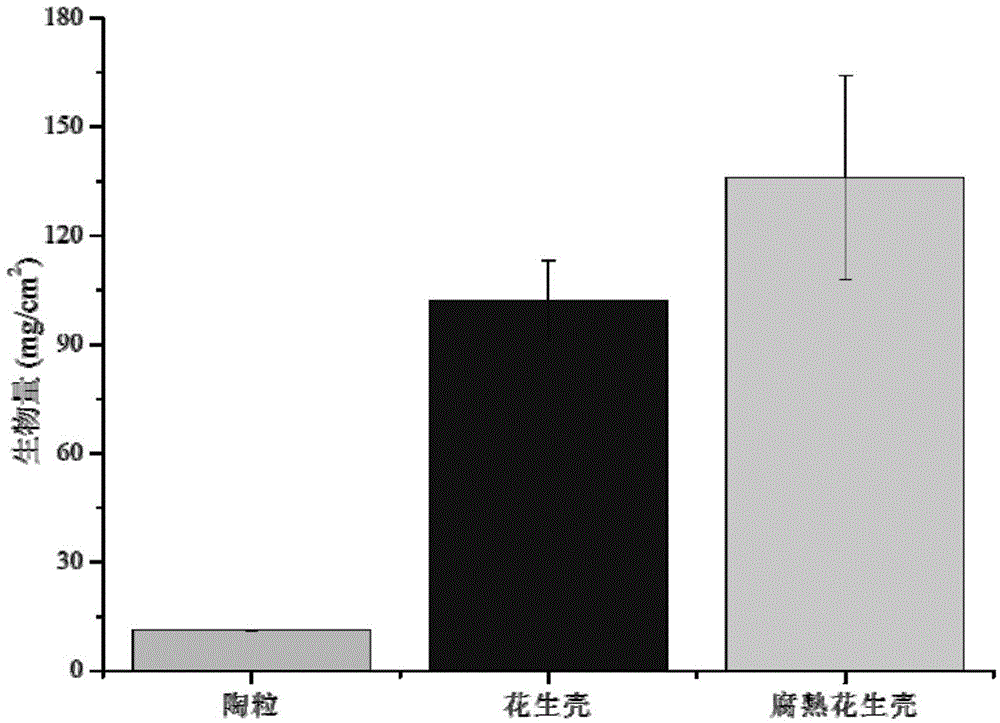
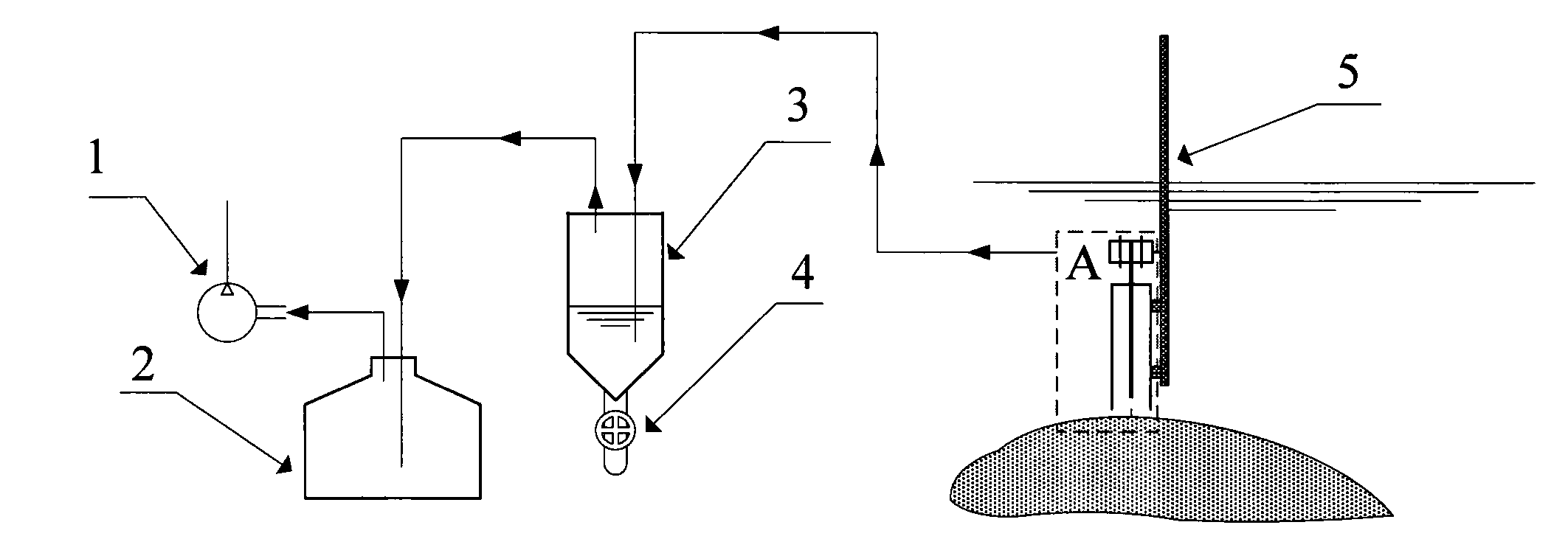
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Periphyton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Periphyton is a complex mixture of algae, cyanobacteria, heterotrophic microbes, and detritus that is attached to submerged surfaces in most aquatic ecosystems. The related term Aufwuchs (German "surface growth" or "overgrowth") refers to the collection of small animals and plants that adhere to open surfaces in aquatic environments, such as parts of rooted plants. Periphyton serves as an important food source for invertebrates, tadpoles, and some fish. It can also absorb contaminants, removing them from the water column and limiting their movement through the environment. The periphyton is also an important indicator of water quality; responses of this community to pollutants can be measured at a variety of scales representing physiological to community-level changes. Periphyton has often been used as an experimental system in, e.g., pollution-induced community tolerance studies.
Antimicrobial composition and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20100086576A1Improve efficacyLow toxicityBiocideDead animal preservationBacteroidesBiofilm
An aqueous composition adapted to kill bacteria in both planktonic and biofilm states is lethal toward a wide spectrum of gram positive and gram negative bacteria as well as other microbes. The composition, which is slightly to moderately acidic, includes a significant amount of one or more surfactants and large amounts of osmotically active solutes. The composition can be applied directly to a site of bacterial growth. Even when the bacteria is in biofilm form, the surfactant component(s) begin to kill the bacteria before the macro-molecular matrix is removed or dislodged from the site.
Owner:NEXT SCI IP HLDG PTY LTD
Method of ecological restoration of water bodies containing excess nutrient
A method of ecological restoration of water bodies containing excess nutrient includes steps of: (a) taming Daphnia magna to be able to eat blue-green algae as an algae eating plankton with a taming composition fermented from spirulina powder, active yeast, and saccharide, so as to digest blue-green algae in the water bodies, and (b) putting the algae eating plankton in the water body polluted by the blue-green algae, wherein the algae eating plankton eats the blue-green algae, so that an eco-system of the water body containing excess nutrient can be restored. The method according to a preferred embodiment further includes a step of: (c) planting submerged plant in the water, wherein the submerged plant includes submerged forest and submerged turf.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAIHE WATER TECH DEV CO LTD
Microbial fuel cell with improved anode
ActiveUS7695834B1Lower resistanceIncrease productionCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsMicrobial fuel cellMicrobial inoculation
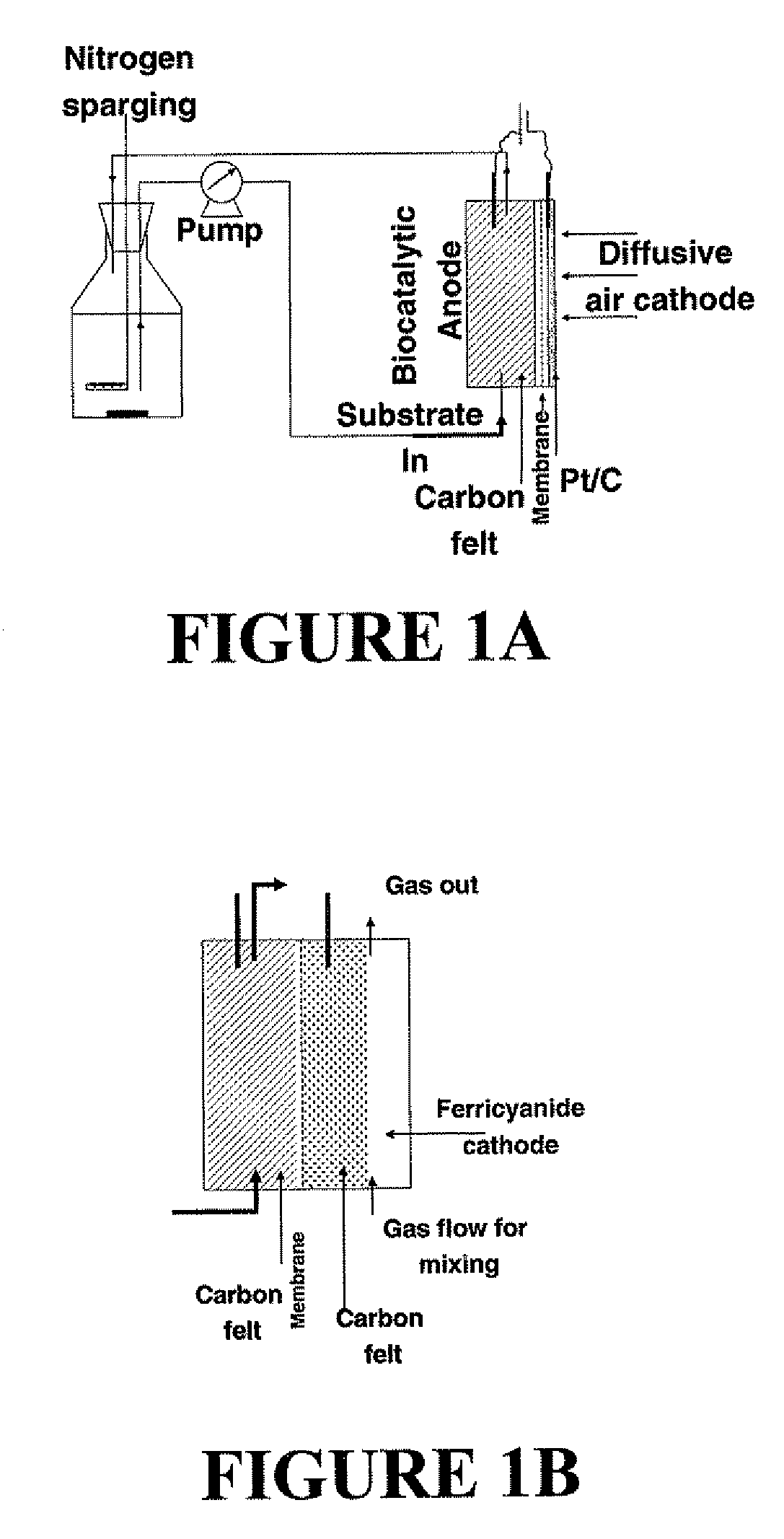
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a microbial fuel cell, wherein the method includes: (i) inoculating an anodic liquid medium in contact with an anode of the microbial fuel cell with one or more types of microorganisms capable of functioning by an exoelectrogenic mechanism; (ii) establishing a biofilm of the microorganisms on and / or within the anode along with a substantial absence of planktonic forms of the microorganisms by substantial removal of the planktonic microorganisms during forced flow and recirculation conditions of the anodic liquid medium; and (iii) subjecting the microorganisms of the biofilm to a growth stage by incorporating one or more carbon-containing nutritive compounds in the anodic liquid medium during biofilm formation or after biofilm formation on the anode has been established.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
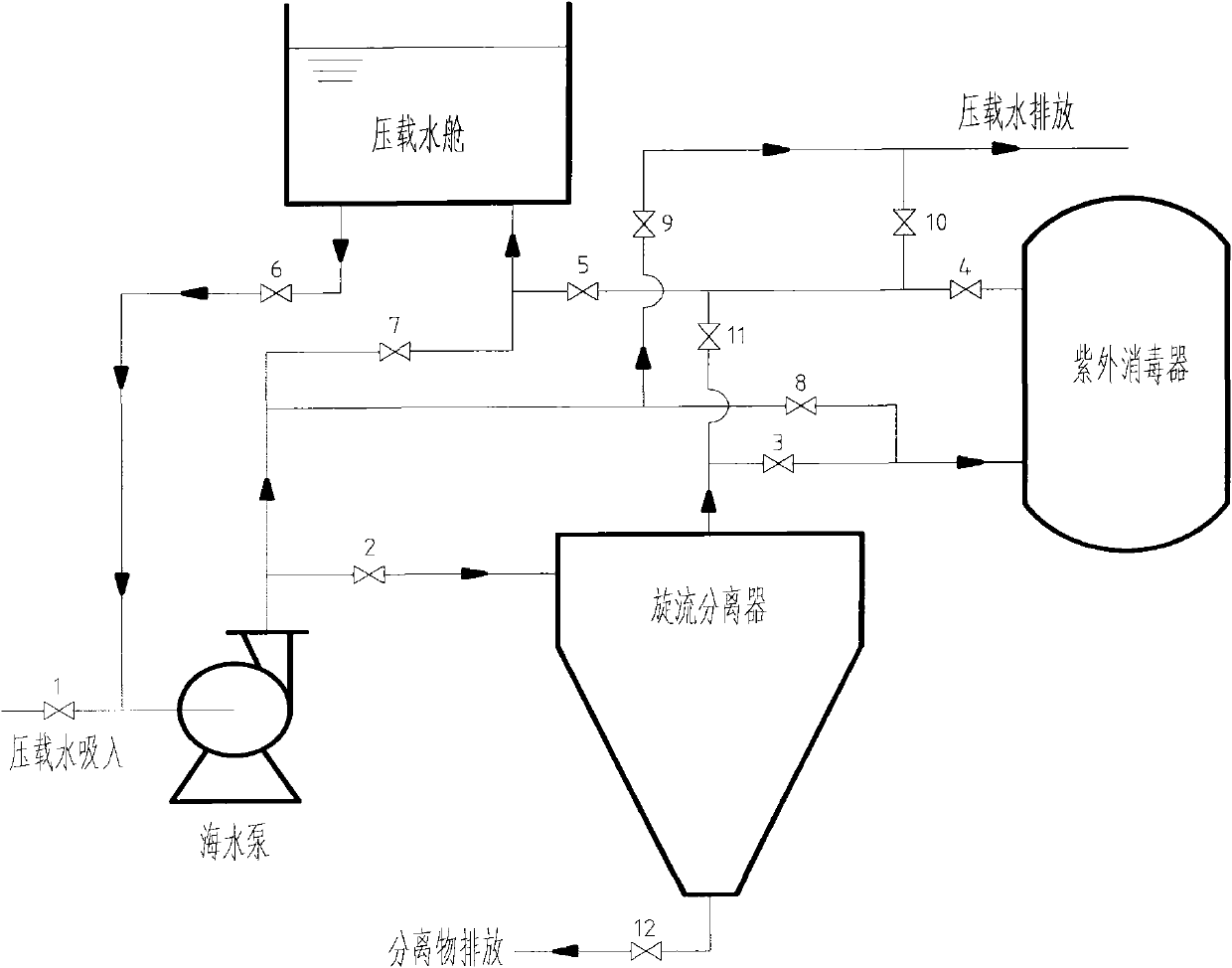
Efficient ship ballast water treating system
InactiveCN101948204AGood removal effectHigh activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMultistage water/sewage treatmentSuspended particlesUltraviolet
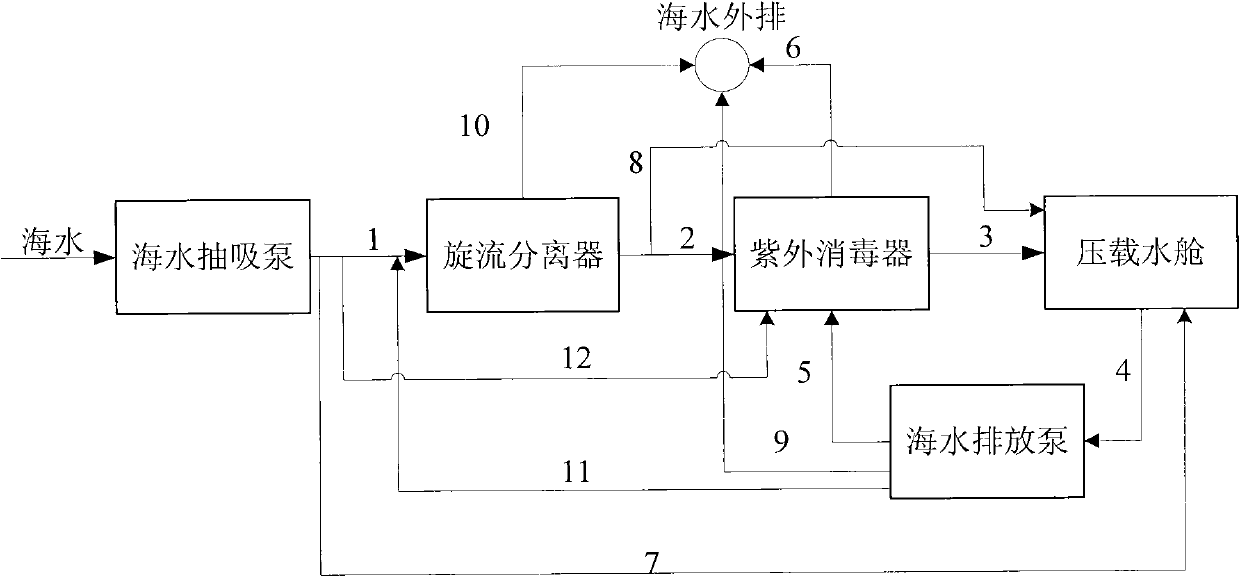
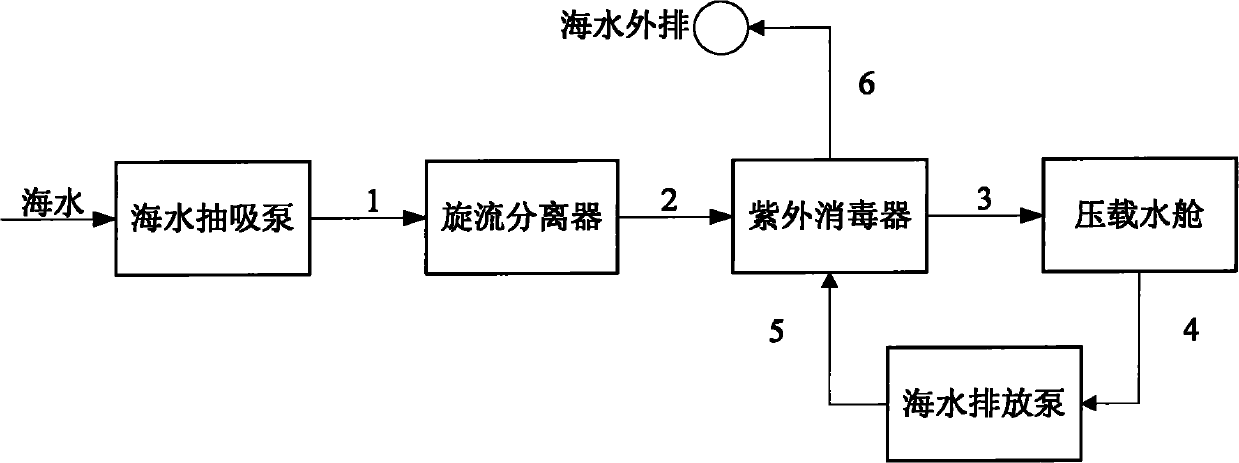
The invention provides an efficient ship ballast water treating system which is mainly used for treating marine organisms in the ballast water of large ships, specifically ocean vessels to remove the effect and damage to the different ocean environments and organisms, belonging to the technical field of environmental protection. The system mainly comprises: a sea water pump, a filter and an ultraviolet sterilizer, etc, wherein the filter utilizes a rotational flow separator to separate the marine organisms, the algae, the planktont and the suspended particle in the sea water through gravity and centrifugal force. The ultraviolet sterilizer can kill the microorganisms (such as bacteria, virus etc) in the water; the discharged water can reach the D-2 discharging standard requirement of the International Ship Ballast Water and Sediment Control and Management Convention. The system has a high removing effect to the marine organisms, the bacterial and the virus in the ballast water; the system does not generate daily substances and dose not have the secondary pollution to the ocean.
