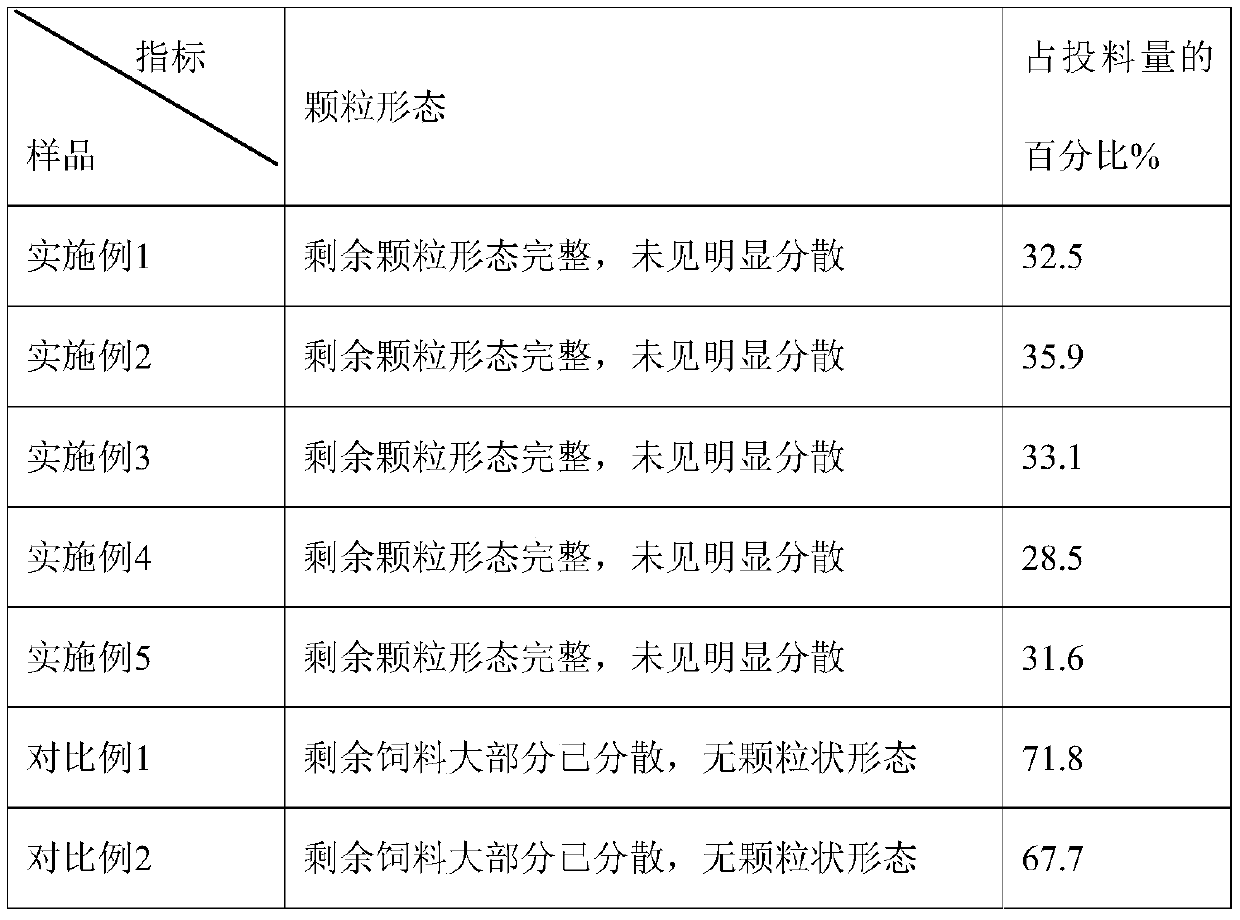
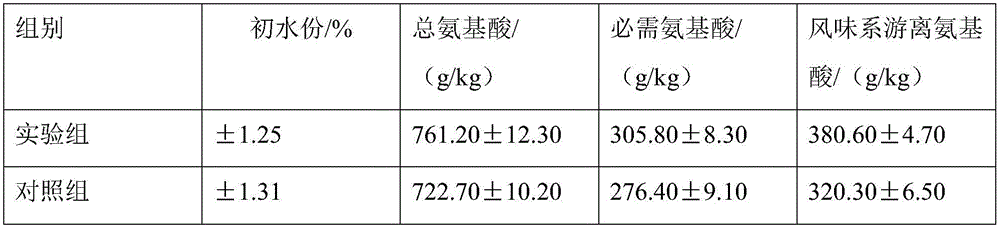
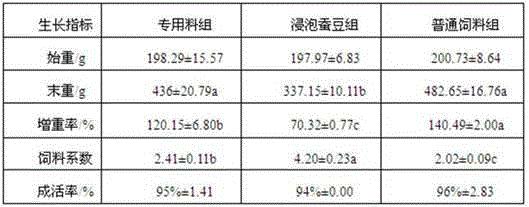
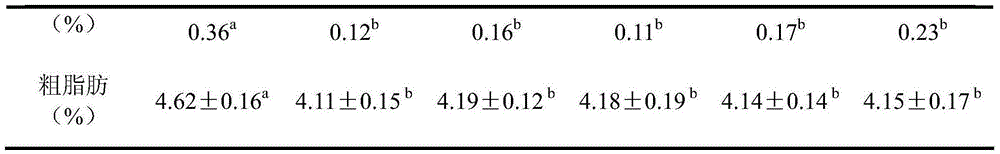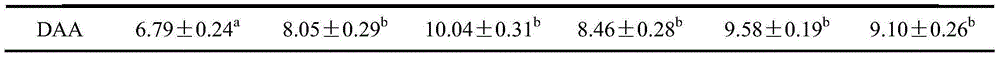Patents
Literature
32results about How to "High in umami amino acids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
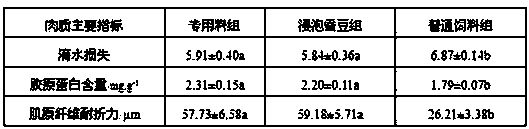
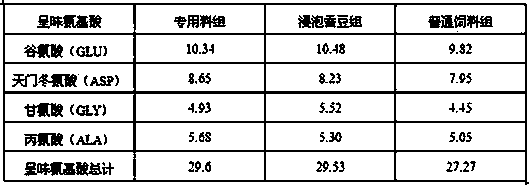
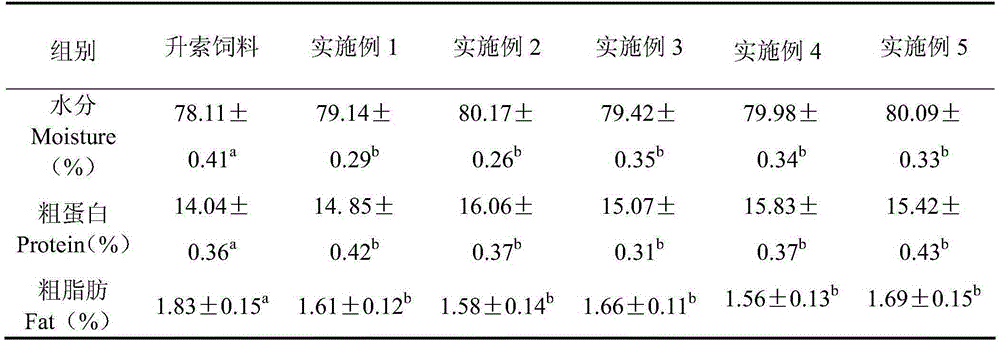
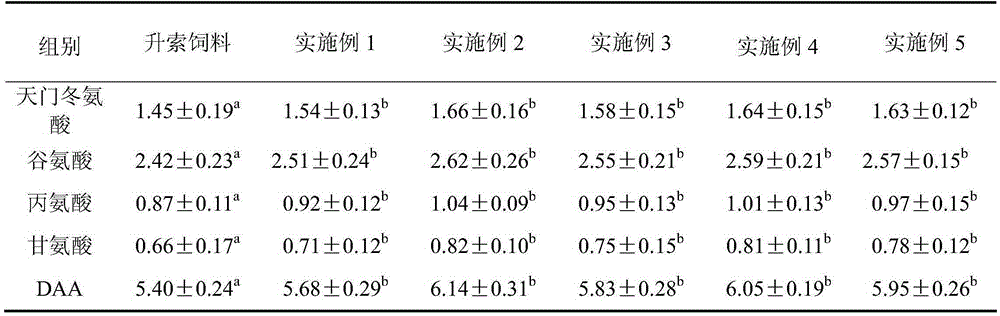
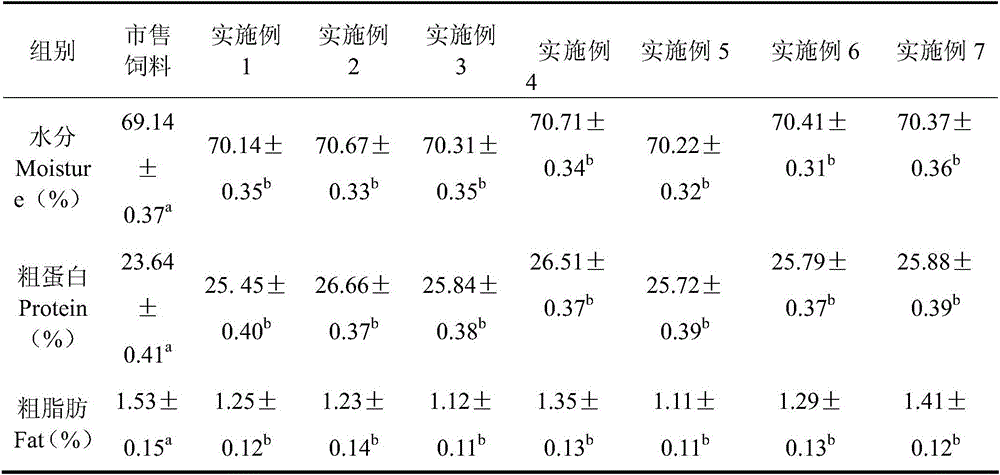
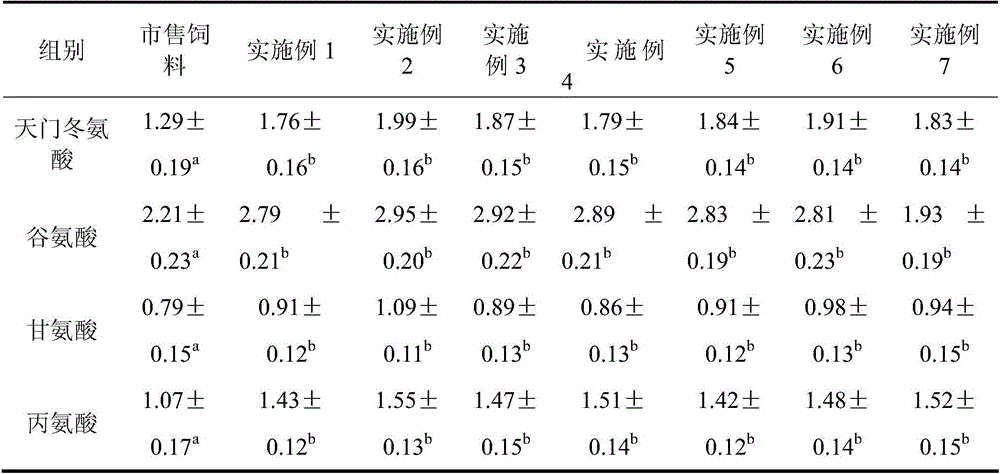
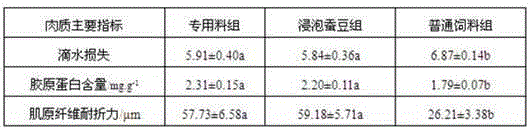
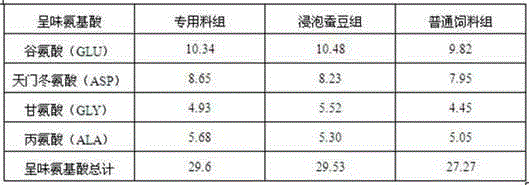
Special formula feed for improving tilapia mossambica meat quality and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103380861AImprove meat qualityFirm and crispy meatClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention relates to the field of aquatic feed, in particular to special formula feed for improving tilapia mossambica meat quality and a preparation method thereof. Ingredients in a feed formula comprise, by weight, 40-70 parts of broad bean, 2-5 parts of fish meal, 7-12 parts of bran, 9-19 parts of rapeseed dregs, 8-19 parts of peanut meal, 1-2 parts of fish oil, 0.3-0.5 part of glycine betaine, 0.4-0.6 part of choline chloride, 0.6-0.8 part of monocalcium phosphate, 0.10-0.13 part of methionine, 0.06-0.1 part of enzyme preparation, 0.02-0.03 part of allicin, 0.4-0.6 part of multivitamins and 1.0-1.2 parts of complex mineral. The preparation method of the feed is further provided. The feed can improve the tilapia mossambica meat quality to be firm, hard, crisp and tasty, improves growth performance of tilapia mossambica, reduces pollution on water quality and production cost and remarkably improves economical and social benefit.
