Algae removal and control method for low-speed small watershed
A technology for small watersheds and water areas, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage treatment of water/sewage, water pollutants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
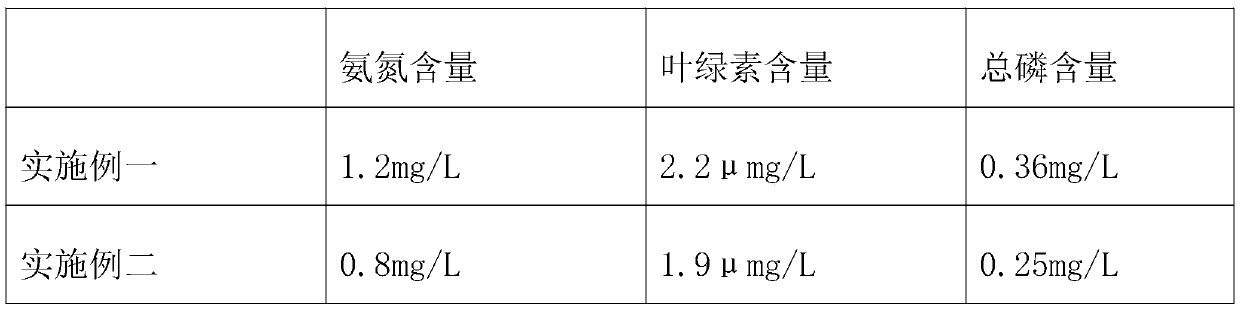
[0040] In the No. 1 simulated lake, a method of algae control in a slow-flow small watershed is adopted, including the following steps:
[0041] (1) Salvage 60% of the algae in the simulated lake;
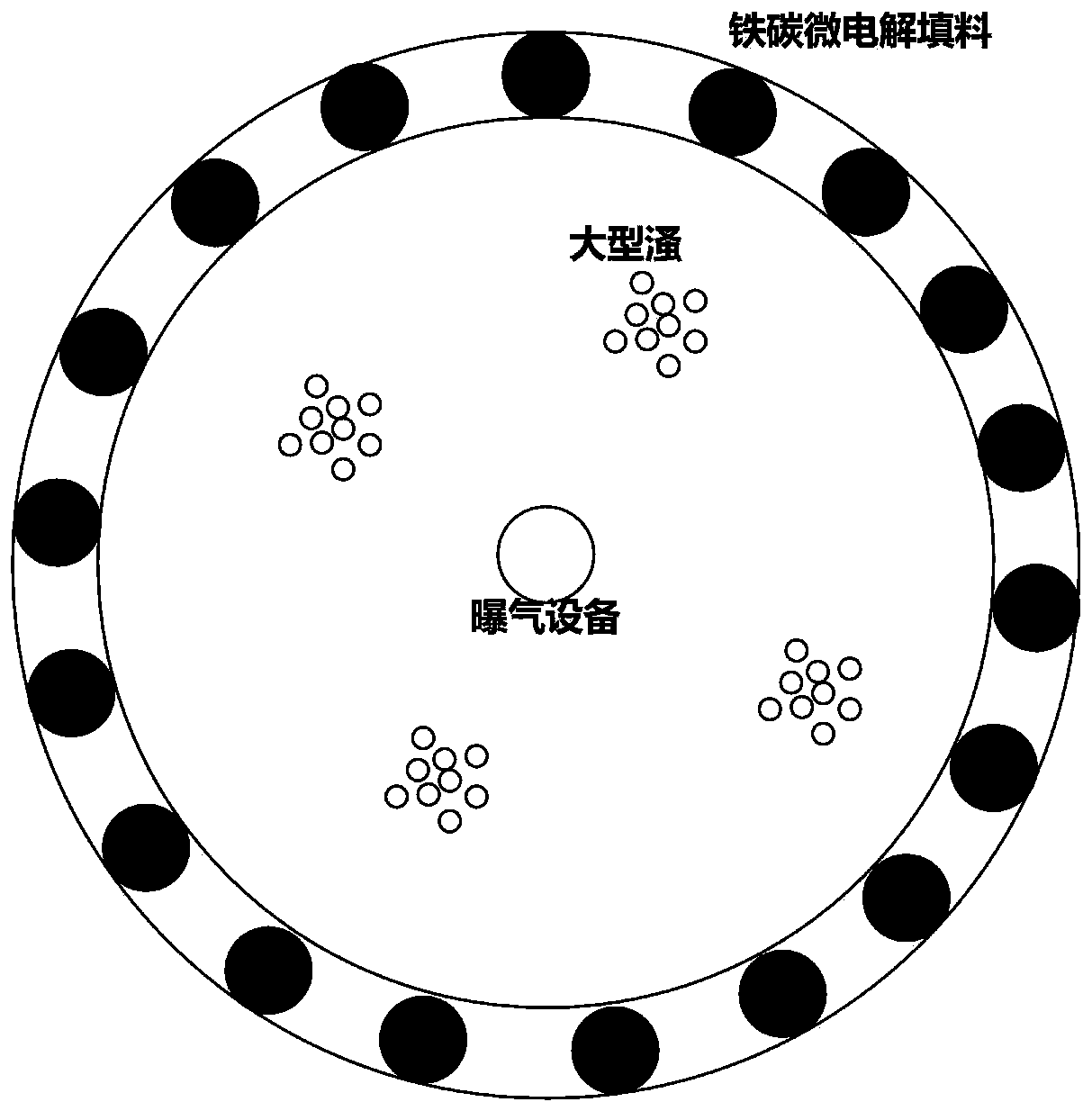
[0042] (2) Arrange the gabion nets equipped with iron-carbon micro-electrolysis filler, 0.05m wide and 0.5m high, along the bank of the simulated lake to remove phosphorus in the water;
[0043] (3) Lay a sunshade net at 0.5m above the water surface, shade it for 10 days, and inhibit the growth of algae;
[0044] (4) Install an aeration device, start aeration after the shading is over, and increase the dissolved oxygen in the water;
[0045] (5) Add 30g / m to the water in the simulated lake 3 The amount of nitrifying bacteria is evenly sprinkled, and a total of 47.1g of nitrifying bacteria are sprinkled in a simulated lake. Under aerobic conditions, nitrifying bacteria degrade ammonia nitrogen in water;
[0046] (6) Add 40g / m to the water in the simulated lake 3 62.8g of phospho...
Embodiment 2
[0049] In the No. 2 simulated lake, a method of algae control in a slow-flow small watershed is adopted, including the following steps:
[0050] (1) Salvage 70% of the algae in the simulated lake;
[0051] (2) Arranging gabion nets equipped with iron-carbon micro-electrolysis fillers with a width of 0.2m and a height of 0.5m along the shore of the simulated lake to remove phosphorus in the water;