Owner:718TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Wet land species diversity habitat system construction method
ActiveCN105248081ANew or restored biological habitat functionsGood breeding placeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTerrainEcological environment
The present invention discloses a wet land species diversity habitat system construction method which comprises the steps of: deep water area construction; shallow water area construction, wherein the area with the water depth being less than 50 cm is 30%-50% of the total water area, and abundant flow state environment is built; sandy beach construction; swamp area construction including the steps of planting pieces of emerged plants having developed subterraneous stems in a low-lying swamp area which is waterlogged all year round, or appropriately accompanying plants such as softstem bulrush, cattail, water horsetail and marsh marigold and the like, or alternately planting sedge; and aquatic vegetation zone construction including the steps of coastwise arranging emerged plant zones and floating-leaved plant zones in a land and water interface hydro-fluctuation belt zone so as to form an isolating barrier, the depth into the water being at least 10 meters. According to the method, the biology habitat function of a wet land can be newly built or recovered, a good growth and propagation place is provided for wet land biology, and an appropriate ecological environment is provided for birds, amphibians, fishes and periphyton.
Owner:南京必蓝环境技术有限公司
Method for realizing ecological larval culture on rapana venosa
InactiveCN102160529AIncrease emergenceReduce manufacturing costClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffWater qualityOrganism
The invention relates to a method for realizing ecological larval culture on rapana venosa. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly selecting a pond which is convenient in water exchange, takes lithoherm and stone bottom as a substrate and is in the size of 2-5Mu; then placing mature rapana venosa with the length of 7-10cm into the pond in the quantity of 100kg per Mu, mating and spawning after the rapana venosa eats ruditapes and mussel for 2-3 days, when enough oocysts are obtained, removing the rapana venosa away, incubating the oocysts for 20-22 days at the water temperature of 20-25 DEG C to obtain planktonic larva, growing the planktonic larva by eating the planktonic larva in the pond, starting to throwing polyethylene corrugated plate adherence ortile under the condition that the water temperature is 22-25 DEG C after 15-16 days, sticking benthic diatom and the planktonic larva onto the polyethylene corrugated plate or tile, transfigurating the planktonic larva of the rapana venosa into young spiral shell after 5-6 days, growing the transfigurated young spiral shell by eating the planktonic larva and benthic diatom on the corrugated plate, wherein the survival rate of the transfigurated young spiral shell on the corrugated plate can reach more than 50%, and feeding small low-value bivalve to the young spiral shell with the length morethan or equal to 3mm. By applying the method provided by the invention, the defects that the survival rate is low and the larval yield is low as bait conversion is difficult and water is polluted when carnivorous fish mice are used as feed in indoor artificial larval culture can be overcome, and the larval yield is improved by more than 50% compared with the indoor artificial larval culture. Meanwhile, the production cost is saved as no bait is thrown into the pond, thus the method is environment-friendly, and the produced larval is strong.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Production method of microbial fish guano
InactiveCN101798145APromote growthGrowth inhibitionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSolubilityHazardous substance
The invention provides a production method of a microbial fish guano. The production method comprises the following steps: fermenting materials, drying, crushing, and adding inorganic fertilizer and solid photosynthetic bacteria. Because all the organic fertilizers are fermented, the invention has a good water solubility and can fast culture pelagic organisms in the water substance, thereby providing adequate feedstuff to fishes and shrimps; the invention improves the culture water environment, and reduces the harmful substances in water, such as ammonia, nitrogen, nitrite, hydrogen sulfide and the like; the invention can realize the intensive alternate-breeding culture and greatly increase the yield per unit culture area, and the yield can be increased by more than 40% based on the current service condition; and the invention has the advantages of low cost, safety, high efficiency, environmental friendliness and no pollution, thereby ensuring the production of pollution-free green food.