Owner:福建省淡水水产研究所
Albumen powder richening in antimicrobial peptide fly maggot, preparation method for albumen powder and feed additive of albumen powder
ActiveCN102894186AHigh content of active ingredientsNo pollutionAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAntimikrobielle peptide
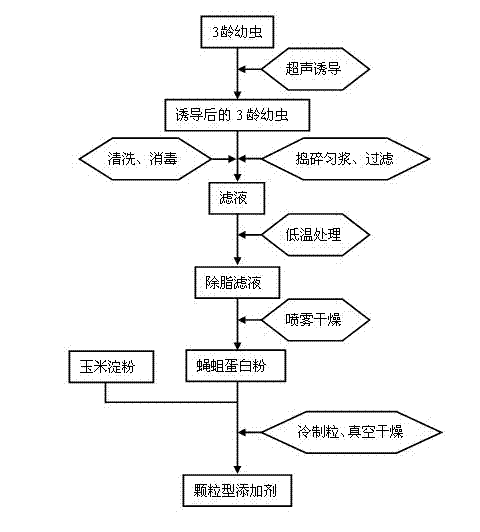
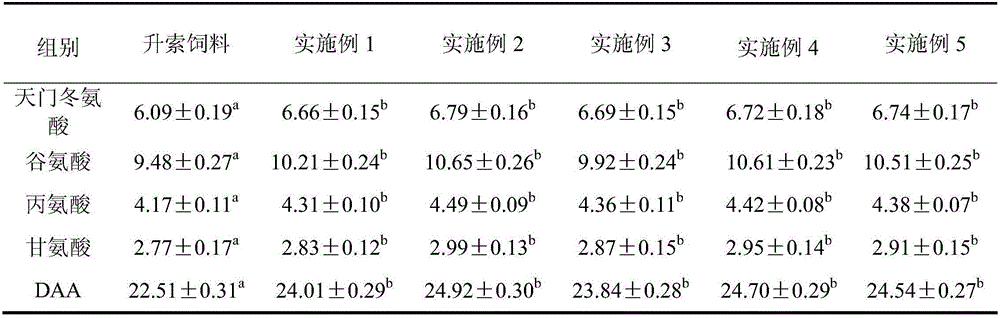
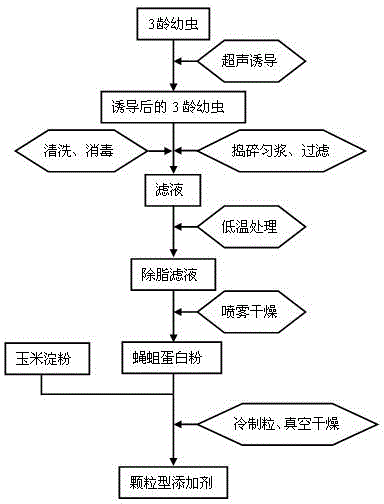
The invention discloses albumen powder richening in antimicrobial peptide fly maggot, a preparation method for the albumen powder and a feed additive of the albumen powder. The albumen powder richening in the antimicrobial peptide fly maggot is prepared by a method comprising the following steps of: (1) feeding flies, luring the flies to lay eggs and feeding larva by using feed after incubation; (2) conducting ultrasound induction on the larva; (3) continuously feeding, collecting the larva, washing, conducting disinfection treatment, and conducting tissue homogenate smashing; and (4) filtering, treating filtrate at 0-5 DEG C, removing surface lipid compositions, drying to obtain the albumen powder; adding auxiliary materials in the albumen powder, pelletizing to obtain the feed additive. A ultrasound stimulation mode under specified conditions is adopted to induce the larva to enable an antimicrobial peptide active ingredient content in a body of a housefly to obviously improve, and the feed additive has certain growth promotion and disease-resistant strengthening effects on litopenaeus vannamei, crucian and the like.
Owner:河北圣土农业科技有限公司
Special compound feed for tilapia meat quality improvement and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103960529AImprove meat qualityFirm and crispy meatClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention relates to the field of aquatic feed and particularly provides special compound feed for tilapia meat quality improvement and a preparation method thereof. The feed comprises the following components in parts by weight: 40-70 parts of broad bean, 2-5 parts of fish meal, 7-12 parts of bran, 9-19 parts of rapeseed mea1, 8-19 parts of peanut meal, 1-2 parts of fish oil, 0.3-0.5 part of glycine betaine, 0.4-0.6 part of choline chloride, 0.6-0.8 part of monocalcium phosphate, 0.10-0.13 part of methionine, 0.06-0.1 part of enzyme preparation, 0.02-0.03 percent of garlicin, 0.4-0.6 percent of compound vitamin and 1.0-1.2 parts of composite mineral salt. The invention also provides a preparation method of the feed. The feed has the benefits that the tilapia meat quality can be improved, so that tilapia meat is hard and crisp; and the growth performance of tilapia is improved, so that the pollution to the water quality is reduced, and the production cost is reduced, therefore, the economic and social benefits are remarkable.
Owner:福建省淡水水产研究所
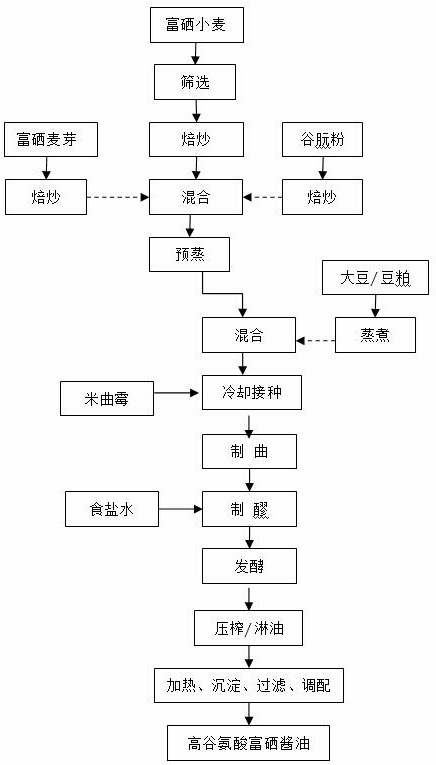
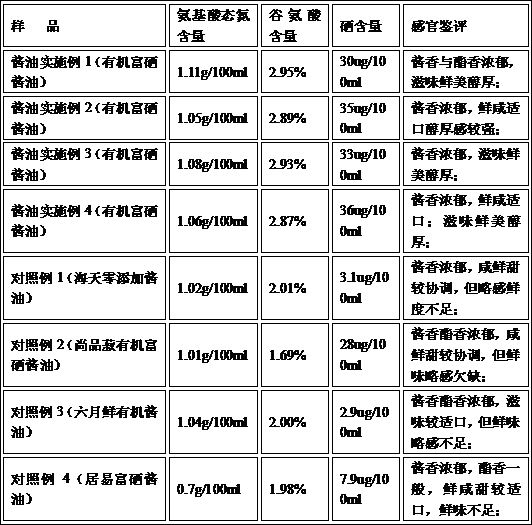
Brewing method of selenium-rich soy sauce with high glutamic acid content
The invention discloses a brewing method of selenium-enriched soy sauce with high glutamic acid content. The brewing method comprises the following steps: step one, treating soybeans or bean pulp, vital gluten, organic selenium malt and selenium-enriched wheat to prepare soy sauce koji; step two, mixing an edible salt solution with a yeast material to prepare soy sauce mash, and conventionally fermenting the soy sauce mash for 90-360 days; and step three, performing squeezing or spraying oil to obtain the selenium-rich soy sauce with high glutamic acid content. The invention provides a novel brewing method for producing the selenium-rich soy sauce with high glutamic acid content and increasing the glutamic acid content of the originally brewed soy sauce, and a fundamental problem of insufficient delicate flavor of the originally brewed soy sauce (without monosodium glutamate and a freshener) can be solved.
