Method for identifying key toxic substances in pesticide wastewater by taking daphnia magna toxicity as guide
A technology for pesticide wastewater and large fleas, which is applied in measurement devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to determine the type of organic matter, and achieve the effect of reducing sample complexity, reducing sample complexity, and high resolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
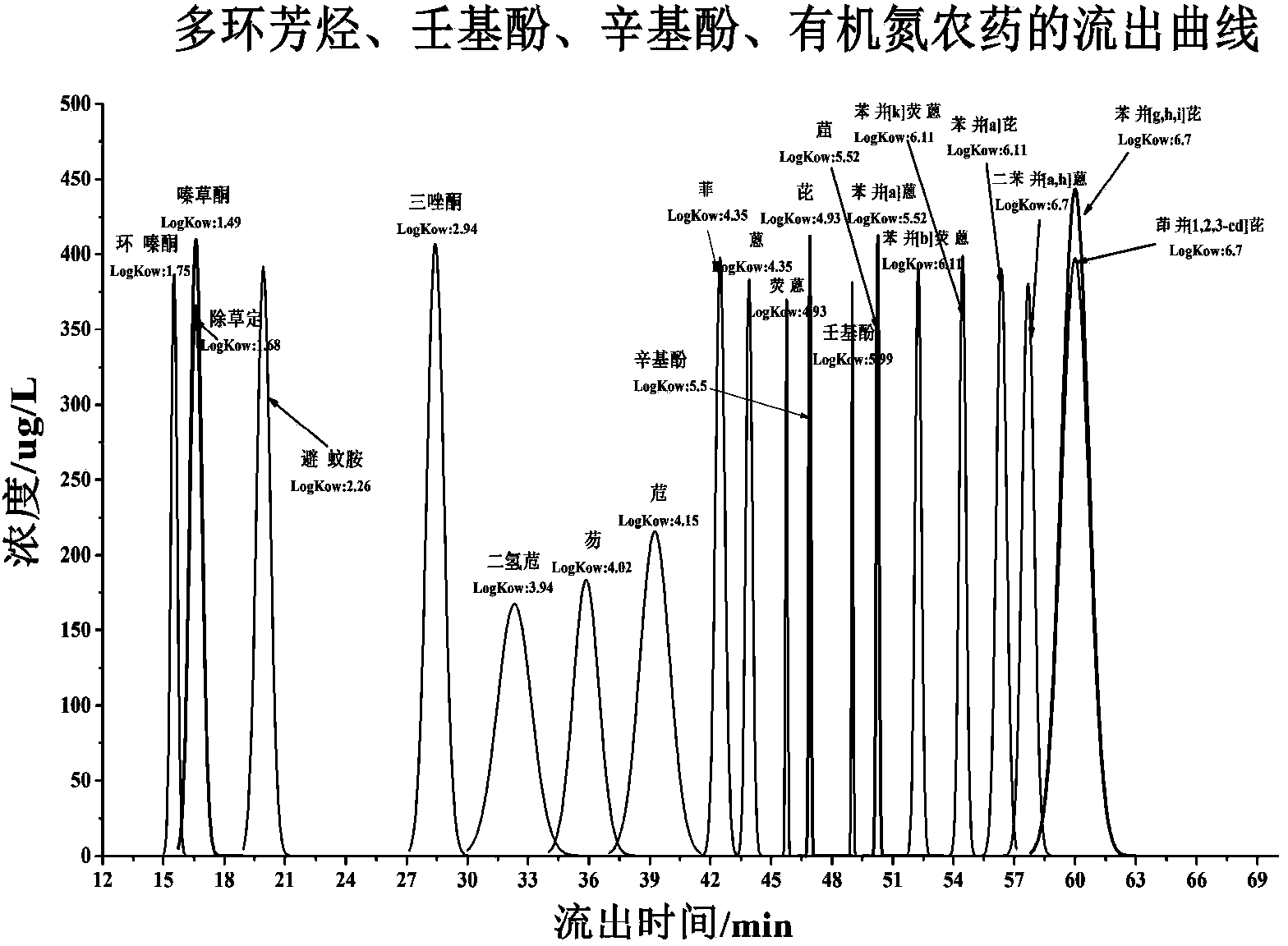
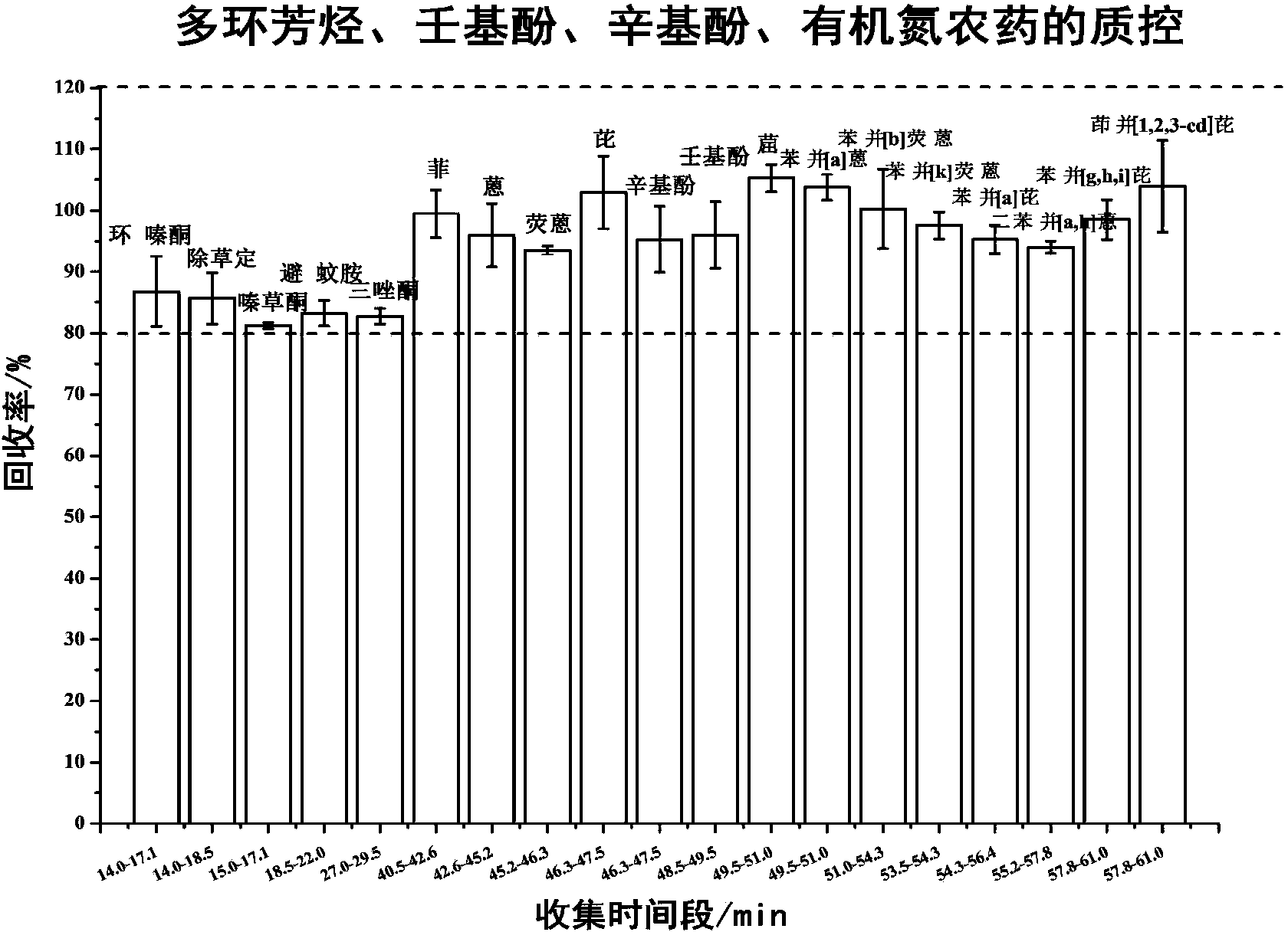
[0041] Establishment of preparative chromatographic separation technology:
[0042] (1) Establishment of the efflux curves of organic nitrogen pesticides (Benzamid, Metrizone, Hexazinone, Triadimefon, DEET), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nonylphenol, and octylphenol: , mecitrione, hexazinone, triadimefon, DEET), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nonylphenol, octylphenol standard samples were separated by preparative chromatography and the separated components were concentrated. Quantitative analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nonylphenol and octylphenol in the separated components was carried out by high performance liquid chromatography. Quantitative analysis of organic nitrogen pesticides in the separated components by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Finally, the distribution of the concentration and efflux time of the compound was obtained, and the efflux of organic nitrogen pesticides (bizamid, metrizone, hexazinone, triadimefon, DE...