Owner:都江堰惠农生物技术有限责任公司
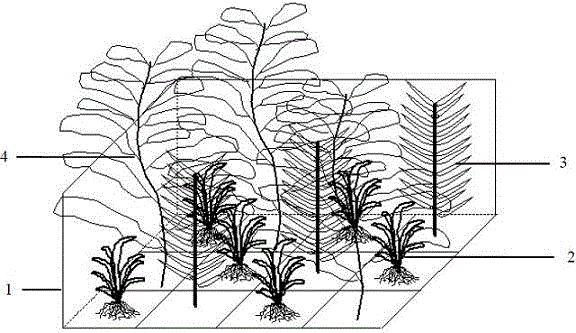
Ecological method for controlling excessive proliferation of periphytic filamentous algae through submerged plant patch mosaic pattern
ActiveCN105830711ASolve the problem of low survival rate and single underwater ecological nicheReasonable designClimate change adaptationSustainable biological treatmentEutrophicationLower grade
The invention discloses an ecological method for controlling excessive proliferation of periphytic filamentous algae through a submerged plant patch mosaic pattern. The ecological method comprises steps as follows: 1), water environment features including water depth, water flow, transparency, sediments, nutritive salts, plankton and the filamentous algae of a to-be-restored area are surveyed; 2), purse seining is performed by the aid of nylon ropes, a purse seine is dropped to be contacted with the sediments, and if a number of herbivorous fishes exist in the submerged plant patch mosaic pattern restoration area, the herbivorous fishes are expelled manually; 3), submerged plant species are selected according to the restoration area water environment obtained through the survey; 4), the submerged plant patch mosaic pattern is designed according to underwater ecological niche, growth and propagation features and water level of submerged plants; 5), submerged planting is performed in a clustering manner according to the designed submerged plant patch mosaic pattern; 6), the growth vigor of the submerged plants is monitored regularly. With the adoption of the ecological method, the problems of low survival rate and single underwater ecological niche of the submerged plants are solved, and the cover degree of the restored submerged plants is up to 70%; abnormal proliferation of the low-grade periphytic filamentous algae in a lake with eutrophication is effectively controlled, and the growth rate of the periphytic filamentous algae is reduced by 35% averagely.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Low-surface-energy stainproof paint preventing ocean periphyton defilement
InactiveCN101117529ASolve the problem of applications that do not meet the required antifouling requirementsWax coatingsAntifouling/underwater paintsCapsaicinEthyl acetate
Owner:TIANJIN ZHENDONG PAINTS CO LTD
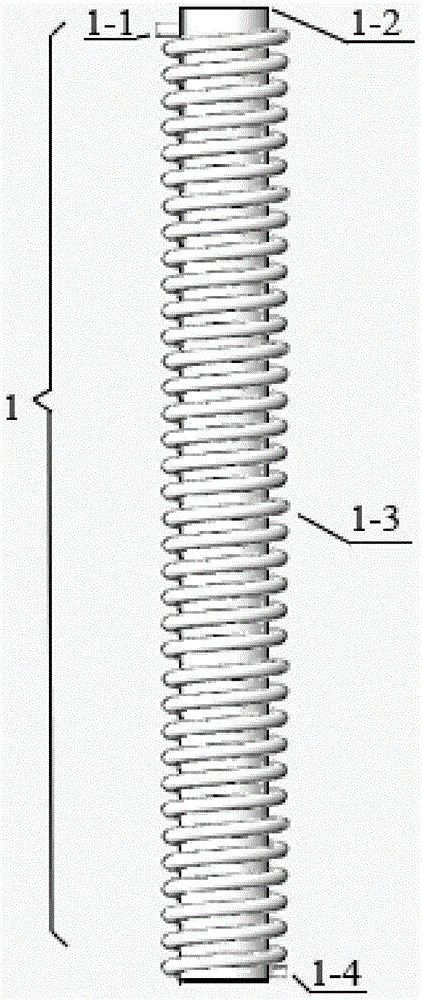
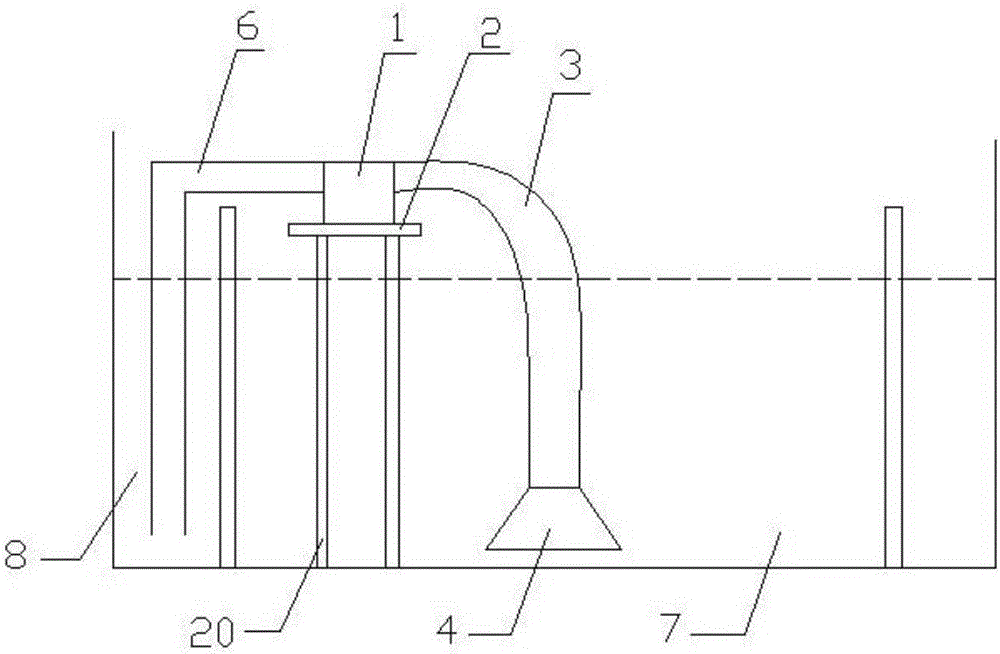
Method and device for efficiently removing organic matters in sewage by using periphyton
InactiveCN104944681AWays to improve immobilizationImprove removal efficiencyMultistage water/sewage treatmentFiltrationSoil organic matter
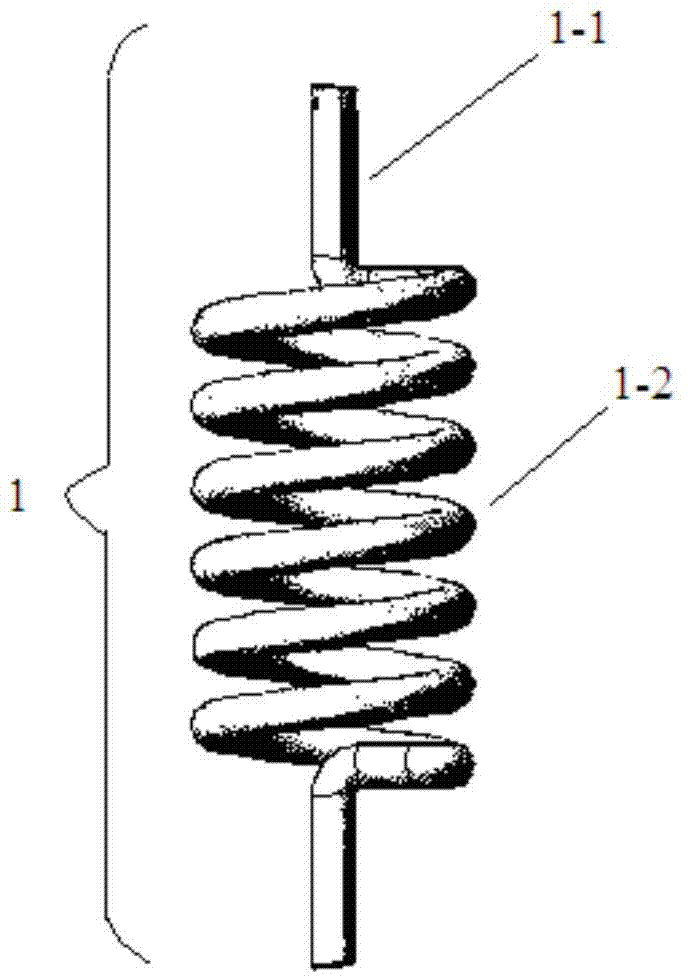
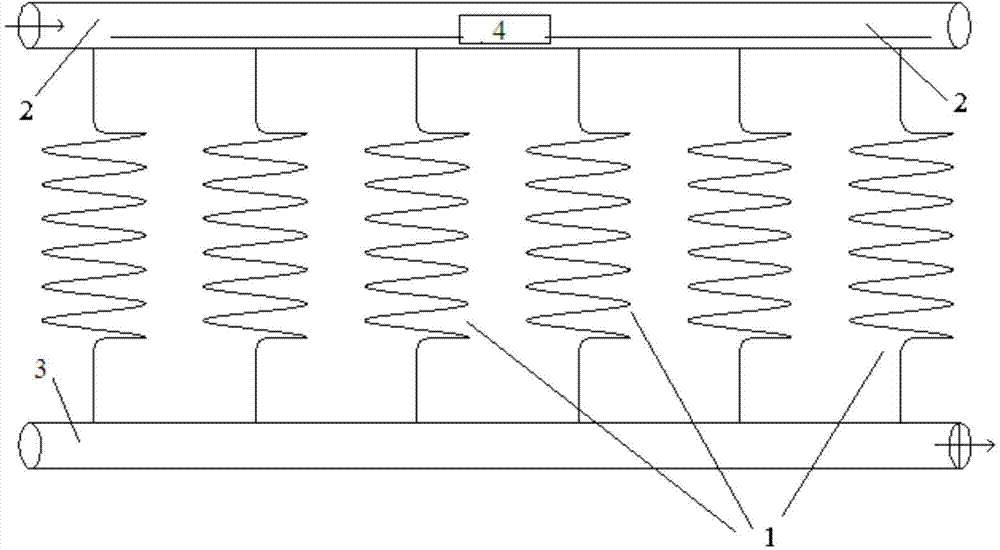
The invention relates to a method and device for efficiently removing organic matters in sewage by using periphyton. The method comprises the following steps: (1) design of spiral periphyton reactor; (2) spiral pipe pretreatment; (3) fixation process of periphyton; (4) design of periphyton treatment system; (5) design of integrated spiral periphyton reaction system; and (6) control of key environmental conditions. The device used by the method is an integrated spiral periphyton reaction system. The adsorption, absorption, biodegradation and other mechanisms of the periphyton are utilized and combined with the traditional precipitation and filtration processes to form the integrated spiral periphyton reactor. The device has the characteristics of high efficiency, small occupied area and high economic and environmental efficiency when being used for purifying organic pollutants in sewage or low-concentration low-C / N-ratio sewage.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method using scratching fish and periphyton for combined control of lake eutrophication
ActiveCN103663672AImprove fish productivityReduce concentrationBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationHabit
The invention discloses a method using scratching fish and periphyton for combined control of lake eutrophication. The method comprises the steps of investigating the quantity of periphyton in a lake, arranging artificial substrates, selecting scratching fish, fishing scratching fish and the like. According to the method, by utilizing the characteristic that periphyton has high absorptivity for nitrogen and phosphorus in a water body, the artificial substrates are arranged to enlarge the quantity of periphyton in the water body so as to increase the amount of absorption and conversion of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water body, and as the baits of scratching fish are exactly periphyton on various substrates, the fishery productivity of the water body can be improved by breeding a certain quantity of scratching fish which has the feeding habit characteristic of being capable of scratching periphyton on various substrates; meanwhile, the concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient substances in the water body can be reduced, so that the method not only has ecological efficiency, but also brings certain economic benefits. Therefore, the effect of comprehensive optimization of ecological efficiency and economic benefits is achieved.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method and device for culturing periphyton
InactiveCN104789472ANot easy to degradeExtended service lifeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutomatic controlDrip irrigation
The invention discloses a method and a device for culturing periphyton. The method for culturing the periphyton comprises the following steps: (1), preparation of a modified carrier, wherein the carrier more favorable for periphyton adhesion is prepared by modifying agricultural byproducts; (2) periphyton culture, wherein water flow is controlled through a floating valve, nourishment is supplied through drip irrigation, and secondary metabolites of the periphyton are taken away while the nourishment in a periphyton culture tank meets microbial growth, so that the periphyton can be massively propagated; (3) control on a key environmental condition, wherein efficient periphyton culture is realized by controlling growth influence factors of the periphyton. The device is capable of automatically controlling sample introduction and realizing integration of periphyton culture and reaction. The selected materials can be all obtained locally and are low in cost and remarkable in effect; the method is suitable for efficient periphyton culture and provides a scientific basis for promotion of application of the periphyton to the natural water body remediation and agricultural area-source pollution control.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
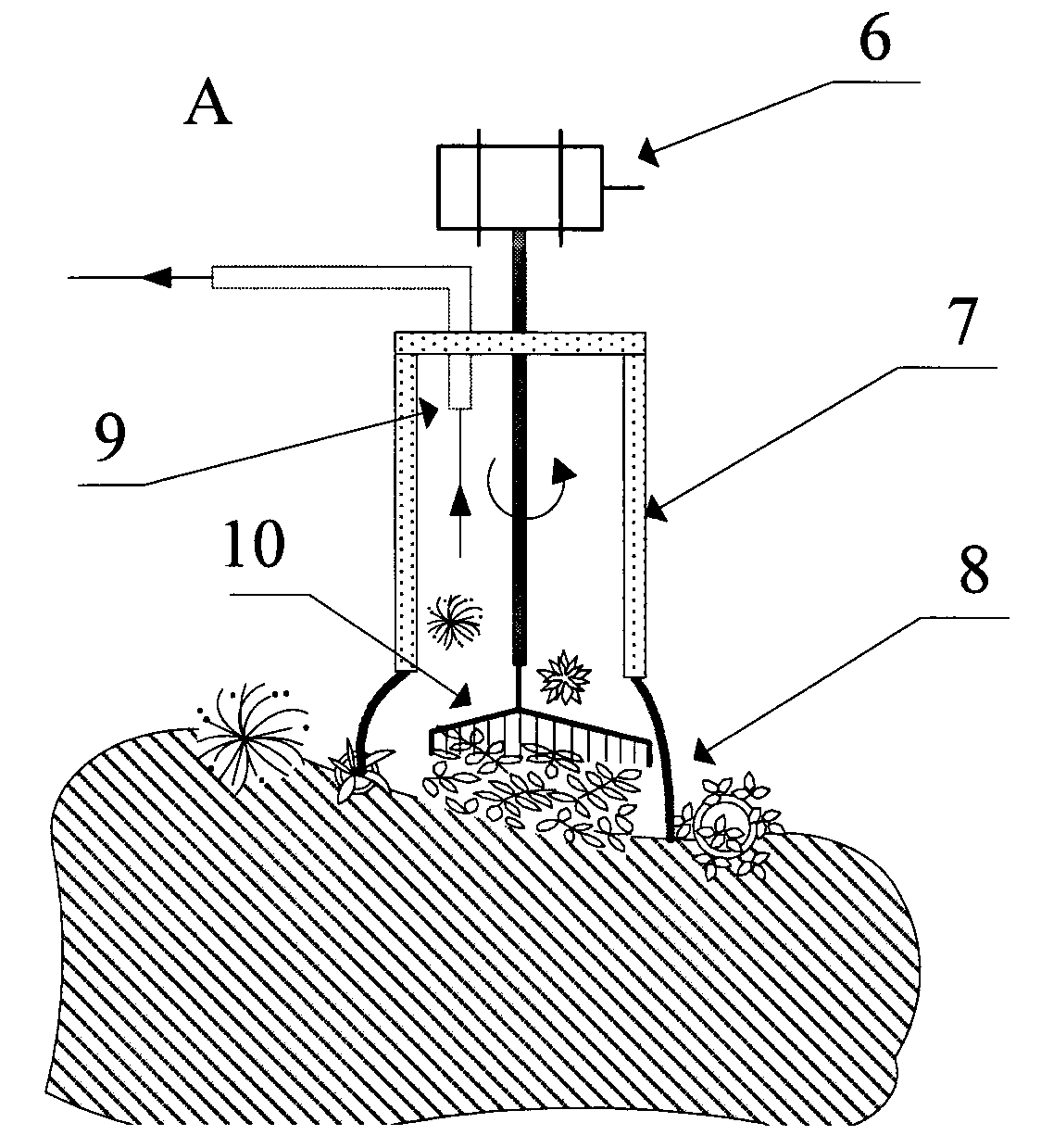