Owner:好记食品酿造股份有限公司
Compound feed for Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and preparation method of compound feed
InactiveCN104957437AMeet nutritional needsImprove qualityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFish oilRapeseed
The invention relates to a fish feed and in particular relates to a compound feed for Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and a preparation method of the compound feed. The compound feed for Pelteobagrus fulvidraco is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of fish meal, 8-15 parts of barley, 7-14 parts of rapeseed meal, 5-9 parts of soybean meal, 6-10 parts of honeysuckle flower powder, 3-8 parts of Portulaca oleracea powder, 3-7 parts of licorice powder, 3-7 parts of green bean powder, 3-5 parts of Lycium barbarum powder, 2-6 parts of mulberry powder, 2-6 parts of fish oil, 1-5 parts of tangerine powder, 1-4 parts of shell powder, 1-4 parts of honey, 1-4 parts of olive oil and 1-4 parts of compound vitamin. Pelteobagrus fulvidraco fed by the Pelteobagrus fulvidraco compound feed has low feed coefficient, and has high crude protein content, low crude fat content and high flavor amino acid content in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco muscles.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIXING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Odontobutis obscurus compound feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105325774AMeet nutritional needsImprove qualityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffFish oilMushroom
The invention relates to fish feed and particularly relates to odontobutis obscurus compound feed. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the odontobutis obscurus compound feed. The odontobutis obscurus compound feed provided by the invention is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 20 to 29 parts of fish meal, 6 to 15 parts of clam worms, 5 to 15 parts of coarse rice powder, 5 to 16 parts of sea clam shells, 7 to 16 parts of Chinese yams, 3 to 11 parts of figs, 4 to 13 parts of arrowheads, 4 to 14 parts of taros, 3 to 10 parts of mushrooms, 2 to 9 parts of broccolis, 2 to 11 parts of longan kernels, 3 to 10 parts of isatis roots, 4 to 14 parts of scutellaria baicalensis, 3 to 9 parts of fish oil, 1 to 4 parts of olive oil and 1 to 4 parts of compound multi-vitamin. After the odontobutis obscurus compound feed provided by the invention is used for feeding, the feed coefficient of odontobutis obscurus feed is low, and odontobutis obscurus meat has high content of crude protein, low content of crude fat and high content of flavor amino acids.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIYUAN INTELLIGENT TECH
Elopichthys bambusa compound feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105325775AMeet nutritional needsImprove qualityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAnimal sciencePumpkin seed
The invention relates to fish feed, in particular to elopichthys bambusa compound feed. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the elopichthys bambusa compound feed. The elopichthys bambusa compound feed comprises the following components in parts by mass: 18 to 27 parts of fish meal, 6 to 15 parts of dried fish, 4 to 18 parts of shrimp head meal, 5 to 16 parts of sweet potato meal, 7 to 19 parts of euphorbia humifusa, 4 to 17 parts of herba polygoni avicularis, 5 to 18 parts of plantago depressa, 4 to 17 parts of geranium strictipes, 3 to 16 parts of wax gourd, 2 to 9 parts of arrowhead, 2 to 13 parts of tricholomagambosum, 3 to 14 parts of pumpkin seed, 4 to 14 parts of semen torreya, 3 to 9 parts of fish oil, 1 to 4 parts of olive oil and 1 to 4 parts of compound Vitamin. After the elopichthys bambusa compound feed provided by the invention is fed, the elopichthys bambusa feed coefficient is low, the crude protein content in the elopichthys bambusa muscle is high, the crude fat content is low, and the flavor amino acid content is high.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIYUAN INTELLIGENT TECH
Blackbone chicken compound feed and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105851651AMeet nutritional needsNutritional balanceAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsFlavorAnimal science
The invention provides a blackbone chicken compound feed and further relates to a preparing method of the blackbone chicken compound feed. The blackbone chicken compound feed is prepared from, by mass, 21-29 parts of corn, 5-15 parts of soybean meal, 4-15 parts of squid meal, 5-14 parts of fish meal, 6-17 parts of almond kernels, 3-11 parts of bitter herb, 5-16 parts of allium macrostemon bunge, 5-14 parts of copperleaf herb, 3-10 parts of horseweed herb, 4-15 parts of brasenia schreberi, 3-15 parts of herba taraxaci, 3-10 parts of herba portulacae, 1-6 parts of lysine, 1-5 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 1-4 parts of methionine, 1-4 parts of microelements and 1-3 parts of olive oil. After blackbone chicken are fed with the blackbone chicken compound feed, the feed coefficient of blackbone chicken is low; in blackbone chicken meat, the content of crude protein is high, the content of crude fat is low, and the content of flavor amino acid is high.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIXING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
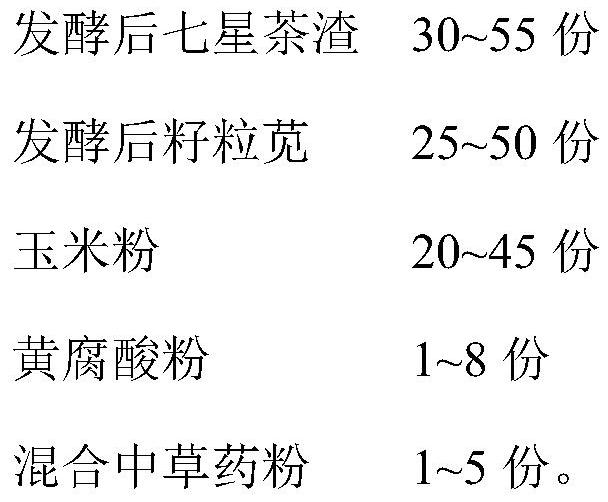
Seven-star tea residue fermented feed for improving quality of pigs bred by using fermentation bed, and preparation method of seven-star tea residue fermented feed
ActiveCN109043166AImprove qualityImprove immunityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffChemistryPollutant
The invention relates to the technical field of feed, in particular to seven-star tea residue fermented feed for improving the quality of pigs bred by using a fermentation bed, and a preparation method of the seven-star tea residue fermented feed. The feed is prepared from 320-60 parts of fermented seven-star tea residue, 20-55 parts of fermented grain amaranth, 15-50 parts of corn flour, 0.5-10 parts of fulvic acid powder and 0.5-5 parts of mixed Chinese herbal medicine powder. The fermented seven-star tea residue contains Chinese herbal medicine components such as semen coicis, fructus crataegi and liquorice root, and is combined with the mixed Chinese herbal medicine powder, so that the effects of improving the immunity of the pigs, promoting the growth of the pigs and improving the pork quality are achieved; all the components have a synergistic effect, so that the growth of microorganisms in the fermentation bed is promoted, the ability to degrade pollutants is improved, and the breeding environment of the pigs is purified.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PUCHUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
Compound feed for channa maculate and preparation method of compound feed
InactiveCN105076830AIncrease crude protein contentLow in crude fatAnimal feeding stuffPumpkin seedFish oil