Embodiment 2
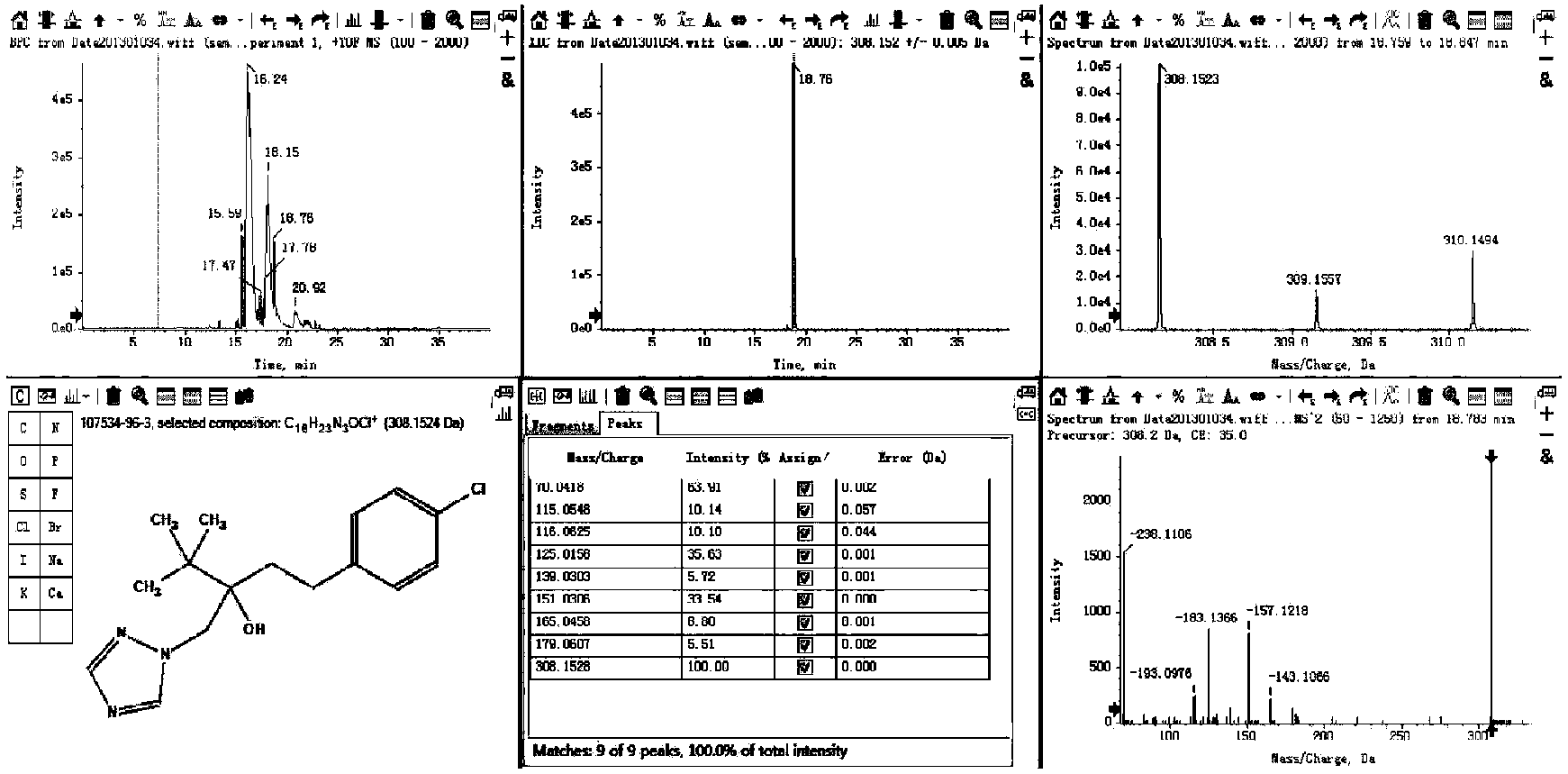
[0046] A method for identifying key toxic substances in pesticide wastewater based on daphnia magna toxicity, the steps of which are: (1) solid phase extraction: the influent of pesticide wastewater treatment plants is filtered through a glass filter with a 0.45um nylon membrane, and the amount The filtered 4L water sample was enriched by Waters Oasis HLB. The column was activated with n-hexane, dichloromethane, methanol and deionized water before use, and the flow rate was controlled at 1-2 Drops per second, each column enriches 500mL of water sample; after the extraction, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 5min to remove the water in the extraction column.
[0047] (2) Enrichment: Use 5mL of n-hexane, 10mL of dichloromethane, and 10mL of methanol to elute the influent organic matter from the solid-phase extraction column and collect the eluate, spin the eluent to evaporate, blow with nitrogen to concentrate, and replace the solvent Then dilute to 1mL and transfer to the injection v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com