In-situ sampling apparatus for epilithic periphyton
The invention discloses an in-situ sampling apparatus for epilithic periphyton. According to the invention, the apparatus fixes a sampling cross-sectional area and uses an eccentric nylon brush which rotates at a high speed under the driving of a motor to brush off epilithic periphyton, wherein the brush is arranged on a probe; negative pressure is formed in a bowl-shaped sealing rubber ring positioned at the end of the probe and in the probe body under the action of a vacuum pump so as to allow water to enter into the probe along a slit between a stone and the sealing rubber ring, so it is guaranteed that periphyton is not taken away by a torrent when brushed off; and periphyton suspension is sucked into a sample collection bottle through a sample suction hole in the probe and deposited at a cone bottom, and a periphyton sample is separated through a sample separation valve. The in-situ sampling apparatus provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, high sample fidelity and a fast sampling speed and overcomes the problem that in-situ collection of epilithic periphyton on a large stone cannot be realized in a torrent. The in-situ sampling apparatus is applicable to a sample region where heterotopic manual sampling can be carried out.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semi-closed floating type multi-layer ecological culture water tank
PendingCN108575845AMeet the requirements of ecological environmental protectionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGratingGroundfish
The invention designs a semi-closed floating type multi-layer ecological culture water tank. The water tank comprises a water tank floating ring, an upper-layer filtering water permeable ring, a watertank upper-edge water partition ring, an upper-layer grating plate, a sealed water tank vertical wall, a middle-layer grating plate, a bottom-layer grating plate, a conical water tank bottom, a sewage discharge filtering cover, a sewage storage tank, an inflation system, a sewage discharge system and a bait feeding system. By using the water tank, planktonic feeding fishes are stocked in an upper-layer culture area, feed eating fishes are stocked in a middle-layer culture area, and bottom fishes are stocked in a bottom-layer culture area. An inflation system is used for conducting inflation and oxygen enrichment on a water area of the water tank, a bait feeding system is used for feeding bait, residual bait enters the bottom-layer culture area to be eaten by the bottom fishes, fish manureand other pollutants are accumulated in the sewage storage tank, and the accumulated pollutants are discharged out through a sewage discharge pump. At the same time, the upper-layer filtering water permeable ring on the upper portion of the water tank body filters surrounding water when the pollutants are discharged, the water then enters the water tank body, only a small amount of water needs tobe supplemented, the culture waste pollutants are extracted from the water area for discharging, the surrounding environment of the culture areas is not influenced, and the requirements for ecological and environmental protection are met.
Owner:魏中成
Penaeus vannamei ecological culture method for improving culture efficiency
ActiveCN106305553AImprove survival ratePromote growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffWater dischargeSludge
The invention discloses a penaeus vannamei ecological culture method for improving the culture efficiency. The method comprises the following steps that a culture pool is selected; water is thoroughly discharged; a sagittaria sagittifolia planting pool is selected on the periphery in the culture pool; a middle part is used as the penaeus vannamei culture pool; sludge in the penaeus vannamei culture pool is cleared way; a plurality of water discharge pipes are laid on the pool bottom of the penaeus vannamei culture pool; water is introduced for soaking sterilization; the water is thoroughly discharged; sagittaria sagittifolia is planted in the sagittaria sagittifolia planting pool; a plurality of pollution suction devices are arranged in the penaeus vannamei culture pool; water is introduced; the pH value of the water is regulated; fertilization is performed; a mixture of straws, chicken manure and cow manure is applied in the sagittaria sagittifolia planting pool for culturing planktonts; shrimp fries and feed are fed; the pollution suction devices are turned on for pollution suction every 10 to 15 days; then, the water discharge pipes are opened for pollution discharge. The penaeus vannamei ecological culture method has the advantages that the growth of the sagittaria sagittifolia can be promoted; the damage to the water quality in the penaeus vannamei culture pool can be prevented; the planktonts cultured in the sagittaria sagittifolia culture pool is food of the sagittaria sagittifolia; the growth of the sagittaria sagittifolia can be promoted; the culture of the planktonts and the culture of the sagittaria sagittifolia have complementary relation.
Owner:唐山市曹妃甸区会达水产养殖有限公司 +1
Periphyton filtration pre- and post-treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050230307A1Reduce the populationReducing and eliminating toxinBiocideEnergy based wastewater treatmentFiltrationBioremediation
Owner:AQUAFIBER TECH CORP
Environment protection type ecology breeding method
InactiveCN101336618AIncrease weightEutrophicationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFecesPolyculture
The invention belongs to the field of aquaculture techniques, particularly an environment-friendly ecological culture method. The method is characterized in that: mussels are cultured in the upper layer of the water body, edible fish is cultured in the lower layer of the water body; the mussels and the edible fish are cultured in the same water body; the edible fish is fed with the fish feed added in the water body; the organic substances in the feces excreted in the growth of the edible fish and the floating organisms serve as feed for the mussels; a fish pond automatic feed dispenser is fixed in the mussel-fish polyculture water body to feed fish on the schedule, thereby establishing conditioned reflex in fish; and a fixed fishing net cage is arranged in the zone free of nacre during the process of throwing the fish feed. Based on the food chain of the aquatic animals in the water body, the method can produce aquatic products such as nacre and establish the ecological positive circulation in the water body. Additionally, the culture method facilitates the fish harvest by adopting a certain fishing method and has high practicability and effectiveness.