The invention relates to fish feed and particularly relates to compound feed for channa maculate; the invention further relates to a preparation method of the compound feed for the channa maculate. The compound feed for the channa maculate comprises the following components in parts by mass: 20 to 30 parts of fish meal, 8 to 15 parts of corn flour, 7 to 14 parts of shrimp meal, 5 to 9 parts of dried blood, 6 to 10 parts of semen raphani, 3 to 7 parts of medicated leaven, 3 to 7 parts of pumpkin seeds, 2 to 5 parts of eclipta, 2 to 6 parts of ganoderma lucidum, 1 to 5 parts of three-colored amaranth, 1 to 4 parts of citrus chirocarpus, 3 to 8 parts of spora lygodii, 1 to4 parts of poria cocos, 2 to 6 parts of fish oil, 1 to 4 parts of olive oil and 1 to 4 parts of calcium hydrophosphate, after using the compound feed for the channa maculate provided by the invention, the feed coefficient of the channa maculate is low, and in the muscle of the channa maculate, the crude protein content is high, the content of crude fat is low, and the flavor amino acid content is high.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIYUAN INTELLIGENT TECH
Application of feed additive to soft-shelled turtle feed capable of improving meat quality and growing performance of soft-shelled turtles
PendingCN108157614AIncrease weight gainIncrease specific growth rateFood processingAnimal feeding stuffGrowth phaseFood additive
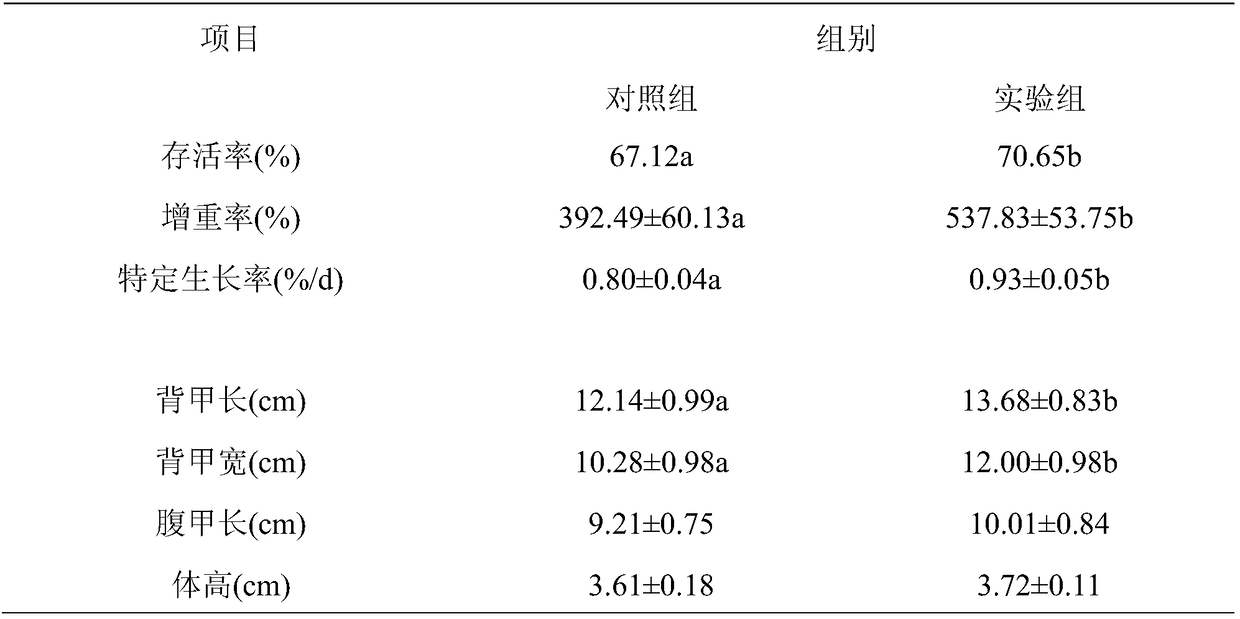
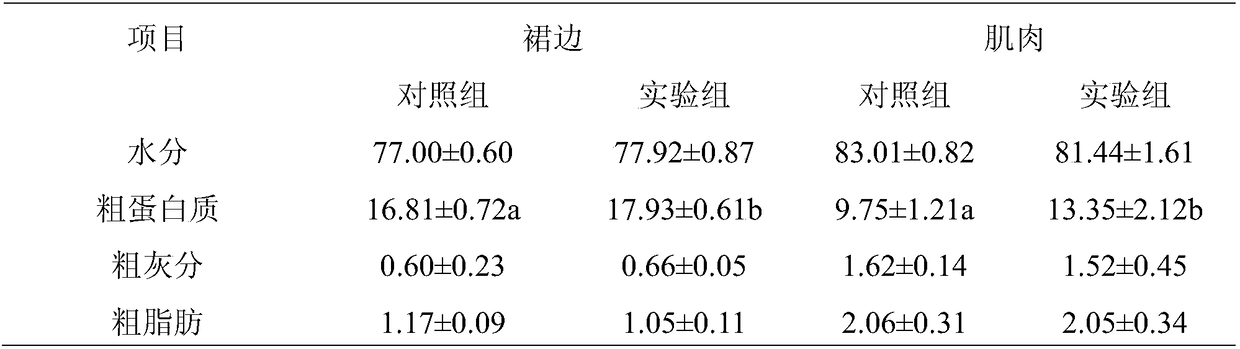
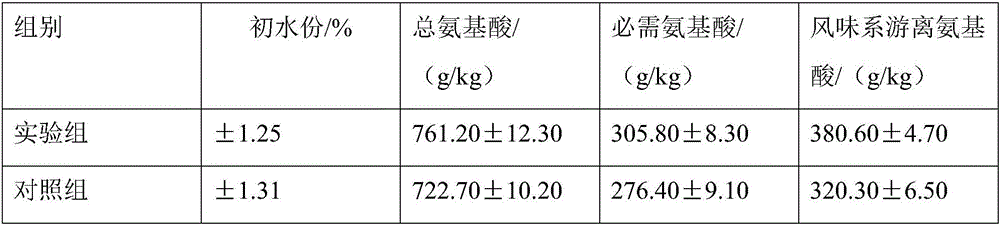
The invention discloses an application of a feed additive to a soft-shelled turtle feed capable of improving meat quality and growing performance of soft-shelled turtles, and belongs to the technicalfield of feed additives. The feed additive comprises 10-45% of glycerol monolaurate, 10-30% of glyceryl dilaurate, 30-55% of glycerol monostearate and 5-15% of a carrier. The glycerol monolaurate, theglyceryl dilaurate, the glycerol monostearate are compounded according to the appropriate content and proportion, so that the feed additive is prepared. The feed additive can be used for trionyx sinensis during growth phase, the growing properties of the trionyx sinensis can be improved, and further, the breeding economic benefits are increased. The feed additive can notably increase the muscle of the trionyx sinensis and the content of crude proteins, the total content of amino acids, the content of necessary amino acids and the content of palatable taste amino acids in turtle edges of the trionyx sinensis can be notably increased, the nutritional quality, the mouth feel and the flavor of the trionyx sinensis are effectively improved, and contradiction between growth rate and quality issolved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Siganus oramin mixed feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105104798AMeet nutritional needsImprove qualityAnimal feeding stuffFish oilChrysanthemum indicum
The invention relates to fish feed and especially relates to Siganus oramin mixed feed and a preparation method of the Siganus oramin mixed feed. The Siganus oramin mixed feed comprises, by mass, 23-30 parts of fish meal, 7-15 parts of wheat bran, 8-14 parts of rice bran, 4-9 parts of corn flour, 6-10 parts of fructus forsythia, 3-8 parts of folium isatidis, 3-7 parts of humifuse euphorbia herb, 3-7 parts of pith of Juncus effusus L., 2-5 parts of paris polyphylla, 2-6 parts of fortune eupatorium herb, 1-5 parts of chrysanthemum indicum, 1-4 parts of radix sophorae subprostratae, 2-6 parts of fish oil, 1-4 parts of honey, 1-4 parts of olive oil and 1-4 parts of composite vitamins. Through use of the Siganus oramin mixed feed, Siganus oramin has a low feed coefficient and has high muscle crude protein content and high flavor amino acid content.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIXING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Purple pennisetum purpureum feed particle additive and preparation method and application thereof
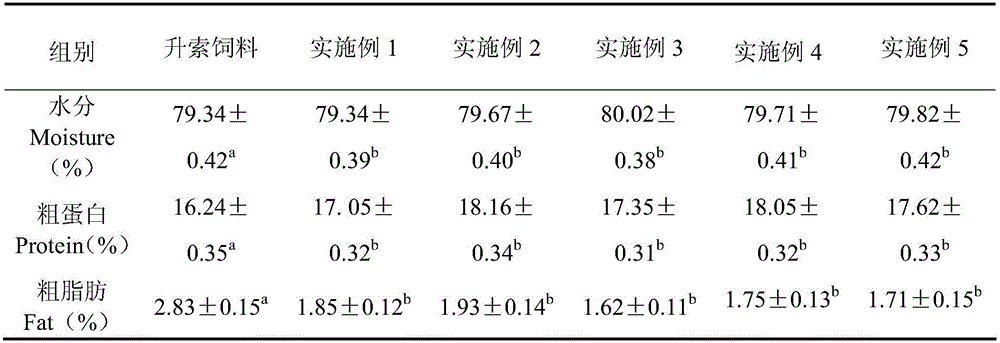
PendingCN110236003AHigh in umami amino acidsImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffPennisetum purpureumBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to the technical field of feed molds and feed processing, in particular to a purple pennisetum purpureum feed particle additive and a preparation method and application thereof. The purple pennisetum purpureum feed particle additive comprises an active ingredient core body, a permeation layer, and a gastric soluble layer, wherein the active ingredient core body is the inner core, the core body is covered with the permeation layer, and the permeation layer is covered with the gastric soluble layer; besides, a plurality of drainage holes are formed in the permeation layer, the drainage holes penetrate through the permeation layer, and the pore diameter of the parts, at the end of the gastric soluble layer, of the drainage holes is 3-4 times the diameter of the parts, at the end of the core body, of the drainage holes. Due to the structure of the purple pennisetum purpureum feed particle additive, the release ability of active ingredients and the shelf life of the additive can be effectively improved. The active ingredients of the feed additive comprise fermented pennisetum purpureum, fermented radix puerariae, aloe polysaccharides, and an amino acid chelating solution. By use of the additive, the dissolution rate of the gastric soluble layer in the gastric juice of a buffalo can be effectively increased, and the palatability, tenderness and flavor of the beef can be improved.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
Crucian carp feed for reducing feed coefficient and preparation method of crucian carp feed
InactiveCN106721599AImprove qualityImprove palatabilityFood processingClimate change adaptationAnimal scienceBran
The invention discloses a crucian carp feed for reducing a feed coefficient and a preparation method of the crucian carp feed. The crucian carp feed is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 700-750 parts of perillafrutescens oil meal, 6-10 parts of calcium gluconate, 12-15 parts of tomatoes, 24-26 parts of goat milk, 5-7 parts of a coconut powder, 3-5 parts of a pleurotus eryngii powder, 34-36 parts of corn germ meal, 52-54 parts of silkworm chrysalis meal, 7-9 parts of lard oil, 12-15 parts of lythrum salicaria, 5-6 parts of caviar, 52-56 parts of sorghum flour, 35-37 parts of sesame bran, 24-26 parts of black glutinous rice flour, 17-19 parts of ginger juice, 0.5-0.8 part of activated lactobacillus, 15-17 parts of a spaghetti squash powder, 12-16 parts of dried meat floss, 5-7 parts of red bean paste and 3-4 parts of sodium alginate. The feed provided by the invention meets nutritional requirements of crucian carps on protein, minerals, vitamins and the like, and has higher quality, good palatability and nutrients easy to be adsorbed; after feeding the feed provided by the invention, the crucian carp feed coefficient is reduced; the content of crude protein in muscles of crucian carps is increased; the content of crude fat is reduced; the content of flavoring amino acid is increased.