[0052] (3) Lay a sunshade net at 0.5m above the water surface, shade it for 10 days, and inhibit the growth of algae;
[0053] (4) Install an aeration device, start aeration after the shading is over, and increase the dissolved oxygen in the water;
[0054] (5) Add 50g / m to the water in the simulated lake 3 The amount of nitrifying bacteria is evenly sprinkled, and a total of 78.5g of nitrifying bacteria are sprinkled in a simulated lake. Under aerobic conditions, nitrifying bacteria degrade ammonia nitrogen in water;
[0055] (6) Add 60g / m to the water in the simulated lake 3 T...
Embodiment 3
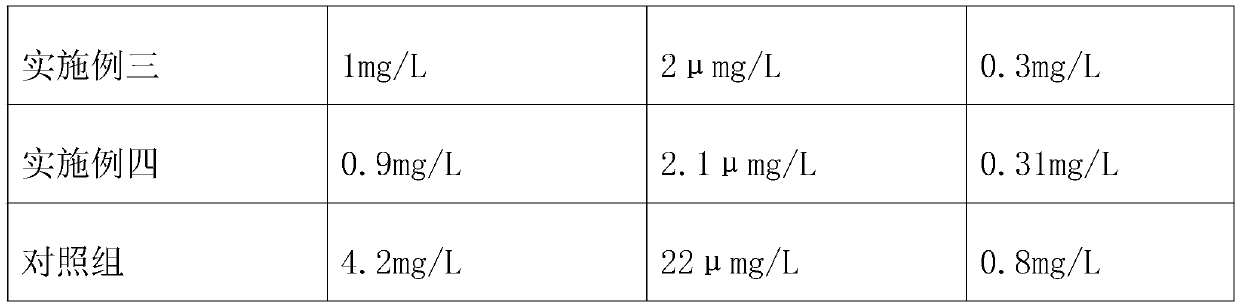
[0058]In the No. 3 simulated lake, a method of algae control in a slow-flow small watershed is adopted, including the following steps:
[0059] (1) Salvage 75% of the algae in the simulated lake;
[0060] (2) Arrange the gabion nets equipped with iron-carbon micro-electrolysis filler, 0.15m wide and 0.5m high, along the bank of the simulated lake to remove phosphorus in the water;
[0061] (3) Lay a sunshade net at 0.5m above the water surface, shade it for 10 days, and inhibit the growth of algae;
[0062] (4) Install an aeration device, start aeration after the shading is over, and increase the dissolved oxygen in the water;
[0063] (5) Add 40g / m to the water in the simulated lake 3 The amount of nitrifying bacteria is evenly sprinkled, and a total of 62.8g of nitrifying bacteria are sprinkled in a simulated lake. Under aerobic conditions, nitrifying bacteria degrade ammonia nitrogen in water;
[0064] (6) Add 50g / m to the water in the simulated lake 3 The amount of pho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com