Owner:张根芳
Efficient breeding method for young lobsters
ActiveCN106259115AImprove immunityReduce the prevalenceFodderClimate change adaptationPrawnWater quality
The invention discloses an efficient breeding method for young lobsters, comprising the steps of: (1) constructing a lobster pond; (2) sterilizing water in the pond; (3) breeding young lobsters; (4) feeding the young lobsters with a young fodder; and (5) performing daily management. By adopting the efficient breeding method for young lobsters, the immunity of the young lobsters can be strengthened, the morbidity rate is reduced to 3%, and the survival rate reaches 92%; comprehensive management is performed from five aspects of construction of the lobster pond, sterilization of pond water, breeding of young lobsters, feeding with the fodder and daily management, the lobster pond is provided with agent holes for placing zeolite, and medical stone is added to the clay ridges, so that toxin can be adsorbed and water can be cleaned; the pond is cleared and disinfected within a fixed time, so that germs are killed thoroughly; the young lobsters are disinfected before being bred and fed with a special fodder for lobsters three times, and planktons are not bred, so that scientific proportioning of the young lobster fodder is ensured, the water is clean, and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms is inhibited; the pond is inspected every day to discover and early treat symptoms, thereby avoiding high loss and improving the economic income by 16.4%.
Owner:ANHUI CHUNSHENG AGRI TECH
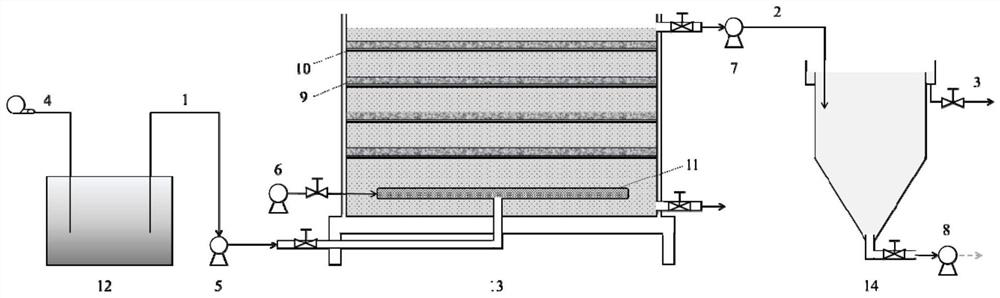
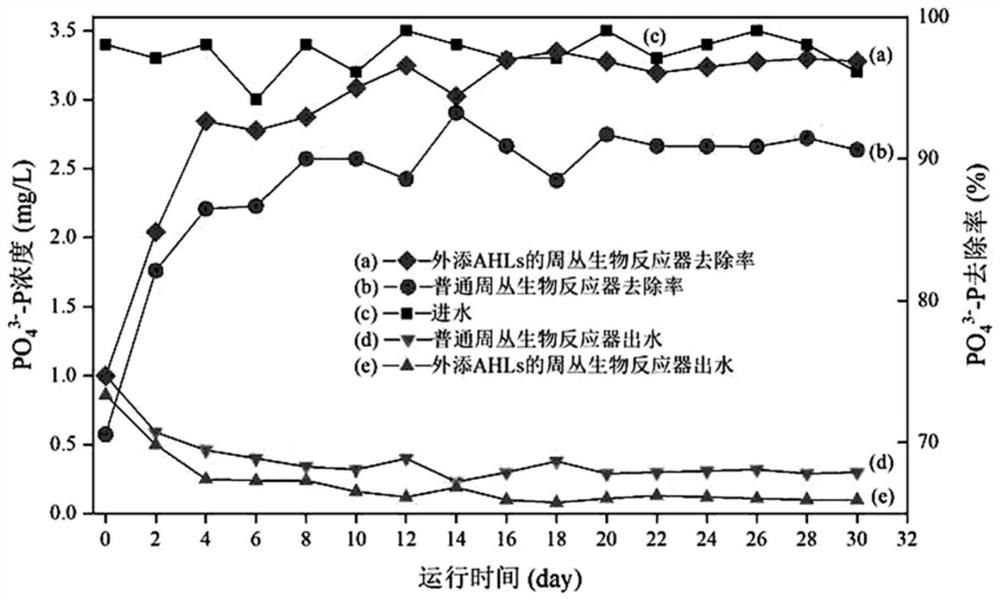
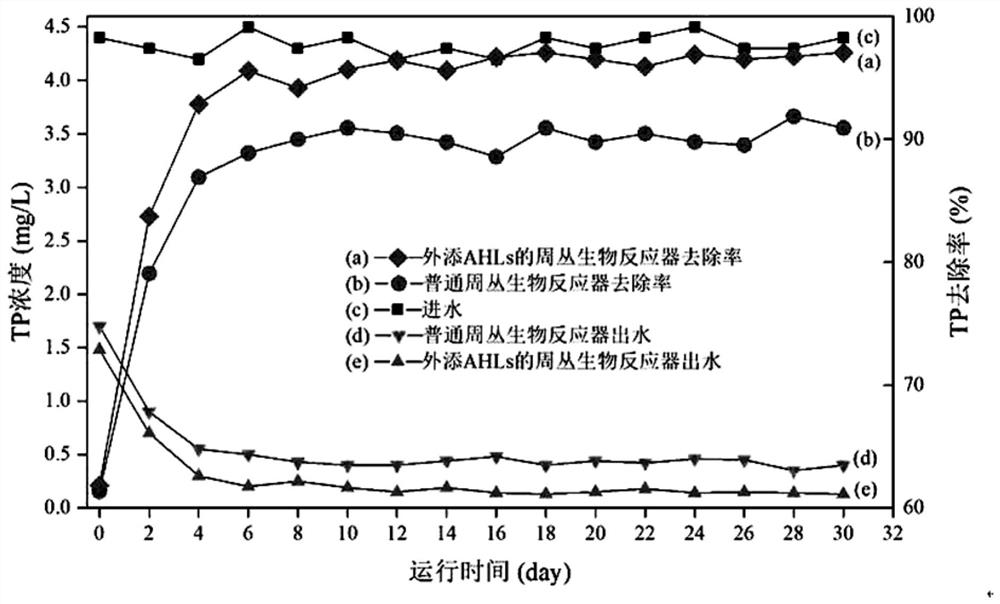
Method for promoting phosphorus removal by stimulating periphyton through AHLs quorum sensing signal molecules and biological phosphorus removal system
ActiveCN111661977AAccelerated growth fixationPromote growthWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for promoting phosphorus removal by stimulating periphyton through AHLs quorum sensing signal molecules and a biological phosphorus removal system, and belongs to thetechnical field of sewage treatment. In a periphyton culture stage and a sewage purification operation stage after culture is finished, AHLs quorum sensing signal molecules are added into a periphytonreactor so that quorum sensing which is crucial to periphyton formation is promoted, microorganism interspecific cooperation is promoted, and the activity of microorganisms is stimulated. An AHLs signal molecule mixture with a certain concentration and a certain proportion is added into theperiphyton reactor so that the fixed growth process of periphyton is accelerated, the biomass is improved, and the phosphorus removal capacity of a periphyton system is optimized. The method has the characteristics of simple process operation requirements, high stability, high treatment efficiency and low investment cost and is suitable for removing and capturing phosphorus in high-concentration phosphorus sewage.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Loach fry cultivation method
InactiveCN105409853AReduce diseasePromote rapid growthFood processingClimate change adaptationWater qualityOrganism
The present invention discloses a loach fry cultivation method. The method comprises 1) fishpond preparation: after a fishpond is disinfected, applying a fermented organic fertilizer or a bio-fertilizer to an inner pond and an outer pond, filling the inner pond and the outer pond with filtered fresh water for detoxification treatment and plankton culture; 2) breeding a fish autumn seedling; 3) cultivation for water cobitinae fries: feeding an egg yolk, rotifera and crushed tubificidae, controlling oxygenation of the pond water, wherein after about one week of cultivation, the water cobitinae fries grow to black child loach fries; and 4) cultivation for the black child loach fries: feeding the black child loach fries with a fish powder feed and limnodrilus with the crude protein content of 40-50%; when the loach fries reach an inch in length, the loach inch fries are strong in physique and high in survival rate, diseases of the loach fries are reduced, and rapid growth of the loach fries is promoted by modifying pond sediment and water quality, improving the structures of natural bait organisms, scientifically feeding bait, controlling toxic and harmful substances such as ammonia and nitrite in the pond by way of improving dissolved oxygen in the pond water and increasing plankton natural bait.