Owner:何俊
Seafood frozen dumplings and production method thereof
InactiveCN104757391AImprove stabilityImprove frost resistanceProtein composition from fishFood preparationAquatic productFish skin
The invention provides seafood frozen dumplings and belongs to the technical field of processing of aquatic products. According to the seafood frozen dumplings, 1.5%-8.0% (by mass percent) of collagen powder is added into frozen dumpling chopped meat; and 1.0%-3.0% (by mass percent) of the collagen powder is added into dumpling wrappers of the frozen dumpling meat. According to the dumpling wrappers and stuffing prepared by the method, the problems that the frozen dumpling wrappers are easy to break and seafood meat cannot be frozen for a long period are solved; and a method for producing the stuffing by the seafood meat and producing the collagen by fish skins is further improved, so that the seafood stuffing is stable and can be stored for long time, and the zero cracking effect of the dumpling wrappers is realized.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Fujian white rabbit compound feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105795148AMeet nutritional needsImprove qualityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffYeastFlavor
The invention relates to feed, in particular to Fujian white rabbit compound feed.The invention further relates to a preparation method of the Fujian white rabbit compound feed.The Fujian white rabbit compound feed is prepared from, by mass, 21-29 parts of straw powder, 15-20 parts of soybean cakes, 5-15 parts of pea powder, 5-10 parts of herba artemisiae scopariae, 4-11 parts of artemisia annua, 3-11 parts of plantago depressa, 5-10 parts of cabbage, 5-10 parts of garlic leaves, 3-10 parts of tenebrio molitor powder, 4-8 parts of endothelium corneum gigeriae galli, 3-9 parts of wheat bran, 2-5 parts of arginine, 1-4 parts of methionine, 2-6 parts of wine yeast, 3-9 parts of bone powder and 1-4 parts of salt.The feed coefficient of Fujian white rabbits fed with the Fujian white rabbit compound feed is low, and muscles of Fujian white rabbits are high in crude protein content, low in crude fat and high in flavor amino acid.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIXING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Processing method of fresh yeast extract paste chicken essence cube
InactiveCN107495272AStrong fragranceImprove decomposition rateLipidic food ingredientsUltra high pressure food processesFlavorChicken Flavor
The invention relates to a processing method of fresh yeast extract paste chicken essence cubes. The processing method is characterized in that yeast extract paste is produced with baker's yeast, beer yeast and torula yeast as raw materials and is used for enhancing flavor and taste and balancing mouth feel; chicken paste is used for enhancing initial flavor; chicken oil brings a natural chicken fragrance to the chicken essence cubes. Through steps of pectin slurry coating, granulation and cube pressing, the raw materials are not liable to deteriorate, and problems that chicken essence is easy to absorb moisture and cake and is liable to deteriorate are solved. The chicken essence cubes have mellow and thick chicken flavor, has outstanding delicate taste and is improved in entire mouth feel.
Owner:安徽悠咔食品有限公司
Compound feed for maccullochella peelii and preparation method of compound feed
The invention relates to a fish feed, in particular to a compound feed for maccullochella peelii, and further relates to a preparation method of the compound feed for the maccullochella peelii. The compound feed for the maccullochella peelii comprises the following components in parts by mass: 21 to 32 parts of fish meal, 7 to 15 parts of small trash fish, 5 to 14 parts of pork powder, 6 to 16 parts of soybean meal, 6 to 14 parts of chinese holly, 3 to 9 parts of pollen pini, 4 to 10 parts of rhizoma atractylodis, 3 to 8 parts of walnut kernel oil, 3 to 7 parts of cloves, 2 to 6 parts of sophora japonica, 2 to 8 parts of lithospermum, 3 to 9 parts of rubia cordifolia, 2 to 8 parts of panax notoginseng, 2 to 6 parts of fish oil, 1 to 4 parts of olive oil and 1 to 4 parts of compound vitamins. After the compound feed for the maccullochella peelii is fed, the feed coefficient of the maccullochella peelii is low; the coarse protein content in muscles of the maccullochella peelii is high, the coarse fat content is low, and the flavor amino acid content is high.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIYUAN INTELLIGENT TECH