Owner:贺代生
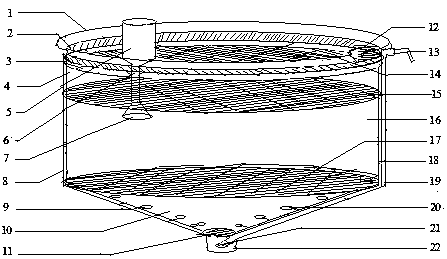
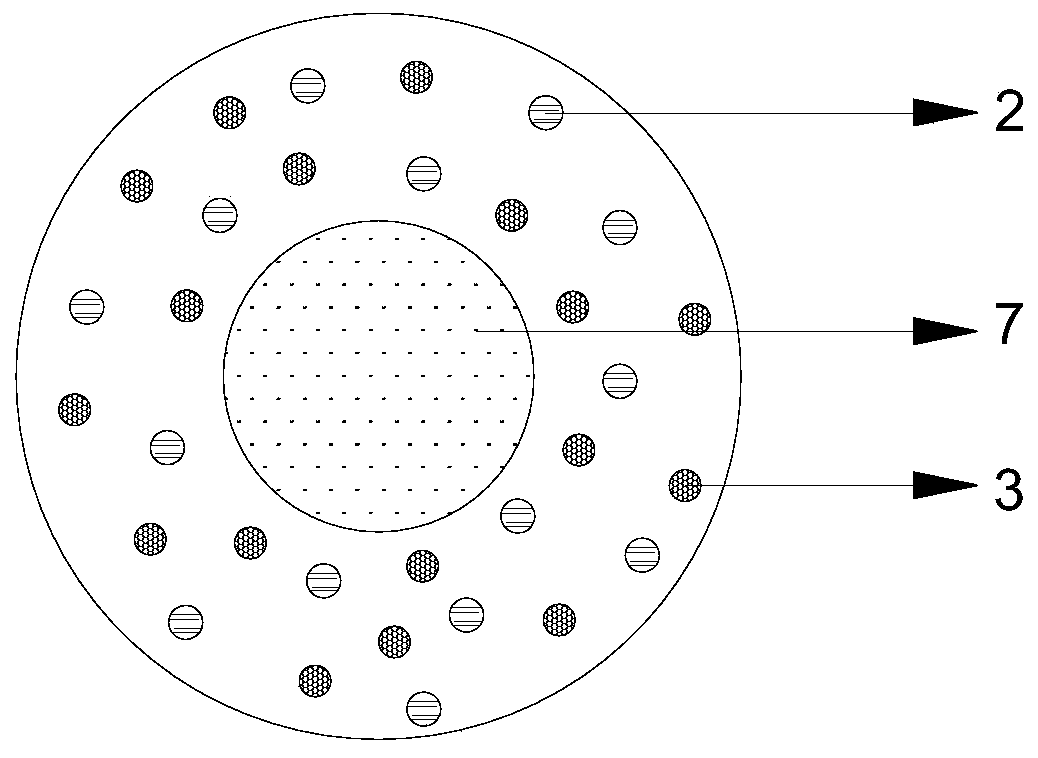
Novel periphyton sampler
InactiveCN101870947ASimple designEasy to operateWithdrawing sample devicesBiological material testing proceduresEutrophicationPeriphyton
The invention relates to a novel periphyton sampler, which mainly comprises a supporting frame structure formed by organic glass materials, a fixation matrix formed by glass slides, a buoyancy carrier formed by foam plastic boards or fixed facilities formed by timber piles and the like. The sampler is mainly used for the relevant study and monitoring in the aspects of natural water bodies, artificial wet land and the like, plays an important role in the aspects of administration of lake eutrophication, ecological restoration, sewage treatment and the like, and has the prominent advantages of simple design, convenient operation, economy, safety and practicality.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
In-situ treatment method for farmland recession
ActiveCN110683659AAchieve coordinated operationBioefficacy coordinationWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
The invention discloses an in-situ treatment method for farmland recession, belongs to the field of ecology and environment protection and in particular relates to a method for removing nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matters from farmland recession by using a multilayer immobilized material of periphyton adhesion composite flora. The method comprises the following steps: performing culture and domestication on ordinary anaerobic granular activated sludge and aerobiotic activated sludge so as to obtain anaerobic ammonia oxidation granular sludge and aerobiotic nitration granular sludge, performing separation screening and activity retention drying so as to obtain the kernel of the multilayer immobilized material of composite flora, and performing pelletizing by using a sphere molding mold, so as to obtain the multilayer immobilized material of the composite flora. The multilayer immobilized material of the composite flora is applied to a recession bank of a farmland, periphyton adhesion growth on the recession bank is achieved, natural seepage of farmland recession passes through the recession bank with sufficient sunshine, and a periphyton intensified denitrification system for farmland recession pollution prevention and control can be constructed. By virtue of the characteristics that an immobilization microorganism technique is high in biological concentration and good in environmental adaptability, successful application of the immobilization microorganism technique in rural water environment control can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of artificial seeds of submerged plants (hydrilla)
InactiveCN103477979AOvercome cumbersomeOvercome riskHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureNutrient solutionBud
The invention relates to a preparation method of artificial seeds of submerged plants (hydrilla). The method comprises the following steps: 1. washing the taken hydrilla seedling with water to remove plankton on the surface of the hydrilla seedling; 2. cutting off the roots and leaves of all the plants, picking up the eugenic plants and washing the eugenic plants with distilled water; 3. cutting off the lateral buds and the terminal buds with internodes and putting the lateral buds and the terminal buds into gel liquid which is formed by mixing of sodium alginate, hoagland's nutrient solution and NAA (nicotinic acid amide); 4. dropping the gel liquid containing hydrilla buds into CaCl2 by a dropper to perform curing reaction, taking out gel liquid after the curing reaction and rinsing with sterile distilled water, and terminating the reaction to obtain the artificial hydrilla seeds. According to the method, the step of plant tissue culture is eliminated, and the method is not required to be implemented under an aseptic condition, the preparation process is greatly reduced, the cost is greatly reduced, the period is shortened, and the survival rate is high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
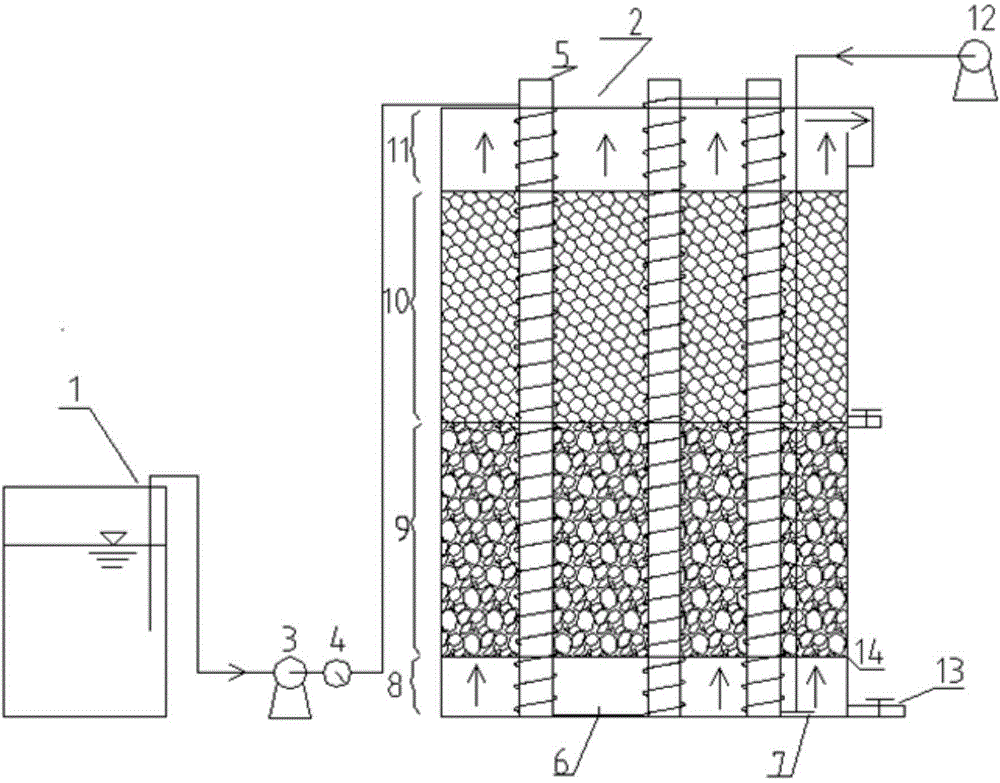
Method and equipment for removing copper in non-point source sewage employing periphyton processing system