Oreochromis sp formula feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105076835AExcellent compound feedMeeting nutritional needsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBarbed Skullcap HerbFish oil
The invention relates to a fish feeder, in particular to an oreochromis sp formula feed, and a preparation method of the oreochromis sp formula feed. The oreochromis sp formula feed comprises the following components in parts by mass: 22 to 31 parts of fish meal, 7 to 15 parts of corn protein powder, 7 to 14 parts of stillage, 4 to 9 parts of bone powder, 6 to 12 parts of herba hyperici japonica, 3 to 7 parts of barbed skullcap herb, 3 to 7 parts of nutgrass galingale rhizome, 2 to 7 parts of pagoda tree flower bud, 2 to 6 parts of Indian kalimeris herb, 1 to 5 parts of platycodon grandiflorum, 1 to 4 parts of broom cypress, 3 to 8 parts of fiddlehead, 2 to 6 parts of fish oil, 1 to 4 parts of honey, 1 to 4 parts of olive oil, and 1 to 4 parts of monocalcium phosphate. The oreochromis sp formula feed has the advantages that after feeding, the coefficient of the oreochromis sp is low; in muscles of the oreochromis sp, the content of crude protein is high, the content of crude fat is low, and the content of flavor amino acid is high.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIYUAN INTELLIGENT TECH
Tilapia mossambica fishy smell removing formula feed and preparation method thereof
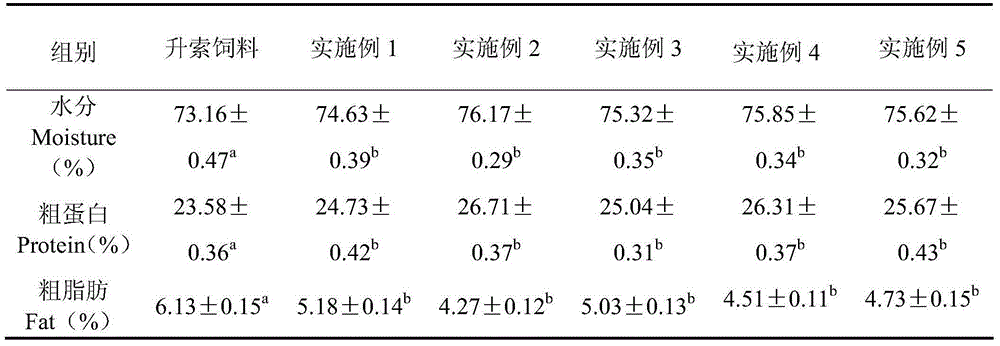
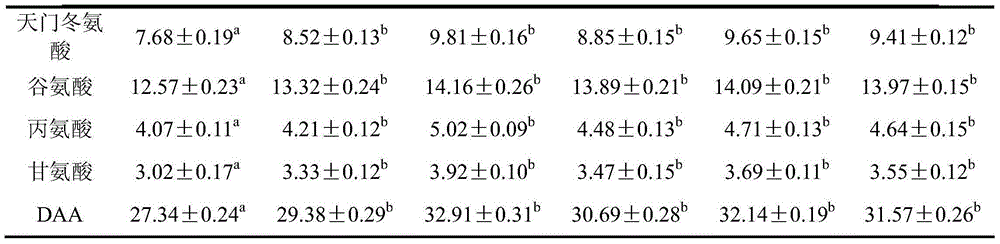
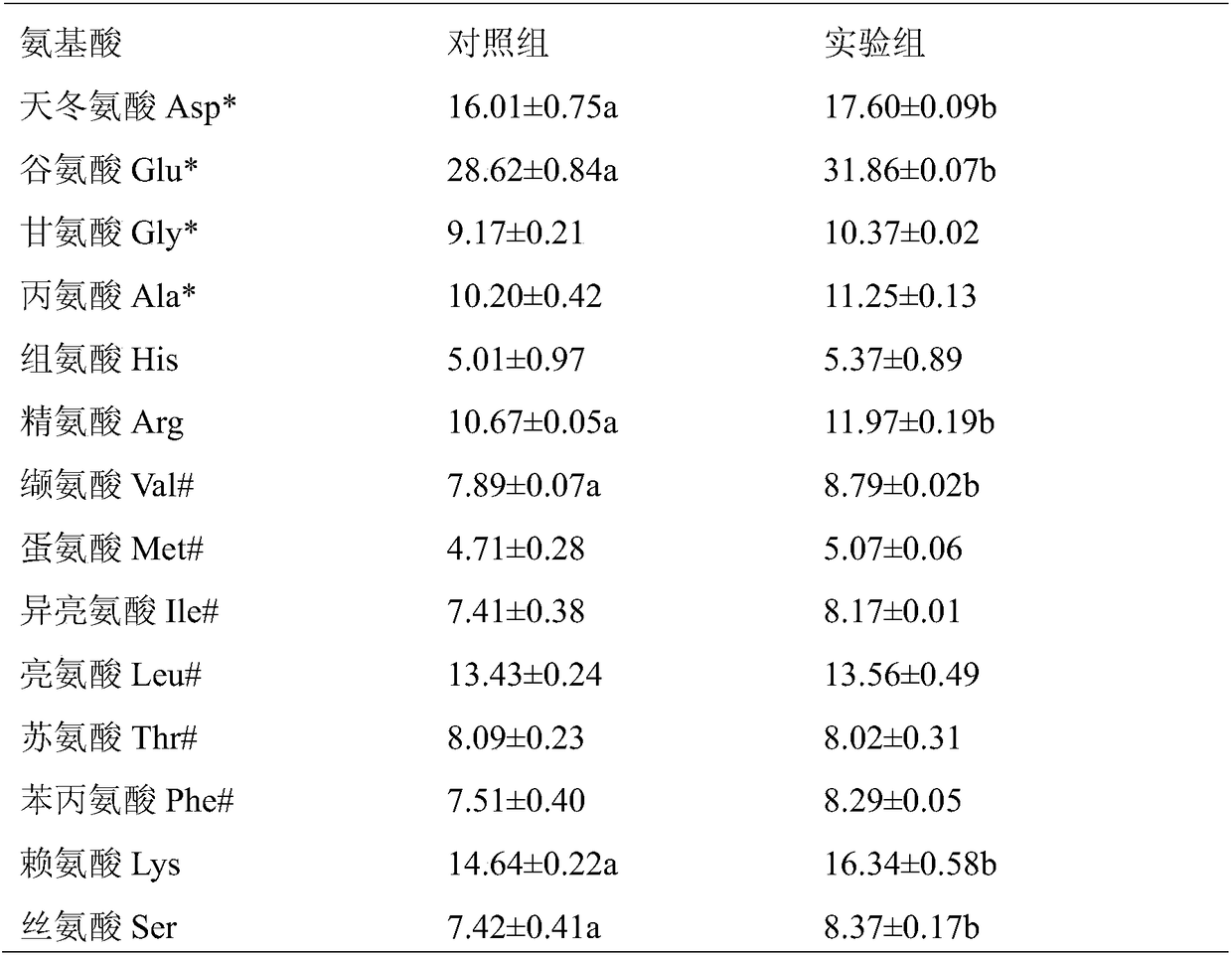
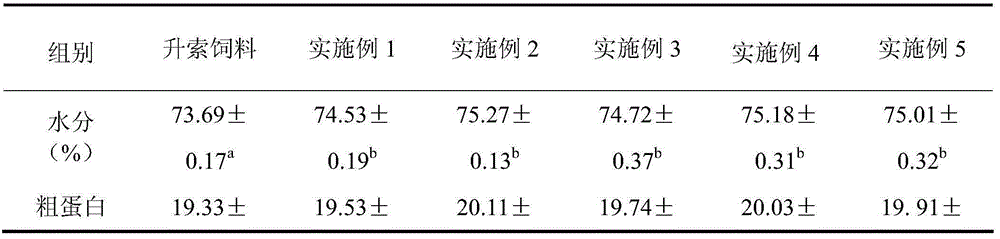
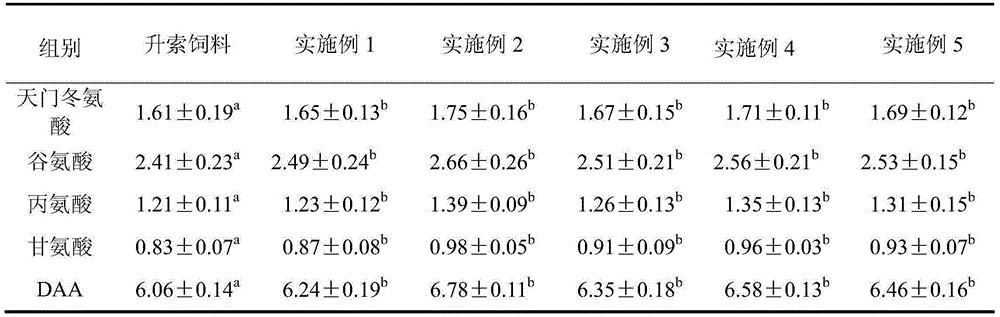
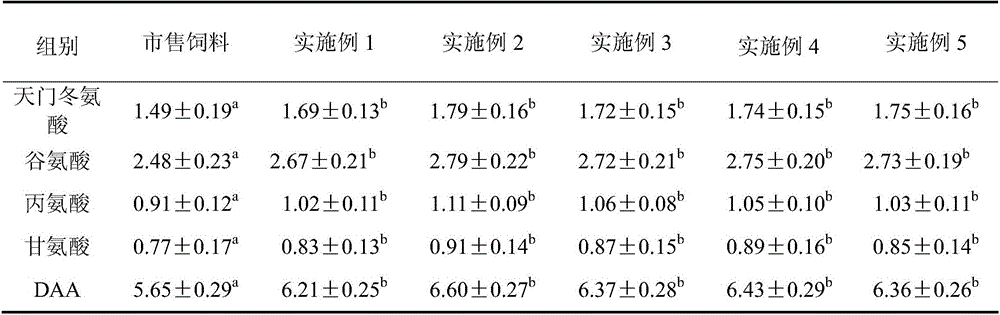
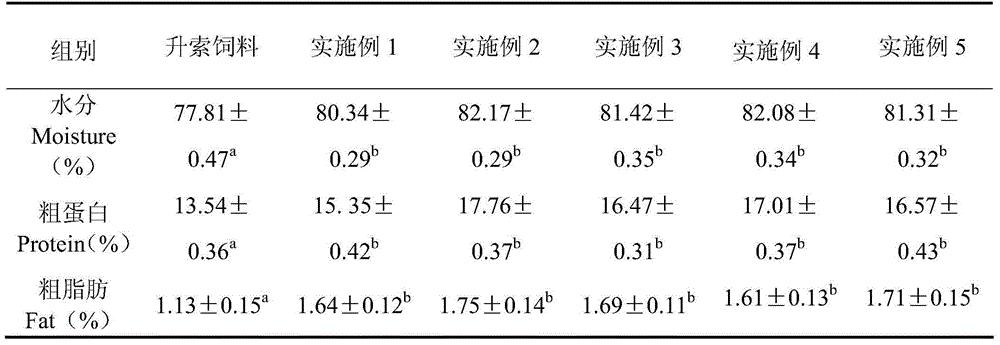
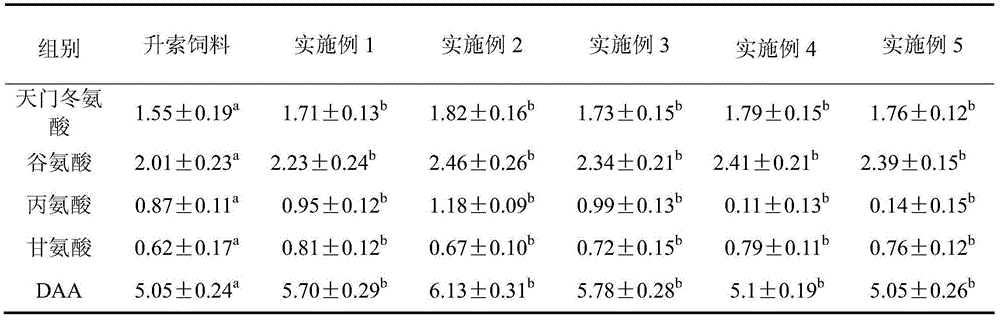
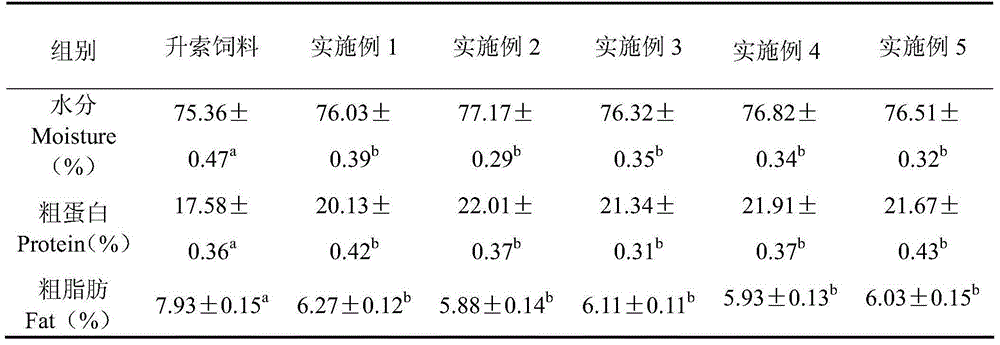
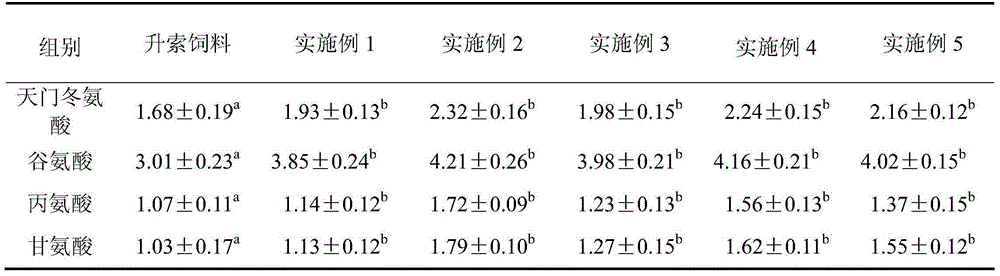
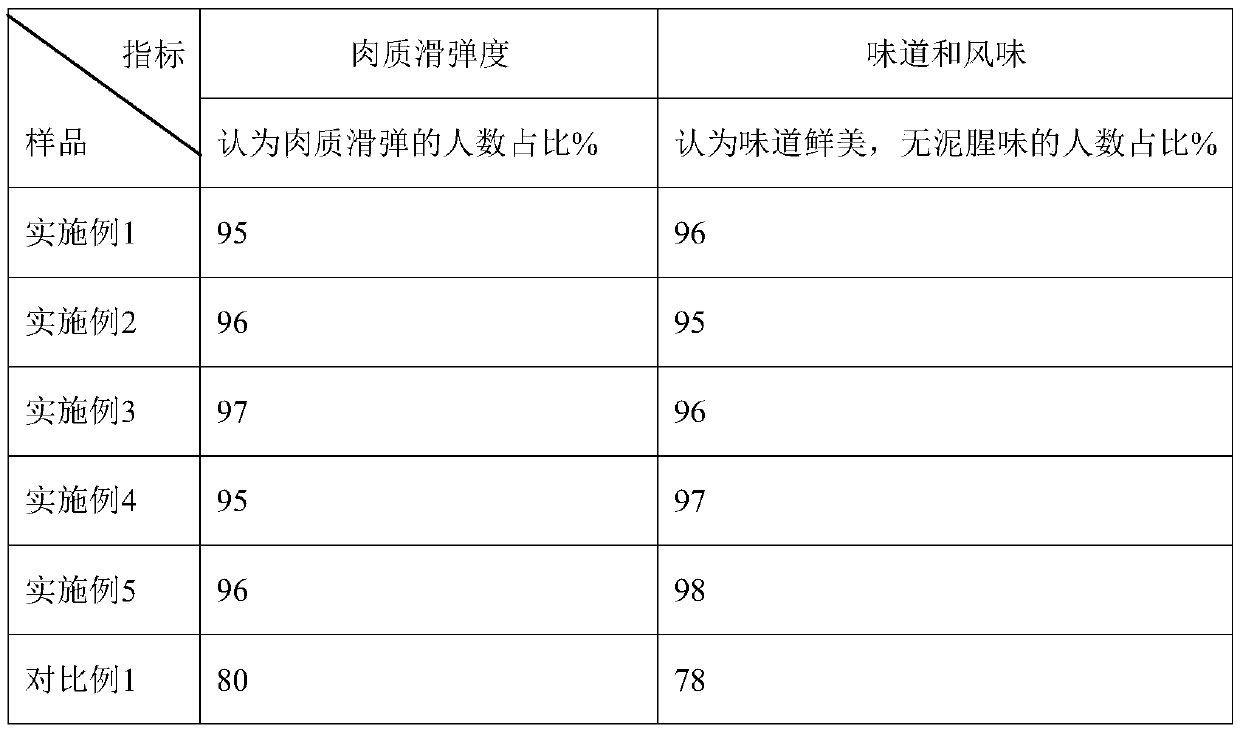
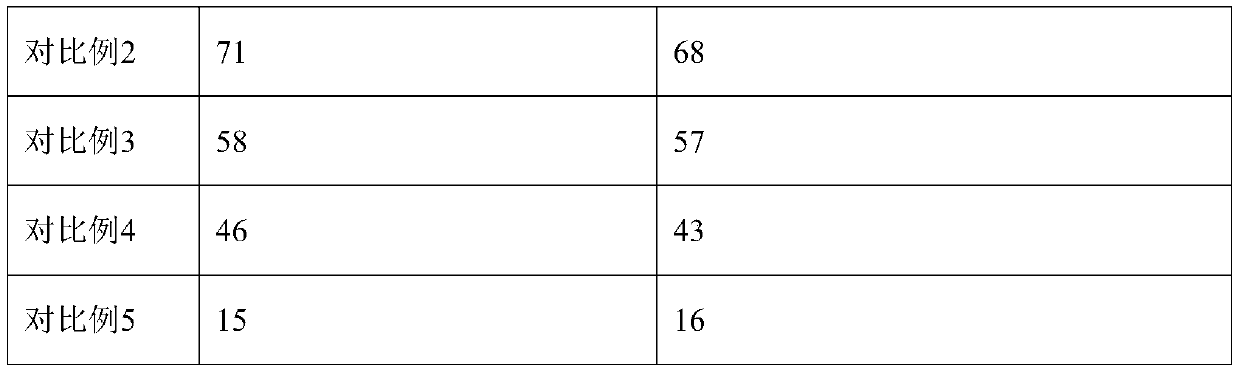
InactiveCN111406853AHigh in umami amino acidsMeet all needsFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyVitamin C
The invention discloses tilapia mossambica fishy smell removing formula feed. The feed includes, in parts by weight, 10-20 parts of fish meal, 10-25 parts of soybean meal, 5-10 parts of marine organism protein hydrolysate, 10-20 parts of rapeseed meal, 10-20 parts of peanut bran, 1-5 parts of fish oil, 1-5 parts of soybean oil, 0.2-1 part of Calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.2-1 part of choline chloride, 0.2-0.6 part of vitamin C and 0.1-0.3 part of multi-vitamins. The marine organism protein hydrolysate is added on the basis of conventional fish feed components; the marine organism protein hydrolysate can increase the taste components having delicate peptides and amino acids in fish bodies; and comprehensive demands of tilapia mossambica for nutrients at growth stages can be effectively met, the delicate amino acid content of the tilapia mossambica can be increased, so that the tilapia mossambica can be delicious in taste and unique in flavor.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN SUNTAI FEEDSTUFF CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of bream and bream hybrid
ActiveCN105684962BImprove adaptabilitySuitable for mass productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaHabitOperability
The invention provides a method for preparing hybrids of bream and triangular bream. The method includes parent selection, intensive cultivation, artificial induction of labor, artificial insemination, hatching and cultivation of seedlings, and other technical links. The invention has strong operability. The obtained hybrid has a beautiful body and obvious growth advantages, and has a mild temperament, does not like jumping, has strong stress resistance, is easy to catch, and has a high survival rate for long-distance transportation of fish species and adults; The degree of tenderness is better than that of triangular bream, and the content of umami amino acids is higher; it has a wider range of feeding habits, better resistance to hypoxia and stress; the hybrid is sexually fertile, providing a source for further tapping the breeding potential of hybrid offspring It is possible to breed new breeds with excellent traits and stable genetics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Nutritive lick blocks suitable for beef cattle and preparation method of nutritive lick blocks