InactiveCN104724834ASimple methodImprove water qualityWater contaminantsEnergy based wastewater treatmentSewagePeriphyton
The invention discloses a method and equipment for removing copper in non-point source sewage employing a periphyton processing system. The method comprises the following steps: (1) design of a periphyton reactor, wherein a main body is made of a transparent material, and comprises a water inlet and out straight pipe section and a spiral coil pipeline; (2) pretreatment of the periphyton reactor, namely, corroding the inner wall to increase the specific surface area; (3) enrichment of periphytons; (4) design of a periphyton processing system, wherein the periphyton processing system is composed of a filter basin, a reaction tank and a sedimentation tank; (5) design of a reaction tank, wherein the reaction tank is arranged between a water inlet aerator pipe and a water outlet aerator pipe, and is connected with a plurality of periphyton reactors which are connected with one another in parallel; (6) control on key environmental conditions; and (7) later disposition of the periphytons in the system, namely, extracting the periphytons from the periphyton reactors, collecting together, carrying out innocent treatment, further collecting copper from the periphytons, and utilizing. Through collecting functions of microorganisms in the periphyton system, the method is high in removal rate on copper in the non-point source sewage, low in operation cost and friendly to environment.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In-situ treatment method of fresh water aquaculture wastewater
ActiveCN110734138ARealize synchronous removalReduce distractionsWater treatment compoundsClimate change adaptationPolyvinyl alcoholNitration
The invention discloses an in-situ treatment method of fresh water aquaculture wastewater. The in-situ treatment method comprises the following specific steps: taking dried anaerobic ammonia oxidationgranular sludge as an inner core, taking polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate and silicon dioxide as outer-layer embedding agents, embedding bacillus amyloliquefaciens and nitrifying bacteria to prepare composite flora embedded spheres, taking the composite flora embedded spheres as a reaction filler, filling the composite flora embedded spheres into a grid wall to form a water-permeable biologicalreaction wall, and growing periphyton in an attached growth manner, so as to realize in-situ remediation of fresh water aquaculture wastewater. The immobilized microorganism technology can realize synchronous removal of organic matters, ammonia nitrogen and nitrite, and has the characteristics of high microorganism concentration, good activity, strong environmental tolerance and the like; meanwhile, the fresh water aquaculture wastewater is remediated in situ by utilizing the embedded spheres, disturbance to beneficial microorganisms in an ecological system is reduced, the water quality of the water body is stabilized, and the ecological balance of the raw water body is kept.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
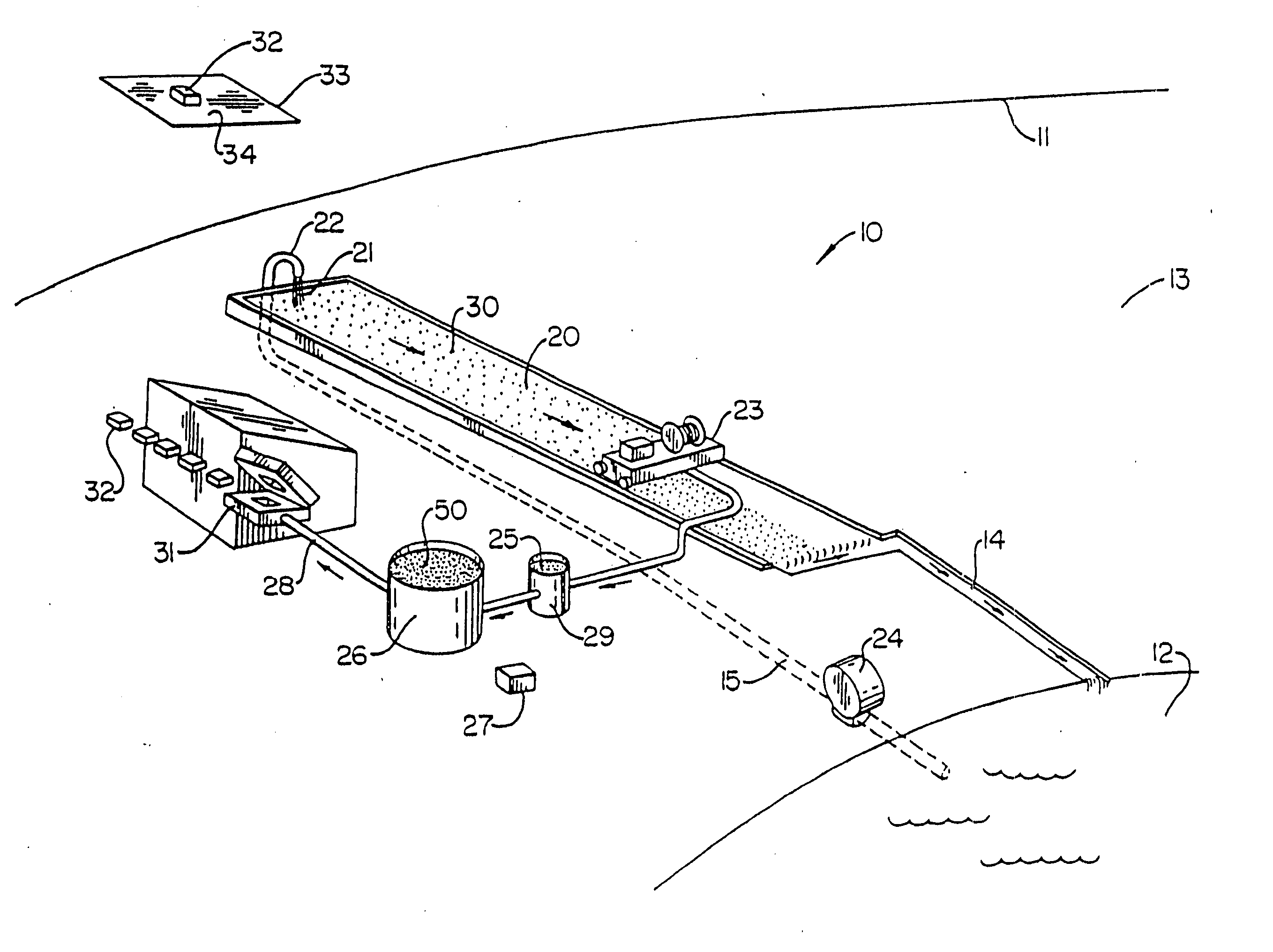
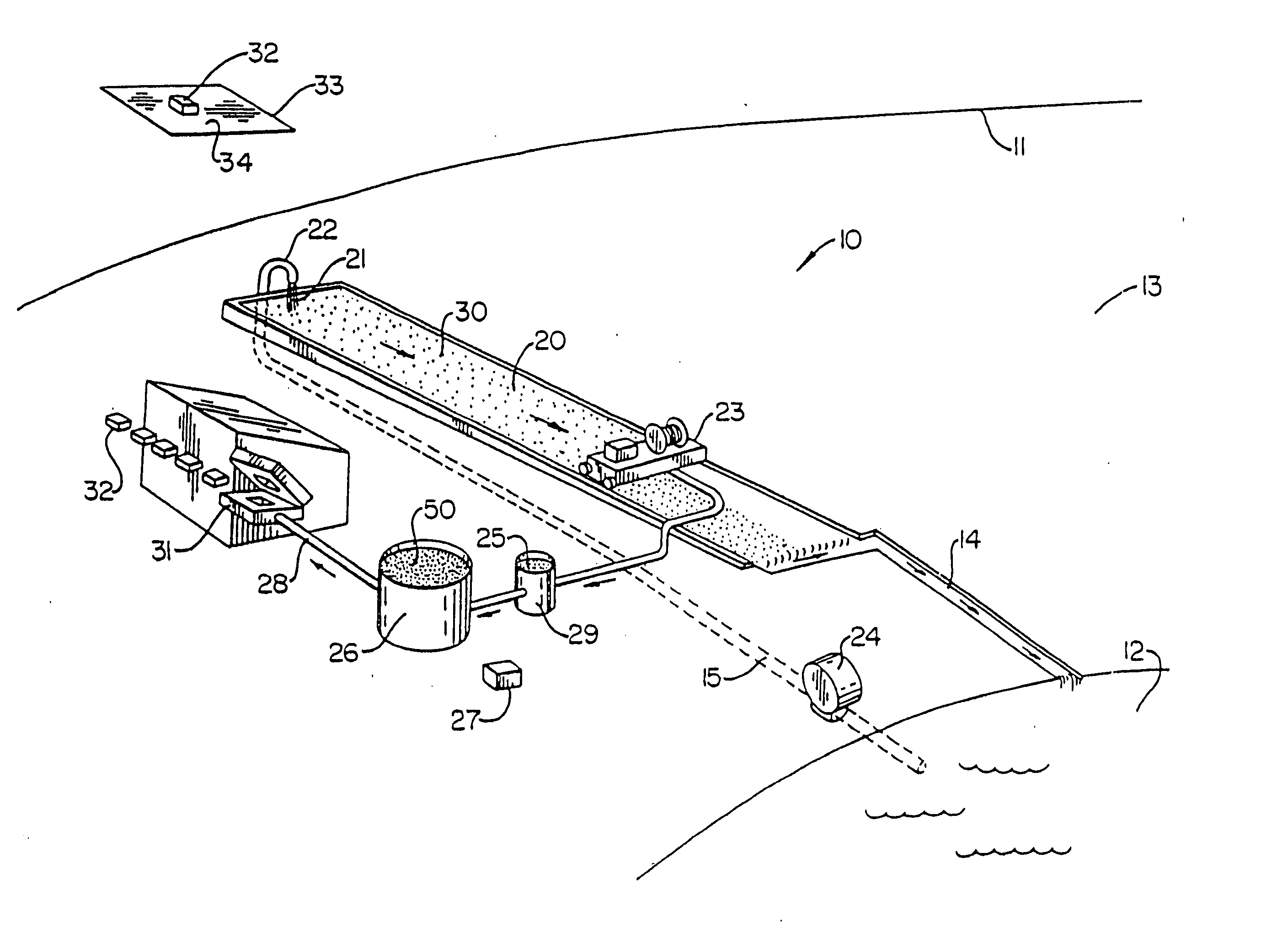
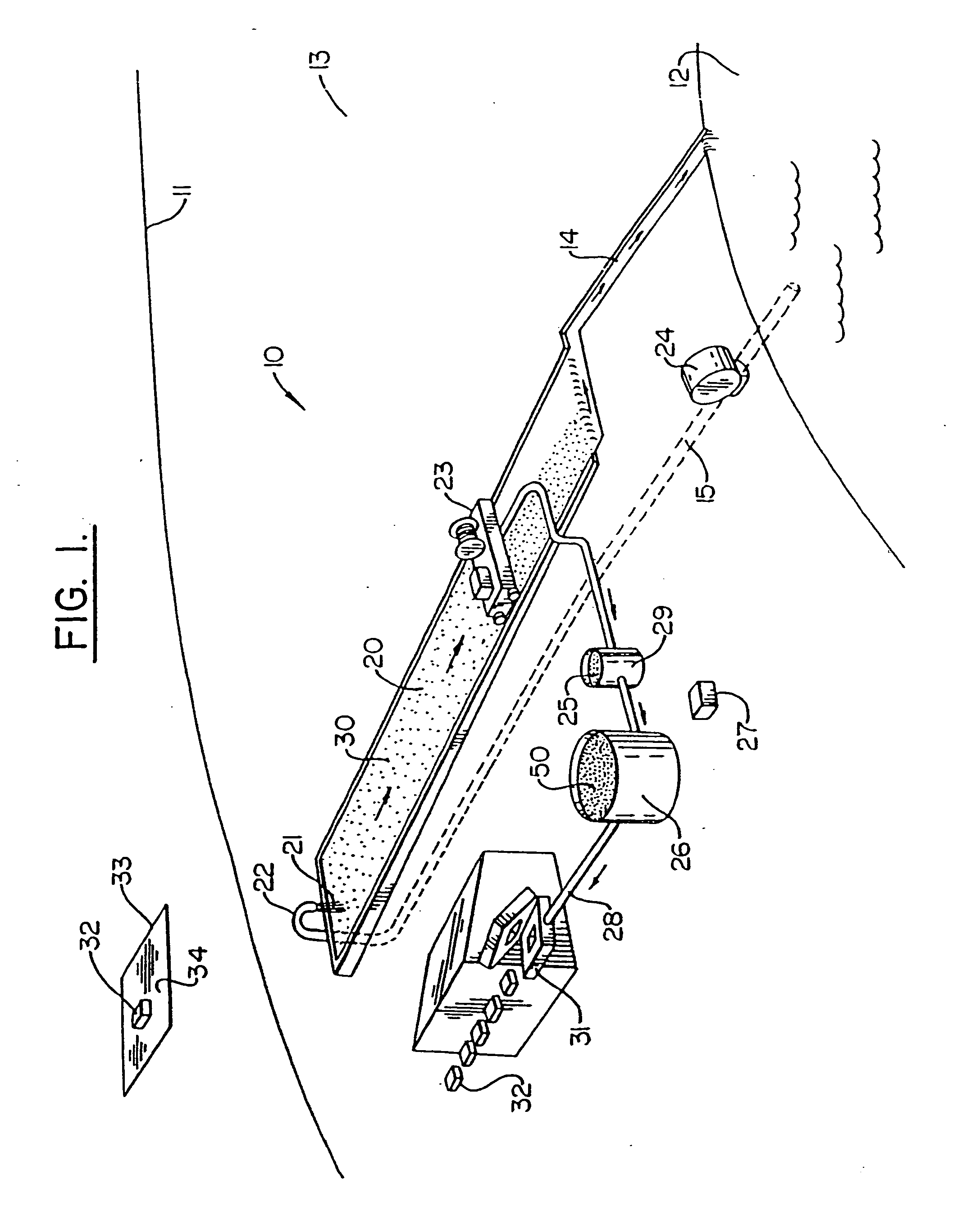
Integrated system and method for purifying water, producing pulp and paper, and improving soil quality
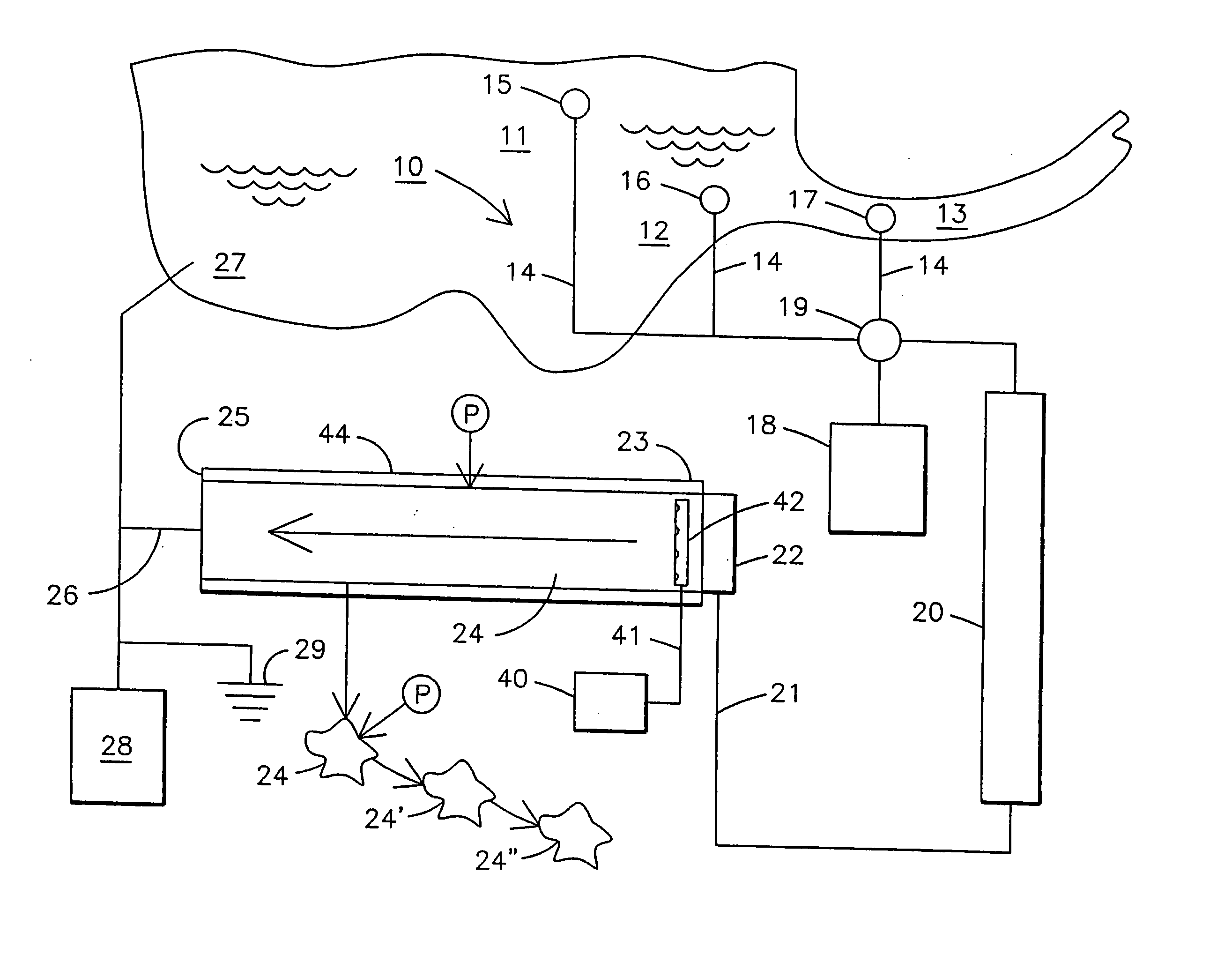
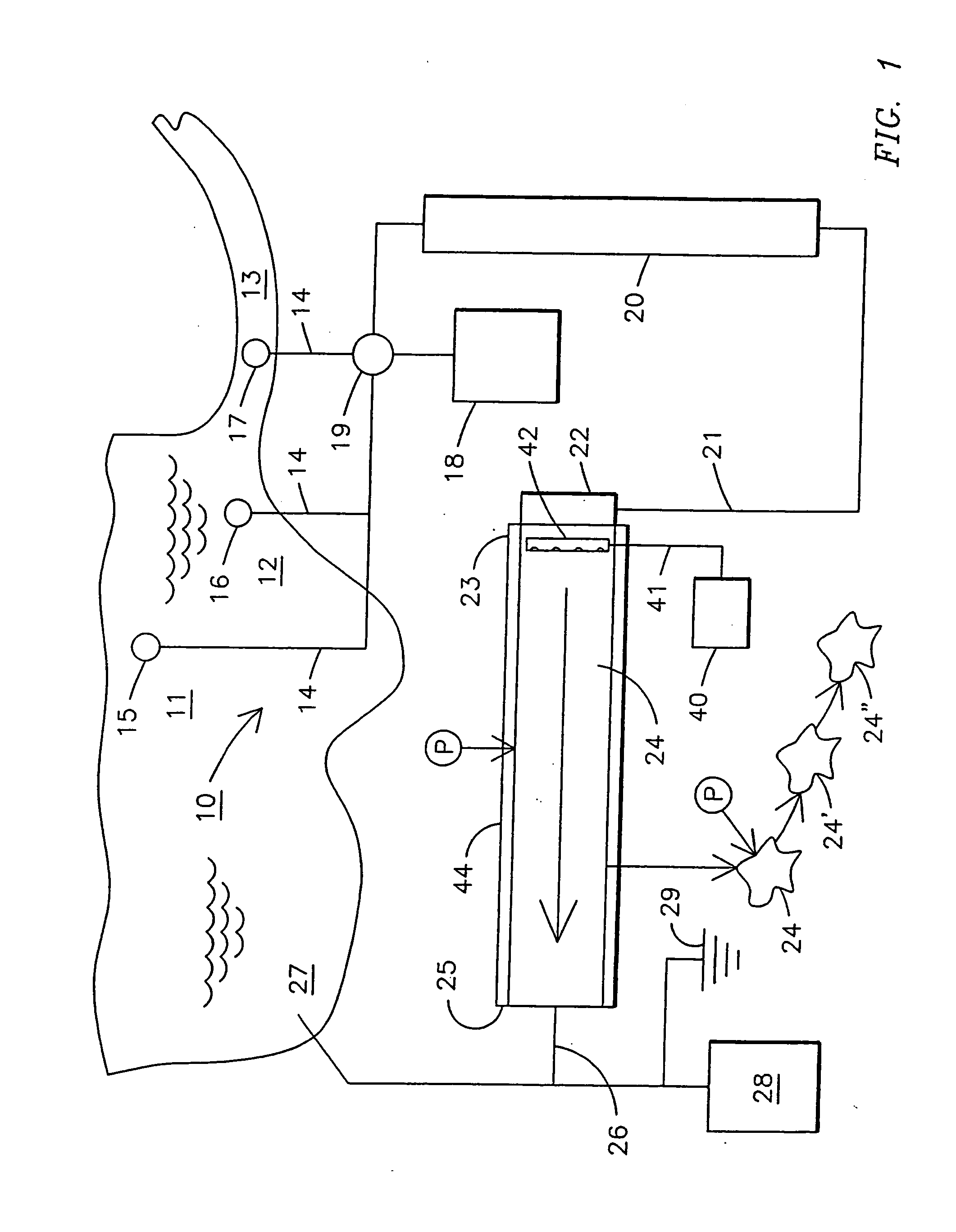
InactiveUS20050178723A1Improve soil qualityIncreasing ecological efficacyNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberDelivery vehicle
An integrated system and method for removing excess nutrients from water, for removing the nutrients from the removal site, for enhancing soil, and for producing pulp and paper products includes bioremediating water to be treated with cultured algae or another suitable plant matter in an attached periphyton bed, harvesting the algae / plant matter to produce a wet algal biomass, and mixing the wet biomass with a shredded fibrous material to produce a pulp. The pulp can be molded into a biodegradable package that can be utilized as a delivery vehicle to a site having nutrient-enrichable soil, where the package can be used as a soil amendment after being used as a delivery vehicle. The pulp can also be made into a paper product that is biodegradable and has the characteristic of enhancing soil quality.