InactiveCN106578436ARaise spiritsImprove meat qualityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffLycopeneAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses nutritive lick blocks suitable for beef cattle and a preparation method of the nutritive lick blocks. The nutritive lick blocks comprise the following raw materials of coarse salt, molasses fermentation liquor, ostrica cruda, zinc sulfate, iron chloride, potassium carbonate, calcium carbonate, manganese oxide, quercetin, lycopene, polyphenols, selenocysteine, genistein, glucurolactone and marjoram essential oil. The nutritive lick blocks disclosed by the invention are convenient to eat and comprehensive in nutrients, and can timely complement nutrient components desired for the growth of the beef cattle.
Owner:方良云
A special compound feed for improving tilapia meat quality and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103960529BImprove meat qualityFirm and crispy meatClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyPeanut meal
The invention relates to the field of aquatic feed, and specifically provides a special compound feed for improving tilapia meat quality and a preparation method thereof. The parts by weight of each component of the feed formula are: 40-70 parts of broad beans, 2-5 parts of fish meal, 7-12 parts of bran, 9-19 parts of rapeseed meal, 8-19 parts of peanut meal, 1-2 parts of fish oil 0.3-0.5 parts of betaine, 0.4-0.6 parts of choline chloride, 0.6-0.8 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.10-0.13 parts of methionine, 0.06-0.1 parts of enzyme preparations, 0.02-0.03 parts of allicin, and 0.4 parts of multivitamins -0.6 parts, 1.0-1.2 parts of compound mineral salt. The invention also provides a preparation method of the above-mentioned feed. The feed of the invention can improve the muscle quality of the tilapia, making the meat firm and crisp; improves the growth performance of the tilapia, reduces water pollution, reduces production costs, and has remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:FUJIAN FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INST
Method for producing flavoring material by double-bacteria fermentation bone paste
The invention discloses a method for producing a flavoring material by double-bacteria fermentation bone paste. The formulation of the fermentation process is as follows: the bacteria inoculation ratio of aspergillusoryzae to bacillus subtilis of 2:1, bacterial inoculation amount of 3%, material-water ratio of 2:3, initial pH of 7, fermentation temperature of 30 DEG C, and fermentation time of 48 hours. The fermentation pig bone paste provided by the invention is utilized, so that the degree of hydrolysis of the protein reaches 53.2% at most, which is remarkably improved in comparison with independent fermentation; the flavor peptide content in the flavor amino acid is improved by 10 times; odor of bacillus subtilis in fermentation liquor is greatly diluted, no objectionable odor is generated after the fermentation liquor is sprayed and dried, and the taste is delicious. The method has the advantages of simple fermentation process, short production period, low cost, high additional value, safety and no toxic and side effect. The product is abundant in micromolecule flavor amino acid and flavor polypeptide, and can be easily absorbed by the body. Besides, the product is safe, nutrient and healthy, can be used as a natural condiment, and also can be used as a health-care product which is directly edible.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENGWEI FOOD +1
Nutrient licking block for mutton sheep and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106562031AHigh hardnessLow expansionAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsGlucurolactoneChemistry
The invention discloses a nutrient licking block for mutton sheep and a preparation method thereof. The nutrient licking block is prepared from the following raw materials: coarse salt, tea fungus, razor clam, zinc lactate, glycine-iron, potassium carbonate, calcium carbonate, manganese citrate, ursolic acid, chlorogenic acid, rhodioloside, selenium malt, genistein, glucurolactone and leptospermum scoparium essential oil. The nutrient licking block is convenient to eat, has comprehensive nutrition, and can be used for supplying nutritional ingredients essential to mutton sheep growth in time.
Owner:方良云
Silurus lanzhouensis compound feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105831488AMeet nutritional needsImprove qualityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAralia elataFish oil
The present invention relates to a fish feed and particularly relates to a silurus lanzhouensis compound feed. The present invention also relates to a preparation method of the silurus lanzhouensis compound feed. The silurus lanzhouensis compound feed comprises the following components in parts by mass: 21-29 parts of fish meal, 5-15 parts of shrimp head powder, 4-15 parts of pea flour, 5-14 parts of silene conoidea seedlings, 6-17 parts of dandelions, 3-11 parts of sonchus oleraceus, 5-16 parts of oenanthe javanica, 5-14 parts of aralia elata, 3-10 parts of Yunlong vegetables, 4-15 parts of brasenia schreberi, 3-15 parts of artemisia selengensis, 3-10 parts of baphicacanthus cusia, 5-14 parts of basil, 3-9 parts of fish oil, 1-4 parts of olive oil and 1-4 parts of compound multi-vitamins. After being fed with the silurus lanzhouensis compound feed, the silurus lanzhouensis is low in feed coefficient. In the muscles of the silurus lanzhouensis, the crude protein content is high, the crude fat content is low, and the flavor amino acid content is high.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIXING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Albumen powder richening in antimicrobial peptide fly maggot, preparation method for albumen powder and feed additive of albumen powder
ActiveCN102894186BHigh content of active ingredientsNo pollutionAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyUltrasound stimulation
Owner:河北圣土农业科技有限公司
Method for improving astaxanthin content of dried freshwater shrimp product through ultrasonic blanching pretreatment
InactiveCN111838583AHigh retention rateReduce volatile base nitrogen contentFood dryingFood ultrasonic treatmentAstaxanthinAmino acid content
The invention relates to a method for improving the astaxanthin content of a dried freshwater shrimp product through ultrasonic blanching pretreatment, and belongs to the field of deep processing of agricultural products. The method comprises the steps: selecting mature and fresh freshwater shrimps as raw materials; cleaning, removing shrimp beards and empennages, and then carrying out variable-frequency ultrasonic blanching pretreatment; in the first stage, putting pretreated freshwater shrimps into clear water according to a material-water ratio of 1 4, and setting the water temperature to be 75-85 DEG C, the ultrasonic frequency to be 60KHz, the power density to be 0.45-0.58 W / cm2 and the treatment time to be 3-5min; in the second stage, taking out he freshwater shrimps and putting intoa NaCl solution with the mass fraction being 2%-4%, wherein the material-liquid ratio is 1 4, the water temperature is set to be 65-75 DEG C, the ultrasonic frequency is set to be 25 KHz, the power density is set to be 0.65-0.72 W / cm2 , and the treatment time is set to be 4-6 min; and finally, performing normal-pressure hot air drying, wherein the hot air drying temperature is set to be 55-65 DEGC, the air speed is set to be 2.0-3.0 ms, and the drying time is set to be 6-8 h. The variable-frequency ultrasonic blanching effectively removes the fishy smell of the freshwater shrimps and reducesthe content of volatile basic nitrogen in the dried products, and compared with conventional blanching, the fresh amino acid content of the dried freshwater shrimp products is increased by 17%-22%, and the astaxanthin content is increased by 18%-23%.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of Qixing tea dregs fermented feed for improving the quality of fermented bed breeding pigs and its preparation method
ActiveCN109043166BDigestiveHas spleen and stomachFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention relates to the technical field of feed, in particular to a seven-star tea dregs fermented feed for improving the quality of pigs in a fermentation bed and a preparation method thereof. It is made of grain amaranth, 15-50 parts of corn flour, 0.5-10 parts of fulvic acid powder and 0.5-5 parts of mixed Chinese herbal medicine powder. Chinese herbal ingredients such as coix seed, hawthorn, and licorice contained in the fermented Qixing tea dregs of the present invention are combined with mixed Chinese herbal medicines to improve the immunity of pigs, promote the growth of pigs, and improve the quality of pork. Promote the growth of microorganisms in the fermentation bed, improve its ability to degrade pollutants, and purify the breeding environment of pigs.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PUCHUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
Health flavor-enhancement cooking wine and preparation method thereof
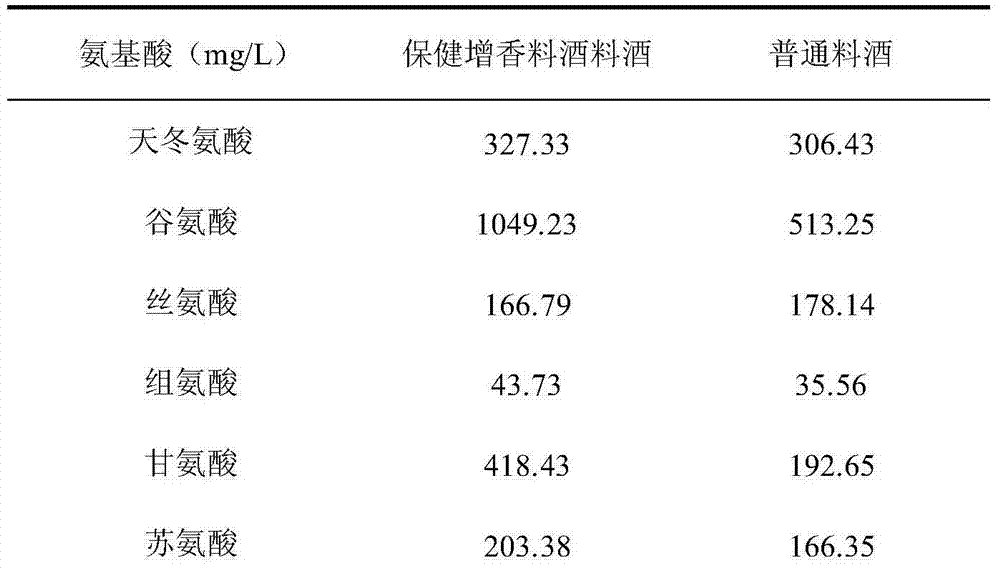
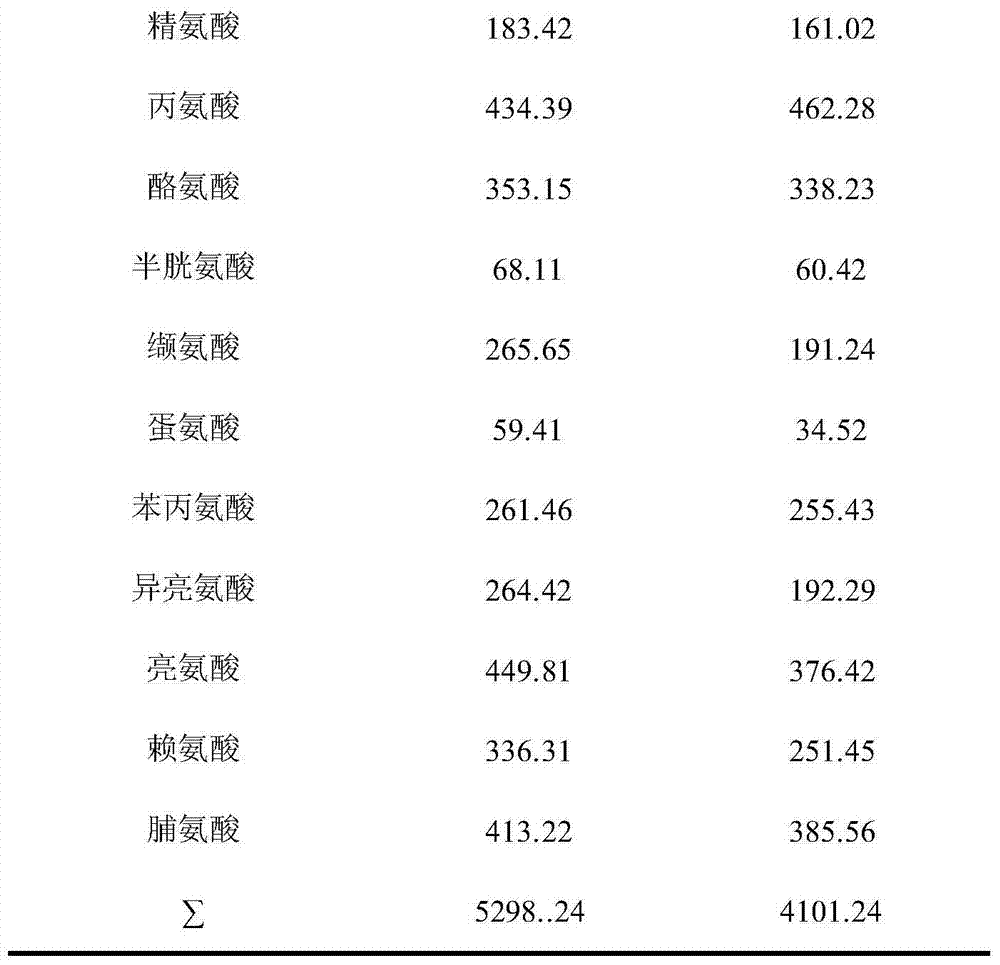
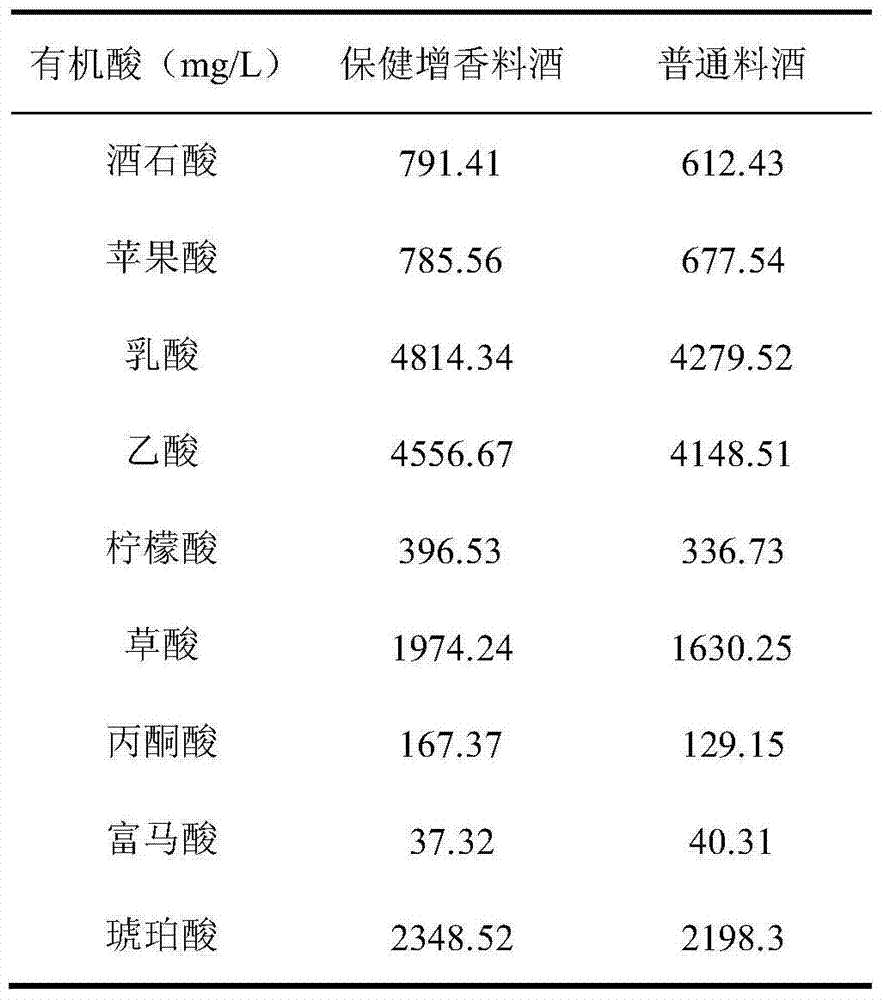
ActiveCN103960630BShorten the timeIncreased organic acid contentNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsGlycineOrganic acid
The invention discloses a health flavor-enhancement cooking wine and a preparation method thereof. The cooking wine comprises the following components: 3.83g / L of polysaccharides, 0.52g / L of flavonoids, 1049.23mg / L of glutamic acid and 418.43mg / L of glycine, wherein polysaccharides and flavonoids serve as functional components. Compared with the conventional cooking wine, the cooking wine produced by adopting the method has the characteristics that the contents of various amino acids in the cooking wine are remarkably increased, especially the content of flavor amino acid is doubled, the content of organic acid is remarkably increased, and the smell-removing and flavor-enhancing effects are remarkable; in addition, the contents of polysaccharides and flavonoids in the cooking wine can reach 3.83g / L and 0.52g / L respectively, and the cooking wine has good health functions of tonifying the spleen, benefiting vital energy, helping digestion, resisting fatigue, improving the immunity of a human body and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com