Owner:LEIDOS
Rapid cultivation method for vitis sinocinerea caulerpa reproductive shoot
ActiveCN105594582AFast growthInhibition of overgrowthCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationShootHabit
The invention provides a rapid cultivation method for a vitis sinocinerea caulerpa reproductive shoot. The rapid cultivation method comprises the following steps: cutting a stolon of 8-10cm as a reproduction mother twig from an end part of a grape caulerpa stolon; burying the reproduction mother twig into sand; covering the shade of a cultivation area with black sunshade net, keeping the light intensity of the cultivation area lower than 1000 lux, keeping the water temperature of the cultivation area to be 28-30 DEG C, and feeding shellfish with plankton feeding habit; applying phosphorus-containing nutritive salt, and when the rhizoid length is greater than 18cm, turning over the sand to collect rhizoid; inserting the collected rhizoid into sand, keeping the light intensity be 1500-2500 lux, and cultivating for 100-120 hours at the water temperature of 25-28 DEG C. By the adoption of the technical scheme of the invention, the vitis sinocinerea caulerpa reproductive shoot can be rapidly cultivated by using an artificial system, and the growth rate and the unit area yield are increased.
Owner:深圳市蓝汀鼎执生物科技有限公司
Device for trapping and collecting zooplankton at base layer of coral reef area
PendingCN109964887AFacilitate identification and countingFor subsequent analysisPisciculture and aquariaZooplanktonTrapping
The invention discloses a device for trapping and collecting zooplankton at a base layer of a coral reef area. The device comprises an upper net bag and a lower net bag, the lower net bag is connectedwith a collecting bottle, a bottle lid is arranged at the bottom of the collecting bottle, and the upper net bag comprises a frame and a netting covering the frame; a collecting port is formed in thenetting, the lower net bag is a non-bracket net bag, and is in seamless joint with the netting of the upper net bag to form an entire net bag, slipknots are arranged at the four corners of the frame,and anchors are connected to the slipknots through strings. The device is placed in the coral reef area, a netting gear is opened and closed through a zipper to collect samples, and the collecting bottle at the bottom of the lower net bag is utilized for collecting the samples. Sufficient zooplankton samples at the base layer of the coral reef are obtained at a special target duration according to research needs; meanwhile, the purity and biomass of the zooplankton at the base layer in the collected samples are increased, the pollution of bottom mud and zooplankton is reduced, the separationtime is shortened, and further identification counting and subsequent analysis of the zooplankton samples at the base layer are facilitated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
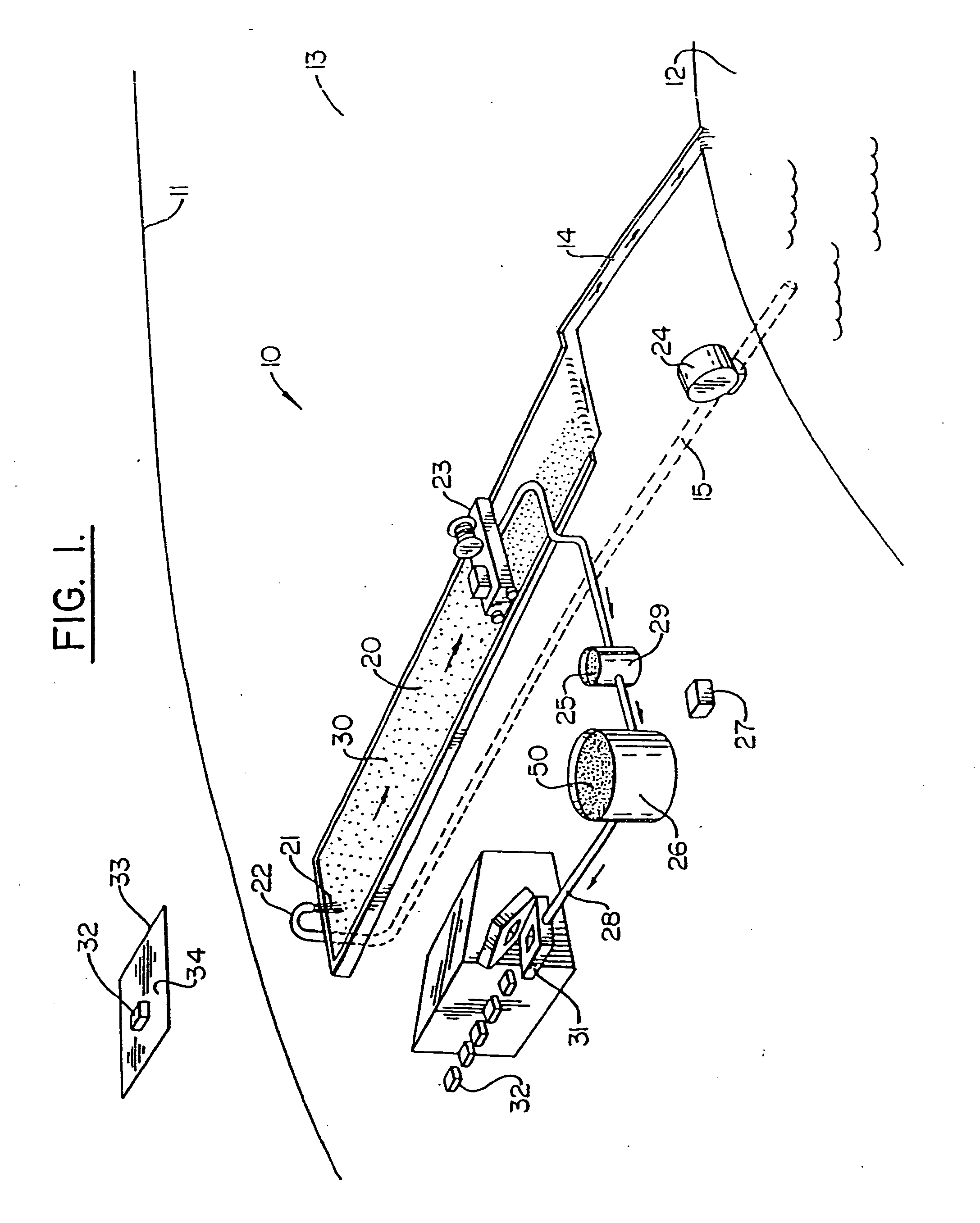
Integrated system and method for purifying water, producing pulp and paper, and improving soil quality
InactiveUS20050178722A1Improve soil qualityIncreasing ecological efficacyNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberDelivery vehicle
An integrated system and method for removing excess nutrients from water, for removing the nutrients from the removal site, for enhancing soil, and for producing pulp and paper products includes bioremediating water to be treated with cultured algae or another suitable plant matter in an attached periphyton bed, harvesting the algae / plant matter to produce a wet algal biomass, and mixing the wet biomass with a shredded fibrous material to produce a pulp. The pulp can be molded into a biodegradable package that can be utilized as a delivery vehicle to a site having nutrient-enrichable soil, where the package can be used as a soil amendment after being used as a delivery vehicle. The pulp can also be made into a paper product that is biodegradable and has the characteristic of enhancing soil quality.
Owner:LEIDOS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com